Inductive and Deductive Reasoning
|
|
|
- Arlene Rose
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inductive and Deductive Reasoning Name General Outcome Develop algebraic and graphical reasoning through the study of relations Specific Outcomes it is expected that students will: Sample Question Student Evidence 11a.l.1. 11a.l.2. Analyze and prove conjectures, using inductive and deductive reasoning, to solve problems. Analyze puzzles and games that involve spatial reasoning, using problem-solving strategies. Achievement Indicators The following set of indicators may be used to determine whether students have met the corresponding specific outcome 11a.l.1. (it is intended that this outcome be integrated throughout the course) Make conjectures by observing patterns and identifying properties, and justify the reasoning. Explain why inductive reasoning may lead to a false conjecture. Compare, using examples, inductive and deductive reasoning. Provide and explain a counterexample to disprove a conjecture. Prove algebraic and number relationships, such as divisibility rules, number properties, mental mathematics strategies, or algebraic number tricks. Prove a conjecture, using deductive reasoning (not limited to two column proofs). Determine if an argument is valid, and justify the reasoning. identify errors in a proof. Solve a contextual problem involving inductive or deductive reasoning. Sample Question Student Evidence 11a.l.2. (it is intended that this outcome be integrated throughout the course by using sliding, rotation, construction, deconstruction, and similar puzzles and games.) Determine, explain and verify a strategy to solve a puzzle or to win a game such as guess and check look for a pattern make a systematic list draw or model eliminate possibilities simplify the original problem work backward develop alternative approaches Identify and correct errors in a solution to a puzzle or in a strategy for winning a game. Create a variation on a puzzle or a game, and describe a strategy for solving the puzzle or winning the game. 1
2 Lesson 1: Making Conjectures: Inductive Reasoning Conjecture: Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure 3 Figure 4 2
3 Inductive Reasoning: For example: Weather Conjectures Long before weather forecasts based on weather stations and satellites were developed, people had to rely on patterns identified from observation of the environment to make predictions about the weather. (From Nelson Foundations of Math.) Animal behaviour: First Nations peoples predicted spring by watching for migratory birds. If smaller birds are spotted, it is a sign that spring is right around the corner. When the crow is spotted, it is a sign that winter is nearly over. Seagulls tend to stop flying and take refuge at the coast when a storm is coming. Turtles often search for higher ground when they expect a large amount of rain. (Turtles are more likely to be seen on roads as much as 1 to 2 days before rain.) Personal: Many people can feel humidity, especially in their hair (it curls up and gets frizzy). High humidity tends to precede heavy rain. 3
4 For Example: Examine the pattern below. Make a prediction about the next numbers. 1 2 = = = = = = Conjecture: For Example: Examine the pattern in the addends and their sums. What conjecture can you make? = = = = 1 6 Conjecture: 4
5 Using Inductive Reasoning to make a Conjecture For Example: Observing the following 3 figures, what conjecture can you make? Conjecture: For Example: Given the following diagram, can you make a conjecture about the number of triangles? Conjecture: 5
6 For Example: A chord is formed between two points on the circumference of a circle. Use inductive reasoning to come up with a conjecture about the number of points and the chords that can be made. Number of Points Number of Chords Conjecture: 6
7 Lesson 2: Exploring the Validity of Conjectures Using inductive reasoning, some conjectures initially seem to be valid, but are shown not to be valid after more evidence is gathered. A conjecture can be supported or disproved with further evidence. You can revise a conjecture in response to new evidence. Reviewing Lesson 1: Conjectures, what can be done to examine the validity of the conjectures we made? Figure 1: Figure 2: Figure 3: Figure 4: The validity of a conjecture can be strengthened by providing more supporting evidence/examples or a tool or device (i.e. such as a ruler, straight edge, etc.). For Example: Are the horizontal lines in this diagram straight or curved? Make a conjecture. Then, check the validity of your conjecture. Conjecture: Checking Validity? 7
8 For Example: Make a conjecture about this pattern. How can you check the validity of your conjecture? = = = = Conjecture: Checking Validity? 8
9 Lesson 3: Using Reasoning to Find a Counterexample to a Conjecture Counterexample: For Example: Examine this pattern in the product of 11 and another two-digit number. 11 X 11 = X 11 = X 11 = X 11 = 473 What conjecture can you make about the pattern? How can you check whether your conjecture is true? Can you come up with a new conjecture? *Counterexamples invalidate conjectures leading to either disgarding or revising the original conjecture. 9
10 Remember the Example: A chord is formed between two points on the circumference of a circle. Use inductive reasoning to come up with a conjecture about the number of points and the chords that can be made. When a chord is formed, it divides the circle into two regions. Use inductive reasoning to come up with a conjecture about the number of points, the number of chords, and/or the regions that can be made. Solution: Number of Points Number of Chords Number of Regions What conjecture can you make about the pattern? Careful, try 6 points Is this more evidence to support your conjecture or a counter example? 10
11 For Example: Jessica stated that: a b = b a. a) Find an example to show that her conjecture is reasonable. b) Find a counterexample to prove that the conjecture is false. For Example: Ryan concluded that whenever he added two prime numbers, the sum was always even. Find a counter example to prove that Ryan s conjecture is false. For Example: Give a counterexample to disprove the following statements: a) All prime numbers are odd. b) A quadrilateral with a pair of parallel sides is a parallelogram. c) If four vertices of a quadrilateral lie on the same circle, then the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. 11
12 Lesson 4: Proving Conjectures: Deductive Reasoning Proof: Generalization: Deductive Reasoning: Transitive Property: Transitive Property Example: Use deductive reasoning to make a conclusion from these statements: All koalas are marsupials. All marsupials are mammals. All mammals are warm-blooded. Barney is a koala. Solution: 12
13 For Example: All Vincent Massey students are cool. James is a Vincent Massey student. Therefore, For Example: Anyone who likes to play badminton likes to play tennis. Jeff likes to play badminton. Therefore, For Example: All students in Gr. 12 must enroll in English. Tracy is a Gr. 12 student. Therefore, 13
14 Using Algebra to Prove Deductive Reasoning: Use deductive reasoning to prove that: "Whenever you square an odd integer, the result is odd." Solution: How do you represent an even integer? an odd integer? Using existing Mathematical Rules and Proofs to Prove Deductive Reasoning arguments: Show deductively that the sum of the measures a, b, and c is 180 o. Solution: a) Draw a triangle and label the inside angles, a, b, and c. b) Use one side as a base and draw a parallel line segment on the opposite vertex. c) Use the known fact that interior opposite angles are equal to show which angles are congruent. And since supplementary angles equal 180, and c is included in both, therefore, the sum of the interior angles of the triangle (a + c + b) also equals 180 o. 14
15 Inductive or Deductive: Which of the conclusions below are valid? a) The sun will rise tomorrow? b) All Vincent Massey students love their calculators. Anyone who hates their calculator must not be a Vincent Massey student. c) There will be snow at Christmas time. d) 3x = 15, x = 5 e) There will be at least one big flood in Winnipeg every 100 years. f) The radius of a circle is 5cm. The area of that circle is 25 cm 2. g) There is a full moon once a month. h) Every time I have a hockey game, I have a test the following day. i) During a statistics project, Jeanine counted the number of cars of different colours that passed her school in 20 minutes. More than half the cars were red. She decided that red is the most popular colour for cars. j) Triangle ABC is an equilateral triangle. We conclude that AB AC. 15
16 Lesson 5: Proofs That Are Not Valid Proving Something Invalid: Premise: Circular Reasoning: Examples: 1. What type of error occurs in this deduction? All people over 65 are retired. Corbin is over 65, so he is retired. 2. What type of error occurs in this deduction? All runners can go one mile without stopping. Tim is a runner. Therefore, Tim can run one mile without stopping Errors in Proofs 3. What type of error occurs in this deduction? 6 = 6 2.5(6) = 2.5(3 + 3) 2.5(6) + 1 = 2.5(3 + 3) = =
17 4. What type of error occurs in this deduction? A is true because B is true; B is true because A is true 5. What type of error occurs in this deduction? Joe: Are electrolytes good for you? Jill: Yeah, they are in Gatorade. Joe: Oh, so is Gatorade good for you? Jill: Yeah, it has got electrolytes. 6. What type of error occurs in this deduction? Let: a = b = 1 To prove: 2 = 0 Proof: a = b a 2 = b 2 a 2 - b 2 = 0 Same operation on both sides Move b 2 to the other side But: a = b = 1 (a - b)(a + b) = 0 Factor a Difference of Squares (a - b)(a + b) = Same operation on both sides (a - b) (a - b) (a + b) = 0 Simplify Therefore: = 0 Substitution 2 = 0 17
18 Lesson 6: Reasoning to Solve Problems Logic Puzzles For Example: Ten cards, numbered from 0 to 9, are divided among five envelopes, with two cards in each envelope. Each envelope shows the sum of the cards inside it. The envelope marked 10 contains the 6 card. The envelope marked 14 contains the 5 card. What pairs of cards does each envelope contain? Explain. Solution:
19 For Example: In the Prisoner s Dilemma, two prisoners are being held by the authorities in separate interrogation rooms. Each prisoner has the same options: he or she can cooperate with the other prisoner by remaining silent, or defect, confessing to the authorities. The results of cooperating or defecting depend on what both prisoners do. If both prisoners cooperate, they are each sentenced to 1 year in prison. If both prisoners defect, they are each sentenced to 3 years. If one prisoner cooperates and the other defects, the defector is sentenced to 6 months and the cooperative prisoner is sentenced to 10 years. a) What would be the best thing for the prisoners to do, and what sentence would they get, if each knew the others decision? b) What do you think the prisoners will actually do, and what sentence will they get, given that they do not know the other's decision? 19
20 Lesson 7: Analyzing Puzzles and Games SUDOKU PUZZLES To solve a Sudoku puzzle: Fill in each empty square with a number from 1 to 9. A number cannot appear twice in a column, row, or 3 X 3 block square. What numbers go in squares A and B of this Sudoku puzzle? 20
21 More Sudoku Puzzles Each number must appear in every row, column and block only once. In the smaller sudoku, use the numbers from 1 to 6, In the larger Sudoku, use the digits 1 to 9. MAGIC SQUARE PUZZLES Fill in the missing numbers, from 1 to 9, so that the sum of the numbers in each row, column, and diagonal is
22 KAKURO PUZZLES To solve a Kakuro puzzle: Fill in each empty square with a number from 1 to 9. Each row must add up to the circled number on the left. Each column must add up to the circled number above. A number cannot appear twice in the same row or column. 22
23 KENKEN PUZZLES To solve a KenKen puzzle: Use only the numbers from 1 to 6. Each number must appear in every row and column. A number may be repeated in a cage(dark outlines), but not a row or column. Use numbers which give the target in each cage by using the given operation. 5 and 6 give a product of 30. 5? 6? 23
24 PASCAL S TRIANGLE Recursive pattern - The numbers are the sum total of the two numbers above it Using Pascal s Triangle to solve the maze: How many ways can the mouse navigate the maze to reach the trail mix, if the mouse can only travel down? 24
25 Inductive and Deductive Reasoning - CHAPTER 1 TEST Name Date 1. Hilary was examining the differences between perfect squares of numbers separated by 5. She made the following conjecture: The differences always have the digit 5 in the ones place. For example: = = 145 a) Gather evidence to support Hilary s conjecture. b) Is her conjecture reasonable? Explain. 2. Denyse works part time at a grocery store. She notices that the store is very busy when she works in the afternoon from 4 to 7 p.m., but it is less busy when she works in the evening from 7 to 10 p.m. What conjecture can you make for this situation? Justify your conjecture. 25
26 3. Heather claimed that the sum of two multiples of 4 is a multiple of 8. Is Heather s conjecture reasonable? Explain. If it is not reasonable, find a counterexample. 4. Prove that the sum of two consecutive perfect squares is always an odd number. 5. Prove that the following number trick will always result in 6: Choose any number. Add 3. Multiply by 2. Add 6. Divide by 2. Subtract your starting number. 26
27 6. Judd presented the following argument: Inuvik, Northwest Territories, is above the Arctic Circle, which is at a latitude of 66 north of the equator. Places north of the Arctic Circle have cold, snowy winters. Winnipeg is at a latitude of 52 north of the equator. Therefore, Winnipeg does not have cold, snowy winters. Is Judd s argument reasonable? If not, identify the errors in his reasoning. 7. Is this proof valid? Explain. 8. Fill in the circles with the appropriate numbers to make the puzzle work
FOM 11 Ch. 1 Practice Test Name: Inductive and Deductive Reasoning
 FOM 11 Ch. 1 Practice Test Name: Inductive and Deductive Reasoning Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Justin gathered the following evidence.
FOM 11 Ch. 1 Practice Test Name: Inductive and Deductive Reasoning Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Justin gathered the following evidence.
FOM 11 Ch. 1 Practice Test Name: Inductive and Deductive Reasoning
 FOM 11 Ch. 1 Practice Test Name: Inductive and Deductive Reasoning Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Justin gathered the following evidence.
FOM 11 Ch. 1 Practice Test Name: Inductive and Deductive Reasoning Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Justin gathered the following evidence.
Ideas beyond Number. Activity worksheets
 Ideas beyond Number Activity sheet 1 Task 1 Some students started to solve this equation in different ways: For each statement tick True or False: = = = = Task 2: Counter-examples The exception disproves
Ideas beyond Number Activity sheet 1 Task 1 Some students started to solve this equation in different ways: For each statement tick True or False: = = = = Task 2: Counter-examples The exception disproves
2 Reasoning and Proof
 www.ck12.org CHAPTER 2 Reasoning and Proof Chapter Outline 2.1 INDUCTIVE REASONING 2.2 CONDITIONAL STATEMENTS 2.3 DEDUCTIVE REASONING 2.4 ALGEBRAIC AND CONGRUENCE PROPERTIES 2.5 PROOFS ABOUT ANGLE PAIRS
www.ck12.org CHAPTER 2 Reasoning and Proof Chapter Outline 2.1 INDUCTIVE REASONING 2.2 CONDITIONAL STATEMENTS 2.3 DEDUCTIVE REASONING 2.4 ALGEBRAIC AND CONGRUENCE PROPERTIES 2.5 PROOFS ABOUT ANGLE PAIRS
2Reasoning and Proof. Prerequisite Skills. Before VOCABULARY CHECK SKILLS AND ALGEBRA CHECK
 2Reasoning and Proof 2.1 Use Inductive Reasoning 2.2 Analyze Conditional Statements 2.3 Apply Deductive Reasoning 2.4 Use Postulates and Diagrams 2.5 Reason Using Properties from Algebra 2.6 Prove Statements
2Reasoning and Proof 2.1 Use Inductive Reasoning 2.2 Analyze Conditional Statements 2.3 Apply Deductive Reasoning 2.4 Use Postulates and Diagrams 2.5 Reason Using Properties from Algebra 2.6 Prove Statements
UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet
 Name Period Date UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet 24.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Explore the Pythagorean theorem numerically, algebraically, and geometrically. Understand a proof
Name Period Date UNIT 6: CONJECTURE AND JUSTIFICATION WEEK 24: Student Packet 24.1 The Pythagorean Theorem Explore the Pythagorean theorem numerically, algebraically, and geometrically. Understand a proof
Ideas beyond Number. Teacher s guide to Activity worksheets
 Ideas beyond Number Teacher s guide to Activity worksheets Learning objectives To explore reasoning, logic and proof through practical, experimental, structured and formalised methods of communication
Ideas beyond Number Teacher s guide to Activity worksheets Learning objectives To explore reasoning, logic and proof through practical, experimental, structured and formalised methods of communication
Grade 6 Math Circles March 7/8, Magic and Latin Squares
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles March 7/8, 2017 Magic and Latin Squares Today we will be solving math and logic puzzles!
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles March 7/8, 2017 Magic and Latin Squares Today we will be solving math and logic puzzles!
CK-12 Geometry Inductive Reasoning
 CK-12 Geometry Inductive Reasoning Learning Objectives Recognize visual and number patterns. Extend and generalize patterns. Write a counterexample. Review Queue a. Look at the patterns of numbers below.
CK-12 Geometry Inductive Reasoning Learning Objectives Recognize visual and number patterns. Extend and generalize patterns. Write a counterexample. Review Queue a. Look at the patterns of numbers below.
Step 2: Extend the compass from the chosen endpoint so that the width of the compass is more than half the distance between the two points.
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Test: 9_12 Mathematics Geometry Exam 1 Description: GEO Topic 1 Test: Tools of Geometry Form: 201 1. A student followed the given
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Miami-Dade County Public Schools Test: 9_12 Mathematics Geometry Exam 1 Description: GEO Topic 1 Test: Tools of Geometry Form: 201 1. A student followed the given
Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem
 UNIT 1 Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem Just for Fun What Do You Notice? Follow the steps. An example is given. Example 1. Pick a 4-digit number with different digits. 3078 2. Find the greatest
UNIT 1 Square Roots and the Pythagorean Theorem Just for Fun What Do You Notice? Follow the steps. An example is given. Example 1. Pick a 4-digit number with different digits. 3078 2. Find the greatest
4.1 Patterns. Example 1 Find the patterns:
 4.1 Patterns One definition of mathematics is the study of patterns. In this section, you will practice recognizing mathematical patterns in various problems. For each example, you will work with a partner
4.1 Patterns One definition of mathematics is the study of patterns. In this section, you will practice recognizing mathematical patterns in various problems. For each example, you will work with a partner
Chapter 4: Patterns and Relationships
 Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Chapter : Patterns and Relationships Getting Started, p. 13 1. a) The factors of 1 are 1,, 3,, 6, and 1. The factors of are 1,,, 7, 1, and. The greatest common factor is. b) The factors of 16 are 1,,,,
Warm Up Classify each angle. Holt McDougal Geometry
 Warm Up Classify each angle. Objectives EQ: How do you use inductive reasoning to identify patterns and make conjectures? How do you find counterexamples to disprove conjectures? Unit 2A Day 4 inductive
Warm Up Classify each angle. Objectives EQ: How do you use inductive reasoning to identify patterns and make conjectures? How do you find counterexamples to disprove conjectures? Unit 2A Day 4 inductive
Warm-Up Up Exercises. 1. Find the value of x. ANSWER 32
 Warm-Up Up Exercises 1. Find the value of x. ANSWER 32 2. Write the converse of the following statement. If it is raining, then Josh needs an umbrella. ANSWER If Josh needs an umbrella, then it is raining.
Warm-Up Up Exercises 1. Find the value of x. ANSWER 32 2. Write the converse of the following statement. If it is raining, then Josh needs an umbrella. ANSWER If Josh needs an umbrella, then it is raining.
Connected Mathematics 2, 6th Grade Units (c) 2006 Correlated to: Utah Core Curriculum for Math (Grade 6)
 Core Standards of the Course Standard I Students will acquire number sense and perform operations with rational numbers. Objective 1 Represent whole numbers and decimals in a variety of ways. A. Change
Core Standards of the Course Standard I Students will acquire number sense and perform operations with rational numbers. Objective 1 Represent whole numbers and decimals in a variety of ways. A. Change
Rosen, Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications, 6th edition Extra Examples
 Rosen, Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications, 6th edition Extra Examples Section 1.7 Proof Methods and Strategy Page references correspond to locations of Extra Examples icons in the textbook. p.87,
Rosen, Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications, 6th edition Extra Examples Section 1.7 Proof Methods and Strategy Page references correspond to locations of Extra Examples icons in the textbook. p.87,
Synergy Round. Warming Up. Where in the World? Scrabble With Numbers. Earning a Gold Star
 Synergy Round Warming Up Where in the World? You re standing at a point on earth. After walking a mile north, then a mile west, then a mile south, you re back where you started. Where are you? [4 points]
Synergy Round Warming Up Where in the World? You re standing at a point on earth. After walking a mile north, then a mile west, then a mile south, you re back where you started. Where are you? [4 points]
Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 MATH 121 SPRING 2017 - PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Given that point P is the midpoint of both and, it follows that. 2. If, then. 3. In a circle (or congruent
MATH 121 SPRING 2017 - PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Given that point P is the midpoint of both and, it follows that. 2. If, then. 3. In a circle (or congruent
Mt. Douglas Secondary
 Foundations of Math 11 Section 4.1 Patterns 167 4.1 Patterns We have stated in chapter 2 that patterns are widely used in mathematics to reach logical conclusions. This type of reasoning is called inductive
Foundations of Math 11 Section 4.1 Patterns 167 4.1 Patterns We have stated in chapter 2 that patterns are widely used in mathematics to reach logical conclusions. This type of reasoning is called inductive
Find the coordinates of the midpoint of a segment having the given endpoints.
 G.(2) Coordinate and transformational geometry. The student uses the process skills to understand the connections between algebra and geometry and uses the one- and two-dimensional coordinate systems to
G.(2) Coordinate and transformational geometry. The student uses the process skills to understand the connections between algebra and geometry and uses the one- and two-dimensional coordinate systems to
2-1 Inductive Reasoning and Conjecture
 Write a conjecture that describes the pattern in each sequence. Then use your conjecture to find the next item in the sequence. 18. 1, 4, 9, 16 1 = 1 2 4 = 2 2 9 = 3 2 16 = 4 2 Each element is the square
Write a conjecture that describes the pattern in each sequence. Then use your conjecture to find the next item in the sequence. 18. 1, 4, 9, 16 1 = 1 2 4 = 2 2 9 = 3 2 16 = 4 2 Each element is the square
Suppose that two squares are cut from opposite corners of a chessboard. Can the remaining squares be completely covered by 31 dominoes?
 Chapter 2 Parent Guide Reasoning in Geometry Reasoning is a thinking process that progresses logically from one idea to another. Logical reasoning advances toward a conclusion in such a way as to be understood
Chapter 2 Parent Guide Reasoning in Geometry Reasoning is a thinking process that progresses logically from one idea to another. Logical reasoning advances toward a conclusion in such a way as to be understood
Downloaded from
 Understanding Elementary Shapes 1 1.In the given figure, lines l and m are.. to each other. (A) perpendicular (B) parallel (C) intersect (D) None of them. 2.a) If a clock hand starts from 12 and stops
Understanding Elementary Shapes 1 1.In the given figure, lines l and m are.. to each other. (A) perpendicular (B) parallel (C) intersect (D) None of them. 2.a) If a clock hand starts from 12 and stops
Geometry Benchmark Assessment #1
 Geometry Benchmark Assessment #1 Multiple Choice Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When the net is folded into the rectangular prism shown beside
Geometry Benchmark Assessment #1 Multiple Choice Circle the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. When the net is folded into the rectangular prism shown beside
The problems in this booklet are organized into strands. A problem often appears in multiple strands. The problems are suitable for most students in
 The problems in this booklet are organized into strands. A problem often appears in multiple strands. The problems are suitable for most students in Grade 7 or higher. Problem C Totally Unusual The dice
The problems in this booklet are organized into strands. A problem often appears in multiple strands. The problems are suitable for most students in Grade 7 or higher. Problem C Totally Unusual The dice
Name: Date: Chapter 2 Quiz Geometry. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Date: Chapter 2 Quiz Geometry Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the value of x? Identify the missing justifications.,, and.
Name: Date: Chapter 2 Quiz Geometry Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What is the value of x? Identify the missing justifications.,, and.
Classwork Example 1: Exploring Subtraction with the Integer Game
 7.2.5 Lesson Date Understanding Subtraction of Integers Student Objectives I can justify the rule for subtraction: Subtracting a number is the same as adding its opposite. I can relate the rule for subtraction
7.2.5 Lesson Date Understanding Subtraction of Integers Student Objectives I can justify the rule for subtraction: Subtracting a number is the same as adding its opposite. I can relate the rule for subtraction
Big Ideas Math: A Common Core Curriculum Geometry 2015 Correlated to Common Core State Standards for High School Geometry
 Common Core State s for High School Geometry Conceptual Category: Geometry Domain: The Number System G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment,
Common Core State s for High School Geometry Conceptual Category: Geometry Domain: The Number System G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment,
Grade 6. Prentice Hall. Connected Mathematics 6th Grade Units Alaska Standards and Grade Level Expectations. Grade 6
 Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics 6th Grade Units 2004 Grade 6 C O R R E L A T E D T O Expectations Grade 6 Content Standard A: Mathematical facts, concepts, principles, and theories Numeration: Understand
Prentice Hall Connected Mathematics 6th Grade Units 2004 Grade 6 C O R R E L A T E D T O Expectations Grade 6 Content Standard A: Mathematical facts, concepts, principles, and theories Numeration: Understand
UKMT UKMT UKMT. Junior Kangaroo Mathematical Challenge. Tuesday 13th June 2017
 UKMT UKMT UKMT Junior Kangaroo Mathematical Challenge Tuesday 3th June 207 Organised by the United Kingdom Mathematics Trust The Junior Kangaroo allows students in the UK to test themselves on questions
UKMT UKMT UKMT Junior Kangaroo Mathematical Challenge Tuesday 3th June 207 Organised by the United Kingdom Mathematics Trust The Junior Kangaroo allows students in the UK to test themselves on questions
2.1 inductive reasoning and conjecture ink.notebook. September 07, Page 55. Ch 2. Reasoning. Page 56. and Proofs. 2.1 Inductive.
 2.1 inductive reasoning and conjecture ink.notebook Page 55 Ch 2 Reasoning and Proofs Page 56 2.1 Inductive Reasoning Lesson Objectives Page 57 Standards Lesson Notes Page 58 2.1 Inductive Reasoning and
2.1 inductive reasoning and conjecture ink.notebook Page 55 Ch 2 Reasoning and Proofs Page 56 2.1 Inductive Reasoning Lesson Objectives Page 57 Standards Lesson Notes Page 58 2.1 Inductive Reasoning and
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet
 GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
GPLMS Revision Programme GRADE 6 Booklet Learner s name: School name: Day 1. 1. a) Study: 6 units 6 tens 6 hundreds 6 thousands 6 ten-thousands 6 hundredthousands HTh T Th Th H T U 6 6 0 6 0 0 6 0 0 0
Name Period GEOMETRY CHAPTER 3 Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Section 3.1 Lines and Angles GOAL 1: Relationship between lines
 Name Period GEOMETRY CHAPTER 3 Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Section 3.1 Lines and Angles GOAL 1: Relationship between lines Two lines are if they are coplanar and do not intersect. Skew lines. Two
Name Period GEOMETRY CHAPTER 3 Perpendicular and Parallel Lines Section 3.1 Lines and Angles GOAL 1: Relationship between lines Two lines are if they are coplanar and do not intersect. Skew lines. Two
A natural number is called a perfect cube if it is the cube of some. some natural number.
 A natural number is called a perfect square if it is the square of some natural number. i.e., if m = n 2, then m is a perfect square where m and n are natural numbers. A natural number is called a perfect
A natural number is called a perfect square if it is the square of some natural number. i.e., if m = n 2, then m is a perfect square where m and n are natural numbers. A natural number is called a perfect
Please bring a laptop or tablet next week! Upcoming Assignment Measurement Investigations Patterns & Algebraic Thinking Investigations Break A Few
 Please bring a laptop or tablet next week! Upcoming Assignment Measurement Investigations Patterns & Algebraic Thinking Investigations Break A Few More Investigations Literature Circles Final Lesson Plan
Please bring a laptop or tablet next week! Upcoming Assignment Measurement Investigations Patterns & Algebraic Thinking Investigations Break A Few More Investigations Literature Circles Final Lesson Plan
Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities
 Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Sharon Rendon (605) 431-0216 sharonrendon@cpm.org 1 2-51. SPECIAL
Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Sharon Rendon (605) 431-0216 sharonrendon@cpm.org 1 2-51. SPECIAL
Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary. Correlations
 Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary Correlations Saxon Math Program Page Math K 2 Math 1 8 Math 2 14 California Math K 21 California Math 1 27 California Math 2 33 1 Saxon Math Manipulatives in
Saxon Math Manipulatives in Motion Primary Correlations Saxon Math Program Page Math K 2 Math 1 8 Math 2 14 California Math K 21 California Math 1 27 California Math 2 33 1 Saxon Math Manipulatives in
MAGIC SQUARES KATIE HAYMAKER
 MAGIC SQUARES KATIE HAYMAKER Supplies: Paper and pen(cil) 1. Initial setup Today s topic is magic squares. We ll start with two examples. The unique magic square of order one is 1. An example of a magic
MAGIC SQUARES KATIE HAYMAKER Supplies: Paper and pen(cil) 1. Initial setup Today s topic is magic squares. We ll start with two examples. The unique magic square of order one is 1. An example of a magic
Math + 4 (Red) SEMESTER 1. { Pg. 1 } Unit 1: Whole Number Sense. Unit 2: Whole Number Operations. Unit 3: Applications of Operations
 Math + 4 (Red) This research-based course focuses on computational fluency, conceptual understanding, and problem-solving. The engaging course features new graphics, learning tools, and games; adaptive
Math + 4 (Red) This research-based course focuses on computational fluency, conceptual understanding, and problem-solving. The engaging course features new graphics, learning tools, and games; adaptive
Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring
 Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring Week 1 Title: Alternating chains Children create chains of alternating positive and negative numbers and look at the patterns in their totals. Skill practised:
Year 5 Problems and Investigations Spring Week 1 Title: Alternating chains Children create chains of alternating positive and negative numbers and look at the patterns in their totals. Skill practised:
6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT. Name Period Date
 6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT Name Period Date Perimeter and Area of Triangles and Rectangles The perimeter is the continuous line forming the boundary of a closed geometric figure.
6.00 Trigonometry Geometry/Circles Basics for the ACT Name Period Date Perimeter and Area of Triangles and Rectangles The perimeter is the continuous line forming the boundary of a closed geometric figure.
I followed the steps to work through four examples. Conjecture: It is 3 times. It worked.
 1.6 Reasoning to Solve Problems GOAL Solve problems using inductive or deductive reasoning. INVESTIGATE the Math Emma was given this math trick: Choose a number. Multiply by 6. Add 4. Divide by 2. Subtract
1.6 Reasoning to Solve Problems GOAL Solve problems using inductive or deductive reasoning. INVESTIGATE the Math Emma was given this math trick: Choose a number. Multiply by 6. Add 4. Divide by 2. Subtract
2005 Galois Contest Wednesday, April 20, 2005
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 2005 Galois Contest Wednesday, April 20, 2005 Solutions
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 2005 Galois Contest Wednesday, April 20, 2005 Solutions
California 1 st Grade Standards / Excel Math Correlation by Lesson Number
 California 1 st Grade Standards / Excel Math Correlation by Lesson Lesson () L1 Using the numerals 0 to 9 Sense: L2 Selecting the correct numeral for a Sense: 2 given set of pictures Grouping and counting
California 1 st Grade Standards / Excel Math Correlation by Lesson Lesson () L1 Using the numerals 0 to 9 Sense: L2 Selecting the correct numeral for a Sense: 2 given set of pictures Grouping and counting
Title: Quadrilaterals Aren t Just Squares
 Title: Quadrilaterals ren t Just Squares Brief Overview: This is a collection of the first three lessons in a series of seven lessons studying characteristics of quadrilaterals, including trapezoids, parallelograms,
Title: Quadrilaterals ren t Just Squares Brief Overview: This is a collection of the first three lessons in a series of seven lessons studying characteristics of quadrilaterals, including trapezoids, parallelograms,
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES -
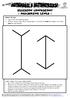 ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
ILLUSION CONFUSION! - MEASURING LINES - WHAT TO DO: 1. Look at the line drawings below. 2. Without using a ruler, which long upright or vertical line looks the longest or do they look the same length?
3.3. You wouldn t think that grasshoppers could be dangerous. But they can damage
 Grasshoppers Everywhere! Area and Perimeter of Parallelograms on the Coordinate Plane. LEARNING GOALS In this lesson, you will: Determine the perimeter of parallelograms on a coordinate plane. Determine
Grasshoppers Everywhere! Area and Perimeter of Parallelograms on the Coordinate Plane. LEARNING GOALS In this lesson, you will: Determine the perimeter of parallelograms on a coordinate plane. Determine
TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 6. Student Book
 TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 6 Student Book TEKSING TOWARD STAAR 2014 Six Weeks 1 Lesson 1 STAAR Category 1 Grade 6 Mathematics TEKS 6.2A/6.2B Problem-Solving Model Step Description of Step 1
TEKSING TOWARD STAAR MATHEMATICS GRADE 6 Student Book TEKSING TOWARD STAAR 2014 Six Weeks 1 Lesson 1 STAAR Category 1 Grade 6 Mathematics TEKS 6.2A/6.2B Problem-Solving Model Step Description of Step 1
18 Two-Dimensional Shapes
 18 Two-Dimensional Shapes CHAPTER Worksheet 1 Identify the shape. Classifying Polygons 1. I have 3 sides and 3 corners. 2. I have 6 sides and 6 corners. Each figure is made from two shapes. Name the shapes.
18 Two-Dimensional Shapes CHAPTER Worksheet 1 Identify the shape. Classifying Polygons 1. I have 3 sides and 3 corners. 2. I have 6 sides and 6 corners. Each figure is made from two shapes. Name the shapes.
Class : VI - Mathematics
 O. P. JINDAL SCHOOL, RAIGARH (CG) 496 001 Phone : 07762-227042, 227293, (Extn. 227001-49801, 02, 04, 06); Fax : 07762-262613; e-mail: opjsraigarh@jspl.com; website : www.opjsrgh.in Class : VI - Mathematics
O. P. JINDAL SCHOOL, RAIGARH (CG) 496 001 Phone : 07762-227042, 227293, (Extn. 227001-49801, 02, 04, 06); Fax : 07762-262613; e-mail: opjsraigarh@jspl.com; website : www.opjsrgh.in Class : VI - Mathematics
CBSE Sample Paper Class 10 Mathematicss
 CBSE Sample Paper Class 10 Mathematicss 1] In the given figure, the respective values of y and x are 30 o and 45 o 60 o and 45 45 o and 60 o 60 o and 30 o 2] The next term of the given series would be
CBSE Sample Paper Class 10 Mathematicss 1] In the given figure, the respective values of y and x are 30 o and 45 o 60 o and 45 45 o and 60 o 60 o and 30 o 2] The next term of the given series would be
During What could you do to the angles to reliably compare their measures?
 Measuring Angles LAUNCH (9 MIN) Before What does the measure of an angle tell you? Can you compare the angles just by looking at them? During What could you do to the angles to reliably compare their measures?
Measuring Angles LAUNCH (9 MIN) Before What does the measure of an angle tell you? Can you compare the angles just by looking at them? During What could you do to the angles to reliably compare their measures?
Winter Quarter Competition
 Winter Quarter Competition LA Math Circle (Advanced) March 13, 2016 Problem 1 Jeff rotates spinners P, Q, and R and adds the resulting numbers. What is the probability that his sum is an odd number? Problem
Winter Quarter Competition LA Math Circle (Advanced) March 13, 2016 Problem 1 Jeff rotates spinners P, Q, and R and adds the resulting numbers. What is the probability that his sum is an odd number? Problem
Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets
 Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets Nevada Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Elko County School District 5 th Grade Math Learning Targets Nevada Content Standard 1.0 Students will accurately calculate and use estimation techniques, number relationships, operation rules, and algorithms;
Triangles, Rectangles, Squares, and Circles
 Triangles, Rectangles, Squares, and Circles Triangle sides Rectangle 4 sides Lesson 21 21 Square length a rectangle with 4 equal sides width Measures of a circle: Radius = 1 diameter Diameter = 2 radius
Triangles, Rectangles, Squares, and Circles Triangle sides Rectangle 4 sides Lesson 21 21 Square length a rectangle with 4 equal sides width Measures of a circle: Radius = 1 diameter Diameter = 2 radius
Grade 7 & 8 Math Circles February 2-3, 2016 Logic Puzzles
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7 & 8 Math Circles February 2-3, 2016 Logic Puzzles Introduction Math is not always numbers, equations
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7 & 8 Math Circles February 2-3, 2016 Logic Puzzles Introduction Math is not always numbers, equations
2.2. Special Angles and Postulates. Key Terms
 And Now From a New Angle Special Angles and Postulates. Learning Goals Key Terms In this lesson, you will: Calculate the complement and supplement of an angle. Classify adjacent angles, linear pairs, and
And Now From a New Angle Special Angles and Postulates. Learning Goals Key Terms In this lesson, you will: Calculate the complement and supplement of an angle. Classify adjacent angles, linear pairs, and
Representing Square Numbers. Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array.
 1.1 Student book page 4 Representing Square Numbers You will need counters a calculator Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array. 5 5 25 number
1.1 Student book page 4 Representing Square Numbers You will need counters a calculator Use materials to represent square numbers. A. Calculate the number of counters in this square array. 5 5 25 number
Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities
 Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Chris Mikles 916-719-3077 chrismikles@cpm.org 1 2 2-51. SPECIAL
Making Middle School Math Come Alive with Games and Activities For more information about the materials you find in this packet, contact: Chris Mikles 916-719-3077 chrismikles@cpm.org 1 2 2-51. SPECIAL
Refer to Blackboard for Activities and/or Resources
 Lafayette Parish School System Curriculum Map Mathematics: Grade 5 Unit 4: Properties in Geometry (LCC Unit 5) Time frame: 16 Instructional Days Assess2know Testing Date: March 23, 2012 Refer to Blackboard
Lafayette Parish School System Curriculum Map Mathematics: Grade 5 Unit 4: Properties in Geometry (LCC Unit 5) Time frame: 16 Instructional Days Assess2know Testing Date: March 23, 2012 Refer to Blackboard
Lesson 2: Using the Number Line to Model the Addition of Integers
 : Using the Number Line to Model the Addition of Integers Classwork Exercise 1: Real-World Introduction to Integer Addition Answer the questions below. a. Suppose you received $10 from your grandmother
: Using the Number Line to Model the Addition of Integers Classwork Exercise 1: Real-World Introduction to Integer Addition Answer the questions below. a. Suppose you received $10 from your grandmother
Inductive Reasoning. L E S S O N 2.1
 Page 1 of 6 L E S S O N 2.1 We have to reinvent the wheel every once in a while, not because we need a lot of wheels; but because we need a lot of inventors. BRUCE JOYCE Language The word geometry means
Page 1 of 6 L E S S O N 2.1 We have to reinvent the wheel every once in a while, not because we need a lot of wheels; but because we need a lot of inventors. BRUCE JOYCE Language The word geometry means
9.1 Properties of Parallelograms
 Name lass ate 9.1 Properties of Parallelograms Essential Question: What can you conclude about the sides, angles, and diagonals of a parallelogram? Explore Investigating Parallelograms quadrilateral is
Name lass ate 9.1 Properties of Parallelograms Essential Question: What can you conclude about the sides, angles, and diagonals of a parallelogram? Explore Investigating Parallelograms quadrilateral is
Geometry Station Activities for Common Core State Standards
 Geometry Station Activities for Common Core State Standards WALCH EDUCATION Table of Contents Standards Correlations...................................................... v Introduction..............................................................vii
Geometry Station Activities for Common Core State Standards WALCH EDUCATION Table of Contents Standards Correlations...................................................... v Introduction..............................................................vii
Fun Challenges Problem Solving Reasoning Deductive Thinking Convergent/Divergent Thinking Mind-Bending Challenges Critical Thinking
 Fun Challenges Problem Solving Reasoning Deductive Thinking Convergent/Divergent Thinking Mind-ending Challenges Critical Thinking Magic Shapes #1 Magic Shapes #1 Directions: Write the numbers 1 through
Fun Challenges Problem Solving Reasoning Deductive Thinking Convergent/Divergent Thinking Mind-ending Challenges Critical Thinking Magic Shapes #1 Magic Shapes #1 Directions: Write the numbers 1 through
Lesson 10: Unknown Angle Proofs Proofs with Constructions
 : Unknown Angle Proofs Proofs with Constructions Student Outcome Students write unknown angle proofs involving auxiliary lines. Lesson Notes On the second day of unknown angle proofs, students incorporate
: Unknown Angle Proofs Proofs with Constructions Student Outcome Students write unknown angle proofs involving auxiliary lines. Lesson Notes On the second day of unknown angle proofs, students incorporate
Mathematical Olympiad for Girls
 UKMT UKMT UKMT United Kingdom Mathematics Trust Mathematical Olympiad for Girls Tuesday 2nd October 208 Organised by the United Kingdom Mathematics Trust These are polished solutions and do not illustrate
UKMT UKMT UKMT United Kingdom Mathematics Trust Mathematical Olympiad for Girls Tuesday 2nd October 208 Organised by the United Kingdom Mathematics Trust These are polished solutions and do not illustrate
Geometry Unit 2 Review Day 1 What to expect on the test:
 Geometry Unit 2 Review Day 1 What to expect on the test: Conditional s Converse Inverse Contrapositive Bi-conditional statements Today we are going to do more work with Algebraic Proofs Counterexamples/Instances
Geometry Unit 2 Review Day 1 What to expect on the test: Conditional s Converse Inverse Contrapositive Bi-conditional statements Today we are going to do more work with Algebraic Proofs Counterexamples/Instances
The problems in this booklet are organized into strands. A problem often appears in multiple strands. The problems are suitable for most students in
 The problems in this booklet are organized into strands. A problem often appears in multiple strands. The problems are suitable for most students in Grade 7 or higher. Problem C Retiring and Hiring A
The problems in this booklet are organized into strands. A problem often appears in multiple strands. The problems are suitable for most students in Grade 7 or higher. Problem C Retiring and Hiring A
Summer Solutions Problem Solving Level 4. Level 4. Problem Solving. Help Pages
 Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
Level Problem Solving 6 General Terms acute angle an angle measuring less than 90 addend a number being added angle formed by two rays that share a common endpoint area the size of a surface; always expressed
LEARNING ABOUT MATH FOR K TO 5. Dorset Public School. April 6, :30 pm 8:00 pm. presented by Kathy Kubota-Zarivnij
 LEARNING ABOUT MATH FOR K TO 5 Dorset Public School April 6, 2016 6:30 pm 8:00 pm presented by Kathy Kubota-Zarivnij kathkubo@rogers.com TODAY S MATH TOOLS FOR colour square tiles Hexalink cubes KKZ, 2016
LEARNING ABOUT MATH FOR K TO 5 Dorset Public School April 6, 2016 6:30 pm 8:00 pm presented by Kathy Kubota-Zarivnij kathkubo@rogers.com TODAY S MATH TOOLS FOR colour square tiles Hexalink cubes KKZ, 2016
TenMarks Curriculum Alignment Guide: EngageNY/Eureka Math, Grade 7
 EngageNY Module 1: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Topic A: Proportional Relationships Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Understand equivalent ratios, rate, and unit rate related to a Understand proportional
EngageNY Module 1: Ratios and Proportional Relationships Topic A: Proportional Relationships Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Understand equivalent ratios, rate, and unit rate related to a Understand proportional
Project Maths Geometry Notes
 The areas that you need to study are: Project Maths Geometry Notes (i) Geometry Terms: (ii) Theorems: (iii) Constructions: (iv) Enlargements: Axiom, theorem, proof, corollary, converse, implies The exam
The areas that you need to study are: Project Maths Geometry Notes (i) Geometry Terms: (ii) Theorems: (iii) Constructions: (iv) Enlargements: Axiom, theorem, proof, corollary, converse, implies The exam
Table of Contents. Standards Correlations...v Introduction...vii Materials List... x
 Table of Contents Standards Correlations...v Introduction...vii Materials List... x...1...1 Set 2: Classifying Triangles and Angle Theorems... 13 Set 3: Corresponding Parts, Transformations, and Proof...
Table of Contents Standards Correlations...v Introduction...vii Materials List... x...1...1 Set 2: Classifying Triangles and Angle Theorems... 13 Set 3: Corresponding Parts, Transformations, and Proof...
The Pythagorean Theorem 8.6.C
 ? LESSON 8.1 The Pythagorean Theorem ESSENTIAL QUESTION Expressions, equations, and relationships 8.6.C Use models and diagrams to explain the Pythagorean Theorem. 8.7.C Use the Pythagorean Theorem...
? LESSON 8.1 The Pythagorean Theorem ESSENTIAL QUESTION Expressions, equations, and relationships 8.6.C Use models and diagrams to explain the Pythagorean Theorem. 8.7.C Use the Pythagorean Theorem...
Shuli s Math Problem Solving Column
 Shuli s Math Problem Solving Column Volume 1, Issue 19 May 1, 2009 Edited and Authored by Shuli Song Colorado Springs, Colorado shuli_song@yahoocom Contents 1 Math Trick: Mental Calculation: 199a 199b
Shuli s Math Problem Solving Column Volume 1, Issue 19 May 1, 2009 Edited and Authored by Shuli Song Colorado Springs, Colorado shuli_song@yahoocom Contents 1 Math Trick: Mental Calculation: 199a 199b
6-3 Conditions for Parallelograms
 Warm Up Justify each statement. 1. 2. Reflex Prop. of Conv. of Alt. Int. s Thm. Evaluate each expression for x = 12 and y = 8.5. 3. 2x + 7 4. 16x 9 31 183 5. (8y + 5) 73 Objective Prove that a given quadrilateral
Warm Up Justify each statement. 1. 2. Reflex Prop. of Conv. of Alt. Int. s Thm. Evaluate each expression for x = 12 and y = 8.5. 3. 2x + 7 4. 16x 9 31 183 5. (8y + 5) 73 Objective Prove that a given quadrilateral
6-1. Angles of Polygons. Lesson 6-1. What You ll Learn. Active Vocabulary
 6-1 Angles of Polygons What You ll Learn Skim Lesson 6-1. Predict two things that you expect to learn based on the headings and figures in the lesson. 1. 2. Lesson 6-1 Active Vocabulary diagonal New Vocabulary
6-1 Angles of Polygons What You ll Learn Skim Lesson 6-1. Predict two things that you expect to learn based on the headings and figures in the lesson. 1. 2. Lesson 6-1 Active Vocabulary diagonal New Vocabulary
Mathematical Olympiads November 19, 2014
 athematical Olympiads November 19, 2014 for Elementary & iddle Schools 1A Time: 3 minutes Suppose today is onday. What day of the week will it be 2014 days later? 1B Time: 4 minutes The product of some
athematical Olympiads November 19, 2014 for Elementary & iddle Schools 1A Time: 3 minutes Suppose today is onday. What day of the week will it be 2014 days later? 1B Time: 4 minutes The product of some
Class 5 Geometry O B A C. Answer the questions. For more such worksheets visit
 ID : in-5-geometry [1] Class 5 Geometry For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) The set square is in the shape of. (2) Identify the semicircle that contains 'C'. A C O B
ID : in-5-geometry [1] Class 5 Geometry For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) The set square is in the shape of. (2) Identify the semicircle that contains 'C'. A C O B
UNC Charlotte 2012 Comprehensive
 March 5, 2012 1. In the English alphabet of capital letters, there are 15 stick letters which contain no curved lines, and 11 round letters which contain at least some curved segment. How many different
March 5, 2012 1. In the English alphabet of capital letters, there are 15 stick letters which contain no curved lines, and 11 round letters which contain at least some curved segment. How many different
Meet #5 March Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts
 Meet #5 March 2008 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet #5 March 2008 Category 1 Mystery 1. In the diagram to the right, each nonoverlapping section of the large rectangle is
Meet #5 March 2008 Intermediate Mathematics League of Eastern Massachusetts Meet #5 March 2008 Category 1 Mystery 1. In the diagram to the right, each nonoverlapping section of the large rectangle is
Geometry Topic 4 Quadrilaterals and Coordinate Proof
 Geometry Topic 4 Quadrilaterals and Coordinate Proof MAFS.912.G-CO.3.11 In the diagram below, parallelogram has diagonals and that intersect at point. Which expression is NOT always true? A. B. C. D. C
Geometry Topic 4 Quadrilaterals and Coordinate Proof MAFS.912.G-CO.3.11 In the diagram below, parallelogram has diagonals and that intersect at point. Which expression is NOT always true? A. B. C. D. C
Investigation. Triangle, Triangle, Triangle. Work with a partner.
 Investigation Triangle, Triangle, Triangle Work with a partner. Materials: centimetre ruler 1-cm grid paper scissors Part 1 On grid paper, draw a large right triangle. Make sure its base is along a grid
Investigation Triangle, Triangle, Triangle Work with a partner. Materials: centimetre ruler 1-cm grid paper scissors Part 1 On grid paper, draw a large right triangle. Make sure its base is along a grid
1. 1 Square Numbers and Area Models (pp. 6-10)
 Math 8 Unit 1 Notes Name: 1. 1 Square Numbers and Area Models (pp. 6-10) square number: the product of a number multiplied by itself; for example, 25 is the square of 5 perfect square: a number that is
Math 8 Unit 1 Notes Name: 1. 1 Square Numbers and Area Models (pp. 6-10) square number: the product of a number multiplied by itself; for example, 25 is the square of 5 perfect square: a number that is
a. $ b. $ c. $
 LESSON 51 Rounding Decimal Name To round decimal numbers: Numbers (page 268) 1. Underline the place value you are rounding to. 2. Circle the digit to its right. 3. If the circled number is 5 or more, add
LESSON 51 Rounding Decimal Name To round decimal numbers: Numbers (page 268) 1. Underline the place value you are rounding to. 2. Circle the digit to its right. 3. If the circled number is 5 or more, add
1Solve linear. 2Solve linear. Then. Now. Why?
 Solving Multi-Step Inequalities Then You solved multistep equations. (Lesson 2-3) Now 1Solve linear inequalities involving more than one operation. 2Solve linear inequalities involving the Distributive
Solving Multi-Step Inequalities Then You solved multistep equations. (Lesson 2-3) Now 1Solve linear inequalities involving more than one operation. 2Solve linear inequalities involving the Distributive
8.3 Prove It! A Practice Understanding Task
 15 8.3 Prove It! A Practice Understanding Task In this task you need to use all the things you know about quadrilaterals, distance, and slope to prove that the shapes are parallelograms, rectangles, rhombi,
15 8.3 Prove It! A Practice Understanding Task In this task you need to use all the things you know about quadrilaterals, distance, and slope to prove that the shapes are parallelograms, rectangles, rhombi,
Downloaded from
 1 IX Mathematics Chapter 8: Quadrilaterals Chapter Notes Top Definitions 1. A quadrilateral is a closed figure obtained by joining four points (with no three points collinear) in an order. 2. A diagonal
1 IX Mathematics Chapter 8: Quadrilaterals Chapter Notes Top Definitions 1. A quadrilateral is a closed figure obtained by joining four points (with no three points collinear) in an order. 2. A diagonal
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines on the Coordinate Plane
 Did You Find a Parking Space? Parallel and Perpendicular Lines on the Coordinate Plane 1.5 Learning Goals Key Term In this lesson, you will: Determine whether lines are parallel. Identify and write the
Did You Find a Parking Space? Parallel and Perpendicular Lines on the Coordinate Plane 1.5 Learning Goals Key Term In this lesson, you will: Determine whether lines are parallel. Identify and write the
Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry
 Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry This Guide Belongs to: Date: Table of Contents Using Sketchpad - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Geometer s Skethchpad 8th Grade Guide to Learning Geometry This Guide Belongs to: Date: Table of Contents Using Sketchpad - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Good Luck To. DIRECTIONS: Answer each question and show all work in the space provided. The next two terms of the sequence are,
 Good Luck To Period Date DIRECTIONS: Answer each question and show all work in the space provided. 1. Find the next two terms of the sequence. 6, 36, 216, 1296, _?_, _?_ The next two terms of the sequence
Good Luck To Period Date DIRECTIONS: Answer each question and show all work in the space provided. 1. Find the next two terms of the sequence. 6, 36, 216, 1296, _?_, _?_ The next two terms of the sequence
18.2 Geometric Probability
 Name Class Date 18.2 Geometric Probability Essential Question: What is geometric probability? Explore G.13.B Determine probabilities based on area to solve contextual problems. Using Geometric Probability
Name Class Date 18.2 Geometric Probability Essential Question: What is geometric probability? Explore G.13.B Determine probabilities based on area to solve contextual problems. Using Geometric Probability
EXPLORING TIC-TAC-TOE VARIANTS
 EXPLORING TIC-TAC-TOE VARIANTS By Alec Levine A SENIOR RESEARCH PAPER PRESENTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE OF STETSON UNIVERSITY IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR
EXPLORING TIC-TAC-TOE VARIANTS By Alec Levine A SENIOR RESEARCH PAPER PRESENTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE OF STETSON UNIVERSITY IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR
Angles and. Learning Goals U N I T
 U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
U N I T Angles and Learning Goals name, describe, and classify angles estimate and determine angle measures draw and label angles provide examples of angles in the environment investigate the sum of angles
Unit 1 Foundations of Geometry: Vocabulary, Reasoning and Tools
 Number of Days: 34 9/5/17-10/20/17 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Using building blocks from Algebra 1, students will use a variety of tools and techniques to construct, understand, and prove geometric
Number of Days: 34 9/5/17-10/20/17 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Using building blocks from Algebra 1, students will use a variety of tools and techniques to construct, understand, and prove geometric
Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers
 LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
LESSON 61 page 328 Squares Multiplication Facts: Square Numbers Name Teacher Notes: Introduce Hint #21 Multiplication/ Division Fact Families. Review Multiplication Table on page 5 and Quadrilaterals on
I.M.O. Winter Training Camp 2008: Invariants and Monovariants
 I.M.. Winter Training Camp 2008: Invariants and Monovariants n math contests, you will often find yourself trying to analyze a process of some sort. For example, consider the following two problems. Sample
I.M.. Winter Training Camp 2008: Invariants and Monovariants n math contests, you will often find yourself trying to analyze a process of some sort. For example, consider the following two problems. Sample
Table of Contents. Table of Contents 1
 Table of Contents 1) The Factor Game a) Investigation b) Rules c) Game Boards d) Game Table- Possible First Moves 2) Toying with Tiles a) Introduction b) Tiles 1-10 c) Tiles 11-16 d) Tiles 17-20 e) Tiles
Table of Contents 1) The Factor Game a) Investigation b) Rules c) Game Boards d) Game Table- Possible First Moves 2) Toying with Tiles a) Introduction b) Tiles 1-10 c) Tiles 11-16 d) Tiles 17-20 e) Tiles
