PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE. Photoacoustic imaging with planoconcave optical microresonator sensors: feasibility studies based on phantom imaging
|
|
|
- Isabel Cooper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROCDINGS OF SPI SPIDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Photoacoustic imaging with planoconcave optical microresonator sensors: feasibility studies based on phantom imaging James A. Guggenheim dward Z. Zhang Paul C. Beard
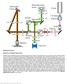
2 Photoacoustic imaging with planoconcave optical microresonator sensors: feasibility studies based on phantom imaging James A. Guggenheim, dward Z. Zhang and Paul C. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical ngineering, University Collegee London, Gower Street, London WC1 6BT, UK. ABSTRACT The planar Fabry-Pérot (FP) sensor provides highh quality photoacoustic (PA) images but beam walk-off limits sensitivity and thus penetration depth to 1 cm. Planoconcave microresonator sensors eliminate beam walk-off enabling sensitivity to be increased by an order-of-magnitude whilst retaining the highly favourable frequency response and directional characteristics of the FP sensor. The first tomographic PA images obtained in a tissue- near realistic phantom using the new sensors are described. These show that the microresonator sensors provide identical image quality as the planar FP sensor but with significantly greater penetration depth (e.g. 2-3cm) due to their higher sensitivity. This offers the prospect of whole body small animal imaging and clinical imaging to depths previously unattainable using the FP planar sensor. 1. INTRODUCTION The thin film polymer Fabry-Pérot (FP) sensor based photoacoustic (PA) imaging system [1] shown in figure 1 is one of several non-traditional ultrasound detection systems based on optical rather than piezoelectric detection schemes. Other such systems include those based on micro-ring resonators [2], fiber Bragg gratings [3], CCDs [4] and probe beam deflection [5]. Polymer spacer Dichroi mirrors Sensor interrogati beam hh Fabry-fDerot sensor head xcite3tion light x -y scanner, Sensor - interroç)ation beam Figure 1: FP sensor based PA imaging system (figure adapted from [6]). The transduction mechanism of the FP sensor [7] is one in whichh an incident acoustic wave modulates its optical thickness resulting in a corresponding modulation in its reflectivity. The latter is detected using a continuous wave interrogation laser beam focussed on the plane of the sensor. The advantage of this approach to ultrasonic detection over conventional piezoelectric detectors is that it provides a highly uniform frequency response (typical -3dB bandwidths of MHz) and a wide directivity due to the small (<Ø100 µm) acoustic element size, both of which impact directly upon PA image quality. The sensitivity in terms of noise equivalent pressure (NP) is in the range Pa with reference to peak (3σ) noise over a 20 MHz measurement bandwidth [1], equivalent to Pa over 20 MHz for root mean squared ( RMS) noise or mpa/ Hz. To put this into perspective a piezoelectric sensor of comparable element size and frequency response would have >2 orders-of-magnitude poorer NP [1]. Photons Plus Ultrasound: Imaging and Sensing 2017, edited by Alexander A. Oraevsky, Lihong V. Wang, Proc. of SPI Vol , V 2017 SPI CCC code: /17/$18 doi: / Proc. of SPI Vol V-1
3 With these characteristics the FP system provides high resolution, high fidelity PA images of tissue with a maximum penetration depth of 10 mmm [8]. There is strong motivation to increase this maximum depth as it would significantly extend the range of available preclinical and clinical applications. This requires a significant improvement in NP but this is limited by the divergent nature of the sensor interrogation beam which encounters beam walk-off inside the FP spacer [9] [11] as shown in figure 2a; the effect of beam-walk is to limit the cavity finesse and therefore the sensitivity. apsulating mer layer ;pacer ar mirror ubstrate Divo ogation - interr eam Ik-off beeam n cap)sulating polyrrier layer Sp)acer - Curvec mirror Beam opticall confine (a) Figure 2: Schematics of (a) planar FP and (b) planoconcave microresonator sensor illustrating beam walk-off in the former and its eliminationn in the latter. To overcome this limitation, planoconcave optical microresonator sensors were developedd with a curved top mirror designed to refocus light upon each round trip in the spacer, thereby eliminating beam walk-off and improving optical confinement [9] [11] as illustrated in figure 2b. With this design it was found that NP could be improved significantly by increasing the mirror reflectance and spacer thickness [11], the latter at a cost to bandwidth as the sensor responds to the spatial integral of the acoustic field. This trade-off enables a family of sensors with different bandwidths and sensitivities to be fabricated. For example, we have previously developed a 100 µm thick sensor with a 9 MHz -3dB bandwidth and NP <10 Pa (3.2 mpa/ Hz) and a 340 µm thick sensor with a 3 MHz -3dB bandwidth and NP <3 Pa (1.6 mpa/ Hz) [11]. The latter represents an order of magnitude improvement in NP over the planar FP sensor. In addition to higher sensitivity the microresonators have the same frequency response and directivity as the FP sensor as they are acoustically identical [11]. This is because both types of sensor are embedded in a planar polymer layer (figure 2) with mirrors that are ultrasonically sub-wavelength and therefore acoustically negligible. These characteristics suggest that when used for PA imagingg the planoconcave microresonator sensors will provide near identical image quality as the planar FP sensor but with significantly greater penetration depth. This paper examines this experimentally. Two experiments are described, the first investigating penetration depth and the second testing image quality. The results demonstrate that planoconcave microresonator sensors achieve deeper imaging with no loss in image quality. 2. IMAGING PNTRATION DPTH To investigate the achievable penetration depth for PA imaging in tomography mode using microresonator sensors, a tissue phantom was imaged in forward mode. Figure 3 shows a schematic of the experimental setup. The phantom consisted of 8 dye-filled in deionised (DI) water. At 1064 nm the medium had µ a = 0.12 cm -1 and µ s = 6 cm -1, polythene tubes arranged vertically in a liquid scattering medium composed of 0.8% Intralipid i.e. μ eff = 1.5 cm -1 ; an attenuation comparable to soft tissues at 750 nm [12]. The tubes had an inner and outer diameter of 580 µm and 960 µm respectively. They contained an Indian ink solution of µ a = 3 cm -1 (at 1064 nm); comparable to 90% oxygenated blood at 750 nm. The excitation source was a fibre-coupled 1064 nm Q-switched ND:YAG laser (Minilite, Continuum Lasers) with a pulse repetition frequency (PRF) of 20 Hz and a pulse-width of 6ns. The pulse energy at the fibre output was 14 mj. The beam was expanded to Ø10 mm yielding a surface fluencee of 18 mj/cmm 2 below the maximum permissible exposure for human skin [13]. The phantom was imaged using a 250 µm thick microresonator sensor with a -3dB bandwidth of 4 MHz and an NP of 2 mpa/ Hz. The sensor was fixed in position and the phantom was mechanically scanned in 2D so as to emulate a 2D array of identical sensors imaging a fixed phantom. Acoustic waveforms were acquired by an oscilloscope (TDS5K, Tektronix) triggered by a photodiode. The total scan area was 41 mm by 12 mm, scanned in (b) Proc. of SPI Vol V-2
4 steps of 100 µm and 2000 µm. No signal averaging was used. The microresonator sensor was then replaced by an FP sensor for comparison and the scan was repeated. XCÍtc3tion light 10( 64 m 18 rmj/ J /cmz r Absorbing Na =3ci j 0580 p / Y Scatteï i ig liquid.5 cm -1 ur=1 Figure 3: xperime Senso Interrogation laser beam ental phantom imaging setup. 3D Images were reconstructed by time reversal using K-wave [14]. Prior to reconstruction waveforms were filtered with a low pass filter with a -3dB cut-off equal to the -3dB bandwidth of the sensor. Reconstructed images were subjected to a 1D fluence correction [15] to aid visualisation. 2D cross-sections through the images are plotted in figure 4. N.v- N 15 mm 15 mm -> (a) (b) Figure 4: 2D cross-sections and vertical profiles through 3D PA images of a tube phantom (figure 3) acquired with (a) an FP sensor and (b) a planoconcave microresonator sensor. Arrows indicate tubes. Compared to typical PA images obtained with the FP sensor both images show significant artefacts. Thesee are a consequence of the experimental conditions; a combination of limited-aperture [16] and tube-related artefacts due to the acoustic mismatch of the tubes to the background. The latter do not appear in vivo and the former can be removed by increasing the size of the scan area whichh was limited here by the mechanical scanning setup. In the FP planar sensor image, only the top 3 tubes are clearly visible and the 4 th is just visible above the evident noise floor. By contrast in the microresonator image all 8 tubes can be seen. This represents an increase of 16 mm in imaging depth. Proc. of SPI Vol V-3
5 3. IMAG QUALITY xcitation LO (Li 4' Sensor Figure 5: Schematic of second phantom. To assess image quality a second phantom was imaged with a 100 µm microresonator. The phantom (figure 5) was 15 mm deep with tubes made of THV of 604 (725) µm inner (outer) diameter. As above, the imaging experiment was repeated using the planar FP sensor for comparison. The results are shown in figure 6. Planar sei nsor image 100 pm nnicrores. ima! ge Laterai profiles v is d 1 True - Planar Microres. Qmm ICI Ve rti cal profiles v mm 6 mm 1 o <- 2 mm True - Planar Microres. Figure 6: xperimental phantom images obtained using the FP sensor and a 100 µm microresonator sensor. The zoomed in images show the middle tube in higher detail. Lateral and vertical profiles are plotted taken through the centre of the middle tube. The images are relatively artefact-frepractically indistinguishable from that of the FP with the only apparent difference being a and provide a sharp, faithful representation of the three tubes. The microresonator image is better SNR due to the higher sensitivity. The profiles through the centre of the middle tube show no noticeable differences and are the expected width given the known size of the tubes. 4. CONCLUSIONS In summary, tomographic PA images obtained by planoconcave microresonator sensors were presented. As compared to the well-established planar FP sensor, the microresonator sensors achieved 16 mm deeper imaging in a tissue-realistic phantom, with no loss in image quality. These sensors therefore offer the prospect of in vivo imaging with high resolution and fidelity and considerably greater (2-3 cm) penetration depth. Imagingg was performed with a single sensor emulating a 2D array but in the future it is anticipated that 2D arrays will be fabricated using techniques such as nano-imprinting. In conjunction with multi-beam interrogation schemes [17] and sub-sampling approaches it will then be possible to perform in vivo imaging in a reasonable time frame (on the scale of seconds). Proc. of SPI Vol V-4
6 It may be also possible to increase sensitivity and penetration depth still further. For instance by fabricating sensors using polymers of lower optical absorption to improve finesse [9] or of lower Young s modulus to increase compliance. This would allow even deeper imaging and enable still more challenging applications such as the noninvasive clinical assessment of breast tumours. ACKNOWLDGMNTS This work was funded by PSRC and uropean Union project FAMOS (FP7 ICT, Contract ). RFRNCS [1]. Zhang, J. Laufer, and P. Beard, Backward-mode multiwavelength photoacoustic scanner using a planar Fabry-Perot polymer film ultrasound sensor for high-resolution three-dimensional imaging of biological tissues, Appl. Opt., vol. 47, no. 4, pp , Mar [2] H. Li, B. Dong, Z. Zhang, H. F. Zhang, and C. Sun, A transparent broadband ultrasonic detector based on an optical micro-ring resonator for photoacoustic microscopy., Sci. Rep., vol. 4, p. 4496, Jan [3] A. Rosenthal, D. Razansky, and V. Ntziachristos, High-sensitivity compact ultrasonic detector based on a pi-phaseshifted fiber Bragg grating., Opt. Lett., vol. 36, no. 10, pp , May [4] R. Nuster, P. Slezak, and G. Paltauf, High resolution three-dimensional photoacoutic tomography with CCD-camera based ultrasound detection, Biomed. Opt. xpress, vol. 5, no. 8, p. 2635, Jul [5] S. M. Maswadi, B. L. Ibey, C. C. Roth, D. A. Tsyboulski, H. T. Beier, R. D. Glickman, and A. A. Oraevsky, All-optical optoacoustic microscopy based on probe beam deflection technique, Photoacoustics, vol. 4, no. 1, pp , [6] J. Laufer, P. Johnson,. Zhang, B. Treeby, B. Cox, B. Pedley, and P. Beard, In vivo preclinical photoacoustic imaging of tumor vasculature development and therapy, J. Biomed. Opt., vol. 17, no. 5, pp , May [7] P. C. Beard, F. Perennes, and T. N. Mills, Transduction mechanisms of the Fabry-Perot polymer film sensing concept for wideband ultrasound detection, I Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control, vol. 46, no. 6, pp , Jan [8] A. P. Jathoul, J. Laufer, O. Ogunlade, B. Treeby, B. Cox,. Zhang, P. Johnson, A. R. Pizzey, B. Philip, T. Marafioti, M. F. Lythgoe, R. B. Pedley, M. a. Pule, and P. Beard, Deep in vivo photoacoustic imaging of mammalian tissues using a tyrosinase-based genetic reporter, Nat. Photonics, vol. 9, no. April, pp , Mar [9] J. A. Guggenheim,. Z. Zhang, and P. C. Beard, Planoconcave optical microresonator sensors for photoacoustic imaging: pushing the limits of sensitivity (Conference Presentation), Proc. SPI, vol p M 97082M 1, [10] J. A. Guggenheim, J. Li,. Z. Zhang, and P. C. Beard, Frequency response and directivity of highly sensitive optical microresonator detectors for photoacoustic imaging, in Proc. of SPI, Photons Plus Ultrasound: Imaging and Sensing, 2015, vol. 9323, p C. [11] J. A. Guggenheim, J. Li, T. J. Allen, R. J. Colchester, S. Noimark, O. Ogunlade, I. P. Parkin, I. Papakonstantinou, A. Desjardins,. Z. Zhang, and P. C. Beard, Ultra-sensitive planoconcave optical microresonators for ultrasound sensing, p. In review. [12] S. L. Jacques, Optical properties of biological tissues: a review, Phys. Med. Biol., vol. 58, no. 14, pp , Jul [13] C. Li and L. V Wang, Photoacoustic tomography and sensing in biomedicine, Phys. Med. Biol., vol. 54, no. 19, pp. R59-97, Oct [14] B.. Treeby and B. T. Cox, k-wave: MATLAB toolbox for the simulation and reconstruction of photoacoustic wave fields, J. Biomed. Opt., vol. 15, no. 2, p , [15] B.. Treeby, J. Jaros, and B. T. Cox, Advanced photoacoustic image reconstruction using the k-wave toolbox, in Proceedings of SPI, 2016, vol. 9708, p P. [16] R. llwood, O. Ogunlade,. Zhang, P. Beard, and B. Cox, Photoacoustic tomography using orthogonal Fabry Pérot sensors, J. Biomed. Opt., vol. 22, no. 4, p , [17] N. Huynh, O. Ogunlade,. Zhang, B. Cox, and P. Beard, Photoacoustic imaging using an 8-beam Fabry-Perot scanner, in Proceedings of SPI, 2016, vol. 9708, p L. Proc. of SPI Vol V-5
Photoacoustic imaging using an 8-beam Fabry-Perot scanner
 Photoacoustic imaging using an 8-beam Fabry-Perot scanner Nam Huynh, Olumide Ogunlade, Edward Zhang, Ben Cox, Paul Beard Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University College London,
Photoacoustic imaging using an 8-beam Fabry-Perot scanner Nam Huynh, Olumide Ogunlade, Edward Zhang, Ben Cox, Paul Beard Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University College London,
A miniature all-optical photoacoustic imaging probe
 A miniature all-optical photoacoustic imaging probe Edward Z. Zhang * and Paul C. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E 6BT, UK http://www.medphys.ucl.ac.uk/research/mle/index.htm
A miniature all-optical photoacoustic imaging probe Edward Z. Zhang * and Paul C. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E 6BT, UK http://www.medphys.ucl.ac.uk/research/mle/index.htm
All-optical endoscopic probe for high resolution 3D photoacoustic tomography
 All-optical endoscopic probe for high resolution 3D photoacoustic tomography R. Ansari, E. Zhang, A. E. Desjardins, and P. C. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University
All-optical endoscopic probe for high resolution 3D photoacoustic tomography R. Ansari, E. Zhang, A. E. Desjardins, and P. C. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University
Multimodal simultaneous photoacoustic tomography, optical resolution microscopy and OCT system
 Multimodal simultaneous photoacoustic tomography, optical resolution microscopy and OCT system Edward Z. Zhang +, Jan Laufer +, Boris Považay *, Aneesh Alex *, Bernd Hofer *, Wolfgang Drexler *, Paul Beard
Multimodal simultaneous photoacoustic tomography, optical resolution microscopy and OCT system Edward Z. Zhang +, Jan Laufer +, Boris Považay *, Aneesh Alex *, Bernd Hofer *, Wolfgang Drexler *, Paul Beard
Ultra-sensitive planoconcave optical microresonators for ultrasound sensing
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 Ultra-sensitive planoconcave optical microresonators for
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 Ultra-sensitive planoconcave optical microresonators for
Novel fibre lasers as excitation sources for photoacoustic tomography and microscopy
 Novel fibre lasers as excitation sources for photoacoustic tomography and microscopy T.J. Allen (1), M.O. Berendt (2), J. Spurrell (2), S.U. Alam (2), E.Z. Zhang (1), D.J. Richardson (2) and P.C. Beard
Novel fibre lasers as excitation sources for photoacoustic tomography and microscopy T.J. Allen (1), M.O. Berendt (2), J. Spurrell (2), S.U. Alam (2), E.Z. Zhang (1), D.J. Richardson (2) and P.C. Beard
Non-contact Photoacoustic Tomography using holographic full field detection
 Non-contact Photoacoustic Tomography using holographic full field detection Jens Horstmann* a, Ralf Brinkmann a,b a Medical Laser Center Lübeck, Peter-Monnik-Weg 4, 23562 Lübeck, Germany; b Institute of
Non-contact Photoacoustic Tomography using holographic full field detection Jens Horstmann* a, Ralf Brinkmann a,b a Medical Laser Center Lübeck, Peter-Monnik-Weg 4, 23562 Lübeck, Germany; b Institute of
Acoustic resolution. photoacoustic Doppler velocimetry. in blood-mimicking fluids. Supplementary Information
 Acoustic resolution photoacoustic Doppler velocimetry in blood-mimicking fluids Joanna Brunker 1, *, Paul Beard 1 Supplementary Information 1 Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University
Acoustic resolution photoacoustic Doppler velocimetry in blood-mimicking fluids Joanna Brunker 1, *, Paul Beard 1 Supplementary Information 1 Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University
Large area laser scanning optical resolution photoacoustic microscopy using a fibre optic sensor
 Vol. 9, No. 2 1 Feb 2018 BIOMEDICAL OPTICS EXPRESS 650 Large area laser scanning optical resolution photoacoustic microscopy using a fibre optic sensor THOMAS J. ALLEN,* OLUMIDE OGUNLADE, EDWARD ZHANG,
Vol. 9, No. 2 1 Feb 2018 BIOMEDICAL OPTICS EXPRESS 650 Large area laser scanning optical resolution photoacoustic microscopy using a fibre optic sensor THOMAS J. ALLEN,* OLUMIDE OGUNLADE, EDWARD ZHANG,
A Real-time Photoacoustic Imaging System with High Density Integrated Circuit
 2011 3 rd International Conference on Signal Processing Systems (ICSPS 2011) IPCSIT vol. 48 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCSIT.2012.V48.12 A Real-time Photoacoustic Imaging System
2011 3 rd International Conference on Signal Processing Systems (ICSPS 2011) IPCSIT vol. 48 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCSIT.2012.V48.12 A Real-time Photoacoustic Imaging System
DEVELOPMENT OF A 50MHZ FABRY-PEROT TYPE FIBRE-OPTIC HYDROPHONE FOR THE CHARACTERISATION OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND FIELDS.
 DEVELOPMENT OF A 50MHZ FABRY-PEROT TYPE FIBRE-OPTIC HYDROPHONE FOR THE CHARACTERISATION OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND FIELDS. P Morris A Hurrell P Beard Dept. Medical Physics and Bioengineering, UCL, Gower Street,
DEVELOPMENT OF A 50MHZ FABRY-PEROT TYPE FIBRE-OPTIC HYDROPHONE FOR THE CHARACTERISATION OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND FIELDS. P Morris A Hurrell P Beard Dept. Medical Physics and Bioengineering, UCL, Gower Street,
High power visible light emitting diodes as pulsed excitation sources for biomedical photoacoustics
 High power visible light emitting diodes as pulsed excitation sources for biomedical photoacoustics Thomas J. Allen * and Paul C. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University
High power visible light emitting diodes as pulsed excitation sources for biomedical photoacoustics Thomas J. Allen * and Paul C. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University
Light emitting diodes as an excitation source for biomedical photoacoustics
 Light emitting diodes as an excitation source for biomedical photoacoustics. J. llen and P.C. eard Department of Medical Physics and ioengineering, University College London, Malet Place Engineering uilding,
Light emitting diodes as an excitation source for biomedical photoacoustics. J. llen and P.C. eard Department of Medical Physics and ioengineering, University College London, Malet Place Engineering uilding,
Edward Zhang,* Jan Laufer, and Paul Beard
 Backward-mode multiwavelength photoacoustic scanner using a planar Fabry Perot polymer film ultrasound sensor for high-resolution three-dimensional imaging of biological tissues Edward Zhang,* Jan Laufer,
Backward-mode multiwavelength photoacoustic scanner using a planar Fabry Perot polymer film ultrasound sensor for high-resolution three-dimensional imaging of biological tissues Edward Zhang,* Jan Laufer,
Photoacoustic imaging with coherent light
 Photoacoustic imaging with coherent light Emmanuel Bossy Institut Langevin, ESPCI ParisTech CNRS UMR 7587, INSERM U979 Workshop Inverse Problems and Imaging Institut Henri Poincaré, 12 February 2014 Background:
Photoacoustic imaging with coherent light Emmanuel Bossy Institut Langevin, ESPCI ParisTech CNRS UMR 7587, INSERM U979 Workshop Inverse Problems and Imaging Institut Henri Poincaré, 12 February 2014 Background:
Transparent Fabry Perot polymer film ultrasound array for backward-mode photoacoustic imaging
 Transparent Fabry Perot polymer film ultrasound array for backward-mode photoacoustic imaging Beard PC 1, Zhang EZ, Cox BT Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, University College London, Shropshire
Transparent Fabry Perot polymer film ultrasound array for backward-mode photoacoustic imaging Beard PC 1, Zhang EZ, Cox BT Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, University College London, Shropshire
Prospects for in vivo blood velocimetry using acoustic resolution photoacoustic Doppler
 Prospects for in vivo blood velocimetry using acoustic resolution photoacoustic Doppler J. Brunker and P. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University College London, Gower
Prospects for in vivo blood velocimetry using acoustic resolution photoacoustic Doppler J. Brunker and P. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University College London, Gower
Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers (CMUTs) for Photoacoustic Imaging
 Invited Paper Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers (CMUTs) for Photoacoustic Imaging Srikant Vaithilingam a,*, Ira O. Wygant a,paulinas.kuo a, Xuefeng Zhuang a, Ömer Oralkana, Peter D. Olcott
Invited Paper Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers (CMUTs) for Photoacoustic Imaging Srikant Vaithilingam a,*, Ira O. Wygant a,paulinas.kuo a, Xuefeng Zhuang a, Ömer Oralkana, Peter D. Olcott
Optical Detection of High-Frequency Ultrasound Using Polymer Microring Resonators
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Optical Detection of High-Frequency Ultrasound Using Polymer Microring Resonators
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Optical Detection of High-Frequency Ultrasound Using Polymer Microring Resonators
Acousto-optic imaging of tissue. Steve Morgan
 Acousto-optic imaging of tissue Steve Morgan Electrical Systems and Optics Research Division, University of Nottingham, UK Steve.morgan@nottingham.ac.uk Optical imaging is useful Functional imaging of
Acousto-optic imaging of tissue Steve Morgan Electrical Systems and Optics Research Division, University of Nottingham, UK Steve.morgan@nottingham.ac.uk Optical imaging is useful Functional imaging of
Ultrasound-modulated optical tomography of absorbing objects buried in dense tissue-simulating turbid media
 Ultrasound-modulated optical tomography of absorbing objects buried in dense tissue-simulating turbid media Lihong Wang and Xuemei Zhao Continuous-wave ultrasonic modulation of scattered laser light was
Ultrasound-modulated optical tomography of absorbing objects buried in dense tissue-simulating turbid media Lihong Wang and Xuemei Zhao Continuous-wave ultrasonic modulation of scattered laser light was
An optical detection system for biomedical photoacoustic imaging
 INVITED PAPER An optical detection system for biomedical photoacoustic imaging Beard PC * and Mills TN Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, University College London, Shropshire House, 11-20
INVITED PAPER An optical detection system for biomedical photoacoustic imaging Beard PC * and Mills TN Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, University College London, Shropshire House, 11-20
Improving the Quality of Photoacoustic Images using the Short-Lag Spatial Coherence Imaging Technique
 Improving the Quality of Photoacoustic Images using the Short-Lag Spatial Coherence Imaging Technique Behanz Pourebrahimi, Sangpil Yoon, Dustin Dopsa, Michael C. Kolios Department of Physics, Ryerson University,
Improving the Quality of Photoacoustic Images using the Short-Lag Spatial Coherence Imaging Technique Behanz Pourebrahimi, Sangpil Yoon, Dustin Dopsa, Michael C. Kolios Department of Physics, Ryerson University,
Broadband All-Optical Ultrasound Transducer
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Broadband All-Optical Ultrasound Transducer Yang HOU 1, Jin-Sung KIM 1, Shai ASHKENAZI
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Broadband All-Optical Ultrasound Transducer Yang HOU 1, Jin-Sung KIM 1, Shai ASHKENAZI
Dual wavelength laser diode excitation source for 2D photoacoustic imaging.
 Dual wavelength laser diode excitation source for 2D photoacoustic imaging. Thomas J. Allen and Paul C. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, Malet Place Engineering Building, Gower Street,
Dual wavelength laser diode excitation source for 2D photoacoustic imaging. Thomas J. Allen and Paul C. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, Malet Place Engineering Building, Gower Street,
Large-field-of-view laser-scanning OR-PAM using a fibre optic sensor
 Large-field-of-view laser-scanning OR-PAM using a fibre optic sensor T. J. Allen, E. Zhang and P.C. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University College London, Gower Street,
Large-field-of-view laser-scanning OR-PAM using a fibre optic sensor T. J. Allen, E. Zhang and P.C. Beard Department of Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, University College London, Gower Street,
ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 Ultra high sensitivity, wideband Fabry Perot ultrasound sensors as an alternative to piezoelectric PVDF transducers for biomedical photoacoustic detection Edward Z. Zhang * and Paul Beard Department of
Ultra high sensitivity, wideband Fabry Perot ultrasound sensors as an alternative to piezoelectric PVDF transducers for biomedical photoacoustic detection Edward Z. Zhang * and Paul Beard Department of
Transmission- and side-detection configurations in ultrasound-modulated optical tomography of thick biological tissues
 Transmission- and side-detection configurations in ultrasound-modulated optical tomography of thick biological tissues Jun Li, Sava Sakadžić, Geng Ku, and Lihong V. Wang Ultrasound-modulated optical tomography
Transmission- and side-detection configurations in ultrasound-modulated optical tomography of thick biological tissues Jun Li, Sava Sakadžić, Geng Ku, and Lihong V. Wang Ultrasound-modulated optical tomography
Wideband Focused Transducer Array for Optoacoustic Tomography
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Wideband Focused Transducer Array for Optoacoustic Tomography Varvara A. SIMONOVA
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Wideband Focused Transducer Array for Optoacoustic Tomography Varvara A. SIMONOVA
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter
 Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
2. Pulsed Acoustic Microscopy and Picosecond Ultrasonics
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Picosecond Ultrasonic Microscopy of Semiconductor Nanostructures Thomas J GRIMSLEY
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Picosecond Ultrasonic Microscopy of Semiconductor Nanostructures Thomas J GRIMSLEY
1002 ieee transactions on ultrasonics, ferroelectrics, and frequency control, vol. 52, no. 6, june 2005
 1002 ieee transactions on ultrasonics, ferroelectrics, and frequency control, vol. 52, no. 6, june 2005 Two-Dimensional Ultrasound Receive Array Using an Angle-Tuned Fabry-Perot Polymer Film Sensor for
1002 ieee transactions on ultrasonics, ferroelectrics, and frequency control, vol. 52, no. 6, june 2005 Two-Dimensional Ultrasound Receive Array Using an Angle-Tuned Fabry-Perot Polymer Film Sensor for
Microwave-induced acoustic imaging of biological tissues
 REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS VOLUME 70, NUMBER 9 SEPTEMBER 1999 Microwave-induced acoustic imaging of biological tissues Lihong V. Wang, Xuemei Zhao, Haitao Sun, and Geng Ku Optical Imaging Laboratory,
REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS VOLUME 70, NUMBER 9 SEPTEMBER 1999 Microwave-induced acoustic imaging of biological tissues Lihong V. Wang, Xuemei Zhao, Haitao Sun, and Geng Ku Optical Imaging Laboratory,
Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating. Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel
 Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel Zhijun Yan *, Pouneh Saffari, Kaiming Zhou, Adedotun Adebay, Lin Zhang Photonic Research Group, Aston
Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel Zhijun Yan *, Pouneh Saffari, Kaiming Zhou, Adedotun Adebay, Lin Zhang Photonic Research Group, Aston
Photoacoustic tomography of biological tissues with high cross-section resolution: Reconstruction and experiment
 Photoacoustic tomography of biological tissues with high cross-section resolution: Reconstruction and experiment Xueding Wang, Yuan Xu, and Minghua Xu Optical Imaging Laboratory, Biomedical Engineering
Photoacoustic tomography of biological tissues with high cross-section resolution: Reconstruction and experiment Xueding Wang, Yuan Xu, and Minghua Xu Optical Imaging Laboratory, Biomedical Engineering
Photoacoustic Imaging of Blood Vessels in Tissue
 of Blood Vessels in Tissue F.F.M. de Mul (University of Twente, Enschede, the Netherlands) FdM [µm] Imaging methods for hidden structures in turbid media (tissue) OCT/ OPS (C)M TOF / FM NIR green C(M)
of Blood Vessels in Tissue F.F.M. de Mul (University of Twente, Enschede, the Netherlands) FdM [µm] Imaging methods for hidden structures in turbid media (tissue) OCT/ OPS (C)M TOF / FM NIR green C(M)
Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics
 1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics Todd W. MURRAY 1,
1st International Symposium on Laser Ultrasonics: Science, Technology and Applications July 16-18 2008, Montreal, Canada Theory and Applications of Frequency Domain Laser Ultrasonics Todd W. MURRAY 1,
Ultrasound Beamforming and Image Formation. Jeremy J. Dahl
 Ultrasound Beamforming and Image Formation Jeremy J. Dahl Overview Ultrasound Concepts Beamforming Image Formation Absorption and TGC Advanced Beamforming Techniques Synthetic Receive Aperture Parallel
Ultrasound Beamforming and Image Formation Jeremy J. Dahl Overview Ultrasound Concepts Beamforming Image Formation Absorption and TGC Advanced Beamforming Techniques Synthetic Receive Aperture Parallel
Miniature probe for all-optical double gradient-index lenses photoacoustic microscopy
 Received: 19 April 2018 Revised: 3 June 2018 Accepted: 11 July 2018 DOI: 10.1002/jbio.201800147 FULL ARTICLE Miniature probe for all-optical double gradient-index lenses photoacoustic microscopy Zhendong
Received: 19 April 2018 Revised: 3 June 2018 Accepted: 11 July 2018 DOI: 10.1002/jbio.201800147 FULL ARTICLE Miniature probe for all-optical double gradient-index lenses photoacoustic microscopy Zhendong
Multi-depth photoacoustic microscopy with a focus tunable lens
 Multi-depth photoacoustic microscopy with a focus tunable lens Kiri Lee a, Euiheon Chung b, Tae Joong Eom a* a Advanced Photonics Research Institute, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, Gwangju,
Multi-depth photoacoustic microscopy with a focus tunable lens Kiri Lee a, Euiheon Chung b, Tae Joong Eom a* a Advanced Photonics Research Institute, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, Gwangju,
Miniature all-optical probe for large synthetic aperture photoacoustic-ultrasound imaging
 Vol. 25, No. 21 16 Oct 2017 OPTICS EXPRESS 25023 Miniature all-optical probe for large synthetic aperture photoacoustic-ultrasound imaging GUANGYAO LI,1 ZHENDONG GUO,1 AND SUNG-LIANG CHEN1,2,* 1 University
Vol. 25, No. 21 16 Oct 2017 OPTICS EXPRESS 25023 Miniature all-optical probe for large synthetic aperture photoacoustic-ultrasound imaging GUANGYAO LI,1 ZHENDONG GUO,1 AND SUNG-LIANG CHEN1,2,* 1 University
Derek Allman a, Austin Reiter b, and Muyinatu Bell a,c
 Exploring the effects of transducer models when training convolutional neural networks to eliminate reflection artifacts in experimental photoacoustic images Derek Allman a, Austin Reiter b, and Muyinatu
Exploring the effects of transducer models when training convolutional neural networks to eliminate reflection artifacts in experimental photoacoustic images Derek Allman a, Austin Reiter b, and Muyinatu
Evaluation of a Chip LED Sensor Module at 770 nm for Fat Thickness Measurement of Optical Tissue Phantoms and Human Body Tissue
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 51, No. 5, November 2007, pp. 1663 1667 Evaluation of a Chip LED Sensor Module at 770 nm for Fat Thickness Measurement of Optical Tissue Phantoms and Human
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 51, No. 5, November 2007, pp. 1663 1667 Evaluation of a Chip LED Sensor Module at 770 nm for Fat Thickness Measurement of Optical Tissue Phantoms and Human
Femtosecond laser microfabrication in. Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca
 Femtosecond laser microfabrication in polymers Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca laser microfabrication focus laser beam on material s surface laser microfabrication laser microfabrication laser microfabrication
Femtosecond laser microfabrication in polymers Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca laser microfabrication focus laser beam on material s surface laser microfabrication laser microfabrication laser microfabrication
A thin foil optical strain gage based on silicon-on-insulator microresonators
 A thin foil optical strain gage based on silicon-on-insulator microresonators D. Taillaert* a, W. Van Paepegem b, J. Vlekken c, R. Baets a a Photonics research group, Ghent University - INTEC, St-Pietersnieuwstraat
A thin foil optical strain gage based on silicon-on-insulator microresonators D. Taillaert* a, W. Van Paepegem b, J. Vlekken c, R. Baets a a Photonics research group, Ghent University - INTEC, St-Pietersnieuwstraat
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE. Teaching multilayer optical coatings with coaxial cables. J. Cos, M. M. Sánchez-López, J. A. Davis, D. Miller, I. Moreno, et al.
 PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Teaching multilayer optical coatings with coaxial cables J. Cos, M. M. Sánchez-López, J. A. Davis, D. Miller, I. Moreno, et al.
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Teaching multilayer optical coatings with coaxial cables J. Cos, M. M. Sánchez-López, J. A. Davis, D. Miller, I. Moreno, et al.
Multi-spectral acoustical imaging
 Multi-spectral acoustical imaging Kentaro NAKAMURA 1 ; Xinhua GUO 2 1 Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan 2 University of Technology, China ABSTRACT Visualization of object through acoustic waves is generally
Multi-spectral acoustical imaging Kentaro NAKAMURA 1 ; Xinhua GUO 2 1 Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan 2 University of Technology, China ABSTRACT Visualization of object through acoustic waves is generally
Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature
 Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature Donghui Zhao.a, Xuewen Shu b, Wei Zhang b, Yicheng Lai a, Lin Zhang a, Ian Bennion a a Photonics Research Group,
Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature Donghui Zhao.a, Xuewen Shu b, Wei Zhang b, Yicheng Lai a, Lin Zhang a, Ian Bennion a a Photonics Research Group,
Non-Contact Ultrasound Characterization of Paper Substrates
 ECNDT 006 - Poster 04 Non-Contact Ultrasound Characterization of Paper Substrates María HELGUERA, J. ARNEY, N. TALLAPALLY, D. ZOLLO., CFC Center for Imaging Science, Rochester Institute of Technology,
ECNDT 006 - Poster 04 Non-Contact Ultrasound Characterization of Paper Substrates María HELGUERA, J. ARNEY, N. TALLAPALLY, D. ZOLLO., CFC Center for Imaging Science, Rochester Institute of Technology,
Photonics and Optical Communication
 Photonics and Optical Communication (Course Number 300352) Spring 2007 Dr. Dietmar Knipp Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/dknipp/ 1 Photonics and Optical Communication
Photonics and Optical Communication (Course Number 300352) Spring 2007 Dr. Dietmar Knipp Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering http://www.faculty.iu-bremen.de/dknipp/ 1 Photonics and Optical Communication
Lecture 21. Wind Lidar (3) Direct Detection Doppler Lidar
 Lecture 21. Wind Lidar (3) Direct Detection Doppler Lidar Overview of Direct Detection Doppler Lidar (DDL) Resonance fluorescence DDL Fringe imaging DDL Scanning FPI DDL FPI edge-filter DDL Absorption
Lecture 21. Wind Lidar (3) Direct Detection Doppler Lidar Overview of Direct Detection Doppler Lidar (DDL) Resonance fluorescence DDL Fringe imaging DDL Scanning FPI DDL FPI edge-filter DDL Absorption
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ULTRASONICS, FERROELECTRICS, AND FREQUENCY CONTROL, VOL. 63, NO. 1, JANUARY
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ULTRASONICS, FERROELECTRICS, AND FREQUENCY CONTROL, VOL. 63, NO. 1, JANUARY 2016 83 Adaptive Light Modulation for Improved Resolution and Efficiency in All-Optical Pulse-Echo Ultrasound
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ULTRASONICS, FERROELECTRICS, AND FREQUENCY CONTROL, VOL. 63, NO. 1, JANUARY 2016 83 Adaptive Light Modulation for Improved Resolution and Efficiency in All-Optical Pulse-Echo Ultrasound
Comparison between optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy and confocal laser scanning microscopy for turbid sample imaging
 Comparison between optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy and confocal laser scanning microscopy for turbid sample imaging Paweena U-Thainual Do-Hyun Kim Journal of Biomedical Optics 20(12), 121202
Comparison between optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy and confocal laser scanning microscopy for turbid sample imaging Paweena U-Thainual Do-Hyun Kim Journal of Biomedical Optics 20(12), 121202
Resolution Enhancement and Frequency Compounding Techniques in Ultrasound.
 Resolution Enhancement and Frequency Compounding Techniques in Ultrasound. Proposal Type: Innovative Student PI Name: Kunal Vaidya PI Department: Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science Position:
Resolution Enhancement and Frequency Compounding Techniques in Ultrasound. Proposal Type: Innovative Student PI Name: Kunal Vaidya PI Department: Chester F. Carlson Center for Imaging Science Position:
Ring cavity tunable fiber laser with external transversely chirped Bragg grating
 Ring cavity tunable fiber laser with external transversely chirped Bragg grating A. Ryasnyanskiy, V. Smirnov, L. Glebova, O. Mokhun, E. Rotari, A. Glebov and L. Glebov 2 OptiGrate, 562 South Econ Circle,
Ring cavity tunable fiber laser with external transversely chirped Bragg grating A. Ryasnyanskiy, V. Smirnov, L. Glebova, O. Mokhun, E. Rotari, A. Glebov and L. Glebov 2 OptiGrate, 562 South Econ Circle,
STUDY ON SAW ATTENUATION OF PMMA USING LASER ULTRASONIC
 STUDY ON SAW ATTENUATION OF PMMA USING LASER ULTRASONIC TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION D. F ei, X. R. Zhang, C. M. Gan, and S. Y. Zhang Lab of Modern Acoustics and Institute of Acoustics Nanjing University, Nanjing,
STUDY ON SAW ATTENUATION OF PMMA USING LASER ULTRASONIC TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION D. F ei, X. R. Zhang, C. M. Gan, and S. Y. Zhang Lab of Modern Acoustics and Institute of Acoustics Nanjing University, Nanjing,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Optically reconfigurable metasurfaces and photonic devices based on phase change materials S1: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. A Ti-Sapphire femtosecond laser (Coherent Chameleon Vision S)
Optically reconfigurable metasurfaces and photonic devices based on phase change materials S1: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. A Ti-Sapphire femtosecond laser (Coherent Chameleon Vision S)
Supplementary Figure S1. Schematic representation of different functionalities that could be
 Supplementary Figure S1. Schematic representation of different functionalities that could be obtained using the fiber-bundle approach This schematic representation shows some example of the possible functions
Supplementary Figure S1. Schematic representation of different functionalities that could be obtained using the fiber-bundle approach This schematic representation shows some example of the possible functions
Methods for parallel-detection-based ultrasound-modulated optical tomography
 Methods for parallel-detection-based ultrasound-modulated optical tomography Jun Li and Lihong V. Wang The research reported here focuses on ultrasound-modulated optical tomography based on parallel speckle
Methods for parallel-detection-based ultrasound-modulated optical tomography Jun Li and Lihong V. Wang The research reported here focuses on ultrasound-modulated optical tomography based on parallel speckle
High-Coherence Wavelength Swept Light Source
 Kenichi Nakamura, Masaru Koshihara, Takanori Saitoh, Koji Kawakita [Summary] Optical technologies that have so far been restricted to the field of optical communications are now starting to be applied
Kenichi Nakamura, Masaru Koshihara, Takanori Saitoh, Koji Kawakita [Summary] Optical technologies that have so far been restricted to the field of optical communications are now starting to be applied
attosnom I: Topography and Force Images NANOSCOPY APPLICATION NOTE M06 RELATED PRODUCTS G
 APPLICATION NOTE M06 attosnom I: Topography and Force Images Scanning near-field optical microscopy is the outstanding technique to simultaneously measure the topography and the optical contrast of a sample.
APPLICATION NOTE M06 attosnom I: Topography and Force Images Scanning near-field optical microscopy is the outstanding technique to simultaneously measure the topography and the optical contrast of a sample.
k λ NA Resolution of optical systems depends on the wavelength visible light λ = 500 nm Extreme ultra-violet and soft x-ray light λ = 1-50 nm
 Resolution of optical systems depends on the wavelength visible light λ = 500 nm Spatial Resolution = k λ NA EUV and SXR microscopy can potentially resolve full-field images with 10-100x smaller features
Resolution of optical systems depends on the wavelength visible light λ = 500 nm Spatial Resolution = k λ NA EUV and SXR microscopy can potentially resolve full-field images with 10-100x smaller features
Fiber-optic Michelson Interferometer Sensor Fabricated by Femtosecond Lasers
 Sensors & ransducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Fiber-optic Michelson Interferometer Sensor Fabricated by Femtosecond Lasers Dong LIU, Ying XIE, Gui XIN, Zheng-Ying LI School of Information
Sensors & ransducers 2013 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Fiber-optic Michelson Interferometer Sensor Fabricated by Femtosecond Lasers Dong LIU, Ying XIE, Gui XIN, Zheng-Ying LI School of Information
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings
 A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
LOPUT Laser: A novel concept to realize single longitudinal mode laser
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 82, No. 2 journal of February 2014 physics pp. 185 190 LOPUT Laser: A novel concept to realize single longitudinal mode laser JGEORGE, KSBINDRAand SMOAK Solid
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 82, No. 2 journal of February 2014 physics pp. 185 190 LOPUT Laser: A novel concept to realize single longitudinal mode laser JGEORGE, KSBINDRAand SMOAK Solid
12/26/2017. Alberto Ardon M.D.
 Alberto Ardon M.D. 1 Preparatory Work Ultrasound Physics http://www.nysora.com/mobile/regionalanesthesia/foundations-of-us-guided-nerve-blockstechniques/index.1.html Basic Ultrasound Handling https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q2otukhrruc
Alberto Ardon M.D. 1 Preparatory Work Ultrasound Physics http://www.nysora.com/mobile/regionalanesthesia/foundations-of-us-guided-nerve-blockstechniques/index.1.html Basic Ultrasound Handling https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q2otukhrruc
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology. April 11, Name: Student ID number: OCT1 1: OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade:
 Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
Examination Optoelectronic Communication Technology April, 26 Name: Student ID number: OCT : OCT 2: OCT 3: OCT 4: Total: Grade: Declaration of Consent I hereby agree to have my exam results published on
101 W of average green beam from diode-side-pumped Nd:YAG/LBO-based system in a relay imaged cavity
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 75, No. 5 journal of November 2010 physics pp. 935 940 101 W of average green beam from diode-side-pumped Nd:YAG/LBO-based system in a relay imaged cavity S K
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 75, No. 5 journal of November 2010 physics pp. 935 940 101 W of average green beam from diode-side-pumped Nd:YAG/LBO-based system in a relay imaged cavity S K
Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques
 Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques Chau-Hwang Lee Associate Research Fellow Research Center for Applied Sciences, Academia Sinica 128 Sec. 2, Academia Rd., Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan E-mail:
Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques Chau-Hwang Lee Associate Research Fellow Research Center for Applied Sciences, Academia Sinica 128 Sec. 2, Academia Rd., Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan E-mail:
Fig. 1
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Fig. 1 shows data for the intensity of a parallel beam of X-rays after penetration through varying thicknesses of a material. intensity / MW m 2 thickness / mm 0.91 0.40 0.69
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Fig. 1 shows data for the intensity of a parallel beam of X-rays after penetration through varying thicknesses of a material. intensity / MW m 2 thickness / mm 0.91 0.40 0.69
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
ADAPTIVE CORRECTION FOR ACOUSTIC IMAGING IN DIFFICULT MATERIALS
 ADAPTIVE CORRECTION FOR ACOUSTIC IMAGING IN DIFFICULT MATERIALS I. J. Collison, S. D. Sharples, M. Clark and M. G. Somekh Applied Optics, Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Nottingham,
ADAPTIVE CORRECTION FOR ACOUSTIC IMAGING IN DIFFICULT MATERIALS I. J. Collison, S. D. Sharples, M. Clark and M. G. Somekh Applied Optics, Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Nottingham,
Linear arrays used in ultrasonic evaluation
 Annals of the University of Craiova, Mathematics and Computer Science Series Volume 38(1), 2011, Pages 54 61 ISSN: 1223-6934 Linear arrays used in ultrasonic evaluation Laura-Angelica Onose and Luminita
Annals of the University of Craiova, Mathematics and Computer Science Series Volume 38(1), 2011, Pages 54 61 ISSN: 1223-6934 Linear arrays used in ultrasonic evaluation Laura-Angelica Onose and Luminita
A 243mJ, Eye-Safe, Injection-Seeded, KTA Ring- Cavity Optical Parametric Oscillator
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Space Dynamics Lab Publications Space Dynamics Lab 1-1-2011 A 243mJ, Eye-Safe, Injection-Seeded, KTA Ring- Cavity Optical Parametric Oscillator Robert J. Foltynowicz
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Space Dynamics Lab Publications Space Dynamics Lab 1-1-2011 A 243mJ, Eye-Safe, Injection-Seeded, KTA Ring- Cavity Optical Parametric Oscillator Robert J. Foltynowicz
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Photoacoustic tomography imaging based on a 4f acoustic lens imaging system
 Photoacoustic tomography imaging based on a 4f acoustic lens imaging system Zhanxu Chen 1, 2, Zhilie Tang 1*, Wei Wan 2 1 School of Physics and Telecom Engineering, South China Normal University, 510006,
Photoacoustic tomography imaging based on a 4f acoustic lens imaging system Zhanxu Chen 1, 2, Zhilie Tang 1*, Wei Wan 2 1 School of Physics and Telecom Engineering, South China Normal University, 510006,
HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM USING AN IMAGING PLATE
 HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM USING AN IMAGING PLATE Takeyuki Hashimoto 1), Morio Onoe 2), Hiroshi Nakamura 3), Tamon Inouye 4), Hiromichi Jumonji 5), Iwao Takahashi 6); 1)Yokohama Soei
HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM USING AN IMAGING PLATE Takeyuki Hashimoto 1), Morio Onoe 2), Hiroshi Nakamura 3), Tamon Inouye 4), Hiromichi Jumonji 5), Iwao Takahashi 6); 1)Yokohama Soei
Impact of the light coupling on the sensing properties of photonic crystal cavity modes Kumar Saurav* a,b, Nicolas Le Thomas a,b,
 Impact of the light coupling on the sensing properties of photonic crystal cavity modes Kumar Saurav* a,b, Nicolas Le Thomas a,b, a Photonics Research Group, Ghent University-imec, Technologiepark-Zwijnaarde
Impact of the light coupling on the sensing properties of photonic crystal cavity modes Kumar Saurav* a,b, Nicolas Le Thomas a,b, a Photonics Research Group, Ghent University-imec, Technologiepark-Zwijnaarde
Improving spatial resolution and contrast in ultrasound modulated optical tomography
 Improving spatial resolution and contrast in ultrasound modulated optical tomography NT Huynh, H Ruan, ML Mather, BR Hayes-Gill, SP Morgan* Electrical Systems and Optics Research Division, Faculty of Engineering,
Improving spatial resolution and contrast in ultrasound modulated optical tomography NT Huynh, H Ruan, ML Mather, BR Hayes-Gill, SP Morgan* Electrical Systems and Optics Research Division, Faculty of Engineering,
GHz ultrasound wave packets in water generated by an Er laser
 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 31 (1998) 2258 2263. Printed in the UK PII: S0022-3727(98)92767-X GHz ultrasound wave packets in water generated by an Er laser U Störkel, K L Vodopyanov and W Grill Hahn-Meitner-Institut,
J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 31 (1998) 2258 2263. Printed in the UK PII: S0022-3727(98)92767-X GHz ultrasound wave packets in water generated by an Er laser U Störkel, K L Vodopyanov and W Grill Hahn-Meitner-Institut,
Transmission of Ultrasonic Waves Via Optical Silica Glass Fiber Doped by 7.5% of TiO 2 with the Use of Power Sandwich Transducer
 ARCHIVES OF ACOUSTICS 36, 1, 141 150 (2011) DOI: 10.2478/v10168-011-0010-3 Transmission of Ultrasonic Waves Via Optical Silica Glass Fiber Doped by 7.5% of TiO 2 with the Use of Power Sandwich Transducer
ARCHIVES OF ACOUSTICS 36, 1, 141 150 (2011) DOI: 10.2478/v10168-011-0010-3 Transmission of Ultrasonic Waves Via Optical Silica Glass Fiber Doped by 7.5% of TiO 2 with the Use of Power Sandwich Transducer
Stabilized Interrogation and Multiplexing. Techniques for Fiber Bragg Grating Vibration Sensors
 Stabilized Interrogation and Multiplexing Techniques for Fiber Bragg Grating Vibration Sensors Hyung-Joon Bang, Chang-Sun Hong and Chun-Gon Kim Division of Aerospace Engineering Korea Advanced Institute
Stabilized Interrogation and Multiplexing Techniques for Fiber Bragg Grating Vibration Sensors Hyung-Joon Bang, Chang-Sun Hong and Chun-Gon Kim Division of Aerospace Engineering Korea Advanced Institute
An Overview Algorithm to Minimise Side Lobes for 2D Circular Phased Array
 An Overview Algorithm to Minimise Side Lobes for 2D Circular Phased Array S. Mondal London South Bank University; School of Engineering 103 Borough Road, London SE1 0AA More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=19093
An Overview Algorithm to Minimise Side Lobes for 2D Circular Phased Array S. Mondal London South Bank University; School of Engineering 103 Borough Road, London SE1 0AA More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=19093
1. INTRODUCTION 2. LASER ABSTRACT
 Compact solid-state laser to generate 5 mj at 532 nm Bhabana Pati*, James Burgess, Michael Rayno and Kenneth Stebbins Q-Peak, Inc., 135 South Road, Bedford, Massachusetts 01730 ABSTRACT A compact and simple
Compact solid-state laser to generate 5 mj at 532 nm Bhabana Pati*, James Burgess, Michael Rayno and Kenneth Stebbins Q-Peak, Inc., 135 South Road, Bedford, Massachusetts 01730 ABSTRACT A compact and simple
High Sensitivity Interferometric Detection of Partial Discharges for High Power Transformer Applications
 High Sensitivity Interferometric Detection of Partial Discharges for High Power Transformer Applications Carlos Macià-Sanahuja and Horacio Lamela-Rivera Optoelectronics and Laser Technology group, Universidad
High Sensitivity Interferometric Detection of Partial Discharges for High Power Transformer Applications Carlos Macià-Sanahuja and Horacio Lamela-Rivera Optoelectronics and Laser Technology group, Universidad
University of Alberta
 University of Alberta Design, Fabrication, and Testing of High-Frequency High-Numerical-Aperture Annular Array Transducer for Improved Depth-of-Field Photoacoustic Microscopy by Huihong Lu A thesis submitted
University of Alberta Design, Fabrication, and Testing of High-Frequency High-Numerical-Aperture Annular Array Transducer for Improved Depth-of-Field Photoacoustic Microscopy by Huihong Lu A thesis submitted
Optical coherence tomography
 Optical coherence tomography Peter E. Andersen Optics and Plasma Research Department Risø National Laboratory E-mail peter.andersen@risoe.dk Outline Part I: Introduction to optical coherence tomography
Optical coherence tomography Peter E. Andersen Optics and Plasma Research Department Risø National Laboratory E-mail peter.andersen@risoe.dk Outline Part I: Introduction to optical coherence tomography
Parallel Digital Holography Three-Dimensional Image Measurement Technique for Moving Cells
 F e a t u r e A r t i c l e Feature Article Parallel Digital Holography Three-Dimensional Image Measurement Technique for Moving Cells Yasuhiro Awatsuji The author invented and developed a technique capable
F e a t u r e A r t i c l e Feature Article Parallel Digital Holography Three-Dimensional Image Measurement Technique for Moving Cells Yasuhiro Awatsuji The author invented and developed a technique capable
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Modal simulation and frequency response of a high- frequency (75- khz) MEMS. a, Modal frequency of the device was simulated using Coventorware and shows
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Modal simulation and frequency response of a high- frequency (75- khz) MEMS. a, Modal frequency of the device was simulated using Coventorware and shows
Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors
 846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
Ultra-short distributed Bragg reflector fiber laser for sensing applications
 Ultra-short distributed Bragg reflector fiber laser for sensing applications Yang Zhang 2, Bai-Ou Guan 1,2,*, and Hwa-Yaw Tam 3 1 Institute of Photonics Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632,
Ultra-short distributed Bragg reflector fiber laser for sensing applications Yang Zhang 2, Bai-Ou Guan 1,2,*, and Hwa-Yaw Tam 3 1 Institute of Photonics Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632,
Ultra-sensitive, room-temperature THz detector using nonlinear parametric upconversion
 15 th Coherent Laser Radar Conference Ultra-sensitive, room-temperature THz detector using nonlinear parametric upconversion M. Jalal Khan Jerry C. Chen Z-L Liau Sumanth Kaushik Ph: 781-981-4169 Ph: 781-981-3728
15 th Coherent Laser Radar Conference Ultra-sensitive, room-temperature THz detector using nonlinear parametric upconversion M. Jalal Khan Jerry C. Chen Z-L Liau Sumanth Kaushik Ph: 781-981-4169 Ph: 781-981-3728
Numerical simulation of a gradient-index fibre probe and its properties of light propagation
 Numerical simulation of a gradient-index fibre probe and its properties of light propagation Wang Chi( ) a), Mao You-Xin( ) b), Tang Zhi( ) a), Fang Chen( ) a), Yu Ying-Jie( ) a), and Qi Bo( ) c) a) Department
Numerical simulation of a gradient-index fibre probe and its properties of light propagation Wang Chi( ) a), Mao You-Xin( ) b), Tang Zhi( ) a), Fang Chen( ) a), Yu Ying-Jie( ) a), and Qi Bo( ) c) a) Department
Introduction. Chapter 16 Diagnostic Radiology. Primary radiological image. Primary radiological image
 Introduction Chapter 16 Diagnostic Radiology Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther In diagnostic radiology
Introduction Chapter 16 Diagnostic Radiology Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther In diagnostic radiology
Research Article A Polymer Film Dye Laser with Spatially Modulated Emission Controlled by Transversely Distributed Pumping
 Optical Technologies Volume 2016, Article ID 1548927, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1548927 Research Article A Polymer Film Dye Laser with Spatially Modulated Emission Controlled by Transversely
Optical Technologies Volume 2016, Article ID 1548927, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1548927 Research Article A Polymer Film Dye Laser with Spatially Modulated Emission Controlled by Transversely
Video-rate all-optical ultrasound imaging
 Vol. 9, No. 1 Aug 1 BIOMEDICAL OPTICS EXPRESS 31 Video-rate all-optical ultrasound imaging E RWIN J. A LLES, 1,,* S ACHA N OIMARK, 1,,3 E FTHYMIOS M ANEAS, 1, E DWARD Z. Z HANG, 1 I VAN P. PARKIN,,3 PAUL
Vol. 9, No. 1 Aug 1 BIOMEDICAL OPTICS EXPRESS 31 Video-rate all-optical ultrasound imaging E RWIN J. A LLES, 1,,* S ACHA N OIMARK, 1,,3 E FTHYMIOS M ANEAS, 1, E DWARD Z. Z HANG, 1 I VAN P. PARKIN,,3 PAUL
Ihor TROTS, Andrzej NOWICKI, Marcin LEWANDOWSKI
 ARCHIVES OF ACOUSTICS 33, 4, 573 580 (2008) LABORATORY SETUP FOR SYNTHETIC APERTURE ULTRASOUND IMAGING Ihor TROTS, Andrzej NOWICKI, Marcin LEWANDOWSKI Institute of Fundamental Technological Research Polish
ARCHIVES OF ACOUSTICS 33, 4, 573 580 (2008) LABORATORY SETUP FOR SYNTHETIC APERTURE ULTRASOUND IMAGING Ihor TROTS, Andrzej NOWICKI, Marcin LEWANDOWSKI Institute of Fundamental Technological Research Polish
Performance characterization of low-cost, highspeed, portable pulsed laser diode photoacoustic tomography (PLD-PAT) system
 Performance characterization of low-cost, highspeed, portable pulsed laser diode photoacoustic tomography (PLD-PAT) system Paul Kumar Upputuri and Manojit Pramanik * School of Chemical and Biomedical Engineering,
Performance characterization of low-cost, highspeed, portable pulsed laser diode photoacoustic tomography (PLD-PAT) system Paul Kumar Upputuri and Manojit Pramanik * School of Chemical and Biomedical Engineering,
Development of a new multi-wavelength confocal surface profilometer for in-situ automatic optical inspection (AOI)
 Development of a new multi-wavelength confocal surface profilometer for in-situ automatic optical inspection (AOI) Liang-Chia Chen 1#, Chao-Nan Chen 1 and Yi-Wei Chang 1 1. Institute of Automation Technology,
Development of a new multi-wavelength confocal surface profilometer for in-situ automatic optical inspection (AOI) Liang-Chia Chen 1#, Chao-Nan Chen 1 and Yi-Wei Chang 1 1. Institute of Automation Technology,
Cavity QED with quantum dots in semiconductor microcavities
 Cavity QED with quantum dots in semiconductor microcavities M. T. Rakher*, S. Strauf, Y. Choi, N.G. Stolz, K.J. Hennessey, H. Kim, A. Badolato, L.A. Coldren, E.L. Hu, P.M. Petroff, D. Bouwmeester University
Cavity QED with quantum dots in semiconductor microcavities M. T. Rakher*, S. Strauf, Y. Choi, N.G. Stolz, K.J. Hennessey, H. Kim, A. Badolato, L.A. Coldren, E.L. Hu, P.M. Petroff, D. Bouwmeester University
