SVD filtering applied to ground-roll attenuation
|
|
|
- Richard Sharp
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 . SVD filtering applied to ground-roll attenuation Milton J. Porsani + Michelângelo G. Silva + Paulo E. M. Melo + and Bjorn Ursin + Centro de Pesquisa em Geofísica e Geologia (UFBA) and National Institute of Science and Technology of Petroleum Geophysics (CNPQ) Instituto de Geociências, Universidade Federal da Bahia. Campus Universitário da Federação Salvador, Bahia, Brasil. porsani@cpgg.ufba.br Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), Department of Petroleum Engineering and Applied Geophysics, S.P. Andersenvei 15A, NO-7491 Trondheim, Norway bjorn.ursin@ntnu.no 1
2 Abstract We present a singular value decomposition (SVD) filtering method for attenuation of the ground roll. Before the SVD computation, normal move-out (NMO) correction is applied to the seismograms, with the purpose of flattening the reflections. SVD is performed on a small number of traces in a sliding window. The output trace is the central trace of the first few eigenimages. These contains mostly horizontally aligned signals, and other noise in the data will be suppressed. By performing this action with the sliding window moving in steps of one trace, the number of output traces is equal to the number of input traces. The new method preserves the character and frequency content of the horizontal reflections and attenuates all other type of events. We illustrate the method using land seismic data of the Tacutu basin, located in the north-east part of Brazil. The results show that the proposed method is effective and is able to reveal reflections masked by the ground-roll. The new SVD filtering approach provides results of better quality, when compared with results obtained from the conventional f-k filtering method. 2
3 Introduction Ground roll is a particular type of Rayleigh wave and has high amplitude, low frequency, and low velocity, being the main type of coherent noise in land seismic surveys. Ground roll is also dispersive and normally overwhelms the desired reflected signal. Because of its dispersive nature, ground-roll masks at short offsets the shallow reflections, and at long offsets the deeper reflections (Claerbout, 1983; Saatçilar and Canitez, 1988; Henley, 2003). Many authors have shown that the ground roll can be attenuated by proper acquisition design and filtering (Harlan et al., 1984; Anstey, 1986; Shieh and Herrmann, 1990; Pritchett, 1991; Brown and Clapp, 2000). Such a strategy may either have logistical limitations or may not be applicable to data already acquired. One of the most simple filtering approaches used in the ground roll attenuation problem is f-k filtering, which is applied in the frequency spatial wavenumber domain. The f-k method uses 2-D Fourier transform (Embree et al., 1963; Wiggins, 1966) and the ground-roll, represented by linear events with low velocities, is mapped as lines in the f-k domain. It can consequently be filtered using a 2D band-pass filter. This has the disadvantage that it also eliminates reflected energy which contributes to the character of reflected events. Various methods to filter ground roll have been proposed in recent years. Deighan and Watts (1997) proposed the use of wavelets which does not assume that the signal is stationary. Liu (1999) and Montagne and Vasconcelos (2006) proposed the use of the Karhunen-Loève transform to estimate and subtract the ground roll from the common-shot gathers. SVD is a coherency-based technique that provides both signal enhancement and noise suppression. It has been implemented in a variety of seismic applications (Freire and Ulrych, 1988, Bekara and van der Baan, 2006). Kendall et al. (2005) proposed a SVD-polarization filter for ground roll attenuation on multicomponent data. Tyapkin et al. (2003) proposed to use the data alignment method of Liu 3
4 (1999) to make the coherent noise horizontally aligned in one or more time sections of a common shot gather. In each of the time sections the noise is represented by the first eigenimages (with a given fraction of the total energy). The remaining eigenimages represent the signal, and this part is transformed back to the original time-space domain. Chiu and Howell (2008) proposed a method that uses SVD to compute eigenimages that represent coherent noise in a localized time-space windows. The data in the local windows is transformed into analytic signal and followed by a complex SVD to decompose the analytic signal into eigenimages that represent the coherent noise model. Yarham et al. (2006) proposed a two stage method of identifying and removing ground roll using the curvelet transform. Karsli and Bayrak (2008) proposed to use a Wiener filter in the estimation of ground roll via a reference noise such as a linear or nonlinear sweep signal. Melo et al. (2009) presented a filtering method for ground-roll attenuation that uses a 2-D time-derivative filter. Bekara and van der Baan (2006) proposed a local SVD approach to noise removal. In each data window the signal is horizontally aligned in time, and after SVD only the first eigenimage is retained. Then the procedure is repeated in the next data window using sliding windows with 50% overlap. Here we proposed a new approach to local SVD noise removal. In each data window (consisting of an odd number of traces) the signal is aligned in time. After SVD only the middle trace of the first one or two eigenimages is retained. Then the data window is moved one trace position and the procedure is repeated. This preserves the amplitude and character of horizontal events and attenuates all other events. We illustrate the method using land seismic data from the Tacutu basin (located in the north-est part of Brazil) acquired by PETROBRAS in 1981 (Eiras and Kinoshita, 1990). The results are compared with f-k filtering. 4
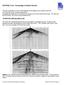
5 SVD Filtering We consider a seismic data set d(t, x n ), t = 1,..., N t, n = 1,..., N x where the primary reflections have been corrected for NMO so that they are horizontally aligned in the x-direction. A windowed data set of 2M + 1 traces centered at x n is given by the matrix D n with components Dtj n = d(t, x n+j ), t = 1,..., N t, j = M,..., 0,..., M. It can be represented by the reduced SVD (Golub & van Loan, 1996): D n = 2M+1 k=1 σ k u k v T k (1) where the left singular vectors u k are orthogonal and the right singular vector v k also are orthogonal. The singular values are sorted such that σ 1 σ 2... σ 2M+1 0. In component form the SVD is D n tj = d(t, x n+j ) = 2M+1 k=1 with t = 1,..., N t and j = M,..., M. σ k u k (t)v k (j) (2) In the filtered output data set only the first K eigenimages or the center trace is being used. That is, the output is d(t, x n ) = K σ k u k (t)v k (0) (3) k=1 The procedure is started at n = M + 1 where the filtered output is the K eigenimages of the first M + 1 traces: 5
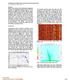
6 K d(t, x M+1+j ) = σ k u k (t)v k (j), j = M,..., 0. (4) k=1 Them n is increase by one and equation (3) is used until n = N x M where the output data are given by the K first eigenimages of the last M + 1 traces. That is d(t, x Nx M+j) = K σ k u k (t)v k (j), j = 0,..., M (5) k=1 The sliding window scheme is shown in Figure 1 for a window of 5 traces (M = 2). The result is a filtered data set d(t, x n ) of the same dimension as the input data set where energy which is not coherent in the x-direction has been attenuated. Both the character and amplitude of the horizontal events are well preserved as they are represented by the first eigenimages which have the largest energy. Data Results The proposed method of SVD filtering was tested on the RL-5090 land seismic line. It contains 179 shots recorded at 4 ms sampling interval. There are 96 channels per shot in a split-spread geometry with offsets m and 50 m between the geophones. The distance between the shots is 200 m giving a low CMP coverage of 12 fold. The data processing was very basic. First a standard processing sequence was applied: geometry, edit, preliminary spherical divergence correction, standard velocity analysis and NMO correction. Due to the limited CMP coverage, the 6
7 data were then resorted into shot gathers before the SVD filtering was applied. In the filtering process we used a 5-trace window (M=2 in equation (1)) for the SVD analysis, and we kept the two most significant central eigentraces (K=2 in equation (3)). The results were compared to a classical f-k filter method where all non-horizontal events were filtered out. Fig. 2a shows a shot gather after NMO-correction. The results after f-k filtering and SVD filtering are shown in Fig. 2b and 2c, respectively. The ground roll is very well filtered in both cases, and the horizontal events which are associated with the reflections of interest are preserved. However, the SVD filtered data exhibit less smear and have more lateral character than the f-k filtered data. In order to compare f-k spectra of the three shot gathers, they were muted, as shown in Fig. 3. The corresponding f-k spectra in Fig. 4 show the severe cut-off characteristic of the f-k filter. The spectra of the f-k filtered ground roll are shown in Fig. 5. From the two last figures one can see that the f-k filter separates the input data in two separate regions of the f-k domain (as expected). The SVD filter has a less dramatic effect, leaving estimated signal in the larger wave-number domain, and it reduces noise also in the low wave-number domain. The three shot-point gathers in Fig. 2 are shown in Fig. 6 after the removal of NMO correction. The effect of f-k filtering and SVD filtering are similar as seen in the NMO corrected gathers. The SVD filter seems to have removed noise in a better way than the f-k filter, preserving the character of the data. The two filtering procedures were applied to the complete NMO corrected data set before stacking. Details from the resulting stacked sections are shown in Fig. 7. Both f-k filtering and SVD filtering have reduced the noise. And again, the SVD filtered section has less smear and more character than the f-k filtered section. 7
8 Conclusions We have developed a new and efficient SVD filter method which enhances horizontal events on seismic sections. The SVD filter process preserves the character and frequency content of the horizontal reflections and attenuate all other types of events. The method was successfully applied to ground roll attenuation on a land seismic data set. In particular, ground roll was virtually absent from the filtered pre-stack gathers. f-k filtering of the same data set also removed the ground roll, but it resulted in loss of lateral variation in the data. Acknowledgements The authors wish to express their gratitude to FINEP, FAPESB and CNPq, Brazil, for financial support. We also thanks PARADIGM, LANDMARK, SEISMIC-MICRO TECHNOLOGY and Schulumberger for the licenses granted to CPGG-UFBA. Bjorn Ursin has received financial support from the VISTA project and from the Norwegian Research Council through the ROSE project. 8
9 References Anstey, N Whatever happened to ground-roll?. The Leading Edge, 5, Bekara, M. and Baan, M. V, 2007, Local singular value decomposition for signal enhancement of seismic data: Geophysics, 72, V59-V65. Brown, M., and R. G. Clapp, 2000, (T-x) domain, pattern-based ground-roll removal: 70th Ann. Internat. Mtg., Soc. Expl. Geophys., Expanded Abstracts, Chiu, S. K. and Howell, J. E., 2008, Attenuation of coherent noise using localizedadaptive eigenimage filter: 78th Ann. Internat. Mtg., Soc. Expl. Geophys., Expanded Abstracts, Claerbout, J. F Ground roll and radial traces: Stanford Exploration Project Report, SEP-35, Eiras, J. F. and Kinoshita, E. M., 1990, Geologia e perspectivas petrolíferas da Bacia do Tacutu, Origem e Evolução das Bacias Sedimentares: PETROBRAS, Anais, Embree, P., Burg, J. P. e Backus, M. M., 1963, Wide-band velocity filtering - the pie-slice process: Geophysics, 28, Deighan, A. J. and Watts, D. R., 1997, Ground-roll suppression using the wavelet transform: Geophysics 62, Freire, S. L. M., and T. J. Ulrych, 1988, Application of singular value decomposition to vertical seismic profiling: Geophysics, 53, Golub, G. H., and C. F. V. Loan, 1996, Matrix computations: Johns Hopkins University Press. 9
10 Harlan, W. S., Claerbout J. F. and Rocca F., 1984, Signal/noise separation and velocity estimation: Geophysics, 49, Henley, D. C., 2003, Coherent noise attenuation in the radial trace domain: Geophysics, 68, Karsli, H. and Bayrak, Y., 2008, Ground-roll attenuation based on Wiener filtering and benefits of time-frequency imaging: The Leading Edge, 27, Kendall R., Jin, S., Ronen, S., 2005, An SVD-polarization filter for ground roll attenuation on multicomponent data: 77th Ann. Internat. Mtg., Soc. Expl. Geophys., Expanded Abstracts, Liu, X, 1999, Ground roll suppression using the Karhunen-Loeve transform: Geophysics 64, Melo, P. E. M., Porsani, M. J. and Silva, M. G, 2009, Ground roll attenuation using a 2D time derivative filter: Geophysical Prospecting. Received May 2007, revision accepted July Montagne, R., and Vasconcelos, G. L., 2006, Optimized suppression of coherent noise from seismic data using the karhunen-loève transform: Physical Review E., 74, 1-9. Pritchett, W., 1991, System design for better seismic data: The Leading Edge, 11, Saatçilar, R. and Canitez, N., 1988, A method of ground-roll elimination: Geophysics 53, Shieh, C. and Herrmann, R. B., 1990, Ground roll: Rejection using polarization filters: Geophysics, 55, Tyapkin, Y. K., Marmalyevskyy, N. Y. and Gornyak, Z. V., 2003, Sourcegenerated noise attenuation using the singular value decomposition: 75th Ann. 10
11 Internat. Mtg. Soc. Expl. Geophys., Expanded Abstracts. Wiggins, R. A., 1966, W-K Filter design: Geophysical Prospecting, 14, Yarham, C., Boeniger, U. and Herrmann, F., 2006, Curvelet-based ground roll removal: 76th Ann. Internat. Mtg., Soc. Expl. Geophys., Expanded Abstracts,
12 Figures FIG. 1. Sliding window SVD filtering scheme. FIG. 2. Comparison of SVD filtering with f-k filtering. (a) input data, (b) output after f-k filtering, (c) output after SVD filtering. FIG. 3. Muted seismograms preserving the ground-roll area. (a) muted input data, (b) after f-k filtering, (c) after SVD filtering. FIG. 4. f-k spectrum of the muted original and filtered seismograms shown in Fig. 3. (a) input data, (b) f-k filtering, (c) SVD filtering. FIG. 5. f-k spectrum of the filtered ground-roll. (a) after f-k filtering and (b) after SVD filtering. FIG. 6. Comparison of SVD filtering with f-k filtering after inverse NMO correction. (a) input data, (b) output after f-k filtering, (c) output after SVD filtering. FIG. 7. Details from the stacked sections: (a) original data (b) f-k filtered data, (c) SVD filtered data. 12
13 Figure 1: Sliding window SVD filtering scheme. 13
14 Traces Traces Traces Time(s) (a) 4.0 (b) 4.0 (c) Figure 2: Comparison of SVD filtering with f-k filtering. (a) input data, (b) output after f-k filtering, (c) output after SVD filtering. 14
15 Traces Traces Traces Time(s) (a) 4.0 (b) 4.0 (c) Figure 3: Muted seismograms preserving the ground-roll area. (a) muted input data, (b) after f-k filtering, (c) after SVD filtering. 15
16 16 Figure 4: f-k spectrum of the muted original and filtered seismograms shown in Fig. 3. (a) input data, (b) f-k filtering, (c) SVD filtering.
17 17 Figure 5: f-k spectrum of the filtered ground-roll. (a) after f-k filtering and (b) after SVD filtering.
18 Traces Traces Traces Time(s) (a) 4.0 (b) 4.0 (c) Figure 6: Comparison of SVD filtering with f-k filtering after inverse NMO correction. (a) input data, (b) output after f-k filtering, (c) output after SVD filtering. 18
19 Distance (Km) Time(s) (a) Distance (Km) Time(s) (b) Distance (Km) Time(s)
Ground-roll attenuation based on SVD filtering Milton J. Porsani, CPGG, Michelngelo G. Silva, CPGG, Paulo E. M. Melo, CPGG and Bjorn Ursin, NTNU
 Ground-roll attenuation based on SVD filtering Milton J. Porsani, CPGG, Michelngelo G. Silva, CPGG, Paulo E. M. Melo, CPGG and Bjorn Ursin, NTNU SUMMARY We present a singular value decomposition (SVD)
Ground-roll attenuation based on SVD filtering Milton J. Porsani, CPGG, Michelngelo G. Silva, CPGG, Paulo E. M. Melo, CPGG and Bjorn Ursin, NTNU SUMMARY We present a singular value decomposition (SVD)
Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise
 Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise Stephen Chiu* ConocoPhillips, Houston, TX, United States stephen.k.chiu@conocophillips.com and Norman Whitmore
Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise Stephen Chiu* ConocoPhillips, Houston, TX, United States stephen.k.chiu@conocophillips.com and Norman Whitmore
Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing Dispersive Ground Roll Noise from Onshore Seismic Data
 Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
Radial trace filtering revisited: current practice and enhancements
 Radial trace filtering revisited: current practice and enhancements David C. Henley Radial traces revisited ABSTRACT Filtering seismic data in the radial trace (R-T) domain is an effective technique for
Radial trace filtering revisited: current practice and enhancements David C. Henley Radial traces revisited ABSTRACT Filtering seismic data in the radial trace (R-T) domain is an effective technique for
Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data
 Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data Patrick Butler, GEDCO, Calgary, Alberta, Canada pbutler@gedco.com Summary A module for removing and replacing strong noise in seismic data is presented.
Strong Noise Removal and Replacement on Seismic Data Patrick Butler, GEDCO, Calgary, Alberta, Canada pbutler@gedco.com Summary A module for removing and replacing strong noise in seismic data is presented.
GROUND ROLL ATTENUATION USING SHAPING FILTERS AND BAND LIMITED SWEEP SIGNALS
 Revista Brasileira de Geofísica (212) 3(4): 545-554 212 Sociedade Brasileira de Geofísica ISSN 12-261X www.scielo.br/rbg GROUND ROLL ATTENUATION USING SHAPING FILTERS AND BAND LIMITED SWEEP SIGNALS Quézia
Revista Brasileira de Geofísica (212) 3(4): 545-554 212 Sociedade Brasileira de Geofísica ISSN 12-261X www.scielo.br/rbg GROUND ROLL ATTENUATION USING SHAPING FILTERS AND BAND LIMITED SWEEP SIGNALS Quézia
Attenuation of high energy marine towed-streamer noise Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco
 Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Ground-roll noise attenuation using a simple and effective approach based on local bandlimited orthogonalization a
 Ground-roll noise attenuation using a simple and effective approach based on local bandlimited orthogonalization a a Published in IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 12, no. 11, 2316-2320 (2015)
Ground-roll noise attenuation using a simple and effective approach based on local bandlimited orthogonalization a a Published in IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 12, no. 11, 2316-2320 (2015)
Seismic processing workflow for supressing coherent noise while retaining low-frequency signal
 Seismic processing for coherent noise suppression Seismic processing workflow for supressing coherent noise while retaining low-frequency signal Patricia E. Gavotti and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT Two different
Seismic processing for coherent noise suppression Seismic processing workflow for supressing coherent noise while retaining low-frequency signal Patricia E. Gavotti and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT Two different
Ocean-bottom hydrophone and geophone coupling
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages 57 70 Ocean-bottom hydrophone and geophone coupling Daniel A. Rosales and Antoine Guitton 1 ABSTRACT We compare two methods for combining hydrophone
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages 57 70 Ocean-bottom hydrophone and geophone coupling Daniel A. Rosales and Antoine Guitton 1 ABSTRACT We compare two methods for combining hydrophone
Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas
 Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas Summary The reliability of seismic attribute estimation depends on reliable signal.
Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas Summary The reliability of seismic attribute estimation depends on reliable signal.
Seismic Reflection Method
 1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 103, April 27, 2000, pages
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 103, April 27, 2000, pages 205 231 204 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 103, April 27, 2000, pages 205 231 Ground roll and the Radial Trace Transform revisited
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 103, April 27, 2000, pages 205 231 204 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 103, April 27, 2000, pages 205 231 Ground roll and the Radial Trace Transform revisited
Random and coherent noise attenuation by empirical mode decomposition Maïza Bekara, PGS, and Mirko van der Baan, University of Leeds
 Random and coherent noise attenuation by empirical mode decomposition Maïza Bekara, PGS, and Mirko van der Baan, University of Leeds SUMMARY This paper proposes a new filtering technique for random and
Random and coherent noise attenuation by empirical mode decomposition Maïza Bekara, PGS, and Mirko van der Baan, University of Leeds SUMMARY This paper proposes a new filtering technique for random and
Random noise attenuation using f-x regularized nonstationary autoregression a
 Random noise attenuation using f-x regularized nonstationary autoregression a a Published in Geophysics, 77, no. 2, V61-V69, (2012) Guochang Liu 1, Xiaohong Chen 1, Jing Du 2, Kailong Wu 1 ABSTRACT We
Random noise attenuation using f-x regularized nonstationary autoregression a a Published in Geophysics, 77, no. 2, V61-V69, (2012) Guochang Liu 1, Xiaohong Chen 1, Jing Du 2, Kailong Wu 1 ABSTRACT We
A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data
 A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data Yessika Blunda*, Pinnacle, Halliburton, Houston, Tx, US yessika.blunda@pinntech.com and Kit Chambers, Pinnacle, Halliburton, St Agnes, Cornwall,
A generic procedure for noise suppression in microseismic data Yessika Blunda*, Pinnacle, Halliburton, Houston, Tx, US yessika.blunda@pinntech.com and Kit Chambers, Pinnacle, Halliburton, St Agnes, Cornwall,
Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Group Array Stack of single sensor data
 P-113 Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Artatran Ojha *, K. Ramakrishna, G. Sarvesam Geophysical Services, ONGC, Chennai Summary Shot generated noise and the cultural noise is a major problem in
P-113 Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Artatran Ojha *, K. Ramakrishna, G. Sarvesam Geophysical Services, ONGC, Chennai Summary Shot generated noise and the cultural noise is a major problem in
Multiple Attenuation - A Case Study
 Multiple Attenuation - A Case Study M.Das, Maharaj Singh, M.Muruganandan* & Dr.D.V.R. Murti RCC, GPS, A&AA Basin, ONGC Jorhat Summary Multiple attenuation is a long standing problem in reflection seismic
Multiple Attenuation - A Case Study M.Das, Maharaj Singh, M.Muruganandan* & Dr.D.V.R. Murti RCC, GPS, A&AA Basin, ONGC Jorhat Summary Multiple attenuation is a long standing problem in reflection seismic
Joint Time/Frequency Analysis, Q Quality factor and Dispersion computation using Gabor-Morlet wavelets or Gabor-Morlet transform
 Joint Time/Frequency, Computation of Q, Dr. M. Turhan (Tury Taner, Rock Solid Images Page: 1 Joint Time/Frequency Analysis, Q Quality factor and Dispersion computation using Gabor-Morlet wavelets or Gabor-Morlet
Joint Time/Frequency, Computation of Q, Dr. M. Turhan (Tury Taner, Rock Solid Images Page: 1 Joint Time/Frequency Analysis, Q Quality factor and Dispersion computation using Gabor-Morlet wavelets or Gabor-Morlet
Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo
 Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo Summary A survey with a novel acquisition technique was acquired
Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo Summary A survey with a novel acquisition technique was acquired
AUTOMATIC FIRST BREAKS PICKING USING LINEAR MOVEOUT CORRECTION AND COMPLEX SEISMIC TRACES
 Revista Brasileira de Geofísica (2016) 34(3): 319-326 2016 Sociedade Brasileira de Geofísica ISSN 0102-261X www.scielo.br/rbg AUTOMATIC FIRST BREAKS PICKING USING LINEAR MOVEOUT CORRECTION AND COMPLEX
Revista Brasileira de Geofísica (2016) 34(3): 319-326 2016 Sociedade Brasileira de Geofísica ISSN 0102-261X www.scielo.br/rbg AUTOMATIC FIRST BREAKS PICKING USING LINEAR MOVEOUT CORRECTION AND COMPLEX
Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data
 Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Stan J. Gorek, Robert R. Stewart, and Mark P. Harrison ABSTRACT During early July, 1995, a large
Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Processing the Blackfoot broad-band 3-C seismic data Stan J. Gorek, Robert R. Stewart, and Mark P. Harrison ABSTRACT During early July, 1995, a large
Applied Methods MASW Method
 Applied Methods MASW Method Schematic illustrating a typical MASW Survey Setup INTRODUCTION: MASW a seismic method for near-surface (< 30 m) Characterization of shear-wave velocity (Vs) (secondary or transversal
Applied Methods MASW Method Schematic illustrating a typical MASW Survey Setup INTRODUCTION: MASW a seismic method for near-surface (< 30 m) Characterization of shear-wave velocity (Vs) (secondary or transversal
FINAL REPORT EL# RS. C. A. Hurich & MUN Seismic Team Earth Sciences Dept. Memorial University Sept. 2009
 FINAL REPORT EL# 09-101-01-RS MUNSIST Seismic Source Test - Five Mile Road C. A. Hurich & MUN Seismic Team Earth Sciences Dept. Memorial University Sept. 2009 1 EL# 09-101-01-RS Five-Mile Road Memorial
FINAL REPORT EL# 09-101-01-RS MUNSIST Seismic Source Test - Five Mile Road C. A. Hurich & MUN Seismic Team Earth Sciences Dept. Memorial University Sept. 2009 1 EL# 09-101-01-RS Five-Mile Road Memorial
Th ELI1 08 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data
 Th ELI1 8 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data P. Edme* (Schlumberger Gould Research), E. Muyzert (Sclumberger Gould Research) & E. Kragh (Schlumberger Gould Research) SUMMARY
Th ELI1 8 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data P. Edme* (Schlumberger Gould Research), E. Muyzert (Sclumberger Gould Research) & E. Kragh (Schlumberger Gould Research) SUMMARY
Processing the Teal South 4C-4D seismic survey
 Processing the Teal South 4C-4D seismic survey Carlos Rodriguez-Suarez, Robert R. Stewart and Han-Xing Lu Processing the Teal South 4C-4D ABSTRACT Repeated 4C-3D seismic surveys have been acquired over
Processing the Teal South 4C-4D seismic survey Carlos Rodriguez-Suarez, Robert R. Stewart and Han-Xing Lu Processing the Teal South 4C-4D ABSTRACT Repeated 4C-3D seismic surveys have been acquired over
Enhanced low frequency signal processing for sub-basalt imaging N. Woodburn*, A. Hardwick and T. Travis, TGS
 Enhanced low frequency signal processing for sub-basalt imaging N. Woodburn*, A. Hardwick and T. Travis, TGS Summary Sub-basalt imaging continues to provide a challenge along the northwest European Atlantic
Enhanced low frequency signal processing for sub-basalt imaging N. Woodburn*, A. Hardwick and T. Travis, TGS Summary Sub-basalt imaging continues to provide a challenge along the northwest European Atlantic
Seismic application of quality factor estimation using the peak frequency method and sparse time-frequency transforms
 Seismic application of quality factor estimation using the peak frequency method and sparse time-frequency transforms Jean Baptiste Tary 1, Mirko van der Baan 1, and Roberto Henry Herrera 1 1 Department
Seismic application of quality factor estimation using the peak frequency method and sparse time-frequency transforms Jean Baptiste Tary 1, Mirko van der Baan 1, and Roberto Henry Herrera 1 1 Department
Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
Attacking localized high amplitude noise in seismic data A method for AVO compliant noise attenuation
 Attacking localized high amplitude noise in seismic data A method for AVO compliant noise attenuation Xinxiang Li and Rodney Couzens Sensor Geophysical Ltd. Summary The method of time-frequency adaptive
Attacking localized high amplitude noise in seismic data A method for AVO compliant noise attenuation Xinxiang Li and Rodney Couzens Sensor Geophysical Ltd. Summary The method of time-frequency adaptive
SPNA 2.3. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2177
 SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
CDP noise attenuation using local linear models
 CDP noise attenuation CDP noise attenuation using local linear models Todor I. Todorov and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Seismic noise attenuation plays an important part in a seismic processing flow. Spatial
CDP noise attenuation CDP noise attenuation using local linear models Todor I. Todorov and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Seismic noise attenuation plays an important part in a seismic processing flow. Spatial
Multicomponent seismic polarization analysis
 Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
P and S wave separation at a liquid-solid interface
 and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface Maria. Donati and Robert R. tewart ABTRACT and seismic waves impinging on a liquid-solid interface give rise
and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface Maria. Donati and Robert R. tewart ABTRACT and seismic waves impinging on a liquid-solid interface give rise
GROUND_ROLL ATTENUATION IN THE RADIAL TRACE DOMAIN
 GROUND_ROLL ATTENUATION IN THE RADIAL TRACE DOMAIN Bagheri, M. -, Dr.Riahi, M.A. -, Khaxar, Z.O. -, Hosseini, M -, Mohseni.D, R -. Adress: - Institute of Geophysics, University of Tehran Kargar Shomali
GROUND_ROLL ATTENUATION IN THE RADIAL TRACE DOMAIN Bagheri, M. -, Dr.Riahi, M.A. -, Khaxar, Z.O. -, Hosseini, M -, Mohseni.D, R -. Adress: - Institute of Geophysics, University of Tehran Kargar Shomali
How to Attenuate Diffracted Noise: (DSCAN) A New Methodology
 How to Attenuate Diffracted Noise: (DSCAN) A New Methodology Ali Karagul* CGG Canada Service Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada akaragul@cgg.com Todd Mojesky and XinXiang Li CGG Canada Service Ltd., Calgary,
How to Attenuate Diffracted Noise: (DSCAN) A New Methodology Ali Karagul* CGG Canada Service Ltd., Calgary, Alberta, Canada akaragul@cgg.com Todd Mojesky and XinXiang Li CGG Canada Service Ltd., Calgary,
Enhanced random noise removal by inversion
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 84, May 9, 2001, pages 1 344 Enhanced random noise removal by inversion Ray Abma 1 ABSTRACT Noise attenuation by prediction filtering breaks down in the presence of
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 84, May 9, 2001, pages 1 344 Enhanced random noise removal by inversion Ray Abma 1 ABSTRACT Noise attenuation by prediction filtering breaks down in the presence of
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG)
 Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
2012 SEG SEG Las Vegas 2012 Annual Meeting Page 1
 Full-wavefield, towed-marine seismic acquisition and applications David Halliday, Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Johan O. A. Robertsson, ETH Zürich, Ivan Vasconcelos, Schlumberger Cambridge Research,
Full-wavefield, towed-marine seismic acquisition and applications David Halliday, Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Johan O. A. Robertsson, ETH Zürich, Ivan Vasconcelos, Schlumberger Cambridge Research,
P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method
 P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method E. Baniasadi* (University of Tehran), M. A. Riahi (University of Tehran) & S. Chaychizadeh (University of Tehran)
P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method E. Baniasadi* (University of Tehran), M. A. Riahi (University of Tehran) & S. Chaychizadeh (University of Tehran)
Application of Coherent Noise Attenuation to 4-C Ocean Bottom Cable Seismic Data from the Niger Delta.
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(10): 4985-4994, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 Application of Coherent Noise Attenuation to 4-C Ocean Bottom Cable Seismic Data from the Niger Delta. 1 D.O. Ogagarue,
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(10): 4985-4994, 2010 ISSN 1991-8178 Application of Coherent Noise Attenuation to 4-C Ocean Bottom Cable Seismic Data from the Niger Delta. 1 D.O. Ogagarue,
Seismic reflection method
 Seismic reflection method Seismic reflection method is based on the reflections of seismic waves occurring at the contacts of subsurface structures. We apply some seismic source at different points of
Seismic reflection method Seismic reflection method is based on the reflections of seismic waves occurring at the contacts of subsurface structures. We apply some seismic source at different points of
Deblending workflow. Summary
 Guillaume Henin*, Didier Marin, Shivaji Maitra, Anne Rollet (CGG), Sandeep Kumar Chandola, Subodh Kumar, Nabil El Kady, Low Cheng Foo (PETRONAS Carigali Sdn. Bhd.) Summary In ocean-bottom cable (OBC) acquisitions,
Guillaume Henin*, Didier Marin, Shivaji Maitra, Anne Rollet (CGG), Sandeep Kumar Chandola, Subodh Kumar, Nabil El Kady, Low Cheng Foo (PETRONAS Carigali Sdn. Bhd.) Summary In ocean-bottom cable (OBC) acquisitions,
T17 Reliable Decon Operators for Noisy Land Data
 T17 Reliable Decon Operators for Noisy Land Data N. Gulunay* (CGGVeritas), N. Benjamin (CGGVeritas) & A. Khalil (CGGVeritas) SUMMARY Interbed multiples for noisy land data that survives the stacking process
T17 Reliable Decon Operators for Noisy Land Data N. Gulunay* (CGGVeritas), N. Benjamin (CGGVeritas) & A. Khalil (CGGVeritas) SUMMARY Interbed multiples for noisy land data that survives the stacking process
Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain
 Predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Marco A. Perez and David C. Henley ABSTRACT Predictive deconvolution has been predominantly
Predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Marco A. Perez and David C. Henley ABSTRACT Predictive deconvolution has been predominantly
Air blast attenuation by combining microphone and geophone signals in the time-frequency domain
 Air blast attenuation in data processing Air blast attenuation by combining microphone and geophone signals in the time-frequency domain Alejandro D. Alcudia and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT Microphone data
Air blast attenuation in data processing Air blast attenuation by combining microphone and geophone signals in the time-frequency domain Alejandro D. Alcudia and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT Microphone data
Downloaded 09/04/18 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion
 Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion Heather J.E. Lloyd*, CREWES / University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta hjelloyd@ucalgary.ca and Gary F. Margrave, CREWES
Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion Heather J.E. Lloyd*, CREWES / University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta hjelloyd@ucalgary.ca and Gary F. Margrave, CREWES
AVO processing of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake heavy oilfield, Saskatchewan
 AVO processing of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake heavy oilfield, Saskatchewan Zimin Zhang, Robert R. Stewart, and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT The AVO processing and analysis of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake
AVO processing of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake heavy oilfield, Saskatchewan Zimin Zhang, Robert R. Stewart, and Don C. Lawton ABSTRACT The AVO processing and analysis of walkaway VSP data at Ross Lake
Microquake seismic interferometry with SV D enhanced Green s function recovery
 Microquake seismic interferometry with SV D enhanced Green s function recovery Gabriela Melo and A lison Malcolm Earth Resources Laboratory - Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department Massachusetts
Microquake seismic interferometry with SV D enhanced Green s function recovery Gabriela Melo and A lison Malcolm Earth Resources Laboratory - Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Department Massachusetts
How to Check the Quality of your Seismic Data Conditioning in Hampson-Russell Software. HRS9 Houston, Texas 2011
 How to Check the Quality of your Seismic Data Conditioning in Hampson-Russell Software HRS9 Houston, Texas 2011 QC Data Conditioning This document guides you through the quality control check process used
How to Check the Quality of your Seismic Data Conditioning in Hampson-Russell Software HRS9 Houston, Texas 2011 QC Data Conditioning This document guides you through the quality control check process used
Coherent noise attenuation: A synthetic and field example
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 108, April 29, 2001, pages 1?? Coherent noise attenuation: A synthetic and field example Antoine Guitton 1 ABSTRACT Noise attenuation using either a filtering or a
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 108, April 29, 2001, pages 1?? Coherent noise attenuation: A synthetic and field example Antoine Guitton 1 ABSTRACT Noise attenuation using either a filtering or a
Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS
 Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS Summary In land AVO processing, near-surface heterogeneity issues are
Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS Summary In land AVO processing, near-surface heterogeneity issues are
Broad-bandwidth data processing of shallow marine conventional streamer data: A case study from Tapti Daman Area, Western Offshore Basin India
 : A case study from Tapti Daman Area, Western Offshore Basin India Subhankar Basu*, Premanshu Nandi, Debasish Chatterjee;ONGC Ltd., India subhankar_basu@ongc.co.in Keywords Broadband, De-ghosting, Notch
: A case study from Tapti Daman Area, Western Offshore Basin India Subhankar Basu*, Premanshu Nandi, Debasish Chatterjee;ONGC Ltd., India subhankar_basu@ongc.co.in Keywords Broadband, De-ghosting, Notch
New technologies in marine seismic surveying: Overview and physical modelling experiments
 New technologies in marine seismic surveying: Overview and physical modelling experiments Eric V. Gallant, Robert R. Stewart, Don C. Lawton, Malcolm B. Bertram, and Carlos Rodriguez ABSTRACT New marine
New technologies in marine seismic surveying: Overview and physical modelling experiments Eric V. Gallant, Robert R. Stewart, Don C. Lawton, Malcolm B. Bertram, and Carlos Rodriguez ABSTRACT New marine
Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results
 Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results David C. Henley and Han-Xing Lu PNG processing ABSTRACT Papua New Guinea is among the most notoriously difficult areas in the world in
Hunting reflections in Papua New Guinea: early processing results David C. Henley and Han-Xing Lu PNG processing ABSTRACT Papua New Guinea is among the most notoriously difficult areas in the world in
Desinging of 3D Seismic Survey And Data Processing of Abu Amood Oil Field Southern of Iraq
 Desinging of 3D Seismic Survey And Data Processing of Abu Amood Oil Field Southern of Iraq Salman Z. Khorshid, Ahmed I. Khaleel Dept.Geology, College of Science, Univercity of Baghdad Abstract 3D seismic
Desinging of 3D Seismic Survey And Data Processing of Abu Amood Oil Field Southern of Iraq Salman Z. Khorshid, Ahmed I. Khaleel Dept.Geology, College of Science, Univercity of Baghdad Abstract 3D seismic
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution
 Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical
 A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical Summary Here we present a method of robust seismic data deghosting for
A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical Summary Here we present a method of robust seismic data deghosting for
Low wavenumber reflectors
 Low wavenumber reflectors Low wavenumber reflectors John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT A numerical modelling environment was created to accurately evaluate reflections from a D interface that has a smooth transition
Low wavenumber reflectors Low wavenumber reflectors John C. Bancroft ABSTRACT A numerical modelling environment was created to accurately evaluate reflections from a D interface that has a smooth transition
Th-P08-11 Deblending of Single Source Vibroseis Land Data in Egypt with V1 Noise Attenuation Algorithm
 Th-P08-11 Deblending of Single Source Vibroseis Land Data in Egypt with V1 Noise Attenuation Algorithm N. Gulunay* (CGG), E. Shaker (CGG), A. Karagul (CGG), A. Ramadan (CGG), T. Bianchi (CGG), J. Ross
Th-P08-11 Deblending of Single Source Vibroseis Land Data in Egypt with V1 Noise Attenuation Algorithm N. Gulunay* (CGG), E. Shaker (CGG), A. Karagul (CGG), A. Ramadan (CGG), T. Bianchi (CGG), J. Ross
Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion
 P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
Comparison of Q-estimation methods: an update
 Q-estimation Comparison of Q-estimation methods: an update Peng Cheng and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT In this article, three methods of Q estimation are compared: a complex spectral ratio method, the centroid
Q-estimation Comparison of Q-estimation methods: an update Peng Cheng and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT In this article, three methods of Q estimation are compared: a complex spectral ratio method, the centroid
INTRODUCTION TO ONSHORE SEISMIC ACQUISITION AND PROCESSING
 INTRODUCTION TO ONSHORE SEISMIC ACQUISITION AND PROCESSING SEPTEMBER 2017 1 SIMPLIFIED DIAGRAM OF SPLIT SPREAD REFLECTION SEISMIC DATA ACQUISITION RECORDING TRUCK ENERGY SOURCE SHOTPOINTS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
INTRODUCTION TO ONSHORE SEISMIC ACQUISITION AND PROCESSING SEPTEMBER 2017 1 SIMPLIFIED DIAGRAM OF SPLIT SPREAD REFLECTION SEISMIC DATA ACQUISITION RECORDING TRUCK ENERGY SOURCE SHOTPOINTS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Tu LHR1 07 MT Noise Suppression for Marine CSEM Data
 Tu LHR1 7 MT Noise Suppression for Marine CSEM Data K.R. Hansen* (EMGS ASA), V. Markhus (EMGS ASA) & R. Mittet (EMGS ASA) SUMMARY We present a simple and effective method for suppression of MT noise in
Tu LHR1 7 MT Noise Suppression for Marine CSEM Data K.R. Hansen* (EMGS ASA), V. Markhus (EMGS ASA) & R. Mittet (EMGS ASA) SUMMARY We present a simple and effective method for suppression of MT noise in
There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to
 Coordinated by JEFF DEERE JOHN GIBSON, FOREST LIN, ALEXANDRE EGRETEAU, and JULIEN MEUNIER, CGGVeritas MALCOLM LANSLEY, Sercel There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to improve the quality
Coordinated by JEFF DEERE JOHN GIBSON, FOREST LIN, ALEXANDRE EGRETEAU, and JULIEN MEUNIER, CGGVeritas MALCOLM LANSLEY, Sercel There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to improve the quality
Using long sweep in land vibroseis acquisition
 Using long sweep in land vibroseis acquisition Authors: Alexandre Egreteau, John Gibson, Forest Lin and Julien Meunier (CGGVeritas) Main objectives: Promote the use of long sweeps to compensate for the
Using long sweep in land vibroseis acquisition Authors: Alexandre Egreteau, John Gibson, Forest Lin and Julien Meunier (CGGVeritas) Main objectives: Promote the use of long sweeps to compensate for the
Summary. Volumetric Q tomography on offshore Brunei dataset
 Success of high-resolution volumetric Q-tomography in the automatic detection of gas anomalies on offshore Brunei data Fatiha Gamar, Diego Carotti *, Patrice Guillaume, Amor Gacha, Laurent Lopes (CGG)
Success of high-resolution volumetric Q-tomography in the automatic detection of gas anomalies on offshore Brunei data Fatiha Gamar, Diego Carotti *, Patrice Guillaume, Amor Gacha, Laurent Lopes (CGG)
Application of complex-trace analysis to seismic data for random-noise suppression and temporal resolution improvement
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 71, NO. 3 MAY-JUNE 2006 ; P. V79 V86, 9 FIGS. 10.1190/1.2196875 Application of complex-trace analysis to seismic data for random-noise suppression and temporal resolution improvement Hakan
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 71, NO. 3 MAY-JUNE 2006 ; P. V79 V86, 9 FIGS. 10.1190/1.2196875 Application of complex-trace analysis to seismic data for random-noise suppression and temporal resolution improvement Hakan
ERTH3021 Note: Terminology of Seismic Records
 ERTH3021 Note: Terminology of Seismic Records This note is intended to assist in understanding of terminology used in practical exercises on 2D and 3D seismic acquisition geometries. A fundamental distinction
ERTH3021 Note: Terminology of Seismic Records This note is intended to assist in understanding of terminology used in practical exercises on 2D and 3D seismic acquisition geometries. A fundamental distinction
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas
 The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
Attenuation estimation with continuous wavelet transforms. Shenghong Tai*, De-hua Han, John P. Castagna, Rock Physics Lab, Univ. of Houston.
 . Shenghong Tai*, De-hua Han, John P. Castagna, Rock Physics Lab, Univ. of Houston. SUMMARY Seismic attenuation measurements from surface seismic data using spectral ratios are particularly sensitive to
. Shenghong Tai*, De-hua Han, John P. Castagna, Rock Physics Lab, Univ. of Houston. SUMMARY Seismic attenuation measurements from surface seismic data using spectral ratios are particularly sensitive to
South Africa CO2 Seismic Program
 1 South Africa CO2 Seismic Program ANNEXURE B Bob A. Hardage October 2016 There have been great advances in seismic technology in the decades following the acquisition of legacy, limited-quality, 2D seismic
1 South Africa CO2 Seismic Program ANNEXURE B Bob A. Hardage October 2016 There have been great advances in seismic technology in the decades following the acquisition of legacy, limited-quality, 2D seismic
Multichannel analysis of surface waves
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 64, NO. 3 (MAY-JUNE 1999); P. 800 808, 7 FIGS. Multichannel analysis of surface waves Choon B. Park, Richard D. Miller, and Jianghai Xia ABSTRACT The frequency-dependent properties of
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 64, NO. 3 (MAY-JUNE 1999); P. 800 808, 7 FIGS. Multichannel analysis of surface waves Choon B. Park, Richard D. Miller, and Jianghai Xia ABSTRACT The frequency-dependent properties of
Seismic source comparison for compressional and convertedwave generation at Spring Coulee, Alberta. Part I: Heavy vibroseis-dynamite comparison
 Seismic source comparison. Part I Seismic source comparison for compressional and convertedwave generation at Spring Coulee, Alberta. Part I: Heavy vibroseis-dynamite comparison Gabriela M. Suarez and
Seismic source comparison. Part I Seismic source comparison for compressional and convertedwave generation at Spring Coulee, Alberta. Part I: Heavy vibroseis-dynamite comparison Gabriela M. Suarez and
Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records
 Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT This paper proposes using microphone recordings of
Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT This paper proposes using microphone recordings of
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data
 Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
Th N Broadband Processing of Variable-depth Streamer Data
 Th N103 16 Broadband Processing of Variable-depth Streamer Data H. Masoomzadeh* (TGS), A. Hardwick (TGS) & S. Baldock (TGS) SUMMARY The frequency of ghost notches is naturally diversified by random variations,
Th N103 16 Broadband Processing of Variable-depth Streamer Data H. Masoomzadeh* (TGS), A. Hardwick (TGS) & S. Baldock (TGS) SUMMARY The frequency of ghost notches is naturally diversified by random variations,
Optimal Processing of Marine High-Resolution Seismic Reflection (Chirp) Data
 Marine Geophysical Researches 20: 13 20, 1998. 1998 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 13 Optimal Processing of Marine High-Resolution Seismic Reflection (Chirp) Data R. Quinn 1,,J.M.Bull
Marine Geophysical Researches 20: 13 20, 1998. 1998 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 13 Optimal Processing of Marine High-Resolution Seismic Reflection (Chirp) Data R. Quinn 1,,J.M.Bull
SAUCE: A new technique to remove cultural noise from HRAM data
 THE METER READER SAUCE: A new technique to remove cultural noise from HRAM data HASSAN H. HASSAN and JOHN W. PEIRCE, GEDCO, Calgary, Alberta, Canada There is little doubt that manual editing to remove
THE METER READER SAUCE: A new technique to remove cultural noise from HRAM data HASSAN H. HASSAN and JOHN W. PEIRCE, GEDCO, Calgary, Alberta, Canada There is little doubt that manual editing to remove
Residual converted wave statics
 Residual converted wave statics Arnim B. Haase and David C. Henley ABSTRACT First estimates of S-wave receiver static shifts are applied to selected common receiver gathers of the Spring Coulee three component
Residual converted wave statics Arnim B. Haase and David C. Henley ABSTRACT First estimates of S-wave receiver static shifts are applied to selected common receiver gathers of the Spring Coulee three component
Downloaded 01/03/14 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 : a case study from Saudi Arabia Joseph McNeely*, Timothy Keho, Thierry Tonellot, Robert Ley, Saudi Aramco, Dhahran, and Jing Chen, GeoTomo, Houston Summary We present an application of time domain early
: a case study from Saudi Arabia Joseph McNeely*, Timothy Keho, Thierry Tonellot, Robert Ley, Saudi Aramco, Dhahran, and Jing Chen, GeoTomo, Houston Summary We present an application of time domain early
THE UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY AND GEOPHYSICS GOPH 703
 THE UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY AND GEOPHYSICS GOPH 703 Arrays Submitted to: Dr. Edward Krebes Dr. Don Lawton Dr. Larry lines Presented by: Yajaira Herrera UCID: 989609
THE UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY AND GEOPHYSICS GOPH 703 Arrays Submitted to: Dr. Edward Krebes Dr. Don Lawton Dr. Larry lines Presented by: Yajaira Herrera UCID: 989609
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis
 Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
A second-order fast marching eikonal solver a
 A second-order fast marching eikonal solver a a Published in SEP Report, 100, 287-292 (1999) James Rickett and Sergey Fomel 1 INTRODUCTION The fast marching method (Sethian, 1996) is widely used for solving
A second-order fast marching eikonal solver a a Published in SEP Report, 100, 287-292 (1999) James Rickett and Sergey Fomel 1 INTRODUCTION The fast marching method (Sethian, 1996) is widely used for solving
A Dissertation Presented for the Doctor of Philosophy Degree. The University of Memphis
 A NEW PROCEDURE FOR ESTIMATION OF SHEAR WAVE VELOCITY PROFILES USING MULTI STATION SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF SURFACE WAVES, REGRESSION LINE SLOPE, AND GENETIC ALGORITHM METHODS A Dissertation Presented for
A NEW PROCEDURE FOR ESTIMATION OF SHEAR WAVE VELOCITY PROFILES USING MULTI STATION SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF SURFACE WAVES, REGRESSION LINE SLOPE, AND GENETIC ALGORITHM METHODS A Dissertation Presented for
Direct Imaging of Group Velocity Dispersion Curves in Shallow Water Christopher Liner*, University of Houston; Lee Bell and Richard Verm, Geokinetics
 Direct Imaging of Group Velocity Dispersion Curves in Shallow Water Christopher Liner*, University of Houston; Lee Bell and Richard Verm, Geokinetics Summary Geometric dispersion is commonly observed in
Direct Imaging of Group Velocity Dispersion Curves in Shallow Water Christopher Liner*, University of Houston; Lee Bell and Richard Verm, Geokinetics Summary Geometric dispersion is commonly observed in
Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation
 Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation T. Elboth* (CGG), H. Shen (CGG), J. Khan (CGG) Summary This paper presents recent advances in the area of seismic interference (SI) attenuation
Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation T. Elboth* (CGG), H. Shen (CGG), J. Khan (CGG) Summary This paper presents recent advances in the area of seismic interference (SI) attenuation
Attenuation compensation for georadar data by Gabor deconvolution
 Attenuation compensation for georadar data by Gabor deconvolution Robert J. Ferguson and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Attenuation compensation It has been shown through previous data examples that nonstationary
Attenuation compensation for georadar data by Gabor deconvolution Robert J. Ferguson and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT Attenuation compensation It has been shown through previous data examples that nonstationary
Vibration and air pressure monitoring of seismic sources
 Vibration monitoring of seismic sources Vibration and air pressure monitoring of seismic sources Alejandro D. Alcudia, Robert R. Stewart, Nanna Eliuk* and Rick Espersen** ABSTRACT Vibration monitoring
Vibration monitoring of seismic sources Vibration and air pressure monitoring of seismic sources Alejandro D. Alcudia, Robert R. Stewart, Nanna Eliuk* and Rick Espersen** ABSTRACT Vibration monitoring
Summary. Introduction
 Multiple attenuation for variable-depth streamer data: from deep to shallow water Ronan Sablon*, Damien Russier, Oscar Zurita, Danny Hardouin, Bruno Gratacos, Robert Soubaras & Dechun Lin. CGGVeritas Summary
Multiple attenuation for variable-depth streamer data: from deep to shallow water Ronan Sablon*, Damien Russier, Oscar Zurita, Danny Hardouin, Bruno Gratacos, Robert Soubaras & Dechun Lin. CGGVeritas Summary
Frequency extrapolation to enhance the deconvolution of transmitted seismic waves
 IOP PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS AND ENGINEERING J. Geophys. Eng. 5 (2008) 118 127 doi:10.1088/1742-2132/5/1/012 Frequency extrapolation to enhance the deconvolution of transmitted seismic waves Saptarshi
IOP PUBLISHING JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS AND ENGINEERING J. Geophys. Eng. 5 (2008) 118 127 doi:10.1088/1742-2132/5/1/012 Frequency extrapolation to enhance the deconvolution of transmitted seismic waves Saptarshi
MEMS-based accelerometers: expectations and practical achievements
 first break volume 29, February 2011 MEMS-based accelerometers: expectations and practical achievements Denis Mougenot, 1* Anatoly Cherepovskiy 1 and Liu JunJie 1 trace the development of MEMS sensors
first break volume 29, February 2011 MEMS-based accelerometers: expectations and practical achievements Denis Mougenot, 1* Anatoly Cherepovskiy 1 and Liu JunJie 1 trace the development of MEMS sensors
Master event relocation of microseismic event using the subspace detector
 Master event relocation of microseismic event using the subspace detector Ibinabo Bestmann, Fernando Castellanos and Mirko van der Baan Dept. of Physics, CCIS, University of Alberta Summary Microseismic
Master event relocation of microseismic event using the subspace detector Ibinabo Bestmann, Fernando Castellanos and Mirko van der Baan Dept. of Physics, CCIS, University of Alberta Summary Microseismic
F-x linear prediction filtering of seismic images
 147 F-x linear prediction filtering of seismic images Mark P. Harrison ABSTRACT The f-x linear prediction filtering algorithm is reviewed and tested on several synthetic images. It is found that the f-x
147 F-x linear prediction filtering of seismic images Mark P. Harrison ABSTRACT The f-x linear prediction filtering algorithm is reviewed and tested on several synthetic images. It is found that the f-x
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency
 25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
Evaluation of a broadband marine source
 Evaluation of a broadband marine source Rob Telling 1*, Stuart Denny 1, Sergio Grion 1 and R. Gareth Williams 1 evaluate far-field signatures and compare processing results for a 2D test-line acquired
Evaluation of a broadband marine source Rob Telling 1*, Stuart Denny 1, Sergio Grion 1 and R. Gareth Williams 1 evaluate far-field signatures and compare processing results for a 2D test-line acquired
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data
 Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Iterative Denoising of Geophysical Time Series Using Wavelets
 5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 943-947 Iterative Denoising of Geophysical Time Series Using Wavelets Nimisha Vedanti Research Scholar Fractals in Geophysics
5th Conference & Exposition on Petroleum Geophysics, Hyderabad-2004, India PP 943-947 Iterative Denoising of Geophysical Time Series Using Wavelets Nimisha Vedanti Research Scholar Fractals in Geophysics
Application of Surface Consistent Amplitude Corrections as a Manual Editing Tool
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 4, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov-Dec. 2016), PP 59-65 www.iosrjournals.org Application of Surface Consistent
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 4, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov-Dec. 2016), PP 59-65 www.iosrjournals.org Application of Surface Consistent
