Questions on Differentiation
|
|
|
- Loreen Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Questions on Differentiation In Questions 3-8 I give some of the eamples of functions that have ha to be ifferentiate in the previous few eams for this course. 3 (2003 Differentiate i ln ( +, for >, twice, : The Sum Rule gives (ln ( + ln ( + +, 2 (ln ( + 2 ( + 2. ii 2 + tan 2, when (2k + π/2 for any k Z. : ( 2 + tan (tan tan ( 2 + tan tan cos 2. (Sum Rule ( tan + tan tan by Prouct Rule When ealing with trigonometric functions it can be har to know how to leave the answer because of the trigonometric ientities. You might think it nicer to epress the answer as (tan ( + tan 2 because no fractions are involve. iii tan, when (2k + π/2 for any k Z. : ( tan ( tan + tan, tan + cos 2. Again you might epress this as tan + ( + tan 2. (Prouct Rule
2 iv e sin, 9 times. : Let f ( e sin. Then f ( ( e sin + e cos, f (2 ( 2e cos, f (3 ( 2e cos + 2e sin, f (4 ( 4e sin, f (5 ( 4e sin 4e cos, f (6 ( 8e cos, f (7 ( 8e cos 8e sin, f (8 ( 6e sin, f (9 ( 6e sin + 6e cos. 4 (2004 Differentiate cos 2, 8 times, : Let g ( cos 2. Then g ( ( 2 cos sin sin 2, g (2 ( 2 cos 2, g (3 ( 4 sin 2, g (4 ( 8 cos 2, g (5 ( 6 sin 2, g (6 ( 32 cos 2, g (7 ( 64 sin 2, g (8 ( 28 cos 2. Note Remembering that 2 sin cos sin 2 makes life a little easier. Otherwise, g ( ( 2 cos sin g (2 ( 2 sin 2 2 cos 2, (Prouct Rule g (3 ( 4 sin cos + 4 cos sin 8 sin cos 4g ( (. Thus further erivatives can be epresse in terms of either g ( of g (2. 2
3 5 (2006 Differentiate when πl/2 for any l Z. : ( sin + cos 6 (2007 Differentiate sin + cos, ( (sin + (cos ( (sin + (sin + (cos i ln 2 ( +, for >, (sin 2 sin sin cos sin 2 + sin cos 2 sin (cos 2 sin cos2 cos 3 + sin 3 sin 2 cos 2 4 sin cos3 sin 2. 2 by the Chain Rule cos This can be one in two ways. First the Prouct Rule gives ln2 ( + (ln ( + ln ( + ln ( + ln ( + + ln ( + + ln ( + + ln ( ln ( +. + ln ( + 3
4 ii Alternatively, the Chain Rule gives for >, 5 times. Let ln2 ( + y y2, where y ln ( +, y ln ( + 2y 2 ln ( + ln f ( ln ( +, + ( +. 2 ln ( +. + There are two ways you coul look at the first erivative. First you coul use the Chain Rule: ( + ln ln y y y, where so Thus y + ( + ln ( + 2 y 2 ( 2. ln y y y y + 2, 2 ( 2 2 ( ( +. ( Alternatively, you can use the properties of logarithm to write ( + f ( ln ln ( + ln (. 4
5 Then the Sum Rule gives ( + ln ln ( + ln ( + +. (2 Check that answers ( an (2 are the same. To continue, it is simpler to start from (2 rather than (: f ( ( f (3 ( f (4 ( f (5 ( + +, so f (2 ( 2 ( ( + 3, 6 ( ( + 4, 24 ( ( + 5. ( 2 + ( + 2, iii tan 2, when (2k + π/2 for any k Z. : It is most straightforwar to use the Prouct Rule but as an eample of the Quotient Rule: tan 2 ( sin 2 cos 2 cos2 sin2 sin 2 cos2 (cos 2 2 cos2 (2 sin cos sin 2 ( 2 cos sin cos 4 2 sin cos2 + sin 3 cos 3 2 sin ( cos 2 + sin 2 cos 3 2 tan cos 2. 5
6 having use sin 2 + cos 2. Further use of trigonometric ientities allow the answer to be written as 2 (tan ( + tan 2. iv e (sin + cos, 6 times, Let f ( e (cos + sin. Then f ( ( e (cos + sin + e ( sin + cos 2e cos, f (2 ( 2e (cos sin, f (3 ( 2e (cos sin + 2e ( sin cos 4e sin, f (4 ( 4e sin 4e cos 4f (, f (5 ( 4f ( ( 8e cos, f (6 ( 4f (2 ( 8e (cos sin. Notice that once we have a relation such as f (4 ( 4f (, then all subsequent erivatives are just multiples of erivatives alreay foun. 7 (2008 Differentiate i 2 2, 3 times. Recall that 2 e ln 2. Thus 2 e ln 2 ey y Write f ( 2 2, then y, y ( ln 2 e ey, where y ln 2, (Chain Rule, e ln 2 ln 2 2 ln 2. f ( ( 2 ln 2 2, f ( ( 2 ln 2 2 2, f (3 ( 2 ln
7 ii for, 5 times. e +, Alternatively, let f ( e / ( + so ( + f ( e an ifferentiate this 5 times. Write f ( e / ( + to get the following: f ( ( f (2 ( f (3 ( f (4 ( f (5 ( e + e ( + 2 e ( + 2, e + 2 e ( e ( + 3 ( + 2 e ( + 3, e + 3 e ( e ( e e + 4 e ( e e ( ( + 5, e + 5 e ( e e 20 ( + 6 e ( ( + 6. ( + 4 ( e ( + 4, ( e ( e ( + 5 ( e ( e The suggeste alternative is: write ( + f ( e. repeate ifferentiation gives ( + f ( ( + f ( e, ( + f (2 ( + 2f ( ( e, ( + f (3 ( + 3f (2 ( e, ( + f (4 ( + 4f (3 ( e, ( + f (5 ( + 5f (4 ( e. ( + 5 In which case These coul be solve to give the erivatives. 7
8 iii sinh + cosh, 6 times : Let h ( sinh + cosh. Then h ( ( 2 sinh + cosh, h (2 ( 3 cosh + sinh, h (3 ( 4 sinh + cosh, h (4 ( 5 cosh + sinh, h (5 ( 6 sinh + cosh, h (6 ( 7 cosh + sinh. 8 (2009 Differentiate i 2 sin π 2. for 0. ( 2 sin π 2 ( 2 sin π + (sin π by the Prouct Rule 2 sin π sin y y y, where y π, 2 by Chain Rule, 2 sin π ( cos y 2π 3 2 sin π 2 2π cos π 2. 8
9 ii ln 2 ( +, for >, 5 times, In Question 6 i you have alreay been aske to ifferentiate this function once. The further erivatives are: f ( ln 2 ( +, f ( ln ( + ( 2 +, f (2 ( 2 ( + 2 2ln ( + ( + 2, f (3 6 ( + ( 3 + 4ln ( + ( + 3, f (4 ( 22 ( + 4 2ln ( + ( + 4, f (5 ( 00 ( ln ( + ( + 5. Practice of ifferentiation. On the basis that you learn mathematics only by oing mathematics here are a series of questions on ifferentiation to help you learn, or perhaps refresh, your facility on ifferentiating stanar functions. 9 Use the Prouct Rule to ifferentiate i e 2 (e 2, e2 (e 2 (e e e e + e e e e + e e 2e 2. (Prouct Rule 9
10 ii e ln, for > 0, e ln e iii (sin (ln, for > 0, ln + e ln e ln + e e ln +. sin ((sin (ln ln + sin ln (Prouct Rule (Prouct Rule cos ln + sin. iv e cos ln, for > 0, (e cos ln (e (cos ln e (cos ln + e (cos ln e (cos ln + e ( cos ln ln + cos (Prouct Rule by a secon application of the prouct rule, e cos ln e sin ln + e cos. 0
11 0 Use the Quotient Rule to ifferentiate i e /e, e ( e e e (e 2 (Quotient Rule e (e 2 e e. ii e /, for 0, iii /e, ( e ( e iv ln / 2, for > 0, ( ln 2 e e 2 e e 2 2 e. (Quotient Rule e e (e 2 (Quotient Rule e e (e 2 e. 2 ln 2 2 ln ( 2 2 (Quotient Rule ln (2 ( ln 3.
12 v 2 / ln, for >, ( 2 ln ln 2 2 ln (ln 2 (Quotient Rule 2 ln 2 ln 2 vi / tan 2, when πl for any l Z. Using the Quotient Rule we have ( tan 2 (2 ln ln 2. ( cos 2 sin 2 sin2 cos2 cos 2 sin2 ( sin sin2 cos sin 2 cos 2 sin cos sin 4 ( sin 2 + cos 2 2 cos 2 cos sin 3 sin 3 Using instea the Chain Rule let u tan 2 which we have ifferentiate in Question 6iii as u 2 tan cos 2. Then ( tan 2 ( u u u 2 2 tan cos 2 which leas to the same result as before. tan 2 tan 4 cos 2, ( u u 2
13 vii (sin + cos / (sin cos, when ( + 4k π/4 for any k Z. ( sin + cos sin cos (sin +cos (sin cos (sin + cos (sin cos 2 (sin cos (cos sin (sin cos 2 by the Quotient Rule (sin + cos (cos + sin (sin cos 2 sin cos sin2 cos 2 + cos sin (sin cos 2 (sin cos sin cos + sin2 + cos 2 + cos sin (sin cos 2 2 sin 2 2 sin cos + cos 2 2 sin 2. Use the Chain Rule to ifferentiate i e 2, Let u 2 so e 2 e u. Then ii e, e 2 eu eu u u e u (2 2e. Let u so e e u. Then (Chain Rule, e eu eu u u e u ( (Chain Rule, e. 3
14 iii cos (/, for 0, Let u / so cos (/ cos u. Then cos (/ cos u cos u u u sin u ( ( sin ( 2 (Chain Rule, sin (/ 2. iv sin (ln, for > 0, Let u ln so sin (ln sin u. Then sin (ln v ln /2, for >, sin u cos u ln sin u u u cos (ln. Let u ln so ln /2 u /2. Then by the Chain Rule, ln /2 u/2 vi ln ( + cos ( /2, for > 0, u/2 u u 2u /2 ln 2 ln /2. by the Chain Rule, This is a function of a function of a function of. Thus given we first calculate v /2. Net we calculate u + cos v ( + cos ( /2 4
15 an finally the function we wish to ifferentiate is ln u. So ln ( + cos ( /2 ln u ln u u u ( + cos ( /2 u u u ( + cos v v v (Chain Rule, ( + cos v u by the Chain Rule, again, /2 ( sin v ( ( sin v u 2 /2 sin ( /2 2 /2 ( + cos ( /2, on substituting for u an v. +sin vii e 2, Let w sin, v + w 2, u +sin v so e 2 e u. Then by the Chain Rule applie three times, e +sin eu eu u v w u v w e u v v e u 2 2w cos v ( + w 2 sin w sin cos + sin 2 e +sin 2 2 Differentiate sin sin 2 e +sin 2. i sin ( ln, for > 0. Let y ln when, by the Prouct Rule y ln ln ln + 5 ln +.
16 Then, by the Chain Rule, sin ( ln sin y y y cos y (ln + (ln + cos ( ln. ii ( /2 sin 2 / ( 2 +, for > 0, ( /2 sin (2 + /2 sin2 /2 sin 2 (2 + ( by Quotient Rule ( ( 2 + sin 2 /2 + /2 sin2 /2 (2 sin 2 ( by Prouct Rule ( ( 2 sin /2 sin cos 2 3/2 sin 2 2 /2 ( (2 + ( sin sin cos 4 2 sin 2 2 /2 ( iii (sin / 2 for 0, Let y sin / when, by the Quotient Rule, y ( sin sin sin 2 cos sin 2. So, by the Chain Rule (sin / 2 y2 y y 2y ( cos sin 2 2 sin ( cos sin 3. 6
17 iv sin (, for 0, The Prouct Rule gives ( sin ( sin ( + ( sin (. For the secon term let y / an use the Chain Rule ( ( sin sin y y y cos y ( ( cos. 2 Combine to get ( ( ( sin sin ( v m sin (, m, n an 0, n cos ( ( m m sin sin n n + m sin ( sin n vi sin m cos n, m, n, By the Prouct Rule. ( n m m + m sin y y y where y / n ( ( sin m m + m cos y n ( m m sin n n n+ ( + n m n cos n (sinm cos n cos n sinm + sin m cosn. m cos n+ sin m n sin m+ cos n sin m cos n ( m cos 2 n sin 2. 7
18 vii 2 sin cos 2, Let y 2 sin cos 2 so y ( 2 sin cos 2 4 sin cos 8 cos sin 4 sin cos 2 sin 2. Then, by the Chain Rule 2 sin cos 2 y y viii m ln n, m, n an > 0, By the Prouct Rule, y 2 ( 2 sin 2 y sin 2 2 sin cos 2. (m ln n ln n m + m lnn. For the secon term use the Chain Rule, so let y ln, then ln n Combining we have i e ln for >, yn y y nyn ln n lnn. (m ln n m m ln n + m n lnn m ln n (m ln + n. Let v ln an u v ln. Then the Chain Rule, applie twice, gives e ln eu u v u v v ln eu v e u 2 v e ln 2 ln. 8
19 e / ln for >, Let v ln an u v /2 / ln. Then the Chain Rule, applie twice, gives i ln ( + + e. ln e u u v e/ u v eu v /2 v e u 2v 3/2 ln e/ 2 ln 3/2. ln Let v + e an u + v + + e. Then the Chain Rule applie twice gives ( ln + + e ln u u u v v u u 2 v e e 2 + e ( + + e e 2 ( + e + + e ( + v ( + e v 9
LESSON 18: INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES MATH FALL 2018
 LESSON 8: INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES MATH 6020 FALL 208 ELLEN WELD. Partial Derivatives We aress how to take a erivative of a function of several variables. Although we won t get into
LESSON 8: INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONS OF SEVERAL VARIABLES MATH 6020 FALL 208 ELLEN WELD. Partial Derivatives We aress how to take a erivative of a function of several variables. Although we won t get into
Figure 5.1. sin θ = AB. cos θ = OB. tan θ = AB OB = sin θ. sec θ = 1. cotan θ = 1
 5 Trigonometric functions Trigonometry is the mathematics of triangles. A right-angle triangle is one in which one angle is 90, as shown in Figure 5.1. The thir angle in the triangle is φ = (90 θ). Figure
5 Trigonometric functions Trigonometry is the mathematics of triangles. A right-angle triangle is one in which one angle is 90, as shown in Figure 5.1. The thir angle in the triangle is φ = (90 θ). Figure
Math 10/11 Honors Section 3.6 Basic Trigonometric Identities
 Math 0/ Honors Section 3.6 Basic Trigonometric Identities 0-0 - SECTION 3.6 BASIC TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Copright all rights reserved to Homework Depot: www.bcmath.ca I) WHAT IS A TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITY?
Math 0/ Honors Section 3.6 Basic Trigonometric Identities 0-0 - SECTION 3.6 BASIC TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Copright all rights reserved to Homework Depot: www.bcmath.ca I) WHAT IS A TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITY?
Math 32A Discussion Session Week 9 Notes November 28 and 30, 2017
 Math 3A Discussion Session Week 9 Notes November 8 an 30, 07 This week we ll explore some of the ieas from chapter 5, focusing mostly on the graient. We ll motivate this exploration with an example that
Math 3A Discussion Session Week 9 Notes November 8 an 30, 07 This week we ll explore some of the ieas from chapter 5, focusing mostly on the graient. We ll motivate this exploration with an example that
Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas
 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas MATH 160, Precalculus J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 011 Objectives In this lesson we will learn to: use multiple-angle formulas to rewrite
Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Formulas MATH 160, Precalculus J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 011 Objectives In this lesson we will learn to: use multiple-angle formulas to rewrite
While you wait: For a-d: use a calculator to evaluate: Fill in the blank.
 While you wait: For a-d: use a calculator to evaluate: a) sin 50 o, cos 40 o b) sin 25 o, cos65 o c) cos o, sin 79 o d) sin 83 o, cos 7 o Fill in the blank. a) sin30 = cos b) cos57 = sin Trigonometric
While you wait: For a-d: use a calculator to evaluate: a) sin 50 o, cos 40 o b) sin 25 o, cos65 o c) cos o, sin 79 o d) sin 83 o, cos 7 o Fill in the blank. a) sin30 = cos b) cos57 = sin Trigonometric
MA 1032 Review for exam III
 MA 10 Review for eam III Name Establish the identit. 1) cot θ sec θ = csc θ 1) ) cscu - cos u sec u= cot u ) ) cos u 1 + tan u - sin u 1 + cot u = cos u - sin u ) ) csc θ + cot θ tan θ + sin θ = csc θ
MA 10 Review for eam III Name Establish the identit. 1) cot θ sec θ = csc θ 1) ) cscu - cos u sec u= cot u ) ) cos u 1 + tan u - sin u 1 + cot u = cos u - sin u ) ) csc θ + cot θ tan θ + sin θ = csc θ
Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I
 MAC 1114 Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Recognize the fundamental identities: reciprocal identities, quotient identities,
MAC 1114 Module 5 Trigonometric Identities I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Recognize the fundamental identities: reciprocal identities, quotient identities,
Honors Algebra 2 w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals
 Honors Algebra w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals By the end of this chapter, you should be able to Identify trigonometric identities. (14.1) Factor trigonometric
Honors Algebra w/ Trigonometry Chapter 14: Trigonometric Identities & Equations Target Goals By the end of this chapter, you should be able to Identify trigonometric identities. (14.1) Factor trigonometric
Principles of Mathematics 12: Explained!
 Principles of Mathematics : Eplained! www.math.com PART I MULTIPLICATION & DIVISION IDENTITLES Algebraic proofs of trigonometric identities In this lesson, we will look at various strategies for proving
Principles of Mathematics : Eplained! www.math.com PART I MULTIPLICATION & DIVISION IDENTITLES Algebraic proofs of trigonometric identities In this lesson, we will look at various strategies for proving
You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3)
 You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3) LEQ: How do we identify and use basic trigonometric identities to find trigonometric values & use basic trigonometric identities to simplify
You found trigonometric values using the unit circle. (Lesson 4-3) LEQ: How do we identify and use basic trigonometric identities to find trigonometric values & use basic trigonometric identities to simplify
Exercise 1. Consider the following figure. The shaded portion of the circle is called the sector of the circle corresponding to the angle θ.
 1 Radian Measures Exercise 1 Consider the following figure. The shaded portion of the circle is called the sector of the circle corresponding to the angle θ. 1. Suppose I know the radian measure of the
1 Radian Measures Exercise 1 Consider the following figure. The shaded portion of the circle is called the sector of the circle corresponding to the angle θ. 1. Suppose I know the radian measure of the
3.3 Properties of Logarithms
 Section 3.3 Properties of Logarithms 07 3.3 Properties of Logarithms Change of Base Most calculators have only two types of log keys, one for common logarithms (base 0) and one for natural logarithms (base
Section 3.3 Properties of Logarithms 07 3.3 Properties of Logarithms Change of Base Most calculators have only two types of log keys, one for common logarithms (base 0) and one for natural logarithms (base
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 0 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometr An angle is in standard position if its verte is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive ais. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 0 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometr An angle is in standard position if its verte is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive ais. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
MATH STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 5
 MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 5 Unit 5 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY MATH 1205 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY INTRODUCTION 3 1. IDENTITIES AND ADDITION FORMULAS 5 FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES 5 PROVING IDENTITIES
MATH STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 5 Unit 5 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY MATH 1205 ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY INTRODUCTION 3 1. IDENTITIES AND ADDITION FORMULAS 5 FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES 5 PROVING IDENTITIES
INTRODUCTION TO LOGARITHMS
 INTRODUCTION TO LOGARITHMS Dear Reader Logarithms are a tool originally designed to simplify complicated arithmetic calculations. They were etensively used before the advent of calculators. Logarithms
INTRODUCTION TO LOGARITHMS Dear Reader Logarithms are a tool originally designed to simplify complicated arithmetic calculations. They were etensively used before the advent of calculators. Logarithms
SSM2040 Filter Analysis Part 1 - Ryan Williams
 SSM2040 Filter Analysis Part 1 - Ryan Williams http://www.siy.org/estrukto The following analysis is use to etermine the maximum bias current neee for the iscrete OTA cells in the ssm2040 filter (René
SSM2040 Filter Analysis Part 1 - Ryan Williams http://www.siy.org/estrukto The following analysis is use to etermine the maximum bias current neee for the iscrete OTA cells in the ssm2040 filter (René
Algebraic Expressions and Equations: Applications I: Translating Words to Mathematical Symbols *
 OpenSta-CNX module: m35046 1 Algebraic Epressions and Equations: Applications I: Translating Words to Mathematical Symbols * Wade Ellis Denny Burzynski This work is produced by OpenSta-CNX and licensed
OpenSta-CNX module: m35046 1 Algebraic Epressions and Equations: Applications I: Translating Words to Mathematical Symbols * Wade Ellis Denny Burzynski This work is produced by OpenSta-CNX and licensed
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 5 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 5.3 Properties of Logarithms Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Use the change-of-base
5 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 5.3 Properties of Logarithms Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Use the change-of-base
Section 6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities
 6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities 47 Section 6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities Double-Angle Identities Half-Angle Identities This section develops another important set of identities
6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities 47 Section 6-3 Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities Double-Angle Identities Half-Angle Identities This section develops another important set of identities
Calculus II Final Exam Key
 Calculus II Final Exam Key Instructions. Do NOT write your answers on these sheets. Nothing written on the test papers will be graded.. Please begin each section of questions on a new sheet of paper. 3.
Calculus II Final Exam Key Instructions. Do NOT write your answers on these sheets. Nothing written on the test papers will be graded.. Please begin each section of questions on a new sheet of paper. 3.
DIVISION BY FRACTIONS
 DIVISION BY FRACTIONS 6.. 6.. Division by fractions introduces three methods to help students understand how dividing by fractions works. In general, think of division for a problem like 8 as, In 8, how
DIVISION BY FRACTIONS 6.. 6.. Division by fractions introduces three methods to help students understand how dividing by fractions works. In general, think of division for a problem like 8 as, In 8, how
4.3. Trigonometric Identities. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Trigonometric Identities 4.3 Introduction trigonometric identity is a relation between trigonometric expressions which is true for all values of the variables (usually angles. There are a very large number
Trigonometric Identities 4.3 Introduction trigonometric identity is a relation between trigonometric expressions which is true for all values of the variables (usually angles. There are a very large number
# 1,5,9,13,...37 (hw link has all odds)
 February 8, 17 Goals: 1. Recognize trig functions and their integrals.. Learn trig identities useful for integration. 3. Understand which identities work and when. a) identities enable substitution by
February 8, 17 Goals: 1. Recognize trig functions and their integrals.. Learn trig identities useful for integration. 3. Understand which identities work and when. a) identities enable substitution by
Using Trigonometric Ratios Part 1: Solving For Unknown Sides
 MPM2D: Principles of Mathematics Using Trigonometric Ratios Part 1: Solving For Unknown Sides J. Garvin Slide 1/15 Recap State the three primary trigonometric ratios for A in ABC. Slide 2/15 Recap State
MPM2D: Principles of Mathematics Using Trigonometric Ratios Part 1: Solving For Unknown Sides J. Garvin Slide 1/15 Recap State the three primary trigonometric ratios for A in ABC. Slide 2/15 Recap State
Transmission Lines. Ranga Rodrigo. January 13, Antennas and Propagation: Transmission Lines 1/46
 Transmission Lines Ranga Rodrigo January 13, 2009 Antennas and Propagation: Transmission Lines 1/46 1 Basic Transmission Line Properties 2 Standing Waves Antennas and Propagation: Transmission Lines Outline
Transmission Lines Ranga Rodrigo January 13, 2009 Antennas and Propagation: Transmission Lines 1/46 1 Basic Transmission Line Properties 2 Standing Waves Antennas and Propagation: Transmission Lines Outline
33. Riemann Summation over Rectangular Regions
 . iemann Summation over ectangular egions A rectangular region in the xy-plane can be defined using compound inequalities, where x and y are each bound by constants such that a x a and b y b. Let z = f(x,
. iemann Summation over ectangular egions A rectangular region in the xy-plane can be defined using compound inequalities, where x and y are each bound by constants such that a x a and b y b. Let z = f(x,
In Exercises 1-12, graph one cycle of the given function. State the period, amplitude, phase shift and vertical shift of the function.
 0.5 Graphs of the Trigonometric Functions 809 0.5. Eercises In Eercises -, graph one ccle of the given function. State the period, amplitude, phase shift and vertical shift of the function.. = sin. = sin.
0.5 Graphs of the Trigonometric Functions 809 0.5. Eercises In Eercises -, graph one ccle of the given function. State the period, amplitude, phase shift and vertical shift of the function.. = sin. = sin.
( x "1) 2 = 25, x 3 " 2x 2 + 5x "12 " 0, 2sin" =1.
 Unit Analytical Trigonometry Classwork A) Verifying Trig Identities: Definitions to know: Equality: a statement that is always true. example:, + 7, 6 6, ( + ) 6 +0. Equation: a statement that is conditionally
Unit Analytical Trigonometry Classwork A) Verifying Trig Identities: Definitions to know: Equality: a statement that is always true. example:, + 7, 6 6, ( + ) 6 +0. Equation: a statement that is conditionally
Learning Log Title: CHAPTER 6: DIVIDING AND BUILDING EXPRESSIONS. Date: Lesson: Chapter 6: Dividing and Building Expressions
 Chapter 6: Dividing and Building Epressions CHAPTER 6: DIVIDING AND BUILDING EXPRESSIONS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 6: Dividing and Building Epressions
Chapter 6: Dividing and Building Epressions CHAPTER 6: DIVIDING AND BUILDING EXPRESSIONS Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Date: Lesson: Learning Log Title: Chapter 6: Dividing and Building Epressions
Trigonometric Identities. Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 5 Trigonometric Identities Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 5.5 Double-Angle Double-Angle Identities An Application Product-to-Sum and Sum-to-Product Identities Copyright 2017, 2013,
5 Trigonometric Identities Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 5.5 Double-Angle Double-Angle Identities An Application Product-to-Sum and Sum-to-Product Identities Copyright 2017, 2013,
Trigonometric Functions. Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 1 Trigonometric Functions Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 1.4 Using the Definitions of the Trigonometric Functions Reciprocal Identities Signs and Ranges of Function Values Pythagorean
1 Trigonometric Functions Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 1.4 Using the Definitions of the Trigonometric Functions Reciprocal Identities Signs and Ranges of Function Values Pythagorean
CHAPTER 6 INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION
 CHAPTER 6 INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION Broadly speaking, system identification is the art and science of using measurements obtained from a system to characterize the system. The characterization
CHAPTER 6 INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION Broadly speaking, system identification is the art and science of using measurements obtained from a system to characterize the system. The characterization
Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas
 Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege Bicycle ramps for advanced riders have a steeper incline than those designed for novices. Bicycle ramps made for competition (see [link])
Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege Bicycle ramps for advanced riders have a steeper incline than those designed for novices. Bicycle ramps made for competition (see [link])
Math 36 "Fall 08" 5.2 "Sum and Di erence Identities" * Find exact values of functions of rational multiples of by using sum and di erence identities.
 Math 36 "Fall 08" 5.2 "Sum and Di erence Identities" Skills Objectives: * Find exact values of functions of rational multiples of by using sum and di erence identities. * Develop new identities from the
Math 36 "Fall 08" 5.2 "Sum and Di erence Identities" Skills Objectives: * Find exact values of functions of rational multiples of by using sum and di erence identities. * Develop new identities from the
Logarithms. Since perhaps it s been a while, calculate a few logarithms just to warm up.
 Logarithms Since perhaps it s been a while, calculate a few logarithms just to warm up. 1. Calculate the following. (a) log 3 (27) = (b) log 9 (27) = (c) log 3 ( 1 9 ) = (d) ln(e 3 ) = (e) log( 100) =
Logarithms Since perhaps it s been a while, calculate a few logarithms just to warm up. 1. Calculate the following. (a) log 3 (27) = (b) log 9 (27) = (c) log 3 ( 1 9 ) = (d) ln(e 3 ) = (e) log( 100) =
Logarithms ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning
 Logarithms ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning History and Uses We noticed that when we multiply two numbers that are the same base raised to different exponents, that the result is the base raised
Logarithms ID1050 Quantitative & Qualitative Reasoning History and Uses We noticed that when we multiply two numbers that are the same base raised to different exponents, that the result is the base raised
J.7 Properties of Logarithms
 J.7. PROPERTIES OF LOGARITHMS 1 J.7 Properties of Logarithms J.7.1 Understanding Properties of Logarithms Product Rule of Logarithms log a MN = log a M +log a N Example J.7.1. Rewrite as a sum of logarithms:
J.7. PROPERTIES OF LOGARITHMS 1 J.7 Properties of Logarithms J.7.1 Understanding Properties of Logarithms Product Rule of Logarithms log a MN = log a M +log a N Example J.7.1. Rewrite as a sum of logarithms:
PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE)
 Theory Class XI TARGET : JEE Main/Adv PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE) MATHEMATICS Trigonometry SHARING IS CARING!! Want to Thank me? Share this Assignment with your friends and show
Theory Class XI TARGET : JEE Main/Adv PREPARED BY: ER. VINEET LOOMBA (B.TECH. IIT ROORKEE) MATHEMATICS Trigonometry SHARING IS CARING!! Want to Thank me? Share this Assignment with your friends and show
1 Mathematical Methods Units 1 and 2
 Mathematical Methods Units and Further trigonometric graphs In this section, we will discuss graphs of the form = a sin ( + c) + d and = a cos ( + c) + d. Consider the graph of = sin ( ). The following
Mathematical Methods Units and Further trigonometric graphs In this section, we will discuss graphs of the form = a sin ( + c) + d and = a cos ( + c) + d. Consider the graph of = sin ( ). The following
Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions. By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh
 Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh Trigonometric Functions This section reviews the basic trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions are important because
Mathematics Lecture. 3 Chapter. 1 Trigonometric Functions By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh Trigonometric Functions This section reviews the basic trigonometric functions. Trigonometric functions are important because
Trigonometric Integrals Section 5.7
 A B I L E N E C H R I S T I A N U N I V E R S I T Y Department of Mathematics Trigonometric Integrals Section 5.7 Dr. John Ehrke Department of Mathematics Spring 2013 Eliminating Powers From Trig Functions
A B I L E N E C H R I S T I A N U N I V E R S I T Y Department of Mathematics Trigonometric Integrals Section 5.7 Dr. John Ehrke Department of Mathematics Spring 2013 Eliminating Powers From Trig Functions
New Assessment Tool for AT-Fieldtest and Monitoring
 31 st Conference of the European Working Group on Acoustic Emission (EWGAE) Th.1.A.4 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=17549 New Assessment Tool for AT-Fieldtest and Monitoring Abstract
31 st Conference of the European Working Group on Acoustic Emission (EWGAE) Th.1.A.4 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=17549 New Assessment Tool for AT-Fieldtest and Monitoring Abstract
8-1 Similarity in Right Triangles
 8-1 Similarity in Right Triangles In this chapter about right triangles, you will be working with radicals, such as 19 and 2 5. radical is in simplest form when: 1. No perfect square factor other then
8-1 Similarity in Right Triangles In this chapter about right triangles, you will be working with radicals, such as 19 and 2 5. radical is in simplest form when: 1. No perfect square factor other then
171S5.4p Properties of Logarithmic Functions. November 20, CHAPTER 5: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Examples. Express as a product.
 MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 5: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 5.1 Inverse Functions 5.2 Exponential Functions and Graphs 5.3 Logarithmic Functions
MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 5: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 5.1 Inverse Functions 5.2 Exponential Functions and Graphs 5.3 Logarithmic Functions
Arkansas Tech University MATH 1203: Trigonometry Dr. Marcel B. Finan. Review Problems for Test #3
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 1203: Trigonometry Dr. Marcel B. Finan Review Problems for Test #3 Exercise 1 The following is one cycle of a trigonometric function. Find an equation of this graph. Exercise
Arkansas Tech University MATH 1203: Trigonometry Dr. Marcel B. Finan Review Problems for Test #3 Exercise 1 The following is one cycle of a trigonometric function. Find an equation of this graph. Exercise
MHF4U. Advanced Functions Grade 12 University Mitchell District High School. Unit 4 Radian Measure 5 Video Lessons
 MHF4U Advanced Functions Grade 12 University Mitchell District High School Unit 4 Radian Measure 5 Video Lessons Allow no more than 1 class days for this unit! This includes time for review and to write
MHF4U Advanced Functions Grade 12 University Mitchell District High School Unit 4 Radian Measure 5 Video Lessons Allow no more than 1 class days for this unit! This includes time for review and to write
Trigonometry, Exam 2 Review, Spring (b) y 4 cos x
 Trigonometr, Eam Review, Spring 8 Section.A: Basic Sine and Cosine Graphs. Sketch the graph indicated. Remember to label the aes (with numbers) and to carefull sketch the five points. (a) sin (b) cos Section.B:
Trigonometr, Eam Review, Spring 8 Section.A: Basic Sine and Cosine Graphs. Sketch the graph indicated. Remember to label the aes (with numbers) and to carefull sketch the five points. (a) sin (b) cos Section.B:
Trigonometry. An Overview of Important Topics
 Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics 1 Contents Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics... 4 UNDERSTAND HOW ANGLES ARE MEASURED... 6 Degrees... 7 Radians... 7 Unit Circle... 9 Practice Problems...
Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics 1 Contents Trigonometry An Overview of Important Topics... 4 UNDERSTAND HOW ANGLES ARE MEASURED... 6 Degrees... 7 Radians... 7 Unit Circle... 9 Practice Problems...
Trigonometric identities
 Trigonometric identities An identity is an equation that is satisfied by all the values of the variable(s) in the equation. For example, the equation (1 + x) = 1 + x + x is an identity. If you replace
Trigonometric identities An identity is an equation that is satisfied by all the values of the variable(s) in the equation. For example, the equation (1 + x) = 1 + x + x is an identity. If you replace
Algebra and Trig. I. In the last section we looked at trigonometric functions of acute angles. Note the angles below are in standard position.
 Algebra and Trig. I 4.4 Trigonometric Functions of Any Angle In the last section we looked at trigonometric functions of acute angles. Note the angles below are in standard position. IN this section we
Algebra and Trig. I 4.4 Trigonometric Functions of Any Angle In the last section we looked at trigonometric functions of acute angles. Note the angles below are in standard position. IN this section we
Trigonometric Functions
 Trigonometric Functions By Daria Eiteneer Topics Covere: Reminer: relationship between egrees an raians The unit circle Definitions of trigonometric functions for a right triangle Definitions of trigonometric
Trigonometric Functions By Daria Eiteneer Topics Covere: Reminer: relationship between egrees an raians The unit circle Definitions of trigonometric functions for a right triangle Definitions of trigonometric
Slinky vs. guitar. W.E. Bailey, APAM/MSE EN1102
 Slinky vs. guitar W.E. Bailey, APAM/MSE EN1102 Differential spring element Figure: Differential length dx of spring under tension T with curvature is not a constant. θ = θ(x) W.E. Bailey, APAM/MSE EN1102
Slinky vs. guitar W.E. Bailey, APAM/MSE EN1102 Differential spring element Figure: Differential length dx of spring under tension T with curvature is not a constant. θ = θ(x) W.E. Bailey, APAM/MSE EN1102
Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities
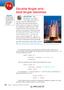 7-4 OBJECTIVE Use the doubleand half-angle identities for the sine, ine, and tangent functions. Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities ARCHITECTURE Mike MacDonald is an architect who designs water fountains.
7-4 OBJECTIVE Use the doubleand half-angle identities for the sine, ine, and tangent functions. Double-Angle and Half-Angle Identities ARCHITECTURE Mike MacDonald is an architect who designs water fountains.
Graphs of Reciprocals
 Graphs of Reciprocals The reciprocal of a number is divided by that number So the reciprocal of 3 is 3 5 The reciprocal of is 5 5 The only number that cannot have a reciprocal is 0 Dividing by zero is
Graphs of Reciprocals The reciprocal of a number is divided by that number So the reciprocal of 3 is 3 5 The reciprocal of is 5 5 The only number that cannot have a reciprocal is 0 Dividing by zero is
INTEGRATING POWERS OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 INTEGRATING POWERS OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS We now consider four cases of integrals involving powers of sine and cosine. The method used in each case is shown by an illustration. CASE 1: sin nn xx dddd
INTEGRATING POWERS OF TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS We now consider four cases of integrals involving powers of sine and cosine. The method used in each case is shown by an illustration. CASE 1: sin nn xx dddd
Chapter 4/5 Part 2- Trig Identities and Equations
 Chapter 4/5 Part 2- Trig Identities and Equations Lesson Package MHF4U Chapter 4/5 Part 2 Outline Unit Goal: By the end of this unit, you will be able to solve trig equations and prove trig identities.
Chapter 4/5 Part 2- Trig Identities and Equations Lesson Package MHF4U Chapter 4/5 Part 2 Outline Unit Goal: By the end of this unit, you will be able to solve trig equations and prove trig identities.
COMPTON SCATTERING. Phys 2010 Brown University March 13, 2009
 COMPTON SCATTERING Phys 00 Brown University March 3, 009 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to verify the energy epenence of gamma raiation upon scattering angle an to compare the ifferential cross
COMPTON SCATTERING Phys 00 Brown University March 3, 009 Purpose The purpose of this experiment is to verify the energy epenence of gamma raiation upon scattering angle an to compare the ifferential cross
cos 2 x + sin 2 x = 1 cos(u v) = cos u cos v + sin u sin v sin(u + v) = sin u cos v + cos u sin v
 Concepts: Double Angle Identities, Power Reducing Identities, Half Angle Identities. Memorized: cos x + sin x 1 cos(u v) cos u cos v + sin v sin(u + v) cos v + cos u sin v Derive other identities you need
Concepts: Double Angle Identities, Power Reducing Identities, Half Angle Identities. Memorized: cos x + sin x 1 cos(u v) cos u cos v + sin v sin(u + v) cos v + cos u sin v Derive other identities you need
HW#02 (18 pts): All recommended exercises from JIT (1 pt/problem)
 Spring 2011 MthSc103 Course Calendar Page 1 of 7 January W 12 Syllabus/Course Policies BST Review Th 13 Basic Skills Test F 14 JIT 1.1 1.3: Numbers, Fractions, Parentheses JIT 1.1: 2, 6, 8, 9 JIT 1.2:
Spring 2011 MthSc103 Course Calendar Page 1 of 7 January W 12 Syllabus/Course Policies BST Review Th 13 Basic Skills Test F 14 JIT 1.1 1.3: Numbers, Fractions, Parentheses JIT 1.1: 2, 6, 8, 9 JIT 1.2:
Functions of several variables
 Chapter 6 Functions of several variables 6.1 Limits and continuity Definition 6.1 (Euclidean distance). Given two points P (x 1, y 1 ) and Q(x, y ) on the plane, we define their distance by the formula
Chapter 6 Functions of several variables 6.1 Limits and continuity Definition 6.1 (Euclidean distance). Given two points P (x 1, y 1 ) and Q(x, y ) on the plane, we define their distance by the formula
Section 7.1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 Section 7.1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine OBJECTIVE 1: Understanding the Graph of the Sine Function and its Properties In Chapter 7, we will use a rectangular coordinate system for a different purpose. We
Section 7.1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine OBJECTIVE 1: Understanding the Graph of the Sine Function and its Properties In Chapter 7, we will use a rectangular coordinate system for a different purpose. We
Sample Problems. Practice Problems
 Lectre Notes Trigonometric Integrals age Samle Problems Comte each of the following integrals.. sin Assme that a an b are ositive nmbers. 8. csc 5. sec ( ). 3. cos 5 cos sin 9.. sin sin 3 6. + cos. csc.
Lectre Notes Trigonometric Integrals age Samle Problems Comte each of the following integrals.. sin Assme that a an b are ositive nmbers. 8. csc 5. sec ( ). 3. cos 5 cos sin 9.. sin sin 3 6. + cos. csc.
CPM EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM
 CPM EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM SAMPLE LESSON: ALGEBRA TILES PART 1: INTRODUCTION TO ALGEBRA TILES The problems in Part 1 introduce algebra tiles to students. These first eleven problems will probably span two
CPM EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM SAMPLE LESSON: ALGEBRA TILES PART 1: INTRODUCTION TO ALGEBRA TILES The problems in Part 1 introduce algebra tiles to students. These first eleven problems will probably span two
Logarithms. In spherical trigonometry
 Logarithms In spherical trigonometry there are many formulas that require multiplying two sines together, e.g., for a right spherical triangle sin b = sin B sin c In the 1590's it was known (as the method
Logarithms In spherical trigonometry there are many formulas that require multiplying two sines together, e.g., for a right spherical triangle sin b = sin B sin c In the 1590's it was known (as the method
Amplitude, Reflection, and Period
 SECTION 4.2 Amplitude, Reflection, and Period Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1 2 3 4 Find the amplitude of a sine or cosine function. Find the period of a sine or
SECTION 4.2 Amplitude, Reflection, and Period Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives 1 2 3 4 Find the amplitude of a sine or cosine function. Find the period of a sine or
MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) (sin x + cos x) 1 + sin x cos x =? 1) ) sec 4 x + sec x tan x - tan 4 x =? ) ) cos
MATH 1040 CP 15 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) (sin x + cos x) 1 + sin x cos x =? 1) ) sec 4 x + sec x tan x - tan 4 x =? ) ) cos
TRANSFORMING TRIG FUNCTIONS
 Chapter 7 TRANSFORMING TRIG FUNCTIONS 7.. 7..4 Students appl their knowledge of transforming parent graphs to the trigonometric functions. The will generate general equations for the famil of sine, cosine
Chapter 7 TRANSFORMING TRIG FUNCTIONS 7.. 7..4 Students appl their knowledge of transforming parent graphs to the trigonometric functions. The will generate general equations for the famil of sine, cosine
Sample Questionnaire I
 Sample Questionnaire I Section I Directions: Below you will find a list of names of many people who work here. Some of these people you may interact with quite frequently; others you may not talk to very
Sample Questionnaire I Section I Directions: Below you will find a list of names of many people who work here. Some of these people you may interact with quite frequently; others you may not talk to very
P1 Chapter 10 :: Trigonometric Identities & Equations
 P1 Chapter 10 :: Trigonometric Identities & Equations jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 20 th August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free
P1 Chapter 10 :: Trigonometric Identities & Equations jfrost@tiffin.kingston.sch.uk www.drfrostmaths.com @DrFrostMaths Last modified: 20 th August 2017 Use of DrFrostMaths for practice Register for free
Algebra 2/Trig AIIT.13 AIIT.15 AIIT.16 Reference Angles/Unit Circle Notes. Name: Date: Block:
 Algebra 2/Trig AIIT.13 AIIT.15 AIIT.16 Reference Angles/Unit Circle Notes Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Trig Functions in a Circle Circle with radius r, centered around origin (x 2 + y 2 = r 2 ) Drop
Algebra 2/Trig AIIT.13 AIIT.15 AIIT.16 Reference Angles/Unit Circle Notes Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Trig Functions in a Circle Circle with radius r, centered around origin (x 2 + y 2 = r 2 ) Drop
Relationships Occurring With Sinusoidal Points March 11, 2002 by Andrew Burnson
 Relationships Occurring With Sinusoidal Points March 11, 2002 by Andrew Burnson I have found that when a sine wave of the form f(x) = Asin(bx+c) passes through three points, several relationships are formed
Relationships Occurring With Sinusoidal Points March 11, 2002 by Andrew Burnson I have found that when a sine wave of the form f(x) = Asin(bx+c) passes through three points, several relationships are formed
Objectives: Students will learn to divide decimals with both paper and pencil as well as with the use of a calculator.
 Unit 3.5: Fractions, Decimals and Percent Lesson: Dividing Decimals Objectives: Students will learn to divide decimals with both paper and pencil as well as with the use of a calculator. Procedure: Dividing
Unit 3.5: Fractions, Decimals and Percent Lesson: Dividing Decimals Objectives: Students will learn to divide decimals with both paper and pencil as well as with the use of a calculator. Procedure: Dividing
Trigonometric Functions
 Trigonometric Functions Q1 : Find the radian measures corresponding to the following degree measures: (i) 25 (ii) - 47 30' (iii) 240 (iv) 520 (i) 25 We know that 180 = π radian (ii) â 47 30' â 47 30' =
Trigonometric Functions Q1 : Find the radian measures corresponding to the following degree measures: (i) 25 (ii) - 47 30' (iii) 240 (iv) 520 (i) 25 We know that 180 = π radian (ii) â 47 30' â 47 30' =
Section 1.5 An Introduction to Logarithms
 Section. An Introduction to Logarithms So far we ve used the idea exponent Base Result from two points of view. When the base and exponent were given, for instance, we simplified to the result 8. When
Section. An Introduction to Logarithms So far we ve used the idea exponent Base Result from two points of view. When the base and exponent were given, for instance, we simplified to the result 8. When
Please grab the warm up off of the chair in the front of the room and begin working!
 Please grab the warm up off of the chair in the front of the room and begin working! add the x! #2 Fix to y = 5cos (2πx 2) + 9 Have your homework out on your desk to be checked. (Pre requisite for graphing
Please grab the warm up off of the chair in the front of the room and begin working! add the x! #2 Fix to y = 5cos (2πx 2) + 9 Have your homework out on your desk to be checked. (Pre requisite for graphing
Trigonometry: A Brief Conversation
 Cit Universit of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works Open Educational Resources Queensborough Communit College 018 Trigonometr: A Brief Conversation Caroln D. King PhD CUNY Queensborough Communit College
Cit Universit of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works Open Educational Resources Queensborough Communit College 018 Trigonometr: A Brief Conversation Caroln D. King PhD CUNY Queensborough Communit College
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Name Date Chapter 3 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Section 3.1 Eponential Functions and Their Graphs Objective: In this lesson ou learned how to recognize, evaluate, and graph eponential functions.
Name Date Chapter 3 Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Section 3.1 Eponential Functions and Their Graphs Objective: In this lesson ou learned how to recognize, evaluate, and graph eponential functions.
Lesson 27: Sine and Cosine of Complementary and Special Angles
 Lesson 7 M Classwork Example 1 If α and β are the measurements of complementary angles, then we are going to show that sin α = cos β. In right triangle ABC, the measurement of acute angle A is denoted
Lesson 7 M Classwork Example 1 If α and β are the measurements of complementary angles, then we are going to show that sin α = cos β. In right triangle ABC, the measurement of acute angle A is denoted
NOTES: SIGNED INTEGERS DAY 1
 NOTES: SIGNED INTEGERS DAY 1 MULTIPLYING and DIVIDING: Same Signs (POSITIVE) + + = + positive x positive = positive = + negative x negative = positive Different Signs (NEGATIVE) + = positive x negative
NOTES: SIGNED INTEGERS DAY 1 MULTIPLYING and DIVIDING: Same Signs (POSITIVE) + + = + positive x positive = positive = + negative x negative = positive Different Signs (NEGATIVE) + = positive x negative
Chapter 3, Part 4: Intro to the Trigonometric Functions
 Haberman MTH Section I: The Trigonometric Functions Chapter, Part : Intro to the Trigonometric Functions Recall that the sine and cosine function represent the coordinates of points in the circumference
Haberman MTH Section I: The Trigonometric Functions Chapter, Part : Intro to the Trigonometric Functions Recall that the sine and cosine function represent the coordinates of points in the circumference
Field Visualization by Image Processing
 The 0th International Symposium on Flow Visualiation August 6-9, 00, Kyoto, Japan F008 Fiel Visualiation by Image Processing Image refining an fiel characteristics arinova, I. *, Eno, H. *, Hayano, S.
The 0th International Symposium on Flow Visualiation August 6-9, 00, Kyoto, Japan F008 Fiel Visualiation by Image Processing Image refining an fiel characteristics arinova, I. *, Eno, H. *, Hayano, S.
EFFECTS OF PHASE AND AMPLITUDE ERRORS ON QAM SYSTEMS WITH ERROR- CONTROL CODING AND SOFT DECISION DECODING
 Clemson University TigerPrints All Theses Theses 8-2009 EFFECTS OF PHASE AND AMPLITUDE ERRORS ON QAM SYSTEMS WITH ERROR- CONTROL CODING AND SOFT DECISION DECODING Jason Ellis Clemson University, jellis@clemson.edu
Clemson University TigerPrints All Theses Theses 8-2009 EFFECTS OF PHASE AND AMPLITUDE ERRORS ON QAM SYSTEMS WITH ERROR- CONTROL CODING AND SOFT DECISION DECODING Jason Ellis Clemson University, jellis@clemson.edu
Math 154 :: Elementary Algebra
 Math :: Elementary Algebra Section 9. Section 9. Section 9. Section 9. Section 9. Section 9.6 Math :: Elementary Algebra Section 9. Introduction to Square Roots. This answer should be in your own words..
Math :: Elementary Algebra Section 9. Section 9. Section 9. Section 9. Section 9. Section 9.6 Math :: Elementary Algebra Section 9. Introduction to Square Roots. This answer should be in your own words..
CHAPTER 14 ALTERNATING VOLTAGES AND CURRENTS
 CHAPTER 4 ALTERNATING VOLTAGES AND CURRENTS Exercise 77, Page 28. Determine the periodic time for the following frequencies: (a) 2.5 Hz (b) 00 Hz (c) 40 khz (a) Periodic time, T = = 0.4 s f 2.5 (b) Periodic
CHAPTER 4 ALTERNATING VOLTAGES AND CURRENTS Exercise 77, Page 28. Determine the periodic time for the following frequencies: (a) 2.5 Hz (b) 00 Hz (c) 40 khz (a) Periodic time, T = = 0.4 s f 2.5 (b) Periodic
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter Homework 1. Table 1: 11.1:8 t x y
 MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 2 Homework Section., pg. 692: 8, 24, 43. Section.2, pg. 72:, 2 (no graph required), 32, 4. Section.3, pg. 73: 4, 2, 54, 8. Section.4, pg. 79: 6, 35, 46. Solutions.:
MATH 255 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 2 Homework Section., pg. 692: 8, 24, 43. Section.2, pg. 72:, 2 (no graph required), 32, 4. Section.3, pg. 73: 4, 2, 54, 8. Section.4, pg. 79: 6, 35, 46. Solutions.:
2.8 Enrichment: more on logarithms EMCFR
 2. Enrichment: more on logarithms EMCFR NOTE: THIS SECTION IS NOT PART OF THE CURRICULUM Laws of logarithms EMCFS Logarithmic law: log a y = log a + log a y ( > 0 and y > 0) Let log a () = m = = a m...
2. Enrichment: more on logarithms EMCFR NOTE: THIS SECTION IS NOT PART OF THE CURRICULUM Laws of logarithms EMCFS Logarithmic law: log a y = log a + log a y ( > 0 and y > 0) Let log a () = m = = a m...
Math Shape and Space: Perimeter
 F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagogy Math Shape and Space: Perimeter Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported by UBC Teaching and Learning Enhancement
F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Department of Curriculum and Pedagogy Math Shape and Space: Perimeter Science and Mathematics Education Research Group Supported by UBC Teaching and Learning Enhancement
Chapter Summary. What did you learn? 270 Chapter 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 0_00R.qd /7/05 0: AM Page 70 70 Chapter Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Chapter Summar What did ou learn? Section. Review Eercises Recognize and evaluate eponential functions with base a (p. ). Graph
0_00R.qd /7/05 0: AM Page 70 70 Chapter Eponential and Logarithmic Functions Chapter Summar What did ou learn? Section. Review Eercises Recognize and evaluate eponential functions with base a (p. ). Graph
The Math Projects Journal
 PROJECT OBJECTIVE The House Painter lesson series offers students firm acquisition of the skills involved in adding, subtracting and multipling polnomials. The House Painter lessons accomplish this b offering
PROJECT OBJECTIVE The House Painter lesson series offers students firm acquisition of the skills involved in adding, subtracting and multipling polnomials. The House Painter lessons accomplish this b offering
An Overview of Mathematics 4
 An Overview of Mathematics 4 Number (N) read, write, represent, and describe whole numbers to 10 000 using concrete materials, pictures, expressions (e.g., 400 + 7), words, place-value charts, and symbols
An Overview of Mathematics 4 Number (N) read, write, represent, and describe whole numbers to 10 000 using concrete materials, pictures, expressions (e.g., 400 + 7), words, place-value charts, and symbols
Trigonometric Identities. Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 5 Trigonometric Identities Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities Difference Identity for Cosine Sum Identity for Cosine Cofunction Identities Applications
5 Trigonometric Identities Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities Difference Identity for Cosine Sum Identity for Cosine Cofunction Identities Applications
INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY
 INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY 7 INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY 8 8. Introduction There is perhaps nothing which so occupies the middle position of mathematics as trigonometry. J.F. Herbart (890) You have
INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY 7 INTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY 8 8. Introduction There is perhaps nothing which so occupies the middle position of mathematics as trigonometry. J.F. Herbart (890) You have
The Analysis and Complementarity of Abbe Principle Application Limited in Coordinate Measurement
 Proceeings of the Worl Congress on Engineering 00 Vol III The Analysis an Complementarity of Abbe Principle Application Limite in Coorinate Measurement Fei Yetai, Shang Ping, Chen Xiaohuai, Huang Qiangxian
Proceeings of the Worl Congress on Engineering 00 Vol III The Analysis an Complementarity of Abbe Principle Application Limite in Coorinate Measurement Fei Yetai, Shang Ping, Chen Xiaohuai, Huang Qiangxian
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Review.1 -. Name Solve the problem. 1) The rabbit population in a forest area grows at the rate of 9% monthl. If there are 90 rabbits in September, find how man rabbits (rounded to the nearest whole number)
Review.1 -. Name Solve the problem. 1) The rabbit population in a forest area grows at the rate of 9% monthl. If there are 90 rabbits in September, find how man rabbits (rounded to the nearest whole number)
5-5 Multiple-Angle and Product-to-Sum Identities
 Find the values of sin 2, cos 2, and tan 2 for the given value and interval. 1. cos =, (270, 360 ) Since on the interval (270, 360 ), one point on the terminal side of θ has x-coordinate 3 and a distance
Find the values of sin 2, cos 2, and tan 2 for the given value and interval. 1. cos =, (270, 360 ) Since on the interval (270, 360 ), one point on the terminal side of θ has x-coordinate 3 and a distance
MATH Week 10. Ferenc Balogh Winter. Concordia University
 MATH 20 - Week 0 Ferenc Balogh Concordia University 2008 Winter Based on the textbook J. Stuart, L. Redlin, S. Watson, Precalculus - Mathematics for Calculus, 5th Edition, Thomson All figures and videos
MATH 20 - Week 0 Ferenc Balogh Concordia University 2008 Winter Based on the textbook J. Stuart, L. Redlin, S. Watson, Precalculus - Mathematics for Calculus, 5th Edition, Thomson All figures and videos
Page 1 of 52 Youtube.com/c/StayLearningNewdelhi
 Page 1 of 52 www.vijayadarsh.com Youtube.com/c/StayLearningNewdelhi Contact@vijayAdarsh.com +919268373738 About StayLearning StayLearning (a Division of AASS) believes in educating their students with
Page 1 of 52 www.vijayadarsh.com Youtube.com/c/StayLearningNewdelhi Contact@vijayAdarsh.com +919268373738 About StayLearning StayLearning (a Division of AASS) believes in educating their students with
Math 180 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes. Professor Miguel Ornelas
 Math 180 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes Professor Miguel Ornelas 1 M. Ornelas Math 180 Lecture Notes Section 6.1 Section 6.1 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Verify the identity. a. sin x + cos x cot x = csc
Math 180 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes Professor Miguel Ornelas 1 M. Ornelas Math 180 Lecture Notes Section 6.1 Section 6.1 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Verify the identity. a. sin x + cos x cot x = csc

 # %
# %