Ezrif a. (12) United States Patent US 7,135,041 B2 V-CHOROID. Nov. 14, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.:
|
|
|
- Rosalyn Edwards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
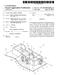
1 US B2 (12) United States Patent Tashiro et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,135,041 B2 Nov. 14, 2006 (54) ARTIFICIAL VISION SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Hiroyuki Tashiro, Aichi (JP): Yasuo Terasawa, Aichi (JP) (73) Assignee: Nidek Co., Ltd., Aichi (JP) (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by 341 days. (21) Appl. No.: 10/650,846 (22) Filed: Aug. 29, 2003 (65) Prior Publication Data US 2004/OO544O7 A1 Mar. 18, 2004 (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Aug. 30, 2002 (JP)... P (51) Int. Cl. A6 IF 2/6 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl /6.22; 623/6.43; 623/6.63: 607/53; 607/54 (58) Field of Classification Search /54, 607/53; 623/6.22, 6.35, 6.43, 6.63 See application file for complete search history. (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,601,545 A 7/1986 Kern ,200 4,628,933 A 12, 1986 Michelson... 6O7.53 4,787,903 A * 11/1988 Grendahl ,622 5,106,179 A 4/1992 Kamaya et al. 5, A * 9/1992 Fedorov et al /9 5,935,155 A * 8/1999 Humayun et al.... 6O7.54 6,120,538 A * 9/2000 Rizzo et al f6.11 6,427,087 B1 * 7/2002 Chow et al.... 6O7.54 6,847,847 B1 * 1/2005 Nisch et al.... 6O7.54 6,976,998 B1* 12/2005 Rizzo et al ( / A1* 4/2004 Suzuki... 6O7.54 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS WO A1 11, 1994 WO 96,39221 A1 12, 1996 WO A1 9, 1999 WO 02/ A1 8, 2002 WO 08/ A1 10, 2002 * cited by examiner Primary Examiner David H. Willse Assistant Examiner Javier G. Blanco (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm Sughrue Mion, PLLC (57) ABSTRACT An artificial vision system for regenerating or restoring vision of an eye of a patient includes: a power acquiring unit which is disposed inside the eye, includes a magnetic core having an opening and a coil wound around the magnetic core, and is adapted to acquire power from outside a body using electromagnetic induction; and a plurality of elec trodes which is provided at a retina and is adapted to electrically stimulate cells constituting the retina. 12 Claims, 6 Drawing Sheets r S RETINA V-CHOROID SCLERA 13b. 13a a Ezrif a 24
2 U.S. Patent Nov. 14, 2006 Sheet 1 of 6 US 7,135,041 B2 FIG r us Š RETNA V-CHOROID SCLERA 5 13b 13 13a 12
3 U.S. Patent Nov. 14, 2006 Sheet 2 of 6 US 7,135,041 B2
4 U.S. Patent Nov. 14, 2006 Sheet 3 of 6 US 7,135,041 B2 FIG. 3A
5 U.S. Patent Nov. 14, 2006 Sheet 4 of 6 US 7,135,041 B2 FIG. 4A
6 U.S. Patent Nov. 14, 2006 Sheet 5 of 6 US 7,135,041 B2 i. i s SN O r
7 U.S. Patent Nov. 14, 2006 Sheet 6 of 6 US 7,135,041 B2 a. 2 H G O O CD i s
8 1. ARTIFICAL VISION SYSTEM BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates to an artificial vision system for regenerating or restoring vision. Recently, a study has been conducted on an artificial vision system that promotes regeneration or restoration of vision by electrically stimulating cells forming the retina with electrodes or the like placed inside the eye. As such an artificial vision system, there are a type that stimulates cells based on an image picked up outside the body (hereinafter, referred to as the external imaging type), a type that stimu lates cells based on an image formed on photodiode arrays or the like placed inside the eye (hereinafter, referred to as the internal imaging type), etc. Regarding the artificial vision system described as above, in order to Supply an apparatus to be placed inside the eye with power wirelessly from outside the body, there has been discussed a method of Supplying power through electromag netic induction using a primary coil placed outside the body and a secondary coil placed inside the eye. However, when a frequency band and magnitude of electromagnetic waves suitable for use in a human body are concerned, it is difficult to supply required power with the secondary coil having an air core, that is, having no mag netic core, and therefore a coil having a magnetic core has to be used. Nevertheless, a coil having a magnetic core is so heavy that it is not suitably placed inside the eye. Moreover, when a coil having a magnetic core is placed in the vicinity of the anterior ocular segment, incoming light from outside the eye may possibly be blocked by the magnetic core in the case of the artificial vision system of the internal imaging type. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The invention was devised in view of the foregoing, and a technical challenge to be met by the invention is therefore to provide an artificial vision system that can efficiently Supply an apparatus to be placed inside the eye with power while being used suitably. In order to solve the aforesaid object, the invention is characterized by having the following arrangement. Aspect 1. An artificial vision system for regenerating or restoring vision of an eye of a patient comprising: a power acquiring unit which is disposed inside the eye, includes a magnetic core having an opening and a coil wound around the magnetic core, and is adapted to acquire power from outside a body using electromagnetic induction; and a plurality of electrodes which is provided at a retina and is adapted to electrically stimulate cells constituting the retina. Aspect 2. The artificial vision system according to the aspect 1, wherein the power acquiring unit is disposed so that the opening of the magnetic core is located at a pupil. Aspect 3. The artificial vision system according to the aspect 2, wherein the opening of the magnetic core is made as large as or larger than a maximum size of the pupil. Aspect 4. The artificial vision system according to the aspect 2 further comprising a plurality of light-receiving ele ments which are provided so as to correspond to the plurality of electrodes and disposed inside the eye so as to receive light from outside the body through the opening of the magnetic core. US 7,135,041 B Aspect 5. The artificial vision system according to the aspect 4 further comprising an optical member which is disposed on an axis of the magnetic core and is adapted to form an image of an object point at a predetermined distance position in front of the eye on a light-receiving Surface of the plurality of light-receiving elements. Aspect 6. The artificial vision system according to the aspect 5, wherein the optical member is placed in the opening of the magnetic core. Aspect 7. The artificial vision system according to the aspect 5 further comprising a moving unit which is adapted to moves the optical member in an axial direction of the magnetic core. Aspect 8. The artificial vision system according to the aspect 2, wherein an iris pattern is provided to one of the magnetic core, a Substrate on which the magnetic core is disposed and a coating Surface embedding the magnetic CO. Aspect 9. The artificial vision system according to the aspect 2 further comprising a power Supply unit which is dis posed in front of the eye, includes a magnetic core having an opening and a coil wound around the magnetic core, and is adapted to Supply the power to the power acquiring unit using the electromagnetic induction. The present disclosure relates to the subject matter con tained in Japanese patent application No (filed on Aug. 30, 2003), which is expressly incorporated herein by reference in their entireties. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of an artificial vision system of an internal imaging type in one embodiment of the invention. FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of an internal apparatus. FIGS. 3A and 3B are schematic diagrams of a power acquiring portion. FIGS. 4A and 4B are schematic diagrams of a vision regenerating portion. FIG. 5 is a schematic block diagram showing a control system in the artificial vision system in the embodiment. FIG. 6 is a schematic block diagram of a control system in an artificial vision system additionally provided with an adjusting mechanism. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS The following description will describe one embodiment of the invention with reference to the drawings. FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of an artificial vision system of the internal imaging type in the embodiment. The artificial vision system is roughly divided into an external apparatus 10 placed outside the body and an inter nal apparatus 20 placed inside the eye. The external appa ratus 10 includes a visor 11 that the user (blind person) can use as if he put eyeglasses on, and a power apparatus 12. The visor 11 is provided with a power supply portion 13 used to supply the internal apparatus 20 with power from the power apparatus 12. The power Supply portion 13 includes a hollow (ring-shaped) magnetic core 13a, and a primary coil 13.b wound around the magnetic core 13a. The magnetic core 13a may be made of a material generally used for a magnetic body, such as ferrite. The primary coil 13b may be made of a material that can be generally used for coil wires, Such as copper, gold, and platinum.
9 US 7,135,041 B2 3 It is arranged in Such a manner that the power Supply portion 13 is situated in front of the eye of the user when the user puts on the visor 11. Because the power Supply portion 13 has the hollow magnetic core 13a (has an opening), the user's view is not blocked even when the power supply 5 portion 13 is situated in front of the eye. Meanwhile, the internal apparatus 20 includes a power acquiring portion 22 and a vision regenerating portion 30 both attached onto a substrate 23. The vision regenerating portion 30 is electrically connected to the power acquiring 10 portion 22 through an electrical line 21 (see FIG. 2). FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of the internal apparatus 20. A material having good biocompatibility as well as a light transmitting property is used for the Substrate 23, and polyimide is used in the embodiment. The substrate comprises a disc portion 23a and a long-plate portion 23b. The power acquiring portion 22 is attached to the disc portion 23a, and the vision regenerating portion 30 is attached to the tip end of the long-plate portion 23b. The long-plate portion 23b in the embodiment has such a length 20 that the vision regenerating portion 30 located at the tip end is situated in the vicinity of the macula of retina along the retina when the disc portion 23a is placed behind the iris in the vicinity thereof. Hence, a length of the substrate 23 from a position at which the power acquiring portion 22 is placed 25 to a position at which the vision regenerating portion 30 is placed is preferably about 20 mm to 40 mm, and more preferably about 25 mm to 35 mm. As shown in the cross section of FIG. 3A, the power acquiring portion 22 includes a hollow (ring-shaped) mag- 30 netic core 22a, and a secondary coil 22b wound around the magnetic core 22a. The magnetic core 22a may be made of a material generally used for a magnetic body, such as ferrite. The secondary coil 22b may be made of a material that can be generally used for coil wires, such as copper, 35 gold, and platinum. In the embodiment, light from outside the eye is intro duced to the eye (fundus) ground through an opening in the magnetic core 22a by situating the opening in the magnetic core 22a at the pupil. For this reason, it is preferable that the 40 opening of the magnetic core 22a is made as large as or larger than the maximum size of the pupil. For example, it is Sufficient to provide an opening of about 2 mm to 7 mm. An optical member (lens) 24 to serve as the crystalline lens of eye is placed in the opening in the magnetic core 22a 45 of the embodiment, which makes it possible to form an image of a given object point at a predetermined distance position in front of the user's eyes on a light-receiving surface of the vision regenerating portion 30 that will be described below. It should be appreciated that the optical 50 member 24 can be placed anywhere on the axis of the magnetic core 22a. For example, it may be placed in front or behind the magnetic core 22a. On the other hand, in a case where the crystalline lens of eye is not removed when the internal apparatus 20 is placed inside the eye, the optical 55 member 24 may be omitted. Also, as shown in the plan view of FIG. 3B, an iris pattern 22c is provided to one Surface of the magnetic core 22a (the Surface situated on the iris side when placed inside the eye, the surface that comes in contact with the substrate 23 in the 60 embodiment). The iris pattern 22c may be provided to a portion to be placed on the periphery of the iris, for example, on the disc portion 23a of the substrate 23 or a coating Surface that embeds the magnetic core 22a. As shown in the plan view of FIG. 4A and the cross 65 section of FIG. 4B, the vision regenerating portion 30 includes a base 31 provided on the substrate 23, light 4 receiving elements 32 comprising photodiodes or the like stimulating electrodes 33, a control circuit 34, etc., which are provided to the base 31, and thereby has an IC (Inte grated Circuit) structure. As shown in FIG. 2, a number of light-receiving elements 32 are provided in two-dimensional arrays to the base 31 on the Surface on the same side where the power acquiring portion 22 is provided on the substrate 23 (on the paper surface side of FIG. 2). Further, the stimulating electrodes 33 in the matching number with the light-receiving elements 32 are correspondingly provided in two-dimensional arrays to the base 31 on the surface opposite to the surface on which the light-receiving element 32 are provided (on the overleaf side of FIG. 2). The stimulating electrodes 33 penetrate through the substrate 23 and are exposed to the outside, so that each stimulating electrode 33 is allowed to come in direct contact with the retina at the tip end when the internal apparatus 20 is placed inside the eye. The respective light receiving elements 32 and the respective Stimulating elec trodes 33 are connected to the control circuit 34 individually through electrical lines (FIGS. 4A and 4B show a state where a plurality of light-receiving elements 32 and stimu lating electrodes 33 are connected to the control circuit 34 in groups for ease of explanation). Numeral 35 denotes tacks used to fixedly hold the vision regenerating portion 30 on the retina. Each tack 35 is shaped like a needle, and four tacks 35 are attached integrally to the base 31 so as to extend respectively from four corners of the base 31 by a certain length in a direction along which the stimulating electrodes 33 protrude. In order to fixedly hold the vision regenerating portion 30, the tacks 35 have a length such that the tip ends thereof reach the choroid or the sclera when they are pushed into the retina to be fully inserted. By inserting the tacks 35 to pierce through the retina and reach the choroid or the sclera, the retina is positioned between the tip ends of the tacks 35 and the stimulating electrodes 33. The tacks 35 are made of a material having electrical conductivity, such as titanium and platinum; moreover, the tacks 35 are insulated with coating except for the tip ends and the rear ends (shaded portions of FIG. 4B). The rear end portions (non-insulated portions) of the tacks 35 have been electrically connected to the control circuit 34. The tacks 35 and the stimulating electrodes 33 are thereby electrically connected to each other, and the tacks 35 serve as reference electrodes. The tacks 35 have been provided fixedly (integrally) to the base 31 in the embodiment. It should be appreciated, however, that the invention is not limited to this arrange ment, and the base 31 may have been provided with only through-holes for the tacks 35 to penetrate through in advance. In Such a case, for example, the base 31 is coated with an electrically conducting material in portions that come in contact with the rear ends of the tacks 35 when the tacks 35 are fit into the through-holes provided in the base 31, and the coated portions are thereby electrically con nected to the control circuit 34. On the other hand, the tacks 35 are insulated except for the tip ends and the rear ends, and when the base 31 is fixed onto the retina with the use of the tacks 35, the rear ends of the tacks 35 come in contact with predetermined portions of the through-holes coated with the electrical conducting material. Numeral 25 denotes openings provided in the disc portion 23a. The openings 25 are formed to situate at positions where no influence of dynamic interference of the iris is given when the disc portion 23a is placed behind the iris. The openings 25 are used to suture the disc portion 23a and
10 5 the iris together to be fixed inside the eye when the internal apparatus 20 is placed inside the eye. After the power acquiring portion 22, the vision regen erating portion 30, etc. are attached to the substrate 23, the internal apparatus 20 is coated entirely with a material having good biocompatibility, such as polyimide, so that body fluid or the like will not come in contact with machines forming the internal apparatus 20. In this instance, neither the electrodes 33 nor the tip ends of the tacks 35 are coated, so that they are allowed to come in direct contact with a living body. Operations of the artificial vision system arranged as above will be described with reference to the block diagram of a control system of FIG. 5. Initially, the crystalline lens in the patient s eye (user's eye) is removed through phacoemulsification and aspiration using a known apparatus for cataract Surgery or the like. Then, an insertion opening is made by incising the Sclera by a predetermined quantity or so in a region at a predetermined distance (for example, about 1.5 mm) from the peripheral cornea on the ear side, and the internal apparatus 20 is inserted into the eye through the insertion opening. The long-plate portion 23b is placed along the retina, so that the vision regenerating portion 30 is situated on the retina in the vicinity of the macula of retina. The vision regenerating portion 30 is fixed inside the eye by pushing the tacks 35 into the retina. When the tacks 35 are pushed into the retina, the tacks 35 penetrate through the retina and the tip ends reach the choroid or the Sclera, whereby the vision regenerating portion 30 is fixedly held on the retina. On the other hand, the disc portion 23a is placed behind the iris in the anterior ocular segment, and the opening in the magnetic core 22a is situated at the pupil. Subsequently, a suture thread is put through the openings 25 provided in the disc portion 23a to suture the iris and the disc portion 23a together. The disc portion 23a is thus fixedly held in the anterior ocular segment. Alternatively, instead of the iris, the openings 25 and the periphery of the ciliary body may be Sutured together. In this case, the disc portion 23a needs to have a diameter large enough for its outer peripheral portion to reach the ciliary groove, while the openings 25 need to be formed at positions to be sutured with the periphery of the ciliary body. When the internal apparatus 20 is placed inside the eye, the iris may undergo abrasion with the substrate 23 and become inflamed, etc. In order to avoid such inconvenience, part of the iris that comes in contact with the substrate 23 may be removed. Removal of the iris causes the outward appearance of the patient s eye to deteriorate. However, in the embodiment, because the iris pattern 22c is provided to one surface of the magnetic core 22a as shown in FIG. 3B. a portion artificially imitating the iris is left behind the iris even when the iris is removed, and deterioration of the outward appearance of the patient's eye is reduced to the least possible degree. Further, the power acquiring portion 22 is placed behind the iris in the embodiment. The invention, however, is not limited to this arrangement, and for example, the power acquiring portion 22 may be placed by positioning the anterior ocular segment on the Surface side of the iris (a space between the cornea and the iris) or the lens capsule to the pupil and the opening in the magnetic core 22a. As has been described, the coil 22b is wound around the magnetic core 22a in the embodiment, which improves power transmission efficiency in comparison with the case of using a coil having an air core. Further, because a hollow magnetic core provided with an opening in the central US 7,135,041 B portion is used as the magnetic core 22a, the magnetic core 22a is lighter in weight than a magnetic core having no opening, and can be therefore readily placed inside the eye. Further, by positioning the opening in the magnetic core 22a at the pupil, it is possible to introduce light from outside the eye to the inside of the eye through the opening. Meanwhile, as to the external apparatus 10, the user puts on the visor 11 and positions the power supply portion 13 in front of his eyes. When a current flows from the power apparatus 12 to the power Supply portion 13, electromag netic induction is induced between the primary coil 13b and the secondary coil 22b, whereby power is supplied to the internal apparatus 20. Light from outside the eye passes through the opening in the magnetic core 13a and reaches inside the eye. The thus-reached light then passes through the opening in the magnetic core 22a, and is received on the light-receiving surface of the light-receiving elements 32 through the opti cal member 24. Signals from the light-receiving elements 32 are transmitted to the control circuit 34. The control circuit 34 converts the thus-received signals into an electrical signal of a pulse shape needed to obtain vision, and applies a predetermined voltage between the tacks 35 and the corre sponding stimulating electrodes 33. When a Voltage is applied between the tacks 35 and the corresponding stimu lating electrodes 33, a current of a specific pulse shape passes through the retina from the stimulating electrodes 33 and raches the tip ends of the tacks 35. Cells forming the retina, such as bipolar cells and retinal gangilion cells, are thereby electrically stimulated, and vision can be thus regen erated or restored. While the embodiment above described the artificial vision system of the internal imaging type, it should be appreciated that the invention is applicable to an artificial vision system of the external imaging type. In this case, the external apparatus 10 is provided with an imaging unit. Such as a CCD camera, an information processing unit for obtain ing stimulating pulse data (control signal) used for regen eration or restoration of vision by applying predetermined processing on image information obtained from the imaging unit, and a transmitting unit for transmitting the stimulating pulse data to the internal apparatus 20. Meanwhile, the internal apparatus 20 is provided with a receiving unit for receiving the stimulating pulse data, instead of the optical member 24 placed in the magnetic core 22a. Alternatively, the power Supply portion 13 and the power acquiring portion 22 may serve as the transmitting unit and the receiving unit, respectively. While the optical member 24 is provided in the magnetic core 22a in the embodiment, an adjusting mechanism may be additionally provided by allowing the optical member 24 to move in the axial direction of the magnetic core 22a. FIG. 6 is a schematic block diagram showing an example when the adjusting mechanism is added. Components having similar functions as those shown in FIG. 5 are labeled with the same reference numerals, and an explanation of Such components is omitted for ease of explanation. Numeral 40 denotes a control portion provided in the external apparatus 10. The control portion 40 is provided with a switch 40a. With the use of the switch 40a, the optical member 24 is moved to focus on a given object point at a predetermined distance position. Further, the control portion 40 converts a power signal from the power apparatus 12 and a signal from the Switch 4.0a into a digital signal, so that power information and driving information of the optical member 24 can be transmitted to the internal apparatus 20 by means of the power Supply portion 13.
11 7 The optical member 24 is attached movably in the axial direction of the magnetic core 22a, and is moved back and forth in the axial direction by a compact motor 41. When the user manipulates the switch 4.0a of the controller 40, a signal is transmitted from the power supply portion 13 to the internal apparatus 20 in the form of a digital signal. The power information and the driving information of the optical member 24 are transmitted in a time divisional manner, and the thus-transmitted power information and driving infor mation of the optical member 24 are received alternately in the power acquiring portion 22 to be further transmitted to the control circuit 34. The control circuit 34 uses the thus-received power information as power to drive the internal apparatus 20. Further, the control circuit 34 drives the compact motor 41 based on the thus-received driving information of the optical member 24, and thereby moves the optical member 24. The user is thus able to bring the focus on a given object point at an arbitrary position freely. By using the arrangement described above, it is possible to provide the internal apparatus 20 with focusing, telescopic, and wide-angle functions. Moreover, a quantity of light or the like can be adjusted by placing an opening-varying mechanism in front or behind the magnetic core 22a or in the opening thereof. Further, such an adjusting mechanism may be provided to the external apparatus 10. In this case, the external apparatus 10 is provided with an optical system enabling focusing, telescopic, and wide-angle functions. The opening in the magnetic core is situated at the pupil in the embodiment. The invention, however, is not limited to this arrangement, and the magnetic core may be situated at a position other than the pupil as long as incoming outside light is not blocked. In this case, light from outside the eye cannot pass through the opening in the magnetic core; however, there are merits in that power Supply efficiency can be increased by winding a coil around the magnetic core, and in that the weight can be reduced by using a hollow magnetic core. AS has been described, according to the invention, the artificial vision system can Supply power efficiently to an apparatus to be placed inside the eye while being used Suitably as an intraocular apparatus. What is claimed is: 1. An artificial vision system for regenerating or restoring vision of an eye of a patient comprising: a power acquiring unit which is disposable inside the eye, in the vicinity of the iris, which unit includes a ring shaped magnetic core having an opening and a coil wound around a periphery of the magnetic core, and is adapted to acquire power from outside a body using electromagnetic induction; and a plurality of electrodes which is adapted to be provided at the retina and is adapted to electrically stimulate cells constituting the retina using power obtained by the power acquiring unit. 2. The artificial vision system according to claim 1, wherein the power acquiring unit is disposed so that the opening of the magnetic core is located at a pupil. 3. The artificial vision system according to claim 2, wherein the opening of the magnetic core is made as large as or larger than a maximum size of the pupil. US 7,135,041 B The artificial vision system according to claim 2 further comprising a plurality of light-receiving elements which are provided so as to correspond to the plurality of electrodes and disposable inside the eye so as to receive light from outside the body through the opening of the magnetic core. 5. The artificial vision system according to claim 4 further comprising an optical member which is disposed on an axis of the magnetic core and is adapted to form an image of an object point at a predetermined distance position in front of the eye on a light-receiving Surface of the plurality of light-receiving elements. 6. The artificial vision system according to claim 5, wherein the optical member is placed in the opening of the magnetic core. 7. The artificial vision system according to claim 5 further comprising a moving unit which is adapted to move the optical member in an axial direction of the magnetic core. 8. The artificial vision system according to claim 2, wherein an iris pattern is provided to one of the magnetic core, a Substrate on which the magnetic core is disposed and a coating Surface embedding the magnetic core. 9. The artificial vision system according to claim 2 further comprising a power Supply unit which is disposable in front of the eye, includes a magnetic core having an opening and a coil wound around the magnetic core, and is adapted to Supply the power to the power acquiring unit using the electromagnetic induction. 10. An artificial vision system for regenerating or restor ing vision of an eye of a patient comprising: a power acquiring unit which is disposable inside the eye, which unit includes a magnetic core having an opening and a coil wound around the magnetic core, and is adapted to acquire power from outside a body using electromagnetic induction; a plurality of electrodes which is adapted to be provided at the retina and is adapted to electrically stimulate cells constituting the retina; a plurality of light-receiving elements which are provided So as to correspond to the plurality of electrodes and disposable inside the eye so as to receive light from outside the body through the opening of the magnetic core; and an optical member which is disposed on an axis of the magnetic core and is adapted to form an image of an object point at a predetermined distance position in front of the eye on a light-receiving surface of the plurality of light-receiving elements; and wherein the power acquiring unit is disposed so that the opening of the magnetic core is located at a pupil. 11. The artificial vision system according to claim 10, wherein the optical member is placed in the opening of the magnetic core. 12. The artificial vision system according to claim 10, further comprising a moving unit which is adapted to move the optical member in an axial direction of the magnetic COC.
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
Kiuchi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2011
 (12) United States Patent US007902952B2 (10) Patent No.: Kiuchi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2011 (54) SHARED REACTOR TRANSFORMER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Hiroshi Kiuchi, Chiyoda-ku
(12) United States Patent US007902952B2 (10) Patent No.: Kiuchi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2011 (54) SHARED REACTOR TRANSFORMER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Hiroshi Kiuchi, Chiyoda-ku
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US008238998B2 (10) Patent No.: Park (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 7, 2012 (54) TAB ELECTRODE 4,653,501 A * 3/1987 Cartmell et al.... 600,392 4,715,382 A * 12/1987 Strand...... 600,392
(12) United States Patent US008238998B2 (10) Patent No.: Park (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 7, 2012 (54) TAB ELECTRODE 4,653,501 A * 3/1987 Cartmell et al.... 600,392 4,715,382 A * 12/1987 Strand...... 600,392
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 Kohayakawa 54) OCULAR LENS MEASURINGAPPARATUS (75) Inventor: Yoshimi Kohayakawa, Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl. No.: 544,486 (22 Filed:
United States Patent 19 Kohayakawa 54) OCULAR LENS MEASURINGAPPARATUS (75) Inventor: Yoshimi Kohayakawa, Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl. No.: 544,486 (22 Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006004.4273A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0044273 A1 Numazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) MOUSE-TYPE INPUT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
US 2006004.4273A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0044273 A1 Numazawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 2, 2006 (54) MOUSE-TYPE INPUT DEVICE (30) Foreign Application
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999
 USOO599.1083A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54) IMAGE DISPLAY APPARATUS 56) References Cited 75 Inventor: Yoshiki Shirochi, Chiba, Japan
USOO599.1083A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54) IMAGE DISPLAY APPARATUS 56) References Cited 75 Inventor: Yoshiki Shirochi, Chiba, Japan
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
(12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,561,977 B2
 US008561977B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,561,977 B2 Chang (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2013 (54) POST-PROCESSINGAPPARATUS WITH (56) References Cited SHEET EUECTION DEVICE (75) Inventor:
US008561977B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,561,977 B2 Chang (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2013 (54) POST-PROCESSINGAPPARATUS WITH (56) References Cited SHEET EUECTION DEVICE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1
 USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
United States Patent (19) Sun
 United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
(19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
202 19' 19 19' (12) United States Patent 202' US 7,050,043 B2. Huang et al. May 23, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.
 US00705.0043B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,050,043 B2 May 23, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 2,
US00705.0043B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,050,043 B2 May 23, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 2,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Schwab et al. US006335619B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR COMPRISING ARESONANT OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT RESPONDING TO CHANGES IN
(12) United States Patent Schwab et al. US006335619B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR COMPRISING ARESONANT OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT RESPONDING TO CHANGES IN
United States Patent (19) Lee
 United States Patent (19) Lee (54) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT FOR DRIVING MAGNETRON 75 Inventor: Kyong-Keun Lee, Suwon, Rep. of Korea 73) Assignee: Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Suweon City, Rep. of Korea (21)
United States Patent (19) Lee (54) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT FOR DRIVING MAGNETRON 75 Inventor: Kyong-Keun Lee, Suwon, Rep. of Korea 73) Assignee: Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Suweon City, Rep. of Korea (21)
TEPZZ 879Z A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0354 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 879Z A_T (11) EP 2 879 023 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.06.1 Bulletin 1/23 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/034 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1419462. (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 879Z A_T (11) EP 2 879 023 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.06.1 Bulletin 1/23 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/034 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1419462. (22) Date of
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009
 (19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
(19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
United States Patent (19) Nihei et al.
 United States Patent (19) Nihei et al. 54) INDUSTRIAL ROBOT PROVIDED WITH MEANS FOR SETTING REFERENCE POSITIONS FOR RESPECTIVE AXES 75) Inventors: Ryo Nihei, Akihiro Terada, both of Fujiyoshida; Kyozi
United States Patent (19) Nihei et al. 54) INDUSTRIAL ROBOT PROVIDED WITH MEANS FOR SETTING REFERENCE POSITIONS FOR RESPECTIVE AXES 75) Inventors: Ryo Nihei, Akihiro Terada, both of Fujiyoshida; Kyozi
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Berweiler USOO6328358B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) COVER PART LOCATED WITHIN THE BEAM PATH OF A RADAR (75) Inventor: Eugen Berweiler, Aidlingen (DE) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent Berweiler USOO6328358B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: (54) COVER PART LOCATED WITHIN THE BEAM PATH OF A RADAR (75) Inventor: Eugen Berweiler, Aidlingen (DE) (73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Onuki et al.
 United States Patent (19) Onuki et al. 54). IGNITION APPARATUS FOR AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE 75 Inventors: Hiroshi Onuki; Takashi Ito, both of Hitachinaka, Katsuaki Fukatsu, Naka-gun; Ryoichi Kobayashi,
United States Patent (19) Onuki et al. 54). IGNITION APPARATUS FOR AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE 75 Inventors: Hiroshi Onuki; Takashi Ito, both of Hitachinaka, Katsuaki Fukatsu, Naka-gun; Ryoichi Kobayashi,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1
 USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2
 US0083 04995 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2 Ku et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) LAMP WITH SNOW REMOVING (56) References Cited STRUCTURE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
US0083 04995 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2 Ku et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) LAMP WITH SNOW REMOVING (56) References Cited STRUCTURE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1
 USOO6386952B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1 White (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) SINGLE STATION BLADE SHARPENING 2,692.457 A 10/1954 Bindszus METHOD AND APPARATUS 2,709,874
USOO6386952B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1 White (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) SINGLE STATION BLADE SHARPENING 2,692.457 A 10/1954 Bindszus METHOD AND APPARATUS 2,709,874
part data signal (12) United States Patent control 33 er m - sm is US 7,119,773 B2
 US007 119773B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING GRAY LEVEL FOR DISPLAY PANEL (75) Inventor: Hak Su Kim, Seoul
US007 119773B2 (12) United States Patent Kim (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 10, 2006 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR CONTROLLING GRAY LEVEL FOR DISPLAY PANEL (75) Inventor: Hak Su Kim, Seoul
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,564,782 B2. Kimura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2017
 USO09564782B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kimura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2017 (54) WINDING, WINDING METHOD, AND (56) References Cited AUTOMOTIVE ROTATING ELECTRIC MACHINE U.S.
USO09564782B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kimura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2017 (54) WINDING, WINDING METHOD, AND (56) References Cited AUTOMOTIVE ROTATING ELECTRIC MACHINE U.S.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent JakobSSOn USOO6608999B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 19, 2003 (54) COMMUNICATION SIGNAL RECEIVER AND AN OPERATING METHOD THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Peter Jakobsson,
(12) United States Patent JakobSSOn USOO6608999B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 19, 2003 (54) COMMUNICATION SIGNAL RECEIVER AND AN OPERATING METHOD THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Peter Jakobsson,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,156,854 B2
 US007 156854B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,156,854 B2 BrOWn et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2007 (54) LENS DELIVERY SYSTEM 5,944,725 A * 8/1999 Cicenas et al.... 606/107 6,241,737
US007 156854B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,156,854 B2 BrOWn et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2007 (54) LENS DELIVERY SYSTEM 5,944,725 A * 8/1999 Cicenas et al.... 606/107 6,241,737
(12) United States Patent
 US008393237B2 (12) United States Patent Arenz et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 12, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) DRIVING DEVICE FOR A HATCH INA MOTOR VEHICLE
US008393237B2 (12) United States Patent Arenz et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 12, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) DRIVING DEVICE FOR A HATCH INA MOTOR VEHICLE
(12) United States Patent
 USOO965 1411 B2 (12) United States Patent Yamaguchi et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,651.411 B2 May 16, 2017 (54) ELECTROMAGNETIC FLOWMETER AND SELF-DAGNOSING METHOD OF EXCITING CIRCUIT
USOO965 1411 B2 (12) United States Patent Yamaguchi et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,651.411 B2 May 16, 2017 (54) ELECTROMAGNETIC FLOWMETER AND SELF-DAGNOSING METHOD OF EXCITING CIRCUIT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
(19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
USOO9443458B2 (12) United States Patent Shang (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.443.458 B2 Sep. 13, 2016 (54) DRIVING CIRCUIT AND DRIVING METHOD, GOA UNIT AND DISPLAY DEVICE (71) Applicant: BOE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Takekuma USOO6850001B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (75) Inventor: Akira Takekuma, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: Agilent Technologies,
(12) United States Patent Takekuma USOO6850001B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (75) Inventor: Akira Takekuma, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: Agilent Technologies,
(12) United States Patent
 US00795.5254B2 (12) United States Patent Hanke (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 7, 2011 (54) MEDICAL VIDEOSCOPE WITH A PIVOTABLY ADJUSTABLE END PART (75) Inventor: Harald Hanke, Hamburg (DE)
US00795.5254B2 (12) United States Patent Hanke (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 7, 2011 (54) MEDICAL VIDEOSCOPE WITH A PIVOTABLY ADJUSTABLE END PART (75) Inventor: Harald Hanke, Hamburg (DE)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2
 USOO6663057B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2 Garelick et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADJUSTABLE PEDESTAL FOR BOAT 5,297.849 A * 3/1994 Chancellor... 297/344.
USOO6663057B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2 Garelick et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADJUSTABLE PEDESTAL FOR BOAT 5,297.849 A * 3/1994 Chancellor... 297/344.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 20050207013A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0207013 A1 Kanno et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) PHOTOELECTRIC ENCODER AND (30) Foreign Application
US 20050207013A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0207013 A1 Kanno et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) PHOTOELECTRIC ENCODER AND (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US00735.5805B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,355,805 B2 Naka0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2008 (54) MAGNETIC TAPE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING MAGNETIC TAPE, 5,689,384 A * 11/1997
(12) United States Patent US00735.5805B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,355,805 B2 Naka0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2008 (54) MAGNETIC TAPE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING MAGNETIC TAPE, 5,689,384 A * 11/1997
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Crompton 54 AMUSEMENT MACHINE 75 Inventor: Gordon Crompton, Kent, United Kingdom 73 Assignee: Cromptons Leisure Machines Limited, Kent, United Kingdom 21 Appl. No.: 08/827,053
United States Patent (19) Crompton 54 AMUSEMENT MACHINE 75 Inventor: Gordon Crompton, Kent, United Kingdom 73 Assignee: Cromptons Leisure Machines Limited, Kent, United Kingdom 21 Appl. No.: 08/827,053
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,729,834 B1
 USOO6729834B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,729,834 B1 McKinley (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) WAFER MANIPULATING AND CENTERING 5,788,453 A * 8/1998 Donde et al.... 414/751 APPARATUS
USOO6729834B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,729,834 B1 McKinley (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) WAFER MANIPULATING AND CENTERING 5,788,453 A * 8/1998 Donde et al.... 414/751 APPARATUS
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
III III 0 IIOI DID IIO 1101 I II 0II II 100 III IID II DI II
 (19) United States III III 0 IIOI DID IIO 1101 I0 1101 0II 0II II 100 III IID II DI II US 200902 19549A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0219549 Al Nishizaka et al. (43) Pub.
(19) United States III III 0 IIOI DID IIO 1101 I0 1101 0II 0II II 100 III IID II DI II US 200902 19549A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0219549 Al Nishizaka et al. (43) Pub.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,715,221 B1. Sasaki (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2004
 USOO671.51B1 (1) United States Patent (10) Patent No. US 6,715,1 B1 Sasaki (45) Date of Patent Apr. 6, 004 (54) FOOT STIMULATING SHOE INSOLE 5,860,9 A * 1/1999 Morgenstern... 36/141 (75) Inventor Manhachi
USOO671.51B1 (1) United States Patent (10) Patent No. US 6,715,1 B1 Sasaki (45) Date of Patent Apr. 6, 004 (54) FOOT STIMULATING SHOE INSOLE 5,860,9 A * 1/1999 Morgenstern... 36/141 (75) Inventor Manhachi
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170176547A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0176547 A1 HONKURA (43) Pub. Date: (54) MAGNETOMETER WITH A DIFFERENTIAL TYPE INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 20170176547A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0176547 A1 HONKURA (43) Pub. Date: (54) MAGNETOMETER WITH A DIFFERENTIAL TYPE INTEGRATED CIRCUIT (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(19) United States US 2003009 1220A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091220 A1 Sato et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Hideaki
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120047754A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047754 A1 Schmitt (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2012 (54) ELECTRICSHAVER (52) U.S. Cl.... 30/527 (57) ABSTRACT
US 20120047754A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0047754 A1 Schmitt (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2012 (54) ELECTRICSHAVER (52) U.S. Cl.... 30/527 (57) ABSTRACT
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Waibel et al. USOO6624881B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) OPTOELECTRONIC LASER DISTANCE MEASURING INSTRUMENT (75) Inventors: Reinhard Waibel, Berneck
(12) United States Patent Waibel et al. USOO6624881B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) OPTOELECTRONIC LASER DISTANCE MEASURING INSTRUMENT (75) Inventors: Reinhard Waibel, Berneck
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030095174A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0095174A1 Terasaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 22, 2003 (54) PRINTER (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 20030095174A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0095174A1 Terasaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 22, 2003 (54) PRINTER (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Chen et al. USOO6692983B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) METHOD OF FORMING A COLOR FILTER ON A SUBSTRATE HAVING PIXELDRIVING ELEMENTS (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent Chen et al. USOO6692983B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) METHOD OF FORMING A COLOR FILTER ON A SUBSTRATE HAVING PIXELDRIVING ELEMENTS (76) Inventors:
(12) United States Patent
 US007098655B2 (12) United States Patent Yamada et al. (54) EDDY-CURRENT SENSOR WITH PLANAR MEANDER EXCITING COIL AND SPIN VALVE MAGNETORESISTIVE ELEMENT FOR NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING (75) Inventors: Sotoshi
US007098655B2 (12) United States Patent Yamada et al. (54) EDDY-CURRENT SENSOR WITH PLANAR MEANDER EXCITING COIL AND SPIN VALVE MAGNETORESISTIVE ELEMENT FOR NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING (75) Inventors: Sotoshi
United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354
![United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354 United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354](/thumbs/92/110916574.jpg) US005746354A United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354 Perkins 45) Date of Patent: May 5, 1998 54 MULTI-COMPARTMENTAEROSOLSPRAY FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS CONTANER 3142205 5/1983 Germany...
US005746354A United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354 Perkins 45) Date of Patent: May 5, 1998 54 MULTI-COMPARTMENTAEROSOLSPRAY FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS CONTANER 3142205 5/1983 Germany...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005O277913A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0277913 A1 McCary (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 15, 2005 (54) HEADS-UP DISPLAY FOR DISPLAYING Publication Classification
US 2005O277913A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0277913 A1 McCary (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 15, 2005 (54) HEADS-UP DISPLAY FOR DISPLAYING Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,262 B2
 USOO8926262B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,262 B2 Tanahashi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2015 (54) CMCTURBINE STATOR BLADE USPC... 415/9, 200, 209.3, 209.4, 210.1, 211.2,
USOO8926262B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,262 B2 Tanahashi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2015 (54) CMCTURBINE STATOR BLADE USPC... 415/9, 200, 209.3, 209.4, 210.1, 211.2,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2
 USOO6543599B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2 Jasinetzky (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) STEP FOR ESCALATORS 5,810,148 A * 9/1998 Schoeneweiss... 198/333 6,398,003 B1
USOO6543599B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2 Jasinetzky (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) STEP FOR ESCALATORS 5,810,148 A * 9/1998 Schoeneweiss... 198/333 6,398,003 B1
Imaging Systems for Eyeglass-Based Display Devices
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Imaging Systems for Eyeglass-Based Display Devices 6-28-2011 Jannick Rolland University of Central Florida Ozan Cakmakci University of Central Florida Find
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Imaging Systems for Eyeglass-Based Display Devices 6-28-2011 Jannick Rolland University of Central Florida Ozan Cakmakci University of Central Florida Find
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005.0070767A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0070767 A1 Maschke (43) Pub. Date: (54) PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 600/300; 128/903 (76)
(19) United States US 2005.0070767A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0070767 A1 Maschke (43) Pub. Date: (54) PATIENT MONITORING SYSTEM (52) U.S. Cl.... 600/300; 128/903 (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0065580 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD
(19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0065580 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 201503185.06A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/031850.6 A1 ZHOU et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 5, 2015 (54) ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DIODE Publication Classification
in-s-he Gua (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,388,499 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 Vddint : SFF LSOUT Tien et al.
 (12) United States Patent Tien et al. USOO6388499B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) LEVEL-SHIFTING SIGNAL BUFFERS THAT SUPPORT HIGHER VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLIES USING LOWER VOLTAGE
(12) United States Patent Tien et al. USOO6388499B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) LEVEL-SHIFTING SIGNAL BUFFERS THAT SUPPORT HIGHER VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLIES USING LOWER VOLTAGE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO900.4986B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,004,986 B2 Byers (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 14, 2015 (54) SHARPENING TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search USPC... 451/557; 76/82, 86, 88
(12) United States Patent USOO900.4986B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9,004,986 B2 Byers (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 14, 2015 (54) SHARPENING TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search USPC... 451/557; 76/82, 86, 88
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) Leonardis
 United States Patent (19) Leonardis 54 SUPPORT STRUCTURE FOR AMOTOR BUS 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Raffaele Leonardis, Turin, Italy Centro Ricerche Fiat S.p.A., Orbassano, Italy (21) Appl. No.: 97,606
United States Patent (19) Leonardis 54 SUPPORT STRUCTURE FOR AMOTOR BUS 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Raffaele Leonardis, Turin, Italy Centro Ricerche Fiat S.p.A., Orbassano, Italy (21) Appl. No.: 97,606
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO867761 OB2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,677,610 B2 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2014 (54) CRIMPING TOOL (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Jen Kai Liu, New Taipei (TW) U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO867761 OB2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,677,610 B2 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2014 (54) CRIMPING TOOL (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Jen Kai Liu, New Taipei (TW) U.S.
(12) United States Patent
 USOO6997228B2 (12) United States Patent Hong (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 14, 2006 (54) LAMINATION APPARATUS FOR AUTOMATED MANUFACTURING SYSTEM OF LITHIUM SECONDARY BATTERY (75) Inventor:
USOO6997228B2 (12) United States Patent Hong (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 14, 2006 (54) LAMINATION APPARATUS FOR AUTOMATED MANUFACTURING SYSTEM OF LITHIUM SECONDARY BATTERY (75) Inventor:
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 LLP 57)
 III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0185581 A1 Xing et al. US 2011 0185581A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) COMPACT CIRCULAR SAW (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0185581 A1 Xing et al. US 2011 0185581A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) COMPACT CIRCULAR SAW (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) Inventors:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) van den Berg et al. 11 Patent Number: Date of Patent: Sep. 8, 1987 54) TRANSDUCING DEVICE FOR CONTACTLESS ULTRASONIC INSPECTION OF PIPELINES OR TUBINGS 75 Inventors: Wilhemus
United States Patent (19) van den Berg et al. 11 Patent Number: Date of Patent: Sep. 8, 1987 54) TRANSDUCING DEVICE FOR CONTACTLESS ULTRASONIC INSPECTION OF PIPELINES OR TUBINGS 75 Inventors: Wilhemus
United States Patent (19) Achatz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Achatz et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 1989 (54) MULTIFOCAL, ESPECIALLY BIFOCAL, INTRAOCULAR, ARTIFICIAL OPHTHALMIC LENS 76) Inventors: Manfred Achatz,
United States Patent (19) Achatz et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 21, 1989 (54) MULTIFOCAL, ESPECIALLY BIFOCAL, INTRAOCULAR, ARTIFICIAL OPHTHALMIC LENS 76) Inventors: Manfred Achatz,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170O80447A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0080447 A1 Rouaud (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2017 (54) DYNAMIC SYNCHRONIZED MASKING AND (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(19) United States US 20170O80447A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0080447 A1 Rouaud (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 23, 2017 (54) DYNAMIC SYNCHRONIZED MASKING AND (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(12) United States Patent
 ............. - (12) United States Patent US007997925B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.997,925 B2 Lam et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 16, 2011 (54) MULTIFUNCTIONAL WALL SOCKET (56) References Cited (76) Inventors:
............. - (12) United States Patent US007997925B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.997,925 B2 Lam et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 16, 2011 (54) MULTIFUNCTIONAL WALL SOCKET (56) References Cited (76) Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. W (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2010
 US 20100080645A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0080645 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2010 (54) WITEBOARD MARKER Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. (76)
US 20100080645A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0080645 A1 W (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 1, 2010 (54) WITEBOARD MARKER Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl. (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0021611A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021611 A1 Onizuka et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) BUS BAR STRUCTURE Related U.S. Application Data
US 2001 0021611A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021611 A1 Onizuka et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) BUS BAR STRUCTURE Related U.S. Application Data
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,593,696 B2
 USOO65.93696B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ding et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 15, 2003 (54) LOW DARK CURRENT LINEAR 5,132,593 7/1992 Nishihara... 315/5.41 ACCELERATOR 5,929,567 A 7/1999
USOO65.93696B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ding et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 15, 2003 (54) LOW DARK CURRENT LINEAR 5,132,593 7/1992 Nishihara... 315/5.41 ACCELERATOR 5,929,567 A 7/1999
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,387,795 B1
 USOO6387795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shao (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) WAFER-LEVEL PACKAGING 5,045,918 A * 9/1991 Cagan et al.... 357/72 (75) Inventor: Tung-Liang Shao, Taoyuan
USOO6387795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shao (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) WAFER-LEVEL PACKAGING 5,045,918 A * 9/1991 Cagan et al.... 357/72 (75) Inventor: Tung-Liang Shao, Taoyuan
(12) United States Patent
 US008133074B1 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 13, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) GUIDED MISSILE/LAUNCHER TEST SET REPROGRAMMING INTERFACE ASSEMBLY
US008133074B1 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 13, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) GUIDED MISSILE/LAUNCHER TEST SET REPROGRAMMING INTERFACE ASSEMBLY
issi Field of search. 348/36, , 33) of the turret punch press machine; an image of the
 US005721587A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,721,587 Hirose 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Primary Examiner Bryan S. Tung NSPECTNG PRODUCT PROCESSED BY Attorney,
US005721587A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,721,587 Hirose 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Primary Examiner Bryan S. Tung NSPECTNG PRODUCT PROCESSED BY Attorney,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,859,376 B2. Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010
 US007859376B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,859,376 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010 (54) ZIGZAGAUTOTRANSFORMER APPARATUS 7,049,921 B2 5/2006 Owen AND METHODS 7,170,268
US007859376B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,859,376 B2 Johnson, Jr. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2010 (54) ZIGZAGAUTOTRANSFORMER APPARATUS 7,049,921 B2 5/2006 Owen AND METHODS 7,170,268
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7768461 B2 (12) United States Patent Cheng et al. (54) ANTENNA DEVICE WITH INSERT-MOLDED ANTENNA PATTERN (75) Inventors: Yu-Chiang Cheng, Taipei (TW); Ping-Cheng Chang, Chaozhou Town (TW); Cheng-Zing
USOO7768461 B2 (12) United States Patent Cheng et al. (54) ANTENNA DEVICE WITH INSERT-MOLDED ANTENNA PATTERN (75) Inventors: Yu-Chiang Cheng, Taipei (TW); Ping-Cheng Chang, Chaozhou Town (TW); Cheng-Zing
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1
 US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.276,333 B1
 USOO9276333B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.276,333 B1 W (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2016 (54) TERMINAL BLOCK WITH IMPROVED 8,647,158 B2 * 2/2014 Kawabata... HO1R 9/2608 RAILENGAGING
USOO9276333B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.276,333 B1 W (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2016 (54) TERMINAL BLOCK WITH IMPROVED 8,647,158 B2 * 2/2014 Kawabata... HO1R 9/2608 RAILENGAGING
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Mack USOO686.0488B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2005 (54) DRILL CHUCK WITH FRONT-END SHIELD (75) Inventor: Hans-Dieter Mack, Sontheim (DE) (73) Assignee: Rohm
(12) United States Patent Mack USOO686.0488B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2005 (54) DRILL CHUCK WITH FRONT-END SHIELD (75) Inventor: Hans-Dieter Mack, Sontheim (DE) (73) Assignee: Rohm
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 (19) United States US 2006OOO1503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0001503 A1 Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (54) MICROSTRIP TO WAVEGUIDE LAUNCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 333/26
(19) United States US 2006OOO1503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0001503 A1 Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (54) MICROSTRIP TO WAVEGUIDE LAUNCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 333/26
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,765,631 B2. Ishikawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2004
 USOO6765631 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,765,631 B2 Ishikawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2004 (54) VEHICLE WINDSHIELD RAIN SENSOR (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Junichi
USOO6765631 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,765,631 B2 Ishikawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2004 (54) VEHICLE WINDSHIELD RAIN SENSOR (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Junichi
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,208,104 B1
 USOO6208104B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Onoue et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) ROBOT CONTROL UNIT (58) Field of Search... 318/567, 568.1, 318/568.2, 568. 11; 395/571, 580;
USOO6208104B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Onoue et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 27, 2001 (54) ROBOT CONTROL UNIT (58) Field of Search... 318/567, 568.1, 318/568.2, 568. 11; 395/571, 580;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 2006O152427A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0152427 A1 Ueda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) ANTENNA COIL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 2006O152427A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0152427 A1 Ueda et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2006 (54) ANTENNA COIL (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,436,044 B1
 USOO643604.4B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wang (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR ADAPTIVE 6,282,963 B1 9/2001 Haider... 73/602 BEAMFORMER APODIZATION 6,312,384
USOO643604.4B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wang (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 20, 2002 (54) SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR ADAPTIVE 6,282,963 B1 9/2001 Haider... 73/602 BEAMFORMER APODIZATION 6,312,384
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,376,238 B1. Rivas et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 20, 2008
 United States Patent USOO7376238B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,376,238 B1 Rivas et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 20, 2008 (54) PULSE RATE, PRESSURE AND HEART 4,658,831 A * 4, 1987 Reinhard et al.... 600,500
United States Patent USOO7376238B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,376,238 B1 Rivas et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 20, 2008 (54) PULSE RATE, PRESSURE AND HEART 4,658,831 A * 4, 1987 Reinhard et al.... 600,500
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,854,310 B2
 US00785431 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,854,310 B2 King et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 2010 (54) PARKING METER 5,841,369 A 1 1/1998 Sutton et al. 5,842,411 A 12/1998 Jacobs
US00785431 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,854,310 B2 King et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 2010 (54) PARKING METER 5,841,369 A 1 1/1998 Sutton et al. 5,842,411 A 12/1998 Jacobs
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,937,567 B2
 US008.937567B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,937,567 B2 Obata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2015 (54) DELTA-SIGMA MODULATOR, INTEGRATOR, USPC... 341/155, 143 AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
US008.937567B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,937,567 B2 Obata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2015 (54) DELTA-SIGMA MODULATOR, INTEGRATOR, USPC... 341/155, 143 AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,705,355 B1
 USOO670.5355B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,705,355 B1 Wiesenfeld (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 16, 2004 (54) WIRE STRAIGHTENING AND CUT-OFF (56) References Cited MACHINE AND PROCESS NEAN
USOO670.5355B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,705,355 B1 Wiesenfeld (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 16, 2004 (54) WIRE STRAIGHTENING AND CUT-OFF (56) References Cited MACHINE AND PROCESS NEAN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 201502272O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0227202 A1 BACKMAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 201502272O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0227202 A1 BACKMAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,347,876 B1
 USOO6347876B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Burton (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) LIGHTED MIRROR ASSEMBLY 1555,478 A * 9/1925 Miller... 362/141 1968,342 A 7/1934 Herbold... 362/141
USOO6347876B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Burton (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 19, 2002 (54) LIGHTED MIRROR ASSEMBLY 1555,478 A * 9/1925 Miller... 362/141 1968,342 A 7/1934 Herbold... 362/141
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,836,894 B2. Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.
 USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
USOO8836894B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Gu et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2014 (54) BACKLIGHT UNIT AND LIQUID CRYSTAL (51) Int. Cl. DISPLAY DEVICE GO2F I/3.3.3 (2006.01) F2/8/00
Sa Sass. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, PACK et al.
 (19) United States US 201701 12163A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0112163 A1 PACK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2017 (54) STAMP PLATE WITH MOULDING STOP (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 201701 12163A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0112163 A1 PACK et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 27, 2017 (54) STAMP PLATE WITH MOULDING STOP (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9463468B2 () Patent No.: Hiley (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2016 (54) COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE RF BO3B 5/08 (2006.01) GENERATOR USING A SELF-RESONANT GOIN 27/62 (2006.01) INDUCTOR
(12) United States Patent USOO9463468B2 () Patent No.: Hiley (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2016 (54) COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE RF BO3B 5/08 (2006.01) GENERATOR USING A SELF-RESONANT GOIN 27/62 (2006.01) INDUCTOR
United States Patent (19)
 US006041720A 11 Patent Number: Hardy (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 2000 United States Patent (19) 54 PRODUCT MANAGEMENT DISPLAY 5,738,019 4/1998 Parker... 108/61 X SYSTEM FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS 75 Inventor:
US006041720A 11 Patent Number: Hardy (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 2000 United States Patent (19) 54 PRODUCT MANAGEMENT DISPLAY 5,738,019 4/1998 Parker... 108/61 X SYSTEM FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS 75 Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,957,665 B2
 USOO6957665B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2005 (54) FLOW FORCE COMPENSATING STEPPED (56) References Cited SHAPE SPOOL VALVE (75) Inventors: Weon
USOO6957665B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2005 (54) FLOW FORCE COMPENSATING STEPPED (56) References Cited SHAPE SPOOL VALVE (75) Inventors: Weon
58 Field of Search /341,484, structed from polarization splitters in series with half-wave
 USOO6101026A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Bane (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 9 2000 54) REVERSIBLE AMPLIFIER FOR OPTICAL FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS NETWORKS 1-274111 1/1990 Japan. 3-125125
USOO6101026A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Bane (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 8, 9 2000 54) REVERSIBLE AMPLIFIER FOR OPTICAL FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS NETWORKS 1-274111 1/1990 Japan. 3-125125
III. United States Patent (19) Ruzskai et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,580,295 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1996
 United States Patent (19) Ruzskai et al. III USOO5580295A 11 Patent Number: 5,580,295 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1996 54 ARMS FOR A TOY FIGURE (75 Inventors: Frank Ruzskai, Copenhagen; Bent Landling,
United States Patent (19) Ruzskai et al. III USOO5580295A 11 Patent Number: 5,580,295 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1996 54 ARMS FOR A TOY FIGURE (75 Inventors: Frank Ruzskai, Copenhagen; Bent Landling,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
