|
|
|
- Harold Nathaniel Sparks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY III YEAR / VI SEMESTER ACADEMIC YEAR (EVEN)
2 EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY L T P C OBJECTIVES: To introduce the concepts of various analog modulations and their spectral characteristics. To understand the properties of random process. To know the effect of noise on communication systems. To study the limits set by Information Theory. UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION 9 Generation and detection of AM wave-spectra-dsbsc, Hilbert Transform, Pre-envelope & complex envelope - SSB and VSB comparison -Superheterodyne Receiver. UNIT II ANGLE MODULATION 9 Phase and frequency modulation-narrow Band and Wind band FM - Spectrum - FM modulation and demodulation FM Discriminator- PLL as FM Demodulator - Transmission bandwidth. UNIT III RANDOM PROCESS 9 Random variables, Central limit Theorem, Random Process, Stationary Processes, Mean, Correlation & Covariance functions, Power Spectral Density, Ergodic Processes, Gaussian Process,Transmission of a Random Process Through a LTI filter. UNIT IV NOISE CHARACTERIZATION 9 Noise sources and types Noise figure and noise temperature Noise in cascaded systems. Narrow band noise PSD of in-phase and quadrature noise Noise performance in AM systems Noise performance in FM systems Pre-emphasis and de-emphasis Capture effect, threshold effect. UNIT V INFORMATION THEORY 9 Entropy - Discrete Memoryless channels - Channel Capacity -Hartley - Shannon law - Source coding theorem - Huffman & Shannon - Fano codes. TOTAL: 45 PERIODS OUTCOMES: At the end of the course, the students would Design AM communication systems. Design Angle modulated communication systems Apply the concepts of Random Process to the design of Communication systems Analyze the noise performance of AM and FM systems TEXT BOOKS: 1. J.G.Proakis, M.Salehi, Fundamentals of Communication Systems, Pearson Education S. Haykin, Digital Communications, John Wiley, REFERENCES: 1. B.P.Lathi, Modern Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 3rd Edition, Oxford University Press, B.Sklar, Digital Communications Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd Edition Pearson Education H P Hsu, Schaum Outline Series - Analog and Digital Communications TMH Couch.L., "Modern Communication Systems", Pearson, 2001.
3 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: IV / II year B.E. UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Generation and detection of AM wave-spectra-dsbsc, Hilbert Transform, Pre-envelope & complex envelope - SSB and VSB comparison -Super heterodyne Receiver. PART A Q.No Questions BT Level Domain 1. What are the advantages of VSB-AM? 2. State heterodyning principle. 3. What are the advantages of modulating low frequency signal into high frequency signal? 4. List the types of AM modulators? 5. Define Coherent Detection. 6. Why do you need modulation in communication systems? 7. Identify the differences between single side band and vestigial side band systems. 8. Write about diagonal clipping and negative peak clipping? 9. Suggest a modulation scheme for broadcast video transmission. 10. Apply the concepts of sensitivity and selectivity in AM receiver Draw the AM modulated wave for modulation index=0.5 and its spectra. 12. Illustrate the applications of Hilbert transform.
4 13. Apply the concepts of power relations and find the total power in a modulated wave if the carrier is 10 watts and amplitude modulated to a depth of 80%. 14. Compare AM with DSB-SC and SSB-SC. 15. Distinguish between high level and low level modulation? 16. Differentiate between linear and nonlinear modulation 17. A transmitter radiates 9kW without modulation and kW after modulation. Determine depth of modulation. 18. When a signal m(t)=3cos(2 x10 3 t) modulates a carrier c(t)=5cos(πx10 6 t), determine the modulation index and transmission bandwidth if the modulation is AM. 19. Summarize the methods for generating SSB-SC signal. 20. Can you formulate the theory for modulation index of an AM signal and write its classification. PART B 1. What is the need for carrier suppression in AM system? Draw and explain the functioning of such system. (16) 2. (i)explain the generation of SSBSC signal using phase shift method. (8) (ii)suggest a scheme for recovering the message signal from the signal s(t)=2m(t)cos2πfct. Explain the same. (8) 3. (i) An AM signal is generated by modulating the carrier fc=800mhz by the signal m(t)=sin3000πt+0.5cos5000πt. The AM signal s(t)=100[1+m(t)] cos2πf c t is fed to a 50ohm load. (8) a) Determine the average power in the carrier and in the sidebands. b) Find the modulation index and peak power delivered to the load. (ii)explain the function of switching modulator in the generation of AM signal. (8) 4. (i)analyze the concepts of AM modulation and derive the equation of an AM wave. Also draw the modulated AM wave for various modulation index. (8) (ii) Summarize the methods of demodulation of DSBSC and explain briefly about costas loop. (8) 5
5 5. (i)draw the VSB spectrum and explain the significance. (8) (ii)how do you demodulate AM signal? Explain. (8) 6. (i)compare the characteristics of DSBFC, DSBSC, SSBFC, SSBSC, SB schemes. (8) (ii)what is heterodyning and explain the operation of Superheterodyne Receiver with a suitable block diagram. (8) 7. (i)what is Hilbert transform? And how it can be used for various applications. (8) (ii)analyze the frequency components present in the output when the 1000kHz carrier is simultaneously AM modulated with 300Hz, 800Hz and 1.5kHz audio sine waves. (8) 8. (i) Apply the concepts of envelope detection for demodulation of AM and explain its operation. (8) (ii)how would you generate SSB using Weavers method? Illustrate with a neat block diagram. (8) 9. (i)construct the balanced modulator circuit for the generation of DSB-SC-AM and explain its operation. (8) (ii)develop the coherent detection method in detail for the detection of DSB-SC and SSB-SC. What happens when there is phase mismatch? (8) 10. (i) How do you apply ring modulator for the generation of DSB-SC signal? (8) (ii) For an AM DSBFC wave with peak unmodulated carrier voltage V c =10V, a load resistance R L =10Ω and a modulation coefficient m a =1,determine (8) a) Powers of the carrier and the upper sidebands b) Total sideband power c) Total power of the modulated wave d) Draw the power spectrum BTL3
6 UNIT II ANGLE MODULATION Phase and frequency modulation-narrow Band and Wind band FM - Spectrum - FM modulation and demodulation FM Discriminator- PLL as FM Demodulator - Transmission bandwidth. PART A Q. No Questions BT Level Domain 1. Compare WBFM and NBFM. 2. State the Carson s rule to determine the bandwidth of FM. 3. Why frequency modulation is more preferred for voice transmission? 4. List the advantages of AM and FM. 5. Apply the concepts of detection for detecting FM signals. 6. Analyze the bandwidth of FM when the carrier is modulated by a sinusoidal modulating frequency of 2kHz resulting in a frequency deviation of 5kHZ. 7. Formulate the difference between the direct method and indirect method of FM. 8. What is the need for pre-emphasis? 9. List the applications of phase locked loop? 10. Draw the block diagram of a method for generating a narrow band FM? 11. Give the mathematical expression for FM and PM. 12. Describe the limitations of slope detector? 13. Summarize the merits and demerits of balanced slope detector. 14. Point out the advantages and disadvantages of Foster-Seely discrimination method? 15. Define modulation index of FM and PM. 16. Differentiate between phase and frequency modulation.
7 17. A carrier of frequency 100MHz is frequency modulated by a signal x(t)=20sin(200πx10 3 t). What is the bandwidth of the FM signal if the frequency sensitivity of the modulator is 25kHz per volt? 18. What is the bandwidth required for an FM wave in which the modulating frequency signal is 2kHz and the maximum frequency deviation is 12kHz? 19. Show that Armstrong method is superior to reactance modulator? 20. Outline the concepts of lock in range and dynamic range of PLL. PART B 1. (i)explain the operation of ratio detector for FM detection. (8) (ii)explain the operation of PLL as a FM demodulator. (8) 2. (i) Explain how FM is achieved using Varactor diodes. (8) (ii)make at least five comparisons of AM and FM systems. (8) 3. Apply the concepts of FM and PM with an angle modulated wave which is described by 10 cos 2 10 ) 0.1sin 10 ) t] a) Considering as PM signal with Kp= 10, find m(t). (8) b) Considering as FM signal with Kp= 10 π, find m(t). (8) 4. A carrier frequency of 80MHz is frequency modulated by a sine wave amplitude of 20volts and frequency of 80MHz and the frequency sensitivity of the modulator is 20KHz/v. (16) a) Determine the appropriate bandwidth of the FM wave by using Carson s Rule b) Determine the bandwidth by transmitting only those frequencies whose amplitude exceed 1% of the unmodulated carrier amplitude. 5. (i)how do you obtain the expression for the single tone frequency modulated signal and hence prove that is the constant envelope modulation requiring infinite bandwidth. (12) (ii)list the components present in the spectrum of the FM. (4) 6. (i)explain the FM discriminator with a suitable diagram. (8) (ii)how FM can be derived from PM and vice versa. (8)
8 7. (i)obtain the mathematical representation of FM and PM waves. (8) (ii) With a neat diagram, analyze the concepts of FM with direct method of generation. (8) 8. (i)define FM and derive the expression for wideband FM in terms of Bessel functions. (10) (ii)how do you obtain FM from PM and vice versa? Explain. (6) 9. (i) What are the methods of FM generation and explain the Armstrong method to generate FM signal. (10) (ii) How do you relate the phase modulation with frequency modulation? (6) 10. (i)when the modulating frequency in an FM system is 400Hz and the modulating voltage is 2.4V and the modulation index is 60.Calculate the maximum deviation. Apply the concepts of modulation index and calculate the modulating index when the modulating frequency is reduced to 250Hz and the modulating voltage is simultaneously raised to 3.2V. (8) (ii)with necessary diagrams, develop the operation of slope detector for demodulating FM signal. (8)
9 UNIT III RANDOM PROCESS Random variables, Central limit Theorem, Random Process, Stationary Processes, Mean, Correlation & Covariance functions, Power Spectral Density, Ergodic Processes, Gaussian Process, Transmission of a Random Process Through a LTI filter. PART A Q.No Questions BT Level Domain 1. Define random variable. Specify the sample space and the random variable for a coin tossing experiment. 2. List the properties of the cumulative distributive function. 3. Demonstrate when random process is called deterministic? 4. Classify random process? Give one example for each. 5. Express the auto correlation function and power spectral density of white noise. 6. State central limit theorem. 7. Write the Rayleigh and Rician probability density functions. 8. Describe mean, autocorrelation and covariance of a random process. 9. Give the conditions to be satisfied for wide sense stationary. 10. What are the properties of an autocorrelation function? 11. Quote Ergodic processes and Gaussian processes. 12. Infer the cross correlation of random processes of X(t) and Y(t)? 13. Show the input output relation for a power spectral density and cross spectral density. 14. Investigate when random processes X(t) is called white process? 15. Summarise an expression for noise equivalent bandwidth. 16. Generalize the power spectral density of X(t). 17. Pointout the properties of Gaussian process. 18. The pdf of a random variable is given as f X (x) =k for a x b and 0 otherwise where k is a constant. Calculate the value of k.
10 19. Evaluate when a random process is called as stationary, deterministic and ergodic. 20. Distinguish between random variable and random process. PART B 1. Explain the following, (i) Random variable (5) (ii) Gaussian process (5) (iii) Central limit theorem (6) 2. (i) Describe and prove the properties of Gaussian Process. (8) (ii) Differentiate the strict-sense stationary with that of wide sense stationary process. (8) 3. (i) Analyze the following terms mean, correlation, covariance, and ergodicity. (8) (ii) Quote the properties of the auto correlation function. (8) 4. (i) An AWGN of power spectral density 1µW is fed through a filter with frequency response H(f) = 1/2 ; f < 40 khz 0 ; elsewhere Calculate the noise power at the output of the filter. (8) (ii)describe about stationary processes and its classifications. (8) 5. Generalize the equation for finding the probability density function of a one to one differential function of a given random variable. (16) 6. (i) Examine about Transmission of random process through a Linear Time Invariant (LTI) filter. (8) (ii) Find the autocorrelation of a sequence x(t) =A cos(2πfc(t+θ)) where A and fc are constant and θ is a random variable that is uniformly distributed over the interval [-π π]. (8) 7. (i) Define autocorrelation. Discuss the properties of autocorrelation function. (8) (ii) Let X(t) and Y(t) be both zero-mean and WSS random processes. Consider the random process z(t) = X(t) + Y(t). Determine the auto correlation and power spectrum of z(t) if X(t) and Y(t) are jointly WSS. (8)
11 8. Discuss and prove the properties of power spectral density. (16) 9. (i) Let X have the uniform distribution given by 12π 0 x 2π f X (x) = 0 Otherwise Calculate mean, mean square value and variance. (8) (ii) Let X(t) = A cos (ωt+φ) and Y(t) = A sin (ωt+φ), where A and ω are constants and Φ is a uniform random variables [0, 2π]. Discover the cross correlation of x(t) and y(t). (8) 10. Given a random process X(t)=A Cos(ωt+θ), where A and ω are constants and θ is a uniform random variable. Judge that X(t) is Ergodic. (16)
12 UNIT IV NOISE CHARACTERIZATION Noise sources and types Noise figure and noise temperature Noise in cascaded systems. Narrow band noise PSD of in-phase and quadrature noise Noise performance in AM systems Noise performance in FM systems Pre-emphasis and de-emphasis Capture effect, threshold effect. PART A Q.No Questions BT Level Domain 1. Describe white noise? Give its Characteristics. 2. Define noise figure and SNR. 3. A Receiver is connected to an antenna of resistance of 50Ω has an equivalent noise resistance of 30Ω. Invent the receiver noise figure. 4. When carrier to noise ratio is high, how will you get figure of merit of FM systems? 5. Formulate the narrow-band noise m(t) at the IF filter output in terms of its in-phase and quadrature components. 6. Discuss the need for pre-emphasis and de-emphasis. 7. Quote threshold effect in AM receiver and Q factor of a receiver. 8. What is FM threshold effect? 9. Distinguish the noise performance of DSBSC receiver using coherent detection with AM receiver using envelope detection. 10. Illustrate coherent system? 11. Classify the methods are to improve FM threshold reduction? 12. The figure of merit of AM system is 1/3 when the modulation is 100 percent and that of FM is (3/2) m f 2.The use of FM offers improved noise performance over AM when (3/2)m f 2 > 1/3. Where m f modulation index in FM. Solve the characteristics of super heterodyne receivers. 13. Name what is capture effect? What do you understand by capture effect in FM? 14. Discuss threshold effect with respect to noise? 15. Label noise equivalent bandwidth. 16. Calculate noise figure and equivalent noise temperature for a receiver connected to an antenna whose resistance is 100Ω and equivalent noise resistance is 50Ω.
13 17. Pointout the characteristic of shot noise. 18. Two resistors of 20 kω, 50 kω are at room temperature (290 o K). For a bandwidth of 100 KHz, Evaluate the thermal noise voltage generated by the two resistors in series. 19. DC current of 2 ma flows through the semiconductor junction. Consider the effective noise bandwidth of 1 khz and Infer the shot noise component. 20. Evaluate thermal noise voltage across the simple parallel RC circuit shown with R =1kΩ and C=1µF at T = 270 o C. PART B 1. (i) Write a short note on shot noise and also explain about power spectral density of shot noise. (8) (ii) Show and discuss the causes and effects of various forms of noise created within a receiver? (8) 2. (i) Describe the following (a) White noise (b) Noise temperature. (8) (ii) Illustrate how to represent narrowband noise. (8) 3. What is coherent detector? Derive an expression for SNR at input (SNRc) and output of (SNRo) of a coherent detector. (16) 4. (i) Express and derive the output SNR for FM reception. (8) (ii) Explain the significance of pre-emphasis and de-emphasis in FM system. (8) 5. (i) Describe and derive the figure of merit of a FM system. (12) (ii) Infer FM threshold effect. (4) 6. (i) Formulate the figure of merit for AM system for noncoherent system, with suitable assumptions. (12) (ii) Formulate the relationship between noise figure and equivalent noise temperature. (4) 7. (i) The three amplifiers 1, 2 and 3 have the following characteristics: F 1 =9dB, G 1 =50dB, F 2 =6dB, G 2 =30dB, F 3 =4db, G 3 =20dB. The amplifiers are connected in tandem. Discover which combination gives the lowest noise figure. (8) (ii) Analyze in detail about narrow band noise and the properties of in-phase and quadrature components of narrow band noise. (8) 8. (i) Solve the expression for figure of merit of DSB-SC receiver using coherent detection. (8) (ii) Define and explain the following: Gaussian noise and Gaussian
14 distribution and thermal noise. What type of PDF does the Gaussian noise follow? (8) 9. (i) Discuss how sine wave plus noise is represented. Obtain the joint PDF of such noise component. (8) (ii) Consider two amplifiers are connected in cascade. First stage amplifier has gain and noise figure as 10 db and 2 db. Second stage has noise figure of 3 db. Estimate the total noise figure. (8) 10. Evaluate the effective noise temperature of a cascade amplifier. Assess how the various noises are generated in the method of representing them. (16)
15 UNIT V INFORMATION THEORY Entropy - Discrete Memoryless channels - Channel Capacity -Hartley - Shannon law - Source coding theorem - Huffman & Shannon - Fano codes PART A Q. No Questions BT Level Domain 1. Define Shannon s channel coding theorem 2. Demonstrate entropy for a discrete memory less source. 3. State channel coding theorem 4. Point out the source coding techniques 5. Give the expression for code efficiency in terms of entropy. 6. Test whether the information of a continuous system is non negative? Give reason? 7. What is prefix code? 8. Calculate the channel capacity of binary synchronous channel with error probability of Define channel redundancy? 10. A telephone network has a bandwidth of 3.4 khz, Solve for the information capacity of the telephone channel for a signal-to-noise ratio of 30dB. 11. Explain the significance of the entropy H(X/Y) of a communication system where X is the transmitter and Y is the receiver. 12. Quote information rate? 13. Identify Shannon s Channel capacity theorem. 14. Summarize the properties of Entropy? 15. An event has six possible outcomes with probabilities 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32, 1/32. Interpret the entropy of the system. 16. Formulate the equation for finding the entropy of a binary source. 17. Generalize the Shannon channel capacity for a discrete memory less channel
16 18. Differentiate between lossless and lossy coding. 19. A source emits one of the four symbols A, B, C and D with probabilities 1/3, 1/6, 1/4, 1/4 respectively the emissions of symbols by the source are statistically independent. Measure the entropy of the system 20. Recognize entropy and find the entropy of a DMS with probability s1=1/4, s2=1/4, and s3=1/4. PART B 1. Discuss Source coding theorem, give the advantage and disadvantage of channel coding in detail, and Summarize the data compaction. (16) 2. (i) Explain in detail Huffman coding algorithm and compare this with the other types of coding. (12) (ii) Describe S/N trade off. (4) 3. (i) Explain how channel capacity could be improved. Demonstrate the S/N trade off in detail. (10) (ii) List out the need for source coding and channel coding. (6) 4. (i) Identify about the lossy source coding schemes. (8) (ii) Source emits one of the five symbols A, B, C, D, E with probabilities 0.4, 0.19, 0.16, 0.15, 0.1 respectively the emissions of symbols by the source are statistically independent. Design a Shannon Fano code for the source. Discover the average code length and efficiency. (8) 5. Explain the properties of entropy and with suitable example, point out the entropy of binary memory less source. (16) 6. (i) What is Entropy? Explain the important properties of entropy. (8) (ii) Show that how will you use the source coding to increase average information per bit. (8) 7. Develop binary optical code for the following probability symbols using Huffman procedure and calculate entropy of the source, average code Length, efficiency, redundancy and variance 0.2, 0.18, 0.12, 0.1, 0.1, 0.08, 0.06, 0.06, 0.06, (16)
17 8. Write short notes on Differential entropy, derive the channel capacity theorem and discuss the implications of the information capacity theorem. (16) 9. Deduce the expression for channel capacity of a continuous channel. Find also the expression for channel capacity of continuous channel of an infinite bandwidth. Comment on the results. (16) 10. Describe binary symmetric channel? Derive channel capacity formula for symmetric Channel. (16)
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: IV / II year B.E.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: IV / II year B.E.
EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE : EC2252 SEM / YEAR : II year SUBJECT NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY UNIT
EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE : EC2252 SEM / YEAR : II year SUBJECT NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY UNIT
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB.NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY SUB.CODE: EC1252 YEAR : II SEMESTER : IV UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION SYSTEMS
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB.NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY SUB.CODE: EC1252 YEAR : II SEMESTER : IV UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION SYSTEMS
15.Calculate the local oscillator frequency if incoming frequency is F1 and translated carrier frequency
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUBJECT NAME:COMMUNICATION THEORY YEAR/SEM: II/IV SUBJECT CODE: EC 6402 UNIT I:l (AMPLITUDE MODULATION) PART A 1. Compute the bandwidth of the AMP
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUBJECT NAME:COMMUNICATION THEORY YEAR/SEM: II/IV SUBJECT CODE: EC 6402 UNIT I:l (AMPLITUDE MODULATION) PART A 1. Compute the bandwidth of the AMP
Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION
 PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATON ENGG. Branch: ECE EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY Semester: IV Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION 1.
PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATON ENGG. Branch: ECE EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY Semester: IV Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION 1.
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]
![(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3] (b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]](/thumbs/85/91561193.jpg) Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC314 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem : III Year, 6th Sem (EEE)
S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC314 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem : III Year, 6th Sem (EEE)
S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4657]-49 S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4657]-49 S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC211 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem
S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC211 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem
Angle Modulated Systems
 Angle Modulated Systems Angle of carrier signal is changed in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal. Two types Frequency Modulation (FM) Phase Modulation (PM) Use Commercial radio
Angle Modulated Systems Angle of carrier signal is changed in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal. Two types Frequency Modulation (FM) Phase Modulation (PM) Use Commercial radio
Communication Channels
 Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I. Review. ELEC 350 Fall
 ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise
 Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise 1. If F X (x) is the distribution function of a random variable X and x 1 x 2, show that F X (x 1 ) F X (x 2 ). 2. Use the definition of the cumulative
Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise 1. If F X (x) is the distribution function of a random variable X and x 1 x 2, show that F X (x 1 ) F X (x 2 ). 2. Use the definition of the cumulative
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS
 EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
V. CHANDRA SEKAR Professor and Head Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SASTRA University, Kumbakonam
 V. CHANDRA SEKAR Professor and Head Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SASTRA University, Kumbakonam 1 Contents Preface v 1. Introduction 1 1.1 What is Communication? 1 1.2 Modulation
V. CHANDRA SEKAR Professor and Head Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SASTRA University, Kumbakonam 1 Contents Preface v 1. Introduction 1 1.1 What is Communication? 1 1.2 Modulation
Communication Systems
 Electrical Engineering Communication Systems Comprehensive Theory with Solved Examples and Practice Questions Publications Publications MADE EASY Publications Corporate Office: 44-A/4, Kalu Sarai (Near
Electrical Engineering Communication Systems Comprehensive Theory with Solved Examples and Practice Questions Publications Publications MADE EASY Publications Corporate Office: 44-A/4, Kalu Sarai (Near
UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System
 UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System Introduction There are three parameters of a carrier that may carry information: Amplitude Frequency Phase Frequency Modulation Power in an FM signal does not vary with modulation
UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System Introduction There are three parameters of a carrier that may carry information: Amplitude Frequency Phase Frequency Modulation Power in an FM signal does not vary with modulation
Theory of Telecommunications Networks
 Theory of Telecommunications Networks Anton Čižmár Ján Papaj Department of electronics and multimedia telecommunications CONTENTS Preface... 5 1 Introduction... 6 1.1 Mathematical models for communication
Theory of Telecommunications Networks Anton Čižmár Ján Papaj Department of electronics and multimedia telecommunications CONTENTS Preface... 5 1 Introduction... 6 1.1 Mathematical models for communication
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers)
 UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
Communication Systems
 Electronics Engineering Communication Systems Comprehensive Theory with Solved Examples and Practice Questions Publications Publications MADE EASY Publications Corporate Office: 44-A/4, Kalu Sarai (Near
Electronics Engineering Communication Systems Comprehensive Theory with Solved Examples and Practice Questions Publications Publications MADE EASY Publications Corporate Office: 44-A/4, Kalu Sarai (Near
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. Semester 1 June COMMUNICATIONS IV (ELEC ENG 4035)
 EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. Semester 1 June 2007 101902 COMMUNICATIONS IV (ELEC ENG 4035) Official Reading Time: Writing Time: Total Duration: 10 mins 120 mins 130 mins Instructions: This is a closed
EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. Semester 1 June 2007 101902 COMMUNICATIONS IV (ELEC ENG 4035) Official Reading Time: Writing Time: Total Duration: 10 mins 120 mins 130 mins Instructions: This is a closed
CHAPTER 3 Noise in Amplitude Modulation Systems
 CHAPTER 3 Noise in Amplitude Modulation Systems NOISE Review: Types of Noise External (Atmospheric(sky),Solar(Cosmic),Hotspot) Internal(Shot, Thermal) Parameters of Noise o Signal to Noise ratio o Noise
CHAPTER 3 Noise in Amplitude Modulation Systems NOISE Review: Types of Noise External (Atmospheric(sky),Solar(Cosmic),Hotspot) Internal(Shot, Thermal) Parameters of Noise o Signal to Noise ratio o Noise
UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION
 UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Prepared by: S.NANDHINI, Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Sriperumbudur, Tamilnadu. CONTENTS Introduction to communication systems
UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Prepared by: S.NANDHINI, Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Sriperumbudur, Tamilnadu. CONTENTS Introduction to communication systems
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
Amplitude Modulated Systems
 Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Amplitude Modulation, II
 Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING 2013 REGULATION 2MARKS UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers)
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING 2013 REGULATION 2MARKS UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING 2013 REGULATION 2MARKS UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY CS6304- ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION BE-CSE/IT SEMESTER III REGULATION 2013 Faculty
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY CS6304- ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION BE-CSE/IT SEMESTER III REGULATION 2013 Faculty Name: S.Kalpana, AP/ECE QUESTION BANK UNIT I ANALOG
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY CS6304- ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION BE-CSE/IT SEMESTER III REGULATION 2013 Faculty Name: S.Kalpana, AP/ECE QUESTION BANK UNIT I ANALOG
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering
 Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
 UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating
UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating
Downloaded from 1
 VII SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2004 Attempt ALL questions. Q. [1] How does Digital communication System differ from Analog systems? Draw functional block diagram of DCS and explain the significance of
VII SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2004 Attempt ALL questions. Q. [1] How does Digital communication System differ from Analog systems? Draw functional block diagram of DCS and explain the significance of
AM Limitations. Amplitude Modulation II. DSB-SC Modulation. AM Modifications
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Amplitude Modulation II
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER GCE@Bodi_ SCIENCE GCE@Bodi_ AND ENIGNEERING GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ Analog and Digital Communication GCE@Bodi_ DEPARTMENT OF CsE Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER GCE@Bodi_ SCIENCE GCE@Bodi_ AND ENIGNEERING GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ Analog and Digital Communication GCE@Bodi_ DEPARTMENT OF CsE Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication
3.1 Introduction to Modulation
 Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Chapter 3: Analog Modulation Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved.
 Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS
 J.P. Linnartz EECS 290i handouts Spring 1993 ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS Amplitude modulation Various methods exist to transmit a baseband message m(t) using an RF carrier signal c(t) =
J.P. Linnartz EECS 290i handouts Spring 1993 ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS Amplitude modulation Various methods exist to transmit a baseband message m(t) using an RF carrier signal c(t) =
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 4TH EDITION Simon Hayhin McMaster University JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. Ш.! [ BACKGROUND AND PREVIEW 1. The Communication Process 1 2. Primary Communication Resources 3 3. Sources of
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 4TH EDITION Simon Hayhin McMaster University JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. Ш.! [ BACKGROUND AND PREVIEW 1. The Communication Process 1 2. Primary Communication Resources 3 3. Sources of
Analog Communication.
 Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATIONS
 PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATIONS Systems, Modulation, and Noise SIXTH EDITION INTERNATIONAL STUDENT VERSION RODGER E. ZIEMER University of Colorado at Colorado Springs WILLIAM H. TRANTER Virginia Polytechnic
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATIONS Systems, Modulation, and Noise SIXTH EDITION INTERNATIONAL STUDENT VERSION RODGER E. ZIEMER University of Colorado at Colorado Springs WILLIAM H. TRANTER Virginia Polytechnic
CHAPTER 2! AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM)
 CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
Wireless Communication Fading Modulation
 EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS. BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4)
 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4) (R15A0409) ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS Course Objectives: Objective of the course is to:
ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4) (R15A0409) ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS Course Objectives: Objective of the course is to:
EE4512 Analog and Digital Communications Chapter 6. Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation
 Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Amplitude Modulation Pages 306-309 309 The analytical signal for double sideband, large carrier amplitude modulation
Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Amplitude Modulation Pages 306-309 309 The analytical signal for double sideband, large carrier amplitude modulation
Silver Oak College of Engineering and Technology
 Silver Oak College of Engineering and Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Syllabus of Midsem I (5 th Sem) Subject Name: Microcontroller & interfacing (2500) Introduction To 8-bit Microcontroller:
Silver Oak College of Engineering and Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Syllabus of Midsem I (5 th Sem) Subject Name: Microcontroller & interfacing (2500) Introduction To 8-bit Microcontroller:
SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ECE COURSE PLAN
 SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ECE COURSE PLAN Course Code : EC0210 Course Title : COMMUNICATION THEORY Semester : IV
SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ECE COURSE PLAN Course Code : EC0210 Course Title : COMMUNICATION THEORY Semester : IV
B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER Third Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 2204 ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION
 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2011. Third Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 2204 ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Time : Three hours Maximum : 100 marks Answer ALL questions.
B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2011. Third Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 2204 ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Time : Three hours Maximum : 100 marks Answer ALL questions.
ANALOG COMMUNICATION
 ANALOG COMMUNICATION TRAINING LAB Analog Communication Training Lab consists of six kits, one each for Modulation (ACL-01), Demodulation (ACL-02), Modulation (ACL-03), Demodulation (ACL-04), Noise power
ANALOG COMMUNICATION TRAINING LAB Analog Communication Training Lab consists of six kits, one each for Modulation (ACL-01), Demodulation (ACL-02), Modulation (ACL-03), Demodulation (ACL-04), Noise power
EE390 Final Exam Fall Term 2002 Friday, December 13, 2002
 Name Page 1 of 11 EE390 Final Exam Fall Term 2002 Friday, December 13, 2002 Notes 1. This is a 2 hour exam, starting at 9:00 am and ending at 11:00 am. The exam is worth a total of 50 marks, broken down
Name Page 1 of 11 EE390 Final Exam Fall Term 2002 Friday, December 13, 2002 Notes 1. This is a 2 hour exam, starting at 9:00 am and ending at 11:00 am. The exam is worth a total of 50 marks, broken down
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE-TRICHY QUESTION BANK UNIT IV PART-A
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE-TRICHY QUESTION BANK SATELLITE COMMUNICATION DEPT./SEM.:ECE/VIII UNIT IV PART-A 1. What are the advantages of the super heterodyne receiver over TRF receiver? (AUC MAY 2004)
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE-TRICHY QUESTION BANK SATELLITE COMMUNICATION DEPT./SEM.:ECE/VIII UNIT IV PART-A 1. What are the advantages of the super heterodyne receiver over TRF receiver? (AUC MAY 2004)
QUESTION BANK. Sandeep Kumar Bansal. Electronics & Communication Department
 QUESTION BANK Sandeep Kumar Bansal Electronics & Communication Department ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION QUESTION BANK BRANCH 4 TH SEM CS/IT UNIT-1 1. Draw the circuit diagram of balanced modulator using
QUESTION BANK Sandeep Kumar Bansal Electronics & Communication Department ANALOG AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION QUESTION BANK BRANCH 4 TH SEM CS/IT UNIT-1 1. Draw the circuit diagram of balanced modulator using
Introduction to Amplitude Modulation
 1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
DIGITAL COMMINICATIONS
 Code No: R346 R Set No: III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 23 DIGITAL COMMINICATIONS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 75 Answer
Code No: R346 R Set No: III B.Tech. I Semester Regular and Supplementary Examinations, December - 23 DIGITAL COMMINICATIONS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 75 Answer
Amplitude Modulation Chapter 2. Modulation process
 Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Charan Langton, Editor
 Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM)
 Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ECE COURSE PLAN
 Course Code Course Title Semester SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ECE COURSE PLAN : EC0210 : COMMUNICATION THEORY : IV
Course Code Course Title Semester SRM UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ECE COURSE PLAN : EC0210 : COMMUNICATION THEORY : IV
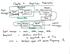 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT. Semester: III Max.Marks: 100
 NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, 639 114 Karur District Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT Branch & Section: II CSE & IT Date & Time: 06.08.15 & 3 Hours Semester: III Max.Marks:
NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, 639 114 Karur District Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT Branch & Section: II CSE & IT Date & Time: 06.08.15 & 3 Hours Semester: III Max.Marks:
Noise and Distortion in Microwave System
 Noise and Distortion in Microwave System Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 1 Introduction Noise is a random process from many sources: thermal,
Noise and Distortion in Microwave System Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 1 Introduction Noise is a random process from many sources: thermal,
DT Filters 2/19. Atousa Hajshirmohammadi, SFU
 1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUBJECT QUESTION BANK : EC6401 ELECTRONICS CIRCUITS-II SEM / YEAR: IV / II year B.E.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING SUBJECT QUESTION BANK : EC6401 ELECTRONICS CIRCUITS-II SEM / YEAR: IV / II year B.E.
PROPOSED SCHEME OF COURSE WORK
 PROPOSED SCHEME OF COURSE WORK Course Details: Course Title : COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Course Code : 13EC1145 L T P C : 4 1 0 3 Program: : B.Tech. Specialization: : Information Technology Semester : V Prerequisites
PROPOSED SCHEME OF COURSE WORK Course Details: Course Title : COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Course Code : 13EC1145 L T P C : 4 1 0 3 Program: : B.Tech. Specialization: : Information Technology Semester : V Prerequisites
4.1 REPRESENTATION OF FM AND PM SIGNALS An angle-modulated signal generally can be written as
 1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II
 EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : EC6404 LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS SEM / YEAR: IV / II year
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : EC6404 LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS SEM / YEAR: IV / II year
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER EI6601 Modern Electronic Instrumentation Regulation
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER EI6601 Modern Electronic Instrumentation Regulation
SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18
 INSTRUCTIONS SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18 The test is 60 minutes long and consists of 40 multiple choice
INSTRUCTIONS SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18 The test is 60 minutes long and consists of 40 multiple choice
Chapter 2: Signal Representation
 Chapter 2: Signal Representation Aveek Dutta Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University at Albany Spring 2018 Images and equations adopted from: Digital Communications
Chapter 2: Signal Representation Aveek Dutta Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University at Albany Spring 2018 Images and equations adopted from: Digital Communications
Dimensional analysis of the audio signal/noise power in a FM system
 Dimensional analysis of the audio signal/noise power in a FM system Virginia Tech, Wireless@VT April 11, 2012 1 Problem statement Jakes in [1] has presented an analytical result for the audio signal and
Dimensional analysis of the audio signal/noise power in a FM system Virginia Tech, Wireless@VT April 11, 2012 1 Problem statement Jakes in [1] has presented an analytical result for the audio signal and
CS311: Data Communication. Transmission of Analog Signal - I
 CS311: Data Communication Transmission of Analog Signal - I by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
CS311: Data Communication Transmission of Analog Signal - I by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering 1
 UNIT I SAMPLING AND QUANTIZATION Pulse Modulation 1. Explain in detail the generation of PWM and PPM signals (16) (M/J 2011) 2. Explain in detail the concept of PWM and PAM (16) (N/D 2012) 3. What is the
UNIT I SAMPLING AND QUANTIZATION Pulse Modulation 1. Explain in detail the generation of PWM and PPM signals (16) (M/J 2011) 2. Explain in detail the concept of PWM and PAM (16) (N/D 2012) 3. What is the
1B Paper 6: Communications Handout 2: Analogue Modulation
 1B Paper 6: Communications Handout : Analogue Modulation Ramji Venkataramanan Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering ramji.v@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term 16 1 / 3 Modulation Modulation
1B Paper 6: Communications Handout : Analogue Modulation Ramji Venkataramanan Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering ramji.v@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term 16 1 / 3 Modulation Modulation
Thus there are three basic modulation techniques: 1) AMPLITUDE SHIFT KEYING 2) FREQUENCY SHIFT KEYING 3) PHASE SHIFT KEYING
 CHAPTER 5 Syllabus 1) Digital modulation formats 2) Coherent binary modulation techniques 3) Coherent Quadrature modulation techniques 4) Non coherent binary modulation techniques. Digital modulation formats:
CHAPTER 5 Syllabus 1) Digital modulation formats 2) Coherent binary modulation techniques 3) Coherent Quadrature modulation techniques 4) Non coherent binary modulation techniques. Digital modulation formats:
Angle Modulation. Frequency Modulation
 Angle Modulation Contrast to AM Generalized sinusoid: v(t)=v max sin(ωt+φ) Instead of Varying V max, Vary (ωt+φ) Angle and Pulse Modulation - 1 Frequency Modulation Instantaneous Carrier Frequency f i
Angle Modulation Contrast to AM Generalized sinusoid: v(t)=v max sin(ωt+φ) Instead of Varying V max, Vary (ωt+φ) Angle and Pulse Modulation - 1 Frequency Modulation Instantaneous Carrier Frequency f i
Q.P. Code : [ TURN OVER]
![Q.P. Code : [ TURN OVER] Q.P. Code : [ TURN OVER]](/thumbs/90/103239233.jpg) Q.P. Code : 587801 8ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC70 6308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703
Q.P. Code : 587801 8ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC70 6308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS. MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications
 DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications Bandpass binary signalling The common techniques of bandpass binary signalling are: - On-off keying (OOK), also known as
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications Bandpass binary signalling The common techniques of bandpass binary signalling are: - On-off keying (OOK), also known as
Digital modulation techniques
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Angle Modulation, II. Lecture topics. FM bandwidth and Carson s rule. Spectral analysis of FM. Narrowband FM Modulation. Wideband FM Modulation
 Angle Modulation, II Lecture topics FM bandwidth and Carson s rule Spectral analysis of FM Narrowband FM Modulation Wideband FM Modulation Bandwidth of Angle-Modulated Waves Angle modulation is nonlinear
Angle Modulation, II Lecture topics FM bandwidth and Carson s rule Spectral analysis of FM Narrowband FM Modulation Wideband FM Modulation Bandwidth of Angle-Modulated Waves Angle modulation is nonlinear
EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. and M.E. Semester
 EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. and M.E. Semester 2 2009 101908 OPTICAL COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING (Elec Eng 4041) 105302 SPECIAL STUDIES IN MARINE ENGINEERING (Elec Eng 7072) Official Reading Time:
EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. and M.E. Semester 2 2009 101908 OPTICAL COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING (Elec Eng 4041) 105302 SPECIAL STUDIES IN MARINE ENGINEERING (Elec Eng 7072) Official Reading Time:
Amplitude Modulation. Ahmad Bilal
 Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
COMM 601: Modulation I
 Prof. Ahmed El-Mahdy, Communications Department The German University in Cairo Text Books [1] Couch, Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 7 th edition, Prentice Hall, 2007. [2] Simon Haykin, Communication
Prof. Ahmed El-Mahdy, Communications Department The German University in Cairo Text Books [1] Couch, Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 7 th edition, Prentice Hall, 2007. [2] Simon Haykin, Communication
Chapter 3. Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques. Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur
 Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur Data Conversion Circuits 2 Digital systems are being used
Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur Data Conversion Circuits 2 Digital systems are being used
END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS ELEC321 Communication Systems (D2) Tuesday, 22 November 2005, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 10 minutes reading time.
 END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS 2005 Unit: Day and Time: Time Allowed: ELEC321 Communication Systems (D2) Tuesday, 22 November 2005, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 10 minutes reading time. Total Number of Questions:
END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS 2005 Unit: Day and Time: Time Allowed: ELEC321 Communication Systems (D2) Tuesday, 22 November 2005, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 10 minutes reading time. Total Number of Questions:
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61)
 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61) Module 1 1. Explain Digital communication system with a neat block diagram. 2. What are the differences between digital and analog communication systems?
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61) Module 1 1. Explain Digital communication system with a neat block diagram. 2. What are the differences between digital and analog communication systems?
AN INTRODUCTION OF ANALOG AND DIGITAL MODULATION TECHNIQUES IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
 AN INTRODUCTION OF ANALOG AND DIGITAL MODULATION TECHNIQUES IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Rashmi Pandey Vedica Institute of Technology, Bhopal Department of Electronics & Communication rashmipandey07@rediffmail.com
AN INTRODUCTION OF ANALOG AND DIGITAL MODULATION TECHNIQUES IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Rashmi Pandey Vedica Institute of Technology, Bhopal Department of Electronics & Communication rashmipandey07@rediffmail.com
Fundamentals of Communication Systems SECOND EDITION
 GLOBAL EDITIO Fundamentals of Communication Systems SECOD EDITIO John G. Proakis Masoud Salehi 78 Effect of oise on Analog Communication Systems Chapter 6 The noise power is P n = ow we can find the output
GLOBAL EDITIO Fundamentals of Communication Systems SECOD EDITIO John G. Proakis Masoud Salehi 78 Effect of oise on Analog Communication Systems Chapter 6 The noise power is P n = ow we can find the output
Solutions to some sampled questions of previous finals
 Solutions to some sampled questions of previous finals First exam: Problem : he modulating signal m(a m coπf m is used to generate the VSB signal β cos[ π ( f c + f m ) t] + (1 β ) cos[ π ( f c f m ) t]
Solutions to some sampled questions of previous finals First exam: Problem : he modulating signal m(a m coπf m is used to generate the VSB signal β cos[ π ( f c + f m ) t] + (1 β ) cos[ π ( f c f m ) t]
Communication Systems Modelling and Simulation
 Communication Systems Modelling and Simulation Using MATLAB and Simulink К С Raveendranathan Professor and Head Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering Government Engineering College Barton
Communication Systems Modelling and Simulation Using MATLAB and Simulink К С Raveendranathan Professor and Head Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering Government Engineering College Barton
Elements of Communication System Channel Fig: 1: Block Diagram of Communication System Terminology in Communication System
 Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Communications IB Paper 6 Handout 2: Analogue Modulation
 Communications IB Paper 6 Handout 2: Analogue Modulation Jossy Sayir Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering University of Cambridge jossy.sayir@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term c Jossy
Communications IB Paper 6 Handout 2: Analogue Modulation Jossy Sayir Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering University of Cambridge jossy.sayir@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term c Jossy
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 1. A cordless telephone using separate frequencies for transmission in base and portable units is known as A. duplex arrangement B. half duplex arrangement C. either (a) or (b) D.
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 1. A cordless telephone using separate frequencies for transmission in base and portable units is known as A. duplex arrangement B. half duplex arrangement C. either (a) or (b) D.
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal
 Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications
 ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
