PHGY Physiology. The Process of Vision. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré. Visible Light. Ocular Anatomy. Ocular Anatomy.
|
|
|
- Charleen Cox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHGY Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca The Process of Vision Vision is the process through which light reflected from objects is translated into a mental image. It involves a sensory organ (the eye), in which light rays are focused by a lens onto the retina, where photoreceptors transduce light energy into electrical signals, which are integrated to create mental images after processing in the cerebral cortex. Visible Light Visible light is composed of electromagnetic waves with frequencies between x hertz and wavelengths between nanometers (nm). The eye is a fluid-filled sphere enclosed by three layers of tissue: 1) The outer layer is composed of the sclera and the cornea. 2) The middle layer includes the iris, the ciliary body, and the choroid. 3) The inner layer is the actual retina containing the photoreceptors. En route to the retina, light successively travels through: 1) the cornea 2) the aqueous humor of the anterior chamber 3) the pupil 4) the lens 5) the vitreous humor The iris contains a musculature controlling the pupil size. Its function is to modulate the amount of light that enters the eyes.
2 The ciliary body encircles the lens. It contains a musculature that adjusts the refractive power of the lens. Together with the cornea, the lens help focusing the image on the retina. The aqueous humor is a clear, watery liquid in the anterior chamber produced by the ciliary body in the posterior chamber. It regulates the intraocular pressure. Schlemm s canal The vitreous humor is a thick gelatinous substance between the back of the lens and the retina. It accounts for the size and shape of the globe. The choroid is a capillary bed. It supplies oxygenation and metabolic sustenance to the cells in the retina, including the photoreceptors. Control of Incoming Light The amount of light that enters the eyes is modulated by changing the size of the pupil. This control originates from the brain stem. Circular muscles under parasympathetic control reduce pupils size. Pupillary Light Reflexes Shining a light into each eye can elicit a direct and a consensual pupillary light reflex. This light reflex tells us about the state of a patient s visual pathways and helps identify the cause of structural coma. Radial muscles under sympathetic control increase pupil size. direct consensual
3 The ability to focus an image on the retina depends on the refractive power of both the cornea and the lens as well as on the shape of the eye globe. The angle of refraction depends on: 1) the difference in density of the two milieus 2) the angle at which the light meets the surface. When the eye is able to bring distant objects to point focus on the retina without the need of a refractive aid, the eye is said to be in a state of emmetropia. When an object is distant, the light rays are essentially parallel and brought to a focus on the retina. If the object moves closer, the focal point then moves behind the retina. To bring the image into focus on the retina, the lens refractive power must be increased. This is the process of accommodation. The lens changes its shape through the action of inelastic fibers called zonulas. Contraction in ciliary muscles relaxes these zonulas, which then allow the lens to assume its natural rounded shape. Accommodation has its limits!!! The closest distance at which your lens can focus on objects is called the near point of accommodation.
4 Problem in Problem in Our lens hardens with age and ciliary muscles weaken. This gradual decreased ability in accommodation is called presbyopia. The solution to presbyopia is a corrective (convex) lens that augments the focusing power to bring the retinal image to a focus on the retina. Problem in Problem in Most of us (~70%) have a refractive error (ametropia), in which light rays come to a point focus either behind the retina (hyperopia) or in front of it (myopia). The solution to hyperopia is a corrective (convex) lens that augments the eye s defective refractive power by converging the light rays to a focus on the retina. Hyperopia (farsighted) Myopia (nearsighted) Problem in Retina The solution to myopia is a corrective (concave) lens that reduces the eye s excess refractive power by diverging the light rays to a focus on the retina. Light strikes photoreceptors only after passing through sensory neurons, except at the central retinal region (fovea) where acuity is best.
5 Retina Retina Visual information is transmitted from photoreceptors to bipolar neurons and ganglion neurons before exiting the eye via the optic nerve. Optic nerve Blind Spot Demonstration
6 Rods: achromatic nighttime vision, when light levels are low. Cones: high-acuity and color vision during daytime, when light levels are higher. Phototransduction Rod System Achromatic Peripheral retina High convergence High light sensitivity Low visual acuity Cone System Chromatic Central retina (fovea) Low convergence Low light sensitivity High visual acuity ON and OFF channels ON and OFF channels The hyperpolarization of photoreceptors elicits both depolarization and hyperpolarization within bipolar and ganglion cells. These graded potentials modulate the discharge rates of ganglion cells. ON and OFF bipolar and ganglion cells respectively detect increases and decreases in luminance. Thanks to lateral inhibition, the receptive fields of ON and OFF ganglion cells have a center-surround organization: stimulation of the region surrounding their receptive fields elicit opposite responses.
7 ON and OFF channels Visual Pathways Center-surround organization serves to emphasize areas of difference (contrast). Our visual system detects local differences in light intensity rather than the absolute amounts of light. Each eye sees a part of the visual space (visual field). The visual fields of both eyes overlap extensively to create a binocular visual field. Visual Pathways Visual Pathways Nerve fibers from the nasal half of each retina cross over at the optic chiasm. The optic tract projects primarily to the thalamus (lateral geniculate nucleus), which projects to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe. The resulting two optic tracts allow right and left visual fields to reach separately the left and right hemispheres. Reading Silverthorn (2 nd edition) Silverthorn (1 st edition) pages pages
PHGY Physiology. SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision. Martin Paré
 PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
PHGY 212 - Physiology SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY Vision Martin Paré Assistant Professor of Physiology & Psychology pare@biomed.queensu.ca http://brain.phgy.queensu.ca/pare The Process of Vision Vision is the process
The Special Senses: Vision
 OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
OLLI Lecture 5 The Special Senses: Vision Vision The eyes are the sensory organs for vision. They collect light waves through their photoreceptors (located in the retina) and transmit them as nerve impulses
Vision. By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd
 Vision By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd Anatomy Outermost part of the eye is the Sclera. Cornea transparent part of outer layer Two cavities by the lens. Anterior cavity = Aqueous humor
Vision By. Leanora Thompson, Karen Vega, and Abby Brainerd Anatomy Outermost part of the eye is the Sclera. Cornea transparent part of outer layer Two cavities by the lens. Anterior cavity = Aqueous humor
November 14, 2017 Vision: photoreceptor cells in eye 3 grps of accessory organs 1-eyebrows, eyelids, & eyelashes 2- lacrimal apparatus:
 Vision: photoreceptor cells in eye 3 grps of accessory organs 1-eyebrows, eyelids, & eyelashes eyebrows: protection from debris & sun eyelids: continuation of skin, protection & lubrication eyelashes:
Vision: photoreceptor cells in eye 3 grps of accessory organs 1-eyebrows, eyelids, & eyelashes eyebrows: protection from debris & sun eyelids: continuation of skin, protection & lubrication eyelashes:
2 The First Steps in Vision
 2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
2 The First Steps in Vision 2 The First Steps in Vision A Little Light Physics Eyes That See light Retinal Information Processing Whistling in the Dark: Dark and Light Adaptation The Man Who Could Not
Sensory receptors External internal stimulus change detectable energy transduce action potential different strengths different frequencies
 General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
General aspects Sensory receptors ; respond to changes in the environment. External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor
Chapter Six Chapter Six
 Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Chapter Six Chapter Six Vision Sight begins with Light The advantages of electromagnetic radiation (Light) as a stimulus are Electromagnetic energy is abundant, travels VERY quickly and in fairly straight
Eye. Eye Major structural layer of the wall of the eye is a thick layer of dense C.T.; that layer has two parts:
 General aspects Sensory receptors ; External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor 1 Major structural layer of the wall
General aspects Sensory receptors ; External or internal environment. A stimulus is a change in the environmental condition which is detectable by a sensory receptor 1 Major structural layer of the wall
EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 Name: Class: Date: EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The eye is the body s organ of sight. It gathers light from the environment and forms an image on specialized nerve cells on the retina. Vision occurs when
Name: Class: Date: EYE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION The eye is the body s organ of sight. It gathers light from the environment and forms an image on specialized nerve cells on the retina. Vision occurs when
Topic 4: Lenses and Vision. Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic
 Topic 4: Lenses and Vision Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic Double Concave Lenses Are thinner and flatter in the middle than around the edges.
Topic 4: Lenses and Vision Lens a curved transparent material through which light passes (transmit) Ex) glass, plastic Double Concave Lenses Are thinner and flatter in the middle than around the edges.
Vision. By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen
 Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Vision By: Karen, Jaqui, and Jen Activity: Directions: Stare at the black dot in the center of the picture don't look at anything else but the black dot. When we switch the picture you can look around
Special Senses. Important Concepts. Anatomy of the Eye. Anatomy of the Eye. Biol 219 Lecture 17 Vision Fall The Eye and Vision
 Special Senses The Eye and Vision Important Concepts Describe the structures of the eye and the role of each structure in vision. Trace the pathway for vis ion from the retina to the visual cortex. Explain
Special Senses The Eye and Vision Important Concepts Describe the structures of the eye and the role of each structure in vision. Trace the pathway for vis ion from the retina to the visual cortex. Explain
Coarse hairs that overlie the supraorbital margins Functions include: Shading the eye Preventing perspiration from reaching the eye
 SPECIAL SENSES (INDERA KHUSUS) Dr.Milahayati Daulay Departemen Fisiologi FK USU Eye and Associated Structures 70% of all sensory receptors are in the eye Most of the eye is protected by a cushion of fat
SPECIAL SENSES (INDERA KHUSUS) Dr.Milahayati Daulay Departemen Fisiologi FK USU Eye and Associated Structures 70% of all sensory receptors are in the eye Most of the eye is protected by a cushion of fat
III: Vision. Objectives:
 III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
III: Vision Objectives: Describe the characteristics of visible light, and explain the process by which the eye transforms light energy into neural. Describe how the eye and the brain process visual information.
ABO Certification Training. Part I: Anatomy and Physiology
 ABO Certification Training Part I: Anatomy and Physiology Major Ocular Structures Centralis Nerve Major Ocular Structures The Cornea Cornea Layers Epithelium Highly regenerative: Cells reproduce so rapidly
ABO Certification Training Part I: Anatomy and Physiology Major Ocular Structures Centralis Nerve Major Ocular Structures The Cornea Cornea Layers Epithelium Highly regenerative: Cells reproduce so rapidly
The Eye. Nakhleh Abu-Yaghi, M.B.B.S Ophthalmology Division
 The Eye Nakhleh Abu-Yaghi, M.B.B.S Ophthalmology Division Coats of the Eyeball 1- OUTER FIBROUS COAT is made up of : Posterior opaque part 2-THE SCLERA the dense white part 1- THE CORNEA the anterior
The Eye Nakhleh Abu-Yaghi, M.B.B.S Ophthalmology Division Coats of the Eyeball 1- OUTER FIBROUS COAT is made up of : Posterior opaque part 2-THE SCLERA the dense white part 1- THE CORNEA the anterior
EYE. The eye is an extension of the brain
 I SEE YOU EYE The eye is an extension of the brain Eye brain proxomity Can you see : the optic nerve bundle? Spinal cord? The human Eye The eye is the sense organ for light. Receptors for light are found
I SEE YOU EYE The eye is an extension of the brain Eye brain proxomity Can you see : the optic nerve bundle? Spinal cord? The human Eye The eye is the sense organ for light. Receptors for light are found
EYE ANATOMY. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. The information in this presentation has been intended to help consumers understand the structure and
Slide 4 Now we have the same components that we find in our eye. The analogy is made clear in this slide. Slide 5 Important structures in the eye
 Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Vision 1 Slide 2 The obvious analogy for the eye is a camera, and the simplest camera is a pinhole camera: a dark box with light-sensitive film on one side and a pinhole on the other. The image is made
Visual System I Eye and Retina
 Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Visual System I Eye and Retina Reading: BCP Chapter 9 www.webvision.edu The Visual System The visual system is the part of the NS which enables organisms to process visual details, as well as to perform
Sensation. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition. All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms
 Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
Sensation. Sensation. Perception. What is Sensation, Perception, and Cognition
 All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
All sensory systems operate the same, they only use different mechanisms Sensation 1. Have a physical stimulus (e.g., light) 2. The stimulus emits some sort of energy 3. Energy activates some sort of receptor
10/8/ dpt. n 21 = n n' r D = The electromagnetic spectrum. A few words about light. BÓDIS Emőke 02 October Optical Imaging in the Eye
 A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
A few words about light BÓDIS Emőke 02 October 2012 Optical Imaging in the Eye Healthy eye: 25 cm, v1 v2 Let s determine the change in the refractive power between the two extremes during accommodation!
Biology 70 Slides for Lecture 1 Fall 2007
 Biology 70 Part II Sensory Systems www.biology.ucsc.edu 1 2 intensity vs spatial position (image formation) color 3 4 motion depth (monocular) 5 6 1 depth (binocular) 1. In the lectures on perception we
Biology 70 Part II Sensory Systems www.biology.ucsc.edu 1 2 intensity vs spatial position (image formation) color 3 4 motion depth (monocular) 5 6 1 depth (binocular) 1. In the lectures on perception we
Chapter 6 Human Vision
 Chapter 6 Notes: Human Vision Name: Block: Human Vision The Humane Eye: 8) 1) 2) 9) 10) 4) 5) 11) 12) 3) 13) 6) 7) Functions of the Eye: 1) Cornea a transparent tissue the iris and pupil; provides most
Chapter 6 Notes: Human Vision Name: Block: Human Vision The Humane Eye: 8) 1) 2) 9) 10) 4) 5) 11) 12) 3) 13) 6) 7) Functions of the Eye: 1) Cornea a transparent tissue the iris and pupil; provides most
Vision. The eye. Image formation. Eye defects & corrective lenses. Visual acuity. Colour vision. Lecture 3.5
 Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Lecture 3.5 Vision The eye Image formation Eye defects & corrective lenses Visual acuity Colour vision Vision http://www.wired.com/wiredscience/2009/04/schizoillusion/ Perception of light--- eye-brain
Objectives. 3. Visual acuity. Layers of the. eye ball. 1. Conjunctiva : is. three quarters. posteriorly and
 OCULAR PHYSIOLOGY (I) Dr.Ahmed Al Shaibani Lab.2 Oct.2013 Objectives 1. Review of ocular anatomy (Ex. after image) 2. Visual pathway & field (Ex. Crossed & uncrossed diplopia, mechanical stimulation of
OCULAR PHYSIOLOGY (I) Dr.Ahmed Al Shaibani Lab.2 Oct.2013 Objectives 1. Review of ocular anatomy (Ex. after image) 2. Visual pathway & field (Ex. Crossed & uncrossed diplopia, mechanical stimulation of
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to:
 SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
11/23/11. A few words about light nm The electromagnetic spectrum. BÓDIS Emőke 22 November Schematic structure of the eye
 11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
11/23/11 A few words about light 300-850nm 400-800 nm BÓDIS Emőke 22 November 2011 The electromagnetic spectrum see only 1/70 of the electromagnetic spectrum The External Structure: The Immediate Structure:
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to:
 SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
SCIENCE 8 WORKBOOK Chapter 6 Human Vision Ms. Jamieson 2018 This workbook belongs to: Eric Hamber Secondary 5025 Willow Street Vancouver, BC Table of Contents A. Chapter 6.1 Parts of the eye.. Parts of
Chapter 25: Applied Optics. PHY2054: Chapter 25
 Chapter 25: Applied Optics PHY2054: Chapter 25 1 Operation of the Eye 24 mm PHY2054: Chapter 25 2 Essential parts of the eye Cornea transparent outer structure Pupil opening for light Lens partially focuses
Chapter 25: Applied Optics PHY2054: Chapter 25 1 Operation of the Eye 24 mm PHY2054: Chapter 25 2 Essential parts of the eye Cornea transparent outer structure Pupil opening for light Lens partially focuses
Handout G: The Eye and How We See
 Handout G: The Eye and How We See Prevent Blindness America. (2003c). The eye and how we see. Retrieved July 31, 2003, from http://www.preventblindness.org/resources/howwesee.html Your eyes are wonderful
Handout G: The Eye and How We See Prevent Blindness America. (2003c). The eye and how we see. Retrieved July 31, 2003, from http://www.preventblindness.org/resources/howwesee.html Your eyes are wonderful
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3.
 AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
AP PSYCH Unit 4.2 Vision 1. How does the eye transform light energy into neural messages? 2. How does the brain process visual information? 3. What theories help us understand color vision? 4. Is your
Exam 3--PHYS 151--S15
 Name: Class: Date: Exam 3--PHYS 151--S15 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider this diagram of the eye and answer the following questions.
Name: Class: Date: Exam 3--PHYS 151--S15 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider this diagram of the eye and answer the following questions.
iris pupil cornea ciliary muscles accommodation Retina Fovea blind spot
 Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Chapter 6 Vision Exam 1 Anatomy of vision Primary visual cortex (striate cortex, V1) Prestriate cortex, Extrastriate cortex (Visual association coretx ) Second level association areas in the temporal and
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2)
 Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
Early Visual Processing: Receptive Fields & Retinal Processing (Chapter 2, part 2) Lecture 5 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Spring 2015 1 Summary of last
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
 L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS SIMPLE MICROSCOPE A simple microscope consists of a single convex lens of a short focal length. The object
L. R. & S. M. VISSANJI ACADEMY SECONDARY SECTION - 2016-17 PHYSICS-GRADE: VIII OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS SIMPLE MICROSCOPE A simple microscope consists of a single convex lens of a short focal length. The object
Vision. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 13. Vision. Vision
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Vision Module 13 2 Vision Vision The Stimulus Input: Light Energy The
Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Lenses convex (converging) concave (diverging) Mirrors Ray Tracing for Mirrors We use three principal rays in finding the image produced by a curved mirror. The parallel ray
Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Lenses convex (converging) concave (diverging) Mirrors Ray Tracing for Mirrors We use three principal rays in finding the image produced by a curved mirror. The parallel ray
Lecture Outline Chapter 27. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 27 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Units of Chapter 27 The Human Eye and the Camera Lenses in Combination and Corrective Optics The Magnifying
Lecture Outline Chapter 27 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Units of Chapter 27 The Human Eye and the Camera Lenses in Combination and Corrective Optics The Magnifying
By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein
 By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein Light is a form of radiant energy, consisting of electromagnetic waves a. Velocity of light: In air it is 300,000 km/second. b. Wave length: The wave-length of visible light to
By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein Light is a form of radiant energy, consisting of electromagnetic waves a. Velocity of light: In air it is 300,000 km/second. b. Wave length: The wave-length of visible light to
HW- Finish your vision book!
 March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
March 1 Table of Contents: 77. March 1 & 2 78. Vision Book Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Vision Notes and Discussion 3. Work on vision book! EQ- How does vision work? Do Now 1.Find your Vision Sensation fill-in-theblanks
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye
 The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 1 - The Eye www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 2 Introduction... 2 Accommodation... 3 The Iris... 4 The Cells in the Retina... 5 Receptive Fields... 8 The
1. Introduction to Anatomy of the Eye and its Adnexa
 1. Introduction to Anatomy of the Eye and its Adnexa Fig 1: A Cross section of the human eye. Let us imagine we are traveling with a ray of light into the eye. The first structure we will encounter is
1. Introduction to Anatomy of the Eye and its Adnexa Fig 1: A Cross section of the human eye. Let us imagine we are traveling with a ray of light into the eye. The first structure we will encounter is
4Basic anatomy and physiology
 Hene_Ch09.qxd 8/30/04 6:51 AM Page 348 348 4Basic anatomy and physiology The eye is a highly specialized organ with an average axial length of 24 mm and a volume of 6.5 ml. Except for its anterior aspect,
Hene_Ch09.qxd 8/30/04 6:51 AM Page 348 348 4Basic anatomy and physiology The eye is a highly specialized organ with an average axial length of 24 mm and a volume of 6.5 ml. Except for its anterior aspect,
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory
 The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Learning - There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different part of the brain. Remembering Mirror Writing Today we will be.
Retina. Convergence. Early visual processing: retina & LGN. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones. Visual Photoreptors: rods and cones.
 Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Announcements 1 st exam (next Thursday): Multiple choice (about 22), short answer and short essay don t list everything you know for the essay questions Book vs. lectures know bold terms for things that
Special Senses: The Eye
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401: Week 9 Special Senses: The Eye 1 VISION As humans, we rely on Vision more than any other special sense. The eye itself is surrounded by accessory structures Eyelids
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401: Week 9 Special Senses: The Eye 1 VISION As humans, we rely on Vision more than any other special sense. The eye itself is surrounded by accessory structures Eyelids
The eye & corrective lenses
 Phys 102 Lecture 20 The eye & corrective lenses 1 Today we will... Apply concepts from ray optics & lenses Simple optical instruments the camera & the eye Learn about the human eye Accommodation Myopia,
Phys 102 Lecture 20 The eye & corrective lenses 1 Today we will... Apply concepts from ray optics & lenses Simple optical instruments the camera & the eye Learn about the human eye Accommodation Myopia,
25 Things To Know. Vision
 25 Things To Know Vision Magnetism Electromagnetic Energy Electricity Magnetism Electromagnetic Energy Electricity Light Frequency Amplitude Light Frequency How often it comes Wave length Peak to peak
25 Things To Know Vision Magnetism Electromagnetic Energy Electricity Magnetism Electromagnetic Energy Electricity Light Frequency Amplitude Light Frequency How often it comes Wave length Peak to peak
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14
 Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
Yokohama City University lecture INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Presentation notes 7/10/14 1. INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN VISION Self introduction Dr. Salmon Northeastern State University, Oklahoma. USA Teach
[Chapter 2] Ocular Geometry and Topography. Elements of Ocular Structure
![[Chapter 2] Ocular Geometry and Topography. Elements of Ocular Structure [Chapter 2] Ocular Geometry and Topography. Elements of Ocular Structure](/thumbs/95/124174711.jpg) [Chapter 2] Ocular Geometry and Topography Before Sam Clemens became Mark Twain, he had been, among other things, a riverboat pilot, a placer miner, and a newspaper reporter, occupations in which success
[Chapter 2] Ocular Geometry and Topography Before Sam Clemens became Mark Twain, he had been, among other things, a riverboat pilot, a placer miner, and a newspaper reporter, occupations in which success
AS Psychology Activity 4
 AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
AS Psychology Activity 4 Anatomy of The Eye Light enters the eye and is brought into focus by the cornea and the lens. The fovea is the focal point it is a small depression in the retina, at the back of
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
Chapter Human Vision
 Chapter 6 6.1 Human Vision How Light Enters the Eye Light enters the eye through the pupil. The pupil appears dark because light passes through it without reflecting back Pupil Iris = Coloured circle of
Chapter 6 6.1 Human Vision How Light Enters the Eye Light enters the eye through the pupil. The pupil appears dark because light passes through it without reflecting back Pupil Iris = Coloured circle of
LECTURE 2. Vision Accomodation& pupillary light reflex By Prof/Faten zakareia
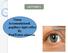 LECTURE 2 Vision Accomodation& pupillary light reflex By Prof/Faten zakareia Objectives: At the end of this lecture,the student should be able to;- -Describe visual acuity & depth perception -Contrast
LECTURE 2 Vision Accomodation& pupillary light reflex By Prof/Faten zakareia Objectives: At the end of this lecture,the student should be able to;- -Describe visual acuity & depth perception -Contrast
General Physics - E&M (PHY 1308) - Lecture Notes. General Physics - E&M (PHY 1308) Lecture Notes
 General Physics - E&M (PHY 1308) Lecture Notes Lecture 036: Application of Lenses - the Human Eye SteveSekula, 1 December 2010 (created 30 November 2010) Goals of this lecture no tags conclude the discussion
General Physics - E&M (PHY 1308) Lecture Notes Lecture 036: Application of Lenses - the Human Eye SteveSekula, 1 December 2010 (created 30 November 2010) Goals of this lecture no tags conclude the discussion
Chapter 29/30. Wave Fronts and Rays. Refraction of Sound. Dispersion in a Prism. Index of Refraction. Refraction and Lenses
 Chapter 29/30 Refraction and Lenses Refraction Refraction the bending of waves as they pass from one medium into another. Caused by a change in the average speed of light. Analogy A car that drives off
Chapter 29/30 Refraction and Lenses Refraction Refraction the bending of waves as they pass from one medium into another. Caused by a change in the average speed of light. Analogy A car that drives off
Aspects of Vision. Senses
 Lab is modified from Meehan (1998) and a Science Kit lab 66688 50. Vision is the act of seeing; vision involves the transmission of the physical properties of an object from an object, through the eye,
Lab is modified from Meehan (1998) and a Science Kit lab 66688 50. Vision is the act of seeing; vision involves the transmission of the physical properties of an object from an object, through the eye,
This question addresses OPTICAL factors in image formation, not issues involving retinal or other brain structures.
 Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
Bonds 1. Cite three practical challenges in forming a clear image on the retina and describe briefly how each is met by the biological structure of the eye. Note that by challenges I do not refer to optical
PSY 214 Lecture # (09/14/2011) (Introduction to Vision) Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 4 Topic: Introduction to Vision Chapter 3, pages 44-54
 Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Corrections: A correction needs to be made to NTCO3 on page 3 under excitatory transmitters. It is possible to excite a neuron without sending information to another neuron. For example, in figure 2.12
Physics Chapter Review Chapter 25- The Eye and Optical Instruments Ethan Blitstein
 Physics Chapter Review Chapter 25- The Eye and Optical Instruments Ethan Blitstein The Human Eye As light enters through the human eye it first passes through the cornea (a thin transparent membrane of
Physics Chapter Review Chapter 25- The Eye and Optical Instruments Ethan Blitstein The Human Eye As light enters through the human eye it first passes through the cornea (a thin transparent membrane of
Physics 11. Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2
 Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2 (c) Refraction (i) Introduction: Snell s law Like water waves, when light is traveling from one medium to another, not only does its wavelength, and in turn the
Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2 (c) Refraction (i) Introduction: Snell s law Like water waves, when light is traveling from one medium to another, not only does its wavelength, and in turn the
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory
 The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Methods of Learning Learning The acquisition of new knowledge and skills. There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different
The Human Brain and Senses: Memory Methods of Learning Methods of Learning Learning The acquisition of new knowledge and skills. There are several types of memory, and each is processed in a different
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to the
Chapter 36 Image Formation Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to the
Visual Optics. Visual Optics - Introduction
 Visual Optics Jim Schwiegerling, PhD Ophthalmology & Optical Sciences University of Arizona Visual Optics - Introduction In this course, the optical principals behind the workings of the eye and visual
Visual Optics Jim Schwiegerling, PhD Ophthalmology & Optical Sciences University of Arizona Visual Optics - Introduction In this course, the optical principals behind the workings of the eye and visual
Materials Cow eye, dissecting pan, dissecting kit, safety glasses, lab apron, and gloves
 Cow Eye Dissection Guide Introduction How do we see? The eye processes the light through photoreceptors located in the eye that send signals to the brain and tells us what we are seeing. There are two
Cow Eye Dissection Guide Introduction How do we see? The eye processes the light through photoreceptors located in the eye that send signals to the brain and tells us what we are seeing. There are two
OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES
 101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
Chapter 25. Optical Instruments
 Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
-eyelashes are richly innervated and triggers reflex blinking
 The Eye and Vision -vision is the dominant sense -70% of all sensory receptors in the body are in the eyes -half of the cerebral cortex is involved in some aspect of visual processing -accessory structures
The Eye and Vision -vision is the dominant sense -70% of all sensory receptors in the body are in the eyes -half of the cerebral cortex is involved in some aspect of visual processing -accessory structures
THE EYE. People of Asian descent have an EPICANTHIC FOLD in the upper eyelid; no functional difference.
 THE EYE The eye is in the orbit of the skull for protection. Within the orbit are 6 extrinsic eye muscles, which move the eye. There are 4 cranial nerves: Optic (II), Occulomotor (III), Trochlear (IV),
THE EYE The eye is in the orbit of the skull for protection. Within the orbit are 6 extrinsic eye muscles, which move the eye. There are 4 cranial nerves: Optic (II), Occulomotor (III), Trochlear (IV),
Vision Basics Measured in:
 Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
Vision Vision Basics Sensory receptors in our eyes transduce light into meaningful images Light = packets of waves Measured in: Brightness amplitude of wave (high=bright) Color length of wave Saturation
 Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World Question 1: What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye? When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thin, the focal length increases, and
Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World Question 1: What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye? When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thin, the focal length increases, and
Physics of the Eye *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42482 1 Physics of the Eye * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain the image formation by
OpenStax-CNX module: m42482 1 Physics of the Eye * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain the image formation by
Human Eye and Colourful World Science. Intext Exercise 1
 Intext Exercise 1 Question 1: What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye? Solution 1: When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thin, the focal length increases, and the distant
Intext Exercise 1 Question 1: What is meant by power of accommodation of the eye? Solution 1: When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thin, the focal length increases, and the distant
Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1
 Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Name: Class: Date: Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 1 Multiple Choice There are 35 multiple choice questions worth one point each. Identify the letter of the choice that best completes
Lecture 8. Lecture 8. r 1
 Lecture 8 Achromat Design Design starts with desired Next choose your glass materials, i.e. Find P D P D, then get f D P D K K Choose radii (still some freedom left in choice of radii for minimization
Lecture 8 Achromat Design Design starts with desired Next choose your glass materials, i.e. Find P D P D, then get f D P D K K Choose radii (still some freedom left in choice of radii for minimization
Special Senses- THE EYE. Pages
 Special Senses- THE EYE Pages 548-569 Accessory Structures Eyebrows Eyelids Conjunctiva Lacrimal Apparatus Extrinsic Eye Muscles EYEBROWS Deflect debris to side of face Facial recognition Nonverbal communication
Special Senses- THE EYE Pages 548-569 Accessory Structures Eyebrows Eyelids Conjunctiva Lacrimal Apparatus Extrinsic Eye Muscles EYEBROWS Deflect debris to side of face Facial recognition Nonverbal communication
Photography (cont d)
 Lecture 13 Ch. 4 Photography continued Ch. 5 The Eye Feb. 23, 2010 Exams will be back on Feb. 25 Homework 5 is due Feb. 25 Read all of Ch. 5. on The Eye. 1 Photography (cont d) Polarizing and haze filters
Lecture 13 Ch. 4 Photography continued Ch. 5 The Eye Feb. 23, 2010 Exams will be back on Feb. 25 Homework 5 is due Feb. 25 Read all of Ch. 5. on The Eye. 1 Photography (cont d) Polarizing and haze filters
30 Lenses. Lenses change the paths of light.
 Lenses change the paths of light. A light ray bends as it enters glass and bends again as it leaves. Light passing through glass of a certain shape can form an image that appears larger, smaller, closer,
Lenses change the paths of light. A light ray bends as it enters glass and bends again as it leaves. Light passing through glass of a certain shape can form an image that appears larger, smaller, closer,
The Human Visual System. Lecture 1. The Human Visual System. The Human Eye. The Human Retina. cones. rods. horizontal. bipolar. amacrine.
 Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Lecture The Human Visual System The Human Visual System Retina Optic Nerve Optic Chiasm Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) Visual Cortex The Human Eye The Human Retina Lens rods cones Cornea Fovea Optic
Visual Perception of Images
 Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Visual Perception of Images A processed image is usually intended to be viewed by a human observer. An understanding of how humans perceive visual stimuli the human visual system (HVS) is crucial to the
Vision. Sensation & Perception. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye. Functional Organization of the Eye
 Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
Vision Sensation & Perception Part 3 - Vision Visible light is the form of electromagnetic radiation our eyes are designed to detect. However, this is only a narrow band of the range of energy at different
INSTRUCTORS GUIDE FOR THE HUMAN EYE AND VISION
 INSTRUCTORS GUIDE FOR THE HUMAN EYE AND VISION Modern Miracle Medical Machines Dyan McBride Based on similar lessons developed by the Hartmut Wiesner & Physics Education Group, LMU Munich Our most important
INSTRUCTORS GUIDE FOR THE HUMAN EYE AND VISION Modern Miracle Medical Machines Dyan McBride Based on similar lessons developed by the Hartmut Wiesner & Physics Education Group, LMU Munich Our most important
Refraction of Light. Refraction of Light
 1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
1 Refraction of Light Activity: Disappearing coin Place an empty cup on the table and drop a penny in it. Look down into the cup so that you can see the coin. Move back away from the cup slowly until the
Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Human Eye and Colourful World
 Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Human Eye and Colourful World Short Answer Questions Question 1. A student sitting at the back of the classroom cannot read clearly the letters written on the
Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Human Eye and Colourful World Short Answer Questions Question 1. A student sitting at the back of the classroom cannot read clearly the letters written on the
Life Science Chapter 2 Study Guide
 Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1
 The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
The Human Eye and a Camera 12.1 The human eye is an amazing optical device that allows us to see objects near and far, in bright light and dim light. Although the details of how we see are complex, the
Further reading. 1. Visual perception. Restricting the light. Forming an image. Angel, section 1.4
 Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
Further reading Angel, section 1.4 Glassner, Principles of Digital mage Synthesis, sections 1.1-1.6. 1. Visual perception Spencer, Shirley, Zimmerman, and Greenberg. Physically-based glare effects for
Retinal stray light originating from intraocular lenses and its effect on visual performance van der Mooren, Marie Huibert
 University of Groningen Retinal stray light originating from intraocular lenses and its effect on visual performance van der Mooren, Marie Huibert IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
University of Groningen Retinal stray light originating from intraocular lenses and its effect on visual performance van der Mooren, Marie Huibert IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's
Refraction Phenomena Apparent Depth & Volume
 Refraction Phenomena Apparent Depth & Volume Refraction can change the perception of depth and volume because the apparent path of light does not equal the actual path of light. 1 Underwater Vision Atmospheric
Refraction Phenomena Apparent Depth & Volume Refraction can change the perception of depth and volume because the apparent path of light does not equal the actual path of light. 1 Underwater Vision Atmospheric
Seeing and Perception. External features of the Eye
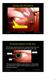 Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
Seeing and Perception Deceives the Eye This is Madness D R Campbell School of Computing University of Paisley 1 External features of the Eye The circular opening of the iris muscles forms the pupil, which
PHYSICS. Chapter 35 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 35 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 35 Optical Instruments IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about some common optical instruments and
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 35 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 35 Optical Instruments IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about some common optical instruments and
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception We ll see the first three steps of the perceptual process for vision https:// 49.media.tumblr.co m/ 87423d97f3fbba8fa4 91f2f1bfbb6893/ tumblr_o1jdiqp4tc1 qabbyto1_500.gif
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes:
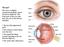 The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
The eye* The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The front part of the eye (the part you see in the mirror) includes: The iris (the pigmented part) The cornea (a clear dome
Name: Hour BE ABLE TO LABEL AN EYE
 Quarter 2: Quiz 3 STUDY GUIDE The scientific method. Measurement system - - metric Metric 1. The metric system is a decimal system of measurement scaled on multiples of 10. OR BASE TEN 1. Types of measure:
Quarter 2: Quiz 3 STUDY GUIDE The scientific method. Measurement system - - metric Metric 1. The metric system is a decimal system of measurement scaled on multiples of 10. OR BASE TEN 1. Types of measure:
better make it a triple (3 x)
 Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Crown 85: Visual Perception: : Structure of and Information Processing in the Retina 1 lectures 5 better make it a triple (3 x) 1 blind spot demonstration (close left eye) blind spot 2 temporal right eye
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 3 Digital Image Fundamentals ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Presentation Outline
Introduction. The Human Eye. Physics 1CL OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS AND THE EYE SPRING 2010
 Introduction Most of the subject material in this lab can be found in Chapter 25 of Serway and Faughn. In this lab, you will make images of images using lenses and the optical bench (Experiment A). IT
Introduction Most of the subject material in this lab can be found in Chapter 25 of Serway and Faughn. In this lab, you will make images of images using lenses and the optical bench (Experiment A). IT
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May
 Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
Lecture 8. Human Information Processing (1) CENG 412-Human Factors in Engineering May 30 2009 1 Outline Visual Sensory systems Reading Wickens pp. 61-91 2 Today s story: Textbook page 61. List the vision-related
