Direct Imaging of Group Velocity Dispersion Curves in Shallow Water Christopher Liner*, University of Houston; Lee Bell and Richard Verm, Geokinetics
|
|
|
- Clementine Moody
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Direct Imaging of Group Velocity Dispersion Curves in Shallow Water Christopher Liner*, University of Houston; Lee Bell and Richard Verm, Geokinetics Summary Geometric dispersion is commonly observed in shallow water marine data due to post-critical multiples in the water layer over a hard seafloor. Characteristics of the guided waves include formation of distinct propagation modes and associated divergence of phase and group velocity. Methods have been available since 1981 to image phase velocity dispersion curves. Here we report a method to directly image the group velocity curves. Introduction where c is phase velocity (m/s), f is frequency (Hz), h is water layer thickness (m), α is compressional or sound speed (m/s), β is shear speed (m/s), and ρ is density (kg/m 3 ). Subscripts 1 and 2 refer to the water layer and the elastic substrate, respectively. Beginning with the work of Pekeris (1948) it has been known that explosive sound in shallow water leads to development of distinct propagation modes. These arise from wide-angle seafloor reflections and subsequent trapping in the water column as post-critical multiples. t certain angles constructive interference is set up depending on water depth and sea floor velocities. Good discussions of the waveguide mode theory can be found in Ewing, Jarketzky, and Press (1957), Officer (1958), Budden (1962), and Grant and West (1965). The reader should note, however, that notation and mode numbering schemes vary widely between authors. The imaging of phase velocity dispersion curves was first published by McMechan and Yedlin (1981) based on slant stack processing of shot records, a method that requires regular spatial sampling. Park et al. (1998) introduced a direct integration method that can be applied to 2D or 3D shot records with irregular trace spacing. We use Park s method here for imaging phase velocity curves. Phase velocity curves can be used for inversion of near surface parameters and to validate processing steps aimed at removal of dispersive waves. Such waves exhibit 2D decay and are typically much stronger than primary reflected waves. For shallow water exploration guided waves dominate shot records at all recording times inside a cone of influence defined by the group velocity min/max values. Inside the cone, phase velocity is defined by the local slope. Figure 1 illustrates the concepts of phase and group velocity, as they would appear on an idealized 2D marine shot record. Figure 1. Features of a dispersive wave train as they would appear in a 2D shot record. The period equation describes the variation of phase velocity with frequency and model parameters Theory of guided wave modes Consider the case of an acoustic medium overlaying an elastic half-space (Ewing, Jarketzky, and Press, 1957, eqn 4-78; Grant and West, 1965, eqn 3-34). We define the following quantities where the modes (0,1,2, ) are enumerated by m. t high frequency the phase velocity is asymptotic to α1, while at low frequency it is asymptotic to Rayleigh wave speed in
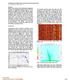
2 the substrate (~ 0.92 β 2 ). Each mode has a cut-off frequency, below which it does not exist. In practice, phase velocities can be calculated by setting the model parameters and mode number, then stepping through phase velocities between the allowed limits and computing (α1 g / h) which is equal to the frequency associated with this phase velocity of this mode. Group velocity can then be calculated numerically using Method and field data example Our data consists of a 4-component ocean bottom cable 3D shot record from offshore ustralia. Three parallel receiver lines include a total of 580 groups. No processing has been applied to the data aside from extraction of the (P,X,Y,Z) components. Using the method of Park (1998), phase velocity curves were computed from P (pressure) and Z (vertical) components. Figure 2 shows the result with clear phase velocity dispersion curves. There are differences in relative mode energy and noise between P and Z, but the story they tell of dispersive modes is basically the same. In an attempt to better understand this dispersive noise, the data was sorted to abs(offset) and every 100 th trace was transformed to (time,scale) space by continuous wavelet transform (CWT) with results shown in Figure 3. complex Morlet wavelet (Torrence and Compo, 1998) was used and several variations of normalization and damping were tested. Normalization sets the relative strength of low and high frequency features in the CWT spectrum. Damping influences time-frequency resolution by controlling the number of oscillations in the analyzing wavelet. More oscillations mean better frequency resolution, while fewer mean better time localization. We note that CWT does not give a true monochromatic timefrequency decomposition, rather the labeled frequency is a center frequency associated with a Gaussian amplitude spectrum. Study of the CWT result revealed the dispersive wave train occupying a short time interval at small offsets, and gradually lengthening as offset increased. Closer inspection at far offsets revealed a curious series of features arcing down and right in each spectrum. The 4194 m offset spectrum in Figure 3 is a good example. With standard dyadic frequency sampling as used here, this direction is toward lower frequency. The immediate interpretation is that low frequencies are arriving later, and thus traveling slower, than high frequencies. This is the opposite of dispersive phase velocity behavior, suggesting group velocity is being observed. Since the trace occupies one offset from the source, each time in the trace is associated with a different group velocity. This follows from the definition of group velocity in this case, the offset divided by travel time from source to receiver. Note that group velocity is a single trace computation, whereas phase velocity is calculated by moveout relative to neighboring offsets. To test the hypothesis that these are in fact dispersive waveguide group velocity curves, the period equation was coded up for visual curve fitting. The CWT was displayed with standard linear frequency sampling as seen in Figure 4, the curve labeled was digitized, and the offset was used to convert to time to velocity. The phase velocity curves and B in Figure 2 (right) were also digitized. From autocorrelation analysis of the near offset traces, a water depth of 55 m was estimated. The other parameters, P and S wave speed in the substrate as well as density ratio, were estimated by manual curve fitting in two ways. First, only the phase velocity values were used for visual fitting, then both phase and group velocities were used. B Figure 2. Phase velocity dispersion curves for ustralian OBC shot record (P,Z) components.
3 Results are shown below, using (left) phase velocity only and (right) phase and group velocity. Figure 5 shows the theoretical dispersion curves (solid) and observed values (dots). Red dots are interpreted as mode 1 values and blue as mode 2. Interestingly, the fundamental mode 0 exists only below 10 Hz and therefore is not clearly observed on either P or Z. Only after including the group velocity information did it become clear that water velocity must deviate slightly from 1500 m/s to achieve a satisfactory match. The 1530 m/s water velocity was independently confirmed by production processing. Inclusion of the group velocity observations also drove interpretation toward lower subtrate VpVs ratio and higher water-to-seafloor density ratio. Conclusions Methods for imaging phase velocity dispersion curves have been available for more than 25 years, but we know of no previously published method for imaging group velocity curves. We have demonstrated a new method of directly imaging group velocity curves in shallow water data using an appropriately tuned continuous wavelet transform. Whereas the phase velocity dispersion curves are imaged by integration over the entire shot record, group velocity behavior can be determined from a single trace. This leads to the possibility of isolating and filtering dispersive events in the CWT domain. By use of both phase and group velocity information, we find that manual estimation of waveguide parameters is much better constrained. We anticipate the same will apply to automated inversion algorithms. The quality of fit between theory and data demonstrates that we have directly imaged a group velocity curve. These may prove very useful for automated parameter estimation of near surface properties. The theoretical dispersion curves are exquisitely sensitive to water depth and shear wave speed in the seafloor. The latter property may prove important in converted wave imaging. Figure 3. CWT spectrum of every 100 th shot record trace showing development of dispersive waves.
4 Figure 4. Wavelet transform linear frequency plot for the 4194 m offset trace. Figure 5. Normal mode analysis comparing theory (lines) to observations (dots). ) Best manual fit using phase velocity observations only, and b) best fit using both phase and group velocity. See text for parameter estimates in each case.
5 References Budden, K. G., 1962, The Wave guide mode theory of wave propagation: Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, N.J. Ewing, W. M., Jardetsky, W. S., and Press, F., 1957, Elastic waves in layered media: McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York Grant, F.S. and West, G.F., 1965, Interpretation theory in applied geophysics, McGraw- Hill Book Company. McMechan, G.., and Yedlin, M. J., 1981, nalysis of dispersive waves by wave field transformation: Geophysics, 46, 869 Officer, C. B., 1958, Introduction to the theory of sound transmission: McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York Park, C. B., Miller R. D., and Xia J., 1998, Imaging of dispersion curves of surface waves on multi-channel record: SEG, Expanded bstracts, 17, no. 1, Pekeris, C. L., 1941, Theory of propagation of explosive sound in shallow water: Geol. Soc. m. Mem. 27. Torrence, C., and Compo, G. P., 1998, Practical guide to wavelet analysis: Bull. mer. Meteor. Soc., 79, 61
Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 80, May 15, 2001, pages 1 356 Amplitude balancing for AVO analysis Arnaud Berlioux and David Lumley 1 ABSTRACT Source and receiver amplitude variations can distort
P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method
 P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method E. Baniasadi* (University of Tehran), M. A. Riahi (University of Tehran) & S. Chaychizadeh (University of Tehran)
P34 Determination of 1-D Shear-Wave Velocity Profileusing the Refraction Microtremor Method E. Baniasadi* (University of Tehran), M. A. Riahi (University of Tehran) & S. Chaychizadeh (University of Tehran)
Joint Time/Frequency Analysis, Q Quality factor and Dispersion computation using Gabor-Morlet wavelets or Gabor-Morlet transform
 Joint Time/Frequency, Computation of Q, Dr. M. Turhan (Tury Taner, Rock Solid Images Page: 1 Joint Time/Frequency Analysis, Q Quality factor and Dispersion computation using Gabor-Morlet wavelets or Gabor-Morlet
Joint Time/Frequency, Computation of Q, Dr. M. Turhan (Tury Taner, Rock Solid Images Page: 1 Joint Time/Frequency Analysis, Q Quality factor and Dispersion computation using Gabor-Morlet wavelets or Gabor-Morlet
Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion
 Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion Heather J.E. Lloyd*, CREWES / University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta hjelloyd@ucalgary.ca and Gary F. Margrave, CREWES
Investigating the low frequency content of seismic data with impedance Inversion Heather J.E. Lloyd*, CREWES / University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta hjelloyd@ucalgary.ca and Gary F. Margrave, CREWES
Analysis and design of filters for differentiation
 Differential filters Analysis and design of filters for differentiation John C. Bancroft and Hugh D. Geiger SUMMARY Differential equations are an integral part of seismic processing. In the discrete computer
Differential filters Analysis and design of filters for differentiation John C. Bancroft and Hugh D. Geiger SUMMARY Differential equations are an integral part of seismic processing. In the discrete computer
High-Frequency Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization
 High-Frequency Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization Kevin D. Heaney Lockheed-Martin ORINCON Corporation, 4350 N. Fairfax Dr., Arlington VA 22203 Abstract. The Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization (RGC) algorithm
High-Frequency Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization Kevin D. Heaney Lockheed-Martin ORINCON Corporation, 4350 N. Fairfax Dr., Arlington VA 22203 Abstract. The Rapid Geo-acoustic Characterization (RGC) algorithm
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis
 Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
Anisotropic Frequency-Dependent Spreading of Seismic Waves from VSP Data Analysis Amin Baharvand Ahmadi* and Igor Morozov, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan amin.baharvand@usask.ca Summary
Presented on. Mehul Supawala Marine Energy Sources Product Champion, WesternGeco
 Presented on Marine seismic acquisition and its potential impact on marine life has been a widely discussed topic and of interest to many. As scientific knowledge improves and operational criteria evolve,
Presented on Marine seismic acquisition and its potential impact on marine life has been a widely discussed topic and of interest to many. As scientific knowledge improves and operational criteria evolve,
This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010.
 This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010. The information herein remains the property of Mustagh
This presentation was prepared as part of Sensor Geophysical Ltd. s 2010 Technology Forum presented at the Telus Convention Center on April 15, 2010. The information herein remains the property of Mustagh
attempt to understand if we can identify a relationship between fundamental mode propagation and the condition of the cement bonds.
 Hua Wang*, Mike Fehler,Earth Resources Lab,Massachusetts Institute of Technology,Cambridge, MA, USA Summary We use a 3D Finite Difference (3DFD) method to simulate monopole wavefields in a singly-cased
Hua Wang*, Mike Fehler,Earth Resources Lab,Massachusetts Institute of Technology,Cambridge, MA, USA Summary We use a 3D Finite Difference (3DFD) method to simulate monopole wavefields in a singly-cased
P and S wave separation at a liquid-solid interface
 and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface Maria. Donati and Robert R. tewart ABTRACT and seismic waves impinging on a liquid-solid interface give rise
and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface and wave separation at a liquid-solid interface Maria. Donati and Robert R. tewart ABTRACT and seismic waves impinging on a liquid-solid interface give rise
Environmental Acoustics and Intensity Vector Acoustics with Emphasis on Shallow Water Effects and the Sea Surface
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Environmental Acoustics and Intensity Vector Acoustics with Emphasis on Shallow Water Effects and the Sea Surface LONG-TERM
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Environmental Acoustics and Intensity Vector Acoustics with Emphasis on Shallow Water Effects and the Sea Surface LONG-TERM
Acoustic propagation affected by environmental parameters in coastal waters
 Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 43(1), January 2014, pp. 17-21 Acoustic propagation affected by environmental parameters in coastal waters Sanjana M C, G Latha, A Thirunavukkarasu & G Raguraman
Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 43(1), January 2014, pp. 17-21 Acoustic propagation affected by environmental parameters in coastal waters Sanjana M C, G Latha, A Thirunavukkarasu & G Raguraman
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG)
 Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain
 High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain Shaowu Wang, Juefu Wang and Tianfei Zhu CGG Summary We present a method to enhance the bandwidth of seismic data in the
High-dimensional resolution enhancement in the continuous wavelet transform domain Shaowu Wang, Juefu Wang and Tianfei Zhu CGG Summary We present a method to enhance the bandwidth of seismic data in the
Estimation of a time-varying sea-surface profile for receiver-side de-ghosting Rob Telling* and Sergio Grion Shearwater Geoservices, UK
 for receiver-side de-ghosting Rob Telling* and Sergio Grion Shearwater Geoservices, UK Summary The presence of a rough sea-surface during acquisition of marine seismic data leads to time- and space-dependent
for receiver-side de-ghosting Rob Telling* and Sergio Grion Shearwater Geoservices, UK Summary The presence of a rough sea-surface during acquisition of marine seismic data leads to time- and space-dependent
WS15-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise
 WS1-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise F. Duret* (CGG) & E. Forgues (CGG) SUMMARY In 4D land seismic and especially for Permanent Reservoir Monitoring (PRM), changes of the near-surface
WS1-B02 4D Surface Wave Tomography Using Ambient Seismic Noise F. Duret* (CGG) & E. Forgues (CGG) SUMMARY In 4D land seismic and especially for Permanent Reservoir Monitoring (PRM), changes of the near-surface
Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo
 Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo Summary A survey with a novel acquisition technique was acquired
Survey results obtained in a complex geological environment with Midwater Stationary Cable Luc Haumonté*, Kietta; Weizhong Wang, Geotomo Summary A survey with a novel acquisition technique was acquired
Low Frequency Bottom Reflectivity from Reflection
 Low Frequency Bottom Reflectivity from Reflection,Alexander Kritski 1 and Chris Jenkins 2 1 School of Geosciences, University of Sydney, NSW, 2 Ocean Sciences Institute, University of Sydney, NSW. Abstract
Low Frequency Bottom Reflectivity from Reflection,Alexander Kritski 1 and Chris Jenkins 2 1 School of Geosciences, University of Sydney, NSW, 2 Ocean Sciences Institute, University of Sydney, NSW. Abstract
MASWaves User manual
 MASWaves User manual Version 1 July 11, 2017 Preface/disclaimers... 2 References... 2 Acknowledgements... 2 1. Introduction... 3 2. Quick start guide... 5 3. MASWaves Dispersion... 11 3.1 Read data (MASWaves_read_data)...
MASWaves User manual Version 1 July 11, 2017 Preface/disclaimers... 2 References... 2 Acknowledgements... 2 1. Introduction... 3 2. Quick start guide... 5 3. MASWaves Dispersion... 11 3.1 Read data (MASWaves_read_data)...
Attenuation estimation with continuous wavelet transforms. Shenghong Tai*, De-hua Han, John P. Castagna, Rock Physics Lab, Univ. of Houston.
 . Shenghong Tai*, De-hua Han, John P. Castagna, Rock Physics Lab, Univ. of Houston. SUMMARY Seismic attenuation measurements from surface seismic data using spectral ratios are particularly sensitive to
. Shenghong Tai*, De-hua Han, John P. Castagna, Rock Physics Lab, Univ. of Houston. SUMMARY Seismic attenuation measurements from surface seismic data using spectral ratios are particularly sensitive to
Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation
 Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation T. Elboth* (CGG), H. Shen (CGG), J. Khan (CGG) Summary This paper presents recent advances in the area of seismic interference (SI) attenuation
Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation T. Elboth* (CGG), H. Shen (CGG), J. Khan (CGG) Summary This paper presents recent advances in the area of seismic interference (SI) attenuation
Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion
 P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical
 A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical Summary Here we present a method of robust seismic data deghosting for
A robust x-t domain deghosting method for various source/receiver configurations Yilmaz, O., and Baysal, E., Paradigm Geophysical Summary Here we present a method of robust seismic data deghosting for
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data
 Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
Tomostatic Waveform Tomography on Near-surface Refraction Data Jianming Sheng, Alan Leeds, and Konstantin Osypov ChevronTexas WesternGeco February 18, 23 ABSTRACT The velocity variations and static shifts
Passive Measurement of Vertical Transfer Function in Ocean Waveguide using Ambient Noise
 Proceedings of Acoustics - Fremantle -3 November, Fremantle, Australia Passive Measurement of Vertical Transfer Function in Ocean Waveguide using Ambient Noise Xinyi Guo, Fan Li, Li Ma, Geng Chen Key Laboratory
Proceedings of Acoustics - Fremantle -3 November, Fremantle, Australia Passive Measurement of Vertical Transfer Function in Ocean Waveguide using Ambient Noise Xinyi Guo, Fan Li, Li Ma, Geng Chen Key Laboratory
Enhanced subsurface response for marine CSEM surveying Frank A. Maaø* and Anh Kiet Nguyen, EMGS ASA
 rank A. Maaø* and Anh Kiet Nguyen, EMGS ASA Summary A new robust method for enhancing marine CSEM subsurface response is presented. The method is demonstrated to enhance resolution and depth penetration
rank A. Maaø* and Anh Kiet Nguyen, EMGS ASA Summary A new robust method for enhancing marine CSEM subsurface response is presented. The method is demonstrated to enhance resolution and depth penetration
HIGH-FREQUENCY ACOUSTIC PROPAGATION IN THE PRESENCE OF OCEANOGRAPHIC VARIABILITY
 HIGH-FREQUENCY ACOUSTIC PROPAGATION IN THE PRESENCE OF OCEANOGRAPHIC VARIABILITY M. BADIEY, K. WONG, AND L. LENAIN College of Marine Studies, University of Delaware Newark DE 19716, USA E-mail: Badiey@udel.edu
HIGH-FREQUENCY ACOUSTIC PROPAGATION IN THE PRESENCE OF OCEANOGRAPHIC VARIABILITY M. BADIEY, K. WONG, AND L. LENAIN College of Marine Studies, University of Delaware Newark DE 19716, USA E-mail: Badiey@udel.edu
Mode Dispersion Curves
 Mode Dispersion Curves Fluid-Filled Pipe using FEM George Grigoropoulos Civil Engineer, MSc. g.grigoropoulos@gmail.com Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Hong Kong University of Science
Mode Dispersion Curves Fluid-Filled Pipe using FEM George Grigoropoulos Civil Engineer, MSc. g.grigoropoulos@gmail.com Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Hong Kong University of Science
Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records
 Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT This paper proposes using microphone recordings of
Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Air-noise reduction on geophone data using microphone records Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT This paper proposes using microphone recordings of
Northing (km)
 Imaging lateral heterogeneity at Coronation Field with surface waves Matthew M. Haney, Boise State University, and Huub Douma, ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging Solutions SUMMARY A longstanding problem in land
Imaging lateral heterogeneity at Coronation Field with surface waves Matthew M. Haney, Boise State University, and Huub Douma, ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging Solutions SUMMARY A longstanding problem in land
Ambient Passive Seismic Imaging with Noise Analysis Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc.
 Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc. SUMMARY The ambient passive seismic imaging technique is capable of imaging repetitive passive seismic events. Here we investigate
Aleksandar Jeremic, Michael Thornton, Peter Duncan, MicroSeismic Inc. SUMMARY The ambient passive seismic imaging technique is capable of imaging repetitive passive seismic events. Here we investigate
The spatial structure of an acoustic wave propagating through a layer with high sound speed gradient
 The spatial structure of an acoustic wave propagating through a layer with high sound speed gradient Alex ZINOVIEV 1 ; David W. BARTEL 2 1,2 Defence Science and Technology Organisation, Australia ABSTRACT
The spatial structure of an acoustic wave propagating through a layer with high sound speed gradient Alex ZINOVIEV 1 ; David W. BARTEL 2 1,2 Defence Science and Technology Organisation, Australia ABSTRACT
Behavior and Sensitivity of Phase Arrival Times (PHASE)
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Behavior and Sensitivity of Phase Arrival Times (PHASE) Emmanuel Skarsoulis Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Behavior and Sensitivity of Phase Arrival Times (PHASE) Emmanuel Skarsoulis Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas
3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion. Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas
 P-75 Summary 3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas Following our previous work on Amplitude Tomography that
P-75 Summary 3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas Following our previous work on Amplitude Tomography that
Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain
 Predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Marco A. Perez and David C. Henley ABSTRACT Predictive deconvolution has been predominantly
Predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Multiple attenuation via predictive deconvolution in the radial domain Marco A. Perez and David C. Henley ABSTRACT Predictive deconvolution has been predominantly
Why not narrowband? Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology
 Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology Summary A 2D towed streamer acquisition experiment was conducted in deep water offshore Gabon to evaluate techniques
Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology Summary A 2D towed streamer acquisition experiment was conducted in deep water offshore Gabon to evaluate techniques
Tu A D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study
 Tu A15 09 4D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study D. Lecerf* (PGS), D. Raistrick (PGS), B. Caselitz (PGS), M. Wingham (BP), J. Bradley (BP), B. Moseley (formaly BP) Summary
Tu A15 09 4D Broadband Towed-Streamer Assessment, West Africa Deep Water Case Study D. Lecerf* (PGS), D. Raistrick (PGS), B. Caselitz (PGS), M. Wingham (BP), J. Bradley (BP), B. Moseley (formaly BP) Summary
Seismic reflection method
 Seismic reflection method Seismic reflection method is based on the reflections of seismic waves occurring at the contacts of subsurface structures. We apply some seismic source at different points of
Seismic reflection method Seismic reflection method is based on the reflections of seismic waves occurring at the contacts of subsurface structures. We apply some seismic source at different points of
Th N Broadband Processing of Variable-depth Streamer Data
 Th N103 16 Broadband Processing of Variable-depth Streamer Data H. Masoomzadeh* (TGS), A. Hardwick (TGS) & S. Baldock (TGS) SUMMARY The frequency of ghost notches is naturally diversified by random variations,
Th N103 16 Broadband Processing of Variable-depth Streamer Data H. Masoomzadeh* (TGS), A. Hardwick (TGS) & S. Baldock (TGS) SUMMARY The frequency of ghost notches is naturally diversified by random variations,
Broadband Temporal Coherence Results From the June 2003 Panama City Coherence Experiments
 Broadband Temporal Coherence Results From the June 2003 Panama City Coherence Experiments H. Chandler*, E. Kennedy*, R. Meredith*, R. Goodman**, S. Stanic* *Code 7184, Naval Research Laboratory Stennis
Broadband Temporal Coherence Results From the June 2003 Panama City Coherence Experiments H. Chandler*, E. Kennedy*, R. Meredith*, R. Goodman**, S. Stanic* *Code 7184, Naval Research Laboratory Stennis
Comparison of Q-estimation methods: an update
 Q-estimation Comparison of Q-estimation methods: an update Peng Cheng and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT In this article, three methods of Q estimation are compared: a complex spectral ratio method, the centroid
Q-estimation Comparison of Q-estimation methods: an update Peng Cheng and Gary F. Margrave ABSTRACT In this article, three methods of Q estimation are compared: a complex spectral ratio method, the centroid
ACOUSTIC MICRO IMAGING ANALYSIS METHODS FOR 3D PACKAGES
 ACOUSTIC MICRO IMAGING ANALYSIS METHODS FOR 3D PACKAGES Janet E. Semmens Sonoscan, Inc. Elk Grove Village, IL, USA Jsemmens@sonoscan.com ABSTRACT Earlier studies concerning evaluation of stacked die packages
ACOUSTIC MICRO IMAGING ANALYSIS METHODS FOR 3D PACKAGES Janet E. Semmens Sonoscan, Inc. Elk Grove Village, IL, USA Jsemmens@sonoscan.com ABSTRACT Earlier studies concerning evaluation of stacked die packages
SUMMARY INTRODUCTION MOTIVATION
 Isabella Masoni, Total E&P, R. Brossier, University Grenoble Alpes, J. L. Boelle, Total E&P, J. Virieux, University Grenoble Alpes SUMMARY In this study, an innovative layer stripping approach for FWI
Isabella Masoni, Total E&P, R. Brossier, University Grenoble Alpes, J. L. Boelle, Total E&P, J. Virieux, University Grenoble Alpes SUMMARY In this study, an innovative layer stripping approach for FWI
Seismic-Acoustic Sensors Topology for Interest Source Position Estimation
 Seismic-Acoustic Sensors Topology for Interest Source Position Estimation Jaroslav Cechak Military Academy in Brno, Kounicova 65, Brno, Czech republic Jaroslav.cechak@vabo.cz Abstract: Estimation of the
Seismic-Acoustic Sensors Topology for Interest Source Position Estimation Jaroslav Cechak Military Academy in Brno, Kounicova 65, Brno, Czech republic Jaroslav.cechak@vabo.cz Abstract: Estimation of the
Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise
 Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise Stephen Chiu* ConocoPhillips, Houston, TX, United States stephen.k.chiu@conocophillips.com and Norman Whitmore
Polarization Filter by Eigenimages and Adaptive Subtraction to Attenuate Surface-Wave Noise Stephen Chiu* ConocoPhillips, Houston, TX, United States stephen.k.chiu@conocophillips.com and Norman Whitmore
Ocean-bottom hydrophone and geophone coupling
 Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages 57 70 Ocean-bottom hydrophone and geophone coupling Daniel A. Rosales and Antoine Guitton 1 ABSTRACT We compare two methods for combining hydrophone
Stanford Exploration Project, Report 115, May 22, 2004, pages 57 70 Ocean-bottom hydrophone and geophone coupling Daniel A. Rosales and Antoine Guitton 1 ABSTRACT We compare two methods for combining hydrophone
Scaled Laboratory Experiments of Shallow Water Acoustic Propagation
 Scaled Laboratory Experiments of Shallow Water Acoustic Propagation Panagiotis Papadakis, Michael Taroudakis FORTH/IACM, P.O.Box 1527, 711 10 Heraklion, Crete, Greece e-mail: taroud@iacm.forth.gr Patrick
Scaled Laboratory Experiments of Shallow Water Acoustic Propagation Panagiotis Papadakis, Michael Taroudakis FORTH/IACM, P.O.Box 1527, 711 10 Heraklion, Crete, Greece e-mail: taroud@iacm.forth.gr Patrick
ON WAVEFORM SELECTION IN A TIME VARYING SONAR ENVIRONMENT
 ON WAVEFORM SELECTION IN A TIME VARYING SONAR ENVIRONMENT Ashley I. Larsson 1* and Chris Gillard 1 (1) Maritime Operations Division, Defence Science and Technology Organisation, Edinburgh, Australia Abstract
ON WAVEFORM SELECTION IN A TIME VARYING SONAR ENVIRONMENT Ashley I. Larsson 1* and Chris Gillard 1 (1) Maritime Operations Division, Defence Science and Technology Organisation, Edinburgh, Australia Abstract
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency
 25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
Summary. Volumetric Q tomography on offshore Brunei dataset
 Success of high-resolution volumetric Q-tomography in the automatic detection of gas anomalies on offshore Brunei data Fatiha Gamar, Diego Carotti *, Patrice Guillaume, Amor Gacha, Laurent Lopes (CGG)
Success of high-resolution volumetric Q-tomography in the automatic detection of gas anomalies on offshore Brunei data Fatiha Gamar, Diego Carotti *, Patrice Guillaume, Amor Gacha, Laurent Lopes (CGG)
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Propagation of Low-Frequency, Transient Acoustic Signals through a Fluctuating Ocean: Development of a 3D Scattering Theory
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Propagation of Low-Frequency, Transient Acoustic Signals through a Fluctuating Ocean: Development of a 3D Scattering Theory
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution
 Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Multichannel analysis of surface waves
 GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 64, NO. 3 (MAY-JUNE 1999); P. 800 808, 7 FIGS. Multichannel analysis of surface waves Choon B. Park, Richard D. Miller, and Jianghai Xia ABSTRACT The frequency-dependent properties of
GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 64, NO. 3 (MAY-JUNE 1999); P. 800 808, 7 FIGS. Multichannel analysis of surface waves Choon B. Park, Richard D. Miller, and Jianghai Xia ABSTRACT The frequency-dependent properties of
Analyzing and Filtering Surface-Wave Energy By Muting Shot Gathers
 307 Analyzing and Filtering Surface-Wave Energy By Muting Shot Gathers Julian Ivanov*, Choon B. Park, Richard D. Miller and Jianghai Xia Kansas Geological Survey, The University of Kansas, 1930 Constant
307 Analyzing and Filtering Surface-Wave Energy By Muting Shot Gathers Julian Ivanov*, Choon B. Park, Richard D. Miller and Jianghai Xia Kansas Geological Survey, The University of Kansas, 1930 Constant
Chapter 5. Signal Analysis. 5.1 Denoising fiber optic sensor signal
 Chapter 5 Signal Analysis 5.1 Denoising fiber optic sensor signal We first perform wavelet-based denoising on fiber optic sensor signals. Examine the fiber optic signal data (see Appendix B). Across all
Chapter 5 Signal Analysis 5.1 Denoising fiber optic sensor signal We first perform wavelet-based denoising on fiber optic sensor signals. Examine the fiber optic signal data (see Appendix B). Across all
2012 SEG SEG Las Vegas 2012 Annual Meeting Page 1
 Full-wavefield, towed-marine seismic acquisition and applications David Halliday, Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Johan O. A. Robertsson, ETH Zürich, Ivan Vasconcelos, Schlumberger Cambridge Research,
Full-wavefield, towed-marine seismic acquisition and applications David Halliday, Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Johan O. A. Robertsson, ETH Zürich, Ivan Vasconcelos, Schlumberger Cambridge Research,
Seismic Reflection Method
 1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
Continuous time and Discrete time Signals and Systems
 Continuous time and Discrete time Signals and Systems 1. Systems in Engineering A system is usually understood to be an engineering device in the field, and a mathematical representation of this system
Continuous time and Discrete time Signals and Systems 1. Systems in Engineering A system is usually understood to be an engineering device in the field, and a mathematical representation of this system
Dispersion of Sound in Marine Sediments
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Dispersion of Sound in Marine Sediments N. Ross Chapman School of Earth and Ocean Sciences University of Victoria 3800
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Dispersion of Sound in Marine Sediments N. Ross Chapman School of Earth and Ocean Sciences University of Victoria 3800
Summary. D Receiver. Borehole. Borehole. Borehole. tool. tool. tool
 n off center quadrupole acoustic wireline : numerical modeling and field data analysis Zhou-tuo Wei*, OSL-UP llied coustic Lab., hina University of Petroleum (UP); Hua Wang, Earth Resources Lab., Massachusetts
n off center quadrupole acoustic wireline : numerical modeling and field data analysis Zhou-tuo Wei*, OSL-UP llied coustic Lab., hina University of Petroleum (UP); Hua Wang, Earth Resources Lab., Massachusetts
Underwater Wideband Source Localization Using the Interference Pattern Matching
 Underwater Wideband Source Localization Using the Interference Pattern Matching Seung-Yong Chun, Se-Young Kim, Ki-Man Kim Agency for Defense Development, # Hyun-dong, 645-06 Jinhae, Korea Dept. of Radio
Underwater Wideband Source Localization Using the Interference Pattern Matching Seung-Yong Chun, Se-Young Kim, Ki-Man Kim Agency for Defense Development, # Hyun-dong, 645-06 Jinhae, Korea Dept. of Radio
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information S1. Theory of TPQI in a lossy directional coupler Following Barnett, et al. [24], we start with the probability of detecting one photon in each output of a lossy, symmetric beam
Supplementary Information S1. Theory of TPQI in a lossy directional coupler Following Barnett, et al. [24], we start with the probability of detecting one photon in each output of a lossy, symmetric beam
Attenuation of high energy marine towed-streamer noise Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco
 Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Processing the Teal South 4C-4D seismic survey
 Processing the Teal South 4C-4D seismic survey Carlos Rodriguez-Suarez, Robert R. Stewart and Han-Xing Lu Processing the Teal South 4C-4D ABSTRACT Repeated 4C-3D seismic surveys have been acquired over
Processing the Teal South 4C-4D seismic survey Carlos Rodriguez-Suarez, Robert R. Stewart and Han-Xing Lu Processing the Teal South 4C-4D ABSTRACT Repeated 4C-3D seismic surveys have been acquired over
Instantaneous frequency-slowness analysis applied to borehole acoustic data
 Instantaneous frequency-slowness analysis applied to borehole acoustic data Marek Kozak, PhD SuperSonic Geophysical LLC Donegal Ct, Newark, CA, USA marek@acousticpulse.com Jefferson Williams SuperSonic
Instantaneous frequency-slowness analysis applied to borehole acoustic data Marek Kozak, PhD SuperSonic Geophysical LLC Donegal Ct, Newark, CA, USA marek@acousticpulse.com Jefferson Williams SuperSonic
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Numerical Modeling of a Time Reversal Experiment in Shallow Singapore Waters
 Numerical Modeling of a Time Reversal Experiment in Shallow Singapore Waters H.C. Song, W.S. Hodgkiss, and J.D. Skinner Marine Physical Laboratory, Scripps Institution of Oceanography La Jolla, CA 92037-0238,
Numerical Modeling of a Time Reversal Experiment in Shallow Singapore Waters H.C. Song, W.S. Hodgkiss, and J.D. Skinner Marine Physical Laboratory, Scripps Institution of Oceanography La Jolla, CA 92037-0238,
A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System
 A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System Per Eivind Dhelie*, PGS, Lysaker, Norway per.eivind.dhelie@pgs.com and Robert Sorley, PGS, Canada Torben Hoy, PGS,
A Step Change in Seismic Imaging Using a Unique Ghost Free Source and Receiver System Per Eivind Dhelie*, PGS, Lysaker, Norway per.eivind.dhelie@pgs.com and Robert Sorley, PGS, Canada Torben Hoy, PGS,
SUMMARY INTRODUCTION GROUP VELOCITY
 Surface-wave inversion for near-surface shear-wave velocity estimation at Coronation field Huub Douma (ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging solutions) and Matthew Haney (Boise State University) SUMMARY We study
Surface-wave inversion for near-surface shear-wave velocity estimation at Coronation field Huub Douma (ION Geophysical/GXT Imaging solutions) and Matthew Haney (Boise State University) SUMMARY We study
UNDERWATER ACOUSTIC CHANNEL ESTIMATION AND ANALYSIS
 Proceedings of the 5th Annual ISC Research Symposium ISCRS 2011 April 7, 2011, Rolla, Missouri UNDERWATER ACOUSTIC CHANNEL ESTIMATION AND ANALYSIS Jesse Cross Missouri University of Science and Technology
Proceedings of the 5th Annual ISC Research Symposium ISCRS 2011 April 7, 2011, Rolla, Missouri UNDERWATER ACOUSTIC CHANNEL ESTIMATION AND ANALYSIS Jesse Cross Missouri University of Science and Technology
Downloaded from library.seg.org by on 10/26/14. For personal use only. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2014
 Ground penetrating abilities of broadband pulsed radar in the 1 70MHz range K. van den Doel, Univ. of British Columbia, J. Jansen, Teck Resources Limited, M. Robinson, G. C, Stove, G. D. C. Stove, Adrok
Ground penetrating abilities of broadband pulsed radar in the 1 70MHz range K. van den Doel, Univ. of British Columbia, J. Jansen, Teck Resources Limited, M. Robinson, G. C, Stove, G. D. C. Stove, Adrok
7. Consider the following common offset gather collected with GPR.
 Questions: GPR 1. Which of the following statements is incorrect when considering skin depth in GPR a. Skin depth is the distance at which the signal amplitude has decreased by a factor of 1/e b. Skin
Questions: GPR 1. Which of the following statements is incorrect when considering skin depth in GPR a. Skin depth is the distance at which the signal amplitude has decreased by a factor of 1/e b. Skin
MATCHED FIELD PROCESSING: ENVIRONMENTAL FOCUSING AND SOURCE TRACKING WITH APPLICATION TO THE NORTH ELBA DATA SET
 MATCHED FIELD PROCESSING: ENVIRONMENTAL FOCUSING AND SOURCE TRACKING WITH APPLICATION TO THE NORTH ELBA DATA SET Cristiano Soares 1, Andreas Waldhorst 2 and S. M. Jesus 1 1 UCEH - Universidade do Algarve,
MATCHED FIELD PROCESSING: ENVIRONMENTAL FOCUSING AND SOURCE TRACKING WITH APPLICATION TO THE NORTH ELBA DATA SET Cristiano Soares 1, Andreas Waldhorst 2 and S. M. Jesus 1 1 UCEH - Universidade do Algarve,
Microtremor Array Measurements and Three-component Microtremor Measurements in San Francisco Bay Area
 Microtremor Array Measurements and Three-component Microtremor Measurements in San Francisco Bay Area K. Hayashi & D. Underwood Geometrics, Inc., United States SUMMARY: Microtremor array measurements and
Microtremor Array Measurements and Three-component Microtremor Measurements in San Francisco Bay Area K. Hayashi & D. Underwood Geometrics, Inc., United States SUMMARY: Microtremor array measurements and
Iterative least-square inversion for amplitude balancing a
 Iterative least-square inversion for amplitude balancing a a Published in SEP report, 89, 167-178 (1995) Arnaud Berlioux and William S. Harlan 1 ABSTRACT Variations in source strength and receiver amplitude
Iterative least-square inversion for amplitude balancing a a Published in SEP report, 89, 167-178 (1995) Arnaud Berlioux and William S. Harlan 1 ABSTRACT Variations in source strength and receiver amplitude
Validation of lateral fraction results in room acoustic measurements
 Validation of lateral fraction results in room acoustic measurements Daniel PROTHEROE 1 ; Christopher DAY 2 1, 2 Marshall Day Acoustics, New Zealand ABSTRACT The early lateral energy fraction (LF) is one
Validation of lateral fraction results in room acoustic measurements Daniel PROTHEROE 1 ; Christopher DAY 2 1, 2 Marshall Day Acoustics, New Zealand ABSTRACT The early lateral energy fraction (LF) is one
The Impact of Very High Frequency Surface Reverberation on Coherent Acoustic Propagation and Modeling
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. The Impact of Very High Frequency Surface Reverberation on Coherent Acoustic Propagation and Modeling Grant B. Deane Marine
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. The Impact of Very High Frequency Surface Reverberation on Coherent Acoustic Propagation and Modeling Grant B. Deane Marine
Multi-survey matching of marine towed streamer data using a broadband workflow: a shallow water offshore Gabon case study. Summary
 Multi-survey matching of marine towed streamer data using a broadband workflow: a shallow water offshore Gabon case study. Nathan Payne, Tony Martin and Jonathan Denly. ION Geophysical UK Reza Afrazmanech.
Multi-survey matching of marine towed streamer data using a broadband workflow: a shallow water offshore Gabon case study. Nathan Payne, Tony Martin and Jonathan Denly. ION Geophysical UK Reza Afrazmanech.
Ocean Acoustics and Signal Processing for Robust Detection and Estimation
 Ocean Acoustics and Signal Processing for Robust Detection and Estimation Zoi-Heleni Michalopoulou Department of Mathematical Sciences New Jersey Institute of Technology Newark, NJ 07102 phone: (973) 596
Ocean Acoustics and Signal Processing for Robust Detection and Estimation Zoi-Heleni Michalopoulou Department of Mathematical Sciences New Jersey Institute of Technology Newark, NJ 07102 phone: (973) 596
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data
 Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Application of Surface Consistent Amplitude Corrections as a Manual Editing Tool
 IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 4, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov-Dec. 2016), PP 59-65 www.iosrjournals.org Application of Surface Consistent
IOSR Journal of Applied Geology and Geophysics (IOSR-JAGG) e-issn: 2321 0990, p-issn: 2321 0982.Volume 4, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov-Dec. 2016), PP 59-65 www.iosrjournals.org Application of Surface Consistent
Applied Methods MASW Method
 Applied Methods MASW Method Schematic illustrating a typical MASW Survey Setup INTRODUCTION: MASW a seismic method for near-surface (< 30 m) Characterization of shear-wave velocity (Vs) (secondary or transversal
Applied Methods MASW Method Schematic illustrating a typical MASW Survey Setup INTRODUCTION: MASW a seismic method for near-surface (< 30 m) Characterization of shear-wave velocity (Vs) (secondary or transversal
Tank experiments of sound propagation over a tilted bottom: Comparison with a 3-D PE model
 Tank experiments of sound propagation over a tilted bottom: Comparison with a 3-D PE model A. Korakas a, F. Sturm a, J.-P. Sessarego b and D. Ferrand c a Laboratoire de Mécanique des Fluides et d Acoustique
Tank experiments of sound propagation over a tilted bottom: Comparison with a 3-D PE model A. Korakas a, F. Sturm a, J.-P. Sessarego b and D. Ferrand c a Laboratoire de Mécanique des Fluides et d Acoustique
MULTI-SHOT PROCESSING FOR BETTER VELOCITY DETERMINATION
 MULTI-SHOT PROCESSING FOR BETTER VELOCITY DETERMINATION by Delaine Thompson Earth Resources Laboratory Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
MULTI-SHOT PROCESSING FOR BETTER VELOCITY DETERMINATION by Delaine Thompson Earth Resources Laboratory Department of Earth, Atmospheric, and Planetary Sciences Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
Summary. Introduction
 Multi survey matching of marine towed streamer data using a broadband workflow: a shallow water offshore Nathan Payne*, Tony Martin and Jonathan Denly. ION GX Technology UK; Reza Afrazmanech. Perenco UK.
Multi survey matching of marine towed streamer data using a broadband workflow: a shallow water offshore Nathan Payne*, Tony Martin and Jonathan Denly. ION GX Technology UK; Reza Afrazmanech. Perenco UK.
Spatial variations in field data
 Chapter 2 Spatial variations in field data This chapter illustrates strong spatial variability in a multi-component surface seismic data set. One of the simplest methods for analyzing variability is looking
Chapter 2 Spatial variations in field data This chapter illustrates strong spatial variability in a multi-component surface seismic data set. One of the simplest methods for analyzing variability is looking
A COMPARISON OF SITE-AMPLIFICATION ESTIMATED FROM DIFFERENT METHODS USING A STRONG MOTION OBSERVATION ARRAY IN TANGSHAN, CHINA
 A COMPARISON OF SITE-AMPLIFICATION ESTIMATED FROM DIFFERENT METHODS USING A STRONG MOTION OBSERVATION ARRAY IN TANGSHAN, CHINA Wenbo ZHANG 1 And Koji MATSUNAMI 2 SUMMARY A seismic observation array for
A COMPARISON OF SITE-AMPLIFICATION ESTIMATED FROM DIFFERENT METHODS USING A STRONG MOTION OBSERVATION ARRAY IN TANGSHAN, CHINA Wenbo ZHANG 1 And Koji MATSUNAMI 2 SUMMARY A seismic observation array for
A NEW APPROACH FOR THE ANALYSIS OF IMPACT-ECHO DATA
 A NEW APPROACH FOR THE ANALYSIS OF IMPACT-ECHO DATA John S. Popovics and Joseph L. Rose Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics The Pennsylvania State University University Park, PA 16802 INTRODUCTION
A NEW APPROACH FOR THE ANALYSIS OF IMPACT-ECHO DATA John S. Popovics and Joseph L. Rose Department of Engineering Science and Mechanics The Pennsylvania State University University Park, PA 16802 INTRODUCTION
Multicomponent seismic polarization analysis
 Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
Isolation Scanner. Advanced evaluation of wellbore integrity
 Isolation Scanner Advanced evaluation of wellbore integrity Isolation Scanner* cement evaluation service integrates the conventional pulse-echo technique with flexural wave propagation to fully characterize
Isolation Scanner Advanced evaluation of wellbore integrity Isolation Scanner* cement evaluation service integrates the conventional pulse-echo technique with flexural wave propagation to fully characterize
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile
 Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
Study of Low-frequency Seismic Events Sources in the Mines of the Verkhnekamskoye Potash Deposit
 Study of Low-frequency Seismic Events Sources in the Mines of the Verkhnekamskoye Potash Deposit D.A. Malovichko Mining Institute, Ural Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences ABSTRACT Seismic networks operated
Study of Low-frequency Seismic Events Sources in the Mines of the Verkhnekamskoye Potash Deposit D.A. Malovichko Mining Institute, Ural Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences ABSTRACT Seismic networks operated
Analysis of Fast Fading in Wireless Communication Channels M.Siva Ganga Prasad 1, P.Siddaiah 1, L.Pratap Reddy 2, K.Lekha 1
 International Journal of ISSN 0974-2107 Systems and Technologies IJST Vol.3, No.1, pp 139-145 KLEF 2010 Fading in Wireless Communication Channels M.Siva Ganga Prasad 1, P.Siddaiah 1, L.Pratap Reddy 2,
International Journal of ISSN 0974-2107 Systems and Technologies IJST Vol.3, No.1, pp 139-145 KLEF 2010 Fading in Wireless Communication Channels M.Siva Ganga Prasad 1, P.Siddaiah 1, L.Pratap Reddy 2,
WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation
 WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), M. Sams (Ikon Science) & K. Waters (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Broadband re-processed seismic
WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), M. Sams (Ikon Science) & K. Waters (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Broadband re-processed seismic
Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas
 Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas Summary The reliability of seismic attribute estimation depends on reliable signal.
Adaptive f-xy Hankel matrix rank reduction filter to attenuate coherent noise Nirupama (Pam) Nagarajappa*, CGGVeritas Summary The reliability of seismic attribute estimation depends on reliable signal.
Time and Frequency Domain Windowing of LFM Pulses Mark A. Richards
 Time and Frequency Domain Mark A. Richards September 29, 26 1 Frequency Domain Windowing of LFM Waveforms in Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing Section 4.7.1 of [1] discusses the reduction of time
Time and Frequency Domain Mark A. Richards September 29, 26 1 Frequency Domain Windowing of LFM Waveforms in Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing Section 4.7.1 of [1] discusses the reduction of time
GEOPIC, Oil & Natural Gas Corporation Ltd, Dehradun ,India b
 Estimation of Seismic Q Using a Non-Linear (Gauss-Newton) Regression Parul Pandit * a, Dinesh Kumar b, T. R. Muralimohan a, Kunal Niyogi a,s.k. Das a a GEOPIC, Oil & Natural Gas Corporation Ltd, Dehradun
Estimation of Seismic Q Using a Non-Linear (Gauss-Newton) Regression Parul Pandit * a, Dinesh Kumar b, T. R. Muralimohan a, Kunal Niyogi a,s.k. Das a a GEOPIC, Oil & Natural Gas Corporation Ltd, Dehradun
HIGH FREQUENCY MASW FOR NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING OF PAVEMENTS ACCELEROMETER APPROACH. Abstract
 HIGH FREQUENCY MASW FOR NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING OF PAVEMENTS ACCELEROMETER APPROACH Downloaded 07/03/14 to 129.237.143.20. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/
HIGH FREQUENCY MASW FOR NON-DESTRUCTIVE TESTING OF PAVEMENTS ACCELEROMETER APPROACH Downloaded 07/03/14 to 129.237.143.20. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/
Summary. Methodology. Selected field examples of the system included. A description of the system processing flow is outlined in Figure 2.
 Halvor Groenaas*, Svein Arne Frivik, Aslaug Melbø, Morten Svendsen, WesternGeco Summary In this paper, we describe a novel method for passive acoustic monitoring of marine mammals using an existing streamer
Halvor Groenaas*, Svein Arne Frivik, Aslaug Melbø, Morten Svendsen, WesternGeco Summary In this paper, we describe a novel method for passive acoustic monitoring of marine mammals using an existing streamer
