Experimental study of broadband trailing edge noise of a linear cascade and its reduction with passive devices
|
|
|
- Dale Gordon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PhD Defense Experimental study of broadband trailing edge noise of a linear cascade and its reduction with passive devices Arthur Finez LMFA/École Centrale de Lyon Thursday 1 th May 212 A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 1 / 37
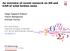
2 Introduction Introduction Noise reduction Why aircraft noise is to be reduced? Orly airport noise disturbance map. : LDEN>7, : LDEN>65, : LDEN>55. [ACNUSA] Noise problems nearby airports. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 2 / 37
3 Introduction Introduction Noise reduction Why aircraft noise is to be reduced? Fan noise contribution Orly airport noise disturbance map. : LDEN>7, : LDEN>65, : LDEN>55. [ACNUSA] Noise problems nearby airports. Engine of an A38 aircraft Take-off and landing : 4%. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 2 / 37
4 Introduction Introduction Discriminating fan noise sources Fan noise composition Tonal noise, significantly reduced in the past decades, Broadband noise, still to be reduced. Many broadband noise sources near the rotor Figure: Axial flow compressor rotor flow phenomena [AGARD-AG-328]. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 3 / 37
5 Introduction Introduction Discriminating fan noise sources Fan noise composition Tonal noise, significantly reduced in the past decades, Broadband noise, still to be reduced. Many broadband noise sources near the rotor - Turbulence - Leading Edge (LE) interaction noise, Figure: Axial flow compressor rotor flow phenomena [AGARD-AG-328]. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 3 / 37
6 Introduction Introduction Discriminating fan noise sources Fan noise composition Tonal noise, significantly reduced in the past decades, Broadband noise, still to be reduced. Many broadband noise sources near the rotor - Turbulence - Leading Edge (LE) interaction noise, - Turbulent Boundary Layer (TBL) - Trailing Edge (TE) interaction noise, Figure: Axial flow compressor rotor flow phenomena [AGARD-AG-328]. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 3 / 37
7 Introduction Introduction Discriminating fan noise sources Fan noise composition Tonal noise, significantly reduced in the past decades, Broadband noise, still to be reduced. Many broadband noise sources near the rotor - Turbulence - Leading Edge (LE) interaction noise, - Turbulent Boundary Layer (TBL) - Trailing Edge (TE) interaction noise, - Blade Tip noise, Figure: Axial flow compressor rotor flow phenomena [AGARD-AG-328]. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 3 / 37
8 Introduction Introduction Discriminating fan noise sources Fan noise composition Tonal noise, significantly reduced in the past decades, Broadband noise, still to be reduced. Many broadband noise sources near the rotor - Turbulence - Leading Edge (LE) interaction noise, - Turbulent Boundary Layer (TBL) - Trailing Edge (TE) interaction noise, - Blade Tip noise, - Turbulence - Shock Surface interaction noise, Figure: Axial flow compressor rotor flow phenomena [AGARD-AG-328]. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 3 / 37
9 Introduction Introduction Discriminating fan noise sources Fan noise composition Tonal noise, significantly reduced in the past decades, Broadband noise, still to be reduced. Many broadband noise sources near the rotor - Turbulence - Leading Edge (LE) interaction noise, - Turbulent Boundary Layer (TBL) - Trailing Edge (TE) interaction noise, - Blade Tip noise, - Turbulence - Shock Surface interaction noise, - Stall noise... Figure: Axial flow compressor rotor flow phenomena [AGARD-AG-328]. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 3 / 37
10 Introduction Introduction Discriminating fan noise sources Fan noise composition Tonal noise, significantly reduced in the past decades, Broadband noise, still to be reduced. Many broadband noise sources near the rotor - Turbulence - Leading Edge (LE) interaction noise, - Turbulent Boundary Layer (TBL) - Trailing Edge (TE) interaction noise, - Blade Tip noise, - Turbulence - Shock Surface interaction noise, - Stall noise... Figure: Axial flow compressor rotor flow phenomena [AGARD-AG-328]. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 3 / 37
11 Introduction Introduction Cascade Effect Blades are not isolated in a fan! - Reflections, - Resonances, - Duct propagation... A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 4 / 37
12 Introduction Introduction Cascade Effect Blades are not isolated in a fan! - Reflections, - Resonances, - Duct propagation... Literature : few studies on cascade trailing edge noise - Analytical modeling : Howe 92 ; Glegg 98 ; - Experiments : Parker 66, Sabah & Roger 1. U 1 β 1 α 1 χ θ U 2 M 7 A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 4 / 37
13 Introduction Introduction Cascade Effect Blades are not isolated in a fan! - Reflections, - Resonances, - Duct propagation... Literature : few studies on cascade trailing edge noise - Analytical modeling : Howe 92 ; Glegg 98 ; - Experiments : Parker 66, Sabah & Roger 1. U 1 β 1 α 1 χ θ U 2 M 7 Need for cascade noise experiment & model validation. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 4 / 37
14 Introduction Introduction Objectives This study aims at - Designing an aeroacoustic cascade set-up, - Measuring cascade TBL-TE noise with various U 1, α Assessing the extent of the cascade effect, - Validating existing cascade noise models, - Reducing cascade noise. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 5 / 37
15 Introduction Outline 1 Cascade Experiment Set-up Aerodynamic Loading Cascade Acoustics 2 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Amiet s Isolated Airfoil Noise Model Glegg s Cascade Noise Model 3 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Acoustic Results PIV results Noise reduction mechanisms A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 6 / 37
16 Cascade Experiment Set-up Outline 1 Cascade Experiment Set-up Aerodynamic Loading Cascade Acoustics 2 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Amiet s Isolated Airfoil Noise Model Glegg s Cascade Noise Model 3 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Acoustic Results PIV results Noise reduction mechanisms A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 7 / 37
17 Cascade Experiment Set-up Experiment Set-up of a unique linear cascade Linear cascade of 7 NACA airfoils, studied by Emery 1. U 1 β 1 α 1 χ θ U 2 M 7 Chord c 1 mm σ = c/s 1.43 Pitch s 7 mm Upstream velocity U 1 8 m/s M.23 Span L 2 mm Re Systematic two-dimensional cascade tests of NACA 65-series compressor blades at low speeds, NACA report 1368, 1957 A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 8 / 37
18 Cascade Experiment Set-up Experiment Improvements from Sabah s set-up 21 : Sabah s PhD thesis - Aim : measurement of cascade leading edge and trailing edge noise, - High background noise level. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 9 / 37
19 Cascade Experiment Set-up Experiment Improvements from Sabah s set-up 21 : Sabah s PhD thesis - Aim : measurement of cascade leading edge and trailing edge noise, - High background noise level. Some improvements - Side panels, - Brushes at the end of wood boards, - No boundary layer exhaust. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 9 / 37
20 Cascade Experiment Set-up Experiment Improvements from Sabah s set-up 21 : Sabah s PhD thesis - Aim : measurement of cascade leading edge and trailing edge noise, - High background noise level. Downstream far-field acoustic spectra 8 7 Some improvements - Side panels, - Brushes at the end of wood boards, - No boundary layer exhaust. PSD, db frequency, Hz Sabah ; Kevlar walls ; Kevlar walls without BL exhaust ; Metal walls without BL exhaust downstream measurements only. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 9 / 37
21 Cascade Experiment Aerodynamic Loading Outline 1 Cascade Experiment Set-up Aerodynamic Loading Cascade Acoustics 2 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Amiet s Isolated Airfoil Noise Model Glegg s Cascade Noise Model 3 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Acoustic Results PIV results Noise reduction mechanisms A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 1 / 37
22 Cascade Experiment Aerodynamic Loading Aerodynamic Loading Validating the cascade design point Reference point near maximum efficiency α 1 = 15, β 1 = 35, U 1 = 8 m/s. (σ = 1.43) A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
23 Cascade Experiment Aerodynamic Loading Aerodynamic Loading Validating the cascade design point Reference point near maximum efficiency α 1 = 15, β 1 = 35, U 1 = 8 m/s. (σ = 1.43) Cp Control on center blade. Measurement, Bock RANS computation, Emery & al., (α 1 = 14.1, β 1 = 3, σ = 1.5) Sabah x/c, % A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
24 Cascade Experiment Aerodynamic Loading Aerodynamic Loading Validating the cascade design point Reference point near maximum efficiency α 1 = 15, β 1 = 35, U 1 = 8 m/s. (σ = 1.43) Cp Control on center blade. Measurement, Bock RANS computation, Emery & al., (α 1 = 14.1, β 1 = 3, σ = 1.5) Sabah x/c, % Cp Control on other blades. At 5% chord, Suction Side, Pressure Side numéro de pale A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
25 Cascade Experiment Cascade Acoustics Outline 1 Cascade Experiment Set-up Aerodynamic Loading Cascade Acoustics 2 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Amiet s Isolated Airfoil Noise Model Glegg s Cascade Noise Model 3 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Acoustic Results PIV results Noise reduction mechanisms A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
26 Cascade Experiment Cascade Acoustics Velocity Dependence Specific frequency scaling PSD (db/hz) Raw PSD 1m/s 8m/s 6m/s DSP (db/hz) Scaled PSD frequency, Hz frequency, Hz Far-field PSD at r=2 m Scaling to U 1 =8 m/s using PSD U 6 1, Frequency axis unchanged He= fl c rather than St= f δ U 1. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
27 Cascade Experiment Cascade Acoustics Acoustic Resonances Near-field / far-field coherence Remote Surface Unsteady Pressure Probes U A B C D Near the center blade trailing edge, midspan plane E F G 1mm - To measure entry data of analytical models (boundary layer statistics), - To investigate near-field/far-field coherence. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
28 Cascade Experiment Cascade Acoustics Acoustic Resonances Near-field / far-field coherence Remote Surface Unsteady Pressure Probes U A B C D Near the center blade trailing edge, midspan plane E F G 1mm - To measure entry data of analytical models (boundary layer statistics), - To investigate near-field/far-field coherence. γ β α γ frequency, Hz θ <, θ >. Parker Resonances : plate nodes mode β A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
29 Cascade Experiment Cascade Acoustics Acoustic Resonances Near-field / far-field coherence Remote Surface Unsteady Pressure Probes U A B C D Near the center blade trailing edge, midspan plane E F G 1mm - To measure entry data of analytical models (boundary layer statistics), - To investigate near-field/far-field coherence. γ β α γ frequency, Hz θ <, θ >. Parker Resonances : plate mode α nodes A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
30 Cascade Experiment Cascade Acoustics Acoustic Resonances Near-field / far-field coherence Remote Surface Unsteady Pressure Probes U A B C D Near the center blade trailing edge, midspan plane E F G 1mm - To measure entry data of analytical models (boundary layer statistics), - To investigate near-field/far-field coherence. γ β α γ frequency, Hz θ <, θ >. Parker Resonances : mode γ A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
31 Cascade Experiment Cascade Acoustics Acoustic Interference Visible in far-field measurements Blade-to-blade reflections 7 PSD, db frequency, Hz A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
32 Cascade Experiment Cascade Acoustics Acoustic Interference Visible in far-field measurements Blade-to-blade reflections 7 PSD, db frequency, Hz A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
33 Cascade Experiment Cascade Acoustics Acoustic Interference Visible in far-field measurements Blade-to-blade reflections 7 PSD, db e ik(δ 1 +δ 2 ) δ 1 δ 2 3 A B frequency, Hz A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
34 Cascade Experiment Cascade Acoustics Acoustic Interference Visible in far-field measurements Blade-to-blade reflections 7 PSD, db e ik(δ 1 +δ 2 ) δ 1 δ 2 3 A B frequency, Hz A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
35 Cascade Experiment Cascade Acoustics Acoustic Interference Visible in far-field measurements Blade-to-blade reflections 7 PSD, db e ik(δ 1 +δ 2 ) δ 1 δ 2 3 A B frequency, Hz Most obvious cascade effects have been observed To go further, need for analytical modeling : computation of the cascade transfer function. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
36 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Outline 1 Cascade Experiment Set-up Aerodynamic Loading Cascade Acoustics 2 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Amiet s Isolated Airfoil Noise Model Glegg s Cascade Noise Model 3 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Acoustic Results PIV results Noise reduction mechanisms A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
37 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Input Data Measurement : BL Statistics Φ pp (ω) PSD, db Cascade, Isolated airfoil, frequency, Hz On center blade, U 1 7 m/s, α 1 = 35, β = 45. A U C B D E F G 1mm A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
38 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Input Data Measurement : BL Statistics Φ pp (ω) PSD, db Cascade, Isolated airfoil, frequency, Hz l z = γ γ(ω, η) cos(k zη)dη frequency, Hz η (mm) : 1, 2.5, 3.5, 5. On center blade, U 1 7 m/s, α 1 = 35, β = 45. A U C B D E F G 1mm A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
39 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Input Data Measurement : BL Statistics Φ pp (ω) PSD, db Cascade, Isolated airfoil, frequency, Hz l z = γ γ(ω, η) cos(k zη)dη frequency, Hz U c η (mm) : 1, 2.5, 3.5, 5. 1 U c /U St= 1 f /U 1 U 1, m/s 6, 7, 8, 1. On center blade, U 1 7 m/s, α 1 = 35, β = 45. A U C B D E F G 1mm A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
40 Analytical Model Validation Amiet s Isolated Airfoil Noise Model Outline 1 Cascade Experiment Set-up Aerodynamic Loading Cascade Acoustics 2 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Amiet s Isolated Airfoil Noise Model Glegg s Cascade Noise Model 3 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Acoustic Results PIV results Noise reduction mechanisms A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
41 Analytical Model Validation Amiet s Isolated Airfoil Noise Model Analytical Models Amiet s isolated airfoil TE noise model Isolated airfoil formulation : ( ) 2 ωyc S pp (n) (x, y, z, ω) = 2L 4πc S 2 I ( ) ω 2 ( ) kz, Φ pp (ω)l z =, ω U c S 7 independant airfoils, observer in the midspan plane, infinite span, shear layer refraction. n=1 y n=4 θ 4 h Measurement, Prediction, x M PSD (db/hz) frequency, Hz A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
42 Analytical Model Validation Glegg s Cascade Noise Model Outline 1 Cascade Experiment Set-up Aerodynamic Loading Cascade Acoustics 2 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Amiet s Isolated Airfoil Noise Model Glegg s Cascade Noise Model 3 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Acoustic Results PIV results Noise reduction mechanisms A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 2 / 37
43 Analytical Model Validation Glegg s Cascade Noise Model Glegg s Analytical Model Original formulation Linear cascade model - Fan azimuthal periodicity periodic sources in linear cascade - Small numbers of propagating modes, - BL information in Q, - 3D : K = (K x, K z). K ϑ x p s = 2πi Bh m=+ m= QH m (K x )e iωt+ikzz K me iγ m (x yd/h) 2iπmy/Bh (2π) 2 i(γ m + K x )J (m) + ( K x)j (m) (γ m) A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
44 Analytical Model Validation Glegg s Cascade Noise Model Glegg s Analytical Model Original formulation Linear cascade model - Fan azimuthal periodicity periodic sources in linear cascade - Small numbers of propagating modes, - BL information in Q, - 3D : K = (K x, K z). K ϑ x p s = 2πi Bh m=+ m= QH m (K x )e iωt+ikzz K me iγ m (x yd/h) 2iπmy/Bh (2π) 2 i(γ m + K x )J (m) + ( K x)j (m) (γ m) y,m 1.5 R(p s), Pa x,m ω = 1 1 propagative mode. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
45 Analytical Model Validation Glegg s Cascade Noise Model Glegg s Analytical Model Original formulation Linear cascade model - Fan azimuthal periodicity periodic sources in linear cascade K - Small numbers of propagating modes, x ϑ - BL information in Q, - 3D : K = (Kx, Kz ). ps = 2πi Bh m=+ X QHm (Kx )e iωt+ikz z m= iγm (x yd/h) 2iπmy/Bh Km e (m) y,m.5 y,m ℜ(ps ), Pa 1 ℜ(ps ), Pa 1 (m) (2π)2 i(γm + Kx )J+ ( Kx )J (γm ) x,m ω = 1 1 propagative mode. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) 1 x,m 2 3 ω = 3 5 propagative modes. PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
46 Analytical Model Validation Glegg s Cascade Noise Model Glegg s Analytical Model Choice of Periodicity Parameter B Choosing B with the aim of isolating a single source contribution. y,m R(p s), Pa x,m.6 B=3 A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
47 Analytical Model Validation Glegg s Cascade Noise Model Glegg s Analytical Model Choice of Periodicity Parameter B Choosing B with the aim of isolating a single source contribution. 1.6 R(p s), Pa y,m.2 y,m x,m.6 B= x,m.6 B=1 A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
48 Analytical Model Validation Glegg s Cascade Noise Model Glegg s Analytical Model Choice of Periodicity Parameter B Choosing B with the aim of isolating a single source contribution. 1.6 R(p s), Pa y,m.2 y,m x,m.6 B= x,m.6 B= y,m x,m B=1 A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
49 Analytical Model Validation Glegg s Cascade Noise Model Glegg s Analytical Model Choice of Periodicity Parameter B Choosing B with the aim of isolating a single source contribution. 1.6 ℜ(ps ), Pa y,m y,m x,m B=3 1 1 x,m 2 3 B= y,m y,m x,m 2 A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) B=1 PhD Defense 1 x,m 2 3 B=1 1/5/ / 37
50 Analytical Model Validation Glegg s Cascade Noise Model Glegg s Analytical Model Choice of Periodicity Parameter B Choosing B with the aim of isolating a single source contribution. 1.6 ℜ(ps ), Pa y,m y,m x,m B=3 1 1 x,m 2 3 B= y,m y,m x,m 2 A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) B=1 PhD Defense 1 x,m 2 3 B=1 1/5/ / 37
51 Analytical Model Validation Glegg s Cascade Noise Model Glegg s Analytical Model Comparison with acoustic measurements Last Steps : - Expressing Q in terms of Φ pp, l z, U c, - Integrating on K z, - Summing over independant blade contributions. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
52 Analytical Model Validation Glegg s Cascade Noise Model Glegg s Analytical Model Comparison with acoustic measurements Last Steps : - Expressing Q in terms of Φ pp, l z, U c, - Integrating on K z, - Summing over independant blade contributions. Results : Suction side θ = 4 Slight modulation of single airfoil results (3 db). PSD, db Measurement, Glegg s model, Amiet s model frequency, Hz A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
53 Analytical Model Validation Glegg s Cascade Noise Model Analytical Models Conclusions Three noise models have been adapted to the test case : - Amiet s isolated airfoil TE noise model, - Glegg s cascade TE noise model, - Howe s cascade TE noise model (not shown). A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
54 Analytical Model Validation Glegg s Cascade Noise Model Analytical Models Conclusions Three noise models have been adapted to the test case : - Amiet s isolated airfoil TE noise model, - Glegg s cascade TE noise model, - Howe s cascade TE noise model (not shown). Results show that : - Cascade effect 3 db, - Experiment variation close to model discrepancies, - Cascade CPU (1min) Isolated Airfoil CPU (1 sec). A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
55 Analytical Model Validation Glegg s Cascade Noise Model Analytical Models Conclusions Three noise models have been adapted to the test case : - Amiet s isolated airfoil TE noise model, - Glegg s cascade TE noise model, - Howe s cascade TE noise model (not shown). Results show that : - Cascade effect 3 db, - Experiment variation close to model discrepancies, - Cascade CPU (1min) Isolated Airfoil CPU (1 sec). Cascade TE noise measured and may be reduced. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
56 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Outline 1 Cascade Experiment Set-up Aerodynamic Loading Cascade Acoustics 2 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Amiet s Isolated Airfoil Noise Model Glegg s Cascade Noise Model 3 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Acoustic Results PIV results Noise reduction mechanisms A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
57 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Introduction Cascade TBL-TE Noise Reduction Successful isolated airfoil noise reduction - Many passive devices tested in the flocon eu project, - te serrations gave best results & were down-selected. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
58 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Introduction Cascade TBL-TE Noise Reduction Successful isolated airfoil noise reduction - Many passive devices tested in the flocon eu project, - te serrations gave best results & were down-selected. Does the noise reduction also occur in a cascade? A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
59 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Introduction Cascade TBL-TE Noise Reduction Successful isolated airfoil noise reduction - Many passive devices tested in the flocon eu project, - te serrations gave best results & were down-selected. Does the noise reduction also occur in a cascade? Serrations sketches 1 - Straight edge Short serrations λ c = 2 mm, 2h = 13 mm - Long serrations λ c = 2 mm, 2h = 2 mm, 2h c λ c e A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
60 Cascade Noise Reduction Acoustic Results Outline 1 Cascade Experiment Set-up Aerodynamic Loading Cascade Acoustics 2 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Amiet s Isolated Airfoil Noise Model Glegg s Cascade Noise Model 3 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Acoustic Results PIV results Noise reduction mechanisms A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
61 Cascade Noise Reduction Acoustic Results Serration Acoustic Results Far field noise reduction, suction side direction θ = straight TE long serrations short serrations Far field PSD, db/hz Noise reduction St Noise increase frequency, Hz 1m/s 8m/s 6m/s 4m/s - Very similar results to single airfoil noise reduction, - Single airfoil St =1.18 ; Cascade St =1.21. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
62 Cascade Noise Reduction PIV results Outline 1 Cascade Experiment Set-up Aerodynamic Loading Cascade Acoustics 2 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Amiet s Isolated Airfoil Noise Model Glegg s Cascade Noise Model 3 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Acoustic Results PIV results Noise reduction mechanisms A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
63 Cascade Noise Reduction PIV results Near Wake Dynamics Mean Velocity U x y location, mm 15 1 Straight Edge U x, m/s 4 3 y location, mm 15 1 Serrated Edge U x, m/s x location, mm x location, mm Observations - Serration wake larger and less deep, - Serrations : through flow with a 1 angle. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/212 3 / 37
64 Cascade Noise Reduction PIV results Near Wake Dynamics Fluctuating velocity u x y location, mm 15 1 Straight Edge u x, m/s y location, mm 15 1 Serrated Edge u x, m/s x location, mm x location, mm Observations - BL removed from the airfoil surface, - Smaller turbulent area in the pressure side wake. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
65 Cascade Noise Reduction Noise reduction mechanisms Outline 1 Cascade Experiment Set-up Aerodynamic Loading Cascade Acoustics 2 Analytical Model Validation Input Data for Models Amiet s Isolated Airfoil Noise Model Glegg s Cascade Noise Model 3 Cascade Noise Reduction Set-up Acoustic Results PIV results Noise reduction mechanisms A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
66 Cascade Noise Reduction Noise reduction mechanisms Serrations Investigation of noise reduction mechanisms Serrations may reduce noise through : - BL ejection, - Spanwise decorrelation, - Local sweep angle? Analytical investigations. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
67 Cascade Noise Reduction Noise reduction mechanisms Serrations Investigation of noise reduction mechanisms Serrations may reduce noise through : - BL ejection, - Spanwise decorrelation, - Local sweep angle? Analytical investigations. Modified Amiet model for sweep angle ϕ : Step 1 : Airfoil response function - compressible unsteady aerodynamics airfoil ϕ =, y U z K z K x U x ϕ ψ U K x ϕ = 15, ϕ = 6, ϕ = 85. P z x/c A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
68 Cascade Noise Reduction Noise reduction mechanisms Serrations Investigation of noise reduction mechanisms Modified Amiet model for sweep angle ϕ : Step 2 : Far-field scattering - Curle s theory airfoil y L z x ϕ x M z ω=1, ω=5, ω=1, ω=2. Wpp, db ϕ, Conclusions : - Serration details cannot be analytically reproduced only a hint, - This new model could be useful for fan noise prediction, - Decrease of noise power in cos ϕ 3. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
69 Conclusions Conclusions Cascade Experiment Cascade rig significantly improved, Cascade trailing edge noise measured, Specific cascade effects observed and analysed. Analytical models Input data measured in cascade, Amiet s model give reasonable prediction ±3 db above 2 Hz, Glegg s cascade model adapted to the experiment, It differs from Amiet s model in level by ±3 db, need for increasing cascade effect via σ. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
70 Conclusions Conclusions Cascade noise reduction Serration inserted in cascade, Reduction at low frequencies, No influence of cascade effect on noise reduction, Candidate mechanism to noise reduction : BL removal, Spanwise decorrelation, Local sweep angle, Amiet s model modified for sweep angle. A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
71 Conclusions Thank you for your attention! A. Finez (LMFA/ECL) PhD Defense 1/5/ / 37
Overview of Turbofan Engine Noise
 Overview of Turbofan Engine Noise Oksana Stalnov Faculty of Aerospace Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology Some statistics Current aircraft are 20-30 db quieter than first generation turbofans
Overview of Turbofan Engine Noise Oksana Stalnov Faculty of Aerospace Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology Some statistics Current aircraft are 20-30 db quieter than first generation turbofans
Noise source characterization by highfrequency surface pressure measurements
 Noise source characterization by highfrequency surface pressure measurements Helge Aagaard Madsen Andreas Fischer Franck Bertagnolio Christian Bak Section Aeroelastic Design Department of Wind Energy hama@dtu.dk
Noise source characterization by highfrequency surface pressure measurements Helge Aagaard Madsen Andreas Fischer Franck Bertagnolio Christian Bak Section Aeroelastic Design Department of Wind Energy hama@dtu.dk
ANALYTICAL NOISE MODELLING OF A CENTRIFUGAL FAN VALIDATED BY EXPERIMENTAL DATA
 ANALYTICAL NOISE MODELLING OF A CENTRIFUGAL FAN VALIDATED BY EXPERIMENTAL DATA Beatrice Faverjon 1, Con Doolan 1, Danielle Moreau 1, Paul Croaker 1 and Nathan Kinkaid 1 1 School of Mechanical and Manufacturing
ANALYTICAL NOISE MODELLING OF A CENTRIFUGAL FAN VALIDATED BY EXPERIMENTAL DATA Beatrice Faverjon 1, Con Doolan 1, Danielle Moreau 1, Paul Croaker 1 and Nathan Kinkaid 1 1 School of Mechanical and Manufacturing
- Selected Final Results -
 PROBAND: Improvement of Fan Broadband Noise Prediction: Experimental investigation and computational modelling - Selected Final Results - Lars Enghardt, DLR Berlin Project Coordinator 1 EU FP6, Call 2,
PROBAND: Improvement of Fan Broadband Noise Prediction: Experimental investigation and computational modelling - Selected Final Results - Lars Enghardt, DLR Berlin Project Coordinator 1 EU FP6, Call 2,
INVESTIGATIONS ON SLAT NOISE REDUCTION TECH- NOLOGIES BASED ON PIEZOELECTRIC MATERIAL, PART II: CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN AND WIND TUNNEL TEST
 INVESTIGATIONS ON SLAT NOISE REDUCTION TECH- NOLOGIES BASED ON PIEZOELECTRIC MATERIAL, PART II: CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN AND WIND TUNNEL TEST Song Xiao, Yu Jinhai, Breard Cyrille and Sun Yifeng Shanghai Aircraft
INVESTIGATIONS ON SLAT NOISE REDUCTION TECH- NOLOGIES BASED ON PIEZOELECTRIC MATERIAL, PART II: CONTROL SYSTEM DESIGN AND WIND TUNNEL TEST Song Xiao, Yu Jinhai, Breard Cyrille and Sun Yifeng Shanghai Aircraft
FLOW INDUCED NOISE CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE WIND TUNNEL TESTING OF A NACA 0015 AIRFOIL WITH SLOTS
 FLOW INDUCED NOISE CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE WIND TUNNEL TESTING OF A NACA 0015 AIRFOIL WITH SLOTS Robert Bruce Alstrom, Pier Marzocca, Goodarz Ahmadi Department of Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering
FLOW INDUCED NOISE CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE WIND TUNNEL TESTING OF A NACA 0015 AIRFOIL WITH SLOTS Robert Bruce Alstrom, Pier Marzocca, Goodarz Ahmadi Department of Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering
Composite aeroacoustic beamforming of an axial fan
 Acoustics Array Systems: Paper ICA2016-122 Composite aeroacoustic beamforming of an axial fan Jeoffrey Fischer (a), Con Doolan (b) (a) School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, UNSW Australia,
Acoustics Array Systems: Paper ICA2016-122 Composite aeroacoustic beamforming of an axial fan Jeoffrey Fischer (a), Con Doolan (b) (a) School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, UNSW Australia,
Experimental Investigation of Unsteady Pressure on an Axial Compressor Rotor Blade Surface
 Energy and Power Engineering, 2010, 2, 131-136 doi:10.4236/epe.2010.22019 Published Online May 2010 (http://www. SciRP.org/journal/epe) 131 Experimental Investigation of Unsteady Pressure on an Axial Compressor
Energy and Power Engineering, 2010, 2, 131-136 doi:10.4236/epe.2010.22019 Published Online May 2010 (http://www. SciRP.org/journal/epe) 131 Experimental Investigation of Unsteady Pressure on an Axial Compressor
An overview of recent research on AM and OAM of wind turbine noise
 An overview of recent research on AM and OAM of wind turbine noise Helge Aagaard Madsen Franck Bertagnolio Andreas Fischer DTU Wind Energy Technical University of Denmark P.O. 49, DK-4000 Roskilde, Denmark
An overview of recent research on AM and OAM of wind turbine noise Helge Aagaard Madsen Franck Bertagnolio Andreas Fischer DTU Wind Energy Technical University of Denmark P.O. 49, DK-4000 Roskilde, Denmark
APPLICATION OF PHASED ARRAY IN THE STUDY OF LINEAR CASCADE NOISE REDUCTION ON THE INDOOR TEST BED
 BeBeC-2014-22 APPLICATION OF PHASED ARRAY IN THE STUDY OF LINEAR CASCADE NOISE REDUCTION ON THE INDOOR TEST BED Weiyang Qiao 1, Liang Ji 2, Fan Tong 3, Kunbo Xu 4, and Weijie Chen 5 School of Power and
BeBeC-2014-22 APPLICATION OF PHASED ARRAY IN THE STUDY OF LINEAR CASCADE NOISE REDUCTION ON THE INDOOR TEST BED Weiyang Qiao 1, Liang Ji 2, Fan Tong 3, Kunbo Xu 4, and Weijie Chen 5 School of Power and
Akustische Rückkopplungen in laminar überströmten Spalten und Methoden zur Abschwächung von Tollmien-Schlichting Wellen
 Akustische Rückkopplungen in laminar überströmten Spalten und Methoden zur Abschwächung von Tollmien-Schlichting Wellen Acoustic Feedback in Gaps and Methods to Weaken Tollmien-Schlichting Waves J. Zahn,
Akustische Rückkopplungen in laminar überströmten Spalten und Methoden zur Abschwächung von Tollmien-Schlichting Wellen Acoustic Feedback in Gaps and Methods to Weaken Tollmien-Schlichting Waves J. Zahn,
1. Introduction The presence of a cavity changes the mean and fluctuating pressure distributions inside and near a cavity [1,2].
![1. Introduction The presence of a cavity changes the mean and fluctuating pressure distributions inside and near a cavity [1,2]. 1. Introduction The presence of a cavity changes the mean and fluctuating pressure distributions inside and near a cavity [1,2].](/thumbs/92/108285851.jpg) 1. Introduction The presence of a cavity changes the mean and fluctuating pressure distributions inside and near a cavity [1,2]. For compressible flow in a rectangular cavity (M = 0.95), the mean and fluctuation
1. Introduction The presence of a cavity changes the mean and fluctuating pressure distributions inside and near a cavity [1,2]. For compressible flow in a rectangular cavity (M = 0.95), the mean and fluctuation
Microphone Array Measurements for High-speed Train
 Microphone Array Measurements for High-speed Train Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science Hyu-Sang Kwon 2016. 05. 31 2 Contents Railway Noise Sound Images Flow Noise Railway Noise Measurement
Microphone Array Measurements for High-speed Train Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science Hyu-Sang Kwon 2016. 05. 31 2 Contents Railway Noise Sound Images Flow Noise Railway Noise Measurement
Ranging detection algorithm for indoor UWB channels and research activities relating to a UWB-RFID localization system
 Ranging detection algorithm for indoor UWB channels and research activities relating to a UWB-RFID localization system Dr Choi Look LAW Founding Director Positioning and Wireless Technology Centre School
Ranging detection algorithm for indoor UWB channels and research activities relating to a UWB-RFID localization system Dr Choi Look LAW Founding Director Positioning and Wireless Technology Centre School
INFLUENCE OF CAPTIVE STORES ON THE UNSTEADY PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION WITHIN A RECTANGULAR CAVITY
 25 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AEROSPACE SCIENCES INFLUENCE OF CAPTIVE STORES ON THE UNSTEADY PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION WITHIN A RECTANGULAR CAVITY D.M. Orchard, B.H.K. Lee and F.C. Tang Aerodynamics
25 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AEROSPACE SCIENCES INFLUENCE OF CAPTIVE STORES ON THE UNSTEADY PRESSURE DISTRIBUTION WITHIN A RECTANGULAR CAVITY D.M. Orchard, B.H.K. Lee and F.C. Tang Aerodynamics
Development of a Reactive Silencer for Turbo Compressors
 Development of a Reactive Silencer for Turbo Compressors Jan Smeulers Nestor Gonzalez TNO Fluid Dynamics TNO Fluid Dynamics Stieltjesweg 1 Stieltjesweg 1 2628CK Delft 2628CK Delft jan.smeulers@tno.nl nestor.gonzalezdiez@tno.nl
Development of a Reactive Silencer for Turbo Compressors Jan Smeulers Nestor Gonzalez TNO Fluid Dynamics TNO Fluid Dynamics Stieltjesweg 1 Stieltjesweg 1 2628CK Delft 2628CK Delft jan.smeulers@tno.nl nestor.gonzalezdiez@tno.nl
Study of Standing Waves to Find Speed of Sound in Air
 Study of Standing Waves to Find Speed of Sound in Air Purpose Using mobile devices as sound analyzer and sound generator to study standing waves and determine the speed of sound in air. Theory The velocity
Study of Standing Waves to Find Speed of Sound in Air Purpose Using mobile devices as sound analyzer and sound generator to study standing waves and determine the speed of sound in air. Theory The velocity
Effects of Angle of Attack and Velocity on Trailing Edge Noise
 42 nd AIA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Reno, NV, January 5-8, 2004 AIAA-2004-1031 Effects of Angle of Attack and Velocity on Trailing Edge Noise Florence V. Hutcheson* Thomas F. Brooks NASA Langley Research
42 nd AIA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Reno, NV, January 5-8, 2004 AIAA-2004-1031 Effects of Angle of Attack and Velocity on Trailing Edge Noise Florence V. Hutcheson* Thomas F. Brooks NASA Langley Research
Source Control of Turbomachine Discrete- Frequency Tone Generation
 Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1996 Source Control of Turbomachine Discrete- Frequency Tone Generation S. Sawyer S. Fleeter Follow this and
Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 1996 Source Control of Turbomachine Discrete- Frequency Tone Generation S. Sawyer S. Fleeter Follow this and
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE MORPHING FLAP AS A LOW NOISE HIGH LIFT DEVICE FOR AIRCRAFT WING
 28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE MORPHING FLAP AS A LOW NOISE HIGH LIFT DEVICE FOR AIRCRAFT WING Yasuhiro TANI*, Yoshiyuki MATSUDA*, Akira DOI*, Yuya
28 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE MORPHING FLAP AS A LOW NOISE HIGH LIFT DEVICE FOR AIRCRAFT WING Yasuhiro TANI*, Yoshiyuki MATSUDA*, Akira DOI*, Yuya
Da-Qing Li Jan Hallander and Roger Karlsson SSPA Sweden AB, Göteborg, Sweden
 Progress in Predicting Pressure Pulses and Underwater Radiated Noise Induced by Propeller with Pressure Side Cavitation Introduction Da-Qing Li (da-qing.li@sspa.se), Jan Hallander (jan.hallander@sspa.se)
Progress in Predicting Pressure Pulses and Underwater Radiated Noise Induced by Propeller with Pressure Side Cavitation Introduction Da-Qing Li (da-qing.li@sspa.se), Jan Hallander (jan.hallander@sspa.se)
WIND TURBINE ACOUSTICS - a sneak preview on research topics- Dr. Andree Altmikus ENERCON Research & Development
 WIND TURBINE ACOUSTICS - a sneak preview on research topics- Dr. Andree Altmikus ENERCON Research & Development 1 INTRODUCTION 1 AERO-ACOUSTICS 2 VIBRO-ACOUSTICS eddys in: STRUCTURAL VIBRATION ATMOSPHERIC
WIND TURBINE ACOUSTICS - a sneak preview on research topics- Dr. Andree Altmikus ENERCON Research & Development 1 INTRODUCTION 1 AERO-ACOUSTICS 2 VIBRO-ACOUSTICS eddys in: STRUCTURAL VIBRATION ATMOSPHERIC
TAU Experiences with Detached-Eddy Simulations
 TAU Experiences with Detached-Eddy Simulations Herbert Rieger & Stefan Leicher EADS Deutschland GmbH Military Aircraft Flight Physics Department Ottobrunn, Germany Outline The Typical Design Problem of
TAU Experiences with Detached-Eddy Simulations Herbert Rieger & Stefan Leicher EADS Deutschland GmbH Military Aircraft Flight Physics Department Ottobrunn, Germany Outline The Typical Design Problem of
Experimental Investigations of Coherence Based Noise Source Identification Techniques for Turbomachinery Applications - Classic and Novel Techniques
 17th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference(32nd AIAA Aeroacoustics Conference) 05-08 June 2011, Portland, Oregon AIAA 2011-2830 Experimental Investigations of Coherence Based Noise Source Identification Techniques
17th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference(32nd AIAA Aeroacoustics Conference) 05-08 June 2011, Portland, Oregon AIAA 2011-2830 Experimental Investigations of Coherence Based Noise Source Identification Techniques
Qualification of Fan-Generated Duct Rumble Noise Part 2: Results
 2008, American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. (www.ashrae.org). ESL-PA-08-06-09 SL-08-003 (RP-1219) Qualification of Fan-Generated Duct Rumble Noise Part 2: Results
2008, American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. (www.ashrae.org). ESL-PA-08-06-09 SL-08-003 (RP-1219) Qualification of Fan-Generated Duct Rumble Noise Part 2: Results
FAN NOISE & VIBRATION
 FAN NOISE & VIBRATION SECTION INDEX 01. FAN NOISE 02. VIBRATION 03. RESONANT FREQUENCIES & HARMONICS 04. SOUND DATA & GURANTEE EXCLUSIONS 05. SOUND DATA MEASURED AT AMCA APPROVED LAB IN USA PFCSL/01 Page
FAN NOISE & VIBRATION SECTION INDEX 01. FAN NOISE 02. VIBRATION 03. RESONANT FREQUENCIES & HARMONICS 04. SOUND DATA & GURANTEE EXCLUSIONS 05. SOUND DATA MEASURED AT AMCA APPROVED LAB IN USA PFCSL/01 Page
Application of Artificial Neural Network for the Prediction of Aerodynamic Coefficients of a Plunging Airfoil
 International Journal of Science and Engineering Investigations vol 1, issue 1, February 212 Application of Artificial Neural Network for the Prediction of Aerodynamic Coefficients of a Plunging Airfoil
International Journal of Science and Engineering Investigations vol 1, issue 1, February 212 Application of Artificial Neural Network for the Prediction of Aerodynamic Coefficients of a Plunging Airfoil
Final Examination. 22 April 2013, 9:30 12:00. Examiner: Prof. Sean V. Hum. All non-programmable electronic calculators are allowed.
 UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 422H1S RADIO AND MICROWAVE WIRELESS SYSTEMS Final Examination
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING The Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 422H1S RADIO AND MICROWAVE WIRELESS SYSTEMS Final Examination
Design and Calibration of a Small Aeroacoustic Beamformer
 Proceedings of 20 th International Congress on Acoustics, ICA 2010 23-27 August 2010, Sydney, Australia Design and Calibration of a Small Aeroacoustic Beamformer Elias J. G. Arcondoulis, Con J. Doolan,
Proceedings of 20 th International Congress on Acoustics, ICA 2010 23-27 August 2010, Sydney, Australia Design and Calibration of a Small Aeroacoustic Beamformer Elias J. G. Arcondoulis, Con J. Doolan,
Particle Image Velocimetry
 Markus Raffel Christian E. Willert Steve T. Wereley Jiirgen Kompenhans Particle Image Velocimetry A Practical Guide Second Edition With 288 Figures and 42 Tables < J Springer Contents Preface V 1 Introduction
Markus Raffel Christian E. Willert Steve T. Wereley Jiirgen Kompenhans Particle Image Velocimetry A Practical Guide Second Edition With 288 Figures and 42 Tables < J Springer Contents Preface V 1 Introduction
About Doppler-Fizeau effect on radiated noise from a rotating source in cavitation tunnel
 PROCEEDINGS of the 22 nd International Congress on Acoustics Signal Processing in Acoustics (others): Paper ICA2016-111 About Doppler-Fizeau effect on radiated noise from a rotating source in cavitation
PROCEEDINGS of the 22 nd International Congress on Acoustics Signal Processing in Acoustics (others): Paper ICA2016-111 About Doppler-Fizeau effect on radiated noise from a rotating source in cavitation
Your title goes here. Aeroacoustics. Methodologies, Validations and Continuing Outlook
 Your title goes here Aeroacoustics Methodologies, Validations and Continuing Outlook Your subtitle goes here Fred Mendonça Some Characteristic Flow Noise Issues Automotive external, sunroof buffeting,
Your title goes here Aeroacoustics Methodologies, Validations and Continuing Outlook Your subtitle goes here Fred Mendonça Some Characteristic Flow Noise Issues Automotive external, sunroof buffeting,
EXPERIMENTS ON PERFORMANCES OF ACTIVE-PASSIVE HYBRID MUFFLERS
 EXPERIMENTS ON PERFORMANCES OF ACTIVE-PASSIVE HYBRID MUFFLERS Hongling Sun, Fengyan An, Ming Wu and Jun Yang Key Laboratory of Noise and Vibration Research, Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
EXPERIMENTS ON PERFORMANCES OF ACTIVE-PASSIVE HYBRID MUFFLERS Hongling Sun, Fengyan An, Ming Wu and Jun Yang Key Laboratory of Noise and Vibration Research, Institute of Acoustics, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Abstract. Vibroacustic Problems in High SpeedmTrains. Felix Sorribe Palmer, Gustavo Alonso Rodrigo, Angel Pedro Snaz Andres
 Vibroacustic Problems in High SpeedmTrains Felix Sorribe Palmer, Gustavo Alonso Rodrigo, Angel Pedro Snaz Andres Abstract Passengers comfort in terms of acoustic noise levels is a key train design parameter,
Vibroacustic Problems in High SpeedmTrains Felix Sorribe Palmer, Gustavo Alonso Rodrigo, Angel Pedro Snaz Andres Abstract Passengers comfort in terms of acoustic noise levels is a key train design parameter,
Active noise control at a moving virtual microphone using the SOTDF moving virtual sensing method
 Proceedings of ACOUSTICS 29 23 25 November 29, Adelaide, Australia Active noise control at a moving rophone using the SOTDF moving sensing method Danielle J. Moreau, Ben S. Cazzolato and Anthony C. Zander
Proceedings of ACOUSTICS 29 23 25 November 29, Adelaide, Australia Active noise control at a moving rophone using the SOTDF moving sensing method Danielle J. Moreau, Ben S. Cazzolato and Anthony C. Zander
Cavity Flow Noise Predictions
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AERODYNAMICS & FLIGHT MECHANICS GROUP Cavity Flow Noise Predictions by Xiaoxian Chen, Neil D. Sandham and Xin Zhang Report No. AFM-07/05 February
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AERODYNAMICS & FLIGHT MECHANICS GROUP Cavity Flow Noise Predictions by Xiaoxian Chen, Neil D. Sandham and Xin Zhang Report No. AFM-07/05 February
Development of a reactive silencer for turbocompressors
 Development of a reactive silencer for turbocompressors N. González Díez, J.P.M. Smeulers, D. Meulendijks 1 S. König TNO Heat Transfer & Fluid Dynamics Siemens AG Energy Sector The Netherlands Duisburg/Germany
Development of a reactive silencer for turbocompressors N. González Díez, J.P.M. Smeulers, D. Meulendijks 1 S. König TNO Heat Transfer & Fluid Dynamics Siemens AG Energy Sector The Netherlands Duisburg/Germany
NASA Langley Activities on Broadband Fan Noise Reduction via Novel Liner Technologies
 NASA Langley Activities on Broadband Fan Noise Reduction via Novel Liner Technologies Michael G. Jones NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, VA CEAS/X-Noise Workshop on Broadband Noise of Rotors and Airframe
NASA Langley Activities on Broadband Fan Noise Reduction via Novel Liner Technologies Michael G. Jones NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton, VA CEAS/X-Noise Workshop on Broadband Noise of Rotors and Airframe
PASSIVE CONTROL OF CAVITY INSTABILITIES AND NOISE
 27 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES PASSIVE CONTROL OF CAVITY INSTABILITIES AND NOISE K Knowles, B Khanal, D Bray, P Geraldes Aeromechanical Systems Group, Cranfield University Defence
27 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES PASSIVE CONTROL OF CAVITY INSTABILITIES AND NOISE K Knowles, B Khanal, D Bray, P Geraldes Aeromechanical Systems Group, Cranfield University Defence
Dynamic Modeling of Air Cushion Vehicles
 Proceedings of IMECE 27 27 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress Seattle, Washington, November -5, 27 IMECE 27-4 Dynamic Modeling of Air Cushion Vehicles M Pollack / Applied Physical Sciences
Proceedings of IMECE 27 27 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress Seattle, Washington, November -5, 27 IMECE 27-4 Dynamic Modeling of Air Cushion Vehicles M Pollack / Applied Physical Sciences
Closed loop control of a flap exposed to harmonic aerodynamic actuation
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jun 08, 018 Closed loop control of a flap exposed to harmonic aerodynamic actuation Velte, Clara Marika; Mikkelsen, Robert Flemming; Sørensen, Jens Nørkær; Kaloyanov, Teodor
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Jun 08, 018 Closed loop control of a flap exposed to harmonic aerodynamic actuation Velte, Clara Marika; Mikkelsen, Robert Flemming; Sørensen, Jens Nørkær; Kaloyanov, Teodor
Active noise control at a moving virtual microphone using the SOTDF moving virtual sensing method
 Proceedings of ACOUSTICS 29 23 25 November 29, Adelaide, Australia Active noise control at a moving rophone using the SOTDF moving sensing method Danielle J. Moreau, Ben S. Cazzolato and Anthony C. Zander
Proceedings of ACOUSTICS 29 23 25 November 29, Adelaide, Australia Active noise control at a moving rophone using the SOTDF moving sensing method Danielle J. Moreau, Ben S. Cazzolato and Anthony C. Zander
Ultrasound Beamforming and Image Formation. Jeremy J. Dahl
 Ultrasound Beamforming and Image Formation Jeremy J. Dahl Overview Ultrasound Concepts Beamforming Image Formation Absorption and TGC Advanced Beamforming Techniques Synthetic Receive Aperture Parallel
Ultrasound Beamforming and Image Formation Jeremy J. Dahl Overview Ultrasound Concepts Beamforming Image Formation Absorption and TGC Advanced Beamforming Techniques Synthetic Receive Aperture Parallel
INFLUENCE OF MEMBRANE AMPLITUDE AND FORCING FREQUENCY ON SYNTHETIC JET VELOCITY
 TASKQUARTERLYvol.19,No2,2015,pp.111 120 INFLUENCE OF MEMBRANE AMPLITUDE AND FORCING FREQUENCY ON SYNTHETIC JET VELOCITY MARCIN KUROWSKI AND PIOTR DOERFFER Institute of Fluid-Flow Machinery, Polish Academy
TASKQUARTERLYvol.19,No2,2015,pp.111 120 INFLUENCE OF MEMBRANE AMPLITUDE AND FORCING FREQUENCY ON SYNTHETIC JET VELOCITY MARCIN KUROWSKI AND PIOTR DOERFFER Institute of Fluid-Flow Machinery, Polish Academy
UNSTEADINESS OF BLADE-PASSING FREQUENCY TONES OF AXIAL FANS
 The 1 st International Congress on Sound and Vibration 13-17 July, 014, Beijing/China UNSTEADINESS OF BLADE-PASSING FREQUENCY TONES OF AXIAL FANS Michael Sturm, Thomas Carolus Institute of Fluid- and Thermodynamics,
The 1 st International Congress on Sound and Vibration 13-17 July, 014, Beijing/China UNSTEADINESS OF BLADE-PASSING FREQUENCY TONES OF AXIAL FANS Michael Sturm, Thomas Carolus Institute of Fluid- and Thermodynamics,
Gravity wave activity and dissipation around tropospheric jet streams
 Gravity wave activity and dissipation around tropospheric jet streams W. Singer, R. Latteck P. Hoffmann, A. Serafimovich Leibniz-Institute of Atmospheric Physics, 185 Kühlungsborn, Germany (email: singer@iap-kborn.de
Gravity wave activity and dissipation around tropospheric jet streams W. Singer, R. Latteck P. Hoffmann, A. Serafimovich Leibniz-Institute of Atmospheric Physics, 185 Kühlungsborn, Germany (email: singer@iap-kborn.de
Microphone Measurements in Aeroacoustic Installations
 Michel ROGER LMFA, Ecole Centrale de Lyon, University of Lyon 36 Avenue Guy de Collongue, 69134 Ecully cedex FRANCE michel.roger@ec-lyon.fr ABSTRACT The lecture is dealing with microphone measurements
Michel ROGER LMFA, Ecole Centrale de Lyon, University of Lyon 36 Avenue Guy de Collongue, 69134 Ecully cedex FRANCE michel.roger@ec-lyon.fr ABSTRACT The lecture is dealing with microphone measurements
Rec. ITU-R P RECOMMENDATION ITU-R P *
 Rec. ITU-R P.682-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R P.682-1 * PROPAGATION DATA REQUIRED FOR THE DESIGN OF EARTH-SPACE AERONAUTICAL MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Question ITU-R 207/3) Rec. 682-1 (1990-1992) The
Rec. ITU-R P.682-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R P.682-1 * PROPAGATION DATA REQUIRED FOR THE DESIGN OF EARTH-SPACE AERONAUTICAL MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Question ITU-R 207/3) Rec. 682-1 (1990-1992) The
THE high level of nuisance noise generated by the take-off and landing of aircraft has a significant impact on the communities
 Bluff Body Noise and Flow Control with Atmospheric Plasma Actuators Xun Huang Xin Zhang and Steve Gabriel University of Southampton, Southampton, SO7 BJ, United Kingdom Plasma actuators operating in atmospheric
Bluff Body Noise and Flow Control with Atmospheric Plasma Actuators Xun Huang Xin Zhang and Steve Gabriel University of Southampton, Southampton, SO7 BJ, United Kingdom Plasma actuators operating in atmospheric
Effect of Flow Impingement on the Acoustic Resonance Excitation in A Shallow Rectangular Cavity
 Effect of Flow Impingement on the Acoustic Resonance Excitation in A Shallow Rectangular Cavity Ahmed Omer 1), Atef Mohany 2) * and Marwan Hassan 3) 1),2) University of Ontario Institute of Technology,
Effect of Flow Impingement on the Acoustic Resonance Excitation in A Shallow Rectangular Cavity Ahmed Omer 1), Atef Mohany 2) * and Marwan Hassan 3) 1),2) University of Ontario Institute of Technology,
DETACHED EDDY SIMULATIONS OF PARTIALLY COVERED AND RAISED CAVITIES. A Thesis by. Sandeep Kumar Gadiparthi
 DETACHED EDDY SIMULATIONS OF PARTIALLY COVERED AND RAISED CAVITIES A Thesis by Sandeep Kumar Gadiparthi Bachelor of Technology, Institute of Aeronautical Engineering, 2007 Submitted to the Department of
DETACHED EDDY SIMULATIONS OF PARTIALLY COVERED AND RAISED CAVITIES A Thesis by Sandeep Kumar Gadiparthi Bachelor of Technology, Institute of Aeronautical Engineering, 2007 Submitted to the Department of
Applications of Monte Carlo Methods in Charged Particles Optics
 Sydney 13-17 February 2012 p. 1/3 Applications of Monte Carlo Methods in Charged Particles Optics Alla Shymanska alla.shymanska@aut.ac.nz School of Computing and Mathematical Sciences Auckland University
Sydney 13-17 February 2012 p. 1/3 Applications of Monte Carlo Methods in Charged Particles Optics Alla Shymanska alla.shymanska@aut.ac.nz School of Computing and Mathematical Sciences Auckland University
Implementation of active noise control in a multi-modal spray dryer exhaust stack
 Implementation of active noise control in a multi-modal spray dryer exhaust stack X. Li a, X. Qiu b, D. L. L. Leclercq a, A. C. Zander a and C. H. Hansen a a School of Mechanical Engineering, The University
Implementation of active noise control in a multi-modal spray dryer exhaust stack X. Li a, X. Qiu b, D. L. L. Leclercq a, A. C. Zander a and C. H. Hansen a a School of Mechanical Engineering, The University
A SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM COMBINED WITH PASSIVE SILENCERS FOR IMPROVED NOISE REDUCTION IN DUCTS SUMMARY INTRODUCTION
 A SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM COMBINED WITH PASSIVE SILENCERS FOR IMPROVED NOISE REDUCTION IN DUCTS Martin LARSSON, Sven JOHANSSON, Lars HÅKANSSON, Ingvar CLAESSON Blekinge
A SYSTEM IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM COMBINED WITH PASSIVE SILENCERS FOR IMPROVED NOISE REDUCTION IN DUCTS Martin LARSSON, Sven JOHANSSON, Lars HÅKANSSON, Ingvar CLAESSON Blekinge
Modal identification of a small-scale ducted fan
 Aeroacoustics Conferences May - June, 6, Lyon, France nd AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference AIAA 6-6 Modal identification of a small-scale ducted fan A. Pereira, E. Salze and P. Souchotte École Centrale
Aeroacoustics Conferences May - June, 6, Lyon, France nd AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference AIAA 6-6 Modal identification of a small-scale ducted fan A. Pereira, E. Salze and P. Souchotte École Centrale
Outline. Aperture function and aperture smoothing function. Aperture and Arrays. INF5410 Array signal processing. Ch. 3: Apertures and Arrays, part I
 INF541 Array signal processing. Ch. 3: Apertures and Arrays, part I Andreas Austeng Department of Informatics, University of Oslo February 1 Outline Finite Continuous Apetrures Aperture and Arrays Aperture
INF541 Array signal processing. Ch. 3: Apertures and Arrays, part I Andreas Austeng Department of Informatics, University of Oslo February 1 Outline Finite Continuous Apetrures Aperture and Arrays Aperture
Multi-channel Active Control of Axial Cooling Fan Noise
 The 2002 International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering Dearborn, MI, USA. August 19-21, 2002 Multi-channel Active Control of Axial Cooling Fan Noise Kent L. Gee and Scott D. Sommerfeldt
The 2002 International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering Dearborn, MI, USA. August 19-21, 2002 Multi-channel Active Control of Axial Cooling Fan Noise Kent L. Gee and Scott D. Sommerfeldt
Photonic time-stretching of 102 GHz millimeter waves using 1.55 µm nonlinear optic polymer EO modulators
 Photonic time-stretching of 10 GHz millimeter waves using 1.55 µm nonlinear optic polymer EO modulators H. Erlig Pacific Wave Industries H. R. Fetterman and D. Chang University of California Los Angeles
Photonic time-stretching of 10 GHz millimeter waves using 1.55 µm nonlinear optic polymer EO modulators H. Erlig Pacific Wave Industries H. R. Fetterman and D. Chang University of California Los Angeles
Travelling Wave, Broadband, and Frequency Independent Antennas. EE-4382/ Antenna Engineering
 Travelling Wave, Broadband, and Frequency Independent Antennas EE-4382/5306 - Antenna Engineering Outline Traveling Wave Antennas Introduction Traveling Wave Antennas: Long Wire, V Antenna, Rhombic Antenna
Travelling Wave, Broadband, and Frequency Independent Antennas EE-4382/5306 - Antenna Engineering Outline Traveling Wave Antennas Introduction Traveling Wave Antennas: Long Wire, V Antenna, Rhombic Antenna
The spatial structure of an acoustic wave propagating through a layer with high sound speed gradient
 The spatial structure of an acoustic wave propagating through a layer with high sound speed gradient Alex ZINOVIEV 1 ; David W. BARTEL 2 1,2 Defence Science and Technology Organisation, Australia ABSTRACT
The spatial structure of an acoustic wave propagating through a layer with high sound speed gradient Alex ZINOVIEV 1 ; David W. BARTEL 2 1,2 Defence Science and Technology Organisation, Australia ABSTRACT
Sensitivity of EFITs to the Form of the MSE Fitting Function
 Sensitivity of EFITs to the Form of the MSE Fitting Function M.A. Makowski, S. Allen, R. Ellis, R. Geer, J. Jayakumar, J. Moller, B. Rice Poster RP1-020 DIII D NATIONAL FUSION FACILITY SAN DIEGO aps01
Sensitivity of EFITs to the Form of the MSE Fitting Function M.A. Makowski, S. Allen, R. Ellis, R. Geer, J. Jayakumar, J. Moller, B. Rice Poster RP1-020 DIII D NATIONAL FUSION FACILITY SAN DIEGO aps01
Off-axis response of Compton and photoelectric polarimeters with a large field of view
 Off-axis response of Compton and photoelectric polarimeters with a large field of view Fabio Muleri fabio.muleri@iaps.inaf.it X-ray polarisation in astrophysics -a window about to open? Stockholm, Sweden,
Off-axis response of Compton and photoelectric polarimeters with a large field of view Fabio Muleri fabio.muleri@iaps.inaf.it X-ray polarisation in astrophysics -a window about to open? Stockholm, Sweden,
Applications area and advantages of the capillary waves method
 Applications area and advantages of the capillary waves method Surface waves at the liquid-gas interface (mainly capillary waves) provide a convenient probe of the bulk and surface properties of liquids.
Applications area and advantages of the capillary waves method Surface waves at the liquid-gas interface (mainly capillary waves) provide a convenient probe of the bulk and surface properties of liquids.
EC6503 Transmission Lines and WaveguidesV Semester Question Bank
 UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines General Solution, Physicasignificance of the equations 1. Derive the two useful forms of equations for voltage and current
UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines General Solution, Physicasignificance of the equations 1. Derive the two useful forms of equations for voltage and current
The Effects of Sweeping Jet Actuator Parameters on Flow Separation Control
 https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?r=20160006025 2019-01-08T00:14:38+00:00Z The Effects of Sweeping Jet Actuator Parameters on Flow Separation Control Mehti Koklu 1 NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton,
https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?r=20160006025 2019-01-08T00:14:38+00:00Z The Effects of Sweeping Jet Actuator Parameters on Flow Separation Control Mehti Koklu 1 NASA Langley Research Center, Hampton,
TOWARDS PRECISE PREDICTION OF FLOW PATTERS OF RESONATORS UNDER GRAZING FLOWS BY USING CARTESIAN- MESH CFD
 6th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM 6) 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) 11 15 June 2018, Glasgow, UK TOWARDS PRECISE PREDICTION OF FLOW PATTERS OF RESONATORS
6th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM 6) 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) 11 15 June 2018, Glasgow, UK TOWARDS PRECISE PREDICTION OF FLOW PATTERS OF RESONATORS
The Analysis of the Airplane Flutter on Low Band Television Broadcasting Signal
 The Analysis of the Airplane Flutter on Low Band Television Broadcasting Signal A. Wonggeeratikun 1,2, S. Noppanakeepong 1, N. Leelaruji 1, N. Hemmakorn 1, and Y. Moriya 1 1 Faculty of Engineering and
The Analysis of the Airplane Flutter on Low Band Television Broadcasting Signal A. Wonggeeratikun 1,2, S. Noppanakeepong 1, N. Leelaruji 1, N. Hemmakorn 1, and Y. Moriya 1 1 Faculty of Engineering and
CREATING OF EXPERIMENTAL ACOUSTIC DATABASE FOR AN ISOLATED HELICOPTER`S MAIN ROTOR
 CREATING OF EXPERIMENTAL ACOUSTIC DATABASE FOR AN ISOLATED HELICOPTER`S MAIN ROTOR G.N. Barakos 1, A.S. Batrakov 2, A.N. Bozhenko 2, L.I. Garipova 2, A.N. Kusuymov 2, S.A. Michailov 2, V.V. Pakhov 2, R.P.
CREATING OF EXPERIMENTAL ACOUSTIC DATABASE FOR AN ISOLATED HELICOPTER`S MAIN ROTOR G.N. Barakos 1, A.S. Batrakov 2, A.N. Bozhenko 2, L.I. Garipova 2, A.N. Kusuymov 2, S.A. Michailov 2, V.V. Pakhov 2, R.P.
Simulation of Cylindrical Resonator with Spiral Neck and Straight Neck to Attenuate the Low Frequency Noise of Muffler
 Simulation of Cylindrical Resonator with Spiral Neck and Straight Neck to Attenuate the Low Frequency Noise of Muffler Dr. Amit Kumar Gupta 1 Devesh Kumar Ratnavat 2 1 Mechanical Engineering Department,
Simulation of Cylindrical Resonator with Spiral Neck and Straight Neck to Attenuate the Low Frequency Noise of Muffler Dr. Amit Kumar Gupta 1 Devesh Kumar Ratnavat 2 1 Mechanical Engineering Department,
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance
 Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
Simple Feedback Structure of Active Noise Control in a Duct
 Strojniški vestnik - Journal of Mechanical Engineering 54(28)1, 649-654 Paper received: 6.9.27 UDC 534.83 Paper accepted: 7.7.28 Simple Feedback Structure of Active Noise Control in a Duct Jan Černetič
Strojniški vestnik - Journal of Mechanical Engineering 54(28)1, 649-654 Paper received: 6.9.27 UDC 534.83 Paper accepted: 7.7.28 Simple Feedback Structure of Active Noise Control in a Duct Jan Černetič
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DIFFERENT MICROPHONE INSTALLATIONS FOR ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL IN DUCTS
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DIFFERENT MICROPHONE INSTALLATIONS FOR ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL IN DUCTS M. Larsson, S. Johansson, L. Håkansson and I. Claesson Department of Signal Processing Blekinge Institute
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS OF DIFFERENT MICROPHONE INSTALLATIONS FOR ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL IN DUCTS M. Larsson, S. Johansson, L. Håkansson and I. Claesson Department of Signal Processing Blekinge Institute
ENHANCEMENT OF THE TRANSMISSION LOSS OF DOUBLE PANELS BY MEANS OF ACTIVELY CONTROLLING THE CAVITY SOUND FIELD
 ENHANCEMENT OF THE TRANSMISSION LOSS OF DOUBLE PANELS BY MEANS OF ACTIVELY CONTROLLING THE CAVITY SOUND FIELD André Jakob, Michael Möser Technische Universität Berlin, Institut für Technische Akustik,
ENHANCEMENT OF THE TRANSMISSION LOSS OF DOUBLE PANELS BY MEANS OF ACTIVELY CONTROLLING THE CAVITY SOUND FIELD André Jakob, Michael Möser Technische Universität Berlin, Institut für Technische Akustik,
Theme 2 The Turbine Dr Geoff Dutton
 SUPERGEN Wind Wind Energy Technology Phase 2 Theme 2 The Turbine Dr Geoff Dutton Supergen Wind Phase 2 General Assembly Meeting 21 March 2012 Normalized spectrum [db] Turbine blade materials The Turbine
SUPERGEN Wind Wind Energy Technology Phase 2 Theme 2 The Turbine Dr Geoff Dutton Supergen Wind Phase 2 General Assembly Meeting 21 March 2012 Normalized spectrum [db] Turbine blade materials The Turbine
Monopile as Part of Aeroelastic Wind Turbine Simulation Code
 Monopile as Part of Aeroelastic Wind Turbine Simulation Code Rune Rubak and Jørgen Thirstrup Petersen Siemens Wind Power A/S Borupvej 16 DK-7330 Brande Denmark Abstract The influence on wind turbine design
Monopile as Part of Aeroelastic Wind Turbine Simulation Code Rune Rubak and Jørgen Thirstrup Petersen Siemens Wind Power A/S Borupvej 16 DK-7330 Brande Denmark Abstract The influence on wind turbine design
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R S *
 Rec. ITU-R S.1339-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R S.1339-1* Rec. ITU-R S.1339-1 SHARING BETWEEN SPACEBORNE PASSIVE SENSORS OF THE EARTH EXPLORATION-SATELLITE SERVICE AND INTER-SATELLITE LINKS OF GEOSTATIONARY-SATELLITE
Rec. ITU-R S.1339-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R S.1339-1* Rec. ITU-R S.1339-1 SHARING BETWEEN SPACEBORNE PASSIVE SENSORS OF THE EARTH EXPLORATION-SATELLITE SERVICE AND INTER-SATELLITE LINKS OF GEOSTATIONARY-SATELLITE
Development of a multi-hole probe for atmospheric boundary layer measurements
 Development of a multi-hole probe for atmospheric boundary layer measurements Árpád Varga a, Márton Balczó a a Theodore von Kármán Wind Tunnel Laboratory, Department of Fluid Mechanics, Budapest University
Development of a multi-hole probe for atmospheric boundary layer measurements Árpád Varga a, Márton Balczó a a Theodore von Kármán Wind Tunnel Laboratory, Department of Fluid Mechanics, Budapest University
PanPhonics Panels in Active Control of Sound
 PanPhonics White Paper PanPhonics Panels in Active Control of Sound Seppo Uosukainen VTT Building and Transport Contents Introduction... 1 Active control of sound... 1 Interference... 2 Control system...
PanPhonics White Paper PanPhonics Panels in Active Control of Sound Seppo Uosukainen VTT Building and Transport Contents Introduction... 1 Active control of sound... 1 Interference... 2 Control system...
Influence of SDBD plasma aerodynamic actuation on flow control by AC power supply and AC-DC power supply
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Influence of SDBD plasma aerodynamic actuation on flow control by AC power supply and AC-DC power supply To cite this article: Xu
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Influence of SDBD plasma aerodynamic actuation on flow control by AC power supply and AC-DC power supply To cite this article: Xu
Active Noise Control: Is it Good for Anything?
 Active Noise Control: Is it Good for Anything? Scott D. Sommerfeldt Acoustics Research Group Dept. of Physics & Astronomy Brigham Young University April 2, 2012 Acoustics AMO Astronomy/Astrophysics Condensed
Active Noise Control: Is it Good for Anything? Scott D. Sommerfeldt Acoustics Research Group Dept. of Physics & Astronomy Brigham Young University April 2, 2012 Acoustics AMO Astronomy/Astrophysics Condensed
Scan-based near-field acoustical holography on rocket noise
 Scan-based near-field acoustical holography on rocket noise Michael D. Gardner N283 ESC Provo, UT 84602 Scan-based near-field acoustical holography (NAH) shows promise in characterizing rocket noise source
Scan-based near-field acoustical holography on rocket noise Michael D. Gardner N283 ESC Provo, UT 84602 Scan-based near-field acoustical holography (NAH) shows promise in characterizing rocket noise source
Active Control of Energy Density in a Mock Cabin
 Cleveland, Ohio NOISE-CON 2003 2003 June 23-25 Active Control of Energy Density in a Mock Cabin Benjamin M. Faber and Scott D. Sommerfeldt Department of Physics and Astronomy Brigham Young University N283
Cleveland, Ohio NOISE-CON 2003 2003 June 23-25 Active Control of Energy Density in a Mock Cabin Benjamin M. Faber and Scott D. Sommerfeldt Department of Physics and Astronomy Brigham Young University N283
Flow around a NACA0018 airfoil with a cavity and its dynamical response to acoustic forcing
 Exp Fluids (2) 5:493 59 DOI.7/s348--65-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Flow around a NACA8 airfoil with a cavity and its dynamical response to acoustic forcing W. F. J. Olsman J. F. H. Willems A. Hirschberg T. Colonius
Exp Fluids (2) 5:493 59 DOI.7/s348--65-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Flow around a NACA8 airfoil with a cavity and its dynamical response to acoustic forcing W. F. J. Olsman J. F. H. Willems A. Hirschberg T. Colonius
The Principle of Superposition
 The Principle of Superposition If wave 1 displaces a particle in the medium by D 1 and wave 2 simultaneously displaces it by D 2, the net displacement of the particle is simply D 1 + D 2. Standing Waves
The Principle of Superposition If wave 1 displaces a particle in the medium by D 1 and wave 2 simultaneously displaces it by D 2, the net displacement of the particle is simply D 1 + D 2. Standing Waves
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R S.1512
 Rec. ITU-R S.151 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R S.151 Measurement procedure for determining non-geostationary satellite orbit satellite equivalent isotropically radiated power and antenna discrimination The ITU
Rec. ITU-R S.151 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R S.151 Measurement procedure for determining non-geostationary satellite orbit satellite equivalent isotropically radiated power and antenna discrimination The ITU
SIGNAL TRANSMISSION CHARACTERISTICS IN STRIPLINE-TYPE BEAM POSITION MONITOR
 SIGNAL TRANSISSION CHARACTERISTICS IN STRIPLINE-TYPE BEA POSITION ONITOR T. Suwada, KEK, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0801, Japan Abstract A new stripline-type beam position monitor (BP) system is under development
SIGNAL TRANSISSION CHARACTERISTICS IN STRIPLINE-TYPE BEA POSITION ONITOR T. Suwada, KEK, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0801, Japan Abstract A new stripline-type beam position monitor (BP) system is under development
Use of Nonlinear Volterra Theory in Predicting the Propagation of Non-uniform Flow Through an Axial Compressor
 Use of Nonlinear Volterra Theory in Predicting the Propagation of Non-uniform Flow Through an Axial Compressor by Jonathan G. Luedke Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute
Use of Nonlinear Volterra Theory in Predicting the Propagation of Non-uniform Flow Through an Axial Compressor by Jonathan G. Luedke Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute
Noise Attenuation by Two One Degree of Freedom Helmholtz Resonators
 Global Science and Technology Journal Vol. 3. No. 1. March 015 Issue. Pp.1-9 Noise Attenuation by Two One Degree of Freedom Helmholtz Resonators Md. Amin Mahmud a*, Md. Zahid Hossain b, Md. Shahriar Islam
Global Science and Technology Journal Vol. 3. No. 1. March 015 Issue. Pp.1-9 Noise Attenuation by Two One Degree of Freedom Helmholtz Resonators Md. Amin Mahmud a*, Md. Zahid Hossain b, Md. Shahriar Islam
INTRODUCTION. Flying freely. Aircraft that do not require a runway. Unconventionally shaped VTOL flying robots
 R E S E A R C H INTRODUCTION Flying freely Aircraft that do not require a runway A runway is generally required for aircraft to take off or land. In contrast, vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft
R E S E A R C H INTRODUCTION Flying freely Aircraft that do not require a runway A runway is generally required for aircraft to take off or land. In contrast, vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft
TURNEX. Turbomachinery noise radiation through the jet exhaust. January December Partners, 4.7 Million Euro
 Turbomachinery noise radiation through the jet exhaust January 2005 - December 2007 12 Partners, 4.7 Million Euro Brian J Tester, TURNEX Co-ordinator, ISVR, Southampton University Daniel Chiron, EC Project
Turbomachinery noise radiation through the jet exhaust January 2005 - December 2007 12 Partners, 4.7 Million Euro Brian J Tester, TURNEX Co-ordinator, ISVR, Southampton University Daniel Chiron, EC Project
Waveguides GATE Problems
 Waveguides GATE Problems One Mark Questions. The interior of a 20 20 cm cm rectangular waveguide is completely 3 4 filled with a dielectric of r 4. Waves of free space wave length shorter than..can be
Waveguides GATE Problems One Mark Questions. The interior of a 20 20 cm cm rectangular waveguide is completely 3 4 filled with a dielectric of r 4. Waves of free space wave length shorter than..can be
Chapter 3 Signal Degradation in Optical Fibers
 What about the loss in optical fiber? Why and to what degree do optical signals gets distorted as they propagate along a fiber? Fiber links are limited by in path length by attenuation and pulse distortion.
What about the loss in optical fiber? Why and to what degree do optical signals gets distorted as they propagate along a fiber? Fiber links are limited by in path length by attenuation and pulse distortion.
Impedance and Loop Antennas
 Impedance and Loop Antennas Ranga Rodrigo University of Moratuwa January 4, 2009 Ranga Rodrigo (University of Moratuwa) Impedance and Loop Antennas January 4, 2009 1 / 41 Gain Summary of Last Week s Lecture
Impedance and Loop Antennas Ranga Rodrigo University of Moratuwa January 4, 2009 Ranga Rodrigo (University of Moratuwa) Impedance and Loop Antennas January 4, 2009 1 / 41 Gain Summary of Last Week s Lecture
Index of refraction varies significantly for broadband pulses
 Index of refraction varies significantly for broadband pulses Δt=10 fs Δλ =90nm index of refraction may vary by nearly 1% phase speed depends on n v φ (λ) = c n(λ) n phase relations will be lost as pulse
Index of refraction varies significantly for broadband pulses Δt=10 fs Δλ =90nm index of refraction may vary by nearly 1% phase speed depends on n v φ (λ) = c n(λ) n phase relations will be lost as pulse
Reduction of Musical Residual Noise Using Harmonic- Adapted-Median Filter
 Reduction of Musical Residual Noise Using Harmonic- Adapted-Median Filter Ching-Ta Lu, Kun-Fu Tseng 2, Chih-Tsung Chen 2 Department of Information Communication, Asia University, Taichung, Taiwan, ROC
Reduction of Musical Residual Noise Using Harmonic- Adapted-Median Filter Ching-Ta Lu, Kun-Fu Tseng 2, Chih-Tsung Chen 2 Department of Information Communication, Asia University, Taichung, Taiwan, ROC
ANALYSE DER WELLENAUSBREITUNG IN TRANSSONISCHER BUFFET-STRÖMUNG
 Fachtagung Lasermethoden in der Strömungsmesstechnik 3. 5. September 2013, München ANALYSE DER WELLENAUSBREITUNG IN TRANSSONISCHER BUFFET-STRÖMUNG ANALYSIS OF WAVE PROPAGATION IN TRANSONIC BUFFET FLOW
Fachtagung Lasermethoden in der Strömungsmesstechnik 3. 5. September 2013, München ANALYSE DER WELLENAUSBREITUNG IN TRANSSONISCHER BUFFET-STRÖMUNG ANALYSIS OF WAVE PROPAGATION IN TRANSONIC BUFFET FLOW
Numerical Study of a High Head Francis Turbine with Measurements from the Francis-99 Project
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Numerical Study of a High Head Francis Turbine with Measurements from the Francis-99 Project To cite this article: H Wallimann and R Neubauer 2015 J. Phys.:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Numerical Study of a High Head Francis Turbine with Measurements from the Francis-99 Project To cite this article: H Wallimann and R Neubauer 2015 J. Phys.:
PRACTICAL IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM IN A HOT EXHAUST STACK
 PRACTICAL IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM IN A HOT EXHAUST STACK Colin H. Hansen, Carl Q. Howard, Kym A. Burgemeister & Ben S. Cazzolato University of Adelaide, South Australia, AUSTRALIA
PRACTICAL IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ACTIVE NOISE CONTROL SYSTEM IN A HOT EXHAUST STACK Colin H. Hansen, Carl Q. Howard, Kym A. Burgemeister & Ben S. Cazzolato University of Adelaide, South Australia, AUSTRALIA
SOUND SPECTRUM MEASUREMENTS IN DUCTED AXIAL FAN UNDER STALL CONDITIONS AT FREQUENCY RANGE FROM 9000 HZ TO 9600 HZ
 Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 2012 Manikandapirapu P K et al., 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 1, No. 2, July 2012 2012 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved SOUND SPECTRUM MEASUREMENTS IN
Int. J. Mech. Eng. & Rob. Res. 2012 Manikandapirapu P K et al., 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2278 0149 www.ijmerr.com Vol. 1, No. 2, July 2012 2012 IJMERR. All Rights Reserved SOUND SPECTRUM MEASUREMENTS IN
Experiment 8 Frequency Response
 Experiment 8 Frequency Response W.T. Yeung, R.A. Cortina, and R.T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Spring 2005 1.0 Objective This lab will introduce the student to frequency response of circuits. The student will
Experiment 8 Frequency Response W.T. Yeung, R.A. Cortina, and R.T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Spring 2005 1.0 Objective This lab will introduce the student to frequency response of circuits. The student will
