A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data
|
|
|
- Franklin West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data Yessika Blunda*, Pinnacle, Halliburton, Houston, Tx, US and Kit Chambers, Pinnacle, Halliburton, St Agnes, Cornwall, UK Summary Here we describe a generic data processing flow that attenuates ringing as well as stationary and transient correlated noise. The procedure consists of two steps; firstly, large errant frequencies are suppressed using a winsorising procedure in the frequency domain, whereby anomalously large frequencies are reset to a median value. Secondly, the data is passed through an adaptive subtraction procedure, where the noise is modeled using a multi-channel Weiner filter (MCWF). The method makes no assumptions regarding the origin of desired signals or their manifestation in the data, for example, it can be applied where the signal moveout is non-linear and or polarities are inconsistent, preserving the original moveout and polarization. This means our procedure can be applied prior to any modeling or subsequent processing operations such as sensor orientation. Using real and semi-synthetic data (synthetic signal plus real noise) we examine the efficacy of the processing flow. Input data for these tests comes from a 40 level downhole array with 3 components stations at each level. We find that whilst the procedure produces fairly modest gains in signal to noise ratio (typically 4-12 db) both geophone ringing and correlated noise from tube waves is effectively removed with minimal distortion to the microseismic waveforms. This suggests the procedure could provide a useful precursor to subsequent processing and analysis. Our experiments also show relatively little sensitivity to the input parameters provided sensible values are chosen. Introduction Despite the best efforts in acquisition microseismic data is often contaminated by noise. This noise can come from a number of sources, for example electrical noise in the geophone may manifest as a ringing frequency. Alternatively (in downhole surveys) tube waves which are manifested as signals with linear moveout along the array may also contaminate microseismic data. Clearly it is desirable to limit the amount of noise contamination during microseismic monitoring as this will lower the detection threshold for microseismic events, leading to a better understanding of the fracturing process. In this study we present and test one such processing flow. In order to examine the efficacy of the processing method we utilize data from a 40x3C downhole array deployed during hydraulic fracturing. We demonstrate aspects of the method using semi-synthetics (a synthetic arrival superimposed upon real noise). Using semi-synthetics with a variety of different settings we gauge the sensitivity of the method to the various input parameters and measure the gains in signal to noise ratio produced by the procedure. Finally we show the results of the processing method applied to a real microseismic arrival. GeoConvention 2013: Integration 1
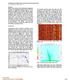
2 Procedure and Semi-Synthetic Example Figure 1 A shows the semi-synthetic data prior to application of any noise suppression. In the plot, ringing frequencies are clearly visible as vertical stripes, whilst tube wave noise is visible as bands with linear moveout. The superimposed synthetic arrival dips from right to left at approximately 0s. The first part of our procedure is designed to attack frequency spikes such as the geophone ringing. These could be suppressed using notch filter; however, this would create un-wanted artifacts particularly in the traces that do not show the ringing. Instead we opt for a procedure that only suppresses anomalous frequencies where they are present. We use a procedure similar to that of (Elboth et al., 2010) to remove high amplitude monochromatic frequency components visible on some of the data. The procedure is as follows: 1. The 2s traces are divided into windows of length 0.2s with the start of successive windows delayed by 0.025s. 2. The data within each time window is transformed to the frequency domain (so called time frequency transform) 3. For each time window and frequency amplitude the median value across the array is computed 4. Frequency amplitudes greater than 3 times the median are, reset to the median value (winsorisation). 5. Traces are transformed back to the time domain for sub sequent processing The procedure has the advantage that it can remove both time and frequency spikes. Additionally traces, frequencies and times that do not have any spurious features are left largely un-altered. Figure 1 B and C display the result and the residual noise removed by the time-frequency winsorisation. The ringing frequencies are completely removed as well as some of the high amplitude tube wave noise on component Z. The signal is now visible in the panels of Figure 1B as the dipping event around 0.s. There is some leakage of the signal into the removed noise; however, this effect is minor. Following time-frequency winsorisation, the panels still contain a large amount of tube wave noise. The most dominant tube wave signal being the wave travelling down the well (left to right in the panels), however, there is also an up going reverberation which has a similar moveout to our desired arrival. The second step in our processing flow is designed to attack this correlated noise. This tube wave noise could be suppressed using a number of different techniques such as tau-p filtering (Claerbout, 1985), SVD or Eigen trace decomposition ((Freire and Ulrych, 1988), (Bekara and Baan, 2007)). However, we adopt an adaptive subtraction technique as it makes no assumptions regarding the nature of the signal we wish to extract. Thus the procedure is applicable in a wide range of settings where source position is unknown. The technique is similar to that used by (Wang et al., 2009), where the noise is simulated in the frequency domain using a multi-channel Weiner filter (MCWF). Mathematically the procedure is summarized as: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) (1) Where, ( ) is the filtered data in channel, and angular frequency,. ( ), is the estimate of the noise on that channel which is formed by applying the linear filter, ( ) to a selection of the reference data channel ( ) The filter coefficients are formed from a sample of the noise, recorded without event arrivals taking place solving the normal equations ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) (2) GeoConvention 2013: Integration 2
3 Where ( ) is the noise channel we are trying to predict, and ( ) are the reference channels being used are using to perform the prediction ( ( ) ( )). ( ) denotes elements of the conjugate transpose of the elements of, ( ). The filter coefficients were computed using a 68 second sample of noise (taken prior to the 2s used to make the semi-synthetic) transformed in to the time-frequency domain using overlapping windows of Length, L, with the start of successive windows delayed by 0.025s. For each data channel reference channels were chosen to be the closest G (group) channels to that particular sensor (but not including channels from the sensor itself). An SVD algorithm was used to solve for filter coefficients, which leads to the third free parameter in the procedure the condition number for the inversion (the ratio of the smallest to the largest eigenvalue used, C) Figure 1D shows the semisynthetic result after adaptive subtraction for L=0.3s G=18 C=0.3. The tube wave noise has now been largely removed. It can also be seen from the residual panel, Figure 1, that there is minimal distortion to the portion of the traces containing the arrival. Figure 1 Panels showing the results of the noise suppression method applied to the semi synthetic data. A Input semi-synthetic input data (ringing frequencies and tube wave noise is clearly visible). B result after time frequency winsorising with window length of 0.3s, C- the noise removed by time-frequency winsorising (i.e. A-B) the ringing frequencies are attenuated but the correlated tube wave noise remains, D the result after adaptive subtraction the tube wave noise has now been removed leaving the arrival we wish to separate, E- the noise removed by the entire procedure (i.e. A-D) GeoConvention 2013: Integration 3
4 SNR Analysis We examine the efficacy of the filter for a variety of input settings. In each case we compute the signal to noise ratio on each channel in decibels ( ) using ( ) (3) Where the signal RMS,, is measured over a short window around the arrival and the is measured over the time window prior to addition of the synthetic arrival. Figure 2 shows the SNR of each channel for the input data, after time-frequency winsorization, as well as for 3 settings of the adaptive subtraction filter. As expected the time-frequency winsorization only produces SNR changes on certain traces. Application of the adaptive subtraction produces further SNR gains across the array. There appears to be little variation in the amount of SNR gain from the different settings for the adaptive subtraction, suggesting the MCWF procedure is relatively insensitivity to input parameters provided sensible values are chosen. In general the SNR gains from the procedure are fairly modest and less than the amount of variation across the array. Figure 2 - Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) for each Channel (same Channel order as Figure 1). The black curve represents the input before noise supression. Blue corresponds to SNR after time-frequency winsorization. The Red, Purple, and Green curves show the results of Multichannel Wiener Filter application with different parameters. The purple line corresponds to the recommended parameters with the highest average SNR: Group Size (G) = 18, Window Length (W) = 200ms, and Condition Number (C) = 0.3. GeoConvention 2013: Integration 4
5 Real data application Figure 3 shows the application of the processing steps to a real microseismic arrival, recorded using the same deployment as used of the semi-synthetic noise. As with the semi-synthetic example the timefrequency winsorisation removes the ringing frequencies, whilst leaving the majority of the data unaltered. The subsequent application of the adaptive subtraction also removes the correlated tubewave noise. The result Figure 3 D shows several clearly delineated arrivals, corresponding to signals from one or more sources. In particular note that complicated waveform features are preserved by the procedure including changes in the arrival slope across the array. Figure 3 - Panels showing the results of the noise suppression method applied to a real microseismic arrival. A Input data, B result after time frequency winsorising with window length of 0.3s and a factor of 12 overlap, C- the noise removed by time-frequency winsorsing (i.e. A-B), D the result after adaptive subtraction, note that the complex nature of the arrival is now much clearer. E- the noise removed by the entire procedure (i.e. A-D) Conclusions Noise Attenuation is a key step in microseismic data processing which enhances signal to noise ratio, enabling accurate interpretation or picking of microseismic wave s arrivals. Here we have described and applied a noise suppression workflow designed to remove ringing frequencies and tube wave noise. The ringing frequencies were attenuated using a time-frequency winsorisation procedure, whereas correlated noise from tube wave was suppressed using an adaptive subtraction method. GeoConvention 2013: Integration 5
6 The method makes no assumptions regarding the origin of signals or its form in the data. For example, it does not require consistent polarities across the array or certain features for the desired signal (such as linear moveout) meaning it can be applied prior to any modeling or subsequent processing operations (such as sensor orientation). Our tests using semi-synthetic and real data indicate that the procedure produces only modest gains in the signal to noise ratio (up to 12dB). Nonetheless the examples show the method is effective at removing the noise and leaving signal preserved. Furthermore there is relatively little sensitivity to variations in the input parameters. Acknowledgements The authors would like to thank Halliburton for permission to present this work. References Bekara, M. and Baan, M.v.d., Local singular value decomposition for signal enhancement of seismic data. Geophysics, 72(2): V59-V65. Claerbout, J.F., Imaging the Earth s Interior. Blackwell. Elboth, T., Vik Presterud, I. and Hermansen, D., Time-frequency seismic data de-noising. Geophysical Prospecting, 58(3): Freire, S.L.M. and Ulrych, T.J., Application of singular value decomposition to vertical sesimic profiling. Geophysics, 53(6): 8. Wang, J., Tilmann, F., White, R.S. and Bordoni, P., Application of frequency-dependent multichannel Wiener filters to detect events in 2D three-component seismometer arrays. Geophysics, 74(6): V133-V141. GeoConvention 2013: Integration 6
Improving microseismic data quality with noise attenuation techniques
 Improving microseismic data quality with noise attenuation techniques Kit Chambers, Aaron Booterbaugh Nanometrics Inc. Summary Microseismic data always contains noise and its effect is to reduce the quality
Improving microseismic data quality with noise attenuation techniques Kit Chambers, Aaron Booterbaugh Nanometrics Inc. Summary Microseismic data always contains noise and its effect is to reduce the quality
Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data
 Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data Patrick Butler, GEDCO, Calgary, Alberta, Canada pbutler@gedco.com Summary A module for removing and replacing strong noise in seismic data is presented.
Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data Patrick Butler, GEDCO, Calgary, Alberta, Canada pbutler@gedco.com Summary A module for removing and replacing strong noise in seismic data is presented.
Application of Multi-channel Wiener Filters to the Suppression of Ambient Seismic Noise in Passive Seismic Arrays
 Application of Multi-channel Wiener Filters to the Suppression of Ambient Seismic Noise in Passive Seismic Arrays J. Wang 1, F. Tilmann 1, R. S. White 1, H. Soosalu 1 and P. Bordoni 2 1. Bullard Laboratories,
Application of Multi-channel Wiener Filters to the Suppression of Ambient Seismic Noise in Passive Seismic Arrays J. Wang 1, F. Tilmann 1, R. S. White 1, H. Soosalu 1 and P. Bordoni 2 1. Bullard Laboratories,
Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring
 Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring Michael Thornton*, MicroSeismic Inc., Houston,Texas mthornton@microseismic.com Summary While related concepts, resolution and uncertainty
Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring Michael Thornton*, MicroSeismic Inc., Houston,Texas mthornton@microseismic.com Summary While related concepts, resolution and uncertainty
Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events
 Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events Natalia Verkhovtseva Pinnacle a Halliburton Service, Calgary, AB Summary Data sampling and its effect on the microseismic
Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events Natalia Verkhovtseva Pinnacle a Halliburton Service, Calgary, AB Summary Data sampling and its effect on the microseismic
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG)
 Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain
 Predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Marco A. Perez and David C. Henley ABSTRACT Predictive deconvolution has been predominantly
Predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Marco A. Perez and David C. Henley ABSTRACT Predictive deconvolution has been predominantly
Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas
 Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas Summary The reliability of seismic attribute estimation depends on reliable signal.
Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas Summary The reliability of seismic attribute estimation depends on reliable signal.
Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise
 Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise Stephen Chiu* ConocoPhillips, Houston, TX, United States stephen.k.chiu@conocophillips.com and Norman Whitmore
Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise Stephen Chiu* ConocoPhillips, Houston, TX, United States stephen.k.chiu@conocophillips.com and Norman Whitmore
Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis
 Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical
 A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical Summary Here we present a method of robust seismic data deghosting for
A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical Summary Here we present a method of robust seismic data deghosting for
Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation
 Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation T. Elboth* (CGG), H. Shen (CGG), J. Khan (CGG) Summary This paper presents recent advances in the area of seismic interference (SI) attenuation
Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation T. Elboth* (CGG), H. Shen (CGG), J. Khan (CGG) Summary This paper presents recent advances in the area of seismic interference (SI) attenuation
Coherent noise attenuation: A synthetic and field example
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 108, April 29, 2001, pages 1?? Coherent noise attenuation: A synthetic and field example Antoine Guitton 1 ABSTRACT Noise attenuation using either a filtering or a
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 108, April 29, 2001, pages 1?? Coherent noise attenuation: A synthetic and field example Antoine Guitton 1 ABSTRACT Noise attenuation using either a filtering or a
Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion
 P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
Random noise attenuation using f-x regularized nonstationary autoregression a
 Random noise attenuation using f-x regularized nonstationary autoregression a a Published in Geophysics, 77, no. 2, V61-V69, (2012) Guochang Liu 1, Xiaohong Chen 1, Jing Du 2, Kailong Wu 1 ABSTRACT We
Random noise attenuation using f-x regularized nonstationary autoregression a a Published in Geophysics, 77, no. 2, V61-V69, (2012) Guochang Liu 1, Xiaohong Chen 1, Jing Du 2, Kailong Wu 1 ABSTRACT We
Downloaded 09/04/18 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Ground-roll attenuation based on SVD filtering Milton J. Porsani, CPGG, Michelngelo G. Silva, CPGG, Paulo E. M. Melo, CPGG and Bjorn Ursin, NTNU
 Ground-roll attenuation based on SVD filtering Milton J. Porsani, CPGG, Michelngelo G. Silva, CPGG, Paulo E. M. Melo, CPGG and Bjorn Ursin, NTNU SUMMARY We present a singular value decomposition (SVD)
Ground-roll attenuation based on SVD filtering Milton J. Porsani, CPGG, Michelngelo G. Silva, CPGG, Paulo E. M. Melo, CPGG and Bjorn Ursin, NTNU SUMMARY We present a singular value decomposition (SVD)
Attenuation of high energy marine towed-streamer noise Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco
 Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Master event relocation of microseismic event using the subspace detector
 Master event relocation of microseismic event using the subspace detector Ibinabo Bestmann, Fernando Castellanos and Mirko van der Baan Dept. of Physics, CCIS, University of Alberta Summary Microseismic
Master event relocation of microseismic event using the subspace detector Ibinabo Bestmann, Fernando Castellanos and Mirko van der Baan Dept. of Physics, CCIS, University of Alberta Summary Microseismic
A k-mean characteristic function to improve STA/LTA detection
 A k-mean characteristic function to improve STA/LTA detection Jubran Akram*,1, Daniel Peter 1, and David Eaton 2 1 King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Saudi Arabia 2 University
A k-mean characteristic function to improve STA/LTA detection Jubran Akram*,1, Daniel Peter 1, and David Eaton 2 1 King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), Saudi Arabia 2 University
Picking microseismic first arrival times by Kalman filter and wavelet transform
 Picking first arrival times Picking microseismic first arrival times by Kalman filter and wavelet transform Baolin Qiao and John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT Due to the high energy content of the ambient noise,
Picking first arrival times Picking microseismic first arrival times by Kalman filter and wavelet transform Baolin Qiao and John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT Due to the high energy content of the ambient noise,
Attacking localized high amplitude noise in seismic data A method for AVO compliant noise attenuation
 Attacking localized high amplitude noise in seismic data A method for AVO compliant noise attenuation Xinxiang Li and Rodney Couzens Sensor Geophysical Ltd. Summary The method of time-frequency adaptive
Attacking localized high amplitude noise in seismic data A method for AVO compliant noise attenuation Xinxiang Li and Rodney Couzens Sensor Geophysical Ltd. Summary The method of time-frequency adaptive
Seismic application of quality factor estimation using the peak frequency method and sparse time-frequency transforms
 Seismic application of quality factor estimation using the peak frequency method and sparse time-frequency transforms Jean Baptiste Tary 1, Mirko van der Baan 1, and Roberto Henry Herrera 1 1 Department
Seismic application of quality factor estimation using the peak frequency method and sparse time-frequency transforms Jean Baptiste Tary 1, Mirko van der Baan 1, and Roberto Henry Herrera 1 1 Department
Ambient Passive Seismic Imaging with Noise Analysis Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc.
 Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc. SUMMARY The ambient passive seismic imaging technique is capable of imaging repetitive passive seismic events. Here we investigate
Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc. SUMMARY The ambient passive seismic imaging technique is capable of imaging repetitive passive seismic events. Here we investigate
Random and coherent noise attenuation by empirical mode decomposition Maïza Bekara, PGS, and Mirko van der Baan, University of Leeds
 Random and coherent noise attenuation by empirical mode decomposition Maïza Bekara, PGS, and Mirko van der Baan, University of Leeds SUMMARY This paper proposes a new filtering technique for random and
Random and coherent noise attenuation by empirical mode decomposition Maïza Bekara, PGS, and Mirko van der Baan, University of Leeds SUMMARY This paper proposes a new filtering technique for random and
Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing Dispersive Ground Roll Noise from Onshore Seismic Data
 Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
Th P6 01 Retrieval of the P- and S-velocity Structure of the Groningen Gas Reservoir Using Noise Interferometry
 Th P6 1 Retrieval of the P- and S-velocity Structure of the Groningen Gas Reservoir Using Noise Interferometry W. Zhou* (Utrecht University), H. Paulssen (Utrecht University) Summary The Groningen gas
Th P6 1 Retrieval of the P- and S-velocity Structure of the Groningen Gas Reservoir Using Noise Interferometry W. Zhou* (Utrecht University), H. Paulssen (Utrecht University) Summary The Groningen gas
=, (1) Summary. Theory. Introduction
 Noise suppression for detection and location of microseismic events using a matched filter Leo Eisner*, David Abbott, William B. Barker, James Lakings and Michael P. Thornton, Microseismic Inc. Summary
Noise suppression for detection and location of microseismic events using a matched filter Leo Eisner*, David Abbott, William B. Barker, James Lakings and Michael P. Thornton, Microseismic Inc. Summary
Enhanced random noise removal by inversion
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 84, May 9, 2001, pages 1 344 Enhanced random noise removal by inversion Ray Abma 1 ABSTRACT Noise attenuation by prediction filtering breaks down in the presence of
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 84, May 9, 2001, pages 1 344 Enhanced random noise removal by inversion Ray Abma 1 ABSTRACT Noise attenuation by prediction filtering breaks down in the presence of
SVD filtering applied to ground-roll attenuation
 . SVD filtering applied to ground-roll attenuation Milton J. Porsani + Michelângelo G. Silva + Paulo E. M. Melo + and Bjorn Ursin + Centro de Pesquisa em Geofísica e Geologia (UFBA) and National Institute
. SVD filtering applied to ground-roll attenuation Milton J. Porsani + Michelângelo G. Silva + Paulo E. M. Melo + and Bjorn Ursin + Centro de Pesquisa em Geofísica e Geologia (UFBA) and National Institute
2D field data applications
 Chapter 5 2D field data applications In chapter 4, using synthetic examples, I showed how the regularized joint datadomain and image-domain inversion methods developed in chapter 3 overcome different time-lapse
Chapter 5 2D field data applications In chapter 4, using synthetic examples, I showed how the regularized joint datadomain and image-domain inversion methods developed in chapter 3 overcome different time-lapse
Seismic Reflection Method
 1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
Th ELI1 08 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data
 Th ELI1 8 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data P. Edme* (Schlumberger Gould Research), E. Muyzert (Sclumberger Gould Research) & E. Kragh (Schlumberger Gould Research) SUMMARY
Th ELI1 8 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data P. Edme* (Schlumberger Gould Research), E. Muyzert (Sclumberger Gould Research) & E. Kragh (Schlumberger Gould Research) SUMMARY
SAUCE: A new technique to remove cultural noise from HRAM data
 THE METER READER SAUCE: A new technique to remove cultural noise from HRAM data HASSAN H. HASSAN and JOHN W. PEIRCE, GEDCO, Calgary, Alberta, Canada There is little doubt that manual editing to remove
THE METER READER SAUCE: A new technique to remove cultural noise from HRAM data HASSAN H. HASSAN and JOHN W. PEIRCE, GEDCO, Calgary, Alberta, Canada There is little doubt that manual editing to remove
P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method
 P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method E. Baniasadi* (University of Tehran), M. A. Riahi (University of Tehran) & S. Chaychizadeh (University of Tehran)
P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method E. Baniasadi* (University of Tehran), M. A. Riahi (University of Tehran) & S. Chaychizadeh (University of Tehran)
Multiple Attenuation - A Case Study
 Multiple Attenuation - A Case Study M.Das, Maharaj Singh, M.Muruganandan* & Dr.D.V.R. Murti RCC, GPS, A&AA Basin, ONGC Jorhat Summary Multiple attenuation is a long standing problem in reflection seismic
Multiple Attenuation - A Case Study M.Das, Maharaj Singh, M.Muruganandan* & Dr.D.V.R. Murti RCC, GPS, A&AA Basin, ONGC Jorhat Summary Multiple attenuation is a long standing problem in reflection seismic
A multi-window algorithm for real-time automatic detection and picking of P-phases of microseismic events
 A multi-window algorithm for real-time automatic detection and picking of P-phases of microseismic events Zuolin Chen and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT There exist a variety of algorithms for the detection
A multi-window algorithm for real-time automatic detection and picking of P-phases of microseismic events Zuolin Chen and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT There exist a variety of algorithms for the detection
Comparison of Q-estimation methods: an update
 Q-estimation Comparison of Q-estimation methods: an update Peng Cheng and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT In this article, three methods of Q estimation are compared: a complex spectral ratio method, the centroid
Q-estimation Comparison of Q-estimation methods: an update Peng Cheng and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT In this article, three methods of Q estimation are compared: a complex spectral ratio method, the centroid
3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion. Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas
 P-75 Summary 3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas Following our previous work on Amplitude Tomography that
P-75 Summary 3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas Following our previous work on Amplitude Tomography that
High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain
 High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain Shaowu Wang, Juefu Wang and Tianfei Zhu CGG Summary We present a method to enhance the bandwidth of seismic data in the
High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain Shaowu Wang, Juefu Wang and Tianfei Zhu CGG Summary We present a method to enhance the bandwidth of seismic data in the
Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results
 Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results David C. Henley and Han-Xing Lu PNG processing ABSTRACT Papua New Guinea is among the most notoriously difficult areas in the world in
Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results David C. Henley and Han-Xing Lu PNG processing ABSTRACT Papua New Guinea is among the most notoriously difficult areas in the world in
Seismic processing workflow for supressing coherent noise while retaining low-frequency signal
 Seismic processing for coherent noise suppression Seismic processing workflow for supressing coherent noise while retaining low-frequency signal Patricia E. Gavotti and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT Two different
Seismic processing for coherent noise suppression Seismic processing workflow for supressing coherent noise while retaining low-frequency signal Patricia E. Gavotti and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT Two different
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data
 Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Group Array Stack of single sensor data
 P-113 Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Artatran Ojha *, K. Ramakrishna, G. Sarvesam Geophysical Services, ONGC, Chennai Summary Shot generated noise and the cultural noise is a major problem in
P-113 Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Artatran Ojha *, K. Ramakrishna, G. Sarvesam Geophysical Services, ONGC, Chennai Summary Shot generated noise and the cultural noise is a major problem in
Microquake seismic interferometry with SV D enhanced Green s function recovery
 Microquake seismic interferometry with SV D enhanced Green s function recovery Gabriela Melo and A lison Malcolm Earth Resources Laboratory - Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department Massachusetts
Microquake seismic interferometry with SV D enhanced Green s function recovery Gabriela Melo and A lison Malcolm Earth Resources Laboratory - Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department Massachusetts
McArdle, N.J. 1, Ackers M. 2, Paton, G ffa 2 - Noreco. Introduction.
 An investigation into the dependence of frequency decomposition colour blend response on bed thickness and acoustic impedance: results from wedge and thin bed models applied to a North Sea channel system
An investigation into the dependence of frequency decomposition colour blend response on bed thickness and acoustic impedance: results from wedge and thin bed models applied to a North Sea channel system
Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion
 Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion Heather J.E. Lloyd*, CREWES / University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta hjelloyd@ucalgary.ca and Gary F. Margrave, CREWES
Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion Heather J.E. Lloyd*, CREWES / University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta hjelloyd@ucalgary.ca and Gary F. Margrave, CREWES
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile
 Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution
 Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Geophones // A COMPLETE PRODUCT LINE. Sercel has a long history in being at the forefront of developing
 Geophones SG-5 // A COMPLETE PRODUCT LINE Sercel has a long history in being at the forefront of developing new cutting-edge technology. Setting new standards for sensors is no exception. Our advanced
Geophones SG-5 // A COMPLETE PRODUCT LINE Sercel has a long history in being at the forefront of developing new cutting-edge technology. Setting new standards for sensors is no exception. Our advanced
Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic
 Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic J. Burren (Petroleum Geo-Services) & D. Lecerf* (Petroleum Geo-Services) SUMMARY Future time-lapse broadband surveys should provide better reservoir monitoring
Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic J. Burren (Petroleum Geo-Services) & D. Lecerf* (Petroleum Geo-Services) SUMMARY Future time-lapse broadband surveys should provide better reservoir monitoring
Seismic acquisition projects 2010
 Acquisition 2010 Seismic acquisition projects 2010 Malcolm B. Bertram, Kevin L. Bertram, Kevin W. Hall, Eric V. Gallant ABSTRACT Acquisition projects since the CREWES meeting in November 2009 include:
Acquisition 2010 Seismic acquisition projects 2010 Malcolm B. Bertram, Kevin L. Bertram, Kevin W. Hall, Eric V. Gallant ABSTRACT Acquisition projects since the CREWES meeting in November 2009 include:
Comparison/sensitivity analysis of various deghosting methods Abdul Hamid
 Master Thesis in Geosciences Comparison/sensitivity analysis of various deghosting methods By Abdul Hamid Comparison/sensitivity analysis of various deghosting methods By ABDUL HAMID MASTER THESIS IN
Master Thesis in Geosciences Comparison/sensitivity analysis of various deghosting methods By Abdul Hamid Comparison/sensitivity analysis of various deghosting methods By ABDUL HAMID MASTER THESIS IN
Extending the useable bandwidth of seismic data with tensor-guided, frequency-dependent filtering
 first break volume 34, January 2016 special topic Extending the useable bandwidth of seismic data with tensor-guided, frequency-dependent filtering Edward Jenner 1*, Lisa Sanford 2, Hans Ecke 1 and Bruce
first break volume 34, January 2016 special topic Extending the useable bandwidth of seismic data with tensor-guided, frequency-dependent filtering Edward Jenner 1*, Lisa Sanford 2, Hans Ecke 1 and Bruce
Evaluation of a broadband marine source
 Evaluation of a broadband marine source Rob Telling 1*, Stuart Denny 1, Sergio Grion 1 and R. Gareth Williams 1 evaluate far-field signatures and compare processing results for a 2D test-line acquired
Evaluation of a broadband marine source Rob Telling 1*, Stuart Denny 1, Sergio Grion 1 and R. Gareth Williams 1 evaluate far-field signatures and compare processing results for a 2D test-line acquired
Iterative least-square inversion for amplitude balancing a
 Iterative least-square inversion for amplitude balancing a a Published in SEP report, 89, 167-178 (1995) Arnaud Berlioux and William S. Harlan 1 ABSTRACT Variations in source strength and receiver amplitude
Iterative least-square inversion for amplitude balancing a a Published in SEP report, 89, 167-178 (1995) Arnaud Berlioux and William S. Harlan 1 ABSTRACT Variations in source strength and receiver amplitude
Tu SRS3 06 Wavelet Estimation for Broadband Seismic Data
 Tu SRS3 06 Wavelet Estimation for Broadband Seismic Data E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), J. Gunning (CSIRO), R. White (Birkbeck University of London) & P. Spaans (Woodside) SUMMARY The volumes of broadband
Tu SRS3 06 Wavelet Estimation for Broadband Seismic Data E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), J. Gunning (CSIRO), R. White (Birkbeck University of London) & P. Spaans (Woodside) SUMMARY The volumes of broadband
SPNA 2.3. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2177
 SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
Efficient Acquisition of Quality Borehole Seismic
 Efficient Acquisition of Quality Borehole Seismic The Versatile Seismic Imager Applications Integrated processing for interpretation of boreholeand surface-seismic data Images for reservoir definition
Efficient Acquisition of Quality Borehole Seismic The Versatile Seismic Imager Applications Integrated processing for interpretation of boreholeand surface-seismic data Images for reservoir definition
Ocean-bottom hydrophone and geophone coupling
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages 57 70 Ocean-bottom hydrophone and geophone coupling Daniel A. Rosales and Antoine Guitton 1 ABSTRACT We compare two methods for combining hydrophone
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages 57 70 Ocean-bottom hydrophone and geophone coupling Daniel A. Rosales and Antoine Guitton 1 ABSTRACT We compare two methods for combining hydrophone
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas
 The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
Deterministic marine deghosting: tutorial and recent advances
 Deterministic marine deghosting: tutorial and recent advances Mike J. Perz* and Hassan Masoomzadeh** *Arcis Seismic Solutions, A TGS Company; **TGS Summary (Arial 12pt bold or Calibri 12pt bold) Marine
Deterministic marine deghosting: tutorial and recent advances Mike J. Perz* and Hassan Masoomzadeh** *Arcis Seismic Solutions, A TGS Company; **TGS Summary (Arial 12pt bold or Calibri 12pt bold) Marine
T17 Reliable Decon Operators for Noisy Land Data
 T17 Reliable Decon Operators for Noisy Land Data N. Gulunay* (CGGVeritas), N. Benjamin (CGGVeritas) & A. Khalil (CGGVeritas) SUMMARY Interbed multiples for noisy land data that survives the stacking process
T17 Reliable Decon Operators for Noisy Land Data N. Gulunay* (CGGVeritas), N. Benjamin (CGGVeritas) & A. Khalil (CGGVeritas) SUMMARY Interbed multiples for noisy land data that survives the stacking process
Understanding Seismic Amplitudes
 Understanding Seismic Amplitudes The changing amplitude values that define the seismic trace are typically explained using the convolutional model. This model states that trace amplitudes have three controlling
Understanding Seismic Amplitudes The changing amplitude values that define the seismic trace are typically explained using the convolutional model. This model states that trace amplitudes have three controlling
Tu A D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study
 Tu A15 09 4D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study D. Lecerf* (PGS), D. Raistrick (PGS), B. Caselitz (PGS), M. Wingham (BP), J. Bradley (BP), B. Moseley (formaly BP) Summary
Tu A15 09 4D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study D. Lecerf* (PGS), D. Raistrick (PGS), B. Caselitz (PGS), M. Wingham (BP), J. Bradley (BP), B. Moseley (formaly BP) Summary
Deblending workflow. Summary
 Guillaume Henin*, Didier Marin, Shivaji Maitra, Anne Rollet (CGG), Sandeep Kumar Chandola, Subodh Kumar, Nabil El Kady, Low Cheng Foo (PETRONAS Carigali Sdn. Bhd.) Summary In ocean-bottom cable (OBC) acquisitions,
Guillaume Henin*, Didier Marin, Shivaji Maitra, Anne Rollet (CGG), Sandeep Kumar Chandola, Subodh Kumar, Nabil El Kady, Low Cheng Foo (PETRONAS Carigali Sdn. Bhd.) Summary In ocean-bottom cable (OBC) acquisitions,
Biosignal filtering and artifact rejection. Biosignal processing, S Autumn 2012
 Biosignal filtering and artifact rejection Biosignal processing, 521273S Autumn 2012 Motivation 1) Artifact removal: for example power line non-stationarity due to baseline variation muscle or eye movement
Biosignal filtering and artifact rejection Biosignal processing, 521273S Autumn 2012 Motivation 1) Artifact removal: for example power line non-stationarity due to baseline variation muscle or eye movement
Basis Pursuit for Seismic Spectral decomposition
 Basis Pursuit for Seismic Spectral decomposition Jiajun Han* and Brian Russell Hampson-Russell Limited Partnership, CGG Geo-software, Canada Summary Spectral decomposition is a powerful analysis tool used
Basis Pursuit for Seismic Spectral decomposition Jiajun Han* and Brian Russell Hampson-Russell Limited Partnership, CGG Geo-software, Canada Summary Spectral decomposition is a powerful analysis tool used
CDP noise attenuation using local linear models
 CDP noise attenuation CDP noise attenuation using local linear models Todor I. Todorov and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Seismic noise attenuation plays an important part in a seismic processing flow. Spatial
CDP noise attenuation CDP noise attenuation using local linear models Todor I. Todorov and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Seismic noise attenuation plays an important part in a seismic processing flow. Spatial
DSU3-428 DIGITAL SENSOR UNITS
 DSU3-428 DIGITAL SENSOR UNITS DSU3-428 The 428XL offers all new hardware and software which is specifi cally designed to address the growing demands of the geophysical industry for even larger channel
DSU3-428 DIGITAL SENSOR UNITS DSU3-428 The 428XL offers all new hardware and software which is specifi cally designed to address the growing demands of the geophysical industry for even larger channel
Optimal Processing of Marine High-Resolution Seismic Reflection (Chirp) Data
 Marine Geophysical Researches 20: 13 20, 1998. 1998 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 13 Optimal Processing of Marine High-Resolution Seismic Reflection (Chirp) Data R. Quinn 1,,J.M.Bull
Marine Geophysical Researches 20: 13 20, 1998. 1998 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 13 Optimal Processing of Marine High-Resolution Seismic Reflection (Chirp) Data R. Quinn 1,,J.M.Bull
Cmin. Cmax. Frac volume. SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting. Summary (1),
 Improving signal-to-noise ratio of passsive seismic data with an adaptive FK filter Chuntao Liang*, Mike P. Thornton, Peter Morton, BJ Hulsey, Andrew Hill, and Phil Rawlins, Microseismic Inc. Summary We
Improving signal-to-noise ratio of passsive seismic data with an adaptive FK filter Chuntao Liang*, Mike P. Thornton, Peter Morton, BJ Hulsey, Andrew Hill, and Phil Rawlins, Microseismic Inc. Summary We
F-x linear prediction filtering of seismic images
 147 F-x linear prediction filtering of seismic images Mark P. Harrison ABSTRACT The f-x linear prediction filtering algorithm is reviewed and tested on several synthetic images. It is found that the f-x
147 F-x linear prediction filtering of seismic images Mark P. Harrison ABSTRACT The f-x linear prediction filtering algorithm is reviewed and tested on several synthetic images. It is found that the f-x
A033 Combination of Multi-component Streamer Pressure and Vertical Particle Velocity - Theory and Application to Data
 A33 Combination of Multi-component Streamer ressure and Vertical article Velocity - Theory and Application to Data.B.A. Caprioli* (Westerneco), A.K. Ödemir (Westerneco), A. Öbek (Schlumberger Cambridge
A33 Combination of Multi-component Streamer ressure and Vertical article Velocity - Theory and Application to Data.B.A. Caprioli* (Westerneco), A.K. Ödemir (Westerneco), A. Öbek (Schlumberger Cambridge
Application of Surface Consistent Amplitude Corrections as a Manual Editing Tool
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 4, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov-Dec. 2016), PP 59-65 www.iosrjournals.org Application of Surface Consistent
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 4, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov-Dec. 2016), PP 59-65 www.iosrjournals.org Application of Surface Consistent
Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS
 Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS Summary In land AVO processing, near-surface heterogeneity issues are
Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS Summary In land AVO processing, near-surface heterogeneity issues are
Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data
 Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Stan J. Gorek, Robert R. Stewart, and Mark P. Harrison ABSTRACT During early July, 1995, a large
Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Stan J. Gorek, Robert R. Stewart, and Mark P. Harrison ABSTRACT During early July, 1995, a large
There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to
 Coordinated by JEFF DEERE JOHN GIBSON, FOREST LIN, ALEXANDRE EGRETEAU, and JULIEN MEUNIER, CGGVeritas MALCOLM LANSLEY, Sercel There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to improve the quality
Coordinated by JEFF DEERE JOHN GIBSON, FOREST LIN, ALEXANDRE EGRETEAU, and JULIEN MEUNIER, CGGVeritas MALCOLM LANSLEY, Sercel There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to improve the quality
Enhancement of Speech Signal Based on Improved Minima Controlled Recursive Averaging and Independent Component Analysis
 Enhancement of Speech Signal Based on Improved Minima Controlled Recursive Averaging and Independent Component Analysis Mohini Avatade & S.L. Sahare Electronics & Telecommunication Department, Cummins
Enhancement of Speech Signal Based on Improved Minima Controlled Recursive Averaging and Independent Component Analysis Mohini Avatade & S.L. Sahare Electronics & Telecommunication Department, Cummins
Time-Frequency Attenuation of Swell Noise on Seismic Data from Offshore Central Niger-Delta, Nigeria.
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 3, Issue 5 Ver. I (Sep. - Oct. 2015), PP 30-35 www.iosrjournals.org Time-Frequency Attenuation of
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 3, Issue 5 Ver. I (Sep. - Oct. 2015), PP 30-35 www.iosrjournals.org Time-Frequency Attenuation of
Ground-roll noise attenuation using a simple and effective approach based on local bandlimited orthogonalization a
 Ground-roll noise attenuation using a simple and effective approach based on local bandlimited orthogonalization a a Published in IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 12, no. 11, 2316-2320 (2015)
Ground-roll noise attenuation using a simple and effective approach based on local bandlimited orthogonalization a a Published in IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 12, no. 11, 2316-2320 (2015)
Observations of the OSOP Sixaola, March 1-3, 2016, at the Albuquerque Seismological Laboratory
 Observations of the OSOP Sixaola, March 1-3, 2016, at the Albuquerque Seismological Laboratory There were two representatives (Angel Rodriquez and David Nelson) from OSOP at ASL March 1-3, 2016, and they
Observations of the OSOP Sixaola, March 1-3, 2016, at the Albuquerque Seismological Laboratory There were two representatives (Angel Rodriquez and David Nelson) from OSOP at ASL March 1-3, 2016, and they
Downloaded 11/02/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Unbiased surface-consistent scalar estimation by crosscorrelation Nirupama Nagarajappa*, Peter Cary, Arcis Seismic Solutions, a TGS Company, Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Summary Surface-consistent scaling
Unbiased surface-consistent scalar estimation by crosscorrelation Nirupama Nagarajappa*, Peter Cary, Arcis Seismic Solutions, a TGS Company, Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Summary Surface-consistent scaling
Multi-survey matching of marine towed streamer data using a broadband workflow: a shallow water offshore Gabon case study. Summary
 Multi-survey matching of marine towed streamer data using a broadband workflow: a shallow water offshore Gabon case study. Nathan Payne, Tony Martin and Jonathan Denly. ION Geophysical UK Reza Afrazmanech.
Multi-survey matching of marine towed streamer data using a broadband workflow: a shallow water offshore Gabon case study. Nathan Payne, Tony Martin and Jonathan Denly. ION Geophysical UK Reza Afrazmanech.
Downloaded 01/03/14 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 : a case study from Saudi Arabia Joseph McNeely*, Timothy Keho, Thierry Tonellot, Robert Ley, Saudi Aramco, Dhahran, and Jing Chen, GeoTomo, Houston Summary We present an application of time domain early
: a case study from Saudi Arabia Joseph McNeely*, Timothy Keho, Thierry Tonellot, Robert Ley, Saudi Aramco, Dhahran, and Jing Chen, GeoTomo, Houston Summary We present an application of time domain early
Radial trace filtering revisited: current practice and enhancements
 Radial trace filtering revisited: current practice and enhancements David C. Henley Radial traces revisited ABSTRACT Filtering seismic data in the radial trace (R-T) domain is an effective technique for
Radial trace filtering revisited: current practice and enhancements David C. Henley Radial traces revisited ABSTRACT Filtering seismic data in the radial trace (R-T) domain is an effective technique for
THE USE OF DIGITAL HYPERBOLIC FILTER AS TOOL TO DENOISING RESISTIVITY DATA MAP OF MOROCCAN PHOSPHATE ANOMALOUS DISTURBANCES
 1. Saad BAKKAI, 2. Mahacine AMRANI TE USE OF DIGITA YPERBOIC FITER AS TOO TO DENOISING RESISTIVITY DATA MAP OF MOROCCAN POSPATE ANOMAOUS DISTURBANCES 1 GEOSCIENCES & ENVIRONMENT GROUP, FACUTY OF SCIENCES
1. Saad BAKKAI, 2. Mahacine AMRANI TE USE OF DIGITA YPERBOIC FITER AS TOO TO DENOISING RESISTIVITY DATA MAP OF MOROCCAN POSPATE ANOMAOUS DISTURBANCES 1 GEOSCIENCES & ENVIRONMENT GROUP, FACUTY OF SCIENCES
Identification and localization of micro-seismic events using the cross-correlation technique for the Ketzin CO2 storage site
 Number of pages Number of appendices 33 (incl. appendices) 3 TNO report Identification and localization of micro-seismic events using the cross-correlation technique for the Ketzin CO2 storage site Date
Number of pages Number of appendices 33 (incl. appendices) 3 TNO report Identification and localization of micro-seismic events using the cross-correlation technique for the Ketzin CO2 storage site Date
Study of Hydrocarbon Detection Methods in Offshore Deepwater Sediments, Gulf of Guinea*
 Study of Hydrocarbon Detection Methods in Offshore Deepwater Sediments, Gulf of Guinea* Guoping Zuo 1, Fuliang Lu 1, Guozhang Fan 1, and Dali Shao 1 Search and Discovery Article #40999 (2012)** Posted
Study of Hydrocarbon Detection Methods in Offshore Deepwater Sediments, Gulf of Guinea* Guoping Zuo 1, Fuliang Lu 1, Guozhang Fan 1, and Dali Shao 1 Search and Discovery Article #40999 (2012)** Posted
Summary. Introduction
 Multi survey matching of marine towed streamer data using a broadband workflow: a shallow water offshore Nathan Payne*, Tony Martin and Jonathan Denly. ION GX Technology UK; Reza Afrazmanech. Perenco UK.
Multi survey matching of marine towed streamer data using a broadband workflow: a shallow water offshore Nathan Payne*, Tony Martin and Jonathan Denly. ION GX Technology UK; Reza Afrazmanech. Perenco UK.
This tutorial describes the principles of 24-bit recording systems and clarifies some common mis-conceptions regarding these systems.
 This tutorial describes the principles of 24-bit recording systems and clarifies some common mis-conceptions regarding these systems. This is a general treatment of the subject and applies to I/O System
This tutorial describes the principles of 24-bit recording systems and clarifies some common mis-conceptions regarding these systems. This is a general treatment of the subject and applies to I/O System
Wave-equation microseismic imaging and event selection in the image domain Brad Artman 1, Ben Witten, Spectraseis Inc.
 Wave-equation microseismic imaging and event selection in the image domain Brad Artman 1, Ben Witten, Spectraseis Inc. Summary Common techniques for locating fracture events, from large earthquakes to
Wave-equation microseismic imaging and event selection in the image domain Brad Artman 1, Ben Witten, Spectraseis Inc. Summary Common techniques for locating fracture events, from large earthquakes to
Tunable Multi Notch Digital Filters A MATLAB demonstration using real data
 Tunable Multi Notch Digital Filters A MATLAB demonstration using real data Jon Bell CSIRO ATNF 27 Sep 2 1 Introduction Many people are investigating a wide range of interference suppression techniques.
Tunable Multi Notch Digital Filters A MATLAB demonstration using real data Jon Bell CSIRO ATNF 27 Sep 2 1 Introduction Many people are investigating a wide range of interference suppression techniques.
Interpretational applications of spectral decomposition in reservoir characterization
 Interpretational applications of spectral decomposition in reservoir characterization GREG PARTYKA, JAMES GRIDLEY, and JOHN LOPEZ, Amoco E&P Technology Group, Tulsa, Oklahoma, U.S. Figure 1. Thin-bed spectral
Interpretational applications of spectral decomposition in reservoir characterization GREG PARTYKA, JAMES GRIDLEY, and JOHN LOPEZ, Amoco E&P Technology Group, Tulsa, Oklahoma, U.S. Figure 1. Thin-bed spectral
Progress in DAS Seismic Methods
 Progress in DAS Seismic Methods A. Mateeva, J. Mestayer, Z. Yang, J. Lopez, P. Wills 1, H. Wu, W. Wong, Barbara Cox (Shell International Exploration and Production, Inc.), J. Roy, T. Bown ( OptaSense )
Progress in DAS Seismic Methods A. Mateeva, J. Mestayer, Z. Yang, J. Lopez, P. Wills 1, H. Wu, W. Wong, Barbara Cox (Shell International Exploration and Production, Inc.), J. Roy, T. Bown ( OptaSense )
A Dissertation Presented for the Doctor of Philosophy Degree. The University of Memphis
 A NEW PROCEDURE FOR ESTIMATION OF SHEAR WAVE VELOCITY PROFILES USING MULTI STATION SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF SURFACE WAVES, REGRESSION LINE SLOPE, AND GENETIC ALGORITHM METHODS A Dissertation Presented for
A NEW PROCEDURE FOR ESTIMATION OF SHEAR WAVE VELOCITY PROFILES USING MULTI STATION SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF SURFACE WAVES, REGRESSION LINE SLOPE, AND GENETIC ALGORITHM METHODS A Dissertation Presented for
SIGNAL MODEL AND PARAMETER ESTIMATION FOR COLOCATED MIMO RADAR
 SIGNAL MODEL AND PARAMETER ESTIMATION FOR COLOCATED MIMO RADAR Moein Ahmadi*, Kamal Mohamed-pour K.N. Toosi University of Technology, Iran.*moein@ee.kntu.ac.ir, kmpour@kntu.ac.ir Keywords: Multiple-input
SIGNAL MODEL AND PARAMETER ESTIMATION FOR COLOCATED MIMO RADAR Moein Ahmadi*, Kamal Mohamed-pour K.N. Toosi University of Technology, Iran.*moein@ee.kntu.ac.ir, kmpour@kntu.ac.ir Keywords: Multiple-input
Evaluation of 3C sensor coupling using ambient noise measurements Summary
 Evaluation of 3C sensor coupling using ambient noise measurements Howard Watt, John Gibson, Bruce Mattocks, Mark Cartwright, Roy Burnett, and Shuki Ronen Veritas Geophysical Corporation Summary Good vector
Evaluation of 3C sensor coupling using ambient noise measurements Howard Watt, John Gibson, Bruce Mattocks, Mark Cartwright, Roy Burnett, and Shuki Ronen Veritas Geophysical Corporation Summary Good vector
Robust Low-Resource Sound Localization in Correlated Noise
 INTERSPEECH 2014 Robust Low-Resource Sound Localization in Correlated Noise Lorin Netsch, Jacek Stachurski Texas Instruments, Inc. netsch@ti.com, jacek@ti.com Abstract In this paper we address the problem
INTERSPEECH 2014 Robust Low-Resource Sound Localization in Correlated Noise Lorin Netsch, Jacek Stachurski Texas Instruments, Inc. netsch@ti.com, jacek@ti.com Abstract In this paper we address the problem
