Tren ds i n Nuclear Security Assessm ents
|
|
|
- Phyllis Bradford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2 Tren ds i n Nuclear Security Assessm ents The l ast deca de of the twentieth century was one of enormous change in the security of the United States and the world. The torrent of changes in Eastern Europe, culminating in the previously unimaginable collapse of the barriers between the two Germanys, shook long-held beliefs about the very foundations for stability and security. The ensuing disintegration of the Soviet Union forced a complete reassessment of national and international security policies amid the most sweeping strategic changes since World War II. The euphoria over the end of the Cold War was tempered, however, as new challenges and uncertainties loomed concerning nuclear proliferation and terrorism. These developments present opportunities and risks that are difficult for scholars, experts, and policymakers to assess, and they are no less challenging for publics the world over. In this chapter, we assess how the American people are adjusting to the momentous security developments of the early post Cold War era. We analyze trends in public views of how the international security environment is evolving to include assessments of strategic threats posed by Russian and Chinese nuclear weapons capabilities. We illustrate how public views of broader external nuclear risks such as the likelihood of nuclear conflict, nuclear proliferation, and nuclear terrorism evolved between 1993 and Also we examine trends in beliefs about the risks associated with our own nuclear arsenal. We chart similar comparisons over time of public beliefs about the external and domestic benefits associated with US nuclear weapons. 1 20
2 trends in nuclear security assessments 21 Trends in Perceptions of the Security Environment Beginning in 1997, we employed the following questions to ask survey participants to rate how international security and US security have changed since the end of the Cold War. (Lead-in) I want to ask you some questions about how you think the world may have changed since the end of the Cold War. We are interested in your perceptions. There are no right or wrong answers. (Q4) Considering the international environment as a whole, and using a scale from one to seven where one means the world is much less secure, and seven means the world is much more secure, how do you think international security has changed since the end of the Cold War? (Q5) Focusing more specifically on the US, and using the same scale from one to seven where one means much less secure, and seven means much more secure, how has US security changed since the end of the Cold War? We compare grouped responses to each question for each of the four measurement periods in figures 2.1 and When we began this series of questions in 1997, a majority of respondents considered international and US security to have improved since the end of the Cold War. This was consistent with much of the considered opinion of the time in which discussion of a peace dividend occupied considerable space in the pages of scholarly and policy opinion as well as popular media. 3 The proportion of respondents perceiving security to have improved declined by about 10 percent between 1997 and 2003, while the proportion of those who consider international and US security to have worsened increased by about the same amount. Changes in means for each question from 1997 to 2003 are statistically significant. While it seems likely the terrorist attacks of 9/11 Figure 2.1. How international security has changed since the Cold War
3 22 chapter 2 Figure 2.2. How US security has changed since the Cold War influenced subsequent assessments, our measurements in 1999 suggest that the downward trend has earlier beginnings. In 2003 most respondents do not consider national or international security to have substantially improved over that which existed during the Cold War. To focus on public understanding of more specific components of strategic security, we also asked the following four questions about current and prospective threats to the United States posed by Russian and Chinese nuclear forces. (Lead-in) Now we want your overall assessment of current and future threats to the US from two sources. (Q51) First, on a scale from zero to ten where zero means no threat, and ten means extreme threat, how would you rate the current threat to the US posed by Russia s nuclear weapons? (Q52) Next, using the same scale from zero to ten where zero means no threat, and ten means extreme threat, how would you rate the current threat to the US from China s nuclear weapons? (Q53) Turning now to your outlook for the future, and using the same scale from zero to ten, how would you rate the threat to the US in the next ten years from Russia s nuclear weapons? (Q54) On the same scale from zero to ten, how would you rate the threat to the US in the next ten years from China s nuclear weapons? We compare trends in grouped assessments of current threats from Russian and Chinese nuclear forces in figures 2.3 and 2.4, and we compare trends in ratings of future strategic nuclear threats in figures 2.5 and 2.6. Several points are apparent. First, the mean public rating of the current nuclear threat from Russia is significantly lower in 2001 and 2003 than in earlier surveys in 1997 and 1999, while the corresponding mean rating of the cur-
4 trends in nuclear security assessments 23 Figure 2.3. Trends in public assessments of the current Russian nuclear threat Figure 2.4. Trends in public assessments of the current Chinese nuclear threat rent threat posed by China s nuclear weapons increases significantly between 2001 and 2003 to a value that statistically is unchanged from Second, the proportion of respondents in 2003 (42 percent) who rate the Chinese nuclear threat in the high range (7 10) is twice the proportion of respondents (21 percent) who rate the nuclear threat from Russia in the same range. Also note that in each measurement period, the mean nuclear threat rating for China is significantly higher than the corresponding rating for Russia (p <.0001 for each of the four years). Thus while our respondents consider general levels of security to be deteriorating, they also judge the more specific and traditional threats posed by Russian nuclear forces to be decreasing. This speaks to public abilities to absorb major strategic changes in nuclear relationships within the larger context of the evolving post Cold War security environment. Figures 2.5 and 2.6 show comparable public assessments of future Russian and Chinese nuclear threats projected over the next ten years.
5 24 chapter 2 Figure 2.5. Trends in public assessments of the future Russian nuclear threat Figure 2.6. Trends in public assessments of the future Chinese nuclear threat Note that the mean future nuclear threat rating for Russia in 2003 changes little from the previous measurement in 2001, but the mean future threat rating for China rises significantly above that measured two years earlier. Again, the mean ratings of future threats are significantly higher for China than for Russia in each of our four surveys (p <.0001 each year). While the public expects the threat posed by Russia s nuclear capabilities to remain at about the same level over the next decade, they predict that the Chinese nuclear threat will grow slightly over the same period. 4 These findings suggest that China has replaced Russia in terms of public expectations of relative current and predicted nuclear threats to US security, and that publicly perceived nuclear threats from each are trending differently. Both current and projected mean nuclear threats from Russia decline significantly over the course of our measurements from 1997 to Mean current and projected nuclear threats from China vary across the different measure-
6 trends in nuclear security assessments 25 ment periods, but by 2003 they are at levels that are statistically unchanged from our first measurements in Trends in External Nuclear Risks In each survey since beginning this project eighteen months after the breakup of the Soviet Union, we asked a series of six questions designed to measure three dimensions of evolving beliefs about external nuclear risks (risks from others nuclear weapons). They consist of the following two questions about the risks of nuclear conflict, two questions about the risks of nuclear proliferation, and two questions about the risks of nuclear terrorism. (Q6) How has the breakup of the Soviet Union affected the chances that the US will be involved in a war with any country in which nuclear weapons are used? (Q7) How has the breakup of the Soviet Union affected the possibility that nuclear weapons will be used by any country against any other country? (Q15) How do you think the breakup of the Soviet Union has affected the likelihood that nuclear weapons will spread to other countries? (Q16) How would you rate the risk to the US if more countries have nuclear weapons? (Q17) How would you rate today s threat of nuclear terrorism occurring anywhere in the world? (Q18) How would you rate the threat of nuclear weapons being used by terrorists anywhere in the world during the next ten years? Table 2.1 compares trends in mean response values for each of the six questions between 1993 and Public assessments of the implications of the Soviet breakup remain remarkably steady over the decade. Respondents are divided about the effects on the likelihood of nuclear conflict, with judgments of the chances the United States will become involved in a nuclear conflict increasing modestly (but statistically significantly) over the period, and assessments of the likelihood that nuclear weapons will be used in nuclear conflict between any two countries holding steady at just above midscale. Opinion is equally steady, and less divided, about the effects of the Soviet demise on further nuclear proliferation, with most participants in each survey judging the risks to be higher. Similarly, most respondents consider the risks to the United States, specifically, of further nuclear proliferation to be higher after the Soviet breakup, and that perspective holds steady throughout the measurement period. As to the current and future threat of nuclear terrorism, participants consider the contemporary threat to be increasing, and forecast no reduction when asked
7 26 chapter 2 Table 2.1. Trends in mean public assessments of external nuclear risks Mean external nuclear risks v 03 p-value Effect of Soviet breakup on chances US will be involved in nuclear war (Q6: 1 = decreased greatly 7 = increased greatly) <.0001 Effect of Soviet breakup on chances nuclear weapons will be used by any country against any other country (Q7: 1 = decreased greatly 7 = increased greatly) Effect of Soviet breakup on further nuclear proliferation (Q15: 0 = greatly reduced 10 = greatly increased) Risk to the US if more countries have nuclear weapons (Q16: 0 = no risk 10 = extreme risk) Threat of nuclear terrorism occurring anywhere in the world today (Q17: 0 = no threat 10 = extreme threat) Threat of nuclear terrorism occurring anywhere in the world in the next 10 years (Q18: 0 = no threat 10 = extreme threat) to consider the next ten years. Clearly, our respondents do not consider the risks of nuclear conflict, nuclear proliferation, or nuclear terrorism to have abated after the Cold War, and judgments about those risks do not show large variations over time. We combine responses to these six questions to form a composite index of external nuclear risks that provides a robust indication, comparable over time, illustrating trends in evolving beliefs about external nuclear weapons risks. 5 In figure 2.7 we show the distribution of responses in 2003, and in figure 2.8 we chart trends in mean external nuclear risk indices between 1993 and In 2003, about 8 percent of respondents judge external nuclear risks to be low (0 3), 49 percent rate them moderate (4 6), and 42 percent place them in the high range (7 10). The modal value is 6.0, and the mean is Mean composite external nuclear risks remain notably steady over the course of the decade, even after the events of 9/11. Thus it appears that the general public differentiates between the nonnuclear risks deriving from the terrorist attacks of 9/11 versus the risks posed by others nuclear weapons including nuclear terrorism and do not conclude that overall external nuclear risks have changed appreciably. As our findings show, from the perspectives of the US general public, average composite external nuclear risks vary only
8 trends in nuclear security assessments 27 Figure 2.7. External nuclear risk index, 2003 Scale midpoint = 5.0 Figure 2.8. Trends in the mean external nuclear risk index, (Note that here and in subsequent trend graphs, we truncate the vertical scale to better illustrate the data. We identify the scale midpoint to help orientation.) 0.34 on a scale from zero to ten over the decade from 1993 to But we note also that mean assessments are well above the scale midpoint of 5.0 in each measurement period, and that a substantial decrease in overall nuclear risks following the end of Cold War hostilities between the United States and the Soviet Union has yet to occur in the judgments of our respondents. Trends in Domestic Nuclear Risks In addition to measuring public assessments of risks deriving from others nuclear weapons, we also measure domestic risks believed to derive from our own nuclear weapons. In each measurement period since 1993, we asked respondents from the general public to rate the domestic risks associated with
9 28 chapter 2 manufacturing, transporting, storing, disassembling, and storing materials from disassembled US nuclear weapons. Additionally, we asked them to rate the likelihood that a US nuclear weapon might be employed without proper national authorization, and the likelihood that an accidental nuclear explosion might occur. The following questions allow us to compare trends in public beliefs about domestic nuclear risks. (Lead-in) The next several questions ask for your perceptions about risks to American society associated with managing US nuclear weapons. Using a scale from zero to ten where zero means no risk, and ten means extreme risk, how would you rate the risk of each of the following items? (Q8) Manufacturing nuclear weapons in the US (Q9) Transporting nuclear weapons in the US (Q10) Storing existing nuclear weapons in the US (Q11) Disassembling nuclear weapons in the US (Q12) Storing radioactive materials in the US from disassembled weapons (Q13) On a scale from zero to ten, where zero means not at all likely, and ten means highly likely, how would you rate the likelihood of a US nuclear weapon being used within the next twenty-five years without presidential authorization? (Q14) On the same scale from zero to ten, how would you rate the likelihood of an accident involving a US nuclear weapon causing an unintended nuclear explosion? In table 2.2, we show mean responses to each question across the six surveys. Note that in contrast to the previously charted steady or increasing public assessments of external nuclear risks, views of domestic nuclear risks deriving from US nuclear weapons capabilities show significant decreases in each category measured over the past decade. The reductions in mean perceived risks from the US nuclear arsenal range from a 14 percent decline in the likelihood of unauthorized use of a US nuclear weapon to a decrease of 23 percent in risks associated with manufacturing components for US nuclear weapons. These observations are recorded during a decade in which the United States is not developing, manufacturing, or testing nuclear weapons, though, presumably, some critical components are remanufactured. Of course, storage and transportation activities are ongoing, and nuclear weapons are being disassembled. By combining responses to these questions we create a robust index of public beliefs about domestic risks associated with US nuclear weapons, as shown in figure By comparing composite mean assessments of the domestic nuclear risk index over time, we illustrate trends in figure Grouped responses in 2003 indicate that 34 percent consider domestic nuclear risks to
10 trends in nuclear security assessments 29 Table 2.2. Trends in mean public assessments of domestic nuclear risks Domestic risk measures v 03 p-value Manufacturing nuclear weapons in the US (Q8: 0 = no risk 10 = extreme risk) <.0001 Transporting nuclear weapons in the US (Q9: 0 = no risk 10 = extreme risk) <.0001 Storing existing nuclear weapons in the US (Q10: 0 = no risk 10 = extreme risk) <.0001 Disassembling nuclear weapons in the US (Q11: 0 = no risk 10 = extreme risk) <.0001 Storing radioactive materials in the US from disassembled weapons (Q12: 0 = no risk 10 = extreme risk) <.0001 Likelihood of unauthorized use of US nuclear weapon in next 25 years (Q13: 0 = not at all likely 10 = extremely likely) <.0001 Likelihood of an unintended US nuclear weapon explosion (Q14: 0 = not at all likely 10 = extremely likely) <.0001 be low (0 3), 47 percent rate them moderate (4 6), and 18 percent judge them to be relatively high (7 10). The modal response is 5.0, and the mean is The downward trend in composite means from 6.06 in 1993 to 4.93 in 2003 clearly is statistically significant. The mean value for combined domestic nuclear risks fell below midscale both in 2001 and 2003, suggesting declining levels of public concern about safeguarding and controlling nuclear weapons. As will be shown in chapter 3, responses to direct questions about trust in Figure 2.9. Domestic nuclear risk index, 2003
11 30 chapter 2 Figure Trends in the mean domestic nuclear risk index, the Departments of Energy and Defense, as well as US national laboratories, reflect substantial levels of public confidence in the US nuclear weapons establishment. Trends in External Nuclear Benefits To measure public assessments of external benefits believed to derive from the US nuclear arsenal, we posed questions about the importance of nuclear weapons for US influence and status, remaining a military superpower, preserving the American way of life, and providing nuclear deterrence. The questions are shown below in summary fashion. (Q19) How important are US nuclear weapons for US influence over international events? (Q20) How important are US nuclear weapons for maintaining US status as a world leader? (Q21) How important is it for the US to remain a military superpower? (Q22) How important have nuclear weapons been to preserving America s way of life? (Lead-in) The next three questions ask about your perceptions of nuclear deterrence, which means preventing someone from using nuclear weapons against us, because they expect that we would retaliate by using nuclear weapons against them. 8 (Q23) First, how important was nuclear deterrence in preventing nuclear conflict during the Cold War? (Q24) How important are US nuclear weapons for preventing other countries from using nuclear weapons against us today?
12 trends in nuclear security assessments 31 (Q25) If more countries acquire nuclear weapons in the future, how effective will nuclear deterrence be in preventing nuclear wars from occurring anywhere in the world? We compare mean responses to each question over time in table 2.3. Mean assessments of the importance of US nuclear weapons for international influence and US status as a world leader, and the importance of remaining a military superpower increase significantly between our first survey in 1993 and our survey in Mean judgments of the importance of nuclear deterrence for preventing nuclear conflict during the Cold War and today are all high, and they remain steady throughout the measurement period. Finally, even when asked to assume that additional countries successfully acquire nuclear weapons, the future effectiveness of nuclear deterrence in a more proliferated world is rated above midscale and varies little over the six surveys. This continued strength of valuations of US nuclear weapons ca- Table 2.3. Trends in mean public assessments of external nuclear benefits Mean external nuclear benefits p-value Importance of nuclear weapons for US international influence (Q19: 0 = not at all important 10 = extremely important) Importance of nuclear weapons for US status as a world leader (Q20: 0 = not at all important 10 = extremely important) Importance of US remaining a military superpower (Q21: 0 = not at all important 10 = extremely important) Importance of nuclear weapons for preserving US way of life (Q22: 0 = not at all important 10 = extremely important) Importance of nuclear deterrence during Cold War (Q23: 0 = not at all important 10 = extremely important) NA Importance of nuclear deterrence today (Q24: 0 = not at all important 10 = extremely important) NA Future effectiveness of nuclear deterrence if more countries acquire nuclear weapons (Q25: 0 = not at all effective 10 = extremely effective) NA v 03 < v 03 < v 03 < v v v v
13 32 chapter 2 pabilities more than a decade after the end of the Cold War is surprising. We anticipated a decline in public views of the importance of US nuclear weapons in the post Cold War era. We combine responses to these questions to form an external nuclear benefit index for which the distribution of responses in 2003 is shown in figure 2.11, and the means are charted over time in figure This distribution pattern clearly shows that respondents in 2003 attribute substantial external security benefits to the US nuclear arsenal. About 58 percent of respondents rate the combined external benefits of nuclear weapons in the high range (7 10), while only about 7 percent of respondents place them in the low range (0 3). About 35 percent rate external nuclear benefits in the middle range (4 6). The modal response is 7.0, and even the mean is in the high range at The trend in our composite index of mean external nuclear benefits since 1995 generally is upward, with a turn downward in Note, however, that mean assessments are well above midscale in each period. A dozen years af- Figure External nuclear benefit index, 2003 Scale midpoint = 5.0 Figure Trends in the mean external nuclear benefit index,
14 trends in nuclear security assessments 33 ter the end of the Cold War, mean public views of the benefits of US nuclear weapons for achieving national objectives have not declined from those values recorded shortly after the collapse of the Soviet Union, and have actually increased somewhat. Clearly, the devaluation of US nuclear weapons we expected in the post Cold War period has not yet occurred. Trends in Domestic Nuclear Benefits Public assessments of domestic benefits related to US nuclear weapons are more difficult to gauge than the other three dimensions of nuclear risks and benefits. Measuring domestic benefits requires differentiating nuclear investments from those that are nonnuclear, and that is problematic. For example, some US weapon systems are designed to employ both nuclear and nonnuclear munitions. In some cases, weapon systems such as aircraft or naval vessels are designed for and employed primarily in conventional, nonnuclear roles, but also have the capacity to be used for employing nuclear weapons. Other systems, such as the B-1 bomber, may originally be designed primarily for nuclear roles but later are adapted to conventional missions. Also, expenditures for personnel and support equipment and facilities are not easily separated into nuclear and conventional components, because many of the same skills and equipment are applicable to both nuclear and nonnuclear combat environments. The same is true for investments in research and development that can encompass both conventional and nuclear systems as well as dual-role systems. Other types of investments, such as those for strategic intelligence and command and control are even harder to differentiate, because they are not publicly reported with sufficient clarity to definitively categorize them as to their nuclear vs. conventional applicability. Some of the investment categories that may be applicable to nuclear systems and capabilities are made outside the defense budget, and tracking all nuclear-related investment categories across the entire federal budget is extremely complex. These and other factors make the separation of nuclear and nonnuclear expenditures and investments very difficult, and thus measuring the domestic benefits of the nuclear categories is a daunting task for technical experts, and is even more problematic for most citizens. 10 For these and other reasons, we limit our questions to three broad inquiries into public beliefs about potential domestic benefits associated with nuclear weapons. As shown below, the three questions address cost trade-offs in nuclear and nonnuclear military capabilities, the economic value of jobs related to defense industries, and the potential benefit of technology transfers from the defense sector to other sectors of the US economy.
15 34 chapter 2 (Q37) Using a scale from one to seven where one means you strongly disagree, and seven means you strongly agree, please respond to the following statement. Having a nuclear arsenal means the US can spend less for national defense than would be necessary without nuclear weapons. (Lead-in) The next two questions deal with the economic value of defense industry jobs and defense-related technologies. Both use a scale from one to seven where one means little economic value, and seven means great economic value. (Q38) First, how do you rate the economic value of defense industry jobs in America? (Q39) Next, how do you rate the economic value of technological advances in defense industries for other areas of the US economy? 11 We compare trends in mean responses to each question in table 2.4. Even in an environment in which the numbers of US nuclear weapons are being reduced, perceived domestic benefits of US nuclear capabilities are not declining; in fact, mean responses to each question have increased significantly since we first asked them. For comparative purposes, we combine responses to each question to form a domestic nuclear benefit index, and we chart the distribution of the index for 2003 in figure Responses are grouped mostly toward the middle and upper portions of the scale, with 40 percent of respondents placing domestic nuclear benefits in the high range (7 10) and 46 percent rating them in the midrange (4 6). About 14 percent of respondents judge them to be low (0 3). The pattern shows a modal response value of 6.0 and a mean of 6.55, which, as shown in figure 2.14, has remained remarkably stable since This pattern of means shows a sustained level of valuation from 1995 (the first year in which all three questions were asked) to 2003 that is well above midscale. The previously discussed difficulties in judging domestic nuclear benefits do not prevent consistent evaluations, and the fact that they are not grouped around midscale suggests that most respondents are able to form Table 2.4. Trends in mean public assessments of domestic nuclear benefits Mean domestic nuclear benefits p-value US nuclear arsenal means we can spend less than would be necessary without nuclear weapons (Q37: 1 = strongly disagree 7 = strongly agree) Economic value of defense industry jobs (Q38: 1 = little value 7 = great value) Economic value of technological advances in defense industries for other areas of US economy (Q39: 1 = little value 7 = great value) NA v 03 < v 03 < v 03 <.0001
16 trends in nuclear security assessments 35 Figure Domestic nuclear benefit index, 2003 Scale midpoint = 5.0 Figure Trends in the mean domestic nuclear benefit index, opinions about the benefits of defense investments for the US domestic economy. We employ these four indices of public beliefs about external and domestic nuclear risks and benefits as important measures of domain beliefs when we analyze mass belief structures in chapter 6. But next we examine trends in public views about specific nuclear security issues, such as the contemporary relevance of nuclear weapons, the efficacy of nuclear deterrence, nuclear security policy and spending preferences, and trust in key elements of the US nuclear weapons establishment.
Special Eurobarometer 460. Summary. Attitudes towards the impact of digitisation and automation on daily life
 Summary Attitudes towards the impact of digitisation and automation on Survey requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General for Communications Networks, Content and Technology and co-ordinated
Summary Attitudes towards the impact of digitisation and automation on Survey requested by the European Commission, Directorate-General for Communications Networks, Content and Technology and co-ordinated
Created by Paul Hallett
 The National Cold War Exhibition covers many aspects of the GCSE Modern World syllabus. This package focuses on: The formation of NATO and the Warsaw Pact, the membership of these organisations and their
The National Cold War Exhibition covers many aspects of the GCSE Modern World syllabus. This package focuses on: The formation of NATO and the Warsaw Pact, the membership of these organisations and their
PUBLIC PERSPECTIVES OF NUCLEAR WEAPONS IN THE POST-COLD WAR ENVIRONMENT
 PUBLIC PERSPECTIVES OF NUCLEAR WEAPONS IN THE POST-COLD WAR ENVIRONMENT Findings and Analysis of the NATIONAL SECURITY SURVEY: PERCEPTIONS AND POLICY CONCERNS 1993-1994 The Institute for Public Policy
PUBLIC PERSPECTIVES OF NUCLEAR WEAPONS IN THE POST-COLD WAR ENVIRONMENT Findings and Analysis of the NATIONAL SECURITY SURVEY: PERCEPTIONS AND POLICY CONCERNS 1993-1994 The Institute for Public Policy
DoD Research and Engineering Enterprise
 DoD Research and Engineering Enterprise 16 th U.S. Sweden Defense Industry Conference May 10, 2017 Mary J. Miller Acting Assistant Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering 1526 Technology Transforming
DoD Research and Engineering Enterprise 16 th U.S. Sweden Defense Industry Conference May 10, 2017 Mary J. Miller Acting Assistant Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering 1526 Technology Transforming
DoD Research and Engineering Enterprise
 DoD Research and Engineering Enterprise 18 th Annual National Defense Industrial Association Science & Emerging Technology Conference April 18, 2017 Mary J. Miller Acting Assistant Secretary of Defense
DoD Research and Engineering Enterprise 18 th Annual National Defense Industrial Association Science & Emerging Technology Conference April 18, 2017 Mary J. Miller Acting Assistant Secretary of Defense
Lesson 17: Science and Technology in the Acquisition Process
 Lesson 17: Science and Technology in the Acquisition Process U.S. Technology Posture Defining Science and Technology Science is the broad body of knowledge derived from observation, study, and experimentation.
Lesson 17: Science and Technology in the Acquisition Process U.S. Technology Posture Defining Science and Technology Science is the broad body of knowledge derived from observation, study, and experimentation.
The Construction Market in Europe: A Supplier s Point of View
 The Construction Market in Europe: A Supplier s Point of View Dr. Walter Nussbaumer Abstract After the 2009 recession and the 2010 stagnation, recovery took place in 2011 when the World Construction Industry
The Construction Market in Europe: A Supplier s Point of View Dr. Walter Nussbaumer Abstract After the 2009 recession and the 2010 stagnation, recovery took place in 2011 when the World Construction Industry
Statement of John S. Foster, Jr. Before the Senate Armed Services Committee October 7, 1999
 Statement of John S. Foster, Jr. Before the Senate Armed Services Committee October 7, 1999 Mr. Chairman, I thank you for the opportunity to appear before the Committee regarding the ratification of the
Statement of John S. Foster, Jr. Before the Senate Armed Services Committee October 7, 1999 Mr. Chairman, I thank you for the opportunity to appear before the Committee regarding the ratification of the
2016 Executive Summary Canada
 5 th Edition 2016 Executive Summary Canada January 2016 Overview Now in its fifth edition and spanning across 23 countries, the GE Global Innovation Barometer is an international opinion survey of senior
5 th Edition 2016 Executive Summary Canada January 2016 Overview Now in its fifth edition and spanning across 23 countries, the GE Global Innovation Barometer is an international opinion survey of senior
Chapter 4. Benefits and Risks From Science
 Chapter 4 Benefits and Risks From Science Chapter 4 Benefits and Risks From Science Public perceptions of the risks and benefits of genetic engineering and biotechnology are probably developed within a
Chapter 4 Benefits and Risks From Science Chapter 4 Benefits and Risks From Science Public perceptions of the risks and benefits of genetic engineering and biotechnology are probably developed within a
Two Presidents, Two Parties, Two Times, One Challenge
 Two Presidents, Two Parties, Two Times, One Challenge David D. Thornburg, PhD Executive Director, Thornburg Center for Space Exploration dthornburg@aol.com www.tcse-k12.org Dwight Eisenhower and Barack
Two Presidents, Two Parties, Two Times, One Challenge David D. Thornburg, PhD Executive Director, Thornburg Center for Space Exploration dthornburg@aol.com www.tcse-k12.org Dwight Eisenhower and Barack
Academic Year
 2017-2018 Academic Year Note: The research questions and topics listed below are offered for consideration by faculty and students. If you have other ideas for possible research, the Academic Alliance
2017-2018 Academic Year Note: The research questions and topics listed below are offered for consideration by faculty and students. If you have other ideas for possible research, the Academic Alliance
Report CREATE THE FUTURE YEAR OLDS
 CREATE THE FUTURE 16-17 YEAR OLDS #QEPrize2016 Contents Introduction 4 Key insights 6 Interest in STEM and engineering as a career path 8 Recognising and understanding engineering 12 Solving the world
CREATE THE FUTURE 16-17 YEAR OLDS #QEPrize2016 Contents Introduction 4 Key insights 6 Interest in STEM and engineering as a career path 8 Recognising and understanding engineering 12 Solving the world
humanitarian impact & risks
 humanitarian impact & risks ICAN CAMPAIGNERS MEETING/GENEVA Humanitarian consequences and risks of nuclear weapons The growing risk that nuclear weapons will be used either deliberately or through some
humanitarian impact & risks ICAN CAMPAIGNERS MEETING/GENEVA Humanitarian consequences and risks of nuclear weapons The growing risk that nuclear weapons will be used either deliberately or through some
Scenario Development Process
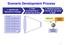 Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
Scenario Development Process 1. Identify Key Elements of Change 2. Filter uncertainties to identify key drivers 3. Develop scenario stories for the world in 2020 Key Uncertainties Text about uncertainties;
April 10, Develop and demonstrate technologies needed to remotely detect the early stages of a proliferant nation=s nuclear weapons program.
 Statement of Robert E. Waldron Assistant Deputy Administrator for Nonproliferation Research and Engineering National Nuclear Security Administration U. S. Department of Energy Before the Subcommittee on
Statement of Robert E. Waldron Assistant Deputy Administrator for Nonproliferation Research and Engineering National Nuclear Security Administration U. S. Department of Energy Before the Subcommittee on
Mars Generation National Opinion Poll
 Mars Generation National Opinion Poll Measuring U.S. Citizen Support for the Exploration of Mars Report by: Explore Mars, Inc. Survey conducted by: Phillips & Company Sponsored by: The Boeing Company March
Mars Generation National Opinion Poll Measuring U.S. Citizen Support for the Exploration of Mars Report by: Explore Mars, Inc. Survey conducted by: Phillips & Company Sponsored by: The Boeing Company March
Ground Robotics Market Analysis
 IHS AEROSPACE DEFENSE & SECURITY (AD&S) Presentation PUBLIC PERCEPTION Ground Robotics Market Analysis AUTONOMY 4 December 2014 ihs.com Derrick Maple, Principal Analyst, +44 (0)1834 814543, derrick.maple@ihs.com
IHS AEROSPACE DEFENSE & SECURITY (AD&S) Presentation PUBLIC PERCEPTION Ground Robotics Market Analysis AUTONOMY 4 December 2014 ihs.com Derrick Maple, Principal Analyst, +44 (0)1834 814543, derrick.maple@ihs.com
Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons (CCW) Meeting of Experts on Lethal Autonomous Weapons Systems (LAWS) April 2016, Geneva
 Introduction Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons (CCW) Meeting of Experts on Lethal Autonomous Weapons Systems (LAWS) 11-15 April 2016, Geneva Views of the International Committee of the Red Cross
Introduction Convention on Certain Conventional Weapons (CCW) Meeting of Experts on Lethal Autonomous Weapons Systems (LAWS) 11-15 April 2016, Geneva Views of the International Committee of the Red Cross
2017 R&D Trends Forecast Results from the Industrial Research Institute s Annual Survey
 FEATURE ARTICLE 2017 R&D Trends Forecast Results from the Industrial Research Institute s Annual Survey Slowing economies slow R&D investments and mute optimism. The Industrial Research Institute The Industrial
FEATURE ARTICLE 2017 R&D Trends Forecast Results from the Industrial Research Institute s Annual Survey Slowing economies slow R&D investments and mute optimism. The Industrial Research Institute The Industrial
Federal Research and Development Contract Trends and the Supporting Industrial Base,
 SEPTEMBER 2016 executive summary Federal Research and Development Contract Trends and the Supporting Industrial Base, 2000 2015 project directors Andrew Hunter Greg Sanders authors Jesse Ellman Kaitlyn
SEPTEMBER 2016 executive summary Federal Research and Development Contract Trends and the Supporting Industrial Base, 2000 2015 project directors Andrew Hunter Greg Sanders authors Jesse Ellman Kaitlyn
DLA Piper TechNOLOGY Leaders
 DLA Piper TechNOLOGY Leaders Forecast Survey FALL 2012 DLA Piper Technology Leaders Forecast Survey q4 2012 Executive Summary In the face of global economic headwinds and amid a high-stakes 2012 presidential
DLA Piper TechNOLOGY Leaders Forecast Survey FALL 2012 DLA Piper Technology Leaders Forecast Survey q4 2012 Executive Summary In the face of global economic headwinds and amid a high-stakes 2012 presidential
Strategic Partner of the Report
 Strategic Partner of the Report Last year s Global Risks Report was published at a time of heightened global uncertainty and strengthening popular discontent with the existing political and economic order.
Strategic Partner of the Report Last year s Global Risks Report was published at a time of heightened global uncertainty and strengthening popular discontent with the existing political and economic order.
INTRODUCTION. Costeas-Geitonas School Model United Nations Committee: Disarmament and International Security Committee
 Committee: Disarmament and International Security Committee Issue: Prevention of an arms race in outer space Student Officer: Georgios Banos Position: Chair INTRODUCTION Space has intrigued humanity from
Committee: Disarmament and International Security Committee Issue: Prevention of an arms race in outer space Student Officer: Georgios Banos Position: Chair INTRODUCTION Space has intrigued humanity from
IXIA S PUBLIC ART SURVEY 2013 SUMMARY AND KEY FINDINGS. Published February 2014
 IXIA S PUBLIC ART SURVEY 2013 SUMMARY AND KEY FINDINGS Published February 2014 ABOUT IXIA ixia is England s public art think tank. We promote and influence the development and implementation of public
IXIA S PUBLIC ART SURVEY 2013 SUMMARY AND KEY FINDINGS Published February 2014 ABOUT IXIA ixia is England s public art think tank. We promote and influence the development and implementation of public
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. St. Louis Region Emerging Transportation Technology Strategic Plan. June East-West Gateway Council of Governments ICF
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY St. Louis Region Emerging Transportation Technology Strategic Plan June 2017 Prepared for East-West Gateway Council of Governments by ICF Introduction 1 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This document
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY St. Louis Region Emerging Transportation Technology Strategic Plan June 2017 Prepared for East-West Gateway Council of Governments by ICF Introduction 1 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This document
What Is a Global Superpower? One World Student Ambassador: Nathan Araya. Unit Resource #2: Understanding the Reflection
 Name: Date: What Is a Global Superpower? One World Student Ambassador: Nathan Araya Unit Resource #2: Understanding the Reflection Directions: Preview the following questions before you read the Reflection.
Name: Date: What Is a Global Superpower? One World Student Ambassador: Nathan Araya Unit Resource #2: Understanding the Reflection Directions: Preview the following questions before you read the Reflection.
ctbuh.org/papers Journals and Patents for Measuring the Development of Technologies in the Area of Supertall Building Title:
 ctbuh.org/papers Title: Authors: Subject: Keyword: Journals and Patents for Measuring the Development of Technologies in the Area of Supertall Building Giu Lee, Researcher, Korea Institute of Construction
ctbuh.org/papers Title: Authors: Subject: Keyword: Journals and Patents for Measuring the Development of Technologies in the Area of Supertall Building Giu Lee, Researcher, Korea Institute of Construction
THE OIL & GAS SERVICES SECTOR: GOOD PROSPECTS FOR THE MEDIUM TO LONG TERM. Dr. Kris R. Nielsen Chairman and President
 www.pegasus-global.com 1750 Emerick Road, Cle Elum, WA 98922 USA +1 (509) 857 2235 Fax: +1 (509) 857 2237 THE OIL & GAS SERVICES SECTOR: GOOD PROSPECTS FOR THE MEDIUM TO LONG TERM Remarks by Dr. Kris R.
www.pegasus-global.com 1750 Emerick Road, Cle Elum, WA 98922 USA +1 (509) 857 2235 Fax: +1 (509) 857 2237 THE OIL & GAS SERVICES SECTOR: GOOD PROSPECTS FOR THE MEDIUM TO LONG TERM Remarks by Dr. Kris R.
Silicon Wafer Demand Outlook: Forecast Update, 2Q03
 Research Brief Silicon Wafer Demand Outlook: Forecast Update, 2Q03 Abstract: The latest silicon wafer demand outlook predicts about 6 percent growth in 2003, nearly the same as the previous forecast. However,
Research Brief Silicon Wafer Demand Outlook: Forecast Update, 2Q03 Abstract: The latest silicon wafer demand outlook predicts about 6 percent growth in 2003, nearly the same as the previous forecast. However,
Technology Needs Assessment
 Technology Needs Assessment CII Research Summary 173-1 Executive Summary The Technology Needs Assessment Research Team was initiated to take a snapshot of current industry technology needs. As a result,
Technology Needs Assessment CII Research Summary 173-1 Executive Summary The Technology Needs Assessment Research Team was initiated to take a snapshot of current industry technology needs. As a result,
DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
 POSITION STATEMENT DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Adopted by the IEEE-USA Board of Directors, 23 November 2013 IEEE-USA strongly supports the Department of Defense (DoD) Science and Technology
POSITION STATEMENT DEPARTMENT OF DEFENSE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Adopted by the IEEE-USA Board of Directors, 23 November 2013 IEEE-USA strongly supports the Department of Defense (DoD) Science and Technology
NATIONAL STRATEGY FOR THE SPACE SECTOR: PROPOSALS MADE BY PROESPAÇO The Portuguese Association of Space Industries MARCH 19, 2012
 NATIONAL STRATEGY FOR THE SPACE SECTOR: PROPOSALS MADE BY PROESPAÇO The Portuguese Association of Space Industries MARCH 19, 2012 VISION FOR THE NEXT 10 YEARS António Neto da Silva * Portugal s space industry
NATIONAL STRATEGY FOR THE SPACE SECTOR: PROPOSALS MADE BY PROESPAÇO The Portuguese Association of Space Industries MARCH 19, 2012 VISION FOR THE NEXT 10 YEARS António Neto da Silva * Portugal s space industry
OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 2008: Highlights
 OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 2008: Highlights Global dynamics in science, technology and innovation Investment in science, technology and innovation has benefited from strong economic
OECD Science, Technology and Industry Outlook 2008: Highlights Global dynamics in science, technology and innovation Investment in science, technology and innovation has benefited from strong economic
Police Technology Jack McDevitt, Chad Posick, Dennis P. Rosenbaum, Amie Schuck
 Purpose Police Technology Jack McDevitt, Chad Posick, Dennis P. Rosenbaum, Amie Schuck In the modern world, technology has significantly affected the way societies police their citizenry. The history of
Purpose Police Technology Jack McDevitt, Chad Posick, Dennis P. Rosenbaum, Amie Schuck In the modern world, technology has significantly affected the way societies police their citizenry. The history of
U.S. National Space Policy
 U.S. National Space Policy Opportunities and Challenges in Shaping the International Space Regime AIAA Space 2007 Long Beach, California 18 September 2007 0 9/18/2007 Dana J. Johnson, Ph.D. Senior Analyst,
U.S. National Space Policy Opportunities and Challenges in Shaping the International Space Regime AIAA Space 2007 Long Beach, California 18 September 2007 0 9/18/2007 Dana J. Johnson, Ph.D. Senior Analyst,
Disarmament and Arms Control An overview of issues and an assessment of the future
 Disarmament and Arms Control An overview of issues and an assessment of the future EU-ISS research staff discussion Jean Pascal Zanders 18 December 2008 Defining the concepts Disarmament: Reduction of
Disarmament and Arms Control An overview of issues and an assessment of the future EU-ISS research staff discussion Jean Pascal Zanders 18 December 2008 Defining the concepts Disarmament: Reduction of
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY (IP) SME SCOREBOARD 2016
 www.euipo.europa.eu INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY (IP) SME SCOREBOARD 2016 Executive Summary JUNE 2016 www.euipo.europa.eu INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY (IP) SME SCOREBOARD 2016 Commissioned to GfK Belgium by the European
www.euipo.europa.eu INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY (IP) SME SCOREBOARD 2016 Executive Summary JUNE 2016 www.euipo.europa.eu INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY (IP) SME SCOREBOARD 2016 Commissioned to GfK Belgium by the European
CCG 360 o Stakeholder Survey
 July 2017 CCG 360 o Stakeholder Survey National report NHS England Publications Gateway Reference: 06878 Ipsos 16-072895-01 Version 1 Internal Use Only MORI This Terms work was and carried Conditions out
July 2017 CCG 360 o Stakeholder Survey National report NHS England Publications Gateway Reference: 06878 Ipsos 16-072895-01 Version 1 Internal Use Only MORI This Terms work was and carried Conditions out
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY (IP) SME SCOREBOARD 2016
 www.euipo.europa.eu INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY (IP) SME SCOREBOARD 2016 Executive Summary JUNE 2016 www.euipo.europa.eu INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY (IP) SME SCOREBOARD 2016 Commissioned to GfK Belgium by the European
www.euipo.europa.eu INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY (IP) SME SCOREBOARD 2016 Executive Summary JUNE 2016 www.euipo.europa.eu INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY (IP) SME SCOREBOARD 2016 Commissioned to GfK Belgium by the European
WNA s Worldwide Overview and Outlook of Global Uranium Mining Supply and Demand
 WNA s Worldwide Overview and Outlook of Global Uranium Mining Supply and Demand - 11685 Sylvain Saint-Pierre and Steve Kidd World Nuclear Association (WNA), London, United Kingdom Abstract This paper presents
WNA s Worldwide Overview and Outlook of Global Uranium Mining Supply and Demand - 11685 Sylvain Saint-Pierre and Steve Kidd World Nuclear Association (WNA), London, United Kingdom Abstract This paper presents
CalsMUN 2019 Future Technology. The Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space. Research Report. Militarising Outer Space
 Future Technology Research Report Forum: Issue: Chairs: COPUOS Militarising Outer Space Björn Overbeek and Thijs de Ruijter RESEARCH REPORT 1 Personal Introduction Björn Overbeek Hi, My name is Björn,
Future Technology Research Report Forum: Issue: Chairs: COPUOS Militarising Outer Space Björn Overbeek and Thijs de Ruijter RESEARCH REPORT 1 Personal Introduction Björn Overbeek Hi, My name is Björn,
Emerging Technologies: What Have We Learned About Governing the Risks?
 Emerging Technologies: What Have We Learned About Governing the Risks? Paul C. Stern, National Research Council, USA Norwegian University of Science and Technology Presentation to Science and Technology
Emerging Technologies: What Have We Learned About Governing the Risks? Paul C. Stern, National Research Council, USA Norwegian University of Science and Technology Presentation to Science and Technology
COST GROWTH, ACQUISITION POLICY, AND BUDGET CLIMATE David L. McNicol
 COST GROWTH, ACQUISITION POLICY, AND BUDGET CLIMATE David L. McNicol The Problem This article asks whether, taking account of funding climate, there is a statistically significant association between changes
COST GROWTH, ACQUISITION POLICY, AND BUDGET CLIMATE David L. McNicol The Problem This article asks whether, taking account of funding climate, there is a statistically significant association between changes
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH AND INNOVATION - DECISIVE FACTORS OF BUSINESS PERFORMANCE
 194ANNALS OF THE UNIVERSITY OF CRAIOVA ECONOMIC SCIENCES Year XXXXI No. 39 2011 SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH AND INNOVATION - DECISIVE FACTORS OF BUSINESS PERFORMANCE Spiridon Cosmin Alexandru Ph. D Student University
194ANNALS OF THE UNIVERSITY OF CRAIOVA ECONOMIC SCIENCES Year XXXXI No. 39 2011 SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH AND INNOVATION - DECISIVE FACTORS OF BUSINESS PERFORMANCE Spiridon Cosmin Alexandru Ph. D Student University
Foresight and Scenario Development
 Foresight and Scenario Development Anita Pirc Velkavrh Head of Foresight and Sustainability group European Environment Agency ESDN Annual conference, 22-23 June 2017, Prague EEA, environmental messages
Foresight and Scenario Development Anita Pirc Velkavrh Head of Foresight and Sustainability group European Environment Agency ESDN Annual conference, 22-23 June 2017, Prague EEA, environmental messages
Civic Scientific Literacy Survey in China
 Journal of Scientific Temper Vol 2(3&4), Jul-Sep & Oct-Dec 2014, pp. 169-182 RESEARCH ARTICLE Civic Scientific Literacy Survey in China HE WEI, REN LEI & ZHANG CHAO Division of Scientific Literacy Research,
Journal of Scientific Temper Vol 2(3&4), Jul-Sep & Oct-Dec 2014, pp. 169-182 RESEARCH ARTICLE Civic Scientific Literacy Survey in China HE WEI, REN LEI & ZHANG CHAO Division of Scientific Literacy Research,
CEO Briefing The Business Agenda for South Africa: Competing in a Digital World
 CEO Briefing 2014 The Business Agenda for South Africa: Competing in a Digital World CEO Briefing 2014 The Business Agenda for South Africa: Competing in a Digital World 3 Contents Introduction 02 South
CEO Briefing 2014 The Business Agenda for South Africa: Competing in a Digital World CEO Briefing 2014 The Business Agenda for South Africa: Competing in a Digital World 3 Contents Introduction 02 South
Census Response Rate, 1970 to 1990, and Projected Response Rate in 2000
 Figure 1.1 Census Response Rate, 1970 to 1990, and Projected Response Rate in 2000 80% 78 75% 75 Response Rate 70% 65% 65 2000 Projected 60% 61 0% 1970 1980 Census Year 1990 2000 Source: U.S. Census Bureau
Figure 1.1 Census Response Rate, 1970 to 1990, and Projected Response Rate in 2000 80% 78 75% 75 Response Rate 70% 65% 65 2000 Projected 60% 61 0% 1970 1980 Census Year 1990 2000 Source: U.S. Census Bureau
The outlook for the oil and gas industry in 2013
 The outlook for the oil and gas industry in 2013 Background to the Research 428 senior professionals and executives across the global oil and gas sector were surveyed by GL Noble Denton during November
The outlook for the oil and gas industry in 2013 Background to the Research 428 senior professionals and executives across the global oil and gas sector were surveyed by GL Noble Denton during November
Nuclear Safety and Security Culture Roles and Responsibilities of Individuals. Middle East Scientific Institute for Security (MESIS)
 Nuclear Safety and Security Culture Roles and Responsibilities of Individuals 8 th Annual RMCC Workshop Middle East Scientific Institute for Security (MESIS) Amman, Jordan June 17-19, 2013 Dr. J. David
Nuclear Safety and Security Culture Roles and Responsibilities of Individuals 8 th Annual RMCC Workshop Middle East Scientific Institute for Security (MESIS) Amman, Jordan June 17-19, 2013 Dr. J. David
Chemistry Based on. Toray Profile: Overview and Philosophy
 Toray Profile: Overview and Philosophy Toray Group, headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, is an integrated chemical group. We are involved in global manufacturing, marketing and sales in three business categories
Toray Profile: Overview and Philosophy Toray Group, headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, is an integrated chemical group. We are involved in global manufacturing, marketing and sales in three business categories
Technologies Worth Watching. Case Study: Investigating Innovation Leader s
 Case Study: Investigating Innovation Leader s Technologies Worth Watching 08-2017 Mergeflow AG Effnerstrasse 39a 81925 München Germany www.mergeflow.com 2 About Mergeflow What We Do Our innovation analytics
Case Study: Investigating Innovation Leader s Technologies Worth Watching 08-2017 Mergeflow AG Effnerstrasse 39a 81925 München Germany www.mergeflow.com 2 About Mergeflow What We Do Our innovation analytics
2018 IIF ANNUAL MEMBERSHIP MEETING
 2018 IIF ANNUAL MEMBERSHIP MEETING October 12-13, 2018 Grand Hyatt Nusa Dua, Bali, Indonesia PRELIMINARY AGENDA *Subject to change* FRIDAY, OCTOBER 12 7:30 am 8:30 am REGISTRATION AND REFRESHMENTS 8:30
2018 IIF ANNUAL MEMBERSHIP MEETING October 12-13, 2018 Grand Hyatt Nusa Dua, Bali, Indonesia PRELIMINARY AGENDA *Subject to change* FRIDAY, OCTOBER 12 7:30 am 8:30 am REGISTRATION AND REFRESHMENTS 8:30
DIGITIZATION IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 3 DESPITE RECORD SALES IN GERMAN SYSTEMS AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING THE GROWTH PROSPECTS IN THE CORE BUSINESS ARE MODERATE. NEW SOLUTION APPROACHES ARE NEEDED TO COUNTERACT THIS TREND. With the development
3 DESPITE RECORD SALES IN GERMAN SYSTEMS AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING THE GROWTH PROSPECTS IN THE CORE BUSINESS ARE MODERATE. NEW SOLUTION APPROACHES ARE NEEDED TO COUNTERACT THIS TREND. With the development
Gerald G. Boyd, Tom D. Anderson, David W. Geiser
 THE ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PROGRAM USES PERFORMANCE MEASURES FOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY TO: FOCUS INVESTMENTS ON ACHIEVING CLEANUP GOALS; IMPROVE THE MANAGEMENT OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY; AND, EVALUATE
THE ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PROGRAM USES PERFORMANCE MEASURES FOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY TO: FOCUS INVESTMENTS ON ACHIEVING CLEANUP GOALS; IMPROVE THE MANAGEMENT OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY; AND, EVALUATE
HISTORY of AIR WARFARE
 INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM 2014 HISTORY of AIR WARFARE Grasp Your History, Enlighten Your Future INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON THE HISTORY OF AIR WARFARE Air Power in Theory and Implementation Air and Space
INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM 2014 HISTORY of AIR WARFARE Grasp Your History, Enlighten Your Future INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON THE HISTORY OF AIR WARFARE Air Power in Theory and Implementation Air and Space
Report to Congress regarding the Terrorism Information Awareness Program
 Report to Congress regarding the Terrorism Information Awareness Program In response to Consolidated Appropriations Resolution, 2003, Pub. L. No. 108-7, Division M, 111(b) Executive Summary May 20, 2003
Report to Congress regarding the Terrorism Information Awareness Program In response to Consolidated Appropriations Resolution, 2003, Pub. L. No. 108-7, Division M, 111(b) Executive Summary May 20, 2003
Figure 1: When asked whether Mexico has the intellectual capacity to perform economic-environmental modeling, expert respondents said yes.
 PNNL-15566 Assessment of Economic and Environmental Modeling Capabilities in Mexico William Chandler Laboratory Fellow, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (retired) 31 October 2005 Purpose This paper
PNNL-15566 Assessment of Economic and Environmental Modeling Capabilities in Mexico William Chandler Laboratory Fellow, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (retired) 31 October 2005 Purpose This paper
Violent Intent Modeling System
 for the Violent Intent Modeling System April 25, 2008 Contact Point Dr. Jennifer O Connor Science Advisor, Human Factors Division Science and Technology Directorate Department of Homeland Security 202.254.6716
for the Violent Intent Modeling System April 25, 2008 Contact Point Dr. Jennifer O Connor Science Advisor, Human Factors Division Science and Technology Directorate Department of Homeland Security 202.254.6716
ALMOST NUCLEAR: INTRODUCING THE NUCLEAR LATENCY DATASET
 ALMOST NUCLEAR: INTRODUCING THE NUCLEAR LATENCY DATASET Matthew Fuhrmann and Benjamin Tkach Alyssa Martinec Nuclear Latency A country having the capacity to quickly produce nuclear weapons in the event
ALMOST NUCLEAR: INTRODUCING THE NUCLEAR LATENCY DATASET Matthew Fuhrmann and Benjamin Tkach Alyssa Martinec Nuclear Latency A country having the capacity to quickly produce nuclear weapons in the event
How U.S. Employment Is Changing
 December 1, 211 How U.S. Employment Is Changing Stephen P. A. Brown and Hui Liu During the most recent recession, U.S. employment fell by 7,49 million jobs (5.4 percent). During the first 8 months of the
December 1, 211 How U.S. Employment Is Changing Stephen P. A. Brown and Hui Liu During the most recent recession, U.S. employment fell by 7,49 million jobs (5.4 percent). During the first 8 months of the
Revista Economică 68:5 (2016) PUBLIC PERCEPTION OF THE ROLE OF SCIENCE AND INNOVATION IN SOLVING THE PROBLEMS EXPERIENCED BY CONTEMPORARY ECONOMY
 PUBLIC PERCEPTION OF THE ROLE OF SCIENCE AND INNOVATION IN SOLVING THE PROBLEMS EXPERIENCED BY CONTEMPORARY ECONOMY DURALIA Oana 1 Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu Abstract: In the context of contemporary
PUBLIC PERCEPTION OF THE ROLE OF SCIENCE AND INNOVATION IN SOLVING THE PROBLEMS EXPERIENCED BY CONTEMPORARY ECONOMY DURALIA Oana 1 Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu Abstract: In the context of contemporary
Dual circulation period in Slovakia
 Flash Eurobarometer 255 The Gallup Organization Analytical Report Flash Eurobarometer European Commission Dual circulation period in Slovakia Analytical report Fieldwork: uary 2009 Report: March 2009 This
Flash Eurobarometer 255 The Gallup Organization Analytical Report Flash Eurobarometer European Commission Dual circulation period in Slovakia Analytical report Fieldwork: uary 2009 Report: March 2009 This
The challenges raised by increasingly autonomous weapons
 The challenges raised by increasingly autonomous weapons Statement 24 JUNE 2014. On June 24, 2014, the ICRC VicePresident, Ms Christine Beerli, opened a panel discussion on The Challenges of Increasingly
The challenges raised by increasingly autonomous weapons Statement 24 JUNE 2014. On June 24, 2014, the ICRC VicePresident, Ms Christine Beerli, opened a panel discussion on The Challenges of Increasingly
Magnitude Scaling. Observations: 1. (Ordinal) Homer Simpson is more humorous than any other character from The Simpsons
 Magnitude Scaling 24.16 39.37 50.00 23.0 29.44 47.8 14.97 37.9 20.75 44.82 140.19 Less Humorous More Humorous 22.5 Observations: 6.92 23.91 38.54 46.4 1. (Ordinal) Homer Simpson is more humorous than any
Magnitude Scaling 24.16 39.37 50.00 23.0 29.44 47.8 14.97 37.9 20.75 44.82 140.19 Less Humorous More Humorous 22.5 Observations: 6.92 23.91 38.54 46.4 1. (Ordinal) Homer Simpson is more humorous than any
STATE REGULATORS PERSPECTIVES ON LTS IMPLEMENTATION AND TECHNOLOGIES Results of an ITRC State Regulators Survey. Thomas A Schneider
 STATE REGULATORS PERSPECTIVES ON LTS IMPLEMENTATION AND TECHNOLOGIES Results of an ITRC State Regulators Survey Thomas A Schneider Ohio Environmental Protection Agency 401 East Fifth Street Dayton OH 45402-2911
STATE REGULATORS PERSPECTIVES ON LTS IMPLEMENTATION AND TECHNOLOGIES Results of an ITRC State Regulators Survey Thomas A Schneider Ohio Environmental Protection Agency 401 East Fifth Street Dayton OH 45402-2911
Silicon Wafer Demand Forecast Update, 4Q03
 Forecast Analysis Silicon Wafer Demand Forecast Update, 4Q03 Abstract: Silicon wafer demand in 2003 will register an 8 percent increase over 2002. Demand will enter an expansion phase in the second quarter
Forecast Analysis Silicon Wafer Demand Forecast Update, 4Q03 Abstract: Silicon wafer demand in 2003 will register an 8 percent increase over 2002. Demand will enter an expansion phase in the second quarter
Empirical Research Regarding the Importance of Digital Transformation for Romanian SMEs. Livia TOANCA 1
 Empirical Research Regarding the Importance of Digital Transformation for Romanian SMEs Livia TOANCA 1 ABSTRACT As the need for digital transformation becomes more and more self-evident with the rapid
Empirical Research Regarding the Importance of Digital Transformation for Romanian SMEs Livia TOANCA 1 ABSTRACT As the need for digital transformation becomes more and more self-evident with the rapid
Comparative study of SME development in Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan. Lyubov Tsoy CWRD intern Supervisor Dai Chai Song
 Comparative study of SME development in Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan Lyubov Tsoy CWRD intern Supervisor Dai Chai Song 1. Background 2. SME development trends (1991-2013) 3. Factors that caused differences
Comparative study of SME development in Uzbekistan and Kazakhstan Lyubov Tsoy CWRD intern Supervisor Dai Chai Song 1. Background 2. SME development trends (1991-2013) 3. Factors that caused differences
ADM STANSFIELD TURNER
 THE DILEMMA OF NUCLEAR WEAPONS ADM STANSFIELD TURNER graduated from the U.S. Naval Academy in 1946 and earned a master s degree from Oxford University as a Rhodes Scholar. In 1967 he commissioned the guided
THE DILEMMA OF NUCLEAR WEAPONS ADM STANSFIELD TURNER graduated from the U.S. Naval Academy in 1946 and earned a master s degree from Oxford University as a Rhodes Scholar. In 1967 he commissioned the guided
REPORT ON THE EUROSTAT 2017 USER SATISFACTION SURVEY
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate A: Cooperation in the European Statistical System; international cooperation; resources Unit A2: Strategy and Planning REPORT ON THE EUROSTAT 2017 USER SATISFACTION
EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate A: Cooperation in the European Statistical System; international cooperation; resources Unit A2: Strategy and Planning REPORT ON THE EUROSTAT 2017 USER SATISFACTION
The Shared Perspective of the World in 2030 and Beyond
 The Shared Perspective of the World in 2030 and Beyond Themes and Drivers Strategic Foresight Analysis Workshop #2 13-14 November, 2012 Budapest, Hungary Organized by Allied Command Transformation, Norfolk
The Shared Perspective of the World in 2030 and Beyond Themes and Drivers Strategic Foresight Analysis Workshop #2 13-14 November, 2012 Budapest, Hungary Organized by Allied Command Transformation, Norfolk
GLOBAL CATASTROPHIC RISKS SURVEY
 GLOBAL CATASTROPHIC RISKS SURVEY (2008) Technical Report 2008/1 Published by Future of Humanity Institute, Oxford University Anders Sandberg and Nick Bostrom At the Global Catastrophic Risk Conference
GLOBAL CATASTROPHIC RISKS SURVEY (2008) Technical Report 2008/1 Published by Future of Humanity Institute, Oxford University Anders Sandberg and Nick Bostrom At the Global Catastrophic Risk Conference
Other Approaches to Civil-Military Integration: The Chinese and Japanese Arms Industries. March OTA-BP-ISS-143 GPO stock #
 Other Approaches to Civil-Military Integration: The Chinese and Japanese Arms Industries March 1995 OTA-BP-ISS-143 GPO stock #052-003-01408-4 Recommended Citation: U.S. Congress, Office of Technology Assessment,
Other Approaches to Civil-Military Integration: The Chinese and Japanese Arms Industries March 1995 OTA-BP-ISS-143 GPO stock #052-003-01408-4 Recommended Citation: U.S. Congress, Office of Technology Assessment,
SACT remarks at. Atlantic Council SFA Washington DC, George Washington University, Elliott School of International Affairs
 SACT remarks at Atlantic Council SFA 2017 Washington DC, George Washington University, Elliott School of International Affairs 16 Nov 2017, 1700-1830 Général d armée aérienne Denis Mercier 1 Thank you
SACT remarks at Atlantic Council SFA 2017 Washington DC, George Washington University, Elliott School of International Affairs 16 Nov 2017, 1700-1830 Général d armée aérienne Denis Mercier 1 Thank you
The Drive for Innovation in Systems Engineering
 The Drive for Innovation in Systems Engineering D. Scott Lucero Office of the Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense for Systems Engineering 20th Annual NDIA Systems Engineering Conference Springfield,
The Drive for Innovation in Systems Engineering D. Scott Lucero Office of the Deputy Assistant Secretary of Defense for Systems Engineering 20th Annual NDIA Systems Engineering Conference Springfield,
Oil & Gas Industry Competitiveness Assessment
 Oil & Gas Industry Competitiveness Assessment Further Analysis on Australia s Position in the Exploration Value Chain March 2017 Global Oil and Gas Exploration Oil and gas exploration across the world
Oil & Gas Industry Competitiveness Assessment Further Analysis on Australia s Position in the Exploration Value Chain March 2017 Global Oil and Gas Exploration Oil and gas exploration across the world
Halliburton and Baker Hughes Creating the leading oilfield services company
 Halliburton and Baker Hughes Creating the leading oilfield services company Halliburton Investor Relations Contacts: Kelly Youngblood, Vice President Scott Danby, Manager 281.871.2688 or investors@halliburton.com
Halliburton and Baker Hughes Creating the leading oilfield services company Halliburton Investor Relations Contacts: Kelly Youngblood, Vice President Scott Danby, Manager 281.871.2688 or investors@halliburton.com
DMSMS Management: After Years of Evolution, There s Still Room for Improvement
 DMSMS Management: After Years of Evolution, There s Still Room for Improvement By Jay Mandelbaum, Tina M. Patterson, Robin Brown, and William F. Conroy dsp.dla.mil 13 Which of the following two statements
DMSMS Management: After Years of Evolution, There s Still Room for Improvement By Jay Mandelbaum, Tina M. Patterson, Robin Brown, and William F. Conroy dsp.dla.mil 13 Which of the following two statements
Analysing Megatrends to Better shape the future of Tourism
 Issues Paper Analysing Megatrends to Better shape the future of Tourism 2-3 October 2017 OECD, Paris 2 Background information This note is provided as background information at the High Level Meeting on
Issues Paper Analysing Megatrends to Better shape the future of Tourism 2-3 October 2017 OECD, Paris 2 Background information This note is provided as background information at the High Level Meeting on
Will Stronger Borders Weaken Innovation?
 October 2017 2017 Global Innovation 1000 Will Stronger Borders Weaken Innovation? Introduction Will Stronger Borders Weaken Innovation? Innovation 1000 update 1 For the 13 th year, Strategy& studied innovation
October 2017 2017 Global Innovation 1000 Will Stronger Borders Weaken Innovation? Introduction Will Stronger Borders Weaken Innovation? Innovation 1000 update 1 For the 13 th year, Strategy& studied innovation
CONTACTS: Michaela Hessling Executive Director Corporate Communications Tel
 Aurubis continues developing its strategy Group working on a more effective organization, an increase in productivity and a sustainable improvement in earnings Resolution for dividend payment of 1.10 per
Aurubis continues developing its strategy Group working on a more effective organization, an increase in productivity and a sustainable improvement in earnings Resolution for dividend payment of 1.10 per
News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons
 www.breaking News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons Russia warns against WMD in space URL: http://www.breakingnewsenglish.com/0506/050603-spacewmd-e.html Today s contents The Article 2 Warm-ups
www.breaking News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons Russia warns against WMD in space URL: http://www.breakingnewsenglish.com/0506/050603-spacewmd-e.html Today s contents The Article 2 Warm-ups
Conference panels considered the implications of robotics on ethical, legal, operational, institutional, and force generation functioning of the Army
 INTRODUCTION Queen s University hosted the 10th annual Kingston Conference on International Security (KCIS) at the Marriott Residence Inn, Kingston Waters Edge, in Kingston, Ontario, from May 11-13, 2015.
INTRODUCTION Queen s University hosted the 10th annual Kingston Conference on International Security (KCIS) at the Marriott Residence Inn, Kingston Waters Edge, in Kingston, Ontario, from May 11-13, 2015.
Confirms 2013 Financial Guidance
 Confirms 2013 Financial Guidance PROVIDENCE, R.I.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul. 17, 2013-- Textron Inc. (NYSE: TXT) today reported second quarter 2013 income from continuing operations of $0.40 per share, compared
Confirms 2013 Financial Guidance PROVIDENCE, R.I.--(BUSINESS WIRE)--Jul. 17, 2013-- Textron Inc. (NYSE: TXT) today reported second quarter 2013 income from continuing operations of $0.40 per share, compared
Technology Insertion: A Way Ahead
 Obsolescence Challenges, Part 2 Technology Insertion: A Way Ahead Brent Hobson In the Summer 2008 issue of the Canadian Naval Review (Volume 4, No. 2), my article, Obsolescence Challenges and the Canadian
Obsolescence Challenges, Part 2 Technology Insertion: A Way Ahead Brent Hobson In the Summer 2008 issue of the Canadian Naval Review (Volume 4, No. 2), my article, Obsolescence Challenges and the Canadian
2. Overall Use of Technology Survey Data Report
 Thematic Report 2. Overall Use of Technology Survey Data Report February 2017 Prepared by Nordicity Prepared for Canada Council for the Arts Submitted to Gabriel Zamfir Director, Research, Evaluation and
Thematic Report 2. Overall Use of Technology Survey Data Report February 2017 Prepared by Nordicity Prepared for Canada Council for the Arts Submitted to Gabriel Zamfir Director, Research, Evaluation and
Produced by the BPDA Research Division:
 Produced by the BPDA Research Division: Alvaro Lima Director Jonathan Lee Deputy Director Christina Kim Research Manager Phillip Granberry Senior Researcher/Demographer Matthew Resseger Senior Researcher/Economist
Produced by the BPDA Research Division: Alvaro Lima Director Jonathan Lee Deputy Director Christina Kim Research Manager Phillip Granberry Senior Researcher/Demographer Matthew Resseger Senior Researcher/Economist
State of IT Research Study
 J M A R K. C O M // 8 4 4-4 4 - J M A R K State of IT Research Study Current State of the I.T. Industry...2 What Do Business Leaders Think?...5 Current Situation...6 Future Perception...6 The Current Reality...7
J M A R K. C O M // 8 4 4-4 4 - J M A R K State of IT Research Study Current State of the I.T. Industry...2 What Do Business Leaders Think?...5 Current Situation...6 Future Perception...6 The Current Reality...7
WEEK 3: OUTBREAKS AND GLOBALIZATION, PART 1
 GOING VIRAL Zombies, Viruses, and the End of the World DAHLIA SCHWEITZER WEEK 3: OUTBREAKS AND GLOBALIZATION, PART 1 Discussion Questions, Going Viral Chapter 1 1. Describe the difference between film
GOING VIRAL Zombies, Viruses, and the End of the World DAHLIA SCHWEITZER WEEK 3: OUTBREAKS AND GLOBALIZATION, PART 1 Discussion Questions, Going Viral Chapter 1 1. Describe the difference between film
Voters Attitudes toward Science and Technology Research and the Role of the Federal Government
 Voters Attitudes toward Science and Technology Research and the Role of the Federal Government Key findings from online national survey among 1,500 registered voters conducted September 28 to October 8,
Voters Attitudes toward Science and Technology Research and the Role of the Federal Government Key findings from online national survey among 1,500 registered voters conducted September 28 to October 8,
2018 IIF ANNUAL MEMBERSHIP MEETING
 2018 IIF ANNUAL MEMBERSHIP MEETING October 12-13, 2018 Grand Hyatt, Bali, Indonesia PRELIMINARY AGENDA *Subject to change* FRIDAY, OCTOBER 12 8:00 am 9:00 am REGISTRATION AND CONTINENTAL BREAKFAST 9:00
2018 IIF ANNUAL MEMBERSHIP MEETING October 12-13, 2018 Grand Hyatt, Bali, Indonesia PRELIMINARY AGENDA *Subject to change* FRIDAY, OCTOBER 12 8:00 am 9:00 am REGISTRATION AND CONTINENTAL BREAKFAST 9:00
INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY 58TH GENERAL CONFERENCE (22 26 September 2014)
 TURKEY INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY 58TH GENERAL CONFERENCE (22 26 September 2014) Allow me at the outset to congratulate you on your assumption of the Presidency of the 58th Session of the IAEA
TURKEY INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY 58TH GENERAL CONFERENCE (22 26 September 2014) Allow me at the outset to congratulate you on your assumption of the Presidency of the 58th Session of the IAEA
Science Impact Enhancing the Use of USGS Science
 United States Geological Survey. 2002. "Science Impact Enhancing the Use of USGS Science." Unpublished paper, 4 April. Posted to the Science, Environment, and Development Group web site, 19 March 2004
United States Geological Survey. 2002. "Science Impact Enhancing the Use of USGS Science." Unpublished paper, 4 April. Posted to the Science, Environment, and Development Group web site, 19 March 2004
ENTREPRENEURSHIP & ACCELERATION
 ENTREPRENEURSHIP & ACCELERATION Questions from the Field Intellectual Property March 2017 Photo by John-Michael Mass/Darby Communications In our work, we see that science and technology-based startups
ENTREPRENEURSHIP & ACCELERATION Questions from the Field Intellectual Property March 2017 Photo by John-Michael Mass/Darby Communications In our work, we see that science and technology-based startups
Re: Examination Guideline: Patentability of Inventions involving Computer Programs
 Lumley House 3-11 Hunter Street PO Box 1925 Wellington 6001 New Zealand Tel: 04 496-6555 Fax: 04 496-6550 www.businessnz.org.nz 14 March 2011 Computer Program Examination Guidelines Ministry of Economic
Lumley House 3-11 Hunter Street PO Box 1925 Wellington 6001 New Zealand Tel: 04 496-6555 Fax: 04 496-6550 www.businessnz.org.nz 14 March 2011 Computer Program Examination Guidelines Ministry of Economic
Globalizing IPR Protection: How Important Might RTAs Be?
 Globalizing IPR Protection: How Important Might RTAs Be? Keith Maskus, University of Colorado Boulder (keith.maskus@colorado.edu) NAS Innovation Policy Forum National and International IP Policies and
Globalizing IPR Protection: How Important Might RTAs Be? Keith Maskus, University of Colorado Boulder (keith.maskus@colorado.edu) NAS Innovation Policy Forum National and International IP Policies and
Privacy and the EU GDPR US and UK Privacy Professionals
 Privacy and the EU GDPR US and UK Privacy Professionals Independent research conducted by Dimensional Research on behalf of TrustArc US 888.878.7830 EU +44 (0)203.078.6495 www.trustarc.com 2017 TrustArc
Privacy and the EU GDPR US and UK Privacy Professionals Independent research conducted by Dimensional Research on behalf of TrustArc US 888.878.7830 EU +44 (0)203.078.6495 www.trustarc.com 2017 TrustArc
Science and Technology for Naval Warfare,
 Science and Technology for Naval Warfare, 2015--2020 Mark Lister Chairman, NRAC NDIA Disruptive Technologies Conference September 4, 2007 Excerpted from the Final Briefing Outline Terms of Reference Panel
Science and Technology for Naval Warfare, 2015--2020 Mark Lister Chairman, NRAC NDIA Disruptive Technologies Conference September 4, 2007 Excerpted from the Final Briefing Outline Terms of Reference Panel
