Review Paper on Frequency Multiplier at Terahertz Range
|
|
|
- Evan Garrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Paper on Frequency Multiplier at Terahertz Range Dhruvi.D. Prajapati PG Stud. Department of E&C L.D. Collage of Engineering Ahmedabad, India Prof. Usha Neelkanthan H.O.D. of E&C department L.D. Collage of Engineering Ahmedabad, India Abstract: Frequency multiplier is an electronic circuit which generates the output frequency which is an integer multiple of the applied frequency. For this purpose, nonlinear devices such as BJT, FET, schottky diode, varactor diode, step recovery diode are used. The nonlinear region of their characteristics is utilized to design frequency multiplier. In terahertz range stability and broad bandwidth are required factors to design heterodyne receiver. For this purpose, only schottky diode is the best option because its cutoff frequency is so high and due to this reason switching frequency of this diode is high compared to its other comparable. The design of frequency multiplier consists of three parts namely the diode structure, input and output matching circuit. The detailed discussion about sources available at terahertz frequency range, different design methods of frequency multiplier with active and passive devices, comparison of available passive frequency multiplier are presented in this paper. Keywords: frequency multiplier, doubler, tripler, schottky diode, antiparallel diode pair, LO, HEMT, HBV ***** 1. Introduction Several recent articles have described the potential capability of terahertz technology and how developing this technology can lead to exciting scientific research for applications in variety of fields. One of most challenging aspects of Terahertz technology is the lack of compact, reliable efficient local oscillator (LO) sources in the terahertz range. Sources available at Terahertz range and their limitations are given below: FIR laser pumped by the gas laser: The power generation method for this type requires several tens of watts of DC power. It is bulky and works at discrete frequencies [1]. Limitation: It is used only at ground based applications where size and power are not an issue [1]. QCLs (quantum Cascade Lasers): They are ultra-compact milliwatt-level terahertz solid state sources. CW mode frequency is lower than 1.2 THz [1]. Limitations: It has tuning problem. It requires cryogenic cooling to approximately 4 0 K for maximum output power [1]. These two sources known as photonic sources are used to generate LO in cryogenic heterodyne receiver. But the main problem is that their output power is in 1-2 THz range which is lower than the power produced by room temperature frequency multiplier [1] Application of high frequency sources: Imaging system: It s able to see through clothing to detect contraband or weapons. Imaging RADAR: For this type of systems the signal to noise ratio and the standoff distance can be improved with higher power sources because spatial resolution is directly proportional to the frequency for a given aperture size. Astrophysics: Heterodyne spectrometer is needed to measure Doppler velocities in the interstellar medium and star forming regions with resolution around 1 km/s. Frequencies ranging from below 100 GHz to at least 5 THz are needed to identify the spectral signature of a wide range of molecules, isotopomers, atoms and ions as well as temperature, density pressure, mass and dynamics of the system observed This article will describe the technologies developed to build frequency multiplier for solid state LO above 100 GHz for a space borne radio telescope. This will address some of the most important questions in cosmology and galaxy evolution. High frequency signals can be generated either using high frequency oscillator or cascading a low frequency source with frequency multipliers. It is difficult to build and realize a high frequency oscillator due to degraded performance such as stability, accuracy and phase noise. To overcome these problems low frequency low phase noise VCO in conjunction with the frequency multiplier is the most preferred and the proposed method [4][6] for our research work. High speed wireless communication: It is used for high speed wireless data communication. This requires open free space path to high speed wireless communication system transferring data at rates of several tens of Gigabytes per seconds [1] 2. Frequency Multiplier Frequency multiplier is an electronics circuit that generates an output signal whose output frequency is a harmonic (multiple) of its input frequency. Frequency multiplier consists of a 228
2 nonlinear circuit that distorts the input signal and consequently fraction of the time that it is on, compared to the entire period generates harmonics of the input signal. At output side called is its duty cycle. By adjusting the duty cycle we can bandpass filter is used to select the desired harmonic maximize the desired output harmonics generated. The higher frequency and remove the unwanted fundamental and other the harmonic, the shorter the duty cycle must be. For a harmonics from the output [2] doubler, the optimum is around 30%, and for a tripler is about 20%. [3] Figure 2.1: frequency multiplier basic block diagram [2] Many types of the frequency multipliers such as doubler and Tripler, quadrupler have been reported. They can be implemented using passive or active circuits. There are 2 Types of Frequency Multipliers for design based on the solid state devices: Active Multiplier and Passive Multiplier The active multipliers using transistors have the advantage of providing conversion gain, but the broadband bandwidth is difficult to achieve due to the stability and power consumption problem. On the other hand, passive multipliers using diodes as a nonlinear deice which provides broader bandwidth and good stability in millimeter wave range. Inp-based high electron mobility transistors (HEMTs) have demonstrated excellent millimeter-wave characteristics, such as low noise figure, and high gain. However, the main drawback of the Inp-substrate is the high cost and limited wafer size availabilities [8] Traditionally, the schottky diode has been the device of choice for the multiplying element and it is still the most common multiplying element available at millimeter wavelength. Recently heterostructure barrier varactors (HBV) or on metamorphic high electron mobility transistors (HEMT) have been developed rapidly. HBVs reach very high efficiencies and output levels but are inherently narrowband devices [4]. HEMT based active multiplier provides very good conversion efficiencies and can be implemented on the same chip with amplifier elements. A disadvantage with active devises is that they cannot usually handle large input power and are not as stable as passive multipliers [8]. Active Multiplier An active frequency multiplier generates harmonics by rectifying the sinusoidal input signal. The principal of operation is that the active devices such as a FET or BJT are biased near its pinch-off point of DC load line. The input sinusoidal turns the device on over part of its cycle. The Figure 2.2: ideal circuit of active frequency multiplier [3] As shown in figure, gate is driven by an RF source. Gate bias voltage is somewhat below (more negative) than pinchoff. So FET conducts only for the period when the gate voltage is above the voltagev p. This whole period is known as duty cycle. Duty cycle of the drain current pulses can be adjusted by changing the DC gate biasv gg. A shorter dutycycle is necessary for higher harmonics because as per the generation of harmonics, number of harmonics is directly proportional to the distortion in applied sinusoidal signal. So, for more harmonics in active multiplier it requires more negative gate voltage v gg and great RF input required. As we continue to decrease the duty cycle in this manner, eventually the negative peaks of the gate voltage reach the gate breakdown voltage [3] The most important characteristic of active multiplier is the possibility of obtaining conversion gain instead of loss. HEMT s have relatively low values of I max and I max is proportional to gate width. Output power depends largely on the size of the device. There is a tradeoff between power against gain. To achieve gain at higher output frequency, C gs must be reduced and this requires a narrow device. A narrow device results in lower output power. [2] FET and BJT frequency multipliers can be made very broadband, but again there is a price, increasing the bandwidth reduces conversion gain. As with other FET circuits, the FET s input Q may be very high, and if the multiplier s 229
3 bandwidth is more than few percent, the input may be impossible to match over the whole band. [3] So, the active multipliers are narrowband and it has some stability problem. Active multiplier cannot be higher order multiplier because if the order of multiplication is high then providing the required matching for higher frequency is difficult. To overcome these all problems, we go with the passive multiplier. Passive Multiplier There are number of efficient ways to generate harmonics with passive devices. The dominant devices are schottky-barrier diode, varactor diode and step-recovery diode. According to diode their resistive or capacitive nonlinearity are used to generate harmonics of input sinusoidal signal. Resistive frequency multiplier: Resistive frequency multipliers use the nonlinear I/V characteristic of a schottky barrier diode to distort a sinusoidal waveform. This distortion generates the harmonics. The optimum efficiency of a resistive frequency multiplier can be no greater than 1/n 2, where n is the harmonic number [3]. Resistive multiplier has broader bandwidth because schottky diode is used as a resistive device and it has inherently very broadband. Varactor multiplier: The nonlinearity of capacitance C/V is used to distort the sinusoidal signal. But one problem is that designing a varactor multiplier is the diode s weak reactive nonlinearity. Without some tricks, the multiplier does not generate harmonics beyond the second. A varactor is capable of higher efficiency and power than a resistive multiplier. If the current in the diode is sinusoidal, the charge function will vary in the same way, and the junction voltage will be roughly proportional to the square of the charge. This means that the varactor multiplier will generates only second harmonics efficiently. For higher harmonics, an idler, a short circuit resonator tuned to the second harmonic in parallel with the diode is used. This idler allows a second harmonic current to circulate through the diode and to mix with the fundamental, producing a third harmonic. [2] Step-recovery diode multiplier: A SRD frequency multiplier is a reactive device, but it operates somewhat differently from a conventional varactor multiplier. SRDs are generating high harmonics from a relatively low frequency excitation. SRDs can generate large pulses a few tens of picoseconds large. Because SRD multipliers invariably are high order, conversion loss can be high. In SRD does not require any type of idler to generate higher order harmonics. SRDs use the diode s diffusion capacitance for charge storage nonlinearity to generate harmonics. [2] From above all multipliers, SRD multiplier and varactors are prone to instability. They also are sensitive to circuit parameters, and requires a high tolerance for frustration. For terahertz application only schottky diode multiplier are used because the switching speed of schottky diode is higher than all other devices. In schottky diode, only majority carriers are participating in any conduction process so, depletion region created at the junction is very narrow. Voltage required to remove this stored charge in the depletion region is very small. So cut-in voltage of schottky diode is very less and switching speed of that diode is high which meets the requirement to design multiplier at terahertz frequency range. 3. Schottky diode frequency multiplier For millimeter and submillimeter wave frequency multipliers, schottky planar varactors are still providing the best performance in terms of efficiency, output power, and instantaneous bandwidth [5]. Planar schottky diodes were introduced over a decade ago [9], [10] and now have been successfully demonstrated well into the terahertz range, replacing whisker-contacted schottky diode [2] Schottky based multipliers can be divided into reactive (varactors diodes) and resistive (varistor diodes) multipliers. Mixed mode of operation is also possible. Varactors multipliers have larger efficiencies and produce more output power than multipliers based on resistive schottky diodes. Resistive multipliers on the other hand have smaller capacitance variation and thus can be designed to cover wider bandwidths than varactors multipliers [7]. Passive multiplier has more advantages over on active multiplier. Passive multiplier using schottky diode handle large input power and it is stable for high frequency. To design a MMIC frequency multiplier for a frequency higher than 100 GHz BES process by United Monolithic Semiconductors (UMS) is use. The main component of BES process is schottky diode because schottky diode s switching frequency is higher than all other diodes. Diode is nonlinear device so it used to design frequency multiplier and its current equation is given by I D = I s [exp q V j ƞkt Where 1] (1) k T q = 25.8 mv for T= 293 K (absolute temperature) V j = junction voltage k = Boltzmann s constant I s = saturation current ƞ= ideality factor In paper [11] the authors have discussed three types of structures to design a multiplier using schottky diode. First one is common balanced tripler whose block diagram is shown in figure 3.1. As shown in this figure on chip capacitor is required for applying DC bias to the schottky diode. Constrained by the technological level, the on chip capacitor cannot be achieved. 230
4 For schottky varactor diode s cutoff frequency should be much higher than the operating frequency [11]. Figure 3.1: block diagram of common balanced tripler [11] To overcome on chip capacitor problem, a tripler is implemented without bias circuit [12] which is shown in below figure 3.2. Here diodes are connected in anti-parallel form. So the even harmonics of the input signal are trapped in a virtual short circuit formed by the diodes and suppressed. And at output side only odd harmonics of the applied signal is available. The disadvantages of this scheme are that the efficiency is relatively low, and heat accumulation happens in the schottky junction when high input power is added due to the poor thermal conductivity of quartz glass [11]. Figure 3.3: block diagram of unbalanced tripler with bias circuit [11] The input circuit as well as the output circuit, consists of the Microstrip-waveguide transition and matching circuit [5].The input and output circuits must fulfill demanding criteria. First, the circuits must obviously let the wanted signal to pass and second, to provide a reasonably large reactive load at other frequencies. In addition, the circuit elements should be as small as possible to minimize the chip size and transmission line losses The tripler consists of input output matching circuits, separates bias routes for both diodes and of a diode pair. In order to suppress the coupled slotline mode and to obtain a symmetric coplanar mode, the circuit was designed to be as symmetric as possible [8]. Figure 3.2: block diagram of tripler without bias circuit [11] To overcome these problems, an unbalanced scheme discussed in [12] with a pair of schottky diode is in parallel is adopted is shown in figure. Because of this type of structure, even harmonics are not suppressed; hence the design process gets more difficult. Design methodology: usually, the first step in the design of frequency multiplier is to determine the characteristics of the diodes along with the operating conditions that best suits the application. Such as a doping level, diode dimensions, and the bias voltage for a given input power once these parameters are fixed and the optimum embedding impedances of the diodes are determined, a linear circuit can be synthesized [5]. The input and output circuits must fulfill a demanding criteria. First, the circuits must obviously let the wanted signal to pass and second, to provide a reasonably large reactive load at other frequencies. In addition, the circuit elements should be as small as possible to minimize the chip size and transmission line losses. [11] The input circuit, as well as the output circuit, consists of the waveguide-microstrip transition and matching circuit. The input circuit consist a low pass filter whose cutoff frequency ω 0 and DC block capacitor. At output side, the short circuit idlers are used for all unwanted harmonics which behave as short circuit for unwanted harmonics and open circuit for wanted harmonic For schematic simulation process the tripler is divided into two parts: a linear network, which is analyzed using Ansys High Frequency Structure Simulator (HFSS) in consideration of the parasitic effects, and nonlinear behavior of the schottky varactor diode, solved by Agilent Advanced Design Simulator (ADS). [11] 231
5 Paper Input frequency (GHz) Output frequency (GHz) Input power (dbm) Output power (dbm) Conversion loss (db) Efficiency (%) [7] [4] to 2 14 to [11] [6] Table 3.1: summary of the performance of previously designed tripler and this work Conclusion: Available frequency sources and their limitations are discussed in this paper. Frequency multiplier is used to multiply low frequency LO source by any integer multiple and convert it into the high frequency. Using frequency multiplier all problems occurring in direct high LO source is removed. As per requirement of terahertz band only passive multiplier is used because stability and frequency bandwidth of passive multiplier is better than the active multiplier. In multiplier design we use diode structure to generate harmonics and to select desired one bandpass filter used at the output side. This diode multiplier demonstrates a broadband LO source with compact chip size References: [1] Maestrini, A., Ward, J., Chattopadhyay, G., Schlecht, E., & Mehdi, I. (2008). Terahertz Sources Based on Frequency Multiplication and Their Applications. Frequenz, 62(5-6). doi: /freq [2] Frequency Multipliers Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, [3] Maas, S. A. (2003). Nonlinear microwave and RF circuits. Boston, MA: Artech Ho [4] Morgan, M., & Weinreb, S. (n.d.). A full waveguide band MMIC tripler for GHz IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (Cat. No.01CH37157). doi: /mwsym [5] Maestrini, A., Ward, J., Gill, J., Javadi, H., Schlecht, E., Tripon-Canseliet, C Mehdi, I. (2005). A GHz high-efficiency four-anode frequency tripler. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 53(9), doi: /tmtt [6] Ward, J., Schlecht, E., Chattopadhyay, G., Maestrini, A., Gill, J., Maiwald, F.,... Mehdi, I. (n.d.). Capability of THz sources based on Schottky diode frequency multiplier chains IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37535). doi: /mwsym [7] Tero Kiuru, Juha Mallat, Antti V. Räisänen, and Tapani Närhi Compactbroadband MMIC Schottky frequency tripler for GHz. In: Proceedings ofthe 6th European Microwave Integrated Circuits Conference (EuMIC 2011).Manchester, UK October Pages ISBN [8] Chen, G., Wu, Y., Chang, H., Hsin, Y., & Chiong, C. (2009). A GHz low conversion loss tripler in µm MHEMT process Asia Pacific Microwave Conference. doi: /apmc [9] W. L. Bishop, K. McKinney, R. J. Mattauch, T.W. Crowe, and G. Green, A novel Whiskerless Schottky diode for millimeter and submillimeterwave application, in IEEE MTT-S Int. Microwave Symp. Dig., vol. 87,Jun. 1987, pp [10] J. W. Archer, R. A. Batchelor, and C. J. Smith, Lowparasitic, planarschottky diodes for millimeter-wave integrated circuits, IEEE Trans.Microw. Theory Tech., vol. 38, no. 1, pp , Jan [11] Meng, J., Zhang, D. H., Yao, C. F., Jiang, C. H., & Zhao, X. (2015). Design Of A 225 GHz High Output Power Tripler Based On Unbalanced Structure. Progress in Electromagnetic Research C, 56, doi: /pierc [12] J., D.-H, M., & C.-H. Jiang, Z. (2008). Research on the practical design method of 225 GHztripler. In Press. [13] Porterfield, D. W. (2007). High-Efficiency Terahertz Frequency tripler IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium. doi: /mwsym [14] Design and Fabrication of Broadband Hybrid GaAsSchottky Diode Frequency Multipliers. 232
Design of Frequency Multiplier at 120 GHz for Sub-Millimeter Wave LO Development
 IJSRD National Conference on Advances in Computer Science Engineering & Technology May 2017 ISSN: 2321-0613 Design of Frequency Multiplier at 120 GHz for Sub-Millimeter Wave LO Development Dhruvi Prajapati
IJSRD National Conference on Advances in Computer Science Engineering & Technology May 2017 ISSN: 2321-0613 Design of Frequency Multiplier at 120 GHz for Sub-Millimeter Wave LO Development Dhruvi Prajapati
Design Considerations for a 1.9 THz Frequency Tripler Based on Membrane Technology
 Design Considerations for a.9 THz Frequency Tripler Based on Membrane Technology Alain Maestrini, David Pukala, Goutam Chattopadhyay, Erich Schlecht and Imran Mehdi Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California
Design Considerations for a.9 THz Frequency Tripler Based on Membrane Technology Alain Maestrini, David Pukala, Goutam Chattopadhyay, Erich Schlecht and Imran Mehdi Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California
ULTRA LOW CAPACITANCE SCHOTTKY DIODES FOR MIXER AND MULTIPLIER APPLICATIONS TO 400 GHZ
 ULTRA LOW CAPACITANCE SCHOTTKY DIODES FOR MIXER AND MULTIPLIER APPLICATIONS TO 400 GHZ Byron Alderman, Hosh Sanghera, Leo Bamber, Bertrand Thomas, David Matheson Abstract Space Science and Technology Department,
ULTRA LOW CAPACITANCE SCHOTTKY DIODES FOR MIXER AND MULTIPLIER APPLICATIONS TO 400 GHZ Byron Alderman, Hosh Sanghera, Leo Bamber, Bertrand Thomas, David Matheson Abstract Space Science and Technology Department,
Frequency Multipliers
 Frequency Multipliers Dr. Alain Maestrini Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, LISIF / Observatoire de Paris, LERMA Formerly at Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology A. Maestrini:
Frequency Multipliers Dr. Alain Maestrini Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, LISIF / Observatoire de Paris, LERMA Formerly at Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology A. Maestrini:
Schottky diode characterization, modelling and design for THz front-ends
 Invited Paper Schottky diode characterization, modelling and design for THz front-ends Tero Kiuru * VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, Communication systems P.O Box 1000, FI-02044 VTT, Finland *
Invited Paper Schottky diode characterization, modelling and design for THz front-ends Tero Kiuru * VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, Communication systems P.O Box 1000, FI-02044 VTT, Finland *
A 200 GHz Broadband, Fixed-Tuned, Planar Doubler
 A 200 GHz Broadband, Fixed-Tuned, Planar Doubler David W. Porterfield Virginia Millimeter Wave, Inc. 706 Forest St., Suite D Charlottesville, VA 22903 Abstract - A 100/200 GHz planar balanced frequency
A 200 GHz Broadband, Fixed-Tuned, Planar Doubler David W. Porterfield Virginia Millimeter Wave, Inc. 706 Forest St., Suite D Charlottesville, VA 22903 Abstract - A 100/200 GHz planar balanced frequency
A Self-Biased Anti-parallel Planar Varactor Diode
 Page 356 A Self-Biased Anti-parallel Planar Varactor Diode Neal R. Erickson Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA 01003 Abstract A set of design criteria are presented
Page 356 A Self-Biased Anti-parallel Planar Varactor Diode Neal R. Erickson Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA 01003 Abstract A set of design criteria are presented
Design of a 212 GHz LO Source Used in the Terahertz Radiometer Front-End
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 66, 65 70, 2017 Design of a 212 GHz LO Source Used in the Terahertz Radiometer Front-End Jin Meng *, De Hai Zhang, Chang Hong Jiang, Xin Zhao, and Xiao
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 66, 65 70, 2017 Design of a 212 GHz LO Source Used in the Terahertz Radiometer Front-End Jin Meng *, De Hai Zhang, Chang Hong Jiang, Xin Zhao, and Xiao
Design of a 225 GHz High Output Power Tripler Based on Unbalanced Structure
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 56, 101 108, 2015 Design of a 225 GHz High Output Power Tripler Based on Unbalanced Structure Jin Meng 1, 2, *, De Hai Zhang 1, Chang Fei Yao 3, Chang Hong
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 56, 101 108, 2015 Design of a 225 GHz High Output Power Tripler Based on Unbalanced Structure Jin Meng 1, 2, *, De Hai Zhang 1, Chang Fei Yao 3, Chang Hong
A 600 GHz Varactor Doubler using CMOS 65nm process
 A 600 GHz Varactor Doubler using CMOS 65nm process S.H. Choi a and M.Kim School of Electrical Engineering, Korea University E-mail : hyperleonheart@hanmail.net Abstract - Varactor and active mode doublers
A 600 GHz Varactor Doubler using CMOS 65nm process S.H. Choi a and M.Kim School of Electrical Engineering, Korea University E-mail : hyperleonheart@hanmail.net Abstract - Varactor and active mode doublers
GHz Membrane Based Schottky Diode Triplers
 1400-1900 GHz Membrane Based Schottky Diode Triplers Alain Maestrini, Goutam Chattopadhyay, Erich Schlecht, David Pukala and Imran Mehdi Jet Propulsion Laboratory, MS 168-314, 4800 Oak Grove Drive, Pasadena,
1400-1900 GHz Membrane Based Schottky Diode Triplers Alain Maestrini, Goutam Chattopadhyay, Erich Schlecht, David Pukala and Imran Mehdi Jet Propulsion Laboratory, MS 168-314, 4800 Oak Grove Drive, Pasadena,
AT millimeter and submillimeter wavelengths quite a few new instruments are being built for astronomical,
 NINTH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON TERAHERTZ ELECTRONICS, OCTOBER 15-16, 20 1 An 800 GHz Broadband Planar Schottky Balanced Doubler Goutam Chattopadhyay, Erich Schlecht, John Gill, Suzanne Martin, Alain
NINTH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON TERAHERTZ ELECTRONICS, OCTOBER 15-16, 20 1 An 800 GHz Broadband Planar Schottky Balanced Doubler Goutam Chattopadhyay, Erich Schlecht, John Gill, Suzanne Martin, Alain
A New Topology of Load Network for Class F RF Power Amplifiers
 A New Topology of Load Network for Class F RF Firas Mohammed Ali Al-Raie Electrical Engineering Department, University of Technology/Baghdad. Email: 30204@uotechnology.edu.iq Received on:12/1/2016 & Accepted
A New Topology of Load Network for Class F RF Firas Mohammed Ali Al-Raie Electrical Engineering Department, University of Technology/Baghdad. Email: 30204@uotechnology.edu.iq Received on:12/1/2016 & Accepted
Broadband Fixed-Tuned Subharmonic Receivers to 640 GHz
 Broadband Fixed-Tuned Subharmonic Receivers to 640 GHz Jeffrey Hesler University of Virginia Department of Electrical Engineering Charlottesville, VA 22903 phone 804-924-6106 fax 804-924-8818 (hesler@virginia.edu)
Broadband Fixed-Tuned Subharmonic Receivers to 640 GHz Jeffrey Hesler University of Virginia Department of Electrical Engineering Charlottesville, VA 22903 phone 804-924-6106 fax 804-924-8818 (hesler@virginia.edu)
Millimeter- and Submillimeter-Wave Planar Varactor Sideband Generators
 Millimeter- and Submillimeter-Wave Planar Varactor Sideband Generators Haiyong Xu, Gerhard S. Schoenthal, Robert M. Weikle, Jeffrey L. Hesler, and Thomas W. Crowe Department of Electrical and Computer
Millimeter- and Submillimeter-Wave Planar Varactor Sideband Generators Haiyong Xu, Gerhard S. Schoenthal, Robert M. Weikle, Jeffrey L. Hesler, and Thomas W. Crowe Department of Electrical and Computer
Planar Frequency Doublers and Triplers for FIRST
 Planar Frequency Doublers and Triplers for FIRST N.R. Erickson and G. Narayanan Dept. of Physics and Astronomy University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA 01003 Introduction R.P. Smith, S.C. Martin and I.
Planar Frequency Doublers and Triplers for FIRST N.R. Erickson and G. Narayanan Dept. of Physics and Astronomy University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA 01003 Introduction R.P. Smith, S.C. Martin and I.
A TRIPLER TO 220 Gliz USING A BACK-TO-BACK BARRIER-N-N + VARACTOR DIODE
 Fifth International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Page 475 A TRIPLER TO 220 Gliz USING A BACK-TO-BACK BARRIER-N-N + VARACTOR DIODE DEBABANI CHOUDHURY, PETER H. SIEGEL, ANTTI V. JUISANEN*, SUZANNE
Fifth International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Page 475 A TRIPLER TO 220 Gliz USING A BACK-TO-BACK BARRIER-N-N + VARACTOR DIODE DEBABANI CHOUDHURY, PETER H. SIEGEL, ANTTI V. JUISANEN*, SUZANNE
White Paper. A High Performance, GHz MMIC Frequency Multiplier with Low Input Drive Power and High Output Power. I.
 A High Performance, 2-42 GHz MMIC Frequency Multiplier with Low Input Drive Power and High Output Power White Paper By: ushil Kumar and Henrik Morkner I. Introduction Frequency multipliers are essential
A High Performance, 2-42 GHz MMIC Frequency Multiplier with Low Input Drive Power and High Output Power White Paper By: ushil Kumar and Henrik Morkner I. Introduction Frequency multipliers are essential
Development of Local Oscillators for CASIMIR
 Development of Local Oscillators for CASIMIR R. Lin, B. Thomas, J. Ward 1, A. Maestrini 2, E. Schlecht, G. Chattopadhyay, J. Gill, C. Lee, S. Sin, F. Maiwald, and I. Mehdi Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California
Development of Local Oscillators for CASIMIR R. Lin, B. Thomas, J. Ward 1, A. Maestrini 2, E. Schlecht, G. Chattopadhyay, J. Gill, C. Lee, S. Sin, F. Maiwald, and I. Mehdi Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California
A FIXED-TUNED 400 GHz SUBHARIVIONIC MIXER
 A FIXED-TUNED 400 GHz SUBHARIVIONIC MIXER USING PLANAR SCHOTTKY DIODES Jeffrey L. Hesler% Kai Hui, Song He, and Thomas W. Crowe Department of Electrical Engineering University of Virginia Charlottesville,
A FIXED-TUNED 400 GHz SUBHARIVIONIC MIXER USING PLANAR SCHOTTKY DIODES Jeffrey L. Hesler% Kai Hui, Song He, and Thomas W. Crowe Department of Electrical Engineering University of Virginia Charlottesville,
QUANTUM WELL DIODE FREQUENCY MULTIPLIER STUDY. Abstract. Quantum Well Diode Odd Harmonic Frequency Multipliers
 Page 226 Second International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology QUANTUM WELL DIODE FREQUENCY MULTIPLIER STUDY R. J. Hwu Department of Electrical Engineering University of Utah N. C. Luhmann, Jr.
Page 226 Second International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology QUANTUM WELL DIODE FREQUENCY MULTIPLIER STUDY R. J. Hwu Department of Electrical Engineering University of Utah N. C. Luhmann, Jr.
Monte Carlo Simulation of Schottky Barrier Mixers and Varactors
 Page 442 Sixth International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Monte Carlo Simulation of Schottky Barrier Mixers and Varactors J. East Center for Space Terahertz Technology The University of Michigan
Page 442 Sixth International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Monte Carlo Simulation of Schottky Barrier Mixers and Varactors J. East Center for Space Terahertz Technology The University of Michigan
The Schottky Diode Mixer. Application Note 995
 The Schottky Diode Mixer Application Note 995 Introduction A major application of the Schottky diode is the production of the difference frequency when two frequencies are combined or mixed in the diode.
The Schottky Diode Mixer Application Note 995 Introduction A major application of the Schottky diode is the production of the difference frequency when two frequencies are combined or mixed in the diode.
A BACK-TO-BACK BARRIER-N-N P (bbbnn) DIODE TRIPLER AT 200 GHz
 Page 274 A BACK-TO-BACK BARRIER-N-N P (bbbnn) DIODE TRIPLER AT 200 GHz Debabani Choudhury, Antti V. Raisänen, R. Peter Smith, and Margaret A. Frerking Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute fo
Page 274 A BACK-TO-BACK BARRIER-N-N P (bbbnn) DIODE TRIPLER AT 200 GHz Debabani Choudhury, Antti V. Raisänen, R. Peter Smith, and Margaret A. Frerking Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute fo
A New Microwave One Port Transistor Amplifier with High Performance for L- Band Operation
 A New Microwave One Port Transistor Amplifier with High Performance for L- Band Operation A. P. VENGUER, J. L. MEDINA, R. CHÁVEZ, A. VELÁZQUEZ Departamento de Electrónica y Telecomunicaciones Centro de
A New Microwave One Port Transistor Amplifier with High Performance for L- Band Operation A. P. VENGUER, J. L. MEDINA, R. CHÁVEZ, A. VELÁZQUEZ Departamento de Electrónica y Telecomunicaciones Centro de
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction of Device Technology Digital wireless communication system has become more and more popular in recent years due to its capability for both voice and data communication.
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction of Device Technology Digital wireless communication system has become more and more popular in recent years due to its capability for both voice and data communication.
High Efficiency Classes of RF Amplifiers
 Rok / Year: Svazek / Volume: Číslo / Number: Jazyk / Language 2018 20 1 EN High Efficiency Classes of RF Amplifiers - Erik Herceg, Tomáš Urbanec urbanec@feec.vutbr.cz, herceg@feec.vutbr.cz Faculty of Electrical
Rok / Year: Svazek / Volume: Číslo / Number: Jazyk / Language 2018 20 1 EN High Efficiency Classes of RF Amplifiers - Erik Herceg, Tomáš Urbanec urbanec@feec.vutbr.cz, herceg@feec.vutbr.cz Faculty of Electrical
Frequency Multipliers Design Techniques and Applications
 Frequency Multipliers Design Techniques and Applications Carlos E. Saavedra Associate Professor Electrical and Computer Engineering Queen s University Kingston, Ontario CANADA Outline Introduction applications
Frequency Multipliers Design Techniques and Applications Carlos E. Saavedra Associate Professor Electrical and Computer Engineering Queen s University Kingston, Ontario CANADA Outline Introduction applications
Sub-millimeter wave MMIC Schottky subharmonic mixer testing at passive cooling temperatures
 15 1 Sub-millimeter wave MMIC Schottky subharmonic mixer testing at passive cooling temperatures B. Thomas, E. Schlecht, A. Maestrini, J. Ward, G. Chattopadhyay, R. Lin, J. Gill, C. Lee, and I. Mehdi Abstract
15 1 Sub-millimeter wave MMIC Schottky subharmonic mixer testing at passive cooling temperatures B. Thomas, E. Schlecht, A. Maestrini, J. Ward, G. Chattopadhyay, R. Lin, J. Gill, C. Lee, and I. Mehdi Abstract
Negative Differential Resistance (NDR) Frequency Conversion with Gain
 Third International Symposium on Space Tcrahertz Technology Page 457 Negative Differential Resistance (NDR) Frequency Conversion with Gain R. J. Hwu, R. W. Aim, and S. C. Lee Department of Electrical Engineering
Third International Symposium on Space Tcrahertz Technology Page 457 Negative Differential Resistance (NDR) Frequency Conversion with Gain R. J. Hwu, R. W. Aim, and S. C. Lee Department of Electrical Engineering
ALMA MEMO 399 Millimeter Wave Generation Using a Uni-Traveling-Carrier Photodiode
 ALMA MEMO 399 Millimeter Wave Generation Using a Uni-Traveling-Carrier Photodiode T. Noguchi, A. Ueda, H.Iwashita, S. Takano, Y. Sekimoto, M. Ishiguro, T. Ishibashi, H. Ito, and T. Nagatsuma Nobeyama Radio
ALMA MEMO 399 Millimeter Wave Generation Using a Uni-Traveling-Carrier Photodiode T. Noguchi, A. Ueda, H.Iwashita, S. Takano, Y. Sekimoto, M. Ishiguro, T. Ishibashi, H. Ito, and T. Nagatsuma Nobeyama Radio
Numerical analysis of a 330 GHz sub-harmonic mixer with planar Schottky diodes, LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France
 Abstract Numerical analysis of a 330 GHz sub-harmonic mixer with planar Schottky diodes, LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France B. Thomas (1), A. Maestrini (1), JC. Orlhac (2), JM. Goutoule (2), G. Beaudin
Abstract Numerical analysis of a 330 GHz sub-harmonic mixer with planar Schottky diodes, LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France B. Thomas (1), A. Maestrini (1), JC. Orlhac (2), JM. Goutoule (2), G. Beaudin
LOW NOISE GHZ RECEIVERS USING SINGLE-DIODE HARMONIC MIXERS
 First International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Page 399 LOW NOISE 500-700 GHZ RECEIVERS USING SINGLE-DIODE HARMONIC MIXERS Neal R. Erickson Millitech Corp. P.O. Box 109 S. Deerfield, MA 01373
First International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Page 399 LOW NOISE 500-700 GHZ RECEIVERS USING SINGLE-DIODE HARMONIC MIXERS Neal R. Erickson Millitech Corp. P.O. Box 109 S. Deerfield, MA 01373
Optoelectronic Oscillator Topologies based on Resonant Tunneling Diode Fiber Optic Links
 Optoelectronic Oscillator Topologies based on Resonant Tunneling Diode Fiber Optic Links Bruno Romeira* a, José M. L Figueiredo a, Kris Seunarine b, Charles N. Ironside b, a Department of Physics, CEOT,
Optoelectronic Oscillator Topologies based on Resonant Tunneling Diode Fiber Optic Links Bruno Romeira* a, José M. L Figueiredo a, Kris Seunarine b, Charles N. Ironside b, a Department of Physics, CEOT,
MEASUREMENT AND OPTIMIZATION OF FREQUENCY MULTIPLIERS USING AN AUTOMATED TEST BENCH
 MEASUREMENT AND OPTIMIZATION OF FREQUENCY MULTIPLIERS USING AN AUTOMATED TEST BENCH Colin Viegas 1, Byron Alderman 2, Jeff Powell 2, Hairui Lui 2 and Robin Sloan 1 1 School of EEE, The University of Manchester,
MEASUREMENT AND OPTIMIZATION OF FREQUENCY MULTIPLIERS USING AN AUTOMATED TEST BENCH Colin Viegas 1, Byron Alderman 2, Jeff Powell 2, Hairui Lui 2 and Robin Sloan 1 1 School of EEE, The University of Manchester,
A Miniaturized Multi-Channel TR Module Design Based on Silicon Substrate
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 74, 117 123, 2018 A Miniaturized Multi-Channel TR Module Design Based on Silicon Substrate Jun Zhou 1, 2, *, Jiapeng Yang 1, Donglei Zhao 1, and Dongsheng
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 74, 117 123, 2018 A Miniaturized Multi-Channel TR Module Design Based on Silicon Substrate Jun Zhou 1, 2, *, Jiapeng Yang 1, Donglei Zhao 1, and Dongsheng
High Power Local Oscillator Sources for 1-2 THz
 High Power Local Oscillator Sources for 1-2 THz Imran Mehdi, Bertrand Thomas, Robert Lin, Alain Maestrini, * John Ward, ** Erich Schlecht, John Gill, Choonsup Lee, Goutam Chattopadhyay, and Frank Maiwald
High Power Local Oscillator Sources for 1-2 THz Imran Mehdi, Bertrand Thomas, Robert Lin, Alain Maestrini, * John Ward, ** Erich Schlecht, John Gill, Choonsup Lee, Goutam Chattopadhyay, and Frank Maiwald
Design and simulation of Parallel circuit class E Power amplifier
 International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 3 Issue 7 Pages 3270-3274 2015 \ Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Design and simulation of Parallel circuit class E Power
International Journal of scientific research and management (IJSRM) Volume 3 Issue 7 Pages 3270-3274 2015 \ Website: www.ijsrm.in ISSN (e): 2321-3418 Design and simulation of Parallel circuit class E Power
Universal Generator of Ultra-Wideband Pulses
 74 P. PROTIVA, J. MRKVICA, J. MACHÁČ, UNIVERSAL GENERATOR OF ULTRA-WIDEBAND PULSES Universal Generator of Ultra-Wideband Pulses Pavel PROTIVA 1, Jan MRKVICA 2, Jan MACHÁČ 1 1 Dept. of Electromagnetic Field,
74 P. PROTIVA, J. MRKVICA, J. MACHÁČ, UNIVERSAL GENERATOR OF ULTRA-WIDEBAND PULSES Universal Generator of Ultra-Wideband Pulses Pavel PROTIVA 1, Jan MRKVICA 2, Jan MACHÁČ 1 1 Dept. of Electromagnetic Field,
WIDE-BAND HIGH ISOLATION SUBHARMONICALLY PUMPED RESISTIVE MIXER WITH ACTIVE QUASI- CIRCULATOR
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 18, 135 143, 2010 WIDE-BAND HIGH ISOLATION SUBHARMONICALLY PUMPED RESISTIVE MIXER WITH ACTIVE QUASI- CIRCULATOR W. C. Chien, C.-M. Lin, C.-H. Liu, S.-H.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 18, 135 143, 2010 WIDE-BAND HIGH ISOLATION SUBHARMONICALLY PUMPED RESISTIVE MIXER WITH ACTIVE QUASI- CIRCULATOR W. C. Chien, C.-M. Lin, C.-H. Liu, S.-H.
Tunable All-Solid-State Local Oscillators to 1900 GHz
 15th International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Tunable All-Solid-State Local Oscillators to 1900 GHz John Ward, Goutam Chattopadhyay, Alain Maestrini 1, Erich Schlecht, John Gill, Hamid Javadi,
15th International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Tunable All-Solid-State Local Oscillators to 1900 GHz John Ward, Goutam Chattopadhyay, Alain Maestrini 1, Erich Schlecht, John Gill, Hamid Javadi,
Wideband 760GHz Planar Integrated Schottky Receiver
 Page 516 Fourth International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology This is a review paper. The material presented below has been submitted for publication in IEEE Microwave and Guided Wave Letters.
Page 516 Fourth International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology This is a review paper. The material presented below has been submitted for publication in IEEE Microwave and Guided Wave Letters.
This article describes a computational
 Computer-Aided Design of Diode Frequency Multipliers This article describes the development and use of the MultFreq program for diode multipliers, and provides a practical example By Cezar A. A. Carioca,
Computer-Aided Design of Diode Frequency Multipliers This article describes the development and use of the MultFreq program for diode multipliers, and provides a practical example By Cezar A. A. Carioca,
Characteristics of InP HEMT Harmonic Optoelectronic Mixers and Their Application to 60GHz Radio-on-Fiber Systems
 . TU6D-1 Characteristics of Harmonic Optoelectronic Mixers and Their Application to 6GHz Radio-on-Fiber Systems Chang-Soon Choi 1, Hyo-Soon Kang 1, Dae-Hyun Kim 2, Kwang-Seok Seo 2 and Woo-Young Choi 1
. TU6D-1 Characteristics of Harmonic Optoelectronic Mixers and Their Application to 6GHz Radio-on-Fiber Systems Chang-Soon Choi 1, Hyo-Soon Kang 1, Dae-Hyun Kim 2, Kwang-Seok Seo 2 and Woo-Young Choi 1
Design of a Broadband HEMT Mixer for UWB Applications
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(26), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i26/97253, July 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Design of a Broadband HEMT Mixer for UWB Applications
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 9(26), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2016/v9i26/97253, July 2016 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Design of a Broadband HEMT Mixer for UWB Applications
20 40 GHz Amplifier. Technical Data HMMC-5040
 2 4 GHz Amplifier Technical Data HMMC-4 Features Large Bandwidth: 2-44 GHz Typical - 4 GHz Specified High : db Typical Saturated Output Power: dbm Typical Supply Bias: 4. volts @ 3 ma Description The HMMC-4
2 4 GHz Amplifier Technical Data HMMC-4 Features Large Bandwidth: 2-44 GHz Typical - 4 GHz Specified High : db Typical Saturated Output Power: dbm Typical Supply Bias: 4. volts @ 3 ma Description The HMMC-4
Preface Introduction p. 1 History and Fundamentals p. 1 Devices for Mixers p. 6 Balanced and Single-Device Mixers p. 7 Mixer Design p.
 Preface Introduction p. 1 History and Fundamentals p. 1 Devices for Mixers p. 6 Balanced and Single-Device Mixers p. 7 Mixer Design p. 9 Monolithic Circuits p. 10 Schottky-Barrier Diodes p. 11 Schottky-Diode
Preface Introduction p. 1 History and Fundamentals p. 1 Devices for Mixers p. 6 Balanced and Single-Device Mixers p. 7 Mixer Design p. 9 Monolithic Circuits p. 10 Schottky-Barrier Diodes p. 11 Schottky-Diode
DESIGN OF AN S-BAND TWO-WAY INVERTED ASYM- METRICAL DOHERTY POWER AMPLIFIER FOR LONG TERM EVOLUTION APPLICATIONS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 39, 73 80, 2013 DESIGN OF AN S-BAND TWO-WAY INVERTED ASYM- METRICAL DOHERTY POWER AMPLIFIER FOR LONG TERM EVOLUTION APPLICATIONS Hai-Jin Zhou * and Hua
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 39, 73 80, 2013 DESIGN OF AN S-BAND TWO-WAY INVERTED ASYM- METRICAL DOHERTY POWER AMPLIFIER FOR LONG TERM EVOLUTION APPLICATIONS Hai-Jin Zhou * and Hua
Design of THz Signal Generation Circuits Using 65nm CMOS Technologies
 Design of THz Signal Generation Circuits Using 65nm CMOS Technologies Hyeong-Jin Kim, Wonseok Choe, and Jinho Jeong Department of Electronics Engineering, Sogang University E-mail: jjeong@sogang.ac.kr
Design of THz Signal Generation Circuits Using 65nm CMOS Technologies Hyeong-Jin Kim, Wonseok Choe, and Jinho Jeong Department of Electronics Engineering, Sogang University E-mail: jjeong@sogang.ac.kr
FABRICATION AND OPTIMISATION OF PLANAR SCHOTTKY DIODES
 Eighth International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology. Harvard University, March 997 FABRICATION AND OPTIMISATION OF PLANAR SCHOTTKY DIODES A. Simon, C. I. Lin #, H. L. Hartnage P. Zimmermann*,
Eighth International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology. Harvard University, March 997 FABRICATION AND OPTIMISATION OF PLANAR SCHOTTKY DIODES A. Simon, C. I. Lin #, H. L. Hartnage P. Zimmermann*,
A High-Power Wideband Cryogenic 200 GHz Schottky Substrateless Multiplier: Modeling, Design and Results
 A High-Power Wideband Cryogenic 2 GHz Schottky Substrateless Multiplier: Modeling, Design and Results E. Schlecht, G. Chattopadhyay, A. Maestrini, D. Pukala, J. Gill, S. Martin*, F. Maiwald and I. Mehdi
A High-Power Wideband Cryogenic 2 GHz Schottky Substrateless Multiplier: Modeling, Design and Results E. Schlecht, G. Chattopadhyay, A. Maestrini, D. Pukala, J. Gill, S. Martin*, F. Maiwald and I. Mehdi
Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent
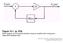 Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent feedback path. Figure 12-2 (p. 579) General circuit for a transistor oscillator. The transistor
Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent feedback path. Figure 12-2 (p. 579) General circuit for a transistor oscillator. The transistor
mhemt based MMICs, Modules, and Systems for mmwave Applications Axel Hülsmann Axel Tessmann Jutta Kühn Oliver Ambacher
 mhemt based MMICs, Modules, and Systems for mmwave Applications Christaweg 54 79114 Freiburg, Germany +49 761 5951 4692 info@ondosense.com www.ondosense.com Axel Hülsmann Axel Tessmann Jutta Kühn Oliver
mhemt based MMICs, Modules, and Systems for mmwave Applications Christaweg 54 79114 Freiburg, Germany +49 761 5951 4692 info@ondosense.com www.ondosense.com Axel Hülsmann Axel Tessmann Jutta Kühn Oliver
PRODUCT APPLICATION NOTES
 Extending the HMC189MS8 Passive Frequency Doubler Operating Range with External Matching General Description The HMC189MS8 is a miniature passive frequency doubler in a plastic 8-lead MSOP package. The
Extending the HMC189MS8 Passive Frequency Doubler Operating Range with External Matching General Description The HMC189MS8 is a miniature passive frequency doubler in a plastic 8-lead MSOP package. The
A COMPACT DOUBLE-BALANCED STAR MIXER WITH NOVEL DUAL 180 HYBRID. National Cheng-Kung University, No. 1 University Road, Tainan 70101, Taiwan
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 24, 147 159, 2011 A COMPACT DOUBLE-BALANCED STAR MIXER WITH NOVEL DUAL 180 HYBRID Y.-A. Lai 1, C.-N. Chen 1, C.-C. Su 1, S.-H. Hung 1, C.-L. Wu 1, 2, and Y.-H.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 24, 147 159, 2011 A COMPACT DOUBLE-BALANCED STAR MIXER WITH NOVEL DUAL 180 HYBRID Y.-A. Lai 1, C.-N. Chen 1, C.-C. Su 1, S.-H. Hung 1, C.-L. Wu 1, 2, and Y.-H.
L AND S BAND TUNABLE FILTERS PROVIDE DRAMATIC IMPROVEMENTS IN TELEMETRY SYSTEMS
 L AND S BAND TUNABLE FILTERS PROVIDE DRAMATIC IMPROVEMENTS IN TELEMETRY SYSTEMS Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Wurth, Timothy J.; Rodzinak, Jason Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering
L AND S BAND TUNABLE FILTERS PROVIDE DRAMATIC IMPROVEMENTS IN TELEMETRY SYSTEMS Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Wurth, Timothy J.; Rodzinak, Jason Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering
A NOVEL BIASED ANTI-PARALLEL SCHOTTKY DIODE STRUCTURE FOR SUBHARMONIC
 Page 342 A NOVEL BIASED ANTI-PARALLEL SCHOTTKY DIODE STRUCTURE FOR SUBHARMONIC Trong-Huang Lee', Chen-Yu Chi", Jack R. East', Gabriel M. Rebeiz', and George I. Haddad" let Propulsion Laboratory California
Page 342 A NOVEL BIASED ANTI-PARALLEL SCHOTTKY DIODE STRUCTURE FOR SUBHARMONIC Trong-Huang Lee', Chen-Yu Chi", Jack R. East', Gabriel M. Rebeiz', and George I. Haddad" let Propulsion Laboratory California
DOUBLE-SIDEBAND MIXER CIRCUITS
 DOUBLE-SIDEBAND MIXER CIRCUITS SBW SERIES Waveguide, SMA / SBB SERIES DC Biasable, Low Power DB, DM SERIES General Purpose SBE SERIES Even Harmonic (1/2 ) TB, TBR SERIES Best Spurs, Overlap / W Y W Y Z
DOUBLE-SIDEBAND MIXER CIRCUITS SBW SERIES Waveguide, SMA / SBB SERIES DC Biasable, Low Power DB, DM SERIES General Purpose SBE SERIES Even Harmonic (1/2 ) TB, TBR SERIES Best Spurs, Overlap / W Y W Y Z
Design of Crossbar Mixer at 94 GHz
 Wireless Sensor Network, 2015, 7, 21-26 Published Online March 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/wsn http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wsn.2015.73003 Design of Crossbar Mixer at 94 GHz Sanjeev Kumar
Wireless Sensor Network, 2015, 7, 21-26 Published Online March 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/wsn http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wsn.2015.73003 Design of Crossbar Mixer at 94 GHz Sanjeev Kumar
POSTER SESSION n'2. Presentation on Friday 12 May 09:00-09:30. Poster session n'2 from 11:00 to 12:30. by Dr. Heribert Eisele & Dr.
 POSTER SESSION n'2 Presentation on Friday 12 May 09:00-09:30 by Dr. Heribert Eisele & Dr. Imran Mehdi Poster session n'2 from 11:00 to 12:30 219 220 Design & test of a 380 GHz sub-harmonic mixer using
POSTER SESSION n'2 Presentation on Friday 12 May 09:00-09:30 by Dr. Heribert Eisele & Dr. Imran Mehdi Poster session n'2 from 11:00 to 12:30 219 220 Design & test of a 380 GHz sub-harmonic mixer using
WIDE-BAND circuits are now in demand as wide-band
 704 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 54, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 Compact Wide-Band Branch-Line Hybrids Young-Hoon Chun, Member, IEEE, and Jia-Sheng Hong, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract
704 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MICROWAVE THEORY AND TECHNIQUES, VOL. 54, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 Compact Wide-Band Branch-Line Hybrids Young-Hoon Chun, Member, IEEE, and Jia-Sheng Hong, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract
MMA RECEIVERS: HFET AMPLIFIERS
 MMA Project Book, Chapter 5 Section 4 MMA RECEIVERS: HFET AMPLIFIERS Marian Pospieszalski Ed Wollack John Webber Last revised 1999-04-09 Revision History: 1998-09-28: Added chapter number to section numbers.
MMA Project Book, Chapter 5 Section 4 MMA RECEIVERS: HFET AMPLIFIERS Marian Pospieszalski Ed Wollack John Webber Last revised 1999-04-09 Revision History: 1998-09-28: Added chapter number to section numbers.
A Varactor-tunable Filter with Constant Bandwidth and Loss Compensation
 A Varactor-tunable Filter with Constant Bandwidth and Loss Compensation April 6, 2... Page 1 of 19 April 2007 Issue: Technical Feature A Varactor-tunable Filter with Constant Bandwidth and Loss Compensation
A Varactor-tunable Filter with Constant Bandwidth and Loss Compensation April 6, 2... Page 1 of 19 April 2007 Issue: Technical Feature A Varactor-tunable Filter with Constant Bandwidth and Loss Compensation
print close Related Low-Cost UWB Source Low-Cost Mixers Build On LTCC Reliability LTCC Launches Miniature, Wideband, Low-Cost Mixers
 print close Design A Simple, Low-Cost UWB Source Microwaves and RF Yeap Yean Wei Fri, 2006-12-15 (All day) Using an inexpensive commercial step recovery diode (SRD) and a handful of passive circuit elements,
print close Design A Simple, Low-Cost UWB Source Microwaves and RF Yeap Yean Wei Fri, 2006-12-15 (All day) Using an inexpensive commercial step recovery diode (SRD) and a handful of passive circuit elements,
Frequency Multiplier Development at e2v Technologies
 Frequency Multiplier Development at e2v Technologies Novak Farrington UK Millimetre-Wave User Group Meeting National Physical Laboratory 05-10-09 Outline Sources available Brief overview of doubler operation
Frequency Multiplier Development at e2v Technologies Novak Farrington UK Millimetre-Wave User Group Meeting National Physical Laboratory 05-10-09 Outline Sources available Brief overview of doubler operation
Varactor Frequency Tripler
 Varactor Frequency Tripler Nonlinear Microwave Design Reto Zingg December 12 th 2 University of Colorado at Boulder Table of Contents 1 Project Goal 3 2 Frequency Multipliers 3 3 Varactor Frequency Multiplier
Varactor Frequency Tripler Nonlinear Microwave Design Reto Zingg December 12 th 2 University of Colorado at Boulder Table of Contents 1 Project Goal 3 2 Frequency Multipliers 3 3 Varactor Frequency Multiplier
An SIS unilateral finline mixer with an ultra-wide IF bandwidth
 An SIS unilateral finline mixer with an ultra-wide IF bandwidth Yangjun Zhou, Jamie Leech, Paul Grimes and Ghassan Yassin Dept. of Physics, University of Oxford, UK Contact: yangjun.zhou@physics.ox.ac.uk,
An SIS unilateral finline mixer with an ultra-wide IF bandwidth Yangjun Zhou, Jamie Leech, Paul Grimes and Ghassan Yassin Dept. of Physics, University of Oxford, UK Contact: yangjun.zhou@physics.ox.ac.uk,
Microwave Office Application Note
 Microwave Office Application Note INTRODUCTION Wireless system components, including gallium arsenide (GaAs) pseudomorphic high-electron-mobility transistor (phemt) frequency doublers, quadruplers, and
Microwave Office Application Note INTRODUCTION Wireless system components, including gallium arsenide (GaAs) pseudomorphic high-electron-mobility transistor (phemt) frequency doublers, quadruplers, and
A 1-W GaAs Class-E Power Amplifier with an FBAR Filter Embedded in the Output Network
 A 1-W GaAs Class-E Power Amplifier with an FBAR Filter Embedded in the Output Network Kyle Holzer and Jeffrey S. Walling University of Utah PERFIC Lab, Salt Lake City, UT 84112, USA Abstract Integration
A 1-W GaAs Class-E Power Amplifier with an FBAR Filter Embedded in the Output Network Kyle Holzer and Jeffrey S. Walling University of Utah PERFIC Lab, Salt Lake City, UT 84112, USA Abstract Integration
EE70 - Intro. Electronics
 EE70 - Intro. Electronics Course website: ~/classes/ee70/fall05 Today s class agenda (November 28, 2005) review Serial/parallel resonant circuits Diode Field Effect Transistor (FET) f 0 = Qs = Qs = 1 2π
EE70 - Intro. Electronics Course website: ~/classes/ee70/fall05 Today s class agenda (November 28, 2005) review Serial/parallel resonant circuits Diode Field Effect Transistor (FET) f 0 = Qs = Qs = 1 2π
A 1.2 THz planar tripler using GaAs membrane based chips
 A 1.2 THz planar tripler using GaAs membrane based chips J. Bruston*, A. Maestrini, D. Pukala, S. Martin, B. Nakamura and I. Mehdi Caltech, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, 4800 Oak Grove dr., Pasadena, CA 91109
A 1.2 THz planar tripler using GaAs membrane based chips J. Bruston*, A. Maestrini, D. Pukala, S. Martin, B. Nakamura and I. Mehdi Caltech, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, 4800 Oak Grove dr., Pasadena, CA 91109
ALMA Memo 436. Band 6 Receiver Noise Measurements using a Pre- Prototype YIG-Tunable LO
 Page: 1 of 11 ALMA Memo 436 Measurements using a Pre- Prototype Eric W. Bryerton, S. K. Pan, Dorsey Thacker, and Kamaljeet Saini National Radio Astronomy Obervatory Charlottesville, VA 2293, USA FEND-.1.6.-1-A-MEM
Page: 1 of 11 ALMA Memo 436 Measurements using a Pre- Prototype Eric W. Bryerton, S. K. Pan, Dorsey Thacker, and Kamaljeet Saini National Radio Astronomy Obervatory Charlottesville, VA 2293, USA FEND-.1.6.-1-A-MEM
A Broadband mm-wave and Terahertz Traveling-Wave Frequency Multiplier on CMOS
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 46, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2011 1 A Broadband mm-wave and Terahertz Traveling-Wave Frequency Multiplier on CMOS Omeed Momeni, Student Member, IEEE, and Ehsan Afshari,
IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 46, NO. 12, DECEMBER 2011 1 A Broadband mm-wave and Terahertz Traveling-Wave Frequency Multiplier on CMOS Omeed Momeni, Student Member, IEEE, and Ehsan Afshari,
ALMA MEMO #360 Design of Sideband Separation SIS Mixer for 3 mm Band
 ALMA MEMO #360 Design of Sideband Separation SIS Mixer for 3 mm Band V. Vassilev and V. Belitsky Onsala Space Observatory, Chalmers University of Technology ABSTRACT As a part of Onsala development of
ALMA MEMO #360 Design of Sideband Separation SIS Mixer for 3 mm Band V. Vassilev and V. Belitsky Onsala Space Observatory, Chalmers University of Technology ABSTRACT As a part of Onsala development of
Research Article A Parallel-Strip Balun for Wideband Frequency Doubler
 Microwave Science and Technology Volume 213, Article ID 8929, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.11/213/8929 Research Article A Parallel-Strip Balun for Wideband Frequency Doubler Leung Chiu and Quan Xue Department
Microwave Science and Technology Volume 213, Article ID 8929, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.11/213/8929 Research Article A Parallel-Strip Balun for Wideband Frequency Doubler Leung Chiu and Quan Xue Department
A Planar Wideband Subharmonic Millimeter-Wave Receiver
 Page 616 Second International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology A Planar Wideband Subharmonic Millimeter-Wave Receiver B. K. Kormanyos, C.C. Ling and G.M. Rebeiz NASA/Center for Space Terahertz Technology
Page 616 Second International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology A Planar Wideband Subharmonic Millimeter-Wave Receiver B. K. Kormanyos, C.C. Ling and G.M. Rebeiz NASA/Center for Space Terahertz Technology
Substrateless Schottky Diodes for THz Applications
 Eighth International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Harvard University March 1997 Substrateless Schottky Diodes for THz Applications C.I. Lin' A. Simon' M. Rodriguez-Gironee H.L. Hartnager P.
Eighth International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Harvard University March 1997 Substrateless Schottky Diodes for THz Applications C.I. Lin' A. Simon' M. Rodriguez-Gironee H.L. Hartnager P.
Integration Techniques for MMICs and Chip Devices in LTCC Multichip Modules for Radio Frequencies
 Integration Techniques for MMICs and Chip Devices in LTCC Multichip Modules for Radio Frequencies R. Kulke *, W. Simon *, M. Rittweger *, I. Wolff *, S. Baker +, R. Powell + and M. Harrison + * Institute
Integration Techniques for MMICs and Chip Devices in LTCC Multichip Modules for Radio Frequencies R. Kulke *, W. Simon *, M. Rittweger *, I. Wolff *, S. Baker +, R. Powell + and M. Harrison + * Institute
GHz Local Oscillators for the Herschel Space Observatory
 14th International Symposium on Space Terahert Technology 1400 1900 GHz Local Oscillators for the Herschel Space Observatory John Ward, Frank Maiwald, Goutam Chattopadhyay, Erich Schlecht, Alain Maestrini
14th International Symposium on Space Terahert Technology 1400 1900 GHz Local Oscillators for the Herschel Space Observatory John Ward, Frank Maiwald, Goutam Chattopadhyay, Erich Schlecht, Alain Maestrini
K-BAND HARMONIC DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OS- CILLATOR USING PARALLEL FEEDBACK STRUC- TURE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 34, 83 90, 2012 K-BAND HARMONIC DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OS- CILLATOR USING PARALLEL FEEDBACK STRUC- TURE Y. C. Du *, Z. X. Tang, B. Zhang, and P. Su School
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 34, 83 90, 2012 K-BAND HARMONIC DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OS- CILLATOR USING PARALLEL FEEDBACK STRUC- TURE Y. C. Du *, Z. X. Tang, B. Zhang, and P. Su School
Simulation of GaAs MESFET and HEMT Devices for RF Applications
 olume, Issue, January February 03 ISSN 78-6856 Simulation of GaAs MESFET and HEMT Devices for RF Applications Dr.E.N.GANESH Prof, ECE DEPT. Rajalakshmi Institute of Technology ABSTRACT: Field effect transistor
olume, Issue, January February 03 ISSN 78-6856 Simulation of GaAs MESFET and HEMT Devices for RF Applications Dr.E.N.GANESH Prof, ECE DEPT. Rajalakshmi Institute of Technology ABSTRACT: Field effect transistor
Design of a Sideband-Separating Balanced SIS Mixer Based on Waveguide Hybrids
 ALMA Memo 316 20 September 2000 Design of a Sideband-Separating Balanced SIS Mixer Based on Waveguide Hybrids S. M. X. Claude 1 and C. T. Cunningham 1, A. R. Kerr 2 and S.-K. Pan 2 1 Herzberg Institute
ALMA Memo 316 20 September 2000 Design of a Sideband-Separating Balanced SIS Mixer Based on Waveguide Hybrids S. M. X. Claude 1 and C. T. Cunningham 1, A. R. Kerr 2 and S.-K. Pan 2 1 Herzberg Institute
A NOVEL SCHEME FOR OPTICAL MILLIMETER WAVE GENERATION USING MZM
 A NOVEL SCHEME FOR OPTICAL MILLIMETER WAVE GENERATION USING MZM Poomari S. and Arvind Chakrapani Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Karpagam College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Tamil
A NOVEL SCHEME FOR OPTICAL MILLIMETER WAVE GENERATION USING MZM Poomari S. and Arvind Chakrapani Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Karpagam College of Engineering, Coimbatore, Tamil
UNIT-4. Microwave Engineering
 UNIT-4 Microwave Engineering Microwave Solid State Devices Two problems with conventional transistors at higher frequencies are: 1. Stray capacitance and inductance. - remedy is interdigital design. 2.Transit
UNIT-4 Microwave Engineering Microwave Solid State Devices Two problems with conventional transistors at higher frequencies are: 1. Stray capacitance and inductance. - remedy is interdigital design. 2.Transit
Prepared by: Dr. Rishi Prakash, Dept of Electronics and Communication Engineering Page 1 of 5
 Microwave tunnel diode Some anomalous phenomena were observed in diode which do not follows the classical diode equation. This anomalous phenomena was explained by quantum tunnelling theory. The tunnelling
Microwave tunnel diode Some anomalous phenomena were observed in diode which do not follows the classical diode equation. This anomalous phenomena was explained by quantum tunnelling theory. The tunnelling
Photodynamics Research Center, The Institute of Physical and Chemical Research, Aza-Koeji, Nagamachi, Aoba-ku, Sendai 980, Japan
 SERIES CONNECTION OF RESONANT TUNNELING DIODES FOR ELIMINATING SPURIOUS OSCILLATIONS Tetsu Fujii 1,2, Olga Boric-Lubecke l, Jongsuck Bae 1.2, and Koji Mizuno 1.2 Photodynamics Research Center, The Institute
SERIES CONNECTION OF RESONANT TUNNELING DIODES FOR ELIMINATING SPURIOUS OSCILLATIONS Tetsu Fujii 1,2, Olga Boric-Lubecke l, Jongsuck Bae 1.2, and Koji Mizuno 1.2 Photodynamics Research Center, The Institute
4th ESA Workshop on Millimetre Wave Technology and Applications. Frequency Multipliers for Local Oscillators at THz Frequencies
 Frequency Multipliers for Local Oscillators at THz Frequencies Alain Maestrini Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris6, LISIF 4 place Jussieu, case 252, 75252 Paris cedex 5, France Email: alain.maestrini@lisif.jussieu.fr
Frequency Multipliers for Local Oscillators at THz Frequencies Alain Maestrini Université Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris6, LISIF 4 place Jussieu, case 252, 75252 Paris cedex 5, France Email: alain.maestrini@lisif.jussieu.fr
Design of Frequency Doubler Using Inductively Compensated Microstrip Ring Resonator
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 32 (2012) 544 549 I-SEEC2011 Design of Frequency Doubler Using Inductively Compensated Microstrip Ring Resonator R. Phromloungsri a, N. Thammawongsa
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 32 (2012) 544 549 I-SEEC2011 Design of Frequency Doubler Using Inductively Compensated Microstrip Ring Resonator R. Phromloungsri a, N. Thammawongsa
325 to 500 GHz Vector Network Analyzer System
 325 to 500 GHz Vector Network Analyzer System By Chuck Oleson, Tony Denning and Yuenie Lau OML, Inc. Abstract - This paper describes a novel and compact WR-02.2 millimeter wave frequency extension transmission/reflection
325 to 500 GHz Vector Network Analyzer System By Chuck Oleson, Tony Denning and Yuenie Lau OML, Inc. Abstract - This paper describes a novel and compact WR-02.2 millimeter wave frequency extension transmission/reflection
Design of Duplexers for Microwave Communication Systems Using Open-loop Square Microstrip Resonators
 International Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications 2016, 6(1): 7-12 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijea.20160601.02 Design of Duplexers for Microwave Communication Charles U. Ndujiuba 1,*, Samuel N. John 1, Taofeek
International Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications 2016, 6(1): 7-12 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijea.20160601.02 Design of Duplexers for Microwave Communication Charles U. Ndujiuba 1,*, Samuel N. John 1, Taofeek
Design and Layout of a X-Band MMIC Power Amplifier in a Phemt Technology
 Design and Layout of a X-Band MMIC Power Amplifier in a Phemt Technology Renbin Dai, and Rana Arslan Ali Khan Abstract The design of Class A and Class AB 2-stage X band Power Amplifier is described in
Design and Layout of a X-Band MMIC Power Amplifier in a Phemt Technology Renbin Dai, and Rana Arslan Ali Khan Abstract The design of Class A and Class AB 2-stage X band Power Amplifier is described in
37-40GHz MMIC Sub-Harmonically Pumped Image Rejection Diode Mixer
 37-40GHz MMIC Sub-Harmonically Pumped Image Rejection Diode Mixer F. Rasà, F. Celestino, M. Remonti, B. Gabbrielli, P. Quentin ALCATEL ITALIA, TSD-HCMW R&D, Str. Provinciale per Monza, 33, 20049 Concorezzo
37-40GHz MMIC Sub-Harmonically Pumped Image Rejection Diode Mixer F. Rasà, F. Celestino, M. Remonti, B. Gabbrielli, P. Quentin ALCATEL ITALIA, TSD-HCMW R&D, Str. Provinciale per Monza, 33, 20049 Concorezzo
High Efficiency Class-F MMIC Power Amplifiers at Ku-Band
 High Efficiency Class-F MMIC Power Amplifiers at Ku-Band Matthew T. Ozalas The MITRE Corporation 2 Burlington Road, Bedford, MA 173 mozalas@mitre.org Abstract Two high efficiency Ku-band phemt power amplifier
High Efficiency Class-F MMIC Power Amplifiers at Ku-Band Matthew T. Ozalas The MITRE Corporation 2 Burlington Road, Bedford, MA 173 mozalas@mitre.org Abstract Two high efficiency Ku-band phemt power amplifier
High Frequency VCO Design and Schematics
 High Frequency VCO Design and Schematics Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul/ This note will review the process by which VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator) designers choose their oscillator
High Frequency VCO Design and Schematics Iulian Rosu, YO3DAC / VA3IUL, http://www.qsl.net/va3iul/ This note will review the process by which VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator) designers choose their oscillator
Linearization Method Using Variable Capacitance in Inter-Stage Matching Networks for CMOS Power Amplifier
 Linearization Method Using Variable Capacitance in Inter-Stage Matching Networks for CMOS Power Amplifier Jaehyuk Yoon* (corresponding author) School of Electronic Engineering, College of Information Technology,
Linearization Method Using Variable Capacitance in Inter-Stage Matching Networks for CMOS Power Amplifier Jaehyuk Yoon* (corresponding author) School of Electronic Engineering, College of Information Technology,
Performance Limitations of Varactor Multipliers.
 Page 312 Fourth International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Performance Limitations of Varactor Multipliers. Jack East Center for Space Terahertz Technology, The University of Michigan Erik Kollberg
Page 312 Fourth International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Performance Limitations of Varactor Multipliers. Jack East Center for Space Terahertz Technology, The University of Michigan Erik Kollberg
Vertical Integration of MM-wave MMIC s and MEMS Antennas
 JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.6, NO.3, SEPTEMBER, 2006 169 Vertical Integration of MM-wave MMIC s and MEMS Antennas Youngwoo Kwon, Yong-Kweon Kim, Sanghyo Lee, and Jung-Mu Kim Abstract
JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.6, NO.3, SEPTEMBER, 2006 169 Vertical Integration of MM-wave MMIC s and MEMS Antennas Youngwoo Kwon, Yong-Kweon Kim, Sanghyo Lee, and Jung-Mu Kim Abstract
Microwave Office Application Note
 Microwave Office Application Note INTRODUCTION Wireless system components, including gallium arsenide (GaAs) pseudomorphic high-electron-mobility transistor (phemt) frequency doublers, quadruplers, and
Microwave Office Application Note INTRODUCTION Wireless system components, including gallium arsenide (GaAs) pseudomorphic high-electron-mobility transistor (phemt) frequency doublers, quadruplers, and
A High Gain and Improved Linearity 5.7GHz CMOS LNA with Inductive Source Degeneration Topology
 A High Gain and Improved Linearity 5.7GHz CMOS LNA with Inductive Source Degeneration Topology Ch. Anandini 1, Ram Kumar 2, F. A. Talukdar 3 1,2,3 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering,
A High Gain and Improved Linearity 5.7GHz CMOS LNA with Inductive Source Degeneration Topology Ch. Anandini 1, Ram Kumar 2, F. A. Talukdar 3 1,2,3 Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering,
Pulsed IV analysis. Performing and Analyzing Pulsed Current-Voltage Measurements PULSED MEASUREMENTS. methods used for pulsed
 From May 2004 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 2004 Summit Technical Media, LLC Performing and Analyzing Pulsed Current-Voltage Measurements By Charles P. Baylis II, Lawrence P. Dunleavy University
From May 2004 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 2004 Summit Technical Media, LLC Performing and Analyzing Pulsed Current-Voltage Measurements By Charles P. Baylis II, Lawrence P. Dunleavy University
