Quantum Dots. a) To whom correspondence should be addressed. E mail:
|
|
|
- Alice Lee
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supporting Information: Persistent Inter Excitonic Quantum Coherence in CdSe Quantum Dots Justin R. Caram 1, Haibin Zheng 1, Peter D. Dahlberg 2, Brian S. Rolczynski 1, Graham B. Griffin 1, Andrew F. Fidler 1, Dmitriy S. Dolzhnikov 3, Dmitri V. Talapin 3, and Gregory S. Engel 1,a 1. Department of Chemistry, The Institute for Biophysical Dynamics, and The James Franck Institute, The University of Chicago, Chicago, Illinois 60637, USA 2. Graduate Program in the Biophysical Sciences, The Institute for Biophysical Dynamics, and The James Franck Institute, The University of Chicago, Chicago, IL Department of Chemistry, and The James Franck Institute, The University of Chicago, Chicago, Illinois 60637, USA a) To whom correspondence should be addressed. E mail: gsengel@uchicago.edu Synthesis of Quantum Dots Large CdSe quantum dots were made using literature procedure mmol of cadmium myristate, 0.2 mmol of selenium dioxide and 0.04 mmol of cadmium acetate were mixed in 12.6 ml of 1 octadecene. The solution was heated to 240 o C (heat rate ~20 o C/min) and stirred. Once the solution reached 230 o C,0.2 ml of oleic acid was added to stabilize the growth of nanocrystals. Quantum dots were precipitated with ethanol and re dispersed in toluene after an hour. Washing was repeated 2 times. We obtained transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images (FEI Tecnai F30 microscope) at 300 kv. To determine zinc blende crystallinity, powder X ray diffraction was collected (Bruker D8 diffractometer). The TEM image and XRD pattern are shown in figure S1a and S1b, with an inset showing a size histogram of dot size. We also plot a histogram of sizes generated by examining the TEM image in the inset. In figure S2, we plot the absorption spectrum fit to Gaussians to estimate the position of the spectral features; our results are consistent with more monodisperse, well resolved preparations. 1
2 C 2DES Apparatus Continuum two dimensional spectroscopy differs from other implementations of 2DES in two specfic ways. First, it utilizes continuum generation in argon to generate ultrabroadband white light, and utilizes that light for all four pulse interactions. 2 These pulses span 400 to 900 nm, from which a 180 nm region in the visible is selected and compressed. The second is that it utilizes an All Reflective Interferometric Delay (ARID) method to introduce the finely controlled pulse delays. This method relies on angled stages (see figure S3) in order to create the coherence time delay with high accuracy and precision. Furthermore, this method elminates relative nonlinear dispersion introduced by previous glass wedge based methods. 3,4 This nonlinear dispersion can lead to distortions in two dimensional spectra. 5,6 In this implementation, continuum pulses were generated by focusing the output of a Ti:Sapphire oscillator seeded regenerative amplifier (4W, 5 khz, 40 fs pulses centered at 800 nm) into 2 atmospheres of argon (f=1m). A dichroic mirror elminate the signal above 700nm. The pulse is compressed using Multiphoton Intrapulse Interference Phase Scan (MIIPS) as described in the text. We use nm pulses with 0.5% stability (std/mean measured at 10 Hz), which are compressed to 8 10fs. Figure S4 plots at typical transient grating and MIIPS autocorrelation trace. Beams 1 and 2 are seperated from beams 3 and 4, and 1 and 2 are delayed using a linear mounted retroreflector (Aerotech). Beam 4 is used as a local oscillator which co propagates with the signal, and is set using a manual delays stage to be approximately 1 ps after the signal, and attennuated by an 3 orders of magnitude. We delay beam 1 relative to 2 using All Reflective Interferometric Delay (ARID). In ARID, angled stages move nearly perpidcular to the direction of propagation of each beam (<0.5 degrees). This translates stage motion into very minimal delay of the beam, approximately 34 fs/mm of motion, compared to ~6660 fs/mm in other reflective implementations, at the cost of a small deviation from the BOXCAR geometry, which can be characterized using solvent transient grating. This deviation is characterized in a recently submitted manuscript. 7 Stages were calibrated using spectral interferometry. All four beams are put into a boxcar geometery with 1.2cm between each beam, and focused onto the sample with an 30 degree off axis parabolic mirror (EFL: 45 cm), to a 100 micron spot size, which minimizes frequency dependent directional filtering. 8 Photon flux was adjusted such that fewer than 0.3 excitations per QD are allowed, to ensure operation in the in the single exciton manifold (14 nj/pulse and sample OD of 0.3 at 630 nm). 9,10 The signal and local oscillator is then focused onto a spectrometer and camera (Andor Shamrock and Newton respectively). Data Processing 2
3 In figure S5, we show the data analysis procedure. We collect an interferogram for each coherence time ranging from 60 to 80 fs. We first Fourier interpolate from wavelength (collected on the camera) to frequency space (λt to ωt), by zero padding the FT of the data by factor of 10, and using the expanded vector to linearly interpolate between points. 11 We then Fourier transform over ωt to create a t vs τ plot, which we apodize in the t domain with a 300 fs window to eliminate scatter and homodyne components. The final 2D spectrum (ωt vs ωτ) is created by Fourier transforming over both domains, for example figure S7. We zero pad by a factor of 2 in the ωτ domain to better resolve features. The experiment was repeated several times (for example, figure S6), and solvent only spectra were taken for comparison, contributing 10% of the signal at T=0, and negligible signal by T=10 fs. 12 To avoid non resonant solvent signals, all analysis is performed for signals after the first 15 fs. Each individual spectrum is phased to separately collected broadband pump broadband probe data (figure S5). 3 Spectrally resolved continuum pump continuumprobe spectra were collected for each waiting time. The pump beam was modulated at 2.5 khz, and pump probe and probe only spectra were collected on a high speed line scan camera. TA spectra were acquired for all time delays corresponding to the waiting times of the 2D spectra. Applying the projection slice theorem, we fit the projection of the real part of the 2D spectrum onto the axis to the TA spectrum. 13 PP t 2 2 T, Re A S, T, i i t i t i t 2 D t exp t 0 c t 0 q 0 d with ϕc, tc, tq, and τc are slight corrections to the measured timings and phase between each electric field. c (S1) 3
4 Figure S1: a) TEM image showing the QD ensemble used in this experiment r=3.0 ±0.3nm. The inset shows a histogram of particle sizes along with the estimate for the Gaussian distribution. b) XRD of the these particles showing zinc blende crystallinity. Figure S2: A fit of the absorption spectrum to a five Gaussian function. The first three peaks in the fit show good agreement to peaks from more monodisperse zinc blende QD preparations. The other states are not clearly distinguishable from very broadband Gaussians, and thus we do not assign them with confidence. 4
5 Figure S3: a) C 2DES setup. The details of this spectrometer and full characterization are the subject of a separate manuscript. 7 Broadband light is generated and compressed as described in the text. The beams are separated using beamsplitters (BS) and amount of glass in all beams is balanced with compensating windows (CW). We introduce a waiting time delay utilizing retroreflectors (RR) and a motorized translation stage (TS). All Reflective Interferometric Delay (ARID) introduces the coherence time delay, and a 30 degree off axis parabolic mirror (PM) focuses the beams to a spot on the sample. All beams are blocked (BB) except the signal and the LO, which are focused on the spectrometer and camera (SC). b) ARID generates time delays by angling the direction of the stage motion nearly perpendicular (0.3 ) to the direction of beam propagation. Therefore a distance Δd leads to a small change Δx in the forward direction of the mirror. 5
6 Figure S4: a) A typical TG FROG trace, taken by overlapping beams 1 and 2 in time and scanning beam 3. The resultant TG signal is frequency resolved on the camera. A typical autocorrelation from this method measured ~ 10fs. b) A pulse duration measurement taken using the Multiphoton Intrapulse Interference Phase Scan (MIIPS) method displays a ~9 fs pulse. 6
7 Figure S5: Representative spectra taken from a typical data analysis procedure. For every coherence time, τ, an interferogram is collected, which represents signal and scatter interfering with the local oscillator. Scatter is collected and subtracted for each coherence time, and the signal is Fourier transformed into t vs τ domain where it is apodized using a Hann window. For clarity, we display the magnitude of the signal in this domain. The t vs τ signal is Fourier transformed over both time domains to generate a magnitude ωt vs. ωt 7
8 spectrum. This spectrum is phased by fitting the summed down the real portion of the 2D spectrum to separately collected pump probe according to equation S1. Figure S6: a) We demonstrate oscillation reproducibility from the same point in the 2D spectrum (ħωτ=2.17, ħωτ=2.05) taken from different days, with different pulse power and pulse compression conditions. The oscillations agree both in character, magnitude and frequency, but show different phase. The phase difference may be a result of small differences in compression (chirp). The pulse energies were 14 nj/pulse for run 1 and 16 nj/pulse for run 2. 8
9 Figure S7: Four 2D spectra from different waiting times. The characteristics of the stimulated emission/ground state bleach signal between the 1P/1S states evident in the lower cross peak are the subject of a separate manuscript.14 9
10 Figure S8: Traces taken from different regions of the spectrum. Trace (a c) are taken from the magnitude of the upper diagonal cross peak between X3> and X1>, while trace (d) is taken from the magnitude of the below diagonal X3>/ X2> peak. (a) Is extracted from the τ>0 rephasing spectra while (b) and (d) are taken from the combined spectrum and (c) is taken from the τ<0 nonrephasing spectrum. As can be seen both trace (a) and (b) show a high amplitude early time coherent oscillations, while (c) shows no clear early time coherent signature, consistent with the expectation for an electronic coherence. Trace (d) demonstrates that the magnitude taken from point A in the main text also shows clear oscillatory dynamics similar to those reported in the phased 2D spectra, indicating that the oscillations are not the result of phasing error. References 1 O. Chen, X. Chen, Y. Yang, J. Lynch, H. Wu, J. Zhuang, and Y.C. Cao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 8638 (2008). 2 D. Kartashov, S. Aliauskas, A. Puglys, A. Voronin, A. Zheltikov, M. Petrarca, P. Béjot, J. Kasparian, J. P. Wolf, and A. Baltuka, Opt. Lett. 37, 3456 (2012). 3 T. Brixner, T. Mančal, I.V. Stiopkin, and G.R. Fleming, J. Chem. Phys. 121, 4221 (2004). 4 M.L. Cowan, J.P. Ogilvie, and R.J.D. Miller, Chem. Phys. Lett. 386, 184 (2004). 5 P.F. Tekavec, J.A. Myers, K.L.M. Lewis, F.D. Fuller, and J.P. Ogilvie, Opt. Express 18, (2010). 6 P.A. Tekavec, K.L.M. Lewis, F.D. Fuller, J.A. Myers, and J.P. Ogilvie, Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, IEEE Journal of 18, 210 (2012). 10
11 7 H. Zheng, J.R. Caram, P.D. Dahlberg, B.S. Rolczynski, S. Viswanathan, D.S. Dolzhnikov, A. Khadivi, D.V. Talapin, and G.S. Engel, (submitted). 8 M.K. Yetzbacher, N. Belabas, K.A. Kitney, and D.M. Jonas, J. Chem. Phys. 126, (2007). 9 E. Harel, S.M. Rupich, R.D. Schaller, D.V. Talapin, and G.S. Engel, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter 86, (2012). 10 V.I. Klimov, J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 6112 (2000). 11 L. Lepetit, G. Chériaux, and M. Joffre, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 12, 2467 (1995). 12 G.B. Griffin, S. Ithurria, D.S. Dolzhnikov, A. Linkin, D.V. Talapin, and G.S. Engel, J. Chem. Phys. 138, (2013). 13 T. Brixner, J. Stenger, H.M. Vaswani, M. Cho, R.E. Blankenship, and G.R. Fleming, Nature 434, 625 (2005). 14 J.R. Caram, H. Zheng, P.D. Dahlberg, B.S. Rolczynski, G.B. Griffin, D.S. Dolzhnikov, D.V. Talapin, and G.S. Engel, (submitted). 11
*Corresponding author.
 Supporting Information for: Ligand-Free, Quantum-Confined Cs 2 SnI 6 Perovskite Nanocrystals Dmitriy S. Dolzhnikov, Chen Wang, Yadong Xu, Mercouri G. Kanatzidis, and Emily A. Weiss * Department of Chemistry,
Supporting Information for: Ligand-Free, Quantum-Confined Cs 2 SnI 6 Perovskite Nanocrystals Dmitriy S. Dolzhnikov, Chen Wang, Yadong Xu, Mercouri G. Kanatzidis, and Emily A. Weiss * Department of Chemistry,
Remote characterization and dispersion compensation of amplified shaped femtosecond pulses using MIIPS
 Remote characterization and dispersion compensation of amplified shaped femtosecond pulses using MIIPS I. Pastirk Biophotonic Solutions, Inc. Okemos, MI 48864 pastirk@biophotonicsolutions.com X. Zhu, R.
Remote characterization and dispersion compensation of amplified shaped femtosecond pulses using MIIPS I. Pastirk Biophotonic Solutions, Inc. Okemos, MI 48864 pastirk@biophotonicsolutions.com X. Zhu, R.
Two-Dimensional Electronic Spectroscopy: A Review. Alicia Swain. A Master s Report Submitted to the Faculty of the COLLEGE OF OPTICAL SCIENCES
 Two-Dimensional Electronic Spectroscopy: A Review by Alicia Swain A Master s Report Submitted to the Faculty of the COLLEGE OF OPTICAL SCIENCES In partial Fulfillment of the Requirements For the Degree
Two-Dimensional Electronic Spectroscopy: A Review by Alicia Swain A Master s Report Submitted to the Faculty of the COLLEGE OF OPTICAL SCIENCES In partial Fulfillment of the Requirements For the Degree
Detection of chemicals at a standoff >10 m distance based on singlebeam coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering
 Detection of chemicals at a standoff >10 m distance based on singlebeam coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering Marcos Dantus* a, Haowen Li b, D. Ahmasi Harris a, Bingwei Xu a, Paul J. Wrzesinski a, Vadim
Detection of chemicals at a standoff >10 m distance based on singlebeam coherent anti-stokes Raman scattering Marcos Dantus* a, Haowen Li b, D. Ahmasi Harris a, Bingwei Xu a, Paul J. Wrzesinski a, Vadim
Chad A. Husko 1,, Sylvain Combrié 2, Pierre Colman 2, Jiangjun Zheng 1, Alfredo De Rossi 2, Chee Wei Wong 1,
 SOLITON DYNAMICS IN THE MULTIPHOTON PLASMA REGIME Chad A. Husko,, Sylvain Combrié, Pierre Colman, Jiangjun Zheng, Alfredo De Rossi, Chee Wei Wong, Optical Nanostructures Laboratory, Columbia University
SOLITON DYNAMICS IN THE MULTIPHOTON PLASMA REGIME Chad A. Husko,, Sylvain Combrié, Pierre Colman, Jiangjun Zheng, Alfredo De Rossi, Chee Wei Wong, Optical Nanostructures Laboratory, Columbia University
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Vibrational Coherence in the Excited State Dynamics of Cr(acac) 3 : Identifying the Reaction Coordinate for Ultrafast Intersystem Crossing Joel N. Schrauben, Kevin L. Dillman,
Supplementary Information for Vibrational Coherence in the Excited State Dynamics of Cr(acac) 3 : Identifying the Reaction Coordinate for Ultrafast Intersystem Crossing Joel N. Schrauben, Kevin L. Dillman,
Modified Spectrum Auto-Interferometric Correlation. (MOSAIC) for Single Shot Pulse Characterization
 To appear in OPTICS LETTERS, October 1, 2007 / Vol. 32, No. 19 Modified Spectrum Auto-Interferometric Correlation (MOSAIC) for Single Shot Pulse Characterization Daniel A. Bender* and Mansoor Sheik-Bahae
To appear in OPTICS LETTERS, October 1, 2007 / Vol. 32, No. 19 Modified Spectrum Auto-Interferometric Correlation (MOSAIC) for Single Shot Pulse Characterization Daniel A. Bender* and Mansoor Sheik-Bahae
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/2/e1700324/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Photocarrier generation from interlayer charge-transfer transitions in WS2-graphene heterostructures Long Yuan, Ting-Fung
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/2/e1700324/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Photocarrier generation from interlayer charge-transfer transitions in WS2-graphene heterostructures Long Yuan, Ting-Fung
Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers
 Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers Dan Fu 1, Gary Holtom 1, Christian Freudiger 1, Xu Zhang 2, Xiaoliang Sunney Xie 1 1. Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard
Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers Dan Fu 1, Gary Holtom 1, Christian Freudiger 1, Xu Zhang 2, Xiaoliang Sunney Xie 1 1. Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard
Directly Chirped Laser Source for Chirped Pulse Amplification
 Directly Chirped Laser Source for Chirped Pulse Amplification Input pulse (single frequency) AWG RF amp Output pulse (chirped) Phase modulator Normalized spectral intensity (db) 64 65 66 67 68 69 1052.4
Directly Chirped Laser Source for Chirped Pulse Amplification Input pulse (single frequency) AWG RF amp Output pulse (chirped) Phase modulator Normalized spectral intensity (db) 64 65 66 67 68 69 1052.4
Simultaneous measurement of two different-color ultrashort pulses on a single shot
 Wong et al. Vol. 29, No. 8 / August 2012 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1889 Simultaneous measurement of two different-color ultrashort pulses on a single shot Tsz Chun Wong,* Justin Ratner, and Rick Trebino School
Wong et al. Vol. 29, No. 8 / August 2012 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1889 Simultaneous measurement of two different-color ultrashort pulses on a single shot Tsz Chun Wong,* Justin Ratner, and Rick Trebino School
Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3000 cm 1
 Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3 cm A.C.W. van Rhijn, S. Postma, J.P. Korterik, J.L. Herek, and H.L. Offerhaus Mesa + Research Institute for Nanotechnology, University
Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3 cm A.C.W. van Rhijn, S. Postma, J.P. Korterik, J.L. Herek, and H.L. Offerhaus Mesa + Research Institute for Nanotechnology, University
Spider Pulse Characterization
 Spider Pulse Characterization Spectral and Temporal Characterization of Ultrashort Laser Pulses The Spider series by APE is an all-purpose and frequently used solution for complete characterization of
Spider Pulse Characterization Spectral and Temporal Characterization of Ultrashort Laser Pulses The Spider series by APE is an all-purpose and frequently used solution for complete characterization of
14. Measuring Ultrashort Laser Pulses I: Autocorrelation
 14. Measuring Ultrashort Laser Pulses I: Autocorrelation The dilemma The goal: measuring the intensity and phase vs. time (or frequency) Why? The Spectrometer and Michelson Interferometer Autocorrelation
14. Measuring Ultrashort Laser Pulses I: Autocorrelation The dilemma The goal: measuring the intensity and phase vs. time (or frequency) Why? The Spectrometer and Michelson Interferometer Autocorrelation
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression
 Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
High-Resolution Bubble Printing of Quantum Dots
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION High-Resolution Bubble Printing of Quantum Dots Bharath Bangalore Rajeeva 1, Linhan Lin 1, Evan P. Perillo 2, Xiaolei Peng 1, William W. Yu 3, Andrew K. Dunn 2, Yuebing Zheng 1,*
SUPPORTING INFORMATION High-Resolution Bubble Printing of Quantum Dots Bharath Bangalore Rajeeva 1, Linhan Lin 1, Evan P. Perillo 2, Xiaolei Peng 1, William W. Yu 3, Andrew K. Dunn 2, Yuebing Zheng 1,*
z t h l g 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Published 2009 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 x w z t h l g Figure 10.1 Photoconductive switch in microstrip transmission-line geometry: (a) top view; (b) side view. Adapted from [579]. Copyright 1983, IEEE. I g G t C g V g V i V r t x u V t Z 0 Z
x w z t h l g Figure 10.1 Photoconductive switch in microstrip transmission-line geometry: (a) top view; (b) side view. Adapted from [579]. Copyright 1983, IEEE. I g G t C g V g V i V r t x u V t Z 0 Z
Figure1. To construct a light pulse, the electric component of the plane wave should be multiplied with a bell shaped function.
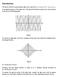 Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
pulsecheck The Modular Autocorrelator
 pulsecheck The Modular Autocorrelator Pulse Measurement Perfection with the Multitalent from APE It is good to have plenty of options at hand. Suitable for the characterization of virtually any ultrafast
pulsecheck The Modular Autocorrelator Pulse Measurement Perfection with the Multitalent from APE It is good to have plenty of options at hand. Suitable for the characterization of virtually any ultrafast
Ultrafast Optical Physics II (SoSe 2017) Lecture 9, June 16
 Ultrafast Optical Physics II (SoSe 2017) Lecture 9, June 16 9 Pulse Characterization 9.1 Intensity Autocorrelation 9.2 Interferometric Autocorrelation (IAC) 9.3 Frequency Resolved Optical Gating (FROG)
Ultrafast Optical Physics II (SoSe 2017) Lecture 9, June 16 9 Pulse Characterization 9.1 Intensity Autocorrelation 9.2 Interferometric Autocorrelation (IAC) 9.3 Frequency Resolved Optical Gating (FROG)
APE Autocorrelator Product Family
 APE Autocorrelator Product Family APE Autocorrelators The autocorrelator product family by APE includes a variety of impressive features and properties, designed to cater for a wide range of ultrafast
APE Autocorrelator Product Family APE Autocorrelators The autocorrelator product family by APE includes a variety of impressive features and properties, designed to cater for a wide range of ultrafast
atom physics seminar ultra short laser pulses
 atom physics seminar ultra short laser pulses creation and application ultra short laser pulses overview what? - why? - how? creation and optimisation typical experimental setup properties of existing
atom physics seminar ultra short laser pulses creation and application ultra short laser pulses overview what? - why? - how? creation and optimisation typical experimental setup properties of existing
Optical coherence tomography
 Optical coherence tomography Peter E. Andersen Optics and Plasma Research Department Risø National Laboratory E-mail peter.andersen@risoe.dk Outline Part I: Introduction to optical coherence tomography
Optical coherence tomography Peter E. Andersen Optics and Plasma Research Department Risø National Laboratory E-mail peter.andersen@risoe.dk Outline Part I: Introduction to optical coherence tomography
GRENOUILLE.
 GRENOUILLE Measuring ultrashort laser pulses the shortest events ever created has always been a challenge. For many years, it was possible to create ultrashort pulses, but not to measure them. Techniques
GRENOUILLE Measuring ultrashort laser pulses the shortest events ever created has always been a challenge. For many years, it was possible to create ultrashort pulses, but not to measure them. Techniques
Outline. Motivation Experimental Set-Up Theory behind the set-up Results Acknowledgements
 Outline Motivation Experimental Set-Up Theory behind the set-up Results Acknowledgements Motivation Attosecond pulses could be used to study time-dependence of atomic dynamics. Greater control of pulse
Outline Motivation Experimental Set-Up Theory behind the set-up Results Acknowledgements Motivation Attosecond pulses could be used to study time-dependence of atomic dynamics. Greater control of pulse
Designing for Femtosecond Pulses
 Designing for Femtosecond Pulses White Paper PN 200-1100-00 Revision 1.1 July 2013 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Calmar s femtosecond laser sources are passively mode-locked fiber lasers.
Designing for Femtosecond Pulses White Paper PN 200-1100-00 Revision 1.1 July 2013 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Calmar s femtosecond laser sources are passively mode-locked fiber lasers.
High Energy Non - Collinear OPA
 High Energy Non - Collinear OPA Basics of Operation FEATURES Pulse Duration less than 10 fs possible High Energy (> 80 microjoule) Visible Output Wavelength Tuning Computer Controlled Tuning Range 250-375,
High Energy Non - Collinear OPA Basics of Operation FEATURES Pulse Duration less than 10 fs possible High Energy (> 80 microjoule) Visible Output Wavelength Tuning Computer Controlled Tuning Range 250-375,
Fundamental Optics ULTRAFAST THEORY ( ) = ( ) ( q) FUNDAMENTAL OPTICS. q q = ( A150 Ultrafast Theory
 ULTRAFAST THEORY The distinguishing aspect of femtosecond laser optics design is the need to control the phase characteristic of the optical system over the requisite wide pulse bandwidth. CVI Laser Optics
ULTRAFAST THEORY The distinguishing aspect of femtosecond laser optics design is the need to control the phase characteristic of the optical system over the requisite wide pulse bandwidth. CVI Laser Optics
Theoretical Approach. Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION:
 Theoretical Approach Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION: Generating ultrashort laser pulses that last a few femtoseconds is a highly active area of research that is finding applications
Theoretical Approach Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION: Generating ultrashort laser pulses that last a few femtoseconds is a highly active area of research that is finding applications
A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier
 Science in China Ser. G Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2004 Vol.47 No.6 767 772 767 A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier ZHU Heyuan, XU Guang, WANG Tao, QIAN Liejia & FAN Dianyuan State
Science in China Ser. G Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2004 Vol.47 No.6 767 772 767 A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier ZHU Heyuan, XU Guang, WANG Tao, QIAN Liejia & FAN Dianyuan State
Nd:YSO resonator array Transmission spectrum (a. u.) Supplementary Figure 1. An array of nano-beam resonators fabricated in Nd:YSO.
 a Nd:YSO resonator array µm Transmission spectrum (a. u.) b 4 F3/2-4I9/2 25 2 5 5 875 88 λ(nm) 885 Supplementary Figure. An array of nano-beam resonators fabricated in Nd:YSO. (a) Scanning electron microscope
a Nd:YSO resonator array µm Transmission spectrum (a. u.) b 4 F3/2-4I9/2 25 2 5 5 875 88 λ(nm) 885 Supplementary Figure. An array of nano-beam resonators fabricated in Nd:YSO. (a) Scanning electron microscope
G. Norris* & G. McConnell
 Relaxed damage threshold intensity conditions and nonlinear increase in the conversion efficiency of an optical parametric oscillator using a bi-directional pump geometry G. Norris* & G. McConnell Centre
Relaxed damage threshold intensity conditions and nonlinear increase in the conversion efficiency of an optical parametric oscillator using a bi-directional pump geometry G. Norris* & G. McConnell Centre
Dispersion measurement in optical fibres over the entire spectral range from 1.1 mm to 1.7 mm
 15 February 2000 Ž. Optics Communications 175 2000 209 213 www.elsevier.comrlocateroptcom Dispersion measurement in optical fibres over the entire spectral range from 1.1 mm to 1.7 mm F. Koch ), S.V. Chernikov,
15 February 2000 Ž. Optics Communications 175 2000 209 213 www.elsevier.comrlocateroptcom Dispersion measurement in optical fibres over the entire spectral range from 1.1 mm to 1.7 mm F. Koch ), S.V. Chernikov,
Terahertz control of nanotip photoemission
 Terahertz control of nanotip photoemission L. Wimmer, G. Herink, D. R. Solli, S. V. Yalunin, K. E. Echternkamp, and C. Ropers Near-infrared pulses of 800 nm wavelength, 50 fs duration and at 1 khz repetition
Terahertz control of nanotip photoemission L. Wimmer, G. Herink, D. R. Solli, S. V. Yalunin, K. E. Echternkamp, and C. Ropers Near-infrared pulses of 800 nm wavelength, 50 fs duration and at 1 khz repetition
Chemistry 524--"Hour Exam"--Keiderling Mar. 19, pm SES
 Chemistry 524--"Hour Exam"--Keiderling Mar. 19, 2013 -- 2-4 pm -- 170 SES Please answer all questions in the answer book provided. Calculators, rulers, pens and pencils permitted. No open books allowed.
Chemistry 524--"Hour Exam"--Keiderling Mar. 19, 2013 -- 2-4 pm -- 170 SES Please answer all questions in the answer book provided. Calculators, rulers, pens and pencils permitted. No open books allowed.
Q-switched resonantly diode-pumped Er:YAG laser
 Q-switched resonantly diode-pumped Er:YAG laser Igor Kudryashov a) and Alexei Katsnelson Princeton Lightwave Inc., 2555 US Route 130, Cranbury, New Jersey, 08512 ABSTRACT In this work, resonant diode pumping
Q-switched resonantly diode-pumped Er:YAG laser Igor Kudryashov a) and Alexei Katsnelson Princeton Lightwave Inc., 2555 US Route 130, Cranbury, New Jersey, 08512 ABSTRACT In this work, resonant diode pumping
High-Conversion-Efficiency Optical Parametric Chirped-Pulse Amplification System Using Spatiotemporally Shaped Pump Pulses
 High-Conversion-Efficiency Optical Parametric Chirped-Pulse Amplification System Using Spatiotemporally Shaped Pump Pulses Since its invention in the early 199s, 1 optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification
High-Conversion-Efficiency Optical Parametric Chirped-Pulse Amplification System Using Spatiotemporally Shaped Pump Pulses Since its invention in the early 199s, 1 optical parametric chirped-pulse amplification
Pulse Shaping Application Note
 Application Note 8010 Pulse Shaping Application Note Revision 1.0 Boulder Nonlinear Systems, Inc. 450 Courtney Way Lafayette, CO 80026-8878 USA Shaping ultrafast optical pulses with liquid crystal spatial
Application Note 8010 Pulse Shaping Application Note Revision 1.0 Boulder Nonlinear Systems, Inc. 450 Courtney Way Lafayette, CO 80026-8878 USA Shaping ultrafast optical pulses with liquid crystal spatial
Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania
 Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania Razvan Dabu, Daniel Ursescu INFLPR, Magurele, Romania Contents GiWALAS laser facility TEWALAS laser facility CETAL project
Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania Razvan Dabu, Daniel Ursescu INFLPR, Magurele, Romania Contents GiWALAS laser facility TEWALAS laser facility CETAL project
Phase-sensitive high-speed THz imaging
 Phase-sensitive high-speed THz imaging Toshiaki Hattori, Keisuke Ohta, Rakchanok Rungsawang and Keiji Tukamoto Institute of Applied Physics, University of Tsukuba, 1-1-1 Tennodai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-8573
Phase-sensitive high-speed THz imaging Toshiaki Hattori, Keisuke Ohta, Rakchanok Rungsawang and Keiji Tukamoto Institute of Applied Physics, University of Tsukuba, 1-1-1 Tennodai, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, 305-8573
picoemerald Tunable Two-Color ps Light Source Microscopy & Spectroscopy CARS SRS
 picoemerald Tunable Two-Color ps Light Source Microscopy & Spectroscopy CARS SRS 1 picoemerald Two Colors in One Box Microscopy and Spectroscopy with a Tunable Two-Color Source CARS and SRS microscopy
picoemerald Tunable Two-Color ps Light Source Microscopy & Spectroscopy CARS SRS 1 picoemerald Two Colors in One Box Microscopy and Spectroscopy with a Tunable Two-Color Source CARS and SRS microscopy
7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP
 7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP Abstract: In this chapter we describe the use of a common path phase sensitive FDOCT set up. The phase measurements
7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP Abstract: In this chapter we describe the use of a common path phase sensitive FDOCT set up. The phase measurements
FPPO 1000 Fiber Laser Pumped Optical Parametric Oscillator: FPPO 1000 Product Manual
 Fiber Laser Pumped Optical Parametric Oscillator: FPPO 1000 Product Manual 2012 858 West Park Street, Eugene, OR 97401 www.mtinstruments.com Table of Contents Specifications and Overview... 1 General Layout...
Fiber Laser Pumped Optical Parametric Oscillator: FPPO 1000 Product Manual 2012 858 West Park Street, Eugene, OR 97401 www.mtinstruments.com Table of Contents Specifications and Overview... 1 General Layout...
PGx11 series. Transform Limited Broadly Tunable Picosecond OPA APPLICATIONS. Available models
 PGx1 PGx3 PGx11 PT2 Transform Limited Broadly Tunable Picosecond OPA optical parametric devices employ advanced design concepts in order to produce broadly tunable picosecond pulses with nearly Fourier-transform
PGx1 PGx3 PGx11 PT2 Transform Limited Broadly Tunable Picosecond OPA optical parametric devices employ advanced design concepts in order to produce broadly tunable picosecond pulses with nearly Fourier-transform
Progress in ultrafast Cr:ZnSe Lasers. Evgueni Slobodtchikov, Peter Moulton
 Progress in ultrafast Cr:ZnSe Lasers Evgueni Slobodtchikov, Peter Moulton Topics Diode-pumped Cr:ZnSe femtosecond oscillator CPA Cr:ZnSe laser system with 1 GW output This work was supported by SBIR Phase
Progress in ultrafast Cr:ZnSe Lasers Evgueni Slobodtchikov, Peter Moulton Topics Diode-pumped Cr:ZnSe femtosecond oscillator CPA Cr:ZnSe laser system with 1 GW output This work was supported by SBIR Phase
Direct observation of beamed Raman scattering
 Supporting Information Direct observation of beamed Raman scattering Wenqi Zhu, Dongxing Wang, and Kenneth B. Crozier* School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Supporting Information Direct observation of beamed Raman scattering Wenqi Zhu, Dongxing Wang, and Kenneth B. Crozier* School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG)
 Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
Improvement of terahertz imaging with a dynamic subtraction technique
 Improvement of terahertz imaging with a dynamic subtraction technique Zhiping Jiang, X. G. Xu, and X.-C. Zhang By use of dynamic subtraction it is feasible to adopt phase-sensitive detection with a CCD
Improvement of terahertz imaging with a dynamic subtraction technique Zhiping Jiang, X. G. Xu, and X.-C. Zhang By use of dynamic subtraction it is feasible to adopt phase-sensitive detection with a CCD
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy
 Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
How to build an Er:fiber femtosecond laser
 How to build an Er:fiber femtosecond laser Daniele Brida 17.02.2016 Konstanz Ultrafast laser Time domain : pulse train Frequency domain: comb 3 26.03.2016 Frequency comb laser Time domain : pulse train
How to build an Er:fiber femtosecond laser Daniele Brida 17.02.2016 Konstanz Ultrafast laser Time domain : pulse train Frequency domain: comb 3 26.03.2016 Frequency comb laser Time domain : pulse train
Thin-Disc-Based Driver
 Thin-Disc-Based Driver Jochen Speiser German Aerospace Center (DLR) Institute of Technical Physics Solid State Lasers and Nonlinear Optics Folie 1 German Aerospace Center! Research Institution! Space Agency!
Thin-Disc-Based Driver Jochen Speiser German Aerospace Center (DLR) Institute of Technical Physics Solid State Lasers and Nonlinear Optics Folie 1 German Aerospace Center! Research Institution! Space Agency!
Ultrafast Surface-Enhanced Raman Probing of the Role of Hot Electrons in Plasmon-Driven Chemistry. Supporting Information
 Methods Ultrafast Surface-Enhanced Raman Probing of the Role of Hot Electrons in Plasmon-Driven Chemistry Sample preparation Supporting Information Nathaniel C. Brandt, Emily L. Keller, and Renee R. Frontiera
Methods Ultrafast Surface-Enhanced Raman Probing of the Role of Hot Electrons in Plasmon-Driven Chemistry Sample preparation Supporting Information Nathaniel C. Brandt, Emily L. Keller, and Renee R. Frontiera
2. Pulsed Acoustic Microscopy and Picosecond Ultrasonics
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Picosecond Ultrasonic Microscopy of Semiconductor Nanostructures Thomas J GRIMSLEY
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Picosecond Ultrasonic Microscopy of Semiconductor Nanostructures Thomas J GRIMSLEY
Supplementary Information. Phase-selective cation-exchange chemistry in sulfide nanowire systems
 Supplementary Information Phase-selective cation-exchange chemistry in sulfide nanowire systems Dandan Zhang,, Andrew B. Wong,, Yi Yu,, Sarah Brittman,, Jianwei Sun,, Anthony Fu,, Brandon Beberwyck,,,
Supplementary Information Phase-selective cation-exchange chemistry in sulfide nanowire systems Dandan Zhang,, Andrew B. Wong,, Yi Yu,, Sarah Brittman,, Jianwei Sun,, Anthony Fu,, Brandon Beberwyck,,,
The Measurement of Ultrashort Laser Pulses
 The Measurement of Ultrashort Laser Pulses To spectrometer SHG crystal Fresnel biprism beamsplitter Cylindrical lens Etalon Oppositely tilted pulses Lens Prof. Rick Trebino Input pulse Georgia Tech & Swamp
The Measurement of Ultrashort Laser Pulses To spectrometer SHG crystal Fresnel biprism beamsplitter Cylindrical lens Etalon Oppositely tilted pulses Lens Prof. Rick Trebino Input pulse Georgia Tech & Swamp
Measuring chromatic aberrations in imaging systems using plasmonic nano particles
 Measuring chromatic aberrations in imaging systems using plasmonic nano particles Sylvain D. Gennaro, Tyler R. Roschuk, Stefan A. Maier, and Rupert F. Oulton* Department of Physics, The Blackett Laboratory,
Measuring chromatic aberrations in imaging systems using plasmonic nano particles Sylvain D. Gennaro, Tyler R. Roschuk, Stefan A. Maier, and Rupert F. Oulton* Department of Physics, The Blackett Laboratory,
Frequency modulation coherent anti-stokes Rama Scattering (FM- CARS) microscopy based on spectral focusing of chirped laser pulses
 Frequency modulation coherent anti-stokes Rama Scattering (FM- ) microscopy based on spectral focusing of chirped laser pulses Bi-Chang Chen, Jiha Sung and Sang-Hyun Lim* Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry,
Frequency modulation coherent anti-stokes Rama Scattering (FM- ) microscopy based on spectral focusing of chirped laser pulses Bi-Chang Chen, Jiha Sung and Sang-Hyun Lim* Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry,
OCT Spectrometer Design Understanding roll-off to achieve the clearest images
 OCT Spectrometer Design Understanding roll-off to achieve the clearest images Building a high-performance spectrometer for OCT imaging requires a deep understanding of the finer points of both OCT theory
OCT Spectrometer Design Understanding roll-off to achieve the clearest images Building a high-performance spectrometer for OCT imaging requires a deep understanding of the finer points of both OCT theory
Spectral Phase Modulation and chirped pulse amplification in High Gain Harmonic Generation
 Spectral Phase Modulation and chirped pulse amplification in High Gain Harmonic Generation Z. Wu, H. Loos, Y. Shen, B. Sheehy, E. D. Johnson, S. Krinsky, J. B. Murphy, T. Shaftan,, X.-J. Wang, L. H. Yu,
Spectral Phase Modulation and chirped pulse amplification in High Gain Harmonic Generation Z. Wu, H. Loos, Y. Shen, B. Sheehy, E. D. Johnson, S. Krinsky, J. B. Murphy, T. Shaftan,, X.-J. Wang, L. H. Yu,
PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
 Becker & Hickl GmbH Kolonnenstr. 29 10829 Berlin Tel. 030 / 787 56 32 Fax. 030 / 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hickl.de http://www.becker-hickl.de PCSAPP.DOC PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
Becker & Hickl GmbH Kolonnenstr. 29 10829 Berlin Tel. 030 / 787 56 32 Fax. 030 / 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hickl.de http://www.becker-hickl.de PCSAPP.DOC PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
Administrative details:
 Administrative details: Anything from your side? www.photonics.ethz.ch 1 What are we actually doing here? Optical imaging: Focusing by a lens Angular spectrum Paraxial approximation Gaussian beams Method
Administrative details: Anything from your side? www.photonics.ethz.ch 1 What are we actually doing here? Optical imaging: Focusing by a lens Angular spectrum Paraxial approximation Gaussian beams Method
taccor Optional features Overview Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser
 taccor Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser Self-locking and maintaining Stable and robust True hands off turn-key system Wavelength tunable Integrated pump laser Overview The taccor is a unique turn-key femtosecond
taccor Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser Self-locking and maintaining Stable and robust True hands off turn-key system Wavelength tunable Integrated pump laser Overview The taccor is a unique turn-key femtosecond
Superconducting single-photon detectors as photon-energy and polarization resolving devices. Roman Sobolewski
 Superconducting single-photon detectors as photon-energy and polarization resolving devices Roman Sobolewski Departments of Electrical and Computing Engineering Physics and Astronomy, Materials Science
Superconducting single-photon detectors as photon-energy and polarization resolving devices Roman Sobolewski Departments of Electrical and Computing Engineering Physics and Astronomy, Materials Science
APPLICATION NOTE. Synchronization of Two Spectra-Physics Spitfire Pro Amplifiers for Pump-Probe Experiments
 APPLICATION NOTE Synchronization of Two Spectra-Physics Spitfire Pro Amplifiers for Pump-Probe Experiments 43 Technology and Applications Center Newport Corporation Introduction: The invention of nanosecond
APPLICATION NOTE Synchronization of Two Spectra-Physics Spitfire Pro Amplifiers for Pump-Probe Experiments 43 Technology and Applications Center Newport Corporation Introduction: The invention of nanosecond
Coherent temporal imaging with analog timebandwidth
 Coherent temporal imaging with analog timebandwidth compression Mohammad H. Asghari 1, * and Bahram Jalali 1,2,3 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095,
Coherent temporal imaging with analog timebandwidth compression Mohammad H. Asghari 1, * and Bahram Jalali 1,2,3 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095,
Ultrafast pulse characterization using XPM in silicon
 Ultrafast pulse characterization using XPM in silicon Nuh S. Yuksek, Xinzhu Sang, En-Kuang Tien, Qi Song, Feng Qian, Ivan V. Tomov, Ozdal Boyraz Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science,
Ultrafast pulse characterization using XPM in silicon Nuh S. Yuksek, Xinzhu Sang, En-Kuang Tien, Qi Song, Feng Qian, Ivan V. Tomov, Ozdal Boyraz Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science,
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET
 LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
Up-conversion Time Microscope Demonstrates 103x Magnification of an Ultrafast Waveforms with 300 fs Resolution. C. V. Bennett B. H.
 UCRL-JC-3458 PREPRINT Up-conversion Time Microscope Demonstrates 03x Magnification of an Ultrafast Waveforms with 3 fs Resolution C. V. Bennett B. H. Kolner This paper was prepared for submittal to the
UCRL-JC-3458 PREPRINT Up-conversion Time Microscope Demonstrates 03x Magnification of an Ultrafast Waveforms with 3 fs Resolution C. V. Bennett B. H. Kolner This paper was prepared for submittal to the
Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics Todd W. MURRAY 1,
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics Todd W. MURRAY 1,
2D IR done cheaper, easier, and faster: design and applications
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Fall 2012 2D IR done cheaper, easier, and faster: design and applications William Thomas Rock University of Iowa Copyright 2012 William
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Fall 2012 2D IR done cheaper, easier, and faster: design and applications William Thomas Rock University of Iowa Copyright 2012 William
Soliton stability conditions in actively modelocked inhomogeneously broadened lasers
 Lu et al. Vol. 20, No. 7/July 2003 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1473 Soliton stability conditions in actively modelocked inhomogeneously broadened lasers Wei Lu,* Li Yan, and Curtis R. Menyuk Department of Computer
Lu et al. Vol. 20, No. 7/July 2003 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1473 Soliton stability conditions in actively modelocked inhomogeneously broadened lasers Wei Lu,* Li Yan, and Curtis R. Menyuk Department of Computer
Implementation of Orthogonal Frequency Coded SAW Devices Using Apodized Reflectors
 Implementation of Orthogonal Frequency Coded SAW Devices Using Apodized Reflectors Derek Puccio, Don Malocha, Nancy Saldanha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Central Florida
Implementation of Orthogonal Frequency Coded SAW Devices Using Apodized Reflectors Derek Puccio, Don Malocha, Nancy Saldanha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Central Florida
ULTRAFAST LASER DIAGNOSTICS
 ULTRAFAST LASER DIAGNOSTICS USE OUR APP IN YOUR LAB The faster way to master nonlinear phenomena... Wavelength conversion calculator Bandwidth and pulse duration Frequency conversion Bandwidth conversion
ULTRAFAST LASER DIAGNOSTICS USE OUR APP IN YOUR LAB The faster way to master nonlinear phenomena... Wavelength conversion calculator Bandwidth and pulse duration Frequency conversion Bandwidth conversion
Applied Physics B Lasers and Optics. m. hirasawa 1,3, n. nakagawa 1,3 k. yamamoto 1,3 r. morita 1,3 h. shigekawa 2,3 m.
 Appl. Phys. B 74 [Suppl.], S225 S229 (2002) DOI: 10.1007/s00340-002-0891-y Applied Physics B Lasers and Optics m. hirasawa 1,3, n. nakagawa 1,3 k. yamamoto 1,3 r. morita 1,3 h. shigekawa 2,3 m. yamashita
Appl. Phys. B 74 [Suppl.], S225 S229 (2002) DOI: 10.1007/s00340-002-0891-y Applied Physics B Lasers and Optics m. hirasawa 1,3, n. nakagawa 1,3 k. yamamoto 1,3 r. morita 1,3 h. shigekawa 2,3 m. yamashita
J-KAREN-P Session 1, 10:00 10:
 J-KAREN-P 2018 Session 1, 10:00 10:25 2018 5 8 Outline Introduction Capabilities of J-KAREN-P facility Optical architecture Status and implementation of J-KAREN-P facility Amplification performance Recompression
J-KAREN-P 2018 Session 1, 10:00 10:25 2018 5 8 Outline Introduction Capabilities of J-KAREN-P facility Optical architecture Status and implementation of J-KAREN-P facility Amplification performance Recompression
Measurement of the group refractive index of air and glass
 Application Note METROLOGY Czech Metrology Institute (CMI), Prague Menlo Systems, Martinsried Measurement of the group refractive index of air and glass Authors: Petr Balling (CMI), Benjamin Sprenger (Menlo
Application Note METROLOGY Czech Metrology Institute (CMI), Prague Menlo Systems, Martinsried Measurement of the group refractive index of air and glass Authors: Petr Balling (CMI), Benjamin Sprenger (Menlo
TIME-PRESERVING MONOCHROMATORS FOR ULTRASHORT EXTREME-ULTRAVIOLET PULSES
 TIME-PRESERVING MONOCHROMATORS FOR ULTRASHORT EXTREME-ULTRAVIOLET PULSES Luca Poletto CNR - Institute of Photonics and Nanotechnologies Laboratory for UV and X-Ray Optical Research Padova, Italy e-mail:
TIME-PRESERVING MONOCHROMATORS FOR ULTRASHORT EXTREME-ULTRAVIOLET PULSES Luca Poletto CNR - Institute of Photonics and Nanotechnologies Laboratory for UV and X-Ray Optical Research Padova, Italy e-mail:
Supplementary information for: Surface passivated GaAsP single-nanowire solar cells exceeding 10% efficiency grown on silicon
 Supplementary information for: Surface passivated GaAsP single-nanowire solar cells exceeding 10% efficiency grown on silicon Jeppe V. Holm 1, Henrik I. Jørgensen 1, Peter Krogstrup 2, Jesper Nygård 2,4,
Supplementary information for: Surface passivated GaAsP single-nanowire solar cells exceeding 10% efficiency grown on silicon Jeppe V. Holm 1, Henrik I. Jørgensen 1, Peter Krogstrup 2, Jesper Nygård 2,4,
Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II
 Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II Generating negative groupdelay dispersion angular dispersion Pulse compression Prisms Gratings Chirped mirrors Chirped vs. transform-limited A transform-limited pulse:
Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II Generating negative groupdelay dispersion angular dispersion Pulse compression Prisms Gratings Chirped mirrors Chirped vs. transform-limited A transform-limited pulse:
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/10/eaao4204/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Enhanced mobility CsPbI3 quantum dot arrays for record-efficiency, high-voltage photovoltaic cells Erin M. Sanehira,
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/10/eaao4204/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Enhanced mobility CsPbI3 quantum dot arrays for record-efficiency, high-voltage photovoltaic cells Erin M. Sanehira,
Fabrication of Photorefractive Grating With 800 nm Femtosecond Lasers in Fe: LiNbO 3 and Rh:BaTiO 3 Crystals
 Fabrication of Photorefractive Grating With 8 nm Femtosecond Lasers in Fe: LiNbO 3 and Rh:BaTiO 3 Crystals Md. Masudul Kabir (D3) Abstract Refractive index gratings have been successfully formed in Fe:LiNbO
Fabrication of Photorefractive Grating With 8 nm Femtosecond Lasers in Fe: LiNbO 3 and Rh:BaTiO 3 Crystals Md. Masudul Kabir (D3) Abstract Refractive index gratings have been successfully formed in Fe:LiNbO
High Power and Energy Femtosecond Lasers
 High Power and Energy Femtosecond Lasers PHAROS is a single-unit integrated femtosecond laser system combining millijoule pulse energies and high average powers. PHAROS features a mechanical and optical
High Power and Energy Femtosecond Lasers PHAROS is a single-unit integrated femtosecond laser system combining millijoule pulse energies and high average powers. PHAROS features a mechanical and optical
Stabilizing an Interferometric Delay with PI Control
 Stabilizing an Interferometric Delay with PI Control Madeleine Bulkow August 31, 2013 Abstract A Mach-Zhender style interferometric delay can be used to separate a pulses by a precise amount of time, act
Stabilizing an Interferometric Delay with PI Control Madeleine Bulkow August 31, 2013 Abstract A Mach-Zhender style interferometric delay can be used to separate a pulses by a precise amount of time, act
Section 2 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENTS
 Section 2 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENTS 2.A High-Power Laser Interferometry Central to the uniformity issue is the need to determine the factors that control the target-plane intensity distribution
Section 2 ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENTS 2.A High-Power Laser Interferometry Central to the uniformity issue is the need to determine the factors that control the target-plane intensity distribution
Ultrafast instrumentation (No Alignment!)
 Ultrafast instrumentation (No Alignment!) We offer products specialized in ultrafast metrology with strong expertise in the production and characterization of high energy ultrashort pulses. We provide
Ultrafast instrumentation (No Alignment!) We offer products specialized in ultrafast metrology with strong expertise in the production and characterization of high energy ultrashort pulses. We provide
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Student Name Date MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161 Modern Optics Project Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 6 Fall 2010 Solid-State
Student Name Date MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161 Modern Optics Project Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 6 Fall 2010 Solid-State
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin
 Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
Supplementary Figure 1. GO thin film thickness characterization. The thickness of the prepared GO thin film is characterized by using an optical profiler (Bruker ContourGT InMotion). Inset: 3D optical
Quantifying noise in ultrafast laser sources and its effect on nonlinear applications
 Quantifying noise in ultrafast laser sources and its effect on nonlinear applications Vadim V. Lozovoy, 1 Gennady Rasskazov, 1 Dmitry Pestov, 3 and Marcos Dantus 1,2,3,* 1 Department of Chemistry, Michigan
Quantifying noise in ultrafast laser sources and its effect on nonlinear applications Vadim V. Lozovoy, 1 Gennady Rasskazov, 1 Dmitry Pestov, 3 and Marcos Dantus 1,2,3,* 1 Department of Chemistry, Michigan
Optical Spectrum Analyzers
 Optical Spectrum Analyzers Broadband Spectrometer and Wavelength Meter in One Thorlabs Optical Spectrum Analyzers obtain highly accurate measurements of the spectra of unknown light sources. They are continuously
Optical Spectrum Analyzers Broadband Spectrometer and Wavelength Meter in One Thorlabs Optical Spectrum Analyzers obtain highly accurate measurements of the spectra of unknown light sources. They are continuously
H. Tu Y. Liu J. Lægsgaard D. Turchinovich M. Siegel D. Kopf H. Li T. Gunaratne S.A. Boppart
 Appl Phys B (2012) 106:379 384 DOI 10.1007/s00340-011-4746-2 Cross-validation of theoretically quantified fiber continuum generation and absolute pulse measurement by MIIPS for a broadband coherently controlled
Appl Phys B (2012) 106:379 384 DOI 10.1007/s00340-011-4746-2 Cross-validation of theoretically quantified fiber continuum generation and absolute pulse measurement by MIIPS for a broadband coherently controlled
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Comprehensive Numerical Modelling of a Low-Gain Optical Parametric Amplifier as a Front-End Contrast Enhancement Unit
 Comprehensive Numerical Modelling of a Low-Gain Optical Parametric Amplifier as a Front-End Contrast Enhancement Unit arxiv:161.5558v1 [physics.optics] 21 Jan 216 A. B. Sharba, G. Nersisyan, M. Zepf, M.
Comprehensive Numerical Modelling of a Low-Gain Optical Parametric Amplifier as a Front-End Contrast Enhancement Unit arxiv:161.5558v1 [physics.optics] 21 Jan 216 A. B. Sharba, G. Nersisyan, M. Zepf, M.
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance
 Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
Jian-Wei Liu, Jing Zheng, Jin-Long Wang, Jie Xu, Hui-Hui Li, Shu-Hong Yu*
 Supporting Information Ultrathin 18 O 49 Nanowire Assemblies for Electrochromic Devices Jian-ei Liu, Jing Zheng, Jin-Long ang, Jie Xu, Hui-Hui Li, Shu-Hong Yu* Experimental Section Synthesis and Assembly
Supporting Information Ultrathin 18 O 49 Nanowire Assemblies for Electrochromic Devices Jian-ei Liu, Jing Zheng, Jin-Long ang, Jie Xu, Hui-Hui Li, Shu-Hong Yu* Experimental Section Synthesis and Assembly
Optomechanical enhancement of doubly resonant 2D optical nonlinearity
 Supporting information Optomechanical enhancement of doubly resonant 2D optical nonlinearity Fei Yi 3+, Mingliang Ren 3+, Jason C Reed 3, Hai Zhu 3, Jiechang Hou 3, Carl H. Naylor 4, Alan T. Charlie Johnson
Supporting information Optomechanical enhancement of doubly resonant 2D optical nonlinearity Fei Yi 3+, Mingliang Ren 3+, Jason C Reed 3, Hai Zhu 3, Jiechang Hou 3, Carl H. Naylor 4, Alan T. Charlie Johnson
On-line spectrometer for FEL radiation at
 On-line spectrometer for FEL radiation at FERMI@ELETTRA Fabio Frassetto 1, Luca Poletto 1, Daniele Cocco 2, Marco Zangrando 3 1 CNR/INFM Laboratory for Ultraviolet and X-Ray Optical Research & Department
On-line spectrometer for FEL radiation at FERMI@ELETTRA Fabio Frassetto 1, Luca Poletto 1, Daniele Cocco 2, Marco Zangrando 3 1 CNR/INFM Laboratory for Ultraviolet and X-Ray Optical Research & Department
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter
 Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Time-Resolved Optical Gating Based on Dispersive Propagation: A New Method to Characterize Optical Pulses
 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 36, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2000 137 Time-Resolved Optical Gating Based on Dispersive Propagation: A New Method to Characterize Optical Pulses Roger G. M. P. Koumans and
IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 36, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2000 137 Time-Resolved Optical Gating Based on Dispersive Propagation: A New Method to Characterize Optical Pulses Roger G. M. P. Koumans and
Broadband 2.12 GHz Ti:sapphire laser compressed to 5.9 femtoseconds using MIIPS
 Broadband 2.12 GHz Ti:sapphire laser compressed to 5.9 femtoseconds using MIIPS Giovana T. Nogueira 1, Bingwei Xu 2, Yves Coello 2, Marcos Dantus 2, and Flavio C. Cruz 1* 1 Gleb Wataghin Physics Institute,
Broadband 2.12 GHz Ti:sapphire laser compressed to 5.9 femtoseconds using MIIPS Giovana T. Nogueira 1, Bingwei Xu 2, Yves Coello 2, Marcos Dantus 2, and Flavio C. Cruz 1* 1 Gleb Wataghin Physics Institute,
S.R.Taplin, A. Gh.Podoleanu, D.J.Webb, D.A.Jackson AB STRACT. Keywords: fibre optic sensors, white light, channeled spectra, ccd, signal processing.
 White-light displacement sensor incorporating signal analysis of channeled spectra S.R.Taplin, A. Gh.Podoleanu, D.J.Webb, D.A.Jackson Applied Optics Group, Physics Department, University of Kent, Canterbury,
White-light displacement sensor incorporating signal analysis of channeled spectra S.R.Taplin, A. Gh.Podoleanu, D.J.Webb, D.A.Jackson Applied Optics Group, Physics Department, University of Kent, Canterbury,
