Summary. Time only. Distance only. Simultaneous Methods. Distance and Time. Slip-Sweeps Dynamic Slip-Sweeps Unconstrained simultaneous sources
|
|
|
- Gregory Arthur Smith
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Over 40,000 VPs per day with real-time quality control: Opportunities and Challenges Peter I. Pecholcs, Stephen K. Lafon, Hafiz Al-Shammery and Panos G. Kelamis (Saudi Aramco) Olivier Winter, Jean-Baptiste Kerboul and Thierry Klein (CGGVeritas) Summary In order to evaluate high density source and receiver land seismic acquisition designs, two sets of simultaneous highproductivity field tests were performed in a relatively flat terrain area with good signal-to-noise ratio. These included distance separated simultaneous sweeping (DSSS) (Bouska, 2009), slip-sweep (Rozemond, 1996), distance separated simultaneous slip-sweep (dynamic slip-sweep) and independent simultaneous sources (ISS) (Howe et. al., 2008) with unique sweeps and real-time QC we were not sweeping blind. The second dynamic slip-sweep field test used a 29Km active fixed super-spread (12 receiver lines separated by 300m) with 20 point vibrator fleets on a 25m x 25m source grid. Ten point vibrators were oriented orthogonal to the receiver spread in the North and ten in the South direction with a lateral separation distance of 14.5Km. This method achieved 30,346 vibration points (VPs) in a 24 hour period. The same fixed active receiver spread was reduced to continuously record the unconstrained simultaneous sources (micro-seismic mode) in 18 quadrants (3x6). Each quadrant was 1.8Km x 1.8Km with 4,320 VPs on a 25m x 25m source grid (77,760 total VPs). The unconstrained stakeless productivity test was first acquired with 18 unique 12s pseudorandom sweeps (Sallas et. al., 2008) and repeated with 18 unique linear upsweeps (14.5s average sweep length). These tests achieved optimum productivity rates of 45,501 and 44,793 VPs per 24 hours, respectively, with real-time QC. Even higher rates could have been achieved with stakeless guidance training of the vibrator drivers. In these field test cases, without any training, high productivity rates were achieved with 72 drivers organized in three 8-hour shifts. Four vibrator pushers were used per shift. Three helped with fleet management and one for TDMA real-time communication between the vibrators and the recorder. Figure 1. Twenty four vibrators used in the 2010 field tests. Introduction In recent years, many oil and gas companies have used new high-channel count recording systems equipped with new vibrator control systems to acquire densely sampled symmetric seismic surveys. From these seismic surveys, decimation studies have shown that a balanced increase in receiver and source density improves the resolution of seismic images at all target depths (Bianchi et. al, 2009). Although we have seen a steady improvement in seismic image quality, we are far from acquiring a true uncommitted 3D stack array acquisition design. The main challenge is how to QC and process mega-channel, continuously recorded seismic data in the field and how to reconfigure in-house processing centers (Denis and Sauzedde, 2009). One method used to compensate for recording channel limitations is to position the vibroseis fleets outside the receiver spread. This increases the crossline offset, at the cost of reoccupying VPs. Combining this method with high-productivity source methods, will allow us to acquire densely sampled wide-azimuth seismic survey designs. The most common simultaneous source high-productivity methods are constrained by distance only, time only, or a combination of both time and distance (Table 1). The important question we need to ask is What is the most productive vibroseis acquisition method that preserves data quality? (Bagaini, 2010). DSSS is the lowest risk method, because each vibroseis record can be treated independently without noise interference given sufficient distance separation. The upper limit in terms of productivity is the unconstrained simultaneous source method. As the distance between independent unconstrained vibroseis fleets is reduced, the increased level of cross-talk interference must be removed in seismic processing without removing prestack signal. Simultaneous Methods DSSS Slip-Sweeps Dynamic Slip-Sweeps Unconstrained simultaneous sources Distance only Time only Distance and Time Table 1. High-productivity distance and time classification. The productivity of each of these methods can be simply improved by increasing the number of vibrator fleets and recording channels. This provides the option to either increase the distance and/or time separation between simultaneous sources. Traditionally, the high-productivity vibroseis acquisition (HPVA) slip-sweep method is designed with point vibrator fleets and organized as a single or multiple salvos. In this case, when the fleets are closely positioned to one another, the slip-time can be increased to mitigate harmonic noise interference or the noise attenuated with special processing
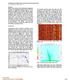
2 algorithms. The same harmonic noise can be avoided in super-spread configuration. If the same receiver spread is reduced by one-half in the cross-line direction, the extra channels can be used to form a super-spread. This allows the fleets to be separated in distance and time and limit the harmonic noise interference to the far offsets. Further improvements in productivity can be gained by using the CGGVeritas fleet management system, where for each fleet specific GPS coordinates and time slots are allocated (Postel, et. al., 2008). In October, 2009 and February, 2010 Saudi Aramco, Argas, and CGGVeritas were given the unique opportunity to test these high-productivity methods with an existing 9,000 channel production seismic crew with 24 point vibrators (Figure 1). This paper reviews these recent dynamic slipsweep and unconstrained simultaneous source methods using unique pseudorandom and linear sweeps. The high-productivity field test methods increased (Figure 9). With this steady increase in VPs per hour, achieving greater than 40,000 VPs per 24 hours, may have been possible, if additional test time had been available. Unconstrained simultaneous source methods The unconstrained simultaneous source field tests acquired in February, 2010, used a reduced active receiver spread with point vibrators isolated in 3 x 6 quadrants, where each quadrant was 1.8Km by 1.8Km with 4,320 VPs on a 25m x 25m source grid (Figure 4 bottom). The unconstrained simultaneous source field test was acquired with 18 unique pseudo-random and linear upsweeps, along with real-time QC. Both sweep designs were designed to reduce the crosstalk noise by 20dB or greater. These field tests were acquired with real-time QC. We were no longer sweeping blind. Both the seismic data and vibrator attributes could be quality controlled in real time. Dynamic slip-sweep method The first dynamic slip-sweep field test used 6 fleets (two vibrators per fleet), 12s linear upsweep, 6s slip-time and the minimum simultaneous separation distance was set to 6.5 Km. Thirteen swaths were recorded into a fixed spread of 24 receiver lines (Figure 2). The combination of sliptime and distance minimized the interference of harmonic noise (Figure 3 top) and proved to have no impact on the final processing results. The production and dynamic slipsweep results were equivalent (Figure 3 - bottom). During this field test we achieved a maximum productivity of 6,000 VPs per day as compared to conventional flip-flop productivity of 3,000 VPs with three fleets. Figure 3. Dynamic slip sweep (upper). Note the lack of harmonic noise contamination. The production (left) and dynamic slip-sweep stack (right) are equivalent. Figure 2. The first dynamic slip-sweep survey design. The second dynamic slip-sweep field test (February, 2010) was repeated in a new location with 20 vibrator trucks (4 spares) on a 25m x 25m source grid. Two salvos with 10 point vibrators per salvo were horizontally separated by 14.5Km along a 29Km super-spread (Figure 4 top). We used a 6s linear upsweep, 3s slip-time and the minimum simultaneous distance was set to 3Km. We achieved 30,346 VPs per 24 hour period after two swaths of acquisition time. As the vibroseis drivers became more familiar with the stakeless guidance monitor, the number of VPs per hour Figure 4. Dynamic slip-sweep super-spread with vibroseis salvos shown in red (top) and unconstrained simultaneous source (bottom) field test designs. Unique linear sweeps The selection of 18 unique linear sweeps was based on the analysis of the maximum amplitude from the crosscorrelation matrix of linear sweeps ranging from 6 to 23s.
3 Cross-correlating any sweep along the diagonal with an adjacent linear sweep with only a one second difference in sweep rate reduces the cross-talk noise by 20dB or more (Figure 5). For this reason, we chose a simple approach and organized the 18 linear sweeps as shown in Table 2. degradation) of radio contact between only one vibrator or more within a fleet can stop or slow down production. In this case, observers would have to consider moving the recorder truck to improve radio communication or implement the use of radio repeaters. Figure 6. Unconstrained simultaneous sweeps using pseudorandom (left), unique linear (middle) and the same linear sweep (right). Note the different levels of cross-talk. Figure 5. Linear sweep cross-correlation matrix from 6s to 23s. Note with only 1 s difference, the cross-talk is reduced by approximately 20dB. Optimized linear sweep lengths per quadrant in seconds Figure 7. Real-time QC of simultaneous sweeps for pseudorandom (left), unique linear (middle) and the same linear sweeps (right) Table 2. After acquiring 50% of the total time to complete the acquisition in quadrant one (1,1), each vibrator changed sweeps from blue to green. The average sweep length for all quadrants was 14.5s. Unique pseudorandom sweeps Eighteen unique pseudorandom sweeps were defined and applied to point vibrators in each quadrant (3x6 quadrants). As described by Sallas et. al. (2009), the objective of using the pseudorandom sweeps was to reduce the cross-talk noise by greater than 20dB and increase the low frequency energy. Unconstrained simultaneous source real-time QC In the past, to speed up acquisition, the recording system sent the start command through the radio to the vibrators and the vibrators sent the ready-to-shake command to the recorder. Now, in continuous recording mode, the vibrators will sweep independently of radio communication. Radio communication is where a great percentage of acquisition time is lost. In flip-flop, slip-sweep (HPVA) and highfidelity vibroseis seismic (HFVS) modes, a loss (or Figure 8. This real-time QC illustrates the vibrator position in each quadrant. The red dots indicate vibrators above predefined distortion threshold. Using the V1 methodology (Postel et. al., 2008) and unconstrained simultaneous source acquisition modes (enhanced with V1 real-time QC modes) the radio communication is no longer needed for source control. We are no longer dependent on distance or terrain conditions. The QC can be monitored either in the recorder truck or in a V1 equipped vehicle. Production is no longer interrupted when a vibrator is out of specification or when radio communication is lost. The vibrators will continue sweeping. During production, the Tablet PC, within each vibrator, stores all the QC attributes such as vibrator phase, distortion, amplitude, position, sweep parameters, and GPS time. These attributes and more can be retrieved by modem at a later time, or relayed by the other vibrators, or repeaters to the recorder. We are aware of the state of each
4 vibrator based upon these QC attributes. These are used to optimize fleet management. Figure 9. Dynamic slip-sweep productivity per hour. How the pseudo real-time QC works The pseudo real-time QC software, can be setup in a light truck in the middle of the vibrator fleets, on a high elevation point, and run by a vibrator pusher. Through repeaters, it can also be monitored in the base camp or other locations. This automatic QC in the vibrator and recorder allows both the vibroseis driver and observer to quickly take decisions about reshooting a VP. This ensures acquisition compliance within pre-plan specifications at high-productivity rates. If an adequate internet connection were available, the software could be run safely (with access through login and password). This interface is currently under development. Conclusions Figure 10. Unconstrained pseudorandom (left) and unique linear simultaneous sweep productivity per hour (right). Peak productivity per hour was 2,064 for unconstrained simultaneous sources. Based on these limited tests, we determined that the use of both distance and time constraints, poses the lowest risk acquisition high-productivity method with our current production seismic crews. Given the opportunity to achieve production levels greater than 40,000 VPs/day, this implies we can finally acquire well sampled wide-azimuth seismic surveys. Currently, we believe the fixed time slot method with both distance and time, can achieve very highproductivity rates with our current production seismic crews. As noted earlier, the unconstrained simultaneous sources technique offers the highest production rates. Seismic processing algorithms will need to be developed and proven to preserve prestack signals. In all the field test cases, it was clear that the vibroseis drivers require proper training with stakeless guidance systems, as shown by the standard deviation for move-up times on a 25m source grid (Figure 9). Figure 11. The median, mean and standard-deviation values for the move-up times for unconstrained simultaneous source field tests using a 25m source grid. Why are we faster today? The answer is very simple - point vibrators or fleets of vibrators are sweeping independently with stakeless guidance systems and real time QC. For example, if the vibrator fleet is out of position (tolerance) the driver will know instantly before sweeping by a synthesized voice from the Tablet PC. The driver will be warned to sweep again without any QC radio communication (Figure 10). Figure 12. Stakeless guidance monitor (Tablet PC) Acknowledgements The authors thank the Saudi Arabian Ministry of Petroleum and Mineral Resources, and the Saudi Arabian Oil Company (Saudi Aramco) for their support and permission to publish this paper. We also like to thank Yi Luo and Shoudong Huo of Saudi Aramco.
5 References Bouska, J., 2009, Distance separated simultaneous sweeping: Efficient 3D Vibroseis acquisition in Oman: 79 th Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts, 1-5. Bianchi, T., Monk D. and Meunier J., 2009, Fold or Force?: 71 st EAGE Conference and Exhibition. Denis, M. and Sauzedde P., 2009, Dukhan 3D: An ultra high density, Full wide azimuth Seismic survey for the future: IPTC, Doha. Howe D., Foster M., Allen T., Taylor B., and Jack I., 2008, Independent simultaneous sweeping a method to increase the productivity of land seismic crews: 78 th Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts, Postel, J.J., Meunier, J., Bianchi, T., and Taylor, R., 2008, V1: Implementation and application of single-vibrator acquisition: The Leading Edge, 27, no. 5, Rozemond, J.H., 1996, Slip-sweep acquisition: 66 th Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts, Sallas, J.J., Gibson, J.B., Lin F., Winter, O., Montgomery, B., and Nagaraiappa P., 2008, Broadband Vibroseis using simultaneous pseudorandom sweeps: 78 th Annual International Meeting, SEG, Expanded Abstracts,
Using long sweep in land vibroseis acquisition
 Using long sweep in land vibroseis acquisition Authors: Alexandre Egreteau, John Gibson, Forest Lin and Julien Meunier (CGGVeritas) Main objectives: Promote the use of long sweeps to compensate for the
Using long sweep in land vibroseis acquisition Authors: Alexandre Egreteau, John Gibson, Forest Lin and Julien Meunier (CGGVeritas) Main objectives: Promote the use of long sweeps to compensate for the
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas
 The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
The case for longer sweeps in vibrator acquisition Malcolm Lansley, Sercel, John Gibson, Forest Lin, Alexandre Egreteau and Julien Meunier, CGGVeritas There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry
Noise Reduction in VibroSeis Source Kaëlig Castor*, Thomas Bianchi, Olivier Winter, Thierry Klein, CGG
 Downloaded //6 to 9..7.. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ Noise Reduction in VibroSeis Source Kaëlig Castor*, Thomas Bianchi, Olivier Winter,
Downloaded //6 to 9..7.. Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at http://library.seg.org/ Noise Reduction in VibroSeis Source Kaëlig Castor*, Thomas Bianchi, Olivier Winter,
There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to
 Coordinated by JEFF DEERE JOHN GIBSON, FOREST LIN, ALEXANDRE EGRETEAU, and JULIEN MEUNIER, CGGVeritas MALCOLM LANSLEY, Sercel There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to improve the quality
Coordinated by JEFF DEERE JOHN GIBSON, FOREST LIN, ALEXANDRE EGRETEAU, and JULIEN MEUNIER, CGGVeritas MALCOLM LANSLEY, Sercel There is growing interest in the oil and gas industry to improve the quality
Th-P08-11 Deblending of Single Source Vibroseis Land Data in Egypt with V1 Noise Attenuation Algorithm
 Th-P08-11 Deblending of Single Source Vibroseis Land Data in Egypt with V1 Noise Attenuation Algorithm N. Gulunay* (CGG), E. Shaker (CGG), A. Karagul (CGG), A. Ramadan (CGG), T. Bianchi (CGG), J. Ross
Th-P08-11 Deblending of Single Source Vibroseis Land Data in Egypt with V1 Noise Attenuation Algorithm N. Gulunay* (CGG), E. Shaker (CGG), A. Karagul (CGG), A. Ramadan (CGG), T. Bianchi (CGG), J. Ross
Simultaneous multi-source acquisition using m-sequences
 Simultaneous source acquisition using m-sequences Simultaneous multi-source acquisition using m-sequences Joe Wong ABSTRACT Maximal length sequences, or m-sequences, are periodic mathematical periodic
Simultaneous source acquisition using m-sequences Simultaneous multi-source acquisition using m-sequences Joe Wong ABSTRACT Maximal length sequences, or m-sequences, are periodic mathematical periodic
T17 Reliable Decon Operators for Noisy Land Data
 T17 Reliable Decon Operators for Noisy Land Data N. Gulunay* (CGGVeritas), N. Benjamin (CGGVeritas) & A. Khalil (CGGVeritas) SUMMARY Interbed multiples for noisy land data that survives the stacking process
T17 Reliable Decon Operators for Noisy Land Data N. Gulunay* (CGGVeritas), N. Benjamin (CGGVeritas) & A. Khalil (CGGVeritas) SUMMARY Interbed multiples for noisy land data that survives the stacking process
Summary. Seismic vibrators are the preferred sources for land seismic ( ) (1) Unfortunately, due to the mechanical and
 Timothy Dean*, John Quigley, Scott MacDonald, and Colin Readman, WesternGeco. Summary Seismic vibrators are the preferred sources for land seismic surveys. Unfortunately, due to the mechanical and hydraulic
Timothy Dean*, John Quigley, Scott MacDonald, and Colin Readman, WesternGeco. Summary Seismic vibrators are the preferred sources for land seismic surveys. Unfortunately, due to the mechanical and hydraulic
Stereo satellite elevation mapping for stakeless 3D seismic surveying. Demonstration Project BP Libya
 Stereo satellite elevation mapping for stakeless 3D seismic surveying. Demonstration Project BP Libya Project Location Gerry Mitchell PhotoSat 16 km 50cm resolution stereo WorldView-2 2 satellite photo
Stereo satellite elevation mapping for stakeless 3D seismic surveying. Demonstration Project BP Libya Project Location Gerry Mitchell PhotoSat 16 km 50cm resolution stereo WorldView-2 2 satellite photo
Summary. Page SEG SEG Denver 2014 Annual Meeting
 Seismo-acoustic characterization of a seismic vibrator Claudio Bagaini*, Martin Laycock and Colin Readman, WesternGeco; Emmanuel Coste, Schlumberger; Colin Anderson, Siemens PLM Software Summary A seismic
Seismo-acoustic characterization of a seismic vibrator Claudio Bagaini*, Martin Laycock and Colin Readman, WesternGeco; Emmanuel Coste, Schlumberger; Colin Anderson, Siemens PLM Software Summary A seismic
Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Group Array Stack of single sensor data
 P-113 Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Artatran Ojha *, K. Ramakrishna, G. Sarvesam Geophysical Services, ONGC, Chennai Summary Shot generated noise and the cultural noise is a major problem in
P-113 Improvement of signal to noise ratio by Artatran Ojha *, K. Ramakrishna, G. Sarvesam Geophysical Services, ONGC, Chennai Summary Shot generated noise and the cultural noise is a major problem in
The transformation of seabed seismic
 first break volume 34, November 2016 The transformation of seabed seismic Tim Bunting 1* and John Moses 1 trace the development of seabed seismic technology. S eabed seismic surveys have been part of the
first break volume 34, November 2016 The transformation of seabed seismic Tim Bunting 1* and John Moses 1 trace the development of seabed seismic technology. S eabed seismic surveys have been part of the
Radial Gain and its Advantages in Seismic Data Acquisition
 P-162 Radial Gain and its Advantages in Seismic Data Acquisition M. Polaiah*, ONGC Ltd. Summary This paper explains the theory behind the radial gain and fixing of the parameters for applying radial gain
P-162 Radial Gain and its Advantages in Seismic Data Acquisition M. Polaiah*, ONGC Ltd. Summary This paper explains the theory behind the radial gain and fixing of the parameters for applying radial gain
Tu N Higher Vibrator Hydraulic Force for Improved High Frequency Generation
 Tu N105 06 Higher Vibrator Hydraulic Force for Improved High Frequency Generation N. Tellier* (Sercel), G. Ollivrin (Sercel) & G. Caradec (Sercel) SUMMARY For conventional deep seismic with heavy vibrators,
Tu N105 06 Higher Vibrator Hydraulic Force for Improved High Frequency Generation N. Tellier* (Sercel), G. Ollivrin (Sercel) & G. Caradec (Sercel) SUMMARY For conventional deep seismic with heavy vibrators,
Attenuation of high energy marine towed-streamer noise Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco
 Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Nick Moldoveanu, WesternGeco Summary Marine seismic data have been traditionally contaminated by bulge waves propagating along the streamers that were generated by tugging and strumming from the vessel,
Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS
 Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS Summary In land AVO processing, near-surface heterogeneity issues are
Surface-consistent phase corrections by stack-power maximization Peter Cary* and Nirupama Nagarajappa, Arcis Seismic Solutions, TGS Summary In land AVO processing, near-surface heterogeneity issues are
Developments in vibrator control
 Geophysical Prospecting, 2010, 58, 33 40 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2478.2009.00848.x Developments in vibrator control D. Boucard and G. Ollivrin Sercel France, PO Box 439, 44474 Carquefou Cedex, France Received
Geophysical Prospecting, 2010, 58, 33 40 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2478.2009.00848.x Developments in vibrator control D. Boucard and G. Ollivrin Sercel France, PO Box 439, 44474 Carquefou Cedex, France Received
OPTIMIZING HIGH FREQUENCY VIBROSEIS DATA. Abstract
 OPTIMIZING HIGH FREQUENCY VIBROSEIS DATA Theresa R. Rademacker, Kansas Geological Survey, Lawrence, KS Richard D. Miller, Kansas Geological Survey, Lawrence, KS Shelby L. Walters, Kansas Geological Survey,
OPTIMIZING HIGH FREQUENCY VIBROSEIS DATA Theresa R. Rademacker, Kansas Geological Survey, Lawrence, KS Richard D. Miller, Kansas Geological Survey, Lawrence, KS Shelby L. Walters, Kansas Geological Survey,
X039 Observations of Surface Vibrator Repeatability in a Desert Environment
 X39 Observations of Surface Vibrator Repeatability in a Desert Environment M.A. Jervis* (Saudi Aramco), A.V. Bakulin (Saudi Aramco), R.M. Burnstad (Saudi Aramco), C. Beron (CGGVeritas) & E. Forgues (CGGVeritas)
X39 Observations of Surface Vibrator Repeatability in a Desert Environment M.A. Jervis* (Saudi Aramco), A.V. Bakulin (Saudi Aramco), R.M. Burnstad (Saudi Aramco), C. Beron (CGGVeritas) & E. Forgues (CGGVeritas)
Downloaded 11/02/15 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Unbiased surface-consistent scalar estimation by crosscorrelation Nirupama Nagarajappa*, Peter Cary, Arcis Seismic Solutions, a TGS Company, Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Summary Surface-consistent scaling
Unbiased surface-consistent scalar estimation by crosscorrelation Nirupama Nagarajappa*, Peter Cary, Arcis Seismic Solutions, a TGS Company, Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Summary Surface-consistent scaling
South Africa CO2 Seismic Program
 1 South Africa CO2 Seismic Program ANNEXURE B Bob A. Hardage October 2016 There have been great advances in seismic technology in the decades following the acquisition of legacy, limited-quality, 2D seismic
1 South Africa CO2 Seismic Program ANNEXURE B Bob A. Hardage October 2016 There have been great advances in seismic technology in the decades following the acquisition of legacy, limited-quality, 2D seismic
Total 3D seismic onshore - a disruptive transition! London, Nov 2011.
 Total 3D seismic onshore - a disruptive transition! London, Nov 2011. Bob Heath - Technical Marketing Manager. iseis Company. Ponca City, Oklahoma, USA. Future-seismic, how universal hardware will improve
Total 3D seismic onshore - a disruptive transition! London, Nov 2011. Bob Heath - Technical Marketing Manager. iseis Company. Ponca City, Oklahoma, USA. Future-seismic, how universal hardware will improve
Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation
 Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation T. Elboth* (CGG), H. Shen (CGG), J. Khan (CGG) Summary This paper presents recent advances in the area of seismic interference (SI) attenuation
Th B3 05 Advances in Seismic Interference Noise Attenuation T. Elboth* (CGG), H. Shen (CGG), J. Khan (CGG) Summary This paper presents recent advances in the area of seismic interference (SI) attenuation
Seismic Reflection Method
 1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
1 of 25 4/16/2009 11:41 AM Seismic Reflection Method Top: Monument unveiled in 1971 at Belle Isle (Oklahoma City) on 50th anniversary of first seismic reflection survey by J. C. Karcher. Middle: Two early
AVO compliant spectral balancing
 Summary AVO compliant spectral balancing Nirupama Nagarajappa CGGVeritas, Calgary, Canada pam.nagarajappa@cggveritas.com Spectral balancing is often performed after surface consistent deconvolution to
Summary AVO compliant spectral balancing Nirupama Nagarajappa CGGVeritas, Calgary, Canada pam.nagarajappa@cggveritas.com Spectral balancing is often performed after surface consistent deconvolution to
Simultaneous Sources: a technology whose time has come Craig J. Beasley, WesternGeco.
 Craig J. Beasley, WesternGeco. Summary It is a rare and exhilarating moment when an emerging technology develops so rapidly that it warrants a special session at the SEG Annual Meeting, while, at the same
Craig J. Beasley, WesternGeco. Summary It is a rare and exhilarating moment when an emerging technology develops so rapidly that it warrants a special session at the SEG Annual Meeting, while, at the same
Introduction. Field Test Description
 GEO21 Seismic Repeatability - Is There a Limit? E. Schissele (CGGVeritas), E. Forgues (CGGVeritas), J. J.Postel* (CGGVeritas), J. Meunier (CGGVeritas), O. de Pellegars (Total) & C. Hubans (Total) SUMMARY
GEO21 Seismic Repeatability - Is There a Limit? E. Schissele (CGGVeritas), E. Forgues (CGGVeritas), J. J.Postel* (CGGVeritas), J. Meunier (CGGVeritas), O. de Pellegars (Total) & C. Hubans (Total) SUMMARY
Th ELI1 07 How to Teach a Neural Network to Identify Seismic Interference
 Th ELI1 07 How to Teach a Neural Network to Identify Seismic Interference S. Rentsch* (Schlumberger), M.E. Holicki (formerly Schlumberger, now TU Delft), Y.I. Kamil (Schlumberger), J.O.A. Robertsson (ETH
Th ELI1 07 How to Teach a Neural Network to Identify Seismic Interference S. Rentsch* (Schlumberger), M.E. Holicki (formerly Schlumberger, now TU Delft), Y.I. Kamil (Schlumberger), J.O.A. Robertsson (ETH
B028 Improved Marine 4D Repeatability Using an Automated Vessel, Source and Receiver Positioning System
 B028 Improved Marine 4D Repeatability Using an Automated Vessel, Source and Receiver Positioning System J.O. Paulsen* (WesternGeco) & G. Brown (WesternGeco) SUMMARY A new automated and integrated, vessel,
B028 Improved Marine 4D Repeatability Using an Automated Vessel, Source and Receiver Positioning System J.O. Paulsen* (WesternGeco) & G. Brown (WesternGeco) SUMMARY A new automated and integrated, vessel,
Can Real-time Wireless Recording Systems be Robust, Reliable and Scalable? Mick Lambert President & C.O.O. Wireless Seismic Inc.
 Can Real-time Wireless Recording Systems be Robust, Reliable and Scalable? Mick Lambert President & C.O.O. Wireless Seismic Inc. Wireless'Seismic'Inc.' HQ in Houston Engineering office near Boulder Sales
Can Real-time Wireless Recording Systems be Robust, Reliable and Scalable? Mick Lambert President & C.O.O. Wireless Seismic Inc. Wireless'Seismic'Inc.' HQ in Houston Engineering office near Boulder Sales
Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion
 P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
P-246 Variable-depth streamer acquisition: broadband data for imaging and inversion Robert Soubaras, Yves Lafet and Carl Notfors*, CGGVeritas Summary This paper revisits the problem of receiver deghosting,
Introduction. Figure 2: Source-Receiver location map (to the right) and geometry template (to the left).
 Advances in interbed multiples prediction and attenuation: Case study from onshore Kuwait Adel El-Emam* and Khaled Shams Al-Deen, Kuwait Oil Company; Alexander Zarkhidze and Andy Walz, WesternGeco Introduction
Advances in interbed multiples prediction and attenuation: Case study from onshore Kuwait Adel El-Emam* and Khaled Shams Al-Deen, Kuwait Oil Company; Alexander Zarkhidze and Andy Walz, WesternGeco Introduction
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency
 25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
25823 Mind the Gap Broadband Seismic Helps To Fill the Low Frequency Deficiency E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), N. Huntbatch (Ikon Science), A. Kielius (Dolphin Geophysical), B. Hannam (Dolphin Geophysical)
Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing Dispersive Ground Roll Noise from Onshore Seismic Data
 Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
Universal Journal of Physics and Application 11(5): 144-149, 2017 DOI: 10.13189/ujpa.2017.110502 http://www.hrpub.org Design of an Optimal High Pass Filter in Frequency Wave Number (F-K) Space for Suppressing
REVISITING THE VIBROSEIS WAVELET
 REVISITING THE VIBROSEIS WAVELET Shaun Strong 1 *, Steve Hearn 2 Velseis Pty Ltd and University of Queensland sstrong@velseis.com 1, steveh@velseis.com 2 Key Words: Vibroseis, wavelet, linear sweep, Vari
REVISITING THE VIBROSEIS WAVELET Shaun Strong 1 *, Steve Hearn 2 Velseis Pty Ltd and University of Queensland sstrong@velseis.com 1, steveh@velseis.com 2 Key Words: Vibroseis, wavelet, linear sweep, Vari
Technology of Adaptive Vibroseis for Wide Spectrum Prospecting
 Technology of Adaptive Vibroseis for Wide Spectrum Prospecting Xianzheng Zhao, Xishuang Wang, A.P. Zhukov, Ruifeng Zhang, Chuanzhang Tang Abstract: Seismic data from conventional vibroseis prospecting
Technology of Adaptive Vibroseis for Wide Spectrum Prospecting Xianzheng Zhao, Xishuang Wang, A.P. Zhukov, Ruifeng Zhang, Chuanzhang Tang Abstract: Seismic data from conventional vibroseis prospecting
Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic
 Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic J. Burren (Petroleum Geo-Services) & D. Lecerf* (Petroleum Geo-Services) SUMMARY Future time-lapse broadband surveys should provide better reservoir monitoring
Repeatability Measure for Broadband 4D Seismic J. Burren (Petroleum Geo-Services) & D. Lecerf* (Petroleum Geo-Services) SUMMARY Future time-lapse broadband surveys should provide better reservoir monitoring
Satinder Chopra 1 and Kurt J. Marfurt 2. Search and Discovery Article #41489 (2014) Posted November 17, General Statement
 GC Autotracking Horizons in Seismic Records* Satinder Chopra 1 and Kurt J. Marfurt 2 Search and Discovery Article #41489 (2014) Posted November 17, 2014 *Adapted from the Geophysical Corner column prepared
GC Autotracking Horizons in Seismic Records* Satinder Chopra 1 and Kurt J. Marfurt 2 Search and Discovery Article #41489 (2014) Posted November 17, 2014 *Adapted from the Geophysical Corner column prepared
Spread spectrum techniques for seismic data acquisition
 Spread spectrum techniques Spread spectrum techniques for seismic data acquisition Joe Wong ABSTRACT Mechanical and piezoelectric vibrators are controllable seismic sources used in seismic surveys for
Spread spectrum techniques Spread spectrum techniques for seismic data acquisition Joe Wong ABSTRACT Mechanical and piezoelectric vibrators are controllable seismic sources used in seismic surveys for
SECTION 2 BROADBAND RF CHARACTERISTICS. 2.1 Frequency bands
 SECTION 2 BROADBAND RF CHARACTERISTICS 2.1 Frequency bands 2.1.1 Use of AMS(R)S bands Note.- Categories of messages, and their relative priorities within the aeronautical mobile (R) service, are given
SECTION 2 BROADBAND RF CHARACTERISTICS 2.1 Frequency bands 2.1.1 Use of AMS(R)S bands Note.- Categories of messages, and their relative priorities within the aeronautical mobile (R) service, are given
Multicomponent seismic polarization analysis
 Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
Saul E. Guevara and Robert R. Stewart ABSTRACT In the 3-C seismic method, the plant orientation and polarity of geophones should be previously known to provide correct amplitude information. In principle
Evaluation of 3C sensor coupling using ambient noise measurements Summary
 Evaluation of 3C sensor coupling using ambient noise measurements Howard Watt, John Gibson, Bruce Mattocks, Mark Cartwright, Roy Burnett, and Shuki Ronen Veritas Geophysical Corporation Summary Good vector
Evaluation of 3C sensor coupling using ambient noise measurements Howard Watt, John Gibson, Bruce Mattocks, Mark Cartwright, Roy Burnett, and Shuki Ronen Veritas Geophysical Corporation Summary Good vector
Deblending workflow. Summary
 Guillaume Henin*, Didier Marin, Shivaji Maitra, Anne Rollet (CGG), Sandeep Kumar Chandola, Subodh Kumar, Nabil El Kady, Low Cheng Foo (PETRONAS Carigali Sdn. Bhd.) Summary In ocean-bottom cable (OBC) acquisitions,
Guillaume Henin*, Didier Marin, Shivaji Maitra, Anne Rollet (CGG), Sandeep Kumar Chandola, Subodh Kumar, Nabil El Kady, Low Cheng Foo (PETRONAS Carigali Sdn. Bhd.) Summary In ocean-bottom cable (OBC) acquisitions,
Th ELI1 08 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data
 Th ELI1 8 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data P. Edme* (Schlumberger Gould Research), E. Muyzert (Sclumberger Gould Research) & E. Kragh (Schlumberger Gould Research) SUMMARY
Th ELI1 8 Efficient Land Seismic Acquisition Sampling Using Rotational Data P. Edme* (Schlumberger Gould Research), E. Muyzert (Sclumberger Gould Research) & E. Kragh (Schlumberger Gould Research) SUMMARY
Downloaded 09/04/18 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
Processing of data with continuous source and receiver side wavefields - Real data examples Tilman Klüver* (PGS), Stian Hegna (PGS), and Jostein Lima (PGS) Summary In this paper, we describe the processing
FINAL REPORT EL# RS. C. A. Hurich & MUN Seismic Team Earth Sciences Dept. Memorial University Sept. 2009
 FINAL REPORT EL# 09-101-01-RS MUNSIST Seismic Source Test - Five Mile Road C. A. Hurich & MUN Seismic Team Earth Sciences Dept. Memorial University Sept. 2009 1 EL# 09-101-01-RS Five-Mile Road Memorial
FINAL REPORT EL# 09-101-01-RS MUNSIST Seismic Source Test - Five Mile Road C. A. Hurich & MUN Seismic Team Earth Sciences Dept. Memorial University Sept. 2009 1 EL# 09-101-01-RS Five-Mile Road Memorial
2012 SEG SEG Las Vegas 2012 Annual Meeting Page 1
 Full-wavefield, towed-marine seismic acquisition and applications David Halliday, Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Johan O. A. Robertsson, ETH Zürich, Ivan Vasconcelos, Schlumberger Cambridge Research,
Full-wavefield, towed-marine seismic acquisition and applications David Halliday, Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Johan O. A. Robertsson, ETH Zürich, Ivan Vasconcelos, Schlumberger Cambridge Research,
Using Frequency Diversity to Improve Measurement Speed Roger Dygert MI Technologies, 1125 Satellite Blvd., Suite 100 Suwanee, GA 30024
 Using Frequency Diversity to Improve Measurement Speed Roger Dygert MI Technologies, 1125 Satellite Blvd., Suite 1 Suwanee, GA 324 ABSTRACT Conventional antenna measurement systems use a multiplexer or
Using Frequency Diversity to Improve Measurement Speed Roger Dygert MI Technologies, 1125 Satellite Blvd., Suite 1 Suwanee, GA 324 ABSTRACT Conventional antenna measurement systems use a multiplexer or
Sharing Considerations Between Small Cells and Geostationary Satellite Networks in the Fixed-Satellite Service in the GHz Frequency Band
 Sharing Considerations Between Small Cells and Geostationary Satellite Networks in the Fixed-Satellite Service in the 3.4-4.2 GHz Frequency Band Executive Summary The Satellite Industry Association ( SIA
Sharing Considerations Between Small Cells and Geostationary Satellite Networks in the Fixed-Satellite Service in the 3.4-4.2 GHz Frequency Band Executive Summary The Satellite Industry Association ( SIA
Multiple Access System
 Multiple Access System TDMA and FDMA require a degree of coordination among users: FDMA users cannot transmit on the same frequency and TDMA users can transmit on the same frequency but not at the same
Multiple Access System TDMA and FDMA require a degree of coordination among users: FDMA users cannot transmit on the same frequency and TDMA users can transmit on the same frequency but not at the same
ADC Based Measurements: a Common Basis for the Uncertainty Estimation. Ciro Spataro
 ADC Based Measurements: a Common Basis for the Uncertainty Estimation Ciro Spataro Department of Electric, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineering - University of Palermo Viale delle Scienze, 90128
ADC Based Measurements: a Common Basis for the Uncertainty Estimation Ciro Spataro Department of Electric, Electronic and Telecommunication Engineering - University of Palermo Viale delle Scienze, 90128
19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007 VIRTUAL AUDIO REPRODUCED IN A HEADREST
 19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007 VIRTUAL AUDIO REPRODUCED IN A HEADREST PACS: 43.25.Lj M.Jones, S.J.Elliott, T.Takeuchi, J.Beer Institute of Sound and Vibration Research;
19 th INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON ACOUSTICS MADRID, 2-7 SEPTEMBER 2007 VIRTUAL AUDIO REPRODUCED IN A HEADREST PACS: 43.25.Lj M.Jones, S.J.Elliott, T.Takeuchi, J.Beer Institute of Sound and Vibration Research;
PC Digital Data Acquisition
 ME 22.302 Mechanical Lab I PC Digital Data Acquisition Dr. Peter Avitabile University of Massachusetts Lowell Digital Data Acquisition 122601-1 Copyright 2001 A general computer data acquisition configuration
ME 22.302 Mechanical Lab I PC Digital Data Acquisition Dr. Peter Avitabile University of Massachusetts Lowell Digital Data Acquisition 122601-1 Copyright 2001 A general computer data acquisition configuration
Advancements in near-surface seismic reflection acquisition
 Advancements in near-surface seismic reflection acquisition Brian E. Miller, George P. Tsoflias, Don W. Steeples Department of Geology and Geophysics, The University of Kansas, 1475 Jayhawk Blvd., Room
Advancements in near-surface seismic reflection acquisition Brian E. Miller, George P. Tsoflias, Don W. Steeples Department of Geology and Geophysics, The University of Kansas, 1475 Jayhawk Blvd., Room
MEMS-based 3C accelerometers for land seismic acquisition: Is it time?
 MEMS-based 3C accelerometers for land seismic acquisition: Is it time? DENIS MOUGENOT, Sercel, Carquefou Cedex, France NIGEL THORBURN, Sercel, Houston, Texas, U.S. Recent advances have allowed development
MEMS-based 3C accelerometers for land seismic acquisition: Is it time? DENIS MOUGENOT, Sercel, Carquefou Cedex, France NIGEL THORBURN, Sercel, Houston, Texas, U.S. Recent advances have allowed development
Latest field trial confirms potential of new seismic method based on continuous source and receiver wavefields
 SPECAL TOPC: MARNE SESMC Latest field trial confirms potential of new seismic method based on continuous source and receiver wavefields Stian Hegna1*, Tilman Klüver1, Jostein Lima1 and Endrias Asgedom1
SPECAL TOPC: MARNE SESMC Latest field trial confirms potential of new seismic method based on continuous source and receiver wavefields Stian Hegna1*, Tilman Klüver1, Jostein Lima1 and Endrias Asgedom1
ISSN Volume 28 Issue 6 June A New Spring for Geoscience. Special Topic
 ISSN 0263-5046 Volume 28 Issue 6 June 2010 Special Topic Technical Articles Multi-azimuth processing and its applications to wide-azimuth OBC seismic data offshore Abu Dhabi Borehole image logs for turbidite
ISSN 0263-5046 Volume 28 Issue 6 June 2010 Special Topic Technical Articles Multi-azimuth processing and its applications to wide-azimuth OBC seismic data offshore Abu Dhabi Borehole image logs for turbidite
Th N Broadband Processing of Variable-depth Streamer Data
 Th N103 16 Broadband Processing of Variable-depth Streamer Data H. Masoomzadeh* (TGS), A. Hardwick (TGS) & S. Baldock (TGS) SUMMARY The frequency of ghost notches is naturally diversified by random variations,
Th N103 16 Broadband Processing of Variable-depth Streamer Data H. Masoomzadeh* (TGS), A. Hardwick (TGS) & S. Baldock (TGS) SUMMARY The frequency of ghost notches is naturally diversified by random variations,
GPR ANTENNA ARRAY FOR THE INSPECTION OF RAILWAY BALLAST
 Proceedings of the National Seminar & Exhibition on Non-Destructive Evaluation NDE 2011, December 8-10, 2011 GPR ANTENNA ARRAY FOR THE INSPECTION OF RAILWAY BALLAST Th. Kind BAM Federal Institute for Materials
Proceedings of the National Seminar & Exhibition on Non-Destructive Evaluation NDE 2011, December 8-10, 2011 GPR ANTENNA ARRAY FOR THE INSPECTION OF RAILWAY BALLAST Th. Kind BAM Federal Institute for Materials
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data
 Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
Tu SRS3 07 Ultra-low Frequency Phase Assessment for Broadband Data F. Yang* (CGG), R. Sablon (CGG) & R. Soubaras (CGG) SUMMARY Reliable low frequency content and phase alignment are critical for broadband
This tutorial describes the principles of 24-bit recording systems and clarifies some common mis-conceptions regarding these systems.
 This tutorial describes the principles of 24-bit recording systems and clarifies some common mis-conceptions regarding these systems. This is a general treatment of the subject and applies to I/O System
This tutorial describes the principles of 24-bit recording systems and clarifies some common mis-conceptions regarding these systems. This is a general treatment of the subject and applies to I/O System
Chapter 7. Multiple Division Techniques
 Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques 1 Outline Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Comparison of FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA Walsh
Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques 1 Outline Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Comparison of FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA Walsh
Desinging of 3D Seismic Survey And Data Processing of Abu Amood Oil Field Southern of Iraq
 Desinging of 3D Seismic Survey And Data Processing of Abu Amood Oil Field Southern of Iraq Salman Z. Khorshid, Ahmed I. Khaleel Dept.Geology, College of Science, Univercity of Baghdad Abstract 3D seismic
Desinging of 3D Seismic Survey And Data Processing of Abu Amood Oil Field Southern of Iraq Salman Z. Khorshid, Ahmed I. Khaleel Dept.Geology, College of Science, Univercity of Baghdad Abstract 3D seismic
G003 Data Preprocessing and Starting Model Preparation for 3D Inversion of Marine CSEM Surveys
 G003 Data Preprocessing and Starting Model Preparation for 3D Inversion of Marine CSEM Surveys J.J. Zach* (EMGS ASA), F. Roth (EMGS ASA) & H. Yuan (EMGS Americas) SUMMARY The marine controlled-source electromagnetic
G003 Data Preprocessing and Starting Model Preparation for 3D Inversion of Marine CSEM Surveys J.J. Zach* (EMGS ASA), F. Roth (EMGS ASA) & H. Yuan (EMGS Americas) SUMMARY The marine controlled-source electromagnetic
Downloaded 01/03/14 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 : a case study from Saudi Arabia Joseph McNeely*, Timothy Keho, Thierry Tonellot, Robert Ley, Saudi Aramco, Dhahran, and Jing Chen, GeoTomo, Houston Summary We present an application of time domain early
: a case study from Saudi Arabia Joseph McNeely*, Timothy Keho, Thierry Tonellot, Robert Ley, Saudi Aramco, Dhahran, and Jing Chen, GeoTomo, Houston Summary We present an application of time domain early
41ST ANNUAL MARINE / OFFSHORE INDUSTRY OUTLOOK CONFERENCE GEOSCIENCE UPDATE: MR. ALAN M. BREED EVP SALES & MARKETING
 41ST ANNUAL MARINE / OFFSHORE INDUSTRY OUTLOOK CONFERENCE GEOSCIENCE UPDATE: MR. ALAN M. BREED EVP SALES & MARKETING AGENDA GEOSCIENCE UPDATE Market Outlook Financial Overview Regulatory Issues Technology
41ST ANNUAL MARINE / OFFSHORE INDUSTRY OUTLOOK CONFERENCE GEOSCIENCE UPDATE: MR. ALAN M. BREED EVP SALES & MARKETING AGENDA GEOSCIENCE UPDATE Market Outlook Financial Overview Regulatory Issues Technology
SEN366 (SEN374) (Introduction to) Computer Networks
 SEN366 (SEN374) (Introduction to) Computer Networks Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (8 th Week) Cellular Wireless Network 8.Outline Principles of Cellular Networks Cellular Network Generations LTE-Advanced
SEN366 (SEN374) (Introduction to) Computer Networks Prof. Dr. Hasan Hüseyin BALIK (8 th Week) Cellular Wireless Network 8.Outline Principles of Cellular Networks Cellular Network Generations LTE-Advanced
SPNA 2.3. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 2177
 SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
SPNA 2.3 Source and receiver amplitude equalization using reciprocity Application to land seismic data Robbert van Vossen and Jeannot Trampert, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Andrew Curtis, Schlumberger
Data and Computer Communications. Tenth Edition by William Stallings
 Data and Computer Communications Tenth Edition by William Stallings Data and Computer Communications, Tenth Edition by William Stallings, (c) Pearson Education - 2013 CHAPTER 10 Cellular Wireless Network
Data and Computer Communications Tenth Edition by William Stallings Data and Computer Communications, Tenth Edition by William Stallings, (c) Pearson Education - 2013 CHAPTER 10 Cellular Wireless Network
3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion. Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas
 P-75 Summary 3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas Following our previous work on Amplitude Tomography that
P-75 Summary 3-D tomographic Q inversion for compensating frequency dependent attenuation and dispersion Kefeng Xin* and Barry Hung, CGGVeritas Following our previous work on Amplitude Tomography that
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG)
 Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
Seismic interference noise attenuation based on sparse inversion Zhigang Zhang* and Ping Wang (CGG) Summary In marine seismic acquisition, seismic interference (SI) remains a considerable problem when
CDMA - QUESTIONS & ANSWERS
 CDMA - QUESTIONS & ANSWERS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/cdma/questions_and_answers.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com 1. What is CDMA? CDMA stands for Code Division Multiple Access. It is a wireless technology
CDMA - QUESTIONS & ANSWERS http://www.tutorialspoint.com/cdma/questions_and_answers.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com 1. What is CDMA? CDMA stands for Code Division Multiple Access. It is a wireless technology
CH 4. Air Interface of the IS-95A CDMA System
 CH 4. Air Interface of the IS-95A CDMA System 1 Contents Summary of IS-95A Physical Layer Parameters Forward Link Structure Pilot, Sync, Paging, and Traffic Channels Channel Coding, Interleaving, Data
CH 4. Air Interface of the IS-95A CDMA System 1 Contents Summary of IS-95A Physical Layer Parameters Forward Link Structure Pilot, Sync, Paging, and Traffic Channels Channel Coding, Interleaving, Data
Accuracy Estimation of Microwave Holography from Planar Near-Field Measurements
 Accuracy Estimation of Microwave Holography from Planar Near-Field Measurements Christopher A. Rose Microwave Instrumentation Technologies River Green Parkway, Suite Duluth, GA 9 Abstract Microwave holography
Accuracy Estimation of Microwave Holography from Planar Near-Field Measurements Christopher A. Rose Microwave Instrumentation Technologies River Green Parkway, Suite Duluth, GA 9 Abstract Microwave holography
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution
 Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
Interferometric Approach to Complete Refraction Statics Solution Valentina Khatchatrian, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada VKhatchatrian@slb.com and Mike Galbraith, WesternGeco, Calgary, Alberta, Canada
WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation
 WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), M. Sams (Ikon Science) & K. Waters (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Broadband re-processed seismic
WS01 B02 The Impact of Broadband Wavelets on Thin Bed Reservoir Characterisation E. Zabihi Naeini* (Ikon Science), M. Sams (Ikon Science) & K. Waters (Ikon Science) SUMMARY Broadband re-processed seismic
Successful mobile-radio tester now with US TDMA and AMPS standards
 Universal Radio Communication Tester CMU200 Successful mobile-radio tester now with US TDMA and AMPS standards Digital TDMA standard TDMA (time-division multiple access) is a mobile-radio system based
Universal Radio Communication Tester CMU200 Successful mobile-radio tester now with US TDMA and AMPS standards Digital TDMA standard TDMA (time-division multiple access) is a mobile-radio system based
Wireless Progresses! Mick Lambert President & C.O.O. Wireless Seismic Inc.
 Wireless Progresses! Mick Lambert President & C.O.O. Wireless Seismic Inc. Finding Petroleum Total 3D seismic onshore a disruptive transition! Nov. 9, 2011 Wireless Networks Easy to use by almost everyone
Wireless Progresses! Mick Lambert President & C.O.O. Wireless Seismic Inc. Finding Petroleum Total 3D seismic onshore a disruptive transition! Nov. 9, 2011 Wireless Networks Easy to use by almost everyone
Cross Spectral Density Analysis for Various Codes Suitable for Spread Spectrum under AWGN conditions with Error Detecting Code
 Cross Spectral Density Analysis for Various Codes Suitable for Spread Spectrum under AWG conditions with Error Detecting Code CH.ISHATHI 1, R.SUDAR RAJA 2 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,
Cross Spectral Density Analysis for Various Codes Suitable for Spread Spectrum under AWG conditions with Error Detecting Code CH.ISHATHI 1, R.SUDAR RAJA 2 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,
Why not narrowband? Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology
 Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology Summary A 2D towed streamer acquisition experiment was conducted in deep water offshore Gabon to evaluate techniques
Philip Fontana* and Mikhail Makhorin, Polarcus; Thomas Cheriyan and Lee Saxton, GX Technology Summary A 2D towed streamer acquisition experiment was conducted in deep water offshore Gabon to evaluate techniques
Long Range Acoustic Classification
 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Long Range Acoustic Classification Authors: Ned B. Thammakhoune, Stephen W. Lang Sanders a Lockheed Martin Company P. O. Box 868 Nashua, New Hampshire
Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Long Range Acoustic Classification Authors: Ned B. Thammakhoune, Stephen W. Lang Sanders a Lockheed Martin Company P. O. Box 868 Nashua, New Hampshire
Looking deeper through Pre Amplifier gain A study
 P-36 Looking deeper through Pre Amplifier gain A study C.V.Jambhekar*, DGM (S) & Paparaju Buddhavarapu, CE (E&T), ONGC, Vadodara, India Summary This article is a report on the experimental study carried
P-36 Looking deeper through Pre Amplifier gain A study C.V.Jambhekar*, DGM (S) & Paparaju Buddhavarapu, CE (E&T), ONGC, Vadodara, India Summary This article is a report on the experimental study carried
Progress in DAS Seismic Methods
 Progress in DAS Seismic Methods A. Mateeva, J. Mestayer, Z. Yang, J. Lopez, P. Wills 1, H. Wu, W. Wong, Barbara Cox (Shell International Exploration and Production, Inc.), J. Roy, T. Bown ( OptaSense )
Progress in DAS Seismic Methods A. Mateeva, J. Mestayer, Z. Yang, J. Lopez, P. Wills 1, H. Wu, W. Wong, Barbara Cox (Shell International Exploration and Production, Inc.), J. Roy, T. Bown ( OptaSense )
CH 5. Air Interface of the IS-95A CDMA System
 CH 5. Air Interface of the IS-95A CDMA System 1 Contents Summary of IS-95A Physical Layer Parameters Forward Link Structure Pilot, Sync, Paging, and Traffic Channels Channel Coding, Interleaving, Data
CH 5. Air Interface of the IS-95A CDMA System 1 Contents Summary of IS-95A Physical Layer Parameters Forward Link Structure Pilot, Sync, Paging, and Traffic Channels Channel Coding, Interleaving, Data
TECHNICAL CONDITIONS FOR RADIO EQUIPMENT OF INMARSAT SHIP EARTH STATIONS, etc
 TECHNICAL CONDITIONS FOR RADIO EQUIPMENT OF INMARSAT SHIP EARTH STATIONS, etc (Article 7 paragraph 21, Article 14 paragraph 3, Article 40.4 paragraph 1 item 5, Article 40.4 paragraph 2 item 4, Article
TECHNICAL CONDITIONS FOR RADIO EQUIPMENT OF INMARSAT SHIP EARTH STATIONS, etc (Article 7 paragraph 21, Article 14 paragraph 3, Article 40.4 paragraph 1 item 5, Article 40.4 paragraph 2 item 4, Article
MEMS-based accelerometers: expectations and practical achievements
 first break volume 29, February 2011 MEMS-based accelerometers: expectations and practical achievements Denis Mougenot, 1* Anatoly Cherepovskiy 1 and Liu JunJie 1 trace the development of MEMS sensors
first break volume 29, February 2011 MEMS-based accelerometers: expectations and practical achievements Denis Mougenot, 1* Anatoly Cherepovskiy 1 and Liu JunJie 1 trace the development of MEMS sensors
A COMPACT, AGILE, LOW-PHASE-NOISE FREQUENCY SOURCE WITH AM, FM AND PULSE MODULATION CAPABILITIES
 A COMPACT, AGILE, LOW-PHASE-NOISE FREQUENCY SOURCE WITH AM, FM AND PULSE MODULATION CAPABILITIES Alexander Chenakin Phase Matrix, Inc. 109 Bonaventura Drive San Jose, CA 95134, USA achenakin@phasematrix.com
A COMPACT, AGILE, LOW-PHASE-NOISE FREQUENCY SOURCE WITH AM, FM AND PULSE MODULATION CAPABILITIES Alexander Chenakin Phase Matrix, Inc. 109 Bonaventura Drive San Jose, CA 95134, USA achenakin@phasematrix.com
Wireless Networks (PHY): Design for Diversity
 Wireless Networks (PHY): Design for Diversity Y. Richard Yang 9/20/2012 Outline Admin and recap Design for diversity 2 Admin Assignment 1 questions Assignment 1 office hours Thursday 3-4 @ AKW 307A 3 Recap:
Wireless Networks (PHY): Design for Diversity Y. Richard Yang 9/20/2012 Outline Admin and recap Design for diversity 2 Admin Assignment 1 questions Assignment 1 office hours Thursday 3-4 @ AKW 307A 3 Recap:
Breaking Through RF Clutter
 Breaking Through RF Clutter A Guide to Reliable Data Communications in Saturated 900 MHz Environments Your M2M Expert Introduction Today, there are many mission-critical applications in industries such
Breaking Through RF Clutter A Guide to Reliable Data Communications in Saturated 900 MHz Environments Your M2M Expert Introduction Today, there are many mission-critical applications in industries such
HD Radio FM Transmission. System Specifications
 HD Radio FM Transmission System Specifications Rev. G December 14, 2016 SY_SSS_1026s TRADEMARKS HD Radio and the HD, HD Radio, and Arc logos are proprietary trademarks of ibiquity Digital Corporation.
HD Radio FM Transmission System Specifications Rev. G December 14, 2016 SY_SSS_1026s TRADEMARKS HD Radio and the HD, HD Radio, and Arc logos are proprietary trademarks of ibiquity Digital Corporation.
Performance Analysis of DSSS and FHSS Techniques over AWGN Channel
 Performance Analysis of DSSS and FHSS Techniques over AWGN Channel M. Katta Swamy, M.Deepthi, V.Mounika, R.N.Saranya Vignana Bharathi Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, and Andhra Pradesh, India. Corresponding
Performance Analysis of DSSS and FHSS Techniques over AWGN Channel M. Katta Swamy, M.Deepthi, V.Mounika, R.N.Saranya Vignana Bharathi Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, and Andhra Pradesh, India. Corresponding
Adaptive Beamforming for Multi-path Mitigation in GPS
 EE608: Adaptive Signal Processing Course Instructor: Prof. U.B.Desai Course Project Report Adaptive Beamforming for Multi-path Mitigation in GPS By Ravindra.S.Kashyap (06307923) Rahul Bhide (0630795) Vijay
EE608: Adaptive Signal Processing Course Instructor: Prof. U.B.Desai Course Project Report Adaptive Beamforming for Multi-path Mitigation in GPS By Ravindra.S.Kashyap (06307923) Rahul Bhide (0630795) Vijay
Agilent AN 1275 Automatic Frequency Settling Time Measurement Speeds Time-to-Market for RF Designs
 Agilent AN 1275 Automatic Frequency Settling Time Measurement Speeds Time-to-Market for RF Designs Application Note Fast, accurate synthesizer switching and settling are key performance requirements in
Agilent AN 1275 Automatic Frequency Settling Time Measurement Speeds Time-to-Market for RF Designs Application Note Fast, accurate synthesizer switching and settling are key performance requirements in
A New Noise Parameter Measurement Method Results in More than 100x Speed Improvement and Enhanced Measurement Accuracy
 MAURY MICROWAVE CORPORATION March 2013 A New Noise Parameter Measurement Method Results in More than 100x Speed Improvement and Enhanced Measurement Accuracy Gary Simpson 1, David Ballo 2, Joel Dunsmore
MAURY MICROWAVE CORPORATION March 2013 A New Noise Parameter Measurement Method Results in More than 100x Speed Improvement and Enhanced Measurement Accuracy Gary Simpson 1, David Ballo 2, Joel Dunsmore
Four-Channel Sample-and-Hold Amplifier AD684
 a FEATURES Four Matched Sample-and-Hold Amplifiers Independent Inputs, Outputs and Control Pins 500 ns Hold Mode Settling 1 s Maximum Acquisition Time to 0.01% Low Droop Rate: 0.01 V/ s Internal Hold Capacitors
a FEATURES Four Matched Sample-and-Hold Amplifiers Independent Inputs, Outputs and Control Pins 500 ns Hold Mode Settling 1 s Maximum Acquisition Time to 0.01% Low Droop Rate: 0.01 V/ s Internal Hold Capacitors
######################################################################
 Write a MATLAB program which asks the user to enter three numbers. - The program should figure out the median value and the average value and print these out. Do not use the predefined MATLAB functions
Write a MATLAB program which asks the user to enter three numbers. - The program should figure out the median value and the average value and print these out. Do not use the predefined MATLAB functions
Enabling autonomous driving
 Automotive fuyu liu / Shutterstock.com Enabling autonomous driving Autonomous vehicles see the world through sensors. The entire concept rests on their reliability. But the ability of a radar sensor to
Automotive fuyu liu / Shutterstock.com Enabling autonomous driving Autonomous vehicles see the world through sensors. The entire concept rests on their reliability. But the ability of a radar sensor to
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile
 Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
Borehole Seismic Processing Summary Checkshot Vertical Seismic Profile COMPANY: Gaz de France WELL: G 14-5 RIG: Noble G.S. FIELD: G 14 LOGGING DATE: COUNTRY: Ref. no: 10-MAR-2005 The Netherlands, Off shore
Isolator-Free 840-nm Broadband SLEDs for High-Resolution OCT
 Isolator-Free 840-nm Broadband SLEDs for High-Resolution OCT M. Duelk *, V. Laino, P. Navaretti, R. Rezzonico, C. Armistead, C. Vélez EXALOS AG, Wagistrasse 21, CH-8952 Schlieren, Switzerland ABSTRACT
Isolator-Free 840-nm Broadband SLEDs for High-Resolution OCT M. Duelk *, V. Laino, P. Navaretti, R. Rezzonico, C. Armistead, C. Vélez EXALOS AG, Wagistrasse 21, CH-8952 Schlieren, Switzerland ABSTRACT
THE EFFECT of multipath fading in wireless systems can
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 47, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 1998 119 The Diversity Gain of Transmit Diversity in Wireless Systems with Rayleigh Fading Jack H. Winters, Fellow, IEEE Abstract In
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON VEHICULAR TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 47, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 1998 119 The Diversity Gain of Transmit Diversity in Wireless Systems with Rayleigh Fading Jack H. Winters, Fellow, IEEE Abstract In
