c a p a b i l i t i e s
|
|
|
- Daniela Lindsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 V I S H AY I N T E R T E C H N O L O G Y, I N C. Shunts, Current Shunts, and Current-Sensing Resistors R e s i s t i v e p r o d u c t s c a p a b i l i t i e s w w w. v i s h a y. c o m
2 SEMICONDUCTORS RECTIFIERS Schottky (single, dual) Standard, Fast, and Ultra-Fast Recovery (single, dual) Bridge Superectifier Sinterglass Avalanche Diodes SMALL-SIGNAL DIODES Schottky and Switching (single, dual) Tuner/Capacitance (single, dual) Bandswitching PIN RF TRANSISTORS Bipolar Transistors (AF and RF) Dual Gate MOSFETs MOSMICs OPTOELECTRONICS IR Emitters and Detectors, and IR Receiver Modules Optocouplers and Solid-State Relays Optical Sensors LEDs and 7-Segment Displays Infrared Data Transceiver Modules Custom Products P r o d u c t L i s t i n G S ZENER AND SUPPRESSOR DIODES Zener (single, dual) TVS (TransZorb, Automotive, ESD, Arrays) MOSFETs Power MOSFETs JFETs Passive Components RESISTIVE PRODUCTS Foil Resistors Film Resistors metal Film Resistors thin Film Resistors thick Film Resistors metal Oxide Film Resistors Carbon Film Resistors Wirewound Resistors Power Metal Strip Resistors Chip Fuses Variable Resistors Cermet Variable Resistors Wirewound Variable Resistors Conductive Plastic Variable Resistors Networks/Arrays Non-linear Resistors ntc Thermistors PTC Thermistors Varistors MAGNETICS Inductors Transformers ICs Power ICs Analog Switches DC/DC Converters RF Transceivers ICs for Optoelectronics CAPACITORS Tantalum Capacitors molded Chip Tantalum Capacitors Coated Chip Tantalum Capacitors Solid Through-Hole Tantalum Capacitors Wet Tantalum Capacitors Ceramic Capacitors multilayer Chip Capacitors disc Capacitors Film Capacitors Power Capacitors Heavy-Current Capacitors Aluminum Capacitors Silicon RF Capacitors STRAIN GAGE TRANSDUCERS and stress analysis systems PhotoStress Strain Gages Load Cells Force Transducers Instruments Weighing Systems
3 Shunts, Current Shunts, and Current-Sensing Resistors, Inc. 63 Lancaster Avenue Malvern, PA United States Phone: Fax:
4 NOTICE Specifications of the products displayed herein are subject to change without notice., Inc., or anyone on its behalf, assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies. Information contained herein is intended to provide a product description only. No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except as provided in Vishay s terms and conditions of sale for such products, Vishay assumes no liability whatsoever, and disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating to sale and/or use of Vishay products including liability or warranties relating to fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability, or infringement of any patent, copyright, or other intellectual property right. The products shown herein are not designed for use in medical, life-saving, or life-sustaining applications. Customers using or selling these products for use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Vishay for any damages resulting from such improper use or sale.
5 Contents Shunts, Current Shunts, and Current Sensing Resistors Introduction 4 Shunt 4 Current Shunt 5 Current Sensor 5 Shunts/Current Sensors 6 Chips and SMD 6 Exposed-Element 7 Shunts, Low-Ohm 8 High-Power (100 W W) 8 Mid-Power (10 W W) 9 Low-Power (1 W - 10 W) 9 Current Sensors, Lower-Ohm 10 Axial Leads 10 Radial Leads 11 Axial/Radial Leads 11 Characteristics and Design Considerations 12 Kelvin Connection 12 Tolerance and Measurement of Resistance at Low Values 12 Power Rating and Thermal Dissipation 13 One Short Pulse 14 Equally Spaced Repetitive Pulses 14 Long Pulses (100 milliseconds to 5 seconds) 14 Current Rating 14 Reactance 14 Impedance 15 Thermal EMF 15 Noise 16 Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR) 18 Design Factors 19 Shunts 19 Sensors 19 Typical Applications 19 T a b l e o f C o n t e n t s 3
6 Introduction Shunt Generally speaking, there is considerable overlapping in the use of the terms shunts, current shunts, and current sensors. Although these three terms are used interchangeably, there are some subtle differences that are worth nothing and that may suggest a preference for one or another term as it relates to a particular application. I n t r o d u c t i o n Shunt A shunt is a resistive device employed to divert most of the current in an electric circuit. The earliest shunts were meter shunts used as external accessories to ammeters allowing one meter to be used for a variety of current levels depending upon which shunt was chosen. These were often massive four-terminal devices with the smaller potential terminals connected to the meter and the larger current terminals connected to the circuit under test. Present day ammeters are more likely to be specific to a particular current range one meter, one internal shunt. These internal shunts are resistors with current connections to the external terminals of the ammeter and voltage connections made internally to the meter movement. In addition to these measurement shunts, power-shunts are used for electric motor starting, braking, and speed control. Loading, neutral grounding, preheating and capacitor unloading are all applications in which a resistor is called upon to shunt large amounts of current. For purposes of this brochure a shunt is defined as any two- or four-terminal resistor of sub-ohmic resistance value and high-current capacity. To fully describe a particular shunt, the following characteristics may require identification: Mechanical (as applicable) All external dimensions Body material and finish Terminal material and finish Mounting method and hardware Maximum internal hot-spot temperature Maximum case temperature and test location (related to hot-spot temperature) External conductors, termination, and method of attachment External heat sink capacity and mounting method Cooling water connection with specified inlet temperature, flow rate, and pressure Part number and part marking Unit packaging method and package marking Unit weight and shipping weight Electrical (as applicable) Resistance value and tolerance (for 4-terminal devices, also the maximum resistance value between the current terminals) Maximum current rating Maximum continuous-duty wattage rating based on specified heat sinking method Maximum pulse power under specified conditions Maximum temperature coefficient of resistance and temperature range and reference Maximum reactance Maximum dielectric withstanding voltage to mounting hardware 4
7 Current Shunt, Current Sensor Current Shunt For the purpose of this brochure, a current shunt is defined as a shunt is capable of current sensing as well as conducting significant current. Current Sensor A curretn sensor is a resistive device employed to sense levels of current. Current sensors are used in applications where the emphasis is on accuracy and repeatability under all conditions and less on high-current capability. Applications such as force-balance scales, E beam deflection systems, and switching power supplies. all rely on current sensors to feed back and control the current. For the purposes of this brochure, a current sensor is defined as a four-terminal resistor of high accuracy and stability and usually of low resistance value. To fully describe a particular current sensor, the following characteristics must be identified: Mechanical (as applicable) All external dimensions Body material and finish Lead material and finish Identification of current and potential leads Part number and part marking Unit packaging method and package marking Unit weight and shipping weight Electrical (as applicable) Resistance value and tolerance Alternate specification: Voltage output and tolerance for a given current throughput: e.g. 50 mv ±0.1 % per A Maximum temperature coefficient of resistance Maximum wattage rating Maximum reactance Maximum dielectric withstanding voltage Maximum current noise Maximum thermal EMF at the terminals I n t r o d u c t i o n 5
8 Shunts/Current Sensors Chips and SMD Chips and SMD These low-ohm chip resistors are examples of the range of capability available. Hybrid packaging and surfacemounting practitioners will find these leadless devices to be solutions to current sensing in small spaces. Brand Product Image Part Number WSL Sizes Available 0603, 0805, 1206, 2010, 2512, 2816, 3921, 5931 Length (inch / [mm]) 0.06 to 0.59 [1.52 to 15] Power Rating (W) 0.1 to 5 Resistance Range, Tolerance, and Other Features Ω to 0.5 Ω Power Metal Strip S h u n t s / C u r r e n t S e n s o r s Vishay Dale WSL (high power) 0603, 0805, 1206, 2010, 2512 WSH 2818 WSR 4527 WSL WSK 2512 WSL...E 1506, 2010, to 0.25 [1.52 to 6.35] [7.1] [11.6] 0.36 [9.14] 0.25 [6.35] 0.15 to 0.25 [3.81 to 6.35] 0.2 to to to Ω to 0.5 Ω Power Metal Strip Ω to Ω Improved thermal management Power Metal Strip Ω to 1 Ω Molded Power Metal Strip Ω to 0.01 Ω 1 % 4-terminal Power Metal Strip Ω to Ω 4-terminal Power Metal Strip 0.5 Ω to 10 kω Flip chip WSC 2012, 2515, 4527, to 0.69 [5.08 to 17.52] 0.5 to Ω to 8 kω Molded wirewound Vishay Sfernice MSP 2715, 4528, to 0.58 [6 to 14.8] 1 to Ω to 15 kω Molded wirewound 6
9 Exposed-Element Exposed-Element These exposed-element devices are examples of the range of capabilities available. Exposed-element devices represent a cost-effective approach to current sensing. Brand Vishay Dale Product Image Part Number SPR-889 SPR-2068 SPR-755 SPR-2166 SPR-513 SPR-2039 SPR-2093 Sizes Available 7 sizes Length (inch / [mm]) 2.4 [61] 4.56 [116] 1.85 [47] 2.75 [70] 2.75 to 3.38 [70 to 86] 1.05 [26.7] 1.4 [35.6] Power Rating (W) Not power rated Resistance Range, Tolerance, and Other Features Ω to Ω 4-terminal Buss block terminals Ω ±2 % Metal bar Ω ±2 % Metal bar Ω to Ω 4-terminal Ω to 0.01 Ω Metal bar Ω to Ω 4-terminal PCB mount Ω to Ω 4-terminal PCB mount S h u n t s / C u r r e n t S e n s o r s SPR [18.8] 0.75 to Ω to Ω ±0.5 % 4-terminal PCB mount SPU [12.7] Ω to 0.01 Ω ±0.1 % 4-terminal PCB mount SPU [8.9] Ω ±0.1 % 4-terminal PCB mount SPU [27.9] Ω to 0.02 Ω ±0.1 % 4-terminal PCB mount 7
10 Shunts, Low Ohms High-Power High-Power (100 W W) These high-power devices are examples of the range of capabilities available. Brand Product Image Part Number HLZ SPR-761 Sizes Available 12 sizes Length (inch / [mm]) 2 to 8.5 [51 to 216] 3.5 [89] Power Rating (W) 35 to Resistance Range, Tolerance, and Other Features 0.05 Ω to 32 Ω ±10 % 375 C max hot spot Air-cooled Ω to 0.01 Ω Chassis mount S h u n t s, L o w - O h m Vishay Dale Vishay Sfernice SPR-1002 SPR-1009 RSO RPS 4 sizes 2 sizes 4.5 [114] 4.5 [114] 5.43 to [138 to 373] 2.87 [73] to and Ω to 37.5 kω Liquid-cooled Ω 4-terminal Chassis mount Ω 450 C temperature rise 0.24 Ω to 1 MΩ Heat sink mounting RTOP 2 sizes 1.5 [38] 100 to Ω to 1 MΩ Multiple resistors in single package Heat sink mounting 8
11 Mid-Power, Low-Power Mid-Power (10 W W) These mid-power devices are examples of the range of capabilities available. Some of these shunts are suitable for precise current sensing and should be considered when a power requirement exists in addition to the precision and stability requirements of current sensoring. Brand Product Image Part Number SPR-390 Sizes Available Length (inch / [mm]) 2.5 [64] Power Rating (W) 50 Resistance Range, Tolerance, and Other Features Ω to 0.01 Ω Chassis mount Vishay Dale SPR [38] Ω to 0.01 Ω Insulated flexible leads Low-Power (1 W - 10 W) These low-power devices are examples of the range of capabilities available. Good practice calls for derating with tolerance to hold the time drift to a level consistent with the initial tolerance. Brand Vishay Dale Product Image Part Number SPR-383 LVR- 1/3/5/10 Sizes Available 4 sizes Length (inch / [mm]) 1.0 [25] to [11 to 46.4] Power Rating (W) 5 1/3/5/10 Resistance Range, Tolerance, and Other Features Ω to 0.01 Ω Special aluminum housing Flexible leads Ω to 0.8 Ω Molded axial leads S h u n t s, L o w - O h m 9
12 Current Sensors, Lower-Ohm Axial Leads Axial Leads These current sensors with axial leads are examples of the range of capabilities available. Some of these current sensors are plastic-encapsulated while others are in metal housings. Metal enclosures provide a more rugged mounting and more thermal conduction. C u r r e n t S e n s o r s, l o w e r - o h m Brand Product Image Part Number SPR-1005 SPR-2013 SPU50/51/52/53 SPR-2073 SPR-2123 Vishay Dale SPR-2091 RH RH Sizes Available 4 sizes Length (inch / [mm]) [24.8] 0.8 [20] 0.66 to 1.87 [16.8 to 47.5] [22.2] [22.2] 1.88 [40] 0.75 [19] [27] Power Rating (W) 5 2 1/2/4/ Resistance Range, Tolerance, and Other Features Ω to 0.5 Ω 4-terminal molded Ω to 0.3 Ω ±0.1 % min 4-terminal molded Ω to 0.5 Ω 4-terminal molded Ω to 0.25 Ω 4-terminal Ceramic case Ω to 0.25 Ω 4-terminal Ceramic case Ω to 0.25 Ω 4-terminal Ceramic case Ω to 6.55 kω 4-terminal Aluminum-housed chassis mount Ω to 13.4 kω 4-terminal Aluminum-housed chassis mount RH [50] Ω to 39.2 kω 4-terminal Aluminum-housed chassis mount SPR and 0.75 [15.9 and 19] Ω to 0.05 Ω min. 4-terminal molded 10
13 Radial Leads, Axial/Radial Leads Radial Leads These current sensors with radial leads are examples of the range of capabilities available. Radial-leaded current sensors take up less board space for a given size. Brands Product Image Part Number Sizes Available Vishay Dale SPR-1012 Vishay Sfernice RTO 2 sizes Length (inch / [mm]) 1.03 [26] 0.59 [15] Power Rating (W) 4 20 and 50 Resistance Range, Tolerance, and Other Features 0.01 Ω / 0.1 Ω, 10 to 1 ratio divider 5-terminal coated Ω to 1 MΩ TO220 package Heat sink mounting Axial/Radial Leads Axial/radial lead configurations have the advantage of short potential connection leads to the PC board thus minimizing thermal EMF generation. Brands Product Image Part Number Sizes Available Vishay Dale SPR-779 Length (inch / [mm]) [17] Power Rating (W) 1 Resistance Range, Tolerance, and Other Features 0.01 Ω to Ω 4-terminal molded C u r r e n t S e n s o r s, l o w e r - o h m 11
14 Characteristics and Design Consider c h a r a c t e r i s t i c s a n d D e s i g n C o n s i d e r a t i o n s Figure 1. The Equivalent Circuit Lead Resistor Lead X X L R L1 r 1 X L2 r 2 Figure 2. The Simplified Circuit Kelvin Connection A Kelvin or four-terminal connection is required in these low-ohmic-value products to measure a precise voltage drop across the resistive element. In these applications, the contact resistance and the lead resistance may be greater than that of the element resistance itself, so lead connection errors and lead temperature coefficient of resistance errors can be significant if only a two-terminal connection is employed. Figure 1 shows a resistor in series with an inductor in parallel with a capacitor including the resistance and inductance of the leads. This is the equivalent circuit of a two-terminal resistor. Lead r 1 Resistor R Lead r 2 Ignoring the inductance and capacitance for now, the two-terminal resistor is now shown in Figure 2. If r 1 = r 2 = r, then the total resistance R T = R + 2 r. The lead resistance r is uncertain because there is no user-assured connection to the lead. Thus, if we allow r to be significant compared to R, small inaccuracies in lead connections become large inaccuracies in reading. Furthermore, since the lead material is likely to be copper (with a resistance change with temperature, or (TCR), of ppm/ C) and the shunt might be manganin (with a TCR of 20 ppm/ C), then r is very large compared to R and the device is useless in a temperature-variable application. In the 19th century, Lord Kelvin developed, among other things, the four-terminal method of measurement, which eliminated both the uncertainty of lead resistance and lead response to temperature. Figure 3 is the Kelvin solution. If the voltage measuring system used here is of a high impedance, then r 5 approaches infinity and the measurement current lm approaches zero. With zero lm there is zero IR drop through r 3 and r 4, and therefore it does not matter whether the contact resistance is large or small. It also does not matter if the contacts have a high TCR. Similarly, the TCR of the current leads is no longer important because the voltage connections are fixed inside the lead resistance, and, the resistance and TCR of the element only are sensed. Any errors associated with the lead resistance, contact resistance, and/or lead TCR are thus eliminated. A Kelvin connection to a four-terminal resistor is essential for precise current sensing. Tolerance and Measurement of Resistance at Low Values The ability to measure low values to tight tolerances is a concern to both the manufacturer and the user. In many cases, coordination of reading ability by exchange of serialized units with recorded readings becomes necessary. The problem is compounded in the cases of high-current shunts where the selfheating will cause the in-service resistance value to be different than that obtained with low-current-level measuring equipment. Therefore, the measurement conditions must be defined (agreed upon) at the time of specification preparation, i.e., resistance value as determined by specified current and measured IR drop following a period of stabilization. R T X c Figure 3. Kelvin Connection I1 r1 R r2 r3 1 r5 (n) r4 I2 12
15 ations Measurement equipment is available from a number of sources with varying stated accuracies. Digital multimeters with from 5-½ to 8-½ digits may have a 1-ohm full-scale range. If the stated accuracy is sufficient, these devices are suitable for direct reading of resistance down to ohms when equipped with Kelvin connections. If indirect readings (calculated from current and voltage readings) are acceptable, then the digital multimeter can be switched from the ohms to the voltage function, and with a constant-current power supply across the known and unknown resistors in series. IR drops across the potential leads can be measured and compared. This method permits measurement at a rated current which is not available with the ohms function of multimeters and/or most lowohm bridges. Thus, measurement with the higher rated current assures correct results at anticipated operating conditions. One useful variation of this scheme is to fixture and read many resistors at one time by passing the constant current through all resistors in series and switching the voltage probes from one resistor to the next. Large quantities are thus measured quickly. It should be noted that manufacturers will generally prefer a resistance specified at room temperature and not have to deal with the stabilization time necessary for rated current readings. If rated current readings are required, a test charge may be imposed. Power Rating and Thermal Dissipation Resistors are energy convertors converting electrical energy to thermal energy in accordance with the formula P = El where the power consumed P watts is the result of impressing E volts across the resistor and producing I current. Also from Ohm s law, these additional formulas are recalled here for convenience- P = I 2 R, P = E 2 /R, and one watt-hour is worth BTUs. The energy converted by the resistor cannot be allowed to continually build up and be stored as heat within the resistor. Eventually it must be passed to an other medium for disposal. Equilibrium is eventually reached such that the heat generation within the resistor is equal to the heat disposal to the other medium and a stable internal temperature results. This temperature must not exceed a tolerable limit since further increase will alter the integrity of the resistor or even destroy it. Since this temperature limit is within the resistor, it is referred to as the maximum internal hot spot temperature as if there were one spot within the device that is most likely to overheat. The internal hot-spot temperature must be limited to that which will not cause a permanent performance change through metallurgical degradation in a metal alloy resistive element or a chemical change in a cermet or other nonmetallic element. More often than not, however, it is limited to the lower temperatures that will be tolerated by any coatings in contact with the element. From the internal hot spot the heat flows through the body of the resistor and (in the absence of a heat sink) passes to the other medium by radiation and convection from the resistor body. With a heat sink, more rapid removal by conduction takes place. In the case of axial-leaded cap and core resistors, the leads act as thermal conductors to the board traces (which act as heat sinks) and dissipate a major amount of the total heat from the resistor. The equilibrium temperature will be reached most rapidly with the resistor in still air. Additional power can be dissipated before reaching the maximum temperature if there is circulation of the air. A heat sink or an oil bath or cooling water circulation becomes necessary to remain below the maximum internal hot spot temperature when dissipating increasingly large amounts of power. The resistor manufacturer has determined the maximum power in still air and/or with a specified heat sink that will limit the resistor internal hot spot temperature to a satisfactory level. This is the rated power and must not be exceeded. A separate power rating for still air and for a specified heat sink may be provided. Also, the other medium may not always be at room temperature, and therefore less power can be dissipated if the other medium is at an elevated temperature. A derating curve may be provided allowing use of the resistor in an elevated temperature environment without exceeding the maximum internal hot-spot temperature. These curves generally derate to zero power at some elevated temperature which is for these purposes the maximum hot spot temperature. While manufacturers power ratings are serious specifications, they cannot be expected to exactly apply in every case. The thermal dissipation in critical applications may require further analysis. To limit the amount of calculation required, the temperature drop from the internal hot spot to some test spot on the body of the resistor is frequently known and available. The thermal analysis is thereby limited to factors associated with the other medium and confirmed by surface pyrometer readings on the test spot. This test spot with its maximum external hot spot temperature is frequently identified for simplicity as the hot spot. c h a r a c t e r i s t i c s a n d D e s i g n C o n s i d e r a t i o n s 13
16 Characteristics and Design Consider c h a r a c t e r i s t i c s a n d D e s i g n C o n s i d e r a t i o n s One Short Pulse The theory of pulse handling depends upon the pulse width. A short pulse of 100 milliseconds or less is assumed to never have time enough to do more than heat the element. Therefore, the calculation is based on the total mass of the element (wire) only being heated to the maximum internal hot-spot temperature. Example: A resistor element consisting of 10 grams of wire with a specific heat of 0.1 heated from 25 C to a maximum internal hot spot temperature of 275 C requires: 10 x 0.1 (275 25) = 0.29 watt-hours of equivalent power 860 Note: A calorie is 1/860 watt-hours. If the pulse width is 10 milliseconds, the pulse power could be: 0.29 x 3600 x = 104,400 watts max. Equally Spaced Repetitive Pulses Here, the average power, which is the peak power multiplied by the pulse width divided by the cycle width, establishes a threshold temperature rise. Above this threshold to the maximum internal hot-spot temperature is additional pulse capacity. In reducing this theory to practice, assignment is given to the percentage of rated power that both the average and pulse power represent. As long as the sum of the two does not exceed 100 % of the rating, the application is satisfied. Example: The pulse power is P = V 2 /R and the average power is P A = Pt/T where t is the pulse width and T is the cycle width. Calculate the average power and the % of rated power for the candidate resistor. Now using the derating curve establish the threshold temperature that results and use it in the pulse calculation above. Calculate the pulse power that can be tolerated in the wire being heated above the new threshold temperature to the internal hot spot temperature. This is the maximum pulse power allowed at this average power level. Long Pulses (100 milliseconds to 5 seconds) Here, the pulse heat generated is no longer retained fully within the wire, but some passes to other body members of the resistor. A short-time overload rating is frequently given, and this can be safely used as the long pulse rating. A factor of 5 times rated power is generally satisfactory for 5 seconds. Allowable pulse power levels for pulses from 1 to 25 seconds long can be found by 25 times rated power divided by the pulse time in seconds. Below 1 second, use the 1-second rating. Above 25 seconds, use rated power. Current Rating Some devices in this range of products are current-limited rather than power-limited. This comes from the fact that as electron flow is increased by increasing the voltage, there comes a point where the current no longer follows Ohm s law. This critical current density varies for different resistance materials, but it must be kept in mind that leads and attachment hardware also have a critical current density. A current density up to 260 KA/in 2 may be tolerated by a particular metal, but the manufacturer s rating is likely to be considerably below this limit for safety reasons. Appropriately size connecting wire must be used and the ratings of the wire manufacturer must be followed. Where a resistor current limit is specified, it must not be exceeded. Under certain circumstances, pulses of current in excess of the current limit can be tolerated. Please contact Technical Support by going to and selecting Contacts. Reactance and Impedance Reactance is the component of an AC impedance that defines a phase shift between the current and the voltage. 14
17 ations Impendance is the ratio of effective voltage over effective current in an AC circuit. Reactance may be inductive or capacitive. In low-value resistors (below 10 ohms), the inductive reactance usually outweighs the capacitive reactance while higher values are more likely to be capacitive with bifilar or Aryton-Perry winding. Pi, bifilar, and Aryton-Perry winding are used to improve reactance. Figure 4 shows the various components of resistor response to an AC signal in vectorial notation. R is the DC resistance of the device and X L and X C are the inductive and capacitive reactances, respectively. Figure 5 shows the sum of XL and XC leaving an effective net reactance X T. The impedance Z is the Pythagorean sum of R and X T. The AC impedance is always greater than the DC resistance unless X L is exactly equal to X C. The products listed in this brochure are largely low-value resistors with little or no response to X T until well up into Figure 4. AC Signal Reactance in Vectorial Notation R X L = 2 πƒl 1 X C = 2 πƒc Figure 5. AC Signal Effective Net Reactance the megahertz range. Therefore, the effect of reactance can largely be ignored referring only special requirements to Applications Engineering. Thermal EMF Dissimilar metals, in contact with each other, produce a small voltage. This voltage is variable with temperature and is therefore called a Thermal EMF or thermocouple effect. The rate of change of voltage with temperature from an intermetallic junction is a function of the metallic combination. The sense of the voltage produced is either positive or negative, depending on which side of the combination is being considered the input. Virtually all resistors have intermetallic combinations, and it is presumed that they will eventually be connected to copper as a final intermetallic junction. Hence, copper is the typical reference metal. Table 2 is a brief synopsis of the thermal EMFs for various metals and alloys used in resistor construction vs. copper as the reference. Thermal EMF is an important consideration in low-value resistors used in DC circuits. (It usually has no importance in AC circuitry.) In particular, its importance in current sensors is obvious since the thermal EMF could be larger than the signal being discriminated. Table 2. Thermal EMF of Selected Metals and Alloys Metal/Alloy Thermal EMF vs. Copper µv/ C Evanohm +2.0 Cupron Manganin -3.0 Zeranin -1.3 Nickel Gold +0.2 Silver -0.2 Aluminum -4.0 Z R X T c h a r a c t e r i s t i c s a n d D e s i g n C o n s i d e r a t i o n s 15
18 Characteristics and Design Consider c h a r a c t e r i s t i c s a n d D e s i g n C o n s i d e r a t i o n s Figure 6. No Thermal Difference End to End 100 µv Cu Min.001 Ω Min Cu + 45 C C µv 60 µv 60 µv Figure Thermal Difference End to End 100 µv Cu Min.001 Ω Min Cu + 45 C C µv 60 µv 90 µv Thermal noise can be obtained from the formula: l=0.1a l=0.1a As noted earlier, thermal EMFs have polarity and so, for example, from copper to manganin and back to copper through a particular resistor, one end is a +3 µv/ C generator and the other end is a -3 µv/ C generator. In the ideal situation of both ends of the resistor being at the same temperature, the thermal EMFs are selfcanceling. The manufacturer minimizes thermal EMF effects through the use of appropriate metals, but it is up to the user to see that the product is installed in such a way that the resistor is not being heated non-uniformly by other components. Figure 6 is the equivalent circuit when both ends of the resistor are at the same temperature. Figure 7 is the equivalent circuit when one end is heated. Note that the 100-µV measured IR drop of Figure 6 becomes a 130-µV apparent drop in Figure 7 when a temperature difference of 10 C is allowed to exist across the resistor. Noise Noise is an unwanted AC signal from within the resistor. Two types of noise exist and can limit product usefulness under certain conditions. Thermal Noise, often called Johnson noise, is due to the random motion of electrons in the resistive material, which creates small fluctuating potential differences across the terminations. Thermal noise is characterized by a continuous frequency spectrum. Its magnitude is independent of the material of the conductive element or its shape, and varies only with temperature and resistance. where K = Boltzmann s constant (1.38 x joules/degree Kelvin) E 2 = 4KTR (f2 f1) t = Absolute temperature ( C + 273) r = Resistance of the conductor e = Root mean square value of the thermal noise voltage (f2 f1) = Bandwidth in hertz The voltage developed by thermal agitation sets a limit on the smallest voltage that can be amplified without being lost in a background of noise. Resistances composed of metal or metal alloys (wirewound, etc.) display the lowest combined noise level and can largely be ignored. However, resistances composed of conductive particles dispersed in an insulating matrix or films with imperfect lattice structure and non-conducting occlusions generate noise far in excess of the thermal agitation 16
19 ations noise when a direct current is passed through the resistance. This type of noise arises from fluctuations in contact resistance between conducting sites within the matrix and is greater in higher values where the sites are fewer. It can also occur at poorly joined metal connections such as cold solder joints. The frequency spectrum of current noise is not continuous and appears in the lower audio frequency range. This may place a limitation on the use of thick film resistors under the circumstances of very small signal discrimination at mid frequencies. The noise index is calculated from the formula: Db = 20 x log 10 = Noise Voltage DC Voltage (over a 1-decade bandwidth) where noise voltage is the RMS current noise voltage generated by the resistor and the DC voltage is the voltage arising out of specified current flowing through the resistor at a specified temperature. The index is usually expressed either as µv/v or in decibels of the ratio of voltages. These are interchangeable as shown in Table 3. Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR) Table 3. Noise Conversion Db µv/v Change in resistance as a function of temperature exists in all resistors to various extents. This change is seldom linear, but for convenience it is usually expressed as a straight line function. Sometimes the change is sought between two specific temperatures. Hence, the general equation for the instantaneous TCR at any temperature is: dr TCR inst = Rdt and the more useful TCR calculated from the chord slope from one temperature to another is: R2 - R1 TCR chord = R1 (T2 - T1) Also, TCR is usually referred to room temperature (25 C) as the reference temperature T1, and the second temperature T2 is either 0 C or + 60 C for end use in instrumentation and -55 C or C for military end use (power resistors to +275 C). Note that TCR can be either positive or negative. By convention, an increase in resistance with an increase in temperature is a positive TCR. Also, note that self-heating causes a resistance change due to TCR. Table 1 gives the TCR for some resistance materials used in the range of products in this brochure. c h a r a c t e r i s t i c s a n d D e s i g n C o n s i d e r a t i o n s Table 1. TCR, ppm/ C of Various Resistor Element Materials Temperature Range -55 C to +25 C 0 C to +25 C +25 C to +60 C +25 C to +125 C Manganin Zeranin +20 ±2.5 ± Evanohm Foil Thin Film Thick Film
20 Design Factors To help customers select the correct components for their application or design new components for specific applications, many design factors must be taken into consideration. Below are the minimum design factors needed before accurate component selection or design can be made. You can obtain more information by sending a request to ww2bresistors@vishay.com or by contacting your local Vishay sales representative. D e s i g n F a c t o r s Shunts 1.0 Power rating required How much power will be dissipated? 2.0 Disposal of heat generated What services are available to remove heat? What services are available to remove forced air? 3.0 Mounting surface and hardware What shock and vibration conditions dictate standard or special mounting? 4.0 Resistance value and tolerance The tolerance must be consistent with the ability to measure. With specific electrical gauge points identified, two-terminal devices can be toleranced to discriminate ohms. Fourterminal devices can be toleranced to discriminate down to ohms. Thus, a two-terminal resistor of 0.1 ohms can be given a tolerance no tighter than ±1.0 % (1.0 % of 0.1 ohms = ohms) while a fourterminal resistor can be given a tolerance as tight as ±0.1 % (0.1 % of 0.1 ohms = ohms). Sensors 1.0 Current Rating How much current is the sensor expected to handle? Continuously? Pulsed? Distortionrestricted? 2.0 Sensitivity How much output signal is required per unit of current? (How much µv or mv per ampere?) This sets the resistance value and the power rating. 3.0 Resistance Value The required sensor resistance is equal to the current rating times the sensitivity divided by the current rating or numerical equivalence to the sensitivity, but in ohms. Example: A 2-A sensor with 100-mV/A sensitivity will have a full scale output of 0.2 V R = E I = = 0.1 ohms 4.0 Power Rating The required power rating may be greater than the product of Emax and Imax if the sensitivity must be the same following self-heating. A positive TCR will cause the resistance value to increase along with the sensitivity. This effect can be minimized by over specifying the power rating or moving to a lower-tcr element. Typical Applications DC/DC converters AC/DC converters Power supplies Motor controls Instrumentation Battery fuel gauges Li-Ion battery management VRMs in notebook computers Automotive applications - Electronic power steering - Body electronics - Engine control modules - ABS - Electric vehicles Household/industrial electric meters 18
21 Notes N o N t o e s t e s 19
22 Notes N o t e s 20
23
24 Semiconductors: Rectifiers High-Power Diodes* and Thyristors* Small-Signal Diodes Zener and Suppressor Diodes FETs RF Transistors Optoelectronics ICs Modules and Assemblies* Passive Components: Resistive Products Magnetics Capacitors Strain Gage Transducers and Stress Analysis Systems *Closing of the planned acquisition of the power control systems business of International Rectifier is expected to occur before the end of March 2007, subject to customary closing conditions. One of the World s Largest Manufacturers of Discrete Semiconductors and Passive Components Worldwide Sales Contacts The Americas united states Vishay Americas One Greenwich Place Shelton, CT United States Ph: Fax: Asia singapore Vishay intertechnology Asia Pte Ltd. 25 Tampines Street 92 Keppel Building #02-00 Singapore Ph: Fax: p.r.c. Vishay Trading (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. (Shanghai Representative Office) Room D, 15F, Sun Tong Infoport plaza 55 huai hai west road shanghai P.R.C. Ph: fax: EUROPE germany Vishay europe sales GmbH Geheimrat-Rosenthal-Str Selb Germany Ph: Fax: france Vishay S.A. 199, blvd de la madeleine nice, cedex 1 France Ph: Fax: netherlands Vishay bccomponents B.V. hurkestraat 31 p.o. box ah eindhoven netherlands Ph: Fax: japan vishay japan CO., LTD. Shibuya 3-chome Square Building 3F Shibuya Shibuya-Ku Tokyo Japan Ph: fax: VMN-PL w w w. v i s h a y. c o m
INTERACTIVE. data book. thick film power resistors. vishay sfernice. vse-db
 VISHAY INTERTECHNOLOGY, INC. INTERACTIVE data book thick film power resistors vishay sfernice vse-db0019-0302 Notes: 1. To navigate: a) Click on the Vishay logo on any datasheet to go to the Contents page
VISHAY INTERTECHNOLOGY, INC. INTERACTIVE data book thick film power resistors vishay sfernice vse-db0019-0302 Notes: 1. To navigate: a) Click on the Vishay logo on any datasheet to go to the Contents page
Manufacturers V I S H AY I N T E R T E C H N O L O G Y, I N C. One of the World s Largest.
 V I S H AY I N T E R T E C H N O L O G Y, I N C. Company overview One of the World s Largest Manufacturers of Discrete Semiconductors and Passive Components www.vishay.com About Vishay Intertechnology
V I S H AY I N T E R T E C H N O L O G Y, I N C. Company overview One of the World s Largest Manufacturers of Discrete Semiconductors and Passive Components www.vishay.com About Vishay Intertechnology
CAPACITORS. Multilayer Ceramic Chip Capacitors PRODUCT OVERVIEW.
 VISHAY INTERTECHNOLOGY, INC. CAPACITORS HVArc GUARD SURFACE MOUNT MLCCs Multilayer Ceramic Chip Capacitors PRODUCT OVERVIEW SEMICONDUCTORS Product Listings Rectifiers Schottky (single, dual) Standard,
VISHAY INTERTECHNOLOGY, INC. CAPACITORS HVArc GUARD SURFACE MOUNT MLCCs Multilayer Ceramic Chip Capacitors PRODUCT OVERVIEW SEMICONDUCTORS Product Listings Rectifiers Schottky (single, dual) Standard,
INTERACTIVE. data book. ESTAmat PFC
 V I S H A Y I N T E R T E C H N O L O G Y, I N C. INTERACTIVE data book ESTAmat PFC vishay ESTA vse-db0050-0509 Notes 1. To navigate a) Click on the Vishay logo on any datasheet to go to the Contents page
V I S H A Y I N T E R T E C H N O L O G Y, I N C. INTERACTIVE data book ESTAmat PFC vishay ESTA vse-db0050-0509 Notes 1. To navigate a) Click on the Vishay logo on any datasheet to go to the Contents page
TABLE 1 - SPECIFICATIONS PARAMETER CSM2512 CSM3637
 Bulk Metal Technology High Precision, Current Sensing, Power Surface Mount, Metal Strip Resistor with Resistance Value from 1 mω, Rated Power up to 3 W and TCR to ± 15 ppm/ C Maximum No minimum order quantity
Bulk Metal Technology High Precision, Current Sensing, Power Surface Mount, Metal Strip Resistor with Resistance Value from 1 mω, Rated Power up to 3 W and TCR to ± 15 ppm/ C Maximum No minimum order quantity
power electronic capacitors
 VISHAY INTERTECHNOLOGY, INC. DATA BOOK power electronic capacitors vishay esta DC-Capacitors www.vishay.com SEMICONDUCTORS Product Listings Rectifiers Schottky (single, dual) Standard, Fast, and Ultra-Fast
VISHAY INTERTECHNOLOGY, INC. DATA BOOK power electronic capacitors vishay esta DC-Capacitors www.vishay.com SEMICONDUCTORS Product Listings Rectifiers Schottky (single, dual) Standard, Fast, and Ultra-Fast
Resistance Value. Interloop capacitance. reduction. in series. Mutual inductance. reduction. due to change in current direction
 UltraHigh-PrecisionThrough-HoleFoilResistorforHighTemperatureApplicationsupto +200 C High Temperature Applications up to +200 C FEATURES Temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR): ±0.2 ppm/ C nominal
UltraHigh-PrecisionThrough-HoleFoilResistorforHighTemperatureApplicationsupto +200 C High Temperature Applications up to +200 C FEATURES Temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR): ±0.2 ppm/ C nominal
Thick Film Resistor Networks Military, MIL-PRF Qualified, Type RZ Dual-In-Line Package, 01, 03, 05 Schematics
 FEATURES MIL-PRF-83401 qualified Epoxy molded construction All device leads are hot-solder dipped Available in tube pack TCR available in "K" (± 100 ppm/ C) or "M" (± 300 ppm/ C) depending on style 100
FEATURES MIL-PRF-83401 qualified Epoxy molded construction All device leads are hot-solder dipped Available in tube pack TCR available in "K" (± 100 ppm/ C) or "M" (± 300 ppm/ C) depending on style 100
IMPROVED PRODUCT DSM. Vishay Foil Resistors FEATURES INTRODUCTION FIGURE 1 - SCHEMATIC
 High Precision Bulk Metal Foil Surface Mount Voltage Divider, TCR Tracking of < 0.5 ppm/ C, Tolerance Match of 0.01 % and Stability of ± 0.005 % (50 ppm) INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal foil technology out-performs
High Precision Bulk Metal Foil Surface Mount Voltage Divider, TCR Tracking of < 0.5 ppm/ C, Tolerance Match of 0.01 % and Stability of ± 0.005 % (50 ppm) INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal foil technology out-performs
V I S H A y I n T E R T E C H n O l O G y, I n C. In D u C T O R S In S T R u C TIO n A l INDuCtOR 101 Gu ID E w w w. v i s h a y.
 VISHAY INTERTECHNOLOGY, INC. INDUCTORS INDUCTOR 101 instructional Guide www.vishay.com Inductor 101 Inductor A passive component designed to resist changes in current. Inductors are often referred to as
VISHAY INTERTECHNOLOGY, INC. INDUCTORS INDUCTOR 101 instructional Guide www.vishay.com Inductor 101 Inductor A passive component designed to resist changes in current. Inductors are often referred to as
Ultra High Precision Z-Foil Voltage Divider and Network Resistor with TCR Tracking to 0.1 ppm/ C and Resistance Match to ± 0.
 Custom Networks, 2-, - or -Resistors (Z-Foil Ultra High Precision Z-Foil Voltage Divider and Network Resistor with TCR Tracking to 0. ppm/ C and Resistance Match to ± 0.00% (0 ppm) NEW Any value at any
Custom Networks, 2-, - or -Resistors (Z-Foil Ultra High Precision Z-Foil Voltage Divider and Network Resistor with TCR Tracking to 0. ppm/ C and Resistance Match to ± 0.00% (0 ppm) NEW Any value at any
Thick Film Resistor Networks, Dual-In-Line, Molded DIP, 01, 03, 05 Schematics
 MDP 01,, 05 Thick Film Resistor Networks, Dual-In-Line, STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS GLOBAL MODEL/ NO. OF PINS MDP 14 MDP 16 SCHEMATIC 01 05 01 RESISTOR POWER RATING Max. AT 70 C W 0.250 0.250 RESISTANCE
MDP 01,, 05 Thick Film Resistor Networks, Dual-In-Line, STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS GLOBAL MODEL/ NO. OF PINS MDP 14 MDP 16 SCHEMATIC 01 05 01 RESISTOR POWER RATING Max. AT 70 C W 0.250 0.250 RESISTANCE
Wirewound Resistors, Military, MIL-PRF Qualified, Type RE, Aluminum Housed, Chassis Mount
 Wirewound Resistors, Military, MIL-PRF-18546 Qualified, Type RE, Aluminum Housed, Chassis Mount STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS MILITARY VISHAY REFERENCE POWER RATING P 25 C W FEATURES Molded construction
Wirewound Resistors, Military, MIL-PRF-18546 Qualified, Type RE, Aluminum Housed, Chassis Mount STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS MILITARY VISHAY REFERENCE POWER RATING P 25 C W FEATURES Molded construction
Bulk Metal Foil Technology Hermetically Sealed Power and Current Sensing Resistor with TCR of 2 ppm/ C and Power up to 10 Watts
 Bulk Metal Foil Technology Hermetically Sealed Power and Current Sensing Resistor with TCR of 2 ppm/ C and Power up to 10 Watts Any value available within resistance range Vishay Bulk Metal Foil power
Bulk Metal Foil Technology Hermetically Sealed Power and Current Sensing Resistor with TCR of 2 ppm/ C and Power up to 10 Watts Any value available within resistance range Vishay Bulk Metal Foil power
DSMZ (Z-Foil) Vishay Foil Resistors FEATURES
 Ultra High Precision Bulk Metal Z-Foil Surface Mount Voltage Divider, TCR Tracking of < 0.1 ppm/ C, PCR of ± 5 ppm at Rated Power and Stability of ± 0.005 % (50 ppm) INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Z-Foil technology
Ultra High Precision Bulk Metal Z-Foil Surface Mount Voltage Divider, TCR Tracking of < 0.1 ppm/ C, PCR of ± 5 ppm at Rated Power and Stability of ± 0.005 % (50 ppm) INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Z-Foil technology
IMPROVED PRODUCT. DSMZ (Z-Foil)
 Ultra High Precision Bulk Metal Z-Foil Surface Mount Voltage Divider, TCR Tracking of < 0.1 ppm/ C, PCR of ± 5 ppm at Rated Power and Stability of ± 0.005 % (50 ppm) INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Z-Foil technology
Ultra High Precision Bulk Metal Z-Foil Surface Mount Voltage Divider, TCR Tracking of < 0.1 ppm/ C, PCR of ± 5 ppm at Rated Power and Stability of ± 0.005 % (50 ppm) INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Z-Foil technology
IMPROVED PRODUCT SMN. Vishay Foil Resistors. RoHS* FEATURES Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR) (- 55 C to C, + 25 C Ref): INTRODUCTION
 High Precision Surface Mount 4 Resistor Network Dual-In-Line Package with TCR Tracking 0.5 ppm/ C, Tolerance Match of 0.01 % and Ratio Stability of 0.005 % Any value and any ratio available within resistance
High Precision Surface Mount 4 Resistor Network Dual-In-Line Package with TCR Tracking 0.5 ppm/ C, Tolerance Match of 0.01 % and Ratio Stability of 0.005 % Any value and any ratio available within resistance
SMR1DZ / SMR3DZ (Z-Foil)
 Ultra High Precision Z-Foil Molded Surface Mount Resistor with TCR down to ±0.2 ppm/ C, PCR of ±5 ppm at Rated Power, Flexible Terminations, and Load-Life Stability of ±0.005 % (50 ppm) FEATURES AND BENEFITS
Ultra High Precision Z-Foil Molded Surface Mount Resistor with TCR down to ±0.2 ppm/ C, PCR of ±5 ppm at Rated Power, Flexible Terminations, and Load-Life Stability of ±0.005 % (50 ppm) FEATURES AND BENEFITS
High Voltage Surge Resistor
 High Voltage Surge Resistor FEATURES High pulse-loading (1 kv as specified) capability (flashes) Good replacement for carbon-composite resistors Lead (Pb)-free solder contacts Pure Tin plating provides
High Voltage Surge Resistor FEATURES High pulse-loading (1 kv as specified) capability (flashes) Good replacement for carbon-composite resistors Lead (Pb)-free solder contacts Pure Tin plating provides
SMN. Vishay Foil Resistors
 High Precision Surface Mount 4 Resistor Network Dual-In-Line Package with TCR Tracking 0.5 ppm/ C, Tolerance Match of 0.01 % and Ratio Stability of 0.005 % Any value and any ratio available within resistance
High Precision Surface Mount 4 Resistor Network Dual-In-Line Package with TCR Tracking 0.5 ppm/ C, Tolerance Match of 0.01 % and Ratio Stability of 0.005 % Any value and any ratio available within resistance
FEATURES. V out VSH144. Interloop Capacitance Reduction in Series. Mutual Inductance Reduction due to Opposing Current in Adjacent Lines
 Bulk Metal Foil Technology Low Profile Conformally Coated High Precision Voltage Divider Resistor with TCR Tracking to 0.5 ppm/ C and Tolerance Match to 0.01 % (100 ppm) APPLICATIONS Instrumentation amplifiers
Bulk Metal Foil Technology Low Profile Conformally Coated High Precision Voltage Divider Resistor with TCR Tracking to 0.5 ppm/ C and Tolerance Match to 0.01 % (100 ppm) APPLICATIONS Instrumentation amplifiers
VHZ Hermetic (Z-Foil)
 New Generation of Secondary Standards Hermetically Sealed Construction Ultra High Precision Z-Foil Technology Resistors with TCR of ± 0.2 ppm/ C, Tolerance of ± 0.005 % and Load Life Stability of ± 0.005
New Generation of Secondary Standards Hermetically Sealed Construction Ultra High Precision Z-Foil Technology Resistors with TCR of ± 0.2 ppm/ C, Tolerance of ± 0.005 % and Load Life Stability of ± 0.005
303139, Vishay Foil Resistors FEATURES INTRODUCTION. TABLE 1 - TOLERANCE AND TCR VS. RESISTANCE VALUE (- 55 C to C, + 25 C ref.
 Models # 303139 and 303140 - Molded Surface Mount Space and Military Grade Resistors SMRxDZ with Screen/Test Flow in Compliance with EEE-INST-002, (Tables 2A and 3A, Film/Foil, Level 1) and MIL-PRF-55182
Models # 303139 and 303140 - Molded Surface Mount Space and Military Grade Resistors SMRxDZ with Screen/Test Flow in Compliance with EEE-INST-002, (Tables 2A and 3A, Film/Foil, Level 1) and MIL-PRF-55182
Thick Film Resistor Networks, Dual-In-Line, Molded DIP, 01, 03, 05 Schematics
 MDP 01,, 05 Thick Film Resistor Networks, Dual-In-Line, STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS GLOBAL MODEL/ NO. OF PINS MDP 14 MDP 16 SCHEMATIC 01 05 01 RESISTOR POWER RATING Max. AT 70 C W 0.250 0.250 RESISTANCE
MDP 01,, 05 Thick Film Resistor Networks, Dual-In-Line, STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS GLOBAL MODEL/ NO. OF PINS MDP 14 MDP 16 SCHEMATIC 01 05 01 RESISTOR POWER RATING Max. AT 70 C W 0.250 0.250 RESISTANCE
Molded Metal Film High Stability (< 0.25 % after 1000 h) High Temperature (up to 175 C) Precision Resistors
 Vishay Sfernice Molded Metal Film High Stability (< 0.25 % after 1000 h) FEATURES 0.1 W to 2 W at 125 C EN140100 CECC 40 101044 High climatic performance 65 C/+ 175 C/56 days High long term stability drift
Vishay Sfernice Molded Metal Film High Stability (< 0.25 % after 1000 h) FEATURES 0.1 W to 2 W at 125 C EN140100 CECC 40 101044 High climatic performance 65 C/+ 175 C/56 days High long term stability drift
High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, Tolerance of ± 0.01 % and Load Life Stability of ± % CECC Qualified
 Vishay Foil Resistors High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Foil (BMF) technology outperforms all other resistor technologies available today for applications that
Vishay Foil Resistors High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Foil (BMF) technology outperforms all other resistor technologies available today for applications that
High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, Tolerance of ± % and Load Life Stability of ± %
 Vishay Foil Resistors High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, Any value at any tolerance available within resistance range INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Foil (BMF) technology outperforms all other
Vishay Foil Resistors High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, Any value at any tolerance available within resistance range INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Foil (BMF) technology outperforms all other
High Precision Wraparound - Wide Ohmic Value Range Thin Film Chip Resistors
 P Vishay Sfernice High Precision Wraparound - Wide Ohmic Value Range For low noise and precision applications, superior stability, low temperature coefficient of resistance, and low voltage coefficient,
P Vishay Sfernice High Precision Wraparound - Wide Ohmic Value Range For low noise and precision applications, superior stability, low temperature coefficient of resistance, and low voltage coefficient,
RCH Vishay Sfernice Power Resistors, for Mounting onto a Heatsink Thick Film Technology
 RCH Power Resistors, for Mounting onto a Heatsink FEATURES 5 W to 50 W High power rating Manufactured in cermet thick film technology, these power resistors exhibit remarkable characteristics and the series
RCH Power Resistors, for Mounting onto a Heatsink FEATURES 5 W to 50 W High power rating Manufactured in cermet thick film technology, these power resistors exhibit remarkable characteristics and the series
FEATURES 200 % 175 % 150 % 125 % 100 % 75 % 50 % 25 %
 Ultra High Precision Z-Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 0.05 ppm/ C, PCR of 5 ppm at Rated Power, Tolerance of ± 0.005 % and Load Life Stability of ± 0.005 % INDUSTRY BREAKTHROUGH Any value at any tolerance
Ultra High Precision Z-Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 0.05 ppm/ C, PCR of 5 ppm at Rated Power, Tolerance of ± 0.005 % and Load Life Stability of ± 0.005 % INDUSTRY BREAKTHROUGH Any value at any tolerance
High Ohmic (up to 33 MΩ)/ High Voltage (up to 3.5 kv) Resistors
 High Ohmic (up to 33 MΩ)/ FEATURES A metal glazed film is deposited on a high grade ceramic body. After a helical groove has been cut in the resistive layer, tinned electrolytic copper wires are welded
High Ohmic (up to 33 MΩ)/ FEATURES A metal glazed film is deposited on a high grade ceramic body. After a helical groove has been cut in the resistive layer, tinned electrolytic copper wires are welded
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. LM134/LM234/LM334 3-Terminal Adjustable Current Sources General Description
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. LM134/LM234/LM334 3-Terminal Adjustable Current Sources General Description
High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, Tolerance of ± % and Load Life Stability of ± %
 High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, Tolerance of ± 0.005 % and Load Life Stability of ± 0.005 % INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Foil (BMF) technology outperforms all other resistor technologies
High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, Tolerance of ± 0.005 % and Load Life Stability of ± 0.005 % INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Foil (BMF) technology outperforms all other resistor technologies
VSH144Z (Z-Foil) Vishay Foil Resistors FEATURES APPLICATIONS TABLE 1A - MODEL VSH144Z SPECIFICATIONS TABLE 1B - MODEL VSH144Z SPECIFICATIONS
 Ultra High Precision Z-Bulk Metal Foil Technology Low Profile Conformally Coated Voltage Divider Resistor with TCR Tracking to 0.1 ppm/ C, Power Coefficient Tracking of 5 ppm at Rated Power, and Tolerance
Ultra High Precision Z-Bulk Metal Foil Technology Low Profile Conformally Coated Voltage Divider Resistor with TCR Tracking to 0.1 ppm/ C, Power Coefficient Tracking of 5 ppm at Rated Power, and Tolerance
High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, Tolerance of ± % and Load Life Stability of ± %
 High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, Tolerance of ± 0.005 % and Load Life Stability of ± 0.005 % INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Foil (BMF) technology outperforms all other resistor technologies
High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, Tolerance of ± 0.005 % and Load Life Stability of ± 0.005 % INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Foil (BMF) technology outperforms all other resistor technologies
Standard Metal Film Resistors
 SFR6S/25/25H Standard Metal Film Resistors FEATURES Low cost Low noise Small size (SFR6S) A homogeneous film of metal alloy is deposited on a high grade ceramic body. After a helical groove has been cut
SFR6S/25/25H Standard Metal Film Resistors FEATURES Low cost Low noise Small size (SFR6S) A homogeneous film of metal alloy is deposited on a high grade ceramic body. After a helical groove has been cut
Metal Film Resistors, Non-Magnetic, Industrial, Precision
 CMF Non-Magnetic Metal Film Resistors, Non-Magnetic, Industrial, Precision STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS GLOBAL HISTORICAL MAXIMUM WORKING VOLTAGE (1) V (1) Continuous working voltage shall be P x
CMF Non-Magnetic Metal Film Resistors, Non-Magnetic, Industrial, Precision STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS GLOBAL HISTORICAL MAXIMUM WORKING VOLTAGE (1) V (1) Continuous working voltage shall be P x
High Stability Thin Film Chip Resistor 0.05 % (1000 h rated power at 70 C)
 TNPW High Stability Thin Film Chip Resistor.5 % ( h rated power at 7 C) FEATURES Metal film layer on high quality ceramic Protective top coat Tin/lead (Pb) solder contacts Excellent overall stability at
TNPW High Stability Thin Film Chip Resistor.5 % ( h rated power at 7 C) FEATURES Metal film layer on high quality ceramic Protective top coat Tin/lead (Pb) solder contacts Excellent overall stability at
Surface Mounted Power Resistor Thick Film Technology
 D2TO35 DIMENSIONS in millimeters 1.6 10.1 Surface Mounted Power Resistor 8.8 1.25 4.5 FEATURES 35 W at 25 C case temperature Surface mounted resistor - TO-263 (D 2 PAK) style package Wide resistance range
D2TO35 DIMENSIONS in millimeters 1.6 10.1 Surface Mounted Power Resistor 8.8 1.25 4.5 FEATURES 35 W at 25 C case temperature Surface mounted resistor - TO-263 (D 2 PAK) style package Wide resistance range
Thick Film Resistor Networks, Dual-In-Line, Molded DIP
 STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS POWER RATING / ELEMENT (1) RANGE NO. OF P 70 C PINS Ω W MDP 14 MDP 16 01 05 01 05 0.2 0.2 Consult factory Consult factory Notes (1) For resistor power ratings at + 25
STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS POWER RATING / ELEMENT (1) RANGE NO. OF P 70 C PINS Ω W MDP 14 MDP 16 01 05 01 05 0.2 0.2 Consult factory Consult factory Notes (1) For resistor power ratings at + 25
Vout SMNZ. Note RESISTANCE RATIO R1/R2 = 1 1 < R1/R < R1/R2 100
 (Z-Foil) Ultra High Precision Z-Foil Surface Mount 4 Resistor Network Dual-In-Line Package with TCR Tracking of 0.1 ppm/ C, PCR Tracking of 5 ppm at Rated Power, and Tolerance Match of 0.01 % Any value
(Z-Foil) Ultra High Precision Z-Foil Surface Mount 4 Resistor Network Dual-In-Line Package with TCR Tracking of 0.1 ppm/ C, PCR Tracking of 5 ppm at Rated Power, and Tolerance Match of 0.01 % Any value
VFB1012D (Z-Foil) Vishay Foil Resistors
 Ultra High Precision Z-Foil BGA Surface Mount Voltage Divider with 0.1 ppm/ C TCR Tracking, Tolerance Match and Load Life Stability Ratio to ± INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Z-foil technology out-performs all
Ultra High Precision Z-Foil BGA Surface Mount Voltage Divider with 0.1 ppm/ C TCR Tracking, Tolerance Match and Load Life Stability Ratio to ± INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Z-foil technology out-performs all
Thick Film Resistor Networks, Military, MIL-PRF Qualified, Type RZ010 and RZ020 Dual-In-Line, Molded DIP
 MDM (Military M831/1 and /2) Thick Film Resistor Networks, Military, MIL-PRF-831 Qualified, Type RZ1 and RZ2 Dual-In-Line, Molded DIP STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS VISHAY DALE MODEL/ PIN NO. MIL STYLE
MDM (Military M831/1 and /2) Thick Film Resistor Networks, Military, MIL-PRF-831 Qualified, Type RZ1 and RZ2 Dual-In-Line, Molded DIP STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS VISHAY DALE MODEL/ PIN NO. MIL STYLE
Wirewound/Metal Film Resistors, Commercial Power, Radial Lead
 RMW, RMF End-of-Life Product FEATURES High power dissipation in small volume Very stable mounting Non-flammable High pulse load handling capabilities High heat and moisture resistance Various terminal
RMW, RMF End-of-Life Product FEATURES High power dissipation in small volume Very stable mounting Non-flammable High pulse load handling capabilities High heat and moisture resistance Various terminal
High Accuracy INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER
 INA High Accuracy INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER FEATURES LOW DRIFT:.µV/ C max LOW OFFSET VOLTAGE: µv max LOW NONLINEARITY:.% LOW NOISE: nv/ Hz HIGH CMR: db AT Hz HIGH INPUT IMPEDANCE: Ω -PIN PLASTIC, CERAMIC
INA High Accuracy INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER FEATURES LOW DRIFT:.µV/ C max LOW OFFSET VOLTAGE: µv max LOW NONLINEARITY:.% LOW NOISE: nv/ Hz HIGH CMR: db AT Hz HIGH INPUT IMPEDANCE: Ω -PIN PLASTIC, CERAMIC
Bulk Metal Foil Technology RNC90Y and RNC90Z (Z-Foil) to MIL-PRF-55182/9
 INTRODUCTION Vishay Military Established Reliability resistors are available in resistance values from 4.99 Ω through 121 kω and for tolerances from ± 0.005 % to ± 1.0 %. The same resistors are also available
INTRODUCTION Vishay Military Established Reliability resistors are available in resistance values from 4.99 Ω through 121 kω and for tolerances from ± 0.005 % to ± 1.0 %. The same resistors are also available
Table of Contents...2. About the Tutorial...6. Audience...6. Prerequisites...6. Copyright & Disclaimer EMI INTRODUCTION Voltmeter...
 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
Thick Film Resistor Networks Single-In-Line, Coated SIP 01, 03, 05 Schematics
 Thick Film Resistor Networks STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS GLOAL / RESISTOR POWER RATING max. at 70 C 1) RANGE Ω A 0.20 W 10-50 xxx01 0.25 W 50.1-2.2M A 0.30 W 10-50 xxx03 0.40 W 50.1-2.2M A 0.20
Thick Film Resistor Networks STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS GLOAL / RESISTOR POWER RATING max. at 70 C 1) RANGE Ω A 0.20 W 10-50 xxx01 0.25 W 50.1-2.2M A 0.30 W 10-50 xxx03 0.40 W 50.1-2.2M A 0.20
Thick Film, Rectangular Chip Resistors for Conductive Gluing
 Thick Film, Rectangular Chip Resistors STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS SIZE RATED LIMITING DISSIPATION ELEMENT MODEL INCH METRIC P 7 VOLTAGE W U max. AC/DC D AP 4 RR M D AP 63 RR 68M D AP 8 RR M D AP
Thick Film, Rectangular Chip Resistors STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS SIZE RATED LIMITING DISSIPATION ELEMENT MODEL INCH METRIC P 7 VOLTAGE W U max. AC/DC D AP 4 RR M D AP 63 RR 68M D AP 8 RR M D AP
CLA LF: Surface Mount Limiter Diode
 DATA SHEET CLA4609-086LF: Surface Mount Limiter Diode Applications Low loss, high power limiters Receiver protectors Features Low thermal resistance: 25 C/W Typical threshold level: +36 dbm Low capacitance:
DATA SHEET CLA4609-086LF: Surface Mount Limiter Diode Applications Low loss, high power limiters Receiver protectors Features Low thermal resistance: 25 C/W Typical threshold level: +36 dbm Low capacitance:
5. The Different Types of Resistors
 5. The Different Types of Resistors Resistors ( R ), are the most fundamental and commonly used of all the electronic components, to the point where they are almost taken for granted. There are many different
5. The Different Types of Resistors Resistors ( R ), are the most fundamental and commonly used of all the electronic components, to the point where they are almost taken for granted. There are many different
High Precision Foil Wraparound Surface Mount Chip Resistor with TCR of ± 2 ppm/ C and Load Life Stability of ± 0.01 % (100 ppm)
 High Precision Foil Wraparound Surface Mount Chip Resistor with TCR of ± 2 ppm/ C and Load Life Stability of ± 0.01 % (100 ppm) Top View Any value at any tolerance within resistance range INTRODUCTION
High Precision Foil Wraparound Surface Mount Chip Resistor with TCR of ± 2 ppm/ C and Load Life Stability of ± 0.01 % (100 ppm) Top View Any value at any tolerance within resistance range INTRODUCTION
LM134/LM234/LM334 3-Terminal Adjustable Current Sources
 3-Terminal Adjustable Current Sources General Description The are 3-terminal adjustable current sources featuring 10,000:1 range in operating current, excellent current regulation and a wide dynamic voltage
3-Terminal Adjustable Current Sources General Description The are 3-terminal adjustable current sources featuring 10,000:1 range in operating current, excellent current regulation and a wide dynamic voltage
Industrial / Power Factory Automation
 Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. Industrial / Power www.vishay.com One of the World s Largest Manufacturers of Discrete Semiconductors and Passive Components Industrial / Power Motor Drives 4 Testers 5 Control
Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. Industrial / Power www.vishay.com One of the World s Largest Manufacturers of Discrete Semiconductors and Passive Components Industrial / Power Motor Drives 4 Testers 5 Control
Adaptive Power MOSFET Driver 1
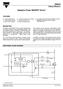 Adaptive Power MOSFET Driver 1 FEATURES dv/dt and di/dt Control Undervoltage Protection Short-Circuit Protection t rr Shoot-Through Current Limiting Low Quiescent Current CMOS Compatible Inputs Compatible
Adaptive Power MOSFET Driver 1 FEATURES dv/dt and di/dt Control Undervoltage Protection Short-Circuit Protection t rr Shoot-Through Current Limiting Low Quiescent Current CMOS Compatible Inputs Compatible
LM675 Power Operational Amplifier
 LM675 Power Operational Amplifier General Description The LM675 is a monolithic power operational amplifier featuring wide bandwidth and low input offset voltage, making it equally suitable for AC and
LM675 Power Operational Amplifier General Description The LM675 is a monolithic power operational amplifier featuring wide bandwidth and low input offset voltage, making it equally suitable for AC and
Power Resistor, for Mounting onto a Heatsink Thick Film Technology
 Power Resistor, for Mounting onto a Heatsink Thick Film Technology FEATURES 5 W to 50 W High power rating DESIGN SUPPORT TOOLS Models Available click logo to get started High overload capabilities up to
Power Resistor, for Mounting onto a Heatsink Thick Film Technology FEATURES 5 W to 50 W High power rating DESIGN SUPPORT TOOLS Models Available click logo to get started High overload capabilities up to
High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES POWER SUPPLIES TO ±0V OUTPUT CURRENT TO 0A PEAK PROGRAMMABLE CURRENT LIMIT INDUSTRY-STANDARD PIN OUT FET INPUT TO- AND LOW-COST POWER PLASTIC PACKAGES
High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES POWER SUPPLIES TO ±0V OUTPUT CURRENT TO 0A PEAK PROGRAMMABLE CURRENT LIMIT INDUSTRY-STANDARD PIN OUT FET INPUT TO- AND LOW-COST POWER PLASTIC PACKAGES
Ultra High Precision Z-Foil Flip Chip Resistor with TCR of ± 0.05 ppm/ C, 35 % Space Saving vs. Wraparound Design and PCR of 5 ppm at Rated Power
 Ultra High Precision Z-Foil Flip Chip Resistor with TCR of ± 0.05 ppm/ C, 35 % Space Saving vs. Wraparound Design and PCR of 5 ppm at Rated Power Bottom View INTRODUCTION One of the most important parameters
Ultra High Precision Z-Foil Flip Chip Resistor with TCR of ± 0.05 ppm/ C, 35 % Space Saving vs. Wraparound Design and PCR of 5 ppm at Rated Power Bottom View INTRODUCTION One of the most important parameters
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. LM138/LM338 5-Amp Adjustable Regulators General Description The LM138 series
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. LM138/LM338 5-Amp Adjustable Regulators General Description The LM138 series
Automotive Full Electric Vehicles (FEVs)
 Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. Automotive Full Electric Vehicles (FEVs) www.vishay.com One of the World s Largest Manufacturers of Discrete Semiconductors and Passive Components Full Electric Vehicles (FEVs)
Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. Automotive Full Electric Vehicles (FEVs) www.vishay.com One of the World s Largest Manufacturers of Discrete Semiconductors and Passive Components Full Electric Vehicles (FEVs)
Power Metal Film Resistors
 PR/2/3 Power Metal Film Resistors FEATURES High power in small packages ( W/27 size to 3 W/67 size) Different lead materials for different applications Defined interruption behaviour Lead (Pb)-free solder
PR/2/3 Power Metal Film Resistors FEATURES High power in small packages ( W/27 size to 3 W/67 size) Different lead materials for different applications Defined interruption behaviour Lead (Pb)-free solder
Current Sense Application Note. Resistors. BI Technologies IRC Welwyn
 Current Sense Resistors Current Sense Resistors The need to measure the flow of current in electronic systems is becoming increasingly widespread. Reasons for this include the growth of battery-powered
Current Sense Resistors Current Sense Resistors The need to measure the flow of current in electronic systems is becoming increasingly widespread. Reasons for this include the growth of battery-powered
Features. Applications SOT-23-5
 135MHz, Low-Power SOT-23-5 Op Amp General Description The is a high-speed, unity-gain stable operational amplifier. It provides a gain-bandwidth product of 135MHz with a very low, 2.4mA supply current,
135MHz, Low-Power SOT-23-5 Op Amp General Description The is a high-speed, unity-gain stable operational amplifier. It provides a gain-bandwidth product of 135MHz with a very low, 2.4mA supply current,
Thick Film Resistor Networks, Dual-In-Line, Molded DIP
 Thick Film Resistor Networks, Dual-In-Line, Molded DIP FEATURES Isolated, bussed, and dual terminator schematics available 0.160" (4.06 mm) maximum seated height and rugged, molded case construction Thick
Thick Film Resistor Networks, Dual-In-Line, Molded DIP FEATURES Isolated, bussed, and dual terminator schematics available 0.160" (4.06 mm) maximum seated height and rugged, molded case construction Thick
Metal Film Resistors, Non-Magnetic, Industrial, Precision
 CMF Non-Magnetic Metal Film Resistors, Non-Magnetic, Industrial, Precision STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS GLOBAL HISTORICAL MAXIMUM WORKING VOLTAGE (1) V (1) Continuous working voltage shall be P x
CMF Non-Magnetic Metal Film Resistors, Non-Magnetic, Industrial, Precision STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS GLOBAL HISTORICAL MAXIMUM WORKING VOLTAGE (1) V (1) Continuous working voltage shall be P x
Metal Film Resistors, Industrial, Precision
 CMF Industrial Metal Film Resistors, Industrial, Precision FEATURES Small size - conformal coated Flame retardant epoxy coating Controlled temperature coefficient Excellent high frequency characteristics
CMF Industrial Metal Film Resistors, Industrial, Precision FEATURES Small size - conformal coated Flame retardant epoxy coating Controlled temperature coefficient Excellent high frequency characteristics
LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF442 dual low power operational amplifiers provide many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM1458 while
LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF442 dual low power operational amplifiers provide many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM1458 while
Thick Film Resistor Networks, Dual-In-Line, Molded DIP
 MDP 01,, 05 STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS POWER RATING / ELEMENT (1) RANGE NO. OF P 70 C PINS Ω W MDP 14 MDP 16 01 05 01 05 0.2 0.2 Consult factory Consult factory Notes (1) For resistor power ratings
MDP 01,, 05 STANDARD ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS POWER RATING / ELEMENT (1) RANGE NO. OF P 70 C PINS Ω W MDP 14 MDP 16 01 05 01 05 0.2 0.2 Consult factory Consult factory Notes (1) For resistor power ratings
LM150/LM350A/LM350 3-Amp Adjustable Regulators
 LM150/LM350A/LM350 3-Amp Adjustable Regulators General Description The LM150 series of adjustable 3-terminal positive voltage regulators is capable of supplying in excess of 3A over a 1.2V to 33V output
LM150/LM350A/LM350 3-Amp Adjustable Regulators General Description The LM150 series of adjustable 3-terminal positive voltage regulators is capable of supplying in excess of 3A over a 1.2V to 33V output
Fast IC Power Transistor with Thermal Protection
 Fast IC Power Transistor with Thermal Protection Introduction Overload protection is perhaps most necessary in power circuitry. This is shown by recent trends in power transistor technology. Safe-area,
Fast IC Power Transistor with Thermal Protection Introduction Overload protection is perhaps most necessary in power circuitry. This is shown by recent trends in power transistor technology. Safe-area,
Metal Film, Cylindrical Resistors
 SMM4 Metal Film, Cylindrical Resistors FEATURES Stable metal film on high quality ceramic Low TC and tight tolerances Excellent stability in different environmental conditions Pure tin termination on nickel
SMM4 Metal Film, Cylindrical Resistors FEATURES Stable metal film on high quality ceramic Low TC and tight tolerances Excellent stability in different environmental conditions Pure tin termination on nickel
LM2935 Low Dropout Dual Regulator
 LM2935 Low Dropout Dual Regulator General Description The LM2935 dual 5V regulator provides a 750 ma output as well as a 10 ma standby output. It features a low quiescent current of 3 ma or less when supplying
LM2935 Low Dropout Dual Regulator General Description The LM2935 dual 5V regulator provides a 750 ma output as well as a 10 ma standby output. It features a low quiescent current of 3 ma or less when supplying
General Purpose Plastic Rectifier
 General Purpose Plastic Rectifier N400 thru N4007 DO-4AL (DO-4) MAJOR RATINGS AND CHARACTERISTICS I F(AV).0 A V RRM V to 00 V I FSM (8.3 ms sine-wave) A I FSM (square wave t p = ms) 45 A V F. V I R 5.0
General Purpose Plastic Rectifier N400 thru N4007 DO-4AL (DO-4) MAJOR RATINGS AND CHARACTERISTICS I F(AV).0 A V RRM V to 00 V I FSM (8.3 ms sine-wave) A I FSM (square wave t p = ms) 45 A V F. V I R 5.0
Driving Success in Automotive Electronics
 Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. Driving Success in Automotive Electronics www.vishay.com One of the World s Largest Manufacturers of Discrete Semiconductors and Passive Components DIODES CapacitorS OPTOELECTRONICS
Vishay Intertechnology, Inc. Driving Success in Automotive Electronics www.vishay.com One of the World s Largest Manufacturers of Discrete Semiconductors and Passive Components DIODES CapacitorS OPTOELECTRONICS
APPLICATION NOTE. Using Current Sense Resistors for Accurate Current Measurement
 Using for Accurate Current Measurement INTRODUCTION Global trends such as the demand for lower CO2 emissions, the smartening of the electricity supply grid and the electrification of our automobiles are
Using for Accurate Current Measurement INTRODUCTION Global trends such as the demand for lower CO2 emissions, the smartening of the electricity supply grid and the electrification of our automobiles are
(SMW) Power Wire Wound Chip Resistors
 Version: July 31, 2017 Electronics Tech. (SMW) Power Wire Wound Chip Resistors Web: www.direct-token.com Email: rfq@direct-token.com Direct Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. China: 12F, Zhong Xing Industry
Version: July 31, 2017 Electronics Tech. (SMW) Power Wire Wound Chip Resistors Web: www.direct-token.com Email: rfq@direct-token.com Direct Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. China: 12F, Zhong Xing Industry
LM2925 Low Dropout Regulator with Delayed Reset
 LM2925 Low Dropout Regulator with Delayed Reset General Description The LM2925 features a low dropout, high current regulator. Also included on-chip is a reset function with an externally set delay time.
LM2925 Low Dropout Regulator with Delayed Reset General Description The LM2925 features a low dropout, high current regulator. Also included on-chip is a reset function with an externally set delay time.
MIC5396/7/8/9. General Description. Features. Applications. Typical Application. Low-Power Dual 300mA LDO in 1.2mm x 1.
 Low-Power Dual 300mA LDO in 1.2mm x 1.6mm Extra Thin DFN General Description The is an advanced dual LDO ideal for powering general purpose portable devices. The provides two high-performance, independent
Low-Power Dual 300mA LDO in 1.2mm x 1.6mm Extra Thin DFN General Description The is an advanced dual LDO ideal for powering general purpose portable devices. The provides two high-performance, independent
High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES POWER SUPPLIES TO ±0V OUTPUT CURRENT TO 0A PEAK PROGRAMMABLE CURRENT LIMIT INDUSTRY-STANDARD PIN OUT FET INPUT TO- AND LOW-COST POWER PLASTIC PACKAGES
High Power Monolithic OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER FEATURES POWER SUPPLIES TO ±0V OUTPUT CURRENT TO 0A PEAK PROGRAMMABLE CURRENT LIMIT INDUSTRY-STANDARD PIN OUT FET INPUT TO- AND LOW-COST POWER PLASTIC PACKAGES
50W TO220 High Power Resistors
 50W TO220 High Power Resistors MHP 50 Non-inductive, thin film technology. Thermally enhanced Industry standard TO220 package. RoHS compliant. Low thermal resistance, 2.3 C/W resistor hot spot to metal
50W TO220 High Power Resistors MHP 50 Non-inductive, thin film technology. Thermally enhanced Industry standard TO220 package. RoHS compliant. Low thermal resistance, 2.3 C/W resistor hot spot to metal
High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, Tolerance of ± % and Load Life Stability of ± %
 High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, Tolerance of ± 0.005 % and Load Life Stability of ± 0.005 % INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Foil (BMF) technology outperforms all other resistor technologies
High Precision Foil Resistor with TCR of ± 2.0 ppm/ C, Tolerance of ± 0.005 % and Load Life Stability of ± 0.005 % INTRODUCTION Bulk Metal Foil (BMF) technology outperforms all other resistor technologies
TS mA / 1.5MHz Synchronous Buck Converter
 SOT-25 Pin Definition: 1. EN 2. Ground 3. Switching Output 4. Input 5. Feedback General Description The TS3406 is a high efficiency monolithic synchronous buck regulator using a 1.5MHz constant frequency,
SOT-25 Pin Definition: 1. EN 2. Ground 3. Switching Output 4. Input 5. Feedback General Description The TS3406 is a high efficiency monolithic synchronous buck regulator using a 1.5MHz constant frequency,
Pulse Load MELF Resistors for High Frequency Applications
 Pulse Load MELF Resistors for High FEATURES Speciality product for RF applications Low-inductance non-helical trimmed product Special carbon film technology ESD capability: 3 kv, Human Body Model Suitable
Pulse Load MELF Resistors for High FEATURES Speciality product for RF applications Low-inductance non-helical trimmed product Special carbon film technology ESD capability: 3 kv, Human Body Model Suitable
Bulk Metal Foil Technology RNC90Y and RNC90Z (Z-Foil) to MIL-PRF-55182/9
 Bulk Metal Foil Technology RNC90Y and RNC90Z (Z-Foil) to MIL-PRF-55182/9 INTRODUCTION Vishay Military Established Reliability resistors are available in resistance values from 4.99 Ω through 121 kω and
Bulk Metal Foil Technology RNC90Y and RNC90Z (Z-Foil) to MIL-PRF-55182/9 INTRODUCTION Vishay Military Established Reliability resistors are available in resistance values from 4.99 Ω through 121 kω and
50 W Power Resistor, Thick Film Technology, TO-220
 50 W Power Resistor, Thick Film Technology, TO-220 FEATURES 50 W at 25 C heatsink mounted Adjusted by sand trimming Leaded or surface mount versions High power to size ratio Non inductive element Material
50 W Power Resistor, Thick Film Technology, TO-220 FEATURES 50 W at 25 C heatsink mounted Adjusted by sand trimming Leaded or surface mount versions High power to size ratio Non inductive element Material
ZXCT1107/1109/1110 LOW POWER HIGH-SIDE CURRENT MONITORS
 Description The ZXCT117/9/1 are high side unipolar current sense monitors. These devices eliminate the need to disrupt the ground plane when sensing a load current. The wide common-mode input voltage range
Description The ZXCT117/9/1 are high side unipolar current sense monitors. These devices eliminate the need to disrupt the ground plane when sensing a load current. The wide common-mode input voltage range
LF353 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 LF353 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
LF353 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
Signal Conditioning Amplifier
 FEATURES Plug-in amplifier design; amplifiers are removable from the front panel without rear access Constant-voltage or constant-current excitation; 0.5 to 15 V or 0.5 to 30 ma; selectable by single internal
FEATURES Plug-in amplifier design; amplifiers are removable from the front panel without rear access Constant-voltage or constant-current excitation; 0.5 to 15 V or 0.5 to 30 ma; selectable by single internal
Low Cost, General Purpose High Speed JFET Amplifier AD825
 a FEATURES High Speed 41 MHz, 3 db Bandwidth 125 V/ s Slew Rate 8 ns Settling Time Input Bias Current of 2 pa and Noise Current of 1 fa/ Hz Input Voltage Noise of 12 nv/ Hz Fully Specified Power Supplies:
a FEATURES High Speed 41 MHz, 3 db Bandwidth 125 V/ s Slew Rate 8 ns Settling Time Input Bias Current of 2 pa and Noise Current of 1 fa/ Hz Input Voltage Noise of 12 nv/ Hz Fully Specified Power Supplies:
Surface Mounted Power Resistor Thick Film Technology
 DIMENSIONS in millimeters FEATURES AEC-Q200 qualified 35 W at 25 C case temperature Surface mounted resistor - TO-263 (D 2 PAK) style package Wide resistance range from 0.01 to 550 k Non inductive Resistor
DIMENSIONS in millimeters FEATURES AEC-Q200 qualified 35 W at 25 C case temperature Surface mounted resistor - TO-263 (D 2 PAK) style package Wide resistance range from 0.01 to 550 k Non inductive Resistor
1.2 A Slew Rate Controlled Load Switch
 1.2 A Slew Rate Controlled Load Switch DESCRIPTION The SiP4282 series is a slew rate controlled high side switch. The switch is of a low ON resistance P-Channel MOSFET that supports continuous current
1.2 A Slew Rate Controlled Load Switch DESCRIPTION The SiP4282 series is a slew rate controlled high side switch. The switch is of a low ON resistance P-Channel MOSFET that supports continuous current
LM3940 1A Low Dropout Regulator for 5V to 3.3V Conversion
 1A Low Dropout Regulator for 5V to 3.3V Conversion General Description The LM3940 is a 1A low dropout regulator designed to provide 3.3V from a 5V supply. The LM3940 is ideally suited for systems which
1A Low Dropout Regulator for 5V to 3.3V Conversion General Description The LM3940 is a 1A low dropout regulator designed to provide 3.3V from a 5V supply. The LM3940 is ideally suited for systems which
Thin Film Mini-MELF Resistors
 FEATURES Advanced thin film technology AEC-Q2 qualified Low TCR and tight tolerances Excellent stability in different environmental conditions Pure tin termination on nickel barrier, plated on press fit
FEATURES Advanced thin film technology AEC-Q2 qualified Low TCR and tight tolerances Excellent stability in different environmental conditions Pure tin termination on nickel barrier, plated on press fit
(FL) Current Shunts Resistors
 Version: January 17, 2017 (FL) Current Shunts Resistors Token Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. Web: www.token.com.tw Email: rfq@token.com.tw Taiwan: No.137, Sec. 1, Zhongxing Rd., Wugu District, New Taipei
Version: January 17, 2017 (FL) Current Shunts Resistors Token Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. Web: www.token.com.tw Email: rfq@token.com.tw Taiwan: No.137, Sec. 1, Zhongxing Rd., Wugu District, New Taipei
LM675 Power Operational Amplifier
 Power Operational Amplifier General Description The LM675 is a monolithic power operational amplifier featuring wide bandwidth and low input offset voltage, making it equally suitable for AC and DC applications.
Power Operational Amplifier General Description The LM675 is a monolithic power operational amplifier featuring wide bandwidth and low input offset voltage, making it equally suitable for AC and DC applications.
Bulk Metal Foil Technology RNC90Y and RNC90Z (Z-Foil) to MIL-PRF-55182/9
 Bulk Metal Foil Technology RNC90Y and RNC90Z (Z-Foil) to MIL-PRF-55182/9 INTRODUCTION Military Established Reliability resistors from Vishay Foil Resistors (VFR) are available in resistance values from
Bulk Metal Foil Technology RNC90Y and RNC90Z (Z-Foil) to MIL-PRF-55182/9 INTRODUCTION Military Established Reliability resistors from Vishay Foil Resistors (VFR) are available in resistance values from
MIC5271. Applications. Low. output current). Zero-current off mode. and reduce power. GaAsFET bias Portable cameras. le enable pin, allowing the user
 µcap Negative Low-Dropout Regulator General Description The is a µcap 100mA negativee regulator in a SOT-23-this regulator provides a very accurate supply voltage for applications that require a negative
µcap Negative Low-Dropout Regulator General Description The is a µcap 100mA negativee regulator in a SOT-23-this regulator provides a very accurate supply voltage for applications that require a negative
Insulated Precision Wirewound Resistors Axial Leads
 Insulated Precision Wirewound Resistors Axial Leads In wirewound precision resistors, the series holds a leading position in professional applications whenever an excellent stability of the ohmic value
Insulated Precision Wirewound Resistors Axial Leads In wirewound precision resistors, the series holds a leading position in professional applications whenever an excellent stability of the ohmic value
TS431-Z Adjustable Precision Shunt Regulator
 SOT-23 TS431-Z Pin Definition: 1. Reference 2. Cathode 3. Anode TS431AR-Z Pin Definition: 1. Cathode 2. Reference 3. Anode General Description TS431 integrated circuits are three-terminal programmable
SOT-23 TS431-Z Pin Definition: 1. Reference 2. Cathode 3. Anode TS431AR-Z Pin Definition: 1. Cathode 2. Reference 3. Anode General Description TS431 integrated circuits are three-terminal programmable
