(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
|
|
|
- Jennifer Blair
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States US A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1 FANTONE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2014 (54) NIGHT VISION ATTACHMENT FOR SMART (57) ABSTRACT CAMERA A night vision attachment for a SmartPhone by which the (71) Applicant: OPTIKOS CORPORATION camera of the SmartPhone is enabled to view or take digital Wakefield, MA (US) s photos of objects under very low light ambient light levels. s The night vision attachment comprises a housing for receiv (72) Inventors: STEPHEN D. FANTONE, Lynnfield, ing and locating components of the attachment and has por MA (US); Bradley S Faecher, Sudbury, tions adapted to mate with a wall ofthe camera through which MA (US); Will Russin, III, Boston, MA the phone camera lens images object space. Located in the (US); Daniel Orband, Boxford, MA attachment housing are animage detector sensitive to infrared (US) (IR), an objective lens for forming images on the image detector whereby the image detector operates to generate (21) Appl. No.: 13/903,374 image output signals representative of detected images, a display arranged to receive the image output signals from the (22) Filed: May 28, 2013 image detector and to generate a visible image; and an eye Publication Classification piece for viewing images formed on the display and permit ting the camera of the phone to focus on the display images when the attachment is mated to a phone. IRLEDs are used to (51) Int. Cl. illuminate scenes. Snap fit connectors releasably hold the HOIL 27/46 ( ) attachment in mating contact with the phone so that the cam (52) U.S. Cl. era of the phone is optically aligned with the axis of the CPC... HOIL 27/14649 ( ) USPC /330; 250/208.1 eyepiece to permit the camera to view images on the display via the eyepiece. : - s - Y -
2 Patent Application Publication Dec. 4, 2014 Sheet 1 of 5 US 2014/ A1 '~~~ ****************azzzzzzz.. &
3 Patent Application Publication Dec. 4, 2014 Sheet 2 of 5 US 2014/ A1 w sy sas XXXXX S wsn
4 Patent Application Publication Dec. 4, 2014 Sheet 3 of 5 US 2014/ A1 & 8. w was x &S wer rea--- y y :.. **********
5 Patent Application Publication Dec. 4, 2014 Sheet 4 of 5 US 2014/ A1 YXat S -- **** *--~~~~ : ~~~~~ ~~~~r--. snan lº y wiwo
6 Patent Application Publication Dec. 4, 2014 Sheet 5 of 5 US 2014/ A1. --~~~~~~ ca sexes eartry's Kassass&
7 US 2014/ A1 Dec. 4, 2014 NIGHT VISION ATTACHMENT FOR SMART CAMERA FIELD OF THE INVENTION This invention generally relates to night vision apparatus and more specifically to an attachment for a cellular or Smartphone for converting its camera for low light level digital imaging. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 0002 Smartphones are handheld electronic devices built on a mobile operating system to provide more advanced com puting capability and connectivity than a conventional cellu lar telephone. The first smartphones combined the functions of a personal digital assistant (FDA) with a mobile phone. Later models added the functionality of portable media play ers, low-end compact digital cameras, pocket video cameras, and GPS navigation units to form one multi-use device. Many modern Smartphones also include high-resolution touch screens and web browsers that can display standard web pages as well as mobile-optimized sites. High-speed data access is provided by Wi-Fi and mobile broadband. In recent years, the rapid development of mobile app markets and of mobile commerce have been drivers of Smartphone adoption The mobile operating systems (OS) used by modern smartphones include Google's Android, Apple's ios, Nokia s Symbian, RIM's BlackBerry OS, Samsung's Bada, Microsoft's Windows Phone, Hewlett-Packard's webos, and embedded Linux distributions such as Maemo and MeeGo. Such operating systems can be installed on many different phone models, and typically each device can receive multiple OS software updates over its lifetime The past several decades has also seen the develop ment of steadily improving lens designs that have evolved to the point where they have become suitable for integration into cellular phones and, more recently, Smartphones. Indeed, the bulk of digital images created today are taken with cellular phones equipped with digital cameras, thus making point and shoot cameras an endangered species. Even so, such phones do have limitations. For example, it is difficult to Snap good close-ups, distant shots, or night vision shots or videos where lighting is so poor the camera is unable to cope While attachments have been provided to improve close-up and distant shots, none exists for permitting a user to take night vision shots or videos or display screen images visible to a user under poor ambient lighting Accordingly, it is a primary object of the present invention to provide an attachment for a Smartphone that will enable a user to take night vision digital photos and videos under poor lighting conditions It is another object of the present invention to pro vide an attachment for a Smartphone that will enable a user to visualize his Surroundings under low light level conditions Other objects of the invention will in part be obvious and will in part appear hereinafter when the following detailed description is read in connection with the accompa nying drawings. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION A night vision attachment for a SmartPhone by which the camera of the SmartPhone is enabled to view or take digital photos and or videos of objects under very low light ambient light levels The night vision attachment is adapted to be used with SmartPhones having cameras and comprises a housing for receiving and locating components of the attachment. The housing has portions adapted to mate with a wall of the camera through which the phone camera lens images object Space Located in the attachment housing are: 0012 an image detector located in the housing along an optical path; 0013 an objective lens located along the optical path for forming images on the image detector whereby the image detector operates to generate image output signals representative of detected images; 0014 a display arranged to receive the image output signals from the image detector and to generate a visible image; and an eyepiece positioned in said housing for view ing images formed on said display and permitting the camera of the phone to focus on said display images when said attachment is mated to a phone Snap fit connectors depend from the housing for Snapping around the camera releasably hold the attachment in mating contact with the phone so that the camera of the phone is optically aligned with the axis of the eyepiece to permit the camera to view images on said display via the eyepiece In an aspect of the invention, the camera and illumi nation system of the attachment comprises a solid State imager having an operating mode having Substantial sensi tivity to infrared radiation within its field of view and adapted to generate an image output signal representative of the Sub ject matter that it observes and a radiation Source to generate infrared radiation and to direct such radiation into the field of view of the Solid state imager In another aspect of the invention, a display is arranged to receive the image output signal from the Solid state imager and to generate an image visible to the Smart Phone camera via the eyepiece. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The structure and operation of the night vision modular system of the present invention, together with other objects and advantages thereof, may best be understood by reading the following detailed description in connection with the drawings in which unique reference numerals have been used throughout for each part and wherein: 0020 FIG. 1A is an exploded diagrammatic perspective view of a SmartPhone and an inventive attachment separated from the SmartPhone; 0021 FIG. 1B is a diagrammatic perspective view of the SmartPhone and attachment of FIG. 1A showing the attach ment mated with the SmartPhone to convert it for use in taking digital photos and or video or allowing a user to visu alize her Surroundings under low ambient light level condi tions; 0022 FIG. 2A is a diagrammatic perspective of the inven tive SmartPhone attachment with parts broken away to visu alize aspects of its optical system; 0023 FIG. 2B is an enlarged diagrammatic perspective of a portion of the inventive attachment shown in FIG. 2A; 0024 FIG. 3A is a diagrammatic perspective of the inven tive SmartPhone attachment with parts broken away to visu alize aspects of its optical and illumination system; 0025 FIG. 3B is an enlarged diagrammatic perspective of a portion of the inventive attachment shown in FIG. 3A:
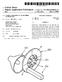
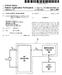
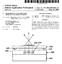
8 US 2014/ A1 Dec. 4, FIG. 4 is a schematic block diagram view of the optical and image-generating components of the inventive SmartPhone attachment shown in FIGS. 1A thru 3B and illustrate the camera and display module used in conjunction with an auxiliary optical module; and 0027 FIG. 5 is a block diagram showing the generation and display of image signals from components of the inven tive modules; and 0028 FIG. 6 is a graph showing a typical spectral response of the Solid State imager and a typical spectra of the emissions from the light emitting diodes shown in FIG. 4 and elsewhere. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION The present invention is an attachment for a Smart Phone, or the like, by which the camera of the SmartPhone can be used to take digital photos and or videos, or its user can visualize his Surroundings, under very low ambient light lev els. Under low light level conditions beneath which the SmartPhone cannot see its surroundings, the attachment operates to provide images to the SmartPhone's camera at light levels that the SmartPhone camera can see and which, in turn, enables the SmartPhone camera to operate normally as though the light levels were higher To understand how the inventive attachment achieves its purpose, reference is now made to FIG.1A which is a diagrammatic view showing in perspective a SmartPhone 10 separated from an inventive attachment SmartPhone 10 may be any of a number of those marketed in large Volumes such as the Apple i-phone series or Samsung Galaxy series, or the like. It is well-known that Such phones have optical systems that may acquire images of their Surroundings and present them for viewing on high resolution touch and display Screens such as that designated generally at 12. Such optical systems, designated generally at 15, typi cally face a scene to be visualized and reside on the side opposite their display screen 12. Other controls such as those designated generally at 14, 16, 18 and 20 are utilized in a well-known manner to select and control other features including, but not limited to, gaining access to the internet, interacting with resident apps, listening to audio files, looking at video files, or the like Referring now to FIG. 18, the low light level attach ment 22 can be seen to have housing 23 that is provided with a shape that is designed to mate in complementary fashion with the back side of the SmartPhone 10 where it is held in place against the back side via three flexible fingers 24, 26 and 28. The flexible fingers 24, 26 and 28 are cantilevered from the attachment 22 via a camming section 29 and flexible cantilevered section 31 that bends under the influence of the camming action of camming section 29 pressed against the edges of the backside of SmartPhone 10. Housing 23 other wise is configured in a well-known manner to receive and position various components of attachment 22 to be described in more detail hereinafter As best shown in FIG. 1A, attachment 22 is pro vided with an aperture 30 that is positioned so that it is automatically aligned with the optical system of SmartPhone 10 when attachment 22 is mated with the SmartPhone 10 as shown in FIG. 1B. Aperture 30 permits the optical system of SmartPhone 10 to view an image formed on a display (See display 166 in FIG. 2B) that forms part of attachment 22's optical and illumination system to be described more fully later. As depicted in FIG. 1B, attachment 22 operates under very low ambient lighting conditions to provide images on screen 12, such at that designated at 32, that SmartPhone 10 would otherwise not be able to provide Attachment 22 is powered either by the internal battery of SmartPhone 10 via a well-known connector 40 into which SmartPhone 10 plugs or by a separate power pack that plugs into the free end of connector 40, i.e. the end that is not occupied by SmartPhone ) Referring now to FIGS. 2A through 3B, the manner by which attachment 22 forms images on display 166 under low light level conditions will now be taken up. Generally, it involves the use of a solid state imager 160 sensitive to infra red radiation, a source for generating infrared radiation (a series of encapsulated IR LEDs 154) within the spectral response range of the Solid state imager 160 and directing this radiation into the field of view of the imager 160, and an image generator 166 that receives the output from the imager 160 and generates a visible image representative of the output of the image at a position visible to SmartPhone 10's camera as seen through aperture 30. Thus, in contrast to passive military night vision apparatus, the night vision attachment of the present invention is an active' apparatus which generates infrared radiation used to form the image. Since the scene being viewed is being illuminated (in the infrared) by the attachment itself, the attachment of the present invention can use a solid state imager much less sensitive, and much less costly, than the image intensifier tube arrangements typically used in military night vision apparatus. The preferred form of Solid state imager for use in the present invention is a comple mentary metal oxide semiconductors (CMOS) device, although other Solid state imagers may also be used As discussed in more detail below with regard to FIG. 6, CMOS imagers are usually sensitive to infrared radia tion only in the range of about 700 to 1000 (or in some case at wavelengths as long as ) nm. CMOS sensors are, of course, also generally sensitive to visible radiation of 400 to 700 nm, and in the present invention, there is no particular reason to exclude visible light from the imager 160, i.e., the imager 160 can be allowed to form an image using both the infrared radiation reflected from the scene viewed and any available ambient visible light. If a CMOS sensor is used in the present invention, the infrared radiation source is chosen to generate infrared radiation within the range of about 700 to 1000 nm to which such imagers are particularly sensitive. Also, it is desireable to illuminate the scene at wavelengths that will not be visible to the user of the device or an indi vidual in the vicinity of the device. Fortunately, inexpensive infrared radiation emitting diodes operating within this range are readily available commercially. Operating in the 700 to 1000 nm range also has the advantage that the images gener ated using Such near infrared radiation are much more similar to visible images than images formed using far infrared radia tion with wavelengths of 2000 nm or more, and hence are easier for inexperienced users to interpret As best seen in FIGS. 2A and B, attachment 22 has an objective lens 158 arranged along optical axis. Objective lens 158 may be an aspherized singlet to bring it to an accept able state of correction or may be of more complex design including more than one element any or all of which may include aspheric surfaces (See FIG. 4). Objective lens 158 is preferably fixed focus set to a hyperfocal distance of may be focusedator near infinity. As may be noted, the optical axis of objective lens 158 is offset with respect to the optical axis of display 166 which in turnis in axial alignment with the taking lens of SmartPhone 10. As such there is some degree of
9 US 2014/ A1 Dec. 4, 2014 parallax between what the SmartPhone 10 would see without attachment 22 and what it sees with the attachment in place but this is negligible and is not noticeable to a user since the user observes images formed by the attachment on Screen Surrounding the optical axis of objective lens 158 are a plurality of IRLEDs 154 which may all be turned on at once to optimize the distance at which images may beformed The camera and illumination system of attachment 22, as best seen in FIGS. 4 and 5, comprises the objective taking lens 158, preferably a centrally located micro video lens, surrounded by the circular pattern of IR LEDs 154. Behind the micro video lens 158 is located a CMOS image sensor 160 (See FIGS. 3B and 3) The LEDs 154 used are preferably of two different types, one having a narrow field of emission and the other having a substantially wider field of emission, with the two types alternating around the circular pattern. It has been found that this arrangement of narrow angle and wide angle diodes provides optimal illumination of the entire field of view of the image sensor 160, the narrow angle diodes illuminating more distant objects while the wide angle diodes the closer objects. However, it will be recognized that one or the other can be used or used in different geometries and quantities consistent with the need to mini mize the power consumption of attachment 22 and hence the drain on batteries A red filter may be mounted forward of the LEDs 154 to pass infrared and visible radiation having wavelengths greater than about 650 nm The other optical and image-forming components are as follows (Refer to FIG. 4): 0043 (a) the micro video lens 158 which extends through a central aperture along the optical axis, gathers infrared and visible radiation, and images this radiation on to 0044 (b) the CMOS sensor 160 mounted along the optical axis in the camera and illumination module 14; 0045 (c) a display elements 25 comprising a back-lighting unit 162 having the form of a green light-emitting diode (see below with reference to FIG. 6) combined with a scattering reflector 174. In FIG. 2B, the scattering reflector 174 and diffuser 164 have been omitted for ease in seeing LCD display 166; 0046 (d) a diffuser 164 disposed adjacent the back-light ing unit 162 to diffuse light emitted from the back-lighting unit; 0047 (e) a liquid crystal display 166 disposed adjacent the diffuse 64 so as to be backlit by light passing therethrough: (f) an auxiliary optics module comprising an eye piece assembly 170 arranged to form provide an image of the display 166 at a distance that can be focused on by the camera lens of SmartPhone 10. Those skilled in the art of optical design will readily be able to adjust the properties of eyepiece 170 to accommodate the SmartPhone's camera lens The mode of operation of the optical and imaging components of the invention will now be explained with reference to FIGS. 4 and 5. As shown schematically in FIG. 4, the infrared LEDs 154 emit infrared radiation that passes through a filter (not shown), is reflected from objects in front of the user, passes back through a centrally located aperture, and is imaged by the two-element micro Video lens 158 on the CMOS sensor 160. As shown in FIG. 5, the sensor 160 generates a standard RS170 video output signal that is fed to a monochrome video display driver 163. The output from driver 163 is fed to the liquid crystal display Returning to FIG. 4, it will be seen that the back lighting unit 162 comprises a green LED 172 lying within a frusto-conical cavity in a scattering reflector 174, the diffuser 164 lying across the wide end of the frusto-conical cavity. A green diode is chosen because this is the color to which the human eye is most sensitive, and hence minimizes light out put and power consumption for an image of any desired intensity. Also, it is reminiscent of the color of phosphors used in Some military night vision systems and provides a desirable user comparison to traditional military night vision systems. The combination of the scattering reflector 174 and the dif fuser 164 provides a substantially uniform distribution of green light across the diffuser 164 and hence substantially uniform back-lighting of the display 166 disposed adjacent the diffuser 164. Green light passing through the display 166 is imaged by the two-element eyepiece assembly 170 of the auxiliary optics module to forman image visible to the Smart Phone camera The arrangement of optical and imaging compo nents shown in FIGS. 4 and 5, in which the sensor 160 and the display 166 are substantially aligned along a common axis, provides an extremely compact and convenient form factor. The arrangement is also designed to avoid two potential prob lems. As shown in FIG. 6, the infrared diodes 154 emit at around 850 nm, the green diode 172 emits around 575 nm, and the sensor 160 has substantial sensitivity over the range of about 475 to about 1075 nm. Accordingly, it is necessary to arrange the optical system so that no light from green diode 172 can reach the sensor 160, since the sensor would be affected by the green light and the desired infrared image would be degraded. The arrangement of the green diode 172 within the frusto-conical cavity of the reflector 174 and the mounting of the sensor 160 immediately adjacent the back surface of the reflector 174 (i.e., the surface facing away from the diffuser 164) prevent light from the green diode 172 reaching the sensor 160. Also, for reasons already noted, it is undesirable for a night vision system to emit any visible light, and proper filtering assures that any light from the green diode 172, which may be reflected forwardly (i.e., away from the user), for example by reflection from the display 166, will not emerge from this module The preferred attachment of the present invention shown in the accompanying drawings is simple, compact and can readily be manufactured using inexpensive, commer cially available components. For example, the monochrome display driver can be a Motorola MCVVQ111 VirtuoVue driver, while the display 166 can be a Cyberdisplay 320 display, available from Kopin Corporation of Taunton Mass., with a 320x240 pixel output. The sensor 160 can be an OmniVision OV5116N CMOS sensor available from OmniVision Technologies, Inc., of Sunnyvale Calif., while the infrared diodes 154 can be Model RT-7507ET from Rodan (Taiwan) Ltd., and the green diode 174 can be a King bright Model AA3528 surface mount LED lamp. Using such components, bright images within the range from about 30 to 100 feet can be readily seen It will readily be apparent to those skilled in the art that numerous changes and modifications can be made to the preferred embodiments of the invention described above without departing from the scope of the invention. For example, the CMOS sensor 160 could be replaced by another type of Solid state imager, for example a charged coupled
10 US 2014/ A1 Dec. 4, 2014 device (CCD). A color camera that also has extended infrared sensitivity could be used in conjunction with a color display to provide a color rendition of the visible scene. Higher reso lution (high-definition) imager and displays could be used with associated higher costs. Therefore, it is intended that the embodiments described herein be considered as illustrative and not be construed in a limiting sense. From the foregoing, it will be seen that the present invention provides a night vision apparatus that is adaptable, inexpensive, compact, robust and well suited for use by the general public, and which does not emit visible radiation permitting observations that can be made at night without notice by or disturbing animals If there is sufficient light, there may be no need for the illumination module to be activated to supply additional illumination to the scene. If a visible light detector is incor porated into the illumination system or if the camera is used (with the illumination system turned off) to measure the amount of ambient light, a determination can he made as to whether additional illumination is required and the output of the illumination Source adjusted to add additional illumina tion. If additional illumination is required to view the scene, either infrared light and/or visible light can be activated. The advantage of using infrared light is that it will not be observed by individuals or animals that are in the immediate area of the illumination system Other embodiments of the invention will be appar ent from its teachings, and Such variants are intended to be within the scope of the appended claims. What is claimed is: 1. An night vision attachment for a phone having a camera with an optical axis, said attachment comprising: a housing for receiving and locating components of the attachment, said housing having portions adapted to mate with a wall of the camera through which the phone camera lens images object space; an image detector located in said housing along an optical path; an objective lens located along said optical path for form ing images on said image detector whereby said image detector generates image output signals representative of detected images; a display arranged to receive said image output signals from said image detector and to generate a visible image; an eyepiece positioned in said housing for viewing images formed on said display and permitting the camera of the phone to focus on said display images when said attach ment is mated to a phone; and a mechanical connector depending from said housing for Snapping around the camera to releasably hold said attachment in mating contact with the phone so that the camera of the phone is optically aligned with the axis of said eyepiece to permit the camera to view images on said display via said eyepiece. 2. The night vision attachment of claim 1 wherein said image detector comprises a solid state imager having an oper ating mode having Substantial sensitivity to infrared radia tion, said solid state imager having a field of view; and wherein said night vision attachment further includes a radia tion source to generate infrared radiation and to direct Such radiation into said field of view of said solid state imager. 3. The night vision attachment of claim 2 wherein said Solid state imager is a complementary metal oxide semicon ductor device. 4. The night vision attachment of claim 2 wherein said Solid state imager is sensitive to infrared radiation in the range of about 700 to about 1000 nm. 5. The night vision attachment of claim 4 wherein said Solid state imager is also sensitive to visible radiation in the range of about 400 to about 700 nm. 6. The night vision attachment of claim 2 wherein said infrared radiation source comprises at least one infrared radiation emitting diode. 7. The night vision attachment of claim 6 wherein said infrared radiation source comprises at least two infrared light emitting diodes, at least one of said diodes being arranged to illuminate a wide area of said field of view of the solid state imager and at least one of said diodes being arranged to illuminate a narrower area adjacent the center of said field of view. 8. The night vision attachment of claim 2 wherein said infrared radiation source comprises at least three radiation emitting diodes arranged on a circle Surrounding said lens. 9. The night vision attachment of claim 1 wherein said display comprises a backlit liquid crystal display. 10. The night vision attachment of claim 9 wherein said liquid crystal display is mounted between said solid state imager and said eyepiece so that the backlight of said liquid crystal display is not visible except via said eyepiece. 11. The night vision attachment of claim 10 wherein the backlight of said liquid crystal display is provided by a visible light emitting diode and a diffuser is provided to diffuse the light from said diode across said liquid crystal display. 12. The night vision attachment of claim 11 wherein said light emitting diode emits green light. k k k k k
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. Penn et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2003
 US 2003O147052A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0147052 A1 Penn et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH CONTRAST PROJECTION Related U.S. Application Data (60) Provisional
US 2003O147052A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0147052 A1 Penn et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH CONTRAST PROJECTION Related U.S. Application Data (60) Provisional
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO3OO63A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0030063 A1 Sosniak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2003 (54) MIXED COLOR LEDS FOR AUTO VANITY MIRRORS AND
(19) United States US 2003OO3OO63A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0030063 A1 Sosniak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2003 (54) MIXED COLOR LEDS FOR AUTO VANITY MIRRORS AND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006004.4273A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0044273 A1 Numazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) MOUSE-TYPE INPUT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 2006004.4273A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0044273 A1 Numazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) MOUSE-TYPE INPUT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,346,966 B1
 USOO6346966B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,346,966 B1 TOh (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 12, 2002 (54) IMAGE ACQUISITION SYSTEM FOR 4,900.934. A * 2/1990 Peeters et al.... 250/461.2 MACHINE
USOO6346966B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,346,966 B1 TOh (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 12, 2002 (54) IMAGE ACQUISITION SYSTEM FOR 4,900.934. A * 2/1990 Peeters et al.... 250/461.2 MACHINE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015 0311941A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0311941 A1 Sorrentino (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) MOBILE DEVICE CASE WITH MOVABLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2015 0311941A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0311941 A1 Sorrentino (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) MOBILE DEVICE CASE WITH MOVABLE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0307772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307772 A1 WU (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) INTERACTIVE PROJECTION SYSTEM WITH (52) U.S. Cl. LIGHT SPOT
(19) United States US 2013 0307772A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0307772 A1 WU (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 21, 2013 (54) INTERACTIVE PROJECTION SYSTEM WITH (52) U.S. Cl. LIGHT SPOT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0323489A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0323489 A1 TANG. et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SMART LIGHTING DEVICE AND RELATED H04N 5/232 (2006.01) CAMERA
(19) United States US 2016.0323489A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0323489 A1 TANG. et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SMART LIGHTING DEVICE AND RELATED H04N 5/232 (2006.01) CAMERA
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O134516A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Du (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) DUAL BAND SLEEVE ANTENNA (52) U.S. Cl.... 3437790 (75) Inventor: Xin Du, Schaumburg,
(19) United States US 2005O134516A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Du (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) DUAL BAND SLEEVE ANTENNA (52) U.S. Cl.... 3437790 (75) Inventor: Xin Du, Schaumburg,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Waibel et al. USOO6624881B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) OPTOELECTRONIC LASER DISTANCE MEASURING INSTRUMENT (75) Inventors: Reinhard Waibel, Berneck
(12) United States Patent Waibel et al. USOO6624881B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) OPTOELECTRONIC LASER DISTANCE MEASURING INSTRUMENT (75) Inventors: Reinhard Waibel, Berneck
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.684,688 B2
 USOO7684688B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.684,688 B2 Torvinen (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 23, 2010 (54) ADJUSTABLE DEPTH OF FIELD 6,308,015 B1 * 10/2001 Matsumoto... 396,89 7,221,863
USOO7684688B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.684,688 B2 Torvinen (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 23, 2010 (54) ADJUSTABLE DEPTH OF FIELD 6,308,015 B1 * 10/2001 Matsumoto... 396,89 7,221,863
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 20150217450A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0217450 A1 HUANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 6, 2015 (54) TEACHING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 20150217450A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0217450 A1 HUANG et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 6, 2015 (54) TEACHING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701 22498A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0122498A1 ZALKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) LAMP DESIGN WITH LED STEM STRUCTURE (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 201701 22498A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0122498A1 ZALKA et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 4, 2017 (54) LAMP DESIGN WITH LED STEM STRUCTURE (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007 172314B2 () Patent No.: Currie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 6, 2007 (54) SOLID STATE ELECTRIC LIGHT BULB (58) Field of Classification Search... 362/2, 362/7, 800, 243,
(12) United States Patent US007 172314B2 () Patent No.: Currie et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 6, 2007 (54) SOLID STATE ELECTRIC LIGHT BULB (58) Field of Classification Search... 362/2, 362/7, 800, 243,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
(19) United States US 2011 O273427A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0273427 A1 Park (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2011 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DISPLAY AND METHOD OF DRIVING THE
A///X 2. N N-14. NetNNNNNNN N. / Et EY / E \ \ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015.0312556A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0312556A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) RGB-IR SENSOR, AND METHOD AND (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2015.0312556A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0312556A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2015 (54) RGB-IR SENSOR, AND METHOD AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O180938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0180938A1 BOk (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) COOLINGAPPARATUS OF COLOR WHEEL OF PROJECTOR (75) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2002O180938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0180938A1 BOk (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 5, 2002 (54) COOLINGAPPARATUS OF COLOR WHEEL OF PROJECTOR (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,836,894 B2. Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.
 USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
of a Panoramic Image Scene
 US 2005.0099.494A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0099494A1 Deng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 12, 2005 (54) DIGITAL CAMERA WITH PANORAMIC (22) Filed: Nov. 10,
US 2005.0099.494A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0099494A1 Deng et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 12, 2005 (54) DIGITAL CAMERA WITH PANORAMIC (22) Filed: Nov. 10,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O2.91546A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0291546 A1 Woida-O Brien (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2016 (54) DIGITAL INFRARED HOLOGRAMS GO2B 26/08 (2006.01)
US 2016O2.91546A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0291546 A1 Woida-O Brien (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 6, 2016 (54) DIGITAL INFRARED HOLOGRAMS GO2B 26/08 (2006.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003.01225O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0122502 A1 Clauberg et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE DRIVER (52) U.S. Cl....
US 2003.01225O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0122502 A1 Clauberg et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 3, 2003 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE DRIVER (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
US 2001 004.8356A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0048356A1 Owen (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 6, 2001 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Related U.S. Application Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Kalevo (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 27, 2008
 US 2008.0075354A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0075354 A1 Kalevo (43) Pub. Date: (54) REMOVING SINGLET AND COUPLET (22) Filed: Sep. 25, 2006 DEFECTS FROM
US 2008.0075354A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0075354 A1 Kalevo (43) Pub. Date: (54) REMOVING SINGLET AND COUPLET (22) Filed: Sep. 25, 2006 DEFECTS FROM
(2) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (2) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Scapa et al. US 20160302277A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) LIGHT AND LIGHT SENSOR Applicant; ilumisys, Inc., Troy,
(19) United States (2) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Scapa et al. US 20160302277A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) LIGHT AND LIGHT SENSOR Applicant; ilumisys, Inc., Troy,
y y (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1 (19) United States (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, C 410C 422b 4200
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0255300 A1 He et al. US 201502553.00A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) DENSELY SPACED FINS FOR
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0255300 A1 He et al. US 201502553.00A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 10, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) DENSELY SPACED FINS FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073337 A1 Liou et al. US 20090073337A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LCD DISPLAY WITH ADJUSTABLE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073337 A1 Liou et al. US 20090073337A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LCD DISPLAY WITH ADJUSTABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O142601A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0142601 A1 Luu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 22, 2004 (54) ADAPTER WALL PLATE ASSEMBLY WITH INTEGRATED ELECTRICAL FUNCTION
(19) United States US 2004O142601A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0142601 A1 Luu (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 22, 2004 (54) ADAPTER WALL PLATE ASSEMBLY WITH INTEGRATED ELECTRICAL FUNCTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150366008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0366008 A1 Barnetson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 17, 2015 (54) LED RETROFIT LAMP WITH ASTRIKE (52) U.S. Cl.
(19) United States US 20150366008A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0366008 A1 Barnetson et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 17, 2015 (54) LED RETROFIT LAMP WITH ASTRIKE (52) U.S. Cl.
58 Field of Search /341,484, structed from polarization splitters in series with half-wave
 USOO6101026A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Bane (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 9 2000 54) REVERSIBLE AMPLIFIER FOR OPTICAL FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS NETWORKS 1-274111 1/1990 Japan. 3-125125
USOO6101026A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Bane (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 9 2000 54) REVERSIBLE AMPLIFIER FOR OPTICAL FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS NETWORKS 1-274111 1/1990 Japan. 3-125125
TEPZZ 7 Z_ 4A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 ( ) G06F 3/0482 (2013.
 (19) TEPZZ 7 Z_ 4A T (11) EP 2 720 134 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/16 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (2013.01) G06F 3/0482 (2013.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 7 Z_ 4A T (11) EP 2 720 134 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 16.04.2014 Bulletin 2014/16 (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0488 (2013.01) G06F 3/0482 (2013.01) (21) Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,314,999 B1 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012
 US0083 l4999bl (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,314,999 B1 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012 (54) OPTICAL IMAGE LENS ASSEMBLY (58) Field Of Classi?cation Search..... 359/715, _ 359/771,
US0083 l4999bl (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,314,999 B1 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012 (54) OPTICAL IMAGE LENS ASSEMBLY (58) Field Of Classi?cation Search..... 359/715, _ 359/771,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006
 (19) United States US 200601 19753A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01 19753 A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006 (54) STACKED STORAGE CAPACITOR STRUCTURE FOR A THIN FILM
(19) United States US 200601 19753A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/01 19753 A1 Luo et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 8, 2006 (54) STACKED STORAGE CAPACITOR STRUCTURE FOR A THIN FILM
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Street et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006
 (19) United States US 2006.00354O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0035402 A1 Street et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) MICROELECTRONIC IMAGING UNITS AND METHODS OF
(19) United States US 2006.00354O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0035402 A1 Street et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 16, 2006 (54) MICROELECTRONIC IMAGING UNITS AND METHODS OF
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,614,995 B2
 USOO6614995B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Tseng (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING AUTO-FOCUS OF IMAGE 6.259.862 B1 * 7/2001 Marino et al.... 396/106
USOO6614995B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Tseng (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 2003 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR COMPENSATING AUTO-FOCUS OF IMAGE 6.259.862 B1 * 7/2001 Marino et al.... 396/106
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120047754A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047754 A1 Schmitt (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2012 (54) ELECTRICSHAVER (52) U.S. Cl.... 30/527 (57) ABSTRACT
US 20120047754A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047754 A1 Schmitt (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2012 (54) ELECTRICSHAVER (52) U.S. Cl.... 30/527 (57) ABSTRACT
R GBWRG B w Bwr G B wird
 US 20090073099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073099 A1 Yeates et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) DISPLAY COMPRISING A PLURALITY OF Publication
US 20090073099A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073099 A1 Yeates et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) DISPLAY COMPRISING A PLURALITY OF Publication
United States Patent (11) 3,626,240
 United States Patent (11) 72) 21 ) 22) () 73 (54) (52) (51) Inventor Alfred J. MacIntyre Nashua, N.H. Appl. No. 884,530 Filed Dec. 12, 1969 Patented Dec. 7, 1971 Assignee Sanders Associates, Inc. Nashua,
United States Patent (11) 72) 21 ) 22) () 73 (54) (52) (51) Inventor Alfred J. MacIntyre Nashua, N.H. Appl. No. 884,530 Filed Dec. 12, 1969 Patented Dec. 7, 1971 Assignee Sanders Associates, Inc. Nashua,
VDD. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. (19) United States. I Data. (76) Inventors: Wen-Cheng Yen, Taichung (TW);
 (19) United States US 2004O150593A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150593 A1 Yen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX LED DISPLAY DRIVING CIRCUIT (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2004O150593A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150593 A1 Yen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) ACTIVE MATRIX LED DISPLAY DRIVING CIRCUIT (76) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109. Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, a. Assistant Examiner-Alan B.
 H HHHHHHH US005299.109A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109 Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 1994 (54) LED EXIT LIGHT FIXTURE 5,138,782 8/1992 Mizobe... 40/219 75) Inventor: Daniel
H HHHHHHH US005299.109A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109 Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 1994 (54) LED EXIT LIGHT FIXTURE 5,138,782 8/1992 Mizobe... 40/219 75) Inventor: Daniel
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0185581 A1 Xing et al. US 2011 0185581A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) COMPACT CIRCULAR SAW (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0185581 A1 Xing et al. US 2011 0185581A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) COMPACT CIRCULAR SAW (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012
 US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
us/ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1 (19) United States / 112 / 108 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb.
 (19) United States US 20080030263A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0030263 A1 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2008 (54) CONTROLLER FOR ORING FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR
(19) United States US 20080030263A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0030263 A1 Frederick et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 7, 2008 (54) CONTROLLER FOR ORING FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999
 USOO599.1083A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54) IMAGE DISPLAY APPARATUS 56) References Cited 75 Inventor: Yoshiki Shirochi, Chiba, Japan
USOO599.1083A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54) IMAGE DISPLAY APPARATUS 56) References Cited 75 Inventor: Yoshiki Shirochi, Chiba, Japan
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009
 (19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
(19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
System and method for focusing a digital camera
 Page 1 of 12 ( 8 of 32 ) United States Patent Application 20060103754 Kind Code A1 Wenstrand; John S. ; et al. May 18, 2006 System and method for focusing a digital camera Abstract A method of focusing
Page 1 of 12 ( 8 of 32 ) United States Patent Application 20060103754 Kind Code A1 Wenstrand; John S. ; et al. May 18, 2006 System and method for focusing a digital camera Abstract A method of focusing
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 Kohayakawa 54) OCULAR LENS MEASURINGAPPARATUS (75) Inventor: Yoshimi Kohayakawa, Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl. No.: 544,486 (22 Filed:
United States Patent 19 Kohayakawa 54) OCULAR LENS MEASURINGAPPARATUS (75) Inventor: Yoshimi Kohayakawa, Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl. No.: 544,486 (22 Filed:
202 19' 19 19' (12) United States Patent 202' US 7,050,043 B2. Huang et al. May 23, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.
 US00705.0043B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,050,043 B2 May 23, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 2,
US00705.0043B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,050,043 B2 May 23, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 2,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0065580 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD
(19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0065580 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0162673A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0162673 A1 Bohn (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 27, 2013 (54) PIXELOPACITY FOR AUGMENTED (52) U.S. Cl. REALITY USPC...
US 2013 0162673A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0162673 A1 Bohn (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 27, 2013 (54) PIXELOPACITY FOR AUGMENTED (52) U.S. Cl. REALITY USPC...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 20050207013A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0207013 A1 Kanno et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) PHOTOELECTRIC ENCODER AND (30) Foreign Application
US 20050207013A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0207013 A1 Kanno et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) PHOTOELECTRIC ENCODER AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O2325O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0232502 A1 Asakawa (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 18, 2003 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING Publication Classification SEMCONDUCTOR
US 2003O2325O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0232502 A1 Asakawa (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 18, 2003 (54) METHOD OF MANUFACTURING Publication Classification SEMCONDUCTOR
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 LLP 57)
 III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
(19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9383 080B1 (10) Patent No.: US 9,383,080 B1 McGarvey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 5, 2016 (54) WIDE FIELD OF VIEW CONCENTRATOR USPC... 250/216 See application file for
(12) United States Patent USOO9383 080B1 (10) Patent No.: US 9,383,080 B1 McGarvey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 5, 2016 (54) WIDE FIELD OF VIEW CONCENTRATOR USPC... 250/216 See application file for
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,068,465 B2
 USOO90684-65B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Keny et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 30, 2015 (54) TURBINE ASSEMBLY USPC... 416/215, 216, 217, 218, 248, 500 See application file for complete
USOO90684-65B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Keny et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 30, 2015 (54) TURBINE ASSEMBLY USPC... 416/215, 216, 217, 218, 248, 500 See application file for complete
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8208048B2 (12) United States Patent Lin et al. (10) Patent No.: US 8,208,048 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) METHOD FOR HIGH DYNAMIC RANGE MAGING
USOO8208048B2 (12) United States Patent Lin et al. (10) Patent No.: US 8,208,048 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 26, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) METHOD FOR HIGH DYNAMIC RANGE MAGING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O24.882OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: MOSer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2005 (54) SYSTEM AND METHODS FOR SPECTRAL Related U.S. Application Data BEAM
US 2005O24.882OA1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: MOSer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 10, 2005 (54) SYSTEM AND METHODS FOR SPECTRAL Related U.S. Application Data BEAM
/ 7. 2 LOWER CASE. (12) United States Patent US 6,856,819 B2. Feb. 15, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: 5 PARASITIC ELEMENT
 (12) United States Patent toh USOO6856819B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2005 (54) PORTABLE WIRELESS UNIT (75) Inventor: Ryoh Itoh, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: NEC Corporation, Tokyo (JP)
(12) United States Patent toh USOO6856819B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2005 (54) PORTABLE WIRELESS UNIT (75) Inventor: Ryoh Itoh, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: NEC Corporation, Tokyo (JP)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120312936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0312936A1 HUANG (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2012 (54) HOLDING DEVICE OF TABLET ELECTRONIC DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl....
US 20120312936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0312936A1 HUANG (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2012 (54) HOLDING DEVICE OF TABLET ELECTRONIC DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 20050214083A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2005 (54) OPTICAL LENS DRILL PRESS Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl."... B23B
US 20050214083A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 29, 2005 (54) OPTICAL LENS DRILL PRESS Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl."... B23B
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005
 US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Eklund (54) HIGH VOLTAGE MOS TRANSISTORS 75) Inventor: Klas H. Eklund, Los Gatos, Calif. 73) Assignee: Power Integrations, Inc., Mountain View, Calif. (21) Appl. No.: 41,994 22
United States Patent (19) Eklund (54) HIGH VOLTAGE MOS TRANSISTORS 75) Inventor: Klas H. Eklund, Los Gatos, Calif. 73) Assignee: Power Integrations, Inc., Mountain View, Calif. (21) Appl. No.: 41,994 22
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1. CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014
 (19) United States US 20140247226A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0247226A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) TOUCH DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. FABRICATING
(19) United States US 20140247226A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0247226A1 CHU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2014 (54) TOUCH DEVICE AND METHOD FOR (52) U.S. Cl. FABRICATING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,436,044 B1
 USOO643604.4B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wang (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR ADAPTIVE 6,282,963 B1 9/2001 Haider... 73/602 BEAMFORMER APODIZATION 6,312,384
USOO643604.4B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wang (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR ADAPTIVE 6,282,963 B1 9/2001 Haider... 73/602 BEAMFORMER APODIZATION 6,312,384
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,525,828 B1
 USOO6525828B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,525,828 B1 Grosskopf (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 25, 2003 (54) CONFOCAL COLOR 5,978,095 A 11/1999 Tanaami... 356/445 6,031,661. A 2/2000 Tanaami...
USOO6525828B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,525,828 B1 Grosskopf (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 25, 2003 (54) CONFOCAL COLOR 5,978,095 A 11/1999 Tanaami... 356/445 6,031,661. A 2/2000 Tanaami...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 200900.00432A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0000432 A1 CHEN (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2009 (54) TOOL HEAD STRUCTURE Publication Classification (51) Int.
US 200900.00432A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0000432 A1 CHEN (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2009 (54) TOOL HEAD STRUCTURE Publication Classification (51) Int.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,512,361 B1
 USOO6512361B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,512,361 B1 Becker (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 28, 2003 (54) 14/42-VOLTAUTOMOTIVE CIRCUIT 5,420.503 5/1995 Beha TESTER 5,517,183 A 5/1996 Bozeman,
USOO6512361B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,512,361 B1 Becker (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 28, 2003 (54) 14/42-VOLTAUTOMOTIVE CIRCUIT 5,420.503 5/1995 Beha TESTER 5,517,183 A 5/1996 Bozeman,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Seavey 11 Patent Number: 4,636,798 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 1987 54 (75) 73 21) 22 51 52 (58) MICROWAVE LENS FOR BEAM BROADENING WITH ANTENNA FEEDS Inventor: Assignee: Appl.
United States Patent (19) Seavey 11 Patent Number: 4,636,798 45 Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 1987 54 (75) 73 21) 22 51 52 (58) MICROWAVE LENS FOR BEAM BROADENING WITH ANTENNA FEEDS Inventor: Assignee: Appl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0052224A1 Yang et al. US 2005OO52224A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 10, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) QUIESCENT CURRENT CONTROL CIRCUIT
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,791,072 B1. Prabhu (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2004
 USOO6791072B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,791,072 B1 Prabhu (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FORMING 2001/0020671 A1 * 9/2001 Ansorge et al.... 250/208.1
USOO6791072B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,791,072 B1 Prabhu (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FORMING 2001/0020671 A1 * 9/2001 Ansorge et al.... 250/208.1
N St. Els"E"" (4) Atomy, Agent, or Firm Steina Brunda Garred &
 USOO6536045B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wilson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2003 (54) TEAR-OFF OPTICAL STACK HAVING 4,716,601. A 1/1988 McNeal... 2/434 PERPHERAL SEAL MOUNT 5,420,649
USOO6536045B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wilson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2003 (54) TEAR-OFF OPTICAL STACK HAVING 4,716,601. A 1/1988 McNeal... 2/434 PERPHERAL SEAL MOUNT 5,420,649
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,388,807 B1. Knebel et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002
 USOO6388807B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Knebel et al. () Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) CONFOCAL LASER SCANNING (56) References Cited MICROSCOPE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO6388807B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Knebel et al. () Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) CONFOCAL LASER SCANNING (56) References Cited MICROSCOPE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
u-2 INVENTOR Dec. 3, P. J. KIBLER 2,412,090 Filed Feb. 14, 1944 PAUL. J. KBLER ATTORNEY TURNSTILE ANTENNA TO TRANSMTTER OR RECEIVER
 Dec. 3, 1946. P. J. KIBLER TURNSTILE ANTENNA Filed Feb. 14, 1944 N TO TRANSMTTER T OR RECEIVER - u-2 TO TRANSMTTER OR RECEIVER INVENTOR PAUL. J. KBLER ATTORNEY Patented Dec. 3, 1946 UNITED STATES PATENT
Dec. 3, 1946. P. J. KIBLER TURNSTILE ANTENNA Filed Feb. 14, 1944 N TO TRANSMTTER T OR RECEIVER - u-2 TO TRANSMTTER OR RECEIVER INVENTOR PAUL. J. KBLER ATTORNEY Patented Dec. 3, 1946 UNITED STATES PATENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090146763A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0146763 A1 Hershtig (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 11, 2009 (54) HIGH Q SURFACE MOUNTTECHNOLOGY Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20090146763A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0146763 A1 Hershtig (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 11, 2009 (54) HIGH Q SURFACE MOUNTTECHNOLOGY Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O116153A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0116153 A1 Hataguchi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2005 (54) ENCODER UTILIZING A REFLECTIVE CYLINDRICAL SURFACE
(19) United States US 2005O116153A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0116153 A1 Hataguchi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2005 (54) ENCODER UTILIZING A REFLECTIVE CYLINDRICAL SURFACE
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Muchel 54) OPTICAL SYSTEM OF WARIABLE FOCAL AND BACK-FOCAL LENGTH (75) Inventor: Franz Muchel, Königsbronn, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73 Assignee: Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung, Heidenheim on
United States Patent (19) Muchel 54) OPTICAL SYSTEM OF WARIABLE FOCAL AND BACK-FOCAL LENGTH (75) Inventor: Franz Muchel, Königsbronn, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73 Assignee: Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung, Heidenheim on
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015 0028681A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0028681 A1 L (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 29, 2015 (54) MULTI-LEVEL OUTPUT CASCODE POWER (57) ABSTRACT STAGE (71)
(19) United States US 2015 0028681A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0028681 A1 L (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 29, 2015 (54) MULTI-LEVEL OUTPUT CASCODE POWER (57) ABSTRACT STAGE (71)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Querry et al. (54) (75) PHASE LOCKED LOOP WITH AUTOMATIC SWEEP Inventors: 73) Assignee: 21) (22 (51) (52) 58 56) Lester R. Querry, Laurel; Ajay Parikh, Gaithersburg, both of Md.
United States Patent (19) Querry et al. (54) (75) PHASE LOCKED LOOP WITH AUTOMATIC SWEEP Inventors: 73) Assignee: 21) (22 (51) (52) 58 56) Lester R. Querry, Laurel; Ajay Parikh, Gaithersburg, both of Md.
United States Patent to 11 3,998,002
 United States Patent to 11 Nathanson 45 Dec. 21, 1976 54 PANEL, HOLDER FOR SMALL STRUCTURES AND TOYS 76 Inventor: Albert Nathanson, 249-26 63rd Ave., Little Neck, N.Y. 11329 22 Filed: Jan. 29, 1975 (21
United States Patent to 11 Nathanson 45 Dec. 21, 1976 54 PANEL, HOLDER FOR SMALL STRUCTURES AND TOYS 76 Inventor: Albert Nathanson, 249-26 63rd Ave., Little Neck, N.Y. 11329 22 Filed: Jan. 29, 1975 (21
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1
 US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007
 US 20070228931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0228931 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) WHITE LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE Publication Classification
US 20070228931A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0228931 A1 Kim et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 4, 2007 (54) WHITE LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) Jawetz
 United States Patent (19) Jawetz 54 MOORING LOCATION SYSTEM 76) Inventor: Ira Jawetz, 9 New Harbor Rd., Eatons Neck, N.Y. 11768 (21) Appl. No.: 926,896 (22 Filed: Nov. 4, 1986 51 Int. Cl."... G08G 3/00;
United States Patent (19) Jawetz 54 MOORING LOCATION SYSTEM 76) Inventor: Ira Jawetz, 9 New Harbor Rd., Eatons Neck, N.Y. 11768 (21) Appl. No.: 926,896 (22 Filed: Nov. 4, 1986 51 Int. Cl."... G08G 3/00;
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,083,443 B1. Circosta et al. 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 27, 2011
 United States Patent USOO8083443B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,083,443 B1 Circosta et al. 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 27, 2011 9 (54) POCKET HOLE PLUG CUTTER 5,800,099 A * 9/1998 Cooper... 408.1 R 5,807,036
United States Patent USOO8083443B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 8,083,443 B1 Circosta et al. 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 27, 2011 9 (54) POCKET HOLE PLUG CUTTER 5,800,099 A * 9/1998 Cooper... 408.1 R 5,807,036
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 201302227 O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222702 A1 WU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) HEADSET, CIRCUIT STRUCTURE OF (52) U.S. Cl. MOBILE
(19) United States US 201302227 O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222702 A1 WU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) HEADSET, CIRCUIT STRUCTURE OF (52) U.S. Cl. MOBILE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
United States Patent to Rioux
 United States Patent to Rioux (54) THREE DIMENSIONAL COLOR IMAGING 75 Inventor: Marc Rioux, Ottawa, Canada 73) Assignee: National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa. Canada 21 Appl. No. 704,092 22 Filed:
United States Patent to Rioux (54) THREE DIMENSIONAL COLOR IMAGING 75 Inventor: Marc Rioux, Ottawa, Canada 73) Assignee: National Research Council of Canada, Ottawa. Canada 21 Appl. No. 704,092 22 Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 O187416A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0187416A1 Bakker (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) SMART DRIVER FOR FLYBACK Publication Classification CONVERTERS
US 2011 O187416A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0187416A1 Bakker (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) SMART DRIVER FOR FLYBACK Publication Classification CONVERTERS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 200901 86.181A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0186181 A1 Mase (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 23, 2009 (54) SCREEN PROTECTOR FILM WITH (30) Foreign Application Priority
(19) United States US 200901 86.181A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0186181 A1 Mase (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 23, 2009 (54) SCREEN PROTECTOR FILM WITH (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) United States Patent
 US007 153067B2 (12) United States Patent GreenW00d et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2006 (54) ROTARY CUTTING TOOL HAVING MULTIPLE HELICAL CUTTING EDGES WITH DIFFERING HELIX ANGLES (76)
US007 153067B2 (12) United States Patent GreenW00d et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 2006 (54) ROTARY CUTTING TOOL HAVING MULTIPLE HELICAL CUTTING EDGES WITH DIFFERING HELIX ANGLES (76)
United States Patent (19) Lin
 United States Patent (19) Lin 11) 45) Dec. 22, 1981 54) (76) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) BUILDING BLOCK SET Inventor: Wen-Ping Lin, 30, Chien-Yung St., Taichung, Taiwan Appl. No.: 187,618 Filed: Sep. 15,
United States Patent (19) Lin 11) 45) Dec. 22, 1981 54) (76) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) BUILDING BLOCK SET Inventor: Wen-Ping Lin, 30, Chien-Yung St., Taichung, Taiwan Appl. No.: 187,618 Filed: Sep. 15,
us Al (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Li et al. (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ Al (43) Pub. Date: Aug.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Li et al. 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 us 20040150613Al (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150613
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication Li et al. 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 us 20040150613Al (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150613
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,923,417 Leis (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 13, 1999
 USOO5923417A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Leis (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 13, 1999 54 SYSTEM FOR DETERMINING THE SPATIAL OTHER PUBLICATIONS POSITION OF A TARGET Original Instruments Product
USOO5923417A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Leis (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 13, 1999 54 SYSTEM FOR DETERMINING THE SPATIAL OTHER PUBLICATIONS POSITION OF A TARGET Original Instruments Product
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201702O8396A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0208396 A1 Dronenburg et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 20, 2017 (54) ACOUSTIC ENERGY HARVESTING DEVICE (52) U.S.
(19) United States US 201702O8396A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0208396 A1 Dronenburg et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 20, 2017 (54) ACOUSTIC ENERGY HARVESTING DEVICE (52) U.S.
