Updated October 2017
|
|
|
- Stewart Taylor
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Updated October 2017
2 Count objects to 100 and read and write numbers in numerals and words Represent numbers to 100 Tens and ones with a part whole model Tens and ones using addition Use a place alue chart Compare objects Compare numbers Order objects and numbers Count in 2s, 5s and 10s Count in 3s Read and write numbers to at least 100 in numerals and in words. Recognise the place alue of each digit in a two digit number (tens, ones) Identify, represent and estimate numbers using different representations including the number line. Compare and order numbers from 0 up to 100; use <, > and = signs. Use place alue and number facts to sole problems. Count in steps of 2, 3 and 5 from 0, and in tens from any number, forward and backward.
3 To build on skills learned in Year 1, children need to be able to count objects to 100 in both numerals and words. Problems should be presented in a ariety of ways e.g. numerals, words and images. Variation should challenge children by proiding them with missing numbers which are nonconsecutie. Count and write the number of cars in the car park. one three four seen eight ten eleen There are. cars in the car park. What numbers are represented below? Write your answer in numerals and words. How can you count the cars? Do you hae a strategy? What is one more/one less? Which is the largest number? Which number is tricky to write in words? Which numbers sound similar? How are 17 and 70 different? Can you show me? Match the numerals to the words Thirty eight Seenty Forty eight Seenteen
4 Year 2 Autumn Term Week 1 to 4 Number: Place Value Count Objects to 100 Reasoning and Problem Soling Tom says he has 61 Is he correct? Explain your reasoning Freddy rolls two dice. One dice shows a 6. What could his total be? Write your answers in words. Tom is not correct because he has 16. He has switched his ten and one around. Freddy s totals could be: seen, eight, nine, ten, eleen and twele. Each bag contains 10 cookies. How many cookies are there altogether? Write your answers in numerals and words. What strategy did you use? There are 48 (forty eight) cookies altogether. (Children may count in 10s and 1s or know that there are 4 tens which equals 40, then count on 8 more.)? How many dots of one die? How did you count the dots? How many dots on a nine sided die? 6 sided die: 21 dots 9 sided die: 50 dots Did your partner use a different method? What is the best strategy to use
5 Children need to be able to represent numbers to 100 using a range of concrete materials. In this small step, children should also be able to state how a number is made up. For example they can express 42 as 4 tens and 2 ones or as 42 ones. Here is part of a bead string. Complete the sentence. There are tens and ones. The number is Represent 45 on a bead string. Match the number to the correct representation. How hae the beads been grouped? How does this help you count? Which part of the resource represents tens/ones? Which resource do you prefer to use for larger numbers? Which is quickest? Which would take a long time? Three tens and four ones Twenty fie 33 Represent 67 in three different ways?
6 Year 2 Autumn Term Week 1 to 4 Number: Place Value Represent Numbers Reasoning and Problem Soling Place 36 on each of the number lines below: How many two digit numbers can you make using the digit cards? One of these images does not show 23. Can you explain the mistake? A B C C does not show 23, it shows 32. They hae reersed the tens and ones. What is the largest number? Proe it by using concrete resources. What is the smallest number? Proe it by using concrete resources. Why can t the 0 be used as a tens number? The largest number is 72 The smallest number is 20.
7 Children now partition numbers and need to hae an understanding of what each digit represents. It is important that children can partition numbers in a ariety of ways, not just as tens and ones. For example, 58 is made up of 5 tens and 8 ones or 4 tens and 18 ones, or 20 and 38, etc. Complete the part whole models Complete the part whole models Which part do we know? How can we use the whole and part to work out the missing part? Can you use concrete materials/draw something to help you partition? How can you rearrange the counters to help you count the lemon and strawberry cupcakes? The ten frames represent lemon and strawberry cupcakes. Draw a part whole model to show how many cupcakes there are altogether.
8 Week 1 to 4 Number: Place Value Charlotte says: In a part whole model you cannot use the same digit twice Disagree- you can use the same digit in a part whole model. i.e Complete the extended part whole model: ? Do you agree with Charlotte? Explain your reasoning. 51?
9 Children will build on preious learning on the part whole model and how tens and ones can be partitioned and recombined to make a total. This small step will focus on using the addition symbol to express numbers to 100. For example 73 can be written as 70 3 = 73 Match the number sentences to the correct number What clues are there in the calculations? Can we look at the tens number or the ones number to help us? What number completes the part-whole model? What is the same and different about the calculations? What are the key bits of information? Can you draw a diagram to help you? Complete the part-whole model and write four number sentences to match Hattie has 20 sweets and Noah has 15 sweets. Represent the total number of sweets: With concrete resources In a part whole model As a number sentence = = = =
10 Year 2 Autumn Term Week 1 to 4 Number: Place Value Tens and Ones (2) Reasoning and Problem Soling Joel thinks that: 40 2 = = 42 Joel has combined the numbers to make 402 Fill in the missing numbers: 1 ten 3 ones = 13 2 tens ones = 23 1 ten 3 ones = 13 2 tens 3 ones = 23 3 tens 3 ones = 33 4 tens 3 ones = 43 Explain the mistake he has made. Can you show the correct answer using concrete resources? 3 tens 3 ones = tens 3 ones = 43 What would the next number in the pattern be? 5 tens 3 ones = 53
11 To build on skills preiously taught, children are now formally presenting their work in the correct place alue columns to aid understanding of place alue. What number is represented in the place alue chart? Tens Ones It is important for children to use concrete, pictorial and abstract representations in their place alue chart. Complete the place alue charts using Base 10 and place alue counters to represent the number 56. Tens Ones Tens Ones How many tens are there? How many ones are there? What is different about using Base 10 and place alue counters? Can you write any other number sentences about the place alue chart? What number is represented in the place alue chart? Tens Ones 9 1 Write two different number sentences for this number. = =
12 Year 2 Autumn Term Place Value Charts Reasoning and Problem Soling How many two digit numbers can you make that hae the same number of tens and ones? Tens Tens Ones Ones Possible answers: Are these two place alue charts of equal alue? A B Yes they are of the same alue = = 41 Same: Both A and B show 41 Different: There are different tens and ones in each place alue chart. Tens Ones What is the same? What is different?
13 Once children are secure with tens and ones and how to place numbers on a place alue chart, comparing objects can be introduced. Children are expected to compare a ariety of objects using the ocabulary more than, less than and equal to and the symbols < and >. How can you arrange the objects to make them easy to compare? Do groups of ten help you count? Why? A packet of sweets contain 10 sweets. Helena s sweets Who has the most sweets? Use cubes to show that: Eleen is less than fifteen. 19 is greater than 9. 2 tens is equal to 20. Put <, > or = in each circle. Zak s sweets
14 Year 2 Autumn Term Comparing Objects Reasoning and Problem Soling Daisy and Dae are comparing numbers that they hae made. Daisy Dae Daisy is incorrect because Dae has 4 tens which makes 40 and Daisy has 3 tens and 6 ones which makes 36 therefore Dae has more. Use Base 10 to make A and B equal: = = Daisy My number is greater because I hae more objects. How could you make B more than A? B can be greater than A if you add more than 34 to it. Is Daisy correct? Explain your answer.
15 Children compare numbers using the language greater than, less than, more than, fewer, most, least and equal to. They are able to use the symbols <, > and = to write number sentences. Complete the statements using more than, less than or equal to. 42 is is is thirty eight Complete the number sentences. 4 tens and 9 ones > < 70 5 Can you proe your answers using concrete resources? Can you proe your answers by drawing a diagram? Is there more than one answer? Do you need to work the number sentences out to decide which is greater? eight tens = Put <, > or = in each circle
16 Year 2 Autumn Term Week 1 to 4 Number: Place Value Comparing Numbers Reasoning and Problem Soling How many different numbers can go in the box? Fill in the missing numbers using 1,2,4 and 7 13 < < 20 True or False: One ten and twele ones is bigger than two tens. Explain how you know. 14,15,16,17,18,19 True: One ten twele ones = 22 Two tens = 20 < < < 9 > < 8 > < or < < > < > < 7 < 8 5 < 6 > 3 21 < 9 > 12
17 Children order numbers and objects from smallest to greatest or greatest to smallest. They should be encouraged to use concrete or pictorial representations to proe or check their answers. Children use the ocabulary smallest and greatest and may also use the < or > symbols to show the order of their numbers. Circle the numbers 48, 43 and 50 on the number line Put the numbers 48, 43 and 50 in order starting with the smallest Use Base 10 to make the numbers sixty, sixteen and twenty six. Write the numbers in order starting with the greatest number. The diagrams represent different numbers. How does the number line help you order the numbers? How does Base 10 proe that your order is correct? Circle the greatest number. Circle the smallest number. Complete the number sentence >
18 Year 2 Autumn Term Week 1 to 4 Number: Place Value Order Numbers and Objects Reasoning and Problem Soling If you ordered the numbers below, which would be the fourth? Explain how you ordered them I ordered them from smallest to largest: 29, 33, 34, 37, 43, would be the fourth number Alternatiely, if I order the numbers from largest to smallest: 53, 43, 37, 34, 33, 29, Bill has written a list of 2 digit numbers. The digits of each number add up to 5. None of the digits are 0. Can you find all the numbers Bill could hae written? Write the numbers in order from smallest to largest. 14, 23, 32, would be the fourth number.
19 Children now need to count on and back in 2s, 5s and 10s. Continue each number sequence. It is important that children do not always start from zero, howeer they should start on a multiple of 2 or 5 when counting in 2s and 5s but can start from any number when counting in 10s. For example when counting in 2s they should not start at 3. Encourage children to look for patterns as they count. What do you notice? Are the numbers getting larger or smaller? Are the numbers getting bigger or smaller each time? By how much? Can you spot a pattern? Why is it the odd one out? Can you correct the mistake? Circle the odd one out in each number pattern. 2, 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, , 5, 10, 20, 30, , 30, 25, 20, 12, 10.. Count forwards and backwards in jumps of ten from: Fifty seen 40 1
20 Year 2 Autumn Term Week 1 to 4 Number: Place Value Counting in 2s, 5s, 10s Reasoning and Problem Soling Alfie says: Do you agree with Alfie? Proe it. If you count in 5s from any number in the fie times table your numbers hae to end in 5 or 0. Agree. Each number in the 5 times tables does end in a 5 or 0. 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50. Using these numbers, trael from 5 to 53 by using the arrows. 10, 29, 43, 15, 17, 45, 39, 19, 41, What do the red arrows show?
21 Children now need to count on and back in 3s from any multiple of 3. Encourage children to look for patterns as they count and use resources such as a number track, a counting stick and concrete representations. What do you notice about the numbers that are circled? Continue the pattern. Complete the number sequence. 15 What do you notice? Are the numbers getting larger or smaller? 9 6 Can you spot a pattern? 0 Sid has 15 stickers. He collects 3 more each day. Complete the number track to show how many he will hae in 6 days. 15
22 Year 2 Autumn Term Counting in 3s Reasoning and Problem Soling True or False I start at 0 and count in 3 s. I say the number 14. False. If I count in 3 s I go: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15 Sid is counting in 2s, Luke is counting in 3s. Sid Luke If Sid and Luke add their numbers together they will be counting in 5s. If Sid and Luke both count in 5s they will be counting in 10s. Sid says: If we add our numbers together as we count we can make a new What pattern do they make? What happens if both Sid and Luke count in 5s and they add them together to make a new pattern?
Read and write numbers to at least 100 in numerals and in words. Recognise the place value of each digit in a two digit number (tens, ones)
 Count objects to 100 and read and write numbers in numerals and words Represent numbers to 100 Tens and ones with a part whole model Tens and ones using addition Use a place alue chart Compare objects
Count objects to 100 and read and write numbers in numerals and words Represent numbers to 100 Tens and ones with a part whole model Tens and ones using addition Use a place alue chart Compare objects
Count in multiples of 6, 7, and Find 1000 more or less than a given number.
 Roman numerals to 100 Round to the nearest 10 Round to the nearest 100 Count in 1,000s 1,000s, 100s, 10s and 1s Partitioning Number line to 10,000 1,000 more or less Compare numbers Order numbers Round
Roman numerals to 100 Round to the nearest 10 Round to the nearest 100 Count in 1,000s 1,000s, 100s, 10s and 1s Partitioning Number line to 10,000 1,000 more or less Compare numbers Order numbers Round
Updated October 2017
 Updated October 2017 Roman numerals to 100 Round to the nearest 10 Round to the nearest 100 Count in 1,000s 1,000s, 100s, 10s and 1s Partitioning Number line to 10,000 1,000 more or less Compare numbers
Updated October 2017 Roman numerals to 100 Round to the nearest 10 Round to the nearest 100 Count in 1,000s 1,000s, 100s, 10s and 1s Partitioning Number line to 10,000 1,000 more or less Compare numbers
Year 1 Spring Term Week 5 to 7 Number: Place Value (within 50)
 1 Numbers to 50 Tens and ones Represent numbers to 50 One more one less Compare objects within 50 Compare numbers within 50 Order numbers within 50 Count in 2s Count in 5s Count to 50 forwards and backwards,
1 Numbers to 50 Tens and ones Represent numbers to 50 One more one less Compare objects within 50 Compare numbers within 50 Order numbers within 50 Count in 2s Count in 5s Count to 50 forwards and backwards,
Released October Year. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 4: Multiplication & Division
 Released October 2017 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Multiplication & Division Multiply and divide numbers mentally drawing upon known facts. Multiples Factors Common factors Prime numbers
Released October 2017 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Multiplication & Division Multiply and divide numbers mentally drawing upon known facts. Multiples Factors Common factors Prime numbers
4 + 3 = 7 10= model. Starting at the bigger number and counting on
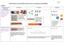 South Wilford C of E Endowed Primary School - Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partpart whole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes
South Wilford C of E Endowed Primary School - Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partpart whole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes
4 + 3 = 7 10= Starting at the bigger number and counting on. Progression in Calculations
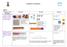 Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes to add two numbers together as a group or in a bar.
Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes to add two numbers together as a group or in a bar.
Progression In Calculations Addition
 Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole model Addition Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes to add two numbers together as a group or in a bar. Use pictures to add two
Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole model Addition Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes to add two numbers together as a group or in a bar. Use pictures to add two
Updated December Year. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 4: Multiplication & Division
 Updated December 2017 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Multiplication & Division Year 5 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Multiples Notes and Guidance Building on their times tables knowledge,
Updated December 2017 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Multiplication & Division Year 5 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Multiples Notes and Guidance Building on their times tables knowledge,
4 + 3 = 7 10= Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole. Starting at the bigger number and counting on
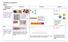 Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies R/Y1 Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes to add two numbers together as a group or in
Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies R/Y1 Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes to add two numbers together as a group or in
Year 3. Term by Term Objectives. Year 3 Overview. Spring Autumn. Summer. Number: Place Value
 Year 3 Autumn Term by Term Objectives Year 3 Year 3 Overview Spring Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Multiplication and Division Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement
Year 3 Autumn Term by Term Objectives Year 3 Year 3 Overview Spring Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Multiplication and Division Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement
Sample pages. Skip Counting. Until we know the pattern of numbers, we can count on from the last answer. Skip count and write the numbers as you go.
 1:01 Skip Counting Until we know the pattern of numbers, we can from the last answer. When I count on, I my fingers. Skip count and write the numbers as you go. a Each time, three more. 3 6 b Each time,
1:01 Skip Counting Until we know the pattern of numbers, we can from the last answer. When I count on, I my fingers. Skip count and write the numbers as you go. a Each time, three more. 3 6 b Each time,
4 + 3 = 7 10= Starting at the bigger number and counting on
 Ladbrooke JMI School Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes to add two numbers together
Ladbrooke JMI School Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes to add two numbers together
Has difficulty in partitioning, for example, 208 into 190 and 18 and 31 into 20 and 11
 Has difficulty in partitioning, for example, 208 into 190 18 31 into 20 11 Opportunity for: developing mental images 2 Y4 / Resources Key vocabulary Three 100-bead strings partition complement add hundreds
Has difficulty in partitioning, for example, 208 into 190 18 31 into 20 11 Opportunity for: developing mental images 2 Y4 / Resources Key vocabulary Three 100-bead strings partition complement add hundreds
Numbers to ten million Compare and order any number Round any numbers Negative numbers
 Numbers to ten million Compare and order any number Round any numbers Negative numbers Read, write, order and compare numbers up to 10,000,000 and determine the value of each digit. Round any whole number
Numbers to ten million Compare and order any number Round any numbers Negative numbers Read, write, order and compare numbers up to 10,000,000 and determine the value of each digit. Round any whole number
There are 5 people upstairs on the bus, there are 4 people downstairs. How many altogether? Write a number sentence to show this.
 National Curriculum Fluency Reasoning Problem Solving Read, write and interpret mathematical statements involving addition (+), subtraction (-) and equals (=) signs. There are 5 people upstairs on the
National Curriculum Fluency Reasoning Problem Solving Read, write and interpret mathematical statements involving addition (+), subtraction (-) and equals (=) signs. There are 5 people upstairs on the
Year 1. Mastery Overview Autumn
 Mastery Overview Autumn SOL Overview As well as providing term by term overviews for the new as a Maths Hub we are aiming to support primary schools by providing more detailed Schemes of Learning, which
Mastery Overview Autumn SOL Overview As well as providing term by term overviews for the new as a Maths Hub we are aiming to support primary schools by providing more detailed Schemes of Learning, which
Children to write number sentences Children to show jumps on laminated number line: Show the jumps on a number line as counting on e.
 Written Methods& Mental Methods & A D D I T I O N FOUNDATION STAGE YEAR 1 YEAR 2 Count with 1:1 correspondence Recognise numbers Count to 20 and beyond Write numbers Order numbers to 20 Know one more than
Written Methods& Mental Methods & A D D I T I O N FOUNDATION STAGE YEAR 1 YEAR 2 Count with 1:1 correspondence Recognise numbers Count to 20 and beyond Write numbers Order numbers to 20 Know one more than
Odd one out. Odd one out
 SAMPLE Odd one out Odd one out NUMBER AND PLACE VALUE Spot the difference Spot the difference The same different NUMBER AND PLACE VALUE Is it sixteen? Is it sixteen? Is it sixteen? Is it sixteen? Is it
SAMPLE Odd one out Odd one out NUMBER AND PLACE VALUE Spot the difference Spot the difference The same different NUMBER AND PLACE VALUE Is it sixteen? Is it sixteen? Is it sixteen? Is it sixteen? Is it
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers
 Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Student Book Series D Mathletics Instant Workbooks Copyright Contents Series D Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Looking at whole numbers reading and
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Student Book Series D Mathletics Instant Workbooks Copyright Contents Series D Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Looking at whole numbers reading and
This policy has been largely adapted from the White Rose Maths Hub Calculation Policy with further material added.
 This policy has been largely adapted from the White Rose Maths Hub Calculation Policy with further material added. St John s RC Primary School Calculation Combining two parts to make a whole: part- whole
This policy has been largely adapted from the White Rose Maths Hub Calculation Policy with further material added. St John s RC Primary School Calculation Combining two parts to make a whole: part- whole
Addition 10=5+5. Vocabulary NB:H=hundreds/T=Tens/O=ones
 Addition Vocabulary NB:H=hundreds/T=Tens/O=ones number bonds, number line, add, more, plus, make, sum, total, altogether, double, how many more?, column addition, partition, counting on, efficient method,
Addition Vocabulary NB:H=hundreds/T=Tens/O=ones number bonds, number line, add, more, plus, make, sum, total, altogether, double, how many more?, column addition, partition, counting on, efficient method,
Use each digit card once to make the decimal number nearest to 20
 NUMBER Level 4 questions 1. Here is a number chart. Circle the smallest number on the chart that is a multiple of both 2 and 7 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95
NUMBER Level 4 questions 1. Here is a number chart. Circle the smallest number on the chart that is a multiple of both 2 and 7 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95
MAKING MATHEMATICS COUNT
 MAKING MATHEMATICS COUNT By Kerry Dalton Using manipulatives from Early Years Foundation Stage to Year 6 10 minutes per day, in addition to the daily mathematics lesson Covers Early Years Foundation Stage
MAKING MATHEMATICS COUNT By Kerry Dalton Using manipulatives from Early Years Foundation Stage to Year 6 10 minutes per day, in addition to the daily mathematics lesson Covers Early Years Foundation Stage
Released November /2. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 4: Measurement - Money
 Released November 2017 1/2 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Measurement - Money Year 1/2 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 1 Year 2 Recognising coins Recognising notes Counting
Released November 2017 1/2 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Measurement - Money Year 1/2 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 1 Year 2 Recognising coins Recognising notes Counting
Addition and Subtraction
 D Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic 1 Addition mental strategies (pp. 114) look for a ten look for patterns doubles and near doubles bridge to ten jump strategy split strategy version 1 split strategy
D Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic 1 Addition mental strategies (pp. 114) look for a ten look for patterns doubles and near doubles bridge to ten jump strategy split strategy version 1 split strategy
Unit 7 Number Sense: Addition and Subtraction with Numbers to 100
 Unit 7 Number Sense: Addition and Subtraction with Numbers to 100 Introduction In this unit, students will review counting and ordering numbers to 100. They will also explore various strategies and tools
Unit 7 Number Sense: Addition and Subtraction with Numbers to 100 Introduction In this unit, students will review counting and ordering numbers to 100. They will also explore various strategies and tools
Stage 2 PROMPT sheet. 2/3 Estimate numbers. 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables. 2/4 Order numbers. Count in 10s.
 Stage 2 PROMPT sheet 2/3 Estimate numbers Eyeball estimate Here are 3 sweets 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables 0 x 2 = 0 1 x 2 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 3 x 2 = 6 4 x 2 = 8 5 x 2 = 10 6 x 2 = 12 7 x 2 = 14 8 x
Stage 2 PROMPT sheet 2/3 Estimate numbers Eyeball estimate Here are 3 sweets 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables 0 x 2 = 0 1 x 2 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 3 x 2 = 6 4 x 2 = 8 5 x 2 = 10 6 x 2 = 12 7 x 2 = 14 8 x
Stage 2 PROMPT sheet. 2/3 Estimate numbers. 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables. 2/4 Order numbers. 2/2 Place value
 tens units tens units Stage 2 PROMPT sheet 2/3 Estimate numbers Eyeball estimate Here are 3 sweets 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables 0 x 2 = 0 1 x 2 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 3 x 2 = 6 4 x 2 = 8 5 x 2 = 10 6 x
tens units tens units Stage 2 PROMPT sheet 2/3 Estimate numbers Eyeball estimate Here are 3 sweets 2/1 Know the 2, 3, 5, 10 times tables 0 x 2 = 0 1 x 2 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 3 x 2 = 6 4 x 2 = 8 5 x 2 = 10 6 x
SERIES Addition and Subtraction
 D Teacher Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic Section Addition Answers mental (pp. 48) strategies (pp. 4) look addition for a mental ten strategies_ look subtraction for patterns_ mental strategies
D Teacher Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic Section Addition Answers mental (pp. 48) strategies (pp. 4) look addition for a mental ten strategies_ look subtraction for patterns_ mental strategies
Number & Place Value: Read, write and represent numbers to 100 Learning focus when objects are rearranged the number remains the same.
 Number & Place Value: Read, write and represent numbers to 100 Learning focus when objects are rearranged the number remains the same. Look at the two sets of shapes. Is there the same number of shapes
Number & Place Value: Read, write and represent numbers to 100 Learning focus when objects are rearranged the number remains the same. Look at the two sets of shapes. Is there the same number of shapes
Counters in a Cup In and Out. The student sets up the cup, drops the counters on it, and records how many landed in and out of the cup.
 Counters in a Cup In and Out Cup Counters Recording Paper The student sets up the cup, drops the counters on it, and records how many landed in and out of the cup. 3 + 4 =7 2 + 5 =7 For subtraction, take
Counters in a Cup In and Out Cup Counters Recording Paper The student sets up the cup, drops the counters on it, and records how many landed in and out of the cup. 3 + 4 =7 2 + 5 =7 For subtraction, take
Hexagon Puzzle. four. ten three. eighteen. twenty-one. six. fourteen. twenty. one hundred. seventeen. sixteen. one quarter. two.
 Cut out the equilateral triangles along the dotted lines. Match the words to the numbers. Fit the triangles together to make one large hexagon. The shaded sections mark the edges of the hexagon. Stick
Cut out the equilateral triangles along the dotted lines. Match the words to the numbers. Fit the triangles together to make one large hexagon. The shaded sections mark the edges of the hexagon. Stick
Two-Digit Numbers. tens ones = tens ones = tens ones = 3 tens 5 ones = 35. tens ones = tens ones =
 Two-Digit Numbers Up to 10s Place Every two-digit whole number has a place and a place. This is how you show and using blocks. Count the blocks and blocks. Fill in the blanks. Then, write the numbers in
Two-Digit Numbers Up to 10s Place Every two-digit whole number has a place and a place. This is how you show and using blocks. Count the blocks and blocks. Fill in the blanks. Then, write the numbers in
Introduction. It gives you some handy activities that you can do with your child to consolidate key ideas.
 (Upper School) Introduction This booklet aims to show you how we teach the 4 main operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) at St. Helen s College. It gives you some handy activities
(Upper School) Introduction This booklet aims to show you how we teach the 4 main operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division) at St. Helen s College. It gives you some handy activities
Series. Student. Numbers. My name
 Series Student My name Copyright 2009 3P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 2009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from 3P Learning Ltd. ISN 978-1-921860-10-2
Series Student My name Copyright 2009 3P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 2009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from 3P Learning Ltd. ISN 978-1-921860-10-2
Numbers. Counting. Key Point. Key Point. Understand what a number is Count from 0 20 in numbers and words Count to 100
 Number - Number and Place Value Numbers and Counting Understand what a number is Count from 0 20 in numbers and words Count to 100 Numbers A number is a symbol used to count how many there are of something.
Number - Number and Place Value Numbers and Counting Understand what a number is Count from 0 20 in numbers and words Count to 100 Numbers A number is a symbol used to count how many there are of something.
Read, write, order and compare numbers to at least and determine the value of each digit.
 Number to 10,000 Roman numerals to 1,000 Round to the nearest 10, 100 and 1,000 Number to 100,000 Compare and order numbers to 100,000 Round numbers within 100,000 Numbers to a million Counting in 10s,
Number to 10,000 Roman numerals to 1,000 Round to the nearest 10, 100 and 1,000 Number to 100,000 Compare and order numbers to 100,000 Round numbers within 100,000 Numbers to a million Counting in 10s,
Year 1. Place Value. Term by Term Objectives. All students Fluency Reasoning Problem Solving. National Curriculum Statement
 National Curriculum Place Value Given a number, identify one more or one less. 9 2 Fill in the missing numbers. Is 1 less than Is 1 more than How many fingers if I put one down? I roll the number that
National Curriculum Place Value Given a number, identify one more or one less. 9 2 Fill in the missing numbers. Is 1 less than Is 1 more than How many fingers if I put one down? I roll the number that
Year 1. Using and applying mathematics. Framework review
 Year 1 Using and applying mathematics Solve problems involving counting, adding, subtracting, doubling or halving in the context of numbers, measures or money, for example to pay and give change I am going
Year 1 Using and applying mathematics Solve problems involving counting, adding, subtracting, doubling or halving in the context of numbers, measures or money, for example to pay and give change I am going
Addition and Subtraction
 Series Student Addition and Subtraction My name D Copyright 2009 3P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 2009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from 3P Learning
Series Student Addition and Subtraction My name D Copyright 2009 3P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 2009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from 3P Learning
Place Value. Get in Place. WRITE how many tens and ones you see. Then WRITE the number they make. 5 3 = 53
 Place Value Get in Place WRITE how many tens and ones you see. Then WRITE the number they make. 1. 2. 5 3 53 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 2 Place Value Get in Place 10 1 1 WRITE how many tens and ones you see. Then
Place Value Get in Place WRITE how many tens and ones you see. Then WRITE the number they make. 1. 2. 5 3 53 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 2 Place Value Get in Place 10 1 1 WRITE how many tens and ones you see. Then
Whole Numbers. Whole Numbers. Curriculum Ready.
 Curriculum Ready www.mathletics.com It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognize their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed when completing
Curriculum Ready www.mathletics.com It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognize their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed when completing
MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING
 MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING 0 1000 Mathematical relational skills and counting 0-1000 ThinkMath 2017 MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING 0 1000 The Mathematical relational skills
MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING 0 1000 Mathematical relational skills and counting 0-1000 ThinkMath 2017 MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING 0 1000 The Mathematical relational skills
Is muddled about the correspondence between multiplication and division facts, recording, for example: 3 5 = 15, so 5 15 = 3
 Is muddled about the correspondence between multiplication and division facts, recording, for example: 3 5 = 15, so 5 15 = 3 Opportunity for: recognising relationships Resources Board with space for four
Is muddled about the correspondence between multiplication and division facts, recording, for example: 3 5 = 15, so 5 15 = 3 Opportunity for: recognising relationships Resources Board with space for four
Meet the Characters 3. Yearly Overview 4. Block 1 Number: Multiplication and Division 5. Block 2 Measurement: Money 25. Block 3 Statistics 37
 1 Meet the Characters 3 Yearly Overview 4 Spring Blocks Block 1 Number: Multiplication and Division 5 Block 2 Measurement: Money 25 Block 3 Statistics 37 Block 4 Measurement: Length and Perimeter 45 Block
1 Meet the Characters 3 Yearly Overview 4 Spring Blocks Block 1 Number: Multiplication and Division 5 Block 2 Measurement: Money 25 Block 3 Statistics 37 Block 4 Measurement: Length and Perimeter 45 Block
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers
 E Student Book Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Thousands 1 Hundreds Tens 1 Units Name Series E Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Contents Topic 1 Looking at whole numbers (pp. 1 8) reading
E Student Book Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Thousands 1 Hundreds Tens 1 Units Name Series E Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Contents Topic 1 Looking at whole numbers (pp. 1 8) reading
Focus on Mathematics
 Focus on Mathematics Year 4 Pre-Learning Tasks Number Pre-learning tasks are used at the start of each new topic in Maths. The children are grouped after the pre-learning task is marked to ensure the work
Focus on Mathematics Year 4 Pre-Learning Tasks Number Pre-learning tasks are used at the start of each new topic in Maths. The children are grouped after the pre-learning task is marked to ensure the work
SERIES Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers
 F Teacher Student Book Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Name Contents Series F Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Section Looking Answers at whole (pp. ) numbers (pp. 8) read looking
F Teacher Student Book Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Name Contents Series F Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Section Looking Answers at whole (pp. ) numbers (pp. 8) read looking
Mathematics Third Practice Test A, B & C - Mental Maths. Mark schemes
 Mathematics Third Practice Test A, B & C - Mental Maths Mark schemes Introduction This booklet contains the mark schemes for the higher tiers tests (Tests A and B) and the lower tier test (Test C). The
Mathematics Third Practice Test A, B & C - Mental Maths Mark schemes Introduction This booklet contains the mark schemes for the higher tiers tests (Tests A and B) and the lower tier test (Test C). The
NS2-45 Skip Counting Pages 1-8
 NS2-45 Skip Counting Pages 1-8 Goals Students will skip count by 2s, 5s, or 10s from 0 to 100, and back from 100 to 0. Students will skip count by 5s starting at multiples of 5, and by 2s or 10s starting
NS2-45 Skip Counting Pages 1-8 Goals Students will skip count by 2s, 5s, or 10s from 0 to 100, and back from 100 to 0. Students will skip count by 5s starting at multiples of 5, and by 2s or 10s starting
Released January Years 3/4. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area
 Released January 208 Years 3/4 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area Year 3/4 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 3 Year 4 Measure length Equivalent lengths
Released January 208 Years 3/4 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area Year 3/4 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 3 Year 4 Measure length Equivalent lengths
GRADE 3 TEXAS. Subtraction WORKSHEETS
 GRADE 3 TEXAS Subtraction WORKSHEETS Subtraction mental strategies related facts Knowing one addition fact means you also know two related subtraction facts. Because 7 + 3 = 10 you also know that 10 7
GRADE 3 TEXAS Subtraction WORKSHEETS Subtraction mental strategies related facts Knowing one addition fact means you also know two related subtraction facts. Because 7 + 3 = 10 you also know that 10 7
Multiplication and Division
 E Student Book 6 7 = 4 Name Series E Contents Topic Multiplication facts (pp. 7) 5 and 0 times tables and 4 times tables 8 times table and 6 times tables Date completed Topic Using known facts (pp. 8 )
E Student Book 6 7 = 4 Name Series E Contents Topic Multiplication facts (pp. 7) 5 and 0 times tables and 4 times tables 8 times table and 6 times tables Date completed Topic Using known facts (pp. 8 )
Maths. Using numbers to carry out calculations and solve problems.
 Maths Using numbers to carry out calculations and solve problems. We want children to be confident manipulating numbers based on their visualisation of quantities. Which group has 30? Children often muddled
Maths Using numbers to carry out calculations and solve problems. We want children to be confident manipulating numbers based on their visualisation of quantities. Which group has 30? Children often muddled
ShillerMath Book 1 Test Answers
 LESSON 1-56 REVIEW TEST #1-1 Now we will have a test to see what you have learned. This will help me understand what I need to do to make our math work more fun. You may take as much time and use whatever
LESSON 1-56 REVIEW TEST #1-1 Now we will have a test to see what you have learned. This will help me understand what I need to do to make our math work more fun. You may take as much time and use whatever
Differentiated Activities by Cognitive Levels. Denise Rawding
 Differentiated Activities by Cognitive Levels Denise Rawding Counting Stations Possibilities 1) Containers filled with small objects and scraps of paper to write the numbers on. As students begin to work
Differentiated Activities by Cognitive Levels Denise Rawding Counting Stations Possibilities 1) Containers filled with small objects and scraps of paper to write the numbers on. As students begin to work
Job Cards and Other Activities. Write a Story for...
 Job Cards and Other Activities Introduction. This Appendix gives some examples of the types of Job Cards and games that we used at the Saturday Clubs. We usually set out one type of card per table, along
Job Cards and Other Activities Introduction. This Appendix gives some examples of the types of Job Cards and games that we used at the Saturday Clubs. We usually set out one type of card per table, along
NS3 Part 1: BLM List. Workbook 3 - Number Sense, Part 1 1 BLACKLINE MASTERS
 NS3 Part 1: BLM List Adding or Trading Game 2 Addition Rummy Blank Cards 3 Addition Rummy Preparation 4 Addition Table (Ordered) 5 Arrays in the Times Tables 6 Counting by 5s 7 Crossword Without Clues
NS3 Part 1: BLM List Adding or Trading Game 2 Addition Rummy Blank Cards 3 Addition Rummy Preparation 4 Addition Table (Ordered) 5 Arrays in the Times Tables 6 Counting by 5s 7 Crossword Without Clues
Whole Numbers. Practice 1 Numbers to 10,000, ,000 four hundred thousand
 Name: Chapter 1 Date: Practice 1 Numbers to 10,000,000 Count on or back by ten thousands or hundred thousands. Then fill in the blanks. 1. 40,000 50,000 60,000 2. 900,000 800,000 700,000 Complete the table.
Name: Chapter 1 Date: Practice 1 Numbers to 10,000,000 Count on or back by ten thousands or hundred thousands. Then fill in the blanks. 1. 40,000 50,000 60,000 2. 900,000 800,000 700,000 Complete the table.
Use repeated addition to find the total number of fingers. Find the total of each group by using repeated addition. Multiplication and Division
 Introducing multiplication groups of 5 Use repeated addition to find the total number of fingers. 5 + 5 + 5 = 5 groups of 5 is equal to 5. Find the total of each group by using repeated addition. a How
Introducing multiplication groups of 5 Use repeated addition to find the total number of fingers. 5 + 5 + 5 = 5 groups of 5 is equal to 5. Find the total of each group by using repeated addition. a How
Hundreds Grid. MathShop: Hundreds Grid
 Hundreds Grid MathShop: Hundreds Grid Kindergarten Suggested Activities: Kindergarten Representing Children create representations of mathematical ideas (e.g., use concrete materials; physical actions,
Hundreds Grid MathShop: Hundreds Grid Kindergarten Suggested Activities: Kindergarten Representing Children create representations of mathematical ideas (e.g., use concrete materials; physical actions,
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers
 Series Student Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers My name D Copyright 2009 P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 2009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from
Series Student Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers My name D Copyright 2009 P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 2009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from
Number Sense Workbook 5, Part 1
 Number Sense Workbook 5, Part 1 page 1 Worksheet NS5-1 page 32 1. b) s c) s d) s e) ten s f) ten s g) hundreds h) tens i) hundreds j) ones k) ten s l) ones 2. a) s b) tens c) s d) ones e) ten s f) tens
Number Sense Workbook 5, Part 1 page 1 Worksheet NS5-1 page 32 1. b) s c) s d) s e) ten s f) ten s g) hundreds h) tens i) hundreds j) ones k) ten s l) ones 2. a) s b) tens c) s d) ones e) ten s f) tens
Year 5. Mathematics A booklet for parents
 Year 5 Mathematics A booklet for parents About the statements These statements show some of the things most children should be able to do by the end of Year 5. A statement might be harder than it seems,
Year 5 Mathematics A booklet for parents About the statements These statements show some of the things most children should be able to do by the end of Year 5. A statement might be harder than it seems,
Does not use partitioning to find double twelve or double thirty-five
 Does not use to find twelve or thirty-five Opportunity for: developing mental images Number cards 0 9 (Resource sheet 1) Doubling cards (Resource sheet 33) Counters/interlocking cubes Additional + cards
Does not use to find twelve or thirty-five Opportunity for: developing mental images Number cards 0 9 (Resource sheet 1) Doubling cards (Resource sheet 33) Counters/interlocking cubes Additional + cards
Fourth Grade Spiraling Review Week 1 of Second Six Weeks
 Week 1 of Second Six Weeks Advanced Preparation: See attachment Spiraling Review Cards Note: Record all work in your math journal. Day 1 Solve the following riddle. If you subtracted 3 ten thousands and
Week 1 of Second Six Weeks Advanced Preparation: See attachment Spiraling Review Cards Note: Record all work in your math journal. Day 1 Solve the following riddle. If you subtracted 3 ten thousands and
Multiplication and Division
 D Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic 1 Introducing multiplication (pp. 1 7) groups of 5 5 times table 10 times table multiplying any number by 10 multiplying numbers by 0 and 1 Date completed Topic
D Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic 1 Introducing multiplication (pp. 1 7) groups of 5 5 times table 10 times table multiplying any number by 10 multiplying numbers by 0 and 1 Date completed Topic
Year 6 Spring Term Week 10 to 11 Number: Ratio
 1 Using ratio language Ratio and fractions Introducing the ratio symbol Calculating ratio Using scale factors Calculating scale factors Ratio and proportion problems Solve problems involving the relative
1 Using ratio language Ratio and fractions Introducing the ratio symbol Calculating ratio Using scale factors Calculating scale factors Ratio and proportion problems Solve problems involving the relative
Please make sure that you print this resource at 100% so that all measurements are correct. To do this, follow the relevant steps below.
 Please make sure that you print this resource at 00% so that all measurements are correct. To do this, follow the relevant steps below. Adobe Reader or Adobe Acrobat Adobe Reader is a free PDF viewer,
Please make sure that you print this resource at 00% so that all measurements are correct. To do this, follow the relevant steps below. Adobe Reader or Adobe Acrobat Adobe Reader is a free PDF viewer,
Whole Numbers WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT.
 WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT www.mathletics.co.uk It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognise their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed
WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT www.mathletics.co.uk It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognise their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed
Important Words in Mathematics
 1 P a g e Important Words in Mathematics... 2 Numbers... 3 Number Words... 4 EVEN OR ODD... 5 PLACE VALUE... 6 PLACE VALUE... 7 VALUE... 8 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 9 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 10
1 P a g e Important Words in Mathematics... 2 Numbers... 3 Number Words... 4 EVEN OR ODD... 5 PLACE VALUE... 6 PLACE VALUE... 7 VALUE... 8 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 9 GREATER THAN OR LESS THAN... 10
MATHEMATICS. Y4 Counting and Understanding Number 4207 Use decimal notation. Order decimal fractions. Equipment
 MATHEMATICS Y4 Counting and Understanding Number 4207 Use decimal notation. Order decimal fractions. Paper, pencil, ruler Calculator Equipment Maths Go Go Go 4207 Use decimal notation Order decimal fractions
MATHEMATICS Y4 Counting and Understanding Number 4207 Use decimal notation. Order decimal fractions. Paper, pencil, ruler Calculator Equipment Maths Go Go Go 4207 Use decimal notation Order decimal fractions
Lesson 1. Numbers Large and Small. Let s Explore
 Math 5 Lesson 1 Numbers Large and Small Let s Explore Exploration 1: Create Large Numbers Materials: 2 sets number cards (0-9) 1. Mix the card sets and place them face down in a stack. Draw three cards
Math 5 Lesson 1 Numbers Large and Small Let s Explore Exploration 1: Create Large Numbers Materials: 2 sets number cards (0-9) 1. Mix the card sets and place them face down in a stack. Draw three cards
Fraction Race. Skills: Fractions to sixths (proper fractions) [Can be adapted for improper fractions]
![Fraction Race. Skills: Fractions to sixths (proper fractions) [Can be adapted for improper fractions] Fraction Race. Skills: Fractions to sixths (proper fractions) [Can be adapted for improper fractions]](/thumbs/84/89643749.jpg) Skills: Fractions to sixths (proper fractions) [Can be adapted for improper fractions] Materials: Dice (2 different colored dice, if possible) *It is important to provide students with fractional manipulatives
Skills: Fractions to sixths (proper fractions) [Can be adapted for improper fractions] Materials: Dice (2 different colored dice, if possible) *It is important to provide students with fractional manipulatives
Year 1 Autumn 1 Progress check
 Year 1 Autumn 1 Progress check Marking guidance NC objective in a year below NC objective in a year above * Key question Qu. National curriculum objectives Progression map outcome Answers Marks Possible
Year 1 Autumn 1 Progress check Marking guidance NC objective in a year below NC objective in a year above * Key question Qu. National curriculum objectives Progression map outcome Answers Marks Possible
Example: I predict odd, roll a 5, and then collect that many counters. Play until time is up. The player with the most counters wins.
 Odds and Evens Skill: Identifying even and odd numbers Materials: 1 die to share 1. Each player takes 5 counters and puts the rest in a pile between them. 2. Player 1 predicts whether he will roll ODD
Odds and Evens Skill: Identifying even and odd numbers Materials: 1 die to share 1. Each player takes 5 counters and puts the rest in a pile between them. 2. Player 1 predicts whether he will roll ODD
Series. Student. Numbers. My name
 Series Student My name opyright 009 P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from P Learning Ltd. ISBN 978--9860--9 Ownership
Series Student My name opyright 009 P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from P Learning Ltd. ISBN 978--9860--9 Ownership
MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING 0 20
 MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING 0 20 Mathematical relational skills and counting 0-20 ThinkMath 2016 MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING 0 20 The Mathematical relational skills and
MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING 0 20 Mathematical relational skills and counting 0-20 ThinkMath 2016 MATHEMATICAL RELATIONAL SKILLS AND COUNTING 0 20 The Mathematical relational skills and
7 + 1 = = = = 5 = 3
 Name MENTAL MATHS Addition & Subtraction 1 1 11 1 1 + 1 = = + 11 = = 1 + = = + 1 = = + 1 = = + + 1 = 1 = = + 1 = = + + = = = 1 + = = + 1 = = Number & Place Value 1 Loop groups of. Then write the total.
Name MENTAL MATHS Addition & Subtraction 1 1 11 1 1 + 1 = = + 11 = = 1 + = = + 1 = = + 1 = = + + 1 = 1 = = + 1 = = + + = = = 1 + = = + 1 = = Number & Place Value 1 Loop groups of. Then write the total.
Maths CAPS. Counting. Fill in the missing numbers: Counts forward and backward in 1s, 2s, 3s, 4s, 5s and 10s from any number between 0 and 200.
 Counting Practise counting in multiples of 1s, 2s, 3s, 4s, 5s, and 10s with learners aloud together regularly. As multiples are counted, point out each number for learners to see on a hundreds chart. a
Counting Practise counting in multiples of 1s, 2s, 3s, 4s, 5s, and 10s with learners aloud together regularly. As multiples are counted, point out each number for learners to see on a hundreds chart. a
Pair counting. Maths focus: Counting on in ones, tens or hundreds from any number. What you need: Instructions
 Cambridge University Press 978-1-107-69401-9 Cambridge Primary Mathematics Stage 3 Cherri Moseley and Janet Rees Excerpt More information Place value games Largest and smallest Maths focus: To understand
Cambridge University Press 978-1-107-69401-9 Cambridge Primary Mathematics Stage 3 Cherri Moseley and Janet Rees Excerpt More information Place value games Largest and smallest Maths focus: To understand
Number Sense 1 AP Book 3.1
 Number Sense 1 AP Book 3.1 page 1 AP Book NS3-1 page 33 1. a) ones b) ones c) tens d) ones e) hundreds f) ones g) tens h) ones i) hundreds j) ones 2. a) tens b) ones c) tens d) hundreds e) ones f) hundreds
Number Sense 1 AP Book 3.1 page 1 AP Book NS3-1 page 33 1. a) ones b) ones c) tens d) ones e) hundreds f) ones g) tens h) ones i) hundreds j) ones 2. a) tens b) ones c) tens d) hundreds e) ones f) hundreds
Free Math print & Go Pages and centers. Created by: The Curriculum Corner.
 Free Math print & Go Pages and centers Created by: The Curriculum Corner 1 x 3 9 x 9 4 x 5 6 x 7 2 x 1 3 x 7 8 x 4 5 x 9 4 x 6 8 x 8 7 x 2 9 x 3 1 x 5 4 x 4 8 x 3 4 x 8 8 x 10 5 x 5 1 x 8 4 x 3 6 x 6 8
Free Math print & Go Pages and centers Created by: The Curriculum Corner 1 x 3 9 x 9 4 x 5 6 x 7 2 x 1 3 x 7 8 x 4 5 x 9 4 x 6 8 x 8 7 x 2 9 x 3 1 x 5 4 x 4 8 x 3 4 x 8 8 x 10 5 x 5 1 x 8 4 x 3 6 x 6 8
California 1 st Grade Standards / Excel Math Correlation by Lesson Number
 California 1 st Grade Standards / Excel Math Correlation by Lesson Lesson () L1 Using the numerals 0 to 9 Sense: L2 Selecting the correct numeral for a Sense: 2 given set of pictures Grouping and counting
California 1 st Grade Standards / Excel Math Correlation by Lesson Lesson () L1 Using the numerals 0 to 9 Sense: L2 Selecting the correct numeral for a Sense: 2 given set of pictures Grouping and counting
Second Grade Fourth Nine- Week Study Guide
 Second Grade Fourth Nine- Week Study Guide Use the study guide to help prepare your child for the fourth nine-week math assessment. The following standards will be assessed on this test. 2.G.1 1. Tom drew
Second Grade Fourth Nine- Week Study Guide Use the study guide to help prepare your child for the fourth nine-week math assessment. The following standards will be assessed on this test. 2.G.1 1. Tom drew
a) Draw half the number of shapes in the picture. b) Draw one third of the number of shapes in the picture.
 MEP Primary Practice Book Yb ANSWERS a) Draw half the number of shapes in the picture. b) Draw one third of the number of shapes in the picture. c) Draw one quarter of the number of shapes in the picture.
MEP Primary Practice Book Yb ANSWERS a) Draw half the number of shapes in the picture. b) Draw one third of the number of shapes in the picture. c) Draw one quarter of the number of shapes in the picture.
E X P L O R I N G. Bev Dunbar E X P L O R I N G M A T H S. Activities, blackline masters & assessment pages that are fun and easy to use
 E X P L O R I N G M A T H S E X P L O R I N G Numeration Bev Dunbar Activities, blackline masters & assessment pages that are fun and easy to use N U M B E R L O W E R P R I M A R Y 6 Exploring 0-100 Numeration
E X P L O R I N G M A T H S E X P L O R I N G Numeration Bev Dunbar Activities, blackline masters & assessment pages that are fun and easy to use N U M B E R L O W E R P R I M A R Y 6 Exploring 0-100 Numeration
Reception Year 1. Counting. Bournmoor Primary School Overview of Strategies and Methods - Counting. How many in a set?
 Counting Overview of Strategies and Methods - Counting How many in a set? How many in a set? Estimate, and encourage estimation, within a range Seven hand claps Estimate, and encourage estimation, within
Counting Overview of Strategies and Methods - Counting How many in a set? How many in a set? Estimate, and encourage estimation, within a range Seven hand claps Estimate, and encourage estimation, within
Teacher Sourcebook. Sample Unit. Authors Rosemary Reuille Irons M Sc Brian Tickle BA James Burnett M Ed
 Teacher Sourcebook Sample Unit Authors Rosemary Reuille Irons M Sc Brian Tickle BA James Burnett M Ed Series Consultants Judith Anderson Ph D Jan Glazier MA Bruce Llewellyn B Sc Counting On Basic Facts
Teacher Sourcebook Sample Unit Authors Rosemary Reuille Irons M Sc Brian Tickle BA James Burnett M Ed Series Consultants Judith Anderson Ph D Jan Glazier MA Bruce Llewellyn B Sc Counting On Basic Facts
Day 1. Mental Arithmetic Questions KS3 MATHEMATICS. 60 X 2 = 120 seconds. 1 pm is 1300 hours So gives 3 hours. Half of 5 is 2.
 Mental Arithmetic Questions. The tally chart shows the number of questions a teacher asked in a lesson. How many questions did the teacher ask? 22 KS MATHEMATICS 0 4 0 Level 4 Answers Day 2. How many seconds
Mental Arithmetic Questions. The tally chart shows the number of questions a teacher asked in a lesson. How many questions did the teacher ask? 22 KS MATHEMATICS 0 4 0 Level 4 Answers Day 2. How many seconds
4 One ticket costs What will four tickets cost? 17.50
 TOP TEN Set X TEST 1 1 Multiply 6.08 by one thousand. 2 Write one quarter as a decimal. 3 35% of a number is 42. What is 70% of the number? 4 One ticket costs 17.50. What will four tickets cost? 17.50
TOP TEN Set X TEST 1 1 Multiply 6.08 by one thousand. 2 Write one quarter as a decimal. 3 35% of a number is 42. What is 70% of the number? 4 One ticket costs 17.50. What will four tickets cost? 17.50
Reception. Year 1. Counting. Overview of strategies and methods Counting. How many in a set? How many in a set?
 Overview of strategies and methods Counting How many in a set? How many in a set? Estimate, and encourage estimation, within a range Counting Estimate, and encourage estimation, within a range Seven hand
Overview of strategies and methods Counting How many in a set? How many in a set? Estimate, and encourage estimation, within a range Counting Estimate, and encourage estimation, within a range Seven hand
Four mice have found a lump of cheese. Draw where they should cut it so that they each have an equal amount. Each mouse has of the c
 MEP Primary Practice Book Y2b a) Draw half the number of shapes in the picture. b) Draw one third of the number of shapes in the picture. c) Draw one quarter of the number of shapes in the picture. 2 There
MEP Primary Practice Book Y2b a) Draw half the number of shapes in the picture. b) Draw one third of the number of shapes in the picture. c) Draw one quarter of the number of shapes in the picture. 2 There
Multiplication and Division
 Series D Student My name Multiplication and Division Copyright 2009 3P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 2009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from 3P Learning
Series D Student My name Multiplication and Division Copyright 2009 3P Learning. All rights reserved. First edition printed 2009 in Australia. A catalogue record for this book is available from 3P Learning
Roll & Make. Represent It a Different Way. Show Your Number as a Number Bond. Show Your Number on a Number Line. Show Your Number as a Strip Diagram
 Roll & Make My In Picture Form In Word Form In Expanded Form With Money Represent It a Different Way Make a Comparison Statement with a Greater than Your Make a Comparison Statement with a Less than Your
Roll & Make My In Picture Form In Word Form In Expanded Form With Money Represent It a Different Way Make a Comparison Statement with a Greater than Your Make a Comparison Statement with a Less than Your
Answers Solving mathematical problems
 Solving mathematical problems 1 in the middle (p.8) Many answers are possible, for example: 10, 11, 1, 13, 14 (on in steps of 1) 14, 13, 1, 11, 10 (back in steps of 1) 8, 10, 1, 14, 16 (on in steps of
Solving mathematical problems 1 in the middle (p.8) Many answers are possible, for example: 10, 11, 1, 13, 14 (on in steps of 1) 14, 13, 1, 11, 10 (back in steps of 1) 8, 10, 1, 14, 16 (on in steps of
Lesson 1: Place Value of Whole Numbers. Place Value, Value, and Reading Numbers in the Billions
 Place Value of Whole Numbers Lesson 1: Place Value, Value, and Reading Numbers in the Billions Jul 15 9:37 PM Jul 16 10:55 PM Numbers vs. Digits Let's begin with some basic vocabulary. First of all, what
Place Value of Whole Numbers Lesson 1: Place Value, Value, and Reading Numbers in the Billions Jul 15 9:37 PM Jul 16 10:55 PM Numbers vs. Digits Let's begin with some basic vocabulary. First of all, what
N Strand. The World of Numbers
 N Strand The World of Numbers WORLD OF NUMBERS INTRODUCTION Numbers are among the most important things that mathematics (at all levels) is about. Mathematicians are interested in numbers just as astronomers
N Strand The World of Numbers WORLD OF NUMBERS INTRODUCTION Numbers are among the most important things that mathematics (at all levels) is about. Mathematicians are interested in numbers just as astronomers
Put these numbers in order from smallest to largest.
 1 Put these numbers in order from smallest to largest. a. 4 9 7 6 b. 11 7 9 1 4 c. 8 0 7 4 1 6 Read the Warm-Up activity page to your students. SAY: Put these numbers in order from smallest to largest.
1 Put these numbers in order from smallest to largest. a. 4 9 7 6 b. 11 7 9 1 4 c. 8 0 7 4 1 6 Read the Warm-Up activity page to your students. SAY: Put these numbers in order from smallest to largest.
