Real Numbers and the Number Line. Unit 1 Lesson 3
|
|
|
- Amice Francis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Real Numbers and the Number Line Unit 1 Lesson 3
2 Students will be able to: graph and compare real numbers using the number line. Key Vocabulary: Real Number Rational Number Irrational number Non-Integers Integers Negative Numbers Numbers Whole Numbers Zero Natural Numbers Number line Graph Plot Absolute Value
3 Real Numbers π, e, 22 7, 2, 3, 7, 3 4, 27, 9i, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, π, e,, 2, 3, 7 7 Irrational Numbers Rational Numbers 3 4, 27, 9i, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, , 27 11, 9i Non-Integers Integers, 3, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 3,, 5, 4, 3, 2 Negative Numbers Whole Numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0 Zero Natural Numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
4 REAL NUMBERS are the set of numbers that is formed by combining the rational numbers and the irrational numbers. IRRATIONAL NUMBERS are the set of all numbers whose decimal representation are neither terminating nor repeating. It cannot be expressed as a quotient of integers. RATIONAL NUMBERS are the set of all numbers which can be expressed in the form: a b, where a and b are integers and b is not equal to 0, written b 0. It can be expressed as terminating or repeating decimals.
5 NON-INTEGERS are the set of all numbers that is neither a positive whole number, nor a negative whole number, nor zero. These include decimals, fractions, and imaginary numbers. INTEGERS are the set of numbers formed by positive whole numbers, negative whole numbers, and zero. NEGATIVE NUMBERS are numbers less than zero and usually mean a value that is a deficit or shortage.
6 WHOLE NUMBERS are the set of numbers formed by adding 0 to the set of natural numbers. ZERO denotes the absence of all magnitude or quantity. NATURAL NUMBERS are used for counting.
7 Sample Problem 1: Determine which of the numbers given below are: a. Integers b. Rational Numbers c. Irrational Numbers d. Real Numbers e. Natural Numbers f. Non-integers π
8 Sample Problem 1: Determine which of the numbers given below are: a. Integers 0, 6, 7, 41, 51 π b. Rational Numbers 0. 2, 0, 0. 3, 6, 7, 41, 51 c. Irrational Numbers , π d. Real Numbers 0. 2, 0, 0. 3, 6, 7, 41, 51, , π e. Natural Numbers 6, 7, 41, 51 f. Non-integers 0. 2, 0. 3
9 NUMBER LINE is used to show the sets of natural numbers, whole numbers, and integers. Also, it can be used to show the set of rational numbers. The point that corresponds to a number is the graph of the number, and drawing the point is called graphing the number or plotting the point. Integers Whole Numbers Natural Numbers Negative Numbers Positive Numbers
10 Sample Problem 2: Graph the numbers 2. 3 and 1 2 line. on the number
11 Sample Problem 2: Graph the numbers 2. 3 and 1 2 line. on the number
12 Sample Problem 3: Graph the numbers 3 and 5 on the number line and write two inequalities that compare the two numbers.
13 Sample Problem 3: Graph the numbers 3 and 5 on the number line and write two inequalities that compare the two numbers < 3 3 > 5
14 Sample Problem 4: Graph the numbers 2, 4, 0, 1. 5, 1 2, 3 2 and 2. 5 on the number line and write the numbers in increasing order.
15 Sample Problem 4: Graph the numbers 2, 4, 0, 1. 5, 1 2, 3 2 and 2. 5 on the number line and write the numbers in increasing order , 2, 3 2, 0, 1, 1. 5, 4 2
16 ABSOLUTE VALUE of a real number is the distance between the origin and the point representing the real number. The symbol x represents the absolute value of a number x. 5 units 5 units = 5 The distance of -5 to the origin is 5 units. 5 = 5 The distance of 5 to the origin is 5 units.
17 Sample Problem 5: Evaluate and graph the numbers 2. 3 and 1 2 on the number line.
18 Sample Problem 5: Evaluate and graph the numbers 2. 3 and 1 2 on the number line. 1 2 units units = 2. 3 units 1 2 = 1 2 units
Order and Compare Rational and Irrational numbers and Locate on the number line
 806.2.1 Order and Compare Rational and Irrational numbers and Locate on the number line Rational Number ~ any number that can be made by dividing one integer by another. The word comes from the word "ratio".
806.2.1 Order and Compare Rational and Irrational numbers and Locate on the number line Rational Number ~ any number that can be made by dividing one integer by another. The word comes from the word "ratio".
Pre-Test Unit 7: Real Numbers KEY
 Pre-Test Unit 7: Real Numbers KEY No calculator necessary. Please do not use a calculator. Convert the following fraction to a decimal or decimal to a fraction. (5 pts; 3 pts for correct set-up/work, 2
Pre-Test Unit 7: Real Numbers KEY No calculator necessary. Please do not use a calculator. Convert the following fraction to a decimal or decimal to a fraction. (5 pts; 3 pts for correct set-up/work, 2
Estimating with Square Roots
 ACTIVITY 3.2 Estimating with Square Roots The square root of most numbers is not an integer. You can estimate the square root of a number that is not a perfect square. Begin by determining the two perfect
ACTIVITY 3.2 Estimating with Square Roots The square root of most numbers is not an integer. You can estimate the square root of a number that is not a perfect square. Begin by determining the two perfect
Pre-Algebra Unit 1: Number Sense Unit 1 Review Packet
 Pre-Algebra Unit 1: Number Sense Unit 1 Review Packet Target 1: Writing Repeating Decimals in Rational Form Remember the goal is to get rid of the repeating decimal so we can write the number in rational
Pre-Algebra Unit 1: Number Sense Unit 1 Review Packet Target 1: Writing Repeating Decimals in Rational Form Remember the goal is to get rid of the repeating decimal so we can write the number in rational
Part I: Bell Work When solving an inequality, when would you flip the inequality sign?
 Algebra 135 Seminar Lesson 55 Part I: Bell Work When solving an inequality, when would you flip the inequality sign? Part II: Mini-Lesson Review for Ch 6 Test Give a review lesson for the Chapter 6 test.
Algebra 135 Seminar Lesson 55 Part I: Bell Work When solving an inequality, when would you flip the inequality sign? Part II: Mini-Lesson Review for Ch 6 Test Give a review lesson for the Chapter 6 test.
constant EXAMPLE #4:
 Linear Equations in One Variable (1.1) Adding in an equation (Objective #1) An equation is a statement involving an equal sign or an expression that is equal to another expression. Add a constant value
Linear Equations in One Variable (1.1) Adding in an equation (Objective #1) An equation is a statement involving an equal sign or an expression that is equal to another expression. Add a constant value
Quantitative Aptitude Preparation Numbers. Prepared by: MS. RUPAL PATEL Assistant Professor CMPICA, CHARUSAT
 Quantitative Aptitude Preparation Numbers Prepared by: MS. RUPAL PATEL Assistant Professor CMPICA, CHARUSAT Numbers Numbers In Hindu Arabic system, we have total 10 digits. Namely, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
Quantitative Aptitude Preparation Numbers Prepared by: MS. RUPAL PATEL Assistant Professor CMPICA, CHARUSAT Numbers Numbers In Hindu Arabic system, we have total 10 digits. Namely, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
Math Fundamentals for Statistics (Math 52) Unit 2:Number Line and Ordering. By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys.
 Math Fundamentals for Statistics (Math 52) Unit 2:Number Line and Ordering By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys Unit 2 Page 1 2.1: Place Values We just looked at graphing ordered
Math Fundamentals for Statistics (Math 52) Unit 2:Number Line and Ordering By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys Unit 2 Page 1 2.1: Place Values We just looked at graphing ordered
G6-M3-Lesson 7: Ordering Integers and Other Rational Numbers
 G6-M3-Lesson 7: Ordering Integers and Other Rational Numbers 1. In the table below, list each set of rational numbers in order from least to greatest. Then, list their opposites. Finally, list the opposites
G6-M3-Lesson 7: Ordering Integers and Other Rational Numbers 1. In the table below, list each set of rational numbers in order from least to greatest. Then, list their opposites. Finally, list the opposites
Alex Benn. Math 7 - Outline First Semester ( ) (Numbers in parentheses are the relevant California Math Textbook Sections) Quarter 1 44 days
 Math 7 - Outline First Semester (2016-2017) Alex Benn (Numbers in parentheses are the relevant California Math Textbook Sections) Quarter 1 44 days 0.1 Classroom Rules Multiplication Table Unit 1 Measuring
Math 7 - Outline First Semester (2016-2017) Alex Benn (Numbers in parentheses are the relevant California Math Textbook Sections) Quarter 1 44 days 0.1 Classroom Rules Multiplication Table Unit 1 Measuring
CK-12 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1
 1.1 Subsets of Real Numbers 1. Rational Number. Irrational Number. Rational Number 4. Whole Number 5. Integer 6. Irrational Number 7. Real, Rational, Integer, Whole, and Natural Number 8. Real and Rational
1.1 Subsets of Real Numbers 1. Rational Number. Irrational Number. Rational Number 4. Whole Number 5. Integer 6. Irrational Number 7. Real, Rational, Integer, Whole, and Natural Number 8. Real and Rational
Topic Proficiency Scale Domain: The Number System Topic: Rational Numbers. I know all of the Simple and Complex Learning Goals.
 Topic Proficiency Scale Domain: The Number System Topic: Rational Numbers 4.0 Going Beyond I know all of the Simple and Complex Learning Goals and my understanding goes beyond the grade level target. I
Topic Proficiency Scale Domain: The Number System Topic: Rational Numbers 4.0 Going Beyond I know all of the Simple and Complex Learning Goals and my understanding goes beyond the grade level target. I
4-2 Using Intercepts. Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz
 4-2 Using Intercepts Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Holt Algebra McDougal 1 Algebra 1 Warm Up Solve each equation. 1. 5x + 0 = 10 2 2. 33 = 0 + 3y 11 3. 1 4. 2x + 14 = 3x + 4 2 5. 5y 1 = 7y +
4-2 Using Intercepts Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz Holt Algebra McDougal 1 Algebra 1 Warm Up Solve each equation. 1. 5x + 0 = 10 2 2. 33 = 0 + 3y 11 3. 1 4. 2x + 14 = 3x + 4 2 5. 5y 1 = 7y +
Quick Answers - Chapter : Relations and Functions: Check for Understanding
 of 38 9/5/2012 8:07 AM Quick Answers - Chapter 1 1-1: Relations and Functions: Check for Understanding 1. 9. 2. 10. 11. 3. 12. 13. 4. 14. 15. of 38 9/5/2012 8:07 AM 5. 16. 6. 7. 8. 1-1: Relations and Functions:
of 38 9/5/2012 8:07 AM Quick Answers - Chapter 1 1-1: Relations and Functions: Check for Understanding 1. 9. 2. 10. 11. 3. 12. 13. 4. 14. 15. of 38 9/5/2012 8:07 AM 5. 16. 6. 7. 8. 1-1: Relations and Functions:
Keystone Exams: Algebra I Assessment Anchors and Eligible Content. Pennsylvania Department of Education
 Keystone Exams: Algebra I Assessment Anchors and Pennsylvania Department of Education www.education.state.pa.us 2010 PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION General Introduction to the Keystone Exam Assessment
Keystone Exams: Algebra I Assessment Anchors and Pennsylvania Department of Education www.education.state.pa.us 2010 PENNSYLVANIA DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION General Introduction to the Keystone Exam Assessment
Roots and Radicals Chapter Questions
 Roots and Radicals Chapter Questions 1. What are the properties of a square? 2. What does taking the square root have to do with the area of a square? 3. Why is it helpful to memorize perfect squares?
Roots and Radicals Chapter Questions 1. What are the properties of a square? 2. What does taking the square root have to do with the area of a square? 3. Why is it helpful to memorize perfect squares?
By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys
 Math Fundamentals for Statistics I (Math 52) Unit 2:Number Line and Ordering By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Math Fundamentals for Statistics I (Math 52) Unit 2:Number Line and Ordering By Scott Fallstrom and Brent Pickett The How and Whys Guys This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Numbers & Operations Chapter Problems
 Numbers & Operations 8 th Grade Chapter Questions 1. What are the properties of a square? 2. What does taking the square root have to do with the area of a square? 3. Why is it helpful to memorize perfect
Numbers & Operations 8 th Grade Chapter Questions 1. What are the properties of a square? 2. What does taking the square root have to do with the area of a square? 3. Why is it helpful to memorize perfect
GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS PACING GUIDE. Algebra I MATHEMATICS G R E A T E R C L A R K C O U N T Y S C H O O L S
 GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS PACING GUIDE Algebra I MATHEMATICS 2014-2015 G R E A T E R C L A R K C O U N T Y S C H O O L S ANNUAL PACING GUIDE Quarter/Learning Check Days (Approx) Q1/LC1 11 Concept/Skill
GREATER CLARK COUNTY SCHOOLS PACING GUIDE Algebra I MATHEMATICS 2014-2015 G R E A T E R C L A R K C O U N T Y S C H O O L S ANNUAL PACING GUIDE Quarter/Learning Check Days (Approx) Q1/LC1 11 Concept/Skill
Published in India by. MRP: Rs Copyright: Takshzila Education Services
 NUMBER SYSTEMS Published in India by www.takshzila.com MRP: Rs. 350 Copyright: Takshzila Education Services All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system,
NUMBER SYSTEMS Published in India by www.takshzila.com MRP: Rs. 350 Copyright: Takshzila Education Services All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system,
Grades 6 8 Innoventure Components That Meet Common Core Mathematics Standards
 Grades 6 8 Innoventure Components That Meet Common Core Mathematics Standards Strand Ratios and Relationships The Number System Expressions and Equations Anchor Standard Understand ratio concepts and use
Grades 6 8 Innoventure Components That Meet Common Core Mathematics Standards Strand Ratios and Relationships The Number System Expressions and Equations Anchor Standard Understand ratio concepts and use
BIG IDEA 1: Develop an understanding of and fluency with multiplication and division of fractions and decimals BIG IDEA 1:
 BIG IDEA 1: Develop an understanding of and fluency with multiplication and division of fractions and decimals Multiplying and Dividing Decimals Explain the difference between an exact answer and an estimated
BIG IDEA 1: Develop an understanding of and fluency with multiplication and division of fractions and decimals Multiplying and Dividing Decimals Explain the difference between an exact answer and an estimated
5-6 Study Guide. Radical Expressions and Rational Exponents. Attendance Problems. Simplify each expression. (No decimal answers!
 Page 1 of 12 Radical Expressions and Rational Exponents Attendance Problems. Simplify each expression. (No decimal answers) 11 8 7 7 2 2.. 2. 11 6. I can rewrite radical expressions by using rational exponents.
Page 1 of 12 Radical Expressions and Rational Exponents Attendance Problems. Simplify each expression. (No decimal answers) 11 8 7 7 2 2.. 2. 11 6. I can rewrite radical expressions by using rational exponents.
TenMarks Curriculum Alignment Guide: EngageNY/Eureka Math, Grade 7
 EngageNY Module 1: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Topic A: Proportional Relationships Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Understand equivalent ratios, rate, and unit rate related to a Understand proportional
EngageNY Module 1: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Topic A: Proportional Relationships Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Understand equivalent ratios, rate, and unit rate related to a Understand proportional
Math 7 Notes Unit 02 Part A: Rational Numbers. Real Numbers
 As we begin this unit it s a good idea to have an overview. When we look at the subsets of the real numbers it helps us organize the groups of numbers students have been exposed to and those that are soon
As we begin this unit it s a good idea to have an overview. When we look at the subsets of the real numbers it helps us organize the groups of numbers students have been exposed to and those that are soon
TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 6. Student Book
 TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 6 Student Book TEKSING TOWARD STAAR 2014 Six Weeks 1 Lesson 1 STAAR Category 1 Grade 6 Mathematics TEKS 6.2A/6.2B Problem-Solving Model Step Description of Step 1
TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 6 Student Book TEKSING TOWARD STAAR 2014 Six Weeks 1 Lesson 1 STAAR Category 1 Grade 6 Mathematics TEKS 6.2A/6.2B Problem-Solving Model Step Description of Step 1
Category A: Estimating Square Roots and Cube Roots - 3
 Category A: Estimating Square Roots and Cube Roots When estimating irrational numbers, the easiest way to compare values is by squaring (or cubing) the given values. Ex: Between which two consecutive numbers
Category A: Estimating Square Roots and Cube Roots When estimating irrational numbers, the easiest way to compare values is by squaring (or cubing) the given values. Ex: Between which two consecutive numbers
7 th grade Math Standards Priority Standard (Bold) Supporting Standard (Regular)
 7 th grade Math Standards Priority Standard (Bold) Supporting Standard (Regular) Unit #1 7.NS.1 Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers;
7 th grade Math Standards Priority Standard (Bold) Supporting Standard (Regular) Unit #1 7.NS.1 Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers;
Can the number be represented as a fraction? What are the different categories of numbers? CPM Materials modified by Mr. Deyo
 Common Core Standard: 8.NS.1, 8.NS.2, 8.EE.2 Can the number be represented as a fraction? What are the different categories of numbers? CPM Materials modified by Mr. Deyo Title: IM8 Ch. 9.2.4 What Kind
Common Core Standard: 8.NS.1, 8.NS.2, 8.EE.2 Can the number be represented as a fraction? What are the different categories of numbers? CPM Materials modified by Mr. Deyo Title: IM8 Ch. 9.2.4 What Kind
UNIT 5 INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS
 UNIT INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will investigate fractions and their multiple meanings. We have seen fractions before in the context of division. For example, we can think
UNIT INTRODUCTION TO FRACTIONS INTRODUCTION In this Unit, we will investigate fractions and their multiple meanings. We have seen fractions before in the context of division. For example, we can think
Developed by Rashmi Kathuria. She can be reached at
 Developed by Rashmi Kathuria. She can be reached at . Photocopiable Activity 1: Step by step Topic Nature of task Content coverage Learning objectives Task Duration Arithmetic
Developed by Rashmi Kathuria. She can be reached at . Photocopiable Activity 1: Step by step Topic Nature of task Content coverage Learning objectives Task Duration Arithmetic
Unit 2: Ratio & Proportion Applications
 Time Frame: Approximately 3-4 Weeks Connections to previous learning: In Grade 6, students develop an understanding of ratio and proportion using ratio tables, tape diagrams, and double number lines. Focus
Time Frame: Approximately 3-4 Weeks Connections to previous learning: In Grade 6, students develop an understanding of ratio and proportion using ratio tables, tape diagrams, and double number lines. Focus
An ordered collection of counters in rows or columns, showing multiplication facts.
 Addend A number which is added to another number. Addition When a set of numbers are added together. E.g. 5 + 3 or 6 + 2 + 4 The answer is called the sum or the total and is shown by the equals sign (=)
Addend A number which is added to another number. Addition When a set of numbers are added together. E.g. 5 + 3 or 6 + 2 + 4 The answer is called the sum or the total and is shown by the equals sign (=)
15 x 15 Multiplication Tables (Blank) X
 15 x 15 Multiplication Tables (Blank) X 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 15 x 15 Multiplication Tables (Completed) X 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 1 1 2 3 4
15 x 15 Multiplication Tables (Blank) X 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 15 x 15 Multiplication Tables (Completed) X 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 1 1 2 3 4
2.1 BASIC CONCEPTS Basic Operations on Signals Time Shifting. Figure 2.2 Time shifting of a signal. Time Reversal.
 1 2.1 BASIC CONCEPTS 2.1.1 Basic Operations on Signals Time Shifting. Figure 2.2 Time shifting of a signal. Time Reversal. 2 Time Scaling. Figure 2.4 Time scaling of a signal. 2.1.2 Classification of Signals
1 2.1 BASIC CONCEPTS 2.1.1 Basic Operations on Signals Time Shifting. Figure 2.2 Time shifting of a signal. Time Reversal. 2 Time Scaling. Figure 2.4 Time scaling of a signal. 2.1.2 Classification of Signals
Connected Mathematics 2, 6th Grade Units (c) 2006 Correlated to: Utah Core Curriculum for Math (Grade 6)
 Core Standards of the Course Standard I Students will acquire number sense and perform operations with rational numbers. Objective 1 Represent whole numbers and decimals in a variety of ways. A. Change
Core Standards of the Course Standard I Students will acquire number sense and perform operations with rational numbers. Objective 1 Represent whole numbers and decimals in a variety of ways. A. Change
Section 2.3 Task List
 Summer 2017 Math 108 Section 2.3 67 Section 2.3 Task List Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook. Section 2.3 Function Notation and Applications
Summer 2017 Math 108 Section 2.3 67 Section 2.3 Task List Work through each of the following tasks, carefully filling in the following pages in your notebook. Section 2.3 Function Notation and Applications
Rational. 8 h 24 h. A rational number is a number that can be written as the ratio of two integers = 1. ACTIVITY: Ordering Rational Numbers
 . rational numbers? How can you use a number line to order The word rational comes from the word ratio. Recall that you can write a ratio using fraction notation. If you sleep for hours in a day, then
. rational numbers? How can you use a number line to order The word rational comes from the word ratio. Recall that you can write a ratio using fraction notation. If you sleep for hours in a day, then
Sect Linear Equations in Two Variables
 99 Concept # Sect. - Linear Equations in Two Variables Solutions to Linear Equations in Two Variables In this chapter, we will examine linear equations involving two variables. Such equations have an infinite
99 Concept # Sect. - Linear Equations in Two Variables Solutions to Linear Equations in Two Variables In this chapter, we will examine linear equations involving two variables. Such equations have an infinite
For more information on the Common Core State Standards, visit Beast Academy Grade 4 Chapters 1-12:
 Beast Academy Scope and Sequence for Grade 4 (books 4A through 4D). The content covered in Beast Academy Grade 4 is loosely based on the standards created by the Common Core State Standards Initiative.
Beast Academy Scope and Sequence for Grade 4 (books 4A through 4D). The content covered in Beast Academy Grade 4 is loosely based on the standards created by the Common Core State Standards Initiative.
Number Sense Unit 1 Math 10F Mrs. Kornelsen R.D. Parker Collegiate
 Unit 1 Math 10F Mrs. Kornelsen R.D. Parker Collegiate Lesson One: Rational Numbers New Definitions: Rational Number Is every number a rational number? What about the following? Why or why not? a) b) c)
Unit 1 Math 10F Mrs. Kornelsen R.D. Parker Collegiate Lesson One: Rational Numbers New Definitions: Rational Number Is every number a rational number? What about the following? Why or why not? a) b) c)
TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 7. Projection Masters
 TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 7 Projection Masters Six Weeks 1 Lesson 1 STAAR Category 1 Grade 7 Mathematics TEKS 7.2A Understanding Rational Numbers A group of items or numbers is called a set.
TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 7 Projection Masters Six Weeks 1 Lesson 1 STAAR Category 1 Grade 7 Mathematics TEKS 7.2A Understanding Rational Numbers A group of items or numbers is called a set.
Fair Game Review. Chapter 2. Name Date. Write the decimal as a fraction Write the fraction as a decimal. 7.
 Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Write the decimal as a fraction.. 0.6. 0.79. 0.7. 0.86 Write the fraction as a decimal.. 8 6. 7. 6 8. 7 0 9. A quarterback completed 0.6 of his passes during a game.
Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Write the decimal as a fraction.. 0.6. 0.79. 0.7. 0.86 Write the fraction as a decimal.. 8 6. 7. 6 8. 7 0 9. A quarterback completed 0.6 of his passes during a game.
Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Grade 6
 Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Grade 6 Write and evaluate numerical expressions involving whole-number exponents. Write, read, and evaluate expressions; identify parts of an expression using mathematical
Core Learning Standards for Mathematics Grade 6 Write and evaluate numerical expressions involving whole-number exponents. Write, read, and evaluate expressions; identify parts of an expression using mathematical
8.1 Exponential Growth 1. Graph exponential growth functions. 2. Use exponential growth functions to model real life situations.
 8.1 Exponential Growth Objective 1. Graph exponential growth functions. 2. Use exponential growth functions to model real life situations. Key Terms Exponential Function Asymptote Exponential Growth Function
8.1 Exponential Growth Objective 1. Graph exponential growth functions. 2. Use exponential growth functions to model real life situations. Key Terms Exponential Function Asymptote Exponential Growth Function
Cardinality and Bijections
 Countable and Cardinality and Bijections Gazihan Alankuş (Based on original slides by Brahim Hnich et al.) August 13, 2012 Countable and Countable and Countable and How to count elements in a set? How
Countable and Cardinality and Bijections Gazihan Alankuş (Based on original slides by Brahim Hnich et al.) August 13, 2012 Countable and Countable and Countable and How to count elements in a set? How
UNIT 2: RATIONAL NUMBER CONCEPTS WEEK 5: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 2: RATIONAL NUMBER CONCEPTS WEEK 5: Student Packet 5.1 Fractions: Parts and Wholes Identify the whole and its parts. Find and compare areas of different shapes. Identify congruent
Name Period Date UNIT 2: RATIONAL NUMBER CONCEPTS WEEK 5: Student Packet 5.1 Fractions: Parts and Wholes Identify the whole and its parts. Find and compare areas of different shapes. Identify congruent
THANK YOU FOR YOUR PURCHASE!
 THANK YOU FOR YOUR PURCHASE! The resources included in this purchase were designed and created by me. I hope that you find this resource helpful in your classroom. Please feel free to contact me with any
THANK YOU FOR YOUR PURCHASE! The resources included in this purchase were designed and created by me. I hope that you find this resource helpful in your classroom. Please feel free to contact me with any
What I can do for this unit:
 Unit 1: Real Numbers Student Tracking Sheet Math 10 Common Name: Block: What I can do for this unit: After Practice After Review How I Did 1-1 I can sort a set of numbers into irrationals and rationals,
Unit 1: Real Numbers Student Tracking Sheet Math 10 Common Name: Block: What I can do for this unit: After Practice After Review How I Did 1-1 I can sort a set of numbers into irrationals and rationals,
Learning Log Title: CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION AND REPRESENTATION. Date: Lesson: Chapter 1: Introduction and Representation
 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION AND REPRESENTATION Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Toolkit 2013 CPM Educational Program. All rights reserved. 1 Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Toolkit 2013 CPM Educational
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION AND REPRESENTATION Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Toolkit 2013 CPM Educational Program. All rights reserved. 1 Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Toolkit 2013 CPM Educational
Table of Contents Left Page
 1 Left Page Table of Contents Right Page Nuggets of Knowledge 0 Table of Contents 1 Table of Contents 2 Table of Contents 3 Module 1 Learning Targts 4 Rate/Ratio/Percent Notes 5 Lesson 6 Gallery Walk 6
1 Left Page Table of Contents Right Page Nuggets of Knowledge 0 Table of Contents 1 Table of Contents 2 Table of Contents 3 Module 1 Learning Targts 4 Rate/Ratio/Percent Notes 5 Lesson 6 Gallery Walk 6
STEM: Electronics Curriculum Map & Standards
 STEM: Electronics Curriculum Map & Standards Time: 45 Days Lesson 6.1 What is Electricity? (16 days) Concepts 1. As engineers design electrical systems, they must understand a material s tendency toward
STEM: Electronics Curriculum Map & Standards Time: 45 Days Lesson 6.1 What is Electricity? (16 days) Concepts 1. As engineers design electrical systems, they must understand a material s tendency toward
Objectives: Students will learn to divide decimals with both paper and pencil as well as with the use of a calculator.
 Unit 3.5: Fractions, Decimals and Percent Lesson: Dividing Decimals Objectives: Students will learn to divide decimals with both paper and pencil as well as with the use of a calculator. Procedure: Dividing
Unit 3.5: Fractions, Decimals and Percent Lesson: Dividing Decimals Objectives: Students will learn to divide decimals with both paper and pencil as well as with the use of a calculator. Procedure: Dividing
We could also take square roots of certain decimals nicely. For example, 0.36=0.6 or 0.09=0.3. However, we will limit ourselves to integers for now.
 7.3 Evaluation of Roots Previously we used the square root to help us approximate irrational numbers. Now we will expand beyond just square roots and talk about cube roots as well. For both we will be
7.3 Evaluation of Roots Previously we used the square root to help us approximate irrational numbers. Now we will expand beyond just square roots and talk about cube roots as well. For both we will be
The Real Number System and Pythagorean Theorem Unit 9 Part B
 The Real Number System and Pythagorean Theorem Unit 9 Part B Standards: 8.NS.1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion;
The Real Number System and Pythagorean Theorem Unit 9 Part B Standards: 8.NS.1 Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion;
Aim #35.1: How do we graph using a table?
 A) Take out last night's homework Worksheet - Aim 34.2 B) Copy down tonight's homework Finish aim 35.1 Aim #35.1: How do we graph using a table? C) Plot the following points... a) (-3, 5) b) (4, -2) c)
A) Take out last night's homework Worksheet - Aim 34.2 B) Copy down tonight's homework Finish aim 35.1 Aim #35.1: How do we graph using a table? C) Plot the following points... a) (-3, 5) b) (4, -2) c)
Radical Expressions and Graph (7.1) EXAMPLE #1: EXAMPLE #2: EXAMPLE #3: Find roots of numbers (Objective #1) Figure #1:
 Radical Expressions and Graph (7.1) Find roots of numbers EXAMPLE #1: Figure #1: Find principal (positive) roots EXAMPLE #2: Find n th roots of n th powers (Objective #3) EXAMPLE #3: Figure #2: 7.1 Radical
Radical Expressions and Graph (7.1) Find roots of numbers EXAMPLE #1: Figure #1: Find principal (positive) roots EXAMPLE #2: Find n th roots of n th powers (Objective #3) EXAMPLE #3: Figure #2: 7.1 Radical
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 4.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Squares and More Using Patterns to Generate Algebraic Functions Vocabulary Match each word with its corresponding definition. 1. linear function a.
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Squares and More Using Patterns to Generate Algebraic Functions Vocabulary Match each word with its corresponding definition. 1. linear function a.
Squares and Square roots
 Squares and Square roots Introduction of Squares and Square Roots: LECTURE - 1 If a number is multiplied by itsely, then the product is said to be the square of that number. i.e., If m and n are two natural
Squares and Square roots Introduction of Squares and Square Roots: LECTURE - 1 If a number is multiplied by itsely, then the product is said to be the square of that number. i.e., If m and n are two natural
Adding Fractions with Different Denominators. Subtracting Fractions with Different Denominators
 Adding Fractions with Different Denominators How to Add Fractions with different denominators: Find the Least Common Denominator (LCD) of the fractions Rename the fractions to have the LCD Add the numerators
Adding Fractions with Different Denominators How to Add Fractions with different denominators: Find the Least Common Denominator (LCD) of the fractions Rename the fractions to have the LCD Add the numerators
Adding and Subtracting Integers. How can you use addition and subtraction of integers to solve real-world problems?
 UNIT 1 Study Guide Review? MODULE 1 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Adding and Subtracting Integers How can you use addition and subtraction of integers to solve real-world problems? Key Vocabulary additive inverse
UNIT 1 Study Guide Review? MODULE 1 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Adding and Subtracting Integers How can you use addition and subtraction of integers to solve real-world problems? Key Vocabulary additive inverse
14.2 Limits and Continuity
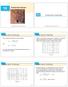 14 Partial Derivatives 14.2 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Let s compare the behavior of the functions Tables 1 2 show values of f(x,
14 Partial Derivatives 14.2 Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Let s compare the behavior of the functions Tables 1 2 show values of f(x,
Algebra 2. Slope of waste pipes
 Algebra 2 Slope of waste pipes Subject Area: Math Grade Levels: 9-12 Date: Aug 25 th -26 th Lesson Overview: Students will first complete a worksheet reviewing slope, rate of change,, and plotting points.
Algebra 2 Slope of waste pipes Subject Area: Math Grade Levels: 9-12 Date: Aug 25 th -26 th Lesson Overview: Students will first complete a worksheet reviewing slope, rate of change,, and plotting points.
Subtracting Rational Numbers
 . How can you use what you know about subtracting integers to subtract rational numbers? ACTIVITY: Work with a partner. Use a number line to find the difference. a. Then move unit left to end at. Subtract.
. How can you use what you know about subtracting integers to subtract rational numbers? ACTIVITY: Work with a partner. Use a number line to find the difference. a. Then move unit left to end at. Subtract.
Solving Equations and Graphing
 Solving Equations and Graphing Question 1: How do you solve a linear equation? Answer 1: 1. Remove any parentheses or other grouping symbols (if necessary). 2. If the equation contains a fraction, multiply
Solving Equations and Graphing Question 1: How do you solve a linear equation? Answer 1: 1. Remove any parentheses or other grouping symbols (if necessary). 2. If the equation contains a fraction, multiply
Pythagorean Theorem Unit
 Pythagorean Theorem Unit TEKS covered: ~ Square roots and modeling square roots, 8.1(C); 7.1(C) ~ Real number system, 8.1(A), 8.1(C); 7.1(A) ~ Pythagorean Theorem and Pythagorean Theorem Applications,
Pythagorean Theorem Unit TEKS covered: ~ Square roots and modeling square roots, 8.1(C); 7.1(C) ~ Real number system, 8.1(A), 8.1(C); 7.1(A) ~ Pythagorean Theorem and Pythagorean Theorem Applications,
Thinking Rationally. Identifying and Ordering Rational Numbers
 Thinking Rationally Identifying and Ordering Rational Numbers 1 WARM UP Determine the fraction represented by the shaded part of each grid. If necessary, rewrite in lowest terms. 1. 2. LEARNING GOALS Understand
Thinking Rationally Identifying and Ordering Rational Numbers 1 WARM UP Determine the fraction represented by the shaded part of each grid. If necessary, rewrite in lowest terms. 1. 2. LEARNING GOALS Understand
Lesson 1 6. Algebra: Variables and Expression. Students will be able to evaluate algebraic expressions.
 Lesson 1 6 Algebra: Variables and Expression Students will be able to evaluate algebraic expressions. P1 Represent and analyze patterns, rules and functions with words, tables, graphs and simple variable
Lesson 1 6 Algebra: Variables and Expression Students will be able to evaluate algebraic expressions. P1 Represent and analyze patterns, rules and functions with words, tables, graphs and simple variable
NAME DATE CLASS NOTES
 NAME DATE CLASS NOTES How do painters design murals so large that you can only see them from a distance? In most cases, designs for large projects like murals are first created as small pieces of art.
NAME DATE CLASS NOTES How do painters design murals so large that you can only see them from a distance? In most cases, designs for large projects like murals are first created as small pieces of art.
Unit 2: Exponents. 8 th Grade Math 8A - Mrs. Trinquero 8B - Dr. Taylor 8C - Mrs. Benefield
 Unit 2: Exponents 8 th Grade Math 8A - Mrs. Trinquero 8B - Dr. Taylor 8C - Mrs. Benefield 1 8 th Grade Math Unit 2: Exponents Standards and Elements Targeted in the Unit: NS 1 Know that numbers that are
Unit 2: Exponents 8 th Grade Math 8A - Mrs. Trinquero 8B - Dr. Taylor 8C - Mrs. Benefield 1 8 th Grade Math Unit 2: Exponents Standards and Elements Targeted in the Unit: NS 1 Know that numbers that are
NAME DATE. b) Then do the same for Jett s pennies (6 sets of 9 pennies with 4 leftover pennies).
 NAME DATE 1.2.2/1.2.3 NOTES 1-51. Cody and Jett each have a handful of pennies. Cody has arranged his pennies into 3 sets of 16, and has 9 leftover pennies. Jett has 6 sets of 9 pennies, and 4 leftover
NAME DATE 1.2.2/1.2.3 NOTES 1-51. Cody and Jett each have a handful of pennies. Cody has arranged his pennies into 3 sets of 16, and has 9 leftover pennies. Jett has 6 sets of 9 pennies, and 4 leftover
Class 8: Square Roots & Cube Roots (Lecture Notes)
 Class 8: Square Roots & Cube Roots (Lecture Notes) SQUARE OF A NUMBER: The Square of a number is that number raised to the power. Examples: Square of 9 = 9 = 9 x 9 = 8 Square of 0. = (0.) = (0.) x (0.)
Class 8: Square Roots & Cube Roots (Lecture Notes) SQUARE OF A NUMBER: The Square of a number is that number raised to the power. Examples: Square of 9 = 9 = 9 x 9 = 8 Square of 0. = (0.) = (0.) x (0.)
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Properties of Logarithms
Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Properties of Logarithms
Students use absolute value to determine distance between integers on the coordinate plane in order to find side lengths of polygons.
 Student Outcomes Students use absolute value to determine distance between integers on the coordinate plane in order to find side lengths of polygons. Lesson Notes Students build on their work in Module
Student Outcomes Students use absolute value to determine distance between integers on the coordinate plane in order to find side lengths of polygons. Lesson Notes Students build on their work in Module
CHAPTER 3 DECIMALS. EXERCISE 8 Page Convert 0.65 to a proper fraction may be written as: 100. i.e = =
 CHAPTER 3 DECIMALS EXERCISE 8 Page 21 1. Convert 0.65 to a proper fraction. 0.65 may be written as: 0.65 100 100 i.e. 0.65 65 100 Dividing both numerator and denominator by 5 gives: 65 13 100 20 Hence,
CHAPTER 3 DECIMALS EXERCISE 8 Page 21 1. Convert 0.65 to a proper fraction. 0.65 may be written as: 0.65 100 100 i.e. 0.65 65 100 Dividing both numerator and denominator by 5 gives: 65 13 100 20 Hence,
Problem Solving: Lesson 12 Symmetry on a Coordinate Graph Lesson 12 Skills Maintenance
 Lesson 1 Skills Maintenance Lesson Planner Skills Maintenance Adding and Subtracting Positive and Negative Integers Symmetry on a Coordinate Graph We review the concept of symmetry and extend it to the
Lesson 1 Skills Maintenance Lesson Planner Skills Maintenance Adding and Subtracting Positive and Negative Integers Symmetry on a Coordinate Graph We review the concept of symmetry and extend it to the
NUMBER, NUMBER SYSTEMS, AND NUMBER RELATIONSHIPS. Kindergarten:
 Kindergarten: NUMBER, NUMBER SYSTEMS, AND NUMBER RELATIONSHIPS Count by 1 s and 10 s to 100. Count on from a given number (other than 1) within the known sequence to 100. Count up to 20 objects with 1-1
Kindergarten: NUMBER, NUMBER SYSTEMS, AND NUMBER RELATIONSHIPS Count by 1 s and 10 s to 100. Count on from a given number (other than 1) within the known sequence to 100. Count up to 20 objects with 1-1
Number Line: Comparing and Ordering Integers (page 6)
 LESSON Name 1 Number Line: Comparing and Ordering Integers (page 6) A number line shows numbers in order from least to greatest. The number line has zero at the center. Numbers to the right of zero are
LESSON Name 1 Number Line: Comparing and Ordering Integers (page 6) A number line shows numbers in order from least to greatest. The number line has zero at the center. Numbers to the right of zero are
Identify if each number is rational or irrational. Click "A" for rational. "B" for irrational
 Bellwork CLICKERS!!!! Identify if each number is rational or irrational. Click "A" for rational. "B" for irrational Today's Agenda: 1. Bell Work: Rational or Irrational 2. CLICKER review Lesson Objective:
Bellwork CLICKERS!!!! Identify if each number is rational or irrational. Click "A" for rational. "B" for irrational Today's Agenda: 1. Bell Work: Rational or Irrational 2. CLICKER review Lesson Objective:
The Basics. GFP - Sohar University. SET 1 - Chapter 1
 The Basics األساسي ات األعداد الحقيقي ة 1-1 Real Numbers Real numbers are used in everyday life to describe quantities such as speed, area, prices, age, temperature, and population. Real numbers are usually
The Basics األساسي ات األعداد الحقيقي ة 1-1 Real Numbers Real numbers are used in everyday life to describe quantities such as speed, area, prices, age, temperature, and population. Real numbers are usually
UNIT 5. Integers and Rational Numbers on the Number Line CCM6 and CCM6+ Name: Math Teacher: Estimated Test Date:
 UNIT 5 Integers and Rational Numbers on the Number Line 2015-2016 CCM6 and CCM6+ Name: Math Teacher: Estimated Test Date: Main Concepts Page(s) Unit 5 Vocabulary 2 Converting Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
UNIT 5 Integers and Rational Numbers on the Number Line 2015-2016 CCM6 and CCM6+ Name: Math Teacher: Estimated Test Date: Main Concepts Page(s) Unit 5 Vocabulary 2 Converting Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
Pre-AP Algebra 2 Unit 8 - Lesson 2 Graphing rational functions by plugging in numbers; feature analysis
 Pre-AP Algebra 2 Unit 8 - Lesson 2 Graphing rational functions by plugging in numbers; feature analysis Objectives: Students will be able to: Analyze the features of a rational function: determine domain,
Pre-AP Algebra 2 Unit 8 - Lesson 2 Graphing rational functions by plugging in numbers; feature analysis Objectives: Students will be able to: Analyze the features of a rational function: determine domain,
The Sine Function. Precalculus: Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 Concepts: Graphs of Sine, Cosine, Sinusoids, Terminology (amplitude, period, phase shift, frequency). The Sine Function Domain: x R Range: y [ 1, 1] Continuity: continuous for all x Increasing-decreasing
Concepts: Graphs of Sine, Cosine, Sinusoids, Terminology (amplitude, period, phase shift, frequency). The Sine Function Domain: x R Range: y [ 1, 1] Continuity: continuous for all x Increasing-decreasing
Lesson Sampling Distribution of Differences of Two Proportions
 STATWAY STUDENT HANDOUT STUDENT NAME DATE INTRODUCTION The GPS software company, TeleNav, recently commissioned a study on proportions of people who text while they drive. The study suggests that there
STATWAY STUDENT HANDOUT STUDENT NAME DATE INTRODUCTION The GPS software company, TeleNav, recently commissioned a study on proportions of people who text while they drive. The study suggests that there
Tennessee Senior Bridge Mathematics
 A Correlation of to the Mathematics Standards Approved July 30, 2010 Bid Category 13-130-10 A Correlation of, to the Mathematics Standards Mathematics Standards I. Ways of Looking: Revisiting Concepts
A Correlation of to the Mathematics Standards Approved July 30, 2010 Bid Category 13-130-10 A Correlation of, to the Mathematics Standards Mathematics Standards I. Ways of Looking: Revisiting Concepts
Algebra/Geometry Session Problems Questions 1-20 multiple choice
 lgebra/geometry Session Problems Questions 1-0 multiple choice nswer only one choice: (a), (b), (c), (d), or (e) for each of the following questions. Only use a number pencil. Make heavy black marks that
lgebra/geometry Session Problems Questions 1-0 multiple choice nswer only one choice: (a), (b), (c), (d), or (e) for each of the following questions. Only use a number pencil. Make heavy black marks that
Example. h + 8 < -13 and b 4 > -6 Multiplying and dividing inequalities
 Unit 2 (continued): Expressions and Equations 2 nd 9 Weeks Suggested Instructional Days: 10 Unit Summary (Learning Target/Goal): Use properties of operations to generate equivalent expressions. CCSS for
Unit 2 (continued): Expressions and Equations 2 nd 9 Weeks Suggested Instructional Days: 10 Unit Summary (Learning Target/Goal): Use properties of operations to generate equivalent expressions. CCSS for
Mathematics Success Grade 6
 T428 Mathematics Success Grade 6 [OBJECTIVE] The students will plot ordered pairs containing rational values to identify vertical and horizontal lengths between two points in order to solve real-world
T428 Mathematics Success Grade 6 [OBJECTIVE] The students will plot ordered pairs containing rational values to identify vertical and horizontal lengths between two points in order to solve real-world
Lesson 1b Linear Equations
 In the first lesson we looked at the concepts and rules of a Function. The first Function that we are going to investigate is the Linear Function. This is a good place to start because with Linear Functions,
In the first lesson we looked at the concepts and rules of a Function. The first Function that we are going to investigate is the Linear Function. This is a good place to start because with Linear Functions,
Write each expression using exponents a b c x x x y y x. x y. x 3 y. x y. x y
 1. Which of the following is equivalent to? 13.40 3.25 0.325 0.325 Write the decimal as a fraction or mixed number in simplest form. 2. 1.35 Replace each with , or = to make a true statement. 3.
1. Which of the following is equivalent to? 13.40 3.25 0.325 0.325 Write the decimal as a fraction or mixed number in simplest form. 2. 1.35 Replace each with , or = to make a true statement. 3.
Activity 1: Play comparison games involving fractions, decimals and/or integers.
 Students will be able to: Lesson Fractions, Decimals, Percents and Integers. Play comparison games involving fractions, decimals and/or integers,. Complete percent increase and decrease problems, and.
Students will be able to: Lesson Fractions, Decimals, Percents and Integers. Play comparison games involving fractions, decimals and/or integers,. Complete percent increase and decrease problems, and.
IIR Filter Design Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Ability to design analog Butterworth filters
 IIR Filter Design Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Ability to design analog Butterworth filters (ii) Ability to design lowpass IIR filters according to predefined specifications based on analog
IIR Filter Design Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Ability to design analog Butterworth filters (ii) Ability to design lowpass IIR filters according to predefined specifications based on analog
Math 8 Homework TRIMESTER 2 November March 2019
 Math 8 Homework TRIMESTER 2 November 2018 - March 2019 MATH XL can be found at www.mrpk.org, press Student button, press Pearson Easy Bridge. Assignments will be found under the selection. Students should
Math 8 Homework TRIMESTER 2 November 2018 - March 2019 MATH XL can be found at www.mrpk.org, press Student button, press Pearson Easy Bridge. Assignments will be found under the selection. Students should
Data Presentation. Esra Akdeniz. February 12th, 2016
 Data Presentation Esra Akdeniz February 12th, 2016 HOW TO DO RESEARCH? Question. Literature research. Hypothesis. Collect data. Analyze data. Interpret and present results. HOW TO DO RESEARCH? Analyze
Data Presentation Esra Akdeniz February 12th, 2016 HOW TO DO RESEARCH? Question. Literature research. Hypothesis. Collect data. Analyze data. Interpret and present results. HOW TO DO RESEARCH? Analyze
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT
 HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Accelerated 7 th Grade Math Second Quarter Unit 3: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Topic C: Ratios and Rates Involving Fractions In Topic C,
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT Accelerated 7 th Grade Math Second Quarter Unit 3: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Topic C: Ratios and Rates Involving Fractions In Topic C,
Lesson 6.1 Linear Equation Review
 Name: Lesson 6.1 Linear Equation Review Vocabulary Equation: a math sentence that contains Linear: makes a straight line (no Variables: quantities represented by (often x and y) Function: equations can
Name: Lesson 6.1 Linear Equation Review Vocabulary Equation: a math sentence that contains Linear: makes a straight line (no Variables: quantities represented by (often x and y) Function: equations can
Mathematics. 6 th Grade Unit 7: Rational Explorations: Numbers and their Opposites
 CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics 6 th Grade Unit 7: Rational Explorations: Numbers and their Opposites These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute
CCGPS Frameworks Student Edition Mathematics 6 th Grade Unit 7: Rational Explorations: Numbers and their Opposites These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute
RATIONAL NUMBER ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION
 14 RATIONAL NUMBER ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION INSTRUCTIONAL ACTIVITY Lesson 3 LEARNING GOAL Students will extend their understanding of integer addition and subtraction, making connections with the number
14 RATIONAL NUMBER ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION INSTRUCTIONAL ACTIVITY Lesson 3 LEARNING GOAL Students will extend their understanding of integer addition and subtraction, making connections with the number
Multiplying and Dividing Fractions and Decimals
 CHAPTER Multiplying and Dividing Fractions and Decimals Lesson. Dividing Fractions Express each improper fraction as a mixed number in simplest form... 6. Express each mixed number as an improper fraction..
CHAPTER Multiplying and Dividing Fractions and Decimals Lesson. Dividing Fractions Express each improper fraction as a mixed number in simplest form... 6. Express each mixed number as an improper fraction..
AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School
 AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved AGS Math Algebra 2 Grade
AGS Math Algebra 2 Correlated to Kentucky Academic Expectations for Mathematics Grades 6 High School Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved AGS Math Algebra 2 Grade
