Read, write, order and compare numbers to at least and determine the value of each digit.
|
|
|
- Harold Lloyd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Number to 10,000 Roman numerals to 1,000 Round to the nearest 10, 100 and 1,000 Number to 100,000 Compare and order numbers to 100,000 Round numbers within 100,000 Numbers to a million Counting in 10s, 100s, 1,000s, 10,000s and 100,000s Compare and order numbers to a million Round numbers to a million Negative numbers Read, write, order and compare numbers to at least and determine the value of each digit. Count forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10 for any given number up to Interpret negative numbers in context, count forwards and backwards with positive and negative whole numbers including through zero. Round any number up to to the nearest 10, 100, 1000, and Solve number problems and practical problems that involve all of the above. Read Roman numerals to 1000 (M) and recognise years written in Roman numerals.
3 Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Children use concrete manipulatives and pictorial diagrams to recap representing numbers up to 10,000 Match the diagram to the number. Within this step, ensure children revise adding and subtracting 10, 100 and 1,000 and discuss what is happening to the place value columns ,005 3,000 4,005 4,500 4,050 Which diagram is the odd one out? 5,000 Show me 8,045 in three different ways. 5 Do you prefer to use concrete objects or draw an image pictorially? Why? 5,000 6, Make 1,500 and explain why you chose to make it this way (use this to see what concrete objects children choose to use) Complete the table. 2,506 7,999 Add 10 Add 100 Add 1,000 6,070
4 Year 5 Autumn Term Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Numbers to 10,000 Reasoning and Problem Solving Harriet has made five numbers, using the digits 1, 2, 3 and 4 She has changed each number into a letter. Her numbers are: 1) 44,213 2) 43,123 3) 13,424 4) 31,413 5) 21,442 Simon says he can order the following numbers by only looking at the first three digits. 12,516 12,679 12,832 He is incorrect because two of the numbers start with twelve thousand, five hundred therefore you need to look at the tens to compare and order. 1) aabdc 2) acdbc 3) dcaba 4) cdadc 5) bdaab 12,538 Is he correct? Explain your answer. 12,794 Here are three clues to work out her numbers: Number 1 is the greatest number. The digits in number 4 total 12 Number 3 is the smallest number.
5 Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Building on their Y4 knowledge of Roman Numerals to 100, children explore Roman Numerals to 1,000. They explore what is the same and what is different between the number systems, for example there is no zero. Teachers could introduce writing the date in Roman Numerals to revise the concept on a daily basis. Lollipop stick activity. The teacher shouts out a number and the children make it with lollipop sticks. Children could also do this in pairs or groups, and for a bit of fun they could test the teacher! Each diagram shows a number in numerals, words and roman numerals. 500 five hundred CCCII Why is there no zero in the Roman numerals? What might it look like? Do you notice any patterns? Look at 30 and 300 How can you check you have represented the Roman numeral correctly? Complete the diagrams. Complete the function machines. CCC +10 1,000 1 DCLXXV
6 Year 5 Autumn Term Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Roman Numerals Reasoning and Problem Solving Solve CCCL + CL = How many calculations, using Roman Numerals, can you write to get the same total? Possible answers: CD + C = D M II = D C + CC + CC = D C V = D Here is part of a Roman Numeral hundred square. Complete the missing values. XLIV XLV XLVII LVI LVII LXIV LXVI LXVII What patterns do you notice?
7 Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Children build on their Year 4 knowledge of rounding to 10, 100 and 1,000. They need to experience rounding up to and within 10,000. Complete the table. Start number Rounded to the nearest 10 Rounded to the nearest 100 Rounded to the nearest 1,000 They need to understand that the column from the question and the column to the right of it are used e.g. round 1,450 to the nearest hundred look at the hundred and tens column DCCLXIX Which place value column do we need to look at when we round the nearest 1,000? When is it best to round to 10? 100? 1,000? Can you give an example of this? Can you justify your reasoning? Is there more than one solution? Will the answers to the nearest 100 and 1,000 be the same or different for the different start numbers? For each number, find five numbers that round to it when rounding to the nearest 100 Complete the table. Start number Nearest 10 Nearest 100 Nearest 1, , ,000 8,900 4,770
8 Year 5 Autumn Term Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Round to 10, 100 and 1,000 Reasoning and Problem Solving My number rounded to the nearest 10 is 1,150 Rounded to the nearest 100 it is 1,200 Rounded to the nearest 1,000 it is 1,000 Nathan 1,150 1,151 1,152 1,153 1,154 2,567 to the nearest 100 is 2,500 Do you agree with Alya? Alya I do not agree with Alya because 2,567 rounded to the nearest 100 is 2,600 I know this because the rule of a tens ending in 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 round up. What could Nathan s number be? Explain why. Can you find all of the possibilities? Regan 4,725 to the nearest 1,000 is 5,025 Explain the mistake Regan has made. Regan has correctly changed four thousand to five thousand but has added the tens and ones back on. When rounded to the nearest thousand, the hundreds, tens and ones will be zeros.
9 Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Children focus on numbers up to 100,000. They represent numbers on a place value grid, read and write numbers and place them on a number line to 100,000. A number is shown in the place value chart. 10,000s 1,000s 100s 10s 1s Using a number line, they find numbers between two points, place a number and estimate where larger numbers will be. Write the number is figures and in words. Ashy adds 10 to this number Zack adds 100 to this number Isobel adds 1,000 to this number Write each of their new numbers in figures and in words. How can we estimate a number on a number line if there are no divisions? Complete the grid to show the same number in different ways. Counters Part-whole model How many digits change when you add 10, 100 or 1000? Do you need to count forwards and backwards to find out if a number is in a number sequence? Explain. Bar model 65,048 Complete the missing numbers. 59,000 = 50, = 30, , ,480 = Number line
10 Year 5 Autumn Term Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Numbers to 100,000 Reasoning and Problem Solving Here is a number line. What is the value of A? B is 40 less than A. What is the value of B? A = 2,700 B = 2,660 Jennie counts forwards and backwards in 10s from 317 Circle the numbers Jennie will count ,666 3,210 5, , C is 500 less than B. Add C to the number line. Here are three ways of partitioning 27, thousands, 650 ones 27 thousands, 5 hundreds and 150 ones 27 thousands and 65 tens Write three more ways Possible answers: 27 thousands, 6 hundreds and 5 tens 27 thousands, 7 thousands and 650 ones 20 thousands, 7 thousands and 650 ones Explain why Jennie will not say the other numbers. Any positive number will always have to end in a 7 Any negative number will always have to end in a 3
11 Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Building on their learning from Year 4 children will compare and order numbers up to 100,000 Children should be able to do this with numbers presented in a variety of ways. Order the following ,130 31,202 10,000s 1,000s 100s 10s 1s Add the symbols <, > and = to make the statements correct. MMXVII , In order to compare what do we need to know? What is the value of each digit? Use 6 counters to make five different 6 digit numbers. 10,000s 1,000s 100s 10s 1s What is the value of in this number? What is the value of the whole? Can you suggest other parts that make the whole? Can you write a story to support your part whole model? Order your numbers from greatest to smallest.
12 Year 5 Autumn Term Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Compare and Order to 100,000 Reasoning and Problem Solving Turn over digit cards 0-9 and select five. Make the greatest number possible and the smallest number possible. How do you know this is the greatest or smallest? Totally dependent on what cards are chosen e.g. 4, 9, 1, 3, 2 Smallest: 12,349 Greatest: 94,321 Using digit cards 0-9, create three different five-digit numbers that fit the following clues: The digit in the hundreds column and ones column has a difference of 2 The digit in the hundreds column and the ten thousands column has a difference of 2 The sum of all the digits totals 19 Possible answers: 81,604 41,608 58,321 18,325
13 Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Children continue with work on rounding now using numbers up to 100,000. They round to the nearest 10, 100, 1,000 and 10,000 Children use their knowledge of multiples to work out what numbers the number they are rounding sits between. Round 85,617 To the nearest 10 To the nearest 100 To the neatest 1,000 To the nearest 10,000 Round the distances to the nearest 1,000 miles. Destination Miles from Manchester airport New York Miles to the nearest 1,000 Sydney 10,562 Which place value column do we need to look at when we round the nearest 1000? Hong Kong 5,979 New Zealand 11,550 When is it best to round to 10? 100? 1,000? Can you give an example of this? Can you justify your reasoning? Complete the table. Rounded to the nearest 100 Start number Rounded to the nearest 1,000 15,999 28,647 56,099
14 Year 5 Autumn Term Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Round within 100,000 Reasoning and Problem Solving Round 59,996 to the nearest 1,000 Round 59,996 to the nearest 10,000 What do you notice about the answers? Can you think of three more numbers where the same thing would happen? Both numbers round to 60,000 Other examples: 19,721 to the nearest 1,000 and 10, to the nearest 10 and 100 Two five-digit numbers have a difference of 5 When they are both rounded to the nearest thousand, the difference is 1,000 What could the numbers be? Two numbers with a difference of two where the last three digits are between 495 and 504 e.g. 52,498 and 52,503 22,982 to the nearest 100 and 1,000
15 Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Children read, write and represent numbers to 1,000,000. Children need to see numbers represented with counters on a place value grid as well as drawing the counters. 100,000s 10,000s 1,000s 100s 10s 1s Use counters to make these numbers on the place value chart. 32, ,301 50,030 Can you say the numbers out loud? Complete the part whole diagrams. If one million is the whole, what could the parts be? Show me 800,500 in three different ways. Where do the commas go in the numbers? How else can the numbers be represented? Katya has the following number. 10,000s 1,000s 100s 10s 1s She adds 4 counters to the hundreds column. What is her new number?
16 Year 5 Autumn Term Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Numbers to a Million Reasoning and Problem Solving Show the value of the digit 7 in each of these numbers. 407,338 7,100,491 25,571 Explain how you know. 407,338: the value is 7 thousand. It is to the left of the hundreds column. 7,100,491: the value is 7 million. It is a 7-digit number and it is on the far left. This is where the millions column is. 25,571; the value is 7 tens. It is second from the right, next to the ones column. The bar models are showing a pattern. Draw the next three. Create your own pattern of bar models for a partner to continue.
17 Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Children complete number sequences and can describe the term to term rule in a sequence e.g. add ten each time. They count forwards and backwards in powers of ten up to 1,000,000 Complete the sequence..,., 2,., 22,..., 32,..,, 62 The rule for this sequence is: Circle and correct the mistake in each sequence. 7,875, 8,875, 9,875, 11,875, 12,875, 13, ,664, 764,664, 664,664, 554,664, 444,664. What happens to the pattern when you move into negative? What do you notice to the pattern when you compare sequences in 10 s, 100 s 1000 s etc? Here is a Gattegno chart showing 32, Cards Can you create a rule for the sequence? ,000-1, ,000-10,000 Give children a target number to make then let them choose a card. Children then need to adjust their number on the Gattengo chart.
18 Year 5 Autumn Term Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Counting in Powers of 10 Reasoning and Problem Solving Daniel writes the first five numbers of a sequence. They are 3,666, 4,666, 5,666, 6,666, 7,666 The 10 th term will be 15,332 because I will double the 5 th term. Daniel The answer would be 12,666 because it is adding 1,000 each time. He should have added 5,000 not double the 5 th term. I am counting in 10s from 184 I will include 224 Ella I am counting in 100s from 604 I will include 1,040 Max Ella has made a mistake. She is counting in 100s therefore the ones column should never change. Is he correct? Explain why. I am counting in 1,000s from 13 I will include 130,000 One person has made a mistake. Henry Identify who has made the mistake and explain how you know.
19 Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Children compare and order numbers up to 1,000,000 using comparison vocabulary and symbols. They use a number line to compare numbers and look at the importance of focusing on the column with the highest place value when comparing numbers. Put the number cards in order of size. 13,010 13,100 13,011 13,110 13,111 Estimate the value of A, B and C. A B C 0 1,000,000 In order to compare what do we need to know? What is the value of each digit? What is the value of in this number? What is the value of the whole? Can you suggest other parts that make the whole? Can you write a story to support your part whole model? Here is a table showing the population in areas of Yorkshire. Halifax 88,134 Brighouse 32,360 Leeds 720,492 Huddersfield 146,234 Wakefield 76,886 Bradford 531,200 Add <, > or = to make the statements correct. The population of Halifax is than the population of Wakefeild. Double the population of Brighouse is than the population of Halifax.
20 Year 5 Autumn Term Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Compare and Order to a Million Reasoning and Problem Solving The number covered by the splat is an odd number. When rounded to the nearest 10,000 it is 440,000 The sum of the digits is 23 Possible answers: 444, , ,502 Here are four number cards. 42,350 43,385 56,995 56,963 Four children take one each and say a clue. Max: 56,995 Ella: 42,350 Henry: 43,385 Kyra: 56,963 My number is 57,000 when rounded to the nearest 100 Max Ella My number has exactly three hundreds in it What could the number be? Can you find three possibilities? My number is 44,000 when rounded to the nearest thousand Henry Kyra My number is exactly 100 less than 57,043 Which card did each child have?
21 Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Children use up to 6 digit numbers to recap previous rounding and learn the new skill of rounding to nearest 100,000. They look at cases when rounding a number for a purpose, and in certain contexts, goes against the general rules of rounding. Round these populations to the nearest 100,000 City Population Leeds 720,492 Durham 87,599 Sheffield 512,827 Birmingham 992,000 Rounded to the nearest 100,000 How many digits does a million have? Partition these numbers. Show me. Which digits do you need to look at when rounding to the nearest 10? 100? 1000? 10,000? 100,000? How do you know which is the greatest value? Show me. Round 450,985 to the nearest ,000 10, ,000 At a festival, 218,712 people attend across the weekend. Tickets come in batches of 100,000 How many batches should the organisers buy? Explain why this goes against the rounding rule.
22 Year 5 Autumn Term Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Round within a Million Reasoning and Problem Solving The difference between two 3-digit numbers is two. When each number is rounded to the nearest 1,000 the difference between them is 1,000 What could the two numbers be? 499 and and 500 The difference between A and B rounded to the nearest 100 is 700 The difference between B and C rounded to the nearest 100 is 400 A, B and C are not multiples of 10 What could A, B and C be? A B = in the range of and including B has to be greater than 400 to complete B C = 400 Possible answer: A = 1,240 B = 506 C = 59
23 Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Children continue to explore negative numbers and their position on a number line. Here are three representations for negative numbers. They need to see and use negative numbers in contexts and be able to count back through zero What is the same and what is different about each representation? Do we include zero when counting backwards? Which is the coldest? Warmest? What was the temperature increase? Decrease? Estimate and label where 0, -12 and -20 will be on the number line Jane visits a zoo. The rainforest room has a temperature of 32 C The artic room has a temperature of -24 C Show the difference in the room temperatures on a number line.
24 Year 5 Autumn Term Week 1 to 3 Number: Place Value Negative Numbers Reasoning and Problem Solving True or False? The temperature outside is -5 degrees, the temperature inside is 25 degree. The difference is 20 degrees. Four less than minus six is minus two. 15 more than -2 is 13 Explain how you know if each statement is true or false. False the difference is 30 degrees because it is 5 degrees from -5 to 0. Added to 25 totals 30 False it is minus 10 because the steps are going further away from zero True Children may use concrete or pictorial resources to explain. Put these statements in order so that the answers are from smallest to greatest The difference between -24 and -76 The even number that is less than -18 but greater -22 The number that is half way between 40 and -50 The difference between -6 and Ordered: -20, -5, 13, 52
Updated October 2017
 Updated October 2017 Roman numerals to 100 Round to the nearest 10 Round to the nearest 100 Count in 1,000s 1,000s, 100s, 10s and 1s Partitioning Number line to 10,000 1,000 more or less Compare numbers
Updated October 2017 Roman numerals to 100 Round to the nearest 10 Round to the nearest 100 Count in 1,000s 1,000s, 100s, 10s and 1s Partitioning Number line to 10,000 1,000 more or less Compare numbers
Count in multiples of 6, 7, and Find 1000 more or less than a given number.
 Roman numerals to 100 Round to the nearest 10 Round to the nearest 100 Count in 1,000s 1,000s, 100s, 10s and 1s Partitioning Number line to 10,000 1,000 more or less Compare numbers Order numbers Round
Roman numerals to 100 Round to the nearest 10 Round to the nearest 100 Count in 1,000s 1,000s, 100s, 10s and 1s Partitioning Number line to 10,000 1,000 more or less Compare numbers Order numbers Round
Numbers to ten million Compare and order any number Round any numbers Negative numbers
 Numbers to ten million Compare and order any number Round any numbers Negative numbers Read, write, order and compare numbers up to 10,000,000 and determine the value of each digit. Round any whole number
Numbers to ten million Compare and order any number Round any numbers Negative numbers Read, write, order and compare numbers up to 10,000,000 and determine the value of each digit. Round any whole number
Focus on Mathematics
 Focus on Mathematics Year 4 Pre-Learning Tasks Number Pre-learning tasks are used at the start of each new topic in Maths. The children are grouped after the pre-learning task is marked to ensure the work
Focus on Mathematics Year 4 Pre-Learning Tasks Number Pre-learning tasks are used at the start of each new topic in Maths. The children are grouped after the pre-learning task is marked to ensure the work
Released October Year. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 4: Multiplication & Division
 Released October 2017 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Multiplication & Division Multiply and divide numbers mentally drawing upon known facts. Multiples Factors Common factors Prime numbers
Released October 2017 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Multiplication & Division Multiply and divide numbers mentally drawing upon known facts. Multiples Factors Common factors Prime numbers
Updated December Year. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 4: Multiplication & Division
 Updated December 2017 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Multiplication & Division Year 5 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Multiples Notes and Guidance Building on their times tables knowledge,
Updated December 2017 Year 5 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Multiplication & Division Year 5 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Multiples Notes and Guidance Building on their times tables knowledge,
Number: Number and Place Value with Reasoning
 count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Number: Number and Place Value with Reasoning +COUNTING Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 count
count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Number: Number and Place Value with Reasoning +COUNTING Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 count
Number: Number and Place Value with Reasoning
 count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Number: Number and Place Value with Reasoning +COUNTING Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 count
count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Number: Number and Place Value with Reasoning +COUNTING Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5 Year 6 count
Updated October 2017
 Updated October 2017 Count objects to 100 and read and write numbers in numerals and words Represent numbers to 100 Tens and ones with a part whole model Tens and ones using addition Use a place alue chart
Updated October 2017 Count objects to 100 and read and write numbers in numerals and words Represent numbers to 100 Tens and ones with a part whole model Tens and ones using addition Use a place alue chart
Read and write numbers to at least 100 in numerals and in words. Recognise the place value of each digit in a two digit number (tens, ones)
 Count objects to 100 and read and write numbers in numerals and words Represent numbers to 100 Tens and ones with a part whole model Tens and ones using addition Use a place alue chart Compare objects
Count objects to 100 and read and write numbers in numerals and words Represent numbers to 100 Tens and ones with a part whole model Tens and ones using addition Use a place alue chart Compare objects
Using only these cards below, what 4-digit 6500 numbers can you make that can be placed on this number line?
 8 Number lines Y4: Order and compare numbers beyond 1000 1. Find the values of x and y if: x y a) is zero and is 2000 b) is 4000 and is 5000 c) is 5600 and is 5700 d) is 9250 and is 9270. Were some parts
8 Number lines Y4: Order and compare numbers beyond 1000 1. Find the values of x and y if: x y a) is zero and is 2000 b) is 4000 and is 5000 c) is 5600 and is 5700 d) is 9250 and is 9270. Were some parts
Assessment Fourth Grade Day 11 Standard(s): 4.NBT.2
 Assessment Fourth Grade Day 11 Standard(s): 4.NBT.2 4.NBT.1: Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. 1. How
Assessment Fourth Grade Day 11 Standard(s): 4.NBT.2 4.NBT.1: Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. 1. How
Number lines. 1. Find the values of x and y if:
 8 Number lines Y4: Order and compare numbers beyond 1000 1. Find the values of x and y if: x y a) is zero and is 2000 b) is 4000 and is 5000 c) is 5600 and is 5700 d) is 9250 and is 9270. Were some parts
8 Number lines Y4: Order and compare numbers beyond 1000 1. Find the values of x and y if: x y a) is zero and is 2000 b) is 4000 and is 5000 c) is 5600 and is 5700 d) is 9250 and is 9270. Were some parts
Number. Place value. Vocabulary. Raphael has eight digit cards. He uses the cards to make two four-digit numbers. He uses each card only once.
 Cambridge Unive 978-1-107-61859-6 Cambridge Primary Mathematics Stage 6 Emma Low Excerpt More information Number Place value Vocabulary Raphael has eight digit cards. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 million: equal to
Cambridge Unive 978-1-107-61859-6 Cambridge Primary Mathematics Stage 6 Emma Low Excerpt More information Number Place value Vocabulary Raphael has eight digit cards. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 million: equal to
Whole Numbers. Practice 1 Numbers to 10,000, ,000 four hundred thousand
 Name: Chapter 1 Date: Practice 1 Numbers to 10,000,000 Count on or back by ten thousands or hundred thousands. Then fill in the blanks. 1. 40,000 50,000 60,000 2. 900,000 800,000 700,000 Complete the table.
Name: Chapter 1 Date: Practice 1 Numbers to 10,000,000 Count on or back by ten thousands or hundred thousands. Then fill in the blanks. 1. 40,000 50,000 60,000 2. 900,000 800,000 700,000 Complete the table.
Edexcel Functional Skills pilot. Maths Level 1. Working with whole numbers. 2 Ordering and comparing whole numbers 4
 Edexcel Functional Skills pilot Maths Level 1 Chapter 1 Working with whole numbers Section 1 Reading and writing whole numbers 2 2 Ordering and comparing whole numbers 4 3 Rounding 5 4 dding whole numbers
Edexcel Functional Skills pilot Maths Level 1 Chapter 1 Working with whole numbers Section 1 Reading and writing whole numbers 2 2 Ordering and comparing whole numbers 4 3 Rounding 5 4 dding whole numbers
Numeracy Warm Up. Introduction
 Numeracy Warm Up Introduction Numeracy Warm Up is a set of numeracy exercises that can be used for starters, main lessons and plenaries. It is aimed at Numeracy lessons covering National Curriculum Levels
Numeracy Warm Up Introduction Numeracy Warm Up is a set of numeracy exercises that can be used for starters, main lessons and plenaries. It is aimed at Numeracy lessons covering National Curriculum Levels
Sample pages. Skip Counting. Until we know the pattern of numbers, we can count on from the last answer. Skip count and write the numbers as you go.
 1:01 Skip Counting Until we know the pattern of numbers, we can from the last answer. When I count on, I my fingers. Skip count and write the numbers as you go. a Each time, three more. 3 6 b Each time,
1:01 Skip Counting Until we know the pattern of numbers, we can from the last answer. When I count on, I my fingers. Skip count and write the numbers as you go. a Each time, three more. 3 6 b Each time,
3Grade. Interactive Notebooks. Ideal for organizing information and applying learning. Perfect for addressing the needs of individual learners
 CD-104648 Interactive Notebooks 3Grade Ideal for organizing information and applying learning Perfect for addressing the needs of individual learners Includes step-by-step instructions for each page Great
CD-104648 Interactive Notebooks 3Grade Ideal for organizing information and applying learning Perfect for addressing the needs of individual learners Includes step-by-step instructions for each page Great
Addition 10=5+5. Vocabulary NB:H=hundreds/T=Tens/O=ones
 Addition Vocabulary NB:H=hundreds/T=Tens/O=ones number bonds, number line, add, more, plus, make, sum, total, altogether, double, how many more?, column addition, partition, counting on, efficient method,
Addition Vocabulary NB:H=hundreds/T=Tens/O=ones number bonds, number line, add, more, plus, make, sum, total, altogether, double, how many more?, column addition, partition, counting on, efficient method,
Year 1. Place Value. Term by Term Objectives. All students Fluency Reasoning Problem Solving. National Curriculum Statement
 National Curriculum Place Value Given a number, identify one more or one less. 9 2 Fill in the missing numbers. Is 1 less than Is 1 more than How many fingers if I put one down? I roll the number that
National Curriculum Place Value Given a number, identify one more or one less. 9 2 Fill in the missing numbers. Is 1 less than Is 1 more than How many fingers if I put one down? I roll the number that
Year 3. Term by Term Objectives. Year 3 Overview. Spring Autumn. Summer. Number: Place Value
 Year 3 Autumn Term by Term Objectives Year 3 Year 3 Overview Spring Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Multiplication and Division Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement
Year 3 Autumn Term by Term Objectives Year 3 Year 3 Overview Spring Autumn Number: Place Value Number: Multiplication and Division Number: Addition and Subtraction Number: Multiplication and Division Measurement
4. Subtracting an even number from another even number gives an odd number. 5. Subtracting an odd number from another odd number gives an even number
 Level A 1. What is 78 32? A) 48 B) 110 C) 46 D) 34 2. What is 57 19? A) 37 B) 38 C) 42 D) 32 3. What is 66 8? A) 58 B) 57 C) 52 D) 42 4. Subtracting an even number from another even number gives an odd
Level A 1. What is 78 32? A) 48 B) 110 C) 46 D) 34 2. What is 57 19? A) 37 B) 38 C) 42 D) 32 3. What is 66 8? A) 58 B) 57 C) 52 D) 42 4. Subtracting an even number from another even number gives an odd
Meet the Characters 3. Yearly Overview 4. Block 1 Number: Multiplication and Division 5. Block 2 Measurement: Money 25. Block 3 Statistics 37
 1 Meet the Characters 3 Yearly Overview 4 Spring Blocks Block 1 Number: Multiplication and Division 5 Block 2 Measurement: Money 25 Block 3 Statistics 37 Block 4 Measurement: Length and Perimeter 45 Block
1 Meet the Characters 3 Yearly Overview 4 Spring Blocks Block 1 Number: Multiplication and Division 5 Block 2 Measurement: Money 25 Block 3 Statistics 37 Block 4 Measurement: Length and Perimeter 45 Block
1 Place value (1) Quick reference. *for NRICH activities mapped to the Cambridge Primary objectives, please visit
 : Core activity 1.2 To 1000 Cambridge University Press 1A 1 Place value (1) Quick reference Number Missing numbers Vocabulary Which game is which? Core activity 1.1: Hundreds, tens and ones (Learner s
: Core activity 1.2 To 1000 Cambridge University Press 1A 1 Place value (1) Quick reference Number Missing numbers Vocabulary Which game is which? Core activity 1.1: Hundreds, tens and ones (Learner s
Patterns and Relationships
 Student ook Patterns and Relationships Name Series Patterns and Relationships Contents Topic Patterns and rules (pp. 6) l continuing patterns l repeating patterns l translating patterns l body patterns
Student ook Patterns and Relationships Name Series Patterns and Relationships Contents Topic Patterns and rules (pp. 6) l continuing patterns l repeating patterns l translating patterns l body patterns
Year 1 Spring Term Week 5 to 7 Number: Place Value (within 50)
 1 Numbers to 50 Tens and ones Represent numbers to 50 One more one less Compare objects within 50 Compare numbers within 50 Order numbers within 50 Count in 2s Count in 5s Count to 50 forwards and backwards,
1 Numbers to 50 Tens and ones Represent numbers to 50 One more one less Compare objects within 50 Compare numbers within 50 Order numbers within 50 Count in 2s Count in 5s Count to 50 forwards and backwards,
MATH NUMBER SENSE 3 Performance Objective Task Analysis Benchmarks/Assessment Students: 1. Students understand place value of whole numbers.
 Students: 1. Students understand place value of whole numbers. 1. Count, read, and write whole numbers to 10,000. Count to 10,000 Which numbers are whole numbers? Whole number 0, 15.3, 4/5, 8, 25 1/2 Count
Students: 1. Students understand place value of whole numbers. 1. Count, read, and write whole numbers to 10,000. Count to 10,000 Which numbers are whole numbers? Whole number 0, 15.3, 4/5, 8, 25 1/2 Count
Released November /2. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 4: Measurement - Money
 Released November 2017 1/2 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Measurement - Money Year 1/2 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 1 Year 2 Recognising coins Recognising notes Counting
Released November 2017 1/2 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 4: Measurement - Money Year 1/2 Autumn Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 1 Year 2 Recognising coins Recognising notes Counting
Sample pages. Multiples, factors and divisibility. Recall 2. Student Book
 52 Recall 2 Prepare for this chapter by attempting the following questions. If you have difficulty with a question, go to Pearson Places and download the Recall from Pearson Reader. Copy and complete these
52 Recall 2 Prepare for this chapter by attempting the following questions. If you have difficulty with a question, go to Pearson Places and download the Recall from Pearson Reader. Copy and complete these
NUMERATION AND NUMBER PROPERTIES
 Section 1 NUMERATION AND NUMBER PROPERTIES Objective 1 Order three or more whole numbers up to ten thousands. Discussion To be able to compare three or more whole numbers in the thousands or ten thousands
Section 1 NUMERATION AND NUMBER PROPERTIES Objective 1 Order three or more whole numbers up to ten thousands. Discussion To be able to compare three or more whole numbers in the thousands or ten thousands
Hundreds Grid. MathShop: Hundreds Grid
 Hundreds Grid MathShop: Hundreds Grid Kindergarten Suggested Activities: Kindergarten Representing Children create representations of mathematical ideas (e.g., use concrete materials; physical actions,
Hundreds Grid MathShop: Hundreds Grid Kindergarten Suggested Activities: Kindergarten Representing Children create representations of mathematical ideas (e.g., use concrete materials; physical actions,
MEP: Primary Project. R: Mental calculation C: Revision: numbers to Writing and ordering. Rounding E: Numbers up to 2000.
 R: Mental calculation C: Revision: numbers to. Writing and ordering. Rounding E: Numbers up to Week Lesson Plan Combinatorics In how many different ways can we write the word 'ONE' if we can read the letters
R: Mental calculation C: Revision: numbers to. Writing and ordering. Rounding E: Numbers up to Week Lesson Plan Combinatorics In how many different ways can we write the word 'ONE' if we can read the letters
Revised Elko County School District 2 nd Grade Math Learning Targets
 Elko County School District 2 nd Grade Math Learning Targets Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Elko County School District 2 nd Grade Math Learning Targets Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Year 1 Objectives: Number 1
 Year 1 Objectives: Number 1 Objective 1:Counting: to 1, forwards and backwards, from any given number Count on from to 2 Count on from to 5 Counting: to 1, forwards and backwards, from any given number
Year 1 Objectives: Number 1 Objective 1:Counting: to 1, forwards and backwards, from any given number Count on from to 2 Count on from to 5 Counting: to 1, forwards and backwards, from any given number
Whole Numbers. Lesson 1.1 Numbers to 10,000,000
 1 CHAPTER Whole Numbers Lesson 1.1 Numbers to 10,000,000 Fill in the table headings. Write Tens, Hundreds, Ten Thousands, or Hundred Thousands. Then write the number in word form and in standard form.
1 CHAPTER Whole Numbers Lesson 1.1 Numbers to 10,000,000 Fill in the table headings. Write Tens, Hundreds, Ten Thousands, or Hundred Thousands. Then write the number in word form and in standard form.
Warm ups PLACE VALUE How many different ways can you make the number 365?
 Warm ups How many different ways can you make the number 365? Write down all you know about the number 24. (It is up to the students to decide how they will display this. They can use numerals, unifix,
Warm ups How many different ways can you make the number 365? Write down all you know about the number 24. (It is up to the students to decide how they will display this. They can use numerals, unifix,
Use each digit card once to make the decimal number nearest to 20
 NUMBER Level 4 questions 1. Here is a number chart. Circle the smallest number on the chart that is a multiple of both 2 and 7 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95
NUMBER Level 4 questions 1. Here is a number chart. Circle the smallest number on the chart that is a multiple of both 2 and 7 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95
Targets - Year 3. By the end of this year most children should be able to
 Targets - Year 3 By the end of this year most children should be able to Read and write numbers up to 1000 and put them in order. Know what each digit is worth. Count on or back in tens or hundreds from
Targets - Year 3 By the end of this year most children should be able to Read and write numbers up to 1000 and put them in order. Know what each digit is worth. Count on or back in tens or hundreds from
Decimals on the Number Line
 Lesson 3.1 Decimals on the Number Line The number line below shows decimal values between 1.0 and 2.0. Which number does point P represent? A P B 1.0 2.0 Since the distance between 1.0 and 2.0 is divided
Lesson 3.1 Decimals on the Number Line The number line below shows decimal values between 1.0 and 2.0. Which number does point P represent? A P B 1.0 2.0 Since the distance between 1.0 and 2.0 is divided
MAKING MATHEMATICS COUNT
 MAKING MATHEMATICS COUNT By Kerry Dalton Using manipulatives from Early Years Foundation Stage to Year 6 10 minutes per day, in addition to the daily mathematics lesson Covers Early Years Foundation Stage
MAKING MATHEMATICS COUNT By Kerry Dalton Using manipulatives from Early Years Foundation Stage to Year 6 10 minutes per day, in addition to the daily mathematics lesson Covers Early Years Foundation Stage
Children to write number sentences Children to show jumps on laminated number line: Show the jumps on a number line as counting on e.
 Written Methods& Mental Methods & A D D I T I O N FOUNDATION STAGE YEAR 1 YEAR 2 Count with 1:1 correspondence Recognise numbers Count to 20 and beyond Write numbers Order numbers to 20 Know one more than
Written Methods& Mental Methods & A D D I T I O N FOUNDATION STAGE YEAR 1 YEAR 2 Count with 1:1 correspondence Recognise numbers Count to 20 and beyond Write numbers Order numbers to 20 Know one more than
SERIES Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers
 F Teacher Student Book Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Name Contents Series F Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Section Looking Answers at whole (pp. ) numbers (pp. 8) read looking
F Teacher Student Book Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Name Contents Series F Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Section Looking Answers at whole (pp. ) numbers (pp. 8) read looking
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
Year 3 Maths Coversheet Week 1 Beginning:
 Learning objectives for this block: Year 3 Maths Coversheet Week 1 Beginning: Number and place value count from 0 in multiples of 100; find 10 or 100 more or less than a given number recognise the place
Learning objectives for this block: Year 3 Maths Coversheet Week 1 Beginning: Number and place value count from 0 in multiples of 100; find 10 or 100 more or less than a given number recognise the place
Study Guide: 5.3 Prime/Composite and Even/Odd
 Standard: 5.1- The student will a) identify and describe the characteristics of prime and composite numbers; and b) identify and describe the characteristics of even and odd numbers. What you need to know
Standard: 5.1- The student will a) identify and describe the characteristics of prime and composite numbers; and b) identify and describe the characteristics of even and odd numbers. What you need to know
Year 1. Mastery Overview Autumn
 Mastery Overview Autumn SOL Overview As well as providing term by term overviews for the new as a Maths Hub we are aiming to support primary schools by providing more detailed Schemes of Learning, which
Mastery Overview Autumn SOL Overview As well as providing term by term overviews for the new as a Maths Hub we are aiming to support primary schools by providing more detailed Schemes of Learning, which
NUMBERS BEYOND Write the number names. (a) 287 (b) 199 (c) 304 (d) Write 26, 87, 19, 145, 52 in ascending order.
 1 NUMBERS BEYND 999 Let s recall... en ones (10 ones) en tens (10 tens) = = ne ten (1 ten) ne hundred (1 hundred) 1. Write the number names. (a) 287 (b) 199 (c) 304 (d) 888 2. Write 26 87 19 145 52 in
1 NUMBERS BEYND 999 Let s recall... en ones (10 ones) en tens (10 tens) = = ne ten (1 ten) ne hundred (1 hundred) 1. Write the number names. (a) 287 (b) 199 (c) 304 (d) 888 2. Write 26 87 19 145 52 in
KEY STAGE 1 NUMERACY PRESENTATION PLACE VALUE & THE NUMBER SYSTEM.
 KEY STAGE 1 NUMERACY PRESENTATION PLACE VALUE & THE NUMBER SYSTEM. LOOKING AT THE NUMBER SYSTEM. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 Our number
KEY STAGE 1 NUMERACY PRESENTATION PLACE VALUE & THE NUMBER SYSTEM. LOOKING AT THE NUMBER SYSTEM. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 Our number
g) 88 h) 19 i) 1512 j) 77 k) 95 l) 921 IV. Solve the given operations and write the answers in Roman numerals: a) = b) XLV V c) XLV + LV =
 ST. MICHAEL S JUNIOR SCHOOL Assignment Sub: Maths Class V Sec 2019-2020 Name: Roll No. Ch: Roman Numerals I. Fill in the blanks: a) Roman numerals, and are never repeated and subtracted. b) XL = 2 x. c)
ST. MICHAEL S JUNIOR SCHOOL Assignment Sub: Maths Class V Sec 2019-2020 Name: Roll No. Ch: Roman Numerals I. Fill in the blanks: a) Roman numerals, and are never repeated and subtracted. b) XL = 2 x. c)
Count in tens/hundreds/thousands from different start numbers. Count backwards.
 Getting Started Number Number and place value Class counting (1) Tell the class the counting you are going to be doing, e.g. counting in thousands starting from five- or six-digit numbers. Tell all the
Getting Started Number Number and place value Class counting (1) Tell the class the counting you are going to be doing, e.g. counting in thousands starting from five- or six-digit numbers. Tell all the
COLUMBIA FOUNDATION SR. SEC SCHOOL
 COLUMBIA FOUNDATION SR. SEC SCHOOL MATHS WORKSHEET NO. 1 KNOWING OUR NUMBERS 1) Write the Roman numeral for each of the following: a) 59 b) 95 c) 324 d) 67 e) 447 2) Write each of the following Roman numerals
COLUMBIA FOUNDATION SR. SEC SCHOOL MATHS WORKSHEET NO. 1 KNOWING OUR NUMBERS 1) Write the Roman numeral for each of the following: a) 59 b) 95 c) 324 d) 67 e) 447 2) Write each of the following Roman numerals
SERIES Addition and Subtraction
 D Teacher Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic Section Addition Answers mental (pp. 48) strategies (pp. 4) look addition for a mental ten strategies_ look subtraction for patterns_ mental strategies
D Teacher Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic Section Addition Answers mental (pp. 48) strategies (pp. 4) look addition for a mental ten strategies_ look subtraction for patterns_ mental strategies
GRADE 4 MATHS SYLLABUS - FIRST TERM SYLLABUS INSTAMATHS WKSHEET 1-14
 GRADE 4 MATHS SYLLABUS - FIRST TERM INSTAMATHS EXERCISES 1; 2; 3; 4; 4; 6; 7; 8; 9; 10; 11; 12; 13; 14; 15; 16; 17; 50; 51; 54; 55; 56; 57; 58; 60; 61; 73; 90;; 92 SYLLABUS INSTAMATHS WKSHEET 1-14 TEXT
GRADE 4 MATHS SYLLABUS - FIRST TERM INSTAMATHS EXERCISES 1; 2; 3; 4; 4; 6; 7; 8; 9; 10; 11; 12; 13; 14; 15; 16; 17; 50; 51; 54; 55; 56; 57; 58; 60; 61; 73; 90;; 92 SYLLABUS INSTAMATHS WKSHEET 1-14 TEXT
Mathematics Success Grade 8
 Mathematics Success Grade 8 T429 [OBJECTIVE] The student will solve systems of equations by graphing. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] solving equations [MATERIALS] Student pages S207 S220 Rulers [ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS]
Mathematics Success Grade 8 T429 [OBJECTIVE] The student will solve systems of equations by graphing. [PREREQUISITE SKILLS] solving equations [MATERIALS] Student pages S207 S220 Rulers [ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS]
3rd Grade. Slide 1 / 268. Slide 2 / 268. Slide 3 / 268. Place Value. Table of Contents Place Value
 Slide 1 / 268 Slide 2 / 268 3rd Grade Place Value 2015-12-14 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 268 - Place Value click on the topic to go to that section - Standard, Numeric and Expanded Forms
Slide 1 / 268 Slide 2 / 268 3rd Grade Place Value 2015-12-14 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 268 - Place Value click on the topic to go to that section - Standard, Numeric and Expanded Forms
3rd Grade Place Value
 Slide 1 / 268 Slide 2 / 268 3rd Grade Place Value 2015-12-14 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 268 Table of Contents - Place Value click on the topic to go to that section - Standard, Numeric and Expanded Forms
Slide 1 / 268 Slide 2 / 268 3rd Grade Place Value 2015-12-14 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 268 Table of Contents - Place Value click on the topic to go to that section - Standard, Numeric and Expanded Forms
ShillerMath Book 1 Test Answers
 LESSON 1-56 REVIEW TEST #1-1 Now we will have a test to see what you have learned. This will help me understand what I need to do to make our math work more fun. You may take as much time and use whatever
LESSON 1-56 REVIEW TEST #1-1 Now we will have a test to see what you have learned. This will help me understand what I need to do to make our math work more fun. You may take as much time and use whatever
find more or less than a given number find 10 or 100 more or less than a given number
 count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Number: Number and Place Value COUNTING Consolidate count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning
count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number Number: Number and Place Value COUNTING Consolidate count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning
Place value disks activity: learn addition and subtraction with large numbers
 Place value disks activity: learn addition and subtraction with large numbers Our place value system can be explained using Singapore Math place value disks and 2 mats. The main rule is: value depends
Place value disks activity: learn addition and subtraction with large numbers Our place value system can be explained using Singapore Math place value disks and 2 mats. The main rule is: value depends
S P R I N G B O A R D 5 S P R I N G B O A R D UNIT SUPPLEMENTARY TEACHING SEQUENCES
 TEACHING SEQUENCES Springboard supplementary Unit SEQUENCE 1 Multiplication sequence RESOURCES: ITP Multiplication Facts (on the accompanying CD-ROM in ITPs Index) or board where arrays can be constructed
TEACHING SEQUENCES Springboard supplementary Unit SEQUENCE 1 Multiplication sequence RESOURCES: ITP Multiplication Facts (on the accompanying CD-ROM in ITPs Index) or board where arrays can be constructed
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy
 The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
The Willows Primary School Mental Mathematics Policy The Willows Primary Mental Maths Policy Teaching methodology and organisation Teaching time All pupils will receive between 10 and 15 minutes of mental
Naming Dollars and Cents Exchanging Dollars, Dimes, and Pennies
 LESSON 21 page 114 Name Naming Dollars and Cents Exchanging Dollars, Dimes, and Pennies Teacher Note: Refer students to Money on page 4 in the Student Reference Guide New Concepts Naming Dollars and Cents
LESSON 21 page 114 Name Naming Dollars and Cents Exchanging Dollars, Dimes, and Pennies Teacher Note: Refer students to Money on page 4 in the Student Reference Guide New Concepts Naming Dollars and Cents
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers
 Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Student Book Series D Mathletics Instant Workbooks Copyright Contents Series D Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Looking at whole numbers reading and
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Student Book Series D Mathletics Instant Workbooks Copyright Contents Series D Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Topic Looking at whole numbers reading and
ON A ROLL TO FACT FLUENCY
 Box Cars and One-Eyed Jacks ON A ROLL TO FACT FLUENCY PRIMARY MATH GAMES JOHN FELLING MPTCA 2016 john@boxcarsandoneeyedjacks.com phone 1-866-342-3386 / 1-780-440-6284 boxcarsandoneeyedjacks.com BoxCarsEduc
Box Cars and One-Eyed Jacks ON A ROLL TO FACT FLUENCY PRIMARY MATH GAMES JOHN FELLING MPTCA 2016 john@boxcarsandoneeyedjacks.com phone 1-866-342-3386 / 1-780-440-6284 boxcarsandoneeyedjacks.com BoxCarsEduc
Lesson 1: Place Value of Whole Numbers. Place Value, Value, and Reading Numbers in the Billions
 Place Value of Whole Numbers Lesson 1: Place Value, Value, and Reading Numbers in the Billions Jul 15 9:37 PM Jul 16 10:55 PM Numbers vs. Digits Let's begin with some basic vocabulary. First of all, what
Place Value of Whole Numbers Lesson 1: Place Value, Value, and Reading Numbers in the Billions Jul 15 9:37 PM Jul 16 10:55 PM Numbers vs. Digits Let's begin with some basic vocabulary. First of all, what
Addition and Subtraction
 D Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic 1 Addition mental strategies (pp. 114) look for a ten look for patterns doubles and near doubles bridge to ten jump strategy split strategy version 1 split strategy
D Student Book Name Series D Contents Topic 1 Addition mental strategies (pp. 114) look for a ten look for patterns doubles and near doubles bridge to ten jump strategy split strategy version 1 split strategy
Day 1. Mental Arithmetic Questions KS3 MATHEMATICS. 60 X 2 = 120 seconds. 1 pm is 1300 hours So gives 3 hours. Half of 5 is 2.
 Mental Arithmetic Questions. The tally chart shows the number of questions a teacher asked in a lesson. How many questions did the teacher ask? 22 KS MATHEMATICS 0 4 0 Level 4 Answers Day 2. How many seconds
Mental Arithmetic Questions. The tally chart shows the number of questions a teacher asked in a lesson. How many questions did the teacher ask? 22 KS MATHEMATICS 0 4 0 Level 4 Answers Day 2. How many seconds
Math Grade 2. Understand that three non-zero digits of a 3-digit number represent amounts of hundreds, tens and ones.
 Number Sense Place value Counting Skip counting Other names for numbers Comparing numbers Using properties or place value to add and subtract Standards to be addressed in Number Sense Standard Topic Term
Number Sense Place value Counting Skip counting Other names for numbers Comparing numbers Using properties or place value to add and subtract Standards to be addressed in Number Sense Standard Topic Term
Curriculum Correlation Number Cluster 6: Early Place Value
 Master 56a Cluster 6: Early Place Value ON 15.1 investigate (e.g., using a number line, a hundreds carpet, a board game with numbered squares) the idea that a number s position in the counting sequence
Master 56a Cluster 6: Early Place Value ON 15.1 investigate (e.g., using a number line, a hundreds carpet, a board game with numbered squares) the idea that a number s position in the counting sequence
Released January Years 3/4. Small Steps Guidance and Examples. Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area
 Released January 208 Years 3/4 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area Year 3/4 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 3 Year 4 Measure length Equivalent lengths
Released January 208 Years 3/4 Small Steps Guidance and Examples Block 2 Length, Perimeter, Area Year 3/4 Spring Term Teaching Guidance Overview Small Steps Year 3 Year 4 Measure length Equivalent lengths
MFL and Numeracy. Teachers of MFL in KS2 and KS3 reinforce:
 MFL and Numeracy "When evaluating the achievement of pupils, inspectors consider...how well pupils develop a range of skills, including reading, writing, communication and mathematical skills, and how
MFL and Numeracy "When evaluating the achievement of pupils, inspectors consider...how well pupils develop a range of skills, including reading, writing, communication and mathematical skills, and how
Foundations of Multiplication and Division
 Grade 2 Module 6 Foundations of Multiplication and Division OVERVIEW Grade 2 Module 6 lays the conceptual foundation for multiplication and division in Grade 3 and for the idea that numbers other than
Grade 2 Module 6 Foundations of Multiplication and Division OVERVIEW Grade 2 Module 6 lays the conceptual foundation for multiplication and division in Grade 3 and for the idea that numbers other than
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 6th Grade Unit 1
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 6th Grade Unit 1 Unit 1 Whole Numbers and Algebra MATH 601 Whole Numbers and Algebra INTRODUCTION 3 1. WHOLE NUMBERS AND THEIR PROPERTIES 5 ROUNDING AND ESTIMATION 7 WHOLE NUMBER OPERATIONS
MATH STUDENT BOOK 6th Grade Unit 1 Unit 1 Whole Numbers and Algebra MATH 601 Whole Numbers and Algebra INTRODUCTION 3 1. WHOLE NUMBERS AND THEIR PROPERTIES 5 ROUNDING AND ESTIMATION 7 WHOLE NUMBER OPERATIONS
Addition quiz. Level A. 1. What is ? A) 100 B) 110 C) 80 D) What is ? A) 76 B) 77 C) 66 D) What is ?
 Level A 1. What is 78 + 32? A) 100 B) 110 C) 80 D) 40 2. What is 57 + 19? A) 76 B) 77 C) 66 D) 87 3. What is 66 + 9? A) 76 B) 79 C) 74 D) 75 4. Adding two even numbers gives an even number. 5. Adding two
Level A 1. What is 78 + 32? A) 100 B) 110 C) 80 D) 40 2. What is 57 + 19? A) 76 B) 77 C) 66 D) 87 3. What is 66 + 9? A) 76 B) 79 C) 74 D) 75 4. Adding two even numbers gives an even number. 5. Adding two
Thousandths are smaller parts than hundredths. If one hundredth is divided into 10 equal parts, each part is one thousandth.
 Lesson 3.1 Reteach Thousandths Thousandths are smaller parts than hundredths. If one hundredth is divided into 10 equal parts, each part is one thousandth. Write the decimal shown by the shaded parts of
Lesson 3.1 Reteach Thousandths Thousandths are smaller parts than hundredths. If one hundredth is divided into 10 equal parts, each part is one thousandth. Write the decimal shown by the shaded parts of
There are 5 people upstairs on the bus, there are 4 people downstairs. How many altogether? Write a number sentence to show this.
 National Curriculum Fluency Reasoning Problem Solving Read, write and interpret mathematical statements involving addition (+), subtraction (-) and equals (=) signs. There are 5 people upstairs on the
National Curriculum Fluency Reasoning Problem Solving Read, write and interpret mathematical statements involving addition (+), subtraction (-) and equals (=) signs. There are 5 people upstairs on the
Example: I predict odd, roll a 5, and then collect that many counters. Play until time is up. The player with the most counters wins.
 Odds and Evens Skill: Identifying even and odd numbers Materials: 1 die to share 1. Each player takes 5 counters and puts the rest in a pile between them. 2. Player 1 predicts whether he will roll ODD
Odds and Evens Skill: Identifying even and odd numbers Materials: 1 die to share 1. Each player takes 5 counters and puts the rest in a pile between them. 2. Player 1 predicts whether he will roll ODD
Mathematics Third Practice Test A, B & C - Mental Maths. Mark schemes
 Mathematics Third Practice Test A, B & C - Mental Maths Mark schemes Introduction This booklet contains the mark schemes for the higher tiers tests (Tests A and B) and the lower tier test (Test C). The
Mathematics Third Practice Test A, B & C - Mental Maths Mark schemes Introduction This booklet contains the mark schemes for the higher tiers tests (Tests A and B) and the lower tier test (Test C). The
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 4 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 4 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. Read carefully: a) The place or position of a digit in a number gives the value of that digit. b) In the number 4237, 4,
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 4 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. Read carefully: a) The place or position of a digit in a number gives the value of that digit. b) In the number 4237, 4,
Whole Numbers WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT.
 WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT www.mathletics.co.uk It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognise their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed
WHOLE NUMBERS PASSPORT www.mathletics.co.uk It is important to be able to identify the different types of whole numbers and recognise their properties so that we can apply the correct strategies needed
MATHEMATICS UTAH CORE GUIDES GRADE 2
 MATHEMATICS UTAH CORE GUIDES GRADE 2 UTAH STATE BOARD OF EDUCATION 250 EAST 500 SOUTH P.O. BOX 144200 SALT LAKE CITY, UTAH 84114-4200 SYDNEE DICKSON, Ed.D., STATE SUPERINTENDENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION Operations
MATHEMATICS UTAH CORE GUIDES GRADE 2 UTAH STATE BOARD OF EDUCATION 250 EAST 500 SOUTH P.O. BOX 144200 SALT LAKE CITY, UTAH 84114-4200 SYDNEE DICKSON, Ed.D., STATE SUPERINTENDENT OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION Operations
NAME DATE. b) Then do the same for Jett s pennies (6 sets of 9 pennies with 4 leftover pennies).
 NAME DATE 1.2.2/1.2.3 NOTES 1-51. Cody and Jett each have a handful of pennies. Cody has arranged his pennies into 3 sets of 16, and has 9 leftover pennies. Jett has 6 sets of 9 pennies, and 4 leftover
NAME DATE 1.2.2/1.2.3 NOTES 1-51. Cody and Jett each have a handful of pennies. Cody has arranged his pennies into 3 sets of 16, and has 9 leftover pennies. Jett has 6 sets of 9 pennies, and 4 leftover
4 + 3 = 7 10= model. Starting at the bigger number and counting on
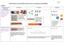 South Wilford C of E Endowed Primary School - Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partpart whole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes
South Wilford C of E Endowed Primary School - Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partpart whole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes
Number. Reading, writing and partitioning numbers. Vocabulary
 Number Reading, writing and partitioning numbers Let s investigate Pablo has these digit cards. He makes three-digit numbers with the cards. Write down all the numbers he could make. 1 8 7 1 Write each
Number Reading, writing and partitioning numbers Let s investigate Pablo has these digit cards. He makes three-digit numbers with the cards. Write down all the numbers he could make. 1 8 7 1 Write each
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 3 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 3 Booklet Learner s name: School name: _ Day 1 1. Read carefully: a) The place or position of a digit in a number gives the value of that digit. b) In the number 273, 2,
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 3 Booklet Learner s name: School name: _ Day 1 1. Read carefully: a) The place or position of a digit in a number gives the value of that digit. b) In the number 273, 2,
Summer Solutions Common Core Mathematics 4. Common Core. Mathematics. Help Pages
 4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
4 Common Core Mathematics 63 Vocabulary Acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 Area the amount of space within a polygon; area is always measured in square units (feet 2, meters 2, ) Congruent figures
4 + 3 = 7 10= Starting at the bigger number and counting on. Progression in Calculations
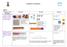 Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes to add two numbers together as a group or in a bar.
Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes to add two numbers together as a group or in a bar.
4 + 3 = 7 10= Starting at the bigger number and counting on
 Ladbrooke JMI School Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes to add two numbers together
Ladbrooke JMI School Progression in Calculations Addition Objective and Strategies Combining two parts to make a whole: partwhole model Concrete Pictorial Abstract Use cubes to add two numbers together
saying the 5 times, 10 times or 2 times table Time your child doing various tasks, e.g.
 Can you tell the time? Whenever possible, ask your child to tell you the time to the nearest 5 minutes. Use a clock with hands as well as a digital watch or clock. Also ask: What time will it be one hour
Can you tell the time? Whenever possible, ask your child to tell you the time to the nearest 5 minutes. Use a clock with hands as well as a digital watch or clock. Also ask: What time will it be one hour
Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers
 E Student Book Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Thousands 1 Hundreds Tens 1 Units Name Series E Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Contents Topic 1 Looking at whole numbers (pp. 1 8) reading
E Student Book Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Thousands 1 Hundreds Tens 1 Units Name Series E Reading and Understanding Whole Numbers Contents Topic 1 Looking at whole numbers (pp. 1 8) reading
Summer Math Completed 5 th grade Entering 6 th grade
 Name Date Summer Math Completed 5 th grade Entering 6 th grade Instructions: Please complete the following problems showing all work. This packet is due on the first day of school and will count as your
Name Date Summer Math Completed 5 th grade Entering 6 th grade Instructions: Please complete the following problems showing all work. This packet is due on the first day of school and will count as your
Roll & Make. Represent It a Different Way. Show Your Number as a Number Bond. Show Your Number on a Number Line. Show Your Number as a Strip Diagram
 Roll & Make My In Picture Form In Word Form In Expanded Form With Money Represent It a Different Way Make a Comparison Statement with a Greater than Your Make a Comparison Statement with a Less than Your
Roll & Make My In Picture Form In Word Form In Expanded Form With Money Represent It a Different Way Make a Comparison Statement with a Greater than Your Make a Comparison Statement with a Less than Your
Objective: Plot points, using them to draw lines in the plane, and describe
 NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 7 5 6 Lesson 7 Objective: Plot points, using them to draw lines in the plane, and describe patterns within the coordinate pairs. Suggested Lesson Structure
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Lesson 7 5 6 Lesson 7 Objective: Plot points, using them to draw lines in the plane, and describe patterns within the coordinate pairs. Suggested Lesson Structure
Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT
 Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT The Coalition Government took office on 11 May 2010. This publication was published prior to that date and may not reflect current government policy. You may choose
Sample lessonsample lessons using ICT The Coalition Government took office on 11 May 2010. This publication was published prior to that date and may not reflect current government policy. You may choose
Unit 7 Number Sense: Addition and Subtraction with Numbers to 100
 Unit 7 Number Sense: Addition and Subtraction with Numbers to 100 Introduction In this unit, students will review counting and ordering numbers to 100. They will also explore various strategies and tools
Unit 7 Number Sense: Addition and Subtraction with Numbers to 100 Introduction In this unit, students will review counting and ordering numbers to 100. They will also explore various strategies and tools
COMING SOON: Place Value, Addition, and Subtraction UNIT TEST
 COMING SOON: Place Value, Addition, and Subtraction UNIT TEST KEY WORDS: millions hundred-thousands ten-thousands thousands hundreds tens ones period place value greater less value equivalent round/estimate
COMING SOON: Place Value, Addition, and Subtraction UNIT TEST KEY WORDS: millions hundred-thousands ten-thousands thousands hundreds tens ones period place value greater less value equivalent round/estimate
This policy has been largely adapted from the White Rose Maths Hub Calculation Policy with further material added.
 This policy has been largely adapted from the White Rose Maths Hub Calculation Policy with further material added. St John s RC Primary School Calculation Combining two parts to make a whole: part- whole
This policy has been largely adapted from the White Rose Maths Hub Calculation Policy with further material added. St John s RC Primary School Calculation Combining two parts to make a whole: part- whole
An ordered collection of counters in rows or columns, showing multiplication facts.
 Addend A number which is added to another number. Addition When a set of numbers are added together. E.g. 5 + 3 or 6 + 2 + 4 The answer is called the sum or the total and is shown by the equals sign (=)
Addend A number which is added to another number. Addition When a set of numbers are added together. E.g. 5 + 3 or 6 + 2 + 4 The answer is called the sum or the total and is shown by the equals sign (=)
Model Place Value Relationships
 Lesson 1.1 Reteach Model Place Value Relationships A hundred grid can help you understand place-value relationships. One small square has been shaded to represent 1. Shade the rest of the first column.
Lesson 1.1 Reteach Model Place Value Relationships A hundred grid can help you understand place-value relationships. One small square has been shaded to represent 1. Shade the rest of the first column.
