Summary. Page SEG SEG Denver 2014 Annual Meeting
|
|
|
- Gavin Greene
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
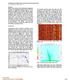
1 Seismo-acoustic characterization of a seismic vibrator Claudio Bagaini*, Martin Laycock and Colin Readman, WesternGeco; Emmanuel Coste, Schlumberger; Colin Anderson, Siemens PLM Software Summary A seismic vibrator generates seismic and acoustic noise as soon as it is pressured up and located in the proximity of a recording spread. The noise in the seismic bandwidth is more critical in vibroseis surveys where a large number of vibrators are used as in the case of simultaneous acquisitions. The noise in the acoustic bandwidth is particularly important when the survey takes place in populated areas. We carried out a seismo-acoustic experiment to characterize these noises. We present the results obtained while the vibrator is pressured up but not sweeping, with the baseplate in contact or not with the ground. We demonstrate that several monochromatic noise components can be related to the cooling and exhaust systems. We also show the effects in the seismic and acoustic bandwidths of modifications to the cooling and exhaust systems. Introduction Over the last three decades, the increase in total productivity in land vibroseis seismic acquisition (here defined as the total number of traces acquired in a time interval) has been mainly due to increases in the recording system channel count. Only in the last few years has the source side substantially contributed to the total productivity, thanks to the widespread use of simultaneous source techniques. However, simultaneous shooting presents in general two types of challenges: one challenge for the acquisition system, and another for the data processing. The challenge for the acquisition system is due to the fact that, to efficiently implement the simultaneous shooting techniques, a continuous recording system with a large channel count must be available. Moreover, the acquisition system must be capable of handling communication between numerous vibrators and the recording truck. The most advanced land acquisition systems fulfil both these requirements. The data processing challenge is due to the fact that the speed-up in acquisition should ideally not affect the final data quality but it should actually be used to improve it by reducing the shot point interval and/or improving the economic acquisition template. It is therefore necessary to either develop algorithms to separate the data by removing the cross-talk noise or to develop new algorithms to process these data without separating them in the early processing stages. In addition to the cross-talk noise, simultaneous vibroseis acquisitions are affected by other noise components. The field experiment described here aimed at acquiring seismic and acoustic data to improve our understanding of noises that affect simultaneous vibroseis surveys, but are different than cross-talk (Figure 1). The first type of noise, often referred to as chimney noise, contaminates the very near offsets, typically less than 2 m. The name comes from its aspect when the data are correlated with the survey sweep and visualized. It is also visible when other vibrator units or vehicles are standing or moving around the active spread (Figure 1 and Figure 2). It is often assumed that it is generated by the vibrator itself (engine, cooling and hydraulic systems, and others). The chimney noise makes the very near offsets practically unusable for applications such as statics estimation and surface-related multiple elimination that benefit from the presence of the very near offsets. The information recorded by the near-offset traces, when they are recorded with point-receiver acquisition systems, can be instrumental for seismic characterization of the nearsurface. Figure 1. A typical vibroseis shot record. Ground-roll, chimney noise and airblast are highlighted. The detrimental effect of the chimney noise is greater in simultaneous vibroseis surveys (Figure 2) because it affects not only the very near offsets of the vibrator that generated it but it also affects the weak signals at the medium-long offsets of other vibrators that emit their signals simultaneously or almost simultaneously. The chimney noise is also generated by vibrators standing along the Page 25
2 spread, but not sweeping. This noise is more critical in simultaneous vibroseis surveys because the number of vibrators in the field is significantly higher than in sequential acquisitions. The second type of noise is the air blast (Sallas and Brook, 1989). Also, this type of noise is more critical in simultaneous vibroseis surveys because the air blast generated by one vibrator may affect several records (Figure 2). Another type of noise often observed during vibroseis surveys using a large number of vibrators is composed of monochromatic components that are generated by seismic vibrators regardless of whether they are sweeping or not. Acoustic and vibrational noise at frequencies beyond the seismic bandwidth are also of interest for their effect on the vibrator personnel and, when operating in populated areas, on nearby inhabitants. To obtain a better insight on these types of noise, we carried out a field test that comprised seismic and acoustic pressure measurements with vibrators in different configurations. We present the results obtained in configurations where the vibrator is pressured up but not sweeping. and PCB 13D21 microphones were installed in the vicinity of the equipment where acoustic energy was expected to be generated. Two different 8,-lbf vibrators were used. The first was a standard vibrator and the second was a modified vibrator. On the second vehicle, the skid unit was replaced by one with an alternative intake, exhaust and cooling system. Figure 3. Acquisition geometry with highlighted geophone and microphone locations. Figure 2. A correlated record from a simultaneous vibroseis acquisition. Field test The acquisition geometry of the field test here described is sketched in Figure 3. The test setup consisted of two distinct but complementary parts. The surface seismic equipment consisted of one Stratavisor NZ recorder, 4 Geode nodes and several GS geophones. The acoustic equipment comprised two types of microphones: PCB 13D21 that were deployed (on a tripod) at 2 m offset and B&K 4189 for longer-offset measurements. The vibrator was equipped with PCB356A2 accelerometers Figure 4 shows a geophone record (located at 5 m offset) during the following sequence: baseplate lowered and in contact with the ground with hold-down weight applied (pad-down configuration), baseplate raised (pad-up) and again in the pad-down configuration. It is clear that, when the baseplate is in contact with the ground, the geophone records a broadband noise in the frequency range. The baseplate is isolated from the vertical vibrations of the truck by air bags whose natural frequency is just above 2.. However, when the vibrator is pressured up and the engine is running, horizontal vibrations are also generated. Horizontal vibrations can, therefore, be transmitted to the ground even if the vibrator is not sweeping. Monochromatic noise components appear in both pad-up and pad-down configurations. The frequencies of 34 and 12 are dominant. The fact that these noise components have approximately the same intensity indicates that they are likely to be airborne. They are recorded by the geophones because of the ground-roll coupling to compressional waves phenomenon (Press and Ewing, 1951). We study these monochromatic noise components in more detail by considering both seismic and acoustic measurements. Page 26
3 Figure 5 shows several geophone and microphone measurements made while the vibrator was in pad-down configuration. They are representative of the geophone recordings at 5 m offset and microphone recording at 2 m offset. Several monochromatic noise components appear in both records, as highlighted in the figures. These monochromatic noise components can be explained by considering the features of the vibrators. The vibrator used for this experiment was equipped with a Caterpillar C-15 engine. This is a 4-stroke diesel engine with 6-cylinders in-line that, during the test, was running at 2,5 rpm. The cooling system is composed of a large fan with 16 blades driven by the engine and running at 16 rpm. The individual monochromatic noises are related to the engine and cooling system as described below ½ order engine (one cylinder fires every two crankshaft revolutions in a 4-stroke engine) st order cooling fan st order engine order engine order engine rd order engine (firing frequency for the 6 cylinder 4-stroke engine running at 25 rpm) rd order engine for a vibrator running at 21 rpm. The engine 3 rd order noise can come from a variety of sources. The 3 rd order engine is the firing frequency, so there will always be significant excitation at this frequency. The fact that the 3 rd order engine ( ) is the strongest component denotes that the engine is well balanced and all the cylinders fire almost evenly. Any small imbalance of the fan generates the 1 st order harmonic of the fan. The 1 st order engine vibration could be caused by imbalance of the parts of the engine which rotate or reciprocate once per revolution. To determine the transmission paths of the noise generated by vibrations and acoustic sources, we followed two methods: 1) Comparison of geophone data with microphone and baseplate data. 2) Comparison of pad-down data with pad-up and ambient noise data. The 3 rd order engine noise is visible in the geophone measurements, but more pronounced in the microphone measurements. Some additional insights on this noise component can be obtained by analyzing some geophone traces acquired while the vibrator was pressured up but not sweeping in pad-up or pad-down configurations (Figure 6). The 3 rd order engine is unchanged when the baseplate is lowered. The analysis of accelerometers mounted on the vibrator highlighted that the effect of the radiation of vibrations at the 3 rd order engine frequency is negligible. We conclude that the 3 rd order engine noise is mainly airborne. Analysis of Figure 5 highlights that the ½ order engine (17.1 ) is mainly structure borne (i.e. skid frame, bushes, vibrator frame, base plate), and transmitted to the ground by means of the baseplate or possibly even from the frame through the tires. The 1 st order cooling fan noise (26.9 ) is also likely to be mainly structure-borne but there is no conclusive evidence of this. Figure 4. Vibrator pressured up and not sweeping. A geophone record obtained during a pad-down, pad-up sequence. Vibrator modifications and noise affecting nearby people A vibrator with a modified cooling system was also tested. The single large engine-driven fan was replaced by several smaller hydraulically driven fan units (operating at a constant speed of around 7 rpm) and a drum-based system. The 1 st order cooling fan (26.9 ) visible in Figure 5 has been completely eliminated in Figure 6. Vibrator noise beyond the seismic bandwidth affects the vibrator personnel and, when operating in populated areas, nearby people. The first and second stages of the exhaust system were modified with a silencer. The effects of these modifications can be seen in Figure 7. The 6 th and 1 th engine order are significantly reduced, along with a general reduction in the frequency range between 1 and. A microphone located at the exhaust orifice (Figure 8) confirms the origin of this noise and the effects of the modified exhaust. A reduction of the acoustic noise between 1 and is obtained when only the first stage is modified. Further attenuation up to 2 k is obtained when both first and second stages are modified. Page 27
4 Frequencies: 26.9 / 34.3 / / F PSD average 2m mic/average 2m mic (2) IOT_SV_D7_b (A) F PSD average 2m mic/average 2m mic (1) SPR1_ModV_ST1_F7_a 82.2 (A) PSD average 2m mic/average 2m mic SPR1_ModV_ST2_F7_a 81.8 (A) F 6 th 1 th engine order (m/s) 2 / (a) Frequencies: 17. / 24.2 / / 85.5 / 12. Average of 4 2m microphones 3 2 Pa 2 / Pa 2 / (A) Figure 7. Vibrator noise beyond the seismic bandwidth. Average of four microphone measurements. Original vibrator (red), vibrator with modified cooling system and first-stage exhaust (green), vibrator with also the second-stage exhaust modified (blue). (b) Figure 5. Seismic and acoustic measurements for a vibrator in paddown configuration (five measurements). (a) Spectral analysis of a geophone (5 m offset) record. (b) Spectral analysis of a microphone (2 m offset) measurement. (m/s) 2 / (m/s) 2 / Trace Trace Figure 6. Spectral analysis of two geophone traces acquired with a modified vibrator in pad-up and pad-down configurations. This vibrator included a modified cooling system that completely removed the 1 st order fan component seen in Figure 5. Spectra of data acquired with pad-up (red), pad-down (green) and ambient noise (blue) are superimposed. Figure 8. Spectrum of a microphone located at the exhaust orifice. Same color convention as in Figure 7. Conclusions A vibrator pressured up and located in the proximity of the receiver spread generates seismic noise that can detrimentally affects the seismic data plus acoustic noise that disturbs nearby people when operating in populated areas. A number of monochromatic noises were measured during a field experiment when a vibrator was pressured-up but not sweeping. A quantitative analysis of these noises measured by geophones and microphones enabled us to relate these noises to the frequency of rotations of both engine and fan. The transmission paths for these noises were identified with a good degree of confidence. It was also observed that a vibrator in pad-down configuration generally emits more structure/ground-borne noise than when it is in pad-up configuration. Modifications in the cooling system eliminated the 1 st order (26.9 ) fan noise and reduced the acoustic noise significantly. Modifications in the exhaust system showed some improvements in the seismic and acoustic bandwidth owing to reductions in the 6 th and 1 th order engine harmonics and in the frequency range up to 2 k. Acknowledgments We thank WesternGeco for permission to publish this work. Page 28
5 EDITED REFERENCES Note: This reference list is a copy-edited version of the reference list submitted by the author. Reference lists for the 214 SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts have been copy edited so that references provided with the online metadata for each paper will achieve a high degree of linking to cited sources that appear on the Web. REFERENCES Press, F., and M. Ewing, 1951, Ground roll coupling to atmospheric compressional waves: Geophysics, 16, , Sallas, J. and Brook, R. A., 1989, Air-coupled noise produced by a seismic P-Wave vibrator: 59 th Annual Meeting and Exhibition, SEG, Expanded Abstracts, Page 29
Summary. Seismic vibrators are the preferred sources for land seismic ( ) (1) Unfortunately, due to the mechanical and
 Timothy Dean*, John Quigley, Scott MacDonald, and Colin Readman, WesternGeco. Summary Seismic vibrators are the preferred sources for land seismic surveys. Unfortunately, due to the mechanical and hydraulic
Timothy Dean*, John Quigley, Scott MacDonald, and Colin Readman, WesternGeco. Summary Seismic vibrators are the preferred sources for land seismic surveys. Unfortunately, due to the mechanical and hydraulic
Noise Reduction in VibroSeis Source Kaëlig Castor*, Thomas Bianchi, Olivier Winter, Thierry Klein, CGG
 Downloaded //6 to 9..7.. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ Noise Reduction in VibroSeis Source Kaëlig Castor*, Thomas Bianchi, Olivier Winter,
Downloaded //6 to 9..7.. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ Noise Reduction in VibroSeis Source Kaëlig Castor*, Thomas Bianchi, Olivier Winter,
SPNA 2.3. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2177
 SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas
 The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
Using long sweep in land vibroseis acquisition
 Using long sweep in land vibroseis acquisition Authors: Alexandre Egreteau, John Gibson, Forest Lin and Julien Meunier (CGGVeritas) Main objectives: Promote the use of long sweeps to compensate for the
Using long sweep in land vibroseis acquisition Authors: Alexandre Egreteau, John Gibson, Forest Lin and Julien Meunier (CGGVeritas) Main objectives: Promote the use of long sweeps to compensate for the
OPTIMIZING HIGH FREQUENCY VIBROSEIS DATA. Abstract
 OPTIMIZING HIGH FREQUENCY VIBROSEIS DATA Theresa R. Rademacker, Kansas Geological Survey, Lawrence, KS Richard D. Miller, Kansas Geological Survey, Lawrence, KS Shelby L. Walters, Kansas Geological Survey,
OPTIMIZING HIGH FREQUENCY VIBROSEIS DATA Theresa R. Rademacker, Kansas Geological Survey, Lawrence, KS Richard D. Miller, Kansas Geological Survey, Lawrence, KS Shelby L. Walters, Kansas Geological Survey,
Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Group Array Stack of single sensor data
 P-113 Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Artatran Ojha *, K. Ramakrishna, G. Sarvesam Geophysical Services, ONGC, Chennai Summary Shot generated noise and the cultural noise is a major problem in
P-113 Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Artatran Ojha *, K. Ramakrishna, G. Sarvesam Geophysical Services, ONGC, Chennai Summary Shot generated noise and the cultural noise is a major problem in
2012 SEG SEG Las Vegas 2012 Annual Meeting Page 1
 Full-wavefield, towed-marine seismic acquisition and applications David Halliday, Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Johan O. A. Robertsson, ETH Zürich, Ivan Vasconcelos, Schlumberger Cambridge Research,
Full-wavefield, towed-marine seismic acquisition and applications David Halliday, Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Johan O. A. Robertsson, ETH Zürich, Ivan Vasconcelos, Schlumberger Cambridge Research,
There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to
 Coordinated by JEFF DEERE JOHN GIBSON, FOREST LIN, ALEXANDRE EGRETEAU, and JULIEN MEUNIER, CGGVeritas MALCOLM LANSLEY, Sercel There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to improve the quality
Coordinated by JEFF DEERE JOHN GIBSON, FOREST LIN, ALEXANDRE EGRETEAU, and JULIEN MEUNIER, CGGVeritas MALCOLM LANSLEY, Sercel There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to improve the quality
Attenuation of high energy marine towed-streamer noise Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco
 Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Tu N Higher Vibrator Hydraulic Force for Improved High Frequency Generation
 Tu N105 06 Higher Vibrator Hydraulic Force for Improved High Frequency Generation N. Tellier* (Sercel), G. Ollivrin (Sercel) & G. Caradec (Sercel) SUMMARY For conventional deep seismic with heavy vibrators,
Tu N105 06 Higher Vibrator Hydraulic Force for Improved High Frequency Generation N. Tellier* (Sercel), G. Ollivrin (Sercel) & G. Caradec (Sercel) SUMMARY For conventional deep seismic with heavy vibrators,
Downloaded 09/04/18 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Th ELI1 08 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data
 Th ELI1 8 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data P. Edme* (Schlumberger Gould Research), E. Muyzert (Sclumberger Gould Research) & E. Kragh (Schlumberger Gould Research) SUMMARY
Th ELI1 8 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data P. Edme* (Schlumberger Gould Research), E. Muyzert (Sclumberger Gould Research) & E. Kragh (Schlumberger Gould Research) SUMMARY
Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records
 Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT This paper proposes using microphone recordings of
Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT This paper proposes using microphone recordings of
FINAL REPORT EL# RS. C. A. Hurich & MUN Seismic Team Earth Sciences Dept. Memorial University Sept. 2009
 FINAL REPORT EL# 09-101-01-RS MUNSIST Seismic Source Test - Five Mile Road C. A. Hurich & MUN Seismic Team Earth Sciences Dept. Memorial University Sept. 2009 1 EL# 09-101-01-RS Five-Mile Road Memorial
FINAL REPORT EL# 09-101-01-RS MUNSIST Seismic Source Test - Five Mile Road C. A. Hurich & MUN Seismic Team Earth Sciences Dept. Memorial University Sept. 2009 1 EL# 09-101-01-RS Five-Mile Road Memorial
Summary. Methodology. Selected field examples of the system included. A description of the system processing flow is outlined in Figure 2.
 Halvor Groenaas*, Svein Arne Frivik, Aslaug Melbø, Morten Svendsen, WesternGeco Summary In this paper, we describe a novel method for passive acoustic monitoring of marine mammals using an existing streamer
Halvor Groenaas*, Svein Arne Frivik, Aslaug Melbø, Morten Svendsen, WesternGeco Summary In this paper, we describe a novel method for passive acoustic monitoring of marine mammals using an existing streamer
Vibration and air pressure monitoring of seismic sources
 Vibration monitoring of seismic sources Vibration and air pressure monitoring of seismic sources Alejandro D. Alcudia, Robert R. Stewart, Nanna Eliuk* and Rick Espersen** ABSTRACT Vibration monitoring
Vibration monitoring of seismic sources Vibration and air pressure monitoring of seismic sources Alejandro D. Alcudia, Robert R. Stewart, Nanna Eliuk* and Rick Espersen** ABSTRACT Vibration monitoring
Applied Methods MASW Method
 Applied Methods MASW Method Schematic illustrating a typical MASW Survey Setup INTRODUCTION: MASW a seismic method for near-surface (< 30 m) Characterization of shear-wave velocity (Vs) (secondary or transversal
Applied Methods MASW Method Schematic illustrating a typical MASW Survey Setup INTRODUCTION: MASW a seismic method for near-surface (< 30 m) Characterization of shear-wave velocity (Vs) (secondary or transversal
On the accuracy reciprocal and direct vibro-acoustic transfer-function measurements on vehicles for lower and medium frequencies
 On the accuracy reciprocal and direct vibro-acoustic transfer-function measurements on vehicles for lower and medium frequencies C. Coster, D. Nagahata, P.J.G. van der Linden LMS International nv, Engineering
On the accuracy reciprocal and direct vibro-acoustic transfer-function measurements on vehicles for lower and medium frequencies C. Coster, D. Nagahata, P.J.G. van der Linden LMS International nv, Engineering
Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation
 Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation T. Elboth* (CGG), H. Shen (CGG), J. Khan (CGG) Summary This paper presents recent advances in the area of seismic interference (SI) attenuation
Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation T. Elboth* (CGG), H. Shen (CGG), J. Khan (CGG) Summary This paper presents recent advances in the area of seismic interference (SI) attenuation
Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS
 Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS Summary In land AVO processing, near-surface heterogeneity issues are
Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS Summary In land AVO processing, near-surface heterogeneity issues are
Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic
 Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic J. Burren (Petroleum Geo-Services) & D. Lecerf* (Petroleum Geo-Services) SUMMARY Future time-lapse broadband surveys should provide better reservoir monitoring
Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic J. Burren (Petroleum Geo-Services) & D. Lecerf* (Petroleum Geo-Services) SUMMARY Future time-lapse broadband surveys should provide better reservoir monitoring
ANALYTICAL NOISE MODELLING OF A CENTRIFUGAL FAN VALIDATED BY EXPERIMENTAL DATA
 ANALYTICAL NOISE MODELLING OF A CENTRIFUGAL FAN VALIDATED BY EXPERIMENTAL DATA Beatrice Faverjon 1, Con Doolan 1, Danielle Moreau 1, Paul Croaker 1 and Nathan Kinkaid 1 1 School of Mechanical and Manufacturing
ANALYTICAL NOISE MODELLING OF A CENTRIFUGAL FAN VALIDATED BY EXPERIMENTAL DATA Beatrice Faverjon 1, Con Doolan 1, Danielle Moreau 1, Paul Croaker 1 and Nathan Kinkaid 1 1 School of Mechanical and Manufacturing
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile
 Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
X039 Observations of Surface Vibrator Repeatability in a Desert Environment
 X39 Observations of Surface Vibrator Repeatability in a Desert Environment M.A. Jervis* (Saudi Aramco), A.V. Bakulin (Saudi Aramco), R.M. Burnstad (Saudi Aramco), C. Beron (CGGVeritas) & E. Forgues (CGGVeritas)
X39 Observations of Surface Vibrator Repeatability in a Desert Environment M.A. Jervis* (Saudi Aramco), A.V. Bakulin (Saudi Aramco), R.M. Burnstad (Saudi Aramco), C. Beron (CGGVeritas) & E. Forgues (CGGVeritas)
Efficient Acquisition of Quality Borehole Seismic
 Efficient Acquisition of Quality Borehole Seismic The Versatile Seismic Imager Applications Integrated processing for interpretation of boreholeand surface-seismic data Images for reservoir definition
Efficient Acquisition of Quality Borehole Seismic The Versatile Seismic Imager Applications Integrated processing for interpretation of boreholeand surface-seismic data Images for reservoir definition
Multi-channel Active Control of Axial Cooling Fan Noise
 The 2002 International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering Dearborn, MI, USA. August 19-21, 2002 Multi-channel Active Control of Axial Cooling Fan Noise Kent L. Gee and Scott D. Sommerfeldt
The 2002 International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering Dearborn, MI, USA. August 19-21, 2002 Multi-channel Active Control of Axial Cooling Fan Noise Kent L. Gee and Scott D. Sommerfeldt
Seismic reflection method
 Seismic reflection method Seismic reflection method is based on the reflections of seismic waves occurring at the contacts of subsurface structures. We apply some seismic source at different points of
Seismic reflection method Seismic reflection method is based on the reflections of seismic waves occurring at the contacts of subsurface structures. We apply some seismic source at different points of
B028 Improved Marine 4D Repeatability Using an Automated Vessel, Source and Receiver Positioning System
 B028 Improved Marine 4D Repeatability Using an Automated Vessel, Source and Receiver Positioning System J.O. Paulsen* (WesternGeco) & G. Brown (WesternGeco) SUMMARY A new automated and integrated, vessel,
B028 Improved Marine 4D Repeatability Using an Automated Vessel, Source and Receiver Positioning System J.O. Paulsen* (WesternGeco) & G. Brown (WesternGeco) SUMMARY A new automated and integrated, vessel,
Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas
 Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas Summary The reliability of seismic attribute estimation depends on reliable signal.
Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas Summary The reliability of seismic attribute estimation depends on reliable signal.
South Africa CO2 Seismic Program
 1 South Africa CO2 Seismic Program ANNEXURE B Bob A. Hardage October 2016 There have been great advances in seismic technology in the decades following the acquisition of legacy, limited-quality, 2D seismic
1 South Africa CO2 Seismic Program ANNEXURE B Bob A. Hardage October 2016 There have been great advances in seismic technology in the decades following the acquisition of legacy, limited-quality, 2D seismic
Summary. Time only. Distance only. Simultaneous Methods. Distance and Time. Slip-Sweeps Dynamic Slip-Sweeps Unconstrained simultaneous sources
 Over 40,000 VPs per day with real-time quality control: Opportunities and Challenges Peter I. Pecholcs, Stephen K. Lafon, Hafiz Al-Shammery and Panos G. Kelamis (Saudi Aramco) Olivier Winter, Jean-Baptiste
Over 40,000 VPs per day with real-time quality control: Opportunities and Challenges Peter I. Pecholcs, Stephen K. Lafon, Hafiz Al-Shammery and Panos G. Kelamis (Saudi Aramco) Olivier Winter, Jean-Baptiste
Why not narrowband? Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology
 Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology Summary A 2D towed streamer acquisition experiment was conducted in deep water offshore Gabon to evaluate techniques
Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology Summary A 2D towed streamer acquisition experiment was conducted in deep water offshore Gabon to evaluate techniques
CDP noise attenuation using local linear models
 CDP noise attenuation CDP noise attenuation using local linear models Todor I. Todorov and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Seismic noise attenuation plays an important part in a seismic processing flow. Spatial
CDP noise attenuation CDP noise attenuation using local linear models Todor I. Todorov and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Seismic noise attenuation plays an important part in a seismic processing flow. Spatial
Presented on. Mehul Supawala Marine Energy Sources Product Champion, WesternGeco
 Presented on Marine seismic acquisition and its potential impact on marine life has been a widely discussed topic and of interest to many. As scientific knowledge improves and operational criteria evolve,
Presented on Marine seismic acquisition and its potential impact on marine life has been a widely discussed topic and of interest to many. As scientific knowledge improves and operational criteria evolve,
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DIFFERENT MICROPHONE INSTALLATIONS FOR ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL IN DUCTS
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DIFFERENT MICROPHONE INSTALLATIONS FOR ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL IN DUCTS M. Larsson, S. Johansson, L. Håkansson and I. Claesson Department of Signal Processing Blekinge Institute
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DIFFERENT MICROPHONE INSTALLATIONS FOR ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL IN DUCTS M. Larsson, S. Johansson, L. Håkansson and I. Claesson Department of Signal Processing Blekinge Institute
Introduction. Figure 2: Source-Receiver location map (to the right) and geometry template (to the left).
 Advances in interbed multiples prediction and attenuation: Case study from onshore Kuwait Adel El-Emam* and Khaled Shams Al-Deen, Kuwait Oil Company; Alexander Zarkhidze and Andy Walz, WesternGeco Introduction
Advances in interbed multiples prediction and attenuation: Case study from onshore Kuwait Adel El-Emam* and Khaled Shams Al-Deen, Kuwait Oil Company; Alexander Zarkhidze and Andy Walz, WesternGeco Introduction
I017 Digital Noise Attenuation of Particle Motion Data in a Multicomponent 4C Towed Streamer
 I017 Digital Noise Attenuation of Particle Motion Data in a Multicomponent 4C Towed Streamer A.K. Ozdemir* (WesternGeco), B.A. Kjellesvig (WesternGeco), A. Ozbek (Schlumberger) & J.E. Martin (Schlumberger)
I017 Digital Noise Attenuation of Particle Motion Data in a Multicomponent 4C Towed Streamer A.K. Ozdemir* (WesternGeco), B.A. Kjellesvig (WesternGeco), A. Ozbek (Schlumberger) & J.E. Martin (Schlumberger)
Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring
 Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring Michael Thornton*, MicroSeismic Inc., Houston,Texas mthornton@microseismic.com Summary While related concepts, resolution and uncertainty
Resolution and location uncertainties in surface microseismic monitoring Michael Thornton*, MicroSeismic Inc., Houston,Texas mthornton@microseismic.com Summary While related concepts, resolution and uncertainty
Analysis of the noise and vibration in the pipe near PIG Launcher
 Analysis of the noise and vibration in the pipe near PIG Launcher JaePil Koh Research & Development Division, Korea Gas Corporation, Il-dong 1248, Suin-Ro, Sangnok-Gu, Ansan-City 425-790, Korea, jpkoh@kogas.or.kr
Analysis of the noise and vibration in the pipe near PIG Launcher JaePil Koh Research & Development Division, Korea Gas Corporation, Il-dong 1248, Suin-Ro, Sangnok-Gu, Ansan-City 425-790, Korea, jpkoh@kogas.or.kr
Ambient Passive Seismic Imaging with Noise Analysis Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc.
 Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc. SUMMARY The ambient passive seismic imaging technique is capable of imaging repetitive passive seismic events. Here we investigate
Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc. SUMMARY The ambient passive seismic imaging technique is capable of imaging repetitive passive seismic events. Here we investigate
Environmental Noise Propagation
 Environmental Noise Propagation How loud is a 1-ton truck? That depends very much on how far away you are, and whether you are in front of a barrier or behind it. Many other factors affect the noise level,
Environmental Noise Propagation How loud is a 1-ton truck? That depends very much on how far away you are, and whether you are in front of a barrier or behind it. Many other factors affect the noise level,
Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure
 Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure Andy St-Onge* 1a, David W. Eaton 1b, and Adam Pidlisecky 1c 1 Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW Calgary,
Borehole vibration response to hydraulic fracture pressure Andy St-Onge* 1a, David W. Eaton 1b, and Adam Pidlisecky 1c 1 Department of Geoscience, University of Calgary, 2500 University Drive NW Calgary,
Field comparison of 3-C geophones and microphones to highprecision
 Geophones, microphones and blasting sensors Field comparison of 3-C geophones and microphones to highprecision blasting sensors Alejandro D. Alcudia, Robert R. Stewart, Kevin W. Hall and Eric V. Gallant
Geophones, microphones and blasting sensors Field comparison of 3-C geophones and microphones to highprecision blasting sensors Alejandro D. Alcudia, Robert R. Stewart, Kevin W. Hall and Eric V. Gallant
NON-SELLABLE PRODUCT DATA. Order Analysis Type 7702 for PULSE, the Multi-analyzer System. Uses and Features
 PRODUCT DATA Order Analysis Type 7702 for PULSE, the Multi-analyzer System Order Analysis Type 7702 provides PULSE with Tachometers, Autotrackers, Order Analyzers and related post-processing functions,
PRODUCT DATA Order Analysis Type 7702 for PULSE, the Multi-analyzer System Order Analysis Type 7702 provides PULSE with Tachometers, Autotrackers, Order Analyzers and related post-processing functions,
THE USE OF VOLUME VELOCITY SOURCE IN TRANSFER MEASUREMENTS
 THE USE OF VOLUME VELOITY SOURE IN TRANSFER MEASUREMENTS N. Møller, S. Gade and J. Hald Brüel & Kjær Sound and Vibration Measurements A/S DK850 Nærum, Denmark nbmoller@bksv.com Abstract In the automotive
THE USE OF VOLUME VELOITY SOURE IN TRANSFER MEASUREMENTS N. Møller, S. Gade and J. Hald Brüel & Kjær Sound and Vibration Measurements A/S DK850 Nærum, Denmark nbmoller@bksv.com Abstract In the automotive
Simultaneous Sources: a technology whose time has come Craig J. Beasley, WesternGeco.
 Craig J. Beasley, WesternGeco. Summary It is a rare and exhilarating moment when an emerging technology develops so rapidly that it warrants a special session at the SEG Annual Meeting, while, at the same
Craig J. Beasley, WesternGeco. Summary It is a rare and exhilarating moment when an emerging technology develops so rapidly that it warrants a special session at the SEG Annual Meeting, while, at the same
ISSN Volume 28 Issue 6 June A New Spring for Geoscience. Special Topic
 ISSN 0263-5046 Volume 28 Issue 6 June 2010 Special Topic Technical Articles Multi-azimuth processing and its applications to wide-azimuth OBC seismic data offshore Abu Dhabi Borehole image logs for turbidite
ISSN 0263-5046 Volume 28 Issue 6 June 2010 Special Topic Technical Articles Multi-azimuth processing and its applications to wide-azimuth OBC seismic data offshore Abu Dhabi Borehole image logs for turbidite
Seismic acquisition projects 2010
 Acquisition 2010 Seismic acquisition projects 2010 Malcolm B. Bertram, Kevin L. Bertram, Kevin W. Hall, Eric V. Gallant ABSTRACT Acquisition projects since the CREWES meeting in November 2009 include:
Acquisition 2010 Seismic acquisition projects 2010 Malcolm B. Bertram, Kevin L. Bertram, Kevin W. Hall, Eric V. Gallant ABSTRACT Acquisition projects since the CREWES meeting in November 2009 include:
Developments in vibrator control
 Geophysical Prospecting, 2010, 58, 33 40 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2478.2009.00848.x Developments in vibrator control D. Boucard and G. Ollivrin Sercel France, PO Box 439, 44474 Carquefou Cedex, France Received
Geophysical Prospecting, 2010, 58, 33 40 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2478.2009.00848.x Developments in vibrator control D. Boucard and G. Ollivrin Sercel France, PO Box 439, 44474 Carquefou Cedex, France Received
Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing Dispersive Ground Roll Noise from Onshore Seismic Data
 Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
Summary. Introduction
 Multi survey matching of marine towed streamer data using a broadband workflow: a shallow water offshore Nathan Payne*, Tony Martin and Jonathan Denly. ION GX Technology UK; Reza Afrazmanech. Perenco UK.
Multi survey matching of marine towed streamer data using a broadband workflow: a shallow water offshore Nathan Payne*, Tony Martin and Jonathan Denly. ION GX Technology UK; Reza Afrazmanech. Perenco UK.
WS15-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise
 WS1-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise F. Duret* (CGG) & E. Forgues (CGG) SUMMARY In 4D land seismic and especially for Permanent Reservoir Monitoring (PRM), changes of the near-surface
WS1-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise F. Duret* (CGG) & E. Forgues (CGG) SUMMARY In 4D land seismic and especially for Permanent Reservoir Monitoring (PRM), changes of the near-surface
SEISMIC, ACOUSTIC, AND MAGNETIC TEST RESULTS FROM US/GERMAN TESTING
 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. SEISMIC, ACOUSTIC, AND MAGNETIC TEST RESULTS FROM US/GERMAN TESTING John Sledge CHICKEN LITTLE Program Office Eglin AFB Florida 32542 ABSTRACT Seismic,
Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. SEISMIC, ACOUSTIC, AND MAGNETIC TEST RESULTS FROM US/GERMAN TESTING John Sledge CHICKEN LITTLE Program Office Eglin AFB Florida 32542 ABSTRACT Seismic,
Visible Light Communication-based Indoor Positioning with Mobile Devices
 Visible Light Communication-based Indoor Positioning with Mobile Devices Author: Zsolczai Viktor Introduction With the spreading of high power LED lighting fixtures, there is a growing interest in communication
Visible Light Communication-based Indoor Positioning with Mobile Devices Author: Zsolczai Viktor Introduction With the spreading of high power LED lighting fixtures, there is a growing interest in communication
Seismic Reflection Method
 1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG)
 Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
DESIGN OF VOICE ALARM SYSTEMS FOR TRAFFIC TUNNELS: OPTIMISATION OF SPEECH INTELLIGIBILITY
 DESIGN OF VOICE ALARM SYSTEMS FOR TRAFFIC TUNNELS: OPTIMISATION OF SPEECH INTELLIGIBILITY Dr.ir. Evert Start Duran Audio BV, Zaltbommel, The Netherlands The design and optimisation of voice alarm (VA)
DESIGN OF VOICE ALARM SYSTEMS FOR TRAFFIC TUNNELS: OPTIMISATION OF SPEECH INTELLIGIBILITY Dr.ir. Evert Start Duran Audio BV, Zaltbommel, The Netherlands The design and optimisation of voice alarm (VA)
Application Note. Airbag Noise Measurements
 Airbag Noise Measurements Headquarters Skovlytoften 33 2840 Holte Denmark Tel: +45 45 66 40 46 E-mail: gras@gras.dk Web: gras.dk Airbag Noise Measurements* Per Rasmussen When an airbag inflates rapidly
Airbag Noise Measurements Headquarters Skovlytoften 33 2840 Holte Denmark Tel: +45 45 66 40 46 E-mail: gras@gras.dk Web: gras.dk Airbag Noise Measurements* Per Rasmussen When an airbag inflates rapidly
=, (1) Summary. Theory. Introduction
 Noise suppression for detection and location of microseismic events using a matched filter Leo Eisner*, David Abbott, William B. Barker, James Lakings and Michael P. Thornton, Microseismic Inc. Summary
Noise suppression for detection and location of microseismic events using a matched filter Leo Eisner*, David Abbott, William B. Barker, James Lakings and Michael P. Thornton, Microseismic Inc. Summary
Vibration studies of a superconducting accelerating
 Vibration studies of a superconducting accelerating module at room temperature and at 4.5 K Ramila Amirikas, Alessandro Bertolini, Wilhelm Bialowons Vibration studies on a Type III cryomodule at room temperature
Vibration studies of a superconducting accelerating module at room temperature and at 4.5 K Ramila Amirikas, Alessandro Bertolini, Wilhelm Bialowons Vibration studies on a Type III cryomodule at room temperature
A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System
 A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System Per Eivind Dhelie*, PGS, Lysaker, Norway per.eivind.dhelie@pgs.com and Robert Sorley, PGS, Canada Torben Hoy, PGS,
A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System Per Eivind Dhelie*, PGS, Lysaker, Norway per.eivind.dhelie@pgs.com and Robert Sorley, PGS, Canada Torben Hoy, PGS,
Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion
 P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency
 25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
NVH analysis of a 3 phase 12/8 SR motor drive for HEV applications
 NVH analysis of a 3 phase 12/8 SR motor drive for HEV applications Mathieu Sarrazin 1, Steven Gillijns 1, Jan Anthonis 1, Karl Janssens 1, Herman van der Auweraer 1, Kevin Verhaeghe 2 1 LMS, a Siemens
NVH analysis of a 3 phase 12/8 SR motor drive for HEV applications Mathieu Sarrazin 1, Steven Gillijns 1, Jan Anthonis 1, Karl Janssens 1, Herman van der Auweraer 1, Kevin Verhaeghe 2 1 LMS, a Siemens
Qualification of Fan-Generated Duct Rumble Noise Part 2: Results
 2008, American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. (www.ashrae.org). ESL-PA-08-06-09 SL-08-003 (RP-1219) Qualification of Fan-Generated Duct Rumble Noise Part 2: Results
2008, American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. (www.ashrae.org). ESL-PA-08-06-09 SL-08-003 (RP-1219) Qualification of Fan-Generated Duct Rumble Noise Part 2: Results
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution
 Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Progress in DAS Seismic Methods
 Progress in DAS Seismic Methods A. Mateeva, J. Mestayer, Z. Yang, J. Lopez, P. Wills 1, H. Wu, W. Wong, Barbara Cox (Shell International Exploration and Production, Inc.), J. Roy, T. Bown ( OptaSense )
Progress in DAS Seismic Methods A. Mateeva, J. Mestayer, Z. Yang, J. Lopez, P. Wills 1, H. Wu, W. Wong, Barbara Cox (Shell International Exploration and Production, Inc.), J. Roy, T. Bown ( OptaSense )
Th-P08-11 Deblending of Single Source Vibroseis Land Data in Egypt with V1 Noise Attenuation Algorithm
 Th-P08-11 Deblending of Single Source Vibroseis Land Data in Egypt with V1 Noise Attenuation Algorithm N. Gulunay* (CGG), E. Shaker (CGG), A. Karagul (CGG), A. Ramadan (CGG), T. Bianchi (CGG), J. Ross
Th-P08-11 Deblending of Single Source Vibroseis Land Data in Egypt with V1 Noise Attenuation Algorithm N. Gulunay* (CGG), E. Shaker (CGG), A. Karagul (CGG), A. Ramadan (CGG), T. Bianchi (CGG), J. Ross
ENERGY- CONTENT AND SPECTRAL ANALYSES OF SHOTS FOR OPTIMUM SEISMOGRAM GENERATION IN THE NIGER DELTA
 ENERGY- CONTENT AND SPECTRAL ANALYSES OF SHOTS FOR OPTIMUM SEISMOGRAM GENERATION IN THE NIGER DELTA Alaminiokuma G.I. and *Emudianughe J.E. Department of Earth Sciences, Federal University of Petroleum
ENERGY- CONTENT AND SPECTRAL ANALYSES OF SHOTS FOR OPTIMUM SEISMOGRAM GENERATION IN THE NIGER DELTA Alaminiokuma G.I. and *Emudianughe J.E. Department of Earth Sciences, Federal University of Petroleum
RP 4.2. Summary. Introduction
 SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 1569 Differential Acoustical Resonance Spectroscopy: An experimental method for estimating acoustic attenuation of porous media Jerry M. Harris*, Youli Quan, Chuntang Xu,
SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 1569 Differential Acoustical Resonance Spectroscopy: An experimental method for estimating acoustic attenuation of porous media Jerry M. Harris*, Youli Quan, Chuntang Xu,
Summary. Introduction
 Multiple attenuation for variable-depth streamer data: from deep to shallow water Ronan Sablon*, Damien Russier, Oscar Zurita, Danny Hardouin, Bruno Gratacos, Robert Soubaras & Dechun Lin. CGGVeritas Summary
Multiple attenuation for variable-depth streamer data: from deep to shallow water Ronan Sablon*, Damien Russier, Oscar Zurita, Danny Hardouin, Bruno Gratacos, Robert Soubaras & Dechun Lin. CGGVeritas Summary
Silent Transformers to Help Consolidated Edison Meet New York City s Ultrastrict Noise Ordinances
 BY DR. RAMSIS GIRGIS, ABB INC. The Sound of Silence: Silent Transformers to Help Consolidated Edison Meet New York City s Ultrastrict Noise Ordinances S ilence is a source of great strength. Although these
BY DR. RAMSIS GIRGIS, ABB INC. The Sound of Silence: Silent Transformers to Help Consolidated Edison Meet New York City s Ultrastrict Noise Ordinances S ilence is a source of great strength. Although these
Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo
 Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo Summary A survey with a novel acquisition technique was acquired
Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo Summary A survey with a novel acquisition technique was acquired
EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS FOR PCM/FM, TIER 1 SOQPSK, AND TIER II MULTI-H CPM WITH CMA EQUALIZATION
 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS FOR PCM/FM, TIER 1 SOQPSK, AND TIER II MULTI-H CPM WITH CMA EQUALIZATION Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Geoghegan, Mark Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS FOR PCM/FM, TIER 1 SOQPSK, AND TIER II MULTI-H CPM WITH CMA EQUALIZATION Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Geoghegan, Mark Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal
Active Control of Energy Density in a Mock Cabin
 Cleveland, Ohio NOISE-CON 2003 2003 June 23-25 Active Control of Energy Density in a Mock Cabin Benjamin M. Faber and Scott D. Sommerfeldt Department of Physics and Astronomy Brigham Young University N283
Cleveland, Ohio NOISE-CON 2003 2003 June 23-25 Active Control of Energy Density in a Mock Cabin Benjamin M. Faber and Scott D. Sommerfeldt Department of Physics and Astronomy Brigham Young University N283
A SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM COMBINED WITH PASSIVE SILENCERS FOR IMPROVED NOISE REDUCTION IN DUCTS SUMMARY INTRODUCTION
 A SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM COMBINED WITH PASSIVE SILENCERS FOR IMPROVED NOISE REDUCTION IN DUCTS Martin LARSSON, Sven JOHANSSON, Lars HÅKANSSON, Ingvar CLAESSON Blekinge
A SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM COMBINED WITH PASSIVE SILENCERS FOR IMPROVED NOISE REDUCTION IN DUCTS Martin LARSSON, Sven JOHANSSON, Lars HÅKANSSON, Ingvar CLAESSON Blekinge
Multicomponent seismic polarization analysis
 Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
Technology of Adaptive Vibroseis for Wide Spectrum Prospecting
 Technology of Adaptive Vibroseis for Wide Spectrum Prospecting Xianzheng Zhao, Xishuang Wang, A.P. Zhukov, Ruifeng Zhang, Chuanzhang Tang Abstract: Seismic data from conventional vibroseis prospecting
Technology of Adaptive Vibroseis for Wide Spectrum Prospecting Xianzheng Zhao, Xishuang Wang, A.P. Zhukov, Ruifeng Zhang, Chuanzhang Tang Abstract: Seismic data from conventional vibroseis prospecting
Simultaneous multi-source acquisition using m-sequences
 Simultaneous source acquisition using m-sequences Simultaneous multi-source acquisition using m-sequences Joe Wong ABSTRACT Maximal length sequences, or m-sequences, are periodic mathematical periodic
Simultaneous source acquisition using m-sequences Simultaneous multi-source acquisition using m-sequences Joe Wong ABSTRACT Maximal length sequences, or m-sequences, are periodic mathematical periodic
A Dissertation Presented for the Doctor of Philosophy Degree. The University of Memphis
 A NEW PROCEDURE FOR ESTIMATION OF SHEAR WAVE VELOCITY PROFILES USING MULTI STATION SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF SURFACE WAVES, REGRESSION LINE SLOPE, AND GENETIC ALGORITHM METHODS A Dissertation Presented for
A NEW PROCEDURE FOR ESTIMATION OF SHEAR WAVE VELOCITY PROFILES USING MULTI STATION SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF SURFACE WAVES, REGRESSION LINE SLOPE, AND GENETIC ALGORITHM METHODS A Dissertation Presented for
Tu A D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study
 Tu A15 09 4D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study D. Lecerf* (PGS), D. Raistrick (PGS), B. Caselitz (PGS), M. Wingham (BP), J. Bradley (BP), B. Moseley (formaly BP) Summary
Tu A15 09 4D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study D. Lecerf* (PGS), D. Raistrick (PGS), B. Caselitz (PGS), M. Wingham (BP), J. Bradley (BP), B. Moseley (formaly BP) Summary
SmartSenseCom Introduces Next Generation Seismic Sensor Systems
 SmartSenseCom Introduces Next Generation Seismic Sensor Systems Summary: SmartSenseCom, Inc. (SSC) has introduced the next generation in seismic sensing technology. SSC s systems use a unique optical sensing
SmartSenseCom Introduces Next Generation Seismic Sensor Systems Summary: SmartSenseCom, Inc. (SSC) has introduced the next generation in seismic sensing technology. SSC s systems use a unique optical sensing
AGN 008 Vibration DESCRIPTION. Cummins Generator Technologies manufacture ac generators (alternators) to ensure compliance with BS 5000, Part 3.
 Application Guidance Notes: Technical Information from Cummins Generator Technologies AGN 008 Vibration DESCRIPTION Cummins Generator Technologies manufacture ac generators (alternators) to ensure compliance
Application Guidance Notes: Technical Information from Cummins Generator Technologies AGN 008 Vibration DESCRIPTION Cummins Generator Technologies manufacture ac generators (alternators) to ensure compliance
VIBROACOUSTIC MEASURMENT FOR BEARING FAULT DETECTION ON HIGH SPEED TRAINS
 VIBROACOUSTIC MEASURMENT FOR BEARING FAULT DETECTION ON HIGH SPEED TRAINS S. BELLAJ (1), A.POUZET (2), C.MELLET (3), R.VIONNET (4), D.CHAVANCE (5) (1) SNCF, Test Department, 21 Avenue du Président Salvador
VIBROACOUSTIC MEASURMENT FOR BEARING FAULT DETECTION ON HIGH SPEED TRAINS S. BELLAJ (1), A.POUZET (2), C.MELLET (3), R.VIONNET (4), D.CHAVANCE (5) (1) SNCF, Test Department, 21 Avenue du Président Salvador
Acceleration Enveloping Higher Sensitivity, Earlier Detection
 Acceleration Enveloping Higher Sensitivity, Earlier Detection Nathan Weller Senior Engineer GE Energy e-mail: nathan.weller@ps.ge.com Enveloping is a tool that can give more information about the life
Acceleration Enveloping Higher Sensitivity, Earlier Detection Nathan Weller Senior Engineer GE Energy e-mail: nathan.weller@ps.ge.com Enveloping is a tool that can give more information about the life
CHAPTER 7 FAULT DIAGNOSIS OF CENTRIFUGAL PUMP AND IMPLEMENTATION OF ACTIVELY TUNED DYNAMIC VIBRATION ABSORBER IN PIPING APPLICATION
 125 CHAPTER 7 FAULT DIAGNOSIS OF CENTRIFUGAL PUMP AND IMPLEMENTATION OF ACTIVELY TUNED DYNAMIC VIBRATION ABSORBER IN PIPING APPLICATION 7.1 INTRODUCTION Vibration due to defective parts in a pump can be
125 CHAPTER 7 FAULT DIAGNOSIS OF CENTRIFUGAL PUMP AND IMPLEMENTATION OF ACTIVELY TUNED DYNAMIC VIBRATION ABSORBER IN PIPING APPLICATION 7.1 INTRODUCTION Vibration due to defective parts in a pump can be
Processing the Teal South 4C-4D seismic survey
 Processing the Teal South 4C-4D seismic survey Carlos Rodriguez-Suarez, Robert R. Stewart and Han-Xing Lu Processing the Teal South 4C-4D ABSTRACT Repeated 4C-3D seismic surveys have been acquired over
Processing the Teal South 4C-4D seismic survey Carlos Rodriguez-Suarez, Robert R. Stewart and Han-Xing Lu Processing the Teal South 4C-4D ABSTRACT Repeated 4C-3D seismic surveys have been acquired over
Please refer to the figure on the following page which shows the relationship between sound fields.
 Defining Sound s Near The near field is the region close to a sound source usually defined as ¼ of the longest wave-length of the source. Near field noise levels are characterized by drastic fluctuations
Defining Sound s Near The near field is the region close to a sound source usually defined as ¼ of the longest wave-length of the source. Near field noise levels are characterized by drastic fluctuations
AERODYNAMIC NOISE RADIATED BY THE INTERCOACH SPACING AND THE BOGIE OF A HIGH-SPEED TRAIN
 Journal of Sound and
Journal of Sound and
Instantaneous Loop. Ideal Phase Locked Loop. Gain ICs
 Instantaneous Loop Ideal Phase Locked Loop Gain ICs PHASE COORDINATING An exciting breakthrough in phase tracking, phase coordinating, has been developed by Instantaneous Technologies. Instantaneous Technologies
Instantaneous Loop Ideal Phase Locked Loop Gain ICs PHASE COORDINATING An exciting breakthrough in phase tracking, phase coordinating, has been developed by Instantaneous Technologies. Instantaneous Technologies
FAULT DIAGNOSIS OF EXCESSIVE PIPE VIBRATION DUE TO BEATING PHENOMENON
 FAULT DIAGNOSIS OF EXCESSIVE PIPE VIBRATION DUE TO BEATING PHENOMENON Meng Hee Lim, Kar Hoou Hui, and Mohd Salman Leong Institute of Noise and Vibration Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Kuala Lumpur Jalan
FAULT DIAGNOSIS OF EXCESSIVE PIPE VIBRATION DUE TO BEATING PHENOMENON Meng Hee Lim, Kar Hoou Hui, and Mohd Salman Leong Institute of Noise and Vibration Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Kuala Lumpur Jalan
TitleApplication of MEMS accelerometer t. AIZAWA, Takao; KIMURA, Toshinori; M Toshifumi; TAKEDA, Tetsuya; ASANO,
 TitleApplication of MEMS accelerometer t Author(s) AIZAWA, Takao; KIMURA, Toshinori; M Toshifumi; TAKEDA, Tetsuya; ASANO, Citation International Journal of the JCRM ( Issue Date 2008-12 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/85166
TitleApplication of MEMS accelerometer t Author(s) AIZAWA, Takao; KIMURA, Toshinori; M Toshifumi; TAKEDA, Tetsuya; ASANO, Citation International Journal of the JCRM ( Issue Date 2008-12 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/85166
Breakthrough Usability for More Efficient Surveys, Higher Quality Data
 Geode DZ Distributed Seismic Acquisition System 3-D Data Acquisition Simplified And Streamlined Breakthrough Usability for More Efficient Surveys, Higher Quality Data Unlike other 3D seismic systems that
Geode DZ Distributed Seismic Acquisition System 3-D Data Acquisition Simplified And Streamlined Breakthrough Usability for More Efficient Surveys, Higher Quality Data Unlike other 3D seismic systems that
Noise Measurements Using a Teledyne LeCroy Oscilloscope
 Noise Measurements Using a Teledyne LeCroy Oscilloscope TECHNICAL BRIEF January 9, 2013 Summary Random noise arises from every electronic component comprising your circuits. The analysis of random electrical
Noise Measurements Using a Teledyne LeCroy Oscilloscope TECHNICAL BRIEF January 9, 2013 Summary Random noise arises from every electronic component comprising your circuits. The analysis of random electrical
Capacitive MEMS accelerometer for condition monitoring
 Capacitive MEMS accelerometer for condition monitoring Alessandra Di Pietro, Giuseppe Rotondo, Alessandro Faulisi. STMicroelectronics 1. Introduction Predictive maintenance (PdM) is a key component of
Capacitive MEMS accelerometer for condition monitoring Alessandra Di Pietro, Giuseppe Rotondo, Alessandro Faulisi. STMicroelectronics 1. Introduction Predictive maintenance (PdM) is a key component of
Natural Frequency Measurement
 Natural Frequency Measurement 'Frequently Asked Questions' F 1 What is the motivation for 'natural frequency testing'? There are different applications which make use of this kind of test: A: Checking
Natural Frequency Measurement 'Frequently Asked Questions' F 1 What is the motivation for 'natural frequency testing'? There are different applications which make use of this kind of test: A: Checking
Ground-roll attenuation based on SVD filtering Milton J. Porsani, CPGG, Michelngelo G. Silva, CPGG, Paulo E. M. Melo, CPGG and Bjorn Ursin, NTNU
 Ground-roll attenuation based on SVD filtering Milton J. Porsani, CPGG, Michelngelo G. Silva, CPGG, Paulo E. M. Melo, CPGG and Bjorn Ursin, NTNU SUMMARY We present a singular value decomposition (SVD)
Ground-roll attenuation based on SVD filtering Milton J. Porsani, CPGG, Michelngelo G. Silva, CPGG, Paulo E. M. Melo, CPGG and Bjorn Ursin, NTNU SUMMARY We present a singular value decomposition (SVD)
An Alternative to Pyrotechnic Testing For Shock Identification
 An Alternative to Pyrotechnic Testing For Shock Identification J. J. Titulaer B. R. Allen J. R. Maly CSA Engineering, Inc. 2565 Leghorn Street Mountain View, CA 94043 ABSTRACT The ability to produce a
An Alternative to Pyrotechnic Testing For Shock Identification J. J. Titulaer B. R. Allen J. R. Maly CSA Engineering, Inc. 2565 Leghorn Street Mountain View, CA 94043 ABSTRACT The ability to produce a
Industrial vibration sensor selection: Piezovelocity transducers
 Industrial vibration sensor selection: Piezovelocity transducers In many industrial monitoring applications, piezovelocity transducers have distinct advantages over piezoelectric accelerometers and traditional
Industrial vibration sensor selection: Piezovelocity transducers In many industrial monitoring applications, piezovelocity transducers have distinct advantages over piezoelectric accelerometers and traditional
