don, G.B. U.S. P. DOCUMENTS spaced by an air gap from the collecting lens. The widths of
|
|
|
- Lionel Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
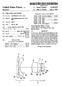
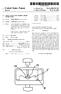
1 United States Patent (19) Wartmann III US A 11 Patent Number: 5,708, Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 1998 (54) DOUBLE-SIDED TELECENTRC /1977 U.S.S.R /663 MEASUREMENT OBJECTIVE /1971 United Kingdom /1972 United Kingdom /663 (75) Inventor: Rolf Wartmann, Hallgarten, Germany /1976 United Kingdom. OTHER PUBLICATIONS 73 Assignee: Jos. Schneider Optische Werke Kreuznach GmbH & Co. KG. Abstract of SU 909,652; Soviet Inventions Illustrated, Week Kreuznach, Germany K01, issued 16 Feb Derwent Publications Ltd, Lon don, G.B. 21 Appl. No.: 659,044 Patent Abstracts of Japan, No , vol. 16, No. 218 (P-1357) Dainippon Screen Mfg Co Ltd, Inventor: Hayashi 22) Filed: Jun. 3, 1996 Naohisa. (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Primary Examiner Thong Nguyen Jun. 3, 1995 EP European Pat. Off Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Herbert Dubno 57 ABSTRACT (51) Int. Cl.... G02B 13/22; G02B 21/02 52 U.S. Cl /663; 359/362; 359/658; A double sided telecentic measurement objective for con 359/756 tactless length measurement in two-dimensional and three 58) Field of Search /362,363, dimensional space. The objective has an image-side optical 359/642, 649, 663, 793, , 733, system consisting of three elements equivalent to those of an 754, 755, 756, object-side optical system but in the reverse order, including a cemented positively refracting lens element turned toward 56 References Cited the object of image respectively, a collecting lens spaced by ATENT an air gap from the cemented lens, and a dispersive meniscus U.S. P. DOCUMENTS spaced by an air gap from the collecting lens. The widths of 4,189,211 2/1980 Taylor /663 the air gaps between the collecting lenses and the meniscus are substantially greater than the widths of air gaps between FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS the cemented lens elements and the collecting lenses /1989 European Pat. Off l/1971 Japan /663 4 Claims, 3 Drawing Sheets 1O OBJECT - K23%-2 4 S&1 r 2 C l3 az22 4 2
2 U.S. Patent Jan. 13, 1998 Sheet 1 of 3 5,708,532
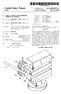
3 U.S. Patent Jan. 13, 1998 Sheet 2 of 3 5,708,532 FIG.2
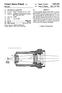
4 U.S. Patent Jan. 13, 1998 Sheet 3 of 3 5,708, FG3
5 1. DOUBLE-SIDED TELECENTRC MEASUREMENT OBJECTIVE FIELD OF THE INVENTION My present invention relates to a double-sided telecentric measuring objective for contactless length measurements in two-dimensional and three-dimensional space. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION For the contactless measurement of objectives in auto matic product lines, video cameras are increasingly of interest as pick-ups for measurement systems. A measuring camera, for example, is described in U.S. Pat. No , 785. The measurement principle utilizes the central projection of object points in an image plane. The image is then digitalized and the digitized image is interpreted in an image-processing computer and stretches between contour features of the object in the image are measured. A precon dition for this type of measurement approach, of course, is a sufficiently precisely defined set of chamber constants and position of the main points photogram-metric. These param eters define the so-called internal orientation of the mea surement camera (see the aforementioned patent). The measurement precision in video measurement tech niques is directly dependent upon the precision and stability of the parameters of the internal orientation. These param eters give the correlation between the measured image size and the geometry of the object. They may be determined by a camera calibration procedure. When a measuring systemisintended not only for a single kind of measurement and the position of the article to be measured cannot be maintained with a high level of precision, camera calibration must be frequent and is expen sive and time-consuming since it must be carried out with each change in the article to be measured or each change in the position of the article. It is known to avoid such camera calibration or at last to reduce the frequency of such calibration by providing tele centric objectives. The use of a telecentric objective makes the image size independent from the object distance and does not require as meticulous adjustment of the measuring unit. By providing telecentric objectives in automatic pro duction lines, the effective quality control can be substan tially simplified. Nevertheless, even with such optical systems, the measurement system must be calibrated and in particular, the dependency of the reduction scale or ratio of the image to the object size must be determined for the selected image plane position. It has already been proposed to completely eliminate the need for camera calibration by providing double-sided tele centric optical systems. Such objectives are comprised of two distinct optical systems or partial systems aligned along a common optical axis which have the same general con structions and between which an iris diaphragm is disposed. The lens elements of the second optical system are disposed in an opposite or reverse order from the sequence of the lens elements of the first optical system. Such telecentric mea suring objectives are afocal and have a fixed image ratio or reduction which is independent not only of the object position but also of the image position. One such afocal and telecentric objective is described in SU Patent Because of the construction of this objective, pupil aberration exists, i.e. in spite of the afocal construction, not all of the major rays are telecentric. The 5, pupil aberration results in a change of distortion upon shifting of the object plane or image plane. This objective is, therefore, unsuitable for measurement purposes. In GB Patent 1423,597, afocal systems for transcription of mark 5 ings is described. This system does not permit correction of pupil aberration and of coma. It is also unsuitable as a measurement objective. EP A2 describes a system which, as a conse quence of its construction, allows only small variation of the 10 object plane or image plane. The optical system of this patent also is not highly suitable for measurement purposes since control of the sharpness is not possible and a scale of reproduction which deviates significantly from -1 cannot be achieved with high image quality. This objective is also 15 costly to produce and with significant variations of the object plane positions, cause a considerable loss of imaging quality. OBJECTS OF THE INVENTION It is, therefore, the principal object of the present inven tion to provide a double-sided measurement objective for contactless measurement systems which makes superfluous internal calibration of the camera, is of simple construction and can ensure high image quality even for a substantial 25 range in variation of the object plane position. Another object of this invention is to provide a telecentric objective for the purposes described whereby drawbacks of the earlier systems described can be avoided. Still another object of the invention is to provide a 30 telecentric objective for a measurement camera which is of simple and economical construction. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION These objects and others which will become apparent 35 hereinafter in a telecentric lens system of the double-sided type having the object-side optical part system and the image-side optical systems as described, each with three lens elements of which a cemented lens element is turned toward the object side or the image side of the respective system, a collecting lens is spaced by an air gap from the cemented lens element and a dispersive meniscus lens is spaced by an air gap from the collecting lens, the image-side optical system thus having lenses equivalent to those of the object-side system but in the reverse order. 45 According to the invention, the cemented positively refracting lens element has a dispersive cemented surface and is made up of a convergent lens and a divergent lens cemented thereto. 50 According to the invention, moreover, the two optical systems are so arranged that the back focal point of the first optical system coincides with the front focal point of the second optical system along the optical axis. The image scale (or magnification or reduction ratio) of the total system 55 is equal to the ratio of the focal lengths of the optical part-systems. It has been found to be important to the invention that the third element of each optical system is a dispersive meniscus whose convex side is turned toward the object. With a construction of this type, a wide range of variation is possible in the selection of the location of the object and image planes. Even in the event that the object or image plane positions are not selected to be optimum, the image can remain free 65 from coma so that a high measurement precision is assured within the total band width of the possible object/image relationship.
6 3 An optical system according to the invention has, if applied to scaled down imaging, and allows an image size aperture of at least It is corrected for an image circle diameter of 0.2f2 where f2 is the focal length of the image-side optical system. A variation of the object plane position in the range of mm (4-) is possible without loss of image quality. In this relationship f1 is the focal length of the object-side optical system. By appropriate selection of the optical systems which are applicable, objectives with various focal lengths for the image-side or the object-side optical systems can be pro vided and the measurement objective can be of the double sided telecentric type for different magnification ratios. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWING The above and other objects, features, and advantages will become more readily apparent from the following description, reference being made to the accompanying drawing in which: FIG. 1 is a diagram of a measurement objective for a magnification or reproduction ratio of -1 according to the invention; FIG. 2 is a diagram of a measurement objective for a magnification or reproduction ratio of -0.5 according to the invention; and FIG. 3 is a diagram of a measurement objective for a magnification or reproduction ratio of according to the invention. SPECIFC DESCRIPTION FIG. 1 shows a double-sided telecentric objective for use in a measurement camera, e.g. of the type described in U.S. Pat No , which comprises an image-side optical system 1 and an object-side optical system 2 for the mea surement of an object 10 and reproduction thereof in an image plane 11. The two optical systems are arrayed along a common optical axis 12 and, in the embodiment of FIG. 1 which is entirely symmetrical, midway between the optical systems, an iris diaphragm 3 is provided. The objective of FIG. 1 has a magnification ratio of -1 and an image size aperture of Each optical system 1, 2 is comprised of a cemented element 4 turned toward the object to be measured and the image plane, respectively, with a positive refractivity and a dispersive cemented surface (the surfaces with radii r and r", respectively. The intermediate lens element of both the object-side and the image-side systems 2, 1, are collecting lenses 5 of a highly respective crown glass. Lying directly opposite the Iris diaphragm 3 are respective dispersive meniscuses 6 whose convex side is turned toward the object and the image respectively. For a two sided telecentic measurement objective with a magnification ratio -1 with a symmetrical configuration of the lenses, the object-image distance may be 284 and a range of object positions between 71 and 77 from the objective can be sustained without a detrimental effect upon the image quality when the image side optical system has for its four lenses L' to L', the radii r' to r, and thicknesses of the lenses and air gaps d' to d, refractive indices and Abbé numbers as given in the follow ing table: 5,708, Lens Radius Thickness le le r' = 130,882 L' d'= r = L' d = r = d = 3.10 r = L' d = r = d = r = I' d = r = focal length: 57 distance to back focal point: all thicknesses, radii, distances and lengths being in the same distance units. In the symmetrical lens system of FIG. 1, the lenses L. through L for radii r to r, and thicknesses d to d6, refraction indices and Abbé numbers correspond to the numerical valves of the foregoing table as well. Throughout this application, r refers to the radius of curvature of the respective lens surfaces, n to the refractive index and V to the Abbé number for the wavelength e=546 nm of the glass from which the lenses are constituted and d represents distances between the respective lens surfaces as measured along the optical axis. In FIG.2, there is shown an embodiment of a double sided telecentric measuring objective with a magnification ratio of -0.5 and an image-side aperture of The position of the object plane can vary within a distance range of 185 to 209 without detriment to the image quality. The object/image distance can then vary between 467 and 485 all thicknesses, radii, distances and lengths being in the same distance units. In this case, for the same construction of the image-side optical system as in FIG. 1, the numerical data of the object-side optical system can correspond to the following table: Lens Radius Thickness le D r = 163,039 L d = r = L2 d = O r = d = r = I d = rs = d = rs = L4 d = r = focal length: 114 distance to back focal point: all thicknesses, radii, distances and lengths being in the same distance units. In the third embodiment illustrated in FIG. 3, for a measuring objective with a magnification ratio of and an image-side aperture of 0.14, the position of the object plane can vary at a distance of 246 through 342 from the objective without detriment to imaging quality. The object/ image distance then varies between 505 and 595. While the image side optical system 1 corresponds to that given in connection with FIG. 1, the object side optical system 8 corresponds to the following numerical data:
7 5 Lens Radius Thickness le l r = 243,547 L1 d = r = L2 d = r = -342,441 d = r = L3 d = r = d = rs = L4 d = r = focal length: 228 distance to back focal point: 4.75 all thicknesses, radii, distances and lengths being in the same distance units. I claim: 1. A double-sided telecentric measurement objective for contactless length measurement in two-dimensional and three-dimensional space, said objective comprising: two optical systems, each comprising three lenses aligned along an optical axis and constituted of an object-side optical system and an image-side optical system, said object-side optical system having in succession from side turned toward an object: a cemented positively refracting lens element and a dispersive cemented surface formed by a convergent lens L with radii of curvature r and r2 and a thickness d and a divergent lens L with radii of curvature r and r and a thickness d, a collecting lens L spaced by an air gap of a thickness d from said cemented lens element and having radii of curvaturer and r and a thickness d of a highly refractive crown glass, and a dispersive meniscus lens L spaced by an air gap of thickness ds from said collecting lens and having radii of curvature of r and r, and a thickness d, and an image-side optical system having in succession from a side turned away from said object: a cemented positively refracting lens element and a dispersive cemented surface formed by a convergent lens L' with radii of curvature r" and r" and a thickness d' and a divergent lens L with radii of curvaturer' and r" and a thickness d". a collecting lens L' spaced by an air gap of a thickness d' from said cemented lens element and having radii of curvaturer and r" and a thickness d'of a highly refractive crown glass, and a dispersive meniscus lens L' spaced by an air gap of thickness d' from said collecting lens and having radii of curvature of r" and r, and a thickness d' with a convex side turned away from said object; widths of air gaps between the respective collecting lenses and the respective meniscuses being substantially greater than widths of air gaps between the cemented lens elements and the respective collecting lenses; a back focal point of said object-side optical system coinciding with a front focal point of said image-side optical system so that a reproduction scale of the objective is equal to a ratio of front and back focal lengths of said optical systems, said image-side optical system having substantially the following numerical parameters wherein n and v are respectively the 5,708, refractive indices and Abbé numbers of the respective lenses: Lens Radius Thickness le r = L' d = ,2 r = L-2' d = r = d = 3.10 r = L' d = r = d = r = L' d = r = focal length: 57 distance to back focal point: 23.20, 2. The objective defined in claim 1 wherein the lenses L. through L have radii of curvaturer through r, and thick nesses d' through do refractive indices and Abbé numbers corresponding to those of the lenses L' to L' for the radii r' through r" and thicknesses d' through d', and the respective refractive indices and Abbé numbers. 3. The objective defined in claim 1 wherein the object side optical system has the following numerical parameter: Lens Radius Thickness r = 163,039 L d = r = L2 d = O r = d = r = La d = rs = d = rs = L4 d = r = focal length: 114 distance to back focal point: The objective defined in claim 1 wherein said object side optical system has the following numerical parameter: Lens Radius Thickness l r = 243,547 L-1 d = r = L2 d = O r = d = r = La d = rs = d = r = 47,746 L4 d = r = 29,641 focal length: 228 distance to back focal point: ck k k is ak
United States Patent (19) Roulot
 United States Patent (19) Roulot 54 LGHT SOURCE WITH ACOUSTO-OPTC OEFLECTOR AND AFOCAL LENS SYSTEM 76 Inventor: Maurice Roulot, 144 Boulevard de la Terrasse, 91400 Orsay, France (21) Appl. No.: 385,196
United States Patent (19) Roulot 54 LGHT SOURCE WITH ACOUSTO-OPTC OEFLECTOR AND AFOCAL LENS SYSTEM 76 Inventor: Maurice Roulot, 144 Boulevard de la Terrasse, 91400 Orsay, France (21) Appl. No.: 385,196
United States Statutory Invention Registration (19) Feb. 28, 1996 JP Japan (51) Int. Cl... GO2B 21/ U.S. Cl...
 USOO4(OO1763B2 United States Statutory Invention Registration (19) Mizusawa 54) MICROSCOPE OBJECTIVE LENS 75 Inventor: Masayuki Mizusawa, Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan 21
USOO4(OO1763B2 United States Statutory Invention Registration (19) Mizusawa 54) MICROSCOPE OBJECTIVE LENS 75 Inventor: Masayuki Mizusawa, Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan 21
24. United States Patent (19) Noé et al. 21 Appl. No. 261,066. least one correcting roller which has an adjustable depth of
 United States Patent (19) Noé et al. 11) 45) US005535610A Patent Number: 5,535,610 Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 1996 54 METHD AND APPARATUS FR ELMINATING CRSSBW IN METAL STRIP 75 Inventors: Rolf Noé; Andreas
United States Patent (19) Noé et al. 11) 45) US005535610A Patent Number: 5,535,610 Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 1996 54 METHD AND APPARATUS FR ELMINATING CRSSBW IN METAL STRIP 75 Inventors: Rolf Noé; Andreas
Oct RETROFOCUS-TYPE WIDE-ANGLE CAMERA LENS Original Filed Dec. 24, 1969
 3 on 460 - SR OR RE Oct. 30 773 RETROFOCUS-TYPE WIDE-ANGLE CAMERA LENS Original Filed Dec. 24, 1969 Re. Li L2 L3 F.G. n STOP -4. L6 \ ) - d d2 d6 d7 dio d5 da del d1 na 7 R rt a?g 10 r -7 L8 L9 \ 2, 5
3 on 460 - SR OR RE Oct. 30 773 RETROFOCUS-TYPE WIDE-ANGLE CAMERA LENS Original Filed Dec. 24, 1969 Re. Li L2 L3 F.G. n STOP -4. L6 \ ) - d d2 d6 d7 dio d5 da del d1 na 7 R rt a?g 10 r -7 L8 L9 \ 2, 5
United States Patent 19
 United States Patent 19 Kohayakawa 54) OCULAR LENS MEASURINGAPPARATUS (75) Inventor: Yoshimi Kohayakawa, Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl. No.: 544,486 (22 Filed:
United States Patent 19 Kohayakawa 54) OCULAR LENS MEASURINGAPPARATUS (75) Inventor: Yoshimi Kohayakawa, Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl. No.: 544,486 (22 Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0132875 A1 Lee et al. US 20070132875A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 14, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE
4,162,827. United Stat to XR 49162,827. U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 1,293,086 2/1919 Graf /234. Jul. 31, Assignee:
 3S() a 483 SR XR 49162,827 United Stat to 11 de- Jul. 31, 1979 54 WIDE ANGLE OBJECTIVE FOR OPHTHALMOSCOPIC INSTRUMENT Yuji Ito, Chigasaki, Japan Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo, Japan Appl. No.: 802,877
3S() a 483 SR XR 49162,827 United Stat to 11 de- Jul. 31, 1979 54 WIDE ANGLE OBJECTIVE FOR OPHTHALMOSCOPIC INSTRUMENT Yuji Ito, Chigasaki, Japan Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo, Japan Appl. No.: 802,877
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Roy et al. USOO6216409 B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,216,409 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2001 (54) CLADDING PANEL FOR FLOORS, WALLS OR THE LIKE (76) Inventors: Valerie Roy, 13,
(12) United States Patent Roy et al. USOO6216409 B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,216,409 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 17, 2001 (54) CLADDING PANEL FOR FLOORS, WALLS OR THE LIKE (76) Inventors: Valerie Roy, 13,
O R 4,720, 1 R 5... United States talent (19) (11 Patent Number; 4,720,183 Dilworth (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1988
 O R 4,720, 1 R 5..... United States talent (19) (11 Patent Number; 4,720,183 Dilworth (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1988 54 EXTREME wrde ANGLEEYEPIECE WITH (56) References Cited - MN MALABERRATIONS. U.S.
O R 4,720, 1 R 5..... United States talent (19) (11 Patent Number; 4,720,183 Dilworth (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 19, 1988 54 EXTREME wrde ANGLEEYEPIECE WITH (56) References Cited - MN MALABERRATIONS. U.S.
Converging Lenses. Parallel rays are brought to a focus by a converging lens (one that is thicker in the center than it is at the edge).
 Chapter 30: Lenses Types of Lenses Piece of glass or transparent material that bends parallel rays of light so they cross and form an image Two types: Converging Diverging Converging Lenses Parallel rays
Chapter 30: Lenses Types of Lenses Piece of glass or transparent material that bends parallel rays of light so they cross and form an image Two types: Converging Diverging Converging Lenses Parallel rays
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20070147825A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0147825 A1 Lee et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2007 (54) OPTICAL LENS SYSTEM OF MOBILE Publication Classification
Lenses Design Basics. Introduction. RONAR-SMITH Laser Optics. Optics for Medical. System. Laser. Semiconductor Spectroscopy.
 Introduction Optics Application Lenses Design Basics a) Convex lenses Convex lenses are optical imaging components with positive focus length. After going through the convex lens, parallel beam of light
Introduction Optics Application Lenses Design Basics a) Convex lenses Convex lenses are optical imaging components with positive focus length. After going through the convex lens, parallel beam of light
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 200801 06809A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0106809 A1 HIRANO (43) Pub. Date: (54) WIDE-ANGLE LENS SYSTEM (75) Inventor: Hiroyuki HIRANO, Kanagawa (JP)
(19) United States US 200801 06809A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0106809 A1 HIRANO (43) Pub. Date: (54) WIDE-ANGLE LENS SYSTEM (75) Inventor: Hiroyuki HIRANO, Kanagawa (JP)
United States Patent (19) Hirakawa
 United States Patent (19) Hirakawa US005233474A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 5,233,474 Aug. 3, 1993 (54) WIDE-ANGLE LENS SYSTEM (75) Inventor: Jun Hirakawa, Tokyo, Japan 73) Assignee: Asahi Kogaku
United States Patent (19) Hirakawa US005233474A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 5,233,474 Aug. 3, 1993 (54) WIDE-ANGLE LENS SYSTEM (75) Inventor: Jun Hirakawa, Tokyo, Japan 73) Assignee: Asahi Kogaku
78r9 for 1234,516. United States Patent (19) 2345 ro. 11) 4,266,860 (45) May 12, Hayashi. taining an excellent image-forming performance em
 5/12/8 OR war v Y 4, 266 860 United States Patent (19) Hayashi 54 WIDE ANGLE ZOOM LENS SYSTEM HAVING SHORTENED CLOSEUP FOCAL LENGTH (75) Inventor: Kiyoshi Hayashi, Yokohama, Japan 73) Assignee: Nippon
5/12/8 OR war v Y 4, 266 860 United States Patent (19) Hayashi 54 WIDE ANGLE ZOOM LENS SYSTEM HAVING SHORTENED CLOSEUP FOCAL LENGTH (75) Inventor: Kiyoshi Hayashi, Yokohama, Japan 73) Assignee: Nippon
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent JO et al. USOO6844989B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2005 (54) LENS SYSTEM INSTALLED IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (75) Inventors: Yong-Joo Jo, Kyunggi-Do
(12) United States Patent JO et al. USOO6844989B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 18, 2005 (54) LENS SYSTEM INSTALLED IN MOBILE COMMUNICATION TERMINAL (75) Inventors: Yong-Joo Jo, Kyunggi-Do
350 a 439 SR x V y (2) slril V -2- OR 3,524,697 - the OS, 0. Aug. 18, 1970 MASAK SSH K ET AL 3,524,697 ACHROMATIC SUPER WIDE-ANGLE LENS
 350 a 439 SR x V y (2) slril V -2- OR - the OS, 0 Aug. 18, 1970 MASAK SSH K ET AL Filed April 23, 1968 2 Sleets-Sheet l F G. Li L-2-3-4-5L6 L7-8 l LiO d7de di-, d2 4. ) -- d2 d\ds iy INA dis r s 58 9 of
350 a 439 SR x V y (2) slril V -2- OR - the OS, 0 Aug. 18, 1970 MASAK SSH K ET AL Filed April 23, 1968 2 Sleets-Sheet l F G. Li L-2-3-4-5L6 L7-8 l LiO d7de di-, d2 4. ) -- d2 d\ds iy INA dis r s 58 9 of
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,314,999 B1 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012
 US0083 l4999bl (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,314,999 B1 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012 (54) OPTICAL IMAGE LENS ASSEMBLY (58) Field Of Classi?cation Search..... 359/715, _ 359/771,
US0083 l4999bl (12) United States Patent (10) Patent N0.: US 8,314,999 B1 Tsai (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2012 (54) OPTICAL IMAGE LENS ASSEMBLY (58) Field Of Classi?cation Search..... 359/715, _ 359/771,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Takekuma USOO6850001B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (75) Inventor: Akira Takekuma, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: Agilent Technologies,
(12) United States Patent Takekuma USOO6850001B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (75) Inventor: Akira Takekuma, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: Agilent Technologies,
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Muchel 54) OPTICAL SYSTEM OF WARIABLE FOCAL AND BACK-FOCAL LENGTH (75) Inventor: Franz Muchel, Königsbronn, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73 Assignee: Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung, Heidenheim on
United States Patent (19) Muchel 54) OPTICAL SYSTEM OF WARIABLE FOCAL AND BACK-FOCAL LENGTH (75) Inventor: Franz Muchel, Königsbronn, Fed. Rep. of Germany 73 Assignee: Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung, Heidenheim on
Lens Design I. Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II Herbert Gross. Summer term
 Lens Design I Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II 207-04-20 Herbert Gross Summer term 207 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule - Lens Design I 207 06.04. Basics 2 3.04. Properties of optical
Lens Design I Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II 207-04-20 Herbert Gross Summer term 207 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule - Lens Design I 207 06.04. Basics 2 3.04. Properties of optical
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1
 USOO6386952B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1 White (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) SINGLE STATION BLADE SHARPENING 2,692.457 A 10/1954 Bindszus METHOD AND APPARATUS 2,709,874
USOO6386952B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1 White (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) SINGLE STATION BLADE SHARPENING 2,692.457 A 10/1954 Bindszus METHOD AND APPARATUS 2,709,874
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Dekerle 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 1991 54 NIPPLE ADAPTER FOR A BOTTLE COMPRISING ASCREW RING 75) Inventor: 73) Assignee: Benoit Dekerle, Evian, France Societe
United States Patent (19) Dekerle 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jun. 18, 1991 54 NIPPLE ADAPTER FOR A BOTTLE COMPRISING ASCREW RING 75) Inventor: 73) Assignee: Benoit Dekerle, Evian, France Societe
-i. DDs. (12) United States Patent US 6,201,214 B1. Mar. 13, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: aeeeeeeea. Duffin
 (12) United States Patent Duffin USOO62O1214B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 13, 2001 (54) LASER DRILLING WITH OPTICAL FEEDBACK (75) Inventor: Jason E. Duffin, Leicestershire (GB) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent Duffin USOO62O1214B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 13, 2001 (54) LASER DRILLING WITH OPTICAL FEEDBACK (75) Inventor: Jason E. Duffin, Leicestershire (GB) (73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Waibel et al. USOO6624881B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) OPTOELECTRONIC LASER DISTANCE MEASURING INSTRUMENT (75) Inventors: Reinhard Waibel, Berneck
(12) United States Patent Waibel et al. USOO6624881B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) OPTOELECTRONIC LASER DISTANCE MEASURING INSTRUMENT (75) Inventors: Reinhard Waibel, Berneck
United States Patent (19) Powell
 United States Patent (19) Powell 54) LINEAR DEIVERGING LENS 75) Inventor: Ian Powell, Gloucester, Canada 73 Assignee: Canadian Patents and Development Limited, Ottawa, Canada 21 Appl. No.: 8,830 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Powell 54) LINEAR DEIVERGING LENS 75) Inventor: Ian Powell, Gloucester, Canada 73 Assignee: Canadian Patents and Development Limited, Ottawa, Canada 21 Appl. No.: 8,830 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Nihei et al.
 United States Patent (19) Nihei et al. 54) INDUSTRIAL ROBOT PROVIDED WITH MEANS FOR SETTING REFERENCE POSITIONS FOR RESPECTIVE AXES 75) Inventors: Ryo Nihei, Akihiro Terada, both of Fujiyoshida; Kyozi
United States Patent (19) Nihei et al. 54) INDUSTRIAL ROBOT PROVIDED WITH MEANS FOR SETTING REFERENCE POSITIONS FOR RESPECTIVE AXES 75) Inventors: Ryo Nihei, Akihiro Terada, both of Fujiyoshida; Kyozi
Lens Design I. Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II Herbert Gross. Summer term
 Lens Design I Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II 205-04-8 Herbert Gross Summer term 206 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule 04.04. Basics 2.04. Properties of optical systrems I 3 8.04.
Lens Design I Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II 205-04-8 Herbert Gross Summer term 206 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule 04.04. Basics 2.04. Properties of optical systrems I 3 8.04.
United States Patent (19) Sun
 United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 201603061.41A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0306141 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) OPTICAL LENS Publication Classification (71) Applicant: ABILITY
US 201603061.41A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0306141 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) OPTICAL LENS Publication Classification (71) Applicant: ABILITY
COURSE NAME: PHOTOGRAPHY AND AUDIO VISUAL PRODUCTION (VOCATIONAL) FOR UNDER GRADUATE (FIRST YEAR)
 COURSE NAME: PHOTOGRAPHY AND AUDIO VISUAL PRODUCTION (VOCATIONAL) FOR UNDER GRADUATE (FIRST YEAR) PAPER TITLE: BASIC PHOTOGRAPHIC UNIT - 3 : SIMPLE LENS TOPIC: LENS PROPERTIES AND DEFECTS OBJECTIVES By
COURSE NAME: PHOTOGRAPHY AND AUDIO VISUAL PRODUCTION (VOCATIONAL) FOR UNDER GRADUATE (FIRST YEAR) PAPER TITLE: BASIC PHOTOGRAPHIC UNIT - 3 : SIMPLE LENS TOPIC: LENS PROPERTIES AND DEFECTS OBJECTIVES By
Performance Factors. Technical Assistance. Fundamental Optics
 Performance Factors After paraxial formulas have been used to select values for component focal length(s) and diameter(s), the final step is to select actual lenses. As in any engineering problem, this
Performance Factors After paraxial formulas have been used to select values for component focal length(s) and diameter(s), the final step is to select actual lenses. As in any engineering problem, this
SW Š. United States Patent (19. Mercado. Mar. 19, 1991 SVS2 ANI-III ,000,548. WAC SaSas. (11) Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent:
 United States Patent (19. Mercado (11) Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 19, 1991 (54) MICROSCOPE OBJECTIVE 75 Inventor: Romeo I. Mercado, San Jose, Calif. (73) Assignee: Lockheed Missiles & Space
United States Patent (19. Mercado (11) Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 19, 1991 (54) MICROSCOPE OBJECTIVE 75 Inventor: Romeo I. Mercado, San Jose, Calif. (73) Assignee: Lockheed Missiles & Space
Ch 24. Geometric Optics
 text concept Ch 24. Geometric Optics Fig. 24 3 A point source of light P and its image P, in a plane mirror. Angle of incidence =angle of reflection. text. Fig. 24 4 The blue dashed line through object
text concept Ch 24. Geometric Optics Fig. 24 3 A point source of light P and its image P, in a plane mirror. Angle of incidence =angle of reflection. text. Fig. 24 4 The blue dashed line through object
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
US 20030091084A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0091084A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 15, 2003 (54) INTEGRATION OF VCSEL ARRAY AND Publication Classification
Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner. Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green
 III United States Patent (19) 11) US005230172A Patent Number: 5,230,172 Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 1993 54 PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner o Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green 76)
III United States Patent (19) 11) US005230172A Patent Number: 5,230,172 Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 1993 54 PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner o Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green 76)
11 Patent Number: 5,331,470 Cook 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 19, ) Inventor: Lacy G. Cook, El Segundo, Calif. Assistant Examiner-James A.
 United States Patent (19) IIIHIIII USOO33147OA 11 Patent Number: Cook 4 Date of Patent: Jul. 19, 1994 4 FAST FOLDED WIDE ANGLE LARGE,170,284 12/1992 Cook... 39/861 RE UNOBSCURED SYSTEM Primary Examiner-Edward
United States Patent (19) IIIHIIII USOO33147OA 11 Patent Number: Cook 4 Date of Patent: Jul. 19, 1994 4 FAST FOLDED WIDE ANGLE LARGE,170,284 12/1992 Cook... 39/861 RE UNOBSCURED SYSTEM Primary Examiner-Edward
--comirator. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 2002O174699A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/017.4699 A1 NOe et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 28, 2002 (54) METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR ELMINATING CROSSBOW
(19) United States US 2002O174699A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/017.4699 A1 NOe et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 28, 2002 (54) METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR ELMINATING CROSSBOW
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,957,665 B2
 USOO6957665B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2005 (54) FLOW FORCE COMPENSATING STEPPED (56) References Cited SHAPE SPOOL VALVE (75) Inventors: Weon
USOO6957665B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 25, 2005 (54) FLOW FORCE COMPENSATING STEPPED (56) References Cited SHAPE SPOOL VALVE (75) Inventors: Weon
Lens Design II Seminar 6 (Solutions)
 2017-01-04 Prof. Herbert Gross Yi Zhong, Norman G. Worku Friedrich Schiller University Jena Institute of Applied Physics Albert-Einstein-Str 15 07745 Jena Lens Design II Seminar 6 (Solutions) 6.1. Correction
2017-01-04 Prof. Herbert Gross Yi Zhong, Norman G. Worku Friedrich Schiller University Jena Institute of Applied Physics Albert-Einstein-Str 15 07745 Jena Lens Design II Seminar 6 (Solutions) 6.1. Correction
III III 0 IIOI DID IIO 1101 I II 0II II 100 III IID II DI II
 (19) United States III III 0 IIOI DID IIO 1101 I0 1101 0II 0II II 100 III IID II DI II US 200902 19549A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0219549 Al Nishizaka et al. (43) Pub.
(19) United States III III 0 IIOI DID IIO 1101 I0 1101 0II 0II II 100 III IID II DI II US 200902 19549A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0219549 Al Nishizaka et al. (43) Pub.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
(19) United States US 20130222876A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0222876 A1 SATO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 29, 2013 (54) LASER LIGHT SOURCE MODULE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... H0IS3/0405
A new prime-focus corrector for paraboloid mirrors
 2013 THOSS Media & DOI 10.1515/aot-2012-0078 Adv. Opt. Techn. 2013; 2(1): 111 116 Research Article Andrew Rakich* and Norman J. Rumsey A new prime-focus corrector for paraboloid mirrors Abstract: A new
2013 THOSS Media & DOI 10.1515/aot-2012-0078 Adv. Opt. Techn. 2013; 2(1): 111 116 Research Article Andrew Rakich* and Norman J. Rumsey A new prime-focus corrector for paraboloid mirrors Abstract: A new
'''S D2 I // EDaDa D7. Ra RoRo Ral DDD RR2R3RRRR. R. R. R3 R5RGR7 RB ROR2, R2, R6R28 VX DIAPHRAGM D26. United States Patent (19) Ikemori
 6/28/85 OR 4 g 39 () 248 United States Patent (19) Ikemori (54) WIDE ANGLE ZOOM LENS (75) Inventor: Keiji Ikemori, Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo, Japan... " (21) Appl. No.:
6/28/85 OR 4 g 39 () 248 United States Patent (19) Ikemori (54) WIDE ANGLE ZOOM LENS (75) Inventor: Keiji Ikemori, Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Canon Kabushiki Kaisha, Tokyo, Japan... " (21) Appl. No.:
(12) United States Patent
 US009 158091B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,158,091 B2 Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) LENS MODULE Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRO-MECHANICS CO.,LTD., Suwon (KR) (72)
US009 158091B2 (12) United States Patent Park et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,158,091 B2 Oct. 13, 2015 (54) (71) LENS MODULE Applicant: SAMSUNGELECTRO-MECHANICS CO.,LTD., Suwon (KR) (72)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Sternbergh 54 75 73 21 22 63 51 52 58 56 MULTILAYER ANT-REFLECTIVE AND ULTRAWOLET BLOCKNG COATNG FOR SUNGLASSES Inventor: James H. Sternbergh, Webster, N.Y. Assignee: Bausch &
United States Patent (19) Sternbergh 54 75 73 21 22 63 51 52 58 56 MULTILAYER ANT-REFLECTIVE AND ULTRAWOLET BLOCKNG COATNG FOR SUNGLASSES Inventor: James H. Sternbergh, Webster, N.Y. Assignee: Bausch &
52 U.S. Cl /193; 206/232; 206/459.5; bridging between the bottom and top, and two flip-lid panels
 US00604.1998A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Goldberg (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 2000 54. FOLDING BOX CONSTRUCTION 4,711,348 12/1987 Schluger... 206/232 5,289.917 3/1994 Chabria...... 206/232
US00604.1998A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Goldberg (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 2000 54. FOLDING BOX CONSTRUCTION 4,711,348 12/1987 Schluger... 206/232 5,289.917 3/1994 Chabria...... 206/232
United States Patent (19) Rottmerhusen
 United States Patent (19) Rottmerhusen USOO5856731A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 1999 54 ELECTRICSCREWDRIVER 75 Inventor: Hermann Rottmerhusen, Tellingstedt, Germany 73 Assignee: Metabowerke
United States Patent (19) Rottmerhusen USOO5856731A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 5, 1999 54 ELECTRICSCREWDRIVER 75 Inventor: Hermann Rottmerhusen, Tellingstedt, Germany 73 Assignee: Metabowerke
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,346,966 B1
 USOO6346966B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,346,966 B1 TOh (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 12, 2002 (54) IMAGE ACQUISITION SYSTEM FOR 4,900.934. A * 2/1990 Peeters et al.... 250/461.2 MACHINE
USOO6346966B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,346,966 B1 TOh (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 12, 2002 (54) IMAGE ACQUISITION SYSTEM FOR 4,900.934. A * 2/1990 Peeters et al.... 250/461.2 MACHINE
(12) United States Patent
 US00755.1711B2 (12) United States Patent Sarment et al. (54) CT SCANNER INCLUDINGA CAMERATO OBTAN EXTERNAL IMAGES OF A PATIENT (75) Inventors: David Phillipe Sarment, Ann Arbor, MI (US); Miodrag Rakic,
US00755.1711B2 (12) United States Patent Sarment et al. (54) CT SCANNER INCLUDINGA CAMERATO OBTAN EXTERNAL IMAGES OF A PATIENT (75) Inventors: David Phillipe Sarment, Ann Arbor, MI (US); Miodrag Rakic,
Image Formation. Light from distant things. Geometrical optics. Pinhole camera. Chapter 36
 Light from distant things Chapter 36 We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can process. This chapter concerns
Light from distant things Chapter 36 We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can process. This chapter concerns
United States Patent (19)
 - A - A /.. 5 CR 4 52 7 8 ft United States Patent (19) Fujioka et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 1985 54 WIDE ANGLE ZOOM LENS 75 Inventors: Yoshisato Fujioka, Higashikurume; Atsushi Kawamura,
- A - A /.. 5 CR 4 52 7 8 ft United States Patent (19) Fujioka et al. 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 1985 54 WIDE ANGLE ZOOM LENS 75 Inventors: Yoshisato Fujioka, Higashikurume; Atsushi Kawamura,
Imaging Systems for Eyeglass-Based Display Devices
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Imaging Systems for Eyeglass-Based Display Devices 6-28-2011 Jannick Rolland University of Central Florida Ozan Cakmakci University of Central Florida Find
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Imaging Systems for Eyeglass-Based Display Devices 6-28-2011 Jannick Rolland University of Central Florida Ozan Cakmakci University of Central Florida Find
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Schwab et al. US006335619B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR COMPRISING ARESONANT OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT RESPONDING TO CHANGES IN
(12) United States Patent Schwab et al. US006335619B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR COMPRISING ARESONANT OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT RESPONDING TO CHANGES IN
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
United States Patent 19 Perets
 United States Patent 19 Perets USOO5623875A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,623,875 Apr. 29, 1997 54 MULTI-COLOR AND EASY TO ASSEMBLE AUTOMATIC RUBBER STAMP 76 Inventor: Mishel Perets, clo M. Perets
United States Patent 19 Perets USOO5623875A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,623,875 Apr. 29, 1997 54 MULTI-COLOR AND EASY TO ASSEMBLE AUTOMATIC RUBBER STAMP 76 Inventor: Mishel Perets, clo M. Perets
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0091458 A1 Asami et al. US 20070091458A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2007 (54) WIDE-ANGLE IMAGING LENS (75) Inventors: Taro Asami,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0091458 A1 Asami et al. US 20070091458A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 26, 2007 (54) WIDE-ANGLE IMAGING LENS (75) Inventors: Taro Asami,
United States Patent (19) Morita et al.
 United States Patent (19) Morita et al. - - - - - 54. TEMPLATE 75 Inventors: Shiro Morita, Sakura; Kazuo Yoshitake, Tokyo, both of Japan 73 Assignee: Yoshitake Seisakujo Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl.
United States Patent (19) Morita et al. - - - - - 54. TEMPLATE 75 Inventors: Shiro Morita, Sakura; Kazuo Yoshitake, Tokyo, both of Japan 73 Assignee: Yoshitake Seisakujo Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,752,496 B2
 USOO6752496 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,752,496 B2 Conner (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 22, 2004 (54) PLASTIC FOLDING AND TELESCOPING 5,929.966 A * 7/1999 Conner... 351/118 EYEGLASS
USOO6752496 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,752,496 B2 Conner (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 22, 2004 (54) PLASTIC FOLDING AND TELESCOPING 5,929.966 A * 7/1999 Conner... 351/118 EYEGLASS
United States Patent (19)
 4 a c (, 42 R 6. A 7 United States Patent (19) Sprague et al. 11 (45) 4,428,647 Jan. 31, 1984 (54) MULTI-BEAM OPTICAL SYSTEM USING LENS ARRAY (75. Inventors: Robert A. Sprague, Saratoga; Donald R. Scifres,
4 a c (, 42 R 6. A 7 United States Patent (19) Sprague et al. 11 (45) 4,428,647 Jan. 31, 1984 (54) MULTI-BEAM OPTICAL SYSTEM USING LENS ARRAY (75. Inventors: Robert A. Sprague, Saratoga; Donald R. Scifres,
Lab 2 Geometrical Optics
 Lab 2 Geometrical Optics March 22, 202 This material will span much of 2 lab periods. Get through section 5.4 and time permitting, 5.5 in the first lab. Basic Equations Lensmaker s Equation for a thin
Lab 2 Geometrical Optics March 22, 202 This material will span much of 2 lab periods. Get through section 5.4 and time permitting, 5.5 in the first lab. Basic Equations Lensmaker s Equation for a thin
Optical Design with Zemax for PhD
 Optical Design with Zemax for PhD Lecture 7: Optimization II 26--2 Herbert Gross Winter term 25 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed content.. Introduction 2 2.2. Basic Zemax
Optical Design with Zemax for PhD Lecture 7: Optimization II 26--2 Herbert Gross Winter term 25 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed content.. Introduction 2 2.2. Basic Zemax
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1. Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009
 (19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
(19) United States US 20090059759A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0059759 A1 Yoshizawa et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 5, 2009 (54) TRANSMISSIVE OPTICAL RECORDING (22) Filed: Apr.
Understanding Optical Specifications
 Understanding Optical Specifications Optics can be found virtually everywhere, from fiber optic couplings to machine vision imaging devices to cutting-edge biometric iris identification systems. Despite
Understanding Optical Specifications Optics can be found virtually everywhere, from fiber optic couplings to machine vision imaging devices to cutting-edge biometric iris identification systems. Despite
Beam expansion standard concepts re-interpreted
 Beam expansion standard concepts re-interpreted Ulrike Fuchs (Ph.D.), Sven R. Kiontke asphericon GmbH Stockholmer Str. 9 07743 Jena, Germany Tel: +49-3641-3100500 Introduction Everyday work in an optics
Beam expansion standard concepts re-interpreted Ulrike Fuchs (Ph.D.), Sven R. Kiontke asphericon GmbH Stockholmer Str. 9 07743 Jena, Germany Tel: +49-3641-3100500 Introduction Everyday work in an optics
United States Patent (19) Marhauer
 United States Patent (19) Marhauer 54 SIDE MIRROR FOR VEHICLES 76 Inventor: Friedrich Marhauer, Buchholzer Strasse 49, 3000 Hannover 61, Fed. Rep. of Germany 21 Appl. No.: 96,162 22 Filed: Nov. 20, 1979
United States Patent (19) Marhauer 54 SIDE MIRROR FOR VEHICLES 76 Inventor: Friedrich Marhauer, Buchholzer Strasse 49, 3000 Hannover 61, Fed. Rep. of Germany 21 Appl. No.: 96,162 22 Filed: Nov. 20, 1979
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,729,834 B1
 USOO6729834B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,729,834 B1 McKinley (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) WAFER MANIPULATING AND CENTERING 5,788,453 A * 8/1998 Donde et al.... 414/751 APPARATUS
USOO6729834B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,729,834 B1 McKinley (45) Date of Patent: May 4, 2004 (54) WAFER MANIPULATING AND CENTERING 5,788,453 A * 8/1998 Donde et al.... 414/751 APPARATUS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O116153A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0116153 A1 Hataguchi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2005 (54) ENCODER UTILIZING A REFLECTIVE CYLINDRICAL SURFACE
(19) United States US 2005O116153A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0116153 A1 Hataguchi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 2, 2005 (54) ENCODER UTILIZING A REFLECTIVE CYLINDRICAL SURFACE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9383 080B1 (10) Patent No.: US 9,383,080 B1 McGarvey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 5, 2016 (54) WIDE FIELD OF VIEW CONCENTRATOR USPC... 250/216 See application file for
(12) United States Patent USOO9383 080B1 (10) Patent No.: US 9,383,080 B1 McGarvey et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 5, 2016 (54) WIDE FIELD OF VIEW CONCENTRATOR USPC... 250/216 See application file for
United States Patent 19) 11 Patent Number: 5,442,436 Lawson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 1995
 I () US005442436A United States Patent 19) 11 Patent Number: Lawson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 1995 54 REFLECTIVE COLLIMATOR 4,109,304 8/1978 Khvalovsky et al.... 362/259 4,196,461 4/1980 Geary......
I () US005442436A United States Patent 19) 11 Patent Number: Lawson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 1995 54 REFLECTIVE COLLIMATOR 4,109,304 8/1978 Khvalovsky et al.... 362/259 4,196,461 4/1980 Geary......
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
Chapter 36 Image Formation Image of Formation Images can result when light rays encounter flat or curved surfaces between two media. Images can be formed either by reflection or refraction due to these
202 19' 19 19' (12) United States Patent 202' US 7,050,043 B2. Huang et al. May 23, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.
 US00705.0043B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,050,043 B2 May 23, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 2,
US00705.0043B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,050,043 B2 May 23, 2006 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (30) Foreign Application Priority Data Sep. 2,
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to the
Chapter 36 Image Formation Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens Denoted by p The image distance is the distance from the image to the
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,877,901 Enomoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 2, 1999
 USOO5877901A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Enomoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 2, 1999 54 SUPER WIDE-ANGLE ZOOM LENS 4,844,599 7/1989 Ito. 4,934,797 6/1990 Hirakawa. 75 Inventors: Takashi
USOO5877901A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Enomoto et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 2, 1999 54 SUPER WIDE-ANGLE ZOOM LENS 4,844,599 7/1989 Ito. 4,934,797 6/1990 Hirakawa. 75 Inventors: Takashi
Laboratory experiment aberrations
 Laboratory experiment aberrations Obligatory laboratory experiment on course in Optical design, SK2330/SK3330, KTH. Date Name Pass Objective This laboratory experiment is intended to demonstrate the most
Laboratory experiment aberrations Obligatory laboratory experiment on course in Optical design, SK2330/SK3330, KTH. Date Name Pass Objective This laboratory experiment is intended to demonstrate the most
United States Patent (19) Miller
 M5 f 85 OR 4 55 O 58 United States Patent (19) Miller (54) (76) FISH EYE LENS SYSTEM Inventor: Rolf Miller, Wienerstr. 3, 7888 Rheinfelden, Fed. Rep. of Germany 1 Appl. No.: 379,76 Filed: May 19, 198 (30)
M5 f 85 OR 4 55 O 58 United States Patent (19) Miller (54) (76) FISH EYE LENS SYSTEM Inventor: Rolf Miller, Wienerstr. 3, 7888 Rheinfelden, Fed. Rep. of Germany 1 Appl. No.: 379,76 Filed: May 19, 198 (30)
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,715,221 B1. Sasaki (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2004
 USOO671.51B1 (1) United States Patent (10) Patent No. US 6,715,1 B1 Sasaki (45) Date of Patent Apr. 6, 004 (54) FOOT STIMULATING SHOE INSOLE 5,860,9 A * 1/1999 Morgenstern... 36/141 (75) Inventor Manhachi
USOO671.51B1 (1) United States Patent (10) Patent No. US 6,715,1 B1 Sasaki (45) Date of Patent Apr. 6, 004 (54) FOOT STIMULATING SHOE INSOLE 5,860,9 A * 1/1999 Morgenstern... 36/141 (75) Inventor Manhachi
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 33 Geometric Optics Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones Aberrations We have continued to make approximations: Paraxial rays Spherical lenses Index of refraction
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 33 Geometric Optics Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones Aberrations We have continued to make approximations: Paraxial rays Spherical lenses Index of refraction
Chapter 36. Image Formation
 Chapter 36 Image Formation Real and Virtual Images Real images can be displayed on screens Virtual Images can not be displayed onto screens. Focal Length& Radius of Curvature When the object is very far
Chapter 36 Image Formation Real and Virtual Images Real images can be displayed on screens Virtual Images can not be displayed onto screens. Focal Length& Radius of Curvature When the object is very far
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,387,795 B1
 USOO6387795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shao (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) WAFER-LEVEL PACKAGING 5,045,918 A * 9/1991 Cagan et al.... 357/72 (75) Inventor: Tung-Liang Shao, Taoyuan
USOO6387795B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Shao (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) WAFER-LEVEL PACKAGING 5,045,918 A * 9/1991 Cagan et al.... 357/72 (75) Inventor: Tung-Liang Shao, Taoyuan
Lens Design I. Lecture 10: Optimization II Herbert Gross. Summer term
 Lens Design I Lecture : Optimization II 5-6- Herbert Gross Summer term 5 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule 3.. Basics.. Properties of optical systrems I 3 7.5..5. Properties of optical systrems
Lens Design I Lecture : Optimization II 5-6- Herbert Gross Summer term 5 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule 3.. Basics.. Properties of optical systrems I 3 7.5..5. Properties of optical systrems
J0 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 22, (54) PHOTOGRAPHICLENS 7, 177,098 B2 * 2/2007 Arai ,715
 (12) United States Patent USOO7321474B1 (10) Patent No.: US 7,321,474 B1 J0 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 22, 2008 (54) PHOTOGRAPHICLENS 7, 177,098 B2 * 2/2007 Arai... 359,715 2005, 0105.194 A1* 5, 2005 Matsui
(12) United States Patent USOO7321474B1 (10) Patent No.: US 7,321,474 B1 J0 (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 22, 2008 (54) PHOTOGRAPHICLENS 7, 177,098 B2 * 2/2007 Arai... 359,715 2005, 0105.194 A1* 5, 2005 Matsui
Lens Design I. Lecture 10: Optimization II Herbert Gross. Summer term
 Lens Design I Lecture : Optimization II 8-6- Herbert Gross Summer term 8 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule - Lens Design I 8.4. Basics 9.4. Properties of optical systems I 3 6.4. Properties of optical
Lens Design I Lecture : Optimization II 8-6- Herbert Gross Summer term 8 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule - Lens Design I 8.4. Basics 9.4. Properties of optical systems I 3 6.4. Properties of optical
Applied Optics. , Physics Department (Room #36-401) , ,
 Applied Optics Professor, Physics Department (Room #36-401) 2290-0923, 019-539-0923, shsong@hanyang.ac.kr Office Hours Mondays 15:00-16:30, Wednesdays 15:00-16:30 TA (Ph.D. student, Room #36-415) 2290-0921,
Applied Optics Professor, Physics Department (Room #36-401) 2290-0923, 019-539-0923, shsong@hanyang.ac.kr Office Hours Mondays 15:00-16:30, Wednesdays 15:00-16:30 TA (Ph.D. student, Room #36-415) 2290-0921,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005
 US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
US 20050284393A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Chen et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 29, 2005 (54) COLOR FILTER AND MANUFACTURING (30) Foreign Application Priority Data
issi Field of search. 348/36, , 33) of the turret punch press machine; an image of the
 US005721587A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,721,587 Hirose 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Primary Examiner Bryan S. Tung NSPECTNG PRODUCT PROCESSED BY Attorney,
US005721587A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: 5,721,587 Hirose 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 24, 1998 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR Primary Examiner Bryan S. Tung NSPECTNG PRODUCT PROCESSED BY Attorney,
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999
 USOO599.1083A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54) IMAGE DISPLAY APPARATUS 56) References Cited 75 Inventor: Yoshiki Shirochi, Chiba, Japan
USOO599.1083A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,991,083 Shirochi (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 23, 1999 54) IMAGE DISPLAY APPARATUS 56) References Cited 75 Inventor: Yoshiki Shirochi, Chiba, Japan
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,948,658 B2
 USOO694.8658B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,948,658 B2 Tsai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR AUTOMATICALLY 5,613,016 A 3/1997 Saitoh... 382/174 INTEGRATING DIGITAL
USOO694.8658B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,948,658 B2 Tsai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR AUTOMATICALLY 5,613,016 A 3/1997 Saitoh... 382/174 INTEGRATING DIGITAL
United States Patent (19) Blackburn et al.
 United States Patent (19) Blackburn et al. 11 Patent Number: (4) Date of Patent: 4,21,042 Jun. 4, 198 4 THREADED CONNECTION 7) Inventors: Jan W. Blackburn, Kingwood; Burl E. Baron, Houston, both of Tex.
United States Patent (19) Blackburn et al. 11 Patent Number: (4) Date of Patent: 4,21,042 Jun. 4, 198 4 THREADED CONNECTION 7) Inventors: Jan W. Blackburn, Kingwood; Burl E. Baron, Houston, both of Tex.
United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354
![United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354 United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354](/thumbs/92/110916574.jpg) US005746354A United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354 Perkins 45) Date of Patent: May 5, 1998 54 MULTI-COMPARTMENTAEROSOLSPRAY FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS CONTANER 3142205 5/1983 Germany...
US005746354A United States Patent (19) [11] Patent Number: 5,746,354 Perkins 45) Date of Patent: May 5, 1998 54 MULTI-COMPARTMENTAEROSOLSPRAY FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS CONTANER 3142205 5/1983 Germany...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 20020O24744A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No. US 2002/0024744 A1 Kasahara (43) Pub. Date Feb. 28, 2002 (54) MICROSCOPE OBJECTIVE LENS (76) Inventor Takashi Kasahara,
(19) United States US 20020O24744A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No. US 2002/0024744 A1 Kasahara (43) Pub. Date Feb. 28, 2002 (54) MICROSCOPE OBJECTIVE LENS (76) Inventor Takashi Kasahara,
Mirrors, Lenses &Imaging Systems
 Mirrors, Lenses &Imaging Systems We describe the path of light as straight-line rays And light rays from a very distant point arrive parallel 145 Phys 24.1 Mirrors Standing away from a plane mirror shows
Mirrors, Lenses &Imaging Systems We describe the path of light as straight-line rays And light rays from a very distant point arrive parallel 145 Phys 24.1 Mirrors Standing away from a plane mirror shows
OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES
 101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
Chapter 29/30. Wave Fronts and Rays. Refraction of Sound. Dispersion in a Prism. Index of Refraction. Refraction and Lenses
 Chapter 29/30 Refraction and Lenses Refraction Refraction the bending of waves as they pass from one medium into another. Caused by a change in the average speed of light. Analogy A car that drives off
Chapter 29/30 Refraction and Lenses Refraction Refraction the bending of waves as they pass from one medium into another. Caused by a change in the average speed of light. Analogy A car that drives off
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2
 USOO6543599B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2 Jasinetzky (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) STEP FOR ESCALATORS 5,810,148 A * 9/1998 Schoeneweiss... 198/333 6,398,003 B1
USOO6543599B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2 Jasinetzky (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) STEP FOR ESCALATORS 5,810,148 A * 9/1998 Schoeneweiss... 198/333 6,398,003 B1
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Mack USOO686.0488B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2005 (54) DRILL CHUCK WITH FRONT-END SHIELD (75) Inventor: Hans-Dieter Mack, Sontheim (DE) (73) Assignee: Rohm
(12) United States Patent Mack USOO686.0488B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 1, 2005 (54) DRILL CHUCK WITH FRONT-END SHIELD (75) Inventor: Hans-Dieter Mack, Sontheim (DE) (73) Assignee: Rohm
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,189,225 B1
 USOO6189225B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,189,225 B1 Jan SSOn (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 20, 2001 (54) ANGLE GAUGE FOR GRINDING SHARP- 2,468.395 4/1949 Fredin... 33/628 EDGED TOOLS
USOO6189225B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,189,225 B1 Jan SSOn (45) Date of Patent: *Feb. 20, 2001 (54) ANGLE GAUGE FOR GRINDING SHARP- 2,468.395 4/1949 Fredin... 33/628 EDGED TOOLS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,915,597 B2. Jungkind (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005
 USOO6915597B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Jungkind (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) SPORTS SHOE 2,523,652 A * 9/1950 Dowd et al.... 36/59 R 3,082.549 A 3/1963 Dolceamore (75) Inventor:
USOO6915597B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Jungkind (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) SPORTS SHOE 2,523,652 A * 9/1950 Dowd et al.... 36/59 R 3,082.549 A 3/1963 Dolceamore (75) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130279021A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279021 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) OPTICAL IMAGE LENS SYSTEM Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20130279021A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0279021 A1 CHEN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 24, 2013 (54) OPTICAL IMAGE LENS SYSTEM Publication Classification
52 U.S. Cl /395 sponding ideal pulse-height spectrum. Comparison of the
 US005545900A United States Patent (19 11) Patent Number: Bolk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 13, 1996 54 RADIATION ANALYSIS APPARATUS 3-179919 8/1991 Japan... 341?2O 75) Inventors: Hendrik J. J. Bolk;
US005545900A United States Patent (19 11) Patent Number: Bolk et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 13, 1996 54 RADIATION ANALYSIS APPARATUS 3-179919 8/1991 Japan... 341?2O 75) Inventors: Hendrik J. J. Bolk;
