Development of 17T-NMR system for measurement of polarized HD and 3He targets
|
|
|
- Lewis Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Development of 17T-NMR system for measurement of polarized HD and 3He targets Research Center for Nuclear Physics, Osaka University, Mihogaoka 10-1, Ibaraki, Osaka , Japan Hideki Kohri a, Masaru Yosoi a, Mamoru Fujiwara a, Masayoshi Tanaka b a Research Center for Nuclear Physics, Osaka University, Mihogaoka 10-1, Ibaraki, Osaka , Japan b Department of Clinical Technology, Kobe Tokiwa University, Ohtani-cho 2-6-2, Nagata, Kobe , Japan Polarized targets for hadron experiment and medical imaging have been developed at RCNP, Osaka University. Concerning the former project, the LEPS group at SPring-8 has studied hadron photo-production experiments of the φ, K, η, and π 0 mesons by using the linear polarized Back Scattering Compton (BCS) γ-rays and unpolarized target in the energy range of Eγ= GeV. An experiment with a complete set of spin observables is, in particular, favorable to investigate the nucleon hidden structure and hadron photo-production dynamics for our future LEPS experiments. This is a major reason why a polarized Hydride Deuterium (HD) target is under development by means of the Brute force method, where a high magnetic field ( 17 T) and an extremely low temperature ( 10 mk) are employed. The polarized HD target is produced at RCNP and transported to the LEPS beam-line at SPring-8 by the ground transportation. To simplify and upgrade the quality for measurement, 700 MHz frequency sweep NMR system was developed allowing the measurement at any magnet field and any frequency without a tuning circuit. XVIth International Workshop in Polarized Sources, Targets, and Polarimetry, PSTP2015, September 2015, Bochum, Germany Speaker. c Copyright owned by the author(s) under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0).
2 1. HD target project in Osaka The hadron physics needs the spin observation in order to understand the fundamental structure of elementally particles. Polarized targets for hadron experiments and medical imaging have been developed at RCNP, Osaka University. Concerning the former project, the LEPS group at SPring-8 has studied hadron photo-production experiment of the φ, K, η, and π 0 mesons by using the linear polarized Back Scattering Compton (BCS) γ-rays and unpolarized target in the energy range of Eγ= GeV. An experiment with a complete set of spin observables is, in particular, favorable to investigate the nucleon hidden structure and hadron photo production dynamics for our future LEPS experiments [1] and reaction mechanisms [2, 3]. For this purpose, we have developed a polarized Hydrogen-Deuteride (HD) [4] target for future experiments at SPring-8/LEPS. Polarized Hydride Deuterium (HD) target is under development by the Brute force method, where a high magnetic field ( 17 Tesla ) and an extremely low temperature ( 10 mk ) are employed [5]. The polarized HD target is produced at RCNP and transported to the LEPS beam-line at SPring-8 by the ground transportation. The polarization degree should be checked not only at RCNP, but also during the transportation and at SPring-8. 5 years ago, we constructed a digital processing NMR system with a digitizer and software for NMR measurement enabling a magnetic field sweeping [6]. This system was the innovative NMR measurement instruments in terms of portability and low cost. Recently, we improved the NMR system working with a frequency sweep instead of a magnet field sweep which caused many problems associated with the heat production due to the change of electric current of the superconducting solenoid coil. Another improvement was that this frequency range is extended up to the 1 GHz by introducing digitizer modules commercially available working in the GHz range. The proton NMR measurement becomes possible with frequency of 700 MHz at 17 Tesla. This success is very important in on-line observation of the target polarization growth at 17 T. This instrument enable us to monitor the polarization degree for a period of three month which are needed for production of the produced polarization target. Meanwhile, this new NMR circuit system will also be used for the hyperpolarized 3 He project aiming at medical imaging, where the the Brute Force method and Pomeranchuk cooling are employed for production of the hyper-polarized 3 He target. This is somewhat in detail described in this workshop by one of our group [7]. In order to achieve high polarizations and long relaxation time of proton and deuteron in the HD target, HD target is kept in the DRS (Dilution refrigerator system) working at low temperature (10 mk) and at high magnetic field (17 T). HD polarization gradually grows up in the spin-flip process between HD molecules and a small amount of ortho-h 2 with spin 1 by spin flip [8, 9]. After a long period of cooling, ortho-h 2 molecules are converted to para-h 2. Since the para-h 2 has a total spin 0, the spin-flip process will stop when all the ortho-h 2 molecules are converted to the para-h 2. If ortho-h 2 does not remain in the HD sample, the relaxation time of hydrogen polarization becomes very long even at a temperature higher than 1 K. The expected polarization exceeds 84% for proton after an aging process for 2-3 months. The polarized HD system consists of five refrigerators called SC (Storage Cryostat), TC1 (Transfer Crryostat), DRS, TC2 (Transfer Cryostat 2) and IBC. All polarization measurements are performed by using the SC. The flow chart of the target transportation is shown in Fig. 1. The DRS is main refrigerator for polarized HD production and having a cooling power of 2500 µw 2
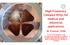
3 at 100mK.. The IBC will be operated under the condition with a magnetic field of 1 Tesla and a temperature of 300 mk during the physics experiment for a few months.the three cryostats SC, TC1, TC2 are liquid- 4 He cryostats used during the transportation of the HD target. At RCNP, pure HD gas with an amount of 1 mole is produced by using the HD gas distillator. The HD gas is solidified in the DRS, and the polarization of the reference HD is measured at 4.2 K. The polarization of the solid HD is grown and frozen by aging at B=17 Tesla and at T=14 mk in the DRS. After polarization is frozen, the target is transferred from the DRS to the SC by using the TC1 and transported to SPring-8/LEPS by a truck. At SPring-8/LEPS, the polarized HD is transferred from the SC to a dilution refrigerator, IBC by using the last 4 He refrigerator, TC2. DIs llator DRS & 17 Magnet TC1 SC TC NMR measurement Figure 1: Transportation diagram for Polarized HD target from production to installing IBC Tesla magnet and Dilution refrigerator The NMR measurement was performed inside DR where the 17 Tesla is produced by the super conducting magnet and DRS. The DRS consists of a liquid nitrogen (LN 2 ) bath, a liquid helium (LHe) bath, and a dilution circular line. The DRS has a hole in the center. The HD target is put and extracted by this hole and transferred to SPring- 8 for hadron experiment. The superconducting magnet cooled by LHe provides the maximum magnetic field of 17.0 T. The homogeneity, B/B, of the magnetic field is in the central region over 300 mm long and 30 mm diameter. The HD gas is solidified in a cell made of Kel-F R (PCTFE:Poly-Chloro-Tri-Fluoro-Ethylene), a hydrogen-free material. We can also observe a Fluorine and Chlorine NMR signals. Since The number of mole of Fluorine and Chlorine unchanges, those NMR signals are used as an relative indicator of proton and deuteron in the HD target. TC2 IBC Figure 2: The HD target cell without coil for the LEPS experiments. The geometry of the cell is 2.5 cm in diameter and 5 cm in length. The coil frame is covered this target when NMR measurement is performed. 3
4 MHz NMR system operated with the frequency sweep The NMR system constructed this time, consists of an RF signal generator module and an ADC module. These modules are put in slots in a PXI (PCI extensions for Instrumentation) chassis and controlled by the software, LabVIEW on the laptop PC with high-speed transmission [10]. This system consists of PXIe-1073 (Chassis), PXIe-5650 (1.3 GHz RF signal generator), and PXI (10 bit, 2.5 GSample/s Digitizer) which are produced by the National Instruments Company (Fig. 3). The LabVIEW has a role as a controller and calculation for signals. The NMR system has a function as an oscilloscope, a lock-in amplifier and a network analyzer on the software. The network analyzer is used for minimizing the power reflection of the NMR circuit by tuning variable capacitors at off-resonance frequencies. The oscilloscope is used to observe the returning signal from the NMR coil. The lock-in amplifier is used to pick up the small RF amplitude with a frequency equal to the frequency of the input signal, then separates detected signal into the absorption and dispersion signal. Even if a noise level is several thousand times higher than a true tiny NMR signal, a signal with a specific frequency can be detected by using a phase sensitive processing in the software. The noises with frequencies other than the reference frequency are rejected. As a result, we can greatly reduce the noise effect in the NMR measurement. As shown in Fig. 4, we introduced a special circuit to cancel the output signals in the case of the non-resonance. The sinusoidal wave output from the signal generator is divided into two components. One is sent the RF signal to the NMR coil and the other is for a reference signal. When the nuclear magnetic resonance occurs, the HD target absorbs an RF energy from the coil, and the absorption signal is measured with the lock-in amplifier when magnetic field (or frequency) is swept. We apply a cross coil method for the NMR measurements [11, 12]. A Teflon coated silver wire with a diameter of 0.1 mm is wounded to form a saddle coil by 1 turn on the coil support frame which is also made of Kel-F R. The polarization of H in the HD is 0.005% at 4.2 K and 1 Tesla. Fig. 5 shows NMR signals obtained in various magnetic fields by the frequency sweep method. The characteristic feature of this NMR system has no tune circuit to measure with the broaden frequency range. On the other hand, the signal to noise ratio becomes bad. Nevertheless NMR signals were visible from 50 MHz (1.17 Tesla) to 727 MHz. During the polarization growth, the NMR measurements keep working for 3 month and monitor the polarization every day. This result shows us that this monitoring is possible irrespectively of the magnetic field. Portable NMR polarimeter system LabVIEW Lock-in amplifier Network analyzer Oscillo scope Signal generator PXI MHz ~ 100MHz ADC PXI MS/s Reference signal Attenuator -20 dbm Preamp +35 dbm Inputl Laptop PC 14bit PXI system ouput Cross coil Figure 3: Photo of 17 tesla NMR monitor. Figure 4: NMR circuit for using 17 tesla NMR monitor 4
5 Figure 5: Measured NMR signals by frequency sweep from 50 MHz (1.17 Tesla) to 727 MHz (17.0 Tesla). Red curves are absorption signals, and black curves are dispersion signals. References [1] A.I. Titov, Y. Oh, and S.N. Yang, Phys. Rev. Lett. 79 (1997) [2] T. Mibe et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 95 (2005) [3] H. Kohri et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 (2010) [4] M. Fujiwara et al., Photoproduction Experiment with polarized HD Target at SPring-8, LEPS/RCNP proposal (2003). [5] A. Honig et al., Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A 356 (1995) 39. [6] T. Ohta et al., Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A 633 (2011) 46. [7] M. Tanaka et al, Physics of Particles and Nuclei, (2013). [8] T. Moriya and K. Motizuki, Progr. Theoret. Phys. 18 (1957) 183. [9] K. Motizuki and T. Nagamiya, J. Phys. Soc. Japan 11 (1956) 93. [10] PXI system alliance: [11] E. Fukushima and S. B. W. Roeder, Experimental Pulse NMR, Westview press, Colorad (1981) p.393. [12] M.P. Klein and D. E. Phelps, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 38 (1967)
Development of large readout area, high time resolution RPCs for LEPS2 at SPring-8
 Development of large readout area, high time resolution RPCs for LEPS2 at SPring-8 1 Department of physics, Kyoto University Kitashirakawa-Oiwakecho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-8502, Japan E-mail: natsuki@scphys.kyoto-u.ac.jp
Development of large readout area, high time resolution RPCs for LEPS2 at SPring-8 1 Department of physics, Kyoto University Kitashirakawa-Oiwakecho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-8502, Japan E-mail: natsuki@scphys.kyoto-u.ac.jp
Development of a new Q-meter module
 A. Berlin,, W. Meyer, G. Reicherz Experimentalphysik I, Ruhr-Universität Bochum E-mail: jonas.herick@rub.de In the research field of polarized target physics the Q-meter is a well established technique
A. Berlin,, W. Meyer, G. Reicherz Experimentalphysik I, Ruhr-Universität Bochum E-mail: jonas.herick@rub.de In the research field of polarized target physics the Q-meter is a well established technique
Trigger Rate Dependence and Gas Mixture of MRPC for the LEPS2 Experiment at SPring-8
 Trigger Rate Dependence and Gas Mixture of MRPC for the LEPS2 Experiment at SPring-8 1 Institite of Physics, Academia Sinica 128 Sec. 2, Academia Rd., Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan cyhsieh0531@gmail.com
Trigger Rate Dependence and Gas Mixture of MRPC for the LEPS2 Experiment at SPring-8 1 Institite of Physics, Academia Sinica 128 Sec. 2, Academia Rd., Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan cyhsieh0531@gmail.com
THE FROZEN SPIN TARGET AT MAMI ANDREAS THOMAS
 Printed ISSN 1330 0016 Online ISSN 1333 9133 CD ISSN 1333 8390 CODEN FIZBE7 THE FROZEN SPIN TARGET AT MAMI ANDREAS THOMAS Institut für Kernphysik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz, J.-J.-Becher-Weg
Printed ISSN 1330 0016 Online ISSN 1333 9133 CD ISSN 1333 8390 CODEN FIZBE7 THE FROZEN SPIN TARGET AT MAMI ANDREAS THOMAS Institut für Kernphysik, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz, J.-J.-Becher-Weg
Los Alamos. Low-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging of. David M. Schmidt, Michelle A. Espy, P-21
 * LA-UR- PI Approved for public release: distribution is unlimited. Title: Low-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Gases Author@): Submitted to Los Alamos David M. Schmidt, Michelle A. Espy, P-21 DOE OFFICE
* LA-UR- PI Approved for public release: distribution is unlimited. Title: Low-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Gases Author@): Submitted to Los Alamos David M. Schmidt, Michelle A. Espy, P-21 DOE OFFICE
RCNP CYCLOTRON FACILITY
 RCNP CYCLOTRON FACILITY K. Hatanaka *, M. Fukuda, T. Yorita, T. Saito, H. Tamura, M. Kibayashi, S. Morinobu, K. Nagayama RCNP, Osaka University, 10-1 Mihogaoka, Ibaraki, Osaka 567-0047, Japan Abstract
RCNP CYCLOTRON FACILITY K. Hatanaka *, M. Fukuda, T. Yorita, T. Saito, H. Tamura, M. Kibayashi, S. Morinobu, K. Nagayama RCNP, Osaka University, 10-1 Mihogaoka, Ibaraki, Osaka 567-0047, Japan Abstract
HETERONUCLEAR IMAGING. Topics to be Discussed:
 HETERONUCLEAR IMAGING BioE-594 Advanced MRI By:- Rajitha Mullapudi 04/06/2006 Topics to be Discussed: What is heteronuclear imaging. Comparing the hardware of MRI and heteronuclear imaging. Clinical applications
HETERONUCLEAR IMAGING BioE-594 Advanced MRI By:- Rajitha Mullapudi 04/06/2006 Topics to be Discussed: What is heteronuclear imaging. Comparing the hardware of MRI and heteronuclear imaging. Clinical applications
A Novel Design of a Low Temperature Preamplifier for Pulsed NMR Experiments of dilute 3 He in Solid 4 He
 Journal of Low Temperature Physics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) A Novel Design of a Low Temperature Preamplifier for Pulsed NMR Experiments of dilute 3 He in Solid 4 He C. Huan 1,2,
Journal of Low Temperature Physics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) A Novel Design of a Low Temperature Preamplifier for Pulsed NMR Experiments of dilute 3 He in Solid 4 He C. Huan 1,2,
Study of the HD target spin rotations during G14
 Study of the HD target spin rotations during G14 A. Deur, deurpam@jlab.org April 18, 2013 1 Introduction During the G14 run, the target spin was reversed using either magnetic field rotations or RF spin
Study of the HD target spin rotations during G14 A. Deur, deurpam@jlab.org April 18, 2013 1 Introduction During the G14 run, the target spin was reversed using either magnetic field rotations or RF spin
Chapter 1. 1 The NMR Spectrometer. 1.1 Components of an NMR Spectrometer The Magnet
 Chapter 1 1 The NMR Spectrometer 1.1 Components of an NMR Spectrometer 1.1.1 The Magnet In most current NMR spectrometers the magnetic field is generated by a superconducting magnet (Fig. 1.1). The first
Chapter 1 1 The NMR Spectrometer 1.1 Components of an NMR Spectrometer 1.1.1 The Magnet In most current NMR spectrometers the magnetic field is generated by a superconducting magnet (Fig. 1.1). The first
Design of a new 18 GHz ECRIS for RIKEN RIBF
 Design of a new 18 GHz ECRIS for RIKEN RIBF Kazutaka Ozeki Yoshihide Higurashi Takahide Nakagawa Jun-ichi Ohnishi RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based Science Contents RIKEN RIBF, RILAC RIKEN 18
Design of a new 18 GHz ECRIS for RIKEN RIBF Kazutaka Ozeki Yoshihide Higurashi Takahide Nakagawa Jun-ichi Ohnishi RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based Science Contents RIKEN RIBF, RILAC RIKEN 18
CULTASK, The Coldest Axion Experiment at CAPP/IBS/KAIST in Korea
 , The Coldest Axion Experiment at CAPP/IBS/KAIST in Korea Center for Axion and Precision Physics Research, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Republic of Korea E-mail: gnuhcw@ibs.re.kr The axion, a hypothetical
, The Coldest Axion Experiment at CAPP/IBS/KAIST in Korea Center for Axion and Precision Physics Research, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Republic of Korea E-mail: gnuhcw@ibs.re.kr The axion, a hypothetical
Spin Manipulation with an RF Wien-Filter at COSY PSTP Workshop 2015
 Spin Manipulation with an RF Wien-Filter at COSY PSTP Workshop 2015 Bochum, September 15, 2015 Forschungszentrum Jülich Sebastian Mey and Ralf Gebel for the JEDI Collaboration Content EDM Measurements
Spin Manipulation with an RF Wien-Filter at COSY PSTP Workshop 2015 Bochum, September 15, 2015 Forschungszentrum Jülich Sebastian Mey and Ralf Gebel for the JEDI Collaboration Content EDM Measurements
7 Equipments. Spectrometers
 7 Equipments Spectrometers There are three spectrometers located in the NMR laboratory: Varian UNITYplus 500 MHz (NMR500), Varian UNITYplus 500 MHz (Nightmare) and Varian INOVA 600 MHz. All spectrometers
7 Equipments Spectrometers There are three spectrometers located in the NMR laboratory: Varian UNITYplus 500 MHz (NMR500), Varian UNITYplus 500 MHz (Nightmare) and Varian INOVA 600 MHz. All spectrometers
MuCool Test Area Experimental Program Summary
 MuCool Test Area Experimental Program Summary Alexey Kochemirovskiy The University of Chicago/Fermilab Alexey Kochemirovskiy NuFact'16 (Quy Nhon, August 21-27, 2016) Outline Introduction Motivation MTA
MuCool Test Area Experimental Program Summary Alexey Kochemirovskiy The University of Chicago/Fermilab Alexey Kochemirovskiy NuFact'16 (Quy Nhon, August 21-27, 2016) Outline Introduction Motivation MTA
A few results [2,3] obtained with the individual cavities inside their horizontal cryostats are summarized in Table I and a typical Q o
![A few results [2,3] obtained with the individual cavities inside their horizontal cryostats are summarized in Table I and a typical Q o A few results [2,3] obtained with the individual cavities inside their horizontal cryostats are summarized in Table I and a typical Q o](/thumbs/78/77724292.jpg) Particle Accelerators, 1990, Vol. 29, pp. 47-52 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1990 Gordon and Breach, Science Publishers, Inc. Printed in the United
Particle Accelerators, 1990, Vol. 29, pp. 47-52 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 1990 Gordon and Breach, Science Publishers, Inc. Printed in the United
Study of RF Breakdown in Strong Magnetic Fields
 The University of Chicago E-mail: kochemir@uchicago.edu Daniel Bowring, Katsuya Yonehara, Alfred Moretti Fermi National Laboratory Yagmur Torun, Ben Freemire Illinois Institute of Technology RF cavities
The University of Chicago E-mail: kochemir@uchicago.edu Daniel Bowring, Katsuya Yonehara, Alfred Moretti Fermi National Laboratory Yagmur Torun, Ben Freemire Illinois Institute of Technology RF cavities
JEDI. Status of the commissioning of the waveguide RF Wien Filter
 COSY Beam Time Request For Lab. use Exp. No.: Session No. E 005.4 7 Collaboration: JEDI Status of the commissioning of the waveguide RF Wien Filter Spokespersons for the beam time: Ralf Gebel (Jülich)
COSY Beam Time Request For Lab. use Exp. No.: Session No. E 005.4 7 Collaboration: JEDI Status of the commissioning of the waveguide RF Wien Filter Spokespersons for the beam time: Ralf Gebel (Jülich)
Review of Progress in Quantitative Nondestructive Evaluation, Vol. 14 Edited by D.O. Thompson and D.E. Chimenti, Plenum Press, New Yorlc,l99S 1749
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND SPECI'ROSCOPY USING SQUID DETECTION S. Kumar, W.F. Avrin, and B.D. Thorson Quantum Magnetics, Inc. 11578 Sorrento Valley Road San Diego, CA 92121 INTRODUCTION Magnetic Resonance
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND SPECI'ROSCOPY USING SQUID DETECTION S. Kumar, W.F. Avrin, and B.D. Thorson Quantum Magnetics, Inc. 11578 Sorrento Valley Road San Diego, CA 92121 INTRODUCTION Magnetic Resonance
The Qweak Experiment at Jefferson Lab
 The Qweak Experiment at Jefferson Lab J. Birchall University of Manitoba for the Qweak Collaboration Elba XII, June 2012 1 Qweak: measurement of the weak charge of the proton Commissioning June - August,
The Qweak Experiment at Jefferson Lab J. Birchall University of Manitoba for the Qweak Collaboration Elba XII, June 2012 1 Qweak: measurement of the weak charge of the proton Commissioning June - August,
MULTIPACTING IN THE CRAB CAVITY
 MULTIPACTING IN TH CRAB CAVITY Y. Morita, K. Hara, K. Hosoyama, A. Kabe, Y. Kojima, H. Nakai, KK, 1-1, Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 3-81, JAPAN Md. M. Rahman, K. Nakanishi, Graduate University for Advanced Studies,
MULTIPACTING IN TH CRAB CAVITY Y. Morita, K. Hara, K. Hosoyama, A. Kabe, Y. Kojima, H. Nakai, KK, 1-1, Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 3-81, JAPAN Md. M. Rahman, K. Nakanishi, Graduate University for Advanced Studies,
Vertical Tests of ILC Cavities and Detection of X-Rays from Field Emission
 Vertical Tests of ILC Cavities and Detection of X-Rays from Field Emission Pardis Niknejadi California State Polytechnic University, Pomona, CA 91768 Elizabeth Olhsson University of Oregon, Eugene, OR
Vertical Tests of ILC Cavities and Detection of X-Rays from Field Emission Pardis Niknejadi California State Polytechnic University, Pomona, CA 91768 Elizabeth Olhsson University of Oregon, Eugene, OR
AC magnetic measurements etc
 physics 590 ruslan prozorov AC magnetic measurements etc lock-in amplifier lock-in summary with integrator integrate out phase-sensitive detector (PSD) AC magnetic susceptibility typical AC susceptometer
physics 590 ruslan prozorov AC magnetic measurements etc lock-in amplifier lock-in summary with integrator integrate out phase-sensitive detector (PSD) AC magnetic susceptibility typical AC susceptometer
Polarization measurement in the COMPASS polarized target
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 526 (24) 7 75 Polarization measurement in the COMPASS polarized target K. Kondo a, *, J. Ball b, G. Baum c, P. Berglund d,e, N. Doshita a, F. Gautheron
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 526 (24) 7 75 Polarization measurement in the COMPASS polarized target K. Kondo a, *, J. Ball b, G. Baum c, P. Berglund d,e, N. Doshita a, F. Gautheron
Timing and cross-talk properties of BURLE multi-channel MCP PMTs
 Timing and cross-talk properties of BURLE multi-channel MCP PMTs Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, University of Maribor, and Jožef Stefan Institute, Ljubljana, Slovenia E-mail: samo.korpar@ijs.si
Timing and cross-talk properties of BURLE multi-channel MCP PMTs Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, University of Maribor, and Jožef Stefan Institute, Ljubljana, Slovenia E-mail: samo.korpar@ijs.si
TOP counter for Belle II - post installation R&Ds
 Raita Omori, Genta Muroyama, Noritsugu Tsuzuki, for the Belle II TOP Group Nagoya University E-mail: raita@hepl.phys.nagoya-u.ac.jp, muroyama@hepl.phys.nagoya-u.ac.jp, noritsugu@hepl.phys.nagoya-u.ac.jp
Raita Omori, Genta Muroyama, Noritsugu Tsuzuki, for the Belle II TOP Group Nagoya University E-mail: raita@hepl.phys.nagoya-u.ac.jp, muroyama@hepl.phys.nagoya-u.ac.jp, noritsugu@hepl.phys.nagoya-u.ac.jp
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 6 Jul 2015
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 6 Jul 2015 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 6 Jul 2015](/thumbs/94/120602675.jpg) July 7, 2015 arxiv:1507.01326v1 [physics.ins-det] 6 Jul 2015 SOIKID, SOI pixel detector combined with superconducting detector KID Hirokazu Ishino, Atsuko Kibayashi, Yosuke Kida and Yousuke Yamada Department
July 7, 2015 arxiv:1507.01326v1 [physics.ins-det] 6 Jul 2015 SOIKID, SOI pixel detector combined with superconducting detector KID Hirokazu Ishino, Atsuko Kibayashi, Yosuke Kida and Yousuke Yamada Department
Hall C Polarimetry at 12 GeV Dave Gaskell Hall C Users Meeting January 14, 2012
 Hall C Polarimetry at 12 GeV Dave Gaskell Hall C Users Meeting January 14, 2012 1. Møller Polarimeter 2. Compton Polarimeter Hall C 12 GeV Polarimetry Møller Polarimeter 6 GeV operation: uses 2 quads to
Hall C Polarimetry at 12 GeV Dave Gaskell Hall C Users Meeting January 14, 2012 1. Møller Polarimeter 2. Compton Polarimeter Hall C 12 GeV Polarimetry Møller Polarimeter 6 GeV operation: uses 2 quads to
FREIA Facility for Research Instrumentation and Accelerator Development Infrastructure and Control Architecture
 FREIA Facility for Research Instrumentation and Accelerator Development Infrastructure and Control Architecture Konrad Gajewski 10 September 2013, Uppsala Why FREIA? Several circumstances test stand for
FREIA Facility for Research Instrumentation and Accelerator Development Infrastructure and Control Architecture Konrad Gajewski 10 September 2013, Uppsala Why FREIA? Several circumstances test stand for
Voltage Biased Superconducting Quantum Interference Device Bootstrap Circuit
 Voltage Biased Superconducting Quantum Interference Device Bootstrap Circuit Xiaoming Xie 1, Yi Zhang 2, Huiwu Wang 1, Yongliang Wang 1, Michael Mück 3, Hui Dong 1,2, Hans-Joachim Krause 2, Alex I. Braginski
Voltage Biased Superconducting Quantum Interference Device Bootstrap Circuit Xiaoming Xie 1, Yi Zhang 2, Huiwu Wang 1, Yongliang Wang 1, Michael Mück 3, Hui Dong 1,2, Hans-Joachim Krause 2, Alex I. Braginski
Status of the ADMX-HF Dark Matter Axion Search
 University of California E-mail: simanovskaia@berkeley.edu Axions are a leading dark matter candidate, and may be detected by their resonant conversion to a monochromatic RF signal in a tunable microwave
University of California E-mail: simanovskaia@berkeley.edu Axions are a leading dark matter candidate, and may be detected by their resonant conversion to a monochromatic RF signal in a tunable microwave
Doppler-Free Spetroscopy of Rubidium
 Doppler-Free Spetroscopy of Rubidium Pranjal Vachaspati, Sabrina Pasterski MIT Department of Physics (Dated: April 17, 2013) We present a technique for spectroscopy of rubidium that eliminates doppler
Doppler-Free Spetroscopy of Rubidium Pranjal Vachaspati, Sabrina Pasterski MIT Department of Physics (Dated: April 17, 2013) We present a technique for spectroscopy of rubidium that eliminates doppler
Double-Resonance Magnetometry in Arbitrarily Oriented Fields. Stuart Ingleby University of Strathclyde
 Ingleby, Stuart and Riis, Erling and Arnold, Aidan and Griffin, Paul and O'Dwyer, Carolyn and Chalmers, Iain (2017) Double-resonance magnetometry in arbitrarily oriented fields. In: Workshop on Optically
Ingleby, Stuart and Riis, Erling and Arnold, Aidan and Griffin, Paul and O'Dwyer, Carolyn and Chalmers, Iain (2017) Double-resonance magnetometry in arbitrarily oriented fields. In: Workshop on Optically
Diagnostic development to measure parallel wavenumber of lower hybrid waves on Alcator C-Mod
 Diagnostic development to measure parallel wavenumber of lower hybrid waves on Alcator C-Mod S. G. Baek, T. Shinya*, G. M. Wallace, S. Shiraiwa, R. R. Parker, Y. Takase*, D. Brunner MIT Plasma Science
Diagnostic development to measure parallel wavenumber of lower hybrid waves on Alcator C-Mod S. G. Baek, T. Shinya*, G. M. Wallace, S. Shiraiwa, R. R. Parker, Y. Takase*, D. Brunner MIT Plasma Science
REVIEW OF HIGH POWER CW COUPLERS FOR SC CAVITIES. S. Belomestnykh
 REVIEW OF HIGH POWER CW COUPLERS FOR SC CAVITIES S. Belomestnykh HPC workshop JLAB, 30 October 2002 Introduction Many aspects of the high-power coupler design, fabrication, preparation, conditioning, integration
REVIEW OF HIGH POWER CW COUPLERS FOR SC CAVITIES S. Belomestnykh HPC workshop JLAB, 30 October 2002 Introduction Many aspects of the high-power coupler design, fabrication, preparation, conditioning, integration
Modifying NMR Probe Electronics in the Muon g-2 Experiment
 Modifying NMR Probe Electronics in the Muon g-2 Experiment AUDREY KVAM University of Washington, 2014 INT REU The intent of the Muon g-2 experiment is to test the completeness of the Standard Model by
Modifying NMR Probe Electronics in the Muon g-2 Experiment AUDREY KVAM University of Washington, 2014 INT REU The intent of the Muon g-2 experiment is to test the completeness of the Standard Model by
THE HIGH LUMINOSITY PERFORMANCE OF CESR WITH THE NEW GENERATION SUPERCONDUCTING CAVITY
 Presented at the 1999 Particle Accelerator Conference, New York City, NY, USA, March 29 April 2 CLNS 99/1614 / SRF 990407-03 THE HIGH LUMINOSITY PERFORMANCE OF CESR WITH THE NEW GENERATION SUPERCONDUCTING
Presented at the 1999 Particle Accelerator Conference, New York City, NY, USA, March 29 April 2 CLNS 99/1614 / SRF 990407-03 THE HIGH LUMINOSITY PERFORMANCE OF CESR WITH THE NEW GENERATION SUPERCONDUCTING
Electron Spin Resonance v2.0
 Electron Spin Resonance v2.0 Background. This experiment measures the dimensionless g-factor (g s ) of an unpaired electron using the technique of Electron Spin Resonance, also known as Electron Paramagnetic
Electron Spin Resonance v2.0 Background. This experiment measures the dimensionless g-factor (g s ) of an unpaired electron using the technique of Electron Spin Resonance, also known as Electron Paramagnetic
Superconducting RF Cavity Performance Degradation after Quenching in Static Magnetic Field
 Superconducting RF Cavity Performance Degradation after Quenching in Static Magnetic Field T. Khabiboulline, D. Sergatskov, I. Terechkine* Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL) *MS-316, P.O. Box
Superconducting RF Cavity Performance Degradation after Quenching in Static Magnetic Field T. Khabiboulline, D. Sergatskov, I. Terechkine* Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (FNAL) *MS-316, P.O. Box
PoS(LHCP2018)031. ATLAS Forward Proton Detector
 . Institut de Física d Altes Energies (IFAE) Barcelona Edifici CN UAB Campus, 08193 Bellaterra (Barcelona), Spain E-mail: cgrieco@ifae.es The purpose of the ATLAS Forward Proton (AFP) detector is to measure
. Institut de Física d Altes Energies (IFAE) Barcelona Edifici CN UAB Campus, 08193 Bellaterra (Barcelona), Spain E-mail: cgrieco@ifae.es The purpose of the ATLAS Forward Proton (AFP) detector is to measure
Medical Imaging. X-rays, CT/CAT scans, Ultrasound, Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Medical Imaging X-rays, CT/CAT scans, Ultrasound, Magnetic Resonance Imaging From: Physics for the IB Diploma Coursebook 6th Edition by Tsokos, Hoeben and Headlee And Higher Level Physics 2 nd Edition
Medical Imaging X-rays, CT/CAT scans, Ultrasound, Magnetic Resonance Imaging From: Physics for the IB Diploma Coursebook 6th Edition by Tsokos, Hoeben and Headlee And Higher Level Physics 2 nd Edition
Gradients. Effects of B0 gradients on transverse magnetisation Similar to figure 10 of Sattler review Progr. NMR 34 (1999), 93
 Gradients 1. What are gradients? Modern high-resolution NMR probes contain -besides the RF coils - additional coils that can be fed a DC current. The coils are built so that a pulse (~1 ms long) of DC
Gradients 1. What are gradients? Modern high-resolution NMR probes contain -besides the RF coils - additional coils that can be fed a DC current. The coils are built so that a pulse (~1 ms long) of DC
RF STATUS OF SUPERCONDUCTING MODULE DEVELOPMENT SUITABLE FOR CW OPERATION: ELBE CRYOSTATS
 RF STATUS OF SUPERCONDUCTING MODULE DEVELOPMENT SUITABLE FOR CW OPERATION: ELBE CRYOSTATS J. Teichert, A. Büchner, H. Büttig, F. Gabriel, P. Michel, K. Möller, U. Lehnert, Ch. Schneider, J. Stephan, A.
RF STATUS OF SUPERCONDUCTING MODULE DEVELOPMENT SUITABLE FOR CW OPERATION: ELBE CRYOSTATS J. Teichert, A. Büchner, H. Büttig, F. Gabriel, P. Michel, K. Möller, U. Lehnert, Ch. Schneider, J. Stephan, A.
PULSED/CW NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE
 PULSED/CW NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE The Second Generation of TeachSpin s Classic Explore NMR for both Hydrogen (at 21 MHz) and Fluorine Nuclei Magnetic Field Stabilized to 1 part in 2 million Homogenize
PULSED/CW NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE The Second Generation of TeachSpin s Classic Explore NMR for both Hydrogen (at 21 MHz) and Fluorine Nuclei Magnetic Field Stabilized to 1 part in 2 million Homogenize
Fundamentals of NMR MRI Workshop Dayananda Sagar Institutes 29 May 2014 K.V.RAMANATHAN NMR Research Centre Indian Institute of Science Bangalore
 Fundamentals of NMR MRI Workshop Dayananda Sagar Institutes 29 May 2014 K.V.RAMANATHAN NMR Research Centre Indian Institute of Science Bangalore NMR It is an Ubiquitous Technique Physics Chemistry Structural
Fundamentals of NMR MRI Workshop Dayananda Sagar Institutes 29 May 2014 K.V.RAMANATHAN NMR Research Centre Indian Institute of Science Bangalore NMR It is an Ubiquitous Technique Physics Chemistry Structural
NMR Basics. Lecture 2
 NMR Basics Lecture 2 Continuous wave (CW) vs. FT NMR There are two ways of tuning a piano: - key by key and recording each sound (or frequency). - or, kind of brutal, is to hit with a sledgehammer and
NMR Basics Lecture 2 Continuous wave (CW) vs. FT NMR There are two ways of tuning a piano: - key by key and recording each sound (or frequency). - or, kind of brutal, is to hit with a sledgehammer and
A DNP-NMR setup for sub-nanoliter samples
 A DNP-NMR setup for sub-nanoliter samples Pedro Freire da Silva, Supervisor(s): Prof. Giovanni Boero, Prof. Pedro Sebastião The electrical and mechanical design for a non-magnetic, 2.5x2.5 cm 2 setup with
A DNP-NMR setup for sub-nanoliter samples Pedro Freire da Silva, Supervisor(s): Prof. Giovanni Boero, Prof. Pedro Sebastião The electrical and mechanical design for a non-magnetic, 2.5x2.5 cm 2 setup with
Superconducting RF Cavities Development at Argonne National Laboratory
 , The University of Chicago Superconducting RF Cavities Development at Argonne National Laboratory Sang-hoon Kim on behalf of Linac Development Group in Physics Division at Argonne National Laboratory
, The University of Chicago Superconducting RF Cavities Development at Argonne National Laboratory Sang-hoon Kim on behalf of Linac Development Group in Physics Division at Argonne National Laboratory
Unpolarized Cluster, Jet and Pellet Targets
 Unpolarized Cluster, Jet and Pellet Targets Intense Electron Beams Workshop Cornell University, June 17-19, 2015 Institut für Kernphysik Typical Requirements on Internal Targets Target material: H 2, D
Unpolarized Cluster, Jet and Pellet Targets Intense Electron Beams Workshop Cornell University, June 17-19, 2015 Institut für Kernphysik Typical Requirements on Internal Targets Target material: H 2, D
Workshop on Rapid Scan EPR. University of Denver EPR Center and Bruker BioSpin July 28, 2013
 Workshop on Rapid Scan EPR University of Denver EPR Center and Bruker BioSpin July 28, 2013 Direct detection Direct detected magnetic resonance that is, without modulation and phase-sensitive detection
Workshop on Rapid Scan EPR University of Denver EPR Center and Bruker BioSpin July 28, 2013 Direct detection Direct detected magnetic resonance that is, without modulation and phase-sensitive detection
Principios Básicos de RMN en sólidos destinado a usuarios. Gustavo Monti. Fa.M.A.F. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba Argentina
 Principios Básicos de RMN en sólidos destinado a usuarios Gustavo Monti Fa.M.A.F. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba Argentina magnet 1 2 4 5 6 computer 3 Block diagrama of a traditional NMR spectrometer.
Principios Básicos de RMN en sólidos destinado a usuarios Gustavo Monti Fa.M.A.F. Universidad Nacional de Córdoba Argentina magnet 1 2 4 5 6 computer 3 Block diagrama of a traditional NMR spectrometer.
Institute for Particle and Nuclear Studies, High Energy Accelerator Research Organization 1-1 Oho, Tsukuba, Ibaraki , Japan
 1, Hiroaki Aihara, Masako Iwasaki University of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan E-mail: chojyuro@gmail.com Manobu Tanaka Institute for Particle and Nuclear Studies, High Energy Accelerator
1, Hiroaki Aihara, Masako Iwasaki University of Tokyo 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0033, Japan E-mail: chojyuro@gmail.com Manobu Tanaka Institute for Particle and Nuclear Studies, High Energy Accelerator
PoS(PhotoDet2015)065. SiPM application for K L /µ detector at Belle II. Timofey Uglov
 National Research Nuclear University MEPhI (Moscow Engineering Physics Institute), Kashirskoe highway 31, Moscow, 115409, Russia E-mail: uglov@itep.ru We report on a new K L and muon detector based on
National Research Nuclear University MEPhI (Moscow Engineering Physics Institute), Kashirskoe highway 31, Moscow, 115409, Russia E-mail: uglov@itep.ru We report on a new K L and muon detector based on
SUPERCONDUCTING GANTRY AND OTHER DEVELOPMENTS AT HIMAC
 SUPERCONDUCTING GANTRY AND OTHER DEVELOPMENTS AT HIMAC Y. Iwata *, K. Noda, T. Shirai, T. Murakami, T. Fujita, T. Furukawa, K. Mizushima, Y. Hara, S. Suzuki, S. Sato, and K. Shouda, NIRS, 4-9-1 Anagawa,
SUPERCONDUCTING GANTRY AND OTHER DEVELOPMENTS AT HIMAC Y. Iwata *, K. Noda, T. Shirai, T. Murakami, T. Fujita, T. Furukawa, K. Mizushima, Y. Hara, S. Suzuki, S. Sato, and K. Shouda, NIRS, 4-9-1 Anagawa,
Polarimetry Concept Based on Heavy Crystal Hadron Calorimeter
 Polarimetry Concept Based on Heavy Crystal Hadron Calorimeter for the JEDI Collaboration CALOR 216 May 17, 216 Irakli Keshelashvili Introduction JEDI Polarimetry Concept MC Simulations Laboratory and Beam
Polarimetry Concept Based on Heavy Crystal Hadron Calorimeter for the JEDI Collaboration CALOR 216 May 17, 216 Irakli Keshelashvili Introduction JEDI Polarimetry Concept MC Simulations Laboratory and Beam
Sustainment and Additional Heating of High-Beta Field-Reversed Configuration Plasmas
 1 Sustainment and Additional Heating of High-Beta Field-Reversed Configuration Plasmas S. Okada, T. Fukuda, K. Kitano, H. Sumikura, T. Higashikozono, M. Inomoto, S. Yoshimura, M. Ohta and S. Goto Science
1 Sustainment and Additional Heating of High-Beta Field-Reversed Configuration Plasmas S. Okada, T. Fukuda, K. Kitano, H. Sumikura, T. Higashikozono, M. Inomoto, S. Yoshimura, M. Ohta and S. Goto Science
Energy in Electromagnetic Waves
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42446 1 Energy in Electromagnetic Waves * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain how the energy
OpenStax-CNX module: m42446 1 Energy in Electromagnetic Waves * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Abstract Explain how the energy
Development of a 1.0 T MR microscope using a Nd-Fe-B permanent magnet
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging 19 (2001) 875 880 Development of a 1.0 T MR microscope using a Nd-Fe-B permanent magnet Tomoyuki Haishi, Takaaki Uematsu, Yoshimasa Matsuda, Katsumi Kose* Institute of Applied
Magnetic Resonance Imaging 19 (2001) 875 880 Development of a 1.0 T MR microscope using a Nd-Fe-B permanent magnet Tomoyuki Haishi, Takaaki Uematsu, Yoshimasa Matsuda, Katsumi Kose* Institute of Applied
Prototype of a Compact Imaging System for GEM Detectors Tomohisa Uchida, Member, IEEE, Yowichi Fujita, Manobu Tanaka, Member, IEEE, and Shoji Uno
 2698 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 55, NO. 5, OCTOBER 2008 Prototype of a Compact Imaging System for GEM Detectors Tomohisa Uchida, Member, IEEE, Yowichi Fujita, Manobu Tanaka, Member, IEEE,
2698 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 55, NO. 5, OCTOBER 2008 Prototype of a Compact Imaging System for GEM Detectors Tomohisa Uchida, Member, IEEE, Yowichi Fujita, Manobu Tanaka, Member, IEEE,
Development of Telescope Readout System based on FELIX for Testbeam Experiments
 Development of Telescope Readout System based on FELIX for Testbeam Experiments, Hucheng Chen, Kai Chen, Francessco Lanni, Hongbin Liu, Lailin Xu Brookhaven National Laboratory E-mail: weihaowu@bnl.gov,
Development of Telescope Readout System based on FELIX for Testbeam Experiments, Hucheng Chen, Kai Chen, Francessco Lanni, Hongbin Liu, Lailin Xu Brookhaven National Laboratory E-mail: weihaowu@bnl.gov,
HIGH POWER COUPLER FOR THE TESLA TEST FACILITY
 Abstract HIGH POWER COUPLER FOR THE TESLA TEST FACILITY W.-D. Moeller * for the TESLA Collaboration, Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY, D-22603 Hamburg, Germany The TeV Energy Superconducting Linear
Abstract HIGH POWER COUPLER FOR THE TESLA TEST FACILITY W.-D. Moeller * for the TESLA Collaboration, Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY, D-22603 Hamburg, Germany The TeV Energy Superconducting Linear
The Pulsed Resistive Low-Field MR Scanner
 39 Chapter 3 The Pulsed Resistive Low-Field MR Scanner 3.1 Background In the remaining part of this work we are going to describe hyperpolarized gas relaxation, diffusion and MR imaging experiments. These
39 Chapter 3 The Pulsed Resistive Low-Field MR Scanner 3.1 Background In the remaining part of this work we are going to describe hyperpolarized gas relaxation, diffusion and MR imaging experiments. These
MRI SYSTEM COMPONENTS Module One
 MRI SYSTEM COMPONENTS Module One 1 MAIN COMPONENTS Magnet Gradient Coils RF Coils Host Computer / Electronic Support System Operator Console and Display Systems 2 3 4 5 Magnet Components 6 The magnet The
MRI SYSTEM COMPONENTS Module One 1 MAIN COMPONENTS Magnet Gradient Coils RF Coils Host Computer / Electronic Support System Operator Console and Display Systems 2 3 4 5 Magnet Components 6 The magnet The
PHY3902 PHY3904. Nuclear magnetic resonance Laboratory Protocol
 PHY3902 PHY3904 Nuclear magnetic resonance Laboratory Protocol PHY3902 PHY3904 Nuclear magnetic resonance Laboratory Protocol GETTING STARTED You might be tempted now to put a sample in the probe and try
PHY3902 PHY3904 Nuclear magnetic resonance Laboratory Protocol PHY3902 PHY3904 Nuclear magnetic resonance Laboratory Protocol GETTING STARTED You might be tempted now to put a sample in the probe and try
S. Ghosh On behalf of Linac, IFR, Cryogenics, RF and beam transport group members. Inter University Accelerator Centre New Delhi India
 S. Ghosh On behalf of Linac, IFR, Cryogenics, RF and beam transport group members Inter University Accelerator Centre New Delhi 110067 India Highlights of presentation 1. Introduction to Linear accelerator
S. Ghosh On behalf of Linac, IFR, Cryogenics, RF and beam transport group members Inter University Accelerator Centre New Delhi 110067 India Highlights of presentation 1. Introduction to Linear accelerator
X-ray polarimetry with a conventional gas proportional counter through rise-time analysis
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 421 (1999) 241 248 X-ray polarimetry with a conventional gas proportional counter through rise-time analysis Kiyoshi Hayashida*, Noriyuki Miura, Hiroshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 421 (1999) 241 248 X-ray polarimetry with a conventional gas proportional counter through rise-time analysis Kiyoshi Hayashida*, Noriyuki Miura, Hiroshi
QUARTER WAVE COAXIAL LINE CAVITY FOR NEW DELHI LINAC BOOSTER*
 QUARTER WAVE COAXIAL LINE CAVITY FOR NEW DELHI LINAC BOOSTER* P.N. Prakash and A.Roy Nuclear Science Centre, P.O.Box 10502, New Delhi 110 067, INDIA and K.W.Shepard Physics Division, Argonne National Laboratory,
QUARTER WAVE COAXIAL LINE CAVITY FOR NEW DELHI LINAC BOOSTER* P.N. Prakash and A.Roy Nuclear Science Centre, P.O.Box 10502, New Delhi 110 067, INDIA and K.W.Shepard Physics Division, Argonne National Laboratory,
Eddy Current Nondestructive Evaluation Using SQUID Sensors
 73 Eddy Current Nondestructive Evaluation Using SQUID Sensors Francesco Finelli Sponsored by: LAPT Introduction Eddy current (EC) nondestructive evaluation (NDE) consists in the use of electromagnetic
73 Eddy Current Nondestructive Evaluation Using SQUID Sensors Francesco Finelli Sponsored by: LAPT Introduction Eddy current (EC) nondestructive evaluation (NDE) consists in the use of electromagnetic
A Complete Digital Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) System at Low Magnetic Field (0.1 Tesla)
 IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Anchorage, AK, USA, 21-23 May 2002 A Complete igital Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) System at Low Magnetic Field (0.1 Tesla) Kosai RAOOF*, IEEE
IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Anchorage, AK, USA, 21-23 May 2002 A Complete igital Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) System at Low Magnetic Field (0.1 Tesla) Kosai RAOOF*, IEEE
Bryn Mawr College Department of Physics Undergraduate Teaching Laboratories Electron Spin Resonance
 Bryn Mawr College Department of Physics Undergraduate Teaching Laboratories Electron Spin Resonance Introduction Electron spin resonance (ESR) (or electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) as it is sometimes
Bryn Mawr College Department of Physics Undergraduate Teaching Laboratories Electron Spin Resonance Introduction Electron spin resonance (ESR) (or electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) as it is sometimes
The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment. Conference Report. Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland
 Available on CMS information server CMS CR -2017/402 The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland 06 November 2017 Commissioning of the
Available on CMS information server CMS CR -2017/402 The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland 06 November 2017 Commissioning of the
SPECIFICATIONS FOR A 4.7 TESLA/310MM BORE ACTIVELY SHIELDED MAGNET SYSTEM
 SPECIFICATIONS FOR A 4.7 TESLA/310MM BORE ACTIVELY SHIELDED MAGNET SYSTEM Prepared by:- Magnex Scientific Limited The Magnet Technology Centre 6 Mead Road Oxford Industrial Park Yarnton, Oxford OX5 1QU,
SPECIFICATIONS FOR A 4.7 TESLA/310MM BORE ACTIVELY SHIELDED MAGNET SYSTEM Prepared by:- Magnex Scientific Limited The Magnet Technology Centre 6 Mead Road Oxford Industrial Park Yarnton, Oxford OX5 1QU,
Proceedings of the 1972 Proton Linear Accelerator Conference, Los Alamos, New Mexico, USA
 STUDY OF HGH-ENERGY PROTON LNAC STRUCTURES by. G. Andreev,. M. Belugin,. G. Kulman, E. A. Mirochnik, and B. M. Pirozhenko Radiotechnical nstitute, USSR Academy of Sciences, Moscow, USSR ABSTRACT Two n2-mode
STUDY OF HGH-ENERGY PROTON LNAC STRUCTURES by. G. Andreev,. M. Belugin,. G. Kulman, E. A. Mirochnik, and B. M. Pirozhenko Radiotechnical nstitute, USSR Academy of Sciences, Moscow, USSR ABSTRACT Two n2-mode
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 5 Apr 2012
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 5 Apr 2012 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 5 Apr 2012](/thumbs/92/110256051.jpg) The Jefferson Lab Frozen Spin Target C.D. Keith a,, J. Brock a, C. Carlin a, S.A. Comer a, D. Kashy a, J. McAndrew b, D.G. Meekins a, E. Pasyuk a, J.J. Pierce a, M.L. Seely a,1 a Thomas Jefferson National
The Jefferson Lab Frozen Spin Target C.D. Keith a,, J. Brock a, C. Carlin a, S.A. Comer a, D. Kashy a, J. McAndrew b, D.G. Meekins a, E. Pasyuk a, J.J. Pierce a, M.L. Seely a,1 a Thomas Jefferson National
Results of FE65-P2 Pixel Readout Test Chip for High Luminosity LHC Upgrades
 for High Luminosity LHC Upgrades R. Carney, K. Dunne, *, D. Gnani, T. Heim, V. Wallangen Lawrence Berkeley National Lab., Berkeley, USA e-mail: mgarcia-sciveres@lbl.gov A. Mekkaoui Fermilab, Batavia, USA
for High Luminosity LHC Upgrades R. Carney, K. Dunne, *, D. Gnani, T. Heim, V. Wallangen Lawrence Berkeley National Lab., Berkeley, USA e-mail: mgarcia-sciveres@lbl.gov A. Mekkaoui Fermilab, Batavia, USA
Current Industrial SRF Capabilities and Future Plans
 and Future Plans Capabilities in view of Design Engineering Manufacturing Preparation Testing Assembly Taking into operation Future Plans Participate in and contribute to development issues, provide prototypes
and Future Plans Capabilities in view of Design Engineering Manufacturing Preparation Testing Assembly Taking into operation Future Plans Participate in and contribute to development issues, provide prototypes
Title detector with operating temperature.
 Title Radiation measurements by a detector with operating temperature cryogen Kanno, Ikuo; Yoshihara, Fumiki; Nou Author(s) Osamu; Murase, Yasuhiro; Nakamura, Masaki Citation REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS
Title Radiation measurements by a detector with operating temperature cryogen Kanno, Ikuo; Yoshihara, Fumiki; Nou Author(s) Osamu; Murase, Yasuhiro; Nakamura, Masaki Citation REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS
STATUS OF THE KOLKATA K500 SUPERCONDUCTING CYCLOTRON
 STATUS OF THE KOLKATA K500 SUPERCONDUCTING CYCLOTRON Rakesh K. Bhandari (for VECC Staff) Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre, Department of Atomic Energy, Kolkata 700 064, India Abstract A superconducting
STATUS OF THE KOLKATA K500 SUPERCONDUCTING CYCLOTRON Rakesh K. Bhandari (for VECC Staff) Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre, Department of Atomic Energy, Kolkata 700 064, India Abstract A superconducting
Power-stabilization of high frequency gyrotrons using a double PID feedback control for applications to many high power THz spectroscopy
 Power-stabilization of high frequency gyrotrons using a double PID feedback control for applications to many high power THz spectroscopy Alexei Kuleshov1,2, Keisuke Ueda3 and Toshitaka Idehara2 Institute
Power-stabilization of high frequency gyrotrons using a double PID feedback control for applications to many high power THz spectroscopy Alexei Kuleshov1,2, Keisuke Ueda3 and Toshitaka Idehara2 Institute
EXP 9 ESR (Electron Spin Resonance)
 EXP 9 ESR (Electron Spin Resonance) Introduction ESR in Theory The basic setup for electron spin resonance is shown in Fig 1. A test sample is placed in a uniform magnetic field. The sample is also wrapped
EXP 9 ESR (Electron Spin Resonance) Introduction ESR in Theory The basic setup for electron spin resonance is shown in Fig 1. A test sample is placed in a uniform magnetic field. The sample is also wrapped
Operation and Performance of the ATLAS Level-1 Calorimeter and Level-1 Topological Triggers in Run 2 at the LHC
 Operation and Performance of the ATLAS Level-1 Calorimeter and Level-1 Topological Triggers in Run 2 at the LHC Kirchhoff-Institute for Physics (DE) E-mail: sebastian.mario.weber@cern.ch ATL-DAQ-PROC-2017-026
Operation and Performance of the ATLAS Level-1 Calorimeter and Level-1 Topological Triggers in Run 2 at the LHC Kirchhoff-Institute for Physics (DE) E-mail: sebastian.mario.weber@cern.ch ATL-DAQ-PROC-2017-026
Low magnetic field dynamic nuclear polarization using a single-coil two-channel probe
 Low magnetic field dynamic nuclear polarization using a single-coil two-channel probe Dinh M. TonThat, a) Matthew P. Augustine, b) Alexander Pines, b) and John Clarke a) University of California, Berkeley,
Low magnetic field dynamic nuclear polarization using a single-coil two-channel probe Dinh M. TonThat, a) Matthew P. Augustine, b) Alexander Pines, b) and John Clarke a) University of California, Berkeley,
SPECIFICATION FOR A 7.0 TESLA/400MM ROOM TEMPERATURE BORE MAGNET SYSTEM
 SPECIFICATION FOR A 7.0 TESLA/400MM ROOM TEMPERATURE BORE MAGNET SYSTEM Prepared by:- Magnex Scientific Limited The Magnet Technology Centre 6 Mead Road Oxford Industrial Park Yarnton, Oxford OX5 1QU,
SPECIFICATION FOR A 7.0 TESLA/400MM ROOM TEMPERATURE BORE MAGNET SYSTEM Prepared by:- Magnex Scientific Limited The Magnet Technology Centre 6 Mead Road Oxford Industrial Park Yarnton, Oxford OX5 1QU,
Cryogenic Operations at SLAC
 Cryogenic Operations at SLAC J. G. Weisend II, A. Candia, W.W. Craddock, E. Thompson CryoOps 2006 5/30/2006 J. G. Weisend II 1 What Do We Do? Cryogenics at SLAC involve: Large scale He refrigerator operation
Cryogenic Operations at SLAC J. G. Weisend II, A. Candia, W.W. Craddock, E. Thompson CryoOps 2006 5/30/2006 J. G. Weisend II 1 What Do We Do? Cryogenics at SLAC involve: Large scale He refrigerator operation
A Study of undulator magnets characterization using the Vibrating Wire technique
 A Study of undulator magnets characterization using the Vibrating Wire technique Alexander. Temnykh a, Yurii Levashov b and Zachary Wolf b a Cornell University, Laboratory for Elem-Particle Physics, Ithaca,
A Study of undulator magnets characterization using the Vibrating Wire technique Alexander. Temnykh a, Yurii Levashov b and Zachary Wolf b a Cornell University, Laboratory for Elem-Particle Physics, Ithaca,
Pulsed NMR Experiment Guide Kenneth Jackson Physics 173, Spring 2014 Professor Tsai
 Pulsed NMR Experiment Guide Kenneth Jackson Physics 173, Spring 2014 Professor Tsai 1. Introduction NMR or nuclear magnetic resonance occurs when nuclei are placed in a magnetic field. It is a physical
Pulsed NMR Experiment Guide Kenneth Jackson Physics 173, Spring 2014 Professor Tsai 1. Introduction NMR or nuclear magnetic resonance occurs when nuclei are placed in a magnetic field. It is a physical
(N)MR Imaging. Lab Course Script. FMP PhD Autumn School. Location: C81, MRI Lab B0.03 (basement) Instructor: Leif Schröder. Date: November 3rd, 2010
 (N)MR Imaging Lab Course Script FMP PhD Autumn School Location: C81, MRI Lab B0.03 (basement) Instructor: Leif Schröder Date: November 3rd, 2010 1 Purpose: Understanding the basic principles of MR imaging
(N)MR Imaging Lab Course Script FMP PhD Autumn School Location: C81, MRI Lab B0.03 (basement) Instructor: Leif Schröder Date: November 3rd, 2010 1 Purpose: Understanding the basic principles of MR imaging
200 MHz 350 MHz 750 MHz Linac2 RFQ2 202 MHz 0.5 MeV /m Weight : 1000 kg/m Ext. diameter : 45 cm
 M. Vretenar, CERN for the HF-RFQ Working Group (V.A. Dimov, M. Garlasché, A. Grudiev, B. Koubek, A.M. Lombardi, S. Mathot, D. Mazur, E. Montesinos, M. Timmins, M. Vretenar) 1 1988-92 Linac2 RFQ2 202 MHz
M. Vretenar, CERN for the HF-RFQ Working Group (V.A. Dimov, M. Garlasché, A. Grudiev, B. Koubek, A.M. Lombardi, S. Mathot, D. Mazur, E. Montesinos, M. Timmins, M. Vretenar) 1 1988-92 Linac2 RFQ2 202 MHz
S600X SQUID M AGNETOMETER. S600X - For better magnetic measurements. The Better Choice. AC and DC measurements.
 S600X SQUID M AGNETOMETER S600X - For better magnetic measurements AC and DC measurements. lo -8 EMU sensitivity for total moment. Oscillator and extraction mode. MilliTesla field resolution and setting.
S600X SQUID M AGNETOMETER S600X - For better magnetic measurements AC and DC measurements. lo -8 EMU sensitivity for total moment. Oscillator and extraction mode. MilliTesla field resolution and setting.
A NOVEL FPGA-BASED DIGITAL APPROACH TO NEUTRON/ -RAY PULSE ACQUISITION AND DISCRIMINATION IN SCINTILLATORS
 10th ICALEPCS Int. Conf. on Accelerator & Large Expt. Physics Control Systems. Geneva, 10-14 Oct 2005, PO2.041-4 (2005) A NOVEL FPGA-BASED DIGITAL APPROACH TO NEUTRON/ -RAY PULSE ACQUISITION AND DISCRIMINATION
10th ICALEPCS Int. Conf. on Accelerator & Large Expt. Physics Control Systems. Geneva, 10-14 Oct 2005, PO2.041-4 (2005) A NOVEL FPGA-BASED DIGITAL APPROACH TO NEUTRON/ -RAY PULSE ACQUISITION AND DISCRIMINATION
20 meter bandstop filter notes
 1 Introduction 20 meter bandstop filter notes Kevin E. Schmidt, W9CF 6510 S. Roosevelt St. Tempe, AZ 85283 USA A shorted half-wavelength stub cut for 20 meters acts as a bandstop filter for 10 and 20 meters,
1 Introduction 20 meter bandstop filter notes Kevin E. Schmidt, W9CF 6510 S. Roosevelt St. Tempe, AZ 85283 USA A shorted half-wavelength stub cut for 20 meters acts as a bandstop filter for 10 and 20 meters,
Zeeman Shifted Modulation Transfer Spectroscopy in Atomic Cesium
 Zeeman Shifted Modulation Transfer Spectroscopy in Atomic Cesium Modulation transfer spectroscopy (MTS) is a useful technique for locking a laser on one of the closed cesium D transitions. We have focused
Zeeman Shifted Modulation Transfer Spectroscopy in Atomic Cesium Modulation transfer spectroscopy (MTS) is a useful technique for locking a laser on one of the closed cesium D transitions. We have focused
Herwig Schopper CERN 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland. Introduction
 THE LEP PROJECT - STATUS REPORT Herwig Schopper CERN 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Introduction LEP is an e + e - collider ring designed and optimized for 2 100 GeV. In an initial phase an energy of 2 55
THE LEP PROJECT - STATUS REPORT Herwig Schopper CERN 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Introduction LEP is an e + e - collider ring designed and optimized for 2 100 GeV. In an initial phase an energy of 2 55
Efficacy of Wavelet Transform Techniques for. Denoising Polarized Target NMR Signals
 Efficacy of Wavelet Transform Techniques for Denoising Polarized Target NMR Signals James Maxwell May 2, 24 Abstract Under the guidance of Dr. Donal Day, mathematical techniques known as Wavelet Transforms
Efficacy of Wavelet Transform Techniques for Denoising Polarized Target NMR Signals James Maxwell May 2, 24 Abstract Under the guidance of Dr. Donal Day, mathematical techniques known as Wavelet Transforms
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS-XII. Physics(Theory)
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS-XII Time allowed: 3 Hrs Physics(Theory) Maximum Marks: 70 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. There are 29 questions in total. Questions 1 to 8 are very
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS-XII Time allowed: 3 Hrs Physics(Theory) Maximum Marks: 70 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS: 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. There are 29 questions in total. Questions 1 to 8 are very
Mass Spectrometry and the Modern Digitizer
 Mass Spectrometry and the Modern Digitizer The scientific field of Mass Spectrometry (MS) has been under constant research and development for over a hundred years, ever since scientists discovered that
Mass Spectrometry and the Modern Digitizer The scientific field of Mass Spectrometry (MS) has been under constant research and development for over a hundred years, ever since scientists discovered that
MOLLER Update. Dustin McNulty Idaho State University for the MOLLER Collaboration June 8, 2012
 MOLLER Update Dustin McNulty Idaho State University mcnulty@jlab.org for the June 8, 2012 Outline Introduction MOLLER Update Motivation (Indirect search for new physics) Search for new contact interactions
MOLLER Update Dustin McNulty Idaho State University mcnulty@jlab.org for the June 8, 2012 Outline Introduction MOLLER Update Motivation (Indirect search for new physics) Search for new contact interactions
NMR Hardware 06/06/2017. Outline. Instrumentation: Magnet. Increasing magnetic field increases Sensitivity, by power of 3/2 Dispersion, linearly
 NMR Hardware Outline Magnet Lock Shims Gradient Probe Signal generation and transmitters Receiver and digitizer Variable temperature system Solids hardware Instrumentation: Magnet Often the most impressive
NMR Hardware Outline Magnet Lock Shims Gradient Probe Signal generation and transmitters Receiver and digitizer Variable temperature system Solids hardware Instrumentation: Magnet Often the most impressive
THE CRYOGENIC SYSTEM OF TESLA
 THE CRYOGENIC SYSTEM OF TESLA S. Wolff, DESY, Notkestr. 85, 22607 Hamburg, Germany for the TESLA collaboration Abstract TESLA, a 33 km long 500 GeV centre-of-mass energy superconducting linear collider
THE CRYOGENIC SYSTEM OF TESLA S. Wolff, DESY, Notkestr. 85, 22607 Hamburg, Germany for the TESLA collaboration Abstract TESLA, a 33 km long 500 GeV centre-of-mass energy superconducting linear collider
The design and performance of the ATLAS jet trigger
 th International Conference on Computing in High Energy and Nuclear Physics (CHEP) IOP Publishing Journal of Physics: Conference Series () doi:.88/7-696/// he design and performance of the ALAS jet trigger
th International Conference on Computing in High Energy and Nuclear Physics (CHEP) IOP Publishing Journal of Physics: Conference Series () doi:.88/7-696/// he design and performance of the ALAS jet trigger
