Easy Transfer Function Measurements with LabVIEW 6i (Lab Skill Exercise X-1)
|
|
|
- Randolph Jordan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Easy Transfer Function Measurements with LabVIEW 6i (Lab Skill Exercise X-1) To exploit fully the potential for computer-based measurements offered by LabVIEW 6i, you need to use your computer and its installed DAQ board for three tasks: 1. Supplying the test signals used for input (analog output, abbreviated AO). 2. Acquiring and storing the measured input and output signals from the circuit (analog input, abbreviated AI), and 3. Computing desired results from the measured data, such as the circuit s transfer function, H ) in this example. One important additional specification: the computer must perform the AO and AI simultaneously in order for the measurement to be meaningful. In the LabVIEW library found at LabVIEW\examples\daq\anlog_io, there is a set of ready-made VI s you can use for this purpose. Choose the Simul AI/AO Buffer (xxx) VI appropriate for your DAQ board and open it. You will see a front panel that looks like Fig. 1. Fig. 1. Front panel 1
2 The following paragraph summarized this VI s operation. Look for the bold-face words in this paragraph on the Fig. 1 front panel: This VI will perform (nearly) simultaneous AO and AI. It calculates sample values for an output waveform and stores them in an output buffer of assigned size. The DAQ board outputs the sequence of voltages in the output buffer at the assigned update rate. At essentially the same time, the DAQ board acquires samples by scanning each of the assigned input channels at the assigned scan rate. It writes these sample values into an input buffer of assigned size, and successively plots snapshots of the acquired waveforms on the acquired data waveform graph. The number of samples used to plot each of the waveforms is the number of scans to read at a time. If all you want to do is measure input and output voltages as functions of time, you can run this VI as is, just setting the scan and update rates appropriately. If your circuit under test were a series RC circuit with the output taken across the capacitor, your wiring diagram for the measurement would look like Fig. 2. Fig. 2. Wiring diagram for input and output measurements using a DAQ board. The front panel after such a measurement looks like Fig. 3. Note how the capacitor voltage charges up and down exponentially, as expected for this circuit. 2
3 Fig. 3. Using the Simul AIAO VI as an oscilloscope to compare input and output waveforms for a series RC circuit like the one in Fig. 2. So far, all you can do with this VI is measure input and output signals from a circuit, Tasks 1 and 2 of the three set forth at the beginning of this document. And you can only do that for a limited set of input functions, the sine wave, square wave, sawtooth and triangle waves available at the signal type control on the front panel in Fig. 3. In order to measure the transfer function of a circuit, the goal of this exercise, you will need to perform Task 3 also, which will involve calculating the transfer function magnitude and phase from the measured input and output waveforms. Circuit theory gives the transfer function in terms of the input and output as functions of time as follows: { vout ( t)} Vout ( ) H ( ), where the operation, { v( t)}, is the complex one-sided { vin ( t)} Vin ( ) Fourier transform of the time signal, v(t). LabVIEW 6i includes a VI called FrequencyResponseFunction (Mag-Phase).vi that performs this calculation on a measured pair of waveforms. It will also take an average over many measurements, if desired. You can find this VI in the Functions Pallette of LabVIEW under Analyze -> Waveform Measurements. 3
4 You do not have to modify the the Simul AI/AO Buffer (xxx).vi much in order to measure transfer functions. First, open its Diagram. It will look like Fig. 4. Fig. 4. The Simultaneous AOAI VI diagram. There are two modifications to be made, in the locations shown: 1. Add a transfer function calculation inside the While Loop (gray-outlined rectangle at right), and 2. Modify the Compute Waveform.vi at the lower left to include a broadband noise input. Figure 5, below, shows how to make the first modification. 4
5 Fig. 5. Modification 1: incorporating the transfer function calculation using the FrequencyResponseFunction(Mag-Phase).vi. (Orange arrow) A brief summary of how you build this VI follows: 1. Create two waveform graphs on the front panel: name one Magnitude and the other Phase. 2. Use two Index Array.vi s to separate the two acquired signals: the output (Column 0) and the input (Column 1). 3. Use two BuildWaveform.vi s to make these columns of data into waveforms. 4. Drop a FrequencyResponseFunction(Mag-Phase).vi. into the diagram and wire the two waveforms to its X and Y terminals. You can right-click on this VI, select Help, and get a short description of how it works. 5. Wire the Magnitude and Phase outputs of the FrequencyResponseFunction(Mag-Phase).vi to the waveform graphs of the same names. 6. Right-click on each of the other inputs to the FrequencyResponseFunction(Mag-Phase).vi and choose Create Control. This will automatically produce the correct controls on the front panel. The next step is to modify the ComputeWaveform.vi to include a noise waveform. If you double-click on the ComputeWaveform.vi where you see it within the diagram for 5
6 the Simultaneous AOAI VI, you will see the diagram below in Fig.6. Fig. 6. The ComputeWaveform.vi diagram, showing the case structure to be modified. Right-click on the case structure and add a case after case 3 as shown below in Fig. 7. Fig. 7. New Case 4 containing a UniformWhiteNoise.vi. Note that you need to re-label the cases so that the new last case has dots after it (4..) and the old last case has no dots (3). Name your modified VI ComputeWaveform(1).vi, and replace the old ComputeWaveform.vi with the new one in the diagram of your main VI. You will also need to delete the signal type control on the front panel of the main VI, and then go back to the diagram and place the wiring tool on the signal type input of the new ComputeWaveform(1).vi, then choose Create Control. This will create a new control on the front panel that has all of the waveform options available. 6
7 If you ve done the above steps correctly, you should be ready to measure a transfer function. Fig. 7. Front Panel of the Transfer Function measuring VI, showing results for an RC low-pass filter like the circuit in Fig. 2. In Fig. 7, the X-scales of the two waveform graphs named magnitude and phase, were switched to logarithmic mapping. You can make these changes by right-clicking on the graphs. The view control switches (lower center of the front panel) were set to display magnitude on a db scale, and to display the phase in degrees. The averaging parameters switches control how the averages over multiple measurements are calculated. Since the network whose transfer function was measured is the one in Fig. 2, we would expect that a Bode plot of its transfer function magnitude would be flat near zero db out to some cutoff frequency, and then roll off at a constant slope (in db/decade) above the cutoff frequency. This is exactly what appears in the magnitude graph. We would also expect the phase shift for this network to be zero at low frequency, and decrease toward 90 o at high frequencies. The measured results agree with this theoretical expectation up to a few hundred Hz of frequency, and then seem to diverge. The fundamental cause of this disagreement between theory and experiment in the phase measurements can be found in the magnitude measurements. Notice that, at the higher frequencies, the magnitude has dropped by at least 20 db. This means that the phase of the (very small) output voltages at these higher frequencies is strongly affected 7
8 by any noise in the measuring circuitry. You can see this noise better if you run a measurement with the averaging mode control set to no averaging. Supplementary Lab Skill Exercise X-1: (Print this part and turn it in) 1. (10%) Put together an RC circuit like the one in Fig. 2 on your proto-board. Wire it to the AO and AI channels of the DAQ interface as in Fig (10%) From the values you chose for R and C, calculate the time-constant of your circuit. Show your calculation and answer here: 3. (20%) Open the Simul AI/AO Buffer (xxx).vi, and use it to measure the time response of your circuit to a square wave. Print out a front panel showing your results and attach it here: 8
9 4. (20%) Modify the ComputeWaveform.vi in the Simul AI/AO Buffer (xxx).vi diagram so that it lets you supply a noise waveform as described above. Run your VI with noise selected as the waveform. Your front panel should look like this. Attach a printout of your front panel over this one. 5. Modify the Simul AI/AO Buffer (xxx).vi to measure transfer functions as described above. Measure the transfer function of your RC circuit up to at least 5000 Hz. Set the number of averages al low as you can consistent with accurate results. 9
10 a) (20%) print out a copy of the diagram of your VI and attach it here. 10
11 b) (20%) Print out a front panel showing the results of your measurements and attach it here. If you were unable to make your own transfer function measuring VI to use, you may use the one provided on the lab computer system, but you will not get the 20% for part 5a). 11
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING
 ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING Objectives: To familiarize the student with the concepts of signal conditioning. At the end of the lab, the student should be able to: Understand the
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING Objectives: To familiarize the student with the concepts of signal conditioning. At the end of the lab, the student should be able to: Understand the
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 8 FREQUENCY ANALYSIS
 ME 365 EXPERIMENT 8 FREQUENCY ANALYSIS Objectives: There are two goals in this laboratory exercise. The first is to reinforce the Fourier series analysis you have done in the lecture portion of this course.
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 8 FREQUENCY ANALYSIS Objectives: There are two goals in this laboratory exercise. The first is to reinforce the Fourier series analysis you have done in the lecture portion of this course.
Lab 3: RC Circuits. Construct circuit 2 in EveryCircuit. Set values for the capacitor and resistor to match those in figure 2 and set the frequency to
 Lab 3: RC Circuits Prelab Deriving equations for the output voltage of the voltage dividers you constructed in lab 2 was fairly simple. Now we want to derive an equation for the output voltage of a circuit
Lab 3: RC Circuits Prelab Deriving equations for the output voltage of the voltage dividers you constructed in lab 2 was fairly simple. Now we want to derive an equation for the output voltage of a circuit
Lab 6: Building a Function Generator
 ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 6: Building a Function Generator Objectives In this lab exercise you will build a function generator capable of generating square, triangle, and sine
ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 6: Building a Function Generator Objectives In this lab exercise you will build a function generator capable of generating square, triangle, and sine
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2009 LAB 2 NON IDEAL OPAMPS
 University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2009 LAB 2 NON IDEAL OPAMPS Issued 10/5/2008 Pre Lab Completed 10/12/2008 Lab Due in Lecture 10/21/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2009 LAB 2 NON IDEAL OPAMPS Issued 10/5/2008 Pre Lab Completed 10/12/2008 Lab Due in Lecture 10/21/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize
Experiment 2: Electronic Enhancement of S/N and Boxcar Filtering
 Experiment 2: Electronic Enhancement of S/N and Boxcar Filtering Synopsis: A simple waveform generator will apply a triangular voltage ramp through an R/C circuit. A storage digital oscilloscope, or an
Experiment 2: Electronic Enhancement of S/N and Boxcar Filtering Synopsis: A simple waveform generator will apply a triangular voltage ramp through an R/C circuit. A storage digital oscilloscope, or an
Part 1. Using LabVIEW to Measure Current
 NAME EET 2259 Lab 11 Studying Characteristic Curves with LabVIEW OBJECTIVES -Use LabVIEW to measure DC current. -Write LabVIEW programs to display the characteristic curves of resistors, diodes, and transistors
NAME EET 2259 Lab 11 Studying Characteristic Curves with LabVIEW OBJECTIVES -Use LabVIEW to measure DC current. -Write LabVIEW programs to display the characteristic curves of resistors, diodes, and transistors
LAB #7: Digital Signal Processing
 LAB #7: Digital Signal Processing Equipment: Pentium PC with NI PCI-MIO-16E-4 data-acquisition board NI BNC 2120 Accessory Box VirtualBench Instrument Library version 2.6 Function Generator (Tektronix
LAB #7: Digital Signal Processing Equipment: Pentium PC with NI PCI-MIO-16E-4 data-acquisition board NI BNC 2120 Accessory Box VirtualBench Instrument Library version 2.6 Function Generator (Tektronix
EE 462G Laboratory #1 Measuring Capacitance
 EE 462G Laboratory #1 Measuring Capacitance Drs. A.V. Radun and K.D. Donohue (1/24/07) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Updated 8/31/2007 by
EE 462G Laboratory #1 Measuring Capacitance Drs. A.V. Radun and K.D. Donohue (1/24/07) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Updated 8/31/2007 by
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 2 ACTIVE FILTERS
 University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 2 ACTIVE FILTERS Issued 9/22/2008 Pre Lab Completed 9/29/2008 Lab Due in Lecture 10/6/2008 Introduction In this lab you will design a
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 2 ACTIVE FILTERS Issued 9/22/2008 Pre Lab Completed 9/29/2008 Lab Due in Lecture 10/6/2008 Introduction In this lab you will design a
Practical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices
 Practical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some points from the lecture courses on Semiconductor Materials and Semiconductor Devices
Practical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some points from the lecture courses on Semiconductor Materials and Semiconductor Devices
Fig. 1. NI Elvis System
 Lab 2: Introduction to I Elvis Environment. Objectives: The purpose of this laboratory is to provide an introduction to the NI Elvis design and prototyping environment. Basic operations provided by Elvis
Lab 2: Introduction to I Elvis Environment. Objectives: The purpose of this laboratory is to provide an introduction to the NI Elvis design and prototyping environment. Basic operations provided by Elvis
Build Your Own Bose WaveRadio Bass Preamp Active Filter Design
 EE230 Filter Laboratory Build Your Own Bose WaveRadio Bass Preamp Active Filter Design Objectives 1) Design an active filter on paper to meet a particular specification 2) Verify your design using Spice
EE230 Filter Laboratory Build Your Own Bose WaveRadio Bass Preamp Active Filter Design Objectives 1) Design an active filter on paper to meet a particular specification 2) Verify your design using Spice
ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis
 ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis All circuit simulation packages that use the Pspice engine allow users to do complex analysis that were once impossible to
ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis All circuit simulation packages that use the Pspice engine allow users to do complex analysis that were once impossible to
ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2016
 ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2016 University of Delaware Dr. Mark Mirotznik Kaleb Burd Patrick Nicholson Aric Lu Kaeini Ekong 1 Table of Contents Lab 1: Intro 3 Lab 2: Resistive Circuits
ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2016 University of Delaware Dr. Mark Mirotznik Kaleb Burd Patrick Nicholson Aric Lu Kaeini Ekong 1 Table of Contents Lab 1: Intro 3 Lab 2: Resistive Circuits
Operational Amplifiers
 Operational Amplifiers Continuing the discussion of Op Amps, the next step is filters. There are many different types of filters, including low pass, high pass and band pass. We will discuss each of the
Operational Amplifiers Continuing the discussion of Op Amps, the next step is filters. There are many different types of filters, including low pass, high pass and band pass. We will discuss each of the
Auntie Spark s Guide to creating a Data Collection VI
 Auntie Spark s Guide to creating a Data Collection VI Suppose you wanted to gather data from an experiment. How would you create a VI to do so? For sophisticated data collection and experimental control,
Auntie Spark s Guide to creating a Data Collection VI Suppose you wanted to gather data from an experiment. How would you create a VI to do so? For sophisticated data collection and experimental control,
LAB II. INTRODUCTION TO LABVIEW
 1. OBJECTIVE LAB II. INTRODUCTION TO LABVIEW In this lab, you are to gain a basic understanding of how LabView operates the lab equipment remotely. 2. OVERVIEW In the procedure of this lab, you will build
1. OBJECTIVE LAB II. INTRODUCTION TO LABVIEW In this lab, you are to gain a basic understanding of how LabView operates the lab equipment remotely. 2. OVERVIEW In the procedure of this lab, you will build
Advanced Lab LAB 6: Signal Acquisition & Spectrum Analysis Using VirtualBench DSA Equipment: Objectives:
 Advanced Lab LAB 6: Signal Acquisition & Spectrum Analysis Using VirtualBench DSA Equipment: Pentium PC with National Instruments PCI-MIO-16E-4 data-acquisition board (12-bit resolution; software-controlled
Advanced Lab LAB 6: Signal Acquisition & Spectrum Analysis Using VirtualBench DSA Equipment: Pentium PC with National Instruments PCI-MIO-16E-4 data-acquisition board (12-bit resolution; software-controlled
Operational Amplifiers 2 Active Filters ReadMeFirst
 Operational Amplifiers 2 Active Filters ReadMeFirst Lab Summary In this lab you will build two active filters on a breadboard, using an op-amp, resistors, and capacitors, and take data for the magnitude
Operational Amplifiers 2 Active Filters ReadMeFirst Lab Summary In this lab you will build two active filters on a breadboard, using an op-amp, resistors, and capacitors, and take data for the magnitude
Physics 303 Fall Module 4: The Operational Amplifier
 Module 4: The Operational Amplifier Operational Amplifiers: General Introduction In the laboratory, analog signals (that is to say continuously variable, not discrete signals) often require amplification.
Module 4: The Operational Amplifier Operational Amplifiers: General Introduction In the laboratory, analog signals (that is to say continuously variable, not discrete signals) often require amplification.
EE 3305 Lab I Revised July 18, 2003
 Operational Amplifiers Operational amplifiers are high-gain amplifiers with a similar general description typified by the most famous example, the LM741. The LM741 is used for many amplifier varieties
Operational Amplifiers Operational amplifiers are high-gain amplifiers with a similar general description typified by the most famous example, the LM741. The LM741 is used for many amplifier varieties
GENERATION OF SIGNALS USING LABVIEW FOR MAGNETIC COILS WITH POWER AMPLIFIERS
 GENERATION OF SIGNALS USING LABVIEW FOR MAGNETIC COILS WITH POWER AMPLIFIERS Ashmi G V 1, Meena M S 2 1 ER&DCI-IT, Centre for Development of Advanced Computing, Thiruvananthapuram(India) 2 LAMP Group,
GENERATION OF SIGNALS USING LABVIEW FOR MAGNETIC COILS WITH POWER AMPLIFIERS Ashmi G V 1, Meena M S 2 1 ER&DCI-IT, Centre for Development of Advanced Computing, Thiruvananthapuram(India) 2 LAMP Group,
Laboratory Experiment #1 Introduction to Spectral Analysis
 J.B.Francis College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department 22-403 Laboratory Experiment #1 Introduction to Spectral Analysis Introduction The quantification of electrical energy can be accomplished
J.B.Francis College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department 22-403 Laboratory Experiment #1 Introduction to Spectral Analysis Introduction The quantification of electrical energy can be accomplished
EE 210 Lab Exercise #5: OP-AMPS I
 EE 210 Lab Exercise #5: OP-AMPS I ITEMS REQUIRED EE210 crate, DMM, EE210 parts kit, T-connector, 50Ω terminator, Breadboard Lab report due at the ASSIGNMENT beginning of the next lab period Data and results
EE 210 Lab Exercise #5: OP-AMPS I ITEMS REQUIRED EE210 crate, DMM, EE210 parts kit, T-connector, 50Ω terminator, Breadboard Lab report due at the ASSIGNMENT beginning of the next lab period Data and results
PHY 351/651 LABORATORY 5 The Diode Basic Properties and Circuits
 Reading Assignment Horowitz, Hill Chap. 1.25 1.31 (p35-44) Data sheets 1N4007 & 1N4735A diodes Laboratory Goals PHY 351/651 LABORATORY 5 The Diode Basic Properties and Circuits In today s lab activities,
Reading Assignment Horowitz, Hill Chap. 1.25 1.31 (p35-44) Data sheets 1N4007 & 1N4735A diodes Laboratory Goals PHY 351/651 LABORATORY 5 The Diode Basic Properties and Circuits In today s lab activities,
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER
 ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER Hand Analysis P1. Determine the DC bias for the BJT Common Emitter Amplifier circuit of Figure 61 (in this lab) including the voltages V B, V C and V
ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER Hand Analysis P1. Determine the DC bias for the BJT Common Emitter Amplifier circuit of Figure 61 (in this lab) including the voltages V B, V C and V
PART I: The questions in Part I refer to the aliasing portion of the procedure as outlined in the lab manual.
 Lab. #1 Signal Processing & Spectral Analysis Name: Date: Section / Group: NOTE: To help you correctly answer many of the following questions, it may be useful to actually run the cases outlined in the
Lab. #1 Signal Processing & Spectral Analysis Name: Date: Section / Group: NOTE: To help you correctly answer many of the following questions, it may be useful to actually run the cases outlined in the
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters
 BME/ISE 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Supplies and Components: Breadboard 4.7 K Resistor 0.047 F Capacitor
BME/ISE 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Supplies and Components: Breadboard 4.7 K Resistor 0.047 F Capacitor
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER
 University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER Issued 10/27/2008 Report due in Lecture 11/10/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize a 2N3904 NPN
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER Issued 10/27/2008 Report due in Lecture 11/10/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize a 2N3904 NPN
Name: Resistors and Basic Resistive Circuits. Objective: To gain experience with data acquisition proto-boards physical resistors. Table of Contents:
 Objective: To gain experience with data acquisition proto-boards physical resistors Table of Contents: Name: Resistors and Basic Resistive Circuits Pre-Lab Assignment 1 Background 2 National Instruments
Objective: To gain experience with data acquisition proto-boards physical resistors Table of Contents: Name: Resistors and Basic Resistive Circuits Pre-Lab Assignment 1 Background 2 National Instruments
ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013
 Signature Name (print, please) Lab section # Lab partner s name (if any) Date(s) lab was performed ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013 In this lab we will demonstrate basic
Signature Name (print, please) Lab section # Lab partner s name (if any) Date(s) lab was performed ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013 In this lab we will demonstrate basic
Pre-Lab. Introduction
 Pre-Lab Read through this entire lab. Perform all of your calculations (calculated values) prior to making the required circuit measurements. You may need to measure circuit component values to obtain
Pre-Lab Read through this entire lab. Perform all of your calculations (calculated values) prior to making the required circuit measurements. You may need to measure circuit component values to obtain
PURPOSE: NOTE: Be sure to record ALL results in your laboratory notebook.
 EE4902 Lab 9 CMOS OP-AMP PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to measure the closed-loop performance of an op-amp designed from individual MOSFETs. This op-amp, shown in Fig. 9-1, combines all of the major
EE4902 Lab 9 CMOS OP-AMP PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to measure the closed-loop performance of an op-amp designed from individual MOSFETs. This op-amp, shown in Fig. 9-1, combines all of the major
RC and RL Circuits Prelab
 RC and RL Circuits Prelab by Dr. Christine P. Cheney, Department of Physics and Astronomy, 401 Nielsen Physics Building, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, Tennessee 37996-1200 2018 by Christine P.
RC and RL Circuits Prelab by Dr. Christine P. Cheney, Department of Physics and Astronomy, 401 Nielsen Physics Building, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, Tennessee 37996-1200 2018 by Christine P.
ECE4902 Lab 5 Simulation. Simulation. Export data for use in other software tools (e.g. MATLAB or excel) to compare measured data with simulation
 ECE4902 Lab 5 Simulation Simulation Export data for use in other software tools (e.g. MATLAB or excel) to compare measured data with simulation Be sure to have your lab data available from Lab 5, Common
ECE4902 Lab 5 Simulation Simulation Export data for use in other software tools (e.g. MATLAB or excel) to compare measured data with simulation Be sure to have your lab data available from Lab 5, Common
Sallen-Key_High_Pass_Filter -- Overview
 Sallen-Key_High_Pass_Filter -- Overview Sallen-Key High Pass Filter Objectives: After performing this lab exercise, learner will be able to: Understand & analyze working of Sallen-Key topology of active
Sallen-Key_High_Pass_Filter -- Overview Sallen-Key High Pass Filter Objectives: After performing this lab exercise, learner will be able to: Understand & analyze working of Sallen-Key topology of active
Lecture 2 Analog circuits. Seeing the light..
 Lecture 2 Analog circuits Seeing the light.. I t IR light V1 9V +V IR detection Noise sources: Electrical (60Hz, 120Hz, 180Hz.) Other electrical IR from lights IR from cameras (autofocus) Visible light
Lecture 2 Analog circuits Seeing the light.. I t IR light V1 9V +V IR detection Noise sources: Electrical (60Hz, 120Hz, 180Hz.) Other electrical IR from lights IR from cameras (autofocus) Visible light
Mechatronics. Analog and Digital Electronics: Studio Exercises 1 & 2
 Mechatronics Analog and Digital Electronics: Studio Exercises 1 & 2 There is an electronics revolution taking place in the industrialized world. Electronics pervades all activities. Perhaps the most important
Mechatronics Analog and Digital Electronics: Studio Exercises 1 & 2 There is an electronics revolution taking place in the industrialized world. Electronics pervades all activities. Perhaps the most important
Lab 1B LabVIEW Filter Signal
 Lab 1B LabVIEW Filter Signal Due Thursday, September 12, 2013 Submit Responses to Questions (Hardcopy) Equipment: LabVIEW Setup: Open LabVIEW Skills learned: Create a low- pass filter using LabVIEW and
Lab 1B LabVIEW Filter Signal Due Thursday, September 12, 2013 Submit Responses to Questions (Hardcopy) Equipment: LabVIEW Setup: Open LabVIEW Skills learned: Create a low- pass filter using LabVIEW and
Lab 7: Let s Make a Little Noise
 Lab 7: Let s Make a Little Noise Introduction Ever had a piece of a song rattling around in your head, but when you tried to sing it, it just did not sound right? What you need is a little keyboard to
Lab 7: Let s Make a Little Noise Introduction Ever had a piece of a song rattling around in your head, but when you tried to sing it, it just did not sound right? What you need is a little keyboard to
VCC. Digital 16 Frequency Divider Digital-to-Analog Converter Butterworth Active Filter Sample-and-Hold Amplifier (part 2) Last Update: 03/19/14
 Digital 16 Frequency Divider Digital-to-Analog Converter Butterworth Active Filter Sample-and-Hold Amplifier (part 2) ECE3204 Lab 5 Objective The purpose of this lab is to design and test an active Butterworth
Digital 16 Frequency Divider Digital-to-Analog Converter Butterworth Active Filter Sample-and-Hold Amplifier (part 2) ECE3204 Lab 5 Objective The purpose of this lab is to design and test an active Butterworth
29:128 Homework Problems
 29:128 Homework Problems Revised 22 Feb 2012 29:128 Homework 1 (15 points) references: Sections 1.6-1.7 & 4.8, Meyer Chapter 1 of Horowitz and Hill, 2nd Edition (1) In the circuit shown below, V in = 9
29:128 Homework Problems Revised 22 Feb 2012 29:128 Homework 1 (15 points) references: Sections 1.6-1.7 & 4.8, Meyer Chapter 1 of Horowitz and Hill, 2nd Edition (1) In the circuit shown below, V in = 9
ECE4902 C Lab 5 MOSFET Common Source Amplifier with Active Load Bandwidth of MOSFET Common Source Amplifier: Resistive Load / Active Load
 ECE4902 C2012 - Lab 5 MOSFET Common Source Amplifier with Active Load Bandwidth of MOSFET Common Source Amplifier: Resistive Load / Active Load PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lab is to measure the
ECE4902 C2012 - Lab 5 MOSFET Common Source Amplifier with Active Load Bandwidth of MOSFET Common Source Amplifier: Resistive Load / Active Load PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lab is to measure the
ME 461 Laboratory #2 Timers and Pulse-Width Modulation
 ME 461 Laboratory #2 Timers and Pulse-Width Modulation Goals: 1. Understand how to use timers to control the frequency at which events occur. 2. Generate PWM signals using Timer A. 3. Explore the frequency
ME 461 Laboratory #2 Timers and Pulse-Width Modulation Goals: 1. Understand how to use timers to control the frequency at which events occur. 2. Generate PWM signals using Timer A. 3. Explore the frequency
Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects
 Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects 11.2.1: Signals with Multiple Frequency Components Overview: In this lab project, we will calculate the magnitude response of an electrical circuit and
Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects 11.2.1: Signals with Multiple Frequency Components Overview: In this lab project, we will calculate the magnitude response of an electrical circuit and
Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited
 Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited In this experiment you will revisit the voltage oscillations of a simple LC circuit. Then you will address circuits made by combining resistors
Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited In this experiment you will revisit the voltage oscillations of a simple LC circuit. Then you will address circuits made by combining resistors
PHYC 500: Introduction to LabView. Exercise 9 (v 1.1) Spectral content of waveforms. M.P. Hasselbeck, University of New Mexico
 PHYC 500: Introduction to LabView M.P. Hasselbeck, University of New Mexico Exercise 9 (v 1.1) Spectral content of waveforms This exercise provides additional experience with the Waveform palette, along
PHYC 500: Introduction to LabView M.P. Hasselbeck, University of New Mexico Exercise 9 (v 1.1) Spectral content of waveforms This exercise provides additional experience with the Waveform palette, along
EE 422G - Signals and Systems Laboratory
 EE 422G - Signals and Systems Laboratory Lab 3 FIR Filters Written by Kevin D. Donohue Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 September 19, 2015 Objectives:
EE 422G - Signals and Systems Laboratory Lab 3 FIR Filters Written by Kevin D. Donohue Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 September 19, 2015 Objectives:
Magnitude and Phase Measurements. Analog Discovery
 Magnitude and Phase Measurements Analog Discovery Set up the oscilloscope to measure the signal of the reference voltage (the input voltage from the arbitrary function generator, in this case) and the
Magnitude and Phase Measurements Analog Discovery Set up the oscilloscope to measure the signal of the reference voltage (the input voltage from the arbitrary function generator, in this case) and the
The above figure represents a two stage circuit. Recall, the transfer function relates. Vout
 LABORATORY 12: Bode plots/second Order Filters Material covered: Multistage circuits Bode plots Design problem Overview Notes: Two stage circuits: Vin1 H1(s) Vout1 Vin2 H2(s) Vout2 The above figure represents
LABORATORY 12: Bode plots/second Order Filters Material covered: Multistage circuits Bode plots Design problem Overview Notes: Two stage circuits: Vin1 H1(s) Vout1 Vin2 H2(s) Vout2 The above figure represents
LIC & COMMUNICATION LAB MANUAL
 LIC & Communication Lab Manual LIC & COMMUNICATION LAB MANUAL FOR V SEMESTER B.E (E& ( E&C) (For private circulation only) NAME: DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION SRI SIDDHARTHA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
LIC & Communication Lab Manual LIC & COMMUNICATION LAB MANUAL FOR V SEMESTER B.E (E& ( E&C) (For private circulation only) NAME: DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION SRI SIDDHARTHA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters
 Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
LLS - Introduction to Equipment
 Published on Advanced Lab (http://experimentationlab.berkeley.edu) Home > LLS - Introduction to Equipment LLS - Introduction to Equipment All pages in this lab 1. Low Light Signal Measurements [1] 2. Introduction
Published on Advanced Lab (http://experimentationlab.berkeley.edu) Home > LLS - Introduction to Equipment LLS - Introduction to Equipment All pages in this lab 1. Low Light Signal Measurements [1] 2. Introduction
ECEN 325 Lab 5: Operational Amplifiers Part III
 ECEN Lab : Operational Amplifiers Part III Objectives The purpose of the lab is to study some of the opamp configurations commonly found in practical applications and also investigate the non-idealities
ECEN Lab : Operational Amplifiers Part III Objectives The purpose of the lab is to study some of the opamp configurations commonly found in practical applications and also investigate the non-idealities
Lab 12 Laboratory 12 Data Acquisition Required Special Equipment: 12.1 Objectives 12.2 Introduction 12.3 A/D basics
 Laboratory 12 Data Acquisition Required Special Equipment: Computer with LabView Software National Instruments USB 6009 Data Acquisition Card 12.1 Objectives This lab demonstrates the basic principals
Laboratory 12 Data Acquisition Required Special Equipment: Computer with LabView Software National Instruments USB 6009 Data Acquisition Card 12.1 Objectives This lab demonstrates the basic principals
ActiveLowPassFilter -- Overview
 ActiveLowPassFilter -- Overview OBJECTIVES: At the end of performing this experiment, learners would be able to: Describe the concept of active Low Pass Butterworth Filter Obtain the roll-off factor and
ActiveLowPassFilter -- Overview OBJECTIVES: At the end of performing this experiment, learners would be able to: Describe the concept of active Low Pass Butterworth Filter Obtain the roll-off factor and
Figure E2-1 The complete circuit showing the oscilloscope and Bode plotter.
 Example 2 An RC network using the oscilloscope and Bode plotter In this example we use the oscilloscope and the Bode plotter in an RC circuit that has an AC source. The circuit which we will construct
Example 2 An RC network using the oscilloscope and Bode plotter In this example we use the oscilloscope and the Bode plotter in an RC circuit that has an AC source. The circuit which we will construct
LABORATORY 7 v2 BOOST CONVERTER
 University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Bernhard Boser LABORATORY 7 v2 BOOST CONVERTER In many situations circuits require a different
University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Bernhard Boser LABORATORY 7 v2 BOOST CONVERTER In many situations circuits require a different
Lab Session 4 Hardware
 Lab Session 4 Hardware Objectives: Upon completion of this experiment, the student will be able to: -Verifying of Transient response, two port network and Fourier analysis circuits Equipment and Components
Lab Session 4 Hardware Objectives: Upon completion of this experiment, the student will be able to: -Verifying of Transient response, two port network and Fourier analysis circuits Equipment and Components
The Oscilloscope. Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift ( ) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope.
 The Oscilloscope Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift (1667-1745) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope. THEORY The oscilloscope, or scope for short, is a device for drawing
The Oscilloscope Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift (1667-1745) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope. THEORY The oscilloscope, or scope for short, is a device for drawing
EE320L Electronics I. Laboratory. Laboratory Exercise #2. Basic Op-Amp Circuits. Angsuman Roy. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 EE320L Electronics I Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #2 Basic Op-Amp Circuits By Angsuman Roy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, Las Vegas Objective: The purpose of
EE320L Electronics I Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #2 Basic Op-Amp Circuits By Angsuman Roy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, Las Vegas Objective: The purpose of
Welcome to your second Electronics Laboratory Session. In this session you will learn about how to use resistors, capacitors and inductors to make
 Welcome to your second Electronics Laboratory Session. In this session you will learn about how to use resistors, capacitors and inductors to make simple circuits. You will find out how these circuits
Welcome to your second Electronics Laboratory Session. In this session you will learn about how to use resistors, capacitors and inductors to make simple circuits. You will find out how these circuits
Lab 15: Lock in amplifier (Version 1.4)
 Lab 15: Lock in amplifier (Version 1.4) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Lab 15: Lock in amplifier (Version 1.4) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1. See suggested breadboard configuration on following page!
 ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1 The Operational Amplifier: Inverting and Non-inverting Gain Configurations Gain-Bandwidth Product Relationship Frequency Response Limitation Transfer Function Measurement DC Errors
ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1 The Operational Amplifier: Inverting and Non-inverting Gain Configurations Gain-Bandwidth Product Relationship Frequency Response Limitation Transfer Function Measurement DC Errors
Using Signal Express to Automate Analog Electronics Experiments
 Session 3247 Using Signal Express to Automate Analog Electronics Experiments B.D. Brannaka, J. R. Porter Engineering Technology and Industrial Distribution Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77843
Session 3247 Using Signal Express to Automate Analog Electronics Experiments B.D. Brannaka, J. R. Porter Engineering Technology and Industrial Distribution Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77843
Frequency Selective Circuits
 Lab 15 Frequency Selective Circuits Names Objectives in this lab you will Measure the frequency response of a circuit Determine the Q of a resonant circuit Build a filter and apply it to an audio signal
Lab 15 Frequency Selective Circuits Names Objectives in this lab you will Measure the frequency response of a circuit Determine the Q of a resonant circuit Build a filter and apply it to an audio signal
University of North Carolina, Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 EE Design II Fall 2009
 University of North Carolina, Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 EE Design II Fall 2009 Lab 1 Power Amplifier Circuits Issued August 25, 2009 Due: September 11, 2009
University of North Carolina, Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 EE Design II Fall 2009 Lab 1 Power Amplifier Circuits Issued August 25, 2009 Due: September 11, 2009
LabVIEW Basics Peter Avitabile,Jeffrey Hodgkins Mechanical Engineering Department University of Massachusetts Lowell
 LabVIEW Basics Peter Avitabile,Jeffrey Hodgkins Mechanical Engineering Department University of Massachusetts Lowell 1 Dr. Peter Avitabile LabVIEW LabVIEW is a data acquisition software package commonly
LabVIEW Basics Peter Avitabile,Jeffrey Hodgkins Mechanical Engineering Department University of Massachusetts Lowell 1 Dr. Peter Avitabile LabVIEW LabVIEW is a data acquisition software package commonly
Laboratory 4. Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes
 Laboratory 4 Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes Required Components: k resistor 0. F capacitor N94 small-signal diode LED 4. Objectives In the previous laboratory exercise you examined the effects of input
Laboratory 4 Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes Required Components: k resistor 0. F capacitor N94 small-signal diode LED 4. Objectives In the previous laboratory exercise you examined the effects of input
ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2017
 ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2017 University of Delaware Dr. Mark Mirotznik Kaleb Burd Aric Lu Patrick Nicholson Colby Banbury Table of Contents Policies Policy Page 3 Labs Lab 1: Intro
ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2017 University of Delaware Dr. Mark Mirotznik Kaleb Burd Aric Lu Patrick Nicholson Colby Banbury Table of Contents Policies Policy Page 3 Labs Lab 1: Intro
EE 233 Circuit Theory Lab 3: First-Order Filters
 EE 233 Circuit Theory Lab 3: First-Order Filters Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Precautions... 1 3 Prelab Exercises... 2 3.1 Inverting Amplifier... 3 3.2 Non-Inverting Amplifier... 4 3.3 Integrating
EE 233 Circuit Theory Lab 3: First-Order Filters Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Precautions... 1 3 Prelab Exercises... 2 3.1 Inverting Amplifier... 3 3.2 Non-Inverting Amplifier... 4 3.3 Integrating
ECE4902 C Lab 7
 ECE902 C2012 - Lab MOSFET Differential Amplifier Resistive Load Active Load PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lab is to measure the performance of the differential amplifier. This is an important topology
ECE902 C2012 - Lab MOSFET Differential Amplifier Resistive Load Active Load PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lab is to measure the performance of the differential amplifier. This is an important topology
Use of the LTI Viewer and MUX Block in Simulink
 Use of the LTI Viewer and MUX Block in Simulink INTRODUCTION The Input-Output ports in Simulink can be used in a model to access the LTI Viewer. This enables the user to display information about the magnitude
Use of the LTI Viewer and MUX Block in Simulink INTRODUCTION The Input-Output ports in Simulink can be used in a model to access the LTI Viewer. This enables the user to display information about the magnitude
EXPERIMENT 4: RC, RL and RD CIRCUITs
 EXPERIMENT 4: RC, RL and RD CIRCUITs Equipment List Resistor, one each of o 330 o 1k o 1.5k o 10k o 100k o 1000k 0.F Ceramic Capacitor 4700H Inductor LED and 1N4004 Diode. Introduction We have studied
EXPERIMENT 4: RC, RL and RD CIRCUITs Equipment List Resistor, one each of o 330 o 1k o 1.5k o 10k o 100k o 1000k 0.F Ceramic Capacitor 4700H Inductor LED and 1N4004 Diode. Introduction We have studied
Notes on Experiment #1
 Notes on Experiment #1 Bring graph paper (cm cm is best) From this week on, be sure to print a copy of each experiment and bring it with you to lab. There will not be any experiment copies available in
Notes on Experiment #1 Bring graph paper (cm cm is best) From this week on, be sure to print a copy of each experiment and bring it with you to lab. There will not be any experiment copies available in
1.5k. (a) Resistive Circuit (b) Capacitive Circuit
 Objective Information The purposes of this laboratory project are to become further acquainted with the use of an oscilloscope, and to observe the behavior of resistor and resistor capacitor circuits.
Objective Information The purposes of this laboratory project are to become further acquainted with the use of an oscilloscope, and to observe the behavior of resistor and resistor capacitor circuits.
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3)
 Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II
 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II LAB 5 INTRO: INTRODUCTION TO INVERTING AMPLIFIERS AND OTHER OP-AMP CIRCUITS GOALS In this lab, you will characterize the gain and frequency dependence of inverting op-amp
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II LAB 5 INTRO: INTRODUCTION TO INVERTING AMPLIFIERS AND OTHER OP-AMP CIRCUITS GOALS In this lab, you will characterize the gain and frequency dependence of inverting op-amp
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5)
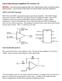 Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response
 ES 3: Introduction to Electrical Systems Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response I. GOALS: In this laboratory, you will build an audio amplifier using an LM386 integrated circuit.
ES 3: Introduction to Electrical Systems Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response I. GOALS: In this laboratory, you will build an audio amplifier using an LM386 integrated circuit.
EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab. Prelab Part I: RC Circuit
 EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab Prelab Part I: RC Circuit 1. Design a high pass filter (Fig. 1) which has a break point f b = 1 khz at 3dB below the midband level (the -3dB
EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab Prelab Part I: RC Circuit 1. Design a high pass filter (Fig. 1) which has a break point f b = 1 khz at 3dB below the midband level (the -3dB
H represents the value of the transfer function (frequency response) at
 Measurements in Electronics and Telecommunication - Laboratory 4 1 Laboratory 4 Measurements of frequency response Purpose: Measuring the cut-off frequency of a filter. The representation of frequency
Measurements in Electronics and Telecommunication - Laboratory 4 1 Laboratory 4 Measurements of frequency response Purpose: Measuring the cut-off frequency of a filter. The representation of frequency
10. Computer-Assisted Data Acquisition and Analysis
 10. Computer-Assisted Data Acquisition and Analysis Objective The purpose of this experiment is to practice computer-assisted data acquisition and analysis. Students use LabVIEW programs to control the
10. Computer-Assisted Data Acquisition and Analysis Objective The purpose of this experiment is to practice computer-assisted data acquisition and analysis. Students use LabVIEW programs to control the
E84 Lab 3: Transistor
 E84 Lab 3: Transistor Cherie Ho and Siyi Hu April 18, 2016 Transistor Testing 1. Take screenshots of both the input and output characteristic plots observed on the semiconductor curve tracer with the following
E84 Lab 3: Transistor Cherie Ho and Siyi Hu April 18, 2016 Transistor Testing 1. Take screenshots of both the input and output characteristic plots observed on the semiconductor curve tracer with the following
BME 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters
 BME 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Laboratory Equipment: Agilent Oscilloscope Model 546A Agilent Function Generator
BME 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Laboratory Equipment: Agilent Oscilloscope Model 546A Agilent Function Generator
Lecture 2 Analog circuits. Seeing the light..
 Lecture 2 Analog circuits Seeing the light.. I t IR light V1 9V +V IR detection Noise sources: Electrical (60Hz, 120Hz, 180Hz.) Other electrical IR from lights IR from cameras (autofocus) Visible light
Lecture 2 Analog circuits Seeing the light.. I t IR light V1 9V +V IR detection Noise sources: Electrical (60Hz, 120Hz, 180Hz.) Other electrical IR from lights IR from cameras (autofocus) Visible light
Cir cuit s 212 Lab. Lab #7 Filter Design. Introductions:
 Cir cuit s 22 Lab Lab #7 Filter Design The purpose of this lab is multifold. This is a three-week experiment. You are required to design a High / Low Pass filter using the LM38 OP AMP. In this lab, you
Cir cuit s 22 Lab Lab #7 Filter Design The purpose of this lab is multifold. This is a three-week experiment. You are required to design a High / Low Pass filter using the LM38 OP AMP. In this lab, you
Low Pass Filter Introduction
 Low Pass Filter Introduction Basically, an electrical filter is a circuit that can be designed to modify, reshape or reject all unwanted frequencies of an electrical signal and accept or pass only those
Low Pass Filter Introduction Basically, an electrical filter is a circuit that can be designed to modify, reshape or reject all unwanted frequencies of an electrical signal and accept or pass only those
EXPERIMENT 4: RC, RL and RD CIRCUITs
 EXPERIMENT 4: RC, RL and RD CIRCUITs Equipment List An assortment of resistor, one each of (330, 1k,1.5k, 10k,100k,1000k) Function Generator Oscilloscope 0.F Ceramic Capacitor 100H Inductor LED and 1N4001
EXPERIMENT 4: RC, RL and RD CIRCUITs Equipment List An assortment of resistor, one each of (330, 1k,1.5k, 10k,100k,1000k) Function Generator Oscilloscope 0.F Ceramic Capacitor 100H Inductor LED and 1N4001
EE 2274 DIODE OR GATE & CLIPPING CIRCUIT
 EE 2274 DIODE OR GATE & CLIPPING CIRCUIT Prelab Part I: Wired Diode OR Gate LTspice use 1N4002 1. Design a diode OR gate, Figure 1 in which the maximum current thru R1 I R1 = 9mA assume Vin = 5Vdc. Design
EE 2274 DIODE OR GATE & CLIPPING CIRCUIT Prelab Part I: Wired Diode OR Gate LTspice use 1N4002 1. Design a diode OR gate, Figure 1 in which the maximum current thru R1 I R1 = 9mA assume Vin = 5Vdc. Design
Electronics. RC Filter, DC Supply, and 555
 Electronics RC Filter, DC Supply, and 555 0.1 Lab Ticket Each individual will write up his or her own Lab Report for this two-week experiment. You must also submit Lab Tickets individually. You are expected
Electronics RC Filter, DC Supply, and 555 0.1 Lab Ticket Each individual will write up his or her own Lab Report for this two-week experiment. You must also submit Lab Tickets individually. You are expected
AC Circuits. "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert ( )
 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits use varying
AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits use varying
2 Oscilloscope Familiarization
 Lab 2 Oscilloscope Familiarization What You Need To Know: Voltages and currents in an electronic circuit as in a CD player, mobile phone or TV set vary in time. Throughout the course you will investigate
Lab 2 Oscilloscope Familiarization What You Need To Know: Voltages and currents in an electronic circuit as in a CD player, mobile phone or TV set vary in time. Throughout the course you will investigate
Lab 2: Introduction to NI ELVIS, Multisim, and LabVIEW
 Page 1 of 19 Lab 2: Introduction to NI ELVIS, Multisim, and LabVIEW Laboratory Goals Familiarize students with the National Instruments hardware ELVIS Learn about the LabVIEW programming environment Demonstrate
Page 1 of 19 Lab 2: Introduction to NI ELVIS, Multisim, and LabVIEW Laboratory Goals Familiarize students with the National Instruments hardware ELVIS Learn about the LabVIEW programming environment Demonstrate
EXPERIMENT 10: SINGLE-TRANSISTOR AMPLIFIERS 10/27/17
 EXPERIMENT 10: SINGLE-TRANSISTOR AMPLIFIERS 10/27/17 In this experiment we will measure the characteristics of the standard common emitter amplifier. We will use the 2N3904 npn transistor. If you have
EXPERIMENT 10: SINGLE-TRANSISTOR AMPLIFIERS 10/27/17 In this experiment we will measure the characteristics of the standard common emitter amplifier. We will use the 2N3904 npn transistor. If you have
Experiment # 4. Frequency Modulation
 ECE 416 Fall 2002 Experiment # 4 Frequency Modulation 1 Purpose In Experiment # 3, a modulator and demodulator for AM were designed and built. In this experiment, another widely used modulation technique
ECE 416 Fall 2002 Experiment # 4 Frequency Modulation 1 Purpose In Experiment # 3, a modulator and demodulator for AM were designed and built. In this experiment, another widely used modulation technique
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Circuits & Electronics Spring 2005
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.002 Circuits & Electronics Spring 2005 Lab #2: MOSFET Inverting Amplifiers & FirstOrder Circuits Introduction
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.002 Circuits & Electronics Spring 2005 Lab #2: MOSFET Inverting Amplifiers & FirstOrder Circuits Introduction
