Distributed Systems. Clocks, Ordering, and Global Snapshots
|
|
|
- Warren Augustine Burke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Distributed Systems Clocks, Ordering, and Global Snapshots Björn Franke University of Edinburgh
2 Logical clocks Why do we need clocks? To determine when one thing happened before another Can we determine that without using a clock at all? Then we don t need to worry about synchronisation, millisecond errors etc.. 2
3 Happened before a b : a happened before b If a and b are successive events in same process then a b Send before receive If a : send event of message m And b : receive event of message m Then a b Transitive: a b and b c a c 3
4 Example p1 e1 e2 p2 e3 p3 e4 e5 4
5 Example Events without a happened before relation are concurrent e1 e2, e3 e4,e1 e5, e5 e2 p1 e1 e2 p2 e3 p3 e4 e5 5
6 Example Events without a happened before relation are concurrent Happened before is a partial ordering p1 e1 e2 p2 e3 p3 e4 e5 6
7 Happened before & causal order Happened before == could have caused/ influenced Preserves causal relations Implies a partial order Implies time ordering between certain pairs of events Does not imply anything about ordering between concurrent events 7
8 Logical clocks Idea: Use a counter at each process Increment after each event Can also increment when there are no events Eg. A clock An actual clock can be thought of as such an event counter It counts the states of the process Each event has an associated time: The count of the state when the event happened 8
9 Lamport clocks Keep a logical clock (counter) Send it with every message On receiving a message, set own clock to max({own counter, message counter}) + 1 For any event e, write c(e) for the logical time Property: If a b, then c(a) < c(b) If a b, then no guarantees 9
10 Lamport clocks: Example 10
11 Concurrency and Lamport clocks If e1 e2 Then no Lamport clock C exists with C(e1)== C(e2) 11
12 Concurrency and Lamport clocks If e1 e2 Then no Lamport clock C exists with C(e1)== C(e2) If e1 e2, then there exists a Lamport clock C such that C(e1)== C(e2) 12
13 The Purpose of Lamport Clocks 13
14 The Purpose of Lamport Clocks If a b, then c(a) < c(b) If we order all events by their Lamport clock times We get a partial order, since some events have same time The partial order satisfies causal relations 14
15 The purpose of Lamport clocks Suppose there are events in different machines Transactions, money in/out, file read, write, copy An ordering of events that guarantees preserving causality 15
16 Total order from Lamport clocks If event e occurs in process j at time C(e) Give it a time (C(e), j) Order events by (C, process id) For events e1 in process i, e2 in process j: If C(e1)<C(e2), then e1<e2 Else if C(e1)==C(e2) and i<j, then e1<e2 Leslie Lamport. Time, clocks and ordering of events in a distributed system. 16
17 Vector Clocks We want a clock such that: If a b, then c(a) < c(b) AND If c(a) < c(b), then a b Ref: Coulouris et al., V. Garg 17
18 Vector Clocks Each process i maintains a vector V i V i has n elements keeps clock V i [j] for every other process j On every local event: V i [i] =V i [i]+1 On sending a message, i sends entire V i On receiving a message at process j: Takes max element by element V j [k] = max(v j [k], V i [k]), for k = 1,2,,n And adds 1 to V j [j] 18
19 Example ff 19
20 Another Example 20
21 Comparing Timestamps V = V iff V[i] == V [i] for i=1,2,,n V < V iff V[i] < V [i] for i=1,2,,n 21
22 Comparing Timestamps V = V iff V[i] == V [i] for i=1,2,,n V < V iff V[i] < V [i] for i=1,2,,n For events a, b and vector clock V a b iff V(a) < V(b) Is this a total order? 22
23 Comparing Timestamps V = V iff V[i] == V [i] for i=1,2,,n V V iff V[i] V [i] for i=1,2,,n For events a, b and vector clock V a b iff V(a) V(b) Two events are concurrent if Neither V(a) < V(b) nor V(b) < V(a) 23
24 Vector Clock Examples (1,2,1) (3,2,1) but (1,2,1) (3,1,2) Also (3,1,2) (1,2,1) No ordering exists 24
25 Vector Clocks What are the drawbacks? What is the communication complexity? 25
26 Vector Clocks What are the drawbacks? Entire vector is sent with message All vector elements (n) have to be checked on every message What is the communication complexity? Ω(n) per message Increases with time 26
27 Logical Clocks There is no way to have perfect knowledge on ordering of events A true ordering may not exist.. Logical and vector clocks give us a way to have ordering consistent with causality 27
28 Distributed Snapshots Take a snapshot of a system E.g. for backup: If system fails, it can start up from a meaningful state Problem: Imagine a sky filled with birds. The sky is too large to cover in a single picture. We want to take multiple pictures that are consistent in a suitable sense Eg. We can correctly count the number of birds from the snapshot 28
29 Distributed Snapshots Global state: State of all processes and communication channels Consistent cuts: A set of states of all processes is a consistent cut if: For any states s, t in the cut, s t If a b, then the following is not allowed: b is before the cut, a is after the cut 29
30 Consistent Cut 30
31 Distributed Snapshot Algorithm Ask each process to record its state The set of states must be a consistent cut Assumptions: Communication channels are FIFO Processes communicate only with neighbors (We assume for now that everyone is neighbor of everyone) Processes do not fail 31
32 Global Snapshot Chandy and Lamport Algorithm One process initiates snapshot and sends a marker Marker is the boundary between before and after snapshot 32
33 Global snapshot: Chandy and Lamport algorithm Marker send rule (Process i) Process i records its state On every outgoing channel where a marker has not been sent: i sends a marker on the channel before sending any other message Marker receive rule (Process i receives marker on channel C) If i has not received the marker before Record state of I Record state of C as empty Follow marker send rule Else: Record the state of C as the set of messages received on C since recording i s state and before receiving marker on C Algorithm stops when all processes have received marker on all incoming channels 33
34 Complexity Message? Time? 34
EECS 498 Introduction to Distributed Systems
 EECS 498 Introduction to Distributed Systems Fall 2017 Harsha V. Madhyastha Replicated State Machine Replica 2 Replica 1 Replica 3 Are we done now that we have logical clocks? Failures! Clients September
EECS 498 Introduction to Distributed Systems Fall 2017 Harsha V. Madhyastha Replicated State Machine Replica 2 Replica 1 Replica 3 Are we done now that we have logical clocks? Failures! Clients September
Global State and Gossip
 Global State and Gossip CS 240: Computing Systems and Concurrency Lecture 6 Marco Canini Credits: Indranil Gupta developed much of the original material. Today 1. Global snapshot of a distributed system
Global State and Gossip CS 240: Computing Systems and Concurrency Lecture 6 Marco Canini Credits: Indranil Gupta developed much of the original material. Today 1. Global snapshot of a distributed system
Synchronisation in Distributed Systems
 Synchronisation in Distributed Systems Distributed Systems Sistemi Distribuiti Andrea Omicini andrea.omicini@unibo.it Ingegneria Due Alma Mater Studiorum Università di Bologna a Cesena Academic Year 2010/2011
Synchronisation in Distributed Systems Distributed Systems Sistemi Distribuiti Andrea Omicini andrea.omicini@unibo.it Ingegneria Due Alma Mater Studiorum Università di Bologna a Cesena Academic Year 2010/2011
Outline for February 6, 2001
 Outline for February 6, 2001 ECS 251 Winter 2001 Page 1 Outline for February 6, 2001 1. Greetings and felicitations! a. Friday times good, also Tuesday 3-4:30. Please send me your preferences! 2. Global
Outline for February 6, 2001 ECS 251 Winter 2001 Page 1 Outline for February 6, 2001 1. Greetings and felicitations! a. Friday times good, also Tuesday 3-4:30. Please send me your preferences! 2. Global
Synchronisation in Distributed Systems
 Synchronisation in Distributed Systems Distributed Systems Sistemi Distribuiti Andrea Omicini andrea.omicini@unibo.it Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria (DISI) Alma Mater Studiorum Università
Synchronisation in Distributed Systems Distributed Systems Sistemi Distribuiti Andrea Omicini andrea.omicini@unibo.it Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria (DISI) Alma Mater Studiorum Università
Distributed Systems. Time Synchronization
 15-440 Distributed Systems Time Synchronization Today's Lecture Need for time synchronization Time synchronization techniques Lamport Clocks Vector Clocks 2 Why Global Timing? Suppose there were a globally
15-440 Distributed Systems Time Synchronization Today's Lecture Need for time synchronization Time synchronization techniques Lamport Clocks Vector Clocks 2 Why Global Timing? Suppose there were a globally
Efficient Detection of Channel Predicates in Distributed Systems 1
 Efficient Detection of Channel Predicates in Distributed Systems 1 V. K. Garg C. M. Chase Richard Kilgore J. Roger Mitchell January 19, 1995 1 This paper is an extended and substially revised version of
Efficient Detection of Channel Predicates in Distributed Systems 1 V. K. Garg C. M. Chase Richard Kilgore J. Roger Mitchell January 19, 1995 1 This paper is an extended and substially revised version of
Today's Lecture. Clocks in a Distributed System. Last Lecture RPC Important Lessons. Need for time synchronization. Time synchronization techniques
 Last Lecture RPC Important Lessons Procedure calls Simple way to pass control and data Elegant transparent way to distribute application Not only way Hard to provide true transparency Failures Performance
Last Lecture RPC Important Lessons Procedure calls Simple way to pass control and data Elegant transparent way to distribute application Not only way Hard to provide true transparency Failures Performance
Link State Routing. Stefano Vissicchio UCL Computer Science CS 3035/GZ01
 Link State Routing Stefano Vissicchio UCL Computer Science CS 335/GZ Reminder: Intra-domain Routing Problem Shortest paths problem: What path between two vertices offers minimal sum of edge weights? Classic
Link State Routing Stefano Vissicchio UCL Computer Science CS 335/GZ Reminder: Intra-domain Routing Problem Shortest paths problem: What path between two vertices offers minimal sum of edge weights? Classic
Game Theory and Randomized Algorithms
 Game Theory and Randomized Algorithms Guy Aridor Game theory is a set of tools that allow us to understand how decisionmakers interact with each other. It has practical applications in economics, international
Game Theory and Randomized Algorithms Guy Aridor Game theory is a set of tools that allow us to understand how decisionmakers interact with each other. It has practical applications in economics, international
2015 Relay School Bus Protection Mike Kockott March, 2015
 2015 Relay School Bus Protection Mike Kockott March, 2015 History of Bus Protection Circulating current differential (1900s) High impedance differential (1940s) Percentage restrained differential (1960s)
2015 Relay School Bus Protection Mike Kockott March, 2015 History of Bus Protection Circulating current differential (1900s) High impedance differential (1940s) Percentage restrained differential (1960s)
Design for Testability & Design for Debug
 EE-382M VLSI II Design for Testability & Design for Debug Bob Molyneaux Mark McDermott Anil Sabbavarapu EE 382M Class Notes Foil # 1 The University of Texas at Austin Agenda Why test? Scan: What is it?
EE-382M VLSI II Design for Testability & Design for Debug Bob Molyneaux Mark McDermott Anil Sabbavarapu EE 382M Class Notes Foil # 1 The University of Texas at Austin Agenda Why test? Scan: What is it?
Fall 2015 COMP Operating Systems. Lab #7
 Fall 2015 COMP 3511 Operating Systems Lab #7 Outline Review and examples on virtual memory Motivation of Virtual Memory Demand Paging Page Replacement Q. 1 What is required to support dynamic memory allocation
Fall 2015 COMP 3511 Operating Systems Lab #7 Outline Review and examples on virtual memory Motivation of Virtual Memory Demand Paging Page Replacement Q. 1 What is required to support dynamic memory allocation
Eliminating Isochronic-Fork Constraints in Quasi-Delay-Insensitive Circuits
 Eliminating Isochronic-Fork Constraints in Quasi-Delay-Insensitive Circuits Nattha Sretasereekul Takashi Nanya RCAST RCAST The University of Tokyo The University of Tokyo Tokyo, 153-8904 Tokyo, 153-8904
Eliminating Isochronic-Fork Constraints in Quasi-Delay-Insensitive Circuits Nattha Sretasereekul Takashi Nanya RCAST RCAST The University of Tokyo The University of Tokyo Tokyo, 153-8904 Tokyo, 153-8904
Graphs and Network Flows IE411. Lecture 14. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Graphs and Network Flows IE411 Lecture 14 Dr. Ted Ralphs IE411 Lecture 14 1 Review: Labeling Algorithm Pros Guaranteed to solve any max flow problem with integral arc capacities Provides constructive tool
Graphs and Network Flows IE411 Lecture 14 Dr. Ted Ralphs IE411 Lecture 14 1 Review: Labeling Algorithm Pros Guaranteed to solve any max flow problem with integral arc capacities Provides constructive tool
Intelligent Handoff in Cellular Data Networks Based on Mobile Positioning
 Intelligent Handoff in Cellular Data Networks Based on Mobile Positioning Prasannakumar J.M. 4 th semester MTech (CSE) National Institute Of Technology Karnataka Surathkal 575025 INDIA Dr. K.C.Shet Professor,
Intelligent Handoff in Cellular Data Networks Based on Mobile Positioning Prasannakumar J.M. 4 th semester MTech (CSE) National Institute Of Technology Karnataka Surathkal 575025 INDIA Dr. K.C.Shet Professor,
Non-linear circuits and sensors
 ELEC3106, Electronics Non-linear circuits and sensors 1 ELEC3106 Electronics: lecture 10 summary Non-linear circuits and sensors Torsten Lehmann School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunication The
ELEC3106, Electronics Non-linear circuits and sensors 1 ELEC3106 Electronics: lecture 10 summary Non-linear circuits and sensors Torsten Lehmann School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunication The
MOBILE COMPUTING NIT Agartala, Dept of CSE Jan-May,2012
 Location Management for Mobile Cellular Systems MOBILE COMPUTING NIT Agartala, Dept of CSE Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com Cellular System
Location Management for Mobile Cellular Systems MOBILE COMPUTING NIT Agartala, Dept of CSE Jan-May,2012 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com Cellular System
Solutions to the problems from Written assignment 2 Math 222 Winter 2015
 Solutions to the problems from Written assignment 2 Math 222 Winter 2015 1. Determine if the following limits exist, and if a limit exists, find its value. x2 y (a) The limit of f(x, y) = x 4 as (x, y)
Solutions to the problems from Written assignment 2 Math 222 Winter 2015 1. Determine if the following limits exist, and if a limit exists, find its value. x2 y (a) The limit of f(x, y) = x 4 as (x, y)
Get Organized! The 5 Keys to Organization & Time Management
 Get Organized! The 5 Keys to Organization & Time Management Frank Buck Consulting, Inc. FrankBuck.org 1 What You Will Learn in This Workshop Thank for your interest in this workshop and for taking the
Get Organized! The 5 Keys to Organization & Time Management Frank Buck Consulting, Inc. FrankBuck.org 1 What You Will Learn in This Workshop Thank for your interest in this workshop and for taking the
A Review of Current Routing Protocols for Ad Hoc Mobile Wireless Networks
 A Review of Current Routing Protocols for Ad Hoc Mobile Wireless Networks Elisabeth M. Royer, Chai-Keong Toh IEEE Personal Communications, April 1999 Presented by Hannu Vilpponen 1(15) Hannu_Vilpponen.PPT
A Review of Current Routing Protocols for Ad Hoc Mobile Wireless Networks Elisabeth M. Royer, Chai-Keong Toh IEEE Personal Communications, April 1999 Presented by Hannu Vilpponen 1(15) Hannu_Vilpponen.PPT
An Adaptive Distributed Channel Allocation Strategy for Mobile Cellular Networks
 Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing 60, 451473 (2000) doi:10.1006jpdc.1999.1614, available online at http:www.idealibrary.com on An Adaptive Distributed Channel Allocation Strategy for Mobile
Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing 60, 451473 (2000) doi:10.1006jpdc.1999.1614, available online at http:www.idealibrary.com on An Adaptive Distributed Channel Allocation Strategy for Mobile
The ternary alphabet is used by alternate mark inversion modulation; successive ones in data are represented by alternating ±1.
 Alphabets EE 387, Notes 2, Handout #3 Definition: An alphabet is a discrete (usually finite) set of symbols. Examples: B = {0,1} is the binary alphabet T = { 1,0,+1} is the ternary alphabet X = {00,01,...,FF}
Alphabets EE 387, Notes 2, Handout #3 Definition: An alphabet is a discrete (usually finite) set of symbols. Examples: B = {0,1} is the binary alphabet T = { 1,0,+1} is the ternary alphabet X = {00,01,...,FF}
22c181: Formal Methods in Software Engineering. The University of Iowa Spring Propositional Logic
 22c181: Formal Methods in Software Engineering The University of Iowa Spring 2010 Propositional Logic Copyright 2010 Cesare Tinelli. These notes are copyrighted materials and may not be used in other course
22c181: Formal Methods in Software Engineering The University of Iowa Spring 2010 Propositional Logic Copyright 2010 Cesare Tinelli. These notes are copyrighted materials and may not be used in other course
Instructions [CT+PT Treatment]
![Instructions [CT+PT Treatment] Instructions [CT+PT Treatment]](/thumbs/84/89527393.jpg) Instructions [CT+PT Treatment] 1. Overview Welcome to this experiment in the economics of decision-making. Please read these instructions carefully as they explain how you earn money from the decisions
Instructions [CT+PT Treatment] 1. Overview Welcome to this experiment in the economics of decision-making. Please read these instructions carefully as they explain how you earn money from the decisions
Application Note 160 Using the DS1808 in Audio Applications
 www.maxim-ic.com Application Note 160 Using the DS1808 in Audio Applications Introduction The DS1808 Dual Log Audio Potentiometer was designed to provide superior audio performance in applications that
www.maxim-ic.com Application Note 160 Using the DS1808 in Audio Applications Introduction The DS1808 Dual Log Audio Potentiometer was designed to provide superior audio performance in applications that
CS 621 Mobile Computing
 Lecture 11 CS 621 Mobile Computing Location Management for Mobile Cellular Systems Zubin Bhuyan, Department of CSE, Tezpur University http://www.tezu.ernet.in/~zubin Several slides and images in this presentation
Lecture 11 CS 621 Mobile Computing Location Management for Mobile Cellular Systems Zubin Bhuyan, Department of CSE, Tezpur University http://www.tezu.ernet.in/~zubin Several slides and images in this presentation
EITF35: Introduction to Structured VLSI Design
 EITF35: Introduction to Structured VLSI Design Part 4.2.1: Learn More Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Crossing clock domain Reset, synchronous or asynchronous? 2 Why two DFFs? 3 Crossing clock
EITF35: Introduction to Structured VLSI Design Part 4.2.1: Learn More Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Crossing clock domain Reset, synchronous or asynchronous? 2 Why two DFFs? 3 Crossing clock
Solutions to Problem Set 6 - Fall 2008 Due Tuesday, Oct. 21 at 1:00
 18.781 Solutions to Problem Set 6 - Fall 008 Due Tuesday, Oct. 1 at 1:00 1. (Niven.8.7) If p 3 is prime, how many solutions are there to x p 1 1 (mod p)? How many solutions are there to x p 1 (mod p)?
18.781 Solutions to Problem Set 6 - Fall 008 Due Tuesday, Oct. 1 at 1:00 1. (Niven.8.7) If p 3 is prime, how many solutions are there to x p 1 1 (mod p)? How many solutions are there to x p 1 (mod p)?
Design of Parallel Algorithms. Communication Algorithms
 + Design of Parallel Algorithms Communication Algorithms + Topic Overview n One-to-All Broadcast and All-to-One Reduction n All-to-All Broadcast and Reduction n All-Reduce and Prefix-Sum Operations n Scatter
+ Design of Parallel Algorithms Communication Algorithms + Topic Overview n One-to-All Broadcast and All-to-One Reduction n All-to-All Broadcast and Reduction n All-Reduce and Prefix-Sum Operations n Scatter
Lecture Notes 3: Paging, K-Server and Metric Spaces
 Online Algorithms 16/11/11 Lecture Notes 3: Paging, K-Server and Metric Spaces Professor: Yossi Azar Scribe:Maor Dan 1 Introduction This lecture covers the Paging problem. We present a competitive online
Online Algorithms 16/11/11 Lecture Notes 3: Paging, K-Server and Metric Spaces Professor: Yossi Azar Scribe:Maor Dan 1 Introduction This lecture covers the Paging problem. We present a competitive online
RW1026 Dot Matrix 48x4 LCD Controller / Driver
 Features Operating voltage: 2.4V~5.5V Internal LCD Bias generation with voltage-follower buffer External resistor CR oscillator External 256k Hz frequency source input Selection of 1/2 or 1/3 bias, and
Features Operating voltage: 2.4V~5.5V Internal LCD Bias generation with voltage-follower buffer External resistor CR oscillator External 256k Hz frequency source input Selection of 1/2 or 1/3 bias, and
Comp551: Advanced Robotics Lab Lecture 7: Consensus CSE481C wi09 - Robotics Capstone, Lec3: Consensus
 Comp551: Advanced Robotics Lab Lecture 7: Consensus 1 intro 3 multi-robot computation model 5 Model: Robot State We can describe the state, s, of a single robot as a tuple of its ID, pose, and private
Comp551: Advanced Robotics Lab Lecture 7: Consensus 1 intro 3 multi-robot computation model 5 Model: Robot State We can describe the state, s, of a single robot as a tuple of its ID, pose, and private
1 2-step and other basic conditional probability problems
 Name M362K Exam 2 Instructions: Show all of your work. You do not have to simplify your answers. No calculators allowed. 1 2-step and other basic conditional probability problems 1. Suppose A, B, C are
Name M362K Exam 2 Instructions: Show all of your work. You do not have to simplify your answers. No calculators allowed. 1 2-step and other basic conditional probability problems 1. Suppose A, B, C are
AC : MEASURING THE JITTER OF CLOCK SIGNAL
 AC 2011-409: MEASURING THE JITTER OF CLOCK SIGNAL Chao Li, Florida A&M University Dr. Chao Li is currently working at Florida A&M University as an assistant professor in Electronic Engineering Technology.
AC 2011-409: MEASURING THE JITTER OF CLOCK SIGNAL Chao Li, Florida A&M University Dr. Chao Li is currently working at Florida A&M University as an assistant professor in Electronic Engineering Technology.
Distributed Network Protocols Lecture Notes 1
 Distributed Network Protocols Lecture Notes 1 Prof. Adrian Segall Department of Electrical Engineering Technion, Israel Institute of Technology segall at ee.technion.ac.il and Department of Computer Engineering
Distributed Network Protocols Lecture Notes 1 Prof. Adrian Segall Department of Electrical Engineering Technion, Israel Institute of Technology segall at ee.technion.ac.il and Department of Computer Engineering
Politecnico di Milano Advanced Network Technologies Laboratory. Radio Frequency Identification
 Politecnico di Milano Advanced Network Technologies Laboratory Radio Frequency Identification RFID in Nutshell o To Enhance the concept of bar-codes for faster identification of assets (goods, people,
Politecnico di Milano Advanced Network Technologies Laboratory Radio Frequency Identification RFID in Nutshell o To Enhance the concept of bar-codes for faster identification of assets (goods, people,
Advanced Automata Theory 4 Games
 Advanced Automata Theory 4 Games Frank Stephan Department of Computer Science Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore fstephan@comp.nus.edu.sg Advanced Automata Theory 4 Games p. 1 Repetition
Advanced Automata Theory 4 Games Frank Stephan Department of Computer Science Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore fstephan@comp.nus.edu.sg Advanced Automata Theory 4 Games p. 1 Repetition
EECS 461, Winter 2009, Problem Set 2 1
 EECS 46, Winter 29, Problem Set 2 issued: Wednesday, January 28, 29 due: Wednesday, February 4, 29.. In all sensor interfacing, it is necessary to minimize the response of the system to noise in the measurements.
EECS 46, Winter 29, Problem Set 2 issued: Wednesday, January 28, 29 due: Wednesday, February 4, 29.. In all sensor interfacing, it is necessary to minimize the response of the system to noise in the measurements.
Raster Based Region Growing
 6th New Zealand Image Processing Workshop (August 99) Raster Based Region Growing Donald G. Bailey Image Analysis Unit Massey University Palmerston North ABSTRACT In some image segmentation applications,
6th New Zealand Image Processing Workshop (August 99) Raster Based Region Growing Donald G. Bailey Image Analysis Unit Massey University Palmerston North ABSTRACT In some image segmentation applications,
Thank you, Honorable Chairperson- Being a good team member
 Session 32 Thank you, Honorable Chairperson- Being a good team member WHOSE FUTURE GOAL 22: You will learn how to plan for a successful Welcome back! You re one step closer to taking more control in your
Session 32 Thank you, Honorable Chairperson- Being a good team member WHOSE FUTURE GOAL 22: You will learn how to plan for a successful Welcome back! You re one step closer to taking more control in your
DISTRIBUTED DYNAMIC CHANNEL ALLOCATION ALGORITHM FOR CELLULAR MOBILE NETWORK
 DISTRIBUTED DYNAMIC CHANNEL ALLOCATION ALGORITHM FOR CELLULAR MOBILE NETWORK 1 Megha Gupta, 2 A.K. Sachan 1 Research scholar, Deptt. of computer Sc. & Engg. S.A.T.I. VIDISHA (M.P) INDIA. 2 Asst. professor,
DISTRIBUTED DYNAMIC CHANNEL ALLOCATION ALGORITHM FOR CELLULAR MOBILE NETWORK 1 Megha Gupta, 2 A.K. Sachan 1 Research scholar, Deptt. of computer Sc. & Engg. S.A.T.I. VIDISHA (M.P) INDIA. 2 Asst. professor,
Intermittent transient earth fault protection
 Intermittent transient earth fault protection The directional intermittent transient earth fault protection is used to detect short intermittent transient faults in compensated cable networks (figure 3).
Intermittent transient earth fault protection The directional intermittent transient earth fault protection is used to detect short intermittent transient faults in compensated cable networks (figure 3).
Learning Outcomes. Spiral 2 3. DeMorgan Equivalents NEGATIVE (ACTIVE LO) LOGIC. Negative Logic One hot State Assignment System Design Examples
 2-3. Learning Outcomes 2-3.2 Spiral 2 3 Negative Logic One hot State Assignment System Design Examples I understand the active low signal convention and how to interface circuits that use both active high
2-3. Learning Outcomes 2-3.2 Spiral 2 3 Negative Logic One hot State Assignment System Design Examples I understand the active low signal convention and how to interface circuits that use both active high
ECOM 4311 Digital System Design using VHDL. Chapter 9 Sequential Circuit Design: Practice
 ECOM 4311 Digital System Design using VHDL Chapter 9 Sequential Circuit Design: Practice Outline 1. Poor design practice and remedy 2. More counters 3. Register as fast temporary storage 4. Pipelined circuit
ECOM 4311 Digital System Design using VHDL Chapter 9 Sequential Circuit Design: Practice Outline 1. Poor design practice and remedy 2. More counters 3. Register as fast temporary storage 4. Pipelined circuit
Interactive 1 Player Checkers. Harrison Okun December 9, 2015
 Interactive 1 Player Checkers Harrison Okun December 9, 2015 1 Introduction The goal of our project was to allow a human player to move physical checkers pieces on a board, and play against a computer's
Interactive 1 Player Checkers Harrison Okun December 9, 2015 1 Introduction The goal of our project was to allow a human player to move physical checkers pieces on a board, and play against a computer's
Game Mechanics Minesweeper is a game in which the player must correctly deduce the positions of
 Table of Contents Game Mechanics...2 Game Play...3 Game Strategy...4 Truth...4 Contrapositive... 5 Exhaustion...6 Burnout...8 Game Difficulty... 10 Experiment One... 12 Experiment Two...14 Experiment Three...16
Table of Contents Game Mechanics...2 Game Play...3 Game Strategy...4 Truth...4 Contrapositive... 5 Exhaustion...6 Burnout...8 Game Difficulty... 10 Experiment One... 12 Experiment Two...14 Experiment Three...16
Increasing Broadcast Reliability for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks. Nathan Balon and Jinhua Guo University of Michigan - Dearborn
 Increasing Broadcast Reliability for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Nathan Balon and Jinhua Guo University of Michigan - Dearborn I n t r o d u c t i o n General Information on VANETs Background on 802.11 Background
Increasing Broadcast Reliability for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Nathan Balon and Jinhua Guo University of Michigan - Dearborn I n t r o d u c t i o n General Information on VANETs Background on 802.11 Background
Eleventh Annual Ohio Wesleyan University Programming Contest April 1, 2017 Rules: 1. There are six questions to be completed in four hours. 2.
 Eleventh Annual Ohio Wesleyan University Programming Contest April 1, 217 Rules: 1. There are six questions to be completed in four hours. 2. All questions require you to read the test data from standard
Eleventh Annual Ohio Wesleyan University Programming Contest April 1, 217 Rules: 1. There are six questions to be completed in four hours. 2. All questions require you to read the test data from standard
Class Project: Low power Design of Electronic Circuits (ELEC 6970) 1
 Power Minimization using Voltage reduction and Parallel Processing Sudheer Vemula Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn, AL. Goal of the project:- To reduce the power consumed
Power Minimization using Voltage reduction and Parallel Processing Sudheer Vemula Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn, AL. Goal of the project:- To reduce the power consumed
Network-Wide Broadcast
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Lecture 10 6.895: Advanced Distributed Algorithms March 15, 2006 Professor Nancy Lynch Network-Wide Broadcast These notes cover the first of two lectures given on
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Lecture 10 6.895: Advanced Distributed Algorithms March 15, 2006 Professor Nancy Lynch Network-Wide Broadcast These notes cover the first of two lectures given on
In this lecture, we will first examine practical digital signals. Then we will discuss the timing constraints in digital systems.
 1 In this lecture, we will first examine practical digital signals. Then we will discuss the timing constraints in digital systems. The important concepts are related to setup and hold times of registers
1 In this lecture, we will first examine practical digital signals. Then we will discuss the timing constraints in digital systems. The important concepts are related to setup and hold times of registers
Student Outcomes. Classwork. Exercise 1 (3 minutes) Discussion (3 minutes)
 Student Outcomes Students learn that when lines are translated they are either parallel to the given line, or the lines coincide. Students learn that translations map parallel lines to parallel lines.
Student Outcomes Students learn that when lines are translated they are either parallel to the given line, or the lines coincide. Students learn that translations map parallel lines to parallel lines.
MIDTERM REVIEW INDU 421 (Fall 2013)
 MIDTERM REVIEW INDU 421 (Fall 2013) Problem #1: A job shop has received on order for high-precision formed parts. The cost of producing each part is estimated to be $65,000. The customer requires that
MIDTERM REVIEW INDU 421 (Fall 2013) Problem #1: A job shop has received on order for high-precision formed parts. The cost of producing each part is estimated to be $65,000. The customer requires that
64/256/512/1K/2K/4K/8K x 9 Synchronous FIFOs
 241/42 fax id: 549 CY7C4421/421/4211/4221 64/256/512/1K/2K/4K/8K x 9 Synchronous FIFOs Features High-speed, low-power, first-in, first-out (FIFO) memories 64 x 9 (CY7C4421) 256 x 9 (CY7C421) 512 x 9 (CY7C4211)
241/42 fax id: 549 CY7C4421/421/4211/4221 64/256/512/1K/2K/4K/8K x 9 Synchronous FIFOs Features High-speed, low-power, first-in, first-out (FIFO) memories 64 x 9 (CY7C4421) 256 x 9 (CY7C421) 512 x 9 (CY7C4211)
CS269I: Incentives in Computer Science Lecture #20: Fair Division
 CS69I: Incentives in Computer Science Lecture #0: Fair Division Tim Roughgarden December 7, 016 1 Cake Cutting 1.1 Properties of the Cut and Choose Protocol For our last lecture we embark on a nostalgia
CS69I: Incentives in Computer Science Lecture #0: Fair Division Tim Roughgarden December 7, 016 1 Cake Cutting 1.1 Properties of the Cut and Choose Protocol For our last lecture we embark on a nostalgia
VCXO Basics David Green & Anthony Scalpi
 VCXO Basics David Green & Anthony Scalpi Overview VCXO, or Voltage Controlled Crystal Oscillators are wonderful devices they function in feedback systems to pull the crystal operating frequency to meet
VCXO Basics David Green & Anthony Scalpi Overview VCXO, or Voltage Controlled Crystal Oscillators are wonderful devices they function in feedback systems to pull the crystal operating frequency to meet
MAT Modular arithmetic and number theory. Modular arithmetic
 Modular arithmetic 1 Modular arithmetic may seem like a new and strange concept at first The aim of these notes is to describe it in several different ways, in the hope that you will find at least one
Modular arithmetic 1 Modular arithmetic may seem like a new and strange concept at first The aim of these notes is to describe it in several different ways, in the hope that you will find at least one
- A CONSOLIDATED PROPOSAL FOR TERMINOLOGY
 ANONYMITY, UNLINKABILITY, UNDETECTABILITY, UNOBSERVABILITY, PSEUDONYMITY, AND IDENTITY MANAGEMENT - A CONSOLIDATED PROPOSAL FOR TERMINOLOGY Andreas Pfitzmann and Marit Hansen Version v0.31, Feb. 15, 2008
ANONYMITY, UNLINKABILITY, UNDETECTABILITY, UNOBSERVABILITY, PSEUDONYMITY, AND IDENTITY MANAGEMENT - A CONSOLIDATED PROPOSAL FOR TERMINOLOGY Andreas Pfitzmann and Marit Hansen Version v0.31, Feb. 15, 2008
Math for Economics 1 New York University FINAL EXAM, Fall 2013 VERSION A
 Math for Economics 1 New York University FINAL EXAM, Fall 2013 VERSION A Name: ID: Circle your instructor and lecture below: Jankowski-001 Jankowski-006 Ramakrishnan-013 Read all of the following information
Math for Economics 1 New York University FINAL EXAM, Fall 2013 VERSION A Name: ID: Circle your instructor and lecture below: Jankowski-001 Jankowski-006 Ramakrishnan-013 Read all of the following information
Mobility Tolerant Broadcast in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks
 Mobility Tolerant Broadcast in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Pradip K Srimani 1 and Bhabani P Sinha 2 1 Department of Computer Science, Clemson University, Clemson, SC 29634 0974 2 Electronics Unit, Indian Statistical
Mobility Tolerant Broadcast in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks Pradip K Srimani 1 and Bhabani P Sinha 2 1 Department of Computer Science, Clemson University, Clemson, SC 29634 0974 2 Electronics Unit, Indian Statistical
performance modeling. He is a subject area editor of the Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, an associate editor
 VLR at the last HLR checkpointing). Thus, the expected number of HLR records need to be updated (with respect to the VLR) in the HLR restoration process is X E[N U ] = np n (7) 0n1 Let E[N V ] be the expected
VLR at the last HLR checkpointing). Thus, the expected number of HLR records need to be updated (with respect to the VLR) in the HLR restoration process is X E[N U ] = np n (7) 0n1 Let E[N V ] be the expected
First Name: Last Name: Lab Cover Page. Teaching Assistant to whom you are submitting
 Student Information First Name School of Computer Science Faculty of Engineering and Computer Science Last Name Student ID Number Lab Cover Page Please complete all (empty) fields: Course Name: DIGITAL
Student Information First Name School of Computer Science Faculty of Engineering and Computer Science Last Name Student ID Number Lab Cover Page Please complete all (empty) fields: Course Name: DIGITAL
Interference-Aware Joint Routing and TDMA Link Scheduling for Static Wireless Networks
 Interference-Aware Joint Routing and TDMA Link Scheduling for Static Wireless Networks Yu Wang Weizhao Wang Xiang-Yang Li Wen-Zhan Song Abstract We study efficient interference-aware joint routing and
Interference-Aware Joint Routing and TDMA Link Scheduling for Static Wireless Networks Yu Wang Weizhao Wang Xiang-Yang Li Wen-Zhan Song Abstract We study efficient interference-aware joint routing and
Deriving Distributed Algorithms from a General Predicate. Detector. J. Roger Mitchell Vijay K. Garg y. The University of Texas at Austin,
 Derivin Distributed Alorithms from a General Predicate Detector J. Roer Mitchell Vijay K. Gar y Parallel and Distributed Systems Lab http://maple.ece.utexas.edu Electrical and Computer Enineerin Department
Derivin Distributed Alorithms from a General Predicate Detector J. Roer Mitchell Vijay K. Gar y Parallel and Distributed Systems Lab http://maple.ece.utexas.edu Electrical and Computer Enineerin Department
18 Completeness and Compactness of First-Order Tableaux
 CS 486: Applied Logic Lecture 18, March 27, 2003 18 Completeness and Compactness of First-Order Tableaux 18.1 Completeness Proving the completeness of a first-order calculus gives us Gödel s famous completeness
CS 486: Applied Logic Lecture 18, March 27, 2003 18 Completeness and Compactness of First-Order Tableaux 18.1 Completeness Proving the completeness of a first-order calculus gives us Gödel s famous completeness
Bisimulation and Modal Logic in Distributed Computing
 Bisimulation and Modal Logic in Distributed Computing Tuomo Lempiäinen Distributed Algorithms group, Department of Computer Science, Aalto University (joint work with Lauri Hella, Matti Järvisalo, Antti
Bisimulation and Modal Logic in Distributed Computing Tuomo Lempiäinen Distributed Algorithms group, Department of Computer Science, Aalto University (joint work with Lauri Hella, Matti Järvisalo, Antti
SPORTident BSF8 stations
 SPORTident BSF8 stations Firmware 6.56 and higher Release notes Product features The SPORTident-Station BSF8 is based on an advanced hardware core. The design offers a number of significant improvements
SPORTident BSF8 stations Firmware 6.56 and higher Release notes Product features The SPORTident-Station BSF8 is based on an advanced hardware core. The design offers a number of significant improvements
Real-Time Digital Image Exposure Status Detection and Circuit Implementation
 Real-Time igital Image Exposure Status etection and Circuit Implementation Li Hongqin School of Electronic and Electrical Engineering Shanghai University of Engineering Science Zhang Liping School of Electronic
Real-Time igital Image Exposure Status etection and Circuit Implementation Li Hongqin School of Electronic and Electrical Engineering Shanghai University of Engineering Science Zhang Liping School of Electronic
Computer Science 1001.py. Lecture 25 : Intro to Error Correction and Detection Codes
 Computer Science 1001.py Lecture 25 : Intro to Error Correction and Detection Codes Instructors: Daniel Deutch, Amiram Yehudai Teaching Assistants: Michal Kleinbort, Amir Rubinstein School of Computer
Computer Science 1001.py Lecture 25 : Intro to Error Correction and Detection Codes Instructors: Daniel Deutch, Amiram Yehudai Teaching Assistants: Michal Kleinbort, Amir Rubinstein School of Computer
CSE 237A Winter 2018 Homework 1
 CSE 237A Winter 2018 Homework 1 Problem 1 [10 pts] a) As discussed in the lecture, ARM based systems are widely used in the embedded computing. Choose one embedded application and compare features (e.g.,
CSE 237A Winter 2018 Homework 1 Problem 1 [10 pts] a) As discussed in the lecture, ARM based systems are widely used in the embedded computing. Choose one embedded application and compare features (e.g.,
5.4 Imperfect, Real-Time Decisions
 116 5.4 Imperfect, Real-Time Decisions Searching through the whole (pruned) game tree is too inefficient for any realistic game Moves must be made in a reasonable amount of time One has to cut off the
116 5.4 Imperfect, Real-Time Decisions Searching through the whole (pruned) game tree is too inefficient for any realistic game Moves must be made in a reasonable amount of time One has to cut off the
PROBLEM SET 1 1. (Geanokoplos, 1992) Imagine three girls sitting in a circle, each wearing either a red hat or a white hat. Each girl can see the colo
 PROBLEM SET 1 1. (Geanokoplos, 1992) Imagine three girls sitting in a circle, each wearing either a red hat or a white hat. Each girl can see the color of the hat of the other two girls, but not the color
PROBLEM SET 1 1. (Geanokoplos, 1992) Imagine three girls sitting in a circle, each wearing either a red hat or a white hat. Each girl can see the color of the hat of the other two girls, but not the color
Multiple Transient Faults in Combinational and Sequential Circuits: A Systematic Approach
 5847 1 Multiple Transient Faults in Combinational and Sequential Circuits: A Systematic Approach Natasa Miskov-Zivanov, Member, IEEE, Diana Marculescu, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract Transient faults in
5847 1 Multiple Transient Faults in Combinational and Sequential Circuits: A Systematic Approach Natasa Miskov-Zivanov, Member, IEEE, Diana Marculescu, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract Transient faults in
UCS-805 MOBILE COMPUTING NIT Agartala, Dept of CSE Jan-May,2011
 Location Management for Mobile Cellular Systems SLIDE #3 UCS-805 MOBILE COMPUTING NIT Agartala, Dept of CSE Jan-May,2011 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com
Location Management for Mobile Cellular Systems SLIDE #3 UCS-805 MOBILE COMPUTING NIT Agartala, Dept of CSE Jan-May,2011 ALAK ROY. Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE NIT Agartala Email-alakroy.nerist@gmail.com
Exercises for Introduction to Game Theory SOLUTIONS
 Exercises for Introduction to Game Theory SOLUTIONS Heinrich H. Nax & Bary S. R. Pradelski March 19, 2018 Due: March 26, 2018 1 Cooperative game theory Exercise 1.1 Marginal contributions 1. If the value
Exercises for Introduction to Game Theory SOLUTIONS Heinrich H. Nax & Bary S. R. Pradelski March 19, 2018 Due: March 26, 2018 1 Cooperative game theory Exercise 1.1 Marginal contributions 1. If the value
FLDIGI Users Manual: WEFAX
 w1hkj.com 10-13 minutes This modem is able to receive and transmit HF-Fax images, traditionally used for weather reports. More technical information is available on the wikipedia article Radiofax. Two
w1hkj.com 10-13 minutes This modem is able to receive and transmit HF-Fax images, traditionally used for weather reports. More technical information is available on the wikipedia article Radiofax. Two
Link State Routing. In particular OSPF. dr. C. P. J. Koymans. Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam. March 4, 2008
 Link State Routing In particular OSPF dr. C. P. J. Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam March 4, 2008 dr. C. P. J. Koymans (UvA) Link State Routing March 4, 2008 1 / 70 1 Link State Protocols
Link State Routing In particular OSPF dr. C. P. J. Koymans Informatics Institute University of Amsterdam March 4, 2008 dr. C. P. J. Koymans (UvA) Link State Routing March 4, 2008 1 / 70 1 Link State Protocols
FREQUENCY AND TIME SYNCHRONIZATION IN DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS NETWORKS
 FREQUENCY AND TIME SYNCHRONIZATION IN DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS NETWORKS M. Kihara and K. Hisadome Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation 1-2356, Take, Yokosuka-shi Kanagawa 23 8-03, Japan ABSTRACT Frequency
FREQUENCY AND TIME SYNCHRONIZATION IN DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS NETWORKS M. Kihara and K. Hisadome Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corporation 1-2356, Take, Yokosuka-shi Kanagawa 23 8-03, Japan ABSTRACT Frequency
Computer Facilities and Network Management BUS3150 Assignment 1
 Computer Facilities and Network Management BUS3150 Assignment 1 Due date: Friday 1st September 2006 (Week 7) This Assignment has 6 questions, and you should complete answers for all 6. The Assignment contributes
Computer Facilities and Network Management BUS3150 Assignment 1 Due date: Friday 1st September 2006 (Week 7) This Assignment has 6 questions, and you should complete answers for all 6. The Assignment contributes
BMT 2018 Combinatorics Test Solutions March 18, 2018
 . Bob has 3 different fountain pens and different ink colors. How many ways can he fill his fountain pens with ink if he can only put one ink in each pen? Answer: 0 Solution: He has options to fill his
. Bob has 3 different fountain pens and different ink colors. How many ways can he fill his fountain pens with ink if he can only put one ink in each pen? Answer: 0 Solution: He has options to fill his
UMLEmb: UML for Embedded Systems. II. Modeling in SysML. Eurecom
 UMLEmb: UML for Embedded Systems II. Modeling in SysML Ludovic Apvrille ludovic.apvrille@telecom-paristech.fr Eurecom, office 470 http://soc.eurecom.fr/umlemb/ @UMLEmb Eurecom Goals Learning objective
UMLEmb: UML for Embedded Systems II. Modeling in SysML Ludovic Apvrille ludovic.apvrille@telecom-paristech.fr Eurecom, office 470 http://soc.eurecom.fr/umlemb/ @UMLEmb Eurecom Goals Learning objective
Technical framework of Operating System using Turing Machines
 Reviewed Paper Technical framework of Operating System using Turing Machines Paper ID IJIFR/ V2/ E2/ 028 Page No 465-470 Subject Area Computer Science Key Words Turing, Undesirability, Complexity, Snapshot
Reviewed Paper Technical framework of Operating System using Turing Machines Paper ID IJIFR/ V2/ E2/ 028 Page No 465-470 Subject Area Computer Science Key Words Turing, Undesirability, Complexity, Snapshot
Cutting a Pie Is Not a Piece of Cake
 Cutting a Pie Is Not a Piece of Cake Julius B. Barbanel Department of Mathematics Union College Schenectady, NY 12308 barbanej@union.edu Steven J. Brams Department of Politics New York University New York,
Cutting a Pie Is Not a Piece of Cake Julius B. Barbanel Department of Mathematics Union College Schenectady, NY 12308 barbanej@union.edu Steven J. Brams Department of Politics New York University New York,
5.4 Imperfect, Real-Time Decisions
 5.4 Imperfect, Real-Time Decisions Searching through the whole (pruned) game tree is too inefficient for any realistic game Moves must be made in a reasonable amount of time One has to cut off the generation
5.4 Imperfect, Real-Time Decisions Searching through the whole (pruned) game tree is too inefficient for any realistic game Moves must be made in a reasonable amount of time One has to cut off the generation
1 2-step and other basic conditional probability problems
 Name M362K Exam 2 Instructions: Show all of your work. You do not have to simplify your answers. No calculators allowed. 1 2-step and other basic conditional probability problems 1. Suppose A, B, C are
Name M362K Exam 2 Instructions: Show all of your work. You do not have to simplify your answers. No calculators allowed. 1 2-step and other basic conditional probability problems 1. Suppose A, B, C are
Strategic Bargaining. This is page 1 Printer: Opaq
 16 This is page 1 Printer: Opaq Strategic Bargaining The strength of the framework we have developed so far, be it normal form or extensive form games, is that almost any well structured game can be presented
16 This is page 1 Printer: Opaq Strategic Bargaining The strength of the framework we have developed so far, be it normal form or extensive form games, is that almost any well structured game can be presented
IOT GEOLOCATION NEW TECHNICAL AND ECONOMICAL OPPORTUNITIES
 IOT GEOLOCATION NEW TECHNICAL AND ECONOMICAL OPPORTUNITIES Florian LECLERE f.leclere@kerlink.fr EOT Conference Herning 2017 November 1st, 2017 AGENDA 1 NEW IOT PLATFORM LoRa LPWAN Platform Geolocation
IOT GEOLOCATION NEW TECHNICAL AND ECONOMICAL OPPORTUNITIES Florian LECLERE f.leclere@kerlink.fr EOT Conference Herning 2017 November 1st, 2017 AGENDA 1 NEW IOT PLATFORM LoRa LPWAN Platform Geolocation
3432 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 53, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2007
 3432 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL 53, NO 10, OCTOBER 2007 Resource Allocation for Wireless Fading Relay Channels: Max-Min Solution Yingbin Liang, Member, IEEE, Venugopal V Veeravalli, Fellow,
3432 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL 53, NO 10, OCTOBER 2007 Resource Allocation for Wireless Fading Relay Channels: Max-Min Solution Yingbin Liang, Member, IEEE, Venugopal V Veeravalli, Fellow,
Modulating control valve
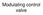 Modulating control valve Automatic modulating valve Automatic modulating valve Diaphragm Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Air filter regulator gauge = AIRSET BALL VALVE GLOBE
Modulating control valve Automatic modulating valve Automatic modulating valve Diaphragm Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Pneumatic Actuator Positioner Air filter regulator gauge = AIRSET BALL VALVE GLOBE
EE595S: Class Lecture Notes Chapter 13: Fully Controlled 3-Phase Bridge Converters. S.D. Sudhoff. Fall 2005
 EE595S: Class Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Fully Controlled 3-Phase Bridge Converters S.D. Sudhoff Fall 2005 3.2 Fully Controlled 3-Phase Bridge Converter Fall 2005 EE595S Electric Drive Systems 2 One Phase
EE595S: Class Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Fully Controlled 3-Phase Bridge Converters S.D. Sudhoff Fall 2005 3.2 Fully Controlled 3-Phase Bridge Converter Fall 2005 EE595S Electric Drive Systems 2 One Phase
Low-Latency Multi-Source Broadcast in Radio Networks
 Low-Latency Multi-Source Broadcast in Radio Networks Scott C.-H. Huang City University of Hong Kong Hsiao-Chun Wu Louisiana State University and S. S. Iyengar Louisiana State University In recent years
Low-Latency Multi-Source Broadcast in Radio Networks Scott C.-H. Huang City University of Hong Kong Hsiao-Chun Wu Louisiana State University and S. S. Iyengar Louisiana State University In recent years
Cardinality revisited
 Cardinality revisited A set is finite (has finite cardinality) if its cardinality is some (finite) integer n. Two sets A,B have the same cardinality iff there is a one-to-one correspondence from A to B
Cardinality revisited A set is finite (has finite cardinality) if its cardinality is some (finite) integer n. Two sets A,B have the same cardinality iff there is a one-to-one correspondence from A to B
Temptation. Temptation. Temptation. Temptation. Temptation START. Lose A Turn. Go Back 1. Move Ahead 1. Roll Again. Move Ahead 1.
 START Go Back 2 FINISH Ahead 2 Resist The START Go Back 2 FINISH Resist The Directions: The objective of the game is to resist the temptation just like Jesus did. Place your markers on the START square.
START Go Back 2 FINISH Ahead 2 Resist The START Go Back 2 FINISH Resist The Directions: The objective of the game is to resist the temptation just like Jesus did. Place your markers on the START square.
CPA Hybrid Profits Make Thousands A Month With The CPA Hybrid Method!
 CPA Hybrid Profits Make Thousands A Month With The CPA Hybrid Method! Thanks for picking up a copy of my latest CPA report. Promise me that you will read every word of this report and take action with
CPA Hybrid Profits Make Thousands A Month With The CPA Hybrid Method! Thanks for picking up a copy of my latest CPA report. Promise me that you will read every word of this report and take action with
and 6.855J. Network Simplex Animations
 .8 and 6.8J Network Simplex Animations Calculating A Spanning Tree Flow -6 7 6 - A tree with supplies and demands. (Assume that all other arcs have a flow of ) What is the flow in arc (,)? Calculating
.8 and 6.8J Network Simplex Animations Calculating A Spanning Tree Flow -6 7 6 - A tree with supplies and demands. (Assume that all other arcs have a flow of ) What is the flow in arc (,)? Calculating
USER MANUAL SATEL i-link I/O-converter Version 1.6
 USER MANUAL SATEL i-link I/O-converter Version 1.6 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 IMPORTANT NOTICE... 3 PRODUCT CONFORMITY... 4 WARRANTY AND SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS... 5 1 GENERAL... 6 1.1 SATEL
USER MANUAL SATEL i-link I/O-converter Version 1.6 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS... 2 IMPORTANT NOTICE... 3 PRODUCT CONFORMITY... 4 WARRANTY AND SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS... 5 1 GENERAL... 6 1.1 SATEL
Final Exam, Math 6105
 Final Exam, Math 6105 SWIM, June 29, 2006 Your name Throughout this test you must show your work. 1. Base 5 arithmetic (a) Construct the addition and multiplication table for the base five digits. (b)
Final Exam, Math 6105 SWIM, June 29, 2006 Your name Throughout this test you must show your work. 1. Base 5 arithmetic (a) Construct the addition and multiplication table for the base five digits. (b)
p-percent Coverage in Wireless Sensor Networks
 p-percent Coverage in Wireless Sensor Networks Yiwei Wu, Chunyu Ai, Shan Gao and Yingshu Li Department of Computer Science Georgia State University October 28, 2008 1 Introduction 2 p-percent Coverage
p-percent Coverage in Wireless Sensor Networks Yiwei Wu, Chunyu Ai, Shan Gao and Yingshu Li Department of Computer Science Georgia State University October 28, 2008 1 Introduction 2 p-percent Coverage
Hitachi P1 Closed Loop Hoist Basic Instruc on Manual
 Hitachi P1 Closed Loop Hoist Basic Instruc on Manual DH Firmware V.18 DETROIT HOIST AND CRANE LLC, CO. 6650 STERLING DRIVE NORTH STERLING HEIGHTS MICHIGAN 48312 Introduction This manual only applies to
Hitachi P1 Closed Loop Hoist Basic Instruc on Manual DH Firmware V.18 DETROIT HOIST AND CRANE LLC, CO. 6650 STERLING DRIVE NORTH STERLING HEIGHTS MICHIGAN 48312 Introduction This manual only applies to
