(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,564,782 B2. Kimura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2017
|
|
|
- Michael Henderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 USO B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kimura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2017 (54) WINDING, WINDING METHOD, AND (56) References Cited AUTOMOTIVE ROTATING ELECTRIC MACHINE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,988,055 A * 1/1991 Sakai... HO1F 5/02 (75) Inventors: Takahiro Kimura, Chiyoda-ku (JP); 242/159 Kazunori Tanaka, Chiyoda-ku (JP) 5,208,571 A * 5/1993 Muller... HO1F 7/20 335,299 (73) Assignee: Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, (Continued) TokVO okyo (JP) (JP FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this CN A 6, 2005 patent is extended or adjusted under 35 JP , 1981 U.S.C. 154(b) by 512 days. (Continued) (21) Appl. No.: 14/116,927 OTHER PUBLICATIONS (22) PCT Filed: Sep. 1, 2011 Communication dated Jul. 15, 2015 from the State Intellectual Property Office of the P.R.C. in counterpart application No O. (86). PCT No.: PCT/UP2011/ (Continued) S 371 (c)(1), Primary Examiner Jose Gonzalez, Quinones (2), (4) Date: Nov. 11, 2013 (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm Sughrue Mion, PLLC; Richard C. Turner (87) PCT Pub. No.: WO2013/0304 (57) ABSTRACT PCT Pub. Date: Mar. 7, 2013 Problem A winding is provided which is so arranged that disengagement of a winding conductor is not caused after a (65) Prior Publication Data winding around being finished. US 2014/ A1 Apr. 3, 2014 Constitution A winding according to the present invention s includes a first descending conductor portion (2818c) being bent from an end-portion (28.18a) of a winding conductor (51) Int. Cl. placed at a top portion of an elevated winding portion (28m) HO2K II/00 ( ) toward an outer lateral side in an axial direction of a winding HO2K 2L/2 ( ) (15), and descending along a side face of the elevated (Continued) winding portion (28m), from the top portion thereof to a predetermined winding layer (2816) among a plurality of (52) U.S. Cl. winding layers constituting the elevated winding portion CPC H02K 3/28 ( ); H02K 3/12 ( ); (28m); a first connection conductor portion (2816a) bent H02K 3/18 ( ); H02K 3/522 ( ); from the first descending conductor portion (2818c) toward H02K 3/528 ( ) an inner lateral side in the axial direction of the winding (58) Field of Classification Search (15), and disposed along the side face of the elevated CPC... H02K 3/46; H02K 3/52 winding portion (28m) in a direction to which a winding (Continued) (Continued) / 288) : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : 2 X X s s e s s t s
2 Page 2 conductor constituting the winding (15) extends; and a (56) second descending conductor portion (2816c) being bent from the first connection conductor portion (2816a) toward the outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding (15), and descending along the side face of the elevated winding portion (28m), from the predetermined winding layer (2816) to another predetermined winding layer (2814). 18 Claims, 3 Drawing Sheets References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 7,202,639 B2 4/2007 Lawahmeh 2005/ A1* /2005 Nakanishi... HO2K 3/18 3,194 JP JP JP WO FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS A 1, A 5, A 2004/ A1 2, , 2004 (51) Int. Cl. HO2K 3/28 ( ) HO2K 3/12 ( ) HO2K 3/8 ( ) HO2K 3/52 ( ) (58) Field of Classification Search USPC... 3/71, , , , See application file for complete search history. OTHER PUBLICATIONS Communication dated Aug. 26, 2014, issued by the Japanese Office Action in counterpart Application No Machine Translation of JP A. Machine Translation of JP A. Machine Translation of WO A1. * cited by examiner
3 U.S. Patent Feb. 7, 2017 Sheet 1 of 3
4 U.S. Patent Feb. 7, 2017 Sheet 2 of 3
5 U.S. Patent Feb. 7, 2017 Sheet 3 of 3
6 1. WINDING, WINDING METHOD, AND AUTOMOTIVE ROTATING ELECTRIC MACHINE CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This application is a National Stage of International Application No. PCT/JP2011/ filed Sep. 1, 2011, the contents of all of which are incorporated herein by reference in their entirety. TECHNICAL FIELD The present invention relates to a winding of ring-shaped structure, a method of winding the winding, and an auto motive rotating electric machine including the winding. BACKGROUND ART For example, an automotive alternating-current generator mounted on a motor vehicle as an automotive rotating electric machine includes an armature winding mounted on a stator as a stator winding (hereinafter referred to as an armature winding), and a field winding mounted on a rotor as a rotor winding (hereinafter referred to as a field wind ing). The field winding generates magnetic field flux when a DC current is supplied to the winding by way of a pair of brushes and a pair of slip rings, and induces an AC voltage in the armature winding by the rotation in an inner space of the stator. The field winding is disposed, for example, in a space where a pair of rotor magnetic poles (claw pole), each including a plurality of claws, is opposing to each other, and an outer circumferential face of the field winding is sur rounded by the plurality of claws of the pair of rotor magnetic poles. In Such an automotive alternating-current generator, there exists a conventional automotive alternating-current genera tor in which, by effectively utilizing a space where the pair of rotor magnetic poles described above is opposing to each other, a winding conductor of field winding is wound up toward undersides of claws of the pair of rotor magnetic poles, and the alternating-current generator is so arranged to achieve output-power enhancement by increasing the num ber of turns of the field winding (for example, refer to Patent Document 1). In the field winding of the conventional automotive alternating-current generator, a central portion of an outer circumferential portion of the field winding is raised to the shape of mound; Such a winding scheme is, usually, referred to an elevated winding scheme. A conventional automotive alternating-current generator disclosed in Patent Document 1 effectively utilizes a space where a pair of rotor magnetic poles is opposing to each other, and adopts an elevated winding structure to a field winding, so that the number of turns of the field winding can be increased as described above, and output-power enhance ment of the automotive alternating-current generator is made possible. Patent Document 1 RELATED ART DOCUMENT Patent Document U.S. Pat. No. 7,202,639 B DISCLOSURE OF THE INVENTION Problems to be Solved by the Invention In the case of field winding in the elevated winding scheme described above, an end-portion of a winding con ductor constituting the field winding is placed at a top portion of an elevated winding portion. Therefore, after ceasing a winding around, it is necessary to guide the end-portion of a winding conductor placed at a top portion of the elevated winding portion toward an end-portion in an axial direction of the field winding, by causing it descending from the top portion, to make the winding conductor itself as an external terminal connection conductor of the field winding, or to connect to an external conductor connection terminal of the field winding provided in advance. However, when the number of overlaps of the elevated winding portion is increased, the height of the top portion of the elevated winding portion becomes larger, so that there arises a necessity of steeply descending the end-portion of the winding conductor placed at the top portion of the elevated winding. Nevertheless, when the winding conductor is caused to steeply descend from a top portion of the elevated winding portion, the descending winding conductor is not sufficiently adhered to another Surface of winding conductor, so that there arises a case in that a winding conductor from the top portion of the elevated winding portion to the external terminal connection terminal of the field winding does not come along with an outer circumferential face of the field winding, causing winding disintegration and disengagement of part of the winding conductor thus easily after the winding around being finished. A winding conductor sepa rated from the field winding in which disengagement and winding disintegration are caused in part of the winding conductor of the field winding has a possibility to make contact with a rotor magnetic pole(s) when the field winding is assembled onto a rotor, so that the field winding becomes under a short-circuiting state during the operation of the automotive alternating-current generator, resulting in not inducing the Voltage in the armature winding, which may give rise to cause a failure due to non-generation of the automotive alternating-current generator. According to the above, in the field winding in a conven tional automotive alternating-current generator, there arises problems in that when the height of an elevated winding portion of the field winding is made larger for the sake of enhanced generator output, portions where the winding conductor does not come along in an outer circumferential portion of the field winding do grow, so that the number of overlaps of the elevated winding portion cannot be increased to a larger extent. The present invention has been directed at solving these problems in a field winding in the conventional automotive alternating-current generator described above, and an object of the invention is to provide a winding, a winding method, and an automotive rotating electric machine that mounts the winding thereon as a field winding which are so arranged that disengagement of the winding conductor is not caused after the winding around being finished. Means for Solving the Problems A winding according to the present invention is a ring-shaped winding including, in an outer circumfer ential portion thereof, an elevated winding portion in which
7 3 a cross-sectional shape thereof takes a shape of mound in an axial direction, wherein the winding comprises a first descending conductor portion being bent from an end-portion of a winding conductor placed at a top portion of the elevated winding portion toward an outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and descending along a side face of the elevated winding portion, from the top portion thereof to a predetermined winding layer among a plurality of winding layers forming the elevated winding portion; a first connection conductor portion bent from the first descending conductor portion toward an inner lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and disposed along the side face of the elevated winding portion in a direction to which a winding conductor constituting the winding extends; and a second descending conductor portion being bent from the first connection conductor portion toward the outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and descending along the side face of the elevated winding portion, from the predetermined winding layer to another predetermined winding layer. In addition, a winding method according to the present invention is the method of winding a ring-shaped winding including, in an outer circumferential portion thereof, an elevated winding portion in which a cross-sectional shape thereof takes a shape of mound in an axial direction, and the method is characterized in that an end-portion of a winding conductor in a top portion of the elevated winding portion descends along a side face of the elevated winding portion, by way of at least two descending conductor portions bent toward an outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding. Moreover, an automotive rotating electric machine according to the present invention includes an automotive alternating-current generator driven by an internal-combustion engine mounted on a motor vehicle, and the machine is characterized in that a ring-shaped winding including, in an outer circumferential portion thereof, an elevated winding portion in which a cross-sectional shape thereof takes a shape of mound in an axial direction is mounted on a rotor as a field winding thereof, and the field winding comprises a first descending conductor portion being bent from an end-portion of a winding conductor placed at a top portion of the elevated winding portion toward an outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and descending along a side face of the elevated winding portion, from the top portion thereof to a predetermined winding layer among a plurality of winding layers forming the elevated winding portion; a first connection conductor portion bent from the first descending conductor portion toward an inner lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and disposed along the side face of the elevated winding portion in a direction to which a winding conductor constituting the winding extends; and a second descending conductor portion being bent from the first connection conductor portion toward the outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and descending along the side face of the elevated winding portion, from the predetermined winding layer to another predetermined winding layer. Effects of the Invention According to a winding in the present invention, the winding comprises a first descending conductor portion being bent from an end-portion of a winding conductor placed at a top portion of an elevated winding portion toward an outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and descending along a side face of the elevated winding por tion, from the top portion thereof to a predetermined wind ing layer among a plurality of winding layers forming the elevated winding portion; a first connection conductor por tion bent from the first descending conductor portion toward an inner lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and disposed along the side face of the elevated winding portion in a direction to which a winding conductor constituting the winding extends; and a second descending conductor por tion being bent from the first connection conductor portion toward the outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and descending along the side face of the elevated winding portion, from the predetermined winding layer to another predetermined winding layer, so that disengagement of the winding conductor is not caused after the winding around being finished even when the height of the elevated winding portion is made larger, enabling to increase the number of turns of the winding by making the height of its elevated winding portion larger. In addition, according to a winding method in the present invention, an end-portion of a winding conductor in a top portion of the elevated winding portion is made in Such a way to descend along a side face of the elevated winding portion, by way of at least two descending conductor por tions bent toward an outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, so that a winding can be obtained in which disengagement of the winding conductor is not caused after the winding around being finished even when the height of the elevated winding portion is made larger. Moreover, according to an automotive rotating electric machine in the present invention, a ring-shaped winding including, in an outer circumferential portion thereof, an elevated winding portion in which a cross-sectional shape thereof takes a shape of mound in an axial direction is mounted as a field winding mounted on a rotor, and the field winding comprises a first descending conductor portion being bent from an end-portion of a winding conductor placed at a top portion of the elevated winding portion toward an outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and descending along a side face of the elevated winding portion, from the top portion thereof to a predeter mined winding layer among a plurality of winding layers forming the elevated winding portion; a first connection conductor portion bent from the first descending conductor portion toward an inner lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and disposed along the side face of the elevated winding portion in a direction to which a winding conductor constituting the winding extends; and a second descending conductor portion being bent from the first connection conductor portion toward the outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and descending along the side face of the elevated winding portion, from the predetermined winding layer to another predetermined winding layer, so that output-power enhancement of the automotive rotating electric machine is achieved by effectively utilizing a space where rotor magnetic poles are opposing to each other, and by increasing the number of turns of the field winding; and moreover, it is possible to obtain an automotive rotating electric machine in which disengagement of the winding conductor is not caused after the winding around being finished, and reliability enhancement can be realized during
8 5 the assembly of the automotive rotating electric machine, without causing a failure Such as short circuiting. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional diagram illustrating an example of an automotive alternating-current generator; FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of part of a field winding of an automotive alternating-current generator according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention; FIG. 3 is an illustrative diagram for explaining the field winding of the automotive alternating-current generator according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention; FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view of part of a field winding of an automotive alternating-current generator which forms foundations for the present invention; and FIG. 5 is an illustrative diagram for explaining the field winding of the automotive alternating-current generator which forms foundations for the present invention. EMBODIMENTS FOR CARRYING OUT THE INVENTION FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional diagram illustrating an example of an automotive alternating-current generator as an auto motive rotating electric machine. In FIG. 1, an automotive alternating-current generator 0 includes a stator 1, a rotor 2 that is inserted within an internal space of the stator 1 and rotates, a rotor shaft 3 that supports the stator 1 and the rotor 2, and brackets 6 and 7 that support the rotor shaft 3 rotationally movable with one another by means of bearings 4 and 5. The stator 1 has an annular stator core 9 including a plurality of stator slots 8 along an inner circumferential face thereof, and an armature winding housed in the stator slots 8 as a stator winding. The rotor 2 has an iron-made first rotor magnetic pole 12 including a plurality of claws 11 extending in an axial direction of the rotor 2, an iron-made second rotor magnetic pole 14 including a plurality of claws 13 extending in the axial direction of the rotor 2, and a field winding 15. The first rotor magnetic pole 12 and the second rotor magnetic pole 14 constitute the rotor magnetic poles. The first rotor magnetic pole 12 and the second rotor magnetic pole 14 abut to each other, and are fixed on a circumferential face of the rotor shaft 3. The plurality of claws 11 of the first rotor magnetic pole 12 is rowed circumferentially interposing space portions, and similarly the plurality of claws 13 of the second rotor magnetic pole 14 is rowed circumferentially interposing space portions. The plurality of claws 11 of the first rotor magnetic pole 12 and the plurality of claws 13 of the second rotor magnetic pole 14 are inserted in respective space portions of other party's rotor magnetic poles opposing to each other, and are alternately disposed to circumferentially interpose predeter mined gaps. An outer circumferential face of the claws 11 of the first rotor magnetic pole 12 and an outer circumferential face of the claws 13 of the second rotor magnetic pole 14 constitute the outer circumferential face of the rotor 2. The field winding 15 is attached in a space portion formed between the first rotor magnetic pole 12 and the second rotor magnetic pole 14 opposing to each other, namely in the space portion in an inner lateral side Surrounded by the claws 11 of the first rotor magnetic pole 12 and the claws 13 of the second rotor magnetic pole 14. The field winding 15 is formed, as this will be described later, by winding a winding conductor in multiple layers around on an outer circumfer ential face of a bobbin. A pair of field-winding external conductors 16 connected to external conductor connection terminals of the field winding 15 is connected to a pair of respective slip rings 17 fixed on the rotor shaft 3. A pair of brushes 18 is supported slidingly movable with each other in a brush holder 19 fixed on the bracket 7, and is pressed to the pair of slip rings 17 described above so as to make slidingly contact therewith due to spring pressure by compression springs 20. The pair of brushes 18 is connected to a DC voltage source (not shown in the figure) such as an automotive battery by way of lead conductors 21. In addi tion, on the bracket 7, there mounted are an electrical power conversion circuit 22 that is made of a plurality of semi conductor devices and performs the electrical power con version between the armature winding and the DC Voltage source Such as the automotive battery, a magnetic field control circuit 23 that controls the magnetic field current of the field winding 15, etc. A pulley 24 fixed on one end of the rotor shaft 3 is joined to an output shaft of an internal-combustion engine (not shown in the figure) by means of a power transmitting member (not shown in the figure) such as a V-belt. The automotive alternating-current generator 0 consti tuted as described above rotates when the rotor shaft 3 and the rotor 2 are driven by an internal-combustion engine by means of a power transmitting member Such as a V-belt, and the pulley 24. At this time, the field winding 15 is energized from a DC voltage source such as a battery by means of the lead conductors 21, the brushes 18, the slip rings 17 and the field-winding external conductors 16, so that magnetic field flux is generated. The magnetic field flux flows in inner parts of the first rotor magnetic pole 12 and the second rotor magnetic pole 14 through gaps where the plurality of claws 11 of the first rotor magnetic pole 12 and the plurality of claws 13 of the second rotor magnetic pole 14 oppose to each other, accordingly, magnetic field flux passing through the aforementioned gaps crosses through the armature wind ing according to the rotation of the rotor 2. Because magnetic field flux passing through each of the gaps where the plurality of claws 11 of the first rotor magnetic pole 12 and the plurality of claws 13 of the second rotor magnetic pole 14 oppose to each other flows in alternately different directions for each of the gaps, an AC Voltage is induced in the armature winding that crosses through the magnetic field flux. The AC voltage induced in the armature winding, and an AC current that flows defined based on the AC voltage are converted into a DC voltage and a DC current by the electrical power conversion circuit 22, and Supplied to an onboard battery, etc. Next, a structure of the field winding 15 and its winding method will be explained. FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view of part of a field winding of an automotive alternating-current generator which forms foundations for the present invention, and FIG. 5 is an illustrative diagram for explaining the field winding of the automotive alternating-current generator which forms foundations for the present invention. In FIG. 4 and FIG. 5, the field winding 15 is formed in multiple layers by sequentially winding a winding conductor 28 around on an outer circumferential face of a cylindrical portion of a bobbin 27 made of a dielectric material having flange portions 25 and 26 each on both ends in an axial direction. The field winding 15 shown in the figures is wound around in eighteen layers, as an example; each of the layers is wound around with an identical width in the axial direc tion from the lowest layer contacting the outer circumfer ential face of the bobbin 27 toward a 14th layer 2814 along the flange portions 25 and 26, whereas the layers are wound
9 7 around so that the number of winding turns sequentially decreases toward a 15th layer 2815, a 16th layer 2816, a 17th layer 2817 and an 18th layer 2818 that is the uppermost layer. Therefore, in the field winding 15, an elevated wind ing portion 28m in which its cross-section takes the shape of 5 mound in the axial direction is formed by the layers from the 15th layer 2815 toward the 18th layer 2818 that is the uppermost layer. The reason why the elevated winding portion 28m is formed in an outer circumferential portion of the field winding 15 is attributed to that, by effectively utilizing space between undersides of the claws 11 of the first rotor mag netic pole 12 and undersides of the claws 13 of the second rotor magnetic pole 14, the number of turns of the field winding is increased. Namely, inner wall portions of the 15 claws 11 of the first rotor magnetic pole 12 and inner wall portions of the claws 13 of the second rotor magnetic pole 14 described above are inclined toward tip portions of each of the claws to a side of outer circumferential face of the rotor, and wall thickness of the tip portions of respective claws 11 and 13 are formed to become thinner; as a result, because a space portion formed by inner wall portions of the claws 11 and inner wall portions of the claws 13 is formed to give a cross-section taking the shape of mound, the elevated winding portion 28m is formed to occupy the space 25 portion so that the number of turns of the field winding 15 is increased. In the case of the field winding 15 which forms founda tions for the present invention, a winding conductor's end portion 2818a residing in the 18th layer 2818 that is a top 30 portion of the elevated winding portion 28m descends, as shown in FIG. 5, in one movement from the 18th layer 2818 to the 14th layer 2814 that is a skirting portion using one descending conductor portion 2818b formed by bending it toward an outer lateral side in the axial direction of the field 35 winding 15 at a predetermined angle. The descending conductor portion 2818b having descended to the 14th layer 2814 is wound for more than or equal to one turn in the 14th layer 2814 as a connection conductor portion 2814a, and thereafter connected to the field-winding external conductor 16 by way of an external conductor connection terminal. As described above, the descending conductor portion 2818b descends, as shown in FIG. 5, from the 18th layer 2818 that is the top portion of the elevated winding portion 28m, passing diagonally across the 17th layer 2817, the 16th layer 2816 and the 15th layer 2815 in one movement, to the 14th layer 2814 that is the skirting portion. Namely, because a position of the winding conductor's end-portion 2818a is placed at a central portion in the axial direction of the field winding 15, it is necessary to provide a process to finish the winding by steeply descending it using the descending conductor portion 2818b, as shown in FIG. 5. Nevertheless, when the finish of winding is performed by steeply descending diagonally across the elevated winding portion 28m using the descending conductor portion 2818b, the descending conductor portion 2818b descends by jump ing over the three layers of 17th layer 2817, 16th layer 2816 and 15th layer 2815 by such movement as shown by the arrow in FIG. 4, thereby there exist problems in that suffi cient adhesion to outer circumferential faces each of the 17th layer 2817, 16th layer 2816 and 15th layer 2815 is not achieved, and disengagement and winding disintegration are likely to be caused thus easily in part of the winding conductor after ceasing the winding around. A field winding of an automotive alternating-current generator according to Embodiment 1 of the present inven tion described below can solve the aforementioned problems in the field winding of the automotive alternating-current generator which forms foundations for the present invention. Embodiment 1 FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view of part of a field winding of an automotive alternating-current generator according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, and FIG. 3 is an illustrative diagram for explaining the field winding of the automotive alternating-current generator according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention; the same reference numerals and symbols designate the same items correspond ing to those in FIG. 4 and FIG. 5 described above. In FIG. 2 and FIG.3, the winding conductor's end-portion 28.18a in the field winding 15 is connected to a field-winding external conductor by way of a first descending conductor portion 2818c, a first connection conductor portion 2816a, a second descending conductor portion 2816c, and a second connection conductor portion 2814a. The winding conduc tor constituting the field winding 15, and the end-portion 28.18a of the conductor, the first descending conductor portion 2818c, the first connection conductor portion 2816a, the second descending conductor portion 2816C, and the second connection conductor portion 2814a are made of the identical winding conductor. The first descending conductor portion 2818c is bent at a first bend position X1 of the end-portion 2818a of the winding conductor placed at a top portion of the elevated winding portion 28m toward the outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding 15 at a predetermined angle 0, and descends along a side face of the elevated winding portion 28m, from the top portion of the elevated winding portion 28m to the 16th layer 2816 that is a predetermined winding layer among a plurality of winding layers forming the elevated winding portion 28m. The first connection conductor portion 2816a is bent at a second bend position X2 of the first descending conductor portion 2818c toward the inner lateral side in the axial direction of the winding 15 at a predetermined angle 0, and wound only for approximately one turn along the side face of the elevated winding portion in a direction to which the winding conductor constituting the winding 15 extends. The second descending conductor portion 2816c is bent at a third bend position X3 of the first connection conductor portion 2816.a toward the outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding 15 at a predetermined angle 0, and descends along the side face of the elevated winding portion 28m, from the aforementioned 16th layer 2816 to the 14th layer 2814 that is another predetermined winding layer. The second connection conductor portion 2814a is bent at a fourth bend position X4 of the second descending con ductor portion 2816c toward the inner lateral side in the axial direction of the winding 15 at a predetermined angle 0. wound for more than or equal to one turn in a direction to which the winding conductor constituting the winding 15 extends, and connected to the field-winding external con ductor 16 by way of an external conductor connection terminal of the field winding 15. The first descending conductor portion 2818c and the second descending conductor portion 2816c are mutually arranged side by side interposing an interspace therebe tween, as shown in FIG. 3. By descending from the end-portion 2818a of the winding conductor at the top portion of the elevated winding portion 28m using the first descending conductor portion 2818c and the second descending conductor portion 2816c as described
10 9 above, it becomes possible to easily connect the winding conductor's end-portion 2818a to the external conductor connection terminal. In addition, by winding the first connection conductor portion 2816.a for more than or equal to half a turn on the side face of the elevated winding portion 28m, adhesive effects of the first descending conductor portion 2818c and the second descending conductor portion 2816c to the winding 15 can be held stronger, so that winding disinte gration and disengagement are difficult to be caused. More over, by winding the second connection conductor portion 2814.a for more than or equal to half a turn, adhesive effects of the first descending conductor portion 2818c and the second descending conductor portion 2816c to the winding 15 can be held further stronger, so that winding disintegra tion and disengagement are difficult to be caused. In Embodiment 1 described above, the plurality of wind ing layers forming the elevated winding portion 28m is formed so that the number of turns of the 18th layer 2818 placed at the uppermost layer is the Smallest in Embodiment 1, and their numbers of turns are sequentially increased in accordance with a lower layer toward the 17th layer 2817, the 16th layer 2816 and the 15th layer Namely, they are configured in Such a manner that the more a winding layer is placed at an upper layer, the less the number of its turns becomes than that of a winding layer placed at an lower layer. The predetermined bend angle 0 at the aforementioned first bend position X1, second bend position X2, third bend position X3 and fourth bend position X4 is the identical angle at them each, and is set in a range from 15 degrees to 30 degrees inclusive, for example. In addition, the lengths of the first descending conductor portion 2818c and the second descending conductor portion 2816c are formed in the identical dimension L. Here, each of the predetermined bend angles 0 described above is set in a range from 15 degrees to 30 degrees inclusive, and each of the bend angles is set at the identical angle. Note that, these bend angles 0 are not necessarily limited to being set at the identical angle, if they are in a range from 15 degrees to 30 degrees inclusive. Note that, the first connection conductor portion 2816a is shown in a case in which it is wound around on a side face of the elevated winding portion 28m for approximately one turn only in Embodiment 1; not necessarily limited thereto, it may be adopted that any number of turns of wounding around is made for, if it is for more than or equal to half a turn. In addition, the second connection conductor portion 2814a is wound around for more than one turn in Embodi ment 1; however, not necessarily limited thereto, it may be adopted that any number of turns of wounding around is made for, if it is for more than or equal to half a turn. Moreover, although the elevated winding portion 28m is formed by overlapping the four layers from the 15th layer 2815 through the 18th layer 2818 in Embodiment 1, it is not necessarily limited to this; it is suitable that overlaps of at least three winding layers may be formed. Note that, other structures are similar to those of the field winding and its winding method shown in aforementioned FIG. 4 and FIG. 5 for the automotive alternating-current generator which forms foundations for the present invention. The automotive alternating-current generator according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention described above gives a concrete form to a winding, a method of the winding, and an automotive alternating-current generator according to the present invention. Namely, the automotive alternating current generator according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention described above subsumes the following inven tions. (1) In a ring-shaped winding including, in an outer circum ferential portion thereof, an elevated winding portion in which a cross-sectional shape thereof takes a shape of mound in an axial direction, the winding is characterized to comprise a first descending conductor portion being bent from an end-portion of a winding conductor placed at a top portion of the elevated winding portion toward an outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and descending along a side face of the elevated winding portion, from the top portion thereof to a predetermined winding layer among a plurality of winding layers forming the elevated winding portion; a first connection conductor portion bent from the first descending conductor portion toward an inner lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and disposed along the side face of the elevated winding portion in a direction to which a winding conductor constituting the winding extends; and a second descending conductor portion being bent from the first connection conductor portion toward the outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and descending along the side face of the elevated winding portion, from the predetermined winding layer to another predetermined winding layer. (2) In the winding, each bending angle is set, preferably, in a range from 15 degrees to 30 degrees inclusive. (3) In the winding, each bending angle is set, preferably, at an identical angle. (4) In the winding, the first connection conductor portion is wound, preferably, for more than or equal to half a turn on the side face of the elevated winding portion. (5) In the winding, the second descending conductor portion is connected, preferably, to an external conductor connection terminal of the winding by way of a second connection conductor portion disposed along the winding conductor constituting the winding. (6) In the winding, the second connection conductor portion is wound, preferably, for more than or equal to half a turn on an outer circumferential portion of the winding. (8) In the winding, the winding conductor constituting the winding, the first descending conductor portion, the first connection conductor portion, the second descending con ductor portion, the second connection conductor portion, and the external conductor connection portion are made, preferably, of an identical conductor continuously extending from the winding conductor. (9) In the winding, the elevated winding portion is formed, preferably, by overlapping at least three winding layers. () In the winding, the plurality of winding layers forming the elevated winding portion is formed, preferably, in Such a manner that the number of turns of a winding layer placed at an upper layer is less than that of a winding layer placed at an lower layer. (11) In the winding, the first descending conductor portion and the second descending conductor portion are mutually arranged, preferably, side by side interposing an interspace therebetween. (12) In a method of winding a ring-shaped winding includ ing, in an outer circumferential portion thereof, an elevated winding portion in which a cross-sectional shape thereof takes a shape of mound in an axial direction, the winding method is characterized in that
11 11 an end-portion of a winding conductor in a top portion of the elevated winding portion descends along a side face of the elevated winding portion, by way of at least two descending conductor portions bent toward an outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding. (13) In the winding method, preferably, a connection con ductor portion mutually connecting between the descending conductor portions is wound for more than or equal to half a turn along the side face of the elevated winding portion. (14) In the winding method, preferably, the at least two descending conductor portions each are bent, with respect to a direction to which the winding conductor constituting the winding extends, toward the outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding in a range from 15 degrees to 30 degrees inclusive. (15) In an automotive rotating electric machine driven by an internal-combustion engine mounted on a motor vehicle, the automotive rotating electric machine is characterized in that the winding as set forth in any one of (1) to (11) is mounted on a rotor as a field winding thereof. (16) In the automotive rotating electric machine, preferably, the rotor comprises a first rotor magnetic pole including a plurality of claws extending in an axial direction of the rotor, and a second rotor magnetic pole being disposed to oppose the first rotor magnetic pole, and including a plurality of claws each opposing to the plurality of claws of the first rotor magnetic pole through predetermined gaps; and the field winding is attached in a space portion Surrounded by the plurality of claws of the first rotor magnetic pole and the plurality of claws of the second rotor magnetic pole. (17) In the automotive rotating electric machine, preferably, inner wall portions of the plurality of claws of the first rotor magnetic pole and inner wall portions of the plurality of claws of the second rotor magnetic pole are formed to incline to a side of outer circumferential face of the rotor, toward tip portions of each of the claws, and an elevated winding portion of the field winding is disposed correspond ing to a space portion formed by the inclined inner wall portions of the claws. INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY The present invention can be utilized, for example, in a field of automotive vehicle industries, and particularly in the field of a rotating electric machine mounted on an automo tive vehicle. EXPLANATION OF NUMERALS AND SYMBOLS Numeral 0' designates an automotive alternating current generator; 1, stator; 2.' rotor; 3, rotor shaft; 4, 5, bracket: 8, stator slot: 9, stator core:, stator winding (armature winding); claw; 12. first rotor magnetic pole; "14. Second rotor magnetic pole; 15. field winding; 16. field-winding external conductor; 17, slip ring: 18, brush: 19, brush holder: 20, compression spring; 21, lead conductor; 22. electrical power conversion circuit: 23 magnetic field control cir cuit; "24, pulley; "24, power transmitting member: 28m. elevated winding portion: 2814, 14th layer: 2815, 15th layer: 2816, 16th layer: 2817, 17th layer: 2818, 18th layer: 28.18a, end-portion of winding conductor; 2818b. descending conductor portion: 2818c, first descending conductor portion: 2816a, first connection conductor por tion: 2816c. second descending conductor portion; 2814a, second connection conductor portion: X1. first bend position: X2, second bend position: 'X3, third bend position; and X4, fourth bend position. What is claimed is: 1. A ring-shaped winding including, in an outer circum ferential portion thereof, an elevated winding portion in which a cross-sectional shape thereof takes a shape of mound in an axial direction, the winding, comprising: a first descending conductor portion being bent from an end-portion of a winding conductor placed at a top portion of the elevated winding portion toward an outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and descending along a side face of the elevated winding portion, from the top portion thereof to a predetermined winding layer among a plurality of winding layers forming the elevated winding portion; a first connection conductor portion bent from the first descending conductor portion toward an inner lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and disposed along the side face of the elevated winding portion in a direction to which a winding conductor constituting the winding extends; and a second descending conductor portion being bent from the first connection conductor portion toward the outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, and descending along the side face of the elevated winding portion, from the predetermined winding layer to another predetermined winding layer. 2. The winding as set forth in claim 1, wherein each bending angle is set in a range from 15 degrees to 30 degrees inclusive. 3. The winding as set forth in claim 1, wherein each bending angle is set at an identical angle. 4. The winding as set forth in claim 1, wherein the first connection conductor portion is wound for more than or equal to half a turn on the side face of the elevated winding portion. 5. The winding as set forth in claim 1, wherein the second descending conductor portion is connected to an external conductor connection terminal of the winding by way of a second connection conductor portion disposed along the winding conductor constituting the winding. 6. The winding as set forth in claim 5, wherein the second connection conductor portion is wound for more than or equal to half a turn on an outer circumferential portion of the winding. 7. The winding as set forth in claim 5, wherein the winding conductor constituting the winding, the first descending conductor portion, the first connection conductor portion, the second descending conductor portion, the sec ond connection conductor portion, and the external conduc tor connection portion are made of an identical conductor continuously extending from the winding conductor. 8. The winding as set forth in claim 1, wherein the elevated winding portion is formed by overlapping at least three winding layers. 9. The winding as set forth in claim 1, wherein the plurality of winding layers forming the elevated winding portion is formed in Such a manner that the number of turns of a winding layer placed at an upper layer is less than that of a winding layer placed at an lower layer.. The winding as set forth in claim 1, wherein the first descending conductor portion and the second descending conductor portion are mutually arranged side by side inter posing an interspace therebetween. 11. A method of winding a ring-shaped winding including, in an outer circumferential portion thereof, an elevated
12 13 winding portion in which a cross-sectional shape thereof takes a shape of mound in an axial direction; the method of winding characterized in that an end-portion of a winding conductor in a top portion of the elevated winding portion descends along a side face of the elevated winding portion, by way of at least two descending conductor portions bent toward an outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding, wherein the at least two descending conductor portions are each separated by a connection conductor portion. 12. The method of winding the winding as set forth in claim 11, wherein the connection conductor portion mutu ally connecting between the descending conductor portions is wound for more than or equal to half a turn along the side face of the elevated winding portion. 13. The method of winding the winding as set forth in claim 11, wherein the at least two descending conductor portions each are bent, with respect to a direction to which the winding conductor constituting the winding extends, toward the outer lateral side in the axial direction of the winding in a range from 15 degrees to 30 degrees inclusive. 14. An automotive rotating electric machine driven by an internal-combustion engine mounted on a motor vehicle, the automotive rotating electric machine characterized in that the winding as set forth in claim 1 is mounted on a rotor as a field winding thereof. 15. The automotive rotating electric machine as set forth in claim 14, wherein the rotor comprises a first rotor magnetic pole including a plurality of claws extending in an axial direction of the rotor, and a second rotor magnetic pole being disposed to oppose the first rotor magnetic pole, and including a plurality of claws each opposing to the plurality of claws of the first rotor magnetic pole through predetermined gaps; and wherein the field winding is attached in a space portion Surrounded by the plurality of claws of the first rotor magnetic pole and the plurality of claws of the second rotor magnetic pole. 16. The automotive rotating electric machine as set forth in claim 14, wherein inner wall portions of the plurality of claws of the first rotor magnetic pole and inner wall portions of the plurality of claws of the second rotor magnetic pole are formed to incline to a side of outer circumferential face of the rotor, toward tip portions of each of the claws, and an elevated winding portion of the field winding is disposed corresponding to a space portion formed by the inclined inner wall portions of the claws. 17. The winding as set forth in claim 1, wherein the first descending portion descends across two winding layers. 18. The method of winding the winding as set forth in claim 11, wherein at least one of the at least two descending conductor portions descends across two winding layers. k k k k k
Kiuchi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2011
 (12) United States Patent US007902952B2 (10) Patent No.: Kiuchi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2011 (54) SHARED REACTOR TRANSFORMER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Hiroshi Kiuchi, Chiyoda-ku
(12) United States Patent US007902952B2 (10) Patent No.: Kiuchi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2011 (54) SHARED REACTOR TRANSFORMER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Hiroshi Kiuchi, Chiyoda-ku
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
(19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
United States Patent (19) Sun
 United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
(12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD21: Last updated: 29th November 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Part PatD21: Last updated: 29th November 2006 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent covers a device which is claimed to have a greater output power than the input
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,262 B2
 USOO8926262B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,262 B2 Tanahashi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2015 (54) CMCTURBINE STATOR BLADE USPC... 415/9, 200, 209.3, 209.4, 210.1, 211.2,
USOO8926262B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,926,262 B2 Tanahashi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 6, 2015 (54) CMCTURBINE STATOR BLADE USPC... 415/9, 200, 209.3, 209.4, 210.1, 211.2,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9206864B2 (12) United States Patent Krusinski et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.206,864 B2 Dec. 8, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) TORQUE CONVERTERLUG
USOO9206864B2 (12) United States Patent Krusinski et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.206,864 B2 Dec. 8, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) TORQUE CONVERTERLUG
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,068,465 B2
 USOO90684-65B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Keny et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 30, 2015 (54) TURBINE ASSEMBLY USPC... 416/215, 216, 217, 218, 248, 500 See application file for complete
USOO90684-65B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Keny et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 30, 2015 (54) TURBINE ASSEMBLY USPC... 416/215, 216, 217, 218, 248, 500 See application file for complete
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices
 A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Device Patent No 30: Last updated: 24th June 2007 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent shows a method of altering a standard electrical generator intended to be
A Practical Guide to Free Energy Devices Device Patent No 30: Last updated: 24th June 2007 Author: Patrick J. Kelly This patent shows a method of altering a standard electrical generator intended to be
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,561,977 B2
 US008561977B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,561,977 B2 Chang (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2013 (54) POST-PROCESSINGAPPARATUS WITH (56) References Cited SHEET EUECTION DEVICE (75) Inventor:
US008561977B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,561,977 B2 Chang (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 22, 2013 (54) POST-PROCESSINGAPPARATUS WITH (56) References Cited SHEET EUECTION DEVICE (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007793.996 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.793,996 B2 Karlander (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2010 (54) CRASH BOX AND A METHOD OF (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/18703,
(12) United States Patent US007793.996 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.793,996 B2 Karlander (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 14, 2010 (54) CRASH BOX AND A METHOD OF (58) Field of Classification Search... 296/18703,
( 12 ) United States Patent
 THI NANIULUH TNICI UNTUK US009941606B1 ( 12 ) United States Patent Hashimoto et al. ( 54 ) COAXIAL CABLE CONNECTOR AND METHOD OF USE THEREOF ( 71 ) Applicant : DAI - ICHI SEIKO CO., LTD., Kyoto ( JP )
THI NANIULUH TNICI UNTUK US009941606B1 ( 12 ) United States Patent Hashimoto et al. ( 54 ) COAXIAL CABLE CONNECTOR AND METHOD OF USE THEREOF ( 71 ) Applicant : DAI - ICHI SEIKO CO., LTD., Kyoto ( JP )
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2
 US0083 04995 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2 Ku et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) LAMP WITH SNOW REMOVING (56) References Cited STRUCTURE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
US0083 04995 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,304,995 B2 Ku et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 6, 2012 (54) LAMP WITH SNOW REMOVING (56) References Cited STRUCTURE U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
III. United States Patent (19) Ruzskai et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,580,295 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1996
 United States Patent (19) Ruzskai et al. III USOO5580295A 11 Patent Number: 5,580,295 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1996 54 ARMS FOR A TOY FIGURE (75 Inventors: Frank Ruzskai, Copenhagen; Bent Landling,
United States Patent (19) Ruzskai et al. III USOO5580295A 11 Patent Number: 5,580,295 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1996 54 ARMS FOR A TOY FIGURE (75 Inventors: Frank Ruzskai, Copenhagen; Bent Landling,
United States Patent (19) Nihei et al.
 United States Patent (19) Nihei et al. 54) INDUSTRIAL ROBOT PROVIDED WITH MEANS FOR SETTING REFERENCE POSITIONS FOR RESPECTIVE AXES 75) Inventors: Ryo Nihei, Akihiro Terada, both of Fujiyoshida; Kyozi
United States Patent (19) Nihei et al. 54) INDUSTRIAL ROBOT PROVIDED WITH MEANS FOR SETTING REFERENCE POSITIONS FOR RESPECTIVE AXES 75) Inventors: Ryo Nihei, Akihiro Terada, both of Fujiyoshida; Kyozi
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,937,567 B2
 US008.937567B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,937,567 B2 Obata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2015 (54) DELTA-SIGMA MODULATOR, INTEGRATOR, USPC... 341/155, 143 AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
US008.937567B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,937,567 B2 Obata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 20, 2015 (54) DELTA-SIGMA MODULATOR, INTEGRATOR, USPC... 341/155, 143 AND WIRELESS COMMUNICATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,705,355 B1
 USOO670.5355B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,705,355 B1 Wiesenfeld (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 16, 2004 (54) WIRE STRAIGHTENING AND CUT-OFF (56) References Cited MACHINE AND PROCESS NEAN
USOO670.5355B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,705,355 B1 Wiesenfeld (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 16, 2004 (54) WIRE STRAIGHTENING AND CUT-OFF (56) References Cited MACHINE AND PROCESS NEAN
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,805,823 B2. Sembritzky et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 2010
 US007805823B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,805,823 B2 Sembritzky et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 2010 (54) AXIAL SWAGE ALIGNMENT TOOL (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: David
US007805823B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,805,823 B2 Sembritzky et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 5, 2010 (54) AXIAL SWAGE ALIGNMENT TOOL (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: David
WA wrippe Z/// (12) United States Patent US 8,091,830 B2. Jan. 10, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Childs
 US008091830B2 (12) United States Patent Childs (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,091,830 B2 Jan. 10, 2012 (54) STRINGER FOR AN AIRCRAFTWING ANDA METHOD OF FORMING THEREOF (75) Inventor: Thomas
US008091830B2 (12) United States Patent Childs (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,091,830 B2 Jan. 10, 2012 (54) STRINGER FOR AN AIRCRAFTWING ANDA METHOD OF FORMING THEREOF (75) Inventor: Thomas
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2
 USOO6663057B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2 Garelick et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADJUSTABLE PEDESTAL FOR BOAT 5,297.849 A * 3/1994 Chancellor... 297/344.
USOO6663057B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2 Garelick et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADJUSTABLE PEDESTAL FOR BOAT 5,297.849 A * 3/1994 Chancellor... 297/344.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Schwab et al. US006335619B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR COMPRISING ARESONANT OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT RESPONDING TO CHANGES IN
(12) United States Patent Schwab et al. US006335619B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR COMPRISING ARESONANT OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT RESPONDING TO CHANGES IN
iii. United States Patent (19) 4,939,441 Dhyanchand Jul. 3, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent:
 United States Patent (19) Dhyanchand 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 1990 54 EXCITATION SYSTEM FOR A BRUSHLESS GENERATOR HAVING SEPARATE AC AND DC EXCTER FELD WINDINGS 75 Inventor: P. John
United States Patent (19) Dhyanchand 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 3, 1990 54 EXCITATION SYSTEM FOR A BRUSHLESS GENERATOR HAVING SEPARATE AC AND DC EXCTER FELD WINDINGS 75 Inventor: P. John
Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner. Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green
 III United States Patent (19) 11) US005230172A Patent Number: 5,230,172 Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 1993 54 PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner o Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green 76)
III United States Patent (19) 11) US005230172A Patent Number: 5,230,172 Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 1993 54 PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner o Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green 76)
(12) United States Patent
 USOO6997228B2 (12) United States Patent Hong (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 14, 2006 (54) LAMINATION APPARATUS FOR AUTOMATED MANUFACTURING SYSTEM OF LITHIUM SECONDARY BATTERY (75) Inventor:
USOO6997228B2 (12) United States Patent Hong (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 14, 2006 (54) LAMINATION APPARATUS FOR AUTOMATED MANUFACTURING SYSTEM OF LITHIUM SECONDARY BATTERY (75) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 US008393237B2 (12) United States Patent Arenz et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 12, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) DRIVING DEVICE FOR A HATCH INA MOTOR VEHICLE
US008393237B2 (12) United States Patent Arenz et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 12, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) (51) (52) (58) DRIVING DEVICE FOR A HATCH INA MOTOR VEHICLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0065580 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD
(19) United States US 2005OO65580A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0065580 A1 Choi (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 24, 2005 (54) BED TYPE HOT COMPRESS AND ACUPRESSURE APPARATUS AND A METHOD
United States Patent (19) Lin
 United States Patent (19) Lin 11) 45) Dec. 22, 1981 54) (76) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) BUILDING BLOCK SET Inventor: Wen-Ping Lin, 30, Chien-Yung St., Taichung, Taiwan Appl. No.: 187,618 Filed: Sep. 15,
United States Patent (19) Lin 11) 45) Dec. 22, 1981 54) (76) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) BUILDING BLOCK SET Inventor: Wen-Ping Lin, 30, Chien-Yung St., Taichung, Taiwan Appl. No.: 187,618 Filed: Sep. 15,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9472442B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.472.442 B2 Priewasser (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 18, 2016 (54) WAFER PROCESSING METHOD H01L 21/304; H01L 23/544; H01L 21/68728; H01L 21/78;
(12) United States Patent USOO9472442B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.472.442 B2 Priewasser (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 18, 2016 (54) WAFER PROCESSING METHOD H01L 21/304; H01L 23/544; H01L 21/68728; H01L 21/78;
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.250,058 B2
 US00925.0058B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.250,058 B2 Backes et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2016 (54) CAPACITIVE ROTARY ENCODER USPC... 324/658, 686, 660, 661, 676, 207.13, 324/207.17,
US00925.0058B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9.250,058 B2 Backes et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 2, 2016 (54) CAPACITIVE ROTARY ENCODER USPC... 324/658, 686, 660, 661, 676, 207.13, 324/207.17,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Kowalewski (54) RADIO FREQUENCY SWITCH EMPLOYING REED SWITCHES AND A QUARTER WAVE LINE 75) inventor: Rolf E. Kowalewski, Palatine, Ill. (73) Assignee: Motorola, Inc., Franklin
United States Patent (19) Kowalewski (54) RADIO FREQUENCY SWITCH EMPLOYING REED SWITCHES AND A QUARTER WAVE LINE 75) inventor: Rolf E. Kowalewski, Palatine, Ill. (73) Assignee: Motorola, Inc., Franklin
IIH. United States Patent (19) Chen. (11) Patent Number: 5,318,090 (45. Date of Patent: Jun. 7, 1994
 United States Patent (19) Chen 54) ROLLER ASSEMBLY FORVENETIAN BLIND 76 Inventor: Cheng-Hsiung Chen, No. 228, Sec. 2, Chung-Te Rd., Taichung City, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 60,278 22 Filed: May 11, 1993 51)
United States Patent (19) Chen 54) ROLLER ASSEMBLY FORVENETIAN BLIND 76 Inventor: Cheng-Hsiung Chen, No. 228, Sec. 2, Chung-Te Rd., Taichung City, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 60,278 22 Filed: May 11, 1993 51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0021611A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021611 A1 Onizuka et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) BUS BAR STRUCTURE Related U.S. Application Data
US 2001 0021611A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021611 A1 Onizuka et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) BUS BAR STRUCTURE Related U.S. Application Data
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030095174A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0095174A1 Terasaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 22, 2003 (54) PRINTER (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 20030095174A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0095174A1 Terasaki et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 22, 2003 (54) PRINTER (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1
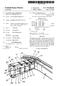
 US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
United States Patent to 11 3,998,002
 United States Patent to 11 Nathanson 45 Dec. 21, 1976 54 PANEL, HOLDER FOR SMALL STRUCTURES AND TOYS 76 Inventor: Albert Nathanson, 249-26 63rd Ave., Little Neck, N.Y. 11329 22 Filed: Jan. 29, 1975 (21
United States Patent to 11 Nathanson 45 Dec. 21, 1976 54 PANEL, HOLDER FOR SMALL STRUCTURES AND TOYS 76 Inventor: Albert Nathanson, 249-26 63rd Ave., Little Neck, N.Y. 11329 22 Filed: Jan. 29, 1975 (21
United States Patent (19) Ohta
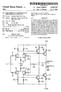 United States Patent (19) Ohta (54) NON-SATURATING COMPLEMENTARY TYPE UNITY GAIN AMPLIFER 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Genichiro Ohta, Ebina, Japan Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan
United States Patent (19) Ohta (54) NON-SATURATING COMPLEMENTARY TYPE UNITY GAIN AMPLIFER 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: Genichiro Ohta, Ebina, Japan Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan
III IIII. United States Patent (19) Hamilton et al. application of welds thereto for attaching the hub member to
 United States Patent (19) Hamilton et al. 54) EARTH SCREW ANCHOR ASSEMBLY HAVING ENHANCED PENETRATING CAPABILITY (75) Inventors: Daniel V. Hamilton; Robert M. Hoyt, both of Centralia; Patricia J. Halferty,
United States Patent (19) Hamilton et al. 54) EARTH SCREW ANCHOR ASSEMBLY HAVING ENHANCED PENETRATING CAPABILITY (75) Inventors: Daniel V. Hamilton; Robert M. Hoyt, both of Centralia; Patricia J. Halferty,
United States Patent (19) Vitale
 United States Patent (19) Vitale 54) ULTRASON CALLY BONDED NON-WOVEN FABRIC 75 (73) Inventor: Assignee: Joseph Vitale, Charlotte, N.C. Perfect Fit Industries, Monroe, N.C. (21) Appl. No.: 756,423 22) Filed:
United States Patent (19) Vitale 54) ULTRASON CALLY BONDED NON-WOVEN FABRIC 75 (73) Inventor: Assignee: Joseph Vitale, Charlotte, N.C. Perfect Fit Industries, Monroe, N.C. (21) Appl. No.: 756,423 22) Filed:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1
 USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,116,081 B2. Wilson (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006
 United States Patent USOO7116081 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Wilson (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006 (54) THERMAL PROTECTION SCHEME FOR 5,497,071 A * 3/1996 Iwatani et al.... 322/28 HIGH OUTPUT VEHICLE ALTERNATOR
United States Patent USOO7116081 B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Wilson (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 3, 2006 (54) THERMAL PROTECTION SCHEME FOR 5,497,071 A * 3/1996 Iwatani et al.... 322/28 HIGH OUTPUT VEHICLE ALTERNATOR
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Mongoven et al. (54) 75 73) 21 22 (51) (52) 58) 56 POWER CRCUT FOR SERIES CONNECTED LOADS Inventors: Michael A. Mongoven, Oak Park; James P. McGee, Chicago, both of 1. Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Mongoven et al. (54) 75 73) 21 22 (51) (52) 58) 56 POWER CRCUT FOR SERIES CONNECTED LOADS Inventors: Michael A. Mongoven, Oak Park; James P. McGee, Chicago, both of 1. Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Minowa
 United States Patent (19) Minowa 54 ANALOG DISPLAY ELECTRONIC STOPWATCH (75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Yoshiki Minowa, Suwa, Japan Kubushiki Kaisha Suwa Seikosha, Tokyo, Japan 21) Appl. No.: 30,963 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Minowa 54 ANALOG DISPLAY ELECTRONIC STOPWATCH (75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Yoshiki Minowa, Suwa, Japan Kubushiki Kaisha Suwa Seikosha, Tokyo, Japan 21) Appl. No.: 30,963 22 Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
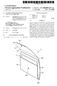 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073337 A1 Liou et al. US 20090073337A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LCD DISPLAY WITH ADJUSTABLE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0073337 A1 Liou et al. US 20090073337A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 19, 2009 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) LCD DISPLAY WITH ADJUSTABLE
Appl. No.: 619,775 Filed: Nov. 29, 1990 Int. Cl... E21B 4/02 U.S. Cl /907. 1; 175/ /95, 97, 282,303,
 United States Patent (19) Justman et al. (54) (75) (73) 21 22 (51) (52) (58) 56) BEARING STRUCTURE FOR DOWNHOLE MOTORS Inventors: Dan B. Justman, Houston; George A. Cross, Kingwood, both of Tex. Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Justman et al. (54) (75) (73) 21 22 (51) (52) (58) 56) BEARING STRUCTURE FOR DOWNHOLE MOTORS Inventors: Dan B. Justman, Houston; George A. Cross, Kingwood, both of Tex. Assignee:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
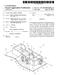 (19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
(19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
United States Patent (19) Putman
 United States Patent (19) Putman 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Sep. 4, 1990 54. RHEOMETER DIE ASSEMBLY 76 Inventor: John B. Putman, 4.638 Commodore Dr., Stow, Ohio 44224 21 Appl. No.: 416,025 22
United States Patent (19) Putman 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Sep. 4, 1990 54. RHEOMETER DIE ASSEMBLY 76 Inventor: John B. Putman, 4.638 Commodore Dr., Stow, Ohio 44224 21 Appl. No.: 416,025 22
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.00200O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0020002 A1 FENG (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) CABLE HAVING ASIMPLIFIED CONFIGURATION TO REALIZE SHIELDING
(19) United States US 2016.00200O2A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0020002 A1 FENG (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 21, 2016 (54) CABLE HAVING ASIMPLIFIED CONFIGURATION TO REALIZE SHIELDING
United States Patent (19) Mori
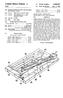 United States Patent (19) Mori 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1991 54 PAPER-CUTTING MACHINE AND METHOD OF CUTTNG PAPER 75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Chuzo Mori, Katsushika, Japan Carl Manufacturing
United States Patent (19) Mori 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 3, 1991 54 PAPER-CUTTING MACHINE AND METHOD OF CUTTNG PAPER 75) Inventor: 73 Assignee: Chuzo Mori, Katsushika, Japan Carl Manufacturing
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Mack USOO686.0488B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2005 (54) DRILL CHUCK WITH FRONT-END SHIELD (75) Inventor: Hans-Dieter Mack, Sontheim (DE) (73) Assignee: Rohm
(12) United States Patent Mack USOO686.0488B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2005 (54) DRILL CHUCK WITH FRONT-END SHIELD (75) Inventor: Hans-Dieter Mack, Sontheim (DE) (73) Assignee: Rohm
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
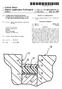 US 2001 0004 175A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0004175 A1 Kelleher (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 21, 2001 (54) GENERATOR STATOR SLOT WEDGE Related U.S. Application
US 2001 0004 175A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0004175 A1 Kelleher (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 21, 2001 (54) GENERATOR STATOR SLOT WEDGE Related U.S. Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 US 20120312936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0312936A1 HUANG (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2012 (54) HOLDING DEVICE OF TABLET ELECTRONIC DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl....
US 20120312936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0312936A1 HUANG (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2012 (54) HOLDING DEVICE OF TABLET ELECTRONIC DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,765,631 B2. Ishikawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2004
 USOO6765631 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,765,631 B2 Ishikawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2004 (54) VEHICLE WINDSHIELD RAIN SENSOR (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Junichi
USOO6765631 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,765,631 B2 Ishikawa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 20, 2004 (54) VEHICLE WINDSHIELD RAIN SENSOR (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Junichi
YARIABLE YEASEf 55. United States Patent (19) 4,743, INPUT OUTPUT, 54 al. Shilling et al. May 10, 1988
 United States Patent (19) Shilling et al. 11 Patent Number: (45. Date of Patent: 4,743,777 May 10, 1988 54 STARTER GENERATOR SYSTEM WITH TWO STATOR EXCITER WINDINGS (75 Inventors: William J. Shilling,
United States Patent (19) Shilling et al. 11 Patent Number: (45. Date of Patent: 4,743,777 May 10, 1988 54 STARTER GENERATOR SYSTEM WITH TWO STATOR EXCITER WINDINGS (75 Inventors: William J. Shilling,
July 28, 1959 S. E. LOVER 2,896,49 1
 July 28, 1959 S. E. LOVER 2,896,49 1 MAGNETIC PICKUP FOR STRINGED MUSICAL INSTRUMENT Filed June 22, 1955 2 Sheets-Sheet 1 July 28, 1959 S. E. LOVER 2,896,49 1 MAGNETIC PICKUP FOi! STRING93 MUSICAL INSTRUMENT
July 28, 1959 S. E. LOVER 2,896,49 1 MAGNETIC PICKUP FOR STRINGED MUSICAL INSTRUMENT Filed June 22, 1955 2 Sheets-Sheet 1 July 28, 1959 S. E. LOVER 2,896,49 1 MAGNETIC PICKUP FOi! STRING93 MUSICAL INSTRUMENT
202 19' 19 19' (12) United States Patent 202' US 7,050,043 B2. Huang et al. May 23, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.
 US00705.0043B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,050,043 B2 May 23, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 2,
US00705.0043B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,050,043 B2 May 23, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 2,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,700 B1. Schmidt et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002
 USOO64627OOB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,700 B1 Schmidt et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) ASYMMETRICAL MULTI-BEAM RADAR 6,028,560 A * 2/2000 Pfizenmaier et al... 343/753
USOO64627OOB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,700 B1 Schmidt et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) ASYMMETRICAL MULTI-BEAM RADAR 6,028,560 A * 2/2000 Pfizenmaier et al... 343/753
(51) Int. Cl... HoH 316 trolling a state of conduction of AC current between the
 USOO58599A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,8,599 ROSenbaum () Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54 GROUND FAULT CIRCUIT INTERRUPTER 57 ABSTRACT SYSTEM WITH UNCOMMITTED CONTACTS A ground fault
USOO58599A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,8,599 ROSenbaum () Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54 GROUND FAULT CIRCUIT INTERRUPTER 57 ABSTRACT SYSTEM WITH UNCOMMITTED CONTACTS A ground fault
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO867761 OB2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,677,610 B2 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2014 (54) CRIMPING TOOL (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Jen Kai Liu, New Taipei (TW) U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO867761 OB2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,677,610 B2 Liu (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2014 (54) CRIMPING TOOL (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Jen Kai Liu, New Taipei (TW) U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090090231A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0090231 A1 Kondo (43) Pub. Date: ADr. 9, 9 2009 (54) BAND SAW MACHINE Publication Classification O O (51)
(19) United States US 20090090231A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0090231 A1 Kondo (43) Pub. Date: ADr. 9, 9 2009 (54) BAND SAW MACHINE Publication Classification O O (51)
Jan. 20, 1970 J. CHASS 3,491,321
 ROTARY WARIABLE DIFFERENTIAL TRANSFORMER USED Filed Nov. 26, 1968 3. Sheets-Sheet apy SaMa 32. 4762 a 76. 5
ROTARY WARIABLE DIFFERENTIAL TRANSFORMER USED Filed Nov. 26, 1968 3. Sheets-Sheet apy SaMa 32. 4762 a 76. 5
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,715,221 B1. Sasaki (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2004
 USOO671.51B1 (1) United States Patent (10) Patent No. US 6,715,1 B1 Sasaki (45) Date of Patent Apr. 6, 004 (54) FOOT STIMULATING SHOE INSOLE 5,860,9 A * 1/1999 Morgenstern... 36/141 (75) Inventor Manhachi
USOO671.51B1 (1) United States Patent (10) Patent No. US 6,715,1 B1 Sasaki (45) Date of Patent Apr. 6, 004 (54) FOOT STIMULATING SHOE INSOLE 5,860,9 A * 1/1999 Morgenstern... 36/141 (75) Inventor Manhachi
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0379053 A1 B00 et al. US 20140379053A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (86) (30) MEDICAL MASK DEVICE
United States Patent (19) Rannou et al.
 United States Patent (19) Rannou et al. (54) (75) 73 22) (21) 30) 52 (51) (58) (56) WIDE-BAND OMNIDIRECTIONAL ANTENNA Inventors: Jean Rannou; William Luther, both of Paris, France Assignee: Thomson-CSF,
United States Patent (19) Rannou et al. (54) (75) 73 22) (21) 30) 52 (51) (58) (56) WIDE-BAND OMNIDIRECTIONAL ANTENNA Inventors: Jean Rannou; William Luther, both of Paris, France Assignee: Thomson-CSF,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0185581 A1 Xing et al. US 2011 0185581A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) COMPACT CIRCULAR SAW (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0185581 A1 Xing et al. US 2011 0185581A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 4, 2011 (54) COMPACT CIRCULAR SAW (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) Inventors:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Yoshida et al. 54 SHAFT WITH GROOVES FOR DYNAMIC PRESSURE GENERATION AND MOTOR EMPLOYNG THE SAME 75 Inventors: Fumio Yoshida, Toride; Mikio Nakasugi, Chofu, both of Japan 73)
United States Patent (19) Yoshida et al. 54 SHAFT WITH GROOVES FOR DYNAMIC PRESSURE GENERATION AND MOTOR EMPLOYNG THE SAME 75 Inventors: Fumio Yoshida, Toride; Mikio Nakasugi, Chofu, both of Japan 73)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,708,159 B2. Darr et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2010
 USOO7708159B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Darr et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2010 (54) PLASTIC CONTAINER 4,830,251 A 5/1989 Conrad 6,085,924 A 7/2000 Henderson (75) Inventors: Richard
USOO7708159B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Darr et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2010 (54) PLASTIC CONTAINER 4,830,251 A 5/1989 Conrad 6,085,924 A 7/2000 Henderson (75) Inventors: Richard
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 201502272O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0227202 A1 BACKMAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 201502272O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0227202 A1 BACKMAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9434098B2 (12) United States Patent Choi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.434,098 B2 Sep. 6, 2016 (54) SLOT DIE FOR FILM MANUFACTURING (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS CO., LTD.,
USOO9434098B2 (12) United States Patent Choi et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.434,098 B2 Sep. 6, 2016 (54) SLOT DIE FOR FILM MANUFACTURING (71) Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRONICS CO., LTD.,
58) Field of Seash, which is located on the first core leg. The fifth winding,
 US006043569A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Ferguson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 2000 54) ZERO PHASE SEQUENCE CURRENT Primary Examiner Richard T. Elms FILTER APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Attorney,
US006043569A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Ferguson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 2000 54) ZERO PHASE SEQUENCE CURRENT Primary Examiner Richard T. Elms FILTER APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Attorney,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007025 1096A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0251096 A1 Smith (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 1, 2007 (54) EGG BREAKING DEVICE INCORPORATING A DURABLE AND RUBBERIZED
(19) United States US 2007025 1096A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0251096 A1 Smith (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 1, 2007 (54) EGG BREAKING DEVICE INCORPORATING A DURABLE AND RUBBERIZED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0081252 A1 Markgraf et al. US 2013 0081252A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) ARRANGEMENT FOR FIXINGA COMPONENT INSIDE OF
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0081252 A1 Markgraf et al. US 2013 0081252A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 4, 2013 (54) ARRANGEMENT FOR FIXINGA COMPONENT INSIDE OF
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090249965A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0249965 A1 Hauser (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIT REMOVER (75) Inventor: Lawrence M. Hauser, Auburn, WA (US) Correspondence
(19) United States US 20090249965A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0249965 A1 Hauser (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIT REMOVER (75) Inventor: Lawrence M. Hauser, Auburn, WA (US) Correspondence
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 LLP 57)
 III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
(12) United States Patent
 US0092.59087B1 (12) United States Patent Hsiao (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.259,087 B1 Feb. 16, 2016 (54) FRONT CONNECTING DEVICE OF CONCEALED SLIDE (71) Applicant: Sun Chain Trading Co.,
US0092.59087B1 (12) United States Patent Hsiao (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.259,087 B1 Feb. 16, 2016 (54) FRONT CONNECTING DEVICE OF CONCEALED SLIDE (71) Applicant: Sun Chain Trading Co.,
United States Patent (19) Lacombe
 United States Patent (19) Lacombe (54) SPACER FOR GLASS SEALED UNT AND INTERLOCK MEMBER THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Gaetan Y. Lacombe, Duvernay, Canada 73 Assignee: D. C. Glass Limited, Anjou, Canada 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Lacombe (54) SPACER FOR GLASS SEALED UNT AND INTERLOCK MEMBER THEREFOR (75) Inventor: Gaetan Y. Lacombe, Duvernay, Canada 73 Assignee: D. C. Glass Limited, Anjou, Canada 21 Appl.
(12) United States Patent
 US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
US009 159725B2 (12) United States Patent Forghani-Zadeh et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) CONTROLLED ON AND OFF TIME SCHEME FORMONOLTHC
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Roy et al. USOO6216409 B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,216,409 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2001 (54) CLADDING PANEL FOR FLOORS, WALLS OR THE LIKE (76) Inventors: Valerie Roy, 13,
(12) United States Patent Roy et al. USOO6216409 B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,216,409 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2001 (54) CLADDING PANEL FOR FLOORS, WALLS OR THE LIKE (76) Inventors: Valerie Roy, 13,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,650,825 B1
 USOO7650825B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 26, 2010 (54) CASE TRIMMER AND CHAMFER TOOL 4.325,282 A 4, 1982 Schaenzer... 86,24 4.385,546 A 5/1983 Lee...
USOO7650825B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 26, 2010 (54) CASE TRIMMER AND CHAMFER TOOL 4.325,282 A 4, 1982 Schaenzer... 86,24 4.385,546 A 5/1983 Lee...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1. T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012
 US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
US 20120326936A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0326936A1 T (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2012 (54) MONOPOLE SLOT ANTENNASTRUCTURE Publication Classification (75)
EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (43) Date of publication: Bulletin 2011/40
 (19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 372 845 A1 (43) Date of publication: 05.10.2011 Bulletin 2011/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 11/28 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10425105.3 (22) Date of filing:
(19) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 2 372 845 A1 (43) Date of publication: 05.10.2011 Bulletin 2011/40 (51) Int Cl.: H01R 11/28 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 10425105.3 (22) Date of filing:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
US 20060239744A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0239744 A1 Hideaki (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 26, 2006 (54) THERMAL TRANSFERTYPE IMAGE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050O28668A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0028668A1 Teel (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 10, 2005 (54) WRIST POSITION TRAINING ASSEMBLY (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(19) United States US 20050O28668A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0028668A1 Teel (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 10, 2005 (54) WRIST POSITION TRAINING ASSEMBLY (76) Inventor: Kenneth
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 (19) United States US 2003OO3OO63A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0030063 A1 Sosniak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2003 (54) MIXED COLOR LEDS FOR AUTO VANITY MIRRORS AND
(19) United States US 2003OO3OO63A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0030063 A1 Sosniak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 13, 2003 (54) MIXED COLOR LEDS FOR AUTO VANITY MIRRORS AND
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US00735.5805B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,355,805 B2 Naka0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2008 (54) MAGNETIC TAPE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING MAGNETIC TAPE, 5,689,384 A * 11/1997
(12) United States Patent US00735.5805B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,355,805 B2 Naka0 et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2008 (54) MAGNETIC TAPE AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING MAGNETIC TAPE, 5,689,384 A * 11/1997
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 (19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
(19) United States US 2001.0020719A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0020719 A1 KM (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) INSULATED GATE BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR (76) Inventor: TAE-HOON
issi Field of search. 348/36, , 33) of the turret punch press machine; an image of the
 US005721587A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,721,587 Hirose 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Primary Examiner Bryan S. Tung NSPECTNG PRODUCT PROCESSED BY Attorney,
US005721587A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,721,587 Hirose 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Primary Examiner Bryan S. Tung NSPECTNG PRODUCT PROCESSED BY Attorney,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160090275A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0090275 A1 Piech et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2016 (54) WIRELESS POWER SUPPLY FOR SELF-PROPELLED ELEVATOR
(19) United States US 20160090275A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0090275 A1 Piech et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2016 (54) WIRELESS POWER SUPPLY FOR SELF-PROPELLED ELEVATOR
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9463468B2 () Patent No.: Hiley (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2016 (54) COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE RF BO3B 5/08 (2006.01) GENERATOR USING A SELF-RESONANT GOIN 27/62 (2006.01) INDUCTOR
(12) United States Patent USOO9463468B2 () Patent No.: Hiley (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2016 (54) COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE RF BO3B 5/08 (2006.01) GENERATOR USING A SELF-RESONANT GOIN 27/62 (2006.01) INDUCTOR
Oct. 25, ,280,665. Filed April 8, ATToRNEYs H. BLOCK. 2 Sheets-Sheet NVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK TWEEZERS
 Oct. 25, 1966 Filed April 8, 1966 H. BLOCK 2 Sheets-Sheet NVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK ATToRNEYs Oct. 25, 1966 Filed April 8, 1966 H, BLOCK 2. Sheets-Sheet 2 ZZZZZZ Taseo (7 INVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK ATTORNEYS United
Oct. 25, 1966 Filed April 8, 1966 H. BLOCK 2 Sheets-Sheet NVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK ATToRNEYs Oct. 25, 1966 Filed April 8, 1966 H, BLOCK 2. Sheets-Sheet 2 ZZZZZZ Taseo (7 INVENTOR HAROLD BLOCK ATTORNEYS United
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 O254338A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0254338 A1 FISHER, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 20, 2011 (54) MULTI-PAWL ROUND-RECLINER MECHANISM (76)
(19) United States US 2011 O254338A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0254338 A1 FISHER, III et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 20, 2011 (54) MULTI-PAWL ROUND-RECLINER MECHANISM (76)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194392 A1 NOUE et al. US 20120194392A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) ANTENNA AND INFORMATION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0194392 A1 NOUE et al. US 20120194392A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 2, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) ANTENNA AND INFORMATION
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,769,908 B1
 US008769908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,769,908 B1 Santini (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2014 (54) MODULAR BUILDING PANEL 4,813,193 A 3, 1989 Altizer.............. (76) Inventor: Patrick
US008769908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,769,908 B1 Santini (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 8, 2014 (54) MODULAR BUILDING PANEL 4,813,193 A 3, 1989 Altizer.............. (76) Inventor: Patrick
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US009682771B2 () Patent No.: Knag et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 20, 2017 (54) CONTROLLING ROTOR BLADES OF A 5,676,334 A * /1997 Cotton... B64C 27.54 SWASHPLATELESS ROTOR 244.12.2
(12) United States Patent US009682771B2 () Patent No.: Knag et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 20, 2017 (54) CONTROLLING ROTOR BLADES OF A 5,676,334 A * /1997 Cotton... B64C 27.54 SWASHPLATELESS ROTOR 244.12.2
United States Patent (19) Lee
 United States Patent (19) Lee (54) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT FOR DRIVING MAGNETRON 75 Inventor: Kyong-Keun Lee, Suwon, Rep. of Korea 73) Assignee: Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Suweon City, Rep. of Korea (21)
United States Patent (19) Lee (54) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT FOR DRIVING MAGNETRON 75 Inventor: Kyong-Keun Lee, Suwon, Rep. of Korea 73) Assignee: Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Suweon City, Rep. of Korea (21)
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109. Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, a. Assistant Examiner-Alan B.
 H HHHHHHH US005299.109A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109 Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 1994 (54) LED EXIT LIGHT FIXTURE 5,138,782 8/1992 Mizobe... 40/219 75) Inventor: Daniel
H HHHHHHH US005299.109A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109 Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 1994 (54) LED EXIT LIGHT FIXTURE 5,138,782 8/1992 Mizobe... 40/219 75) Inventor: Daniel
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
US 2013 0334265A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0334265 A1 AVis0n et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 19, 2013 (54) BRASTORAGE DEVICE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,880,737 B2
 USOO6880737B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bauer (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) CELL PHONE HOLSTER SUBSIDIARY 5,217,294 A 6/1993 Liston STRAP AND HOLDER 5,503,316 A 4/1996 Stewart
USOO6880737B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Bauer (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) CELL PHONE HOLSTER SUBSIDIARY 5,217,294 A 6/1993 Liston STRAP AND HOLDER 5,503,316 A 4/1996 Stewart
