Global Challenges 12. Executive Summary. Risks that threaten. Global System Collapse. Major Asteroid Impact. Global Pandemic.
|
|
|
- Karin Jackson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Challenges Risks that threaten human civilisation Governance Governance System Governance Governance System Executive Summary Climate Change Nuclear Governance War System The case for a new category Climate Change Governance System Governance
2 Introduction Introduction This is the executive summary of a report about a limited number of global s that pose a threat to human civilisation, or even possibly to all human life. With such a focus it may surprise some readers to find that the report s essential aim is to inspire action and dialogue as well as an increased use of the methodologies used for assessment. The real focus is not on the almost unimaginable impacts of the s the report outlines. Its fundamental purpose is to encourage global collaboration and to use this new category of as a driver for innovation. The Challenges Foundation works to raise awareness of the greatest threats facing humanity. In particular climate change, other environmental damage and political violence, and how these threats are linked to poverty and the rapid growth in global population. These problems appear insurmountable without an international body with decision-making mandate. The Foundation is therefore working to identify possible solutions and models as to how the United Nations can develop, and initiate new ideas on working global governance. The idea that we face a number of global challenges threatening the very basis of our civilisation at the beginning of the st century is well accepted in the scientific community, and is studied at a number of leading universities. But there is still no coordinated approach to address this group of challenges and turn them into opportunities. Full report can be downloaded at globalchallenges.org/globals Contents - Introduction - s - The goals of the report - Report structure - A new category of global - Infinite impacts and thresholds - Methodology - Quick overview of each - Relations between global s - The technical difficulty of reducing the and the difficulty of collaboration - Uncertainties - Probability - Possible ways forward page History: the LA-60 document It is only 70 years ago that Edward Teller, one of the greatest physicists of his time, with his back-of-the-envelope calculations, produced results that differed drastically from all that had gone before.his calculations showed that the explosion of a nuclear bomb a creation of some of the brightest minds on the planet, including Teller himself could result in a chain reaction so powerful that it would ignite the world s atmosphere, thereby ending human life on Earth. Robert Oppenheimer, who led the Manhattan Project to develop the nuclear bomb, halted the project to see whether Teller s calculations were correct. The resulting document, LA-60: Ignition of the Atmosphere with Nuclear Bombs, concluded that Teller was wrong. But the sheer complexity drove the assessors to end their study by writing that further work on the subject [is] highly desirable. The LA-60 document can be seen as the first global challenge report addressing a category of s where the worst possible impact in all practical senses is infinite. Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary
3 s s icial ligence s This report has, to the best of the authors knowledge, created the first list of global s with impacts that for all practical purposes can be called infinite. It is also the first structured overview of key events related to such challenges and has tried to provide initial rough quantifications for the probabilities of these impacts. The report conducts its exploration within carefully defined bounds, resulting in a list of twelve s with a possible infinite outcome There were many challenges which might have been included on the list because of their ability to pose severe damage to humanity. They were excluded for one or more of three reasons:. Limited impact tsunamis, for example, and chemical pollution.. No effective countermeasures the report focuses on promoting effective interventions and so ignores challenges where nothing useful can be done to prevent or mitigate the impact, as with nearby gamma-ray bursts.. Included in other challenges. Many challenges are already covered by others, or are very similar to them. Population growth, for one, is significant for climate change and ecosystem catastrophe, but without direct large-scale impacts of its own. Governance It is worth noting that complex systems are often stable only within certain boundaries outside which the system can collapse and rapidly change to a new stable state. Such a collapse can trigger a process where change continues for a long time until a new stable state is found. None of the s in this report is likely to result directly in an infinite impact, and some cannot do so physically. All the s however are big enough to reach a threshold where the social and ecological systems become so unstable that an infinite impact could ensue. This is a report about two extremes, not one. It is about how a better understanding of the magnitude of the challenges can help the world to address the s it faces, and can help to create a path towards more sustainable development. It is a scientific assessment about the possibility of oblivion, certainly, Governance Governance but even more it is a call for action based on the assumption that humanity is able to rise to challenges and turn them into opportunities. We are confronted with possibly the greatest challenge ever and our response need to match this thorough global collaboration in new and innovative ways. System Nuclear War Governance System System Governance Major Asteroid Nuclear War logical strophe Bad Governance Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary
4 The goals of the report Report structure The goals of the report The four main goals of this report are to acknowledge, inspire, connect and deliver. The first of the report s goals acknowledging the existence of s with potential infinite impact seeks to help key stakeholders to acknowledge the existence of the category of s that could result in infinite impact and to show them that we can reduce or even eliminate most of them. The second inspires by showing the practical action that is taking place today. This report seeks to show that helping to meet these global challenges is perhaps the most important contribution anyone can make today, and highlights concrete examples to inspire a new generation of leaders. The third goal is to connect different groups at every level, so that leaders in different sectors connect with each other to encourage collaboration. This will need a specific focus on financial and security policy where significant s combine to demand action beyond the incremental. The fourth goal is to deliver actual strategies and initiatives that produce actual results. The report is a first step and its success will ultimately be measured only on how it contributes to concrete results. The report will have achieved its goals when key decision-makers recognise the magnitude of the possible s and our ability to reduce or even eliminate most of them. Report structure The first part of the report introduces and defines the global challenges and includes the methodology for selecting them. The second part is an overview of the twelve challenges and key events that illustrate strategic work to address them. It also lists for each challenge five important factors that influence its probability or impact. The challengesare divided into four different categories: current challenges includes those which currently threaten humanity because of its economic and technological development; exogenic challenges are those where the basic probability of an event is beyond human control, but where the probability and magnitude of the impact can be influenced; emerging challenges could both help to reduce the s associated with current challenges and also result in infinite impacts; The third part of the report discusses the relationship between the different challenges, because action to address one can increase the of another. Many solutions can also address multiple challenges, so there are significant benefits from understanding how they are linked. The fourth part is an overview, the first ever to the authors knowledge, of the probabilities of global challenges with potential infinite impacts. The fifth presents some of the most important underlying trends that influence the challenges, which often build up slowly to a threshold where very rapid changes can ensue. The sixth part presents an overview of possible ways forward. the last of the twelve is defined as a global policy challenge, a threat arising from future global governance as it resorts to destructive policies in response to the categories of challenge listed above. The goals. to acknowledge the existence of s with potential infinite impact. to inspire by showing the practical action that is taking place today.. to connect different groups at every level.. to deliver actual strategies and initiatives that produce actual results. Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary
5 A new category of global Infinite impacts and thresholds A new category of global The idea that there may be s where the impact can be described as infinite, defined as the end of human civilisation or even human life, is not new. However, it excites relatively little political or academic interest and the way it is treated in popular culture makes a serious discussion harder. For several reasons the potentially infinite impacts of the challenges in this report are not as well known as they should be. One reason is the way that extreme impacts are often masked by most of the theories and models used by governments and business today. Climate change is a good example, where almost all of the focus is on the most likely scenarios and there are few public studies that include the low-probability high-impact scenarios. In most reports about climate impacts, those caused by warming beyond five or six degrees Celsius are omitted from tables and graphs. Other aspects that contribute to this relative invisibility include the fact that extreme impacts are difficult to translate into monetary terms, they have a global scope, and they often require a timehorizon of a century or more. They cannot be understood simply by linear extrapolation of current trends, and they lack historical precedents. There is also the fact that the measures required to significantly reduce the probability of infinite impacts will be radical compared to a business-as-usual scenario. A scientific approach requires us to base our decisions on the whole probability distribution. The review of literature indicate that, under a business as usual scenario, new s with potential infinite impact is probably inseparable from the rapid technological development in areas like synthetic biology, nanotechnology and AI. Most s are linked to increased knowledge, economic and technical development that has brought many benefits. E.g. climate change is a result from the industrial revolution and fossil fuelbased development. The increased potential for global pandemics is one consequence of an integrated global economy where goods and services move quickly internationally. Similar challenges can be expected for synthetic biology, nanotechnology and AI. There are remedies, including technological and institutional, for all s. But they will require collaboration of a sort humanity has not achieved before, and the creation of systems which can deal with problems pre-emptively. It is important to understand that much of the knowledge and many tools that we have, and will develop, can be both a and a solution to s depending on context. Infinite impacts and thresholds probability There is a clear ethical dimension to the concept of infinite impact, because a very small group alive today can take decisions that will fundamentally affect all future generations. Its equally clear economic component can generate disagreement over issues such as discounting, which the report examines in some detail,considering for example the role of tipping points. The report distinguishes between the concepts of infinite impact where civilisation collapses to a state of great suffering and do not recover, or a situation where all human life end and infinite impact threshold an impact that can trigger a chain of Normal Risks Traditional measures and tools applicable events that could result first in a civilisation collapse, and then later result in an infinite impact. Such thresholds are especially important to recognise in a complex and interconnected society where resilience is decreeing. A collapse of civilisation is defined as a drastic decrease in human population size and political/ economic/social complexity, globally for an extended time. New Category Requires new measures and tools Threshold Risk = Probability x 0 impact 6 Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary 7
6 Quick overview of each Methodology In order to establish a list of global challenges with potential infinite impact a methodological triangulation was used, consisting of: Methodology A quantitative assessment of relevant literature. A strategic selection of relevant organisations and their priorities. A qualitative assessment with the help of expert workshops. Quick overview of each Two workshops were arranged where the selection of challenges was discussed, one with experts in Oxford at the Future of Humanity Institute and the other in London with experts from the financial sector. No challenge was excluded at the workshops, but one was added: the participants agreed to include System as a category. Current Relevant literature Estimations of impact Only literature where there is some estimation of impact that indicates the possibility of an infinite impact is included. Leading organisations priorities Possibility of addressing the : From the s gathered from literature and organisations only those where the probability or impact can be affected by human actions are included. Expert review Governance Climate Change Governance Qualitative assessment: Expert review in order to increase the probability of covering all relevant global s. Climate Change Governance System Nuclear War Current Climate Change System Future Bad Governance Current Future Bad Governance Governance Climate Change System Future Bad Governance Future BadSystem Governance Nuclear War Nuclear War System System Major Asteroid System Governance System 6 Nuclear War Governance Emerging Governance System Emerging Emerging System Exogenic Emerging Exogenic In order to increase the probability of covering all relevant s an overview of leading organisations' work was conducted. This list was then compared with the initial list and subjected to the same filter regarding the possibility to affect the probability or impact. Possibility of addressing the Current Identification of credible sources: search relevant literature in academic literature included in World of Knowledge and Google Scholar. Current Policy List of s Result: List of s with potentially infinite impacts. 8 Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary System Climate Change Governance 9 Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary
7 Quick overview of each - Climat Change / Quick overview of each - / Current Current key key The uncertainties in climate sensitivity models, including the tail. The likelihood - or not - of global coordination on controlling emissions. The future uptake of low carbon economies, including energy, mobility and food systems. Whether technological innovations will improve or worsen the situation, and by how much. The long-term climate impact caused by global warming. As for all s there are uncertainties in the estimates, and warming could be much more extreme than the middle estimates suggest. Feedback loops could mean global average temperatures increase by C or even 6 C over pre-industrial levels. Feedbacks could be the release of methane from permafrost or the dieback of the Amazon rainforest. The impact of global warming would be strongest in poorer countries, which could become completely uninhabitable for the highest range of warming. Mass deaths and famines, social collapse and mass migration are certainly possible in this scenario. Combined with shocks to the agriculture and biosphere-dependent industries of the more developed countries, this could lead to global conflict and possibly civilisation collapse. Further evidence of the comes from signs that past civilisation collapses have been driven by climate change. What the true probability distribution for pandemics is, especially at the tail. The capacity of international health systems to deal with an extreme pandemic. How fast medical research can proceed in an emergency. How mobility of goods and people, as well as population density, will affect pandemic transmission. Whether humans can develop novel and effective anti-pandemic solutions. An epidemic of infectious disease that has spread through human populations across a large region or even worldwide. There are grounds for suspecting that such a highimpact epidemic is more probable than usually assumed. All the features of an extremely devastating disease already exist in nature: essentially incurable (Ebola), nearly always fatal (rabies), extremely infectious (common cold), and long incubation periods (HIV). If a pathogen were to emerge that somehow combined these features (and influenza has demonstrated antigenic shift, the ability to combine features from different viruses), its death toll would be extreme. The world has changed considerably, making comparisons with the past problematic.today it has better sanitation and medical research, as well as national and supra-national institutions dedicated to combating diseases. But modern transport and dense human population allow infections to spread much more rapidly, and slums can be breeding grounds for disease. Current Current key key How relations between current and future nuclear powers develop. The probability of accidental war. Whether disarmament efforts will succeed in reducing the number of nuclear warheads. The likelihood of a nuclear winter. The long-term effects of a nuclear war on climate, infrastructure and technology. A new category of global. The likelihood of a full-scale nuclear war between the USA and Russia has probably decreased. Still, the potential for deliberate or accidental nuclear conflict has not been removed, with some estimates putting the in the next century or so at around 0%. A larger impact would depend on whether or not the war triggered what is often called a nuclear winter or something similar the creation of a pall of smoke high in the stratosphere that would plunge temperatures below freezing around the globe and possibly also destroy most of the ozone layer. The detonations would need to start firestorms in the targeted cities, which could lift the soot up into the stratosphere. The s are severe and recent models have confirmed the earlier analysis. The disintegration of the global food supply would make mass starvation and state collapse likely. The extent to which humans are dependent on the ecosystem. Whether there will be effective political measures taken to protect the ecosystem on a large scale. The likelihood of the emergence of sustainable economies. The positive and negative impacts on the ecosystems of both wealth and poverty. The long-term effects of an ecological collapse on ecosystems. This is where an ecosystem suffers a drastic, possibly permanent, reduction in carrying capacity for all organisms, often resulting in mass extinction. Humans are part of the global ecosystem and so fundamentally depend on it. Species extinction is now far faster than the historic rate, and attempts to quantify a safe ecological operating space place humanity well outside it. Many of the problems of ecological degradation interact to multiply the damage and (unlike previous, localised collapses) the whole world is potentially at. It seems plausible that some human lifestyles could be sustained in a relatively ecosystem independent way, at relatively low costs. Whether this can be achieved on a large scale in practice, especially during a collapse, will be a technological challenge and whether it is something we want is an ethical question. 0 Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary
8 Quick overview of each - System / Quick overview of each - / Current Exogenic key System key Whether global system collapse will trigger subsequent collapses or fragility in other areas. What the true trade-off is between efficiency and resilience. Whether effective regulation and resilience can be developed. Whether an external disruption will trigger a collapse. Whether an internal event will trigger a collapse. An economic or societal collapse on the global scale. The term has been used to describe a broad range of conditions. Often economic collapse is accompanied by social chaos, civil unrest and sometimes a breakdown of law and order. Societal collapse usually refers to the fall or disintegration of human societies, often along with their life support systems. The world economic and political system is made up of many actors with many objectives and many links between them. Such intricate, interconnected systems are subject to unexpected system-wide failures caused by the structure of the network even if each component of the network is reliable. This gives rise to systemic, when parts that individually may function well become vulnerable when connected as a system to a self-reinforcing joint that can spread from part to part, potentially affecting the entire system and possibly spilling over to related outside systems. Such effects have been observed in ecology, finance and critical infrastructure such as power grids. The possibility of collapse becomes more acute when several independent networks depend on each other. Whether countries will coordinate globally against super-volcano and damage. The predictability of supervolcanic eruptions. How directly destructive an eruption would be. The effectiveness of general mitigation efforts. How severe the long-term climate effects would be. Any volcano capable of producing an eruption with an ejecta volume greater than,000 km. This is thousands of times larger than normal eruptions. The danger from super-volcanoes is the amount of aerosols and dust projected into the upper atmosphere. This dust would absorb the Sun s rays and cause a global volcanic winter. The Mt Pinatubo eruption of 99 caused an average global cooling of surface temperatures by 0. C over three years, while the Toba eruption around 70,000 years ago is thought by some to have cooled global temperatures for over two centuries. The effect of these eruptions could be best compared with that of a nuclear war. The eruption would be more violent than the nuclear explosions, but would be less likely to ignite firestorms and other secondary effects. Exogenic Emerging key key Whether detection and tracking of asteroids and other dangerous space objects is sufficiently exhaustive. How feasible it is to deflect an asteroid. Whether measures such as evacuation could reduce the damage of an impact. The short- and long-term climate consequences of a collision. Whether our current civilisation could adapt to a post-impact world. Large asteroid collisions with objects km or more in size happen about once every twenty million years and would have an energy a hundred thousand times greater than the largest bomb ever detonated. A land impact would destroy an area the size of a nation like Holland. Larger asteroids could be extinction-level events. Asteroid impacts are probably one of the best understood of all s in this report. There has been some discussion about possible methods for deflecting asteroids found on a collision course with the planet. Should an impact occur the main destruction will not be from the initial impact, but from the clouds of dust projected into the upper atmosphere. The damage from such an impact winter could affect the climate, damage the biosphere, affect food supplies, and create political instability. The true destructive potential of synthetic biology, especially the tail. Whether the field will be successfully regulated, or successfully manage to regulate itself. Whether the field will usher in a new era of bio-warfare. Whether the tools of synthetic biology can be used defensively to create effective counter measures. The dangers of relying on synthetic biologists to estimate the danger of synthetic biology. The design and construction of biological devices and systems for useful purposes, but adding human intentionality to traditional pandemic s. Attempts at regulation or self-regulation are currently in their infancy, and may not develop as fast as research does. One of the most damaging impacts from synthetic biology would come from an engineered pathogen targeting humans or a crucial component of the ecosystem. This could emerge through military or commercial bio-warfare, bioterrorism (possibly using dual-use products developed by legitimate researchers, and currently unprotected by international legal regimes), or dangerous pathogens leaked from a lab. Of relevance is whether synthetic biology products become integrated into the global economy or biosphere. This could lead to additional vulnerabilities (a benign but widespread synthetic biology product could be specifically targeted as an entry point through which to cause damage). Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary
9 Quick overview of each - / Quick overview of each - / Governance Emerging Emerging key key The timeline for nanotech development. Which aspects of nanotech research will progress in what order. Whether small groups can assemble a weapons arsenal quickly. Whether nanotech tools can be used defensively or for surveillance. Whether nanotech tools or weaponry are made to be outside human control. Atomically precise manufacturing, the creation of effective, highthroughput manufacturing processes that operate at the atomic or molecular level. It could create new products such as smart or extremely resilient materials and would allow many different groups or even individuals to manufacture a wide range of things. This could lead to the easy construction of large arsenals of conventional or more novel weapons made possible by atomically precise manufacturing. Of particular relevance is whether nanotechnology allows the construction of nuclear bombs. But many of the world s current problems may be solvable with the manufacturing possibilities that nanotechnology would offer, such as depletion of natural resources, pollution, climate change, clean water and even poverty. Some have conjectured special self-replicating nanomachines which would be engineered to consume the entire environment. The misuse of medical nanotechnology is another scenario. Whether there will be extensive research into unknown s and their probabilities. The capacity to develop methods for limiting the combined probability of all uncertain s The capacity for estimating out of-model s. The culture of assessment in potentially y areas Whether general, non-specific mitigation or resilience measures are implemented. These represent the unknown unknowns in the family of global catastrophic challenges. They constitute an amalgamation of all the s that can appear extremely unlikely in isolation, but can combine to represent a not insignificant proportion of the exposure. One resolution to the Fermi paradox the apparent absence of alien life in the galaxy is that intelligent life destroys itself before beginning to expand into the galaxy. Results that increase or decrease the probability of this explanation modify the generic probability of intelligent life (self-)destruction, which includes uncertain s. Anthropic reasoning can also bound the total of human extinction, and hence estimate the unknown component. Nonspecific resilience and post-disaster rebuilding efforts will also reduce the damage from uncertain s, as would appropriate national and international regulatory regimes. Most of these methods would also help with the more conventional, known s, and badly need more investment. Emerging Policy key The reliability of AI predictions. Whether there will be a single dominant AI or a plethora of entities. How intelligent AIs will become. Whether extremely intelligent AIs can be controlled, and how. Whether whole brain emulations (human minds in computer form) will arrive before true AIs. AI is the intelligence exhibited by machines or software, and the branch of computer science that develops machines and software with human-level intelligence. The field is often defined as the study and design of intelligent agents, systems that perceive their environment and act to maximise their chances of success. Such extreme intelligences could not easily be controlled (either by the groups creating them, or by some international regulatory regime), and would probably act to boost their own intelligence and acquire maximal resources for almost all initial AI motivations. And if these motivations do not detail the survival and value of humanity, the intelligence will be driven to construct a world without humans. This makes extremely intelligent AIs a unique, in that extinction is more likely than lesser impacts. On a more positive note, an intelligence of such power could easily combat most other s in this report, making extremely intelligent AI into a tool of great potential. There is also the possibility of AI-enabled warfare and all the s of the technologies that AIs would make possible. An interesting version of this scenario is the possible creation of whole brain emulations, human brains scanned and physically represented in a machine. This would make the AIs into properly human minds, possibly alleviating a lot of problems. key How the severity of nondeadly policy failures can be compared with potential casualties. Whether poor governance will result in a collapse of the world system. How mass surveillance and other technological innovations will affect governance. Whether there will be new systems of governance in the future. Whether a world dictatorship may end up being constructed. Governance There are two main divisions in governance disasters: failing to solve major solvable problems, and actively causing worse outcomes. An example of the first would be failing to alleviate absolute poverty; of the second, constructing a global totalitarian state. Technology, political and social change may enable the construction of new forms of governance, which may be either much better or much worse. Two issues with governance disasters are first, the difficulty of estimating their probability, and second, the dependence of the impact of these disasters on subjective comparative evaluations: it is not impartially obvious how to rank continued poverty and global totalitarianism against billions of casualties or civilisation collapse. Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary
10 Relations between global s The technical difficulty of reducing the and the difficulty of collaboration Relations between global s Two things make the understanding of the relation between the global s particularly important.. s: The s are interconnected in different ways. Often the situation resembles a set of dominoes: if one falls, many follow. Even small impacts can start a process where different s interact.. Specific measures to address a : s often require significant changes, which will result in situations where measures to reduce the in one area affect the probability and/or the impact in other areas, for better or worse. The technical difficulty of reducing the and the difficulty of collaboration In order to better understand the relations between different global s work could start to analyse similarities and differences. Below is an example of an overview of how different global s can be plotted depending on the technical difficulty of reducing the and the difficulty of collaborating to reduce it. ALL RISKS first worsens second solving first improves second both of the above technical difficulty of reducing collaboration difficulty of reducing 6 Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary 7
11 Uncertainties Probability As the different challenges are very different and the status of probability estimates varies significantly, the initial probability numbers are provided together with estimates regarding: Uncertainties Probability These estimates are an attempt to assemble existing estimates in order to encourage efforts to improve the numbers. They express estimates of probabilities over 00 years, except in the case of extreme climate change, where the time frame is 00 years.. Understanding.. Understanding of sequence of of sequence. Data. Data. availability Data availability. Existing probability. estimation Existing probability estimation challenges need to be seen in the light of trends which help to shape the wider society. These include: Poverty although it has fallen, it could increase again. This is especially relevant to climate change and pandemics. Population growth the UN s estimates range from 6.8 billion people by 00 to a high-variant projection of 6.6 bn (which would require the resources of 0 Earth-like planets to provide everyone with a modern Western lifestyle). Other trends include technological development and demographic changes. none at all some parts most parts all parts none at all some parts most parts all parts none at all none at all some parts some parts most most parts parts all parts degree degree of events of events from today s from today s actions actions to infinite to infinite impact impact no data no data no data some some data data some data most data most most data data all data all data no data some data most data all data amount amount of data of to data make to make probability probability assessment assessment on all on relevant all relevant steps steps of the of sequence the sequence calculations calculations with with small uncertainty small uncertainty calculations with large uncertainty calculations with large uncertainty calculations with large uncertainty best guesses by experts best guesses by experts best guesses by experts no estimates no estimates no estimates kind of estimation and uncertainty n / a n / a n / a n / a n / a % 0.000% 0.000% 0.00% 0.0% 0.% 0-0% Probability of infinite impact (%) 0.00% 0.0% 0.% 0.8% % % 0-0% degree of events from today s actions to infinite impact degree of events degree from of events today s from actions today s actions to infinite impact to infinite impact amount of data to make probability assessment on all relevant steps amount of the sequence of data to make probability assessment on all relevant steps of the sequence kind of estimation and uncertainty kind of estimation and uncertainty Probability of reaching or exceeding the infinite threshold (%) % one in hundred million % one in ten million 0.000% one in a million 0.00% one in hundred thousand 0.0% one in ten thousand 0.% one in a thousand % one in a hundred 0% one in ten 00% one in one 8 Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary 9
12 Possible ways forward Possible ways forward There are ten areas that could help mitigate immediate threats while also contributing to a future global governance system capable of addressing global s with a potential infinite impact:.... challenges leadership networks Better quality assessment for global challenges Development of early warning systems Encouraging visualisation of complex systems The main authors of this report are Dennis Pamlin, Executive Project Manager, Challenges Foundation and Dr Stuart Armstrong, James Martin Research Fellow, Future of Humanity Institute, Oxford Martin School & Faculty of Philosophy, University of Oxford. Stuart Armstrong wrote the chapter covering the twelve global challenges, under the direction of Dennis Pamlin who served as project manager and himself wrote and edited the rest of the report. Seth Baum, Executive Director of the Catastrophic Risk Institute and affiliate researcher at the Center for Research on Environmental Decisions, Columbia University, also played an important role as he helped develop the methodology chapter regarding the selection of the global s with a potentially infinite impact as well as providing helpful input throughout the process. But the report is the result of a collaborative approach where many people have provided invaluable contributions. The authors would therefore like to thank a few people in particular. First and foremost László Szombatfalvy, chairman of Challenges Foundation, whose work is the basis for this report and whose guidance on all levels has been invaluable. The rest of the board of the Challenges Foundation have also contributed in many different ways, in particular Johan Rockström has provided important input regarding the structure and methodology. Outside the foundation Prof Nick Bostrom, Professor & Director of the Future of Humanity Institute, Oxford Martin School & Faculty of Philosophy, University of Oxford, who initiated the possibility of working with the Future of Humanity Institute at the University of Oxford, played a particularly important role. Patrick McSharry, head of Smith School s Risk Financing research area, provided invaluable input regarding complex systems and ways that the economic system can respond to s with potentially infinite impacts. Alex Kirby also played a key part as he did so much more than proofread the text; the report would hardly be possible to read without his help. Others that must be mentioned, including those who participated in the workshop on January th 0, at the Future of Humanity Institute (FHI), University of Oxford and the workshop at the Munich RE office in London, January th 0, and helped provide input regarding the economic and finance aspects, include (in alphabetical order): Highlighting early movers Including the whole probability distribution Increasing the focus on the probability of extreme events Encouraging appropriate language to describe extreme s Establishing a Risk and Opportunity Indicator to guide governance Explore the possibility of establishing a Risk Organisation (GRO) Dr Nick Beckstead, Research Fellow, Future of Humanity Institute, Oxford Martin School & Faculty of Philosophy, University of Oxford Kennette Benedict, Executive Director and Publisher of the Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists Oliver Bettis, pricing actuary Munich RE and fellow of the Chartered Insurance Institute and the Institute & Faculty of Actuaries. Dr Eric Drexler, Academic Visitor, Future of Humanity Institute, Oxford Martin School & Faculty of Philosophy, University of Oxford Madeleine Enarsson, Transformative Catalyst, st Century Frontiers Dr Seán Ó héigeartaigh, Senior Academic Manager, Future of Humanity Institute, University of Oxford and Executive Director, Centre for the Study of Existential Risk, University of Cambridge Martin Hellman, Professor Emeritus of Electrical Engineering, Stanford University Pan Jiahua, Director of the Institute for Urban and Environmental Studies, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS); professor of economics at CASS; vice president Chinese Society for Economics; member National Expert Panel on and National Foreign Policy Advisory Committee, China Aled Jones, Director of the Sustainability Institute (GSI) at Anglia Ruskin University Nick Mabey, Chief Executive and a founder director of EG (Third Generation Environmentalism) Jennifer Morgan, Founder & Co-Convener, the finance lab Prof Vincent Müller, James Martin Research Fellow, Future of Humanity Institute, Oxford Martin School & Faculty of Philosophy, University of Oxford Robert de Neufville, Professional Associate, Catastrophic Risk Institute Dr Toby Ord, James Martin Research Fellow, Future of Humanity Institute, Oxford Martin School & Faculty of Philosophy, University of Oxford Jules Peck, Founding Partner, Jericho Chambers; Trustee, New Economics Foundation Dr Anders Sandberg, James Martin Research Fellow, Future of Humanity Institute, Oxford Martin School & Faculty of Philosophy, University of Oxford Nick Silver, director of Callund Consulting and founder and director of the Climate Bonds Initiative (CBI) Andrew Simms, Author, Fellow at the New Economics Foundation and Chief Analyst at Witness Andrew Snyder-Beattie, Academic Project Manager, Future of Humanity Institute, Oxford Martin School & Faculty of Philosophy, University of Oxford James Taplan, Principal Sustainability Advisor, Forum for the Future Raj Thamotheram, CEO, Preventable Surprises Nathan Wolfe, Director of Viral and the Lorry I. Lokey Visiting Professor in Human at Stanford University. Liang Yin, Investment Consultant at Towers Watson 0 Challenges Twelve s that threaten human civilisation Executive summary design by wearebwa.co.uk
13 Published February 0 by Challenges Foundation globalchallenges.org Challenges Foundation Stureplan C Stockholm The opinions expressed in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of Challenges Foundation. Any inaccuracies in the report remain the responsibility of the authors. The material and the geographical designations in this report do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of Challenges Foundation, concerning the legal status of any country, territory, or area, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. For comments and/or queries on this report, please contact the co-authors: Dennis Pamlin Executive Project Manager Risks Challenges Foundation dennis@globalchallenges.org globalchallenges.org Dr Stuart Armstrong James Martin Research Fellow, Future of Humanity Institute, Oxford Martin School & Faculty of Philosophy, University of Oxford stuart.armstrong@philosophy.ox.ac.uk fhi.ox.ac.uk
GLOBAL CATASTROPHIC RISKS SURVEY
 GLOBAL CATASTROPHIC RISKS SURVEY (2008) Technical Report 2008/1 Published by Future of Humanity Institute, Oxford University Anders Sandberg and Nick Bostrom At the Global Catastrophic Risk Conference
GLOBAL CATASTROPHIC RISKS SURVEY (2008) Technical Report 2008/1 Published by Future of Humanity Institute, Oxford University Anders Sandberg and Nick Bostrom At the Global Catastrophic Risk Conference
Strategic Partner of the Report
 Strategic Partner of the Report Last year s Global Risks Report was published at a time of heightened global uncertainty and strengthening popular discontent with the existing political and economic order.
Strategic Partner of the Report Last year s Global Risks Report was published at a time of heightened global uncertainty and strengthening popular discontent with the existing political and economic order.
ASTEROID THREATS: A CALL FOR GLOBAL RESPONSE
 2008 ASTEROID THREATS: A CALL FOR GLOBAL RESPONSE A report on the need to develop an international decision-making program for global response to Near Earth Object threats. Submitted for consideration
2008 ASTEROID THREATS: A CALL FOR GLOBAL RESPONSE A report on the need to develop an international decision-making program for global response to Near Earth Object threats. Submitted for consideration
Scenario Development Process
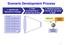 Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Please send your responses by to: This consultation closes on Friday, 8 April 2016.
 CONSULTATION OF STAKEHOLDERS ON POTENTIAL PRIORITIES FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION IN THE 2018-2020 WORK PROGRAMME OF HORIZON 2020 SOCIETAL CHALLENGE 5 'CLIMATE ACTION, ENVIRONMENT, RESOURCE EFFICIENCY AND
CONSULTATION OF STAKEHOLDERS ON POTENTIAL PRIORITIES FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION IN THE 2018-2020 WORK PROGRAMME OF HORIZON 2020 SOCIETAL CHALLENGE 5 'CLIMATE ACTION, ENVIRONMENT, RESOURCE EFFICIENCY AND
The Study of Knowledge Innovation Based on Enterprise Knowledge Ecosystem
 The Study of Knowledge Innovation Based on Enterprise Knowledge Ecosystem Mingkui Huo 1 1 School of Economics and Management, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun 130022, China Correspondence:
The Study of Knowledge Innovation Based on Enterprise Knowledge Ecosystem Mingkui Huo 1 1 School of Economics and Management, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun 130022, China Correspondence:
Participatory backcasting: A tool for involving stakeholders in long term local development planning
 Erasmus Intensive Programme Equi Agry June 29 July 11, Foggia Participatory backcasting: A tool for involving stakeholders in long term local development planning Dr. Maurizio PROSPERI ( maurizio.prosperi@unifg.it
Erasmus Intensive Programme Equi Agry June 29 July 11, Foggia Participatory backcasting: A tool for involving stakeholders in long term local development planning Dr. Maurizio PROSPERI ( maurizio.prosperi@unifg.it
The future agenda of research for sustainable development
 The future agenda of research for sustainable development Heide Hackmann Executive Director: International Social Science Council Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research Overview The global environment
The future agenda of research for sustainable development Heide Hackmann Executive Director: International Social Science Council Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research Overview The global environment
Tren ds i n Nuclear Security Assessm ents
 2 Tren ds i n Nuclear Security Assessm ents The l ast deca de of the twentieth century was one of enormous change in the security of the United States and the world. The torrent of changes in Eastern Europe,
2 Tren ds i n Nuclear Security Assessm ents The l ast deca de of the twentieth century was one of enormous change in the security of the United States and the world. The torrent of changes in Eastern Europe,
Responsibility in Wealth
 Responsibility in Wealth The Kaiser Partner Special Report Series Issue #1/June 2012 With great wealth comes great responsibility. Introduction At Kaiser Partner, we understand that the world is changing
Responsibility in Wealth The Kaiser Partner Special Report Series Issue #1/June 2012 With great wealth comes great responsibility. Introduction At Kaiser Partner, we understand that the world is changing
Inter and Transdisciplinarity in Social Sciences. Approaches and lessons learned
 Inter and Transdisciplinarity in Social Sciences Approaches and lessons learned Symposium on Sustainability Science, 19 December 2016 Overview 1. The ISSC: short intro 2. ID and TD research 3. ISSC s initiatives:
Inter and Transdisciplinarity in Social Sciences Approaches and lessons learned Symposium on Sustainability Science, 19 December 2016 Overview 1. The ISSC: short intro 2. ID and TD research 3. ISSC s initiatives:
Executive summary. AI is the new electricity. I can hardly imagine an industry which is not going to be transformed by AI.
 Executive summary Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly driving important developments in technology and business, from autonomous vehicles to medical diagnosis to advanced manufacturing. As AI
Executive summary Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly driving important developments in technology and business, from autonomous vehicles to medical diagnosis to advanced manufacturing. As AI
The Landscape of Global Risks and Global Opportunities: Transforming the Biodiversity Agenda in a Changing Global Context
 The Landscape of Global Risks and Global Opportunities: Transforming the Biodiversity Agenda in a Changing Global Context Dominic Waughray: Head, World Economic Forum Centre for Global Public Goods CBD
The Landscape of Global Risks and Global Opportunities: Transforming the Biodiversity Agenda in a Changing Global Context Dominic Waughray: Head, World Economic Forum Centre for Global Public Goods CBD
United Nations Environment Programme 12 February 2019* Guidance note: Leadership Dialogues at fourth session of the UN Environment Assembly
 United Nations Environment Programme 12 February 2019* Guidance note: Leadership Dialogues at fourth session of the UN Environment Assembly A key feature of the high/level segment of the 2019 UN Environment
United Nations Environment Programme 12 February 2019* Guidance note: Leadership Dialogues at fourth session of the UN Environment Assembly A key feature of the high/level segment of the 2019 UN Environment
The global in the social sciences and humanities
 The global in the social sciences and humanities What does global mean? The planet earth is a single unit or space Global issues transcend humanity and human society Human activity is having global effects:
The global in the social sciences and humanities What does global mean? The planet earth is a single unit or space Global issues transcend humanity and human society Human activity is having global effects:
Five-year strategy. Harnessing the power of evidence and ideas. Evidence. Ideas. Change. Evidence. Ideas. Change.
 ODI 203 Blackfriars Road London SE1 8NJ +44 (0)20 7922 0300 odi.org Evidence. Ideas. Change. Five-year strategy Harnessing the power of evidence and ideas Evidence. Ideas. Change. Follow us on Twitter
ODI 203 Blackfriars Road London SE1 8NJ +44 (0)20 7922 0300 odi.org Evidence. Ideas. Change. Five-year strategy Harnessing the power of evidence and ideas Evidence. Ideas. Change. Follow us on Twitter
Integrated Transformational and Open City Governance Rome May
 Integrated Transformational and Open City Governance Rome May 9-11 2016 David Ludlow University of the West of England, Bristol Workshop Aims Key question addressed - how do we advance towards a smart
Integrated Transformational and Open City Governance Rome May 9-11 2016 David Ludlow University of the West of England, Bristol Workshop Aims Key question addressed - how do we advance towards a smart
 UN Global Sustainable Development Report 2013 Annotated outline UN/DESA/DSD, New York, 5 February 2013 Note: This is a living document. Feedback welcome! Forewords... 1 Executive Summary... 1 I. Introduction...
UN Global Sustainable Development Report 2013 Annotated outline UN/DESA/DSD, New York, 5 February 2013 Note: This is a living document. Feedback welcome! Forewords... 1 Executive Summary... 1 I. Introduction...
Nuclear weapons: Ending a threat to humanity
 International Review of the Red Cross (2015), 97 (899), 887 891. The human cost of nuclear weapons doi:10.1017/s1816383116000060 REPORTS AND DOCUMENTS Nuclear weapons: Ending a threat to humanity Speech
International Review of the Red Cross (2015), 97 (899), 887 891. The human cost of nuclear weapons doi:10.1017/s1816383116000060 REPORTS AND DOCUMENTS Nuclear weapons: Ending a threat to humanity Speech
Development for a Finite Planet:
 Call for Papers NFU Conference 2012 Development for a Finite Planet: Grassroots perspectives and responses to climate change, resource extraction and economic development Date and Venue: 26-27 November
Call for Papers NFU Conference 2012 Development for a Finite Planet: Grassroots perspectives and responses to climate change, resource extraction and economic development Date and Venue: 26-27 November
Foresight and Scenario Development
 Foresight and Scenario Development Anita Pirc Velkavrh Head of Foresight and Sustainability group European Environment Agency ESDN Annual conference, 22-23 June 2017, Prague EEA, environmental messages
Foresight and Scenario Development Anita Pirc Velkavrh Head of Foresight and Sustainability group European Environment Agency ESDN Annual conference, 22-23 June 2017, Prague EEA, environmental messages
Expression Of Interest
 Expression Of Interest Modelling Complex Warfighting Strategic Research Investment Joint & Operations Analysis Division, DST Points of Contact: Management and Administration: Annette McLeod and Ansonne
Expression Of Interest Modelling Complex Warfighting Strategic Research Investment Joint & Operations Analysis Division, DST Points of Contact: Management and Administration: Annette McLeod and Ansonne
The Global in the social science and humanities
 The Global in the social science and humanities Well, I hope Dave and I did not throw too much at you in the first day of class! My objective on the first day was to introduce some basic themes that we
The Global in the social science and humanities Well, I hope Dave and I did not throw too much at you in the first day of class! My objective on the first day was to introduce some basic themes that we
The work under the Environment under Review subprogramme focuses on strengthening the interface between science, policy and governance by bridging
 The work under the Environment under Review subprogramme focuses on strengthening the interface between science, policy and governance by bridging the gap between the producers and users of environmental
The work under the Environment under Review subprogramme focuses on strengthening the interface between science, policy and governance by bridging the gap between the producers and users of environmental
Future of Financing. For more information visit ifrc.org/s2030
 Future of Financing The gap between humanitarian and development needs and financing is growing, yet largely we still rely on just a few traditional sources of funding. How do we mobilize alternate sources
Future of Financing The gap between humanitarian and development needs and financing is growing, yet largely we still rely on just a few traditional sources of funding. How do we mobilize alternate sources
An Innovative Public Private Approach for a Technology Facilitation Mechanism (TFM)
 Summary An Innovative Public Private Approach for a Technology Facilitation Mechanism (TFM) July 31, 2012 In response to paragraph 265 276 of the Rio+20 Outcome Document, this paper outlines an innovative
Summary An Innovative Public Private Approach for a Technology Facilitation Mechanism (TFM) July 31, 2012 In response to paragraph 265 276 of the Rio+20 Outcome Document, this paper outlines an innovative
g~:~: P Holdren ~\k, rjj/1~
 July 9, 2015 M-15-16 OF EXECUTIVE DEPARTMENTS AND AGENCIES FROM: g~:~: P Holdren ~\k, rjj/1~ Office of Science a~fechno!o;} ~~~icy SUBJECT: Multi-Agency Science and Technology Priorities for the FY 2017
July 9, 2015 M-15-16 OF EXECUTIVE DEPARTMENTS AND AGENCIES FROM: g~:~: P Holdren ~\k, rjj/1~ Office of Science a~fechno!o;} ~~~icy SUBJECT: Multi-Agency Science and Technology Priorities for the FY 2017
Is Resilience Enough?
 Is Resilience Enough? Anthony Hodgson F.R.S.A Decision Integrity Limited International Futures Forum D I L Thursday March 8 th 2011 Glasgow Centre for Population Health The Lighthouse, Glasgow IFF 1 Why
Is Resilience Enough? Anthony Hodgson F.R.S.A Decision Integrity Limited International Futures Forum D I L Thursday March 8 th 2011 Glasgow Centre for Population Health The Lighthouse, Glasgow IFF 1 Why
"How to ensure a secure supply of raw materials in the global economy"
 SPEECH/12/304 Antonio TAJANI Vice-President of the European Commission responsible for Industry and Entrepreneurship "How to ensure a secure supply of raw materials in the global economy" Bundestag Berlin,
SPEECH/12/304 Antonio TAJANI Vice-President of the European Commission responsible for Industry and Entrepreneurship "How to ensure a secure supply of raw materials in the global economy" Bundestag Berlin,
Key Concept 6.1 Science and the Environment
 Key Concept 6.1 Science and the Environment Rapid advances in science altered the understanding of the universe and the natural world and led to the development of new technologies. These changes enabled
Key Concept 6.1 Science and the Environment Rapid advances in science altered the understanding of the universe and the natural world and led to the development of new technologies. These changes enabled
ClusterNanoRoad
 ClusterNanoRoad 723630 Expert Advisory Board Meeting Brussels April 11th, 2018 WP1 ClusterNanoRoad (723630) VALUE CHAIN OPPORTUNITIES: mapping and benchmarking of Cluster-NMBP RIS3 good practices [M1-M7]
ClusterNanoRoad 723630 Expert Advisory Board Meeting Brussels April 11th, 2018 WP1 ClusterNanoRoad (723630) VALUE CHAIN OPPORTUNITIES: mapping and benchmarking of Cluster-NMBP RIS3 good practices [M1-M7]
Science Impact Enhancing the Use of USGS Science
 United States Geological Survey. 2002. "Science Impact Enhancing the Use of USGS Science." Unpublished paper, 4 April. Posted to the Science, Environment, and Development Group web site, 19 March 2004
United States Geological Survey. 2002. "Science Impact Enhancing the Use of USGS Science." Unpublished paper, 4 April. Posted to the Science, Environment, and Development Group web site, 19 March 2004
A New Perspective in the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence
 A New Perspective in the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence A new study conducted by Dr. Nicolas Prantzos of the Institut d Astrophysique de Paris (Paris Institute of Astrophysics) takes a fresh
A New Perspective in the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence A new study conducted by Dr. Nicolas Prantzos of the Institut d Astrophysique de Paris (Paris Institute of Astrophysics) takes a fresh
Scoping Paper for. Horizon 2020 work programme Societal Challenge 4: Smart, Green and Integrated Transport
 Scoping Paper for Horizon 2020 work programme 2018-2020 Societal Challenge 4: Smart, Green and Integrated Transport Important Notice: Working Document This scoping paper will guide the preparation of the
Scoping Paper for Horizon 2020 work programme 2018-2020 Societal Challenge 4: Smart, Green and Integrated Transport Important Notice: Working Document This scoping paper will guide the preparation of the
Horizon Scanning. Why & how to launch it in Lithuania? Prof. Dr. Rafael Popper
 VTT TECHNICAL RESEARCH CENTRE OF FINLAND LTD Horizon Scanning Why & how to launch it in Lithuania? Prof. Dr. Rafael Popper Principal Scientist in Business, Innovation and Foresight VTT Technical Research
VTT TECHNICAL RESEARCH CENTRE OF FINLAND LTD Horizon Scanning Why & how to launch it in Lithuania? Prof. Dr. Rafael Popper Principal Scientist in Business, Innovation and Foresight VTT Technical Research
WMD Events and Other Catastrophes
 WMD Events and Other Catastrophes 2012 Joint CBRN Conference National Defense Industrial Association March 13, 2012 Tara O Toole, M.D., M.P.H. Under Secretary for Science and Technology U.S. Department
WMD Events and Other Catastrophes 2012 Joint CBRN Conference National Defense Industrial Association March 13, 2012 Tara O Toole, M.D., M.P.H. Under Secretary for Science and Technology U.S. Department
Emerging biotechnologies. Nuffield Council on Bioethics Response from The Royal Academy of Engineering
 Emerging biotechnologies Nuffield Council on Bioethics Response from The Royal Academy of Engineering June 2011 1. How would you define an emerging technology and an emerging biotechnology? How have these
Emerging biotechnologies Nuffield Council on Bioethics Response from The Royal Academy of Engineering June 2011 1. How would you define an emerging technology and an emerging biotechnology? How have these
Science Policy and Social Change. December 2003
 Science Policy and Social Change December 2003 S&T Drive Economic Growth Scientific and technical changes accounts for as much as 50% of long-run economic growth, even perhaps as much as 75%. Public Science
Science Policy and Social Change December 2003 S&T Drive Economic Growth Scientific and technical changes accounts for as much as 50% of long-run economic growth, even perhaps as much as 75%. Public Science
The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) reports that there were more than 15,000 nuclear warheads on Earth as of 2016.
 The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) reports that there were more than 15,000 nuclear warheads on Earth as of 2016. The longer these weapons continue to exist, the greater the likelihood
The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) reports that there were more than 15,000 nuclear warheads on Earth as of 2016. The longer these weapons continue to exist, the greater the likelihood
Development and Integration of Artificial Intelligence Technologies for Innovation Acceleration
 Development and Integration of Artificial Intelligence Technologies for Innovation Acceleration Research Supervisor: Minoru Etoh (Professor, Open and Transdisciplinary Research Initiatives, Osaka University)
Development and Integration of Artificial Intelligence Technologies for Innovation Acceleration Research Supervisor: Minoru Etoh (Professor, Open and Transdisciplinary Research Initiatives, Osaka University)
The global in the social sciences and humanities
 The global in the social sciences and humanities Key Points Understanding global issues requires an understanding of both the physical and life sciences and the social sciences and humanities The importance
The global in the social sciences and humanities Key Points Understanding global issues requires an understanding of both the physical and life sciences and the social sciences and humanities The importance
Responding to the Potential Threat of a Near-Earth-Object Impact
 Responding to the Potential Threat of a Near-Earth-Object Impact An AIAA Position Paper Prepared by the Space Systems Technical Committee and the Systems Engineering Technical Committee Approved by the
Responding to the Potential Threat of a Near-Earth-Object Impact An AIAA Position Paper Prepared by the Space Systems Technical Committee and the Systems Engineering Technical Committee Approved by the
The global in the social sciences and humanities
 The global in the social sciences and humanities Key Points Understanding global issues requires an understanding of both the physical and life sciences and the social sciences and humanities The importance
The global in the social sciences and humanities Key Points Understanding global issues requires an understanding of both the physical and life sciences and the social sciences and humanities The importance
Responsible innovation and synthetic biology. Prof Phil Macnaghten Knowledge, Technology and Innovation Wageningen University (NL)
 Responsible innovation and synthetic biology Prof Phil Macnaghten Knowledge, Technology and Innovation Wageningen University (NL) 1. What is responsible innovation and what is different about it? 2. Why
Responsible innovation and synthetic biology Prof Phil Macnaghten Knowledge, Technology and Innovation Wageningen University (NL) 1. What is responsible innovation and what is different about it? 2. Why
Center for Ocean Solutions
 Center for Ocean Solutions The Stanford Center for Ocean Solutions catalyzes research innovation and action to improve the health of the oceans for the people who depend on them most. Oceans are vital
Center for Ocean Solutions The Stanford Center for Ocean Solutions catalyzes research innovation and action to improve the health of the oceans for the people who depend on them most. Oceans are vital
A SYSTEMIC APPROACH TO KNOWLEDGE SOCIETY FORESIGHT. THE ROMANIAN CASE
 A SYSTEMIC APPROACH TO KNOWLEDGE SOCIETY FORESIGHT. THE ROMANIAN CASE Expert 1A Dan GROSU Executive Agency for Higher Education and Research Funding Abstract The paper presents issues related to a systemic
A SYSTEMIC APPROACH TO KNOWLEDGE SOCIETY FORESIGHT. THE ROMANIAN CASE Expert 1A Dan GROSU Executive Agency for Higher Education and Research Funding Abstract The paper presents issues related to a systemic
19 - LIFETIMES OF TECHNOLOGICAL CIVILIZATIONS
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 19 - LIFETIMES OF TECHNOLOGICAL CIVILIZATIONS Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ THE FERMI PARADOX THE DRAKE EQUATION LEADS
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 19 - LIFETIMES OF TECHNOLOGICAL CIVILIZATIONS Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics, CSUSB http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen/ THE FERMI PARADOX THE DRAKE EQUATION LEADS
The Global in the social science and humanities
 The Global in the social science and humanities Well, I hope Dave and I did not throw too much at you in the first day of class! My objective on the first day was to introduce some basic themes that we
The Global in the social science and humanities Well, I hope Dave and I did not throw too much at you in the first day of class! My objective on the first day was to introduce some basic themes that we
WFEO STANDING COMMITTEE ON ENGINEERING FOR INNOVATIVE TECHNOLOGY (WFEO-CEIT) STRATEGIC PLAN ( )
 WFEO STANDING COMMITTEE ON ENGINEERING FOR INNOVATIVE TECHNOLOGY (WFEO-CEIT) STRATEGIC PLAN (2016-2019) Hosted by The China Association for Science and Technology March, 2016 WFEO-CEIT STRATEGIC PLAN (2016-2019)
WFEO STANDING COMMITTEE ON ENGINEERING FOR INNOVATIVE TECHNOLOGY (WFEO-CEIT) STRATEGIC PLAN (2016-2019) Hosted by The China Association for Science and Technology March, 2016 WFEO-CEIT STRATEGIC PLAN (2016-2019)
MEGATRENDS THE TREND TOWARDS
 01: DEMOGRAPHIC CHANGE 02: INDIVIDUALISATION REACHES A NEW STAGE 03: HEALTH THRIVES 04: WOMEN ON THE RISE 05: CULTURAL DIVERSITY 06: NEW PATTERNS OF MOBILITY 07: DIGITAL LIFESTYLE 08: BIOMIMICRY, OR, LEARNING
01: DEMOGRAPHIC CHANGE 02: INDIVIDUALISATION REACHES A NEW STAGE 03: HEALTH THRIVES 04: WOMEN ON THE RISE 05: CULTURAL DIVERSITY 06: NEW PATTERNS OF MOBILITY 07: DIGITAL LIFESTYLE 08: BIOMIMICRY, OR, LEARNING
Social Innovation and new pathways to social changefirst insights from the global mapping
 Social Innovation and new pathways to social changefirst insights from the global mapping Social Innovation2015: Pathways to Social change Vienna, November 18-19, 2015 Prof. Dr. Jürgen Howaldt/Antonius
Social Innovation and new pathways to social changefirst insights from the global mapping Social Innovation2015: Pathways to Social change Vienna, November 18-19, 2015 Prof. Dr. Jürgen Howaldt/Antonius
Our digital future. SEPA online. Facilitating effective engagement. Enabling business excellence. Sharing environmental information
 Our digital future SEPA online Facilitating effective engagement Sharing environmental information Enabling business excellence Foreword Dr David Pirie Executive Director Digital technologies are changing
Our digital future SEPA online Facilitating effective engagement Sharing environmental information Enabling business excellence Foreword Dr David Pirie Executive Director Digital technologies are changing
AI for Global Good Summit. Plenary 1: State of Play. Ms. Izumi Nakamitsu. High Representative for Disarmament Affairs United Nations
 AI for Global Good Summit Plenary 1: State of Play Ms. Izumi Nakamitsu High Representative for Disarmament Affairs United Nations 7 June, 2017 Geneva Mr Wendall Wallach Distinguished panellists Ladies
AI for Global Good Summit Plenary 1: State of Play Ms. Izumi Nakamitsu High Representative for Disarmament Affairs United Nations 7 June, 2017 Geneva Mr Wendall Wallach Distinguished panellists Ladies
K.1 Structure and Function: The natural world includes living and non-living things.
 Standards By Design: Kindergarten, First Grade, Second Grade, Third Grade, Fourth Grade, Fifth Grade, Sixth Grade, Seventh Grade, Eighth Grade and High School for Science Science Kindergarten Kindergarten
Standards By Design: Kindergarten, First Grade, Second Grade, Third Grade, Fourth Grade, Fifth Grade, Sixth Grade, Seventh Grade, Eighth Grade and High School for Science Science Kindergarten Kindergarten
17.181/ SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Theory and Policy
 17.181/17.182 SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Theory and Policy Department of Political Science Fall 2016 Professor N. Choucri 1 ` 17.181/17.182 Week 1 Introduction-Leftover Item 1. INTRODUCTION Background Early
17.181/17.182 SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT Theory and Policy Department of Political Science Fall 2016 Professor N. Choucri 1 ` 17.181/17.182 Week 1 Introduction-Leftover Item 1. INTRODUCTION Background Early
Innovation in the Energy Sector: Which Technologies do we need after 2030 and which policies do we need now?
 15th IAEE European Conference 2017 Heading Towards Sustainable Energy Systems: Evolution or Revolution? 3rd to 6th September 2017, Hofburg Congress Center, Vienna, Austria Innovation in the Energy Sector:
15th IAEE European Conference 2017 Heading Towards Sustainable Energy Systems: Evolution or Revolution? 3rd to 6th September 2017, Hofburg Congress Center, Vienna, Austria Innovation in the Energy Sector:
6/14/2017. Engineering Future Cities The Value of Extreme Scenario Methodologies
 Engineering Future Cities The Value of Extreme Scenario Methodologies Resilience Through Innovation Critical Local Transport and Utility Infrastructure Professor Chris Rogers University of Birmingham 12
Engineering Future Cities The Value of Extreme Scenario Methodologies Resilience Through Innovation Critical Local Transport and Utility Infrastructure Professor Chris Rogers University of Birmingham 12
Our position. ICDPPC declaration on ethics and data protection in artificial intelligence
 ICDPPC declaration on ethics and data protection in artificial intelligence AmCham EU speaks for American companies committed to Europe on trade, investment and competitiveness issues. It aims to ensure
ICDPPC declaration on ethics and data protection in artificial intelligence AmCham EU speaks for American companies committed to Europe on trade, investment and competitiveness issues. It aims to ensure
SACT remarks at. Atlantic Council SFA Washington DC, George Washington University, Elliott School of International Affairs
 SACT remarks at Atlantic Council SFA 2017 Washington DC, George Washington University, Elliott School of International Affairs 16 Nov 2017, 1700-1830 Général d armée aérienne Denis Mercier 1 Thank you
SACT remarks at Atlantic Council SFA 2017 Washington DC, George Washington University, Elliott School of International Affairs 16 Nov 2017, 1700-1830 Général d armée aérienne Denis Mercier 1 Thank you
Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved
 Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved 6-15-2017 Learner Objective: Students will be able to independently use their learning to develop the ability to make informed decisions
Modern World History Grade 10 - Learner Objectives BOE approved 6-15-2017 Learner Objective: Students will be able to independently use their learning to develop the ability to make informed decisions
Topic and Reading Schedule
 Technological, Social, and Sustainable Systems Topic and Reading Schedule Topic and Reading Schedule The topics of the lectures, and the chapters of the text with which it is associated, are given for
Technological, Social, and Sustainable Systems Topic and Reading Schedule Topic and Reading Schedule The topics of the lectures, and the chapters of the text with which it is associated, are given for
Policy Evaluation as if sustainable development really mattered: Rethinking evaluation in light of Europe s 2050 Agenda
 Policy Evaluation as if sustainable development really mattered: Rethinking evaluation in light of Europe s 2050 Agenda EEEN Forum, Helsinki, April 28-29, 2014 Dr Hans Bruyninckx Executive Director, European
Policy Evaluation as if sustainable development really mattered: Rethinking evaluation in light of Europe s 2050 Agenda EEEN Forum, Helsinki, April 28-29, 2014 Dr Hans Bruyninckx Executive Director, European
DIGITAL FINLAND FRAMEWORK FRAMEWORK FOR TURNING DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION TO SOLUTIONS TO GRAND CHALLENGES
 DIGITAL FINLAND FRAMEWORK FRAMEWORK FOR TURNING DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION TO SOLUTIONS TO GRAND CHALLENGES 1 Digital transformation of industries and society is a key element for growth, entrepreneurship,
DIGITAL FINLAND FRAMEWORK FRAMEWORK FOR TURNING DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION TO SOLUTIONS TO GRAND CHALLENGES 1 Digital transformation of industries and society is a key element for growth, entrepreneurship,
Revista Economică 68:5 (2016) PUBLIC PERCEPTION OF THE ROLE OF SCIENCE AND INNOVATION IN SOLVING THE PROBLEMS EXPERIENCED BY CONTEMPORARY ECONOMY
 PUBLIC PERCEPTION OF THE ROLE OF SCIENCE AND INNOVATION IN SOLVING THE PROBLEMS EXPERIENCED BY CONTEMPORARY ECONOMY DURALIA Oana 1 Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu Abstract: In the context of contemporary
PUBLIC PERCEPTION OF THE ROLE OF SCIENCE AND INNOVATION IN SOLVING THE PROBLEMS EXPERIENCED BY CONTEMPORARY ECONOMY DURALIA Oana 1 Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu Abstract: In the context of contemporary
International Efforts for Transparency and Confidence-Building Measures (TCBM) and Japan s Contribution
 International Efforts for Transparency and Confidence-Building Measures (TCBM) and Japan s Contribution Atsushi SAITO 4 th March, 2016 1 1. International Rules On Outer Space (1) Committee on the Peaceful
International Efforts for Transparency and Confidence-Building Measures (TCBM) and Japan s Contribution Atsushi SAITO 4 th March, 2016 1 1. International Rules On Outer Space (1) Committee on the Peaceful
Partnerships for the 2030 Agenda: Role of Science, Technology, and Innovation
 Partnerships for the 2030 Agenda: Role of Science, Technology, and Innovation United Nations University October 18, 2018 Tokyo, Japan 0 Mahmoud Mohieldin Senior Vice President @wbg2030 worldbank.org/sdgs
Partnerships for the 2030 Agenda: Role of Science, Technology, and Innovation United Nations University October 18, 2018 Tokyo, Japan 0 Mahmoud Mohieldin Senior Vice President @wbg2030 worldbank.org/sdgs
U.S. National Space Policy
 U.S. National Space Policy Opportunities and Challenges in Shaping the International Space Regime AIAA Space 2007 Long Beach, California 18 September 2007 0 9/18/2007 Dana J. Johnson, Ph.D. Senior Analyst,
U.S. National Space Policy Opportunities and Challenges in Shaping the International Space Regime AIAA Space 2007 Long Beach, California 18 September 2007 0 9/18/2007 Dana J. Johnson, Ph.D. Senior Analyst,
Innovation Economy. Creating the. Dr. G. Wayne Clough President, Georgia Institute of Technology
 Creating the Innovation Economy Dr. G. Wayne Clough President, Georgia Institute of Technology IBM Systems & Technology Group Leadership Development Meeting January 19, 2005 Powerful trends reshape the
Creating the Innovation Economy Dr. G. Wayne Clough President, Georgia Institute of Technology IBM Systems & Technology Group Leadership Development Meeting January 19, 2005 Powerful trends reshape the
Establishing The Second Task of PHPR. Miguel A. Sanchez-Rey
 Establishing The Second Task of PHPR Miguel A. Sanchez-Rey Table of Contents Introduction Space-Habitats Star Gates and Interstellar Travel Extraterrestrial Encounter Defensive Measures Through Metaspace
Establishing The Second Task of PHPR Miguel A. Sanchez-Rey Table of Contents Introduction Space-Habitats Star Gates and Interstellar Travel Extraterrestrial Encounter Defensive Measures Through Metaspace
Who cares about the future anyway? We all should!
 Who cares about the future anyway? We all should! Jonathan Veale M.Des., M.E.S. CASHC/TORONTO May 21, 2015 Government and public service is too important for it to fail through lack of care; through the
Who cares about the future anyway? We all should! Jonathan Veale M.Des., M.E.S. CASHC/TORONTO May 21, 2015 Government and public service is too important for it to fail through lack of care; through the
Canada-Italy Innovation Award Call for Proposals
 Embassy of Canada to Italy Canada-Italy Innovation Award 2018 Public Affairs and Advocacy www.canada.it Canada-Italy Innovation Award 2018 Call for Proposals Overview The Embassy of Canada to Italy is
Embassy of Canada to Italy Canada-Italy Innovation Award 2018 Public Affairs and Advocacy www.canada.it Canada-Italy Innovation Award 2018 Call for Proposals Overview The Embassy of Canada to Italy is
Discussion Topics. How do we imagine will society change? What will be the drivers of change? What do we think will be the future needs of society?
 Looking Beyond 2010 Jack Smith National Research Council of Canada and the Telfer School of Management, University of Ottawa jesmith@telfer.uottawa.ca; Discussion Topics How do we imagine will society
Looking Beyond 2010 Jack Smith National Research Council of Canada and the Telfer School of Management, University of Ottawa jesmith@telfer.uottawa.ca; Discussion Topics How do we imagine will society
Nanotechnology and Artificial Life. Intertwined from the beginning. Living systems are frequently held up as proof that nano-machines are feasible.
 Nanotechnology and Artificial Life Intertwined from the beginning Living systems are frequently held up as proof that nano-machines are feasible. Nano-machines are difficult to fabricate in large quantities,
Nanotechnology and Artificial Life Intertwined from the beginning Living systems are frequently held up as proof that nano-machines are feasible. Nano-machines are difficult to fabricate in large quantities,
JTC1 Smart Ci,es workshop. Welcome!
 JTC1 Smart Ci,es workshop Welcome! British Standards smart cities programme Saviour Alfino, Project Manager Smart Cities Standards Strategy, BSI 2 nd September 2014 03/09/2014 Overview 1. Common city challenges
JTC1 Smart Ci,es workshop Welcome! British Standards smart cities programme Saviour Alfino, Project Manager Smart Cities Standards Strategy, BSI 2 nd September 2014 03/09/2014 Overview 1. Common city challenges
Impacts of the circular economy transition in Europe CIRCULAR IMPACTS Final Conference Summary
 Impacts of the circular economy transition in Europe CIRCULAR IMPACTS Final Conference Summary Brussels, 05 September 2018 Venue: CEPS, Place du Congrès 1, 1000 Brussels Attendees included officials from
Impacts of the circular economy transition in Europe CIRCULAR IMPACTS Final Conference Summary Brussels, 05 September 2018 Venue: CEPS, Place du Congrès 1, 1000 Brussels Attendees included officials from
HIGHLIGHTS OF THE LATIN AMERICAN AND CARIBBEAN REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT (Santiago, Chile, 5-75
 HIGHLIGHTS OF THE LATIN AMERICAN AND CARIBBEAN REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT (Santiago, Chile, 5-75 7 March 2002) Gilberto Gallopín Synthesis Workshop on Science
HIGHLIGHTS OF THE LATIN AMERICAN AND CARIBBEAN REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT (Santiago, Chile, 5-75 7 March 2002) Gilberto Gallopín Synthesis Workshop on Science
Dublin City Schools Science Graded Course of Study Environmental Science
 I. Content Standard: Earth and Space Sciences Students demonstrate an understanding about how Earth systems and processes interact in the geosphere resulting in the habitability of Earth. This includes
I. Content Standard: Earth and Space Sciences Students demonstrate an understanding about how Earth systems and processes interact in the geosphere resulting in the habitability of Earth. This includes
International Collaborative Initiative. Enhancing Foresight and Scenario Analysis for Global Food Systems
 International Collaborative Initiative Enhancing Foresight and Scenario Analysis for Global Food Systems Foresight is a key tool that governments, private sector and civil society can jointly use to better
International Collaborative Initiative Enhancing Foresight and Scenario Analysis for Global Food Systems Foresight is a key tool that governments, private sector and civil society can jointly use to better
An Introduction to China s Science and Technology Policy
 An Introduction to China s Science and Technology Policy SHANG Yong, Ph.D. Vice Minister Ministry of Science and Technology, China and Senior Fellow Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs
An Introduction to China s Science and Technology Policy SHANG Yong, Ph.D. Vice Minister Ministry of Science and Technology, China and Senior Fellow Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs
Twenty-Thirty Health care Scenarios - exploring potential changes in health care in England over the next 20 years
 Twenty-Thirty Health care Scenarios - exploring potential changes in health care in England over the next 20 years Chris Evennett & Professor James Barlow The context Demographics On-going financial constraints
Twenty-Thirty Health care Scenarios - exploring potential changes in health care in England over the next 20 years Chris Evennett & Professor James Barlow The context Demographics On-going financial constraints
April 10, Develop and demonstrate technologies needed to remotely detect the early stages of a proliferant nation=s nuclear weapons program.
 Statement of Robert E. Waldron Assistant Deputy Administrator for Nonproliferation Research and Engineering National Nuclear Security Administration U. S. Department of Energy Before the Subcommittee on
Statement of Robert E. Waldron Assistant Deputy Administrator for Nonproliferation Research and Engineering National Nuclear Security Administration U. S. Department of Energy Before the Subcommittee on
Doing, supporting and using public health research. The Public Health England strategy for research, development and innovation
 Doing, supporting and using public health research The Public Health England strategy for research, development and innovation Draft - for consultation only About Public Health England Public Health England
Doing, supporting and using public health research The Public Health England strategy for research, development and innovation Draft - for consultation only About Public Health England Public Health England
Latin-American non-state actor dialogue on Article 6 of the Paris Agreement
 Latin-American non-state actor dialogue on Article 6 of the Paris Agreement Summary Report Organized by: Regional Collaboration Centre (RCC), Bogota 14 July 2016 Supported by: Background The Latin-American
Latin-American non-state actor dialogue on Article 6 of the Paris Agreement Summary Report Organized by: Regional Collaboration Centre (RCC), Bogota 14 July 2016 Supported by: Background The Latin-American
Ministerial Conference on Nuclear Science and Technology: Addressing Current and Emerging Challenges Vienna, November 2018
 Ministerial Conference on Nuclear Science and Technology: Addressing Current and Emerging Challenges Vienna, 28-30 November 2018 Concluding Summary by the Co-Chairs of the Conference 1. The International
Ministerial Conference on Nuclear Science and Technology: Addressing Current and Emerging Challenges Vienna, 28-30 November 2018 Concluding Summary by the Co-Chairs of the Conference 1. The International
Welcome to the future of energy
 Welcome to the future of energy Sustainable Innovation Jobs The Energy Systems Catapult - why now? Our energy system is radically changing. The challenges of decarbonisation, an ageing infrastructure and
Welcome to the future of energy Sustainable Innovation Jobs The Energy Systems Catapult - why now? Our energy system is radically changing. The challenges of decarbonisation, an ageing infrastructure and
APSEC President s Report
 2015/EWG49/008 Agenda Item: 5a APSEC President s Report Purpose: Information Submitted by: APSEC 49 th Energy Working Group Meeting Gyeongju, Korea 22 26 June 2015 Report on APEC Sustainable Energy Center
2015/EWG49/008 Agenda Item: 5a APSEC President s Report Purpose: Information Submitted by: APSEC 49 th Energy Working Group Meeting Gyeongju, Korea 22 26 June 2015 Report on APEC Sustainable Energy Center
Almost by definition, issues of risk are both complex and complicated.
 E d itorial COMPLEXITY, RISK AND EMERGENCE: ELEMENTS OF A MANAGEMENT DILEMMA Risk Management (2006) 8, 221 226. doi: 10.1057/palgrave.rm.8250024 Introduction Almost by definition, issues of risk are both
E d itorial COMPLEXITY, RISK AND EMERGENCE: ELEMENTS OF A MANAGEMENT DILEMMA Risk Management (2006) 8, 221 226. doi: 10.1057/palgrave.rm.8250024 Introduction Almost by definition, issues of risk are both
CHAPTER 1 PURPOSES OF POST-SECONDARY EDUCATION
 CHAPTER 1 PURPOSES OF POST-SECONDARY EDUCATION 1.1 It is important to stress the great significance of the post-secondary education sector (and more particularly of higher education) for Hong Kong today,
CHAPTER 1 PURPOSES OF POST-SECONDARY EDUCATION 1.1 It is important to stress the great significance of the post-secondary education sector (and more particularly of higher education) for Hong Kong today,
Background Key point:
 Systems Innovation 1 Background Key point: Systemic innovation has gained added importance because of systems failure: a widespread perception that many of the systems supporting daily life need radical
Systems Innovation 1 Background Key point: Systemic innovation has gained added importance because of systems failure: a widespread perception that many of the systems supporting daily life need radical
Customising Foresight
 Customising Foresight Systemic and Synergistic Foresight Approaches Systemic and Synergistic Foresight Approaches in a small country context Higher School of Economics Moscow 13.10.2011 Ozcan Saritas &
Customising Foresight Systemic and Synergistic Foresight Approaches Systemic and Synergistic Foresight Approaches in a small country context Higher School of Economics Moscow 13.10.2011 Ozcan Saritas &
The Shared Perspective of the World in 2030 and Beyond
 The Shared Perspective of the World in 2030 and Beyond Themes and Drivers Strategic Foresight Analysis Workshop #2 13-14 November, 2012 Budapest, Hungary Organized by Allied Command Transformation, Norfolk
The Shared Perspective of the World in 2030 and Beyond Themes and Drivers Strategic Foresight Analysis Workshop #2 13-14 November, 2012 Budapest, Hungary Organized by Allied Command Transformation, Norfolk
Refining foresight approaches to crisis, inertia and transition
 Refining foresight approaches to crisis, inertia and transition 25-27 April 2017 Aalto University, Espoo, Finland Jennifer Cassingena Harper, Malta Council for Science and Technology This presentation
Refining foresight approaches to crisis, inertia and transition 25-27 April 2017 Aalto University, Espoo, Finland Jennifer Cassingena Harper, Malta Council for Science and Technology This presentation
Call for Papers & Workshops. Global Forum on Business as an Agent of World Benefit: Managing as Designing in an Era of Massive Innovation
 Call for Papers & Workshops Global Forum on Business as an Agent of World Benefit: Managing as Designing in an Era of Massive Innovation June 2 5, 2009 (500 word abstracts due December 1, 2008) What is
Call for Papers & Workshops Global Forum on Business as an Agent of World Benefit: Managing as Designing in an Era of Massive Innovation June 2 5, 2009 (500 word abstracts due December 1, 2008) What is
CSCM World Congress on CBRNe Science and Consequence Management. Remarks by Ahmet Üzümcü, Director-General OPCW. Monday 2 June 2014 Tbilisi, Georgia
 1 CSCM World Congress on CBRNe Science and Consequence Management Remarks by Ahmet Üzümcü, Director-General OPCW Monday 2 June 2014 Tbilisi, Georgia H.E. the Minister of Internal Affairs, H.E. the Minister
1 CSCM World Congress on CBRNe Science and Consequence Management Remarks by Ahmet Üzümcü, Director-General OPCW Monday 2 June 2014 Tbilisi, Georgia H.E. the Minister of Internal Affairs, H.E. the Minister
COMMISSION STAFF WORKING PAPER EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF THE IMPACT ASSESSMENT. Accompanying the
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 30.11.2011 SEC(2011) 1428 final Volume 1 COMMISSION STAFF WORKING PAPER EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF THE IMPACT ASSESSMENT Accompanying the Communication from the Commission 'Horizon
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 30.11.2011 SEC(2011) 1428 final Volume 1 COMMISSION STAFF WORKING PAPER EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF THE IMPACT ASSESSMENT Accompanying the Communication from the Commission 'Horizon
Enhancing Government through the Transforming Application of Foresight
 Addressing g the Future: Enhancing Government through the Transforming Application of Foresight Professor Ron Johnston Australian Centre for Innovation University of Sydney www.aciic.org.au Helsinki Institute
Addressing g the Future: Enhancing Government through the Transforming Application of Foresight Professor Ron Johnston Australian Centre for Innovation University of Sydney www.aciic.org.au Helsinki Institute
Table of Contents. Two Cultures of Ecology...0 RESPONSES TO THIS ARTICLE...3
 Table of Contents Two Cultures of Ecology...0 RESPONSES TO THIS ARTICLE...3 Two Cultures of Ecology C.S. (Buzz) Holling University of Florida This editorial was written two years ago and appeared on the
Table of Contents Two Cultures of Ecology...0 RESPONSES TO THIS ARTICLE...3 Two Cultures of Ecology C.S. (Buzz) Holling University of Florida This editorial was written two years ago and appeared on the
humanitarian impact & risks
 humanitarian impact & risks ICAN CAMPAIGNERS MEETING/GENEVA Humanitarian consequences and risks of nuclear weapons The growing risk that nuclear weapons will be used either deliberately or through some
humanitarian impact & risks ICAN CAMPAIGNERS MEETING/GENEVA Humanitarian consequences and risks of nuclear weapons The growing risk that nuclear weapons will be used either deliberately or through some
Towards a World in Common Strategy. #WorldInCommon
 Towards a World in Common 2018-2022 Strategy #WorldInCommon Our vision A World in Common AFD Group has a mission to help construct a world in common, a world that preserves and protects five important
Towards a World in Common 2018-2022 Strategy #WorldInCommon Our vision A World in Common AFD Group has a mission to help construct a world in common, a world that preserves and protects five important
Universities and Sustainable Development Towards the Global Goals
 Universities and Sustainable Development Towards the Global Goals Universities promote sustainable development The unique contribution of universities Sustainable Development Goals Sustainable development
Universities and Sustainable Development Towards the Global Goals Universities promote sustainable development The unique contribution of universities Sustainable Development Goals Sustainable development
