Manual version 1.1, September 5th, HF Projects 6 Meter VHF Packer Amplifier Project Manual
|
|
|
- Clifford Harvey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Manual version 1.1, September 5th, 29 HF Projects 6 Meter VHF Packer Amplifier Project Manual
2 Table of Contents 1 Introduction Description Features Procedure Preparation Faults Soldering Technique Suggested Tools Component Installation Board Cleaning Chassis Fabrication Template Procedure Bottom Cover Fabrication Chassis component mounting Cable Assemblies Power Cable Assembly RF Cable Assembly Switch Cable Wiring Circuit Board Construction Install Capacitors Install Resistors Install Connectors Install ICs, Transistors, Diodes and Relay Install Other Components Fabricate and Install T Fabricate and Install L1 and L Install Circuit Board and Amplifier Module Install Circuit Board Install Amplifier Module Testing Procedures Initial Checks Setting Bias Current Filter Circuit Alignment of L1 and L Power Output Test
3 8 Operating Procedure Schematic, Parts List, Templates, Module DataSheet...2 3
4 1 Introduction 1.1 Description This project will provide you with an excellent source of fun, interest and skill building challenge. In the end you will have a compact 3 watt linear amplifier for use with QRP 6m transmitters, which can be powered from a 12 volt DC supply. The design is a good balance between output power, physical size and battery power consumption. The completed amplifier will reward the builder with a clean, more powerful output signal from a 6M QRP transmitter. The product uses the Mitsubishi RA3H68M RF mosfet module mounted on a heat sink. ( ). This 3-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module is designed for 12.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the 66- to 88-MHz range on SSB, CW and FM modes. 1.2 Features All parts, circuit board, case and heat sink provided 5 ohm resistive pi network input: 1W drive = 3W output Filtered Anderson Power Pole DC Input: 6.2A Low Pass Filter on-board; Filtered RF Input and RF Output Bypass / Operate Switch with TX LED COR Carrier Operated Relay Size: 5.25 x 3 x 3 inches ; Weight is less than 1 pound Accurate Drill templates provided for easy case fabrication Construction manual provided on a CD 4
5 2 Procedure The basic concept to building this amplifier is to prepare the chassis, the cables, the circuit board and the amplifier board (in that order) and pretest them before final assembly and final testing. This manual is thus organized with this concept in mind and consists of distinct chapters for each module assembly process: 1. Introduction 2. Procedure (this chapter) 3. Chassis Fabrication 4. Cable Assemblies 5. Circuit Board Construction 6. Install Circuit Board and Amplifier Assembly 7. Testing Procedures 8. Operating Procedures 2.1 Preparation The most important preparation step is to read this manual before assembly. This will familiarize you with the project, its circuitry, building requirements and components. You should also do an inventory of parts. In the unlikely event that you appear to have missing parts, duplicates or wrong parts please first double check for the parts in all bags, recheck the inventory and if you appear to still be missing parts please contact the project organizer 2.2 Faults It is a fact that 9-95% of problems with completed electronics projects are due to either component misplacement or soldering faults. We cannot stress highly enough the importance of reading the manual thoroughly, double checking component installation before soldering and then good soldering technique in order to have a working amplifier at the end of this project. Other builder faults are active component damage due to overheating and damage to circuit board pads and tracks caused by faulty de-soldering, too high a wattage of soldering iron or carelessness. It is very rare indeed to have initially faulty components or printed circuit boards (PCBs). 2.3 Soldering Technique use a watt soldering iron with a clean, non-corroded, well-tinned, fine tip keep the tip clean by frequently rubbing it along a wet sponge keep the tip tinned with a thin film of solder 5
6 ensure all circuit board pads and component leads are clean (not a problem with this project because boards and components are new) insert the component in the holes associated with the component outline. Bend the leads at a 45 degree angle to hold the part in place ensure the soldering iron tip is at its working temperature and is in contact simultaneously with both surfaces to be soldered (the pad and the component) let the contact zones heat before applying only electronics grade rosin cored solder (usually 3-6 seconds will do) apply the solder to the two surfaces (not the iron tip) and only enough solder to coat both surfaces ensure that the joint does not move after you remove the soldering iron tip and until the solder has solidified (approx 5-7 seconds) clip the leads very close to the circuit board surface check that the resultant solder joint is shiny, in perfect contact with pad and wire and has a concave upwards appearance if not, renew the solder joint by reheating and reflowing the solder joint with the tip of the soldering iron special care for toroid coils: the toroids and inductors you will wind and solder in this project use enamel coated magnet wire. You must remove this insulation coating at the ends of the wires prior to soldering. Two techniques are: 1) use a small butane cigarette lighter to burn off the insulation material or 2) take a large drop of hot solder on your soldering iron tip and run the wire end through the hot solder blob to remove the insulation (this may not work with low wattage irons). Other methods such as using sandpaper or a razor knife will work but you may damage the wire or the toroid windings if you are not careful. Desoldering: we recommend using desoldering wick. This thin flexible copper braid heats rapidly, sucks up solder well and is inexpensive. (Solder suckers are difficult to hold in place and the solder may re-solidify before you are able to press the suck button). To use desoldering wick (braid) heat the wick first before applying any heat to the joint, lay the wick over the joint and put the tip of the iron on the wick. It will take a second or two to heat up, but once it is hot you will feel the wick slide and you should then see the solder flow into it. You probably won't have to repeat this step. Once a section of wick is filled with solder, it is used up and must be cut off the rest of the braid. Since the wick comes on a spool, all you need to do is cut off the used sections and take some more off the spool. 2.4 Suggested Tools watt electronics soldering iron with stand and sponge electronics grade solder de-soldering braid and/or de-soldering pump or bulb fine needle nose pliers, small fine wire cutters, wire stripper multi-meter, test leads small nutdriver set, English 5 ohm Dummy Load Also, the following tools are needed to fabricate the chassis: 6
7 3/8 inch wood boring bit 1 5/8 inch wood boring bit 7/32 inch drill bit 5/32 inch drill bit 1/8 inch drill bit 1/16 inch drill bit for pilot holes Nibbler tool for cutouts Hand drill and/or drill press Small and medium flat file Tools necessary for Testing: Multi-meter capable of measuring volts, ohms and amps. LCR meter for testing low pass filter (other methods possible if you don't have this) Dummy load, 5 ohms for output testing (capable of 5W) Dummy load, 5 ohms to terminate the input (BNC 5 ohm plug) Current measurement test cable (to make life easy) 12V source for testing (a small battery is ok) Nice to have (but not necessary tools): GC/Waldom W-HT1821 crimp tool (for blue flag terminals) West Mountain Radio Power Pole Crimpers Wire strippers, Klein Tools 1146 Molex Crimp tool EDP# ; ENG# CR2262C (22-3 AWG) Heat Gun for shrink tubing 2.5 Component Installation For each component and throughout this manual, our word Install generally means: 1 A wood boring bit works well when drilling through soft aluminum and makes a nice neat hole. 7
8 1. Pick the correct part to start with in the assembly notes that follow you will get a complete description of the part to install. You must find this part using the Bill of Materials for the specific module you are constructing. This parts list is located at the end of this document (see the Table of Contents). Parts will be located in their appropriate module bag. 2. Insert the component into the correct PCB position. Refer to the appropriate PCB component outline diagrams and follow the text. 3. Orient it correctly, following the PC board outline. This is vital for active components, electrolytic and tantalum capacitors and diodes. Also, it is good practice to mount resistors and capacitors in identical orientations (for resistors normally read color code left to right in same direction as the silkscreen on the PC board). This makes component checks easier. 4. Install all low profile components first: usually resistors, capacitors, diodes, then electrolytics and active components. The text will normally guide you to the most efficient method of what to install when. 5. Resistors, capacitors, relays and connectors should be mounted flush with the board. 6. Bend the wires of the components at the bottom side slightly outwards in order to hold the component in place for soldering. 7. Solder as per techniques described above. 8. Trim excess wire leads. 9. Mark off each installation step in sequence as you complete it, in the box provided (e.g. ). The usual sequence of assembly is to place all the small resistors and capacitors first. The order given is by position on the board. Generally, the flow is from upper left to lower right to aid you in locating the next component. Sort all the resistors by component value from left to right. You may wish to use a strip of scotch tape on a scrap of paper and slip a lead of the resistor under the tape. Use your ohm meter and resistor color code (see end of this document) to identify each of the small resistor values. Group the same component values together and then follow the text procedure exactly. A parts placement diagram is provided at the end of each module assembly section for reference. 2.6 Board Cleaning PCB cleaning is recommended after soldering all components. This removes residue that might provide a conduction path at high frequencies and subvert the overall frequency response of the filters. TechSpray Blue Shower is a good product and is available from Mouser Electronics. Use the spray in a well ventilated area (e.g. outside) to remove solder flux from the board. Follow directions on the can. 8
9 3 Chassis Fabrication 3.1 Template Procedure Ensure your printer is set for no shrink so that no distortion of scale occurs upon printout. Print out 2 copies of the drill templates (one to read the other to use). See Illustration 1 as an example. Cut out the top and end panels and tape. Put the box back together again for strength. Using the heat sink plate (rectangle, approximate size of cutout) as a straight edge, score the outline with a hobby knife or straight-edge razor blade to mark the outline. Use a chassis-punch to mark all the holes for drilling. Mark all three sides of the chassis for the cutouts or holes to drill. After you cut through the paper, remove the rectangle cutout and place a piece of scotch tape over the cutout. Score the outline again to leave a tape outline of the area to be removed. Drill small 1/16 inch pilot holes at all hole locations. Drill all holes before removing the drill template as it very hard to see the marks. Remove the drill template. You will be left with tape outlines to help you see the cutout area clearly. Drill a 3/8 inch hole in the center of the larger cutouts. Use a couple adjacent ¼ inch holes on the smaller cutouts and file large enough diameter to accept the nibbler tool. Use the Nibbler tool to cut close to the edge of the scribed line of the cutout. Use a file to finish up the cutouts to dimension. Install the chassis switch components into the cutouts. Use a file to achieve the final dimension necessary to install the component. It is important to note that the two terminals should be oriented towards the outside for proper switch logic. Precisely attach the drill template for the heat sink plate (rectangle piece). Center punch and drill the 6 holes starting with a small drill bit diameter and graduate to the final bit size. Remove rough edges so the plate will mount flat against the heat sink. A ¼ inch drill bit rotated by hand will clean up the edge. Trial fit the heat sink plate on the heat sink into the chassis. The heat sink plate should be parallel to the heat sink edge and spaced about.5 inch from the edge. Align the amp module mounting holes in the heat sink plate with the tapped holes in the heat sink. This is of primary importance. Apply a thin even layer of thermal grease between the heat sink plate and heat sink. Use four 4-4 x 5/16 inch screws to attach the heat sink plate to the heat sink. Attach four Jack screws to the four holes that will be the board mounting location. Trial fit the heat sink into the chassis. File the length or width of the slot as necessary to achieve fit. Elongate a hole, if necessary (to compensate for fabricating tolerance variation). Side pressure with the hand drill can make small adjustments for better fit. 9
10 Illustration 1: Preparing the templates for chassis fabrication 3.2 Bottom Cover Fabrication Cut out drill template for bottom cover. Tape to the bottom of the case. Chassis punch four holes. Drill pilot holes. Drill 7/32 inch diameter holes. Use a large bit on the inside to de-burr the holes. Attach four rubber feet into the holes. 3.3 Chassis component mounting Attach the heat sink assembly to the case. Use four 4-4 x 5/16 inch screws with lock washers. (You should already have the two switches mounted in the case). Attach the power pole connectors using 4-4 x 3/8 inch screws, lock washers and #4 nuts. The extra screw length helps with assembly. 1
11 The Power Poles have a mounting convention to properly mate with a power pole cable. View from outside the box, the red housing should be on the left with the metal contact in the bottom quadrant. The black housing is physically combined with the red housing. Place the top power pole retainer piece first, loosely attached with a 3/8 inch length 4-4 screw, lock washer and nut. Insert the power pole retainer into the metal retaining tab. Tighten up the mounting screw. Install the other screw, power pole retainer, washer and nut. Even up the hardware and tighten. We will insert the wire later. Attach the SO239 connector with two sets of 4-4 x 3/8 inch screws, lock washers and #4 nuts. The flange is placed inside the enclosure. Attach the BNC connector. Use a ½ inch wrench to tighten securely to the case. Trim the LED length to 6 inch. Install two crimp terminals to the ends of the wires. Insert the LED through the chassis. Slip the crimp terminals into the housing. The red lead will ultimately plug into the square pad at the D3 connector on the circuit board. 4 Cable Assemblies 4.1 Power Cable Assembly Cut the red wire to make a 7 inch length. Crimp a Power Pole terminal to one end and a blue flag terminal to the other end. Plug in on a power switch tab. Trim the black wire to make a 7 inch length. Crimp a Power Pole terminal to one end and a blue flag terminal to the other end. This wire will connect to the circuit board when installed. Insert the wires into the power pole housing. It is important that the connector tab be fully inserted for proper assembly. Use a small flat blade screw driver to push on the back end of the terminal with the terminal inserted in the housing. You should hear a click when the mating ends of the terminals join together. Trim the remaining red wire to 3 inch. Crimp a blue flag terminal to each end. Plug in on a power switch tab. This wire will connect to the circuit board when installed. 4.2 RF Cable Assembly Cut two four inch lengths of RG174 coax. Remove the insulation ¾ inch from the wire end. Thread four ferrite cores over each wire. Comb out the braid and twist into a pig tail. Trim the pig tail to ¼ inch. Tin the wire at the tip. Cut six ½ inch lengths of the black shrink tubing. Place over the four ferrite cores in the middle of the wire and heat shrink to hold in place. Locate the black hook up wire. Cut four 2 inch lengths. Strip ¼ inch insulation from each end. Tin one end of each wire. Solder one end of each black wire to the ends of the cable. Place a ½ inch length of shrink tubing over each end of the cables. The black wire should be formed so both the black and center conductor are the same length. Heat shrink the tubing. 11
12 Crimp a terminal pin to one end of each cable. Crimp a terminal pin to same end of the coax center connector. Insert the terminal pins into the connector housings. The coax center pin will plug into the circuit board at the square pad position. Tin the wires at the other end of the two cables. Solder the red ring terminal to the black lead of one of the cables. This establishes this cable as the RF Output cable. The other cable is the RF Input cable. Solder the RF Output cable to the SO239 connector. The red ring terminal is placed under a SO239 mounting screw. See Illustration 2. Solder the RF Input cable to the BNC connector. Make sure the ground connection is not a cold solder joint. See illustration Switch Cable Wiring Illustration 2: Completed RF cables. Cut two 6 ½ inch lengths of hook up wire. Strip ¼ inch insulation from each end. Tin the wires on one end. Attach crimp terminals to the unsoldered end of each wire. Insert into a 2-pin housing. Solder the other end of each wire to the Bypass/Inline switch. 12
13 5 Circuit Board Construction 5.1 Install Capacitors C5 47pf C2 18 pf C4 1 pf (11) C1 5.6pf C14.1uF (13) C3 56 pf C15.1uf (13) C12.68uf (684) (observe polarity) C9 1nf (12) same as 1 pf C6 1nf (12) C1.1uf (13) C13.1uf (13) C7.1uf (14) 5.2 Install Resistors R5 1K BRN, BLK, ORN 1/8W R6 42 Blue body 1% 1/8W R7 1K BRN, BLK, ORN 1/8W R8 1K BRN, BLK, RED 1/8W R4 jumper R3 1 1W (measure) R1 68 1W (measure) R2 1 1W (measure) 5.3 Install Connectors J1 2 pin friction lock header 13
14 J2 2 pin friction lock header D3 2 pin friction lock header SW1 2 pin friction lock header TEST 2 pin header 5.4 Install ICs, Transistors, Diodes and Relay U1 78L5 Q2 2N396 Q3 2N589 D2 1N5711 (observe polarity stripe) D1 1N47 (observe polarity stripe) K1 Relay, 12V DPDT (solder 1 pin, reheat and align, solder all pins) 5.5 Install Other Components L4 Ferrite Tube (use a wire from component clipping) L3 Multi-hole Ferrite C8.68uF surface mount (684) Tin 1 pad. Place component and solder. Solder other lead J3 Tab Solder 1 pin, reheat and align, solder other pin J4 Tab Solder 1 pin, reheat and align, solder other pin VR1 POT 2 ohm (adjustment screw aligned with square pad) Turn pot fully CCW (no stop) C11 68uF (observe polarity) 5.6 Fabricate and Install T1 Cut a 15 inch length of #24 AWG wire Fold in half and thread ferrite core on the wire. Hold core between thumb and fore finger with the wires pointing up Grasp the wire under your fore finger wind 13 turns on the core. Wind 12 turns with the remaining wire for a total of 26 passes through the core. 14
15 Trim the ends to 3/8 inch. Remove the insulation on the wire (file, Dremel tool, etc.) Tin the leads and insert into holes 1 and 4 (upper right square pad and lower left round pad) and solder. Insert a 1 inch length of insulated wire (small insulated bus wire) through the center of T1 and attach to holes 2 and 3 (upper left, lower right) and solder. 5.7 Fabricate and Install L1 and L2 Cut a 5 inch length of #24AWG enamel wire. Scrape the last ¼ inch to remove insulation and tin the ends. Wrap the wire tightly around a ¼ inch drill bit to form an air coil. Form the leads and solder into L1 position. Cut a 4 inch length of #24AWG enamel wire. Scrape the last ¼ inch to remove insulation and tin the ends. Wrap the wire tightly around a ¼ inch drill bit to form an air coil. Form the leads and solder into L2 position. 6 Install Circuit Board and Amplifier Module 6.1 Install Circuit Board Attach circuit board to case using four 4-4 x ¼ inch black screws. Place the shorter locking lug terminal under the screws at upper left and upper right. These will be soldered to the amp module lug terminals when the amp module is installed. Plug in RF In cable to IN. Keep coax tight and next to RF IN connector. Plug in RF Out cable to OUT. Route cable to be under SO239 connector. Route LED wires below power cable down the length of the case and plug into D3 location. Route switch cable in the same manner as the LED cable. Plug in the power cable to J3 and J4. The plus (red) lead connects to J3. The minus (black) connects to J Install Amplifier Module Read the RA3H68M data sheet located at the end of this document and heed the warning concerning handling and operation. Attach four TO22 Thermasil pads on the heat sink surface of the Amp Module Ensure you do not bend the leads of the device. Solder the leads only after the module and circuit board are mounted and in their final resting place. 15
16 Clip ¼ inch off the length of the four pins attached to the amp module. Apply a thin coat of thermal grease under each mounting wing of the amp module Place the amp module on the heat sink plate. Place a lug locking terminal on each 4-4 x 3/8 inch mounting screw. Screw until just tight but not cinched down yet. Position the lug locking terminal to contact the lug locking terminals mounted on the circuit board. Firm up the screws a bit more and solder the lug locking terminals together. Tighten the amp module mounting screws firm. Amplifier module connections on the circuit board are pins 1-4 (left to right) Solder pins 1, 2 and 4 to the circuit board and isolate pin 3 with small of paper between the pin and the circuit board. We will attach pin 3 to the 12V in a later step after initial check out has been completed. See Illustrations 6, 7 and 8 regarding completed and assembled amplifier chassis, boards and module. Illustration 3: Thermalsil III is.152mm (.6") thick and grey green in color. A finely woven glass cloth provides the thinnest possible matrix for enhanced thermal resistance. 16
17 7 Testing Procedures 7.1 Initial Checks Connect a multi-meter to measure ohms on the DC input (power pole connectors). The resistance should be in the high megaohms. A typical is greater than 5Meg ohms with the power switch ON. Connect a multi-meter to measure volts. One lead to ground (case). Place the positive lead on pin 2 of the amp module. This is the BIAS pin. Turn power on. The voltage on pin 2 should be zero volts. Attach a jumper to the TEST jack (use an small alligator clip for this purpose). Reading should be about 3.2 VDC. Rotate the pot clockwise a few turns and observe that the voltage begins to rise. This will confirm the adjustment circuit is functional and the pot is installed correctly. Disconnect from power. Remove the paper insulator and solder pin 3 to the circuit board. 7.2 Setting Bias Current Configure the multi-meter to measure current. Place the meter in the circuit to measure the current. A typical configuration would be to place the meter in series with the positive DC Volts lead to the amp from the power source. Set the meter to measure DC AMPS. Turn on the amp. The current reading should be zero amps. There will be an initial small surge current that quickly drops to zero. Jumper the TEST jack. The current will be approximately 36mA. Operating the amp in SSB mode requires setting the bias current to.7a. For FM or digital modes, set the bias current to.5a. Connect a 5 ohm load to the OUTPUT and INPUT. Failure to terminate may result in oscillation and high current. Turn the pot slowly clockwise and set the BIAS current. No oscillation or erratic behavior should be observed. 17
18 7.3 Filter Circuit The low pass filter is designed to band stop frequencies above the 6 meter band with notch filters for the 2 nd and 3 rd harmonics. Illustration 4: Low Pass Filter characteristics. 7.4 Alignment of L1 and L2 Alignment of the low pass filter is done by squeezing or pulling L1 and L2 - but only one at a time (see Illustration 5 below). Adjust L1 until the dip is at 15 MHz and similarly for L4 on 1 MHz. The inevitable attenuation in the pass band should not be affected by the tuning of L1 and L2. Otherwise there is something seriously wrong with the coils. If you do not have the necessary instruments to align the filter apply a small but known signal level at 5 MHz and measure it before and after the low pass filter. The maximum attenuation should not exceed 1%. 18
19 Building the filter and L1-L2 according to the directions in this manual shouldhave your inductance will be reasonably close to the schematic values listed. Illustration 5: L1 and L2 low pass filter. 7.5 Power Output Test Attach a Power Out/SWR Meter to the RF Output. Attach a dummy load. Attach a transceiver set to only 1 watt drive on 6M to the RF Input. Monitor the DC Current with a multi-meter set to the AMPs. Connect a 12VDC Source capable of delivering 1A. Momentarily put the transceiver into TUNE (CW signal): RF Power Out should be about 3W SWR should be 1.:1 DC Current should be about 6A 19
20 Illustration 7: Front panel controls. Illustration 6: Rear panel controls. Illustration 8: Inside view of completed amplifier. 2
21 8 Operating Procedure Connect a fused 12VDC source to the amplifier Power Pole inputs. Tune your antenna with the front panel switch in BYPASS. Operate QRP with the switch in BYPASS. Place a meter to measure SWR in series from the RF OUT to the SWR meter and Antenna. The Transceiver driving the amp will see a 5 ohm load and a low SWR when driving the amp with the switch in OPERATE. The TX light will light when a sufficient RF signal triggers the carrier operated T/R switch. Do not exceed 1W of RF drive. The standby current is very low (less than 1 ma). The transmit current will peak about 6A. Do not attempt to operate with the RF Output connector not connected to an antenna or dummy load. If your power exceeds 3W, you should take steps to reduce power out by either reducing drive or lowering the applied DC Voltage. Enjoy! 9 Schematic, Parts List, Templates and Module DataSheet Follow on below. 21
22 6M PACKER AMP Revised: Thursday, Aug 13, 29 Item Quantity Ref Description Part Number Capacitor 5.6pF 5V 5.6pF 14-5N2-5R6C- 1 1 C1 NPO RC 2 1 C2 Capacitor 18pF 5V 18pF NPO 14-5N5-18J-RC 3 1 C3 Capacitor 56pF 5V 56pF NPO 14-5N5-56J-RC 4 1 C4 Capacitor 1pF 5V 1pF NPO 14-5N5-11J-RC 5 1 C5 Capacitor 47pF 5V 47pF NPO 14-5N5-47J-RC 6 2 C6,C9 7 1 C7 8 1 C8 Cap 1pf Kemet Conformally Coated Radial Ceramic Capacitors 1V X7R 8-C315C12K1R ; Vishay Capacitor.1uF Cap,.1uF 1V 1% X7R SR21C14KAR AVX Capacitor.68 uf SMD Cap Cerm.68uf 1% 25V X7R 126 AVX 1263C684KAT2A 8-C315C12K1R Mouser 581- SR21C14KAR ; Allied stk C684K Mouser 9 4 C1,C13, C14,C15 Cap,.1uF SR151C13K AVX 1V 1% 581-SR151C13K AVX 1V 1% 1C1X7R13K5B Vishay Capacitor, Al Electrolytic; 68uF; 25VDC; +/-2%; Radial; 1.mmDia.; 2.mmL; 32VDC Mouser 581- SR151C13K; Allied stk C11 687KXM25M 11 1 C12 Capacitor.68uF 1% 35V 8-T35A684K D D2 J1, 14 4 J2,D1,S J3, J K L1,L2 Standard Recovery Rectifier 1V 1A Standard (Subminiature case) ON Semiconductor 1N47 Mouser 863-1N47G Diode, Schottkey 1N5711 STM Electronics Allied Header.1 K.K. Friction lock Molex CKT 221 KeyStone Electronics.25 PCB TAB 32TPBR Mouser Relay, 12VDC Non-latching Single coil P2 Tyco Electronics/ Axicom FUTURE V2379A13B31 1 TYCO INDUCTOR 24AWG fabricated
23 18 1 L3 Inductor VK2 3A Inductor VK2 3A 19 1 L4 Ferrite Bead EMI/RFI Supressors & Ferrites Fair-Rite EMI Shield Beads 1MHz Fair-Rite Mouser Q1 Amplifier Module RA3H68M 68-88MHz 3W 12V 21 1 Q2 Transistor 2N N Q3 2N589 Small Signal Transistors NPN Gen Pur SS Central Semiconductor 2N N589 Mouser 23 1 R1 Resistor 68ohms 5% Tol RC 24 2 R2, R3 Resistor 1 ohm 5% Tol RC 25 1 VR1 Potentiometer 2 3/8" 2 ohms Sealed 67WR2LF 26 1 R8 Resistor 1K 5% 1/8W Carbon Film XICON 299-1K 299-1K-RC 27 2 R7,R5 Resistor 1K 1/8W 1% Metal Film 1% 5PPM XICON 27-1K-RC Mouser 27-1K-RC 28 1 R6 Resistor 42ohms 1% RC 29 1 T1 Toroid, FT U1 5V Regulator, Fairchild 512- LM78L5ACZ Mouser 512- LM78L5ACZX Switch, Rocker; SPST; VAC, 1 25 VAC; 125/25; On-None-Off Allied DA12J12S215HQF 33 1 Circuit Board HF Projects 34 1 HeatSink, AAVID 64693B46 Norvell 64693B HeatSink Plate HF Projects 36 1 Case Metal Enclosures BOX Black finish Heeger LMB model J Crimp Terminal MOLEX MOLEX Locking Ramp Housing 2P MOLEX AMP Faston Terminals FLAG RECP M Insulated Terminals RING AWG S-P A 41 1 Wire 14AWG RED 11" 42 1 Wire 14AWG BLK 8.5" 43 2 Red 1327 Power Pole Connector Black 1327G6 Power Pole Connector 83-1
24 45 4 Contacts, 3A 1331BK Power Pole Power Pole Plate Set 1462G Screw 4-4 x 1/ Screw 4-4 x 3/ Nut #4 5 2 Washer # G1 ST/ Connector, BNC R.A. JACK 5 OHM Emerson CP194AST Allied Coaxial Connector, UHF, Female Chassis Mount Emerson LED Red Snap-In Allied F 54 4 Foot, Black elastomer; fits all LMB enclosures Mouser 537-F2 Switch, Rocker, ULTRA Miniature, ON-OFF, NO LEGEND Mfr's Part#: PRK22J5BBBNN Allied Stk#: VERT PCB HDR 2P.1 K.K. Mouser hookup wire 8 inch black 58 1 hookup wire 15 inch any color 59 8 T1 FT23-77 Core 6 2 Coax RG174, 6 inch 61 4 Screw, 4-4 x 5/ AWG Enamel wire 9 inch AWG Enamel wire 16 inch 64 Heat Shrink, 1/4 inch V inch Mouser 66 4 M/F Spacer.187 Keystone 7228 Jack Screws, Length.25; No Hardware Allied Lug, Locking Tinned #4 Keystone 93 Terminal; Lockwasher;.12 in.; 3/32 in.; 7/8 in.;.18 in.; 5/16 in. Lug, Locking Tinned #4 Keystone 98 Terminal; Lockwasher; 3/32 in.; 5/8 in.;.18 in ACG TO-22 THERMASIL III Allied Stk#: Allied Stk#: Mouser
25 7 1 Heat Transfer Compound; Silicone; white paste;.14 oz x 1 pkts MG Chemicals 86-4G Allied Sequential Serial Number Techiant LLC
26 D Q1 RA3H68M D C B J1 OUT 1 2 J2 IN 1 2 D2 1N5711 C13.1 1T:26T 3 AWG 15 inch A C T1 F R4 ohms + C12.68uF Q3 2N589 12V D1 1N47 JP1 TEST V R7 1K R5 1K K1 R8 1K Q2 2N C TX D3 U1 78L5 VIN GND 1dB R1 68 R2 1 VOUT 12V R R3 1 1 VR C15.1 C6 1nF C9 1nF 1 2 C7.1uF L3 VK2 3A C V C3 56pF C8.68 uf L4 C uf C1 5.6pF L1 186nH C4 15MHz 1pF C2 18pF L2 139nH C5 1MHz 47pF 2 1 J3 2 1 J4 PWR+ PWR- C B STDBY OPER 1 2 SW1 SW SPST 3 A A Title B HF PROJECTS 29 6M PACKER AMP Size Document Number Rev 6MAV1 Thursday, August 13, Date: Sheet of 1
27 M M CUT OUT 1. TYP. OF 4 D AA A BB A A.35 M M LMB JIFFY BOX J88.. E.25 B A.6.7 E J.95 L E K D 1.47 AA BB 1.81 E A=3/8 inch DIA. B=5/8 inch DIA. D=5/32 inch DIA E=1/8 inch DIA J =.68 x.36 inch rectangle.6 Radius K =.76 x.51 inch rectangle.3 Radius L =. 539 x.362 rectangle.6 Radius M = 3/16 inch DIA, 4 places VHF PACKER 6M AMP VER 29 C:\Documents and Settings\virgil\My Documents\ALL PROJECTS\6M AMP\6M AmpChassis29.cmp.VCD 8/15/29
28 FAB PER LMB JIFFY BOX J88 MATERIAL: ALUM THICK PAINT: GLOSS BLACK POWDER COAT A = 7/32 inch DIA. VHF PACKER 6M AMP 29 HF PROJECTS (rubber feet) A A A A /8 INCH DIMPLE OUT 4 PLACES TYPICAL (Do not drill) C:\DOCUME~1\VIRGIL\MYDOCU~1\ALLPRO~1\6MAMP~1\VHFPAC~1.VCD 8/3/29
29 Material: Heat Sink, AAVID 4.6 x 2.25 inch Drill and Tap 4-4 holes through 18 places HF PROJECTS Heat Sink Modification 7/26/
30 Material: 1/8 inch aluminum, no finish 6 holes: 9/64 inch dia. through HF PROJECTS Heat Sink Plate 7/26/
31 ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA3H68M RoHS Compliance, 66-88MHz 3W 12.5V, 2 stage Amp. for MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA3H68M is a 3-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 12.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the 66- to 88-MHz range. The battery can be connected directly to the drain of the enhancement-mode MOSFET transistors. Without the gate voltage (V GG =V), only a small leakage current flows into the drain and the RF input signal attenuates up to 6 db. The output power and drain current increase as the gate voltage increases. With a gate voltage around 3V (minimum), output power and drain current increases substantially. The nominal output power becomes available at 4V (typical) and 5V (maximum). At V GG =5V, the typical gate current is 1 ma. This module is designed for non-linear FM modulation, but may also be used for linear modulation by setting the drain quiescent current with the gate voltage and controlling the output power with the input power. FEATURES Enhancement-Mode MOSFET Transistors (I V DD =12.5V, V GG =V) P out >3W, η T V DD =12.5V, V GG =5V, P in =5mW Broadband Frequency Range: 66-88MHz Low-Power Control Current I GG =1mA (typ) at V GG =5V Module Size: 66 x 21 x 9.88 mm Linear operation is possible by setting the quiescent drain current with the gate voltage and controlling the output power with the input power BLOCK DIAGRAM RF Input (P in ) 2 Gate Voltage (V GG ), Power Control 3 Drain Voltage (V DD ), Battery 4 RF Output (P out ) 5 RF Ground (Case) PACKAGE CODE: H2S 4 5 RoHS COMPLIANCE RA3H68M-11 is a RoHS compliant products. RoHS compliance is indicate by the letter G after the Lot Marking. This product include the lead in the Glass of electronic parts and the lead in electronic Ceramic parts. How ever,it applicable to the following exceptions of RoHS Directions. 1.Lead in the Glass of a cathode-ray tube, electronic parts, and fluorescent tubes. 2.Lead in electronic Ceramic parts. ORDERING INFORMATION: ORDER NUMBER RA3H68M-11 SUPPLY FORM Antistatic tray, 1 modules/tray RA3H68M MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC 24 Jan 26 1/8
32 ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS MAXIMUM RATINGS (T case =+25 C, unless otherwise specified) RoHS COMPLIANCE MITSUBISHI RF POWER MODULE RA3H68M SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS RATING UNIT V DD Drain Voltage V GG <5V, Z G =Z L =5Ω 17 V V GG Gate Voltage V DD <12.5V, P in =5mW, Z G =Z L =5Ω 6 V P in Input Power f=66-88mhz, V GG <5V 1 mw P out Output Power f=66-88mhz, V GG <5V (Note 2) 45 W T case(op) Operation Case Temperature Range f=66-88mhz, V GG <5V -3 to +11 C T stg Storage Temperature Range -4 to +11 C Note 1: The above parameters are independently guaranteed. Note 2: This device may destroyed in a few minutes when output power from module is more than 45W. Therefore, please keep the output power of device less than 45W even operating under the high load VSWR conditions. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (T case =+25 C, Z G =Z L =5Ω, unless otherwise specified) SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT f Frequency Range MHz P out Output Power 3 W η T Total Efficiency V DD =12.5V 4 % 2f o 2 nd Harmonic V GG =5V P in =5mW -25 dbc ρ in Input VSWR 3:1 I GG Gate Current Stability Load VSWR Tolerance V DD = V, P in =25-7mW, P out <3W (V GG control), Load VSWR=3:1 V DD =15.2V, P in =5mW, P out =3W (V GG control), Load VSWR=2:1(all phase) 1 ma No parasitic oscillation No degradation or destroy All parameters, conditions, ratings, and limits are subject to change without notice. RA3H68M MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC 24 Jan 26 2/8
33 ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS RoHS COMPLIANCE MITSUBISHI RF POWER MODULE RA3H68M TYPICAL PERFORMANCE (T case =+25 C, Z G =Z L =5Ω, unless otherwise specified) OUTPUT POWER Pout(W) INPUT VSWR ρin (-) OUTPUT POWER, TOTAL EFFICIENCY, and INPUT VSWR versus FREQUENCY P out ρ in V DD =12.5V V GG =5V P in =5mW FREQUENCY f(mhz) η T TOTAL EFFICIENCY ηt(%) HARMONICS (dbc) 2 nd, 3 rd HARMONICS versus FREQUENCY rd 2 nd V DD =12.5V V GG =5V P in =5mW FREQUENCY f(mhz) OUTPUT POWER Pout(dBm) POWER GAIN Gp(dB) OUTPUT POWER, POWER GAIN and DRAIN CURRENT versus INPUT POWER Gp I DD P out f=66mhz, 1 V DD =12.5V, 4 V GG =5V INPUT POWER P in (dbm) OUTPUT POWER, POWER GAIN and DRAIN CURRENT versus INPUT POWER DRAIN CURRENT IDD(A) OUTPUT POWER Pout(dBm) POWER GAIN Gp(dB) OUTPUT POWER, POWER GAIN and DRAIN CURRENT versus INPUT POWER Gp I DD f=77mhz, V DD =12.5V, V GG =5V INPUT POWER P in (dbm) P out DRAIN CURRENT I DD (A) OUTPUT POWER Pout(dBm) POWER GAIN Gp(dB) Gp I DD f=88mhz, 1 4 V DD =12.5V, V GG =5V INPUT POWER P in (dbm) P out DRAIN CURRENT IDD(A) OUTPUT POWER Pout(W) OUTPUT POWER and DRAIN CURRENT versus DRAIN VOLTAGE f=66mhz, V GG =5V, P in =5mW P out I DD DRAIN VOLTAGE V DD (V) DRAIN CURRENT IDD(A) OUTPUT POWER Pout(W) OUTPUT POWER and DRAIN CURRENT versus DRAIN VOLTAGE f=77mhz, V GG =5V, P in =5mW P out I DD DRAIN VOLTAGE V DD (V) DRAIN CURRENT IDD(A) RA3H68M MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC 24 Jan 26 3/8
34 ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS RoHS COMPLIANCE MITSUBISHI RF POWER MODULE RA3H68M TYPICAL PERFORMANCE (T case =+25 C, Z G =Z L =5Ω, unless otherwise specified) OUTPUT POWER Pout(W) OUTPUT POWER and DRAIN CURRENT versus DRAIN VOLTAGE f=88mhz, V GG =5V, P in =5mW P out I DD DRAIN VOLTAGE V DD (V) DRAIN CURRENT IDD(A) OUTPUT POWER Pout(W) OUTPUT POWER and DRAIN CURRENT versus GATE VOLTAGE f=66mhz, V DD =12.5V, P in =5mW P out I DD GATE VOLTAGE V GG (V) DRAIN CURRENT IDD(A) OUTPUT POWER Pout(W) OUTPUT POWER and DRAIN CURRENT versus GATE VOLTAGE f=77mhz, V DD =12.5V, P in =5mW P out I DD GATE VOLTAGE V GG (V) DRAIN CURRENT IDD(A) OUTPUT POWER Pout(W) OUTPUT POWER and DRAIN CURRENT versus GATE VOLTAGE f=88mhz, V DD =12.5V, P in =5mW P out I DD GATE VOLTAGE V GG (V) DRAIN CURRENT IDD(A) RA3H68M MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC 24 Jan 26 4/8
35 ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS RoHS COMPLIANCE MITSUBISHI RF POWER MODULE RA3H68M OUTLINE DRAWING (mm) 66. ±.5 3. ± ±.8 6. ± ±.5 2-R2 ± ±1 21. ± ±.5 2. ± Ø.45 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± /-.4.9 ± ±.5 (9.88) 2.3 ±.3 (5.4) 1 RF Input (P in ) 2 Gate Voltage (V GG ) 3 Drain Voltage (V DD ) 4 RF Output (P out ) 5 RF Ground (Case) RA3H68M MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC 24 Jan 26 5/8
36 ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS RoHS COMPLIANCE MITSUBISHI RF POWER MODULE RA3H68M TEST BLOCK DIAGRAM Power Meter DUT 5 Spectrum Analyzer Signal Generator Attenuator Preamplifier Attenuator Directional Coupler Z G =5Ω Z L =5Ω Directional Coupler Attenuator Power Meter C1 C2 C1, C2: 47pF, 22uF in parallel - + DC Power Supply V GG + - DC Power Supply V DD 1 RF Input (P in ) 2 Gate Voltage (V GG ) 3 Drain Voltage (V DD ) 4 RF Output (P out ) 5 RF Ground (Case) EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT RA3H68M MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC 24 Jan 26 6/8
37 ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS RoHS COMPLIANCE MITSUBISHI RF POWER MODULE RA3H68M PRECAUTIONS, RECOMMENDATIONS, and APPLICATION INFORMATION: Construction: This module consists of an alumina substrate soldered onto a copper flange. For mechanical protection, a plastic cap is attached with silicone. The MOSFET transistor chips are die bonded onto metal, wire bonded to the substrate, and coated with resin. Lines on the substrate (eventually inductors), chip capacitors, and resistors form the bias and matching circuits. Wire leads soldered onto the alumina substrate provide the DC and RF connection. Following conditions must be avoided: a) Bending forces on the alumina substrate (for example, by driving screws or from fast thermal changes) b) Mechanical stress on the wire leads (for example, by first soldering then driving screws or by thermal expansion) c) Defluxing solvents reacting with the resin coating on the MOSFET chips (for example, Trichloroethylene) d) Frequent on/off switching that causes thermal expansion of the resin e) ESD, surge, overvoltage in combination with load VSWR, and oscillation ESD: This MOSFET module is sensitive to ESD voltages down to 1V. Appropriate ESD precautions are required. Mounting: Heat sink flatness must be less than 5 µm (a heat sink that is not flat or particles between module and heat sink may cause the ceramic substrate in the module to crack by bending forces, either immediately when driving screws or later when thermal expansion forces are added). A thermal compound between module and heat sink is recommended for low thermal contact resistance and to reduce the bending stress on the ceramic substrate caused by the temperature difference to the heat sink. The module must first be screwed to the heat sink, then the leads can be soldered to the printed circuit board. M3 screws are recommended with a tightening torque of.4 to.6 Nm. Soldering and Defluxing: This module is designed for manual soldering. The leads must be soldered after the module is screwed onto the heat sink. The temperature of the lead (terminal) soldering should be lower than 35 C and shorter than 3 second. Ethyl Alcohol is recommend for removing flux. Trichloroethylene solvents must not be used (they may cause bubbles in the coating of the transistor chips which can lift off the bond wires). Thermal Design of the Heat Sink: At P out =3W, V DD =12.5V and P in =5mW each stage transistor operating conditions are: Stage P in (W) P out (W) R th(ch-case) ( C/W) I η T =4% (A) 1 st nd The channel temperatures of each stage transistor T ch = T case + (V DD x I DD - P out + P in ) x R th(ch-case) are: T ch1 = T case + (12.5V x.36a - 3.W +.5W) x 23. C/W = T case C T ch2 = T case + (12.5V x 5.6A - 3.W + 3.W) x 1.2 C/W = T case C For long-term reliability, it is best to keep the module case temperature (T case ) below 9 C. For an ambient temperature T air =6 C and P out =3W, the required thermal resistance R th (case-air) = ( T case - T air ) / ( (P out / η T ) - P out + P in ) of the heat sink, including the contact resistance, is: R th(case-air) = (9 C - 6 C) / (3W/4% 3W +.5W) =.67 C/W When mounting the module with the thermal resistance of.67 C/W, the channel temperature of each stage transistor is: T ch1 = T air C T ch2 = T air C The 175 C maximum rating for the channel temperature ensures application under derated conditions. V DD (V) RA3H68M MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC 24 Jan 26 7/8
38 ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS RoHS COMPLIANCE MITSUBISHI RF POWER MODULE RA3H68M Output Power Control: Depending on linearity, the following two methods are recommended to control the output power: a) Non-linear FM modulation: By the gate voltage (V GG ). When the gate voltage is close to zero, the RF input signal is attenuated up to 6 db and only a small leakage current flows from the battery into the drain. Around V GG =3V, the output power and drain current increases substantially. Around V GG =4V (typical) to V GG =5V (maximum), the nominal output power becomes available. b) Linear AM modulation: By RF input power P in. The gate voltage is used to set the drain s quiescent current for the required linearity. Oscillation: To test RF characteristics, this module is put on a fixture with two bias decoupling capacitors each on gate and drain, a 4.7 pf chip capacitor, located close to the module, and a 22 µf (or more) electrolytic capacitor. When an amplifier circuit around this module shows oscillation, the following may be checked: a) Do the bias decoupling capacitors have a low inductance pass to the case of the module? b) Is the load impedance Z L =5Ω? c) Is the source impedance Z G =5Ω? Frequent on/off switching: In base stations, frequent on/off switching can cause thermal expansion of the resin that coats the transistor chips and can result in reduced or no output power. The bond wires in the resin will break after long-term thermally induced mechanical stress. Quality: Mitsubishi Electric is not liable for failures resulting from base station operation time or operating conditions exceeding those of mobile radios. This module technology results from more than 2 years of experience, field proven in tens of millions of mobile radios. Currently, most returned modules show failures such as ESD, substrate crack, and transistor burnout, which are caused by improper handling or exceeding recommended operating conditions. Few degradation failures are found. Keep safety first in your circuit designs! Mitsubishi Electric Corporation puts the maximum effort into making semiconductor products better and more reliable, but there is always the possibility that trouble may occur. Trouble with semiconductors may lead to personal injury, fire or property damage. Remember to give due consideration to safety when making your circuit designs, with appropriate measures such as (i) placement of substitutive, auxiliary circuits, (ii) use of non-flammable material, or (iii) prevention against any malfunction or mishap. RA3H68M MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC 24 Jan 26 8/8
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA30H1317M
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA3H1317M RoHS Compliance, 135-175MHz 3W 1.5V Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA3H1317M is a 3-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA3H1317M RoHS Compliance, 135-175MHz 3W 1.5V Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA3H1317M is a 3-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA45H4047M
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA5H7M RoHS Compliance, -7MHz 5W.5V, 3 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA5H7M is a 5-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA5H7M RoHS Compliance, -7MHz 5W.5V, 3 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA5H7M is a 5-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA30H1317M1. RoHS Compliance, MHz 30W 12.5V 2 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA3H1317M1 RoHS Compliance, 135-175MHz 3W 1.5V Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO TENTATIVE DESCRIPTION The RA3H1317M1 is a 3-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA3H1317M1 RoHS Compliance, 135-175MHz 3W 1.5V Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO TENTATIVE DESCRIPTION The RA3H1317M1 is a 3-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA07H0608M
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA7H8M RoHS Compliance,8-88MHz 7W.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA7H8M is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt portable radios that operate in the
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA7H8M RoHS Compliance,8-88MHz 7W.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA7H8M is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt portable radios that operate in the
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA07M3843M
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA7MM RoHS Compliance, 7-MHz 7W 7.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA7MM is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 7.-volt portable radios that operate in the
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA7MM RoHS Compliance, 7-MHz 7W 7.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA7MM is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 7.-volt portable radios that operate in the
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA07M4047MSA
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RoHS Compliance, -7MHz 7.W 7.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 7.-volt portable radios that operate in the - to 7-MHz
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RoHS Compliance, -7MHz 7.W 7.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 7.-volt portable radios that operate in the - to 7-MHz
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA33H1516M1
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RoHS Compliance, 15-1MHz 33W 1.5V Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a 33watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5volt mobile radios that operate in the 15- to 1MHz
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RoHS Compliance, 15-1MHz 33W 1.5V Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a 33watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5volt mobile radios that operate in the 15- to 1MHz
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA7H7M -7MHz 7W.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE/ MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA7H7M is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt portable/ mobile radios that operate in the
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA7H7M -7MHz 7W.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE/ MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA7H7M is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt portable/ mobile radios that operate in the
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE -7MHz 7W 7.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 7.-volt portable radios that operate in the - to 7-MHz range. The battery
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE -7MHz 7W 7.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 7.-volt portable radios that operate in the - to 7-MHz range. The battery
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE 135-175MHz 8W 12.5V PORTABLE/MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a 8-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 12.5-volt portable/ mobile radios that operate in the 135- to 175-MHz range.
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE 135-175MHz 8W 12.5V PORTABLE/MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a 8-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 12.5-volt portable/ mobile radios that operate in the 135- to 175-MHz range.
RA30H4452M MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE 1/9 ELECTROSTATIC SENSITIVE DEVICE OBSERVE HANDLING PRECAUTIONS MHz 30W 12.
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA3H5M -5MHz 3W 1.5V MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA3H5M is a 3-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the - to 5-MHz range. The battery
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA3H5M -5MHz 3W 1.5V MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA3H5M is a 3-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the - to 5-MHz range. The battery
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA35H1516M
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RoHS Compliance, 15-1MHz W 1.5V, Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the 15- to 1-MHz
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RoHS Compliance, 15-1MHz W 1.5V, Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the 15- to 1-MHz
<Silicon RF Power Modules > RA55H4452M RoHS Compliance, MHz 55W 12.5V, 3 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO
 RAHM RoHS Compliance, -MHz W.V, 3 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RAHM is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt mobile radios that operate in the - to -MHz range. The battery can be
RAHM RoHS Compliance, -MHz W.V, 3 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RAHM is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt mobile radios that operate in the - to -MHz range. The battery can be
<Silicon RF Power Modules > RA60H1317M RoHS Compliance, MHz 60W 12.5V, 3 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO
 RAH1317M RoHS Compliance, 13-17MHz W 1.V, 3 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RAH1317M is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.-volt mobile radios that operate in the 13- to 17-MHz range.
RAH1317M RoHS Compliance, 13-17MHz W 1.V, 3 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RAH1317M is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.-volt mobile radios that operate in the 13- to 17-MHz range.
<Silicon RF Power Modules > RA30H1721M RoHS Compliance, MHz 30W 12.5V, 2 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION
 RA3H171M RoHS Compliance, 17-1MHz 3W 1.V, Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA3H171M is a 3-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.-volt mobile radios that operate in the 17- to 1-MHz range. The
RA3H171M RoHS Compliance, 17-1MHz 3W 1.V, Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA3H171M is a 3-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.-volt mobile radios that operate in the 17- to 1-MHz range. The
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE 15-1MHz W 1.5V, Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the 15- to 1-MHz range. The battery
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE 15-1MHz W 1.5V, Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the 15- to 1-MHz range. The battery
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE -MHz 5W 1.5V, 3 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a 5-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the - to -MHz range. The battery
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE -MHz 5W 1.5V, 3 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a 5-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the - to -MHz range. The battery
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA3H17M 1-7MHz 3W 1.5V, Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA3H17M is a 3-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the 1- to 7-MHz
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA3H17M 1-7MHz 3W 1.5V, Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA3H17M is a 3-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the 1- to 7-MHz
07H4452M RA07H4452. Silicon RF Power Semiconductors 1/9. RoHS Compliance, MHz 7W 12.5V, 2 Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO
 RA7H 7HM RoHS Compliance,-MHz 7W.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA7HM is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt portable radios that operate in the - to -MHz range. The battery
RA7H 7HM RoHS Compliance,-MHz 7W.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA7HM is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt portable radios that operate in the - to -MHz range. The battery
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA01L9595M
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA1L9595M RoHS Compliance, 952-954MHz 1.4W 3.3V, 2 Stage Amp. For RFID READER / WRITER DESCRIPTION The RA1L9595M is a 1.4-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module. The battery can be
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA1L9595M RoHS Compliance, 952-954MHz 1.4W 3.3V, 2 Stage Amp. For RFID READER / WRITER DESCRIPTION The RA1L9595M is a 1.4-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module. The battery can be
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA7M7M -7MHz 7W 7.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA7M7M is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 7.-volt portable radios that operate in the - to 7-MHz range.
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA7M7M -7MHz 7W 7.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA7M7M is a 7-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 7.-volt portable radios that operate in the - to 7-MHz range.
Silicon RF Power Semiconductors RA03M4547MD
 RoHS Compliance, 45-47MHz 38dBm 7.2V, 2 Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a 38 dbm output RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 7.2 volt portable radios that operate in the 45 to 47 MHz range.
RoHS Compliance, 45-47MHz 38dBm 7.2V, 2 Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The is a 38 dbm output RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 7.2 volt portable radios that operate in the 45 to 47 MHz range.
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA60H4047M1
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RAH7M RoHS Compliance, -7MHz W.V, Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RAH7M is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt mobile radios that operate in the - to 7-MHz
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RAH7M RoHS Compliance, -7MHz W.V, Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RAH7M is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt mobile radios that operate in the - to 7-MHz
< Silicon RF Power Modules > RA33H1516M1 RoHS Compliance, MHz 33W 12.5V 2 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO
 DESCRIPTION The is a 33watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5volt mobile radios that operate in the 15- to 1MHz range. The battery can be connected directly to the drain of the enhancement-mode MOSFET
DESCRIPTION The is a 33watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5volt mobile radios that operate in the 15- to 1MHz range. The battery can be connected directly to the drain of the enhancement-mode MOSFET
< Silicon RF Power Modules > RA60H3847M1 RoHS Compliance, MHz 60W 12.5V, 2 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO
 DESCRIPTION The is a 60-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 12.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the 378- to 470-MHz range. The battery can be connected directly to the drain of the enhancement-mode
DESCRIPTION The is a 60-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 12.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the 378- to 470-MHz range. The battery can be connected directly to the drain of the enhancement-mode
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA3H47M -47MHz 3W 12.5V MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA3H47M is a 3-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 12.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the - to 47-MHz range. The battery
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA3H47M -47MHz 3W 12.5V MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA3H47M is a 3-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 12.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the - to 47-MHz range. The battery
<Silicon RF Power Modules > RA08H1317M RoHS Compliance, MHz 8W 12.5V, 2 Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO
 DESCRIPTION The is a 8-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 12.5-volt portable radios that operate in the 135- to 175-MHz range. The battery can be connected directly to the drain of the enhancement-mode
DESCRIPTION The is a 8-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 12.5-volt portable radios that operate in the 135- to 175-MHz range. The battery can be connected directly to the drain of the enhancement-mode
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE
 MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA1H113G 1.-1.3GHz 1W 1.5V, 3 stage amplifier for MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA1H113G is a 1-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the
MITSUBISHI RF MOSFET MODULE RA1H113G 1.-1.3GHz 1W 1.5V, 3 stage amplifier for MOBILE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RA1H113G is a 1-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the
Assembly Instructions for the FRB FET FM 70 Watt Amp
 Assembly Instructions for the FRB FET FM 70 Watt Amp 1.) Orient the circuit board with the diagram 2.) Use a narrow chisel tip 25-30 watt soldering iron for assembly 3.) All the small parts are taped onto
Assembly Instructions for the FRB FET FM 70 Watt Amp 1.) Orient the circuit board with the diagram 2.) Use a narrow chisel tip 25-30 watt soldering iron for assembly 3.) All the small parts are taped onto
< Silicon RF Power Modules > RA60H4452M1 RoHS Compliance, MHz 60W 12.5V, 2 Stage Amp. For MOBILE RADIO
 DESCRIPTION The is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the - to -MHz range. The battery can be connected directly to the drain of the enhancement-mode MOSFET transistors.
DESCRIPTION The is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt mobile radios that operate in the - to -MHz range. The battery can be connected directly to the drain of the enhancement-mode MOSFET transistors.
Assembly Instructions for the 1.5 Watt Amplifier Kit
 Assembly Instructions for the 1.5 Watt Amplifier Kit 1.) All of the small parts are attached to a sheet of paper indicating both their value and id. 2.) Leave the parts affixed to the paper until you are
Assembly Instructions for the 1.5 Watt Amplifier Kit 1.) All of the small parts are attached to a sheet of paper indicating both their value and id. 2.) Leave the parts affixed to the paper until you are
Read This Page First
 Read This Page First If you are reading this you know the manuals are always available at QRPKITS.com. If you have questions contact qrpkits.com@gmail.com There is no need to print out the whole assembly
Read This Page First If you are reading this you know the manuals are always available at QRPKITS.com. If you have questions contact qrpkits.com@gmail.com There is no need to print out the whole assembly
Read This Page First
 Pacific Antenna 0 Watt HF Amplifier Kit Manual This is Version 5.5 dated 060505 Read This Page First If you are reading this you know the manuals are always available at QRPKITS.com. If you have questions
Pacific Antenna 0 Watt HF Amplifier Kit Manual This is Version 5.5 dated 060505 Read This Page First If you are reading this you know the manuals are always available at QRPKITS.com. If you have questions
< Silicon RF Power Modules > RA60H1317M1B RoHS Compliance, MHz 60W 12.5V, 2 Stage Amp. for Digital Mobile Radio
 RAH1317M1B RoHS Compliance, 13-17MHz W.5V, Stage Amp. for Digital Mobile Radio DESCRIPTION The RAH1317M1B is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.5-volt digital mobile radios of TDMA that operate in
RAH1317M1B RoHS Compliance, 13-17MHz W.5V, Stage Amp. for Digital Mobile Radio DESCRIPTION The RAH1317M1B is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.5-volt digital mobile radios of TDMA that operate in
Pacific Antenna 10 Watt HF Amplifier Kit
 Pacific Antenna 0 Watt HF Amplifier Kit Description Our 0 watt Linear, HF amplifier kit is designed to increase the power output of low power transmitters. Gives up to 5dB gain and includes an input attenuator
Pacific Antenna 0 Watt HF Amplifier Kit Description Our 0 watt Linear, HF amplifier kit is designed to increase the power output of low power transmitters. Gives up to 5dB gain and includes an input attenuator
Easy Transmitter. Support ETX_REV5_Manual V2.7 Revised
 Easy Transmitter Introduction The Easy Transmitter kit from qrpkits.com provides a basic, crystal controlled transmitter with VXO tuning to provide a small tuning range around the crystal frequency. It
Easy Transmitter Introduction The Easy Transmitter kit from qrpkits.com provides a basic, crystal controlled transmitter with VXO tuning to provide a small tuning range around the crystal frequency. It
< Silicon RF Power Modules > RA03M8087M RoHS Compliance, MHz 3.6W 7.2V, 2 Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO
 RAMM RoHS Compliance, -MHz.W.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RAMM is a.-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt portable radios that operate in the to -MHz range. The battery can be
RAMM RoHS Compliance, -MHz.W.V, Stage Amp. For PORTABLE RADIO DESCRIPTION The RAMM is a.-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt portable radios that operate in the to -MHz range. The battery can be
Pacific Antenna Easy Transmitter Kit
 Pacific Antenna Easy Transmitter Kit Introduction The Easy Transmitter kit from qrpkits.com provides a crystal controlled transmitter with VXO tuning. The circuit consists of a N3904 based crystal oscillator
Pacific Antenna Easy Transmitter Kit Introduction The Easy Transmitter kit from qrpkits.com provides a crystal controlled transmitter with VXO tuning. The circuit consists of a N3904 based crystal oscillator
Read This Page First
 Read This Page First If you are reading this you know the manuals are always available at QRPKITS.com. This is version 8.0 of the manual dated 4/27/2016. There is no need to print out the whole assembly
Read This Page First If you are reading this you know the manuals are always available at QRPKITS.com. This is version 8.0 of the manual dated 4/27/2016. There is no need to print out the whole assembly
SoftRock v6.0 Builder s Notes. May 22, 2006
 SoftRock v6.0 Builder s Notes May 22, 2006 Be sure to use a grounded tip soldering iron in building the v6.0 SoftRock circuit board. The soldering iron needs to have a small tip, (0.05-0.1 inch diameter),
SoftRock v6.0 Builder s Notes May 22, 2006 Be sure to use a grounded tip soldering iron in building the v6.0 SoftRock circuit board. The soldering iron needs to have a small tip, (0.05-0.1 inch diameter),
RF Linear Amplifier PCB Assembly Manual
 Page 1 of 46 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Required Parts List... 4 Before You Start... 6 Assembly Instructions... 7 Step #1 - Spacer (SPACER1, SPACER2, SPACER3, SPACER4)... 7 Step #2 - Transformer
Page 1 of 46 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Required Parts List... 4 Before You Start... 6 Assembly Instructions... 7 Step #1 - Spacer (SPACER1, SPACER2, SPACER3, SPACER4)... 7 Step #2 - Transformer
WA3RNC 30 METER CRYSTALPLEXER TRANSMITTER KIT ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
 WA3RNC 30 METER CRYSTALPLEXER TRANSMITTER KIT ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS Description The WA3RNC 30 Meter Crystalplexer is a low power crystal controlled QRP transmitter offering a significantly improved tuning
WA3RNC 30 METER CRYSTALPLEXER TRANSMITTER KIT ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS Description The WA3RNC 30 Meter Crystalplexer is a low power crystal controlled QRP transmitter offering a significantly improved tuning
Pacific Antenna Field Strength Indicator Kit
 Pacific Antenna Field Strength Indicator Kit Description The Field Strength Indicator kit from Pacific Antenna provides a visual way to monitor the presence and relative strength RF fields through the
Pacific Antenna Field Strength Indicator Kit Description The Field Strength Indicator kit from Pacific Antenna provides a visual way to monitor the presence and relative strength RF fields through the
Pacific Antenna Easy TR Switch
 Pacific Antenna Easy TR Switch Kit Description The Easy TR Switch is an RF sensing circuit with a double pole double throw relay that can be used to automatically switch an antenna between a separate receiver
Pacific Antenna Easy TR Switch Kit Description The Easy TR Switch is an RF sensing circuit with a double pole double throw relay that can be used to automatically switch an antenna between a separate receiver
Building the Sawdust Regenerative Receiver
 Building the Sawdust Regenerative Receiver Introduction The Sawdust is a super regenerative receiver using the basic Armstrong design architecture. The receiver uses one toroidal transformer to provide
Building the Sawdust Regenerative Receiver Introduction The Sawdust is a super regenerative receiver using the basic Armstrong design architecture. The receiver uses one toroidal transformer to provide
HF SuperPacker Pro 100W Amp Low Pass Filter Module LPF-100 R3B. Construction Manual for Model LPF-100 R3B June 22, 2013
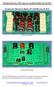 HF SuperPacker Pro W Amp Low Pass Filter Module LPF- RB Construction Manual for Model LPF- RB June, LPF RB TOP LPF RB BOTTOM The LPF- RB design is electrically the same as RA but has been changed for improved
HF SuperPacker Pro W Amp Low Pass Filter Module LPF- RB Construction Manual for Model LPF- RB June, LPF RB TOP LPF RB BOTTOM The LPF- RB design is electrically the same as RA but has been changed for improved
PM124 Installation Instructions. See important note about revisions of this board on the last page.
 Marchand Electronics Inc. PO Box 473, Webster, NY 14580 Tel:(716) 872-0980 Fax:(716) 872-1960 info@marchandelec.com http://www.marchandelec.com (c)1997 Marchand Electronics Inc. PM124 Installation Instructions
Marchand Electronics Inc. PO Box 473, Webster, NY 14580 Tel:(716) 872-0980 Fax:(716) 872-1960 info@marchandelec.com http://www.marchandelec.com (c)1997 Marchand Electronics Inc. PM124 Installation Instructions
Pacific Antenna - Easy TR Switch
 Pacific Antenna - Easy TR Switch Kit Description The Easy TR Switch is an RF sensing switch that can be used to switch an antenna between a receiver and transmitter. It also has a second switched pair
Pacific Antenna - Easy TR Switch Kit Description The Easy TR Switch is an RF sensing switch that can be used to switch an antenna between a receiver and transmitter. It also has a second switched pair
DEM Part Number L144-28INTCK 144 MHz Transverter Kit and complete kit
 DEM Part Number L144-28INTCK 144 MHz Transverter Kit and complete kit Power Out: Noise Figure and Gain: DC Power Requirement: 50 mw linear minimum 3.5 db NF nominal, 5 dbg maximum 12-15.5 VDC, 13.8 nominal
DEM Part Number L144-28INTCK 144 MHz Transverter Kit and complete kit Power Out: Noise Figure and Gain: DC Power Requirement: 50 mw linear minimum 3.5 db NF nominal, 5 dbg maximum 12-15.5 VDC, 13.8 nominal
LED Field Strength Indicator Kit
 LED Field Strength Indicator Kit Description The Field Strength Indicator kit from Qrpkits.com provides a visual way to monitor RF fields through the brightness of an LED. It will respond to RF fields
LED Field Strength Indicator Kit Description The Field Strength Indicator kit from Qrpkits.com provides a visual way to monitor RF fields through the brightness of an LED. It will respond to RF fields
Building the Sawdust Regenerative Receiver
 Building the Sawdust Regenerative Receiver Introduction The Sawdust is a super regenerative receiver using the basic Armstrong design architecture. The receiver uses one toroidal transformer to provide
Building the Sawdust Regenerative Receiver Introduction The Sawdust is a super regenerative receiver using the basic Armstrong design architecture. The receiver uses one toroidal transformer to provide
SUBJECT: PRECAUTIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC SILICON RF POWER SEMICONDUCTORS GENERAL:
 APPLICATION NOTE Silicon RF Power Document NO. Date : 30 th May 2001 Rev. date : 22 th.jun. 2010 Prepared : K. Kajiwara T.Okawa Confirmed : T. Okawa (Taking charge of Silicon RF by MIYOSHI Electronics)
APPLICATION NOTE Silicon RF Power Document NO. Date : 30 th May 2001 Rev. date : 22 th.jun. 2010 Prepared : K. Kajiwara T.Okawa Confirmed : T. Okawa (Taking charge of Silicon RF by MIYOSHI Electronics)
G6ALU 20W FET PA Construction Information
 G6ALU 20W FET PA Construction Information The requirement This amplifier was designed specifically to complement the Pic-A-Star transceiver developed by Peter Rhodes G3XJP. From the band pass filter an
G6ALU 20W FET PA Construction Information The requirement This amplifier was designed specifically to complement the Pic-A-Star transceiver developed by Peter Rhodes G3XJP. From the band pass filter an
SoftRock v6.0 Builder s Notes. April 6, 2006
 SoftRock v6.0 Builder s Notes April 6, 006 Be sure to use a grounded tip soldering iron in building the v6.0 SoftRock circuit board. The soldering iron needs to have a small tip, (0.05-0. inch diameter),
SoftRock v6.0 Builder s Notes April 6, 006 Be sure to use a grounded tip soldering iron in building the v6.0 SoftRock circuit board. The soldering iron needs to have a small tip, (0.05-0. inch diameter),
THE AGGRESSOR (K-995)
 THE AGGRESSOR (K-99) TONE VOLUME DISTORTION MID-SHIFT SWITCH LED The Aggressor Distortion Pedal Modkitsdiy.com 9 VDC CENTER (-) ADAPTER TO AMP IN FROM GUITAR OUT Unplug when not in use to save battery
THE AGGRESSOR (K-99) TONE VOLUME DISTORTION MID-SHIFT SWITCH LED The Aggressor Distortion Pedal Modkitsdiy.com 9 VDC CENTER (-) ADAPTER TO AMP IN FROM GUITAR OUT Unplug when not in use to save battery
KN-Q10 Assembly Manual
 KN-Q10 Assembly Manual Translated by Adam Rong, BD6CR/4 with permission from Ke Shi, BA6BF Edited by Stephen, VK2RH Revision B, Oct 14, 2010 Thank you for purchasing the KN-Q10 4 Band SSB/CW Dual Mode
KN-Q10 Assembly Manual Translated by Adam Rong, BD6CR/4 with permission from Ke Shi, BA6BF Edited by Stephen, VK2RH Revision B, Oct 14, 2010 Thank you for purchasing the KN-Q10 4 Band SSB/CW Dual Mode
< Silicon RF Power Modules > RA30H4452M1A RoHS Compliance, MHz 30W 12.5V, 2 Stage Amp. For Digital Mobile Radio
 DESCRIPTION The is a 30-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 12.5-volt digital mobile radios of TDMA that operate in the 440- to 520-MHz range. The battery can be connected directly to the drain of the
DESCRIPTION The is a 30-watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 12.5-volt digital mobile radios of TDMA that operate in the 440- to 520-MHz range. The battery can be connected directly to the drain of the
Assembly Instructions
 Assembly Instructions For the SSQ-2F 3.1 MHz Rife Controller Board Kit v1.41 Manual v1.00 2012 by Ralph Hartwell Spectrotek Services GENERAL ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS Arrange for a clean work surface with
Assembly Instructions For the SSQ-2F 3.1 MHz Rife Controller Board Kit v1.41 Manual v1.00 2012 by Ralph Hartwell Spectrotek Services GENERAL ASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS Arrange for a clean work surface with
< Silicon RF Power Modules > RA60H4452M1A RoHS Compliance, MHz 60W 12.5V, 2 Stage Amp. For Digital Mobile Radio
 RAH5M1A RoHS Compliance, -5MHz W 1.5V, Stage Amp. For Digital Mobile Radio DESCRIPTION The RAH5M1A is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt digital mobile radios of TDMA that operate in the-
RAH5M1A RoHS Compliance, -5MHz W 1.5V, Stage Amp. For Digital Mobile Radio DESCRIPTION The RAH5M1A is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for 1.5-volt digital mobile radios of TDMA that operate in the-
HAMTRONICS LPA 2-25R REPEATER POWER AMPLIFIER: ASSEMBLY, INSTALLATION, & MAINTENANCE
 HAMTRONICS LPA 2-25R REPEATER POWER AMPLIFIER: ASSEMBLY, INSTALLATION, & MAINTENANCE GENERAL INFORMATION. The Power Amplifier is a class C device designed to be installed as an integral part of a transmitter
HAMTRONICS LPA 2-25R REPEATER POWER AMPLIFIER: ASSEMBLY, INSTALLATION, & MAINTENANCE GENERAL INFORMATION. The Power Amplifier is a class C device designed to be installed as an integral part of a transmitter
Pacific Antenna Low Pass Filter Kit
 Pacific Antenna Low Pass Filter Kit Description Many basic transmitter and/or transceiver designs have minimal filtering on their output and frequently have significant harmonic content in their signals.
Pacific Antenna Low Pass Filter Kit Description Many basic transmitter and/or transceiver designs have minimal filtering on their output and frequently have significant harmonic content in their signals.
QRPGuys Michigan Mighty Might Plus 40M Transmitter
 QRPGuys Michigan Mighty Might Plus 40M Transmitter First, familiarize yourself with the parts and check for all the components. If a part is missing, please contact us and we will send one. You must use
QRPGuys Michigan Mighty Might Plus 40M Transmitter First, familiarize yourself with the parts and check for all the components. If a part is missing, please contact us and we will send one. You must use
QRP to 30-35W HF Packer Amp minihfpa Edition. Beat the downturn in HF conditions! Make your SOTA/NPOTA/WWF activations a success every time!
 QRP to 30-35W HF Packer Amp minihfpa Edition Beat the downturn in HF conditions! Make your SOTA/NPOTA/WWF activations a success every time! The minihfpa is a 5th generation HF PackerAmp optimized for your
QRP to 30-35W HF Packer Amp minihfpa Edition Beat the downturn in HF conditions! Make your SOTA/NPOTA/WWF activations a success every time! The minihfpa is a 5th generation HF PackerAmp optimized for your
PM24 Installation Instructions
 Marchand Electronics Inc. PO Box 473, Webster, NY 14580 Tel:(716) 872-0980 Fax:(716) 872-1960 info@marchandelec.com http://www.marchandelec.com (c)1997 Marchand Electronics Inc. PM24 Installation Instructions
Marchand Electronics Inc. PO Box 473, Webster, NY 14580 Tel:(716) 872-0980 Fax:(716) 872-1960 info@marchandelec.com http://www.marchandelec.com (c)1997 Marchand Electronics Inc. PM24 Installation Instructions
< Silicon RF Power Modules > RA30H1317M1A RoHS Compliance, MHz 30W 12.5V, 2 Stage Amp. for Digital Mobile Radio
 RAHMA RoHS Compliance, -MHz W.V, Stage Amp. for Digital Mobile Radio DESCRIPTION The RAHMA is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt digital mobile radios of TDMA that operate in the - to -MHz range.
RAHMA RoHS Compliance, -MHz W.V, Stage Amp. for Digital Mobile Radio DESCRIPTION The RAHMA is a -watt RF MOSFET Amplifier Module for.-volt digital mobile radios of TDMA that operate in the - to -MHz range.
SoftRock v5.0 Builder s Notes. December 12, Building a QSD Kit
 SoftRock v5.0 Builder s Notes December 12, 2005 Building a QSD Kit Be sure to use a grounded tip soldering iron in building the QSD board. The soldering iron needs to have a small tip, (0.05-0.1 inch diameter),
SoftRock v5.0 Builder s Notes December 12, 2005 Building a QSD Kit Be sure to use a grounded tip soldering iron in building the QSD board. The soldering iron needs to have a small tip, (0.05-0.1 inch diameter),
QRPme.com Kits. Tx/Tuna Topper. Assembly and Operation Guide. Kits for the QRP and Electronics Hobbyist. Heatsink left off for better assembly viewing
 QRPme.com Kits Kits for the QRP and Electronics Hobbyist Tx/Tuna Topper Heatsink left off for better assembly viewing QRMme.com Kits Tx/Tuna Topper Contents Figures and Illustrations...............................
QRPme.com Kits Kits for the QRP and Electronics Hobbyist Tx/Tuna Topper Heatsink left off for better assembly viewing QRMme.com Kits Tx/Tuna Topper Contents Figures and Illustrations...............................
HFpacker Amplifier Project Manual
 HFpacker Amplifier Project Manual (Manual version: Sept. 2003) Virgil Stamps K5OOR and volunteers HFpacker-Amp 1 Introduction Welcome all builders to the homebrew Hfpacker-Amp Project. This project and
HFpacker Amplifier Project Manual (Manual version: Sept. 2003) Virgil Stamps K5OOR and volunteers HFpacker-Amp 1 Introduction Welcome all builders to the homebrew Hfpacker-Amp Project. This project and
Pacific Antenna Easy SWR Indicator Kit
 Pacific Antenna Easy SWR Indicator Kit Description Monitoring the match of an antenna to your transmitter or adjusting an antenna tuner for best match requires an indicator of the reflected power as an
Pacific Antenna Easy SWR Indicator Kit Description Monitoring the match of an antenna to your transmitter or adjusting an antenna tuner for best match requires an indicator of the reflected power as an
V6.2 SoftRock Lite Builder s Notes. November 17, 2006
 V6.2 SoftRock Lite Builder s Notes November 17, 2006 Be sure to use a grounded tip soldering iron in building the v6.2 SoftRock circuit board. The soldering iron needs to have a small tip, (0.05-0.1 inch
V6.2 SoftRock Lite Builder s Notes November 17, 2006 Be sure to use a grounded tip soldering iron in building the v6.2 SoftRock circuit board. The soldering iron needs to have a small tip, (0.05-0.1 inch
THE RING RESONATOR (K-975)
 THE RING RESONATOR (K-975) OUTPUT BOOST The Ring Resonator An Octave Up Fuzz Modkitsdiy.com 9 VDC CENTER (-) ADAPTER TO AMP IN FROM GUITAR OUT Unplug when not in use to save battery life. Use these instructions
THE RING RESONATOR (K-975) OUTPUT BOOST The Ring Resonator An Octave Up Fuzz Modkitsdiy.com 9 VDC CENTER (-) ADAPTER TO AMP IN FROM GUITAR OUT Unplug when not in use to save battery life. Use these instructions
Building a Bitx20 Version 3
 Building a Bitx20 Version 3 The board can be broken into sections and then built and tested one section at a time. This will make troubleshooting easier as any problems will be confined to one small section.
Building a Bitx20 Version 3 The board can be broken into sections and then built and tested one section at a time. This will make troubleshooting easier as any problems will be confined to one small section.
CONSTRUCTION. Refer to schematic and component location diagrams during assembly
 HAMTRONICS VHF RECEIVING CONVERTERS CONSTRUCTION, ALIGNMENT, & INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS GENERAL DESCRIPTION. The CA( ) series of VHF Receiving Converter modules are designed to amplify and convert the
HAMTRONICS VHF RECEIVING CONVERTERS CONSTRUCTION, ALIGNMENT, & INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS GENERAL DESCRIPTION. The CA( ) series of VHF Receiving Converter modules are designed to amplify and convert the
PAC-12 Kit Contents. Tools Needed Soldering iron Phillips screwdriver Wire stripper Wrenches, 7/16 and 1/2 Terminal crimp tool Pliers Solder
 PAC-2 Kit Contents Part Quantity Screws: 8/32 x 3/8 Screws: 8-32 x 5/6 Screw: 8-32 x /4 #8 internal tooth washers #8 solder lug ring terminals Bolt: Aluminum, /4-20 x.5 /4 internal tooth washer Nut: Aluminum
PAC-2 Kit Contents Part Quantity Screws: 8/32 x 3/8 Screws: 8-32 x 5/6 Screw: 8-32 x /4 #8 internal tooth washers #8 solder lug ring terminals Bolt: Aluminum, /4-20 x.5 /4 internal tooth washer Nut: Aluminum
Manual AMERITRON QSK-5PC T/R SWITCH PC BOARD INTRODUCTION
 Manual Instruction AMERITRON QSK-5PC T/R SWITCH PC BOARD INTRODUCTION The Ameritron QSK-5PC is a PIN diode QSK circuit board designed for use in Ameritron's AL-80A, AL-80B, AL-82, AL-1500 and AL- 1200
Manual Instruction AMERITRON QSK-5PC T/R SWITCH PC BOARD INTRODUCTION The Ameritron QSK-5PC is a PIN diode QSK circuit board designed for use in Ameritron's AL-80A, AL-80B, AL-82, AL-1500 and AL- 1200
MINI FM PHONE TRANSMITTER KIT
 MINI FM PHONE TRANSMITTER KIT Description: This is a subminiature FM telephone transmitter capable of transmitting both sides of a telephone conversation to most any FM receiver up to 1/4 mile away. When
MINI FM PHONE TRANSMITTER KIT Description: This is a subminiature FM telephone transmitter capable of transmitting both sides of a telephone conversation to most any FM receiver up to 1/4 mile away. When
RF Current Meter Kit
 Kit When assembled, this kit provides you with a simple but effective means of measuring the current in antenna wires, and of looking for braid currents on coax feeders. The more current you can get flowing
Kit When assembled, this kit provides you with a simple but effective means of measuring the current in antenna wires, and of looking for braid currents on coax feeders. The more current you can get flowing
Cricket 80a Assembly Manual v Copyright David Cripe NM0S The 4 State QRP Group
 Cricket 80a Assembly Manual v. 1.0 Copyright 2017 David Cripe NM0S The 4 State QRP Group Introduction Thank you for purchasing a CRICKET 80a Transceiver. We hope you will enjoy building it and find it
Cricket 80a Assembly Manual v. 1.0 Copyright 2017 David Cripe NM0S The 4 State QRP Group Introduction Thank you for purchasing a CRICKET 80a Transceiver. We hope you will enjoy building it and find it
Building the Toothpick Audio CW Filter
 Building the Toothpick Audio CW Filter Introduction The toothpick is a simple variable bandpass audio filter designed to compliment the Splinter QRPp Trans-Receiver. The filter also contains an audio amplifier
Building the Toothpick Audio CW Filter Introduction The toothpick is a simple variable bandpass audio filter designed to compliment the Splinter QRPp Trans-Receiver. The filter also contains an audio amplifier
HT-1A Dual Band CW QRP Transceiver. Kit Building Instructions
 HT-A Dual Band CW QRP Transceiver Kit Building Instructions Rev B, July 8, 08 Designed by BD4RG Exclusively distributed by CRKITS.COM and its worldwide distributors Join the group http://groups.io/g/crkits
HT-A Dual Band CW QRP Transceiver Kit Building Instructions Rev B, July 8, 08 Designed by BD4RG Exclusively distributed by CRKITS.COM and its worldwide distributors Join the group http://groups.io/g/crkits
DIODE / TRANSISTOR TESTER KIT
 DIODE / TRANSISTOR TESTER KIT MODEL DT-100K Assembly and Instruction Manual Elenco Electronics, Inc. Copyright 1988 Elenco Electronics, Inc. Revised 2002 REV-K 753110 DT-100 PARTS LIST If you are a student,
DIODE / TRANSISTOR TESTER KIT MODEL DT-100K Assembly and Instruction Manual Elenco Electronics, Inc. Copyright 1988 Elenco Electronics, Inc. Revised 2002 REV-K 753110 DT-100 PARTS LIST If you are a student,
10W HF Linear PA. A low-cost, high-performance HF Linear PA covering 2-30MHz. 10W HF Linear Power Amplifier kit assembly manual
 10W HF Linear PA 10W HF Linear Power Amplifier kit assembly manual A low-cost, high-performance HF Linear PA covering 2-30MHz Designed and produced by QRP Labs, 2018 10W HF Linear PA kit assembly 1.01
10W HF Linear PA 10W HF Linear Power Amplifier kit assembly manual A low-cost, high-performance HF Linear PA covering 2-30MHz Designed and produced by QRP Labs, 2018 10W HF Linear PA kit assembly 1.01
Assembly Instructions
 Assembly Instructions for the PA3 v2.0 Amplifier Kit PA3 Amplifier shown mounted on HS2 Heat Sink (The HS2 shown here is not included with this kit.) 27 February 2016 2013-2016 by Ralph Hartwell Spectrotek
Assembly Instructions for the PA3 v2.0 Amplifier Kit PA3 Amplifier shown mounted on HS2 Heat Sink (The HS2 shown here is not included with this kit.) 27 February 2016 2013-2016 by Ralph Hartwell Spectrotek
Manual Version July 2007
 Manual Version 1.2 - July 2007 Page 1 Table of Contents Section1: M3 Phono Board Build...3 Phono Board Parts List...3 Preparation...4 Fitting the Valve Bases...6 Installing the Resistors...7 Starting the
Manual Version 1.2 - July 2007 Page 1 Table of Contents Section1: M3 Phono Board Build...3 Phono Board Parts List...3 Preparation...4 Fitting the Valve Bases...6 Installing the Resistors...7 Starting the
THE THUNDERDRIVE (K-950)
 THE THUNDERDRIVE (K-950) OUTPUT DISTORTION Unplug when not in use to save battery life. TO AMP IN The Thunderdrive Modkitsdiy.com FROM GUITAR OUT Use these instructions to learn: How to build an effects
THE THUNDERDRIVE (K-950) OUTPUT DISTORTION Unplug when not in use to save battery life. TO AMP IN The Thunderdrive Modkitsdiy.com FROM GUITAR OUT Use these instructions to learn: How to build an effects
Foxhunt Offset Attenuator. Parts List:
 When your closing in on the fox you may find the signals to be so strong that you can no longer find a peak or null with your antenna. Sometimes the signal is so strong that the RF will leak straight into
When your closing in on the fox you may find the signals to be so strong that you can no longer find a peak or null with your antenna. Sometimes the signal is so strong that the RF will leak straight into
REPAIRING THE RM KL400 LINEAR AMPLIFIER.
 REPAIRING THE RM KL400 LINEAR AMPLIFIER. Les Carpenter G4CNH December 2012 Page 1 of 20 The following is a step by step guide to fixing your KL400 amplifier. Each part will be individually tested up to
REPAIRING THE RM KL400 LINEAR AMPLIFIER. Les Carpenter G4CNH December 2012 Page 1 of 20 The following is a step by step guide to fixing your KL400 amplifier. Each part will be individually tested up to
NEW DESIGN***DEM Part Number FRS***NEW DESIGN Low power 144 MHz Transverter for the Flex Radio System SDR-1000 Operating Specifications:
 NEW DESIGN***DEM Part Number 144-28FRS***NEW DESIGN Low power 144 MHz Transverter for the Flex Radio System SDR-1000 Operating Specifications: Operating Voltage: 12.0-15.5 VDC, 13.8 nominal Current Drain:
NEW DESIGN***DEM Part Number 144-28FRS***NEW DESIGN Low power 144 MHz Transverter for the Flex Radio System SDR-1000 Operating Specifications: Operating Voltage: 12.0-15.5 VDC, 13.8 nominal Current Drain:
Pacific Antenna 20 and 40M Lightweight Dipole Kit
 Pacific Antenna 20 and 40M Lightweight Dipole Kit Antenna diagram showing configuration and lengths when assembled 7 8 16 9 16 9 Description The Pacific Antenna lightweight dual band dipole kit provides
Pacific Antenna 20 and 40M Lightweight Dipole Kit Antenna diagram showing configuration and lengths when assembled 7 8 16 9 16 9 Description The Pacific Antenna lightweight dual band dipole kit provides
S-Pixie QRP Kit. Student Manual. Revision V 1-0
 S-Pixie QRP Kit Student Manual Revision V 1-0 Introduction The Pixie 2 is a small, versatile radio transceiver that is very popular with QRP (low power) amateur radio operators the world over. It reflects
S-Pixie QRP Kit Student Manual Revision V 1-0 Introduction The Pixie 2 is a small, versatile radio transceiver that is very popular with QRP (low power) amateur radio operators the world over. It reflects
The Tellun Corporation. TLN-861 Dunsel. User Guide, Rev Scott Juskiw The Tellun Corporation
 The Tellun Corporation TLN-861 Dunsel User Guide, Rev. 1.0 Scott Juskiw The Tellun Corporation scott@tellun.com TLN-861 User Guide Revision 1.0 August 31, 2006 1. Introduction The TLN-861 Dunsel is a collection
The Tellun Corporation TLN-861 Dunsel User Guide, Rev. 1.0 Scott Juskiw The Tellun Corporation scott@tellun.com TLN-861 User Guide Revision 1.0 August 31, 2006 1. Introduction The TLN-861 Dunsel is a collection
LPF-9B Nine band low pass filter module kit ( meters)
 LPF-9B Nine band low pass filter module kit (80-60-40-30-20-17-15-12-10 meters) Assembly manual Last update: March 1, 2018 ea3gcy@gmail.com Most recent updates and news at: www.ea3gcy.com Thanks for constructing
LPF-9B Nine band low pass filter module kit (80-60-40-30-20-17-15-12-10 meters) Assembly manual Last update: March 1, 2018 ea3gcy@gmail.com Most recent updates and news at: www.ea3gcy.com Thanks for constructing
The W3FF Portable Dipole
 The W3FF Portable Dipole This is the antenna I designed for my 'walking portable' station. It is a dipole constructed out of the plastic plumbing pipe CPVC. There are telescoping whips at the ends of each
The W3FF Portable Dipole This is the antenna I designed for my 'walking portable' station. It is a dipole constructed out of the plastic plumbing pipe CPVC. There are telescoping whips at the ends of each
Custom Front Panel Upgrade Instructions
 Custom Front Panel Upgrade Instructions Here are the directions for upgrading your SP-II to an SP-IIB, with a custom blackanodized front panel and engraved lettering. There are only forty SP-IIB s in existence
Custom Front Panel Upgrade Instructions Here are the directions for upgrading your SP-II to an SP-IIB, with a custom blackanodized front panel and engraved lettering. There are only forty SP-IIB s in existence
Pacific Antenna 20 and 40M Lightweight Dipole Kit
 Pacific Antenna 20 and 40M Lightweight Dipole Kit Diagram showing configuration and approximate lengths 8 3 16 9 16 9 8 3 Description The Pacific Antenna lightweight dual band, trap dipole kit provides
Pacific Antenna 20 and 40M Lightweight Dipole Kit Diagram showing configuration and approximate lengths 8 3 16 9 16 9 8 3 Description The Pacific Antenna lightweight dual band, trap dipole kit provides
Assembly Manual V1R2B-Rev1.0D
 Assembly Manual V1R2B-Rev1.0D for 4 State QRP MagicBox - Solid State Transmit/Receive System Designed by: Jim Kortge, K8IQY Copyright 2009-2012 - All rights reserved This system is the result of some brainstorming
Assembly Manual V1R2B-Rev1.0D for 4 State QRP MagicBox - Solid State Transmit/Receive System Designed by: Jim Kortge, K8IQY Copyright 2009-2012 - All rights reserved This system is the result of some brainstorming
DC Injector (Bias Tee) kit. Technical Manual
 DC Injector (Bias Tee) kit Technical Manual Document Author Dave Powis, G4HUP Date 7 Jan 2017 Version Issue 2_0 Document Ref HUP-05-020 http://huprf.com Tel +44 (0)1473 737717 g4hup@outlook.com Contents
DC Injector (Bias Tee) kit Technical Manual Document Author Dave Powis, G4HUP Date 7 Jan 2017 Version Issue 2_0 Document Ref HUP-05-020 http://huprf.com Tel +44 (0)1473 737717 g4hup@outlook.com Contents
Instructions for Building the Pulsed Width Modulation Circuit. MC-12 (DC Motor Controller or PWM) From Electronic Light Inc. (revised kit 10/03/08)
 Instructions for Building the Pulsed Width Modulation Circuit MC-12 (DC Motor Controller or PWM) From Electronic Light Inc. (revised kit 10/03/08) Congratulations on your purchase of the MC-12 DC Motor
Instructions for Building the Pulsed Width Modulation Circuit MC-12 (DC Motor Controller or PWM) From Electronic Light Inc. (revised kit 10/03/08) Congratulations on your purchase of the MC-12 DC Motor
Repairing your Porsche 928 Central Warning System (CWS) controller
 Repairing your Porsche 928 Central Warning System (CWS) controller Disclaimer: This procedure is for a 1984 Porsche 928 S controller. Overview: Under the left foot pedal (dead pedal) of the Porsche 928
Repairing your Porsche 928 Central Warning System (CWS) controller Disclaimer: This procedure is for a 1984 Porsche 928 S controller. Overview: Under the left foot pedal (dead pedal) of the Porsche 928
The ability to make basic voltage and resistance measurements using a digital multimeter
 Congratulations on your purchase of a new OneShot chassis! The PC01 OneShot combines a rugged enclosure, power supply, and discrete instrument DI in a compact 1/4U package. A few minutes of assembly are
Congratulations on your purchase of a new OneShot chassis! The PC01 OneShot combines a rugged enclosure, power supply, and discrete instrument DI in a compact 1/4U package. A few minutes of assembly are
