Conservation of energy during the reflection and transmission of microwaves
|
|
|
- Erika Glenn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
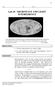
1 Related topics Microwaves, electromagnetic waves, reflection, transmission, polarisation, conservation of energy, conservation laws Principle When electromagnetic waves impinge on an obstacle, reflection, transmission, and refraction may occur. The aim of this experiment is to describe the relationship between reflection and transmission with the aid of a polarisation grating and to verify conservation of energy. Note Prior to performing this experiment, it would be helpful, though not mandatory, to perform the experiments P "Polarisation of microwaves", P "Reflection, transmission and refraction of microwaves" and P "Standing waves in the microwave range". Equipment () Microwave set Microwave control unit Microwave transmitter Microwave probe Angle scale Meter rule Grating Additional equipment Multi-range meter, analogue Connecting cord, 32 A, 750 mm, red Connecting cord, 32 A, 750 mm, blue Barrel base PHYWE Support rod, stainless steel 8/8, l = 250 mm, d = 0 mm Right angle clamp PHYWE Plate holder, opening width 0-0 mm Geometry set square Fig. : Experiment set-up P246060
2 Tasks Use a polarisation grating in order to demonstrate the relationship between reflection and transmission. Theory When electromagnetic waves impinge on a surface, different interactions may result: Part of the radiation will be reflected, transmitted, and absorbed (energy will be transferred to the material). The reflection follows the law of reflection (angle of incidence = angle of reflection). During the transition into another medium, a change in propagation time and, thereby, a change of the direction of propagation of the wave (refraction) may occur (see also the experiment P "Reflection, transmission and refraction of microwaves"). The aim of the following experiment is to examine the partial reflection from and transmission through a polarisation grating. In order to understand the phenomena of reflection and transmission, we will look at the amplitude of the electric field strength during the reflection. Since a standing wave forms between the reflecting object (here: metal plate) and the transmitter (metallic housing) (see also the experiment P "Standing waves"), the amplitude ES that is measured in the antinode includes the part ER (amplitude of the reflected wave) and the part (amplitude of the primary radiation of the transmitter). The following applies: E S =E 0+E R () The following is true for the part of the radiation that is reflected: R= ER (2) Accordingly, the following is true for the part of the radiation that is transmitted: T= ET (3) Here, ET is the amplitude of the transmitted radiation. The sum of the reflected part R and transmitted part T is constant due to the conservation of energy. Since it is a relative quantity (percentage) by definition, the following must be true for the sum: R+T = (4) As far as this experiment is concerned, the quantities R and T are not directly accessible, since intensities (and not amplitudes) are measured. Since the amplitudes are included in the intensity in a square manner, they can be obtained from the voltage signals, which is proportional to the intensity. R= ER or T= 2 ET = = UR U0 UT U0 (5) (6) P246060
3 When determining the reflected part R, it must be taken into consideration that, at the location of the measurement, the reflected intensity is superimposed by the primary beam of the microwave transmitter (see equation ). This is why, for the determination of UR, first the superimposed signal US is measured. Then, it its corrected based on the proportion of the primary beam U0: U = U U R S 0 (7) In the present experiment, a polarisation grating is used for adjusting various reflection and transmission parts. With this grating made of metal bars, the transmissivity depends on the angular orientation of the grating (angle α) relative to the constant polarisation of the microwaves as it is defined by the transmitter: Only the projection of the electric field vector in the transmitting direction will actually be transmitted; the remaining part of the radiation will be reflected by the metallic grating (a detailed description concerning the polarisation can be found in the experiment P "Polarisation of microwaves"). The part of the transmitted intensity I(α) follows 2 I (α)=i 0 cos (α) (8) As a consequence, the reflection and transmission parts can be adjusted in an infinitely variable manner by turning the grating in the beam. For this experiment, five angular alignments are used as an example for the demonstration of the law of conservation of energy. The absorption on the grating can be neglected. Please note that microwaves that are reflected by the grating will be reflected to the transmitter. This transmitter has a metallic housing, which is also reflective, so that a standing wave will form between the transmitter and grating. This means that, among other things, the intensity will disappear at the location of the grating, since there is an oscillation node. If the reflected part of the intensity is to be determined, this must be performed at a different location, i.e. at the location of the antinode. A detailed description of standing waves can be found in the experiment P "Standing waves in the microwave range". P
4 Set-up and procedure Set the experiment up as shown in Fig. 2. Fig. 2: Experiment set-up Connect the microwave transmitter and probe to their associated sockets of the control unit. Connect the multi-range meter to the voltmeter output of the control unit and select the 0 V measuring range (direct voltage). The loudspeaker and internal or external modulation are not required for this experiment. Combine the angle scale and meter rule by way of the screw on the back of the angle scale and the recess in the meter rule. Turn the meter rule in order to align the reference mark (arrow) on the angle scale with the one of the meter rule so that they coincide (see Fig. 3). Fig. 3: Set-up and alignment of the angle scale and meter rule Install the grating in the holder in the centre of rotation of the angle scale so that the grating rods are aligned horizontally. Secure the grating by way of the screws so that it cannot tilt or fall over. It must be absolutely ensured that the grating maintains its upright position during the experiment. Otherwise, the measurement would be severely invalidated. Mount the probe on the support rod in the barrel base by way of the right angle clamp and plate holder (see Fig. 4). Ensure that the round mark near the measuring head points upwards. Position the transmitter at the far end of the angle scale (e.g. at 20 mm). 4 P246060
5 Fig. 3: Transmission measurement with a horizontally aligned grating Fig. 4: 5: Fastening of the probe and transmission measurement (here: horizontally aligned grating) Position the probe in the beam path behind the grating so that the measuring head is located directly above the meter rule without being turned with regard to the direction of propagation of the radiation (see Fig. 4). Switch the microwave transmitter on by connecting the control unit to the mains power supply and set the amplitude controller to maximum. Check the height of the probe in its holder by varying the height of the right angle clamp in order to maximise the voltmeter reading. Move and turn the probe in order to test and ensure that it receives the maximum signal of the transmitted radiation. Fig. 5: Reflection measurement (here: vertically aligned grating) Measure the voltage UT as a measure of the intensity of the transmitted microwaves. Then, position the probe in front of the grating so that the measuring head faces the grating (see Fig. 5). Align the probe in the beam path as described above and ensure the exact determination of the position in the direction of the beam. To do so, move the probe in the direction of the beam to the location of the antinode of the standing wave between the transmitter and grating (see above). Measure the voltage (US) at this location. Then, remove the grating from the beam path in order to measure the intensity without the grating (U0). Repeat the measurement of the three voltages UT, US, and U0 for various angles α by fastening the grating in the holder several times, each time turned by 45 (see Fig. 6). Use the set square in order to verify the angle (see also the experiment P "Polarisation of microwaves"). P
6 Fig. 6: Transmission measurement with various angles Note During the experiment, do not stand in the direct vicinity of the beam path when reading the voltmeter values. The human body reflects microwaves so that the measurement result may be invalidated. The same applies to all types of metallic objects. If several experiments are performed simultaneously in a laboratory, ensure sufficient distance between the experiment stations in order to avoid interference signals caused by reflected radiation and/or scattered radiation from the other set-ups. 6 P246060
7 Evaluation and result Determine the reflection part R and the transmission part T for various angles and compare the sum R+T to the expected value of. Angle in UT in V US in V U0 in V UT in V US in V U0 in V UR in V R = UR/ U T = UT/ U R+T Deviation in % Table : Reflection and transmission parts for various angles Table shows that the measurement values are subject to considerable errors. The prediction that R+T= could be confirmed (within the scope of the measurement accuracy). If the values result in R+T, this may be caused by a deviation of the probe position from the location of the antinode during the measurement of the reflected part or by turning the probe against the beam path. If the grating is not aligned absolutely precisely with regard to the intended angles, the result will also differ. In addition, a tilted grating or a grating that is twisted in the two remaining directions of rotation, or interference signals caused by reflections in the surroundings, may invalidate the measurement result regardless of any reading inaccuracies. A loss of radiation intensity through absorption or the transfer of heat into the grating (energy dissipation) does not have to be taken into consideration with the present set-up. P
Standing waves in the microwave range
 Related topics Microwaves, electromagnetic waves, reflection, inverse square law Principle If electromagnetic waves are reflected to and fro between two reflectors, a standing wave results. The wavelength
Related topics Microwaves, electromagnetic waves, reflection, inverse square law Principle If electromagnetic waves are reflected to and fro between two reflectors, a standing wave results. The wavelength
Electricity. Interference of microwaves Electromagnetic Oscillations and Waves. What you need:
 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Waves Electricity What you can learn about Wavelength Standing wave Reflection Transmission Michelson interferometer Principle: A microwave beam, after reflection from
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Waves Electricity What you can learn about Wavelength Standing wave Reflection Transmission Michelson interferometer Principle: A microwave beam, after reflection from
Part 1: Standing Waves - Measuring Wavelengths
 Experiment 7 The Microwave experiment Aim: This experiment uses microwaves in order to demonstrate the formation of standing waves, verifying the wavelength λ of the microwaves as well as diffraction from
Experiment 7 The Microwave experiment Aim: This experiment uses microwaves in order to demonstrate the formation of standing waves, verifying the wavelength λ of the microwaves as well as diffraction from
9. Microwaves. 9.1 Introduction. Safety consideration
 MW 9. Microwaves 9.1 Introduction Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths of the order of 1 mm to 1 m, or equivalently, with frequencies from 0.3 GHz to 0.3 THz, are commonly known as microwaves, sometimes
MW 9. Microwaves 9.1 Introduction Electromagnetic waves with wavelengths of the order of 1 mm to 1 m, or equivalently, with frequencies from 0.3 GHz to 0.3 THz, are commonly known as microwaves, sometimes
Microwave Optics. Department of Physics & Astronomy Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, TX. January 16, 2014
 Microwave Optics Department of Physics & Astronomy Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, TX January 16, 2014 1 Introduction Optical phenomena may be studied at microwave frequencies. Visible light has
Microwave Optics Department of Physics & Astronomy Texas Christian University, Fort Worth, TX January 16, 2014 1 Introduction Optical phenomena may be studied at microwave frequencies. Visible light has
Experiment 19. Microwave Optics 1
 Experiment 19 Microwave Optics 1 1. Introduction Optical phenomena may be studied at microwave frequencies. Using a three centimeter microwave wavelength transforms the scale of the experiment. Microns
Experiment 19 Microwave Optics 1 1. Introduction Optical phenomena may be studied at microwave frequencies. Using a three centimeter microwave wavelength transforms the scale of the experiment. Microns
Fig On Fig. 6.1 label one set of the lines in the first order spectrum R, G and V to indicate which is red, green and violet.
 1 This question is about the light from low energy compact fluorescent lamps which are replacing filament lamps in the home. (a) The light from a compact fluorescent lamp is analysed by passing it through
1 This question is about the light from low energy compact fluorescent lamps which are replacing filament lamps in the home. (a) The light from a compact fluorescent lamp is analysed by passing it through
Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II
 Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II 3.1 Applications of the Quantum Model of Radiant Energy 1) Photon Absorption and Emission 12/29/04 The diagrams below illustrate an atomic nucleus
Period 3 Solutions: Electromagnetic Waves Radiant Energy II 3.1 Applications of the Quantum Model of Radiant Energy 1) Photon Absorption and Emission 12/29/04 The diagrams below illustrate an atomic nucleus
TAP 313-1: Polarisation of waves
 TAP 313-1: Polarisation of waves How does polarisation work? Many kinds of polariser filter out waves, leaving only those with a polarisation along the direction allowed by the polariser. Any kind of transverse
TAP 313-1: Polarisation of waves How does polarisation work? Many kinds of polariser filter out waves, leaving only those with a polarisation along the direction allowed by the polariser. Any kind of transverse
[4] (b) Fig. 6.1 shows a loudspeaker fixed near the end of a tube of length 0.6 m. tube m 0.4 m 0.6 m. Fig. 6.
![[4] (b) Fig. 6.1 shows a loudspeaker fixed near the end of a tube of length 0.6 m. tube m 0.4 m 0.6 m. Fig. 6. [4] (b) Fig. 6.1 shows a loudspeaker fixed near the end of a tube of length 0.6 m. tube m 0.4 m 0.6 m. Fig. 6.](/thumbs/82/84801740.jpg) 1 (a) Describe, in terms of vibrations, the difference between a longitudinal and a transverse wave. Give one example of each wave.................... [4] (b) Fig. 6.1 shows a loudspeaker fixed near the
1 (a) Describe, in terms of vibrations, the difference between a longitudinal and a transverse wave. Give one example of each wave.................... [4] (b) Fig. 6.1 shows a loudspeaker fixed near the
Experiment 12: Microwaves
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2005 OBJECTIVES Experiment 12: Microwaves To observe the polarization and angular dependence of radiation from a microwave generator
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2005 OBJECTIVES Experiment 12: Microwaves To observe the polarization and angular dependence of radiation from a microwave generator
28 The diagram shows an experiment which has been set up to demonstrate two-source interference, using microwaves of wavelength λ.
 PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 28 The diagram shows an experiment which has been set up to demonstrate two-source interference, using microwaves of wavelength λ. 9702/1/M/J/02 X microwave transmitter S 1 S 2
PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 28 The diagram shows an experiment which has been set up to demonstrate two-source interference, using microwaves of wavelength λ. 9702/1/M/J/02 X microwave transmitter S 1 S 2
1 Diffraction of Microwaves
 1 Diffraction of Microwaves 1.1 Purpose In this lab you will investigate the coherent scattering of electromagnetic waves from a periodic structure. The experiment is a direct analog of the Bragg diffraction
1 Diffraction of Microwaves 1.1 Purpose In this lab you will investigate the coherent scattering of electromagnetic waves from a periodic structure. The experiment is a direct analog of the Bragg diffraction
2. Refraction and Reflection
 2. Refraction and Reflection In this lab we will observe the displacement of a light beam by a parallel plate due to refraction. We will determine the refractive index of some liquids from the incident
2. Refraction and Reflection In this lab we will observe the displacement of a light beam by a parallel plate due to refraction. We will determine the refractive index of some liquids from the incident
Physics 4C Chabot College Scott Hildreth
 Physics 4C Chabot College Scott Hildreth The Inverse Square Law for Light Intensity vs. Distance Using Microwaves Experiment Goals: Experimentally test the inverse square law for light using Microwaves.
Physics 4C Chabot College Scott Hildreth The Inverse Square Law for Light Intensity vs. Distance Using Microwaves Experiment Goals: Experimentally test the inverse square law for light using Microwaves.
MICROWAVE OPTICS. Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model WA-9314B G
 Includes Teacher's Notes and Typical Experiment Results Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model WA-9314B 012-04630G MICROWAVE OPTICS 10101 Foothills Blvd. Roseville, CA 95678-9011
Includes Teacher's Notes and Typical Experiment Results Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model WA-9314B 012-04630G MICROWAVE OPTICS 10101 Foothills Blvd. Roseville, CA 95678-9011
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET
 LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
LOS 1 LASER OPTICS SET Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 Light interference 5 2.1 Light interference on a thin glass plate 6 2.2 Michelson s interferometer 7 3 Light diffraction 13 3.1 Light diffraction on a
Lab 12 Microwave Optics.
 b Lab 12 Microwave Optics. CAUTION: The output power of the microwave transmitter is well below standard safety levels. Nevertheless, do not look directly into the microwave horn at close range when the
b Lab 12 Microwave Optics. CAUTION: The output power of the microwave transmitter is well below standard safety levels. Nevertheless, do not look directly into the microwave horn at close range when the
NTT DOCOMO Technical Journal. Method for Measuring Base Station Antenna Radiation Characteristics in Anechoic Chamber. 1.
 Base Station Antenna Directivity Gain Method for Measuring Base Station Antenna Radiation Characteristics in Anechoic Chamber Base station antennas tend to be long compared to the wavelengths at which
Base Station Antenna Directivity Gain Method for Measuring Base Station Antenna Radiation Characteristics in Anechoic Chamber Base station antennas tend to be long compared to the wavelengths at which
Wave Motion Demonstrator. Instruction Manual
 Wave Motion Demonstrator Instruction Manual CONTENTS 4 INTRODUCTION 6 THEORY 7 DEMONSTRATIONS 16 APPENDIX 18 GENERAL INFORMATION 3 INTRODUCTION The Wave Motion Demonstrator (WMD) uses mechanical waves
Wave Motion Demonstrator Instruction Manual CONTENTS 4 INTRODUCTION 6 THEORY 7 DEMONSTRATIONS 16 APPENDIX 18 GENERAL INFORMATION 3 INTRODUCTION The Wave Motion Demonstrator (WMD) uses mechanical waves
Exercise 1-4. The Radar Equation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION OUTLINE DISCUSSION OF FUNDAMENTALS
 Exercise 1-4 The Radar Equation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the different parameters in the radar equation, and with the interaction between these
Exercise 1-4 The Radar Equation EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the different parameters in the radar equation, and with the interaction between these
Speed of Sound in Air
 Speed of Sound in Air OBJECTIVE To explain the condition(s) necessary to achieve resonance in an open tube. To understand how the velocity of sound is affected by air temperature. To determine the speed
Speed of Sound in Air OBJECTIVE To explain the condition(s) necessary to achieve resonance in an open tube. To understand how the velocity of sound is affected by air temperature. To determine the speed
PHYS2090 OPTICAL PHYSICS Laboratory Microwaves
 PHYS2090 OPTICAL PHYSICS Laboratory Microwaves Reference Hecht, Optics, (Addison-Wesley) 1. Introduction Interference and diffraction are commonly observed in the optical regime. As wave-particle duality
PHYS2090 OPTICAL PHYSICS Laboratory Microwaves Reference Hecht, Optics, (Addison-Wesley) 1. Introduction Interference and diffraction are commonly observed in the optical regime. As wave-particle duality
Standing Waves and Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR)
 Exercise 3-1 Standing Waves and Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) EXERCISE OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this exercise, you will know how standing waves are created on transmission lines. You will be
Exercise 3-1 Standing Waves and Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) EXERCISE OBJECTIVES Upon completion of this exercise, you will know how standing waves are created on transmission lines. You will be
Physics 476LW. Advanced Physics Laboratory - Microwave Optics
 Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Microwave Radiation Introduction Setup The purpose of this lab is to better understand the various ways that interference of EM radiation manifests itself. However,
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Microwave Radiation Introduction Setup The purpose of this lab is to better understand the various ways that interference of EM radiation manifests itself. However,
M1.D [1] M2.C [1] Suitable experiment eg diffraction through a door / out of a pipe
![M1.D [1] M2.C [1] Suitable experiment eg diffraction through a door / out of a pipe M1.D [1] M2.C [1] Suitable experiment eg diffraction through a door / out of a pipe](/thumbs/78/77338681.jpg) M.D [] M.C [] M3.(a) Suitable experiment eg diffraction through a door / out of a pipe (b) Using c = d / t t = 500 / 480 = 5. s (c) (Measured time is difference between time taken by light and time taken
M.D [] M.C [] M3.(a) Suitable experiment eg diffraction through a door / out of a pipe (b) Using c = d / t t = 500 / 480 = 5. s (c) (Measured time is difference between time taken by light and time taken
Lab 10 - MICROWAVE AND LIGHT INTERFERENCE
 181 Name Date Partners Lab 10 - MICROWAVE AND LIGHT INTERFERENCE Amazing pictures of the microwave radiation from the universe have helped us determine the universe is 13.7 billion years old. This picture
181 Name Date Partners Lab 10 - MICROWAVE AND LIGHT INTERFERENCE Amazing pictures of the microwave radiation from the universe have helped us determine the universe is 13.7 billion years old. This picture
6 Experiment II: Law of Reflection
 Lab 6: Microwaves 3 Suggested Reading Refer to the relevant chapters, 1 Introduction Refer to Appendix D for photos of the apparatus This lab allows you to test the laws of reflection, refraction and diffraction
Lab 6: Microwaves 3 Suggested Reading Refer to the relevant chapters, 1 Introduction Refer to Appendix D for photos of the apparatus This lab allows you to test the laws of reflection, refraction and diffraction
Practical Considerations for Radiated Immunities Measurement using ETS-Lindgren EMC Probes
 Practical Considerations for Radiated Immunities Measurement using ETS-Lindgren EMC Probes Detectors/Modulated Field ETS-Lindgren EMC probes (HI-6022/6122, HI-6005/6105, and HI-6053/6153) use diode detectors
Practical Considerations for Radiated Immunities Measurement using ETS-Lindgren EMC Probes Detectors/Modulated Field ETS-Lindgren EMC probes (HI-6022/6122, HI-6005/6105, and HI-6053/6153) use diode detectors
KULLIYYAH OF ENGINEERING
 KULLIYYAH OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION LABORATORY (ECE 4103) EXPERIMENT NO 3 RADIATION PATTERN AND GAIN CHARACTERISTICS OF THE DISH (PARABOLIC)
KULLIYYAH OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION LABORATORY (ECE 4103) EXPERIMENT NO 3 RADIATION PATTERN AND GAIN CHARACTERISTICS OF THE DISH (PARABOLIC)
Introduction. Equipment
 MICROWAVE OPTICS Microwave Optics Introduction There are many advantages to studying optical phenomena at microwave frequencies. Using a 2.85 centimeter microwave wavelength transforms the scale of the
MICROWAVE OPTICS Microwave Optics Introduction There are many advantages to studying optical phenomena at microwave frequencies. Using a 2.85 centimeter microwave wavelength transforms the scale of the
A progressive wave of frequency 150 Hz travels along a stretched string at a speed of 30 m s 1.
 1. progressive wave of frequency 150 Hz travels along a stretched string at a speed of 30 m s 1. What is the phase difference between two points that are 50 mm apart on the string? zero 90 180 360 2 Which
1. progressive wave of frequency 150 Hz travels along a stretched string at a speed of 30 m s 1. What is the phase difference between two points that are 50 mm apart on the string? zero 90 180 360 2 Which
Lab in a Box Microwave Interferometer
 In 1887 Michelson and Morley used an optical interferometer (a device invented by Michelson to accurately detect aether flow) to try and detect the relative motion of light through the luminous either.
In 1887 Michelson and Morley used an optical interferometer (a device invented by Michelson to accurately detect aether flow) to try and detect the relative motion of light through the luminous either.
7. Experiment K: Wave Propagation
 7. Experiment K: Wave Propagation This laboratory will be based upon observing standing waves in three different ways, through coaxial cables, in free space and in a waveguide. You will also observe some
7. Experiment K: Wave Propagation This laboratory will be based upon observing standing waves in three different ways, through coaxial cables, in free space and in a waveguide. You will also observe some
3/23/2015. Chapter 11 Oscillations and Waves. Contents of Chapter 11. Contents of Chapter Simple Harmonic Motion Spring Oscillations
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 11 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli Chapter 11 and Waves This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 11 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli Chapter 11 and Waves This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use
Experimental Competition
 37 th International Physics Olympiad Singapore 8 17 July 2006 Experimental Competition Wed 12 July 2006 Experimental Competition Page 2 List of apparatus and materials Label Component Quantity Label Component
37 th International Physics Olympiad Singapore 8 17 July 2006 Experimental Competition Wed 12 July 2006 Experimental Competition Page 2 List of apparatus and materials Label Component Quantity Label Component
Chapter 21. Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal
Chapter 21 Alternating Current Circuits and Electromagnetic Waves AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal
YOUNGS MODULUS BY UNIFORM & NON UNIFORM BENDING OF A BEAM
 YOUNGS MODULUS BY UNIFORM & NON UNIFORM BENDING OF A BEAM RECTANGULAR BEAM PLACED OVER TWO KNIFE EDGES & DISTANCE BETWEEN KNIFE EDGES IS KEPT CONSTANT AS l= 50cm UNIFORM WEIGHT HANGERS ARE SUSPENDED WITH
YOUNGS MODULUS BY UNIFORM & NON UNIFORM BENDING OF A BEAM RECTANGULAR BEAM PLACED OVER TWO KNIFE EDGES & DISTANCE BETWEEN KNIFE EDGES IS KEPT CONSTANT AS l= 50cm UNIFORM WEIGHT HANGERS ARE SUSPENDED WITH
Microwave Diffraction and Interference
 Microwave Diffraction and Interference Department of Physics Ryerson University rev.2014 1 Introduction The object of this experiment is to observe interference and diffraction of microwave radiation,
Microwave Diffraction and Interference Department of Physics Ryerson University rev.2014 1 Introduction The object of this experiment is to observe interference and diffraction of microwave radiation,
EC ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION
 EC6602 - ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION FUNDAMENTALS PART-B QUESTION BANK UNIT 1 1. Define the following parameters w.r.t antenna: i. Radiation resistance. ii. Beam area. iii. Radiation intensity. iv. Directivity.
EC6602 - ANTENNA AND WAVE PROPAGATION FUNDAMENTALS PART-B QUESTION BANK UNIT 1 1. Define the following parameters w.r.t antenna: i. Radiation resistance. ii. Beam area. iii. Radiation intensity. iv. Directivity.
Resonance Tube. 1 Purpose. 2 Theory. 2.1 Air As A Spring. 2.2 Traveling Sound Waves in Air
 Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Lab 10 - MICROWAVE AND LIGHT INTERFERENCE
 179 Name Date Partners Lab 10 - MICROWAVE AND LIGHT INTERFERENCE Amazing pictures of the microwave radiation from the universe have helped us determine the universe is 13.7 billion years old. This picture
179 Name Date Partners Lab 10 - MICROWAVE AND LIGHT INTERFERENCE Amazing pictures of the microwave radiation from the universe have helped us determine the universe is 13.7 billion years old. This picture
Q1. The figure below shows two ways in which a wave can travel along a slinky spring.
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. The figure below shows two ways in which a wave can travel along a slinky spring. (a) State and explain which wave is longitudinal..... On the figure above, (i) clearly indicate
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. The figure below shows two ways in which a wave can travel along a slinky spring. (a) State and explain which wave is longitudinal..... On the figure above, (i) clearly indicate
Goals. Introduction. To understand the use of root mean square (rms) voltages and currents.
 Lab 10. AC Circuits Goals To show that AC voltages cannot generally be added without accounting for their phase relationships. That is, one must account for how they vary in time with respect to one another.
Lab 10. AC Circuits Goals To show that AC voltages cannot generally be added without accounting for their phase relationships. That is, one must account for how they vary in time with respect to one another.
SHIELDING EFFECTIVENESS
 SHIELDING Electronic devices are commonly packaged in a conducting enclosure (shield) in order to (1) prevent the electronic devices inside the shield from radiating emissions efficiently and/or (2) prevent
SHIELDING Electronic devices are commonly packaged in a conducting enclosure (shield) in order to (1) prevent the electronic devices inside the shield from radiating emissions efficiently and/or (2) prevent
Resonance Tube. 1 Purpose. 2 Theory. 2.1 Air As A Spring. 2.2 Traveling Sound Waves in Air
 Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adapters, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
Resonance Tube Equipment Capstone, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adapters, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads (2), (room) thermometer, flat rubber
SCATTERING POLARIMETRY PART 1. Dr. A. Bhattacharya (Slide courtesy Prof. E. Pottier and Prof. L. Ferro-Famil)
 SCATTERING POLARIMETRY PART 1 Dr. A. Bhattacharya (Slide courtesy Prof. E. Pottier and Prof. L. Ferro-Famil) 2 That s how it looks! Wave Polarisation An electromagnetic (EM) plane wave has time-varying
SCATTERING POLARIMETRY PART 1 Dr. A. Bhattacharya (Slide courtesy Prof. E. Pottier and Prof. L. Ferro-Famil) 2 That s how it looks! Wave Polarisation An electromagnetic (EM) plane wave has time-varying
Goals. Introduction. To understand the use of root mean square (rms) voltages and currents.
 Lab 10. AC Circuits Goals To show that AC voltages cannot generally be added without accounting for their phase relationships. That is, one must account for how they vary in time with respect to one another.
Lab 10. AC Circuits Goals To show that AC voltages cannot generally be added without accounting for their phase relationships. That is, one must account for how they vary in time with respect to one another.
SECTION A Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 2. A string is firmly attached at both ends. When a frequency of 60 Hz is applied, the string vibrates in the standing wave
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 2. A string is firmly attached at both ends. When a frequency of 60 Hz is applied, the string vibrates in the standing wave
POLARISATION OF LIGHT. Polarisation: It is the phenomenon by which the vibrations in a transverse wave are confined to one particular direction only.
 POLARISATION OF LIGHT Polarisation: It is the phenomenon by which the vibrations in a transverse wave are confined to one particular direction only. Polarisation is a phenomenon exhibited only by transverse
POLARISATION OF LIGHT Polarisation: It is the phenomenon by which the vibrations in a transverse wave are confined to one particular direction only. Polarisation is a phenomenon exhibited only by transverse
Friday 20 January 2012 Morning
 Friday 20 January 2012 Morning AS GCE PHYSICS A G482 Electrons, Waves and Photons *G411580112* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data, Formulae and Relationships Booklet
Friday 20 January 2012 Morning AS GCE PHYSICS A G482 Electrons, Waves and Photons *G411580112* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data, Formulae and Relationships Booklet
Resonance Tube Lab 9
 HB 03-30-01 Resonance Tube Lab 9 1 Resonance Tube Lab 9 Equipment SWS, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads
HB 03-30-01 Resonance Tube Lab 9 1 Resonance Tube Lab 9 Equipment SWS, complete resonance tube (tube, piston assembly, speaker stand, piston stand, mike with adaptors, channel), voltage sensor, 1.5 m leads
VectaStar 3500 METHODS FOR SUCCESSFUL ANTENNA DEPLOYMENT
 VectaStar 3500 METHODS FOR SUCCESSFUL ANTENNA DEPLOYMENT Cambridge Broadband Limited D000114 Issue A01 Mark Jackson 1 INTRODUCTION 3 1.1 The purpose of antennas 3 2 ANTENNA CHARACTERISTICS 4 2.1 Antenna
VectaStar 3500 METHODS FOR SUCCESSFUL ANTENNA DEPLOYMENT Cambridge Broadband Limited D000114 Issue A01 Mark Jackson 1 INTRODUCTION 3 1.1 The purpose of antennas 3 2 ANTENNA CHARACTERISTICS 4 2.1 Antenna
3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS
 3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS Equipment Set for Wave Optics with Laser 1003053 Instruction sheet 06/18 Alf 1. Safety instructions The laser emits visible radiation at a wavelength of 635 nm with a maximum power
3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS Equipment Set for Wave Optics with Laser 1003053 Instruction sheet 06/18 Alf 1. Safety instructions The laser emits visible radiation at a wavelength of 635 nm with a maximum power
Physics B Waves and Sound Name: AP Review. Show your work:
 Physics B Waves and Sound Name: AP Review Mechanical Wave A disturbance that propagates through a medium with little or no net displacement of the particles of the medium. Parts of a Wave Crest: high point
Physics B Waves and Sound Name: AP Review Mechanical Wave A disturbance that propagates through a medium with little or no net displacement of the particles of the medium. Parts of a Wave Crest: high point
The spatial structure of an acoustic wave propagating through a layer with high sound speed gradient
 The spatial structure of an acoustic wave propagating through a layer with high sound speed gradient Alex ZINOVIEV 1 ; David W. BARTEL 2 1,2 Defence Science and Technology Organisation, Australia ABSTRACT
The spatial structure of an acoustic wave propagating through a layer with high sound speed gradient Alex ZINOVIEV 1 ; David W. BARTEL 2 1,2 Defence Science and Technology Organisation, Australia ABSTRACT
Exp No.(8) Fourier optics Optical filtering
 Exp No.(8) Fourier optics Optical filtering Fig. 1a: Experimental set-up for Fourier optics (4f set-up). Related topics: Fourier transforms, lenses, Fraunhofer diffraction, index of refraction, Huygens
Exp No.(8) Fourier optics Optical filtering Fig. 1a: Experimental set-up for Fourier optics (4f set-up). Related topics: Fourier transforms, lenses, Fraunhofer diffraction, index of refraction, Huygens
3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS
 3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS Equipment Set for Wave Optics with Laser U17303 Instruction sheet 10/08 Alf 1. Safety instructions The laser emits visible radiation at a wavelength of 635 nm with a maximum power
3B SCIENTIFIC PHYSICS Equipment Set for Wave Optics with Laser U17303 Instruction sheet 10/08 Alf 1. Safety instructions The laser emits visible radiation at a wavelength of 635 nm with a maximum power
SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION AND Q-SWITCHING
 SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION AND Q-SWITCHING INTRODUCTION In this experiment, the following learning subjects will be worked out: 1) Characteristics of a semiconductor diode laser. 2) Optical pumping on
SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION AND Q-SWITCHING INTRODUCTION In this experiment, the following learning subjects will be worked out: 1) Characteristics of a semiconductor diode laser. 2) Optical pumping on
Interference and Diffraction of Microwaves
 Interference and Diffraction of Microwaves References: Equipment: Ford, Kenneth W., Classical and Modern Physics Vol2 Xerox College Publishing 1972 pp. 850-871. Pasco Instruction Manual and Experiment
Interference and Diffraction of Microwaves References: Equipment: Ford, Kenneth W., Classical and Modern Physics Vol2 Xerox College Publishing 1972 pp. 850-871. Pasco Instruction Manual and Experiment
UNIT Derive the fundamental equation for free space propagation?
 UNIT 8 1. Derive the fundamental equation for free space propagation? Fundamental Equation for Free Space Propagation Consider the transmitter power (P t ) radiated uniformly in all the directions (isotropic),
UNIT 8 1. Derive the fundamental equation for free space propagation? Fundamental Equation for Free Space Propagation Consider the transmitter power (P t ) radiated uniformly in all the directions (isotropic),
AS Physics Unit 5 - Waves 1
 AS Physics Unit 5 - Waves 1 WHAT IS WAVE MOTION? The wave motion is a means of transferring energy from one point to another without the transfer of any matter between the points. Waves may be classified
AS Physics Unit 5 - Waves 1 WHAT IS WAVE MOTION? The wave motion is a means of transferring energy from one point to another without the transfer of any matter between the points. Waves may be classified
Acoustic Doppler Effect
 Acoustic Doppler Effect TEP Related Topics Wave propagation, Doppler shift of frequency Principle If an emitter of sound or a detector is set into motion relative to the medium of propagation, the frequency
Acoustic Doppler Effect TEP Related Topics Wave propagation, Doppler shift of frequency Principle If an emitter of sound or a detector is set into motion relative to the medium of propagation, the frequency
Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color
 Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. What causes color? What causes reflection? What causes color?
Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. What causes color? What causes reflection? What causes color?
Electromagnetic Radiation
 Electromagnetic Radiation EMR Light: Interference and Optics I. Light as a Wave - wave basics review - electromagnetic radiation II. Diffraction and Interference - diffraction, Huygen s principle - superposition,
Electromagnetic Radiation EMR Light: Interference and Optics I. Light as a Wave - wave basics review - electromagnetic radiation II. Diffraction and Interference - diffraction, Huygen s principle - superposition,
Thursday 9 June 2016 Afternoon
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Thursday 9 June 2016 Afternoon AS GCE PHYSICS A G482/01 Electrons, Waves and Photons *1164935362* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data, Formulae
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Thursday 9 June 2016 Afternoon AS GCE PHYSICS A G482/01 Electrons, Waves and Photons *1164935362* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: Data, Formulae
SECTION A Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 1. Which of the following statements about the speed of waves on a string are true? I. The speed depends on the tension in
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 1. Which of the following statements about the speed of waves on a string are true? I. The speed depends on the tension in
Wave optics and interferometry
 11b, 2013, lab 7 Wave optics and interferometry Note: The optical surfaces used in this experiment are delicate. Please do not touch any of the optic surfaces to avoid scratches and fingerprints. Please
11b, 2013, lab 7 Wave optics and interferometry Note: The optical surfaces used in this experiment are delicate. Please do not touch any of the optic surfaces to avoid scratches and fingerprints. Please
Transmission Line Transient Overvoltages (Travelling Waves on Power Systems)
 Transmission Line Transient Overvoltages (Travelling Waves on Power Systems) The establishment of a potential difference between the conductors of an overhead transmission line is accompanied by the production
Transmission Line Transient Overvoltages (Travelling Waves on Power Systems) The establishment of a potential difference between the conductors of an overhead transmission line is accompanied by the production
Laboratory 7: Properties of Lenses and Mirrors
 Laboratory 7: Properties of Lenses and Mirrors Converging and Diverging Lens Focal Lengths: A converging lens is thicker at the center than at the periphery and light from an object at infinity passes
Laboratory 7: Properties of Lenses and Mirrors Converging and Diverging Lens Focal Lengths: A converging lens is thicker at the center than at the periphery and light from an object at infinity passes
1 (a) State two properties which distinguish electromagnetic waves from other transverse waves [2] lamp eye
![1 (a) State two properties which distinguish electromagnetic waves from other transverse waves [2] lamp eye 1 (a) State two properties which distinguish electromagnetic waves from other transverse waves [2] lamp eye](/thumbs/88/115297818.jpg) 1 (a) State two properties which distinguish electromagnetic waves from other transverse waves............. [2] (b) (i) Describe what is meant by a plane polarised wave.... [2] (ii) Light from a filament
1 (a) State two properties which distinguish electromagnetic waves from other transverse waves............. [2] (b) (i) Describe what is meant by a plane polarised wave.... [2] (ii) Light from a filament
Radial Polarization Converter With LC Driver USER MANUAL
 ARCoptix Radial Polarization Converter With LC Driver USER MANUAL Arcoptix S.A Ch. Trois-portes 18 2000 Neuchâtel Switzerland Mail: info@arcoptix.com Tel: ++41 32 731 04 66 Principle of the radial polarization
ARCoptix Radial Polarization Converter With LC Driver USER MANUAL Arcoptix S.A Ch. Trois-portes 18 2000 Neuchâtel Switzerland Mail: info@arcoptix.com Tel: ++41 32 731 04 66 Principle of the radial polarization
Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus
 Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus Reference http://chaos.swarthmore.edu/courses/physics50_2008/p50_optics/04_polariz_matrices.pdf Theory In Jones calculus, the polarization state of light is
Polarization Experiments Using Jones Calculus Reference http://chaos.swarthmore.edu/courses/physics50_2008/p50_optics/04_polariz_matrices.pdf Theory In Jones calculus, the polarization state of light is
Antennas and Propagation
 Antennas and Propagation Chapter 5 Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space Reception - collects electromagnetic
Antennas and Propagation Chapter 5 Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space Reception - collects electromagnetic
Antennas and Propagation
 Mobile Networks Module D-1 Antennas and Propagation 1. Introduction 2. Propagation modes 3. Line-of-sight transmission 4. Fading Slides adapted from Stallings, Wireless Communications & Networks, Second
Mobile Networks Module D-1 Antennas and Propagation 1. Introduction 2. Propagation modes 3. Line-of-sight transmission 4. Fading Slides adapted from Stallings, Wireless Communications & Networks, Second
Video. Part I. Equipment
 1 of 7 11/8/2013 11:32 AM There are two parts to this lab that can be done in either order. In Part I you will study the Laws of Reflection and Refraction, measure the index of refraction of glass and
1 of 7 11/8/2013 11:32 AM There are two parts to this lab that can be done in either order. In Part I you will study the Laws of Reflection and Refraction, measure the index of refraction of glass and
(A) 2f (B) 2 f (C) f ( D) 2 (E) 2
 1. A small vibrating object S moves across the surface of a ripple tank producing the wave fronts shown above. The wave fronts move with speed v. The object is traveling in what direction and with what
1. A small vibrating object S moves across the surface of a ripple tank producing the wave fronts shown above. The wave fronts move with speed v. The object is traveling in what direction and with what
Session2 Antennas and Propagation
 Wireless Communication Presented by Dr. Mahmoud Daneshvar Session2 Antennas and Propagation 1. Introduction Types of Anttenas Free space Propagation 2. Propagation modes 3. Transmission Problems 4. Fading
Wireless Communication Presented by Dr. Mahmoud Daneshvar Session2 Antennas and Propagation 1. Introduction Types of Anttenas Free space Propagation 2. Propagation modes 3. Transmission Problems 4. Fading
CHAPTER 2 WIRELESS CHANNEL
 CHAPTER 2 WIRELESS CHANNEL 2.1 INTRODUCTION In mobile radio channel there is certain fundamental limitation on the performance of wireless communication system. There are many obstructions between transmitter
CHAPTER 2 WIRELESS CHANNEL 2.1 INTRODUCTION In mobile radio channel there is certain fundamental limitation on the performance of wireless communication system. There are many obstructions between transmitter
Lab 10 - Microwave and Light Interference
 Lab 10 Microwave and Light Interference L10-1 Name Date Partners Lab 10 - Microwave and Light Interference Amazing pictures of the microwave radiation from the universe have helped us determine the universe
Lab 10 Microwave and Light Interference L10-1 Name Date Partners Lab 10 - Microwave and Light Interference Amazing pictures of the microwave radiation from the universe have helped us determine the universe
FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION
 FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION Revised November 15, 2017 INTRODUCTION The simplest and most commonly described examples of diffraction and interference from two-dimensional apertures
FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION Revised November 15, 2017 INTRODUCTION The simplest and most commonly described examples of diffraction and interference from two-dimensional apertures
AP Chemistry Cell Phone Spectroscopy Lab Adopted from Alexander Scheeline Department of Chemistry University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 AP Chemistry Cell Phone Spectroscopy Lab Adopted from Alexander Scheeline Department of Chemistry University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Back Ground Electromagnetic radiation Electromagnetic radiation
AP Chemistry Cell Phone Spectroscopy Lab Adopted from Alexander Scheeline Department of Chemistry University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Back Ground Electromagnetic radiation Electromagnetic radiation
Antennas and Propagation. Chapter 5
 Antennas and Propagation Chapter 5 Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space Reception - collects electromagnetic
Antennas and Propagation Chapter 5 Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space Reception - collects electromagnetic
Antennas and Propagation. Chapter 5
 Antennas and Propagation Chapter 5 Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space Reception - collects electromagnetic
Antennas and Propagation Chapter 5 Introduction An antenna is an electrical conductor or system of conductors Transmission - radiates electromagnetic energy into space Reception - collects electromagnetic
Atmospheric Effects. Attenuation by Atmospheric Gases. Atmospheric Effects Page 1
 Atmospheric Effects Page 1 Atmospheric Effects Attenuation by Atmospheric Gases Uncondensed water vapour and oxygen can be strongly absorptive of radio signals, especially at millimetre-wave frequencies
Atmospheric Effects Page 1 Atmospheric Effects Attenuation by Atmospheric Gases Uncondensed water vapour and oxygen can be strongly absorptive of radio signals, especially at millimetre-wave frequencies
This manual will aid in the assembly of the FireBall V90 and FireBall X90. The assembly of both machines will be identical, unless specified.
 This manual will aid in the assembly of the FireBall V90 and FireBall X90. The assembly of both machines will be identical, unless specified. Step #1 Lay all parts out to verify quantities. (2) 2 x 25-1/4
This manual will aid in the assembly of the FireBall V90 and FireBall X90. The assembly of both machines will be identical, unless specified. Step #1 Lay all parts out to verify quantities. (2) 2 x 25-1/4
MICROWAVE OPTICS. Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model WA-9314B F 4/ PASCO scientific $10.
 Includes Teacher's Notes and Typical Experiment Results Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model WA-9314B 012-04630F 4/99 MICROWAVE OPTICS 1991 PASCO scientific $10.00 012-04630F
Includes Teacher's Notes and Typical Experiment Results Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model WA-9314B 012-04630F 4/99 MICROWAVE OPTICS 1991 PASCO scientific $10.00 012-04630F
Unguided Transmission Media
 CS311 Data Communication Unguided Transmission Media by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
CS311 Data Communication Unguided Transmission Media by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
Range Sensing strategies
 Range Sensing strategies Active range sensors Ultrasound Laser range sensor Slides adopted from Siegwart and Nourbakhsh 4.1.6 Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Large range distance measurement -> called
Range Sensing strategies Active range sensors Ultrasound Laser range sensor Slides adopted from Siegwart and Nourbakhsh 4.1.6 Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Large range distance measurement -> called
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems. Sound Waves. If the speed of sound in air is not given in the problem, take it as 343 m/s.
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 17 Sound Waves Sound waves Interference of sound waves Intensity & level Resonance in tubes Doppler effect If the speed of sound in air is not given in the problem,
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 17 Sound Waves Sound waves Interference of sound waves Intensity & level Resonance in tubes Doppler effect If the speed of sound in air is not given in the problem,
Propagation Mechanism
 Propagation Mechanism ELE 492 FUNDAMENTALS OF WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS 1 Propagation Mechanism Simplest propagation channel is the free space: Tx free space Rx In a more realistic scenario, there may be
Propagation Mechanism ELE 492 FUNDAMENTALS OF WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS 1 Propagation Mechanism Simplest propagation channel is the free space: Tx free space Rx In a more realistic scenario, there may be
PHYS 3153 Methods of Experimental Physics II O2. Applications of Interferometry
 Purpose PHYS 3153 Methods of Experimental Physics II O2. Applications of Interferometry In this experiment, you will study the principles and applications of interferometry. Equipment and components PASCO
Purpose PHYS 3153 Methods of Experimental Physics II O2. Applications of Interferometry In this experiment, you will study the principles and applications of interferometry. Equipment and components PASCO
Radio Propagation Fundamentals
 Radio Propagation Fundamentals Concept of Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Mechanisms Modes of Propagation Propagation Models Path Profiles Link Budget Fading Channels Electromagnetic (EM) Waves EM Wave
Radio Propagation Fundamentals Concept of Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Mechanisms Modes of Propagation Propagation Models Path Profiles Link Budget Fading Channels Electromagnetic (EM) Waves EM Wave
Wind Direction Transmitter - compact
 THE WORLD OF WEATHER DATA - THE WORLD OF WEATHER DATA - THE WORLD OF WEATHER DATA Instruction for Use 021542/06/05 Wind Direction Transmitter - compact 4.3129.03.141 4.3129.53.141 ADOLF THIES GmbH & Co.
THE WORLD OF WEATHER DATA - THE WORLD OF WEATHER DATA - THE WORLD OF WEATHER DATA Instruction for Use 021542/06/05 Wind Direction Transmitter - compact 4.3129.03.141 4.3129.53.141 ADOLF THIES GmbH & Co.
The cross directional coupler
 Fundamentals General properties of waveguide (directional) couplers is a special type of directional coupler. Thus, it makes sense to follow with a general explanation applicable to the function of all
Fundamentals General properties of waveguide (directional) couplers is a special type of directional coupler. Thus, it makes sense to follow with a general explanation applicable to the function of all
General Physics Laboratory Experiment Report 2nd Semester, Year 2018
 PAGE 1/13 Exp. #2-7 : Measurement of the Characteristics of the Light Interference by Using Double Slits and a Computer Interface Measurement of the Light Wavelength and the Index of Refraction of the
PAGE 1/13 Exp. #2-7 : Measurement of the Characteristics of the Light Interference by Using Double Slits and a Computer Interface Measurement of the Light Wavelength and the Index of Refraction of the
Lap Triggers. Application Note. McLaren Electronic Systems McLaren Technology Centre Chertsey Road Woking Surrey GU21 4YH UK
 McLaren Technology Centre Chertsey Road Woking Surrey GU1 YH UK McLaren Electronics Inc. Suite 11 Bostick Building 9801 West Kincey Avenue Huntersville NC 8078 USA Copyright McLaren Electronics 01 Revision
McLaren Technology Centre Chertsey Road Woking Surrey GU1 YH UK McLaren Electronics Inc. Suite 11 Bostick Building 9801 West Kincey Avenue Huntersville NC 8078 USA Copyright McLaren Electronics 01 Revision
Waves Q1. MockTime.com. (c) speed of propagation = 5 (d) period π/15 Ans: (c)
 Waves Q1. (a) v = 5 cm (b) λ = 18 cm (c) a = 0.04 cm (d) f = 50 Hz Q2. The velocity of sound in any gas depends upon [1988] (a) wavelength of sound only (b) density and elasticity of gas (c) intensity
Waves Q1. (a) v = 5 cm (b) λ = 18 cm (c) a = 0.04 cm (d) f = 50 Hz Q2. The velocity of sound in any gas depends upon [1988] (a) wavelength of sound only (b) density and elasticity of gas (c) intensity
CHARACTERISATION OF IN -HOUSE EMC TESTING FACILITIES FOR PRODUCT DESIGNERS. Paul Kay* and Andrew Nafalski**
 CHARACTERISATION OF IN -HOUSE EMC TESTING FACILITIES FOR PRODUCT DESIGNERS Paul Kay* and Andrew Nafalski** *Austest Laboratories, Adelaide **University of South Australia School of Electrical and Information
CHARACTERISATION OF IN -HOUSE EMC TESTING FACILITIES FOR PRODUCT DESIGNERS Paul Kay* and Andrew Nafalski** *Austest Laboratories, Adelaide **University of South Australia School of Electrical and Information
QDV120 Operation and Pointing manual
 QDV120 Operation and Pointing manual MPAD1 Plus OP-080316-E1 page 1 Contents Item Description Page 1.0 Health and Safety for Operators and Installation Staff 3 2.0 Transit case Reflector/Mount/BUC/LNB
QDV120 Operation and Pointing manual MPAD1 Plus OP-080316-E1 page 1 Contents Item Description Page 1.0 Health and Safety for Operators and Installation Staff 3 2.0 Transit case Reflector/Mount/BUC/LNB
