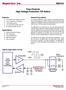
Supertex inc. HV9973. Isolated, Constant Current LED Driver HV9973. Features. General Description. Applications. Typical Application Circuit
|
|
|
- Deirdre Stafford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Isolated, Constant Current LED Driver Features Programmable true constant current operation ±3% LED current accuracy Adaptive to external component tolerances and parasitics Primary-side current sensing Output open circuit protection Output short circuit protection Input under voltage lockout PWM dimming / enable VDC input Applications Lighting fixtures with 6-50W power range General Description The is a primary-side control IC for driving a discontinuous conduction mode DCM) flyback LED driver. The IC is optimized for operation at a constant full-load switching frequency of 100kHz and the high input DC voltage range of VDC. It maintains 3% variation of the LED current setting, and features tight line and load regulation. The proprietary primary-side output current control employed in the makes the output current setting insensitive to most component tolerances and parasitics without use of an opto-coupler feedback. The LED driver is fully protected against output open and short circuit conditions and input under-voltage. It also offers a logic input for dimming the LED light output by means of pulsewidth modulation of the output current. The is ideally suited for driving high-brightness LEDs in low-power lighting fixtures such as incandescent bulb retrofits. Typical Application Circuit V IN R IN VIN PWMD VD GATE GND CS BIAS VDD R S R BIAS C DD
2 Ordering Information Pin Configuration Part Number Package Option Packing LG-G 8-Lead SOIC 500/Reel -G indicates package is RoHS compliant Green ) VIN VD VDD GND PWMD BIAS CS 4 5 GATE 8-Lead SOIC Absolute Maximum Ratings* Parameter VIN, VD, BIAS current VDD voltage VDD current Value ±5.0mA -0.3V to VDD SHUNT) 10mA Product Marking YWW H9973 LLLL Y Last Digit of Year Sealed WW Week Sealed L Lot Number Green Packaging Package may or may not include the following marks Si or 8-Lead SOIC GATE voltage -0.3V to V DD +0.3V CS, PWMD voltage -0.3V to 6.0V Continuous power dissipation T A +5 C) derate 6.3mW/ C above +5 C) 630mW Typical Thermal Resistance Package 8-Lead SOIC θ ja 101 O C/W Junction temperature Storage temperature range +15 C -65 C to +150 C * All voltages referenced to GND pin. Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated in the operational sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. Electrical Characteristics Specifications are at T A 5 C, V DD 10V, I IN 00µA, C GATE 750pF, BIAS open, unless otherwise noted). Sym Description Min Typ Max Units Conditions Power Supply VDD) V DDSHUNT) Shunt voltage * V --- V DDSTART) Start voltage * V V DD rising V DDSTOP) Under voltage threshold * V V DD falling I DDQ Supply standby current ma Gate open I DDQSTART) Start-up current * μa V DD 10V Notes * Specifications which apply over the full operating ambient temperature range of -40 O C < T A < +15 O C. Parameters guaranteed by design
3 Electrical Characteristics Sym Description Min Typ Max Units Conditions Feed Forward Inputs VD, VIN) and Oscillator I IN Operating current range * μa --- I D Operating current range * μa --- ΔQ INMAX) V IN Input charge swing * pf I IN 00μA, I D 0 K Osc Oscillator coefficient * V D VD voltage * mv --- F SSTART) Start-up frequency khz --- K C Effective integrator capacitance ratio V IN to V D Bias Current Generator BIAS) V BIAS Output voltage * mv --- GATE Output T RISE GATE output rise time ns --- T FALL GATE output fall time ns --- Current Sense Comparator V CSTH) CS trip threshold * mv --- T DELAY Propagation delay CS to GATE * ns V CS - V CSTH) ) 0mV T BLANK Leading edge blanking delay * ns --- VIN Under Voltage Comparator I INUVLO) V IN undervoltage threshold current μa V IN falling ΔI INUVLO) V DD undervoltage lockout hysteresis μa V IN rising Open Circuit Protection I DOV) Output open circuit threshold μa --- PWM Dimming V PWMD,HI PWMD input high voltage * V --- V PWMD,LO PWMD input low voltage * V --- Effective Current Sense Reference Voltage V EFF Effective reference voltage mv ΔV EFF /V EFF I IN, I D regulation of V EFF % Notes * specifications which apply over the full operating ambient temperature range of -40 O C < T A < +15 O C. Parameters guaranteed by design. 1. Effective output current V EFF 0.5 V CS K Osc. Trimmed to the product of V CS K Osc. I IN 16.5μA, I D 10μA, See Note 1. 15μA I IN 185μA, 40μA I D 10μA 3
4 Functional Block Diagram VD VIN VDD UVLO 11V i D i IN Start-Up Oscillator Shunt Reg..44V Current Mirror S&H Shutdown PWMD i IN GATE i IN i D - i BIAS <i D - i BIAS > sampled) UV Power-On Reset UV VIN UVLO Oscillator & Parasitics Compensator Q R S + - L/E Blanking 1.V CLK CS i UV OVP Shutdown Q S Power-On Reset BIAS R <i D - i BIAS > sampled) 1.V i OVP GND i BIAS BIAS 4
5 Functional Description Power Topology and Control Method The regulates the constant output current of a discontinuous conduction mode DCM) flyback converter. Although it can be used in other applications, it is optimized for operating from a high DC line input voltage of VDC. The is a fully integrated peak-current PWM controller IC. It does not require an optocoupler feedback, and includes protection from output open-circuit, short-circuit, and input under-voltage conditions. A proprietary control scheme permits accurate primary-side control of output current, insensitive to most circuit parasitics, external component tolerances and output voltage variation. Output current of an flyback converter can be expressed as where V OR n V O ) 6) In the equation 5), L m is magnetizing inductance of the transformer primary winding, and V F is the forward voltage drop at the output rectifier diode. Note that the switching frequency is not a function of the internal timing components of the or the absolute value of R IN and ). Proper selection of maximum switching frequency F SMAX) at full load, in combination with maximum V ORMAX) is critical for proper operation of the. The oscillator circuit ramp may saturate when the maximum charge swing ΔQ INMAX) 400pC is exceeded at V IN. Therefore, the circuit components should be selected such that I n K PK Osc 1) ΔQ IN V IN T ON ΔQ INMAX) 7) R IN Where K Osc 0.57 is an oscillator coefficient, n is flyback transformer turns ratio of primary to secondary winding, and where I PK is peak primary winding current given by I PK V CSTH) R S In ), V CSTH) is the reference voltage of the current sense comparator at CS, and R S is the current sense resistance. Combining 1) and ), we can write the output current as V n K CSTH) Osc n V EFF R S R S The effective reference voltage V EFF 347mV. Hence, the desired LED current is programmed by merely selecting the current sense resistor as ) 3) R S n V EFF 4) Note that the output current of the LED driver is independent of the input and output voltage, the switching frequency or the transformer inductance. The switching frequency at a given output voltage V O can be estimated as F S n V + V ) K O F Osc V K OR Osc L m I PK L m I PK 5) Note, that the is protected against incorrect oscillator setup. When saturation of the oscillator ramp occurs, the shuts off and attempts to go through a start-up cycle again. The transformer magnetic flux equals the volt-seconds at the transformer winding in the DCM flyback converter V IN T ON L M I PK 8) Therefore, the charge swing ΔQ IN varies only as a function of external component tolerances and circuit parasitic, and it is the same for all V IN and V O operating conditions. Combining equations 5), 7) and 8), and taking into consideration tolerances for L m, R S and V CSTH), we get the following design criterion V ORMAX) K OscMAX) L mmax) V CSTH)MAX R SMAX) ΔQ F INMAX) SMAX) R INMIN) L mmin) V CSTH)MIN R SMIN) 9) The equation 9) gives the condition for selecting proper ratio of V ORmax) /F SMAX), which guarantees ΔQ IN Q INMAX). Selection of the resistor R IN is dictated by the desired input under-voltage UV). The recommended selection of R IN.0MΩ produces a UV shutdown at V IN < 40VDC. As an example, we can assume the tolerances of L m and R S as ±10% and ±1% correspondingly. We shall also limit the switching frequency under F SMAX) 130KHz. With these assumption, the equation 9) gives V ORMAX) 134.1V. Apparently, there 5
6 is also limitation on V OR)MAX related to open circuit protection V OR)MAX < R INMIN) I DOV)MIN 9A). In our case V OR)MAX < 10.V and the least of two values should be used. With some margin we should choose V OR)MAX 10V. The above example takes full advantage of the available V IN input dynamic range, and, therefore, achieves the most accurate control over the LED current. For this reason, we will use V ORMAX) 10V and F SMAX) 130KHz in the following equations, as our recommended design inputs. Given, the primary-to-secondary turn ratio is determined simply as V ORMAX) 10V n 10) V OMAX) ) V OMAX) ) The maximum magnetizing inductance of the primary winding L mmax) is obtained by combining the equations ), 7) and 8) L mmax) ΔQ INMAX) R INMIN) R SMIN) V CSTH)MAX 11) If we assume the primary inductance tolerance of ±10%, the nominal value of L m is determined simply as L m L mmax) 1.1 1) Selection of the maximum magnetizing inductance in accordance with 11) guarantees DCM operation in the entire working range of the input voltage with the proper selection of the input under-voltage and output over-voltage thresholds. See Input Under-Voltage Protection and Output Open and Short Circuit Protection below.) Due to presence of the leakage inductance L LK, a voltage spike occurs at the primary winding of the transformer. Although the eliminates the effect of the leakage inductance on the LED current, the duration of this spike should be minimized for best efficiency. The time t LK is the leakage spike duration, determined by L LK I PK t LK 13) V Z n V OMAX) ) Here, L LK is primary winding leakage inductance, V Z is the Zener clamp voltage. Hence, the Zener clamp voltage V Z should be selected significantly higher than n V OMAX) ). V Z must also exceed the open-circuit protection threshold. The is powered by an internal shunt regulator, clamping VDD at V DDREG) 11V. The IC shuts down when the voltage at VDD falls below V DDUV) 7.0V. Under steadystate operation, the IC is powered by an auxiliary bootstrap winding through a ballast resistor D. The primary-to-auxiliary winding turn ratio and the value of D should be selected carefully to ensure operation throughout the input and output voltage range with minimum power dissipation in D. Note that the polarity of the auxiliary winding is opposite of the polarity of the secondary winding, such that the auxiliary winding voltage is positive during the on time. The following formulas are providing optimal values for and D, given the output voltage range V OMIN), V OMAX) and the input voltage range V INMIN), V INMAX) V INMIN) V INMAX) V V V V DDUV) INMAX) INMIN) DDREG) D W DD V DDUV) V DDREG) V INMIN) V INMAX) 14) 15) n V OMAX) ) K Osc 16) D V INMAX) where W DD is power dissipation in D, and I DDQ is the quiescent current of the. n V OMIN) ) K Osc I DDQ + Q GATE V OMIN) ) F SMAX) VOMAX) ) V INMAX) V DDREG) Start-Up Upon applying the input AC power, the input current of VIN is diverted into the hold-up capacitor connected at VDD. The consumes less than 60µA in this mode, and its GATE output is off. When a threshold of V DD 10.5V is reached at VDD, VIN is disconnected from VDD, and the GATE output turns on. The GATE turns off upon reaching V CSTH) 1.V at CS. The frequency of the GATE pulses is determined by the oscillator circuit or by the 10kHz start-up clock, whichever frequency is higher. The hold-up capacitor connected at VDD must store enough energy to supply power to the until adequate bootstrap power supply becomes available. The stops switching and makes another attempt to charge the hold-up capacitor, if the voltage at VDD falls below 7.0V. Although the resistor R IN serves a different purpose in operation, its value must be selected with care to ensure the required 60µA start-up current at V INMIN). 6
7 Current Sense Comparator The peak current comparator is using an external sense resistor R S to compare the primary winding current to the reference voltage V CSTH) 1.V. The corresponding peak current I PK is given by equation ). When the current in the primary winding exceeds I PK, the comparator resets the PWM flip-flop circuit, and the output pulse is terminated. The next cycle begins upon receiving a clock signal from an internal oscillator circuit. A 300ns leading-edge blanking delay is applied to prevent false triggering of the current sense comparator. Oscillator Circuit Upon the end of the start-up cycle, the input current of V IN is reverted to a current mirror circuit for generating the current i IN in accordance with the following equation i IN V IN 1V V IN R IN R IN 17) Accordingly, the input current i D is derived by connecting a resistor from the bootstrap winding to V D. However, since >> 1 normally, the voltage V AUX is much higer in comparison to the voltage at the VD pin V D.44V). Hence, the current i D through the resistor can be expressed as i D V D V AUX 18) From this equation, the current i D is not directly proportional to V AUX. The offset current is given by the following equation i OS V D 19) The cancels out this offset internally by subtracting a current of the same magnitude as i OS. This correction current is programmed by connecting a resistor at the BIAS pin in accordance with V BIAS i OR V V D AUX V AUX 3.5 R BIAS ) Sampled during the conduction time of the transformer secondary winding, this current represents the reflected output voltage V O ), where V F is the voltage drop across the output rectified diode. The value of should scale with R IN in accordance with R IN K C k 3) In 3), k is the coupling coefficient between the primary and the bootstrap windings. The coupling coefficient can be determined by measuring the leakage inductance L SAUX) of the auxiliary winding with respect to the primary winding and calculating it in accordance with the equation k 1 L SAUX) L AUX 4) Here, L AUX is the bootstrap winding inductance. Since the value of the k is normally very close to 1, then k 1 could be used as a first approximation. With proper selection of the resistor in accordance with 3), the oscillator circuit then generates switching frequency F S n V + V ) K R O F Osc S L m V CSTH) 5) Output Open and Short Circuit Protection The provides a very reliable open circuit protection. If the sampled current i OR exceeds the 140µA threshold, the is forced to go through a power-up cycle again. The corresponding output voltage threshold can be calculated as i BIAS V BIAS 0) 3.5 i OS V OLIM) 66.5µA VF 6) n In 0), V BIAS V D / is the voltage at the BIAS pin. Combining the equations 19) and 0) gives formula for calculating R BIAS simply as R BIAS 7 1) The resulting current i OR i D - i OS ) represents the instantaneous voltage across the transformer bootstrap winding Normal operation resumes when the adequate LED load is connected. Output short circuit protection is inherent to the since the switching frequency is directly proportional to the output voltage. Moreover, loss of output voltage is likely to cause insufficient bootstrap power at VDD, resulting in a hiccup operating mode and repetitive restart attempts. 7
8 Input Under-Voltage Protection The GATE output of the becomes inhibited when the input current at VIN falls below 10µA. The GATE output is enabled again when the VIN current exceeds 140µA. The corresponding input under-voltage thresholds can be calculated as V INSTOP) R IN 10µA 7) V INSTART) R IN 140µA 8) R-C Snubber Design Considerations Detection of t LK given by the equation 13) is crucial for proper operation of the. Upon the turn-off of the switching MOSFET, the voltage spike caused by the transformer leakage inductance is followed by high-frequency oscillation. The oscillation occurs at the transformer windings with the period equal to π L LK C OSS, where C OSS is the output capacitance of the MOSFET. This oscillation is damped naturally by copper and core losses of the transformer, and it subsides during conduction time of the secondary winding. However, extra damping is usually required. Insufficiently damped, the post-spike oscillation may adversely affect accuracy of the output current regulation as well as EMI performance of the LED driver. Damping of the post-spike oscillation is achieved by connecting of a snubber network R SN, C SN ) across the switching MOSFET. Selection of the R SN and C SN values is based on achieving sufficient damping while minimizing the power losses in the snubber network. At the same time, the oscillation should not be over-damped, as this will prevent detection of t LK. We recommend the following choice of the snubber network components C SN C OSS 9) than being wired to ground or across the primary winding. Otherwise, the current from C SN may cause false tripping of the CS comparator. Power dissipation in R SN can be estimated by the following formula W RSN C SN V INMAX) F SMAX) 31) Layout Considerations The signal inputs VIN and VD operate at relatively low input current ranging from hundreds down to tens of microamps. Therefore, proximity of the switching potential of the MOSFET drain can cause a displacement current in VD and VIN affecting the normal operation of the. Proper PCB layout should avoid direct proximity of the VD and VIN inputs to the high-voltage switching potential. The resistor should be placed as close as possible to the VD input. Otherwise, a long VD trace can be susceptible to noise coupling, or it can introduce parasitic capacitance with respect to ground capable of distorting the VD input signal. Design example The following example illustrates LED driver design with for the following conditions 1. Input V INMIN) 40V, V INMAX) 375V. Output V OMIN) 6.0V, V OMAX) 18V, V F 0.7V, 0.5A 3. Maximum switching frequency F SMAX) 130kHz 4. V INSTOP) 40V Design 1. Using formula 7), calculate value of the resistor R IN R IN V INSTOP).0MΩ 10µA R SN 1.6 L LK 30) C SN. Using formula 9), calculate V ORMAX) Note that the output capacitance C OSS is a nonlinear function of the drain voltage. Most datasheets give the C OSS value at the drain voltage of V DS 5V. Typically, the output capacitance characteristic as a function of V DS is provided in the MOSFET datasheet as well. The equation 9) should use the C OSS value at V DS V INMIN) + n V OMIN) ), or at the highest V DS given in the plot, whichever voltage is lower. Also note that the R-C snubber network must be connected between the drain and the source of the MOSFET, rather V OR ΔQ INMAX) F SMAX) R IN 77.6% 134.1V K OscMAX) Using formula 9A), calculate V OR)MAX base on OV protection V OR R INMIN) I DOV)MIN 131.7V Choose V OR)MAX 10V based on 8-10% margin from lower value. 8
9 3. Using formula 10), calculate primary-to-secondary turns ratio of the flyback transformer V ORMAX) 115V n V OMAX) ) V OMAX) ) 4. Using formula 4), calculate value of the current sense resistor R S n V EFF 4.47Ω 5. Using formula ), calculate value of the maximum peak current I PKMAX) V V CSTH)MAX CSTH)MAX 0.77A R SMIN) 0.99 R S 6. Using formula 11), calculate maximum value of the magnetizing inductance L m L mmax) ΔQ INMAX) 0.99R IN 0.99R S.564µH 110% V CSTH)MAX 110% 9. Using formula 15), calculate value of the resistor D V DDUV) V DDREG) n V VINMIN) V OMIN) ) K OscMAX) INMAX) D I DDQ + Q GATE V + V ) 6.0Ω OMIN) F F SMAX) VOMAX) ) We have assumed Q GATE 15nC and V DDMIN) 8V to account for the forward voltage drop at the bootstrap winding diode.) 10. Using formula 18), calculate the maximum power dissipation W DD in the resistor D W DD V INMAX) V DDREG) n V OMAX) ) K OscMAX) 0.08W D V INMAX) 11. Using formula 30), calculate the resistor R SN. Assume C OSS 33pF IRFUC0, 600V, 1A MOSFET), L LK 0μH 7. Using formula 14), calculate turns ratio primary-to-auxiliary winding of the flyback transformer V INMIN) V INMAX) 6.7 V DDUV) V INMAX) V INMIN) V DDREG) C SN 33pF R SN 1.6 L LK 1.5k Ω C SN 8. Using formulas 1) and 3), calculate values of the resistors, R BIAS R IN 38.9kΩ 1. Using formula 30), calculate the maximum power dissipation W RSN in the resistor R SN W RSN C SN V INMAX) F SMAX) 0.6W R BIAS 5.56kΩ 7 9
10 Pin Description Pin # Function Description 1 VIN This pin is the input voltage feed forward input. Connect a resistor from this pin to the input side of the primary winding of the transformer to program the VIN current. The same resistor is also used for start-up upon initial application of power. VD This pin is the auxiliary winding feedback input. Connect a resistor from this pin to the transformer bootstrap winding. 3 VDD This is a power supply pin for all internal circuits. It must be bypassed with a low ESR capacitor to GND. The capacitor must be able to store sufficient energy for starting up the converter. 4 CS This pin is for sensing peak output voltage at an external current sense resistor.. 5 GATE This pin is the output gate driver for an external N-channel power MOSFET. 6 BIAS This pin is used for generating a correction current to account for the.44v offset at VD. Connect a resistor to ground to program. 7 PWMD When this pin is pulled to GND, switching of the is disabled. When the PWM pin is released, or external TTL high level is applied to it, switching will resume. 8 GND This pin is the common return for all the internal circuits. 10
11 8-Lead SOIC Narrow Body) Package Outline LG) 4.90x3.90mm body, 1.75mm height max), 1.7mm pitch D θ1 8 Note 1 Index Area D/ x E1/) E1 E L Gauge Plane 1 L L1 Seating Plane Top View A A A1 e b Seating Plane Side View A A θ View B View B Note 1 h h View A-A Note 1. This chamfer feature is optional. A Pin 1 identifier must be located in the index area indicated. The Pin 1 identifier can be a molded mark/identifier; an embedded metal marker; or a printed indicator. Dimension mm) The package drawings) in this data sheet may not reflect the most current specifications. For the latest package outline information go to http///packaging.html.) does not recommend the use of its products in life support applications, and will not knowingly sell them for use in such applications unless it receives an adequate product liability indemnification insurance agreement. does not assume responsibility for use of devices described, and limits its liability to the replacement of the devices determined defective due to workmanship. No responsibility is assumed for possible omissions and inaccuracies. Circuitry and specifications are subject to change without notice. For the latest product specifications refer to the website http//) 01 All rights reserved. Unauthorized use or reproduction is prohibited. Symbol A A1 A b D E E1 e h L L1 L θ θ1 MIN 1.35* * 5.80* 3.80* O 5 O NOM BSC REF BSC MAX * * 6.0* 4.00* O 15 O JEDEC Registration MS-01, Variation AA, Issue E, Sept * This dimension is not specified in the JEDEC drawing. Drawings are not to scale. Supertex Doc. # DSPD-8SOLGTG, Version I Bordeaux Drive, Sunnyvale, CA Tel
Supertex inc. HV9910B. Universal High Brightness LED Driver. Features. General Description. Applications. Typical Application Circuit HV9910B
 Supertex inc. HV9910B Universal High Brightness LED Driver Features Switch mode controller for single switch LED drivers Enhanced drop-in replacement to the HV9910 Open loop peak current controller Internal
Supertex inc. HV9910B Universal High Brightness LED Driver Features Switch mode controller for single switch LED drivers Enhanced drop-in replacement to the HV9910 Open loop peak current controller Internal
HV9931 Unity Power Factor LED Lamp Driver
 Unity Power Factor LED Lamp Driver Features Constant output current Large step-down ratio Unity power factor Low input current harmonic distortion Fixed frequency or fixed off-time operation Internal 450V
Unity Power Factor LED Lamp Driver Features Constant output current Large step-down ratio Unity power factor Low input current harmonic distortion Fixed frequency or fixed off-time operation Internal 450V
Supertex inc. HV9861A. LED Driver with Average-Mode, Constant Current Control HV9861A. Features. General Description. Applications
 Supertex inc. LED Driver with Average-Mode, Constant Current Control Features Fast average current control Programmable constant off-time switching PWM / linear dimming input Output short circuit protection
Supertex inc. LED Driver with Average-Mode, Constant Current Control Features Fast average current control Programmable constant off-time switching PWM / linear dimming input Output short circuit protection
24/48V Fan Driver/Controller With High-Side Drive
 24/48V Fan Driver/Controller With High-Side Drive Features High-side drive allows use of tachs Direct interface to host controller Noise-immune linear speed control 4-bit digital speed control Operates
24/48V Fan Driver/Controller With High-Side Drive Features High-side drive allows use of tachs Direct interface to host controller Noise-immune linear speed control 4-bit digital speed control Operates
3-Channel LED Array Driver IC
 -Channel LED Array Driver IC Features Integrated 00V, 5Ω (typ.) MOSFETs Programmable output current to 80mA per channel TTL compatible PWM dimming inputs -Phase synchronous operation Leading edge blanking
-Channel LED Array Driver IC Features Integrated 00V, 5Ω (typ.) MOSFETs Programmable output current to 80mA per channel TTL compatible PWM dimming inputs -Phase synchronous operation Leading edge blanking
High Input Voltage, Adjustable 3-Terminal Linear Regulator
 High Input Voltage, Adjustable 3-Terminal Linear Regulator Features 13.2 to 100V input voltage range Stable with output capacitor Adjustable 1.20 to 88V output regulation 5% reference voltage tolerance
High Input Voltage, Adjustable 3-Terminal Linear Regulator Features 13.2 to 100V input voltage range Stable with output capacitor Adjustable 1.20 to 88V output regulation 5% reference voltage tolerance
Supertex inc. HV7801 HV7801. High Side Current Monitor 8.0 to 450V Voltage Gain of 5. Features. General Description. Applications
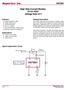 High Side Current Monitor 80 to 450V Voltage Gain of 5 Features Supply voltage 8V to 450V Voltage output device Typical gain 50±1% Max 500mV Fast rise and fall time, 700ns to 20µs Maximum quiescent current
High Side Current Monitor 80 to 450V Voltage Gain of 5 Features Supply voltage 8V to 450V Voltage output device Typical gain 50±1% Max 500mV Fast rise and fall time, 700ns to 20µs Maximum quiescent current
Supertex inc. HV Pin Switch-Mode LED Lamp Driver IC HV9922
 Supertex inc. HV99 3-Pin Switch-Mode LED Lamp Driver IC Features Constant output current: 50mA Universal 85-65VAC operation Fixed off-time buck converter Internal 475V power MOSFET Applications Decorative
Supertex inc. HV99 3-Pin Switch-Mode LED Lamp Driver IC Features Constant output current: 50mA Universal 85-65VAC operation Fixed off-time buck converter Internal 475V power MOSFET Applications Decorative
Supertex inc. CL7. Linear, 100mA, Constant Current LED Driver with Enable Input CL7. Features. General Description. Applications
 Linear, 100mA, Constant Current LED Driver with Enable Input Features 100mA ±5% constant current drive Built-in reverse polarity protection Logic level enable Dimmable via pin Overtemperature protection
Linear, 100mA, Constant Current LED Driver with Enable Input Features 100mA ±5% constant current drive Built-in reverse polarity protection Logic level enable Dimmable via pin Overtemperature protection
Supertex inc. HV809. Off-Line, High Voltage EL Lamp Driver. Features. General Description. Applications. Block Diagram.
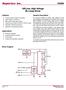 Off-Line, High Voltage EL Lamp Driver Features Processed with HVCMOS technology Input voltage up to 200V DC 400V peak-to-peak output voltage Output load up to 30nF (00in 2 for 3.nF/in 2 lamp) djustable
Off-Line, High Voltage EL Lamp Driver Features Processed with HVCMOS technology Input voltage up to 200V DC 400V peak-to-peak output voltage Output load up to 30nF (00in 2 for 3.nF/in 2 lamp) djustable
Supertex inc. TN2640. N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FETs. Features
 TN264 Features Low threshold (2.V max.) High input impedance Low input capacitance Fast switching speeds Low on-resistance Free from secondary breakdown Low input and output leakage pplications Logic level
TN264 Features Low threshold (2.V max.) High input impedance Low input capacitance Fast switching speeds Low on-resistance Free from secondary breakdown Low input and output leakage pplications Logic level
3-Channel 25mA Linear LED Driver
 -Channel 5mA Linear LED Driver Features ±6% current accuracy @.0-5V 90V standoff voltage Separate enable pins for each channel allow for PWM dimming Over-temperature protection 8-Lead SOIC (w/heat Slug)
-Channel 5mA Linear LED Driver Features ±6% current accuracy @.0-5V 90V standoff voltage Separate enable pins for each channel allow for PWM dimming Over-temperature protection 8-Lead SOIC (w/heat Slug)
Supertex inc. HV816. High Voltage, Dimmable EL Lamp Driver. Features. Applications. General Description
 Supertex inc. HV816 High Voltage, Dimmable EL Lamp Driver Features 360V PP output voltage for high brightness Large output load capability of up to 150nF 2.7 to 5.5V operating supply voltage Single lithium
Supertex inc. HV816 High Voltage, Dimmable EL Lamp Driver Features 360V PP output voltage for high brightness Large output load capability of up to 150nF 2.7 to 5.5V operating supply voltage Single lithium
High-Voltage Current-Mode PWM Controller
 HV9112 High-Voltage Current-Mode PWM Controller Features 9. to 8V input voltage range Current-mode control High efficiency Up to 1.MHz internal oscillator Internal start-up circuit Low internal noise 5%
HV9112 High-Voltage Current-Mode PWM Controller Features 9. to 8V input voltage range Current-mode control High efficiency Up to 1.MHz internal oscillator Internal start-up circuit Low internal noise 5%
Electronic Telephone Line Switch
 Electronic Telephone Line Switch Features 350V breakdown voltage 18Ω maximum switch resistance Current limiting protection Operates at 2.3V input Applications General Description The Supertex LG is an
Electronic Telephone Line Switch Features 350V breakdown voltage 18Ω maximum switch resistance Current limiting protection Operates at 2.3V input Applications General Description The Supertex LG is an
High Input Voltage SMPS Start-up / Linear Regulator
 High Input Voltage SMPS Start-up / Linear Regulator Features ccepts inputs from 15 to 450V Output currents up to 3.0m continuous, 30m peak Supply current typically 50µ Line regulation typically 0.1mV/V
High Input Voltage SMPS Start-up / Linear Regulator Features ccepts inputs from 15 to 450V Output currents up to 3.0m continuous, 30m peak Supply current typically 50µ Line regulation typically 0.1mV/V
Supertex inc. HV825. High Voltage EL Lamp Driver IC. Features
 High Voltage EL Lamp Driver IC Features Processed with HVCMOS technology.0 to.6v operating supply voltage DC to C conversion Output load of typically up to 6.0nF djustable output lamp frequency djustable
High Voltage EL Lamp Driver IC Features Processed with HVCMOS technology.0 to.6v operating supply voltage DC to C conversion Output load of typically up to 6.0nF djustable output lamp frequency djustable
High Voltage, Low Noise, Inductorless EL Lamp Driver. = 3.4V to 4.2V only) VDD HV850 REL GND 4 CLKIN CLKEN 5
 Supertex inc. High Voltage, Low Noise, Inductorless Lamp Driver Features No external components required when using an external clock frequency frequency can be set by an external resistor Low noise DC
Supertex inc. High Voltage, Low Noise, Inductorless Lamp Driver Features No external components required when using an external clock frequency frequency can be set by an external resistor Low noise DC
Capacitor-Coupled, Switched Shunt, (CCSS) Regulator. All components except for C S D OUT OUT D6 D12 D24 SR10 FB PGND AGND. C FB 470pF D6 D12 D24 SR10
 Supertex inc. Capacitor-Coupled, Switched Shunt, (CCSS) Regulator Features Efficiencies up to 75% at 20mA Less than 20mW standby power Optional 6., 12V or 24V fixed output voltage, or adjustable from 6.
Supertex inc. Capacitor-Coupled, Switched Shunt, (CCSS) Regulator Features Efficiencies up to 75% at 20mA Less than 20mW standby power Optional 6., 12V or 24V fixed output voltage, or adjustable from 6.
Supertex inc. HV264. Quad, High Voltage, Amplifier Array. Features. General Description. Applications. Block Diagram. Supertex inc.
 Quad, High Voltage, Amplifier Array Features Four independent high voltage amplifiers 190V output swing 9.0V/µs typical output slew rate Fixed gain of 66.7V/V High value internal feedback resistors Very
Quad, High Voltage, Amplifier Array Features Four independent high voltage amplifiers 190V output swing 9.0V/µs typical output slew rate Fixed gain of 66.7V/V High value internal feedback resistors Very
Supertex inc. CL525 Linear, Fixed Constant Current LED Driver Features General Description Applications Typical Application Circuit VIN 4.
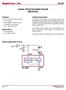 Linear, Fixed Constant Current LED Driver Features 25mA ±10% constant current drive 1.0V dropout 90V rating for transient immunity Temperature compensated 4.75-90V supply range Applications Specialty lighting
Linear, Fixed Constant Current LED Driver Features 25mA ±10% constant current drive 1.0V dropout 90V rating for transient immunity Temperature compensated 4.75-90V supply range Applications Specialty lighting
Supertex inc. HV892 HV892. Inductorless Liquid Lens Driver. General Description. Features. Applications. Typical Application Circuit. Supertex inc.
 Inductorless Liquid Lens Driver Features Drives capacitive loads up to 200pF Programmable drive amplitude (compatible with 40V RMS to 60V RMS lenses) On-chip boost converter No external inductor I 2 C
Inductorless Liquid Lens Driver Features Drives capacitive loads up to 200pF Programmable drive amplitude (compatible with 40V RMS to 60V RMS lenses) On-chip boost converter No external inductor I 2 C
HV311. Hot Swap Controller. Features. General Description. Applications. Typical Application Circuit HV311
 Hot Swap Controller Features 0 to 90V operation, positive or negative supply / lock out & power-on-reset Circuit breaker 00ms startup timer Automatic retry or latched operation Low Power, 400µA sleep mode
Hot Swap Controller Features 0 to 90V operation, positive or negative supply / lock out & power-on-reset Circuit breaker 00ms startup timer Automatic retry or latched operation Low Power, 400µA sleep mode
Supertex inc. CL2. Simple 90V, 20mA, Temperature Compensated Constant Current LED Driver IC. General Description. Features.
 Simple 90V, 20mA, Temperature Compensated Constant Current LED Driver IC Features 5.0 to 90V operating range (V A-B ) 20mA ±10% at 5.0-90V 0.01%/ C typical temperature coefficient Available in TO-243AA
Simple 90V, 20mA, Temperature Compensated Constant Current LED Driver IC Features 5.0 to 90V operating range (V A-B ) 20mA ±10% at 5.0-90V 0.01%/ C typical temperature coefficient Available in TO-243AA
Switch-Mode LED Driver IC with High Current Accuracy
 Features Switch mode controller for single switch drivers Buck Boost Buck-boost SEPIC Works with high side current sensing Closed loop control of output current High PWM dimming ratio Internal 250V linear
Features Switch mode controller for single switch drivers Buck Boost Buck-boost SEPIC Works with high side current sensing Closed loop control of output current High PWM dimming ratio Internal 250V linear
AC/DC WLED Driver with External MOSFET Universal High Brightness
 AC/DC WLED Driver with External MOSFET Universal High Brightness DESCRIPTION The is an open loop, current mode control LED driver IC. It can be programmed to operate in either a constant frequency or constant
AC/DC WLED Driver with External MOSFET Universal High Brightness DESCRIPTION The is an open loop, current mode control LED driver IC. It can be programmed to operate in either a constant frequency or constant
Supertex inc. HV Pin Hotswap, Inrush Current Limiter Controllers (Negative Supply Rail) Features. General Description.
 3-Pin Hotswap, Inrush Current Limiter Controllers (Negative Supply Rail) Features Pass element is only external part No sense resistor required Auto-adapt to pass element Short circuit protection UV &
3-Pin Hotswap, Inrush Current Limiter Controllers (Negative Supply Rail) Features Pass element is only external part No sense resistor required Auto-adapt to pass element Short circuit protection UV &
High Speed, 200V, Full H-Bridge MOSFET Driver
 High Speed, 2V, Full H-Bridge MOSFET MD72 Features HVCMOS technology for high performance All N-MOSFET full-bridge driver Designed for 2V bridge supply voltage Up to.mhz operation frequency Greater than
High Speed, 2V, Full H-Bridge MOSFET MD72 Features HVCMOS technology for high performance All N-MOSFET full-bridge driver Designed for 2V bridge supply voltage Up to.mhz operation frequency Greater than
Supertex inc. LR8 High Input Voltage, Adjustable 3-Terminal Linear Regulator Features General Description Applications Typical Application Circuit
 Supertex inc. High Input Voltage, Adjustable 3-Terminal Linear Regulator Features 13.2-45 input voltage range Adjustable 1.20-44 output regulation 5% output voltage tolerance Output current limiting 10µA
Supertex inc. High Input Voltage, Adjustable 3-Terminal Linear Regulator Features 13.2-45 input voltage range Adjustable 1.20-44 output regulation 5% output voltage tolerance Output current limiting 10µA
Supertex inc. HV Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs. General Description. Features.
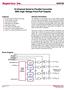 32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs Features Processed with HVCMOS technology Output voltages up to 80V Low power level shifting Shift register speed 8.0MHz ed data
32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs Features Processed with HVCMOS technology Output voltages up to 80V Low power level shifting Shift register speed 8.0MHz ed data
Simple, 90V, 20mA, Temperature Compensated, Constant Current, LED Driver IC
 Simple, 90V, 20mA, Temperature Compensated, Constant Current, LED Driver IC Features 5.0 to 90V operating range (V A-B ) 20mA ±5% at 45V (V A-B ) -8.5µA/ C typical temperature coefficient Available in
Simple, 90V, 20mA, Temperature Compensated, Constant Current, LED Driver IC Features 5.0 to 90V operating range (V A-B ) 20mA ±5% at 45V (V A-B ) -8.5µA/ C typical temperature coefficient Available in
Linear, Fixed Constant Current LED Driver
 Linear, Fixed Constant Current LED Driver Features ±10% constant current drive 1.0V dropout 90V rating for transient immunity Temperature compensated 4.75-90V supply range Applications Specialty lighting
Linear, Fixed Constant Current LED Driver Features ±10% constant current drive 1.0V dropout 90V rating for transient immunity Temperature compensated 4.75-90V supply range Applications Specialty lighting
High Input Voltage, Adjustable 3-Terminal Linear Regulator
 High Input Voltage, Adjustable 3-Terminal Linear Regulator Features 13.2-450V input voltage range Adjustable 1.20-440V output regulation 5% output voltage tolerance Output current limiting 10µA typical
High Input Voltage, Adjustable 3-Terminal Linear Regulator Features 13.2-450V input voltage range Adjustable 1.20-440V output regulation 5% output voltage tolerance Output current limiting 10µA typical
Supertex inc. CL220. Simple, 220V, 20mA, Temperature-Compensated, Constant Current, LED Driver IC. Functional Circuit Diagram.
 Supertex inc. CL220 Simple, 220V,, Temperature-Compensated, Constant Current, LED Driver IC Features 5.0 to 220V operating range (V -B ) ±10% at 5.0-160V 0.01% / C typical temperature coefficient vailable
Supertex inc. CL220 Simple, 220V,, Temperature-Compensated, Constant Current, LED Driver IC Features 5.0 to 220V operating range (V -B ) ±10% at 5.0-160V 0.01% / C typical temperature coefficient vailable
Supertex inc. HV Channel Serial To Parallel Converter With Open Drain Outputs. Features. General Description. Applications.
 Supertex inc. HV5523 32-Channel Serial To Parallel Converter With Open Drain Outputs Features Processed with HVCMOS technology Sink current minimum 00mA Shift register speed 6MHz Polarity and blanking
Supertex inc. HV5523 32-Channel Serial To Parallel Converter With Open Drain Outputs Features Processed with HVCMOS technology Sink current minimum 00mA Shift register speed 6MHz Polarity and blanking
Supertex inc. TP2540. P-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET. Features. General Description. Applications. Ordering Information.
 Features Low threshold (-2.4V max.) High input impedance Low input capacitance (6pF typical) Fast switching speeds Low on-resistance Free from secondary breakdown Low input and output leakage Applications
Features Low threshold (-2.4V max.) High input impedance Low input capacitance (6pF typical) Fast switching speeds Low on-resistance Free from secondary breakdown Low input and output leakage Applications
Boost LED Driver with Low-side LED Wiring Fault Detection. General Description C O R OVP1 R 1 ZD 1 R CS R SC D 1 R OVP2 C VIN R 2
 HV9966 Boost LED Driver with Lowside LED Wiring Fault Detection Features Switch mode controller for boost LED driver High output current accuracy Constant frequency operation Hiccup mode protection for
HV9966 Boost LED Driver with Lowside LED Wiring Fault Detection Features Switch mode controller for boost LED driver High output current accuracy Constant frequency operation Hiccup mode protection for
Supertex inc. MD1210. High Speed Dual MOSFET Driver. Supertex MD1210. Features. General Description. Applications. Typical Application Circuit
 Supertex inc. MD0 High Speed Dual MOSFET Driver Features 6ns rise and fall time with 000pF load.0a peak output source/sink current.v to 5.0V input CMOS compatible 4.5V to 3V single positive supply voltage
Supertex inc. MD0 High Speed Dual MOSFET Driver Features 6ns rise and fall time with 000pF load.0a peak output source/sink current.v to 5.0V input CMOS compatible 4.5V to 3V single positive supply voltage
32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs VPP. High Voltage. Level Translators & Push-Pull Output Buffers
 32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs Features Processed with HVCMOS technology Low power level shifting Source/sink current minimum 20mA Shift register speed 8.0MHz
32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs Features Processed with HVCMOS technology Low power level shifting Source/sink current minimum 20mA Shift register speed 8.0MHz
Supertex inc. HV9150 HV9150. High Voltage Output Hysteretic Mode Step Up DC/DC Controller. Features. General Description. Applications.
 High Voltage Output Hysteretic Mode Step Up DC/DC Controller Features Wide output voltage range: 6V to 500V Low input voltage: 2.7V 5W maximum output power with external MOSFET driver Built-in charge pump
High Voltage Output Hysteretic Mode Step Up DC/DC Controller Features Wide output voltage range: 6V to 500V Low input voltage: 2.7V 5W maximum output power with external MOSFET driver Built-in charge pump
Supertex inc. TC8220. Two Pair, N- and P-Channel Enhancement-Mode MOSFET. Features. General Description. Applications. Typical Application Circuit
 Supertex inc. TC8220 Two Pair, N- and P-Channel Enhancement-Mode MOSFET Features High voltage Vertical DMOS technology Integrated gate-to-source resistor Integrated gate-to-source Zener diode Low threshold,
Supertex inc. TC8220 Two Pair, N- and P-Channel Enhancement-Mode MOSFET Features High voltage Vertical DMOS technology Integrated gate-to-source resistor Integrated gate-to-source Zener diode Low threshold,
Supertex inc. TP2510. P-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET TP5AW. Features. General Description. Applications. Ordering Information
 TP251 P-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET Features Low threshold (-2.4V max.) High input impedance Low input capacitance (125pF max.) Fast switching speeds Low on-resistance Free from secondary
TP251 P-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET Features Low threshold (-2.4V max.) High input impedance Low input capacitance (125pF max.) Fast switching speeds Low on-resistance Free from secondary
TC7320 Six Pair, N- and P-Channel Enhancement-Mode MOSFET
 Six Pair, N- and P-Channel Enhancement-Mode MOSFET Features Six N- and P-channel MOSFET pairs Integrated gate-to-source resistor Integrated gate-to-source Zener diode Low threshold Low on-resistance Low
Six Pair, N- and P-Channel Enhancement-Mode MOSFET Features Six N- and P-channel MOSFET pairs Integrated gate-to-source resistor Integrated gate-to-source Zener diode Low threshold Low on-resistance Low
Simple, 90V, 20mA, Temperature Compensated, Constant Current, LED Driver IC
 Simple, 90V, 20mA, Temperature Compensated, Constant Current, LED Driver IC Features 5.0 to 90V operating range (V A-B ) 20mA ±10% at 5.0-90V 0.01%/ C typical temperature coefficient Available in TO-243AA
Simple, 90V, 20mA, Temperature Compensated, Constant Current, LED Driver IC Features 5.0 to 90V operating range (V A-B ) 20mA ±10% at 5.0-90V 0.01%/ C typical temperature coefficient Available in TO-243AA
8-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter with High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs, POL, Hi-Z, and Short Circuit Detect. General Description
 Features HVCMOS technology Operating output voltage of 250V Low power level shifting from 5.0 to 250V Shift register speed.0mhz @ V DD = 5.0V latch data outputs Output polarity and blanking Output short
Features HVCMOS technology Operating output voltage of 250V Low power level shifting from 5.0 to 250V Shift register speed.0mhz @ V DD = 5.0V latch data outputs Output polarity and blanking Output short
N- and P-Channel Enhancement-Mode Dual MOSFET
 N- and P-Channel Enhancement-Mode Dual MOSFET TC2320 Features Low threshold Low on-resistance Low input capacitance Fast switching speeds Freedom from secondary breakdown Low input and output leakage Independent,
N- and P-Channel Enhancement-Mode Dual MOSFET TC2320 Features Low threshold Low on-resistance Low input capacitance Fast switching speeds Freedom from secondary breakdown Low input and output leakage Independent,
Supertex inc. TN0702. N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET. Features
 TN72 Features Low threshold - 1.6V max. High input impedance Low input capacitance - 13pF typical Fast switching speeds Low on-resistance guaranteed at = 2, 3, and 5V Free from secondary breakdown Low
TN72 Features Low threshold - 1.6V max. High input impedance Low input capacitance - 13pF typical Fast switching speeds Low on-resistance guaranteed at = 2, 3, and 5V Free from secondary breakdown Low
BV /BV DS(ON) D(ON) DSS DGS
 TP61T P-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET Features High input impedance and high gain Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability
TP61T P-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET Features High input impedance and high gain Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability
Supertex inc. HV Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With Open Drain Outputs. Features. General Description. Functional Block Diagram
 32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With Open Drain Outputs Features Processed with HVCMOS technology Output voltages to 225V using a ramped supply voltage SINK current minimum 100mA Shift register
32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With Open Drain Outputs Features Processed with HVCMOS technology Output voltages to 225V using a ramped supply voltage SINK current minimum 100mA Shift register
Supertex inc. TN2510. N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET. Features. General Description. Applications. Ordering Information.
 TN51 N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET Features Low threshold (.V max.) High input impedance Low input capacitance (15pF max.) Fast switching speeds Low on-resistance Free from secondary breakdown
TN51 N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET Features Low threshold (.V max.) High input impedance Low input capacitance (15pF max.) Fast switching speeds Low on-resistance Free from secondary breakdown
Dimmable, Low Noise, Dual EL Lamp Driver. 100µH Coilcraft LPS MΩ VREG VOUT LX CS 3 12 VDD EL1 2.0MΩ HV861K7-G. REL-Osc COM1 2. RSW-Osc.
 Supertex inc. HV86 Features Adjustable output regulation for dimming Lamp fade-in/fade-out capability Low audible noise 80V PP output voltage for higher brightness.v enable input logic high Single cell
Supertex inc. HV86 Features Adjustable output regulation for dimming Lamp fade-in/fade-out capability Low audible noise 80V PP output voltage for higher brightness.v enable input logic high Single cell
Supertex inc. TN0106. N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET
 TN16 N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET Features Low threshold - 2.V max. High input impedance Low input capacitance - 5pF typical Fast switching speeds Low on-resistance Free from secondary
TN16 N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET Features Low threshold - 2.V max. High input impedance Low input capacitance - 5pF typical Fast switching speeds Low on-resistance Free from secondary
Inductorless, Dual Output Off-Line Regulators
 Inductless, Dual Output Off-Line Regulats Features Accepts peak input voltages up to 700V Operates directly off of rectified 120 230VAC Integrated linear regulat Minimal power dissipation No high voltage
Inductless, Dual Output Off-Line Regulats Features Accepts peak input voltages up to 700V Operates directly off of rectified 120 230VAC Integrated linear regulat Minimal power dissipation No high voltage
Supertex inc. CL8801. Sequential Linear LED Driver CL8801 GND SET1 SET2 SET3 SET4. Features. General Description. Applications
 Sequential Linear LED Driver Features Minimal component count (base config: + 4 resistors + diode bridge) No magnetics, no capacitors Up to 3W output >5Lm/W using efficient LEDs 85-90% electrical efficiency
Sequential Linear LED Driver Features Minimal component count (base config: + 4 resistors + diode bridge) No magnetics, no capacitors Up to 3W output >5Lm/W using efficient LEDs 85-90% electrical efficiency
16-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter with High Voltage Backplane Driver and Push-Pull Outputs
 16-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter with High Voltage Backplane Driver and Push-Pull Outputs Features HVCMOS technology Output voltage up to +200V Shift register speed 500kHz @ V DD = 1.7V 16 high
16-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter with High Voltage Backplane Driver and Push-Pull Outputs Features HVCMOS technology Output voltage up to +200V Shift register speed 500kHz @ V DD = 1.7V 16 high
Supertex inc. LN V Cascoded N-Channel MOSFET L 100 YWLL
 Features 1200V breakdown voltage Low threshold, 1.V max. High input impedance Low input capacitance Integrated high voltage resistor divider Integrated 1000:1 resistor divider Compact 3x3 LFGA package
Features 1200V breakdown voltage Low threshold, 1.V max. High input impedance Low input capacitance Integrated high voltage resistor divider Integrated 1000:1 resistor divider Compact 3x3 LFGA package
Supertex inc. TN2106. N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET. Features. General Description. Applications. Ordering Information.
 Features Free from secondary breakdown Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability Integral source-drain diode High input impedance and
Features Free from secondary breakdown Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability Integral source-drain diode High input impedance and
32-Channel, 256 Gray-Shade High Voltage Driver. General Description. High Voltage. Power Supply. High Voltage
 Supertex inc. Features HVCMOS technology 5.0V CMOS inputs Output voltage up to +0V PWM gray shade conversion Capable of 256 levels of gray shading 0MHz shift and count clock frequency 20MHz data throughput
Supertex inc. Features HVCMOS technology 5.0V CMOS inputs Output voltage up to +0V PWM gray shade conversion Capable of 256 levels of gray shading 0MHz shift and count clock frequency 20MHz data throughput
Supertex inc. TP0610T. P-Channel Enhancement Mode Vertical DMOS FETs. Features. General Description. Applications. Ordering Information
 Supertex inc. P-Channel Enhancement Mode Vertical DMOS FETs Features High input impedance and high gain Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal
Supertex inc. P-Channel Enhancement Mode Vertical DMOS FETs Features High input impedance and high gain Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal
Supertex inc. TP2104. P-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET. Features. General Description. Applications. Ordering Information.
 TP214 Features High input impedance and high gain Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability Integral source-drain diode Free from secondary
TP214 Features High input impedance and high gain Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability Integral source-drain diode Free from secondary
Supertex inc. TC7920. Two Pair, N- and P-Channel Enhancement-Mode MOSFET with Drain-Diodes
 Two Pair, N- and P-Channel Enhancement-Mode MOSFET with Drain-Diodes Features High voltage Vertical DMOS technology Integrated drain output high voltage diodes Integrated gate-to-source resistor Integrated
Two Pair, N- and P-Channel Enhancement-Mode MOSFET with Drain-Diodes Features High voltage Vertical DMOS technology Integrated drain output high voltage diodes Integrated gate-to-source resistor Integrated
BV /BV DS(ON) D(ON) DSS DGS
 P-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FETs VP216 Features Free from secondary breakdown Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability
P-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FETs VP216 Features Free from secondary breakdown Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD UCSR3651S Preliminary CMOS IC
 UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD UCSR3651S Preliminary CMOS IC HIGH PRECISION CC/CV PRIMARY-SIDE PWM POWER SWITCH DESCRIPTION The UTC UCSR3651S is a primary control switch mode charger and adapter applications.
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD UCSR3651S Preliminary CMOS IC HIGH PRECISION CC/CV PRIMARY-SIDE PWM POWER SWITCH DESCRIPTION The UTC UCSR3651S is a primary control switch mode charger and adapter applications.
Supertex inc. MD0105. Four-Channel High Voltage Protection T/R Switch. Features. General Description. Applications. Typical Application Circuit +130V
 Four-Channel High Voltage Protection T/R Switch Features Up to ±30V input voltage protection Low on resistance - 5Ω typical Fast switching speed Four electrically isolated channels No external supplies
Four-Channel High Voltage Protection T/R Switch Features Up to ±30V input voltage protection Low on resistance - 5Ω typical Fast switching speed Four electrically isolated channels No external supplies
DSX DGS DS(ON) D(ON) (V)
 N7 N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FETs Features Free from secondary breakdown Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability Integral
N7 N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FETs Features Free from secondary breakdown Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability Integral
16-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter with High Voltage Backplane Driver and Push-Pull Outputs
 16-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter with High Voltage Backplane Driver and Push-Pull Outputs Features HVCMOS technology Output voltage up to +200V Shift register speed 500kHz @ = 2.0V 16 high voltage
16-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter with High Voltage Backplane Driver and Push-Pull Outputs Features HVCMOS technology Output voltage up to +200V Shift register speed 500kHz @ = 2.0V 16 high voltage
64-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs
 64-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs Features Processed with HVCMOS technology Operating output voltages to 300V Low power level shifting from 5.0 to 300V Shift register
64-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs Features Processed with HVCMOS technology Operating output voltages to 300V Low power level shifting from 5.0 to 300V Shift register
Supertex inc. HV7022C. 34-Channel Symmetric Row Driver. General Description. Features. Functional Block Diagram. Supertex inc.
 34-Channel Symmetric Row Driver Features HVCMOS technology Symmetric row drive (reduces latent imaging in ACTFEL displays) Output voltage up to +230V Low power level shifting Source/sink current minimum
34-Channel Symmetric Row Driver Features HVCMOS technology Symmetric row drive (reduces latent imaging in ACTFEL displays) Output voltage up to +230V Low power level shifting Source/sink current minimum
Primary-Side Regulation PWM Controller for PFC LED Driver
 Preliminary R7304 Primary-Side Regulation PWM Controller for PFC LED Driver General Description RT7304 is an active power factor controller specifically designed for use as a constant current LED driver.
Preliminary R7304 Primary-Side Regulation PWM Controller for PFC LED Driver General Description RT7304 is an active power factor controller specifically designed for use as a constant current LED driver.
Supertex inc. HV2661 Low Charge Injection 24-Channel High Voltage Analog Switch. General Description. Features. Applications.
 Low Charge Injection 24-Channel High Voltage Analog Switch Features 24 Channels of high voltage analog switch 3.3 or 5.0V CMOS input logic level 3:1 MUX-deMUX with 8 states 20MHz data shift clock frequency
Low Charge Injection 24-Channel High Voltage Analog Switch Features 24 Channels of high voltage analog switch 3.3 or 5.0V CMOS input logic level 3:1 MUX-deMUX with 8 states 20MHz data shift clock frequency
ML4818 Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller
 Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller www.fairchildsemi.com Features Full bridge phase modulation zero voltage switching circuit with programmable ZV transition times Constant frequency operation
Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller www.fairchildsemi.com Features Full bridge phase modulation zero voltage switching circuit with programmable ZV transition times Constant frequency operation
Supertex inc. VN0109. N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET. Features. General Description. Applications. Ordering Information.
 VN19 N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET Features Free from secondary breakdown Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability
VN19 N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET Features Free from secondary breakdown Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability
Supertex inc. HV Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With Open Drain Outputs. Features. General Description. Functional Block Diagram
 Supertex inc. HV5522 32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With Open Drain Outputs Features General Description Processed with HVCMOS technology Sink current minimum 00mA Shift register speed 8.0MHz
Supertex inc. HV5522 32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With Open Drain Outputs Features General Description Processed with HVCMOS technology Sink current minimum 00mA Shift register speed 8.0MHz
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD UC1103 Preliminary CMOS IC
 UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD HIGH PRECISION CC/CV PRIMARY SIDE SWITCHING REGULATOR DESCRIPTION The UTC UC1103 is a primary control unit for switch mode charger and adapter applications. The controlled
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD HIGH PRECISION CC/CV PRIMARY SIDE SWITCHING REGULATOR DESCRIPTION The UTC UC1103 is a primary control unit for switch mode charger and adapter applications. The controlled
Supertex inc. MD0105. Four-Channel High Voltage Protection T/R Switch. Features. General Description. Applications. Typical Application Circuit +130V
 Supertex inc. Four-Channel High Voltage Protection T/R Switch Features Up to ±130V input voltage protection Low on resistance - 15Ω typical Fast switching speed Four electrically isolated channels No external
Supertex inc. Four-Channel High Voltage Protection T/R Switch Features Up to ±130V input voltage protection Low on resistance - 15Ω typical Fast switching speed Four electrically isolated channels No external
Supertex inc. TN0604. N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET. Features. General Description. Applications. Ordering Information.
 TN64 N-Channel Enhancement-Mode ertical DMOS FET Features Low threshold (1.6 max.) High input impedance Low input capacitance (14pF typical) Fast switching speeds Low on-resistance Free from secondary
TN64 N-Channel Enhancement-Mode ertical DMOS FET Features Low threshold (1.6 max.) High input impedance Low input capacitance (14pF typical) Fast switching speeds Low on-resistance Free from secondary
Supertex inc. HV9120. High-Voltage, Current-Mode PWM Controller
 Features 1 to 45V input voltage range 1.MHz clock >2:1 dynamic range @ 5KHz 49% Maximum duty cycle version Low internal noise Applications Off-line high frequency power supplies
Features 1 to 45V input voltage range 1.MHz clock >2:1 dynamic range @ 5KHz 49% Maximum duty cycle version Low internal noise Applications Off-line high frequency power supplies
32-Channel High Voltage Amplifier Array
 32-Channel High Voltage Amplifier Array Features 32 independent high voltage amplifiers 3 operating voltage 295V output voltage 2.2V/µs typical output slew rate Adjustable output current source limit Adjustable
32-Channel High Voltage Amplifier Array Features 32 independent high voltage amplifiers 3 operating voltage 295V output voltage 2.2V/µs typical output slew rate Adjustable output current source limit Adjustable
Low Charge Injection 8-Channel High Voltage Analog Switches with Bleed Resistors. Level Shifters. Latches D LE CL D LE CL D LE CL D LE CL D LE CL
 Low Charge Injection 8-Channel High Voltage Analog Switches with Bleed Resistors Features HVCMOS technology for high performance Very low quiescent power dissipation (10µA max.) Output on-resistance (22Ω
Low Charge Injection 8-Channel High Voltage Analog Switches with Bleed Resistors Features HVCMOS technology for high performance Very low quiescent power dissipation (10µA max.) Output on-resistance (22Ω
MP2494 2A, 55V, 100kHz Step-Down Converter
 The Future of Analog IC Technology MP2494 2A, 55V, 100kHz Step-Down Converter DESCRIPTION The MP2494 is a monolithic step-down switch mode converter. It achieves 2A continuous output current over a wide
The Future of Analog IC Technology MP2494 2A, 55V, 100kHz Step-Down Converter DESCRIPTION The MP2494 is a monolithic step-down switch mode converter. It achieves 2A continuous output current over a wide
N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FETs
 2N72 N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FETs Features Free from secondary breakdown Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability
2N72 N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FETs Features Free from secondary breakdown Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability
Supertex inc. VN10K. N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET. Features. General Description. Applications. Ordering Information.
 VN1K N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET Features Free from secondary breakdown Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability
VN1K N-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET Features Free from secondary breakdown Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds Excellent thermal stability
Supertex inc. VP2206. P-Channel Enhancement-Mode Vertical DMOS FET. Features. General Description. Applications. Ordering Information.
 Features Free from secondary breakdown Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds High input impedance and high gain Excellent thermal stability Integral source-to-drain
Features Free from secondary breakdown Low power drive requirement Ease of paralleling Low C ISS and fast switching speeds High input impedance and high gain Excellent thermal stability Integral source-to-drain
HV Channel, Low Harmonic Distortion, High Voltage Analog Switch with Bleed Resistors. General Description
 Supertex inc. HV2733 16-Channel, Low Harmonic istortion, Analog Switch with Bleed Resistors Features Low harmonic distortion Integrated bleed resistors on the outputs 3.3 or 5.5V CMOS input logic level
Supertex inc. HV2733 16-Channel, Low Harmonic istortion, Analog Switch with Bleed Resistors Features Low harmonic distortion Integrated bleed resistors on the outputs 3.3 or 5.5V CMOS input logic level
Low Charge Injection 32-Channel High Voltage Analog Switch. General Description. Level Shifters. Latches D LE CLR D LE CLR D LE CLR D LE CLR D LE CLR
 Low Charge Injection 32-Channel High Voltage Analog Switch Features 32-Channel high voltage analog switch 2:1 Multiplexer / emultiplexer 3.3V or 5.0V CMOS input logic level 20MHz data shift clock frequency
Low Charge Injection 32-Channel High Voltage Analog Switch Features 32-Channel high voltage analog switch 2:1 Multiplexer / emultiplexer 3.3V or 5.0V CMOS input logic level 20MHz data shift clock frequency
Supertex inc. HV859. High Voltage EL Lamp Driver for Low Noise Applications. Features. General Description. Applications. Typical Application Circuit
 High Voltage EL Lamp river for Low Noise Applications Features Patented audible noise reduction Patented lamp aging compensation 0 V PP output voltage for higher brightness Patented output timing for high
High Voltage EL Lamp river for Low Noise Applications Features Patented audible noise reduction Patented lamp aging compensation 0 V PP output voltage for higher brightness Patented output timing for high
32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs VPP. High Voltage. Level Translators & Push-Pull Output Buffers
 Supertex inc. HV5308B 32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs Features General Description Processed with HVCMOS technology Low power level shifting Source/sink current
Supertex inc. HV5308B 32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs Features General Description Processed with HVCMOS technology Low power level shifting Source/sink current
D8020. Universal High Integration Led Driver Description. Features. Typical Applications
 Universal High Integration Led Driver Description The D8020 is a highly integrated Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) high efficiency LED driver IC. It requires as few as 6 external components. This IC allows
Universal High Integration Led Driver Description The D8020 is a highly integrated Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) high efficiency LED driver IC. It requires as few as 6 external components. This IC allows
FL103 Primary-Side-Regulation PWM Controller for LED Illumination
 FL103 Primary-Side-Regulation PWM Controller for LED Illumination Features Low Standby Power: < 30mW High-Voltage Startup Few External Component Counts Constant-Voltage (CV) and Constant-Current (CC) Control
FL103 Primary-Side-Regulation PWM Controller for LED Illumination Features Low Standby Power: < 30mW High-Voltage Startup Few External Component Counts Constant-Voltage (CV) and Constant-Current (CC) Control
MP6902 Fast Turn-off Intelligent Controller
 MP6902 Fast Turn-off Intelligent Controller The Future of Analog IC Technology DESCRIPTION The MP6902 is a Low-Drop Diode Emulator IC for Flyback converters which combined with an external switch replaces
MP6902 Fast Turn-off Intelligent Controller The Future of Analog IC Technology DESCRIPTION The MP6902 is a Low-Drop Diode Emulator IC for Flyback converters which combined with an external switch replaces
32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs VPP. High Voltage. Level Translators & Push-Pull Output Buffers
 Supertex inc. HV5408B 32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs Features Processed with HVCMOS technology Low power level shifting SOURCE/SINK current minimum 20mA Shift
Supertex inc. HV5408B 32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs Features Processed with HVCMOS technology Low power level shifting SOURCE/SINK current minimum 20mA Shift
Supertex inc. AT9932. Automotive Boost-Buck LED Lamp Driver IC. Features
 Supertex inc Automotive BoostBuck LED Lamp Driver IC Features Constant output current Steps output voltage up or down Very low susceptibility to Input voltage transients Frequency jitter Externally programmable
Supertex inc Automotive BoostBuck LED Lamp Driver IC Features Constant output current Steps output voltage up or down Very low susceptibility to Input voltage transients Frequency jitter Externally programmable
32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs
 32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs Features General Description Processed with HVCMOS technology Low power level shifting Source/sink current minimum 20mA Shift
32-Channel Serial to Parallel Converter With High Voltage Push-Pull Outputs Features General Description Processed with HVCMOS technology Low power level shifting Source/sink current minimum 20mA Shift
MP A, 55V, 100kHz Step-Down Converter with Programmable Output OVP Threshold
 The Future of Analog IC Technology MP24943 3A, 55V, 100kHz Step-Down Converter with Programmable Output OVP Threshold DESCRIPTION The MP24943 is a monolithic, step-down, switch-mode converter. It supplies
The Future of Analog IC Technology MP24943 3A, 55V, 100kHz Step-Down Converter with Programmable Output OVP Threshold DESCRIPTION The MP24943 is a monolithic, step-down, switch-mode converter. It supplies
MP2497-A 3A, 50V, 100kHz Step-Down Converter with Programmable Output OVP Threshold
 The Future of Analog IC Technology MP2497-A 3A, 50V, 100kHz Step-Down Converter with Programmable Output OVP Threshold DESCRIPTION The MP2497-A is a monolithic step-down switch mode converter with a programmable
The Future of Analog IC Technology MP2497-A 3A, 50V, 100kHz Step-Down Converter with Programmable Output OVP Threshold DESCRIPTION The MP2497-A is a monolithic step-down switch mode converter with a programmable
HIGH SPEED, 100V, SELF OSCILLATING 50% DUTY CYCLE, HALF-BRIDGE DRIVER
 Data Sheet No. 60206 HIGH SPEED, 100V, SELF OSCILLATING 50% DUTY CYCLE, HALF-BRIDGE DRIVER Features Simple primary side control solution to enable half-bridge DC-Bus Converters for 48V distributed systems
Data Sheet No. 60206 HIGH SPEED, 100V, SELF OSCILLATING 50% DUTY CYCLE, HALF-BRIDGE DRIVER Features Simple primary side control solution to enable half-bridge DC-Bus Converters for 48V distributed systems
TS19460 AC/DC WLED Driver with Average-Mode Constant Current Control
 SOP-8 Pin Definition: 1. VIN 8. RT 2. CS 7. LD 3. GND 6. VDD 4. Gate 5. PWMD General Description The TS19460 is an average current mode control LED driver IC operating in a constant off-time mode. It greatly
SOP-8 Pin Definition: 1. VIN 8. RT 2. CS 7. LD 3. GND 6. VDD 4. Gate 5. PWMD General Description The TS19460 is an average current mode control LED driver IC operating in a constant off-time mode. It greatly
12-Channel High Voltage Analog Switch
 12-Channel Analog Switch Features HVCMOS technology for high performance Operating voltage of up to 200V Output on-resistance typically 22Ω Integrated bleed resistors on the outputs 5.0V to 12.0V CMOS
12-Channel Analog Switch Features HVCMOS technology for high performance Operating voltage of up to 200V Output on-resistance typically 22Ω Integrated bleed resistors on the outputs 5.0V to 12.0V CMOS
Universal High Brightness LED Driver
 FEATURES Over 90% Efficiency 10V to 600V Input Range Constant Current LED Driver Applications from a few ma to more than 1A output LED String From One to Hundreds of Diodes Linear and PWM Dimming Capability
FEATURES Over 90% Efficiency 10V to 600V Input Range Constant Current LED Driver Applications from a few ma to more than 1A output LED String From One to Hundreds of Diodes Linear and PWM Dimming Capability
EM8631S. Green mode PWM Flyback Controller. Features. General Description. Ordering Information. Applications. Typical Application Circuit
 Green mode PWM Flyback Controller General Description is a high performance, low startup current, low cost, current mode PWM controller with green mode power saving. The integrates functions of Soft Start(SS),
Green mode PWM Flyback Controller General Description is a high performance, low startup current, low cost, current mode PWM controller with green mode power saving. The integrates functions of Soft Start(SS),
