Year 9 Product Design - Introduction
|
|
|
- Dorcas Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Year 9 Product Design - Introduction PURPOSE The purpose of this project is to design and create a product with an end user in mind. The end user will be your client this may be yourself, another student, a teacher or someone from outside the school. STATEMENT OF INQUIRY Students will understand that in order to design and create a product, certain processes must be undertaken through an inquiry into the MYP design cycle and how each part are implemented during the product design processes. FASHION SHOW/EXHIBITION Your final product design will be part of a fashion show at the end of the school year. If you do not wish to model the product yourself, you will be responsible for finding a model for your product. Your presentation and product will also be displayed during the Year 9 Graduation. PRODUCT DESIGN PROCESSES The product design process is the application of design thinking that involves the use of strategies for understanding design needs and opportunities, visualising and generating creative and innovative ideas, planning, and analysing and evaluating the ideas that best meet the criteria. The use of creative and critical thinking techniques enables students to develop, articulate, analyse and reflect on the product design process. Consideration of economic, environmental and social impacts that result from designed solutions are core to design thinking and the product design process. The product design process has four stages (See MYP Design Cycle) Textiles & Design, Alamanda College. Year 9 design brief Calico Challenge 1
2 PRODUCT DESIGN FACTORS The following product design factors and parameters are integral to framing product design. These factors influence the design of a product. Some will be included in a design brief and may also be used in product evaluation. In the following table, the factors have been placed into broad categories, with parameters overlapping and interconnecting, depending on the individual context. Product design factors Purpose, function and context User-centered design Innovation and creativity Visual, tactile and aesthetic Sustainability Economics time and cost Legal responsibilities Materials characteristics and properties Technologies tools, processes and manufacturing methods Parameters Includes the reason or need for a product, in the context and environment of its use. This includes its operation, performance, reliability and quality. The primary function and secondary functions that support its use are considered. End-user/s problems or needs identified to improve wellbeing and/or quality of life. In response to these needs, considerations include culture and religion, age, economic status, emotional and sensory appeal, universal design, social and physical needs, fashion and trends. Safety, accessibility, comfort, ergonomics and anthropometric data should also be considered. Innovation requires a creative approach to develop new or improved solutions to unsolved problems and opportunities. This involves invention, improvement, modification, incremental progress, experimentation and pushing the boundaries. Opportunities are identified from research and development, end-user/s feedback, new ideas and knowledge, new materials and emerging technologies. Relate to the product s form, appearance and feel. Design elements include: point, line, shape, form, texture, tone, colour, transparency, translucency and opacity. Natural forms, patterns and structures along with geometry and mathematics can also be employed to create aesthetic appeal. Design principles of: balance, contrast, repetition, movement/rhythm, pattern, proportion, asymmetry/symmetry, negative/positive space and surface qualities are used to combine and arrange the design elements. Involves the connection and interaction between three pillars of sustainability: social, economic and environmental systems. Underpinning factors include: life cycle analysis/ assessment (LCA) and life cycle thinking, emotional attachment, carbon footprints, fair trade, embodied energy and water use, distribution (product miles) and use of renewable energy and resources. Costing a product takes into account materials, labour and use of plant (equipment and machinery) but must give value to the end-user/s. Time management and material availability are critical issues to consider. The legal aspects of product design are: intellectual property (IP) particularly Patents and Design Registration; Australian and International (ISO) standards, regulations and legislation (including OH&S). Products must be produced safely and be safe for the end-user/s. Materials are selected for use based on their properties (their performance and behaviour both chemically and physically under certain conditions) and characteristics (visible features). These properties and characteristics include strength, durability, thermal resistance, hardness, density, rigidity, flexibility, corrosiveness and compatibility with other materials. Conversion techniques (changing raw materials into usable forms) and production processes are reliant on and affected by available tools, equipment, machines, and expertise. Suitable and accurate methods are selected to perform the following: marking/ setting out, cutting/shaping/forming, joining/assembling/constructing, decorating/ embellishing/finishing. Textiles & Design, Alamanda College. Year 9 Product Design 2
3 Year 9 Product Design Summary JOURNAL Throughout this product design process, you will be required to keep a record of all your planning, research, records, ideas, wonderings, etc. You will record all this information in your journal book, which you can use to create your final portfolio. You may like to scan pages of your journal to include in your portfolio, or retype your work, or a combination of both. You will be required to keep your journal up to date at all times. PORTFOLIO PRESENTATION For this project, you will produce a presentation style report (using software such as PowerPoint, Keynote or Prezi). You will need to include photos of your progress throughout the semester. These will be uploaded onto SeeSaw for later use. Use the following headings/sections to structure your presentation: Investigating and Defining, Design, Planning and Management, Production Journal and Evaluation (based on your own criteria). PART 1: INVESTIGATING AND DEFINING This section will have the following subsections (see details overleaf): Client Profile: Identify end user/client. Establish your client s needs for their intended product (you will need to interview them). Design brief: outline of the context, constraints and considerations. Evaluation criteria: development of the criteria to evaluate how well the finished product satisfies the design brief. Research: research into factors related to the design brief, including materials and process investigations. PART 2: DESIGNING AND DEVELOPMENT This section will have the following subsections (see details overleaf): Visualisations: concept sketches and drawings of ideas to meet the needs of the design brief. Design options: presentation of drawings, selection and justification of the preferred option, how this option meets the design brief. You are required to develop at least three design options to choose from. Record feedback from your client. Present the chosen design of your product. Working drawings: drawings including technical drawings, showing product specifications, (i.e. sizes and construction methods) needed for production planning. This should include fabric swatches. Textiles & Design, Alamanda College. Year 9 Product Design 3
4 PART 3: PLANNING AND PRODUCTION This section will have the following subsections (see details overleaf): Scheduled production plan: sequence plan and timeline, listing tools, equipment and machines required. Production: Product and production record. Refinements and modifications including pattern drafting/adapting may be made throughout production. Justify any modifications you make to your original plan. PART 4: EVALUATING You are to develop your own evaluation criteria from the design brief. These criteria are used to inform and justify the selected design option, and evaluate the success of the finished product in relation to solving the design problem for the end-user/s. You need to: Design testing methods Evaluate the success of the product, including quality and sustainability Explain how the product could be improved Explain how satisfied your client is with the product (review) THE VCE PRODUCT DESIGN CYCLE Textiles & Design, Alamanda College. Year 9 Product Design 4
5 Year 9 Product Design The Details PART 1: INVESTIGATING AND DEFINING Part 1.1: Client Profile Before you can write your design brief, you must first identify your client. This could be yourself, a friend, a teacher or a family member. Include the following in your client profile: Name Age Gender Photo of client Contact details Occupation Personality Fashion sense Colouring Colours that may compliment their colouring Ethical or social concerns Body measurements: chest, waist, hips, skirt length, outseam, arm length. Create interview questions you can ask your client during your consultation. The answers to these will help determine your brief. Some examples include: What is the intended purpose of the product? Will it be used for other occasions? Who will use the product? Will other people use the garment? Is this a formal or casual occasion? What are your preferences regarding size, colour, comfort? How will you maintain and store the product? Do you want the garment to be highly fashionable, classical or costume style? Do you have a colour scheme in mind? Is sustainability an important issue for you in regard to its disposal or re-use? Part 1.2: Design Brief Based on your interview with your client, you can now create your design brief specifications. Your design brief should outline of the context, constraints and considerations of your product design. Use the information you gained during your consultation to fill in the chart on the next page. You will need to also create a chart with the following information: Outline of the context (from your design web) include primary and secondary functions. Information about the user (relevant to the design of the product, e.g. size, colour). Constraints and considerations including budget and time. Textiles & Design, Alamanda College. Year 9 Product Design 5
6 Design Brief Web Textiles & Design, Alamanda College. Year 9 Product Design 6
7 Part 1.3: Developing Your Evaluation Criteria Evaluation criteria for your product design should come from your design brief, particularly the constraints and considerations. You need to cover functionality, aesthetics, material requirements, quality and client satisfaction. Include one criterion for design and planning, and at least five criteria for production and the finished product. For each criterion, you need to write: The criterion question A justification (reason why it is important) Description of how you might check this once the product is finished. Part 1.4: Research You need to research into factors related to the design brief, including materials and process investigations. This includes inspiration and information related to the construction. Thinking about your research Search supplier (spotlight) for materials and notions. o Your budget is $50. You need to ensure you are able to purchase all your required items for that amount. o Compare the costs of different materials. Explore different materials to become familiar with their characteristics and properties thinking about what they look like and their suitability. Take required measurements. Try out different processes (practical trials). Look at the work of other designers. Collect printed or digital images of objects, shapes, textures, etc. that interest you/your client. Refer to subject-specific texts on how to complete processes or construction techniques. Textiles & Design, Alamanda College. Year 9 design brief Calico Challenge 7
8 PART 2: DESIGNING AND DEVELOPMENT Part 2.1: Visualisations Concept sketches and drawings of ideas to meet the needs of the design brief. Include a mood board of colours and fashion found on the web or in magazines etc. Visualisations are sketches and models that you carry out to explore your ideas for your product design. It is important to do this so you don t lose any of your great ideas when carrying out your research. Your visulisations could be the entire look, or just one section of the garment you are designing. These sketches don t need to polished get your ideas down quickly while they are fresh in your mind. Part 2.2: Design Options Design options are informative and are drawn as presentation drawings. They need to be clear and fully worked out design ideas. Your drawings should give an accurate sense of what you intend the product to look like. It is crucial to include comments or annotations. Your annotations could highlight or describe: Materials being used Stitching, if obvious Folds and draping of the fabric Any notions or components needed Modifications made to the original design How the product fulfils the requirements of your brief. Use your visualisations as the basis for developing your design options. You are required to develop at least three design options to choose from. Record feedback from your client. Present the chosen design of your product. Part 2.3: Working Drawings Drawings including technical drawings, showing product specifications, (i.e. sizes and construction methods) needed for production planning. This should include fabric swatches. Your working drawings should show the details of the design you have chosen to make. One drawing should be a flat, showing the front and back view with all construction details clearly drawn, detailed measurements and information provided about the materials and notions used. Other drawings can show steps in construction or enlarged details. If you are using existing commercial patterns, you can include diagrams of your adjustments to these patterns. Include a photo/scan of the pattern design in your portfolio. Textiles & Design, Alamanda College. Year 9 design brief Calico Challenge 8
9 PART 3: PLANNING AND PRODUCTION Part 3.1: Materials list and costing of the preferred option This provides details of the materials that would be required to make this design option. It should include all of the different types of fabrics needed, any notions, embellishments, patterns, particular tools or pieces of equipment that might need to be purchased. Complete the following chart Product description: Part of the design or garment Material name (fabrics and fibres) or notion description Amount needed Cost per meter Total cost Other needs notions, patterns etc Description Where it will be used (if applicable) Cost per item Total cost Total amount (remember the budget is $50): Textiles & Design, Alamanda College. Year 9 Product Design 9
10 Part 3.2: Scheduled production plan This is a detailed sequence plan and timeline, listing tools, fabrics, equipment and machines required. Use the following template to create your plan. Step no. Description of the step or processes Materials or parts needed Equipment Estimated time Part 3.3: Production Product and production record. Refinements and modifications including pattern drafting/ adapting may be made throughout production. Justify any modifications you make to your original plan. Keep a journal of your progress. It is important to note: The date that you completed processes and the time taken Any change in the order of the sequence, responsibilities, planned processes Problems or errors that forced a change in plans Time saved or skills that improved vastly The equipment, tools, machines and safety procedures that you used. You will need this information for your evaluation report (written when the product is finished) to compare what you actually did with your production plants. This could be enhanced with the use of digital photos and captions. Textiles & Design, Alamanda College. Year 9 design brief Calico Challenge 10
11 PART 4: EVALUATION Part 4.1: Evaluating your Finished Product Respond to your evaluation criteria use the criteria you created to assess your finished product. Create and complete a table with your evaluation criteria (see example below). Evaluation criterion: How it was checked: Observations, feedback and response: Part 4.2: Evaluating your design, planning and production activities In this subsection, you are required to evaluate the activities and methods used. Use the questions in the table below to help you evaluate your activities, and use your evaluation criteria that you wrote earlier. Activities: Methods used: Observations, feedback and response: Design Visualisations, design options, working drawings compared with finished product. Planning Sequence plan, timeline, materials list and costing compared with your journal. Production Accuracy and quality of processes. What do you think were good about your designs? How do you think these could have been improved? Your own criterion. Was your planning helpful? Did you keep on track? Your own criterion. Did you follow your plan and use time effectively? How could the result of these processes be improved or what alternative processes would have been more suitable? Were there any factors that made your progress slower or faster than expected? Your own criterion. Part 4.3: Reflection Write a detailed reflection on your Product Design process. Textiles & Design, Alamanda College. Year 9 Product Design 11
DESIGN BRIEF Calico Challenge
 Name: DESIGN BRIEF Calico Challenge BACKGROUND Calico is a woven fabric made from 100% cotton fibres. It is unbleached, undyed and not fully processed during production. This results in the fabric being
Name: DESIGN BRIEF Calico Challenge BACKGROUND Calico is a woven fabric made from 100% cotton fibres. It is unbleached, undyed and not fully processed during production. This results in the fabric being
Product Design and Technology (PD&T) Unit 3&4 2015
 Product Design and Technology (PD&T) Unit 3&4 2015 Transition/ Holiday homework Resources required: A3 Visual Diary, coloured pencils, 2B and HB pencils Teacher: Mr Devine devine.mark.a@edumail.vic.gov.au
Product Design and Technology (PD&T) Unit 3&4 2015 Transition/ Holiday homework Resources required: A3 Visual Diary, coloured pencils, 2B and HB pencils Teacher: Mr Devine devine.mark.a@edumail.vic.gov.au
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS MATERIALS DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY ATAR YEAR 12
 SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS MATERIALS DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY ATAR YEAR 1 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 015 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS MATERIALS DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY ATAR YEAR 1 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 015 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
Outcome 3 Evaluate the outcomes of the design and production activities, and promote the product's design features to the client and/or end-user.
 2010 School-assessed Task Report Design and Technology: Units 3 and 4 BACKGROUND INFORMATION The School-assessed Task is commenced in Unit 3 and completed in Unit 4. Components of the task relate to Unit
2010 School-assessed Task Report Design and Technology: Units 3 and 4 BACKGROUND INFORMATION The School-assessed Task is commenced in Unit 3 and completed in Unit 4. Components of the task relate to Unit
Design, Technology and Engineering
 BOARD-ACCREDITED, PRE-EDITED DRAFT Design, Technology and Engineering 2020 Subject Outline Stage 1 and Stage 2 This subject outline has been accredited. It is provided in draft, pre-edited form for planning
BOARD-ACCREDITED, PRE-EDITED DRAFT Design, Technology and Engineering 2020 Subject Outline Stage 1 and Stage 2 This subject outline has been accredited. It is provided in draft, pre-edited form for planning
VCE Product Design and Technology: Administrative information for Schoolbased Assessment in 2018
 VCE Product Design and Technology: Administrative information for Schoolbased Assessment in 2018 Units 3 and 4 School-assessed Task The School-assessed Task contributes 50 per cent to the study score and
VCE Product Design and Technology: Administrative information for Schoolbased Assessment in 2018 Units 3 and 4 School-assessed Task The School-assessed Task contributes 50 per cent to the study score and
AQA GCSE Design and Technology 8552
 AQA GCSE Design and Technology 8552 Investigation, primary and secondary data Unit 6 Designing principles 1 Objectives Understand how primary and secondary data can be collected to assist the understanding
AQA GCSE Design and Technology 8552 Investigation, primary and secondary data Unit 6 Designing principles 1 Objectives Understand how primary and secondary data can be collected to assist the understanding
Eco Lamp Assessment Task
 Eco Lamp Assessment Task Length: See folio guide Marks / value: Folio: 25% Project: 25% Date due: Design Folio Progress Mark Term 1 Week 10 Design Folio Term 2 Week 9 Design Project Term 2 Week 9 Purpose
Eco Lamp Assessment Task Length: See folio guide Marks / value: Folio: 25% Project: 25% Date due: Design Folio Progress Mark Term 1 Week 10 Design Folio Term 2 Week 9 Design Project Term 2 Week 9 Purpose
APPROVAL CRITERIA FOR GCE AS AND A LEVEL DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY
 APPROVAL CRITERIA FOR GCE AS AND A LEVEL DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY JULY 2016 Contents Page number Introduction 1 Subject aims and objectives 2 Subject content 3 Core technical principles 3 Core designing and
APPROVAL CRITERIA FOR GCE AS AND A LEVEL DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY JULY 2016 Contents Page number Introduction 1 Subject aims and objectives 2 Subject content 3 Core technical principles 3 Core designing and
Design and technology
 Design and technology Programme of study for key stage 3 and attainment target (This is an extract from The National Curriculum 2007) Crown copyright 2007 Qualifications and Curriculum Authority 2007 Curriculum
Design and technology Programme of study for key stage 3 and attainment target (This is an extract from The National Curriculum 2007) Crown copyright 2007 Qualifications and Curriculum Authority 2007 Curriculum
Industrial Practices, Systems and Control at Key Stage 4
 Industrial Practices, Systems and Control at Key Stage 4 Abstract This article discusses the relationship between designing and making processes followed in design and technology and industrial and commercial
Industrial Practices, Systems and Control at Key Stage 4 Abstract This article discusses the relationship between designing and making processes followed in design and technology and industrial and commercial
CLANCY CATHOLIC COLLEGE TAS Year 8 - Rotation 1: Mixed Materials (Gumball)
 CLANCY CATHOLIC COLLEGE TAS- 2014 Year 8 - Rotation 1: Mixed Materials (Gumball) Handed Out: Term 1 Week 3 (Circle) 10/2/14 11/2/14 12/2/14 13/2/14 14/2/14 Period: Term 2 Week 2 (Circle) 5/5/14 6/5/14
CLANCY CATHOLIC COLLEGE TAS- 2014 Year 8 - Rotation 1: Mixed Materials (Gumball) Handed Out: Term 1 Week 3 (Circle) 10/2/14 11/2/14 12/2/14 13/2/14 14/2/14 Period: Term 2 Week 2 (Circle) 5/5/14 6/5/14
Design and Technologies: Engineering principles and systems and Materials and technologies specialisations Automatons
 Sample assessment task Year level 10 Learning area Subject Title of task Task details of task Type of assessment Purpose of assessment Assessment strategy Evidence to be collected Technologies Design and
Sample assessment task Year level 10 Learning area Subject Title of task Task details of task Type of assessment Purpose of assessment Assessment strategy Evidence to be collected Technologies Design and
Unit Title: Drawing Concept Art for Computer Games
 Unit Credit Value: 10 Unit Level: Three Unit Guided Learning Hours: 60 Ofqual Unit Reference Number: A/502/5675 Unit Review Date: 31/12/2016 Unit Sector: 9.3 Media and Communication Unit Summary The aim
Unit Credit Value: 10 Unit Level: Three Unit Guided Learning Hours: 60 Ofqual Unit Reference Number: A/502/5675 Unit Review Date: 31/12/2016 Unit Sector: 9.3 Media and Communication Unit Summary The aim
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS MATERIALS DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY GENERAL YEAR 12
 SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS MATERIALS DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY GENERAL YEAR 1 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 01 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS MATERIALS DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY GENERAL YEAR 1 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 01 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
Grade Descriptors: Design & Technology
 Grade Descriptors: Design & Technology Investigating the Design Context Development of the Design Proposals Making Testing and Evaluation Communication Grade 9 Discrimination show when selecting and acquiring
Grade Descriptors: Design & Technology Investigating the Design Context Development of the Design Proposals Making Testing and Evaluation Communication Grade 9 Discrimination show when selecting and acquiring
Design and Technologies: Materials and technologies specialisations
 Sample assessment task Year level 5 Learning area Subject Title of task Task details of task Type of assessment Purpose of assessment Assessment strategy Evidence to be collected Suggested time Content
Sample assessment task Year level 5 Learning area Subject Title of task Task details of task Type of assessment Purpose of assessment Assessment strategy Evidence to be collected Suggested time Content
Years 9 and 10 standard elaborations Australian Curriculum: Design and Technologies
 Purpose The standard elaborations (SEs) provide additional clarity when using the Australian Curriculum achievement standard to make judgments on a five-point scale. They can be used as a tool for: making
Purpose The standard elaborations (SEs) provide additional clarity when using the Australian Curriculum achievement standard to make judgments on a five-point scale. They can be used as a tool for: making
GCSE Design and Technology Specification - NEA Guidance
 GCSE Design and Technology 2017 Specification - NEA Guidance Non Examined Assessment NEA Non Examined Assessment 50% of the qualification. Approximately 35 hrs of candidate work. Design & Make task from
GCSE Design and Technology 2017 Specification - NEA Guidance Non Examined Assessment NEA Non Examined Assessment 50% of the qualification. Approximately 35 hrs of candidate work. Design & Make task from
CATHOLIC REGIONAL COLLEGE SYDENHAM. Study: Studio Arts
 CATHOLIC REGIONAL COLLEGE SYDENHAM Study: Studio Arts Rationale: The creative nature of visual art provides individuals with the opportunity for personal growth, the expression of ideas and a process for
CATHOLIC REGIONAL COLLEGE SYDENHAM Study: Studio Arts Rationale: The creative nature of visual art provides individuals with the opportunity for personal growth, the expression of ideas and a process for
The Wool4School Design Competition is designed to support the curriculum taught in Design and Technology subjects across Australia.
 CURRICULUM LINKS Introduction ADVICE FOR TEACHERS The Wool4School Design Competition is designed to support the curriculum taught in Design and Technology subjects across Australia. Listed on the Wool4School
CURRICULUM LINKS Introduction ADVICE FOR TEACHERS The Wool4School Design Competition is designed to support the curriculum taught in Design and Technology subjects across Australia. Listed on the Wool4School
Area of Learning: APPLIED DESIGN, SKILLS, AND TECHNOLOGIES Graphic Production Grade 12 BIG IDEAS
 BIG IDEAS Design for the life cycle includes consideration of social and environmental impacts. Design choices require the evaluation and refinement of skills. Tools and technologies can be adapted for
BIG IDEAS Design for the life cycle includes consideration of social and environmental impacts. Design choices require the evaluation and refinement of skills. Tools and technologies can be adapted for
CURRICULUM MAP. Rota Product design Earphone Wrap
 CURRICULUM MAP Subject: & Technology, Product & Textiles Key Stage 3 Number of lessons 36 in each rota Healthy Cafe Product design Earphone Wrap Textiles & make Kites preparation & nutrition Textiles Product
CURRICULUM MAP Subject: & Technology, Product & Textiles Key Stage 3 Number of lessons 36 in each rota Healthy Cafe Product design Earphone Wrap Textiles & make Kites preparation & nutrition Textiles Product
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS MATERIALS DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY ATAR YEAR 11
 SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS MATERIALS DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY ATAR YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS MATERIALS DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY ATAR YEAR 11 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 014 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
GCSE Design and Technology Specification - NEA Guidance
 GCSE Design and Technology 2017 Specification - NEA Guidance Non Examined Assessment NEA Non Examined Assessment 50% of the qualification. Approximately 35 hrs of candidate work. Design & Make task from
GCSE Design and Technology 2017 Specification - NEA Guidance Non Examined Assessment NEA Non Examined Assessment 50% of the qualification. Approximately 35 hrs of candidate work. Design & Make task from
VCE Product Design and Technology
 VCE Product Design and Technology Written examination November Examination specifications Overall conditions The examination will be scheduled at a time and date to be set annually by the Victorian Curriculum
VCE Product Design and Technology Written examination November Examination specifications Overall conditions The examination will be scheduled at a time and date to be set annually by the Victorian Curriculum
YEAR 7 & 8 THE ARTS. The Visual Arts
 VISUAL ARTS Year 7-10 Art VCE Art VCE Media Certificate III in Screen and Media (VET) Certificate II in Creative Industries - 3D Animation (VET)- Media VCE Studio Arts VCE Visual Communication Design YEAR
VISUAL ARTS Year 7-10 Art VCE Art VCE Media Certificate III in Screen and Media (VET) Certificate II in Creative Industries - 3D Animation (VET)- Media VCE Studio Arts VCE Visual Communication Design YEAR
Submissions for Art, Craft and Design should aim to present evidence of the following in order to meet assessment objective requirements.
 GCE AS ART AND DESIGN UNIT ONE PERSONAL CREATIVE ENQUIRY GUIDANCE: INDICATIVE CONTENT FOR ART AND DESIGN (ART, CRAFT AND DESIGN) four assessment objectives. Teachers may refer to this indicative content
GCE AS ART AND DESIGN UNIT ONE PERSONAL CREATIVE ENQUIRY GUIDANCE: INDICATIVE CONTENT FOR ART AND DESIGN (ART, CRAFT AND DESIGN) four assessment objectives. Teachers may refer to this indicative content
Study Skills Course Milestones for Students
 Study Skills Course Milestones for Students Course Title: Design & Manufacture Level: National 5 Work to be covered/topics/activities/assignments Month Unit 1 Design Unit 2 Materials & Manufacturing Unit
Study Skills Course Milestones for Students Course Title: Design & Manufacture Level: National 5 Work to be covered/topics/activities/assignments Month Unit 1 Design Unit 2 Materials & Manufacturing Unit
Home Economics Lower Secondary Subject Area Guidelines. November 2011
 Home Economics Lower Secondary Subject Area Guidelines November 2011 Contents Rationale... 1 Planning using these guidelines... 2 Mapping of Essential Learnings and Year 10 Guidelines... 3 Essential Learnings
Home Economics Lower Secondary Subject Area Guidelines November 2011 Contents Rationale... 1 Planning using these guidelines... 2 Mapping of Essential Learnings and Year 10 Guidelines... 3 Essential Learnings
COSTUME DESIGN & RENDERING INTEGRATED DRAMA & DESIGN PROJECT
 COSTUME DESIGN & RENDERING INTEGRATED DRAMA & DESIGN PROJECT Essential Question: How can costume design enhance a role? OVERALL EXPECTATIONS: A. TECHNOLOGY FUNDAMENTALS A1. demonstrate an understanding
COSTUME DESIGN & RENDERING INTEGRATED DRAMA & DESIGN PROJECT Essential Question: How can costume design enhance a role? OVERALL EXPECTATIONS: A. TECHNOLOGY FUNDAMENTALS A1. demonstrate an understanding
Environmental Design. Floor Plan. Planometric Drawing. Target Audience. Media. Materials
 Environmental Design The design of large-scale aspects of the environment by means of architecture, interior design, way-finding, landscape architecture, etc. Floor Plan A scale diagram of the arrangement
Environmental Design The design of large-scale aspects of the environment by means of architecture, interior design, way-finding, landscape architecture, etc. Floor Plan A scale diagram of the arrangement
Kingsdale School Technology FACULTY Scheme of Work
 Project Title: Monster s Year Group: 7&8 Length in weeks: 12-14 Kingsdale School Technology FACULTY Scheme of Work Lesson Objectives, Key Skills and Key Words Activity Notes and Resources 1 To be able
Project Title: Monster s Year Group: 7&8 Length in weeks: 12-14 Kingsdale School Technology FACULTY Scheme of Work Lesson Objectives, Key Skills and Key Words Activity Notes and Resources 1 To be able
VCE Systems Engineering: Administrative information for Schoolbased Assessment in 2019
 VCE Systems Engineering: Administrative information for Schoolbased Assessment in 2019 Units 3 and 4 School-assessed Task The School-assessed Task contributes 50 per cent to the study score and is commenced
VCE Systems Engineering: Administrative information for Schoolbased Assessment in 2019 Units 3 and 4 School-assessed Task The School-assessed Task contributes 50 per cent to the study score and is commenced
2017 VCE Product Design and Technology examination report
 2017 VCE Product Design and Technology examination report General comments Overall, in the 2017 VCE Product Design and Technology examination, students who produced high-scoring responses understood the
2017 VCE Product Design and Technology examination report General comments Overall, in the 2017 VCE Product Design and Technology examination, students who produced high-scoring responses understood the
Information and Communication Technology
 Information and Communication Technology Lower Secondary Subject Area Guidelines November 2011 Contents Rationale... 3 Planning using these guidelines... 4 Mapping Essential Learnings and Year 10 Guidelines...
Information and Communication Technology Lower Secondary Subject Area Guidelines November 2011 Contents Rationale... 3 Planning using these guidelines... 4 Mapping Essential Learnings and Year 10 Guidelines...
Technology Engineering and Design Education
 Technology Engineering and Design Education Grade: Grade 6-8 Course: Technological Systems NCCTE.TE02 - Technological Systems NCCTE.TE02.01.00 - Technological Systems: How They Work NCCTE.TE02.02.00 -
Technology Engineering and Design Education Grade: Grade 6-8 Course: Technological Systems NCCTE.TE02 - Technological Systems NCCTE.TE02.01.00 - Technological Systems: How They Work NCCTE.TE02.02.00 -
Years 5 and 6 standard elaborations Australian Curriculum: Design and Technologies
 Purpose The standard elaborations (SEs) provide additional clarity when using the Australian Curriculum achievement standard to make judgments on a five-point scale. They can be used as a tool for: making
Purpose The standard elaborations (SEs) provide additional clarity when using the Australian Curriculum achievement standard to make judgments on a five-point scale. They can be used as a tool for: making
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit. State Examinations Commission. Leaving Certificate Examination 2010
 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission Leaving Certificate Examination 2010 Technology Coursework Briefs Ordinary Level and Higher Level 200 marks The Thematic Briefs for the Leaving
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission Leaving Certificate Examination 2010 Technology Coursework Briefs Ordinary Level and Higher Level 200 marks The Thematic Briefs for the Leaving
CLANCY CATHOLIC COLLEGE
 CLANCY CATHOLIC COLLEGE Year 8 Technology Mandatory Rotation 3 GUMBALL Portfolio & Project Task 4 NAME: TEACHER: Term 4 Week 6 (Circle) 10/11/14 11/11/14 12/11/14 13/11/14 14/11/14 Period: KLA: TAS WEIGHTING:
CLANCY CATHOLIC COLLEGE Year 8 Technology Mandatory Rotation 3 GUMBALL Portfolio & Project Task 4 NAME: TEACHER: Term 4 Week 6 (Circle) 10/11/14 11/11/14 12/11/14 13/11/14 14/11/14 Period: KLA: TAS WEIGHTING:
Foundation - 2. Exploring how local products, services and environments are designed by people for a purpose and meet social needs
 Foundation - 2 LEGO Education Technologies and society Identify how people design and produce familiar products, services and environments and consider sustainability to meet personal and local community
Foundation - 2 LEGO Education Technologies and society Identify how people design and produce familiar products, services and environments and consider sustainability to meet personal and local community
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit. State Examinations Commission. Leaving Certificate Examination, 2018
 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission 208. M03P 208. M04P Leaving Certificate Examination, 208 Technology Coursework Briefs Ordinary Level and Higher Level 200 marks The Thematic
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission 208. M03P 208. M04P Leaving Certificate Examination, 208 Technology Coursework Briefs Ordinary Level and Higher Level 200 marks The Thematic
Introduction. Unit 1. Unit 2. 2D and 3D Visual Language. Materials, Techniques and Technology
 Introduction Unit 1 2D and 3D Visual Language These units introduce the student to several themes which can be reinforced through an exploration of their application in the workplace. They include; and
Introduction Unit 1 2D and 3D Visual Language These units introduce the student to several themes which can be reinforced through an exploration of their application in the workplace. They include; and
Unit 5: Product Design Portfolio/Project Appendix 3:
 Unit 5: Product Design Portfolio/Project Appendix 3: Design Portfolio 20% Mark Descriptors Amplification of Mark Descriptors Mark Band 1)A design opportunity described or problem identified, including
Unit 5: Product Design Portfolio/Project Appendix 3: Design Portfolio 20% Mark Descriptors Amplification of Mark Descriptors Mark Band 1)A design opportunity described or problem identified, including
PowerAnchor STEM Curriculum mapping Year 9
 PowerAnchor STEM Curriculum mapping Year 9 *NOTE: Bullet points are ACARA provided elaborations for each outcome for this year level. Content Area Science Content Science Understanding Physical sciences:
PowerAnchor STEM Curriculum mapping Year 9 *NOTE: Bullet points are ACARA provided elaborations for each outcome for this year level. Content Area Science Content Science Understanding Physical sciences:
PowerAnchor Curriculum mapping Year 7
 PowerAnchor Curriculum mapping Year 7 *NOTE: Bullet points are ACARA provided elaborations for each outcome for this year level. Content Area Science Content Science Understanding Earth and space sciences:
PowerAnchor Curriculum mapping Year 7 *NOTE: Bullet points are ACARA provided elaborations for each outcome for this year level. Content Area Science Content Science Understanding Earth and space sciences:
KNES Art & Design Course Outline. Year 9
 KNES Art & Design Course Outline Year 9 Art & Design stimulates creativity and imagination. It provides visual, tactile and sensory experiences and a unique way of understanding and responding to the world.
KNES Art & Design Course Outline Year 9 Art & Design stimulates creativity and imagination. It provides visual, tactile and sensory experiences and a unique way of understanding and responding to the world.
AS ART AND DESIGN COMPONENT PERSONAL CREATIVE ENQUIRY
 AS ART AND DESIGN COMPONENT PERSONAL CREATIVE ENQUIRY GUIDANCE: INDICATIVE CONTENT FOR ART AND DESIGN (ART, CRAFT AND DESIGN) four assessment objectives. Teachers may refer to this indicative content for
AS ART AND DESIGN COMPONENT PERSONAL CREATIVE ENQUIRY GUIDANCE: INDICATIVE CONTENT FOR ART AND DESIGN (ART, CRAFT AND DESIGN) four assessment objectives. Teachers may refer to this indicative content for
Communicating your design
 Communicating your design Who to? ideas Design proposals for new or improved textile products can only be turned into saleable items if the design team communicates these proposals effectively to clients,
Communicating your design Who to? ideas Design proposals for new or improved textile products can only be turned into saleable items if the design team communicates these proposals effectively to clients,
Technology (mandatory) Years 7 8 Syllabus. Stage 4. Plan it: a native garden/walk
 Technology (mandatory) Years 7 8 Syllabus Stage 4 1 Length of unit: 20 weeks (50 hours) Area of study: Built Environments Design specialisation: Landscape Design Technology: Model Making Technologies Unit
Technology (mandatory) Years 7 8 Syllabus Stage 4 1 Length of unit: 20 weeks (50 hours) Area of study: Built Environments Design specialisation: Landscape Design Technology: Model Making Technologies Unit
in the New Zealand Curriculum
 Technology in the New Zealand Curriculum We ve revised the Technology learning area to strengthen the positioning of digital technologies in the New Zealand Curriculum. The goal of this change is to ensure
Technology in the New Zealand Curriculum We ve revised the Technology learning area to strengthen the positioning of digital technologies in the New Zealand Curriculum. The goal of this change is to ensure
IB DESIGN TECHNOLOGY SL: YEAR 2
 FREEHOLD REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION INTERNATIONAL BACCALAUREATE PROGRAM IB DESIGN TECHNOLOGY SL: YEAR 2 Grade Level: 12 Credits: 5 BOARD OF EDUCATION ADOPTION DATE:
FREEHOLD REGIONAL HIGH SCHOOL DISTRICT OFFICE OF CURRICULUM AND INSTRUCTION INTERNATIONAL BACCALAUREATE PROGRAM IB DESIGN TECHNOLOGY SL: YEAR 2 Grade Level: 12 Credits: 5 BOARD OF EDUCATION ADOPTION DATE:
VCE Studio Arts Study Design. Implementation briefing July August 2016
 VCE Studio Arts Study Design 2017 2021 Implementation briefing July August 2016 Victorian Curriculum and Assessment Authority 2016 The copyright in this PowerPoint presentation is owned by the Victorian
VCE Studio Arts Study Design 2017 2021 Implementation briefing July August 2016 Victorian Curriculum and Assessment Authority 2016 The copyright in this PowerPoint presentation is owned by the Victorian
SAMPLE COURSE OUTLINE VISUAL ARTS ATAR YEAR 12
 SAMPLE COURSE OUTLINE VISUAL ARTS ATAR YEAR 12 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2015 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it may be freely copied,
SAMPLE COURSE OUTLINE VISUAL ARTS ATAR YEAR 12 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2015 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it may be freely copied,
Area of Study. Design & Technologies Handbook
 Area of Study Design & Technologies Contents Why study Design & Technology?... 3 Pathway Information: Technology... 4 Resistant Materials: Timber, Metal, Plastic... 4 Non-Resistant Materials: Textiles...
Area of Study Design & Technologies Contents Why study Design & Technology?... 3 Pathway Information: Technology... 4 Resistant Materials: Timber, Metal, Plastic... 4 Non-Resistant Materials: Textiles...
YEAR 10 TEXTILES THEME Textiles around the world HEALTH AND HEALING INFLUENCES/SOURCES
 YEAR 10 TEXTILES THEME Textiles around the world HEALTH AND HEALING INFLUENCES/SOURCES Pupils will develop ideas using primary and secondary images inspired by health and healing: Health and healing objects
YEAR 10 TEXTILES THEME Textiles around the world HEALTH AND HEALING INFLUENCES/SOURCES Pupils will develop ideas using primary and secondary images inspired by health and healing: Health and healing objects
Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Technology Level 1. Resource title: Personal Storage Item: Develop a Conceptual Design
 Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Technology Level 1 Resource title: Personal Storage Item: Develop a Conceptual Design This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard 91046 Demonstrate
Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Technology Level 1 Resource title: Personal Storage Item: Develop a Conceptual Design This exemplar supports assessment against: Achievement Standard 91046 Demonstrate
Year 13 - DVC NCEA LEVEL 3 Course Outline 2017 Technology Dept. Huntly College
 Year 13 - DVC NCEA LEVEL 3 Course Outline 2017 Technology Dept. Huntly College What is Design and Visual Communication? The term 'visual presentation' is used to refer to the actual presentation of information
Year 13 - DVC NCEA LEVEL 3 Course Outline 2017 Technology Dept. Huntly College What is Design and Visual Communication? The term 'visual presentation' is used to refer to the actual presentation of information
Materials Design and Technology General Course Year 12. Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the. Externally set task 2018
 Materials Design and Technology General Course Year 12 Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the Externally set task 2018 This document is an extract from the Materials Design and Technology General Course
Materials Design and Technology General Course Year 12 Selected Unit 3 syllabus content for the Externally set task 2018 This document is an extract from the Materials Design and Technology General Course
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
 TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION visual merchandising/ Window Dressing WorldSkills International TD44 v4.0 WSC2013 WorldSkills International, by a resolution of the Technical Committee and in accordance with the
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION visual merchandising/ Window Dressing WorldSkills International TD44 v4.0 WSC2013 WorldSkills International, by a resolution of the Technical Committee and in accordance with the
Make props using mixed media
 Training Package Title Unit code CUEPRP07A Entertainment (CUE03) Make props using mixed media Unit Descriptor This unit describes the skills and knowledge required to interpret props production schedules
Training Package Title Unit code CUEPRP07A Entertainment (CUE03) Make props using mixed media Unit Descriptor This unit describes the skills and knowledge required to interpret props production schedules
DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY
 Victorian Certificate of Education 2009 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words Section DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY Written examination Monday 9 November 2009 Reading time:
Victorian Certificate of Education 2009 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE STUDENT NUMBER Letter Figures Words Section DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY Written examination Monday 9 November 2009 Reading time:
2012 HSC Textiles and Design Marking Guidelines
 01 HSC Textiles and Design Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer 1 B D 3 A 4 C 5 B 6 A 7 C 8 B 9 D 10 C 1 01 HSC Textiles and Design Marking Guidelines Section II Question
01 HSC Textiles and Design Marking Guidelines Section I Multiple-choice Answer Key Question Answer 1 B D 3 A 4 C 5 B 6 A 7 C 8 B 9 D 10 C 1 01 HSC Textiles and Design Marking Guidelines Section II Question
Design Technology. IB DP course syllabus
 Design Technology IB DP course syllabus 2016-2018 School of Young Politicians Gymnasium 1306 Teacher: Mariam Ghukasyan Nature of design technology Design, and the resultant development of new technologies,
Design Technology IB DP course syllabus 2016-2018 School of Young Politicians Gymnasium 1306 Teacher: Mariam Ghukasyan Nature of design technology Design, and the resultant development of new technologies,
Area of Learning: APPLIED DESIGN, SKILLS, AND TECHNOLOGIES Media Design Grade 11 BIG IDEAS
 Area of Learning: APPLIED DESIGN, SKILLS, AND TECHNOLOGIES Media Design Grade 11 BIG IDEAS Design for the life cycle includes consideration of social and environmental impacts. Personal design choices
Area of Learning: APPLIED DESIGN, SKILLS, AND TECHNOLOGIES Media Design Grade 11 BIG IDEAS Design for the life cycle includes consideration of social and environmental impacts. Personal design choices
Praxis Technology Education (5051) Study Plan Description of content
 Page 1 I. Technology and Society (15%) A. Understands the nature of technology, technology education, and technological literacy B. Understands how invention and innovation occur, how they are influenced
Page 1 I. Technology and Society (15%) A. Understands the nature of technology, technology education, and technological literacy B. Understands how invention and innovation occur, how they are influenced
KNES Art & Design Course Outline. Year 8
 KNES Art & Design Course Outline Year 8 Art & Design stimulates creativity and imagination. It provides visual, tactile and sensory experiences and a unique way of understanding and responding to the world.
KNES Art & Design Course Outline Year 8 Art & Design stimulates creativity and imagination. It provides visual, tactile and sensory experiences and a unique way of understanding and responding to the world.
BIG IDEAS. Personal design interests require the evaluation and refinement of skills. Learning Standards
 Area of Learning: APPLIED DESIGN, SKILLS, AND TECHNOLOGIES BIG IDEAS Design for the life cycle includes consideration of social and environmental impacts. Personal design interests require the evaluation
Area of Learning: APPLIED DESIGN, SKILLS, AND TECHNOLOGIES BIG IDEAS Design for the life cycle includes consideration of social and environmental impacts. Personal design interests require the evaluation
ART AND DESIGN POLICY
 ART AND DESIGN POLICY Date: March 2018 Signed: Review: March 2019 Art, craft and design embody some of the highest forms of human creativity. A high-quality art and design education should engage, inspire
ART AND DESIGN POLICY Date: March 2018 Signed: Review: March 2019 Art, craft and design embody some of the highest forms of human creativity. A high-quality art and design education should engage, inspire
Product Design and Technology
 Product Design and Technology Victorian Certificate of Education Study Design Victorian Curriculum and Assessment Authority 2011 COVER ARTWORK WAS SELECTED FROM THE TOP ARTS EXHIBITION. COPYRIGHT REMAINS
Product Design and Technology Victorian Certificate of Education Study Design Victorian Curriculum and Assessment Authority 2011 COVER ARTWORK WAS SELECTED FROM THE TOP ARTS EXHIBITION. COPYRIGHT REMAINS
Product Design. Higher Prelim Notes
 Product Design Higher Prelim Notes TIPS -When you are asked to STATE something you are only being asked to name whatever you are being asked e.g. State 2 materials that could be used? Aluminium and Stainless
Product Design Higher Prelim Notes TIPS -When you are asked to STATE something you are only being asked to name whatever you are being asked e.g. State 2 materials that could be used? Aluminium and Stainless
Guidance for applying to study design
 Guidance for applying to study design 1 Contents Guidance for art, design and media arts applications 4 Guidelines for applications to undergraduate 5 courses in design BA (Honours) Fashion Design 7 MDes
Guidance for applying to study design 1 Contents Guidance for art, design and media arts applications 4 Guidelines for applications to undergraduate 5 courses in design BA (Honours) Fashion Design 7 MDes
Study: Visual Communication & Design
 CATHOLIC REGIONAL COLLEGE SYDENHAM Rationale: Study: Visual Communication & Design Visual Communication is a bridge between an idea and its intended audience. In the fields of architecture, engineering,
CATHOLIC REGIONAL COLLEGE SYDENHAM Rationale: Study: Visual Communication & Design Visual Communication is a bridge between an idea and its intended audience. In the fields of architecture, engineering,
Design and Technology
 2005 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Design and Technology Total marks 40 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 1 1 2 hours Write using black or blue pen Write your Centre Number
2005 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION Design and Technology Total marks 40 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 1 1 2 hours Write using black or blue pen Write your Centre Number
Years 3 and 4 standard elaborations Australian Curriculum: Design and Technologies
 Purpose The standard elaborations (SEs) provide additional clarity when using the Australian Curriculum achievement standard to make judgments on a five-point scale. They can be used as a tool for: making
Purpose The standard elaborations (SEs) provide additional clarity when using the Australian Curriculum achievement standard to make judgments on a five-point scale. They can be used as a tool for: making
Production Techniques for Fashion and Clothing
 Unit 124: Production Techniques for Fashion and Clothing Unit code: QCF Level 3: Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose H/502/5024 BTEC National The aim of this unit is to develop learners
Unit 124: Production Techniques for Fashion and Clothing Unit code: QCF Level 3: Credit value: 10 Guided learning hours: 60 Aim and purpose H/502/5024 BTEC National The aim of this unit is to develop learners
Knowledge, Skills and Understanding breakdown for Art. Year 1 Drawing Painting Printing Textiles. 3D Collage Use of IT Knowledge
 Knowledge, Skills and Understanding breakdown for Art Year 1 Drawing Painting Printing Textiles Can they communicate something about themselves in their drawing? Can they create moods in their drawings?
Knowledge, Skills and Understanding breakdown for Art Year 1 Drawing Painting Printing Textiles Can they communicate something about themselves in their drawing? Can they create moods in their drawings?
PowerAnchor STEM Curriculum mapping Year 10
 PowerAnchor STEM Curriculum mapping Year 10 *NOTE: Bullet points are ACARA provided elaborations for each outcome for this year level. Content Area Science Content Science Understanding Physical sciences:
PowerAnchor STEM Curriculum mapping Year 10 *NOTE: Bullet points are ACARA provided elaborations for each outcome for this year level. Content Area Science Content Science Understanding Physical sciences:
Graphic Communication Assignment General assessment information
 Graphic Communication Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the assignment Component of Higher Graphic Communication
Graphic Communication Assignment General assessment information This pack contains general assessment information for centres preparing candidates for the assignment Component of Higher Graphic Communication
Revision. Product Design GCSE
 GCSE Product Design Revision The following pages are a guide to the key areas you will need to have knowledge of in order to successfully complete your GCSE exam. At the end of each of the four sections,
GCSE Product Design Revision The following pages are a guide to the key areas you will need to have knowledge of in order to successfully complete your GCSE exam. At the end of each of the four sections,
Higher National Unit specification. General information for centres. Photography: Darkroom Techniques. Unit code: DW81 34
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Photography: Darkroom Techniques Unit code: DW81 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable the candidate to research,
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Photography: Darkroom Techniques Unit code: DW81 34 Unit purpose: This Unit is designed to enable the candidate to research,
Art & Design Curriculum Policy Statement
 Art & Design Curriculum Policy Statement WOODSTOCK CE PRIMARY SCHOOL Art & Design Curriculum Policy Statement PURPOSE OF STUDY Art, craft and design embody some of the highest forms of human creativity.
Art & Design Curriculum Policy Statement WOODSTOCK CE PRIMARY SCHOOL Art & Design Curriculum Policy Statement PURPOSE OF STUDY Art, craft and design embody some of the highest forms of human creativity.
CAMBRIDGE NATIONAL IN ENGINEERING
 CAMBRIDGE NATIONAL IN ENGINEERING Engineering Design R105, R106, R107, R108 A comprehensive 99 page overview of how the following qualifications match to the Learning Outcomes for National in Engineering,
CAMBRIDGE NATIONAL IN ENGINEERING Engineering Design R105, R106, R107, R108 A comprehensive 99 page overview of how the following qualifications match to the Learning Outcomes for National in Engineering,
DT MIND MAPS. Application. Information. Steps. Planning. Creativity Process. Analysis MIND MAPS NAME.
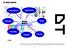 DT MIND MAPS Information Steps MIND MAPS Creativity Process Analysis DT Planning Application NAME. These mind maps are a visual thinking tool that helps structure information, helping to better analyse,
DT MIND MAPS Information Steps MIND MAPS Creativity Process Analysis DT Planning Application NAME. These mind maps are a visual thinking tool that helps structure information, helping to better analyse,
Year 11 GCSE Revision - Resistant Materials Topics for revision Re-visit work Suggested activities
 Week beginning 6 th Year 11 GCSE Revision - Resistant Materials Topics for revision Re-visit work Suggested activities Materials Woods-hard, soft, manufactured Metals-ferrous, non-ferrous, alloys Recognise
Week beginning 6 th Year 11 GCSE Revision - Resistant Materials Topics for revision Re-visit work Suggested activities Materials Woods-hard, soft, manufactured Metals-ferrous, non-ferrous, alloys Recognise
Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Visual Arts Level 2. Resource title: Still life
 Exemplar for internal assessment resource Visual Arts Painting 2.3 for Achievement Standard 91316 Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Visual Arts Level 2 Resource title: Still life This exemplar
Exemplar for internal assessment resource Visual Arts Painting 2.3 for Achievement Standard 91316 Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Visual Arts Level 2 Resource title: Still life This exemplar
Year 11 General Studies Visual Arts UNIT 1 EXPERIENCES (13 weeks) 2017 PROGRAMME
 Year 11 General Studies Visual Arts 1 EXPERIENCES (13 weeks) 2017 PROGRAMME DESCRIPTION: Experiences is the theme studied throughout this unit. Students develop artworks based on their lives and personal
Year 11 General Studies Visual Arts 1 EXPERIENCES (13 weeks) 2017 PROGRAMME DESCRIPTION: Experiences is the theme studied throughout this unit. Students develop artworks based on their lives and personal
DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY
 N E W S O U T H W A L E S HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 1997 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 2/3 UNIT (COMMON) (40 Marks) Time allowed One hour and a half (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES
N E W S O U T H W A L E S HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 1997 DESIGN AND TECHNOLOGY 2/3 UNIT (COMMON) (40 Marks) Time allowed One hour and a half (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES
RIVERSDALE PRIMARY SCHOOL. Design & Technology Policy
 RIVERSDALE PRIMARY SCHOOL Design & Technology Policy EQUALITY At Riversdale we have due regard for our duties under the Equality Act 2010. Through the use of the library, we will ensure that we: eliminate
RIVERSDALE PRIMARY SCHOOL Design & Technology Policy EQUALITY At Riversdale we have due regard for our duties under the Equality Act 2010. Through the use of the library, we will ensure that we: eliminate
Scope and Sequence Chart Subject Area: Food Technology Year Level: 9 TERM 1 TERM 2 TERM 3 TERM 4
 Scope and Sequence Chart Subject Area: Food Technology TERM 1 TERM 2 TERM 3 TERM 4 UNIT 1- Food handling/kitchen safety and hygiene (1 week) UNIT 2- Global goodies Indigenous Australians - History of Australia
Scope and Sequence Chart Subject Area: Food Technology TERM 1 TERM 2 TERM 3 TERM 4 UNIT 1- Food handling/kitchen safety and hygiene (1 week) UNIT 2- Global goodies Indigenous Australians - History of Australia
Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work
 Number of weeks (between 6&8) Content of the unit Assumed prior learning (tested at the beginning of the unit) 16 weeks No. of lessons: 24 (1:40 minutes each) Unit 1: Written Paper (40% of the course)
Number of weeks (between 6&8) Content of the unit Assumed prior learning (tested at the beginning of the unit) 16 weeks No. of lessons: 24 (1:40 minutes each) Unit 1: Written Paper (40% of the course)
The. Nuts and Bolts of an. MYP Unit Shaker MYP Professional Development November 24, 2015
 The Nuts and Bolts of an MYP Unit Shaker MYP Professional Development November 24, 2015 Statement of Inquiry: Informed educators design MYP units of inquiry with knowledge of the necessary nuts and bolts
The Nuts and Bolts of an MYP Unit Shaker MYP Professional Development November 24, 2015 Statement of Inquiry: Informed educators design MYP units of inquiry with knowledge of the necessary nuts and bolts
HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION TEXTILES AND DESIGN 2/3 UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time)
 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 1999 TEXTILES AND DESIGN 2/3 UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES This paper is divided into THREE sections.
HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 1999 TEXTILES AND DESIGN 2/3 UNIT (COMMON) Time allowed Three hours (Plus 5 minutes reading time) DIRECTIONS TO CANDIDATES This paper is divided into THREE sections.
Design and Technology
 2013 H I G H E R S C H O O L C E R T I F I C A T E E X A M I N A T I O N Design and Technology Total marks 40 Section I Pages 2 4 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 1 1 hours 2 Write
2013 H I G H E R S C H O O L C E R T I F I C A T E E X A M I N A T I O N Design and Technology Total marks 40 Section I Pages 2 4 General Instructions Reading time 5 minutes Working time 1 1 hours 2 Write
2000 HSC Notes from the Examination Centre Textiles and Design
 2000 HSC Notes from the Examination Centre Textiles and Design Board of Studies 2001 Published by Board of Studies NSW GPO Box 5300 Sydney NSW 2001 Australia Tel: (02) 9367 8111 Fax: (02) 9262 6270 Internet:
2000 HSC Notes from the Examination Centre Textiles and Design Board of Studies 2001 Published by Board of Studies NSW GPO Box 5300 Sydney NSW 2001 Australia Tel: (02) 9367 8111 Fax: (02) 9262 6270 Internet:
WORLDSKILLS STANDARD SPECIFICATION
 WSC2015_WSSS05 WORLDSKILLS STANDARD SPECIFICATION Skill 05 Mechanical Engineering Design - CAD THE WORLDSKILLS STANDARDS SPECIFICATION (WSSS) GENERAL NOTES ON THE WSSS The WSSS specifies the knowledge,
WSC2015_WSSS05 WORLDSKILLS STANDARD SPECIFICATION Skill 05 Mechanical Engineering Design - CAD THE WORLDSKILLS STANDARDS SPECIFICATION (WSSS) GENERAL NOTES ON THE WSSS The WSSS specifies the knowledge,
learning progression diagrams
 Technological literacy: implications for Teaching and learning learning progression diagrams The connections in these Learning Progression Diagrams show how learning progresses between the indicators within
Technological literacy: implications for Teaching and learning learning progression diagrams The connections in these Learning Progression Diagrams show how learning progresses between the indicators within
Draft Shape of the Australian Curriculum: Technologies
 November 2010 Draft Shape of the Australian Curriculum: Technologies March 2012 www.acara.edu.au Contents Purpose... 1 Background... 1 Introduction... 2 The contribution of technologies education to students
November 2010 Draft Shape of the Australian Curriculum: Technologies March 2012 www.acara.edu.au Contents Purpose... 1 Background... 1 Introduction... 2 The contribution of technologies education to students
Curriculum rationale Faculty : Design Lead : M Jones What is your curriculum statement for each key stage?
 What is your curriculum statement for each key stage? There are also some characteristics distinct to our subject. Design Technology is taught at KS2 to widely varying levels, students join us with a range
What is your curriculum statement for each key stage? There are also some characteristics distinct to our subject. Design Technology is taught at KS2 to widely varying levels, students join us with a range
Transportation. Inspiring aesthetics for your visions
 Transportation and Product Design Inspiring aesthetics for your visions Our Benchmark: The Human Being We develop, simulate, test and analyse for visions of the future. Our passion: Mobility and Sports.
Transportation and Product Design Inspiring aesthetics for your visions Our Benchmark: The Human Being We develop, simulate, test and analyse for visions of the future. Our passion: Mobility and Sports.
