Introduction to Mechatronics Programming a robot
|
|
|
- Lorin Mills
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Mechatronics Programming a robot Lecturer Filippo Sanfilippo Faculty of Aalesund University College, Filippo Sanfilippo 1
2 Filippo Sanfilippo 2
3 Content of today s lecture! Programming and software engineering in mechantronics! The Robot Control Loop! Communication! Robot Programming Systems Manual Programming Automatic Programming Software Architecture! Programming in practice: Arduino Programming a modular robot Programming a delta robot Filippo Sanfilippo 3
4 Schedule! Overview and Introduction! Evolutionary Robotics (GAs and Proximal vs. Distal Description)! Neural Networks (Theoretical Introduction and examples) Arduino Seminar Prototyping and Mechanics Seminar Filippo Sanfilippo 4
5 Lecture material! A survey of robot programming systems, Biggs, G. and MacDonald, B., Proceedings of the Australasian conference on robotics and automation, pp. 1-3, 2003! Programming robots, Robot Programming Code, Arduino, Getting Started with Arduino, Massimo Banzi, O'Reilly Media / Make, 2008! Making Things Talk, Practical Methods for Connecting Physical Objects, Tom Igoe, O'Reilly Media / Make, 2007! The Mechatronics Handbook, Robert H. Bishop CRC Press, 2002 Filippo Sanfilippo 5
6 Programming and software engineering in mechantronics! Mechatronics is more than the sum of its parts! Mechatronics as a way of thinking! Mechanics, electronics and software are considered together and then simultaneously conceived, planned and implemented with interdisciplinary coordination > Software is the glue! Filippo Sanfilippo 6
7 Programming and software engineering in mechantronics! Software vs. Information Technology Filippo Sanfilippo 7
8 Programming and software engineering in mechantronics! A little bit of history Filippo Sanfilippo 8
9 Programming and software engineering in mechantronics! Several overlaps between hardware and software! Es. Mobile phone keyboard! Analogic vs. Digital Filippo Sanfilippo 9
10 Programming and software engineering in mechantronics! Some properties of Conventional and Mechatronic Design Systems Filippo Sanfilippo 10
11 The Robot Control Loop Open talk and sketches on the whiteboard Take some notes! Filippo Sanfilippo 11
12 The Robot Control Loop Filippo Sanfilippo 12
13 The Robot Control Loop Filippo Sanfilippo 13
14 Communications Access control Filippo Sanfilippo 14
15 Robot Programming Systems Filippo Sanfilippo 15
16 Manual Programming Systems! Users of a manual programming systems must create the robot program by hand, which is typically performed without the robot. The finished program is loaded into the robot afterwards.! These are often off-line programming systems, where a robot is not present while programming! It is conceivable for manual programming to control a robot online, using for example an interpreted language, where there are no safety concerns Filippo Sanfilippo 16
17 Manual Programming Systems Graphical -based Filippo Sanfilippo 17
18 Controller-Specific Languages! Controller-specific languages were the original method of controlling industrial robots, and are still the most common method today! Every robot controller has some form of machine language, and there is usually a programming language to go with it that can be used to create programs for that robot! These programming languages are usually very simple, with a BASIClike syntax and simple commands for controlling the robot and program flow Filippo Sanfilippo 18
19 Controller-Specific Languages The KUKA programming environment and robot programming language Filippo Sanfilippo 19
20 Controller-Specific Languages! Drawbacks Despite having existed for as long as industrial robots have been in use, controller-specific languages have seen only minor advances The biggest problem is the lack of a universal standard between languages from different robot manufacturers If a factory uses robots from many different manufacturers then they will need to either train their programmers for each one, or pay the manufacturer to develop the required programs for them Commercial systems have concentrated their advances on overcoming these lacks by providing more advanced programming systems that remove the need for the programmer to write the robot code by hand Filippo Sanfilippo 20
21 Generic Procedure Languages! Generic languages provide an alternative to controller-specific languages for programming robots. "Generic" means a high-level multipurpose language, for example C++ or JAVA! particularly common in research environments, where generic languages are extended to meet the needs of the research project! The choice of the base language varies, depending upon what the researchers are trying to achieve (for example, procedural or behavioral programming) Filippo Sanfilippo 21
22 Generic Procedure Languages! Advantages The most common extension to a multi-purpose language is a robot abstraction, which is a set of classes, methods, or similar constructs that provides access to common robot functions in a simple way They remove the need to handle low-level functionality such as setting output ports high, to turn on motors or translating raw sensor data It might also provide higher-level abstractions, such as methods to make the robot move to a point using path planning Filippo Sanfilippo 22
23 Generic Procedure Languages! Drawbacks these abstractions suffer from the same fault as controller-specific language. They are still specific to the robot they are designed for! Possible improvements many researches have developed their own robot abstraction systems some examples: Player/stage [Vaughan et al., 2003] Motion Description Language [Kanayama and Wu, 2000] Filippo Sanfilippo 23
24 Generic Procedure Languages! Methodology to develop abstractions it is interesting to note that a abstractions are commonly implemented using an object-oriented methodology McKee et al. [2001] state that a rigorous object-oriented approach to robotics is important to clearly define robotic entities relationships. They describe the MARS model of object-oriented robots, and define robots comprised of "resources", which are then modeled as "modules". They draw clear parallels between object-oriented concepts such as inheritance, and the modules of a robot. Example: a tool on the end of an arm, simply by being on the end of an arm, inherits the ability to move. Filippo Sanfilippo 24
25 Behaviour-based Languages! They typically specify how the robot should react to different conditions, rather than providing a procedural description! A behavioral system is more likely to be used by a robot developer than the end user. The developer would use it to define functionality that the end user would use to perform tasks! Example: a set of behaviors would be to follow a wall from one point to another (a profile path is provided to the robot) Filippo Sanfilippo 25
26 Graphical Systems! Graphical (or icon-based) programming systems provide an alternative to text-based methods for manual programming! they are a small step closer to automatic programming, as they provide a graphical medium for programming! they require manual input to specify actions and program flow.! Graphical systems typically use a graph, flow-chart or diagram view of the robot system Filippo Sanfilippo 26
27 Graphical Systems! One advantage of graphical systems is their ease of use, which is achieved at the cost of text-based programming's flexibility! They are typically used for robotic applications rather than system programming! Perhaps the most successful graphical system using the flow-chart approach is employed by the Lego Mindstorms robotics kit [Lego, 2003] Filippo Sanfilippo 27
28 Automatic Programming Systems! Automatic programming systems provide little or no direct control over the program code the robot will run! robot code is generated from information entered into the system in a variety of indirect ways! often a robot system must be running while automatic programming is performed, and these systems have been referred to as "online" programming systems! automatic programming may also be performed on simulated or virtual robots Filippo Sanfilippo 28
29 Automatic Programming Systems Filippo Sanfilippo 29
30 Learning Systems! Learning systems create a program by inductive inference from user provided examples and self-exploration by the robot! Initially the robot watches as the task is performed. Successively the robot attempts to perform the task on its own! Examples include a hierarchy of neural networks developed for learning the motion of a human arm in 3D [Billard and Schaal, 2001], a robot that can learn simple behaviours and chain these together to form larger behaviours [Weng and Zhang, 2002],... Filippo Sanfilippo 30
31 Programming by Demonstration! This is the most common method of automatic programming! PbD systems may use touch/pendants for the demonstration, or they may use other, more natural communication methods such as gestures and voice Filippo Sanfilippo 31
32 Programming by Demonstration! A traditional PbD system uses a teach-pendant to demonstrate the movements the robot should perform! The demonstrator performs the task (for example, an assembly task) using the teach pendant! The position of the pendant is recorded and the results used to generate a robot program that will move the robot arm through the same motions! Alternatively, the demonstrator may move the robot arm through the required motions either physically or using a controller. In this case, the joint positions are recorded and used to generate the robot program. Filippo Sanfilippo 32
33 Instructive Systems! Instructive systems are given a sequence of instructions, usually in realtime.! The technique is best suited for commanding robots to carry out tasks that they have already been trained or programmed to perform! it could be considered the highest level of programming. Typically, gesture recognition or voice recognition is used Filippo Sanfilippo 33
34 Programming in practice! Robots have become significantly more powerful and intelligent over the last decade! Robots will more often be used by people with minimal technical skills! Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) and Open source hardware (OSHW) can bee seen as very promising means for the technological progress Filippo Sanfilippo 34
35 Arduino: introduction! What is Arduino? It's an open-source physical computing platform based on a simple microcontroller board (Atmel's ATMEGA8 and ATMEGA168 microcontrollers), and a development environment for writing software for the board. It can be used to develop interactive objects, taking inputs from a variety of switches or sensors, and controlling a variety of lights, motors, and other physical outputs. Arduino projects can be stand-alone, or they can be communicate with software running on a computer (e.g. Flash, Processing, MaxMSP.) The boards can be assembled by hand or purchased preassembled; the open-source IDE can be downloaded for free. Arduino The Documentary: Filippo Sanfilippo 35
36 Arduino: introduction! Why Arduino? Arduino simplifies the process of working with microcontrollers. It also offers the following advantages: Inexpensive compared to other microcontroller platforms. Cross-platform - Windows, Macintosh OSX, and Linux. Simple, clear programming environment Open source and extensible software - The Arduino software and is published as open source tools, available for extension by experienced programmers. Open source and extensible hardware - The plans for the modules are published under a Creative Commons license, so experienced circuit designers can make their own version of the module, extending it and improving it. Filippo Sanfilippo 36
37 Arduino: getting started! Installation Step-by-step instructions for setting up the Arduino software and connecting it to an Arduino Uno, Mega2560, Duemilanove, Mega, or Diecimila. Windows Mac OS X Linux (on the playground wiki) Environment: Description of the Arduino development environment. Troubleshooting: Advice on what to do if things don't work. Filippo Sanfilippo 37
38 Arduino: hardware! Official Arduino boards Arduino Uno Arduino LilyPad Arduino Pro Arduino Nano Arduino Mini Filippo Sanfilippo 38
39 Arduino: hardware! Official Arduino Shields and Modules Arduino Ethernet Shield Arduino Wireless Shield GPRS Quadband Module LCD Module GPS Module Touch Sensor Accelerometer IR Receiver Filippo Sanfilippo 39
40 Arduino: learning! Sketch: Arduino uses for a program. It's the unit of code that is uploaded to and run on an Arduino board. Comments Everything between the /* and */ is ignored by the Arduino when it runs the sketch. There's another style for short, single-line comments. These start with // and continue to the end of the line. Variables A variable is a place for storing a piece of data. It has a name, a type, and a value. There's more information in the Variables tutorial. NOTE: refear to the Blink example. Filippo Sanfilippo 40
41 Arduino: learning Sketch Functions A function (otherwise known as a procedure or sub-routine) is a named piece of code that can be used from elsewhere in a sketch. You can call a function that's already been defined (either in your sketch or as part of the Arduino language). setup() and loop() There are two special functions that are a part of every Arduino sketch: setup() and loop(). The setup() is called once, when the sketch starts. It's a good place to do setup tasks like setting pin modes or initializing libraries. The loop() function is called over and over and is heart of most sketches. You need to include both functions in your sketch, even if you don't need them for anything. Filippo Sanfilippo 41
42 Arduino: learning Microcontrollers Digital Pins The pins on the Arduino can be configured as either inputs or outputs. Arduino (Atmega) pins default to inputs, so they don't need to be explicitly declared as inputs with pinmode(). Analog Input Pins The Atmega controllers used for the Arduino contain an onboard 6 channel analog-to-digital (A/D) converter. While the main function of the analog pins for most Arduino users is to read analog sensors, the analog pins also have all the functionality of general purpose input/ output (GPIO) pins (the same as digital pins 0 13). The analog pins can be used identically to the digital pins, using the aliases A0 (for analog input 0), A1, etc. Filippo Sanfilippo 42
43 Arduino: learning Microcontrollers PWM Pulse Width Modulation, or PWM, is a technique for getting analog results with digital means. Digital control is used to create a square wave, a signal switched between on and off. The Fading example demonstrates the use of analog output (PWM) to fade an LED. It is available in the File->Sketchbook->Examples->Analog menu of the Arduino software. Filippo Sanfilippo 43
44 Arduino: learning Microcontrollers Memory There are three pools of memory in the microcontroller used on Arduino boards (ATmega168): Flash memory (program space), is where the Arduino sketch is stored. SRAM (static random access memory) is where the sketch creates and manipulates variables when it runs. EEPROM is memory space that programmers can use to store longterm information. Filippo Sanfilippo 44
45 Arduino: learning Programming Technique Functions Filippo Sanfilippo 45
46 Arduino: learning by doing Examples Blink Circuit To build the circuit, attach a 220-ohm resistor to pin 13. Then attach the long leg of an LED (the positive leg, called the anode) to the resistor. Attach the short leg (the negative leg, called the cathode) to ground. Then plug your Arduino board into your computer. In the program below, the first thing you do is to initialize pin 13 as an output pin with the line pinmode(13, OUTPUT); In the main loop, you turn the LED on with the line: digitalwrite(13, HIGH); check out:! Blink! Blink without delay This supplies 5 volts to pin 13. That creates a voltage difference across the pins of the LED, and lights it up. Then you turn it off with the line: digitalwrite(13, LOW); Filippo Sanfilippo 46
47 Arduino: learning by doing Examples Button check out:! Button Circuit Connect three wires to the Arduino board. The first two, red and black, connect to the two long vertical rows on the side of the breadboard to provide access to the 5 volt supply and ground. The third wire goes from digital pin 2 to one leg of the pushbutton. That same leg of the button connects through a pull-down resistor (here 10 KOhms) to ground. The other leg of the button connects to the 5 volt supply. void setup() { pinmode(ledpin, OUTPUT); pinmode(buttonpin, INPUT); }... buttonstate = digitalread(buttonpin); if (buttonstate == HIGH) { digitalwrite(ledpin, HIGH); } else { digitalwrite(ledpin, LOW); } Filippo Sanfilippo 47
48 Arduino: learning by doing Examples Analog Input Circuit Connect three wires to the Arduino board. The first goes to ground from one of the outer pins of the potentiometer. The second goes from 5 volts to the other outer pin of the potentiometer. The third goes from analog input 0 to the middle pin of the potentiometer. void loop() { // read the value from the sensor: sensorvalue = analogread(sensorpin); // turn the ledpin on digitalwrite(ledpin, HIGH); // stop the program for <sensorvalue> milliseconds: delay(sensorvalue); // turn the ledpin off: digitalwrite(ledpin, LOW); // stop the program for for <sensorvalue> milliseconds: delay(sensorvalue); } check out:! Analog Input Filippo Sanfilippo 48
49 Arduino: learning by doing Examples Graph Circuit This example shows you how to send a byte of data from the Arduino to a personal computer and graph the result. This is called serial communication. You can use the Arduino serial monitor to view the sent data, or it can be read by Processing. check out:! Graph! Processing Filippo Sanfilippo 49
50 Arduino: learning by doing Examples Accelerometer Circuit You'll use three of the analog input pins as digital I/O pins, for power and ground to the accelerometer, and for the self-test pin. You'll use the other three analog inputs to read the acclerometer's analog outputs. Reads an Analog Devices ADXL3xx accelerometer and communicates the acceleration to the computer. check out: void loop() { Serial.print(analogRead(xpin)); Serial.print("\t"); Serial.print(analogRead(ypin)); Serial.print("\t"); Serial.print(analogRead(zpin)); Serial.println(); // delay before next reading: delay(100); }! Accelerometer Filippo Sanfilippo 50
51 Arduino: learning by doing Examples Knob Circuit Servo motors have three wires: power, ground, and signal. The power wire is typically red, and should be connected to the 5V pin on the Arduino board. The ground wire is typically black or brown and should be connected to a ground pin on the Arduino board. The signal pin is typically yellow or orange and should be connected to pin 9 on the Arduino board. The potentiometer should be wired so that its two outer pins are connected to power (+5V) and ground, and its middle pin is connected to analog input 0 on the Arduino. void loop() { val = analogread(potpin); val = map(val, 0, 1023, 0, 179); myservo.write(val); delay(15); } check out:! Knob Filippo Sanfilippo 51
52 Parallel robots A parallel robot is a closed loop chain, whereas a serial robot is an open loop chain (a hybrid mechanism is one with both closed and open chains). Major industrial applications of these devices are:! flight simulators! automobile simulators! in work processes! photonics / optical fiber alignment They also become more popular:! in high speed, high-accuracy positioning with limited workspace, such as in assembly of PCBs! as micro manipulators mounted on the end effector of larger but slower serial manipulators! as high speed/high-precision milling machines Filippo Sanfilippo 52
53 Parallel robots Two examples of popular parallel robots are the Stewart platform and the Delta robot. Stewart platform Delta robot Filippo Sanfilippo 53
54 Delta robot A delta robot is a type of parallel robot. It consists of three arms connected to universal joints at the base. The key design feature is the use of parallelograms in the arms, which maintains the orientation of the end effector. The key concept of the Delta robot is the use of parallelograms. These parallelograms restrict the movement of the end platform to pure translation (only movement in the X, Y or Z direction). Because the actuators are all located in the base, and the arms can be made of a light composite material the moving parts of the Delta robot have a small inertia. This allows for very high accelerations. Check out: Kinematics Model Filippo Sanfilippo 54
55 Programming a delta robot The robot can be controlled by using:! keyboard! joystick! mouse! accelerometer!... Check out: A parallel delta robotcontrolled via iphone accelerometer Filippo Sanfilippo 55
56 Homework 01: Servo as input device Reading the voltage from the center pin of the a servo s potentiometer so that it can be used as an input as well as an output device. Useful for: Collision detection on unpowered arms (or even poor man s torque detection by measuring the difference between what you requested and the actual position, assuming the servo doesn t break); Physical keyframing; you move the arms of the thing you are animating manually, then press a button to record that position, repeat a number of times and then have the computer play it back; Haptic feedback, if you can control the servo fast enough (doubtful, but worth a try). Check out: Servo as input device Robot Arm Remote Control Interface Filippo Sanfilippo 56
57 Homework 01: Servo as input device Hack-free/ Check out: Servo as input device Robot Arm Remote Control Interface Filippo Sanfilippo 57
58 Homework 02: Web Based Servo Control Check out: Web Based Servo Control Filippo Sanfilippo 58
59 Homework 03: Arduino 3DOF Head Tracker Check out: Arduino 3DOF Head Tracker Filippo Sanfilippo 59
60 Homework 04: Pong with the Arduino Check out: Pong with the Arduino Filippo Sanfilippo 60
61 Homework 05: Arduino Robotic Arm Build a basic Arduino robotic arm using 3 servos. Check out: Arduino robotic arm Filippo Sanfilippo 61
62 Exercises - Binary LEDs Clock - Temperature monitor (LCD and some LEDs) - Finger controlled servo (using a flex sensor) - Relaxing light (photo resistor and LEDs) Filippo Sanfilippo 62
63 Other material (AI and ANN) Filippo Sanfilippo 63
64 Thanks for your attention! Any questions? Filippo Sanfilippo 64
Intelligent Systems Design in a Non Engineering Curriculum. Embedded Systems Without Major Hardware Engineering
 Intelligent Systems Design in a Non Engineering Curriculum Embedded Systems Without Major Hardware Engineering Emily A. Brand Dept. of Computer Science Loyola University Chicago eabrand@gmail.com William
Intelligent Systems Design in a Non Engineering Curriculum Embedded Systems Without Major Hardware Engineering Emily A. Brand Dept. of Computer Science Loyola University Chicago eabrand@gmail.com William
Rodni What will yours be?
 Rodni What will yours be? version 4 Welcome to Rodni, a modular animatronic animal of your own creation for learning how easy it is to enter the world of software programming and micro controllers. During
Rodni What will yours be? version 4 Welcome to Rodni, a modular animatronic animal of your own creation for learning how easy it is to enter the world of software programming and micro controllers. During
Disclaimer. Arduino Hands-On 2 CS5968 / ART4455 9/1/10. ! Many of these slides are mine. ! But, some are stolen from various places on the web
 Arduino Hands-On 2 CS5968 / ART4455 Disclaimer! Many of these slides are mine! But, some are stolen from various places on the web! todbot.com Bionic Arduino and Spooky Arduino class notes from Tod E.Kurt!
Arduino Hands-On 2 CS5968 / ART4455 Disclaimer! Many of these slides are mine! But, some are stolen from various places on the web! todbot.com Bionic Arduino and Spooky Arduino class notes from Tod E.Kurt!
Arduino Digital Out_QUICK RECAP
 Arduino Digital Out_QUICK RECAP BLINK File> Examples>Digital>Blink int ledpin = 13; // LED connected to digital pin 13 // The setup() method runs once, when the sketch starts void setup() // initialize
Arduino Digital Out_QUICK RECAP BLINK File> Examples>Digital>Blink int ledpin = 13; // LED connected to digital pin 13 // The setup() method runs once, when the sketch starts void setup() // initialize
You'll create a lamp that turns a light on and off when you touch a piece of conductive material
 TOUCHY-FEELY LAMP You'll create a lamp that turns a light on and off when you touch a piece of conductive material Discover : installing third party libraries, creating a touch sensor Time : 5 minutes
TOUCHY-FEELY LAMP You'll create a lamp that turns a light on and off when you touch a piece of conductive material Discover : installing third party libraries, creating a touch sensor Time : 5 minutes
Coding with Arduino to operate the prosthetic arm
 Setup Board Install FTDI Drivers This is so that your RedBoard will be able to communicate with your computer. If you have Windows 8 or above you might already have the drivers. 1. Download the FTDI driver
Setup Board Install FTDI Drivers This is so that your RedBoard will be able to communicate with your computer. If you have Windows 8 or above you might already have the drivers. 1. Download the FTDI driver
FABO ACADEMY X ELECTRONIC DESIGN
 ELECTRONIC DESIGN MAKE A DEVICE WITH INPUT & OUTPUT The Shanghaino can be programmed to use many input and output devices (a motor, a light sensor, etc) uploading an instruction code (a program) to it
ELECTRONIC DESIGN MAKE A DEVICE WITH INPUT & OUTPUT The Shanghaino can be programmed to use many input and output devices (a motor, a light sensor, etc) uploading an instruction code (a program) to it
.:Twisting:..:Potentiometers:.
 CIRC-08.:Twisting:..:Potentiometers:. WHAT WE RE DOING: Along with the digital pins, the also has 6 pins which can be used for analog input. These inputs take a voltage (from 0 to 5 volts) and convert
CIRC-08.:Twisting:..:Potentiometers:. WHAT WE RE DOING: Along with the digital pins, the also has 6 pins which can be used for analog input. These inputs take a voltage (from 0 to 5 volts) and convert
Lab 2: Blinkie Lab. Objectives. Materials. Theory
 Lab 2: Blinkie Lab Objectives This lab introduces the Arduino Uno as students will need to use the Arduino to control their final robot. Students will build a basic circuit on their prototyping board and
Lab 2: Blinkie Lab Objectives This lab introduces the Arduino Uno as students will need to use the Arduino to control their final robot. Students will build a basic circuit on their prototyping board and
Welcome to Arduino Day 2016
 Welcome to Arduino Day 2016 An Intro to Arduino From Zero to Hero in an Hour! Paul Court (aka @Courty) Welcome to the SLMS Arduino Day 2016 Arduino / Genuino?! What?? Part 1 Intro Quick Look at the Uno
Welcome to Arduino Day 2016 An Intro to Arduino From Zero to Hero in an Hour! Paul Court (aka @Courty) Welcome to the SLMS Arduino Day 2016 Arduino / Genuino?! What?? Part 1 Intro Quick Look at the Uno
Attribution Thank you to Arduino and SparkFun for open source access to reference materials.
 Attribution Thank you to Arduino and SparkFun for open source access to reference materials. Contents Parts Reference... 1 Installing Arduino... 7 Unit 1: LEDs, Resistors, & Buttons... 7 1.1 Blink (Hello
Attribution Thank you to Arduino and SparkFun for open source access to reference materials. Contents Parts Reference... 1 Installing Arduino... 7 Unit 1: LEDs, Resistors, & Buttons... 7 1.1 Blink (Hello
EE-110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Labs Introduction to Arduino
 EE-110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Labs 10-11 Introduction to Arduino In this lab we will introduce the idea of using a microcontroller as a tool for controlling
EE-110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Labs 10-11 Introduction to Arduino In this lab we will introduce the idea of using a microcontroller as a tool for controlling
Introduction to. An Open-Source Prototyping Platform. Hans-Petter Halvorsen
 Introduction to An Open-Source Prototyping Platform Hans-Petter Halvorsen Contents 1.Overview 2.Installation 3.Arduino Starter Kit 4.Arduino TinkerKit 5.Arduino Examples 6.LabVIEW Interface for Arduino
Introduction to An Open-Source Prototyping Platform Hans-Petter Halvorsen Contents 1.Overview 2.Installation 3.Arduino Starter Kit 4.Arduino TinkerKit 5.Arduino Examples 6.LabVIEW Interface for Arduino
For this exercise, you will need a partner, an Arduino kit (in the plastic tub), and a laptop with the Arduino programming environment.
 Physics 222 Name: Exercise 6: Mr. Blinky This exercise is designed to help you wire a simple circuit based on the Arduino microprocessor, which is a particular brand of microprocessor that also includes
Physics 222 Name: Exercise 6: Mr. Blinky This exercise is designed to help you wire a simple circuit based on the Arduino microprocessor, which is a particular brand of microprocessor that also includes
Lab 5: Arduino Uno Microcontroller Innovation Fellows Program Bootcamp Prof. Steven S. Saliterman
 Lab 5: Arduino Uno Microcontroller Innovation Fellows Program Bootcamp Prof. Steven S. Saliterman Exercise 5-1: Familiarization with Lab Box Contents Objective: To review the items required for working
Lab 5: Arduino Uno Microcontroller Innovation Fellows Program Bootcamp Prof. Steven S. Saliterman Exercise 5-1: Familiarization with Lab Box Contents Objective: To review the items required for working
Computational Crafting with Arduino. Christopher Michaud Marist School ECEP Programs, Georgia Tech
 Computational Crafting with Arduino Christopher Michaud Marist School ECEP Programs, Georgia Tech Introduction What do you want to learn and do today? Goals with Arduino / Computational Crafting Purpose
Computational Crafting with Arduino Christopher Michaud Marist School ECEP Programs, Georgia Tech Introduction What do you want to learn and do today? Goals with Arduino / Computational Crafting Purpose
Industrial Automation Training Academy. Arduino, LabVIEW & PLC Training Programs Duration: 6 Months (180 ~ 240 Hours)
 nfi Industrial Automation Training Academy Presents Arduino, LabVIEW & PLC Training Programs Duration: 6 Months (180 ~ 240 Hours) For: Electronics & Communication Engineering Electrical Engineering Instrumentation
nfi Industrial Automation Training Academy Presents Arduino, LabVIEW & PLC Training Programs Duration: 6 Months (180 ~ 240 Hours) For: Electronics & Communication Engineering Electrical Engineering Instrumentation
Training Schedule. Robotic System Design using Arduino Platform
 Training Schedule Robotic System Design using Arduino Platform Session - 1 Embedded System Design Basics : Scope : To introduce Embedded Systems hardware design fundamentals to students. Processor Selection
Training Schedule Robotic System Design using Arduino Platform Session - 1 Embedded System Design Basics : Scope : To introduce Embedded Systems hardware design fundamentals to students. Processor Selection
Analog Feedback Servos
 Analog Feedback Servos Created by Bill Earl Last updated on 2018-01-21 07:07:32 PM UTC Guide Contents Guide Contents About Servos and Feedback What is a Servo? Open and Closed Loops Using Feedback Reading
Analog Feedback Servos Created by Bill Earl Last updated on 2018-01-21 07:07:32 PM UTC Guide Contents Guide Contents About Servos and Feedback What is a Servo? Open and Closed Loops Using Feedback Reading
Lecture 4: Basic Electronics. Lecture 4 Brief Introduction to Electronics and the Arduino
 Lecture 4: Basic Electronics Lecture 4 Page: 1 Brief Introduction to Electronics and the Arduino colintan@nus.edu.sg Lecture 4: Basic Electronics Page: 2 Objectives of this Lecture By the end of today
Lecture 4: Basic Electronics Lecture 4 Page: 1 Brief Introduction to Electronics and the Arduino colintan@nus.edu.sg Lecture 4: Basic Electronics Page: 2 Objectives of this Lecture By the end of today
3-Degrees of Freedom Robotic ARM Controller for Various Applications
 3-Degrees of Freedom Robotic ARM Controller for Various Applications Mohd.Maqsood Ali M.Tech Student Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering, VNR Vignana Jyothi Institute of Engineering
3-Degrees of Freedom Robotic ARM Controller for Various Applications Mohd.Maqsood Ali M.Tech Student Department of Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering, VNR Vignana Jyothi Institute of Engineering
MAKEVMA502 BASIC DIY KIT WITH ATMEGA2560 FOR ARDUINO USER MANUAL
 BASIC DIY KIT WITH ATMEGA2560 FOR ARDUINO USER MANUAL USER MANUAL 1. Introduction To all residents of the European Union Important environmental information about this product This symbol on the device
BASIC DIY KIT WITH ATMEGA2560 FOR ARDUINO USER MANUAL USER MANUAL 1. Introduction To all residents of the European Union Important environmental information about this product This symbol on the device
Workshops Elisava Introduction to programming and electronics (Scratch & Arduino)
 Workshops Elisava 2011 Introduction to programming and electronics (Scratch & Arduino) What is programming? Make an algorithm to do something in a specific language programming. Algorithm: a procedure
Workshops Elisava 2011 Introduction to programming and electronics (Scratch & Arduino) What is programming? Make an algorithm to do something in a specific language programming. Algorithm: a procedure
Arduino Platform Capabilities in Multitasking. environment.
 7 th International Scientific Conference Technics and Informatics in Education Faculty of Technical Sciences, Čačak, Serbia, 25-27 th May 2018 Session 3: Engineering Education and Practice UDC: 004.42
7 th International Scientific Conference Technics and Informatics in Education Faculty of Technical Sciences, Čačak, Serbia, 25-27 th May 2018 Session 3: Engineering Education and Practice UDC: 004.42
1 Introduction. 2 Embedded Electronics Primer. 2.1 The Arduino
 Beginning Embedded Electronics for Botballers Using the Arduino Matthew Thompson Allen D. Nease High School matthewbot@gmail.com 1 Introduction Robotics is a unique and multidisciplinary field, where successful
Beginning Embedded Electronics for Botballers Using the Arduino Matthew Thompson Allen D. Nease High School matthewbot@gmail.com 1 Introduction Robotics is a unique and multidisciplinary field, where successful
TWEAK THE ARDUINO LOGO
 TWEAK THE ARDUINO LOGO Using serial communication, you'll use your Arduino to control a program on your computer Discover : serial communication with a computer program, Processing Time : 45 minutes Level
TWEAK THE ARDUINO LOGO Using serial communication, you'll use your Arduino to control a program on your computer Discover : serial communication with a computer program, Processing Time : 45 minutes Level
BEYOND TOYS. Wireless sensor extension pack. Tom Frissen s
 LEGO BEYOND TOYS Wireless sensor extension pack Tom Frissen s040915 t.e.l.n.frissen@student.tue.nl December 2008 Faculty of Industrial Design Eindhoven University of Technology 1 2 TABLE OF CONTENT CLASS
LEGO BEYOND TOYS Wireless sensor extension pack Tom Frissen s040915 t.e.l.n.frissen@student.tue.nl December 2008 Faculty of Industrial Design Eindhoven University of Technology 1 2 TABLE OF CONTENT CLASS
Arduino
 Arduino Class Kit Contents A Word on Safety Electronics can hurt you Lead in some of the parts Wash up afterwards You can hurt electronics Static-sensitive: don t shuffle your feet & touch Wires only
Arduino Class Kit Contents A Word on Safety Electronics can hurt you Lead in some of the parts Wash up afterwards You can hurt electronics Static-sensitive: don t shuffle your feet & touch Wires only
Lecture 6. Interfacing Digital and Analog Devices to Arduino. Intro to Arduino
 Lecture 6 Interfacing Digital and Analog Devices to Arduino. Intro to Arduino PWR IN USB (to Computer) RESET SCL\SDA (I2C Bus) POWER 5V / 3.3V / GND Analog INPUTS Digital I\O PWM(3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11) Components
Lecture 6 Interfacing Digital and Analog Devices to Arduino. Intro to Arduino PWR IN USB (to Computer) RESET SCL\SDA (I2C Bus) POWER 5V / 3.3V / GND Analog INPUTS Digital I\O PWM(3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11) Components
Arduino STEAM Academy Arduino STEM Academy Art without Engineering is dreaming. Engineering without Art is calculating. - Steven K.
 Arduino STEAM Academy Arduino STEM Academy Art without Engineering is dreaming. Engineering without Art is calculating. - Steven K. Roberts Page 1 See Appendix A, for Licensing Attribution information
Arduino STEAM Academy Arduino STEM Academy Art without Engineering is dreaming. Engineering without Art is calculating. - Steven K. Roberts Page 1 See Appendix A, for Licensing Attribution information
CONSTRUCTION GUIDE IR Alarm. Robobox. Level I
 CONSTRUCTION GUIDE Robobox Level I This month s montage is an that will allow you to detect any intruder. When a movement is detected, the alarm will turn its LEDs on and buzz to a personalized tune. 1X
CONSTRUCTION GUIDE Robobox Level I This month s montage is an that will allow you to detect any intruder. When a movement is detected, the alarm will turn its LEDs on and buzz to a personalized tune. 1X
Montgomery Village Arduino Meetup Dec 10, 2016
 Montgomery Village Arduino Meetup Dec 10, 2016 Making Microcontrollers Multitask or How to teach your Arduinos to walk and chew gum at the same time (metaphorically speaking) Background My personal project
Montgomery Village Arduino Meetup Dec 10, 2016 Making Microcontrollers Multitask or How to teach your Arduinos to walk and chew gum at the same time (metaphorically speaking) Background My personal project
1Getting Started SIK BINDER //3
 SIK BINDER //1 SIK BINDER //2 1Getting Started SIK BINDER //3 Sparkfun Inventor s Kit Teacher s Helper These worksheets and handouts are supplemental material intended to make the educator s job a little
SIK BINDER //1 SIK BINDER //2 1Getting Started SIK BINDER //3 Sparkfun Inventor s Kit Teacher s Helper These worksheets and handouts are supplemental material intended to make the educator s job a little
Lesson 3: Arduino. Goals
 Introduction: This project introduces you to the wonderful world of Arduino and how to program physical devices. In this lesson you will learn how to write code and make an LED flash. Goals 1 - Get to
Introduction: This project introduces you to the wonderful world of Arduino and how to program physical devices. In this lesson you will learn how to write code and make an LED flash. Goals 1 - Get to
Arduino Workshop 01. AD32600 Physical Computing Prof. Fabian Winkler Fall 2014
 AD32600 Physical Computing Prof. Fabian Winkler Fall 2014 Arduino Workshop 01 This workshop provides an introductory overview of the Arduino board, basic electronic components and closes with a few basic
AD32600 Physical Computing Prof. Fabian Winkler Fall 2014 Arduino Workshop 01 This workshop provides an introductory overview of the Arduino board, basic electronic components and closes with a few basic
Arduino An Introduction
 Arduino An Introduction Hardware and Programming Presented by Madu Suthanan, P. Eng., FEC. Volunteer, Former Chair (2013-14) PEO Scarborough Chapter 2 Arduino for Mechatronics 2017 This note is for those
Arduino An Introduction Hardware and Programming Presented by Madu Suthanan, P. Eng., FEC. Volunteer, Former Chair (2013-14) PEO Scarborough Chapter 2 Arduino for Mechatronics 2017 This note is for those
MICROCONTROLLERS BASIC INPUTS and OUTPUTS (I/O)
 PH-315 Portland State University MICROCONTROLLERS BASIC INPUTS and OUTPUTS (I/O) ABSTRACT A microcontroller is an integrated circuit containing a processor and programmable read-only memory, 1 which is
PH-315 Portland State University MICROCONTROLLERS BASIC INPUTS and OUTPUTS (I/O) ABSTRACT A microcontroller is an integrated circuit containing a processor and programmable read-only memory, 1 which is
Demon Pumpkin APPROXIMATE TIME (EXCLUDING PREPARATION WORK): 1 HOUR PREREQUISITES: PART LIST:
 Demon Pumpkin This is a lab guide for creating your own simple animatronic pumpkin. This project encourages students and makers to innovate upon the base design to add their own personal touches. APPROXIMATE
Demon Pumpkin This is a lab guide for creating your own simple animatronic pumpkin. This project encourages students and makers to innovate upon the base design to add their own personal touches. APPROXIMATE
Arduino Robotic Projects By Richard Grimmett
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with arduino robotic projects
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with arduino robotic projects
Total Hours Registration through Website or for further details please visit (Refer Upcoming Events Section)
 Total Hours 110-150 Registration Q R Code Registration through Website or for further details please visit http://www.rknec.edu/ (Refer Upcoming Events Section) Module 1: Basics of Microprocessor & Microcontroller
Total Hours 110-150 Registration Q R Code Registration through Website or for further details please visit http://www.rknec.edu/ (Refer Upcoming Events Section) Module 1: Basics of Microprocessor & Microcontroller
HAW-Arduino. Sensors and Arduino F. Schubert HAW - Arduino 1
 HAW-Arduino Sensors and Arduino 14.10.2010 F. Schubert HAW - Arduino 1 Content of the USB-Stick PDF-File of this script Arduino-software Source-codes Helpful links 14.10.2010 HAW - Arduino 2 Report for
HAW-Arduino Sensors and Arduino 14.10.2010 F. Schubert HAW - Arduino 1 Content of the USB-Stick PDF-File of this script Arduino-software Source-codes Helpful links 14.10.2010 HAW - Arduino 2 Report for
Advanced Mechatronics 1 st Mini Project. Remote Control Car. Jose Antonio De Gracia Gómez, Amartya Barua March, 25 th 2014
 Advanced Mechatronics 1 st Mini Project Remote Control Car Jose Antonio De Gracia Gómez, Amartya Barua March, 25 th 2014 Remote Control Car Manual Control with the remote and direction buttons Automatic
Advanced Mechatronics 1 st Mini Project Remote Control Car Jose Antonio De Gracia Gómez, Amartya Barua March, 25 th 2014 Remote Control Car Manual Control with the remote and direction buttons Automatic
MICROCONTROLLERS BASIC INPUTS and OUTPUTS (I/O)
 PH-315 Portland State University MICROCONTROLLERS BASIC INPUTS and OUTPUTS (I/O) ABSTRACT A microcontroller is an integrated circuit containing a processor and programmable read-only memory, 1 which is
PH-315 Portland State University MICROCONTROLLERS BASIC INPUTS and OUTPUTS (I/O) ABSTRACT A microcontroller is an integrated circuit containing a processor and programmable read-only memory, 1 which is
Objectives: Learn what an Arduino is and what it can do Learn what an LED is and how to use it Be able to wire and program an LED to blink
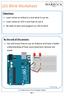 Objectives: Learn what an Arduino is and what it can do Learn what an LED is and how to use it Be able to wire and program an LED to blink By the end of this session: You will know how to use an Arduino
Objectives: Learn what an Arduino is and what it can do Learn what an LED is and how to use it Be able to wire and program an LED to blink By the end of this session: You will know how to use an Arduino
Embedded Systems & Robotics (Winter Training Program) 6 Weeks/45 Days
 Embedded Systems & Robotics (Winter Training Program) 6 Weeks/45 Days PRESENTED BY RoboSpecies Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Office: W-53G, Sector-11, Noida-201301, U.P. Contact us: Email: stp@robospecies.com
Embedded Systems & Robotics (Winter Training Program) 6 Weeks/45 Days PRESENTED BY RoboSpecies Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Office: W-53G, Sector-11, Noida-201301, U.P. Contact us: Email: stp@robospecies.com
Saturday Academy Program
 Lesson Plans High School Courses Donald L. McCoy K-to-College STEM Education Consultant thempitman@gmail.com Last Update: October 17, 2018 Virtual Reality Coding using PlayCanvas RobotC Coding Applications
Lesson Plans High School Courses Donald L. McCoy K-to-College STEM Education Consultant thempitman@gmail.com Last Update: October 17, 2018 Virtual Reality Coding using PlayCanvas RobotC Coding Applications
ARDUINO / GENUINO. start as professional. short course in a book. faculty of engineering technology
 ARDUINO / GENUINO start as professional short course in a book faculty of engineering technology Publisher Universiti Malaysia Pahang Kuantan 2017 Copyright Universiti Malaysia Pahang, 2017 First Published,
ARDUINO / GENUINO start as professional short course in a book faculty of engineering technology Publisher Universiti Malaysia Pahang Kuantan 2017 Copyright Universiti Malaysia Pahang, 2017 First Published,
Mechatronics Engineering and Automation Faculty of Engineering, Ain Shams University MCT-151, Spring 2015 Lab-4: Electric Actuators
 Mechatronics Engineering and Automation Faculty of Engineering, Ain Shams University MCT-151, Spring 2015 Lab-4: Electric Actuators Ahmed Okasha, Assistant Lecturer okasha1st@gmail.com Objective Have a
Mechatronics Engineering and Automation Faculty of Engineering, Ain Shams University MCT-151, Spring 2015 Lab-4: Electric Actuators Ahmed Okasha, Assistant Lecturer okasha1st@gmail.com Objective Have a
LESSONS Lesson 1. Microcontrollers and SBCs. The Big Idea: Lesson 1: Microcontrollers and SBCs. Background: What, precisely, is computer science?
 LESSONS Lesson Lesson : Microcontrollers and SBCs Microcontrollers and SBCs The Big Idea: This book is about computer science. It is not about the Arduino, the C programming language, electronic components,
LESSONS Lesson Lesson : Microcontrollers and SBCs Microcontrollers and SBCs The Big Idea: This book is about computer science. It is not about the Arduino, the C programming language, electronic components,
NAMASKAR ROBOT-WHICH PROVIDES SERVICE
 Int. J. Elec&Electr.Eng&Telecoms. 2014 V Sai Krishna and R Sunitha, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2319 2518 www.ijeetc.com Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2014 2014 IJEETC. All Rights Reserved NAMASKAR ROBOT-WHICH PROVIDES
Int. J. Elec&Electr.Eng&Telecoms. 2014 V Sai Krishna and R Sunitha, 2014 Research Paper ISSN 2319 2518 www.ijeetc.com Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2014 2014 IJEETC. All Rights Reserved NAMASKAR ROBOT-WHICH PROVIDES
A Do-and-See Approach for Learning Mechatronics Concepts
 Proceedings of the 5 th International Conference of Control, Dynamic Systems, and Robotics (CDSR'18) Niagara Falls, Canada June 7 9, 2018 Paper No. 124 DOI: 10.11159/cdsr18.124 A Do-and-See Approach for
Proceedings of the 5 th International Conference of Control, Dynamic Systems, and Robotics (CDSR'18) Niagara Falls, Canada June 7 9, 2018 Paper No. 124 DOI: 10.11159/cdsr18.124 A Do-and-See Approach for
APDS-9960 RGB and Gesture Sensor Hookup Guide
 Page 1 of 12 APDS-9960 RGB and Gesture Sensor Hookup Guide Introduction Touchless gestures are the new frontier in the world of human-machine interfaces. By swiping your hand over a sensor, you can control
Page 1 of 12 APDS-9960 RGB and Gesture Sensor Hookup Guide Introduction Touchless gestures are the new frontier in the world of human-machine interfaces. By swiping your hand over a sensor, you can control
Arduino Sensor Beginners Guide
 Arduino Sensor Beginners Guide So you want to learn arduino. Good for you. Arduino is an easy to use, cheap, versatile and powerful tool that can be used to make some very effective sensors. This guide
Arduino Sensor Beginners Guide So you want to learn arduino. Good for you. Arduino is an easy to use, cheap, versatile and powerful tool that can be used to make some very effective sensors. This guide
ISSN: [Singh* et al., 6(6): June, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116
![ISSN: [Singh* et al., 6(6): June, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116 ISSN: [Singh* et al., 6(6): June, 2017] Impact Factor: 4.116](/thumbs/96/126741285.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY WORKING, OPERATION AND TYPES OF ARDUINO MICROCONTROLLER Bhupender Singh, Manisha Verma Assistant Professor, Electrical Department,
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY WORKING, OPERATION AND TYPES OF ARDUINO MICROCONTROLLER Bhupender Singh, Manisha Verma Assistant Professor, Electrical Department,
CURIE Academy, Summer 2014 Lab 2: Computer Engineering Software Perspective Sign-Off Sheet
 Lab : Computer Engineering Software Perspective Sign-Off Sheet NAME: NAME: DATE: Sign-Off Milestone TA Initials Part 1.A Part 1.B Part.A Part.B Part.C Part 3.A Part 3.B Part 3.C Test Simple Addition Program
Lab : Computer Engineering Software Perspective Sign-Off Sheet NAME: NAME: DATE: Sign-Off Milestone TA Initials Part 1.A Part 1.B Part.A Part.B Part.C Part 3.A Part 3.B Part 3.C Test Simple Addition Program
100UF CAPACITOR POTENTIOMETER SERVO MOTOR MOTOR ARM. MALE HEADER PIN (3 pins) INGREDIENTS
 05 POTENTIOMETER SERVO MOTOR MOTOR ARM 100UF CAPACITOR MALE HEADER PIN (3 pins) INGREDIENTS 63 MOOD CUE USE A SERVO MOTOR TO MAKE A MECHANICAL GAUGE TO POINT OUT WHAT SORT OF MOOD YOU RE IN THAT DAY Discover:
05 POTENTIOMETER SERVO MOTOR MOTOR ARM 100UF CAPACITOR MALE HEADER PIN (3 pins) INGREDIENTS 63 MOOD CUE USE A SERVO MOTOR TO MAKE A MECHANICAL GAUGE TO POINT OUT WHAT SORT OF MOOD YOU RE IN THAT DAY Discover:
Arduino: Sensors for Fun and Non Profit
 Arduino: Sensors for Fun and Non Profit Slides and Programs: http://pamplin.com/dms/ Nicholas Webb DMS: @NickWebb 1 Arduino: Sensors for Fun and Non Profit Slides and Programs: http://pamplin.com/dms/
Arduino: Sensors for Fun and Non Profit Slides and Programs: http://pamplin.com/dms/ Nicholas Webb DMS: @NickWebb 1 Arduino: Sensors for Fun and Non Profit Slides and Programs: http://pamplin.com/dms/
Setup Download the Arduino library (link) for Processing and the Lab 12 sketches (link).
 Lab 12 Connecting Processing and Arduino Overview In the previous lab we have examined how to connect various sensors to the Arduino using Scratch. While Scratch enables us to make simple Arduino programs,
Lab 12 Connecting Processing and Arduino Overview In the previous lab we have examined how to connect various sensors to the Arduino using Scratch. While Scratch enables us to make simple Arduino programs,
Arduino Lesson 1. Blink. Created by Simon Monk
 Arduino Lesson 1. Blink Created by Simon Monk Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview Parts Part Qty The 'L' LED Loading the 'Blink' Example Saving a Copy of 'Blink' Uploading Blink to the Board How 'Blink'
Arduino Lesson 1. Blink Created by Simon Monk Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview Parts Part Qty The 'L' LED Loading the 'Blink' Example Saving a Copy of 'Blink' Uploading Blink to the Board How 'Blink'
Module: Arduino as Signal Generator
 Name/NetID: Teammate/NetID: Module: Laboratory Outline In our continuing quest to access the development and debugging capabilities of the equipment on your bench at home Arduino/RedBoard as signal generator.
Name/NetID: Teammate/NetID: Module: Laboratory Outline In our continuing quest to access the development and debugging capabilities of the equipment on your bench at home Arduino/RedBoard as signal generator.
Embedded systems. Exercise session 1. Introduction and project presentation
 Embedded systems Exercise session 1 Introduction and project presentation Introduction Contact Mail : michael.fonder@ulg.ac.be Office : 1.82a, Montefiore Website for the exercise sessions and the project
Embedded systems Exercise session 1 Introduction and project presentation Introduction Contact Mail : michael.fonder@ulg.ac.be Office : 1.82a, Montefiore Website for the exercise sessions and the project
Programming a Servo. Servo. Red Wire. Black Wire. White Wire
 Programming a Servo Learn to connect wires and write code to program a Servo motor. If you have gone through the LED Circuit and LED Blink exercises, you are ready to move on to programming a Servo. A
Programming a Servo Learn to connect wires and write code to program a Servo motor. If you have gone through the LED Circuit and LED Blink exercises, you are ready to move on to programming a Servo. A
Adafruit 16-Channel Servo Driver with Arduino
 Adafruit 16-Channel Servo Driver with Arduino Created by Bill Earl Last updated on 2015-09-29 06:19:37 PM EDT Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview Assembly Install the Servo Headers Solder all pins Add
Adafruit 16-Channel Servo Driver with Arduino Created by Bill Earl Last updated on 2015-09-29 06:19:37 PM EDT Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview Assembly Install the Servo Headers Solder all pins Add
UTILIZATION OF ROBOTICS AS CONTEMPORARY TECHNOLOGY AND AN EFFECTIVE TOOL IN TEACHING COMPUTER PROGRAMMING
 UTILIZATION OF ROBOTICS AS CONTEMPORARY TECHNOLOGY AND AN EFFECTIVE TOOL IN TEACHING COMPUTER PROGRAMMING Aaron R. Rababaah* 1, Ahmad A. Rabaa i 2 1 arababaah@auk.edu.kw 2 arabaai@auk.edu.kw Abstract Traditional
UTILIZATION OF ROBOTICS AS CONTEMPORARY TECHNOLOGY AND AN EFFECTIVE TOOL IN TEACHING COMPUTER PROGRAMMING Aaron R. Rababaah* 1, Ahmad A. Rabaa i 2 1 arababaah@auk.edu.kw 2 arabaai@auk.edu.kw Abstract Traditional
Servomotor Control with Arduino Integrated Development Environment. Application Notes. Bingyang Wu Mar 27, Introduction
 Servomotor Control with Arduino Integrated Development Environment Application Notes Bingyang Wu Mar 27, 2015 Introduction Arduino is a tool for making computers that can sense and control more of the
Servomotor Control with Arduino Integrated Development Environment Application Notes Bingyang Wu Mar 27, 2015 Introduction Arduino is a tool for making computers that can sense and control more of the
Experiment 1 Identification of Components and Breadboard Realization
 Experiment 1 Identification of Components and Breadboard Realization Aim: Introduction to the lab and identification of various components and realization using bread board. Hardware/Software Required:
Experiment 1 Identification of Components and Breadboard Realization Aim: Introduction to the lab and identification of various components and realization using bread board. Hardware/Software Required:
Lab 06: Ohm s Law and Servo Motor Control
 CS281: Computer Systems Lab 06: Ohm s Law and Servo Motor Control The main purpose of this lab is to build a servo motor control circuit. As with prior labs, there will be some exploratory sections designed
CS281: Computer Systems Lab 06: Ohm s Law and Servo Motor Control The main purpose of this lab is to build a servo motor control circuit. As with prior labs, there will be some exploratory sections designed
Arduino Uno Pinout Book
 Arduino Uno Pinout Book 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Arduino Uno Pinout Book Arduino Uno pinout - Power Supply. There are 3 ways to power the Arduino Uno: Barrel Jack - The Barrel jack, or DC Power Jack can be used
Arduino Uno Pinout Book 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Arduino Uno Pinout Book Arduino Uno pinout - Power Supply. There are 3 ways to power the Arduino Uno: Barrel Jack - The Barrel jack, or DC Power Jack can be used
OTTO THE BIPEDAL ROBOT
 Item 19 - Otto Monday, 15 October 2018 12:35 PM OTTO THE BIPEDAL ROBOT EXPLORE WALT: definition and decomposition of complex problems in terms of functional and non-functional requirements WILF - Defined
Item 19 - Otto Monday, 15 October 2018 12:35 PM OTTO THE BIPEDAL ROBOT EXPLORE WALT: definition and decomposition of complex problems in terms of functional and non-functional requirements WILF - Defined
1. Introduction to Analog I/O
 EduCake Analog I/O Intro 1. Introduction to Analog I/O In previous chapter, we introduced the 86Duino EduCake, talked about EduCake s I/O features and specification, the development IDE and multiple examples
EduCake Analog I/O Intro 1. Introduction to Analog I/O In previous chapter, we introduced the 86Duino EduCake, talked about EduCake s I/O features and specification, the development IDE and multiple examples
MAE106 Laboratory Exercises Lab # 1 - Laboratory tools
 MAE106 Laboratory Exercises Lab # 1 - Laboratory tools University of California, Irvine Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Goals To learn how to use the oscilloscope, function generator,
MAE106 Laboratory Exercises Lab # 1 - Laboratory tools University of California, Irvine Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Goals To learn how to use the oscilloscope, function generator,
Internet of Things Student STEM Project Jackson High School. Lesson 3: Arduino Solar Tracker
 Internet of Things Student STEM Project Jackson High School Lesson 3: Arduino Solar Tracker Lesson 3 Arduino Solar Tracker Time to complete Lesson 60-minute class period Learning objectives Students learn
Internet of Things Student STEM Project Jackson High School Lesson 3: Arduino Solar Tracker Lesson 3 Arduino Solar Tracker Time to complete Lesson 60-minute class period Learning objectives Students learn
A servo is an electric motor that takes in a pulse width modulated signal that controls direction and speed. A servo has three leads:
 Project 4: Arduino Servos Part 1 Description: A servo is an electric motor that takes in a pulse width modulated signal that controls direction and speed. A servo has three leads: a. Red: Current b. Black:
Project 4: Arduino Servos Part 1 Description: A servo is an electric motor that takes in a pulse width modulated signal that controls direction and speed. A servo has three leads: a. Red: Current b. Black:
Arduino Setup & Flexing the ExBow
 Arduino Setup & Flexing the ExBow What is Arduino? Before we begin, We must first download the Arduino and Ardublock software. For our Set-up we will be using Arduino. Arduino is an electronics platform.
Arduino Setup & Flexing the ExBow What is Arduino? Before we begin, We must first download the Arduino and Ardublock software. For our Set-up we will be using Arduino. Arduino is an electronics platform.
Proseminar Roboter und Aktivmedien. Outline of today s lecture. Acknowledgments. Educational robots achievements and challenging
 Proseminar Roboter und Aktivmedien Educational robots achievements and challenging Lecturer Lecturer Houxiang Houxiang Zhang Zhang TAMS, TAMS, Department Department of of Informatics Informatics University
Proseminar Roboter und Aktivmedien Educational robots achievements and challenging Lecturer Lecturer Houxiang Houxiang Zhang Zhang TAMS, TAMS, Department Department of of Informatics Informatics University
User Interface Engineering FS 2013
 User Interface Engineering FS 2013 Input Fundamentals 23.09.2013 1 Last Week Brief Overview of HCI as a discipline History of the UI Product perspective Research perspective Overview of own research as
User Interface Engineering FS 2013 Input Fundamentals 23.09.2013 1 Last Week Brief Overview of HCI as a discipline History of the UI Product perspective Research perspective Overview of own research as
Yihao Qian Team A: Aware Teammates: Amit Agarwal Harry Golash Menghan Zhang Zihao (Theo) Zhang ILR01 Oct.14, 2016
 Yihao Qian Team A: Aware Teammates: Amit Agarwal Harry Golash Menghan Zhang Zihao (Theo) Zhang ILR01 Oct.14, 2016 Individual Progress For sensors and motors lab, I was in charge of the servo and force
Yihao Qian Team A: Aware Teammates: Amit Agarwal Harry Golash Menghan Zhang Zihao (Theo) Zhang ILR01 Oct.14, 2016 Individual Progress For sensors and motors lab, I was in charge of the servo and force
Arduino as a tool for physics experiments
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Arduino as a tool for physics experiments To cite this article: Giovanni Organtini 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1076 012026 View the article online
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Arduino as a tool for physics experiments To cite this article: Giovanni Organtini 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1076 012026 View the article online
Programming 2 Servos. Learn to connect and write code to control two servos.
 Programming 2 Servos Learn to connect and write code to control two servos. Many students who visit the lab and learn how to use a Servo want to use 2 Servos in their project rather than just 1. This lesson
Programming 2 Servos Learn to connect and write code to control two servos. Many students who visit the lab and learn how to use a Servo want to use 2 Servos in their project rather than just 1. This lesson
RESET SIK GUIDE SCL SCA AREF GND ~11 ~10 13 RX TX ~9 8 7 ~6 ~5 4 ~3 DIGITAL (PWM~) 7-15V ON
 .V V IOREF -V A POWER ANALOG IN A A A A A VIN ~ ~ SCL SDA AREF ISP ~ ON DIGITAL (PWM~) ~ ~ ~ SIK GUIDE SCL SCA AREF ~ ~ Your guide to the SparkFun Inventor s Kit for the SparkFun RedBoard ~ ~ ~ ~ DIGITAL
.V V IOREF -V A POWER ANALOG IN A A A A A VIN ~ ~ SCL SDA AREF ISP ~ ON DIGITAL (PWM~) ~ ~ ~ SIK GUIDE SCL SCA AREF ~ ~ Your guide to the SparkFun Inventor s Kit for the SparkFun RedBoard ~ ~ ~ ~ DIGITAL
Pulse Width Modulation and
 Pulse Width Modulation and analogwrite ( ); 28 Materials needed to wire one LED. Odyssey Board 1 dowel Socket block Wire clip (optional) 1 Female to Female (F/F) wire 1 F/F resistor wire LED Note: The
Pulse Width Modulation and analogwrite ( ); 28 Materials needed to wire one LED. Odyssey Board 1 dowel Socket block Wire clip (optional) 1 Female to Female (F/F) wire 1 F/F resistor wire LED Note: The
CPSC 226 Lab Four Spring 2018
 CPSC 226 Lab Four Spring 2018 Directions. This lab is a quick introduction to programming your Arduino to do some basic internal operations and arithmetic, perform character IO, read analog voltages, drive
CPSC 226 Lab Four Spring 2018 Directions. This lab is a quick introduction to programming your Arduino to do some basic internal operations and arithmetic, perform character IO, read analog voltages, drive
ZX Distance and Gesture Sensor Hookup Guide
 Page 1 of 13 ZX Distance and Gesture Sensor Hookup Guide Introduction The ZX Distance and Gesture Sensor is a collaboration product with XYZ Interactive. The very smart people at XYZ Interactive have created
Page 1 of 13 ZX Distance and Gesture Sensor Hookup Guide Introduction The ZX Distance and Gesture Sensor is a collaboration product with XYZ Interactive. The very smart people at XYZ Interactive have created
Sensors and Sensing Motors, Encoders and Motor Control
 Sensors and Sensing Motors, Encoders and Motor Control Todor Stoyanov Mobile Robotics and Olfaction Lab Center for Applied Autonomous Sensor Systems Örebro University, Sweden todor.stoyanov@oru.se 05.11.2015
Sensors and Sensing Motors, Encoders and Motor Control Todor Stoyanov Mobile Robotics and Olfaction Lab Center for Applied Autonomous Sensor Systems Örebro University, Sweden todor.stoyanov@oru.se 05.11.2015
Introduction to the VEX Robotics Platform and ROBOTC Software
 Introduction to the VEX Robotics Platform and ROBOTC Software Computer Integrated Manufacturing 2013 Project Lead The Way, Inc. VEX Robotics Platform: Testbed for Learning Programming VEX Structure Subsystem
Introduction to the VEX Robotics Platform and ROBOTC Software Computer Integrated Manufacturing 2013 Project Lead The Way, Inc. VEX Robotics Platform: Testbed for Learning Programming VEX Structure Subsystem
2.017 DESIGN OF ELECTROMECHANICAL ROBOTIC SYSTEMS Fall 2009 Lab 4: Motor Control. October 5, 2009 Dr. Harrison H. Chin
 2.017 DESIGN OF ELECTROMECHANICAL ROBOTIC SYSTEMS Fall 2009 Lab 4: Motor Control October 5, 2009 Dr. Harrison H. Chin Formal Labs 1. Microcontrollers Introduction to microcontrollers Arduino microcontroller
2.017 DESIGN OF ELECTROMECHANICAL ROBOTIC SYSTEMS Fall 2009 Lab 4: Motor Control October 5, 2009 Dr. Harrison H. Chin Formal Labs 1. Microcontrollers Introduction to microcontrollers Arduino microcontroller
Arduino. AS220 Workshop. Part II Interactive Design with advanced Transducers Lutz Hamel
 AS220 Workshop Part II Interactive Design with advanced Transducers Lutz Hamel hamel@cs.uri.edu www.cs.uri.edu/~hamel/as220 How we see the computer Image source: Considering the Body, Kate Hartman, 2008.
AS220 Workshop Part II Interactive Design with advanced Transducers Lutz Hamel hamel@cs.uri.edu www.cs.uri.edu/~hamel/as220 How we see the computer Image source: Considering the Body, Kate Hartman, 2008.
VEX Robotics Platform and ROBOTC Software. Introduction
 VEX Robotics Platform and ROBOTC Software Introduction VEX Robotics Platform: Testbed for Learning Programming VEX Structure Subsystem VEX Structure Subsystem forms the base of every robot Contains square
VEX Robotics Platform and ROBOTC Software Introduction VEX Robotics Platform: Testbed for Learning Programming VEX Structure Subsystem VEX Structure Subsystem forms the base of every robot Contains square
TOP SERVO SIGNAL 5 SERVO SIGNAL 3 SERVO SIGNAL 4 SERVO SIGNAL 6 T B T B T B T B T B SERVO TRIGGER 1 BOTTOM
 Micro Miniatures Servo Controller Channel Location of connections and switches TOP SERVO SIGNAL SERVO SIGNAL 7 SERVO SIGNAL 6 SERVO SIGNAL 5 SERVO SIGNAL SERVO SIGNAL SERVO SIGNAL SERVO SIGNAL SIGNAL COMMON
Micro Miniatures Servo Controller Channel Location of connections and switches TOP SERVO SIGNAL SERVO SIGNAL 7 SERVO SIGNAL 6 SERVO SIGNAL 5 SERVO SIGNAL SERVO SIGNAL SERVO SIGNAL SERVO SIGNAL SIGNAL COMMON
PCB & Circuit Designing (Summer Training Program) 6 Weeks/ 45 Days PRESENTED BY
 PCB & Circuit Designing (Summer Training Program) 6 Weeks/ 45 Days PRESENTED BY RoboSpecies Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Office: D-66, First Floor, Sector- 07, Noida, UP Contact us: Email: stp@robospecies.com
PCB & Circuit Designing (Summer Training Program) 6 Weeks/ 45 Days PRESENTED BY RoboSpecies Technologies Pvt. Ltd. Office: D-66, First Floor, Sector- 07, Noida, UP Contact us: Email: stp@robospecies.com
Inspiring Creative Fun Ysbrydoledig Creadigol Hwyl. S4A - Scratch for Arduino Workbook
 Inspiring Creative Fun Ysbrydoledig Creadigol Hwyl S4A - Scratch for Arduino Workbook 1) Robotics Draw a robot. Consider the following and annotate: What will it look like? What will it do? How will you
Inspiring Creative Fun Ysbrydoledig Creadigol Hwyl S4A - Scratch for Arduino Workbook 1) Robotics Draw a robot. Consider the following and annotate: What will it look like? What will it do? How will you
AN ARDUINO CONTROLLED CHAOTIC PENDULUM FOR A REMOTE PHYSICS LABORATORY
 AN ARDUINO CONTROLLED CHAOTIC PENDULUM FOR A REMOTE PHYSICS LABORATORY J. C. Álvarez, J. Lamas, A. J. López, A. Ramil Universidade da Coruña (SPAIN) carlos.alvarez@udc.es, jlamas@udc.es, ana.xesus.lopez@udc.es,
AN ARDUINO CONTROLLED CHAOTIC PENDULUM FOR A REMOTE PHYSICS LABORATORY J. C. Álvarez, J. Lamas, A. J. López, A. Ramil Universidade da Coruña (SPAIN) carlos.alvarez@udc.es, jlamas@udc.es, ana.xesus.lopez@udc.es,
Understanding the Arduino to LabVIEW Interface
 E-122 Design II Understanding the Arduino to LabVIEW Interface Overview The Arduino microcontroller introduced in Design I will be used as a LabVIEW data acquisition (DAQ) device/controller for Experiments
E-122 Design II Understanding the Arduino to LabVIEW Interface Overview The Arduino microcontroller introduced in Design I will be used as a LabVIEW data acquisition (DAQ) device/controller for Experiments
introduction to Digital Electronics Install the Arduino IDE on your laptop if you haven t already!
 introduction to Digital Electronics Install the Arduino IDE 1.8.5 on your laptop if you haven t already! Electronics can add interactivity! Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from
introduction to Digital Electronics Install the Arduino IDE 1.8.5 on your laptop if you haven t already! Electronics can add interactivity! Any sufficiently advanced technology is indistinguishable from
Sten-Bot Robot Kit Stensat Group LLC, Copyright 2013
 Sten-Bot Robot Kit Stensat Group LLC, Copyright 2013 Legal Stuff Stensat Group LLC assumes no responsibility and/or liability for the use of the kit and documentation. There is a 90 day warranty for the
Sten-Bot Robot Kit Stensat Group LLC, Copyright 2013 Legal Stuff Stensat Group LLC assumes no responsibility and/or liability for the use of the kit and documentation. There is a 90 day warranty for the
Experiment 1: Robot Moves in 3ft squared makes sound and
 Experiment 1: Robot Moves in 3ft squared makes sound and turns on an LED at each turn then stop where it started. Edited: 9-7-2015 Purpose: Press a button, make a sound and wait 3 seconds before starting
Experiment 1: Robot Moves in 3ft squared makes sound and turns on an LED at each turn then stop where it started. Edited: 9-7-2015 Purpose: Press a button, make a sound and wait 3 seconds before starting
J. La Favre Using Arduino with Raspberry Pi February 7, 2018
 As you have already discovered, the Raspberry Pi is a very capable digital device. Nevertheless, it does have some weaknesses. For example, it does not produce a clean pulse width modulation output (unless
As you have already discovered, the Raspberry Pi is a very capable digital device. Nevertheless, it does have some weaknesses. For example, it does not produce a clean pulse width modulation output (unless
Sensors and Sensing Motors, Encoders and Motor Control
 Sensors and Sensing Motors, Encoders and Motor Control Todor Stoyanov Mobile Robotics and Olfaction Lab Center for Applied Autonomous Sensor Systems Örebro University, Sweden todor.stoyanov@oru.se 13.11.2014
Sensors and Sensing Motors, Encoders and Motor Control Todor Stoyanov Mobile Robotics and Olfaction Lab Center for Applied Autonomous Sensor Systems Örebro University, Sweden todor.stoyanov@oru.se 13.11.2014
Adafruit 16-Channel Servo Driver with Arduino
 Adafruit 16-Channel Servo Driver with Arduino Created by Bill Earl Last updated on 2017-11-26 09:41:23 PM UTC Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview Assembly Install the Servo Headers Solder all pins Add
Adafruit 16-Channel Servo Driver with Arduino Created by Bill Earl Last updated on 2017-11-26 09:41:23 PM UTC Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview Assembly Install the Servo Headers Solder all pins Add
Adafruit 16-Channel PWM/Servo HAT & Bonnet for Raspberry Pi
 Adafruit 16-Channel PWM/Servo HAT & Bonnet for Raspberry Pi Created by lady ada Last updated on 2018-03-21 09:56:10 PM UTC Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview Powering Servos Powering Servos / PWM OR
Adafruit 16-Channel PWM/Servo HAT & Bonnet for Raspberry Pi Created by lady ada Last updated on 2018-03-21 09:56:10 PM UTC Guide Contents Guide Contents Overview Powering Servos Powering Servos / PWM OR
