Photonic Bandgap Fibres for Broadband Transmission of SWIR Wavelengths. Southampton SO17 1BJ, UK
|
|
|
- Deborah Craig
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Photonic Bandgap Fibres for Broadband Transmission of SWIR Wavelengths. M.N. Petrovich 1, R. AmezcuaCorrea 1, N.G. Broderick 1, D.J. Richardson 1, T. Delmonte 2, M.A. Watson 2, E.J. O'Driscoll 2 1 Optoelectronics Research Centre, University of Southampton, Southampton SO17 1BJ, UK 2 BAE SYSTEMS Advanced Technology Centre, Sowerby Building, FPC 267, PO Box 5, Filton, Bristol, BS34 7QW Abstract Hollow core photonic bandgap fibres can achieve light guidance in air, which offers a number of potential benefits for applications relevant to electromagnetic remote sensing, including higher nonlinear and damage thresholds for high power beam delivery and operation at wavelengths that are not feasible using conventional fibres. Because they rely on coherent scattering from a highly ordered lattice of air holes as the mechanism of light guidance, bandgap fibres can only operate over a finite range of wavelengths. This paper investigates the parameters affecting the bandwidth of transmission in PBGFs and identifies realistic PBGF structures for widebandwidth operation in the SWIR wavelength region. Keywords: Microstructured fibres, photonic bandgap fibres, infrared fibres Introduction Photonic bandgap fibres (PBGFs) are an emerging class of optical fibres that exploit photonic bandgap effects, rather than total internal reflection, as the mechanism of light guidance [1]. These fibres possess a periodic lattice of air holes acting as the cladding, in which light propagation is prohibited for welldefined ranges of optical frequencies. Optical modes are confined in a central core defect, which can have lower refractive index than the cladding. Hollow core PBGFs are obtained by introducing an oversized air hole at the centre of the photonic crystal cladding. Such fibres allow for a very weak interaction of the guided mode with the fibre structure, which paves the way to novel and technologically enabling properties, such as low nonlinearity, high damage thresholds and transmission beyond silica s own transparency window [2]. Figure 1. Cross section of a highair filling factor PBGF and parameters used to define the structure. PBGFs are manufactured by the stackanddraw method [2], much in the same way as indexguiding holey fibres. Fabrication of PBGFs is however more challenging because a very large air filling factor (>75%) and a small pitch are required for low loss operation [3]. Moreover, since light guidance in PBGFs relies upon resonant scattering from the photonic crystal lattice, the fibre transmission is strongly dependent on the structure and very sensitive to imperfections and to structural variations along the fibre length.
2 The position of the bandgap is primarily determined by the holetohole spacing, Λ, and by the hole size and shape; since PBGFs require a high air filling factor, the holes are hexagonal with rounded corners and are generally described via two parameters (Fig 1): the relative hole diameter, d/λ and the shape factor, i.e. the relative radii of curvature at the corners, D C /Λ [4]. The goal of this study is to develop PBGFs with broadband transmission in the shortwavelength infrared region (SWIR). To this end, two distinct factors must be considered. The first is the width of the optical bandgap, which is determined by the properties of the photonic crystal cladding. Secondly, the operational bandwidth of a PBGF must also take into account its wavelength dependent transmission loss. In particular, it is well established that PBGFs can support both core and surface modes [5] and coupling between these modes is a major source of loss in these fibres, and can drastically reduce the fibre s transmission bandwidth. In this paper we present a detailed study of idealised but realistic PBGF structures, investigate the impact of key structural parameters and identify regimes that are robustly free of surface modes. Fibres fabricated with an optimised structure exhibit a wide lowloss operational bandwidth in good agreement with our theoretical predictions. Transmission properties of PBGFs Fig. 2 shows the optical bandgaps calculated for three different PBGF structures using a plane wave expansion method [6]. For a fixed wavelength λ 0, optical modes with effective index, n eff (λ 0 ), within the shaded areas cannot propagate in the photonic crystal cladding and are confined to the core. The fundamental airguided mode has a dispersion curve (dashed line), which lies just below the air line (n eff =1), thus the theoretical bandwidth of transmission ( Λ MAX ) can be approximated by the intersection of the bandgap edges with the air line. Based on this definition, Λ MAX is only dependent on the properties of the cladding. Fig. 2 shows that increasing the hole size has a dramatic effect on the transmission bandwidth: as d/λ is increased by less than 3% from 0.95 to 0.98, the bandgap almost doubles in width. This implies that a structure with very thin silica struts is preferable in order to achieve wide bandwidth PBGFs. The width of the bandgap is also found to depend on the shape factor, which also affects the air filling factor. Wavelength (µm) Figure 2: Optical bandgap of PBGF structures with d/λ = 0.95, 0.96 and 0.98 for a fixed shape factor D C /Λ 0.6 As stated above, the operational bandwidth of PBGFs depends on both the width of the optical bandgap and on the presence of surface modes (SMs). We employed a full vector finite element method (FEM) to accurately predict the dispersion curves of the optical modes supported by different PBGF structures. Fig. 3 shows a typical result for a fibre supporting one SM in addition to the fundamental core mode. The top graph shows the dispersion curves (solid lines) superimposed on the optical bandgap (shaded region). The inserts show the mode profiles corresponding to the core mode (FM), with most of the optical power located in air, and of the SM, which is concentrated in the thin core boundary
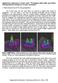
3 region instead. An anticrossing between modes occurs within the bandgap, which is indicated by a dashed square. The impact of such an interaction between these modes can clearly be seen as a dip in the percentage of power in the core for the fundamental mode (bottom graph). Because surface modes are intrinsically lossy, an increase in the transmission loss of the FM is always observed at the anticrossing points [5]. The operational bandwidth is thus correspondingly reduced. Optimisation of Fibre Design In real PBGFs the core is defined by a thin noncircular silica ring of nearly constant thickness at the boundary with the cladding. During the fabrication at least two of the core parameters can be controlled, i.e. the thickness of the silica ring and the core diameter, while keeping the parameters of the cladding constant. Hence we have focused our study on the effects on the fibre s transmission properties due to the modification of these two parameters. The thickness of the core ring is described by the parameter T C, while the size of the core is determined by its radii, R C (Fig.1). Variations of R C were modelled considering that only the first ring of holes is affected and the rest of the cladding is unchanged; this assumption was justified based on experimental observations, as clearly shown by two SEM micrographs of PBGFs with compressed and expanded cores (Fig. 4). Operational bandwidth Maximum bandwidth Figure 3. (Top) Effective index of modes vs wavelength. (Bottom) Percentage of power in the core of the fundamental mode. Shaded regions represent the bandgap. To summarize, in order to achieve maximum bandwidth suitable PBGF structures must be identified where: a) the optical bandgap is widest and b) SMs are ideally eliminated, or at least their impact on the fibre transmission is minimised. This in turn involves two equally critical steps of optimizing both the cladding structure, which determines the width of the optical bandgap, and the design of the core boundary, which determines the presence of SMs and their position within the optical bandgap. (a) (b) Figure 4. SEM images of hollowcore PBGFs, with (a) compressed and (b) expanded core. We initially varied the core thickness T C while holding the core size constant and calculated the optical modes within the bandgap. The analysis was then repeated for different values of R C. Our detailed calculations showed a strong dependence of the number and position of SMs interacting with the core mode on T C. It was however possible to identify a design regime, which is free of surface modes [7]. This optimum core design regime requires the core ring to have a thickness of about half that of the struts within the photonic crystal cladding. Our calculations also showed that a further improvement in the operational bandwidth can be achieved in a design with a slightly compressed core [7]. By
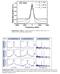
4 performing a systematic study we established this to be a robust effect that does not critically depend on the core size or cladding properties. Furthermore, we have confirmed that the result holds true for both 7cell core structures as well as for structures with a larger 19cell core. The modal and transmission properties of a PBGF with optimised structure are shown in Fig. 5, clearly demonstrating a huge improvement as compared to the unoptimized fibre structure in Fig. 2. Here SMs only occur either outside the optical bandgap or very close to its edges, hence they have very little impact on the fibre s transmission. Shaded areas indicate the width of the optical bandgap ( Λ MAX ), which in this case approximately coincides with the operating bandwidth. Operational bandwidth Figure 6. SEM images of fabricated PBGFs bandwidth operation. Fig. 6 shows a crosssectional SEM image of a fibre with a 7cell core and seven rings surrounding it, plus one incomplete ring to facilitate stacking and structure integrity during fibre fabrication. The fibre has a high air filling factor and the pitch of the photonic crystal cladding is in this case optimised for operation at about 2µm. The fibre transmission was measured using an OPO source, which could be continuously tuned across the bandgap. Fig. 7 shows a plot of the total loss (fibre loss plus coupling loss) vs. wavelength. A 6m length was used in the measurements, which is deemed to be suitable for the end application of the present study. Little variation in the fibre transmission at the centre of the bandgap was however observed between samples with different fibre lengths, which indicates low fibre loss and good structural uniformity. Light transmitted at 2µm showed good beam quality (M 2 1.4). 30 Figure 5. Modal dispersion curves of PBGFs with an optimised structure. Fibre Fabrication Fabrication of PBGFs with optimised structure was then undertaken. Several fibres were produced with bandgaps covering the range from 1.5 to 2.5µm. Detailed structural analysis was performed by scanning electron microscopy, which allowed us verification that the fibre s parameters were within the regime for wide Total Transmission Loss (db) Length: 1m Length: 6m 3dB Bandwidth Wavelength (µm) Figure 7. Bandwidth of transmission of a PBGF designed for operation at 2µm.
5 All fibres produced showed a wide, low loss region completely free of surface modes; from the data shown in Fig.7, we estimated an operational bandwidth spanning approximately 350nm for the fibre operating at 2µm. This result is in very good agreement with the predictions of modelling shown in Fig. 5. Conclusions A detailed investigation of the factors affecting the bandwidth of transmission of PBGFs was presented. Through computer simulations we have shown that by carefully selecting the structural parameters it is possible to design PBGFs with high air filling fractions for which the fundamental mode is not affected by surface modes at all wavelengths within the bandgap, allowing maximum operational bandwidth. Several fibres with an optimized structure and operating wavelengths in the range 1.5 to 2.5µm were produced, demonstrating that the regimes identified through modeling are realistic and that the predicted operational bandwidths within these regimes closely match those experimentally measured in real fibres. 7 AmezcuaCorrea, R, Broderick, NGB, Petrovich, MN, Poletti, F, Richardson, DJ, Finazzi, V and Monro, TM, 2006, Proc OFC, paper OFC1 Acknowledgements The work reported in this paper was funded by the ElectroMagnetic Remote Sensing (EMRS) Defence Technology Centre, established by the UK Ministry of Defence and run by a consortium of SELEX Sensors & Airborne Systems, Thales Defence, Roke Manor Research and Filtronic. R.A.C. thanks the Mexican Council for Science and Technology for support. References 1 Cregan, R.F., Mangan, B.J., Knight, J.C., Birks, T.A., Russell, P.St.J., Roberts, P.J. and Allan, D.C., 1999, Science 285, Russell, P.St.J., Science 299, 2003, Brandon Shaw, L., Sanghera, J.S., Aggarwal, I.D. and Kung, F.H., 2003, Optics Express 11(25), Mortensen, N.A., Nielsen, M.D., Opt. Lett. 29(4), Smith, C.M., Venkataraman, N., Gallagher, M.T., Muller, D., West, J.A., Borrelli, NF, Allan, DC and Koch, KW, Nature 424 (2003) Johnson, SG and Joannopoulos, JD, 2001 Optics Express 8, (3),
GREAT interest has recently been shown for photonic
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 22, NO. 1, JANUARY 2004 11 Air-Guiding Photonic Bandgap Fibers: Spectral Properties, Macrobending Loss, and Practical Handling Theis P. Hansen, Jes Broeng, Christian
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 22, NO. 1, JANUARY 2004 11 Air-Guiding Photonic Bandgap Fibers: Spectral Properties, Macrobending Loss, and Practical Handling Theis P. Hansen, Jes Broeng, Christian
Splice losses in holey optical fibers
 Splice losses in holey optical fibers J.T. Lizier and G.E. Town School of Electrical and Information Engineering (J03), University of Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia. Tel: +612-9351-2110, Fax: +612-9351-3847,
Splice losses in holey optical fibers J.T. Lizier and G.E. Town School of Electrical and Information Engineering (J03), University of Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia. Tel: +612-9351-2110, Fax: +612-9351-3847,
On-chip Si-based Bragg cladding waveguide with high index contrast bilayers
 On-chip Si-based Bragg cladding waveguide with high index contrast bilayers Yasha Yi, Shoji Akiyama, Peter Bermel, Xiaoman Duan, and L. C. Kimerling Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts
On-chip Si-based Bragg cladding waveguide with high index contrast bilayers Yasha Yi, Shoji Akiyama, Peter Bermel, Xiaoman Duan, and L. C. Kimerling Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77 Massachusetts
New possibilities with hollow core antiresonant fibers
 1 New possibilities with hollow core antiresonant fibers Walter Belardi Optoelectronics Research Centre, University of Southampton, Southampton, SO17 1BJ, UK w.belardi@soton.ac.uk Abstract Hollow core
1 New possibilities with hollow core antiresonant fibers Walter Belardi Optoelectronics Research Centre, University of Southampton, Southampton, SO17 1BJ, UK w.belardi@soton.ac.uk Abstract Hollow core
Title. Author(s)Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanori. CitationOptics Letters, 31(1): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type.
 Title Polarization-independent optical directional coupler Author(s)Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Letters, 31(1): 56-58 Issue Date 2006 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/948 Rights
Title Polarization-independent optical directional coupler Author(s)Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Letters, 31(1): 56-58 Issue Date 2006 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/948 Rights
Keywords: Photonic crystal fibers (PCFs), Chromatic dispersion, Confinement losses, SVEI Method. Linear waveguide.
 Volume 3, Issue 11, November 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Analysis of
Volume 3, Issue 11, November 2013 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Analysis of
CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING
 CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING Siti Aisyah bt. Ibrahim and Chong Wu Yi Photonics Research Center Department of Physics,
CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING Siti Aisyah bt. Ibrahim and Chong Wu Yi Photonics Research Center Department of Physics,
Photonic crystal distributed feedback fiber lasers with Bragg gratings Søndergaard, Thomas
 Aalborg Universitet Photonic crystal distributed feedback fiber lasers with Bragg gratings Søndergaard, Thomas Published in: Journal of Lightwave Technology DOI (link to publication from Publisher): 10.1109/50.838134
Aalborg Universitet Photonic crystal distributed feedback fiber lasers with Bragg gratings Søndergaard, Thomas Published in: Journal of Lightwave Technology DOI (link to publication from Publisher): 10.1109/50.838134
Antiresonant Hollow Core Fiber with an Octave Spanning Bandwidth for Short Haul Data Communications
 > REPLACE THIS LINE WITH YOUR PAPER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (DOUBLE-CLICK HERE TO EDIT) < 1 Antiresonant Hollow Core Fiber with an Octave Spanning Bandwidth for Short Haul Data Communications J.R. Hayes,
> REPLACE THIS LINE WITH YOUR PAPER IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (DOUBLE-CLICK HERE TO EDIT) < 1 Antiresonant Hollow Core Fiber with an Octave Spanning Bandwidth for Short Haul Data Communications J.R. Hayes,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Silver permittivity used in the simulations Silver permittivity values are obtained from Johnson & Christy s experimental data 31 and are fitted with a spline interpolation in order to estimate the permittivity
Silver permittivity used in the simulations Silver permittivity values are obtained from Johnson & Christy s experimental data 31 and are fitted with a spline interpolation in order to estimate the permittivity
Fiber Optic Communication Systems. Unit-05: Types of Fibers. https://sites.google.com/a/faculty.muet.edu.pk/abdullatif
 Unit-05: Types of Fibers https://sites.google.com/a/faculty.muet.edu.pk/abdullatif Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro 1 Optical Fiber Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro
Unit-05: Types of Fibers https://sites.google.com/a/faculty.muet.edu.pk/abdullatif Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro 1 Optical Fiber Department of Telecommunication, MUET UET Jamshoro
Ultra-Compact Photonic Crystal Based Water Temperature Sensor
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 3, 2016: 274 278 Ultra-Compact Photonic Crystal Based Water Temperature Sensor Mahmoud NIKOUFARD *, Masoud KAZEMI ALAMOUTI, and Alireza ADEL Department of Electronics, Faculty
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 3, 2016: 274 278 Ultra-Compact Photonic Crystal Based Water Temperature Sensor Mahmoud NIKOUFARD *, Masoud KAZEMI ALAMOUTI, and Alireza ADEL Department of Electronics, Faculty
Completely Rewrite Industry s Understanding of Transmitting. High Quality Laser Processing Light over Long Distances
 25 April, 2018 Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Completely Rewrite Industry s Understanding of Transmitting High Quality Laser Processing Light over Long Distances
25 April, 2018 Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. Completely Rewrite Industry s Understanding of Transmitting High Quality Laser Processing Light over Long Distances
Bangladesh 1
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 232-3331, Volume 11, Issue 4 Ver. IV (Jul. Aug. 216), PP 19-24 www.iosrjournals.org Characterization of Hexagonal
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 232-3331, Volume 11, Issue 4 Ver. IV (Jul. Aug. 216), PP 19-24 www.iosrjournals.org Characterization of Hexagonal
Two bit optical analog-to-digital converter based on photonic crystals
 Two bit optical analog-to-digital converter based on photonic crystals Binglin Miao, Caihua Chen, Ahmed Sharkway, Shouyuan Shi, and Dennis W. Prather University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 976 binglin@udel.edu
Two bit optical analog-to-digital converter based on photonic crystals Binglin Miao, Caihua Chen, Ahmed Sharkway, Shouyuan Shi, and Dennis W. Prather University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 976 binglin@udel.edu
Fiber-Optic Polarizer Using Resonant Tunneling through a Multilayer Overlay
 Fiber-Optic Polarizer Using Resonant Tunneling through a Multilayer Overlay Arun Kumar, Rajeev Jindal, and R. K. Varshney Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi 110 016 India
Fiber-Optic Polarizer Using Resonant Tunneling through a Multilayer Overlay Arun Kumar, Rajeev Jindal, and R. K. Varshney Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi 110 016 India
Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors
 846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 12, Number 3, 2009, 308 316 Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals Daniela DRAGOMAN 1, Adrian DINESCU 2, Raluca MÜLLER2, Cristian KUSKO 2, Alex.
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 12, Number 3, 2009, 308 316 Waveguiding in PMMA photonic crystals Daniela DRAGOMAN 1, Adrian DINESCU 2, Raluca MÜLLER2, Cristian KUSKO 2, Alex.
Visible to infrared high-speed WDM transmission over PCF
 Visible to infrared high-speed WDM transmission over PCF Koji Ieda a), Kenji Kurokawa, Katsusuke Tajima, and Kazuhide Nakajima NTT Access Network Service Systems Laboratories, NTT Corporation, 1 7 1 Hanabatake,
Visible to infrared high-speed WDM transmission over PCF Koji Ieda a), Kenji Kurokawa, Katsusuke Tajima, and Kazuhide Nakajima NTT Access Network Service Systems Laboratories, NTT Corporation, 1 7 1 Hanabatake,
Title. Author(s)Saitoh, Fumiya; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori. CitationOptics Express, 18(5): Issue Date Doc URL.
 Title A design method of a fiber-based mode multi/demultip Author(s)Saitoh, Fumiya; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Express, 18(5): 4709-4716 Issue Date 2010-03-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/46825
Title A design method of a fiber-based mode multi/demultip Author(s)Saitoh, Fumiya; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Express, 18(5): 4709-4716 Issue Date 2010-03-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/46825
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter
 Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression
 Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
10 Gb/s transmission over 5 km at 850 nm using single-mode photonic crystal fiber, single-mode VCSEL, and Si-APD
 10 Gb/s transmission over 5 km at 850 nm using single-mode photonic crystal fiber, single-mode VCSEL, and Si-APD Hideaki Hasegawa a), Yosuke Oikawa, Masato Yoshida, Toshihiko Hirooka, and Masataka Nakazawa
10 Gb/s transmission over 5 km at 850 nm using single-mode photonic crystal fiber, single-mode VCSEL, and Si-APD Hideaki Hasegawa a), Yosuke Oikawa, Masato Yoshida, Toshihiko Hirooka, and Masataka Nakazawa
Design, Simulation & Optimization of 2D Photonic Crystal Power Splitter
 Optics and Photonics Journal, 2013, 3, 13-19 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/opj.2013.32a002 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/opj) Design, Simulation & Optimization of 2D Photonic Crystal
Optics and Photonics Journal, 2013, 3, 13-19 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/opj.2013.32a002 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/opj) Design, Simulation & Optimization of 2D Photonic Crystal
Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices
 644 Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices Kin Seng Chiang,* Sin Yip Cheng, Hau Ping Chan, Qing Liu, Kar Pong Lor, and Chi Kin Chow Department of Electronic Engineering,
644 Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices Kin Seng Chiang,* Sin Yip Cheng, Hau Ping Chan, Qing Liu, Kar Pong Lor, and Chi Kin Chow Department of Electronic Engineering,
UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS
 UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS The Signal Transmitting through the fiber is degraded by two mechanisms. i) Attenuation ii) Dispersion Both are important to determine the transmission characteristics
UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS The Signal Transmitting through the fiber is degraded by two mechanisms. i) Attenuation ii) Dispersion Both are important to determine the transmission characteristics
Higher-order mode suppression in chalcogenide negative curvature fibers
 Higher-order mode suppression in chalcogenide negative curvature fibers Chengli Wei, 1 Robinson A. Kuis, 2 Francois Chenard, 3 Curtis R. Menyuk, 2 and Jonathan Hu 1, 1 Baylor University, One Bear Place
Higher-order mode suppression in chalcogenide negative curvature fibers Chengli Wei, 1 Robinson A. Kuis, 2 Francois Chenard, 3 Curtis R. Menyuk, 2 and Jonathan Hu 1, 1 Baylor University, One Bear Place
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information "Large-scale integration of wavelength-addressable all-optical memories in a photonic crystal chip" SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Eiichi Kuramochi*, Kengo Nozaki, Akihiko Shinya,
Supplementary Information "Large-scale integration of wavelength-addressable all-optical memories in a photonic crystal chip" SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Eiichi Kuramochi*, Kengo Nozaki, Akihiko Shinya,
Optical properties of small-bore hollow glass waveguides
 Optical properties of small-bore hollow glass waveguides Yuji Matsuura, Todd Abel, and James. A. Harrington Hollow glass waveguides with a 250-µm i.d. have been fabricated with a liquid-phase deposition
Optical properties of small-bore hollow glass waveguides Yuji Matsuura, Todd Abel, and James. A. Harrington Hollow glass waveguides with a 250-µm i.d. have been fabricated with a liquid-phase deposition
Enhanced bandwidth of supercontinuum generated in microstructured fibers
 Enhanced bandwidth of supercontinuum generated in microstructured fibers G. Genty, M. Lehtonen, and H. Ludvigsen Fiber-Optics Group, Department of Electrical and Communications Engineering, Helsinki University
Enhanced bandwidth of supercontinuum generated in microstructured fibers G. Genty, M. Lehtonen, and H. Ludvigsen Fiber-Optics Group, Department of Electrical and Communications Engineering, Helsinki University
Implementation of Orthogonal Frequency Coded SAW Devices Using Apodized Reflectors
 Implementation of Orthogonal Frequency Coded SAW Devices Using Apodized Reflectors Derek Puccio, Don Malocha, Nancy Saldanha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Central Florida
Implementation of Orthogonal Frequency Coded SAW Devices Using Apodized Reflectors Derek Puccio, Don Malocha, Nancy Saldanha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Central Florida
CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
 43 CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This work begins with design of reflectarrays with conventional patches as unit cells for operation at Ku Band in
43 CHAPTER 2 MICROSTRIP REFLECTARRAY ANTENNA AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION 2.1 INTRODUCTION This work begins with design of reflectarrays with conventional patches as unit cells for operation at Ku Band in
Waveguide Bragg Gratings and Resonators LUMERICAL SOLUTIONS INC
 Waveguide Bragg Gratings and Resonators JUNE 2016 1 Outline Introduction Waveguide Bragg gratings Background Simulation challenges and solutions Photolithography simulation Initial design with FDTD Band
Waveguide Bragg Gratings and Resonators JUNE 2016 1 Outline Introduction Waveguide Bragg gratings Background Simulation challenges and solutions Photolithography simulation Initial design with FDTD Band
Differential Mode Group Delay (DMGD) in Few Mode Fibers (FMF)
 Differential Mode Group Delay (DMGD) in Few Mode Fibers (FMF) Microwave Interferometric Technique for Characterizing Few Mode Fibers Abstract We propose and experimentally demonstrate a simple and accurate
Differential Mode Group Delay (DMGD) in Few Mode Fibers (FMF) Microwave Interferometric Technique for Characterizing Few Mode Fibers Abstract We propose and experimentally demonstrate a simple and accurate
Wavelength-independent coupler from fiber to an on-chip cavity, demonstrated over an 850nm span
 Wavelength-independent coupler from fiber to an on-chip, demonstrated over an 85nm span Tal Carmon, Steven Y. T. Wang, Eric P. Ostby and Kerry J. Vahala. Thomas J. Watson Laboratory of Applied Physics,
Wavelength-independent coupler from fiber to an on-chip, demonstrated over an 85nm span Tal Carmon, Steven Y. T. Wang, Eric P. Ostby and Kerry J. Vahala. Thomas J. Watson Laboratory of Applied Physics,
Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating. Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel
 Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel Zhijun Yan *, Pouneh Saffari, Kaiming Zhou, Adedotun Adebay, Lin Zhang Photonic Research Group, Aston
Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel Zhijun Yan *, Pouneh Saffari, Kaiming Zhou, Adedotun Adebay, Lin Zhang Photonic Research Group, Aston
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin
 Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
Multi-mode to single-mode conversion in a 61 port photonic lantern
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 13, 2018 Multi-mode to single-mode conversion in a 61 port photonic lantern Noordegraaf, Danny; Skovgaard, Peter M.W.; Maack, Martin D.; Bland-Hawthorn, Joss; Lægsgaard,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 13, 2018 Multi-mode to single-mode conversion in a 61 port photonic lantern Noordegraaf, Danny; Skovgaard, Peter M.W.; Maack, Martin D.; Bland-Hawthorn, Joss; Lægsgaard,
C. J. S. de Matos and J. R. Taylor. Femtosecond Optics Group, Imperial College, Prince Consort Road, London SW7 2BW, UK
 Multi-kilowatt, all-fiber integrated chirped-pulse amplification system yielding 4 pulse compression using air-core fiber and conventional erbium-doped fiber amplifier C. J. S. de Matos and J. R. Taylor
Multi-kilowatt, all-fiber integrated chirped-pulse amplification system yielding 4 pulse compression using air-core fiber and conventional erbium-doped fiber amplifier C. J. S. de Matos and J. R. Taylor
A new design of a 4-channel optical demultiplexer based on photonic crystal ring resonator using a modified Y-branch
 Optica Applicata, Vol. XLVIII, No. 2, 2018 DOI: 10.5277/oa180203 A new design of a 4-channel optical demultiplexer based on photonic crystal ring resonator using a modified Y-branch VAHID FALLAHI, MAHMOOD
Optica Applicata, Vol. XLVIII, No. 2, 2018 DOI: 10.5277/oa180203 A new design of a 4-channel optical demultiplexer based on photonic crystal ring resonator using a modified Y-branch VAHID FALLAHI, MAHMOOD
Cavity QED with quantum dots in semiconductor microcavities
 Cavity QED with quantum dots in semiconductor microcavities M. T. Rakher*, S. Strauf, Y. Choi, N.G. Stolz, K.J. Hennessey, H. Kim, A. Badolato, L.A. Coldren, E.L. Hu, P.M. Petroff, D. Bouwmeester University
Cavity QED with quantum dots in semiconductor microcavities M. T. Rakher*, S. Strauf, Y. Choi, N.G. Stolz, K.J. Hennessey, H. Kim, A. Badolato, L.A. Coldren, E.L. Hu, P.M. Petroff, D. Bouwmeester University
Dispersion measurement in optical fibres over the entire spectral range from 1.1 mm to 1.7 mm
 15 February 2000 Ž. Optics Communications 175 2000 209 213 www.elsevier.comrlocateroptcom Dispersion measurement in optical fibres over the entire spectral range from 1.1 mm to 1.7 mm F. Koch ), S.V. Chernikov,
15 February 2000 Ž. Optics Communications 175 2000 209 213 www.elsevier.comrlocateroptcom Dispersion measurement in optical fibres over the entire spectral range from 1.1 mm to 1.7 mm F. Koch ), S.V. Chernikov,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:0.038/nature727 Table of Contents S. Power and Phase Management in the Nanophotonic Phased Array 3 S.2 Nanoantenna Design 6 S.3 Synthesis of Large-Scale Nanophotonic Phased
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:0.038/nature727 Table of Contents S. Power and Phase Management in the Nanophotonic Phased Array 3 S.2 Nanoantenna Design 6 S.3 Synthesis of Large-Scale Nanophotonic Phased
Nanoscale effects on multichannel add/drop filter based on 2-D photonic crystal ring-resonator heterostructure
 Pezeshki and Ahmadi Journal of Theoretical and Applied Physics 2012, 6:12 RESEARCH Open Access Nanoscale effects on multichannel add/drop filter based on 2-D photonic crystal ring-resonator heterostructure
Pezeshki and Ahmadi Journal of Theoretical and Applied Physics 2012, 6:12 RESEARCH Open Access Nanoscale effects on multichannel add/drop filter based on 2-D photonic crystal ring-resonator heterostructure
Low-loss single-mode hollow-core fiber with anisotropic anti-resonant elements
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 06, 2018 Low-loss single-mode hollow-core fiber with anisotropic anti-resonant elements Habib, Selim; Bang, Ole; Bache, Morten Published in: Optics Express Link to
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 06, 2018 Low-loss single-mode hollow-core fiber with anisotropic anti-resonant elements Habib, Selim; Bang, Ole; Bache, Morten Published in: Optics Express Link to
First Observation of Stimulated Coherent Transition Radiation
 SLAC 95 6913 June 1995 First Observation of Stimulated Coherent Transition Radiation Hung-chi Lihn, Pamela Kung, Chitrlada Settakorn, and Helmut Wiedemann Applied Physics Department and Stanford Linear
SLAC 95 6913 June 1995 First Observation of Stimulated Coherent Transition Radiation Hung-chi Lihn, Pamela Kung, Chitrlada Settakorn, and Helmut Wiedemann Applied Physics Department and Stanford Linear
Impact of Cladding Tubes in Chalcogenide Negative Curvature Fibers
 Impact of Cladding Tubes in Chalcogenide Negative Curvature Fibers Volume 8, Number 3, June 2016 Chengli Wei Curtis R. Menyuk Jonathan Hu DOI: 10.1109/JPHOT.2016.2577711 1943-0655 Ó 2016 IEEE Impact of
Impact of Cladding Tubes in Chalcogenide Negative Curvature Fibers Volume 8, Number 3, June 2016 Chengli Wei Curtis R. Menyuk Jonathan Hu DOI: 10.1109/JPHOT.2016.2577711 1943-0655 Ó 2016 IEEE Impact of
Index. Cambridge University Press Silicon Photonics Design Lukas Chrostowski and Michael Hochberg. Index.
 absorption, 69 active tuning, 234 alignment, 394 396 apodization, 164 applications, 7 automated optical probe station, 389 397 avalanche detector, 268 back reflection, 164 band structures, 30 bandwidth
absorption, 69 active tuning, 234 alignment, 394 396 apodization, 164 applications, 7 automated optical probe station, 389 397 avalanche detector, 268 back reflection, 164 band structures, 30 bandwidth
Tunable Color Filters Based on Metal-Insulator-Metal Resonators
 Chapter 6 Tunable Color Filters Based on Metal-Insulator-Metal Resonators 6.1 Introduction In this chapter, we discuss the culmination of Chapters 3, 4, and 5. We report a method for filtering white light
Chapter 6 Tunable Color Filters Based on Metal-Insulator-Metal Resonators 6.1 Introduction In this chapter, we discuss the culmination of Chapters 3, 4, and 5. We report a method for filtering white light
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 77. Table of Contents 1
 Efficient single photon detection from 500 nm to 5 μm wavelength: Supporting Information F. Marsili 1, F. Bellei 1, F. Najafi 1, A. E. Dane 1, E. A. Dauler 2, R. J. Molnar 2, K. K. Berggren 1* 1 Department
Efficient single photon detection from 500 nm to 5 μm wavelength: Supporting Information F. Marsili 1, F. Bellei 1, F. Najafi 1, A. E. Dane 1, E. A. Dauler 2, R. J. Molnar 2, K. K. Berggren 1* 1 Department
TAPERED MEANDER SLOT ANTENNA FOR DUAL BAND PERSONAL WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 are closer to grazing, where 50. However, once the spectral current distribution is windowed, and the level of the edge singularity is reduced by this process, the computed RCS shows a much better agreement
are closer to grazing, where 50. However, once the spectral current distribution is windowed, and the level of the edge singularity is reduced by this process, the computed RCS shows a much better agreement
Horizontal single and multiple slot waveguides: optical transmission at λ = 1550 nm
 Horizontal single and multiple slot waveguides: optical transmission at λ = 1550 nm Rong Sun 1 *, Po Dong 2 *, Ning-ning Feng 1, Ching-yin Hong 1, Jurgen Michel 1, Michal Lipson 2, Lionel Kimerling 1 1Department
Horizontal single and multiple slot waveguides: optical transmission at λ = 1550 nm Rong Sun 1 *, Po Dong 2 *, Ning-ning Feng 1, Ching-yin Hong 1, Jurgen Michel 1, Michal Lipson 2, Lionel Kimerling 1 1Department
Lectureo5 FIBRE OPTICS. Unit-03
 Lectureo5 FIBRE OPTICS Unit-03 INTRODUCTION FUNDAMENTAL IDEAS ABOUT OPTICAL FIBRE Multimode Fibres Multimode Step Index Fibres Multimode Graded Index Fibres INTRODUCTION In communication systems, there
Lectureo5 FIBRE OPTICS Unit-03 INTRODUCTION FUNDAMENTAL IDEAS ABOUT OPTICAL FIBRE Multimode Fibres Multimode Step Index Fibres Multimode Graded Index Fibres INTRODUCTION In communication systems, there
Ultracompact and low power optical switch based on silicon. photonic crystals
 Ultracompact and low power optical switch based on silicon photonic crystals Daryl M. Beggs 1, *, Thomas P. White 1, Liam O Faolain 1 and Thomas F. Krauss 1 1 School of Physics and Astronomy, University
Ultracompact and low power optical switch based on silicon photonic crystals Daryl M. Beggs 1, *, Thomas P. White 1, Liam O Faolain 1 and Thomas F. Krauss 1 1 School of Physics and Astronomy, University
Section B Lecture 5 FIBER CHARACTERISTICS
 Section B Lecture 5 FIBER CHARACTERISTICS Material absorption Losses Material absorption is a loss mechanism related to material composition and fabrication process for the fiber. This results in dissipation
Section B Lecture 5 FIBER CHARACTERISTICS Material absorption Losses Material absorption is a loss mechanism related to material composition and fabrication process for the fiber. This results in dissipation
2D silicon-based surface-normal vertical cavity photonic crystal waveguide array for high-density optical interconnects
 2D silicon-based surface-normal vertical cavity photonic crystal waveguide array for high-density optical interconnects JaeHyun Ahn a, Harish Subbaraman b, Liang Zhu a, Swapnajit Chakravarty b, Emanuel
2D silicon-based surface-normal vertical cavity photonic crystal waveguide array for high-density optical interconnects JaeHyun Ahn a, Harish Subbaraman b, Liang Zhu a, Swapnajit Chakravarty b, Emanuel
HIGH-EFFICIENCY MQW ELECTROABSORPTION MODULATORS
 HIGH-EFFICIENCY MQW ELECTROABSORPTION MODULATORS J. Piprek, Y.-J. Chiu, S.-Z. Zhang (1), J. E. Bowers, C. Prott (2), and H. Hillmer (2) University of California, ECE Department, Santa Barbara, CA 93106
HIGH-EFFICIENCY MQW ELECTROABSORPTION MODULATORS J. Piprek, Y.-J. Chiu, S.-Z. Zhang (1), J. E. Bowers, C. Prott (2), and H. Hillmer (2) University of California, ECE Department, Santa Barbara, CA 93106
Optically reconfigurable balanced dipole antenna
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Optically reconfigurable balanced dipole antenna This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation:
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Optically reconfigurable balanced dipole antenna This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation:
Compact hybrid TM-pass polarizer for silicon-on-insulator platform
 Compact hybrid TM-pass polarizer for silicon-on-insulator platform Muhammad Alam,* J. Stewart Aitchsion, and Mohammad Mojahedi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto,
Compact hybrid TM-pass polarizer for silicon-on-insulator platform Muhammad Alam,* J. Stewart Aitchsion, and Mohammad Mojahedi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto,
Plane wave excitation by taper array for optical leaky waveguide antenna
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.15, No.2, 1 6 Plane wave excitation by taper array for optical leaky waveguide antenna Hiroshi Hashiguchi a), Toshihiko Baba, and Hiroyuki Arai Graduate School of
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.15, No.2, 1 6 Plane wave excitation by taper array for optical leaky waveguide antenna Hiroshi Hashiguchi a), Toshihiko Baba, and Hiroyuki Arai Graduate School of
ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES
 ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN: 1995-0772 Published BYAENSI Publication EISSN: 1998-1090 http://www.aensiweb.com/anas 2017 June 11(8): pages 639-644 Open Access Journal Design And Implementation
ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN: 1995-0772 Published BYAENSI Publication EISSN: 1998-1090 http://www.aensiweb.com/anas 2017 June 11(8): pages 639-644 Open Access Journal Design And Implementation
Measuring bend losses in large-mode-area fibers
 Measuring bend losses in large-mode-area fibers Changgeng Ye,* Joona Koponen, Ville Aallos, Teemu Kokki, Laeticia Petit, Ossi Kimmelma nlght Corporation, Sorronrinne 9, 08500 Lohja, Finland ABSTRACT We
Measuring bend losses in large-mode-area fibers Changgeng Ye,* Joona Koponen, Ville Aallos, Teemu Kokki, Laeticia Petit, Ossi Kimmelma nlght Corporation, Sorronrinne 9, 08500 Lohja, Finland ABSTRACT We
Photonic Crystal Fiber Polarization Filter Based on Surface Plasmon Polaritons
 DOI 10.1007/s11468-015-0026-z Photonic Crystal Fiber Polarization Filter Based on Surface Plasmon Polaritons Jianchen Zi 1 & Shuguang Li 1 & Hailiang Chen 1 & Jianshe Li 1 & Hui Li 1 Received: 14 April
DOI 10.1007/s11468-015-0026-z Photonic Crystal Fiber Polarization Filter Based on Surface Plasmon Polaritons Jianchen Zi 1 & Shuguang Li 1 & Hailiang Chen 1 & Jianshe Li 1 & Hui Li 1 Received: 14 April
Designing an ultra negative dispersion Photonic Crystal Fiber (PCFs) with square lattice geometry
 Designing an ultra negative dispersion Photonic Crystal Fiber (PCFs) with square lattice geometry Partha Sona Maji and Partha Roy Chaudhuri Department of Physics & Meteorology, Indian Institute of Technology
Designing an ultra negative dispersion Photonic Crystal Fiber (PCFs) with square lattice geometry Partha Sona Maji and Partha Roy Chaudhuri Department of Physics & Meteorology, Indian Institute of Technology
Luminous Equivalent of Radiation
 Intensity vs λ Luminous Equivalent of Radiation When the spectral power (p(λ) for GaP-ZnO diode has a peak at 0.69µm) is combined with the eye-sensitivity curve a peak response at 0.65µm is obtained with
Intensity vs λ Luminous Equivalent of Radiation When the spectral power (p(λ) for GaP-ZnO diode has a peak at 0.69µm) is combined with the eye-sensitivity curve a peak response at 0.65µm is obtained with
H.-W. Wu Department of Computer and Communication Kun Shan University No. 949, Dawan Road, Yongkang City, Tainan County 710, Taiwan
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 107, 21 30, 2010 COMPACT MICROSTRIP BANDPASS FILTER WITH MULTISPURIOUS SUPPRESSION H.-W. Wu Department of Computer and Communication Kun Shan University No.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 107, 21 30, 2010 COMPACT MICROSTRIP BANDPASS FILTER WITH MULTISPURIOUS SUPPRESSION H.-W. Wu Department of Computer and Communication Kun Shan University No.
Photonic Crystal Slot Waveguide Spectrometer for Detection of Methane
 Photonic Crystal Slot Waveguide Spectrometer for Detection of Methane Swapnajit Chakravarty 1, Wei-Cheng Lai 2, Xiaolong (Alan) Wang 1, Che-Yun Lin 2, Ray T. Chen 1,2 1 Omega Optics, 10306 Sausalito Drive,
Photonic Crystal Slot Waveguide Spectrometer for Detection of Methane Swapnajit Chakravarty 1, Wei-Cheng Lai 2, Xiaolong (Alan) Wang 1, Che-Yun Lin 2, Ray T. Chen 1,2 1 Omega Optics, 10306 Sausalito Drive,
High-power All-Fiber components: The missing link for high power fiber lasers
 High- All-Fiber components: The missing link for high lasers François Gonthier, Lilian Martineau, Nawfel Azami, Mathieu Faucher, François Séguin, Damien Stryckman, Alain Villeneuve ITF Optical Technologies
High- All-Fiber components: The missing link for high lasers François Gonthier, Lilian Martineau, Nawfel Azami, Mathieu Faucher, François Séguin, Damien Stryckman, Alain Villeneuve ITF Optical Technologies
Two compact structures for perpendicular coupling of optical signals between dielectric and photonic crystal waveguides
 Two compact structures for perpendicular coupling of optical signals between dielectric and photonic crystal waveguides Michael E. Potter Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of
Two compact structures for perpendicular coupling of optical signals between dielectric and photonic crystal waveguides Michael E. Potter Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of
Integrated Photonics based on Planar Holographic Bragg Reflectors
 Integrated Photonics based on Planar Holographic Bragg Reflectors C. Greiner *, D. Iazikov and T. W. Mossberg LightSmyth Technologies, Inc., 86 W. Park St., Ste 25, Eugene, OR 9741 ABSTRACT Integrated
Integrated Photonics based on Planar Holographic Bragg Reflectors C. Greiner *, D. Iazikov and T. W. Mossberg LightSmyth Technologies, Inc., 86 W. Park St., Ste 25, Eugene, OR 9741 ABSTRACT Integrated
Chapter Ray and Wave Optics
 109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology. April 11, Name: Student ID number: OCT1 1: OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade:
 Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Industrial Automation
 OPTICAL FIBER. SINGLEMODE OR MULTIMODE It is important to understand the differences between singlemode and multimode fiber optics before selecting one or the other at the start of a project. Its different
OPTICAL FIBER. SINGLEMODE OR MULTIMODE It is important to understand the differences between singlemode and multimode fiber optics before selecting one or the other at the start of a project. Its different
Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings
 Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu Optical Engineering 52(9), 091708 (September 2013) Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu
Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu Optical Engineering 52(9), 091708 (September 2013) Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu
ISSN: [Akther* et al., 6(11): November, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116
![ISSN: [Akther* et al., 6(11): November, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116 ISSN: [Akther* et al., 6(11): November, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116](/thumbs/82/85804846.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY DESIGN OF A WIDEBAND 1 2 Y-BRANCH OPTICAL BEAM SPLITTER USING GaAs BASED PHOTONIC CRYSTAL Md. Shoaib Akther 1, Md. Rupam Khandkar
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY DESIGN OF A WIDEBAND 1 2 Y-BRANCH OPTICAL BEAM SPLITTER USING GaAs BASED PHOTONIC CRYSTAL Md. Shoaib Akther 1, Md. Rupam Khandkar
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Design and fabrication of indium phosphide air-bridge waveguides with MEMS functionality
 Design and fabrication of indium phosphide air-bridge waveguides with MEMS functionality Wing H. Ng* a, Nina Podoliak b, Peter Horak b, Jiang Wu a, Huiyun Liu a, William J. Stewart b, and Anthony J. Kenyon
Design and fabrication of indium phosphide air-bridge waveguides with MEMS functionality Wing H. Ng* a, Nina Podoliak b, Peter Horak b, Jiang Wu a, Huiyun Liu a, William J. Stewart b, and Anthony J. Kenyon
Intra-cavity active optics in lasers
 Intra-cavity active optics in lasers W. Lubeigt, A. Kelly, V. Savitsky, D. Burns Institute of Photonics, University of Strathclyde Wolfson Centre,106 Rottenrow Glasgow G4 0NW, UK J. Gomes, G. Brown, D.
Intra-cavity active optics in lasers W. Lubeigt, A. Kelly, V. Savitsky, D. Burns Institute of Photonics, University of Strathclyde Wolfson Centre,106 Rottenrow Glasgow G4 0NW, UK J. Gomes, G. Brown, D.
Supporting Information: Achromatic Metalens over 60 nm Bandwidth in the Visible and Metalens with Reverse Chromatic Dispersion
 Supporting Information: Achromatic Metalens over 60 nm Bandwidth in the Visible and Metalens with Reverse Chromatic Dispersion M. Khorasaninejad 1*, Z. Shi 2*, A. Y. Zhu 1, W. T. Chen 1, V. Sanjeev 1,3,
Supporting Information: Achromatic Metalens over 60 nm Bandwidth in the Visible and Metalens with Reverse Chromatic Dispersion M. Khorasaninejad 1*, Z. Shi 2*, A. Y. Zhu 1, W. T. Chen 1, V. Sanjeev 1,3,
Supplementary information to Nature article: Wavelength-scalable hollow optical fibres with large photonic band gaps for CO 2 laser transmission
 Supplementary information to Nature article: Wavelength-scalable hollow optical fibres with large photonic band gaps for CO 2 laser transmission I. Modal characteristics of CO 2 laser guiding fibres Due
Supplementary information to Nature article: Wavelength-scalable hollow optical fibres with large photonic band gaps for CO 2 laser transmission I. Modal characteristics of CO 2 laser guiding fibres Due
Effects of Two Dimensional Electromagnetic Bandgap (EBG) Structures on the Performance of Microstrip Patch Antenna Arrays
 Effects of Two Dimensional Electromagnetic Bandgap (EBG) Structures on the Performance of Microstrip Patch Antenna Arrays Mr. F. Benikhlef 1 and Mr. N. Boukli-Hacen 2 1 Research Scholar, telecommunication,
Effects of Two Dimensional Electromagnetic Bandgap (EBG) Structures on the Performance of Microstrip Patch Antenna Arrays Mr. F. Benikhlef 1 and Mr. N. Boukli-Hacen 2 1 Research Scholar, telecommunication,
An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm
 An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm Ma Yangwu *, Liang Di ** Center for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Lab of Modern Optical
An Optical Characteristic Testing System for the Infrared Fiber in a Transmission Bandwidth 9-11μm Ma Yangwu *, Liang Di ** Center for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Lab of Modern Optical
Supercontinuum and four-wave mixing with Q-switched pulses in endlessly single-mode photonic crystal fibres
 Supercontinuum and four-wave mixing with Q-switched pulses in endlessly single-mode photonic crystal fibres W. J. Wadsworth, N. Joly, J. C. Knight, T. A. Birks, F. Biancalana, P. St. J. Russell Optoelectronics
Supercontinuum and four-wave mixing with Q-switched pulses in endlessly single-mode photonic crystal fibres W. J. Wadsworth, N. Joly, J. C. Knight, T. A. Birks, F. Biancalana, P. St. J. Russell Optoelectronics
Diamond X-ray Rocking Curve and Topograph Measurements at CHESS
 Diamond X-ray Rocking Curve and Topograph Measurements at CHESS G. Yang 1, R.T. Jones 2, F. Klein 3 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK G12 8QQ. 2 University of Connecticut
Diamond X-ray Rocking Curve and Topograph Measurements at CHESS G. Yang 1, R.T. Jones 2, F. Klein 3 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK G12 8QQ. 2 University of Connecticut
Fiber Optic Communications Communication Systems
 INTRODUCTION TO FIBER-OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS A fiber-optic system is similar to the copper wire system in many respects. The difference is that fiber-optics use light pulses to transmit information down
INTRODUCTION TO FIBER-OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS A fiber-optic system is similar to the copper wire system in many respects. The difference is that fiber-optics use light pulses to transmit information down
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 25 Aug 2003
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 25 Aug 2003 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.optics] 25 Aug 2003](/thumbs/84/90868967.jpg) arxiv:physics/0308087v1 [physics.optics] 25 Aug 2003 Multi-mode photonic crystal fibers for VCSEL based data transmission N. A. Mortensen, 1 M. Stach, 2 J. Broeng, 1 A. Petersson, 1 H. R. Simonsen, 1 and
arxiv:physics/0308087v1 [physics.optics] 25 Aug 2003 Multi-mode photonic crystal fibers for VCSEL based data transmission N. A. Mortensen, 1 M. Stach, 2 J. Broeng, 1 A. Petersson, 1 H. R. Simonsen, 1 and
 Chapter 5 5.1 What are the factors that determine the thickness of a polystyrene waveguide formed by spinning a solution of dissolved polystyrene onto a substrate? density of polymer concentration of polymer
Chapter 5 5.1 What are the factors that determine the thickness of a polystyrene waveguide formed by spinning a solution of dissolved polystyrene onto a substrate? density of polymer concentration of polymer
Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide
 Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide Hwee-Gee Teo, 1 Ming-Bin Yu, 1 Guo-Qiang Lo, 1 Kazuhiro Goi, 2 Ken Sakuma, 2 Kensuke Ogawa, 2 Ning Guan, 2 and Yong-Tsong Tan 2 Silicon photonics
Silicon Photonic Device Based on Bragg Grating Waveguide Hwee-Gee Teo, 1 Ming-Bin Yu, 1 Guo-Qiang Lo, 1 Kazuhiro Goi, 2 Ken Sakuma, 2 Kensuke Ogawa, 2 Ning Guan, 2 and Yong-Tsong Tan 2 Silicon photonics
Session 2: Silicon and Carbon Photonics (11:00 11:30, Huxley LT311)
 Session 2: Silicon and Carbon Photonics (11:00 11:30, Huxley LT311) (invited) Formation and control of silicon nanocrystals by ion-beams for photonic applications M Halsall The University of Manchester,
Session 2: Silicon and Carbon Photonics (11:00 11:30, Huxley LT311) (invited) Formation and control of silicon nanocrystals by ion-beams for photonic applications M Halsall The University of Manchester,
Supplementary Figure 1. Pump linewidth for different input power at a pressure of 20 bar and fibre length of 20 m
 Power = 29 W Power = 16 W Power = 9 W Supplementary Figure 1. Pump linewidth for different input power at a pressure of 20 bar and fibre length of 20 m 20bar Forward Stokes Backward Stokes Transmission
Power = 29 W Power = 16 W Power = 9 W Supplementary Figure 1. Pump linewidth for different input power at a pressure of 20 bar and fibre length of 20 m 20bar Forward Stokes Backward Stokes Transmission
Impact of the light coupling on the sensing properties of photonic crystal cavity modes Kumar Saurav* a,b, Nicolas Le Thomas a,b,
 Impact of the light coupling on the sensing properties of photonic crystal cavity modes Kumar Saurav* a,b, Nicolas Le Thomas a,b, a Photonics Research Group, Ghent University-imec, Technologiepark-Zwijnaarde
Impact of the light coupling on the sensing properties of photonic crystal cavity modes Kumar Saurav* a,b, Nicolas Le Thomas a,b, a Photonics Research Group, Ghent University-imec, Technologiepark-Zwijnaarde
Absorption: in an OF, the loss of Optical power, resulting from conversion of that power into heat.
 Absorption: in an OF, the loss of Optical power, resulting from conversion of that power into heat. Scattering: The changes in direction of light confined within an OF, occurring due to imperfection in
Absorption: in an OF, the loss of Optical power, resulting from conversion of that power into heat. Scattering: The changes in direction of light confined within an OF, occurring due to imperfection in
CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY AND SOFTWARE TOOLS
 CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY AND SOFTWARE TOOLS Microstrip Patch Antenna Design In this chapter, the procedure for designing of a rectangular microstrip patch antenna is described. The proposed broadband rectangular
CHAPTER 3 METHODOLOGY AND SOFTWARE TOOLS Microstrip Patch Antenna Design In this chapter, the procedure for designing of a rectangular microstrip patch antenna is described. The proposed broadband rectangular
SELF COLLIMATION IN PILLAR TYPE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL USING COMSOL
 SELF COLLIMATION IN PILLAR TYPE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL USING COMSOL S.Hemalatha 1, K.Shanthalakshmi 2 1 ME Communication Systems Department of ECE Adhiyamaan College Of Engineering, Hosur, India 2 Associate
SELF COLLIMATION IN PILLAR TYPE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL USING COMSOL S.Hemalatha 1, K.Shanthalakshmi 2 1 ME Communication Systems Department of ECE Adhiyamaan College Of Engineering, Hosur, India 2 Associate
Rogério Nogueira Instituto de Telecomunicações Pólo de Aveiro Departamento de Física Universidade de Aveiro
 Fiber Bragg Gratings for DWDM Optical Networks Rogério Nogueira Instituto de Telecomunicações Pólo de Aveiro Departamento de Física Universidade de Aveiro Overview Introduction. Fabrication. Physical properties.
Fiber Bragg Gratings for DWDM Optical Networks Rogério Nogueira Instituto de Telecomunicações Pólo de Aveiro Departamento de Física Universidade de Aveiro Overview Introduction. Fabrication. Physical properties.
Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: Signature:
 Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: PID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. TWO 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: PID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. TWO 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
A COMPACT DEFECTED GROUND MICROSTRIP DEVICE WITH PHOTONIC BANDGAP EFFECTS
 J. of Electromagn. Waves and Appl., Vol. 23, 255 266, 29 A COMPACT DEFECTED GROUND MICROSTRIP DEVICE WITH PHOTONIC BANDGAP EFFECTS S. K. Gupta and K. J. Vinoy Microwave Laboratory Department of Electrical
J. of Electromagn. Waves and Appl., Vol. 23, 255 266, 29 A COMPACT DEFECTED GROUND MICROSTRIP DEVICE WITH PHOTONIC BANDGAP EFFECTS S. K. Gupta and K. J. Vinoy Microwave Laboratory Department of Electrical
Supplementary Figure 1 Reflective and refractive behaviors of light with normal
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Reflective and refractive behaviors of light with normal incidence in a three layer system. E 1 and E r are the complex amplitudes of the incident wave and
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Reflective and refractive behaviors of light with normal incidence in a three layer system. E 1 and E r are the complex amplitudes of the incident wave and
Ultra-Low-Loss Athermal AWG Module with a Large Number of Channels
 Ultra-Low-Loss Athermal AWG Module with a Large Number of Channels by Junichi Hasegawa * and Kazutaka Nara * There is an urgent need for an arrayed waveguide grating (AWG), the device ABSTRACT that handles
Ultra-Low-Loss Athermal AWG Module with a Large Number of Channels by Junichi Hasegawa * and Kazutaka Nara * There is an urgent need for an arrayed waveguide grating (AWG), the device ABSTRACT that handles
High-power fibre Raman lasers at the University of Southampton
 High-power fibre Raman lasers at the University of Southampton Industry Day Southampton, April 2 2014 Johan Nilsson Optoelectronics Research Centre University of Southampton, England Also consultant to
High-power fibre Raman lasers at the University of Southampton Industry Day Southampton, April 2 2014 Johan Nilsson Optoelectronics Research Centre University of Southampton, England Also consultant to
