Th P6 01 Retrieval of the P- and S-velocity Structure of the Groningen Gas Reservoir Using Noise Interferometry
|
|
|
- Elwin Atkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Th P6 1 Retrieval of the P- and S-velocity Structure of the Groningen Gas Reservoir Using Noise Interferometry W. Zhou* (Utrecht University), H. Paulssen (Utrecht University) Summary The Groningen gas field in the Netherlands is the world's 7th largest onshore gas field and has been producing from Since 213, the reservoir has been monitored by two geophone strings at reservoir level (3 km). For borehole SDM, 1 geophones with a natural frequency of 15-Hz are positioned from the top to bottom of the reservoir. We used seismic interferometry to determine, as accurately as possible, the inter-geophone P- and S- wave velocities from ambient noise. Cross-correlations were stacked for every 1 hour and 24(hours)*33(days) segments were obtained for each station pair. The cross-correlations show both diurnal and weekly variations reflecting fluctuations in cultural noise. The apparent P-wave travel time for each geophone pair is measured from the maximum of the vertical component cross-correlation for each of the hourly stacks. We used Kernel density estimations to obtain the maximum likelihood travel times of all the geophone pairs which were subsequently used to determine inter-geophone P-wave velocities. A good agreement was found between our estimated P velocity structure and well logging data. The S-velocity structure was obtained from the eastcomponent cross-correlations. Because of the interference with P wave in east-component, the inferred S- velocity structure is less accurate.
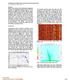
2 Introduction The Groningen gas field (Fig. 1 left) in the Netherlands is one of the world s largest onshore gas fields and has been producing from As a result of gas extraction, subsidence and induced seismicity occur, causing damage and concern in the area. Since 213, which was the year with the highest level of induced seismicity, two geophone strings have been placed in two boreholes to monitor the reservoir. For borehole SDM (Fig. 1 right), 1 geophones are positioned almost vertically from the top to the bottom of the reservoir with a geophone spacing of 3 m. We used the ambient noise data recorded in this borehole to determine the 1D P and S wave velocity structure within the reservoir. Figure 1: Left: Groningen gas field (green) with seismicity (ML.1-3.5; ), and two borehole locations (blue inverted triangles). Right: P wave velocity model and borehole monitoring system. Empirical Green s function and data processing In this study ambient noise interferometry was used to determine the velocity profile along the borehole. Under the assumption that ambient seismic noise is isotropically distributed, cross-correlation of records at two sensors provides an estimate of the Green s function between them (Snieder 24; Wapenaar et al. 21). For deep borehole data, the assumption can be satisfied for noise distributions mainly above or below the vertically aligned sensors. Previous studies have shown that body waves along borehole can be extracted by stacking noise cross-correlations over certain time (Miyazawa et al. 28; Grechka and Zhao 212; Vaezi and Van der Baan 215; Behm 216). Here we calculated the normalized crosscorrelation Csr (t) (Richter et al. 214; Durand et al. 211): Csr (t) = S(t) R(t)?. k S(t) k k R(t) k Where S(t) is the record at the reference geophone, R(t) the record at receiver geophone,? stands for correlation, and kk for the L2 norm. Continuous data from 21st November to 23rd December 213 was used. A bandpass filter from 3 to 4 Hz was applied. After filtering, we used 1-bit normalization, setting all positive amplitudes to 1 while negative amplitudes were set to -1. This is a treatment to remove amplitude bias in the time domain. Spectral whitening was also applied to remove frequency bias. The normalized crosscorrelations were calculated for 6 second segments with 4 second overlap. These segmented crosscorrelations were stacked over 1 hour. Further processing was based on these stacks. Figure 2 displays cross-correlation functions (CCFs) with the top geophone as a virtual-source for a 24-hour stack. In the left panel of Fig. 2, CCFs of vertical components of the 1 geophones are shown. A strong signal with an average velocity of about 38 m/s is interpreted as the direct P wave. In the right-hand panel, CCFs of east components are shown. The two signals with apparent velocity 38 m/s and 22 m/s correspond to the direct P and S wave, respectively. 79th EAGE Conference & Exhibition 217
3 Geophone depth (m) Geophone depth (m) Figure 2: Left: Vertical component cross-correlations with top geophone. Right: East component cross-correlations. Blue and red lines indicate P and S wave arrivals, respectively /11/13 1/12 8/12 date-time of records 15/12 22/12 The causal parts of the hourly CCFs between the top and the bottom geophone are shown in Fig. 3 for the entire period of over 1 month of data. For each hourly stack an estimate of the travel time, given by the maimum of the CCF, is marked with a black dot. Figure 3 shows diurnal and weekly variation of the CCFs for both vertical and horizontal components. This indicates that the noise is dominated by cultural noise from the surface /11/13 1/12 8/12 date-time of records 15/12 22/12 Figure 3: Causal part of the CCFs between the top and the bottom geophone for the vertical component (left) and the east component (right). Black dots indicate estimated travel times obtained from the CCFs. The colorbar shows retrieved waveform amplitudes. Travel time estimation and velocity profile The apparent P wave travel time for each geophone pair was measured from the maximum of the vertical component cross-correlation for each of the hourly stacks (Fig. 3 left). There are 33 (days) * 24 (hours) hourly stacks, so there are 33*24 P wave travel times for each geophone pair. We did the same for east component CCFs that showed the S arrival. In order to reduce the influence from the early arriving P waves, we set a time window with apparent velocity from 15 m/s to 35 m/s for S wave picking. For each geophone pair, the travel times of the 33*24 hourly stacks were plotted as a histogram. Because the distribution of these apparent travel times is skewed for both the P and the S wave, we used the kernel density estimation (Botev et al. 21) to obtain probability density functions (PDFs) of the travel times (Fig. 4). The maximum likelihood travel times of all the 45 geophone pairs were subsequently used to estimate the inter-geophone P and S wave velocities. We treated the 45 maximum likelihood P wave travel times of all geophone pairs with a linear least square method, to determine the best fitting inter-geophone travel times and velocities. We could not use all S wave timings because of the interference of the P with the S wave (Fig. 2 right). Therefore only 79th EAGE Conference & Exhibition 217
4 t=.74s 5 t=.111s 5 Number of samples Probability density function Number of samples Probability density function Figure 4: Histogram (blue) for P wave (left) and S wave (right) travel times obtained from the CCFs between the top and the bottom geophone. Red lines represent PDFs obtained by kernel density estimation. geophones with a spacing larger than 3*3 m to the reference geophone were used. The inferred P and S velocity structure is shown in Fig. 5. Errors are estimated as twice the diagonal of the model covariance matrix. We found a good agreement between our P velocity structure and the acoustic logging, with differences less than 5% Depth (m) Depth (m) V P logging geophone location V P estimation Apparent velocity in U (m/s) 3 35 NAM V S average model geophone location V S estimation Apparent velocity in E (m/s) Figure 5: Left: Estimated P velocity profile (blue) together with well logging data. Right: S velocity profile (red) with average S velocity. Well logging data and average S velocity in the reservoir (green) were provided by the NAM. Conclusion In order to monitor the reservoir of Groningen gas field, we analyzed the data from the 1 vertically aligned geophones in borehole SDM that are positioned from the top to the bottom of the reservoir with 3 m geophone spacing. Using seismic noise interferometry, 33 days of continuous recording was analysed and clear direct P and S wave were obtained. We found that the CCFs showed both diurnal and weekly variations reflecting fluctuations in cultural noise. Probability density estimations for the distributions of P and S travel times for each geophone pair were used to accurately determine the inter-geophone P and S travel times. A good agreement was found between our estimated P wave velocity structure and well logs, within 5%. S wave velocity was obtained with larger uncertainty. It is concluded that noise interferometry can be used to determine the seismic velocity structure from deep borehole data. In the future we will use this technique to monitor seismic velocity variations in the reservoir.
5 Acknowledgements We thank NAM and Remco Romijn for providing us with the data. This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 22 research and innovation programme under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No ITN CREEP. References Behm, M. [216] Feasibility of borehole ambient noise interferometry for permanent reservoir monitoring. Geophysical Prospecting, doi: / Botev, Z.I., Grotowski, J.F., Kroese, D.P. et al. [21] Kernel density estimation via diffusion. The Annals of Statistics, 38(5), Durand, S., Montagner, J.P., Roux, P., Brenguier, F., Nadeau, R.M. and Ricard, Y. [211] Passive monitoring of anisotropy change associated with the Parkfield 24 earthquake. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(13), doi:1.129/211gl L1333. Grechka, V. and Zhao, Y. [212] Microseismic interferometry. The Leading Edge, 31(12), Miyazawa, M., Snieder, R. and Venkataraman, A. [28] Application of seismic interferometry to extract P-and S-wave propagation and observation of shear-wave splitting from noise data at Cold Lake, Alberta, Canada. Geophysics, 73(4), D35 D4. Richter, T., Sens-Schönfelder, C., Kind, R. and Asch, G. [214] Comprehensive observation and modeling of earthquake and temperature-related seismic velocity changes in northern Chile with passive image interferometry. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 119(6), Snieder, R. [24] Extracting the Green s function from the correlation of coda waves: A derivation based on stationary phase. Physical Review E, 69(4), Vaezi, Y. and Van der Baan, M. [215] Interferometric assessment of clamping quality of borehole geophones. Geophysics, 8(6), WC89 WC98. Wapenaar, K., Draganov, D., Snieder, R., Campman, X. and Verdel, A. [21] Tutorial on seismic interferometry: Part 1 - Basic principles and applications. Geophysics, 75(5), 75A195 75A29.
Multicomponent seismic polarization analysis
 Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
PASSIVE ACOUSTIC AND SEISMIC TOMOGRAPHY WITH OCEAN AMBIENT NOISE IN ORION
 Proceedings of the International Conference Underwater Acoustic Measurements: Technologies &Results Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 28 th June 1 st July 2005 PASSIVE ACOUSTIC AND SEISMIC TOMOGRAPHY WITH OCEAN
Proceedings of the International Conference Underwater Acoustic Measurements: Technologies &Results Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 28 th June 1 st July 2005 PASSIVE ACOUSTIC AND SEISMIC TOMOGRAPHY WITH OCEAN
Microquake seismic interferometry with SV D enhanced Green s function recovery
 Microquake seismic interferometry with SV D enhanced Green s function recovery Gabriela Melo and A lison Malcolm Earth Resources Laboratory - Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department Massachusetts
Microquake seismic interferometry with SV D enhanced Green s function recovery Gabriela Melo and A lison Malcolm Earth Resources Laboratory - Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department Massachusetts
Coda Waveform Correlations
 Chapter 5 Coda Waveform Correlations 5.1 Cross-Correlation of Seismic Coda 5.1.1 Introduction In the previous section, the generation of the surface wave component of the Green s function by the correlation
Chapter 5 Coda Waveform Correlations 5.1 Cross-Correlation of Seismic Coda 5.1.1 Introduction In the previous section, the generation of the surface wave component of the Green s function by the correlation
=, (1) Summary. Theory. Introduction
 Noise suppression for detection and location of microseismic events using a matched filter Leo Eisner*, David Abbott, William B. Barker, James Lakings and Michael P. Thornton, Microseismic Inc. Summary
Noise suppression for detection and location of microseismic events using a matched filter Leo Eisner*, David Abbott, William B. Barker, James Lakings and Michael P. Thornton, Microseismic Inc. Summary
Master event relocation of microseismic event using the subspace detector
 Master event relocation of microseismic event using the subspace detector Ibinabo Bestmann, Fernando Castellanos and Mirko van der Baan Dept. of Physics, CCIS, University of Alberta Summary Microseismic
Master event relocation of microseismic event using the subspace detector Ibinabo Bestmann, Fernando Castellanos and Mirko van der Baan Dept. of Physics, CCIS, University of Alberta Summary Microseismic
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis
 Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
Extracting time-domain Green s function estimates from ambient seismic noise
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32,, doi:10.1029/2004gl021862, 2005 Extracting time-domain Green s function estimates from ambient seismic noise Karim G. Sabra, Peter Gerstoft, Philippe Roux, and W.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32,, doi:10.1029/2004gl021862, 2005 Extracting time-domain Green s function estimates from ambient seismic noise Karim G. Sabra, Peter Gerstoft, Philippe Roux, and W.
X039 Observations of Surface Vibrator Repeatability in a Desert Environment
 X39 Observations of Surface Vibrator Repeatability in a Desert Environment M.A. Jervis* (Saudi Aramco), A.V. Bakulin (Saudi Aramco), R.M. Burnstad (Saudi Aramco), C. Beron (CGGVeritas) & E. Forgues (CGGVeritas)
X39 Observations of Surface Vibrator Repeatability in a Desert Environment M.A. Jervis* (Saudi Aramco), A.V. Bakulin (Saudi Aramco), R.M. Burnstad (Saudi Aramco), C. Beron (CGGVeritas) & E. Forgues (CGGVeritas)
P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method
 P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method E. Baniasadi* (University of Tehran), M. A. Riahi (University of Tehran) & S. Chaychizadeh (University of Tehran)
P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method E. Baniasadi* (University of Tehran), M. A. Riahi (University of Tehran) & S. Chaychizadeh (University of Tehran)
WS15-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise
 WS1-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise F. Duret* (CGG) & E. Forgues (CGG) SUMMARY In 4D land seismic and especially for Permanent Reservoir Monitoring (PRM), changes of the near-surface
WS1-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise F. Duret* (CGG) & E. Forgues (CGG) SUMMARY In 4D land seismic and especially for Permanent Reservoir Monitoring (PRM), changes of the near-surface
Seismic application of quality factor estimation using the peak frequency method and sparse time-frequency transforms
 Seismic application of quality factor estimation using the peak frequency method and sparse time-frequency transforms Jean Baptiste Tary 1, Mirko van der Baan 1, and Roberto Henry Herrera 1 1 Department
Seismic application of quality factor estimation using the peak frequency method and sparse time-frequency transforms Jean Baptiste Tary 1, Mirko van der Baan 1, and Roberto Henry Herrera 1 1 Department
Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure
 Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure Andy St-Onge* 1a, David W. Eaton 1b, and Adam Pidlisecky 1c 1 Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW Calgary,
Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure Andy St-Onge* 1a, David W. Eaton 1b, and Adam Pidlisecky 1c 1 Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW Calgary,
A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data
 A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data Yessika Blunda*, Pinnacle, Halliburton, Houston, Tx, US yessika.blunda@pinntech.com and Kit Chambers, Pinnacle, Halliburton, St Agnes, Cornwall,
A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data Yessika Blunda*, Pinnacle, Halliburton, Houston, Tx, US yessika.blunda@pinntech.com and Kit Chambers, Pinnacle, Halliburton, St Agnes, Cornwall,
Passive fathometer processing
 Passive fathometer processing Peter Gerstoft and William S. Hodgkiss Marine Physical Laboratory, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, California 92093-0238 Martin Siderius HLS Research Inc.,
Passive fathometer processing Peter Gerstoft and William S. Hodgkiss Marine Physical Laboratory, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, La Jolla, California 92093-0238 Martin Siderius HLS Research Inc.,
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data
 Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation
 WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), M. Sams (Ikon Science) & K. Waters (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Broadband re-processed seismic
WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), M. Sams (Ikon Science) & K. Waters (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Broadband re-processed seismic
SUMMARY INTRODUCTION GROUP VELOCITY
 Surface-wave inversion for near-surface shear-wave velocity estimation at Coronation field Huub Douma (ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging solutions) and Matthew Haney (Boise State University) SUMMARY We study
Surface-wave inversion for near-surface shear-wave velocity estimation at Coronation field Huub Douma (ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging solutions) and Matthew Haney (Boise State University) SUMMARY We study
EENG473 Mobile Communications Module 3 : Week # (12) Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Path Loss
 EENG473 Mobile Communications Module 3 : Week # (12) Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Path Loss Introduction Small-scale fading is used to describe the rapid fluctuation of the amplitude of a radio
EENG473 Mobile Communications Module 3 : Week # (12) Mobile Radio Propagation: Small-Scale Path Loss Introduction Small-scale fading is used to describe the rapid fluctuation of the amplitude of a radio
A multi-window algorithm for real-time automatic detection and picking of P-phases of microseismic events
 A multi-window algorithm for real-time automatic detection and picking of P-phases of microseismic events Zuolin Chen and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT There exist a variety of algorithms for the detection
A multi-window algorithm for real-time automatic detection and picking of P-phases of microseismic events Zuolin Chen and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT There exist a variety of algorithms for the detection
Time Domain Classification and Quantification of Seismic Noise
 Time Domain Classification and Quantification of Seismic Noise Jörn Groos 1, Joachim R. R. Ritter 1 1 Geophysikalisches Institut, Universität Karlsruhe (TH), Germany, E-mail: joern.groos@gpi.unikarlsruhe.de,
Time Domain Classification and Quantification of Seismic Noise Jörn Groos 1, Joachim R. R. Ritter 1 1 Geophysikalisches Institut, Universität Karlsruhe (TH), Germany, E-mail: joern.groos@gpi.unikarlsruhe.de,
TREBALL FI DE CARRERA
 - TREBALL FI DE CARRERA Títol Development of an automated microseismic event detection method and analysis of a microseismic dataset from hydraulic fracture stimulation to characterise natural and induced
- TREBALL FI DE CARRERA Títol Development of an automated microseismic event detection method and analysis of a microseismic dataset from hydraulic fracture stimulation to characterise natural and induced
Ambient Passive Seismic Imaging with Noise Analysis Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc.
 Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc. SUMMARY The ambient passive seismic imaging technique is capable of imaging repetitive passive seismic events. Here we investigate
Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc. SUMMARY The ambient passive seismic imaging technique is capable of imaging repetitive passive seismic events. Here we investigate
Green s Function Extraction from Ambient Seismic Field: Analysis of Seasonal Variations
 Green s Function Extraction from Ambient Seismic Field: Analysis of Seasonal Variations Sutton Chiorini 1 Supervisor: Kazuki Koketsu 2 Supporter: Loïc Viens 2 1 University of Maryland, College Park, U.S.A,
Green s Function Extraction from Ambient Seismic Field: Analysis of Seasonal Variations Sutton Chiorini 1 Supervisor: Kazuki Koketsu 2 Supporter: Loïc Viens 2 1 University of Maryland, College Park, U.S.A,
Tu SRS3 06 Wavelet Estimation for Broadband Seismic Data
 Tu SRS3 06 Wavelet Estimation for Broadband Seismic Data E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), J. Gunning (CSIRO), R. White (Birkbeck University of London) & P. Spaans (Woodside) SUMMARY The volumes of broadband
Tu SRS3 06 Wavelet Estimation for Broadband Seismic Data E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), J. Gunning (CSIRO), R. White (Birkbeck University of London) & P. Spaans (Woodside) SUMMARY The volumes of broadband
Identification and localization of micro-seismic events using the cross-correlation technique for the Ketzin CO2 storage site
 Number of pages Number of appendices 33 (incl. appendices) 3 TNO report Identification and localization of micro-seismic events using the cross-correlation technique for the Ketzin CO2 storage site Date
Number of pages Number of appendices 33 (incl. appendices) 3 TNO report Identification and localization of micro-seismic events using the cross-correlation technique for the Ketzin CO2 storage site Date
Corresponding Author William Menke,
 Waveform Fitting of Cross-Spectra to Determine Phase Velocity Using Aki s Formula William Menke and Ge Jin Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Corresponding Author William Menke, MENKE@LDEO.COLUMBIA.EDU,
Waveform Fitting of Cross-Spectra to Determine Phase Velocity Using Aki s Formula William Menke and Ge Jin Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Corresponding Author William Menke, MENKE@LDEO.COLUMBIA.EDU,
INVESTIGATION OF AMBIENT SEISMIC NOISE USING SEISMIC INTERFEROMETRY IN WESTERN MONTANA
 Montana Tech Library Digital Commons @ Montana Tech Graduate Theses & Non-Theses Student Scholarship Fall 2015 INVESTIGATION OF AMBIENT SEISMIC NOISE USING SEISMIC INTERFEROMETRY IN WESTERN MONTANA Natalia
Montana Tech Library Digital Commons @ Montana Tech Graduate Theses & Non-Theses Student Scholarship Fall 2015 INVESTIGATION OF AMBIENT SEISMIC NOISE USING SEISMIC INTERFEROMETRY IN WESTERN MONTANA Natalia
Cmin. Cmax. Frac volume. SEG Houston 2009 International Exposition and Annual Meeting. Summary (1),
 Improving signal-to-noise ratio of passsive seismic data with an adaptive FK filter Chuntao Liang*, Mike P. Thornton, Peter Morton, BJ Hulsey, Andrew Hill, and Phil Rawlins, Microseismic Inc. Summary We
Improving signal-to-noise ratio of passsive seismic data with an adaptive FK filter Chuntao Liang*, Mike P. Thornton, Peter Morton, BJ Hulsey, Andrew Hill, and Phil Rawlins, Microseismic Inc. Summary We
Wave-equation microseismic imaging and event selection in the image domain Brad Artman 1, Ben Witten, Spectraseis Inc.
 Wave-equation microseismic imaging and event selection in the image domain Brad Artman 1, Ben Witten, Spectraseis Inc. Summary Common techniques for locating fracture events, from large earthquakes to
Wave-equation microseismic imaging and event selection in the image domain Brad Artman 1, Ben Witten, Spectraseis Inc. Summary Common techniques for locating fracture events, from large earthquakes to
Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion
 Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion Heather J.E. Lloyd*, CREWES / University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta hjelloyd@ucalgary.ca and Gary F. Margrave, CREWES
Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion Heather J.E. Lloyd*, CREWES / University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta hjelloyd@ucalgary.ca and Gary F. Margrave, CREWES
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency
 25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
Observations of the OSOP Sixaola, March 1-3, 2016, at the Albuquerque Seismological Laboratory
 Observations of the OSOP Sixaola, March 1-3, 2016, at the Albuquerque Seismological Laboratory There were two representatives (Angel Rodriquez and David Nelson) from OSOP at ASL March 1-3, 2016, and they
Observations of the OSOP Sixaola, March 1-3, 2016, at the Albuquerque Seismological Laboratory There were two representatives (Angel Rodriquez and David Nelson) from OSOP at ASL March 1-3, 2016, and they
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/11/e1501057/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Earthquake detection through computationally efficient similarity search The PDF file includes: Clara E. Yoon, Ossian
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/11/e1501057/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Earthquake detection through computationally efficient similarity search The PDF file includes: Clara E. Yoon, Ossian
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas
 The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
Retrieving Focal Mechanism of Earthquakes Using the CAP Method
 Retrieving Focal Mechanism of Earthquakes Using the CAP Method Hongfeng Yang April 11, 2013 1 Introduction Waveforms recorded at a seismic station, W (t), compose of three components: W (t) = S(t) G(t)
Retrieving Focal Mechanism of Earthquakes Using the CAP Method Hongfeng Yang April 11, 2013 1 Introduction Waveforms recorded at a seismic station, W (t), compose of three components: W (t) = S(t) G(t)
Micro-Seismic Interpretation of Hydraulic Fracture Treatments. Hans de Pater Pinnacle Technologies Delft
 Micro-Seismic Interpretation of Hydraulic Fracture Treatments Hans de Pater Pinnacle Technologies Delft Outline Micro Seismic Technology in the Oil industry Velocity Structure Examples Fault interaction
Micro-Seismic Interpretation of Hydraulic Fracture Treatments Hans de Pater Pinnacle Technologies Delft Outline Micro Seismic Technology in the Oil industry Velocity Structure Examples Fault interaction
Microtremor Array Measurements and Three-component Microtremor Measurements in San Francisco Bay Area
 Microtremor Array Measurements and Three-component Microtremor Measurements in San Francisco Bay Area K. Hayashi & D. Underwood Geometrics, Inc., United States SUMMARY: Microtremor array measurements and
Microtremor Array Measurements and Three-component Microtremor Measurements in San Francisco Bay Area K. Hayashi & D. Underwood Geometrics, Inc., United States SUMMARY: Microtremor array measurements and
Characterization of a Very Shallow Water Acoustic Communication Channel MTS/IEEE OCEANS 09 Biloxi, MS
 Characterization of a Very Shallow Water Acoustic Communication Channel MTS/IEEE OCEANS 09 Biloxi, MS Brian Borowski Stevens Institute of Technology Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer
Characterization of a Very Shallow Water Acoustic Communication Channel MTS/IEEE OCEANS 09 Biloxi, MS Brian Borowski Stevens Institute of Technology Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer
ESTIMATING LOCAL AND NEAR-REGIONAL VELOCITY AND ATTENUATION STRUCTURE FROM SEISMIC NOISE. Sponsored by Air Force Research Laboratory
 ESTIMATING LOCAL AND NEAR-REGIONAL VELOCITY AND ATTENUATION STRUCTURE FROM SEISMIC NOISE Peter Gerstoft 1, Jian Zhang 1, William A Kuperman 1, Nick Harmon 1, Karim G. Sabra 2, Michael C Fehler 3, Steven
ESTIMATING LOCAL AND NEAR-REGIONAL VELOCITY AND ATTENUATION STRUCTURE FROM SEISMIC NOISE Peter Gerstoft 1, Jian Zhang 1, William A Kuperman 1, Nick Harmon 1, Karim G. Sabra 2, Michael C Fehler 3, Steven
Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing Dispersive Ground Roll Noise from Onshore Seismic Data
 Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
SUMMARY INTRODUCTION MOTIVATION
 Isabella Masoni, Total E&P, R. Brossier, University Grenoble Alpes, J. L. Boelle, Total E&P, J. Virieux, University Grenoble Alpes SUMMARY In this study, an innovative layer stripping approach for FWI
Isabella Masoni, Total E&P, R. Brossier, University Grenoble Alpes, J. L. Boelle, Total E&P, J. Virieux, University Grenoble Alpes SUMMARY In this study, an innovative layer stripping approach for FWI
Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion
 P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
New Metrics Developed for a Complex Cepstrum Depth Program
 T3.5-05 Robert C. Kemerait Ileana M. Tibuleac Jose F. Pascual-Amadeo Michael Thursby Chandan Saikia Nuclear Treaty Monitoring, Geophysics Division New Metrics Developed for a Complex Cepstrum Depth Program
T3.5-05 Robert C. Kemerait Ileana M. Tibuleac Jose F. Pascual-Amadeo Michael Thursby Chandan Saikia Nuclear Treaty Monitoring, Geophysics Division New Metrics Developed for a Complex Cepstrum Depth Program
Surface wave analysis for P- and S-wave velocity models
 Distinguished Lectures in Earth Sciences, Napoli, 24 Maggio 2018 Surface wave analysis for P- and S-wave velocity models Laura Valentina Socco, Farbod Khosro Anjom, Cesare Comina, Daniela Teodor POLITECNICO
Distinguished Lectures in Earth Sciences, Napoli, 24 Maggio 2018 Surface wave analysis for P- and S-wave velocity models Laura Valentina Socco, Farbod Khosro Anjom, Cesare Comina, Daniela Teodor POLITECNICO
Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS
 Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS Summary In land AVO processing, near-surface heterogeneity issues are
Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS Summary In land AVO processing, near-surface heterogeneity issues are
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2015) 203, 1149 1163 GJI Seismology doi: 10.1093/gji/ggv357 Extracting seismic attenuation coefficients from cross-correlations of ambient noise at linear
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2015) 203, 1149 1163 GJI Seismology doi: 10.1093/gji/ggv357 Extracting seismic attenuation coefficients from cross-correlations of ambient noise at linear
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile
 Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
Microseismic events enhancement and detection in sensor arrays using autocorrelation-based filtering
 Geophysical Prospecting, 7 doi:./3-78.9 Microseismic events enhancement and detection in sensor arrays using autocorrelation-based filtering Entao Liu, Lijun Zhu, Anupama Govinda Raj, James H. McClellan,
Geophysical Prospecting, 7 doi:./3-78.9 Microseismic events enhancement and detection in sensor arrays using autocorrelation-based filtering Entao Liu, Lijun Zhu, Anupama Govinda Raj, James H. McClellan,
Improving microseismic data quality with noise attenuation techniques
 Improving microseismic data quality with noise attenuation techniques Kit Chambers, Aaron Booterbaugh Nanometrics Inc. Summary Microseismic data always contains noise and its effect is to reduce the quality
Improving microseismic data quality with noise attenuation techniques Kit Chambers, Aaron Booterbaugh Nanometrics Inc. Summary Microseismic data always contains noise and its effect is to reduce the quality
Coda Wave Interferometry used to detect loads and cracks in a concrete structure under field conditions
 9 th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring July 10-13, 2018, Manchester, United Kingdom Coda Wave Interferometry used to detect loads and cracks in a concrete structure under field conditions
9 th European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring July 10-13, 2018, Manchester, United Kingdom Coda Wave Interferometry used to detect loads and cracks in a concrete structure under field conditions
Application of Low Frequency Passive Seismic Method for Hydrocarbon Detection in S Field, South Sumatra Basin
 Abstract Application of Low Frequency Passive Seismic Method for Hydrocarbon Detection in S Field, South Sumatra Basin Andika Perbawa, Danar Yudhatama, and M. Aidil Arham PT. Medco E&P Indonesia, Jakarta
Abstract Application of Low Frequency Passive Seismic Method for Hydrocarbon Detection in S Field, South Sumatra Basin Andika Perbawa, Danar Yudhatama, and M. Aidil Arham PT. Medco E&P Indonesia, Jakarta
Matching and Locating of Cloud to Ground Lightning Discharges
 Charles Wang Duke University Class of 05 ECE/CPS Pratt Fellow Matching and Locating of Cloud to Ground Lightning Discharges Advisor: Prof. Steven Cummer I: Introduction When a lightning discharge occurs
Charles Wang Duke University Class of 05 ECE/CPS Pratt Fellow Matching and Locating of Cloud to Ground Lightning Discharges Advisor: Prof. Steven Cummer I: Introduction When a lightning discharge occurs
Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results
 Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results David C. Henley and Han-Xing Lu PNG processing ABSTRACT Papua New Guinea is among the most notoriously difficult areas in the world in
Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results David C. Henley and Han-Xing Lu PNG processing ABSTRACT Papua New Guinea is among the most notoriously difficult areas in the world in
A COMPARISON OF SITE-AMPLIFICATION ESTIMATED FROM DIFFERENT METHODS USING A STRONG MOTION OBSERVATION ARRAY IN TANGSHAN, CHINA
 A COMPARISON OF SITE-AMPLIFICATION ESTIMATED FROM DIFFERENT METHODS USING A STRONG MOTION OBSERVATION ARRAY IN TANGSHAN, CHINA Wenbo ZHANG 1 And Koji MATSUNAMI 2 SUMMARY A seismic observation array for
A COMPARISON OF SITE-AMPLIFICATION ESTIMATED FROM DIFFERENT METHODS USING A STRONG MOTION OBSERVATION ARRAY IN TANGSHAN, CHINA Wenbo ZHANG 1 And Koji MATSUNAMI 2 SUMMARY A seismic observation array for
Passive (Micro-)Seismic Event Detection
 Passive (Micro-)Seismic Event Detection Introduction Among engineers there is considerable interest in the real-time identification of events within time series data with a low signal to noise ratio (S/N).
Passive (Micro-)Seismic Event Detection Introduction Among engineers there is considerable interest in the real-time identification of events within time series data with a low signal to noise ratio (S/N).
Reconstructing Green s function by correlation of the coda of the correlation (C 3 ) of ambient seismic noise
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 11, B1106, doi:10.1029/2008jb00569, 2008 Reconstructing Green s function by correlation of the coda of the correlation (C ) of ambient
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 11, B1106, doi:10.1029/2008jb00569, 2008 Reconstructing Green s function by correlation of the coda of the correlation (C ) of ambient
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution
 Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Innovative Solutions Across the E&P Lifecycle. ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT PRODUCTION
 Innovative Solutions Across the E&P Lifecycle. ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT PRODUCTION Innovative Solutions, from Access to Production Uncertainty Knowledge ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT
Innovative Solutions Across the E&P Lifecycle. ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT PRODUCTION Innovative Solutions, from Access to Production Uncertainty Knowledge ACCESS EXPLORATION APPRAISAL DEVELOPMENT
Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring
 Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring Michael Thornton*, MicroSeismic Inc., Houston,Texas mthornton@microseismic.com Summary While related concepts, resolution and uncertainty
Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring Michael Thornton*, MicroSeismic Inc., Houston,Texas mthornton@microseismic.com Summary While related concepts, resolution and uncertainty
ISSN Volume 28 Issue 6 June A New Spring for Geoscience. Special Topic
 ISSN 0263-5046 Volume 28 Issue 6 June 2010 Special Topic Technical Articles Multi-azimuth processing and its applications to wide-azimuth OBC seismic data offshore Abu Dhabi Borehole image logs for turbidite
ISSN 0263-5046 Volume 28 Issue 6 June 2010 Special Topic Technical Articles Multi-azimuth processing and its applications to wide-azimuth OBC seismic data offshore Abu Dhabi Borehole image logs for turbidite
Overview ta3520 Introduction to seismics
 Overview ta3520 Introduction to seismics Fourier Analysis Basic principles of the Seismic Method Interpretation of Raw Seismic Records Seismic Instrumentation Processing of Seismic Reflection Data Vertical
Overview ta3520 Introduction to seismics Fourier Analysis Basic principles of the Seismic Method Interpretation of Raw Seismic Records Seismic Instrumentation Processing of Seismic Reflection Data Vertical
TRAIN INDUCED SEISMIC NOISE OF ACCELERATING AND DECELERATING TRAIN SETS
 TRAIN INDUCED SEISMIC NOISE OF ACCELERATING AND DECELERATING TRAIN SETS ABSTRACT: M. Çetin 1, A. Tongut 2, S.Ü. Dikmen 3 and Ali Pınar 4 1 Civil Eng., Dept. of Earthquake Engineering, KOERI, Bogazici University,
TRAIN INDUCED SEISMIC NOISE OF ACCELERATING AND DECELERATING TRAIN SETS ABSTRACT: M. Çetin 1, A. Tongut 2, S.Ü. Dikmen 3 and Ali Pınar 4 1 Civil Eng., Dept. of Earthquake Engineering, KOERI, Bogazici University,
NPAL Acoustic Noise Field Coherence and Broadband Full Field Processing
 NPAL Acoustic Noise Field Coherence and Broadband Full Field Processing Arthur B. Baggeroer Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 Phone: 617 253 4336 Fax: 617 253 2350 Email: abb@boreas.mit.edu
NPAL Acoustic Noise Field Coherence and Broadband Full Field Processing Arthur B. Baggeroer Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 02139 Phone: 617 253 4336 Fax: 617 253 2350 Email: abb@boreas.mit.edu
A Combined Multi-Temporal InSAR Method: Incorporating Persistent Scatterer and Small Baseline Approaches. Andy Hooper University of Iceland
 A Combined Multi-Temporal InSAR Method: Incorporating Persistent Scatterer and Small Baseline Approaches Andy Hooper University of Iceland Time Multi-Temporal InSAR Same area imaged each time Multi-Temporal
A Combined Multi-Temporal InSAR Method: Incorporating Persistent Scatterer and Small Baseline Approaches Andy Hooper University of Iceland Time Multi-Temporal InSAR Same area imaged each time Multi-Temporal
Attenuation of high energy marine towed-streamer noise Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco
 Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Shallow shear wave velocity structure in two sites of Khartoum, Sudan using methods of seismic dispersion and ambient noise.
 Norwegian National Seismic Network Technical Report No. 25 Shallow shear wave velocity structure in two sites of Khartoum, Sudan using methods of seismic dispersion and ambient noise. Prepared by Miguel
Norwegian National Seismic Network Technical Report No. 25 Shallow shear wave velocity structure in two sites of Khartoum, Sudan using methods of seismic dispersion and ambient noise. Prepared by Miguel
Antennas and Propagation. Chapter 5c: Array Signal Processing and Parametric Estimation Techniques
 Antennas and Propagation : Array Signal Processing and Parametric Estimation Techniques Introduction Time-domain Signal Processing Fourier spectral analysis Identify important frequency-content of signal
Antennas and Propagation : Array Signal Processing and Parametric Estimation Techniques Introduction Time-domain Signal Processing Fourier spectral analysis Identify important frequency-content of signal
Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events
 Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events Natalia Verkhovtseva Pinnacle a Halliburton Service, Calgary, AB Summary Data sampling and its effect on the microseismic
Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events Natalia Verkhovtseva Pinnacle a Halliburton Service, Calgary, AB Summary Data sampling and its effect on the microseismic
Study of Hydrocarbon Detection Methods in Offshore Deepwater Sediments, Gulf of Guinea*
 Study of Hydrocarbon Detection Methods in Offshore Deepwater Sediments, Gulf of Guinea* Guoping Zuo 1, Fuliang Lu 1, Guozhang Fan 1, and Dali Shao 1 Search and Discovery Article #40999 (2012)** Posted
Study of Hydrocarbon Detection Methods in Offshore Deepwater Sediments, Gulf of Guinea* Guoping Zuo 1, Fuliang Lu 1, Guozhang Fan 1, and Dali Shao 1 Search and Discovery Article #40999 (2012)** Posted
Some observations of data quality at global seismic stations
 Some observations of data quality at global seismic stations Meredith Nettles and Göran Ekström Global CMT Project Waveform Quality Center SITS, 2009/11/10 1. Data quality control using signals 1a. Sensor
Some observations of data quality at global seismic stations Meredith Nettles and Göran Ekström Global CMT Project Waveform Quality Center SITS, 2009/11/10 1. Data quality control using signals 1a. Sensor
Monitoring a Building Using Deconvolution Interferometry. II: Ambient- Vibration Analysis
 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol., No., pp. 3, February, doi:.7/3 Monitoring a Building Using Deconvolution Interferometry. II: Ambient- Vibration Analysis by Nori Nakata and Roel
Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, Vol., No., pp. 3, February, doi:.7/3 Monitoring a Building Using Deconvolution Interferometry. II: Ambient- Vibration Analysis by Nori Nakata and Roel
There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to
 Coordinated by JEFF DEERE JOHN GIBSON, FOREST LIN, ALEXANDRE EGRETEAU, and JULIEN MEUNIER, CGGVeritas MALCOLM LANSLEY, Sercel There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to improve the quality
Coordinated by JEFF DEERE JOHN GIBSON, FOREST LIN, ALEXANDRE EGRETEAU, and JULIEN MEUNIER, CGGVeritas MALCOLM LANSLEY, Sercel There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to improve the quality
Tu A D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study
 Tu A15 09 4D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study D. Lecerf* (PGS), D. Raistrick (PGS), B. Caselitz (PGS), M. Wingham (BP), J. Bradley (BP), B. Moseley (formaly BP) Summary
Tu A15 09 4D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study D. Lecerf* (PGS), D. Raistrick (PGS), B. Caselitz (PGS), M. Wingham (BP), J. Bradley (BP), B. Moseley (formaly BP) Summary
Seismic interferometry turning noise into signal
 Seismic interferometry turning noise into signal ANDREW CURTIS, University of Edinburgh, UK PETER GERSTOFT, University of California at San Diego, USA HARUO SATO, Tokoku University, Japan ROEL SNIEDER,
Seismic interferometry turning noise into signal ANDREW CURTIS, University of Edinburgh, UK PETER GERSTOFT, University of California at San Diego, USA HARUO SATO, Tokoku University, Japan ROEL SNIEDER,
Extending the useable bandwidth of seismic data with tensor-guided, frequency-dependent filtering
 first break volume 34, January 2016 special topic Extending the useable bandwidth of seismic data with tensor-guided, frequency-dependent filtering Edward Jenner 1*, Lisa Sanford 2, Hans Ecke 1 and Bruce
first break volume 34, January 2016 special topic Extending the useable bandwidth of seismic data with tensor-guided, frequency-dependent filtering Edward Jenner 1*, Lisa Sanford 2, Hans Ecke 1 and Bruce
attempt to understand if we can identify a relationship between fundamental mode propagation and the condition of the cement bonds.
 Hua Wang*, Mike Fehler,Earth Resources Lab,Massachusetts Institute of Technology,Cambridge, MA, USA Summary We use a 3D Finite Difference (3DFD) method to simulate monopole wavefields in a singly-cased
Hua Wang*, Mike Fehler,Earth Resources Lab,Massachusetts Institute of Technology,Cambridge, MA, USA Summary We use a 3D Finite Difference (3DFD) method to simulate monopole wavefields in a singly-cased
Infrasonic Observations of the Hekla Eruption of February 26, 2000
 JOURNAL OF LOW FREQUENCY NOISE, VIBRATION AND ACTIVE CONTROL Pages 1 8 Infrasonic Observations of the Hekla Eruption of February 26, 2000 Ludwik Liszka 1 and Milton A. Garces 2 1 Swedish Institute of Space
JOURNAL OF LOW FREQUENCY NOISE, VIBRATION AND ACTIVE CONTROL Pages 1 8 Infrasonic Observations of the Hekla Eruption of February 26, 2000 Ludwik Liszka 1 and Milton A. Garces 2 1 Swedish Institute of Space
Efficient Acquisition of Quality Borehole Seismic
 Efficient Acquisition of Quality Borehole Seismic The Versatile Seismic Imager Applications Integrated processing for interpretation of boreholeand surface-seismic data Images for reservoir definition
Efficient Acquisition of Quality Borehole Seismic The Versatile Seismic Imager Applications Integrated processing for interpretation of boreholeand surface-seismic data Images for reservoir definition
Application of Multi-channel Wiener Filters to the Suppression of Ambient Seismic Noise in Passive Seismic Arrays
 Application of Multi-channel Wiener Filters to the Suppression of Ambient Seismic Noise in Passive Seismic Arrays J. Wang 1, F. Tilmann 1, R. S. White 1, H. Soosalu 1 and P. Bordoni 2 1. Bullard Laboratories,
Application of Multi-channel Wiener Filters to the Suppression of Ambient Seismic Noise in Passive Seismic Arrays J. Wang 1, F. Tilmann 1, R. S. White 1, H. Soosalu 1 and P. Bordoni 2 1. Bullard Laboratories,
JournalofGeophysicalResearch: SolidEarth
 JournalofGeophysicalResearch: olidearth REEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: We extract body waves from ambient noise recorded by a dense network Two signal-processing filters are applied to retrieve clear body
JournalofGeophysicalResearch: olidearth REEARCH ARTICLE Key Points: We extract body waves from ambient noise recorded by a dense network Two signal-processing filters are applied to retrieve clear body
This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010.
 This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010. The information herein remains the property of Mustagh
This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010. The information herein remains the property of Mustagh
Ambient seismic noise tomography at Ekofisk
 Chapter 6 Ambient seismic noise tomography at Ekofisk In Chapter 2 to 5 I presented an extensive characterization of noise and noise correlations for ambient seismic recordings made at Valhall. Here I
Chapter 6 Ambient seismic noise tomography at Ekofisk In Chapter 2 to 5 I presented an extensive characterization of noise and noise correlations for ambient seismic recordings made at Valhall. Here I
JUMPSTARTING NEURAL NETWORK TRAINING FOR SEISMIC PROBLEMS
 JUMPSTARTING NEURAL NETWORK TRAINING FOR SEISMIC PROBLEMS Fantine Huot (Stanford Geophysics) Advised by Greg Beroza & Biondo Biondi (Stanford Geophysics & ICME) LEARNING FROM DATA Deep learning networks
JUMPSTARTING NEURAL NETWORK TRAINING FOR SEISMIC PROBLEMS Fantine Huot (Stanford Geophysics) Advised by Greg Beroza & Biondo Biondi (Stanford Geophysics & ICME) LEARNING FROM DATA Deep learning networks
AVO processing of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake heavy oilfield, Saskatchewan
 AVO processing of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake heavy oilfield, Saskatchewan Zimin Zhang, Robert R. Stewart, and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT The AVO processing and analysis of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake
AVO processing of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake heavy oilfield, Saskatchewan Zimin Zhang, Robert R. Stewart, and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT The AVO processing and analysis of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake
Northing (km)
 Imaging lateral heterogeneity at Coronation Field with surface waves Matthew M. Haney, Boise State University, and Huub Douma, ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging Solutions SUMMARY A longstanding problem in land
Imaging lateral heterogeneity at Coronation Field with surface waves Matthew M. Haney, Boise State University, and Huub Douma, ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging Solutions SUMMARY A longstanding problem in land
IOMAC'13 5 th International Operational Modal Analysis Conference
 IOMAC'13 5 th International Operational Modal Analysis Conference 2013 May 13-15 Guimarães - Portugal STRUCTURAL HEALTH MONITORING OF A MID HEIGHT BUILDING IN CHILE R. Boroschek 1, A. Aguilar 2, J. Basoalto
IOMAC'13 5 th International Operational Modal Analysis Conference 2013 May 13-15 Guimarães - Portugal STRUCTURAL HEALTH MONITORING OF A MID HEIGHT BUILDING IN CHILE R. Boroschek 1, A. Aguilar 2, J. Basoalto
Seismic Reflection Method
 1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
Seismic fault detection based on multi-attribute support vector machine analysis
 INT 5: Fault and Salt @ SEG 2017 Seismic fault detection based on multi-attribute support vector machine analysis Haibin Di, Muhammad Amir Shafiq, and Ghassan AlRegib Center for Energy & Geo Processing
INT 5: Fault and Salt @ SEG 2017 Seismic fault detection based on multi-attribute support vector machine analysis Haibin Di, Muhammad Amir Shafiq, and Ghassan AlRegib Center for Energy & Geo Processing
Geophysical Journal International
 Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2014) 197, 458 463 Advance Access publication 2014 January 20 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt516 An earthquake detection algorithm with pseudo-probabilities of
Geophysical Journal International Geophys. J. Int. (2014) 197, 458 463 Advance Access publication 2014 January 20 doi: 10.1093/gji/ggt516 An earthquake detection algorithm with pseudo-probabilities of
SPNA 2.3. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2177
 SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
Optimize Full Waveform Sonic Processing
 Optimize Full Waveform Sonic Processing Diego Vasquez Technical Sales Advisor. Paradigm Technical Session. May 18 th, 2016. AGENDA Introduction to Geolog. Introduction to Full Waveform Sonic Processing
Optimize Full Waveform Sonic Processing Diego Vasquez Technical Sales Advisor. Paradigm Technical Session. May 18 th, 2016. AGENDA Introduction to Geolog. Introduction to Full Waveform Sonic Processing
McArdle, N.J. 1, Ackers M. 2, Paton, G ffa 2 - Noreco. Introduction.
 An investigation into the dependence of frequency decomposition colour blend response on bed thickness and acoustic impedance: results from wedge and thin bed models applied to a North Sea channel system
An investigation into the dependence of frequency decomposition colour blend response on bed thickness and acoustic impedance: results from wedge and thin bed models applied to a North Sea channel system
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data
 Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Downloaded 11/02/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Unbiased surface-consistent scalar estimation by crosscorrelation Nirupama Nagarajappa*, Peter Cary, Arcis Seismic Solutions, a TGS Company, Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Summary Surface-consistent scaling
Unbiased surface-consistent scalar estimation by crosscorrelation Nirupama Nagarajappa*, Peter Cary, Arcis Seismic Solutions, a TGS Company, Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Summary Surface-consistent scaling
2D field data applications
 Chapter 5 2D field data applications In chapter 4, using synthetic examples, I showed how the regularized joint datadomain and image-domain inversion methods developed in chapter 3 overcome different time-lapse
Chapter 5 2D field data applications In chapter 4, using synthetic examples, I showed how the regularized joint datadomain and image-domain inversion methods developed in chapter 3 overcome different time-lapse
Downloaded 09/04/18 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Here I briefly describe the daily seismicity analysis procedure: Table 1
 A: More on Daily Seismicity Analysis Here I briefly describe the daily seismicity analysis procedure: Table 1 The broadband continuous data set was acquired as hour-long files. For this purpose I wrote
A: More on Daily Seismicity Analysis Here I briefly describe the daily seismicity analysis procedure: Table 1 The broadband continuous data set was acquired as hour-long files. For this purpose I wrote
Site-specific seismic hazard analysis
 Site-specific seismic hazard analysis ABSTRACT : R.K. McGuire 1 and G.R. Toro 2 1 President, Risk Engineering, Inc, Boulder, Colorado, USA 2 Vice-President, Risk Engineering, Inc, Acton, Massachusetts,
Site-specific seismic hazard analysis ABSTRACT : R.K. McGuire 1 and G.R. Toro 2 1 President, Risk Engineering, Inc, Boulder, Colorado, USA 2 Vice-President, Risk Engineering, Inc, Acton, Massachusetts,
