Interactive Learning Media for Lenses and Their Applications Using Macro Visual Basic in Microsoft PowerPoint
|
|
|
- Jeffery Clyde Arnold
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Interactive Learning Media for Lenses and Their Applications Using Macro Visual Basic in Microsoft PowerPoint To cite this article: Sari Sami Novita et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser Related content - Excel VBA for Physicists: Introduction B V Liengme - The Euler s Graphical User Interface Spreadsheet Calculator for Solving Ordinary Differential Equations by Visual Basic for Application Programming Kim Gaik Tay, Tau Han Cheong, Ming Foong Lee et al. - Preparing content-rich learning environments with VPython and Excel, controlled byvisual Basic for Applications Chandra Prayaga View the article online for updates and enhancements. This content was downloaded from IP address on 14/02/2018 at 18:41
2 Interactive Learning Media for Lenses and Their Applications Using Macro Visual Basic in Microsoft PowerPoint Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science Institut Teknologi Bandung a) b) c) Abstract. There are two types of lenses are used, namely a convex lens and a concave lens. Microscope is a tool that uses two convex lenses as the eyepiece and objective lens because it can form a magnified image. Instead concave lens is usually used as a spectacle lens for nearsightedness patients because the distance of image formed is closer than the distance of the object. Just like a mirror, the image formation by lenses also can be conveniently determined with ray diagrams. Therefore, this research aims to create a simulation of ray diagrams in the process of image formation by lenses and their applications using Macro Visual Basic in Microsoft PowerPoint. Lenses applications made are the microscope simulation and the combined lenses which consist of a concave-convex lens combined and a convex-concave lens combined. This research begins with the preparation of material on the image formation by lenses and their application. Second, made an appearance on the program which consists of a PowerPoint slide, CommandButton, Textbox, OptionButton, Shape and others then wrote programs in Macro Visual Basic procedure to active the command to do. Input of this simulation can be given in the form of object distance, focal point distance of lens and height of objects. The data will be processed according to commands contained in macros procedure to result image distance, image height, image magnification and the properties of image. In addition to result the data, media can also provide output in the form of ray diagrams simulation on the image formation that can be used to assist students understanding the image formation by lenses. 1. Physics is one of science that studies about nature. Physics makes significant contributions in human life. Much existing technology development can not be separated from physics. Nevertheless, most of students assumed physics as a difficult and terrify subject [1]. Physics is a natural science based on experiments, measurements and mathematical analysis to find quantitative physical laws or theory. As natural science based on experiments, teaching physics at school is usually equipped with simple laboratory activities. But in fact, laboratory activities of physics in school still have a lot of experience barriers. Based on a survey conducted by Yennita et al [2], the barriers are reinforced by reluctance of teachers held laboratory activities because of limited lab equipments. In addition, laboratory activities require a lot of time. One of topics in physics that have lab activities is image formation by lens. Lens is an optics device for gathers or diffusing light beam [3]. Lenses are commonly used to form images in optical instruments, such as microscope. Microscope is a tool that uses two convex lenses as the eyepiece and objective lens because it can form a magnified image. Another kind of lens is a concave lens that commonly uses as a spectacle lens for nearsightness patients. The image distance that formed by concave lens is closer than the object distance. Therefore it can help the nearsightness patients to see the distant object. Content from this work may be used under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 licence. Any further distribution of this work must maintain attribution to the author(s) and the title of the work, journal citation and DOI. Published under licence by Ltd 1
3 Some learning medias and learning methods on the topic of the lenses have been developed. This media aims to help students, especially first grade students on senior high school, to figure out about lense and the proccess of image formation by lenses. Sambudi and Mosik [4] using media tools to teaching about optics, include the topic of lenses. Nowdays, computer-based learning media of lense has been developed. Fakhriyah, et al. [5] teached about lense through development of geometrical optics learning media, using Macromedia Flash CS5. But there is no studies that use Visual Basic macros in Microsoft Powerpoint to develop a learning media of lenses. 1.1 Microsoft Power point 2010 PowerPoint is a Microsoft s presentation tool widely used in education. PowerPoint has some slides that can be changed by simply clicking one button. So that PowerPoint can visualize text, images, animation, sound, and video in the form of presentation. Even the last few years PowerPoint has been equipped with hyperlinks and buttons to give more interactive presentation appearance [6]. Microsoft PowerPoint has encountered several renewal. Each of these programs that have been updated are named according to the renewals, for example, Microsoft PowerPoint 1995, 1997, 2003, 2007, 2010, and This interactive-learning media using Microsoft PowerPoint The initial view of Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 can be seen in Figure 1. Initial view of Microsoft PowerPoint 2010 Although it has many advantages, PowerPoint also has limitations. One of them is users have to use a lot of slides in a presentation that will spend a large enough memory capacity. To overcome these limitations, users can use Visual Basic for Applications (VBA). 1.2 Visual Basic for Application (VBA) Visual Basic for Application (VBA) is a programming language based "object oriented" by using the Visual Basic that can be used to support the functions of Microsoft Office, one of them is PowerPoint. Basically VBA is integrated with Mirosoft Office and used by writing a script or procedure on macro sheet. The macros are usually referred to Visual Basic macros [5]. Although integrated with Microsoft Office, VBA by default not displayed in Microsoft Office window. If you want to use VBA, you must bring up the Developer tab first. Developer tab contains menus necessary to make macros procedure. How to display the Developer tab is shown in Figure 2. After displaying the Developer tab, then the user can write macros in a VBA macros sheet. 2
4 . How to display the Developer tab in Microsoft PowerPoint. 2. H I L M Developer tab generally contains three main parts, namely the Code, Controls and Modify. In Controls, there are several tools that are often used to create macros procedures. Macros procedures written in Visual Basic Editor by: 1. Click Macros in the Developer tab. 2. Type the name of the procedure that will be written (for example, "Hello") under Macro Name in the Macros dialog box.. Appearance of Macros dialog box 3. Click Create button, and the Visual Basic Editor will appear as shown in Figure 4. Macros procedure is ready to written.. Visual Basic Editor PowerPoint
5 Macros procedure also can be run using the Shapes. We can find the Shapes on the Insert tab in PowerPoint. The use of Shapes as a button requires user s creativity to create macros procedures. By using Shapes as a button we can set the size, shape, and color are more varied. Make a button using Shapes can be done by: a. Create a macros procedure in the Visual Basic Editor. b. Choose one of Shapes on Insert Tab (eg. oval).. Choose the Shapes on Insert Tab c. Click the choosen Shapes, then click Action in Insert Tab. On Run Macro, choose the procedure will be run using Shapes. d. Click ok.. Choose the procedure will be run using Shapes on Run Macro Figure 7 is one of macros procedures on program of Interactive-Leraning Media running by Shapes. 4
6 . One of macro procedures macro on Interactive-Leraning Media program running by Shapes 3. I M L T 3.1 Image Image formed when light rays encounter flat and spherical surfaces. We know two kind of image formed by a lens, they are virtual image and real image. Virtual image cannot be displayed on a screen and real image can be displayed on a screen. In this interactive-learning media Virtual image is simulated by dotted line and real image is simulated by straight line. To be able to show the image formation by lenses, this interactive learning media can do the commands to rescale image formed. If the image are formed exceeds the screen, the program will automatically reduce the size of the simulation so the image can be displayed completely on screen. (a). The simulation (a) before rescaled, (b) after rescaled (b) 3.2 Image Formation by Convex Lens and Concave Lens Convex lens is a thin lens that its refractive surface can converge the parallel rays (convergent lens). Just like in a concave mirror, parallel rays on convex lens will also be collected at the focal point in the main axis, which is behind the lens. So that the focal point of the convex lens is positive. 5
7 Concave lens is a thin lens that its refractive surface can diverge parallel the parallel rays (divergent lens). Parallel rays in a concave lens also will spread and seems to come from a gathering point located in front of the lens. Therefore, the focus of a concave lens is negative and located in front of a concave lens. The lens equation is f p q (1) And lateral magnification of lens is h q M ' h p (2) To determine the image formation of the lens we can use the geometric approach, using diagram rays. The following diagram rays for lens are: 1. Ray 1 is drawn parallel to the principal axis. After being refracted by the lens, this ray passes through the focal point on the back side of the lens. 2. Ray 2 is drawn through the center of the lens and continues in a straight line. 3. Ray 3 is drawn through the focal point on the front side of the lens (or as if coming from the focal point, if p > f) and emerges from the lens parallel to the principal axis.. Rays diagram of convex lens and concave lens Simulation of the image formation on interactive learning media that have been made located on the simulation slide. On simulation slide, user can see the result of the integration between VBA and PowerPoint. VBA is used to activate the command in order to produce the desired output. You can change any value of f, p, and q by click the red button. After that you can click Gambar Bayangan button to active macros procedure. Simulation of convex lens after Gambar Bayangan button clicked 6
8 3.3 Applications of Lens This media have two kind application of image formation by lens. They are microscope and combined lens. Just as simulations for the formation of a shadow on the convex lens and a concave lens, simulations for lens applications were also made to process input into output is numeric and numeric simulations. Making the application simulation lens also uses shapes as buttons, textbox, CommandButton, and option button.. One of image formation application 3.4 Simulation Test A short field test consists of testing a convex lens and a concave lens that is presented in two different slides.. A short field test consists of testing a convex lens after the "Periksa Jawaban" is clicked On each slide a short field user can change the amount of which is given in the matter, namely by replacing the value of F, P, or h. To answer each question, the user can write the answers on a black textbox and click one of the options for the properties of the image produced. If the user has been convinced by the answer, the user can correct their own answers by clicking the "Periksa Jawaban". Automatically media will give the mark " " if the answer is correct and the "x" if the answer is wrong and the value box will appear on the user earned value questions. Simulation of the formation of shadows remain displayed on this test to inform the correct answer from the given problem. 7
9 4. Interactive learning media for lenses and their applications using Macro Visual Basic in Microsoft PowerPoint has been created and can be used by students to figure out the process of image formation by thin lenses and their applications in several optics devices through a simple simulation. The following are some things that media can do: 1. Visualize simulation 2. Simulation test 3. Rescale simulation A Gratefully acknowledge the suggestions and comments of Mrs. Siti Nurul Khotimah (Institute Teknologi Bandung) and Mr. Wahyu Hidayat (Institute Teknolohi Bandung) as supervisor of Interactive Learning Media Research. Also, special thanks to Physics Laboratory of Mathematics and Natural Science Faculty of ITB that supported and provided valuable advices. 1. Kontributor Wikipedia, "Lensa", Wikipedia, Ensiklopedi Bebas. [June 23rd 2015] 2. Yennita, Mugi Sukmawati, dan Zulirfan, Hambatan Pelaksanaan Praktikum IPA Fisika yang Dihadapi Guru SMP Negeri Kota di Pekanbaru. Scientific Article Laboratorium Pendidikan Fisika departement PMIPA FKIP Universitas Riau. 3. R. A. Serway dan J. W. Jewett, Physics for Scientists and Engineers, James Madison University- California State Polytechnic University, 2004, p A. Sambudi dan Mosik, Penggunaan Alat Peraga Papan Optik untuk Meningkatkan Hasil Belajar Pemantulan Cahaya pada Siswa Kelas VIII, Journal on Jurnal Pendidikan Fisika Indonesia 5, (2009) 5. Wahyuni Ainun Fakhriyah (1), Muhardjito, Sentot Kusairi, Pengembangan Media Pembelajaran IPA Fisika Berbasis Multimedia Flash CS5 Pokok Bahasan Optika Geometri untuk Meningkatkan Pemahaman Konsep Siswa Kelas VIII SMP Negeri 1 Winongan, Journal on journal-online UM. [June 21st 2015] 6. David M. Marcovitz, Powerful PowerPoint for Educators Using Visual Basic for Application to Make PowerPoint Interactive, Santa Barbara - California, Second Edition, 2012, p
Complete the diagram to show what happens to the rays. ... (1) What word can be used to describe this type of lens? ... (1)
 Q1. (a) The diagram shows two parallel rays of light, a lens and its axis. Complete the diagram to show what happens to the rays. (2) Name the point where the rays come together. (iii) What word can be
Q1. (a) The diagram shows two parallel rays of light, a lens and its axis. Complete the diagram to show what happens to the rays. (2) Name the point where the rays come together. (iii) What word can be
Chapter 23. Mirrors and Lenses
 Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to
Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to
Algebra Based Physics. Reflection. Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66. Slide 3 / 66. Slide 4 / 66. Slide 5 / 66. Slide 6 / 66.
 Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 66 Slide 4 / 66 Table of ontents lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Refraction and Snell's
Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 Algebra Based Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 66 Slide 4 / 66 Table of ontents lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Refraction and Snell's
Spherical Mirrors. Concave Mirror, Notation. Spherical Aberration. Image Formed by a Concave Mirror. Image Formed by a Concave Mirror 4/11/2014
 Notation for Mirrors and Lenses Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to
Notation for Mirrors and Lenses Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to
King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept.
 King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 111 (GENERAL PHYSICS 2) CHAPTER 36: Image Formation LECTURE NO. 9 Presented by Nouf Saad Alkathran 36.1 Images Formed by Flat Mirrors
King Saud University College of Science Physics & Astronomy Dept. PHYS 111 (GENERAL PHYSICS 2) CHAPTER 36: Image Formation LECTURE NO. 9 Presented by Nouf Saad Alkathran 36.1 Images Formed by Flat Mirrors
Converging Lenses. Parallel rays are brought to a focus by a converging lens (one that is thicker in the center than it is at the edge).
 Chapter 30: Lenses Types of Lenses Piece of glass or transparent material that bends parallel rays of light so they cross and form an image Two types: Converging Diverging Converging Lenses Parallel rays
Chapter 30: Lenses Types of Lenses Piece of glass or transparent material that bends parallel rays of light so they cross and form an image Two types: Converging Diverging Converging Lenses Parallel rays
Chapter 23. Mirrors and Lenses
 Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses Mirrors and Lenses The development of mirrors and lenses aided the progress of science. It led to the microscopes and telescopes. Allowed the study of objects from microbes
Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses Mirrors and Lenses The development of mirrors and lenses aided the progress of science. It led to the microscopes and telescopes. Allowed the study of objects from microbes
Name: Lab Partner: Section:
 Chapter 10 Thin Lenses Name: Lab Partner: Section: 10.1 Purpose In this experiment, the formation of images by concave and convex lenses will be explored. The application of the thin lens equation and
Chapter 10 Thin Lenses Name: Lab Partner: Section: 10.1 Purpose In this experiment, the formation of images by concave and convex lenses will be explored. The application of the thin lens equation and
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Real and Virtual Images Real images can be displayed on screens Virtual Images can not be displayed onto screens. Focal Length& Radius of Curvature When the object is very far
Chapter 36 Image Formation Real and Virtual Images Real images can be displayed on screens Virtual Images can not be displayed onto screens. Focal Length& Radius of Curvature When the object is very far
Gaussian Ray Tracing Technique
 Gaussian Ray Tracing Technique Positive Lenses. A positive lens has two focal points one on each side of the lens; both are at the same focal distance f from the lens. Parallel rays of light coming from
Gaussian Ray Tracing Technique Positive Lenses. A positive lens has two focal points one on each side of the lens; both are at the same focal distance f from the lens. Parallel rays of light coming from
Notation for Mirrors and Lenses. Chapter 23. Types of Images for Mirrors and Lenses. More About Images
 Notation for Mirrors and Lenses Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses Sections: 4, 6 Problems:, 8, 2, 25, 27, 32 The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image
Notation for Mirrors and Lenses Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses Sections: 4, 6 Problems:, 8, 2, 25, 27, 32 The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image
Chapter 2 - Geometric Optics
 David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 The human eye is a visual system that collects light and forms an image on the retina. The human eye is a visual system that collects light and forms an image
David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 214 The human eye is a visual system that collects light and forms an image on the retina. The human eye is a visual system that collects light and forms an image
Unit 3: Energy On the Move
 14 14 Table of Contents Unit 3: Energy On the Move Chapter 14: Mirrors and Lenses 14.1: Mirrors 14.2: Lenses 14.3: Optical Instruments 14.1 Mirrors How do you use light to see? When light travels from
14 14 Table of Contents Unit 3: Energy On the Move Chapter 14: Mirrors and Lenses 14.1: Mirrors 14.2: Lenses 14.3: Optical Instruments 14.1 Mirrors How do you use light to see? When light travels from
Chapter 23. Light Geometric Optics
 Chapter 23. Light Geometric Optics There are 3 basic ways to gather light and focus it to make an image. Pinhole - Simple geometry Mirror - Reflection Lens - Refraction Pinhole Camera Image Formation (the
Chapter 23. Light Geometric Optics There are 3 basic ways to gather light and focus it to make an image. Pinhole - Simple geometry Mirror - Reflection Lens - Refraction Pinhole Camera Image Formation (the
Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Lenses convex (converging) concave (diverging) Mirrors Ray Tracing for Mirrors We use three principal rays in finding the image produced by a curved mirror. The parallel ray
Chapter 24 Geometrical Optics Lenses convex (converging) concave (diverging) Mirrors Ray Tracing for Mirrors We use three principal rays in finding the image produced by a curved mirror. The parallel ray
Chapter 23. Mirrors and Lenses
 Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to
Chapter 23 Mirrors and Lenses Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to
Algebra Based Physics. Reflection. Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66. Slide 3 / 66. Slide 4 / 66. Slide 5 / 66. Slide 6 / 66.
 Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 lgebra ased Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 66 Slide 4 / 66 Table of ontents lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Refraction and Snell's
Slide 1 / 66 Slide 2 / 66 lgebra ased Physics Geometric Optics 2015-12-01 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 66 Slide 4 / 66 Table of ontents lick on the topic to go to that section Reflection Refraction and Snell's
Optics Practice. Version #: 0. Name: Date: 07/01/2010
 Optics Practice Date: 07/01/2010 Version #: 0 Name: 1. Which of the following diagrams show a real image? a) b) c) d) e) i, ii, iii, and iv i and ii i and iv ii and iv ii, iii and iv 2. A real image is
Optics Practice Date: 07/01/2010 Version #: 0 Name: 1. Which of the following diagrams show a real image? a) b) c) d) e) i, ii, iii, and iv i and ii i and iv ii and iv ii, iii and iv 2. A real image is
Ch 24. Geometric Optics
 text concept Ch 24. Geometric Optics Fig. 24 3 A point source of light P and its image P, in a plane mirror. Angle of incidence =angle of reflection. text. Fig. 24 4 The blue dashed line through object
text concept Ch 24. Geometric Optics Fig. 24 3 A point source of light P and its image P, in a plane mirror. Angle of incidence =angle of reflection. text. Fig. 24 4 The blue dashed line through object
PHYS 160 Astronomy. When analyzing light s behavior in a mirror or lens, it is helpful to use a technique called ray tracing.
 Optics Introduction In this lab, we will be exploring several properties of light including diffraction, reflection, geometric optics, and interference. There are two sections to this lab and they may
Optics Introduction In this lab, we will be exploring several properties of light including diffraction, reflection, geometric optics, and interference. There are two sections to this lab and they may
Geometric Optics. Ray Model. assume light travels in straight line uses rays to understand and predict reflection & refraction
 Geometric Optics Ray Model assume light travels in straight line uses rays to understand and predict reflection & refraction General Physics 2 Geometric Optics 1 Reflection Law of reflection the angle
Geometric Optics Ray Model assume light travels in straight line uses rays to understand and predict reflection & refraction General Physics 2 Geometric Optics 1 Reflection Law of reflection the angle
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT. Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring Lab #8: Thin Lenses
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring 2018 Lab #8: Thin Lenses Lab Writeup Due: Mon/Wed/Thu/Fri, April 2/4/5/6, 2018 Background In the previous lab
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring 2018 Lab #8: Thin Lenses Lab Writeup Due: Mon/Wed/Thu/Fri, April 2/4/5/6, 2018 Background In the previous lab
2015 EdExcel A Level Physics EdExcel A Level Physics. Lenses
 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Lenses Types of lenses Converging lens bi-convex has two convex surfaces Diverging lens bi-concave has two concave surfaces Thin
2015 EdExcel A Level Physics 2015 EdExcel A Level Physics Topic Topic 5 5 Lenses Types of lenses Converging lens bi-convex has two convex surfaces Diverging lens bi-concave has two concave surfaces Thin
Option G 2: Lenses. The diagram below shows the image of a square grid as produced by a lens that does not cause spherical aberration.
 Name: Date: Option G 2: Lenses 1. This question is about spherical aberration. The diagram below shows the image of a square grid as produced by a lens that does not cause spherical aberration. In the
Name: Date: Option G 2: Lenses 1. This question is about spherical aberration. The diagram below shows the image of a square grid as produced by a lens that does not cause spherical aberration. In the
Readings: Hecht, Chapter 24
 5. GEOMETRIC OPTICS Readings: Hecht, Chapter 24 Introduction In this lab you will measure the index of refraction of glass using Snell s Law, study the application of the laws of geometric optics to systems
5. GEOMETRIC OPTICS Readings: Hecht, Chapter 24 Introduction In this lab you will measure the index of refraction of glass using Snell s Law, study the application of the laws of geometric optics to systems
Physics 228 Lecture 3. Today: Spherical Mirrors Lenses.
 Physics 228 Lecture 3 Today: Spherical Mirrors Lenses www.physics.rutgers.edu/ugrad/228 a) Santa as he sees himself in a mirrored sphere. b) Santa as he sees himself in a flat mirror after too much eggnog.
Physics 228 Lecture 3 Today: Spherical Mirrors Lenses www.physics.rutgers.edu/ugrad/228 a) Santa as he sees himself in a mirrored sphere. b) Santa as he sees himself in a flat mirror after too much eggnog.
Laboratory 7: Properties of Lenses and Mirrors
 Laboratory 7: Properties of Lenses and Mirrors Converging and Diverging Lens Focal Lengths: A converging lens is thicker at the center than at the periphery and light from an object at infinity passes
Laboratory 7: Properties of Lenses and Mirrors Converging and Diverging Lens Focal Lengths: A converging lens is thicker at the center than at the periphery and light from an object at infinity passes
CH. 23 Mirrors and Lenses HW# 6, 7, 9, 11, 13, 21, 25, 31, 33, 35
 CH. 23 Mirrors and Lenses HW# 6, 7, 9, 11, 13, 21, 25, 31, 33, 35 Mirrors Rays of light reflect off of mirrors, and where the reflected rays either intersect or appear to originate from, will be the location
CH. 23 Mirrors and Lenses HW# 6, 7, 9, 11, 13, 21, 25, 31, 33, 35 Mirrors Rays of light reflect off of mirrors, and where the reflected rays either intersect or appear to originate from, will be the location
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 27 Geometric Optics Spring 205 Semester Matthew Jones Sign Conventions > + = Convex surface: is positive for objects on the incident-light side is positive for
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 27 Geometric Optics Spring 205 Semester Matthew Jones Sign Conventions > + = Convex surface: is positive for objects on the incident-light side is positive for
Gaussian Ray Tracing Technique
 Gaussian Ray Tracing Technique Positive Lenses. A positive lens has two focal points one on each side of the lens; both are at the same focal distance f from the lens. Parallel rays of light coming from
Gaussian Ray Tracing Technique Positive Lenses. A positive lens has two focal points one on each side of the lens; both are at the same focal distance f from the lens. Parallel rays of light coming from
Geometric Optics Practice Problems. Ray Tracing - Draw at least two principle rays and show the image created by the lens or mirror.
 Geometric Optics Practice Problems Ray Tracing - Draw at least two principle rays and show the image created by the lens or mirror. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Practice Problems - Mirrors Classwork
Geometric Optics Practice Problems Ray Tracing - Draw at least two principle rays and show the image created by the lens or mirror. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Practice Problems - Mirrors Classwork
Activity 6.1 Image Formation from Spherical Mirrors
 PHY385H1F Introductory Optics Practicals Day 6 Telescopes and Microscopes October 31, 2011 Group Number (number on Intro Optics Kit):. Facilitator Name:. Record-Keeper Name: Time-keeper:. Computer/Wiki-master:..
PHY385H1F Introductory Optics Practicals Day 6 Telescopes and Microscopes October 31, 2011 Group Number (number on Intro Optics Kit):. Facilitator Name:. Record-Keeper Name: Time-keeper:. Computer/Wiki-master:..
Image Formation. Light from distant things. Geometrical optics. Pinhole camera. Chapter 36
 Light from distant things Chapter 36 We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can process. This chapter concerns
Light from distant things Chapter 36 We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can process. This chapter concerns
Chapter 23. Geometrical Optics: Mirrors and Lenses and other Instruments
 Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics: Mirrors and Lenses and other Instruments HITT 1 You stand two feet away from a plane mirror. How far is it from you to your image? a. 2.0 ft b. 3.0 ft c. 4.0 ft d. 5.0 ft
Chapter 23 Geometrical Optics: Mirrors and Lenses and other Instruments HITT 1 You stand two feet away from a plane mirror. How far is it from you to your image? a. 2.0 ft b. 3.0 ft c. 4.0 ft d. 5.0 ft
Instructions. To run the slideshow:
 Instructions To run the slideshow: Click: view full screen mode, or press Ctrl +L. Left click advances one slide, right click returns to previous slide. To exit the slideshow press the Esc key. Optical
Instructions To run the slideshow: Click: view full screen mode, or press Ctrl +L. Left click advances one slide, right click returns to previous slide. To exit the slideshow press the Esc key. Optical
INSIDE LAB 6: The Properties of Lenses and Telescopes
 INSIDE LAB 6: The Properties of Lenses and Telescopes OBJECTIVE: To construct a simple refracting telescope and to measure some of its properties. DISCUSSION: In tonight s lab we will build a simple telescope
INSIDE LAB 6: The Properties of Lenses and Telescopes OBJECTIVE: To construct a simple refracting telescope and to measure some of its properties. DISCUSSION: In tonight s lab we will build a simple telescope
AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light
 AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light 1. 1974-3 (Geometric Optics) An object 1.0 cm high is placed 4 cm away from a converging lens having a focal length of 3 cm. a. Sketch a principal ray diagram for
AP Physics Problems -- Waves and Light 1. 1974-3 (Geometric Optics) An object 1.0 cm high is placed 4 cm away from a converging lens having a focal length of 3 cm. a. Sketch a principal ray diagram for
Chapter 34 Geometric Optics
 Chapter 34 Geometric Optics Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Goals of Chapter 34 To see how plane and curved mirrors form images To learn how lenses form images To understand how a simple image system works Reflection
Chapter 34 Geometric Optics Lecture by Dr. Hebin Li Goals of Chapter 34 To see how plane and curved mirrors form images To learn how lenses form images To understand how a simple image system works Reflection
Reading: Lenses and Mirrors; Applications Key concepts: Focal points and lengths; real images; virtual images; magnification; angular magnification.
 Reading: Lenses and Mirrors; Applications Key concepts: Focal points and lengths; real images; virtual images; magnification; angular magnification. 1.! Questions about objects and images. Can a virtual
Reading: Lenses and Mirrors; Applications Key concepts: Focal points and lengths; real images; virtual images; magnification; angular magnification. 1.! Questions about objects and images. Can a virtual
Lab 11: Lenses and Ray Tracing
 Name: Lab 11: Lenses and Ray Tracing Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Materials: Ray box, two different converging lenses, one diverging lens, screen, lighted object, three stands, meter stick, two letter
Name: Lab 11: Lenses and Ray Tracing Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Materials: Ray box, two different converging lenses, one diverging lens, screen, lighted object, three stands, meter stick, two letter
10.2 Images Formed by Lenses SUMMARY. Refraction in Lenses. Section 10.1 Questions
 10.2 SUMMARY Refraction in Lenses Converging lenses bring parallel rays together after they are refracted. Diverging lenses cause parallel rays to move apart after they are refracted. Rays are refracted
10.2 SUMMARY Refraction in Lenses Converging lenses bring parallel rays together after they are refracted. Diverging lenses cause parallel rays to move apart after they are refracted. Rays are refracted
LECTURE 17 MIRRORS AND THIN LENS EQUATION
 LECTURE 17 MIRRORS AND THIN LENS EQUATION 18.6 Image formation with spherical mirrors Concave mirrors Convex mirrors 18.7 The thin-lens equation Sign conventions for lenses and mirrors Spherical mirrors
LECTURE 17 MIRRORS AND THIN LENS EQUATION 18.6 Image formation with spherical mirrors Concave mirrors Convex mirrors 18.7 The thin-lens equation Sign conventions for lenses and mirrors Spherical mirrors
Chapter 18 Optical Elements
 Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Chapter 18 Optical Elements GOALS When you have mastered the content of this chapter, you will be able to achieve the following goals: Definitions Define each of the following terms and use it in an operational
Converging Lens. Goal: To measure the focal length of a converging lens using various methods and to study how a converging lens forms a real image.
 Converging Lens Goal: To measure the focal length of a converging lens using various methods and to study how a converging lens forms a real image. Lab Preparation The picture on the screen in a movie
Converging Lens Goal: To measure the focal length of a converging lens using various methods and to study how a converging lens forms a real image. Lab Preparation The picture on the screen in a movie
Physics 222, October 25
 Physics 222, October 25 Key Concepts: Image formation by refraction Thin lenses The eye Optical instruments A single flat interface Images can be formed by refraction, when light traverses a boundary between
Physics 222, October 25 Key Concepts: Image formation by refraction Thin lenses The eye Optical instruments A single flat interface Images can be formed by refraction, when light traverses a boundary between
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
Physics 4L Spring 2010 Problem set 1 Due Tuesday 26 January in class
 Physics 4L Spring 2010 Problem set 1 Due Tuesday 26 January in class From Wolfson: Chapter 30 problem 36 (the flashlight beam comes out of the water some distance from the edge of the lake; the figure
Physics 4L Spring 2010 Problem set 1 Due Tuesday 26 January in class From Wolfson: Chapter 30 problem 36 (the flashlight beam comes out of the water some distance from the edge of the lake; the figure
Lab 8 Microscope. Name. I. Introduction/Theory
 Lab 8 Microscope Name I. Introduction/Theory The purpose of this experiment is to construct a microscope and determine the magnification. A microscope magnifies an object that is close to the microscope.
Lab 8 Microscope Name I. Introduction/Theory The purpose of this experiment is to construct a microscope and determine the magnification. A microscope magnifies an object that is close to the microscope.
CHAPTER 18 REFRACTION & LENSES
 Physics Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 18 REFRACTION & LENSES Day Plans for the day Assignments for the day 1 18.1 Refraction of Light o Snell
Physics Approximate Timeline Students are expected to keep up with class work when absent. CHAPTER 18 REFRACTION & LENSES Day Plans for the day Assignments for the day 1 18.1 Refraction of Light o Snell
Lecture Outline Chapter 27. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 27 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Units of Chapter 27 The Human Eye and the Camera Lenses in Combination and Corrective Optics The Magnifying
Lecture Outline Chapter 27 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 27 Optical Instruments Units of Chapter 27 The Human Eye and the Camera Lenses in Combination and Corrective Optics The Magnifying
PHYSICS 289 Experiment 8 Fall Geometric Optics II Thin Lenses
 PHYSICS 289 Experiment 8 Fall 2005 Geometric Optics II Thin Lenses Please look at the chapter on lenses in your text before this lab experiment. Please submit a short lab report which includes answers
PHYSICS 289 Experiment 8 Fall 2005 Geometric Optics II Thin Lenses Please look at the chapter on lenses in your text before this lab experiment. Please submit a short lab report which includes answers
Test Review # 8. Physics R: Form TR8.17A. Primary colors of light
 Physics R: Form TR8.17A TEST 8 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 8 Light and Color. Color comes from light, an electromagnetic wave that travels in straight lines in all directions from a light source
Physics R: Form TR8.17A TEST 8 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 8 Light and Color. Color comes from light, an electromagnetic wave that travels in straight lines in all directions from a light source
Physics 11. Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2
 Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2 (c) Refraction (i) Introduction: Snell s law Like water waves, when light is traveling from one medium to another, not only does its wavelength, and in turn the
Physics 11 Unit 8 Geometric Optics Part 2 (c) Refraction (i) Introduction: Snell s law Like water waves, when light is traveling from one medium to another, not only does its wavelength, and in turn the
Rutgers Analytical Physics 750:228, Spring 2013 ( RUPHYS228S13 ) My Courses Course Settings University Physics with Modern Physics, 13e Young/Freedman
 Signed in as RONALD GILMAN, Instructor Help Sign Out Rutgers Analytical Physics 750:228, Spring 2013 ( RUPHYS228S13 ) My Courses Course Settings University Physics with Modern Physics, 13e Young/Freedman
Signed in as RONALD GILMAN, Instructor Help Sign Out Rutgers Analytical Physics 750:228, Spring 2013 ( RUPHYS228S13 ) My Courses Course Settings University Physics with Modern Physics, 13e Young/Freedman
LENSES. A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved.
 1 LENSES A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of Lenses There are two types of basic lenses: Converging/
1 LENSES A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of Lenses There are two types of basic lenses: Converging/
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to the
Chapter 36 Image Formation Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to the
Dr. Todd Satogata (ODU/Jefferson Lab) Monday, April
 University Physics 227N/232N Mirrors and Lenses Homework Optics 2 due Friday AM Quiz Friday Optional review session next Monday (Apr 28) Bring Homework Notebooks to Final for Grading Dr. Todd Satogata
University Physics 227N/232N Mirrors and Lenses Homework Optics 2 due Friday AM Quiz Friday Optional review session next Monday (Apr 28) Bring Homework Notebooks to Final for Grading Dr. Todd Satogata
Geometric Optics. Objective: To study the basics of geometric optics and to observe the function of some simple and compound optical devices.
 Geometric Optics Objective: To study the basics of geometric optics and to observe the function of some simple and compound optical devices. Apparatus: Pasco optical bench, mounted lenses (f= +100mm, +200mm,
Geometric Optics Objective: To study the basics of geometric optics and to observe the function of some simple and compound optical devices. Apparatus: Pasco optical bench, mounted lenses (f= +100mm, +200mm,
Physics 2310 Lab #6: Multiple Thin Lenses Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming)
 Physics 2310 Lab #6: Multiple Thin Lenses Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming) Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to investigate the properties of multiple thin lenses. The primary goals are to understand
Physics 2310 Lab #6: Multiple Thin Lenses Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming) Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to investigate the properties of multiple thin lenses. The primary goals are to understand
Final Reg Optics Review SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Final Reg Optics Review 1) How far are you from your image when you stand 0.75 m in front of a vertical plane mirror? 1) 2) A object is 12 cm in front of a concave mirror, and the image is 3.0 cm in front
Final Reg Optics Review 1) How far are you from your image when you stand 0.75 m in front of a vertical plane mirror? 1) 2) A object is 12 cm in front of a concave mirror, and the image is 3.0 cm in front
Mirrors, Lenses &Imaging Systems
 Mirrors, Lenses &Imaging Systems We describe the path of light as straight-line rays And light rays from a very distant point arrive parallel 145 Phys 24.1 Mirrors Standing away from a plane mirror shows
Mirrors, Lenses &Imaging Systems We describe the path of light as straight-line rays And light rays from a very distant point arrive parallel 145 Phys 24.1 Mirrors Standing away from a plane mirror shows
Lenses. Light refracts at both surfaces. Non-parallel surfaces results in net bend.
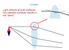 Lenses Light refracts at both surfaces. Non-parallel surfaces results in net bend. Lenses Focusing power of the lens is function of radius of curvature of each surface and index of refraction of lens.
Lenses Light refracts at both surfaces. Non-parallel surfaces results in net bend. Lenses Focusing power of the lens is function of radius of curvature of each surface and index of refraction of lens.
13. Optical Instruments*
 13. Optical Instruments* Objective: Here what you have been learning about thin lenses is applied to make a telescope. In the process you encounter general optical instrument design concepts. The learning
13. Optical Instruments* Objective: Here what you have been learning about thin lenses is applied to make a telescope. In the process you encounter general optical instrument design concepts. The learning
Chapter 34. Images. Copyright 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 34 Images Copyright 34-1 Images and Plane Mirrors Learning Objectives 34.01 Distinguish virtual images from real images. 34.02 Explain the common roadway mirage. 34.03 Sketch a ray diagram for
Chapter 34 Images Copyright 34-1 Images and Plane Mirrors Learning Objectives 34.01 Distinguish virtual images from real images. 34.02 Explain the common roadway mirage. 34.03 Sketch a ray diagram for
UNIT SUMMARY: Electromagnetic Spectrum, Color, & Light Name: Date:
 UNIT SUMMARY: Electromagnetic Spectrum, Color, & Light Name: Date: Topics covered in the unit: 1. Electromagnetic Spectrum a. Order of classifications and respective wavelengths b. requency, wavelength,
UNIT SUMMARY: Electromagnetic Spectrum, Color, & Light Name: Date: Topics covered in the unit: 1. Electromagnetic Spectrum a. Order of classifications and respective wavelengths b. requency, wavelength,
Mirrors and Lenses. Images can be formed by reflection from mirrors. Images can be formed by refraction through lenses.
 Mirrors and Lenses Images can be formed by reflection from mirrors. Images can be formed by refraction through lenses. Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object
Mirrors and Lenses Images can be formed by reflection from mirrors. Images can be formed by refraction through lenses. Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object
2. The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal length?
 1. Define the principle focus of a concave mirror? The principle focus of a concave mirror is a point on its principle axis to which all the light rays which are parallel and close to the axis, converge
1. Define the principle focus of a concave mirror? The principle focus of a concave mirror is a point on its principle axis to which all the light rays which are parallel and close to the axis, converge
REFLECTION THROUGH LENS
 REFLECTION THROUGH LENS A lens is a piece of transparent optical material with one or two curved surfaces to refract light rays. It may converge or diverge light rays to form an image. Lenses are mostly
REFLECTION THROUGH LENS A lens is a piece of transparent optical material with one or two curved surfaces to refract light rays. It may converge or diverge light rays to form an image. Lenses are mostly
LENSES. a. To study the nature of image formed by spherical lenses. b. To study the defects of spherical lenses.
 Purpose Theory LENSES a. To study the nature of image formed by spherical lenses. b. To study the defects of spherical lenses. formation by thin spherical lenses s are formed by lenses because of the refraction
Purpose Theory LENSES a. To study the nature of image formed by spherical lenses. b. To study the defects of spherical lenses. formation by thin spherical lenses s are formed by lenses because of the refraction
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS CLASS X REFLECTION AND REFRACTION OF LIGHT QUESTION BANK
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS CLASS X REFLECTION AND REFRACTION OF LIGHT QUESTION BANK 1. Q. A small candle 2.5cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of concave mirror of radius
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS CLASS X REFLECTION AND REFRACTION OF LIGHT QUESTION BANK 1. Q. A small candle 2.5cm in size is placed at 27 cm in front of concave mirror of radius
Physics Chapter Review Chapter 25- The Eye and Optical Instruments Ethan Blitstein
 Physics Chapter Review Chapter 25- The Eye and Optical Instruments Ethan Blitstein The Human Eye As light enters through the human eye it first passes through the cornea (a thin transparent membrane of
Physics Chapter Review Chapter 25- The Eye and Optical Instruments Ethan Blitstein The Human Eye As light enters through the human eye it first passes through the cornea (a thin transparent membrane of
LAB 12 Reflection and Refraction
 Cabrillo College Physics 10L Name LAB 12 Reflection and Refraction Read Hewitt Chapters 28 and 29 What to learn and explore Please read this! When light rays reflect off a mirror surface or refract through
Cabrillo College Physics 10L Name LAB 12 Reflection and Refraction Read Hewitt Chapters 28 and 29 What to learn and explore Please read this! When light rays reflect off a mirror surface or refract through
CHAPTER 3LENSES. 1.1 Basics. Convex Lens. Concave Lens. 1 Introduction to convex and concave lenses. Shape: Shape: Symbol: Symbol:
 CHAPTER 3LENSES 1 Introduction to convex and concave lenses 1.1 Basics Convex Lens Shape: Concave Lens Shape: Symbol: Symbol: Effect to parallel rays: Effect to parallel rays: Explanation: Explanation:
CHAPTER 3LENSES 1 Introduction to convex and concave lenses 1.1 Basics Convex Lens Shape: Concave Lens Shape: Symbol: Symbol: Effect to parallel rays: Effect to parallel rays: Explanation: Explanation:
Light: Lenses and. Mirrors. Test Date: Name 1ÿ-ÿ. Physics. Light: Lenses and Mirrors
 Name 1ÿ-ÿ Physics Light: Lenses and Mirrors i Test Date: "Shadows cannot see themselves in the mirror of the sun." -Evita Peron What are lenses? Lenses are made from transparent glass or plastice and refract
Name 1ÿ-ÿ Physics Light: Lenses and Mirrors i Test Date: "Shadows cannot see themselves in the mirror of the sun." -Evita Peron What are lenses? Lenses are made from transparent glass or plastice and refract
Lenses. A transparent object used to change the path of light Examples: Human eye Eye glasses Camera Microscope Telescope
 SNC2D Lenses A transparent object used to change the path of light Examples: Human eye Eye glasses Camera Microscope Telescope Reading stones used by monks, nuns, and scholars ~1000 C.E. Lenses THERE ARE
SNC2D Lenses A transparent object used to change the path of light Examples: Human eye Eye glasses Camera Microscope Telescope Reading stones used by monks, nuns, and scholars ~1000 C.E. Lenses THERE ARE
Determination of Focal Length of A Converging Lens and Mirror
 Physics 41 Determination of Focal Length of A Converging Lens and Mirror Objective: Apply the thin-lens equation and the mirror equation to determine the focal length of a converging (biconvex) lens and
Physics 41 Determination of Focal Length of A Converging Lens and Mirror Objective: Apply the thin-lens equation and the mirror equation to determine the focal length of a converging (biconvex) lens and
Thin Lenses. Lecture 25. Chapter 23. Ray Optics. Physics II. Course website:
 Lecture 25 Chapter 23 Physics II Ray Optics Thin Lenses Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov201415/physics2spring.html
Lecture 25 Chapter 23 Physics II Ray Optics Thin Lenses Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Lecture Capture: http://echo360.uml.edu/danylov201415/physics2spring.html
PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II
 PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II Laboratory Advanced Sheet Thin Lenses 1. Objectives. The objectives of this laboratory are a. to be able to measure the focal length of a converging lens.
PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II Laboratory Advanced Sheet Thin Lenses 1. Objectives. The objectives of this laboratory are a. to be able to measure the focal length of a converging lens.
Assignment X Light. Reflection and refraction of light. (a) Angle of incidence (b) Angle of reflection (c) principle axis
 Assignment X Light Reflection of Light: Reflection and refraction of light. 1. What is light and define the duality of light? 2. Write five characteristics of light. 3. Explain the following terms (a)
Assignment X Light Reflection of Light: Reflection and refraction of light. 1. What is light and define the duality of light? 2. Write five characteristics of light. 3. Explain the following terms (a)
General Physics II. Optical Instruments
 General Physics II Optical Instruments 1 The Thin-Lens Equation 2 The Thin-Lens Equation Using geometry, one can show that 1 1 1 s+ =. s' f The magnification of the lens is defined by For a thin lens,
General Physics II Optical Instruments 1 The Thin-Lens Equation 2 The Thin-Lens Equation Using geometry, one can show that 1 1 1 s+ =. s' f The magnification of the lens is defined by For a thin lens,
The Optics of Mirrors
 Use with Text Pages 558 563 The Optics of Mirrors Use the terms in the list below to fill in the blanks in the paragraphs about mirrors. reversed smooth eyes concave focal smaller reflect behind ray convex
Use with Text Pages 558 563 The Optics of Mirrors Use the terms in the list below to fill in the blanks in the paragraphs about mirrors. reversed smooth eyes concave focal smaller reflect behind ray convex
Unit 2: Optics Part 2
 Unit 2: Optics Part 2 Refraction of Visible Light 1. Bent-stick effect: When light passes from one medium to another (for example, when a beam of light passes through air and into water, or vice versa),
Unit 2: Optics Part 2 Refraction of Visible Light 1. Bent-stick effect: When light passes from one medium to another (for example, when a beam of light passes through air and into water, or vice versa),
Physics II. Chapter 23. Spring 2018
 Physics II Chapter 23 Spring 2018 IMPORTANT: Except for multiple-choice questions, you will receive no credit if you show only an answer, even if the answer is correct. Always show in the space on your
Physics II Chapter 23 Spring 2018 IMPORTANT: Except for multiple-choice questions, you will receive no credit if you show only an answer, even if the answer is correct. Always show in the space on your
Lenses. Not in your text book
 Lenses Not in your text book Objectives: 1. Students will be able to draw a ray diagram for a lens 2. Students will be able to explain the difference between a real and a virtual image Different Lenses,
Lenses Not in your text book Objectives: 1. Students will be able to draw a ray diagram for a lens 2. Students will be able to explain the difference between a real and a virtual image Different Lenses,
Academic Year: 2017/2018 Term 3 Physics - Grade 10 Revision sheet Chapter 13: section 1,2,3 / Chapter 14: section 1 pages: ( ),( )
 Academic Year: 2017/2018 Term 3 Physics - Grade 10 Revision sheet Chapter 13: section 1,2,3 / Chapter 14: section 1 pages: (442-462),(482-487) Spherical curved mirrors : a mirror that has the shape of
Academic Year: 2017/2018 Term 3 Physics - Grade 10 Revision sheet Chapter 13: section 1,2,3 / Chapter 14: section 1 pages: (442-462),(482-487) Spherical curved mirrors : a mirror that has the shape of
Class-X Assignment (Chapter-10) Light-Reflection & Refraction
 Class-X Assignment (Chapter-10) Light-Reflection & Refraction Q 1. How does light enable us to see an object? Q 2. What is a concave mirror? Q 3. What is the relationship between focal length and radius
Class-X Assignment (Chapter-10) Light-Reflection & Refraction Q 1. How does light enable us to see an object? Q 2. What is a concave mirror? Q 3. What is the relationship between focal length and radius
Refraction is the when a ray changes mediums. Examples of mediums:
 Refraction and Lenses Refraction is the when a ray changes mediums. Examples of mediums: Lenses are optical devices which take advantage of the refraction of light to 1. produces images real and 2. change
Refraction and Lenses Refraction is the when a ray changes mediums. Examples of mediums: Lenses are optical devices which take advantage of the refraction of light to 1. produces images real and 2. change
Optical Systems. The normal eye
 Optical Systems The normal eye The ciliary muscles can adjust the shape of the lens of the human eye. As the eye attempts to see objects at different distances, the muscles will adjust the focal length
Optical Systems The normal eye The ciliary muscles can adjust the shape of the lens of the human eye. As the eye attempts to see objects at different distances, the muscles will adjust the focal length
Image Formation by Lenses
 Image Formation by Lenses Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Lenses are found in a huge array of optical instruments, ranging from a simple magnifying glass to the eye to a camera s zoom lens. In this section, we will
Image Formation by Lenses Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Lenses are found in a huge array of optical instruments, ranging from a simple magnifying glass to the eye to a camera s zoom lens. In this section, we will
Chapter 29/30. Wave Fronts and Rays. Refraction of Sound. Dispersion in a Prism. Index of Refraction. Refraction and Lenses
 Chapter 29/30 Refraction and Lenses Refraction Refraction the bending of waves as they pass from one medium into another. Caused by a change in the average speed of light. Analogy A car that drives off
Chapter 29/30 Refraction and Lenses Refraction Refraction the bending of waves as they pass from one medium into another. Caused by a change in the average speed of light. Analogy A car that drives off
Geometric Optics. Find the focal lengths of lenses and mirrors; Draw and understand ray diagrams; and Build a simple telescope
 Geometric Optics I. OBJECTIVES Galileo is known for his many wondrous astronomical discoveries. Many of these discoveries shook the foundations of Astronomy and forced scientists and philosophers alike
Geometric Optics I. OBJECTIVES Galileo is known for his many wondrous astronomical discoveries. Many of these discoveries shook the foundations of Astronomy and forced scientists and philosophers alike
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
Part 1 Investigating Snell s Law
 Geometric Optics with Lenses PURPOSE: To observe the refraction of light off through lenses; to investigate the relationship between objects and images; to study the relationship between object distance,
Geometric Optics with Lenses PURPOSE: To observe the refraction of light off through lenses; to investigate the relationship between objects and images; to study the relationship between object distance,
General Physics II. Ray Optics
 General Physics II Ray Optics 1 Dispersion White light is a combination of all the wavelengths of the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Red light has the longest wavelengths and violet light
General Physics II Ray Optics 1 Dispersion White light is a combination of all the wavelengths of the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Red light has the longest wavelengths and violet light
Physics 208 Spring 2008 Lab 2: Lenses and the eye
 Name Section Physics 208 Spring 2008 Lab 2: Lenses and the eye Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. You must use complete sentences and clearly explain
Name Section Physics 208 Spring 2008 Lab 2: Lenses and the eye Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. You must use complete sentences and clearly explain
Unit 3: Chapter 6. Refraction
 Unit 3: Chapter 6 Refraction Refraction of Visible Light 2 Examples: 1. Bent-stick effect: When light passes from one medium to another (ex: from air into water), the change of speed causes it to change
Unit 3: Chapter 6 Refraction Refraction of Visible Light 2 Examples: 1. Bent-stick effect: When light passes from one medium to another (ex: from air into water), the change of speed causes it to change
Test Review # 9. Physics R: Form TR9.15A. Primary colors of light
 Physics R: Form TR9.15A TEST 9 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 9 Light and Color. Color comes from light, an electromagnetic wave that travels in straight lines in all directions from a light source
Physics R: Form TR9.15A TEST 9 REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 9 Light and Color. Color comes from light, an electromagnetic wave that travels in straight lines in all directions from a light source
Lenses. A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved.
 PHYSICS NOTES ON A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of There are two types of basic lenses. (1.)
PHYSICS NOTES ON A lens is any glass, plastic or transparent refractive medium with two opposite faces, and at least one of the faces must be curved. Types of There are two types of basic lenses. (1.)
Thin Lenses. Physics 227 Lab. Introduction:
 Introduction: From last week's lab, Reflection and Refraction, you should already be familiar with the following terms: principle axis, focal point, focal length,f, converging lens (f is +), and diverging
Introduction: From last week's lab, Reflection and Refraction, you should already be familiar with the following terms: principle axis, focal point, focal length,f, converging lens (f is +), and diverging
Focus on an optical blind spot A closer look at lenses and the basics of CCTV optical performances,
 Focus on an optical blind spot A closer look at lenses and the basics of CCTV optical performances, by David Elberbaum M any security/cctv installers and dealers wish to know more about lens basics, lens
Focus on an optical blind spot A closer look at lenses and the basics of CCTV optical performances, by David Elberbaum M any security/cctv installers and dealers wish to know more about lens basics, lens
