Recognizing the source of the lamp
|
|
|
- Beatrix Carpenter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Recognizing the source of the lamp In an earlier publication How illuminated is the light, a new pictogram is proposed on the packaging of lamps. The motives behind that are substantiated below. Preliminary draft pictogram light from heat light from discharge The usual names in the world of lamps are characterized by a series of phenomena which coincide with the form or functioning of the lamp. Ball lamp, incandescent lamp, candle lamp, fluorescent lamp, mercury-vapor lamp, metal-halide lamp, low and high pressure sodium lamp, LED lamp etc. are characteristic names which have been formed to designate these lamps. Even type numbers of some suppliers can describe the lamp type: TL-lamp, Son-T lamp, etc. That need not change, the addition of the pictogram is only intended to provide a means to distinguish between the different sources of externally similar lamps. The term light source indicates the source also characterizes an important element of the lamp. A distinction between lamps with light from heat and light from discharge constitutes a basic, original classification of lamps. An almost forgotten optical experiment can show a surprising aspect of the light source. When a projector projects a simple parallel beam of light, the filaments of the light source can appear on the screen when a magnifying glass is placed in the beam at the focal distance. This experiment is so surprising because it shows that the light of the projector comprises the image of the source that remains visible. Without external mirrors or other resources, but with a simple magnifying glass, the filaments become visible on the
2 screen in the light surface. The light, which is invisible itself, apparently contains the image of the source behind the lens of the projector that one never sees without the magnifying glass! Light from heat As long as mankind can remember, it has used light from heat. With fires, torches, oil- and gas lamps the nightly darkness has been conquered until the nineteenth century. The appearance of electricity made the incandescent lamp possible, with a filament which still generated light by heat. Light from heat invokes comfortable feelings in us. With candlelight, a burning wood fire in an open fireplace or the warmth of the sunlight in the right dosage generally pleasantness can be experienced. Light from discharge Not long ago in human history, in the course of the 20th century, the first discharge lamps appeared. The first were carbon arc lamps, later came mercury vapor and fluorescent lamps. In these lamps light and electromagnetic radiation is emitted when in a supercharged state an atomic system returns to its original state. The nature of the radiation and the wavelengths can differ very much per substance, so that the source can be recognized in the spectral composition. Here too, the source remains visible even till in the light of stars and planets, which is worked with intensively in spectrographic analysis and astronomy. Infrared and ultra violet light Light from heat is characterized mainly by a relative substantial part of infrared and near infrared radiation (750 nm 10 ꙡm ) besides the visible light for the eye ( nm). Aside from the visible light, light from heat also produces short ultra-violet waves ( nm) which are potentially transformed by fluorescence processes in the visible area. The tones of both light sources surround the natural sunlight on two sides, so to speak. 1 When the total human body is viewed as an instrument for the light then it is remarkable that infrared light penetrates the skin deeply whereas ultra violet light only gets stuck at the surface. Penetration by wavelength of the skin 2
3 Within the skin the infrared component takes care of multiple complex cyclic cell processes. Four other optical sensors are discovered in the eye beside the wellknown optical sensitive rods and cylinders, which has specific effects on countless bio-chemical and hormonal processes in the body. The infrared- and ultraviolet light are both responsible for the total wellness of mankind. A day at the beach, a holiday in the sun, a visit to the (infrared) sauna and the quick healing of a wound in the daylight shows every clear-thinking human being, even those without scientific and bio-chemical backgrounds, the very special function of light for mankind. Partial, excessive dosage of infrared- and ultraviolet light furnish adverse phenomena such as burning, skin cancer and eye deflection, etc. Source as image The sun, which creates the conditions for life on earth, contains in her light a power, which we try to understand in her wave character in a materialistic way as a vibration. In her life and form-creating character, this light still holds an unsolved mystery of life. Every dewdrop, that the translucent round shape of a magnifying glass makes with his cohesion, reflects the sun as light source. Which effects of the source carries the also invisible artificial light? Beside a candle and the campfire everybody experiences a change of mood, so that many restaurants gladly offer their clients hearths. Light from heat, however, is different from light from discharge. This source also influences our mood, but with the blue light components it cannot give us this warming mood and creates much more a chilly atmosphere. The question is whether fluorescent processes, which paint the UV light component in warmer hues, can also lead to the same warmness feeling as the candle and the fire do. As opposed to the development of the halogen incandescent lamp the fluorescent lamps with the warm color temperatures have not been able to conquer our living rooms in the past decades. The heat source as well as the discharge source both have their counterparts in nature with fire and lightning. As such they do not ask for a judgment of value in the sense of good or bad, but they do evoke a basis for a mood of the human sensory system. Epileptics and highly sensitive people will therefore experience these sources in a different way than other people. However, a recent study by Dr. U. Geier also shows the remarkable differences in learning in teaching rooms of same classes equipped with LED and with halogen incandescent lamps. 3 The errors in a dictation with LED lighting were 310% more numerous than when halogen incandescent lighting was used. Copying of text from a blackboard also delivered an alarming increase in errors of 313%. The impressions of comparing the installations were described in a free expression as follows 4 :
4 Of course such scientific research asks of course for verification and repetition, but the very scarce financial means for that uphold a wrongful perception of reality by many people, that light from discharge evokes a different mood than light from heat. The normative eye function in light technology for the visibility of objects with illumination intensity masks also these differences in experiences. Consumer market Now that the energy saving LED alternatives of the halogen incandescent lamps are actually produced en masse with a great diversity and can be found in stores, the unsuspected consumer does not possess the information which is vital when he makes his choice. It is inconceivable that the LED development should not find its justified application with the consumer. It is equally inconceivable that special applications in children s rooms or study rooms or as a reading lamp, do not have the same qualities as light from heat. The partial promotion of one of both light sources is not justified for the well-advised and justified decision of every individual user in his individual application. Essen-Wildert Henk Stolk President Obtrusive Light expert group Nederlandse Stichting Voor Verlichtingskunde (on a personal basis)
5 1 For spectral comparison sun/incadescent lamp/led H. Stolk Wie heeft de kennis van wetten over licht? image Alexander Wunsch Light Symposium Wismar Alexander Wunsch Light Symposium Wismar Uwe Geier WirkSensorik GmbH Light Symposium Wismar Uwe Geier WirkSensorik GmbH Light Symposium Wismar
Designing with daylighting
 Designing with daylighting Pharmacy Faculty, Portugal central atrium 4-windows elements small apertures on vaults east and west overhangs Figure by MIT OCW. Designing with daylighting Collège La Vanoise,
Designing with daylighting Pharmacy Faculty, Portugal central atrium 4-windows elements small apertures on vaults east and west overhangs Figure by MIT OCW. Designing with daylighting Collège La Vanoise,
Westinghouse. Lamps 101
 Westinghouse Lamps 101 Objectives Explain common lighting terminology to your customers Examine color temperature and explain the Kelvin scale List features and benefits of various lamp types, including:
Westinghouse Lamps 101 Objectives Explain common lighting terminology to your customers Examine color temperature and explain the Kelvin scale List features and benefits of various lamp types, including:
17-1 Electromagnetic Waves
 17-1 Electromagnetic Waves transfers energy called electromagnetic radiation no medium needed transverse some electrical, some magnetic properties speed is 300,000,000 m/s; nothing is faster; at this speed
17-1 Electromagnetic Waves transfers energy called electromagnetic radiation no medium needed transverse some electrical, some magnetic properties speed is 300,000,000 m/s; nothing is faster; at this speed
LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points
 WRITE ON SCANTRON WITH NUMBER 2 PENCIL DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or
WRITE ON SCANTRON WITH NUMBER 2 PENCIL DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or
Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 13 Electromagnetic Waves 13.1 Gamma Rays Gamma rays have a very short wavelength and are very penetrating. They are produced by radioactive substances and are very dangerous to humans unless used
Chapter 13 Electromagnetic Waves 13.1 Gamma Rays Gamma rays have a very short wavelength and are very penetrating. They are produced by radioactive substances and are very dangerous to humans unless used
Electromagnetic Waves
 Electromagnetic Waves What is an Electromagnetic Wave? An EM Wave is a disturbance that transfers energy through a field. A field is a area around an object where the object can apply a force on another
Electromagnetic Waves What is an Electromagnetic Wave? An EM Wave is a disturbance that transfers energy through a field. A field is a area around an object where the object can apply a force on another
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION METHOD
 ABSTRACT This research project aims to investigate and illustrate the effects a light source s spectral distribution and colour temperature has on photographic image colour reproduction, and how this often
ABSTRACT This research project aims to investigate and illustrate the effects a light source s spectral distribution and colour temperature has on photographic image colour reproduction, and how this often
LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola LIGHT a form of radiant energy from natural sources and artificial sources. travels in the form of an electromagnetic wave, so it has
LIGHT AND LIGHTING FUNDAMENTALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola LIGHT a form of radiant energy from natural sources and artificial sources. travels in the form of an electromagnetic wave, so it has
Topic 1 - What is Light? 1. Radiation is the type of energy transfer which does not require... A matter B heat C waves D light
 Grade 8 Unit 1 Test Student Class Topic 1 - What is Light? 1. Radiation is the type of energy transfer which does not require... A matter B heat C waves D light 2. Light-producing technologies, such as
Grade 8 Unit 1 Test Student Class Topic 1 - What is Light? 1. Radiation is the type of energy transfer which does not require... A matter B heat C waves D light 2. Light-producing technologies, such as
Optics & Light. See What I m Talking About. Grade 8 - Science OPTICS - GRADE 8 SCIENCE 1
 Optics & Light See What I m Talking About Grade 8 - Science OPTICS - GRADE 8 SCIENCE 1 Overview In this cluster, students broaden their understanding of how light is produced, transmitted, and detected.
Optics & Light See What I m Talking About Grade 8 - Science OPTICS - GRADE 8 SCIENCE 1 Overview In this cluster, students broaden their understanding of how light is produced, transmitted, and detected.
Form 4: Integrated Science Notes TOPIC NATURAL AND ARTIFICIAL LIGHTING
 Form 4: Integrated Science Notes TOPIC NATURAL AND ARTIFICIAL LIGHTING OBJECTIVES: 1. Define natural and artificial lighting. 2. Use of fluorescent and filament lamps. 3. Investigation of white light and
Form 4: Integrated Science Notes TOPIC NATURAL AND ARTIFICIAL LIGHTING OBJECTIVES: 1. Define natural and artificial lighting. 2. Use of fluorescent and filament lamps. 3. Investigation of white light and
Basic Lighting Design Seminar
 Basic Lighting Design Seminar GEWISS GULF - Dubai Date: 29 th May 2009 GEWISS GULF welcomes all members of IIEE. PROGRAM: Basic Lighting Design Seminar 1. BASIC LIGHTING PRINCIPLES 2. INDUSTRIAL& COMMERCIAL
Basic Lighting Design Seminar GEWISS GULF - Dubai Date: 29 th May 2009 GEWISS GULF welcomes all members of IIEE. PROGRAM: Basic Lighting Design Seminar 1. BASIC LIGHTING PRINCIPLES 2. INDUSTRIAL& COMMERCIAL
National 3 Physics Waves and Radiation. 1. Wave Properties
 1. Wave Properties What is a wave? Waves are a way of transporting energy from one place to another. They do this through some form of vibration. We see waves all the time, for example, ripples on a pond
1. Wave Properties What is a wave? Waves are a way of transporting energy from one place to another. They do this through some form of vibration. We see waves all the time, for example, ripples on a pond
H22: Lamps and Colour
 page 1 of 5 H22: Lamps and Colour James H Nobbs Colour4Free.org Each type of light source provides a different distribution of power within the spectrum. For example, daylight has more power in the blue/green
page 1 of 5 H22: Lamps and Colour James H Nobbs Colour4Free.org Each type of light source provides a different distribution of power within the spectrum. For example, daylight has more power in the blue/green
Answers to Chapter 11
 Answers to Chapter 11 11.1 What is Light? #1 Radiation (light) does NOT need a medium to travel through. Conduction needs a solid medium and convection needs liquid or gas medium to travel through. #2
Answers to Chapter 11 11.1 What is Light? #1 Radiation (light) does NOT need a medium to travel through. Conduction needs a solid medium and convection needs liquid or gas medium to travel through. #2
Uses of Electromagnetic Waves
 Uses of Electromagnetic Waves 1 of 42 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Uses of Electromagnetic Waves 2 of 42 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are radio waves? 3 of 42 Boardworks Ltd 2016 The broadcast of every radio and television
Uses of Electromagnetic Waves 1 of 42 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Uses of Electromagnetic Waves 2 of 42 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are radio waves? 3 of 42 Boardworks Ltd 2016 The broadcast of every radio and television
INDEX 1.- LIGHT. DEFINITION 2.- TYPES OF LIGHT
 LIGHT INDEX 1.- LIGHT. DEFINITION 2.- TYPES OF LIGHT a.- NATURAL LIGHT b.- ARTIFICIAL LIGHT 3.- THE CONCEPT OF LIGHT AS A GRAPHIC SYMBOL. TONE AND VALUE 4.- SHADOWS. TYPES OF SHADOWS USE OF SHADOWS 5.-
LIGHT INDEX 1.- LIGHT. DEFINITION 2.- TYPES OF LIGHT a.- NATURAL LIGHT b.- ARTIFICIAL LIGHT 3.- THE CONCEPT OF LIGHT AS A GRAPHIC SYMBOL. TONE AND VALUE 4.- SHADOWS. TYPES OF SHADOWS USE OF SHADOWS 5.-
Section 18.3 Behavior of Light
 Light and Materials When light hits an object it can be Section 18.3 Behavior of Light Light and Materials Objects can be classified as Transparent Translucent Opaque Transparent, Translucent, Opaque Transparent
Light and Materials When light hits an object it can be Section 18.3 Behavior of Light Light and Materials Objects can be classified as Transparent Translucent Opaque Transparent, Translucent, Opaque Transparent
Light sources. Daylight Electric light. Daylight source direct sunlight or diffuse skylight) Indirect light reflected or modified from its primary
 Light sources Daylight Electric light Daylight source direct sunlight or diffuse skylight) Indirect light reflected or modified from its primary Artificial light source incandescent lamps (including tungsten-halogen
Light sources Daylight Electric light Daylight source direct sunlight or diffuse skylight) Indirect light reflected or modified from its primary Artificial light source incandescent lamps (including tungsten-halogen
Light can be described as a wave of Electromagnetic Radiation, located near the center of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
 LED Color Basics The Spectrum Light can be described as a wave of Electromagnetic Radiation, located near the center of the Electromagnetic Spectrum Different wavelengths are interpreted by the eye as
LED Color Basics The Spectrum Light can be described as a wave of Electromagnetic Radiation, located near the center of the Electromagnetic Spectrum Different wavelengths are interpreted by the eye as
INFS 423 Preservation of Information Resources
 INFS 423 Preservation of Information Resources Lecture 4 Deterioration by Light Lecturer(s): Prof. Harry Akussah & Mr. Michael Allotey Contact Information: mallotey@ug.edu.gh, hakussah@ug.edu.gh School
INFS 423 Preservation of Information Resources Lecture 4 Deterioration by Light Lecturer(s): Prof. Harry Akussah & Mr. Michael Allotey Contact Information: mallotey@ug.edu.gh, hakussah@ug.edu.gh School
How can we "see" using the Infrared?
 The Infrared Infrared light lies between the visible and microwave portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Infrared light has a range of wavelengths, just like visible light has wavelengths that range
The Infrared Infrared light lies between the visible and microwave portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Infrared light has a range of wavelengths, just like visible light has wavelengths that range
CHAPTER VII ELECTRIC LIGHTING
 CHAPTER VII ELECTRIC LIGHTING 7.1 INTRODUCTION Light is a form of wave energy, with wavelengths to which the human eye is sensitive. The radiant-energy spectrum is shown in Figure 7.1. Light travels through
CHAPTER VII ELECTRIC LIGHTING 7.1 INTRODUCTION Light is a form of wave energy, with wavelengths to which the human eye is sensitive. The radiant-energy spectrum is shown in Figure 7.1. Light travels through
Basic Lighting Terms Glossary (Terms included in the basic lighting course are italicized and underlined)
 Basic Lighting Terms Glossary (Terms included in the basic lighting course are italicized and underlined) Accent Lighting Directional lighting to emphasize a particular object or draw attention to a display
Basic Lighting Terms Glossary (Terms included in the basic lighting course are italicized and underlined) Accent Lighting Directional lighting to emphasize a particular object or draw attention to a display
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION
 THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE PHYSICS A Electrons, Waves and Photons G482 *OCE/23017* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: Data, Formulae and Relationships
THIS IS A NEW SPECIFICATION ADVANCED SUBSIDIARY GCE PHYSICS A Electrons, Waves and Photons G482 *OCE/23017* Candidates answer on the Question Paper OCR Supplied Materials: Data, Formulae and Relationships
UNIT 3 LIGHT AND SOUND
 NIT 3 LIGHT AND SOUND Primary Colours Luminous Sources of Light Colours sources is divided Secondary Colours includes Illıminated Sources of Light LIGHT Illumination is form Travels in Spaces Shadow Reflection
NIT 3 LIGHT AND SOUND Primary Colours Luminous Sources of Light Colours sources is divided Secondary Colours includes Illıminated Sources of Light LIGHT Illumination is form Travels in Spaces Shadow Reflection
Chapter 23 Study Questions Name: Class:
 Chapter 23 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When you look at yourself in a plane mirror, you
Chapter 23 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When you look at yourself in a plane mirror, you
Application Notes Photoconductive Cells
 APPLICATION NOTE #1 Light - Some Physical Basics Light is produced by the release of energy from the atoms of a material when they are excited by heat, chemical reaction or other means. Light travels through
APPLICATION NOTE #1 Light - Some Physical Basics Light is produced by the release of energy from the atoms of a material when they are excited by heat, chemical reaction or other means. Light travels through
If you forgot about the homework due today: textbook page 542 data analysis questions, I'll collect them tomorrow along with binder pages
 Light & the Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic waves > transverse waves consisting of changing electric & magnetic fields; carry energy from place to place; differ from mechanical
Light & the Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic waves > transverse waves consisting of changing electric & magnetic fields; carry energy from place to place; differ from mechanical
Color Temperature Color temperature is distinctly different from color and also it is different from the warm/cold contrast described earlier.
 Color Temperature Color temperature is distinctly different from color and also it is different from the warm/cold contrast described earlier. Color temperature describes the actual temperature of a black
Color Temperature Color temperature is distinctly different from color and also it is different from the warm/cold contrast described earlier. Color temperature describes the actual temperature of a black
LAB 11 Color and Light
 Cabrillo College Name LAB 11 Color and Light Bring colored pencils or crayons to lab if you already have some. What to learn and explore In the previous lab, we discovered that some sounds are simple,
Cabrillo College Name LAB 11 Color and Light Bring colored pencils or crayons to lab if you already have some. What to learn and explore In the previous lab, we discovered that some sounds are simple,
Term Info Picture. A wave that has both electric and magnetic fields. They travel through empty space (a vacuum).
 Waves S8P4. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to support the claim that electromagnetic (light) waves behave differently than mechanical (sound) waves. A. Ask questions to develop explanations
Waves S8P4. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate information to support the claim that electromagnetic (light) waves behave differently than mechanical (sound) waves. A. Ask questions to develop explanations
Chapter 9: Light, Colour and Radiant Energy. Passed a beam of white light through a prism.
 Chapter 9: Light, Colour and Radiant Energy Where is the colour in sunlight? In the 17 th century (1600 s), Sir Isaac Newton conducted a famous experiment. Passed a beam of white light through a prism.
Chapter 9: Light, Colour and Radiant Energy Where is the colour in sunlight? In the 17 th century (1600 s), Sir Isaac Newton conducted a famous experiment. Passed a beam of white light through a prism.
Exercise 8: Interference and diffraction
 Physics 223 Name: Exercise 8: Interference and diffraction 1. In a two-slit Young s interference experiment, the aperture (the mask with the two slits) to screen distance is 2.0 m, and a red light of wavelength
Physics 223 Name: Exercise 8: Interference and diffraction 1. In a two-slit Young s interference experiment, the aperture (the mask with the two slits) to screen distance is 2.0 m, and a red light of wavelength
simply providing that illuminance is not enough to ensure good quality lighting (SLL 2012)
 simply providing that illuminance is not enough to ensure good quality lighting (SLL 2012) Light is the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum The main source of our natural light is the sun, which
simply providing that illuminance is not enough to ensure good quality lighting (SLL 2012) Light is the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum The main source of our natural light is the sun, which
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals
 Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 13: LIGHT WAVES This lecture will help you understand: Electromagnetic Spectrum Transparent and Opaque Materials Color Why the Sky is Blue, Sunsets are Red, and
Conceptual Physics Fundamentals Chapter 13: LIGHT WAVES This lecture will help you understand: Electromagnetic Spectrum Transparent and Opaque Materials Color Why the Sky is Blue, Sunsets are Red, and
Here is a glossary of terms about Lighting that is great knowledge to understand when growing cannabis, whether indoors our outside in a greenhouse.
 Here is a glossary of terms about Lighting that is great knowledge to understand when growing cannabis, whether indoors our outside in a greenhouse. AMPERE (AMP) - The unit used to measure the strength
Here is a glossary of terms about Lighting that is great knowledge to understand when growing cannabis, whether indoors our outside in a greenhouse. AMPERE (AMP) - The unit used to measure the strength
the physics of different light sources incandescence and blackbody radiation the concept of photons
 Notes for teachers on module 06: Making light The generation of a photon is not just a physical effect. Ever since the first beacon fires were lit in caves, the making of light has been important for our
Notes for teachers on module 06: Making light The generation of a photon is not just a physical effect. Ever since the first beacon fires were lit in caves, the making of light has been important for our
Ultraviolet Visible Infrared Instrumentation
 Ultraviolet Visible Infrared Instrumentation Focus our attention on measurements in the UV-vis region of the EM spectrum Good instrumentation available Very widely used techniques Longstanding and proven
Ultraviolet Visible Infrared Instrumentation Focus our attention on measurements in the UV-vis region of the EM spectrum Good instrumentation available Very widely used techniques Longstanding and proven
Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II
 Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II 3.1 Applications of the Quantum Model of Radiant Energy 1) Photon Absorption and Emission 12/29/04 The diagrams below illustrate an atomic nucleus
Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II 3.1 Applications of the Quantum Model of Radiant Energy 1) Photon Absorption and Emission 12/29/04 The diagrams below illustrate an atomic nucleus
G1 THE NATURE OF EM WAVES AND LIGHT SOURCES
 G1 THE NATURE OF EM WAVES AND LIGHT SOURCES G2 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS HW/Study Packet Required: READ Tsokos, pp 598-620 SL/HL Supplemental: Hamper, pp 411-450 DO Questions p 605 #1,3 pp 621-623 #6,8,15,18,19,24,26
G1 THE NATURE OF EM WAVES AND LIGHT SOURCES G2 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS HW/Study Packet Required: READ Tsokos, pp 598-620 SL/HL Supplemental: Hamper, pp 411-450 DO Questions p 605 #1,3 pp 621-623 #6,8,15,18,19,24,26
THE EXAMINATION OF WORKS OF ART USING ELECTROMAGNETIC RAYS
 THE EXAMINATION OF WORKS OF ART USING ELECTROMAGNETIC RAYS A work of art is assessed, judged and commented on by a person viewing the object, itself dependant on the presence and intensity of light that
THE EXAMINATION OF WORKS OF ART USING ELECTROMAGNETIC RAYS A work of art is assessed, judged and commented on by a person viewing the object, itself dependant on the presence and intensity of light that
LASERS. & Protective Glasses. Your guide to Lasers and the Glasses you need to wear for protection.
 LASERS & Protective Glasses Your guide to Lasers and the Glasses you need to wear for protection. FACTS Light & Wavelengths Light is a type of what is called electromagnetic radiation. Radio waves, x-rays,
LASERS & Protective Glasses Your guide to Lasers and the Glasses you need to wear for protection. FACTS Light & Wavelengths Light is a type of what is called electromagnetic radiation. Radio waves, x-rays,
Optics Review (Chapters 11, 12, 13)
 Optics Review (Chapters 11, 12, 13) Complete the following questions in preparation for your test on FRIDAY. The notes that you need are in italics. Try to answer it on your own first, then check with
Optics Review (Chapters 11, 12, 13) Complete the following questions in preparation for your test on FRIDAY. The notes that you need are in italics. Try to answer it on your own first, then check with
Note 2 Electromagnetic waves N2/EMWAVES/PHY/XII/CHS2012
 ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Electromagnetic waves include visible light waves, X-rays, gamma rays, radio waves, microwaves, ultraviolet and infrared waves. The classification of em waves according to frequency
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM Electromagnetic waves include visible light waves, X-rays, gamma rays, radio waves, microwaves, ultraviolet and infrared waves. The classification of em waves according to frequency
HSL HUMAN SUN LIGHTING
 HSL HUMAN SUN LIGHTING Innovative lighting technology Lighting to protect vision Contents Overview Principle of lighting to protect vision Advantages of the new lighting to protect vision Patents relating
HSL HUMAN SUN LIGHTING Innovative lighting technology Lighting to protect vision Contents Overview Principle of lighting to protect vision Advantages of the new lighting to protect vision Patents relating
Illumination Guide. Choosing the right lighting to evaluate products
 Illumination Guide Choosing the right lighting to evaluate products Illumination Guide Companies that are concerned with the color quality of their products may use sophisticated instruments to make sure
Illumination Guide Choosing the right lighting to evaluate products Illumination Guide Companies that are concerned with the color quality of their products may use sophisticated instruments to make sure
HOME SCIENCE CHAPTER 3: LIGHTING IN THE HOME Class: X
 HOME SCIENCE CHAPTER 3: LIGHTING IN THE HOME Class: X 2017-18 Answer the following questions. 1 What is a foot candle? Ans Light is usually measured in terms of Foot candles. A Foot Candle is the degree
HOME SCIENCE CHAPTER 3: LIGHTING IN THE HOME Class: X 2017-18 Answer the following questions. 1 What is a foot candle? Ans Light is usually measured in terms of Foot candles. A Foot Candle is the degree
Light Transmission and Reflectance
 T E C H N I C A L D A T A CYRO Industries 279 Interpace Parkway Parsippany, NJ 07054 www.cyro.com Light Transmission and Reflectance Light and Radiation Light or electromagnetic radiation can be divided
T E C H N I C A L D A T A CYRO Industries 279 Interpace Parkway Parsippany, NJ 07054 www.cyro.com Light Transmission and Reflectance Light and Radiation Light or electromagnetic radiation can be divided
Test 1: Example #2. Paul Avery PHY 3400 Feb. 15, Note: * indicates the correct answer.
 Test 1: Example #2 Paul Avery PHY 3400 Feb. 15, 1999 Note: * indicates the correct answer. 1. A red shirt illuminated with yellow light will appear (a) orange (b) green (c) blue (d) yellow * (e) red 2.
Test 1: Example #2 Paul Avery PHY 3400 Feb. 15, 1999 Note: * indicates the correct answer. 1. A red shirt illuminated with yellow light will appear (a) orange (b) green (c) blue (d) yellow * (e) red 2.
28 Color. The colors of the objects depend on the color of the light that illuminates them.
 The colors of the objects depend on the color of the light that illuminates them. Color is in the eye of the beholder and is provoked by the frequencies of light emitted or reflected by things. We see
The colors of the objects depend on the color of the light that illuminates them. Color is in the eye of the beholder and is provoked by the frequencies of light emitted or reflected by things. We see
Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color
 Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. What causes color? What causes reflection? What causes color?
Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. What causes color? What causes reflection? What causes color?
Colorado State Standards Mathematics Standards 3.4 Science Standard 1, 2, 4, 5
 Lesson Summary In this activity, students build and decorate their own spectrographs using simple materials and holographic diffraction gratings. After building the spectrographs, they observe the spectra
Lesson Summary In this activity, students build and decorate their own spectrographs using simple materials and holographic diffraction gratings. After building the spectrographs, they observe the spectra
Colours Learning Outcomes
 1 Colours Learning Outcomes Associate the wavelength of light with its colour. Describe the electromagnetic spectrum in terms of frequency and wavelength. Detect UV and IR radiation. Discuss UV radiation
1 Colours Learning Outcomes Associate the wavelength of light with its colour. Describe the electromagnetic spectrum in terms of frequency and wavelength. Detect UV and IR radiation. Discuss UV radiation
Colours Learning Outcomes. Colours Learning Outcomes. Electromagnetic Spectrum
 by Abstruse Goose CC-BY-NC-3.0 1 Colours Learning Outcomes Associate the wavelength of light with its colour. Describe the electromagnetic spectrum in terms of frequency and wavelength. Detect UV and IR
by Abstruse Goose CC-BY-NC-3.0 1 Colours Learning Outcomes Associate the wavelength of light with its colour. Describe the electromagnetic spectrum in terms of frequency and wavelength. Detect UV and IR
Bulletin Post. Metamerism and Illuminants C O A T S S E W I N G S O L U T I O N S. Contents. Introduction. What is Metamerism? Kinds of Metamerism
 C O A T S S E W I N G S O L U T I O N S Metamerism and Illuminants Contents Introduction What is Metamerism? Kinds of Metamerism Importance of Light in Metamerism What are Illuminants? What is the difference
C O A T S S E W I N G S O L U T I O N S Metamerism and Illuminants Contents Introduction What is Metamerism? Kinds of Metamerism Importance of Light in Metamerism What are Illuminants? What is the difference
LIGHT & COLOR. Thoughts on Color
 LIGHT & COLOR www.physics.ohio-state.edu/~gilmore/images/collection/misc/prism.gif Ball State Architecture ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS 1 Grondzik 1 Thoughts on Color I fly on the breeze of my mind and I pour
LIGHT & COLOR www.physics.ohio-state.edu/~gilmore/images/collection/misc/prism.gif Ball State Architecture ENVIRONMENTAL SYSTEMS 1 Grondzik 1 Thoughts on Color I fly on the breeze of my mind and I pour
Light, Color, Spectra 05/30/2006. Lecture 17 1
 What do we see? Light Our eyes can t t detect intrinsic light from objects (mostly infrared), unless they get red hot The light we see is from the sun or from artificial light When we see objects, we see
What do we see? Light Our eyes can t t detect intrinsic light from objects (mostly infrared), unless they get red hot The light we see is from the sun or from artificial light When we see objects, we see
Vision Lighting Seminar
 Creators of Evenlite Vision Lighting Seminar Daryl Martin Midwest Sales & Support Manager Advanced illumination 734-213 213-13121312 dmartin@advill.com www.advill.com 2005 1 Objectives Lighting Source
Creators of Evenlite Vision Lighting Seminar Daryl Martin Midwest Sales & Support Manager Advanced illumination 734-213 213-13121312 dmartin@advill.com www.advill.com 2005 1 Objectives Lighting Source
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND LIGHT. Physics 5 th Six Weeks
 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND LIGHT Physics 5 th Six Weeks What are Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic Waves Sound and water waves are examples of waves resulting from energy being transferred from particle
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND LIGHT Physics 5 th Six Weeks What are Electromagnetic Waves Electromagnetic Waves Sound and water waves are examples of waves resulting from energy being transferred from particle
Energy Efficient Lighting
 Energy Efficient Lighting Watt You Need To Know Tuesday, October 8th, 2013 1:00 PM Presented By: Bryan Heitzmann, Training & Edu. Dev. Specialist Pennsylvania Housing Research Center www.engr.psu.edu/phrc
Energy Efficient Lighting Watt You Need To Know Tuesday, October 8th, 2013 1:00 PM Presented By: Bryan Heitzmann, Training & Edu. Dev. Specialist Pennsylvania Housing Research Center www.engr.psu.edu/phrc
07-Lighting Concepts. EE570 Energy Utilization & Conservation Professor Henry Louie
 07-Lighting Concepts EE570 Energy Utilization & Conservation Professor Henry Louie 1 Overview Light Luminosity Function Lumens Candela Illuminance Luminance Design Motivation Lighting comprises approximately
07-Lighting Concepts EE570 Energy Utilization & Conservation Professor Henry Louie 1 Overview Light Luminosity Function Lumens Candela Illuminance Luminance Design Motivation Lighting comprises approximately
Competitive Analysis, Color Rendering in White Light
 Comparing Metal Halide, Fluorescent, and Solid State Technologies Jim Dilbeck, May, 2012 Scope This study compares the color rendition characteristics of the three most common commercial lighting technologies;
Comparing Metal Halide, Fluorescent, and Solid State Technologies Jim Dilbeck, May, 2012 Scope This study compares the color rendition characteristics of the three most common commercial lighting technologies;
THE CANDELA - UNIT OF LUMINOUS INTENSITY
 THE CANDELA - UNIT OF LUMINOUS INTENSITY Light is that part of the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation that the human eye can see. It lies between about 400 and 700 nanometers. All the units for measuring
THE CANDELA - UNIT OF LUMINOUS INTENSITY Light is that part of the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation that the human eye can see. It lies between about 400 and 700 nanometers. All the units for measuring
Sensory Room. Policy for. Vicarage School
 Sensory Room Policy for Vicarage School 2016-17 (Reviewed October 2016) Contents. 1) Rationale. 2) Responsible Person Details & Responsibilities. 3) Philosophy of the Room. 4) Description of Equipment
Sensory Room Policy for Vicarage School 2016-17 (Reviewed October 2016) Contents. 1) Rationale. 2) Responsible Person Details & Responsibilities. 3) Philosophy of the Room. 4) Description of Equipment
Science Focus 8. Light and Optical Systems. Pop Quiz Master (5 questions) for each Topic A C B D C C B C C A D B C A B B C C A C A C D B A C B B C D
 Science Focus 8 Pop Quiz Master (5 questions) for each Topic Light and Optical Systems Answer Key Science Focus 8 Questions Topics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Topic 1 - What is Light? A C B D C Topic 2 Reflection C
Science Focus 8 Pop Quiz Master (5 questions) for each Topic Light and Optical Systems Answer Key Science Focus 8 Questions Topics 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Topic 1 - What is Light? A C B D C Topic 2 Reflection C
THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR
 THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR Colour can be described as a light wavelength coming from a light source striking the surface of an object which in turns reflects the incoming light from were it is received by the
THE SCIENCE OF COLOUR Colour can be described as a light wavelength coming from a light source striking the surface of an object which in turns reflects the incoming light from were it is received by the
Human Retina. Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve
 I am Watching YOU!! Human Retina Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve Human Vision Optical Antennae: Rods & Cones Rods: Intensity Cones: Color Energy of Light 6 10 ev 10 ev 4 1 2eV 40eV KeV MeV Energy
I am Watching YOU!! Human Retina Sharp Spot: Fovea Blind Spot: Optic Nerve Human Vision Optical Antennae: Rods & Cones Rods: Intensity Cones: Color Energy of Light 6 10 ev 10 ev 4 1 2eV 40eV KeV MeV Energy
Lighting with artificial light
 Lighting with artificial light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is necessary Our vision and thus our contact
Lighting with artificial light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is necessary Our vision and thus our contact
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course
 Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C ONTENT S TANDARDS 4.1 Describe the measurable properties of waves (velocity, frequency, wavelength, amplitude, period)
Introductory Physics, High School Learning Standards for a Full First-Year Course I. C ONTENT S TANDARDS 4.1 Describe the measurable properties of waves (velocity, frequency, wavelength, amplitude, period)
Unit 1.5 Waves. The number waves per second. 1 Hz is 1waves per second. If there are 40 waves in 10 seconds then the frequency is 4 Hz.
 Unit 1.5 Waves Basic information Transverse: The oscillations of the particles are at right angles (90 ) to the direction of travel (propagation) of the wave. Examples: All electromagnetic waves (Light,
Unit 1.5 Waves Basic information Transverse: The oscillations of the particles are at right angles (90 ) to the direction of travel (propagation) of the wave. Examples: All electromagnetic waves (Light,
SER: Biological Stains Visualization with Alternate Light Sources
 Sources Safety SAFETY WARNING! Do not look directly into the beam. Safety glasses with the proper viewing filters must always be worn to protect the eyes from the intense light emitted by a forensic light
Sources Safety SAFETY WARNING! Do not look directly into the beam. Safety glasses with the proper viewing filters must always be worn to protect the eyes from the intense light emitted by a forensic light
TECHNOLOGY INFORMATION SHEET
 TECHNOLOGY INFORMATION SHEET LIGHTING BASICS Topics covered by this information sheet: 1. Light as Service 2. What is Light - How is it Defined 3. Light Quality - How Much and What Type of Light 4. Sources
TECHNOLOGY INFORMATION SHEET LIGHTING BASICS Topics covered by this information sheet: 1. Light as Service 2. What is Light - How is it Defined 3. Light Quality - How Much and What Type of Light 4. Sources
2 nd Term Final. Revision Sheet. Students Name: Subject: Science. Teacher Signature
 2 nd Term Final Revision Sheet Students Name: Grade: 8 A/B Subject: Science Teacher Signature Grade 8 2nd Term Final Revision Sheet Science True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1.
2 nd Term Final Revision Sheet Students Name: Grade: 8 A/B Subject: Science Teacher Signature Grade 8 2nd Term Final Revision Sheet Science True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1.
Announcements. EM Induction. Faraday s Law 4/24/15. Why is current induced? EM Induction: Current is Induced
 Announcements Today: Induction & transformers Wednesday: Finish transformers, start light Reading: review Fig. 26.3 and Fig. 26.8 Recall: N/S poles (opposites attract) Moving electrical charges produce
Announcements Today: Induction & transformers Wednesday: Finish transformers, start light Reading: review Fig. 26.3 and Fig. 26.8 Recall: N/S poles (opposites attract) Moving electrical charges produce
THEIMER - lamps. The optimal type for every application. Ga - Fe doped: Multi spectrum type TH...2 Ga - Pb doped: Dual spectrum type THS...
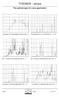 The optimal type for every application 12 12 1 1 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 3 35 4 45 5 55 6 65 7 Xenon puls: For reprographic camera type KX... 3 32 34 36 38 4 42 44 46 48 5 52 54 56 58 6 Hg undoped: For UV curing
The optimal type for every application 12 12 1 1 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 3 35 4 45 5 55 6 65 7 Xenon puls: For reprographic camera type KX... 3 32 34 36 38 4 42 44 46 48 5 52 54 56 58 6 Hg undoped: For UV curing
Innovative optical solutions. Inspector M2 Manual
 Innovative optical solutions Inspector M2 Manual DANGER Ultraviolet radiation emitted from this product. Avoid exposure. Never look directly into the lamp. Exposure can cause eye and skin allergy and allergic
Innovative optical solutions Inspector M2 Manual DANGER Ultraviolet radiation emitted from this product. Avoid exposure. Never look directly into the lamp. Exposure can cause eye and skin allergy and allergic
Answers to SNC 2DI Review for Unit Test #3: Geometric Optics
 Answers to SNC 2DI Review for Unit Test #3: Geometric Optics 1. Know the meanings of the following terms and be able to apply them for multiple choice questions: physics non-luminous regular reflection
Answers to SNC 2DI Review for Unit Test #3: Geometric Optics 1. Know the meanings of the following terms and be able to apply them for multiple choice questions: physics non-luminous regular reflection
Life Science Chapter 2 Study Guide
 Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND THE EM SPECTRUM MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND THE EM SPECTRUM MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Do not need matter to transfer energy. Made by vibrating electric charges. When an electric charge vibrates,
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES AND THE EM SPECTRUM MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Do not need matter to transfer energy. Made by vibrating electric charges. When an electric charge vibrates,
Unit 3: Energy On the Move
 13 13 Table of Contents Unit 3: Energy On the Move Chapter 13: Light 13.1: The Behavior of Light 13.2: Light and Color 13.3: Producing Light 13.4: Using Light 13.1 The Behavior of Light Light and Matter
13 13 Table of Contents Unit 3: Energy On the Move Chapter 13: Light 13.1: The Behavior of Light 13.2: Light and Color 13.3: Producing Light 13.4: Using Light 13.1 The Behavior of Light Light and Matter
The White Paper: Considerations for Choosing White Point Chromaticity for Digital Cinema
 The White Paper: Considerations for Choosing White Point Chromaticity for Digital Cinema Matt Cowan Loren Nielsen, Entertainment Technology Consultants Abstract Selection of the white point for digital
The White Paper: Considerations for Choosing White Point Chromaticity for Digital Cinema Matt Cowan Loren Nielsen, Entertainment Technology Consultants Abstract Selection of the white point for digital
Physical Science Physics
 Name Physical Science Physics C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points PSP 5W4 Seeing Problems (divide by 11) Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers
Name Physical Science Physics C/By Due Date Code Period Earned Points PSP 5W4 Seeing Problems (divide by 11) Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers
PHYSICS. Speed of Sound. Mr R Gopie
 Speed of Sound Mr R Gopie a) Reciprocal firing Methods of determining the speed of sound in air include: Diag. 20 The time interval, t, between the flash and the sound represents the time taken for sound
Speed of Sound Mr R Gopie a) Reciprocal firing Methods of determining the speed of sound in air include: Diag. 20 The time interval, t, between the flash and the sound represents the time taken for sound
The ultimate guide To living green Wall lighting
 The ultimate guide To living green Wall lighting by Eric Westerduin of Suite Plants Page 1 Table of Contents Introduction 4 Types of Light 6 Measuring Light Intensity 7 Light Quality 8 Selecting the Right
The ultimate guide To living green Wall lighting by Eric Westerduin of Suite Plants Page 1 Table of Contents Introduction 4 Types of Light 6 Measuring Light Intensity 7 Light Quality 8 Selecting the Right
ULTRAVIOLET and INFRARED Photography Summarized
 ULTRAVIOLET and INFRARED Photography Summarized Andrew Davidhazy School of Photographic Arts and Sciences Imaging and Photographic Technology Department Rochester Institute of Technology A large part of
ULTRAVIOLET and INFRARED Photography Summarized Andrew Davidhazy School of Photographic Arts and Sciences Imaging and Photographic Technology Department Rochester Institute of Technology A large part of
Traditional lighting technologies
 Traditional lighting technologies Traditional lighting technologies Traditional lighting technologies Incandescent (filament) lamps i n Incandescent lamps n Halogen lamps Traditional lighting technologies
Traditional lighting technologies Traditional lighting technologies Traditional lighting technologies Incandescent (filament) lamps i n Incandescent lamps n Halogen lamps Traditional lighting technologies
S200 Course LECTURE 1 TEM
 S200 Course LECTURE 1 TEM Development of Electron Microscopy 1897 Discovery of the electron (J.J. Thompson) 1924 Particle and wave theory (L. de Broglie) 1926 Electromagnetic Lens (H. Busch) 1932 Construction
S200 Course LECTURE 1 TEM Development of Electron Microscopy 1897 Discovery of the electron (J.J. Thompson) 1924 Particle and wave theory (L. de Broglie) 1926 Electromagnetic Lens (H. Busch) 1932 Construction
Light-Emitting Diodes
 445.664 Light-Emitting Diodes Chapter 16. Human eye sensitivity and photometric quantities Euijoon Yoon Human vision Ganglion cell (circadian receptor) Cones: provide color sensitivity Rods : color insensitive
445.664 Light-Emitting Diodes Chapter 16. Human eye sensitivity and photometric quantities Euijoon Yoon Human vision Ganglion cell (circadian receptor) Cones: provide color sensitivity Rods : color insensitive
skip chap. 8 for now Chap. 9 Color (continued) Lecture 19 Tuesday, October 26
 skip chap. 8 for now Chap. 9 Color (continued) Lecture 19 Tuesday, October 26 Next time: Chapter 10, start reading. Nov. 2: exam review Nov. 4: exam II There are computer problems with clicker registration.
skip chap. 8 for now Chap. 9 Color (continued) Lecture 19 Tuesday, October 26 Next time: Chapter 10, start reading. Nov. 2: exam review Nov. 4: exam II There are computer problems with clicker registration.
Seeing the Invisible. Activity J11. Tips and Suggestions. What s This Activity About? What Will Students Do? What Will Students Learn?
 J11 Seeing the Invisible Activity J11 Grade Level: 7 12 Source: This activity is section 3 of Active Astronomy, a series of educational materials on infrared astronomy sponsored by NASA s Stratospheric
J11 Seeing the Invisible Activity J11 Grade Level: 7 12 Source: This activity is section 3 of Active Astronomy, a series of educational materials on infrared astronomy sponsored by NASA s Stratospheric
Gas-discharge lamp From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 Page 1 of 8 Gas-discharge lamp From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Gas-discharge lamps are a family of artificial light sources that generate light by sending an electrical discharge through an ionized
Page 1 of 8 Gas-discharge lamp From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Gas-discharge lamps are a family of artificial light sources that generate light by sending an electrical discharge through an ionized
Visual Effects of Light. Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana
 Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Visual Effects of Light Prof. Grega Bizjak, PhD Laboratory of Lighting and Photometry Faculty of Electrical Engineering University of Ljubljana Light is life If sun would turn off the life on earth would
Notes: Light and Optics. Reflection. Refraction. Law of Reflection. Light goes straight 12/13/2012
 Notes: Light and Optics Light goes straight Light travels in a straight line unless it interacts with a medium. The material through which a wave travels is called a medium. Light can be reflected, refracted
Notes: Light and Optics Light goes straight Light travels in a straight line unless it interacts with a medium. The material through which a wave travels is called a medium. Light can be reflected, refracted
LED: Light Emitting Diodes FACTS GUIDE
 LED: Light Emitting Diodes FACTS GUIDE A.D.COLA LIGHTING 86 Worcester St. Natick MA 800-698-LITE www.adcola.com 2 Photo Courtesy of Feiss Lighting your home efficiently is continually becoming more popular.
LED: Light Emitting Diodes FACTS GUIDE A.D.COLA LIGHTING 86 Worcester St. Natick MA 800-698-LITE www.adcola.com 2 Photo Courtesy of Feiss Lighting your home efficiently is continually becoming more popular.
4.6.1 Waves in air, fluids and solids Transverse and longitudinal waves Properties of waves
 4.6 Waves Wave behaviour is common in both natural and man-made systems. Waves carry energy from one place to another and can also carry information. Designing comfortable and safe structures such as bridges,
4.6 Waves Wave behaviour is common in both natural and man-made systems. Waves carry energy from one place to another and can also carry information. Designing comfortable and safe structures such as bridges,
UV RADIATION AND LIGHT
 Deep dyed polyester color filters UV RADIATION AND LIGHT UVA UVB UVC Presented in conjunction with Safe.T.C, Exclusive Representative in Israel - www.safetc.com Prepared for Responsibility for Conservation
Deep dyed polyester color filters UV RADIATION AND LIGHT UVA UVB UVC Presented in conjunction with Safe.T.C, Exclusive Representative in Israel - www.safetc.com Prepared for Responsibility for Conservation
Match the correct description with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Interactions of Light with Matter REFLECTION Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What happens when light travels through a material
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Interactions of Light with Matter REFLECTION Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What happens when light travels through a material
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Waves
 A Waves in air, fluids and solids 1. The diagrams below show two types of wave produced on a slinky spring. A B a. Which one is a transverse wave? (1) Wave B b. What is the name of the other type of wave?
A Waves in air, fluids and solids 1. The diagrams below show two types of wave produced on a slinky spring. A B a. Which one is a transverse wave? (1) Wave B b. What is the name of the other type of wave?
Section Electromagnetic Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
 Section 17.6 Electromagnetic Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic Waves Can you name all the colors of the rainbow? Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet Electromagnetic Waves
Section 17.6 Electromagnetic Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic Waves Can you name all the colors of the rainbow? Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet Electromagnetic Waves
