Seismic acquisition projects 2010
|
|
|
- Allison Elliott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acquisition 2010 Seismic acquisition projects 2010 Malcolm B. Bertram, Kevin L. Bertram, Kevin W. Hall, Eric V. Gallant ABSTRACT Acquisition projects since the CREWES meeting in November 2009 include: a) a VSP test of a new downhole tool based on the Vectorseis MEMs sensor at the Priddis test site in the existing 130m deep well; b) a 3C-3D survey over the southern field at Priddis to further investigate locations for the planned injection well site for CO2 sequestration; c) a test on the University of Calgary campus of the AWD thumper to quantify output versus band tension; d) the 2010 GOPH549 undergraduate Field School project which shot a 3C 2D line along a road allowance on the southern boundary of the Priddis test site, continuing west for a total length of 2.5 km. INTRODUCTION The first project was carried out in December 2009 and involved a test of a new downhole tool based on the Vectorseis MEMs three component sensor. This was undertaken along with two short orthogonal lines of surface 3C geophones meeting at the well. This survey was to test the new downhole array as well as attempt to refine knowledge of the shallow aquifers which the well intercepted. The work was carried out in conjunction with High-Definition Seismic Corporation who supplied the tool and Geokinetics who supplied the Vectorseis sensors and the recorder. Sources used were the University of Calgary EnviroVibe, and the new thumper constructed by CREWES. The second project was an extensive 3C 3D survey of the southern field at Priddis in May For this survey the Aries three component system was provided by Aram Rental Corporation. Seven lines of SM7 3C geophones were laid out east-west, and fifteen shot lines oriented north-south were shot using the University of Calgary EnviroVibe. Both geophone and shot spacing was 10m, with 50m between lines. The thumper test was carried out on the west end of the University of Calgary campus and was intended to show the changes in output both in frequency and amplitude from changes in elastic belt tension on the accelerated weight drop unit constructed by the CREWES project in The Geophysics Field School line was shot by the GOPH549 undergraduates and was designed to provide more information about the shallow structure beneath the Priddis test site, extending west to cross the surface expression of the east dipping sandstone layers on the east side of the triangle zone. This line was shot using the Aries three component recording system provided by Aram Rental Corporation. Geophone spacing was 10m and the University of Calgary EnviroVibe was again used as the source with a VP spacing of 10m. VECTORSEIS VSP TOOL TESTS The Vectorseis VSP tool was developed by High-Definition Seismic Corporation for shallow high resolution VSP surveys. The system uses standard Vectorseis sensors and CREWES Research Report Volume 22 (2010) 1
2 Bertram et al. needs to be installed in a dry hole. Since the University of Calgary Priddis test site has a 130m well which could be pumped out, and there was an interest in trying to refine our knowledge of the shallow aquifers in the region for ground water studies, a joint project was conducted between High-Definition Seismic Corporation, Geokinetics and CREWES. The Vectorseis tool was installed in the well with a spacing of 2m between sensors, and two surface lines planted, one east-west, the other north-south with the intersection at the well head. The east-west line was connected as two lines with the sensor nearest the wellhead being the first trace on each. The University of Calgary EnviroVibe was used as a source, providing multi-azimuth locations at various offsets. A number of different sweeps were used, firstly Hz, then 2-15Hz, 10-25Hz, 15-35Hz, 25-50Hz, 40-70Hz, Hz, and Hz. The AWD thumper was also used as a source for this survey. The layout of the survey with the occupied source points is shown in Figure 1. Vectorseis VSP spread layout Line 3 Line 2 130m well Line 1 Shot points FIG 1. Layout of VSP survey December 2009 A gather from the survey is shown is Figure 2. This is the vertical component of the 3C sensors, with the three surface lines on the left side of the figure and the downhole array on the right. This gather is from a zero offset Hz sweep by the EnviroVibe. There are some issues with casing bonding in this well, giving some areas where coupling is poor and data loss occurs. Figure 3 shows a thumper shot at zero offset with a Hz filter applied. The Vectorseis VSP tool proved to be a good high resolution system, since the whole well depth was recorded as a single spread with 2m spacing, providing the ability to record the entire depth with a single shot. 2 CREWES Research Report Volume 22 (2010)
3 Acquisition 2010 FIG 2. A correlated EnviroVibe gather from the VSP survey. The left half has the three surface lines, the right half is the downhole array. Filter of applied. FIG 3. A thumper shot gather for zero offset. Filter of applied. CREWES Research Report Volume 22 (2010) 3
4 Bertram et al. MAY 3C 3D SURVEY This survey was designed to establish the preferred location for the injection well location for the planned CO2 test site at Priddis. The survey layout is shown in Figure 4. Geophone lines were east-west and shot lines north-south. FIG 4. The layout for the May C-2D survey. Receiver lines in blue, shot lines in red. The spacing between both receiver lines and shot lines was 50m, with geophones and shots spaced at 10m on their respective lines. The receiver lines each had 72 3C Sensor SM7 geophones deployed. The geophones and 24 channel RAMs for the survey were provided by Aram Rental Corporation. The source for the survey was the University of Calgary EnviroVibe, with a sweep of 10 to 200Hz over 20 seconds; 4 sweeps per vibe point. Data was recorded on the University of Calgary SPMLite Aries recording system. The data from two receiver lines is shown on Figure 5. Data was of reasonable quality, with reflections visible to greater than 2 seconds. A cube of the first second of processed data is shown in Figure 6, showing a number of horizons dipping east in the shallow section. At depth, the structure is horizontal, showing that this is the effect of the typical triangle zone wedging caused by thrusting from the west. These are interpreted to be sandstone horizons and some can be found outcropping to the west. Some samples were taken of one outcrop to establish porosity and permeability parameters. The 2010 Field School seismic line crosses some of the outcrops as shown later in this paper. The converted wave data from this survey has not yet been completely processed, but is currently being worked on. 4 CREWES Research Report Volume 22 (2010)
5 Acquisition 2010 FIG 5. An example of the data quality fron the May C 3D survey at Priddis. This show two receiver lines from the patch with no filtering applied. FIG 6. A chair display of the cube showing the shallow reflectors which outcrop to the west. North is in the X-line direction. CREWES Research Report Volume 22 (2010) 5
6 Bertram et al. THUMPER TESTS To analyze the output from the new thumper which was constructed in 2009 by the CREWES project, a small survey was set up on the west section of the University of Calgary campus in August A spread of 80 geophones was set out at a spacing of 2m and the thumper positioned in the centre of this spread. A number of shots were recorded at different setting of tension on the elastic bands used to accelerate the hammer. A video camera was also deployed to attempt to measure the impact velocity of the hammer, but results from this were not conclusive. At the time this survey was done, the trigger system for the source was incomplete, so a manual start time on the recording instruments was utilized to capture the impacts. This turned out to be serendipitous as there is an event visible on the records which is the release of the hammer at the start of the drop. By the time difference between release and impact, a measure of the relative velocity for different tensions is possible. Figure 7 shows one record from this survey, with the release time evident at about 350 msec, and the impact on the base plate at about 550 msec. FIG 7. An example record from the thumper tests with the release of the hammer, and the impact both visible. Figure 8 shows the changes in the travel time of the hammer for the cases of tension increasing and decreasing. There is some hysteresis apparent as the bands tend to settle after several thumps, thereby losing a small amount of tension. It is apparent that the change in drop time is almost three times (100msec to about 300msec). 6 CREWES Research Report Volume 22 (2010)
7 Acquisition 2010 Drop Time (msec) Drop Time vs Tension Tension (Inches) Increasing decreasing FIG 8. The travel times for the hammer for increasing tension and decreasing tension. Another parameter measuerd was the maximum amplitude measured for each setting of the tension control. As is shown in Figure 9, there is a three times change in amplitude over the range of tension adjustment. Max Amplitude (Volts) Amplitude vs Tension Tension (Inches) Increasing Decreasing FIG 9. The maximum amplitude related to different tensions. A cross plot of drop time and amplitude is shown in Figure 10. The relationship appears fairly linear for drop times less than 150msec. It is likely that with no tension on the bands, the hammer release is not as immediate due to friction in the system in fact there were times when the hammer did stick in the raised position. The measurements with no bands installed are therefore suspect, and should not be included in the analysis. CREWES Research Report Volume 22 (2010) 7
8 Bertram et al. Max Amplitude (Volts) Amplitude Drop Time (msec) Amplitude FIG 10. The cross plot of Drop Time vs Max Amplitude. Below 150msec this is linear. The next measurement was the spectrum for each different tension. These are shown overlaid in Figure 11 for one gather from each different tension during increasing tension positions. The graphs are very similar, showing no major change in spectrum between no tension and maximum tension. The tension is given in inches, as this was the easiest way to set the elastic bands on the machine. A better measure is the holding pressure in the hydraulics which would be more consistent, but this was not available for this test. Blue : 19 0 in Purple: 24 5 in Orange: in Red: in Green: in Grey: in Olive : in FIG 11. An overlay of spectra for seven different thumper band tensions. A zoom of the first 100Hz of the spectra is shown in Figure 12 and demonstrated a small amount of amplitude change around 30Hz. The amplitude only increases by a few 8 CREWES Research Report Volume 22 (2010)
9 Acquisition 2010 decibels over the range of tensions, showing that there is no apparent high frequency content with higher tension. Further analysis if thumper output is required to further quantify this change. This will include the accurate measurement of impact velocity of the hammer related to apparent energy, and the hydraulic pressure monitoring on the elastic frame cylinders. Blue : 19 0 in Purple: 24 5 in Orange: in Red: in Green: in Grey: in Olive : in FIG 12. A zoom of the first 100Hz of the thumper spectra GEOPHYSICS FIELD SCHOOL This year the seismic section of the University of Calgary Geophysics Field School was held at Priddis, with the major component being a 3C 2D seismic line shot over 2.5Km along a road allowance running east-west from the south of the University of Calgary Rothney Astrophysical Observatory to the Priddis Valley Road. The line is on the east flank of the triangle zone, and was intended to provide a better interpretation of the structure underlying the south field of the observatory property. Geophone spacing was 10m and shots were every station. The geophones were SM7 three component singles and were provided by ARAM Rental Corporation, who also provided the 24 channel RAM units for data acquisition. The recorder was the University of Calgary SPMLite and the source was the University of Calgary EnviroVibe. Data quality was good, with similar results to the 3C-3D shot in May mentioned above. Figure 13 is a sample record from this survey. Events are visible down to 2500msec in this data, and there is a great deal of detail in the shallow section. CREWES Research Report Volume 22 (2010) 9
10 Bertram et al. FIG 13. A record from the U of C 2010 Geophysics Field School survey. The processed section in Figure 14 shows several deep horizons and the east dipping shallow structure which outcrops along the line. These shallow events are the main focus of the ongoing work at Priddis, as they consist of the sandstone / shale sequence being investigated for carbon dioxide sequestration over the next few years. Some of the sandstone layers outcrop on the seismic line, in some places forming local ridges or high points, one of which is shown by the elevation profile (green in Figure 11) at approximately CDP 870. FIG 14. The processed section from the 2010 Geophysics Field School line. 10 CREWES Research Report Volume 22 (2010)
11 Acquisition 2010 CONCLUSIONS Data from all these field projects is available. The Vectoreseis VSP was a successful first deployment of this tool, and provided some interesting results. This tool is now in use as a VSP system for shallow work, and has shown some excellent results. The 3C 3D survey at Priddis gave some expected results, but came up short on the converted wave data quality, mainly due to the restricted offset range. Another survey here is indicated, with an expanded shot spread to the east and west of the receiver spread area. Work will be continuing on the thumper analysis to try to increase the output frequency, since the device was designed for shallow high resolution work. The Field School line provided good quality data, with further processing yet to be completed. As a further guide to the structure of the area, a parallel line one mile to the north is being investigated for Field School next year. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Thanks to High-Definition Seismic Corporation for the supply of the Vectorseis VSP tool, and Geokinetics for the use of the surface Vectorseis sensors, and the recording system, and personnel from both companies who assisted in the field for the survey. Thanks to Aram Rental Corporation for the use of the Sensor 3C SM7 geophones and the 24 channel RAM units for the May C 3D survey and the 2010 Field School project. We thank all the students and staff of CREWES for their assistance on these field projects, and the GOPH549 undergraduate students for their work during the Field School project. Thanks to GEDCO for the use of the Vista Seismic Data Processing software. Thanks to NSERC and the sponsors of the CREWES consortium for their ongoing support. CREWES Research Report Volume 22 (2010) 11
Recent fieldwork activities and analysis. Malcolm Bertram
 Recent fieldwork activities and analysis Malcolm Bertram Covered in this talk The pulse-probe experiment Sources Sensors Autoseis system Near surface survey Aries Geodes Resisitivity New equipment Shear
Recent fieldwork activities and analysis Malcolm Bertram Covered in this talk The pulse-probe experiment Sources Sensors Autoseis system Near surface survey Aries Geodes Resisitivity New equipment Shear
and Hussar Malcolm B. Bertram, J. Helen Isaac, Kevin W. Hall, Kevin L. Bertram and Gary F. Margrave
 Source and receiver comparisons from Priddis and Hussar Malcolm B. Bertram, J. Helen Isaac, Kevin W. Hall, Kevin L. Bertram and Gary F. Margrave Guaranteed 100% real data. No artificial additives. No math.
Source and receiver comparisons from Priddis and Hussar Malcolm B. Bertram, J. Helen Isaac, Kevin W. Hall, Kevin L. Bertram and Gary F. Margrave Guaranteed 100% real data. No artificial additives. No math.
Comparison of low-frequency data from co-located receivers using frequency dependent least-squares-subtraction scalars
 Receiver comparison Comparison of low-frequency data from co-located receivers using frequency dependent least-squares-subtraction scalars Kevin W. Hall, Gary F. Margrave and Malcolm B. Bertram ABSTRACT
Receiver comparison Comparison of low-frequency data from co-located receivers using frequency dependent least-squares-subtraction scalars Kevin W. Hall, Gary F. Margrave and Malcolm B. Bertram ABSTRACT
Comparisons between data recorded by several 3-component coil geophones and a MEMS sensor at the Violet Grove monitor seismic survey
 Geophone and sensor comparisons Comparisons between data recorded by several 3-component coil geophones and a MEMS sensor at the Violet Grove monitor seismic survey Don C. Lawton, Malcolm B. Bertram, Gary
Geophone and sensor comparisons Comparisons between data recorded by several 3-component coil geophones and a MEMS sensor at the Violet Grove monitor seismic survey Don C. Lawton, Malcolm B. Bertram, Gary
New seismic reflection and other geophysical equipment available to CREWES
 New geophysical equipment New seismic reflection and other geophysical equipment available to CREWES Malcolm B. Bertram, Don C. Lawton, Eric V. Gallant, Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT A new 600 channel seismic
New geophysical equipment New seismic reflection and other geophysical equipment available to CREWES Malcolm B. Bertram, Don C. Lawton, Eric V. Gallant, Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT A new 600 channel seismic
Multicomponent seismic polarization analysis
 Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
Earthquake on the Hussar low-frequency experiment
 Earthquake Earthquake on the Hussar low-frequency experiment Kevin W. Hall and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT On the last day of acquisition on the Hussar low-frequency line, a magnitude 6.3 earthquake occurred
Earthquake Earthquake on the Hussar low-frequency experiment Kevin W. Hall and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT On the last day of acquisition on the Hussar low-frequency line, a magnitude 6.3 earthquake occurred
Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion
 Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion Heather J.E. Lloyd*, CREWES / University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta hjelloyd@ucalgary.ca and Gary F. Margrave, CREWES
Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion Heather J.E. Lloyd*, CREWES / University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta hjelloyd@ucalgary.ca and Gary F. Margrave, CREWES
Seismic Reflection Method
 1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
FINAL REPORT EL# RS. C. A. Hurich & MUN Seismic Team Earth Sciences Dept. Memorial University Sept. 2009
 FINAL REPORT EL# 09-101-01-RS MUNSIST Seismic Source Test - Five Mile Road C. A. Hurich & MUN Seismic Team Earth Sciences Dept. Memorial University Sept. 2009 1 EL# 09-101-01-RS Five-Mile Road Memorial
FINAL REPORT EL# 09-101-01-RS MUNSIST Seismic Source Test - Five Mile Road C. A. Hurich & MUN Seismic Team Earth Sciences Dept. Memorial University Sept. 2009 1 EL# 09-101-01-RS Five-Mile Road Memorial
AVO processing of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake heavy oilfield, Saskatchewan
 AVO processing of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake heavy oilfield, Saskatchewan Zimin Zhang, Robert R. Stewart, and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT The AVO processing and analysis of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake
AVO processing of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake heavy oilfield, Saskatchewan Zimin Zhang, Robert R. Stewart, and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT The AVO processing and analysis of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake
This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010.
 This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010. The information herein remains the property of Mustagh
This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010. The information herein remains the property of Mustagh
Air blast attenuation by combining microphone and geophone signals in the time-frequency domain
 Air blast attenuation in data processing Air blast attenuation by combining microphone and geophone signals in the time-frequency domain Alejandro D. Alcudia and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT Microphone data
Air blast attenuation in data processing Air blast attenuation by combining microphone and geophone signals in the time-frequency domain Alejandro D. Alcudia and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT Microphone data
Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Group Array Stack of single sensor data
 P-113 Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Artatran Ojha *, K. Ramakrishna, G. Sarvesam Geophysical Services, ONGC, Chennai Summary Shot generated noise and the cultural noise is a major problem in
P-113 Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Artatran Ojha *, K. Ramakrishna, G. Sarvesam Geophysical Services, ONGC, Chennai Summary Shot generated noise and the cultural noise is a major problem in
Auto-levelling geophone development and testing
 Auto-levelling geophone development Auto-levelling geophone development and testing Malcolm B. Bertram, Eric V. Gallant and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT An auto-levelling, motion sensor (multi-component
Auto-levelling geophone development Auto-levelling geophone development and testing Malcolm B. Bertram, Eric V. Gallant and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT An auto-levelling, motion sensor (multi-component
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data
 Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis
 Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data
 Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Stan J. Gorek, Robert R. Stewart, and Mark P. Harrison ABSTRACT During early July, 1995, a large
Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Stan J. Gorek, Robert R. Stewart, and Mark P. Harrison ABSTRACT During early July, 1995, a large
Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing Dispersive Ground Roll Noise from Onshore Seismic Data
 Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
INTRODUCTION TO ONSHORE SEISMIC ACQUISITION AND PROCESSING
 INTRODUCTION TO ONSHORE SEISMIC ACQUISITION AND PROCESSING SEPTEMBER 2017 1 SIMPLIFIED DIAGRAM OF SPLIT SPREAD REFLECTION SEISMIC DATA ACQUISITION RECORDING TRUCK ENERGY SOURCE SHOTPOINTS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
INTRODUCTION TO ONSHORE SEISMIC ACQUISITION AND PROCESSING SEPTEMBER 2017 1 SIMPLIFIED DIAGRAM OF SPLIT SPREAD REFLECTION SEISMIC DATA ACQUISITION RECORDING TRUCK ENERGY SOURCE SHOTPOINTS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records
 Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT This paper proposes using microphone recordings of
Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT This paper proposes using microphone recordings of
Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
COMPARISON OF FIBER OPTIC MONITORING AT AQUISTORE WITH CONVENTIONAL GEOPHONE SYSTEM. Tom Daley Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
 IEAGHG 10 th Monitoring Network Meeting Berkeley, California June 10-12, 2015 COMPARISON OF FIBER OPTIC MONITORING WITH CONVENTIONAL GEOPHONE SYSTEM AT AQUISTORE Tom Daley Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
IEAGHG 10 th Monitoring Network Meeting Berkeley, California June 10-12, 2015 COMPARISON OF FIBER OPTIC MONITORING WITH CONVENTIONAL GEOPHONE SYSTEM AT AQUISTORE Tom Daley Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Advancements in near-surface seismic reflection acquisition
 Advancements in near-surface seismic reflection acquisition Brian E. Miller, George P. Tsoflias, Don W. Steeples Department of Geology and Geophysics, The University of Kansas, 1475 Jayhawk Blvd., Room
Advancements in near-surface seismic reflection acquisition Brian E. Miller, George P. Tsoflias, Don W. Steeples Department of Geology and Geophysics, The University of Kansas, 1475 Jayhawk Blvd., Room
TitleApplication of MEMS accelerometer t. AIZAWA, Takao; KIMURA, Toshinori; M Toshifumi; TAKEDA, Tetsuya; ASANO,
 TitleApplication of MEMS accelerometer t Author(s) AIZAWA, Takao; KIMURA, Toshinori; M Toshifumi; TAKEDA, Tetsuya; ASANO, Citation International Journal of the JCRM ( Issue Date 2008-12 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/85166
TitleApplication of MEMS accelerometer t Author(s) AIZAWA, Takao; KIMURA, Toshinori; M Toshifumi; TAKEDA, Tetsuya; ASANO, Citation International Journal of the JCRM ( Issue Date 2008-12 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/85166
Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results
 Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results David C. Henley and Han-Xing Lu PNG processing ABSTRACT Papua New Guinea is among the most notoriously difficult areas in the world in
Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results David C. Henley and Han-Xing Lu PNG processing ABSTRACT Papua New Guinea is among the most notoriously difficult areas in the world in
Seismic processing workflow for supressing coherent noise while retaining low-frequency signal
 Seismic processing for coherent noise suppression Seismic processing workflow for supressing coherent noise while retaining low-frequency signal Patricia E. Gavotti and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT Two different
Seismic processing for coherent noise suppression Seismic processing workflow for supressing coherent noise while retaining low-frequency signal Patricia E. Gavotti and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT Two different
Seismic source comparison for compressional and convertedwave generation at Spring Coulee, Alberta. Part I: Heavy vibroseis-dynamite comparison
 Seismic source comparison. Part I Seismic source comparison for compressional and convertedwave generation at Spring Coulee, Alberta. Part I: Heavy vibroseis-dynamite comparison Gabriela M. Suarez and
Seismic source comparison. Part I Seismic source comparison for compressional and convertedwave generation at Spring Coulee, Alberta. Part I: Heavy vibroseis-dynamite comparison Gabriela M. Suarez and
Field Tests of 3-Component geophones Don C. Lawton and Malcolm B. Bertram
 Field Tests of 3-Component geophones Don C. Lawton and Malcolm B. Bertram ABSTRACT Field tests of Litton, Geosource and Oyo 3-component geophones showed similar performance characteristics for all three
Field Tests of 3-Component geophones Don C. Lawton and Malcolm B. Bertram ABSTRACT Field tests of Litton, Geosource and Oyo 3-component geophones showed similar performance characteristics for all three
New technologies in marine seismic surveying: Overview and physical modelling experiments
 New technologies in marine seismic surveying: Overview and physical modelling experiments Eric V. Gallant, Robert R. Stewart, Don C. Lawton, Malcolm B. Bertram, and Carlos Rodriguez ABSTRACT New marine
New technologies in marine seismic surveying: Overview and physical modelling experiments Eric V. Gallant, Robert R. Stewart, Don C. Lawton, Malcolm B. Bertram, and Carlos Rodriguez ABSTRACT New marine
Technology of Adaptive Vibroseis for Wide Spectrum Prospecting
 Technology of Adaptive Vibroseis for Wide Spectrum Prospecting Xianzheng Zhao, Xishuang Wang, A.P. Zhukov, Ruifeng Zhang, Chuanzhang Tang Abstract: Seismic data from conventional vibroseis prospecting
Technology of Adaptive Vibroseis for Wide Spectrum Prospecting Xianzheng Zhao, Xishuang Wang, A.P. Zhukov, Ruifeng Zhang, Chuanzhang Tang Abstract: Seismic data from conventional vibroseis prospecting
7. Consider the following common offset gather collected with GPR.
 Questions: GPR 1. Which of the following statements is incorrect when considering skin depth in GPR a. Skin depth is the distance at which the signal amplitude has decreased by a factor of 1/e b. Skin
Questions: GPR 1. Which of the following statements is incorrect when considering skin depth in GPR a. Skin depth is the distance at which the signal amplitude has decreased by a factor of 1/e b. Skin
Distributed Fiber Optic Arrays: Integrated Temperature and Seismic Sensing for Detection of CO 2 Flow, Leakage and Subsurface Distribution
 Distributed Fiber Optic Arrays: Integrated Temperature and Seismic Sensing for Detection of CO 2 Flow, Leakage and Subsurface Distribution Robert C. Trautz Technical Executive US-Taiwan International CCS
Distributed Fiber Optic Arrays: Integrated Temperature and Seismic Sensing for Detection of CO 2 Flow, Leakage and Subsurface Distribution Robert C. Trautz Technical Executive US-Taiwan International CCS
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile
 Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
Applied Methods MASW Method
 Applied Methods MASW Method Schematic illustrating a typical MASW Survey Setup INTRODUCTION: MASW a seismic method for near-surface (< 30 m) Characterization of shear-wave velocity (Vs) (secondary or transversal
Applied Methods MASW Method Schematic illustrating a typical MASW Survey Setup INTRODUCTION: MASW a seismic method for near-surface (< 30 m) Characterization of shear-wave velocity (Vs) (secondary or transversal
ERTH3021 Note: Terminology of Seismic Records
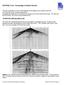 ERTH3021 Note: Terminology of Seismic Records This note is intended to assist in understanding of terminology used in practical exercises on 2D and 3D seismic acquisition geometries. A fundamental distinction
ERTH3021 Note: Terminology of Seismic Records This note is intended to assist in understanding of terminology used in practical exercises on 2D and 3D seismic acquisition geometries. A fundamental distinction
Evaluation of 3C sensor coupling using ambient noise measurements Summary
 Evaluation of 3C sensor coupling using ambient noise measurements Howard Watt, John Gibson, Bruce Mattocks, Mark Cartwright, Roy Burnett, and Shuki Ronen Veritas Geophysical Corporation Summary Good vector
Evaluation of 3C sensor coupling using ambient noise measurements Howard Watt, John Gibson, Bruce Mattocks, Mark Cartwright, Roy Burnett, and Shuki Ronen Veritas Geophysical Corporation Summary Good vector
Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion
 P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
Field comparison of 3-C geophones and microphones to highprecision
 Geophones, microphones and blasting sensors Field comparison of 3-C geophones and microphones to highprecision blasting sensors Alejandro D. Alcudia, Robert R. Stewart, Kevin W. Hall and Eric V. Gallant
Geophones, microphones and blasting sensors Field comparison of 3-C geophones and microphones to highprecision blasting sensors Alejandro D. Alcudia, Robert R. Stewart, Kevin W. Hall and Eric V. Gallant
There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to
 Coordinated by JEFF DEERE JOHN GIBSON, FOREST LIN, ALEXANDRE EGRETEAU, and JULIEN MEUNIER, CGGVeritas MALCOLM LANSLEY, Sercel There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to improve the quality
Coordinated by JEFF DEERE JOHN GIBSON, FOREST LIN, ALEXANDRE EGRETEAU, and JULIEN MEUNIER, CGGVeritas MALCOLM LANSLEY, Sercel There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to improve the quality
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas
 The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
Residual converted wave statics
 Residual converted wave statics Arnim B. Haase and David C. Henley ABSTRACT First estimates of S-wave receiver static shifts are applied to selected common receiver gathers of the Spring Coulee three component
Residual converted wave statics Arnim B. Haase and David C. Henley ABSTRACT First estimates of S-wave receiver static shifts are applied to selected common receiver gathers of the Spring Coulee three component
Presented on. Mehul Supawala Marine Energy Sources Product Champion, WesternGeco
 Presented on Marine seismic acquisition and its potential impact on marine life has been a widely discussed topic and of interest to many. As scientific knowledge improves and operational criteria evolve,
Presented on Marine seismic acquisition and its potential impact on marine life has been a widely discussed topic and of interest to many. As scientific knowledge improves and operational criteria evolve,
Low wavenumber reflectors
 Low wavenumber reflectors Low wavenumber reflectors John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT A numerical modelling environment was created to accurately evaluate reflections from a D interface that has a smooth transition
Low wavenumber reflectors Low wavenumber reflectors John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT A numerical modelling environment was created to accurately evaluate reflections from a D interface that has a smooth transition
ENERGY- CONTENT AND SPECTRAL ANALYSES OF SHOTS FOR OPTIMUM SEISMOGRAM GENERATION IN THE NIGER DELTA
 ENERGY- CONTENT AND SPECTRAL ANALYSES OF SHOTS FOR OPTIMUM SEISMOGRAM GENERATION IN THE NIGER DELTA Alaminiokuma G.I. and *Emudianughe J.E. Department of Earth Sciences, Federal University of Petroleum
ENERGY- CONTENT AND SPECTRAL ANALYSES OF SHOTS FOR OPTIMUM SEISMOGRAM GENERATION IN THE NIGER DELTA Alaminiokuma G.I. and *Emudianughe J.E. Department of Earth Sciences, Federal University of Petroleum
Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo
 Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo Summary A survey with a novel acquisition technique was acquired
Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo Summary A survey with a novel acquisition technique was acquired
Downloaded 09/04/18 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Eric V. Gallant, Malcolm B. Bertram, Don C. Lawton, R. James Brown, and Robert R. Stewart
 Physical modellinq update Physical modelling update Eric V. Gallant, Malcolm B. Bertram, Don C. Lawton, R. James Brown, and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT This is a short note on some of the physical models
Physical modellinq update Physical modelling update Eric V. Gallant, Malcolm B. Bertram, Don C. Lawton, R. James Brown, and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT This is a short note on some of the physical models
Summary. Page SEG SEG Denver 2014 Annual Meeting
 Seismo-acoustic characterization of a seismic vibrator Claudio Bagaini*, Martin Laycock and Colin Readman, WesternGeco; Emmanuel Coste, Schlumberger; Colin Anderson, Siemens PLM Software Summary A seismic
Seismo-acoustic characterization of a seismic vibrator Claudio Bagaini*, Martin Laycock and Colin Readman, WesternGeco; Emmanuel Coste, Schlumberger; Colin Anderson, Siemens PLM Software Summary A seismic
Summary. Theory. Introduction
 round motion through geophones and MEMS accelerometers: sensor comparison in theory modeling and field data Michael Hons* Robert Stewart Don Lawton and Malcolm Bertram CREWES ProjectUniversity of Calgary
round motion through geophones and MEMS accelerometers: sensor comparison in theory modeling and field data Michael Hons* Robert Stewart Don Lawton and Malcolm Bertram CREWES ProjectUniversity of Calgary
South Africa CO2 Seismic Program
 1 South Africa CO2 Seismic Program ANNEXURE B Bob A. Hardage October 2016 There have been great advances in seismic technology in the decades following the acquisition of legacy, limited-quality, 2D seismic
1 South Africa CO2 Seismic Program ANNEXURE B Bob A. Hardage October 2016 There have been great advances in seismic technology in the decades following the acquisition of legacy, limited-quality, 2D seismic
Efficient Acquisition of Quality Borehole Seismic
 Efficient Acquisition of Quality Borehole Seismic The Versatile Seismic Imager Applications Integrated processing for interpretation of boreholeand surface-seismic data Images for reservoir definition
Efficient Acquisition of Quality Borehole Seismic The Versatile Seismic Imager Applications Integrated processing for interpretation of boreholeand surface-seismic data Images for reservoir definition
ISSN Volume 28 Issue 6 June A New Spring for Geoscience. Special Topic
 ISSN 0263-5046 Volume 28 Issue 6 June 2010 Special Topic Technical Articles Multi-azimuth processing and its applications to wide-azimuth OBC seismic data offshore Abu Dhabi Borehole image logs for turbidite
ISSN 0263-5046 Volume 28 Issue 6 June 2010 Special Topic Technical Articles Multi-azimuth processing and its applications to wide-azimuth OBC seismic data offshore Abu Dhabi Borehole image logs for turbidite
Investigating power variation in first breaks, reflections, and ground roll from different charge sizes
 Investigating power variation in first breaks, reflections, and ground roll from different charge sizes Christopher C. Petten*, University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta ccpetten@ucalgary.ca and Gary F.
Investigating power variation in first breaks, reflections, and ground roll from different charge sizes Christopher C. Petten*, University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta ccpetten@ucalgary.ca and Gary F.
Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure
 Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure Andy St-Onge* 1a, David W. Eaton 1b, and Adam Pidlisecky 1c 1 Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW Calgary,
Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure Andy St-Onge* 1a, David W. Eaton 1b, and Adam Pidlisecky 1c 1 Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW Calgary,
Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic
 Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic J. Burren (Petroleum Geo-Services) & D. Lecerf* (Petroleum Geo-Services) SUMMARY Future time-lapse broadband surveys should provide better reservoir monitoring
Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic J. Burren (Petroleum Geo-Services) & D. Lecerf* (Petroleum Geo-Services) SUMMARY Future time-lapse broadband surveys should provide better reservoir monitoring
X039 Observations of Surface Vibrator Repeatability in a Desert Environment
 X39 Observations of Surface Vibrator Repeatability in a Desert Environment M.A. Jervis* (Saudi Aramco), A.V. Bakulin (Saudi Aramco), R.M. Burnstad (Saudi Aramco), C. Beron (CGGVeritas) & E. Forgues (CGGVeritas)
X39 Observations of Surface Vibrator Repeatability in a Desert Environment M.A. Jervis* (Saudi Aramco), A.V. Bakulin (Saudi Aramco), R.M. Burnstad (Saudi Aramco), C. Beron (CGGVeritas) & E. Forgues (CGGVeritas)
Understanding Seismic Amplitudes
 Understanding Seismic Amplitudes The changing amplitude values that define the seismic trace are typically explained using the convolutional model. This model states that trace amplitudes have three controlling
Understanding Seismic Amplitudes The changing amplitude values that define the seismic trace are typically explained using the convolutional model. This model states that trace amplitudes have three controlling
A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data
 A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data Yessika Blunda*, Pinnacle, Halliburton, Houston, Tx, US yessika.blunda@pinntech.com and Kit Chambers, Pinnacle, Halliburton, St Agnes, Cornwall,
A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data Yessika Blunda*, Pinnacle, Halliburton, Houston, Tx, US yessika.blunda@pinntech.com and Kit Chambers, Pinnacle, Halliburton, St Agnes, Cornwall,
DSU3-428 DIGITAL SENSOR UNITS
 DSU3-428 DIGITAL SENSOR UNITS DSU3-428 The 428XL offers all new hardware and software which is specifi cally designed to address the growing demands of the geophysical industry for even larger channel
DSU3-428 DIGITAL SENSOR UNITS DSU3-428 The 428XL offers all new hardware and software which is specifi cally designed to address the growing demands of the geophysical industry for even larger channel
Enhanced low frequency signal processing for sub-basalt imaging N. Woodburn*, A. Hardwick and T. Travis, TGS
 Enhanced low frequency signal processing for sub-basalt imaging N. Woodburn*, A. Hardwick and T. Travis, TGS Summary Sub-basalt imaging continues to provide a challenge along the northwest European Atlantic
Enhanced low frequency signal processing for sub-basalt imaging N. Woodburn*, A. Hardwick and T. Travis, TGS Summary Sub-basalt imaging continues to provide a challenge along the northwest European Atlantic
Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events
 Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events Natalia Verkhovtseva Pinnacle a Halliburton Service, Calgary, AB Summary Data sampling and its effect on the microseismic
Effect of data sampling on the location accuracy of high frequency microseismic events Natalia Verkhovtseva Pinnacle a Halliburton Service, Calgary, AB Summary Data sampling and its effect on the microseismic
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency
 25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method
 P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method E. Baniasadi* (University of Tehran), M. A. Riahi (University of Tehran) & S. Chaychizadeh (University of Tehran)
P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method E. Baniasadi* (University of Tehran), M. A. Riahi (University of Tehran) & S. Chaychizadeh (University of Tehran)
Processing the Teal South 4C-4D seismic survey
 Processing the Teal South 4C-4D seismic survey Carlos Rodriguez-Suarez, Robert R. Stewart and Han-Xing Lu Processing the Teal South 4C-4D ABSTRACT Repeated 4C-3D seismic surveys have been acquired over
Processing the Teal South 4C-4D seismic survey Carlos Rodriguez-Suarez, Robert R. Stewart and Han-Xing Lu Processing the Teal South 4C-4D ABSTRACT Repeated 4C-3D seismic surveys have been acquired over
Progress in DAS Seismic Methods
 Progress in DAS Seismic Methods A. Mateeva, J. Mestayer, Z. Yang, J. Lopez, P. Wills 1, H. Wu, W. Wong, Barbara Cox (Shell International Exploration and Production, Inc.), J. Roy, T. Bown ( OptaSense )
Progress in DAS Seismic Methods A. Mateeva, J. Mestayer, Z. Yang, J. Lopez, P. Wills 1, H. Wu, W. Wong, Barbara Cox (Shell International Exploration and Production, Inc.), J. Roy, T. Bown ( OptaSense )
Simultaneous multi-source acquisition using m-sequences
 Simultaneous source acquisition using m-sequences Simultaneous multi-source acquisition using m-sequences Joe Wong ABSTRACT Maximal length sequences, or m-sequences, are periodic mathematical periodic
Simultaneous source acquisition using m-sequences Simultaneous multi-source acquisition using m-sequences Joe Wong ABSTRACT Maximal length sequences, or m-sequences, are periodic mathematical periodic
Why not narrowband? Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology
 Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology Summary A 2D towed streamer acquisition experiment was conducted in deep water offshore Gabon to evaluate techniques
Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology Summary A 2D towed streamer acquisition experiment was conducted in deep water offshore Gabon to evaluate techniques
SCANNING METHOD. Olson Instruments Impact Echo Scanner. incorporating source and receiver. Overlay. Sound joint between. overlay and bridge deck
 IE Method N D E I M P A C T E C H O S C A N N I N G A PPLICATION Impact Echo (IE) investigations are performed to assess the condition of slabs, beams, columns, walls, pavements, runways, tunnels, and
IE Method N D E I M P A C T E C H O S C A N N I N G A PPLICATION Impact Echo (IE) investigations are performed to assess the condition of slabs, beams, columns, walls, pavements, runways, tunnels, and
REVISITING THE VIBROSEIS WAVELET
 REVISITING THE VIBROSEIS WAVELET Shaun Strong 1 *, Steve Hearn 2 Velseis Pty Ltd and University of Queensland sstrong@velseis.com 1, steveh@velseis.com 2 Key Words: Vibroseis, wavelet, linear sweep, Vari
REVISITING THE VIBROSEIS WAVELET Shaun Strong 1 *, Steve Hearn 2 Velseis Pty Ltd and University of Queensland sstrong@velseis.com 1, steveh@velseis.com 2 Key Words: Vibroseis, wavelet, linear sweep, Vari
Geophysical Applications Seismic Reflection Surveying
 Seismic sources and receivers Basic requirements for a seismic source Typical sources on land and on water Basic impact assessment environmental and social concerns EPS435-Potential-08-01 Basic requirements
Seismic sources and receivers Basic requirements for a seismic source Typical sources on land and on water Basic impact assessment environmental and social concerns EPS435-Potential-08-01 Basic requirements
Th-P08-11 Deblending of Single Source Vibroseis Land Data in Egypt with V1 Noise Attenuation Algorithm
 Th-P08-11 Deblending of Single Source Vibroseis Land Data in Egypt with V1 Noise Attenuation Algorithm N. Gulunay* (CGG), E. Shaker (CGG), A. Karagul (CGG), A. Ramadan (CGG), T. Bianchi (CGG), J. Ross
Th-P08-11 Deblending of Single Source Vibroseis Land Data in Egypt with V1 Noise Attenuation Algorithm N. Gulunay* (CGG), E. Shaker (CGG), A. Karagul (CGG), A. Ramadan (CGG), T. Bianchi (CGG), J. Ross
Desinging of 3D Seismic Survey And Data Processing of Abu Amood Oil Field Southern of Iraq
 Desinging of 3D Seismic Survey And Data Processing of Abu Amood Oil Field Southern of Iraq Salman Z. Khorshid, Ahmed I. Khaleel Dept.Geology, College of Science, Univercity of Baghdad Abstract 3D seismic
Desinging of 3D Seismic Survey And Data Processing of Abu Amood Oil Field Southern of Iraq Salman Z. Khorshid, Ahmed I. Khaleel Dept.Geology, College of Science, Univercity of Baghdad Abstract 3D seismic
Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data
 Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data Patrick Butler, GEDCO, Calgary, Alberta, Canada pbutler@gedco.com Summary A module for removing and replacing strong noise in seismic data is presented.
Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data Patrick Butler, GEDCO, Calgary, Alberta, Canada pbutler@gedco.com Summary A module for removing and replacing strong noise in seismic data is presented.
TREBALL FI DE CARRERA
 - TREBALL FI DE CARRERA Títol Development of an automated microseismic event detection method and analysis of a microseismic dataset from hydraulic fracture stimulation to characterise natural and induced
- TREBALL FI DE CARRERA Títol Development of an automated microseismic event detection method and analysis of a microseismic dataset from hydraulic fracture stimulation to characterise natural and induced
Seismic reflection method
 Seismic reflection method Seismic reflection method is based on the reflections of seismic waves occurring at the contacts of subsurface structures. We apply some seismic source at different points of
Seismic reflection method Seismic reflection method is based on the reflections of seismic waves occurring at the contacts of subsurface structures. We apply some seismic source at different points of
Looking deeper through Pre Amplifier gain A study
 P-36 Looking deeper through Pre Amplifier gain A study C.V.Jambhekar*, DGM (S) & Paparaju Buddhavarapu, CE (E&T), ONGC, Vadodara, India Summary This article is a report on the experimental study carried
P-36 Looking deeper through Pre Amplifier gain A study C.V.Jambhekar*, DGM (S) & Paparaju Buddhavarapu, CE (E&T), ONGC, Vadodara, India Summary This article is a report on the experimental study carried
ARIES II recording system
 GROUND EQUIPMENT RAM (REMOTE ACQUISITION MODULE) 24-bit Delta-Sigma A/D Conversion 6 or 8 channels per RAM Supports ARIES Capacity on Demand and automatic transmission load balancing Fully redundant quad-telemetry
GROUND EQUIPMENT RAM (REMOTE ACQUISITION MODULE) 24-bit Delta-Sigma A/D Conversion 6 or 8 channels per RAM Supports ARIES Capacity on Demand and automatic transmission load balancing Fully redundant quad-telemetry
AVO compliant spectral balancing
 Summary AVO compliant spectral balancing Nirupama Nagarajappa CGGVeritas, Calgary, Canada pam.nagarajappa@cggveritas.com Spectral balancing is often performed after surface consistent deconvolution to
Summary AVO compliant spectral balancing Nirupama Nagarajappa CGGVeritas, Calgary, Canada pam.nagarajappa@cggveritas.com Spectral balancing is often performed after surface consistent deconvolution to
Design of Geophysical Surveys in Transportation
 Boise State University ScholarWorks CGISS Publications and Presentations Center for Geophysical Investigation of the Shallow Subsurface (CGISS) 1-1-2004 Design of Geophysical Surveys in Transportation
Boise State University ScholarWorks CGISS Publications and Presentations Center for Geophysical Investigation of the Shallow Subsurface (CGISS) 1-1-2004 Design of Geophysical Surveys in Transportation
JULY AUG 2010 INNOVATING WHILE DRILLING REGIONAL FOCUS: EUROPE & THE NORTH SEA
 DRILLING C O N T R A C T O R OFFICIAL MAGAZINE OF THE INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF DRILLING S C O N T R A C T O R Multi-zone, expandable completions JULY AUG 2010 New technologies provide more options
DRILLING C O N T R A C T O R OFFICIAL MAGAZINE OF THE INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF DRILLING S C O N T R A C T O R Multi-zone, expandable completions JULY AUG 2010 New technologies provide more options
Analysis of PS-to-PP amplitude ratios for seismic reflector characterisation: method and application
 Analysis of PS-to-PP amplitude ratios for seismic reflector characterisation: method and application N. Maercklin, A. Zollo RISSC, Italy Abstract: Elastic parameters derived from seismic reflection data
Analysis of PS-to-PP amplitude ratios for seismic reflector characterisation: method and application N. Maercklin, A. Zollo RISSC, Italy Abstract: Elastic parameters derived from seismic reflection data
P and S wave separation at a liquid-solid interface
 and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface Maria. Donati and Robert R. tewart ABTRACT and seismic waves impinging on a liquid-solid interface give rise
and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface Maria. Donati and Robert R. tewart ABTRACT and seismic waves impinging on a liquid-solid interface give rise
Overview ta3520 Introduction to seismics
 Overview ta3520 Introduction to seismics Fourier Analysis Basic principles of the Seismic Method Interpretation of Raw Seismic Records Seismic Instrumentation Processing of Seismic Reflection Data Vertical
Overview ta3520 Introduction to seismics Fourier Analysis Basic principles of the Seismic Method Interpretation of Raw Seismic Records Seismic Instrumentation Processing of Seismic Reflection Data Vertical
CDP noise attenuation using local linear models
 CDP noise attenuation CDP noise attenuation using local linear models Todor I. Todorov and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Seismic noise attenuation plays an important part in a seismic processing flow. Spatial
CDP noise attenuation CDP noise attenuation using local linear models Todor I. Todorov and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Seismic noise attenuation plays an important part in a seismic processing flow. Spatial
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution
 Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Evaluation of a broadband marine source
 Evaluation of a broadband marine source Rob Telling 1*, Stuart Denny 1, Sergio Grion 1 and R. Gareth Williams 1 evaluate far-field signatures and compare processing results for a 2D test-line acquired
Evaluation of a broadband marine source Rob Telling 1*, Stuart Denny 1, Sergio Grion 1 and R. Gareth Williams 1 evaluate far-field signatures and compare processing results for a 2D test-line acquired
Spectral Detection of Attenuation and Lithology
 Spectral Detection of Attenuation and Lithology M S Maklad* Signal Estimation Technology Inc., Calgary, AB, Canada msm@signalestimation.com and J K Dirstein Total Depth Pty Ltd, Perth, Western Australia,
Spectral Detection of Attenuation and Lithology M S Maklad* Signal Estimation Technology Inc., Calgary, AB, Canada msm@signalestimation.com and J K Dirstein Total Depth Pty Ltd, Perth, Western Australia,
Refraction: Solutions
 Introduction to Refraction Tomography Geop402-Senior Project Introduction Refraction Design Geophone Setup Software Results Refraction: Solutions Brute Force High-energy Source Survey Design Source Location
Introduction to Refraction Tomography Geop402-Senior Project Introduction Refraction Design Geophone Setup Software Results Refraction: Solutions Brute Force High-energy Source Survey Design Source Location
Development and Field Testing of a Seismic System for Locating Trapped Miners - Progress Report. Yi Luo, Keith A. Heasley and Syd S.
 Development and Field Testing of a Seismic System for Locating Trapped Miners - Progress Report Yi Luo, Keith A. Heasley and Syd S. Peng Department of Mining Engineering West Virginia University Acknowledgements
Development and Field Testing of a Seismic System for Locating Trapped Miners - Progress Report Yi Luo, Keith A. Heasley and Syd S. Peng Department of Mining Engineering West Virginia University Acknowledgements
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. Microphone and geophone data analysis for noise characterization. and seismic signal enhancement. Alejandro David Alcudia León
 Important Notice This copy may be used only for the purposes of research and private study, and any use of the copy for a purpose other than research or private study may require the authorization of the
Important Notice This copy may be used only for the purposes of research and private study, and any use of the copy for a purpose other than research or private study may require the authorization of the
Breakthrough Usability for More Efficient Surveys, Higher Quality Data
 Geode DZ Distributed Seismic Acquisition System 3-D Data Acquisition Simplified And Streamlined Breakthrough Usability for More Efficient Surveys, Higher Quality Data Unlike other 3D seismic systems that
Geode DZ Distributed Seismic Acquisition System 3-D Data Acquisition Simplified And Streamlined Breakthrough Usability for More Efficient Surveys, Higher Quality Data Unlike other 3D seismic systems that
The Hodogram as an AVO Attribute
 The Hodogram as an AVO Attribute Paul F. Anderson* Veritas GeoServices, Calgary, AB Paul_Anderson@veritasdgc.com INTRODUCTION The use of hodograms in interpretation of AVO cross-plots is a relatively recent
The Hodogram as an AVO Attribute Paul F. Anderson* Veritas GeoServices, Calgary, AB Paul_Anderson@veritasdgc.com INTRODUCTION The use of hodograms in interpretation of AVO cross-plots is a relatively recent
SPNA 2.3. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2177
 SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
Applied Geophysics Nov 2 and 4
 Applied Geophysics Nov 2 and 4 Effects of conductivity Surveying geometries Noise in GPR data Summary notes with essential equations Some Case histories EOSC 350 06 Slide 1 GPR Ground Penetrating Radar
Applied Geophysics Nov 2 and 4 Effects of conductivity Surveying geometries Noise in GPR data Summary notes with essential equations Some Case histories EOSC 350 06 Slide 1 GPR Ground Penetrating Radar
Vibration and air pressure monitoring of seismic sources
 Vibration monitoring of seismic sources Vibration and air pressure monitoring of seismic sources Alejandro D. Alcudia, Robert R. Stewart, Nanna Eliuk* and Rick Espersen** ABSTRACT Vibration monitoring
Vibration monitoring of seismic sources Vibration and air pressure monitoring of seismic sources Alejandro D. Alcudia, Robert R. Stewart, Nanna Eliuk* and Rick Espersen** ABSTRACT Vibration monitoring
Interpretational applications of spectral decomposition in reservoir characterization
 Interpretational applications of spectral decomposition in reservoir characterization GREG PARTYKA, JAMES GRIDLEY, and JOHN LOPEZ, Amoco E&P Technology Group, Tulsa, Oklahoma, U.S. Figure 1. Thin-bed spectral
Interpretational applications of spectral decomposition in reservoir characterization GREG PARTYKA, JAMES GRIDLEY, and JOHN LOPEZ, Amoco E&P Technology Group, Tulsa, Oklahoma, U.S. Figure 1. Thin-bed spectral
Summary. Seismic vibrators are the preferred sources for land seismic ( ) (1) Unfortunately, due to the mechanical and
 Timothy Dean*, John Quigley, Scott MacDonald, and Colin Readman, WesternGeco. Summary Seismic vibrators are the preferred sources for land seismic surveys. Unfortunately, due to the mechanical and hydraulic
Timothy Dean*, John Quigley, Scott MacDonald, and Colin Readman, WesternGeco. Summary Seismic vibrators are the preferred sources for land seismic surveys. Unfortunately, due to the mechanical and hydraulic
Marine Imaging Systems (Streamer & Seabed)
 Marine Imaging Systems (Streamer & Seabed) Investor Education Series Presented by Jeff Cunkelman, VP Marketing (Marine Imaging Systems) May 2010 FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENT The information included herein
Marine Imaging Systems (Streamer & Seabed) Investor Education Series Presented by Jeff Cunkelman, VP Marketing (Marine Imaging Systems) May 2010 FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENT The information included herein
Vertical Seismic Profile (PIVSP) Downgoing tube wave. Upgoing tube wave.
 Vertical Seismic Profile (PIVSP) Downgoing tube wave Upgoing tube wave Contents VSP Acquisition System (PIVSP) PI Vertical Seismic Profile System (PIVSP) Slim Vertical Seismic Profile Tool (SlimVSP) Multilevel
Vertical Seismic Profile (PIVSP) Downgoing tube wave Upgoing tube wave Contents VSP Acquisition System (PIVSP) PI Vertical Seismic Profile System (PIVSP) Slim Vertical Seismic Profile Tool (SlimVSP) Multilevel
