DESIGN AND MODELLING OF A 1 N ALL- OPTICAL NONLINEAR MACH-ZEHNDER SWITCH CONTROLLED BY WAVELENGTH AND INPUT POWER
|
|
|
- Marjorie Harrington
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 28, , 2013 DESIGN AND MODELLING OF A 1 N ALL- OPTICAL NONLINEAR MACH-ZEHNDER SWITCH CONTROLLED BY WAVELENGTH AND INPUT POWER Saeed Karimi, Majid Ebnali-Heidari *, and Farnaz Forootan Faculty of Engineering, Shahrekord University, Shahrekord , Iran Abstract The authors propose two 1 N all optical switches by taking the advantage of the accelerating behaviour of a spatial soliton in a Mach-Zehnder waveguide and the soliton s oscillating behaviour while propagating inside the nonlinear waveguide. The proposed switches consist of asymmetric and symmetric Mach- Zehnder waveguides followed by a homogenous Kerr medium, which is terminated by N parallel trapezoidal waveguides. In these switches, the signal is dropped from one of the desired output channels by changing the input pulse of wavelength or power. The numerical results confirm the switching application and show that the proposed 1 N switches can be used for wide ranges of wavelength and power, which are suitable for optical communication networks and optical data processing systems. 1. INTRODUCTION Researchers are encouraged to design all optical devices in telecommunication industries due to their advantages such as ultra-high spectral bandwidth, great flexibility, and low attenuation. The development of all optical devices is too fast, as a result, variety of all optical devices such as switches [1 4], wavelength converters [5, 6], routers [7], modulator [8], gates [9], demultiplexers [10], and filters [11, 12] have been designed and produced recently. All-optical ultrafast photonic switches based on the nonlinear Kerr effect in an optical waveguide draw particular attention toward high-bit-rate optical communication systems and ultrafast information processing [13]. Optical switches Received 5 October 2012, Accepted 26 December 2012, Scheduled 7 January 2013 * Corresponding author: Majid Ebnali-Heidari (ma.ebnali@gmail.com).
2 102 Karimi, Ebnali-Heidari, and Forootan can change the signal path toward our desired output. In some waveguide based switches, by linear or nonlinear changing of the refractive indices in a homogenous Kerr medium of the waveguide and choosing a suitable wavelength and power of the input signal, the desired switch output channel is simply selected [14, 15]. Recently, soliton s oscillating behavior in nonlinear waveguides with different transverse index profiles has been studied [16 19]. In this paper, we propose a 1 N (input output) optical which includes three segments that in the first one both symmetric and asymmetric Mach-Zehnder waveguides are used. Mach-Zehnder is one of the most available optical interferometers, which we use on the first segment of proposed switches to make the phases difference at the output. And it also takes the advantage of the soliton s oscillating behavior while propagating inside the nonlinear waveguide in the second section and finally the last segment uses some output channels. This simple structure has many applications for signal switching to the desired output channel according to their wavelength and power. It also helps engineers to design all-optical broadband systems based on code division multiple access (CDMA) with many applications on third generation of cellular telecommunication network. This paper is organized as follows: In Section 2, the physical models for two types of 1 5 Mach-Zehnder switches are proposed. Mathematical analysis is briefly presented in Section 3. Section 4 shows the simulation results using difference beam propagation method (FD- BPM) and finally Section 5 concludes the paper. 2. PHYSICAL MODEL The schematic of our design, both asymmetric and symmetric Mach- Zehnder interferometer arms switch are displayed in Figures 1(a) and 1(b), respectively. In this figure the red and yellow marked are belong to nonlinear, and linear switch section, respectively. These structures comprise of three segments with various transverse refractive index profiles. The compound structures are followed by a homogeneous Kerr medium, which in turn is terminated by a trapezoidal waveguides. Each segment depending on its power and wavelength has a specified duty to control and guide its input signal toward next segment. Increasing the nonlinear refractive index in each segment caused by Kerr effect will increase the light intensities and leads to appear some nonlinear phenomena such as self-phase modulation (SPM). SPM leads to spectral broadening of the input pulse and simultaneously an important linear effect, which is called group velocity dispersion (GVD), results in temporal broadening. To
3 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 28, (a) (b) Figure 1. (a) 1 5 all-optical asymmetric Mach-Zehnder switch with nonlinear arms. (b) 1 5 all-optical symmetric Mach-Zehnder switch with linear-nonlinear arms. prevent both SPM and GVD effects, soliton wave as the input signal is used. These waves propagate within a nonlinear medium without spectral and temporal broadening. This remarkable feature is due to the balancing of the wave s natural tendency to disperse with the opposing nonlinearity of the system. Solitons are special solutions of the nonlinear Schrödinger (NLS) equation that describe the paraxial propagation of an optical field in a Kerr medium [19 21]. All the segments have solitonic behaviors that cause the output signal to be unchanged. The main reason for using nonlinear-nonlinear asymmetric and linear-nonlinear symmetric Mach-Zehnder arms as the input segment, is to create a phase difference between the received signals of the right and left arms and finally creating either constructive or destructive resultant signal at the next segment. The arms difference in both asymmetric and symmetric Mach-Zehnder is the source of the phase delay. The scheme employs angular deflection of spatial solitons controlled by phase modulation created in the Mach-Zehnder, which acts as a phase shifter. However, practical implementation of the structure shown in Figure 1(b) is simpler because of symmetric arms. The aim of using nonlinear Kerr medium as the second segment of the switch is to reduce the speed of propagating signal (speed of light), enhance the nonlinear effects, and create the signal swing mode which is completely discussed in [22]. All these approaches help signal guide toward one of the desired output channels in the last segment based on its power and wavelength. In both Figures 1(a) and 1(b) the output channels consist of five trapezoidal waveguides which are also extendable to N waveguides that is discussed in the following. However there are some other forms of waveguide, but trapezoidal one has advantage to prevent the disordered changing of the output
4 104 Karimi, Ebnali-Heidari, and Forootan channel [23]. Moreover, these proposed switches have been designed according to international telecommunication union (ITU) standard. It means that the wavelength range of the first output channel is designed for C and L bands while the second output channel is designed for U- band. 3. FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS According to Section 2, the input pulse has the soliton shape as follows: ( ) T x(t) = P 0 sec, (1) where P 0, T 0 and T are the peak power, duration of the input pulse, and time parameter, respectively. Input pulse is launched into the first segment of switch. For simplicity and due to the non-periodic structure of the proposed 1 N switch, the TM and TE mode analyses are the same. So we consider the case of TE waves propagating along the structure as: ε(x, z, t) = E(x, z) exp[j(ωt βk 0 z)], (2) where k 0 is the wave number in free space, β the effective refractive index, ω the angular frequency, and E the electrical field of propagation signal. Also, the field has been assumed to be homogeneous in the y direction. Taking into account the slowly varying envelope approximation, E(x, z) is obtained as follows [22, 23]: [ n 2 i E 2jβk 0 z + 2 E ( x 2 + k2 0 x, z, E 2) β 2] = 0. (3) For Kerr-type nonlinear medium, the total refractive index n i can be written as [24]: n i = n i0 + n i1 I (4) In which n i0 and n i1 are the linear and nonlinear refractive indices of the nonlinear medium, and I is the signal intensity. The phase difference between two Mach-Zehnder arms is given by [25]: φ = n i1 k 0 L 1 I (5) where L 1 is the length of Mach-Zehnder optical path (according to Figure 1) and I the intensity difference between two received signals of both arms. φ is an important parameter to define the output intensity in each position at the output of the first segment. For example φ equals to 0 and 180, results in constructive and destructive fields, respectively. The constructive field effect just happens in a special position which determines the signal path at the next segment. T 0
5 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 28, NUMERICAL RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS In this section, the switches performance and applications are numerically investigated. For simulation of the signal propagation along proposed switches finite difference beam propagation method (FD-BPM) [26, 27] is used. There are several reasons for selecting the FD-BPM; one of the most significant reasons includes that it is conceptually straightforward, which allows rapid implementation of the basic technique. This conceptual simplicity also benefits the user of the FD-BPM based modeling tool as well as the implementer, since an understanding of the results and proper usage of the tool can be readily grasped by a non-expert in numerical methods. In spite of the relative Table 1. The device parameters for both structures shown in Figure 1. Description L 1 L 2 L 3 L T Figure 1(a) Figure 1(b) Description Figure 1(a) Figure 1(b) W 1 2 Nonlinear arm 2 Linear arm W 2 3 Nonlinear arm 2 Nonlinear arm W 3 W Table 2. The output channel number versus the wavelength range of the input signal for P 0 equals to 18 W for both proposed switches as illustrated in Figure 1. Output Channel #1 Channel #2 Channel #3 Figure 1(a) wavelength Figure 1(b) wavelength Output Channel #4 Channel #5 - Figure 1(a) wavelength Figure 1(b) wavelength
6 106 Karimi, Ebnali-Heidari, and Forootan simplicity, FD-BPM is generally an efficient method, which makes the characteristic of computational complexity optimal in most cases, i.e., the computational effort is directly proportional to the number of grid points used in the numerical simulation. Another characteristic of FD-BPM method is that the approach is readily applied to complex geometries without any necessity to develop specialized versions of it. Furthermore, the approach automatically includes the effects of both guided and radiating fields as well as mode coupling and conversion. Finally, the -FBPM technique is very flexible and extensible, allowing inclusion of most effects of interest (e.g., polarization, nonlinearities) by extensions of the basic method that fit within the same overall framework. The device parameters and values related to both proposed switches are given in Table 1 in which L 1, L 2 and L 3 are the lengths of the first, second and third segments of the switch, respectively. W 1 and W 2 are the left and right arm widths of the Mach-Zehnder waveguide. W 3 is the width of the second segment (homogenous Kerr medium) and W 4 the width of each channel of the output segment. In the first simulation related to structure shown in Figure 1(a), the peak power of the input pulse was kept as a constant value of 18 W, and only its wavelength is changed from 1.5 µm to 2.05 µm. Here the proposed switches rely on the wavelength variations, which causes phases difference in the first output segment of the switches and the signal to appear in different spatial locations of Mach-Zehnder output. This difference along with second segment swing properties causes the signal to extract in different channels due to input power and wavelength. The evolutions of such a input pulse with constant power propagating along 1 5 all-optical switch are demonstrated in Figure 2. Figure 2 and Table 2 reveal that when input signal wavelength is between 1.5 µm to µm, the coupled signal passes from channel #1. For another case with wavelength between µm to 1.73 µm, it passes from channel #2. The other results of the switch function related to wavelength ranges according to Table 2 present in Figures 2(c), 2(d), and 2(e). One of the most important characteristic of the designed switch is that by increasing the wavelength of the input signal, it sequentially switches to the output channel as desired which is demonstrated in Figure 2 and Table 2. Moreover, the simulations were repeated for the second structure shown in Figure 1(b) with the same peak power as mentioned above, and the results are given in Table 2 in which they also confirm that increasing the input signal wavelength shifts it toward the output channel sequentially, which means that by using symmetric Mach-Zhender, beside easier and cheaper fabrication process, similar results to the asymmetric one are obtained. Our simulations are followed for the case where the input signal
7 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 28, (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Figure 2. The evolutions of the input pulse propagating along 1 5 all-optical switch based on Figure 1(a) for constant power of 18 W and wavelength range of the input signal from (a) 1.5 µm to µm, (b) µm to 1.73 µm, (c) µm to 1.9 µm, (d) µm to 2 µm and (e) µm to 2.05 µm. Table 3. The output channel number versus the peak power of the input signal for a constant wavelength of 1.55 µm. Output Channel #5 Channel #4 Channel #3 Figure 1(b) Input peak power (W) Figure 1(a) input peak power (W) Output Channel #2 Channel #1 - Figure 1(b) Input peak power (W) Figure 1(a) input peak power (W)
8 108 Karimi, Ebnali-Heidari, and Forootan wavelength is assumed to be constant with 1.55 µm, and its only peak power changes from 10 to 40 W. Here as before, the simulations are repeated for both structures of Figure 1, and the results of simulation for both Figures 1(a) and 1(b) are given in Table 3. Moreover, the input pulse propagation along switch shown in Figure 1(b) is depicted in Figure 3 for different values of its peak power as Table 3. Figure 3 also shows and confirms that just by changing the input signal peak power, the desired output channel will be obtained. According to the results of Table 3, for fixed wavelength of the input signal, both switches have the same behaviour. So we prefer to use the second one because of the easier and cheaper fabrication process. The signal position shifts versus the wavelength for different values of the input peak power are calculated, and finally the related curves for both structures are depicted in Figure 4. According to Figure 4(a), related to the first structure, the most position shift occurs at p = 17.9 W; however there is not any positions shift in Figure 4(b), related to the second one, in that power and range (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) Figure 3. The evolutions of the input pulse propagating along 1 5 all-optical switch based on Figure 1(b) for constant wavelength equals to 1.55 µm and power range of the input signal from (a) 10 W to 1.62 W, (b) W to W, (c) W to W, (d) W to W and (e) W to 40 W.
9 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 28, (a) (b) Figure 4. (a) Position shift versus wavelength in different values of the input power for structure as Figure 1(a). (b) Position shift versus wavelength for different values of input power for structure as Figure 1(b). Figure 5. A 1 N all-optical nonlinear Mach-Zehnder switch. of the wavelength. The simulation results curves also show that the switch in the condition of Fig. 4(b) can work in lower powers than that in the situation of Fig. 4(a) for the same position shift which is another reason for choosing the second switch as desired. Figures 4(a) and 4(b) show that by increasing the input peak power, the position shift is reduced; however the curves are almost linear. Linear curves help us extend our method to design a 1 N switch as illustrated in Figure 5 by N trapezoidal waveguides. Now, for an optimal design of switch, the length of homogeneous Kerr medium for both symmetric and asymmetry 1 N all optical
10 110 Karimi, Ebnali-Heidari, and Forootan Figure 6. Width of homogeneous Kerr medium versus number of output channel (from N = 5 to N = 30). switches should be computed. In the proposed switches, X T is a place in homogeneous Kerr medium that the signal propagates directly from the first segment toward the last output channel without any variations. The design rule for 1 N channel switch is based on generalizing switch 1 5 and repetition of second segment and output channels until it reaches 1 N switch channel. According to our simulations for mentioned switches consisting of five-channel output, X T is 24 µm, and for another switch with ten-channel output, it is around 46 µm, which means that by increasing the number of output channels by a factor of two, the width of homogeneous Kerr medium is approximately doubled. By repeating our simulations for many switches with different numbers of output channels, we can generalize the principle for N-channel output switch as follows: where N is the number of output channel. 5. CONCLUSION x T 4N (6) We propose two all optical switches controlled by both input peak power and wavelength. Each one includes a Mach-Zehnder waveguide followed by a homogenous Kerr medium, which in turn was terminated by N parallel trapezoidal waveguides. The Mach-Zehnder waveguide was symmetric for one of them and asymmetric for the other one. The numerical results showed that the signal was dropped from one of the desired output channels by changing either the wavelength of input pulse or power. They also confirmed that the proposed switches can be used for wide range of wavelength and power, which makes the device suitable for optical communication networks and optical data
11 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 28, processing systems. We also showed that the switch can be utilized to be a 1 N, by either reducing the widths of output channels or increasing the length of the Kerr medium as the proposed equation which is obtained by the simulation results. REFERENCES 1. Nakamura, H., Y. Sugimoto, and K. Asakawa, Ultra-fast photonic crystal/quantum dot all-optical switch for future photonic networks, Optics Express, Vol. 12, No. 26, , Beggs, D. M., et al., Ultra compact and low-power optical switch based on silicon photonic crystals, Optics Letters, Vol. 33, No. 2, , Cho, S. Y. and R. Soref, Interferometer microring-resonant 2 2 optical switches, Optics Express, Vol. 16, No. 17, , Ridolfo, A., et al., All optical switch of vacuum Rabi oscillations: The ultrafast quantum eraser, Phys. Rev. Lett., Vol. 106, No. 1, , Lal, V., et al., Monolithic wavelength converters for high-speed packet-switched optical networks, IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, Vol. 13, No. 1, 49 57, Ebnali-Heidari, M., M. K. Moravvej-Farshi, and A. Zarifkar, Multi channel wavelength conversion using fourth-order soliton decay, Journal of Lightwave Technology, Vol. 25, No. 9, , Sherwood-Droz, N., et al., Optical 4 4 hitless slicon router for optical networks-on-chip (NoC), Optics Express, Vol. 16, No. 20, , Bakhshi, S., M. K. Moravvej-Farshi, and M. Ebnali-Heidari, Design of an ultracompact low-power all-optical modulator by means of dispersion engineered slow light regime in a photonic crystal Mach-Zehnder interferometer, Applied Optics, Vol. 51, No. 14, , Lai, D. M., C. Kwok, and K. K. Wong, All-optical picoseconds logic gates based on a fiber optical parametric amplifier, Optics Express, Vol. 16, No. 22, , Gayen, D. K. and J. N. Roy, All-optical arithmetic unit with the help of terahertz-optical-asymmetric-demultiplexer-based tree architecture, Applied Optics, Vol. 47, No. 7, , 2008.
12 112 Karimi, Ebnali-Heidari, and Forootan 11. Tu, X., F. Liu, and N. Xu, Design of high channel-count optical fiber filters based on sampled Bragg grating with discrete linear chirp structure, Optics and Precision Engineering, Bitarafan, M., M. Moravvej-Farshi, and M. Ebnali-Heidari, Proposal for postfabrication fine-tuning of three-port photonic crystal channel drop filters by means of optofluidic infiltration, Applied Optics, Vol. 50, No. 17, , Lu, H., et al., Ultrafast all-optical switching in nanoplasmonic waveguide with Kerr nonlinear resonator, Optics Express, Vol. 19, No. 4, , Wu, Y. D., et al., All-optical switch based on the local nonlinear Mach-Zehnder interferometer, Optics Express, Vol. 15, No. 16, , Camargo, E., H. Chong, and R. de la Rue, 2D photonic crystal thermo-optic switch based on AlGaAs/GaAs epitaxial structure, Optics Express, Vol. 12, No. 4, , Garzia, F., C. Sibilia, and M. Bertolotti, Swing effect of spatial soliton, Optics Communications, Vol. 139, No. 4 6, , Suryanto, A. and E. van Groesen, On the swing effect of spatial inhomogeneous NLS solitons, Journal of Nonlinear Optical Physics and Materials, Vol. 10, No. 2, , Suryanto, A. and E. van Groesen, Break up of bound-n-spatialsoliton in a ramp waveguide, Optical and Quantum Electronics, Vol. 34, No. 5, , Moravvej-Farshi, M., M. E. Heidari, and A. Zarifkar, Spatial solitons in compound ramp waveguides, Proceedings of CAOL 2005 Second International Conference on Advanced Optoelectronics and Lasers, Vol. 2, , Agrawal, G. P., Nonlinear Fiber Optics, 2nd Edition, Academic Press, Agrawal, G. P., Fiber Optic Communication Systems, Wiley- Interscience, Ebnali-Heidari, M., M. K. Moravvej-Farshi, and A. Zarifkar, Swing effect of spatial solitons propagating through Gaussian and triangular waveguides, Applied Optics, Vol. 48, No. 26, , Aceves, A. B., J. V. Moloney, and A. C. Newell, Theory of lightbeam propagation at nonlinear interfaces. I. Equivalent-particle theory for a single interface, Phys. Rev. A, Vol. 39, , 1989.
13 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 28, Kuo, C. W., et al., Analyzing multilayer optical waveguide with all nonlinear layers, Optics Express, Vol. 15, No. 5, , Berrettini, G., et al., Ultrafast integrable and reconfigurable XNOR, AND, NOR, and NOT photonic logic gate, IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, Vol. 18, No. 8, , Niwa, S., et al., Experimental demonstration of 1 4 InP/InGaAsP optical integrated multimode interference waveguide switch, 20th International Conference on Indium Phosphide and Related Materials, 2008, IPRM 2008, 1 4, Scarmozzino, R., et al., Numerical techniques for modeling guided-wave photonic devices, IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, Vol. 6, No. 1, , 2000.
Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p.
 Preface p. xiii Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p. 6 Plastic Optical Fibers p. 9 Microstructure Optical
Preface p. xiii Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p. 6 Plastic Optical Fibers p. 9 Microstructure Optical
Fiber-Optic Communication Systems
 Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Second Edition GOVIND P. AGRAWAL The Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY A WILEY-iNTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. NEW YORK / CHICHESTER
Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Second Edition GOVIND P. AGRAWAL The Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY A WILEY-iNTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. NEW YORK / CHICHESTER
Chad A. Husko 1,, Sylvain Combrié 2, Pierre Colman 2, Jiangjun Zheng 1, Alfredo De Rossi 2, Chee Wei Wong 1,
 SOLITON DYNAMICS IN THE MULTIPHOTON PLASMA REGIME Chad A. Husko,, Sylvain Combrié, Pierre Colman, Jiangjun Zheng, Alfredo De Rossi, Chee Wei Wong, Optical Nanostructures Laboratory, Columbia University
SOLITON DYNAMICS IN THE MULTIPHOTON PLASMA REGIME Chad A. Husko,, Sylvain Combrié, Pierre Colman, Jiangjun Zheng, Alfredo De Rossi, Chee Wei Wong, Optical Nanostructures Laboratory, Columbia University
All-Optical Logic Gates Based on No Title Waveguide Couplers. Author(s) Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba,
 All-Optical Logic Gates Based on No Title Waveguide Couplers Author(s) Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanor Journal of the Optical Society of A Citation Physics, 23(4): 684-691 Issue 2006-04-01 Date Type
All-Optical Logic Gates Based on No Title Waveguide Couplers Author(s) Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanor Journal of the Optical Society of A Citation Physics, 23(4): 684-691 Issue 2006-04-01 Date Type
All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration
 1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
A GENERAL RULE FOR DESIGNING MULTIBRANCH HIGH-ORDER MODE CONVERTER. of Applied Sciences, Kaohsiung 807, Taiwan, R.O.C.
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 138, 327 336, 2013 A GENERAL RULE FOR DESIGNING MULTIBRANCH HIGH-ORDER MODE CONVERTER Yaw-Dong Wu 1, *, Chih-Wen Kuo 2, Shih-Yuan Chen 2, and Mao-Hsiung Chen
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 138, 327 336, 2013 A GENERAL RULE FOR DESIGNING MULTIBRANCH HIGH-ORDER MODE CONVERTER Yaw-Dong Wu 1, *, Chih-Wen Kuo 2, Shih-Yuan Chen 2, and Mao-Hsiung Chen
Index. Cambridge University Press Silicon Photonics Design Lukas Chrostowski and Michael Hochberg. Index.
 absorption, 69 active tuning, 234 alignment, 394 396 apodization, 164 applications, 7 automated optical probe station, 389 397 avalanche detector, 268 back reflection, 164 band structures, 30 bandwidth
absorption, 69 active tuning, 234 alignment, 394 396 apodization, 164 applications, 7 automated optical probe station, 389 397 avalanche detector, 268 back reflection, 164 band structures, 30 bandwidth
Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides
 Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides Yaming Li, Chong Li, Chuanbo Li, Buwen Cheng, * and Chunlai Xue State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics,
Compact two-mode (de)multiplexer based on symmetric Y-junction and Multimode interference waveguides Yaming Li, Chong Li, Chuanbo Li, Buwen Cheng, * and Chunlai Xue State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics,
Performance of Optical Encoder and Optical Multiplexer Using Mach-Zehnder Switching
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Performance of Optical Encoder and Optical Multiplexer Using Mach-Zehnder Switching Abhishek Raj 1, A.K. Jaiswal 2, Mukesh Kumar 3, Rohini Saxena 4, Neelesh Agrawal 5 1 PG
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Performance of Optical Encoder and Optical Multiplexer Using Mach-Zehnder Switching Abhishek Raj 1, A.K. Jaiswal 2, Mukesh Kumar 3, Rohini Saxena 4, Neelesh Agrawal 5 1 PG
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 35. Self-Phase-Modulation
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 35 Self-Phase-Modulation (SPM) Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 35 Self-Phase-Modulation (SPM) Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
STUDY OF CHIRPED PULSE COMPRESSION IN OPTICAL FIBER FOR ALL FIBER CPA SYSTEM
 International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJECE) ISSN(P): 78-991; ISSN(E): 78-991X Vol. 4, Issue 6, Oct - Nov 15, 9-16 IASE SUDY OF CHIRPED PULSE COMPRESSION IN OPICAL FIBER FOR
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJECE) ISSN(P): 78-991; ISSN(E): 78-991X Vol. 4, Issue 6, Oct - Nov 15, 9-16 IASE SUDY OF CHIRPED PULSE COMPRESSION IN OPICAL FIBER FOR
Analysis and Design of Semiconductor Photonic Crystal Double Bandpass Filter for CWDM Systems
 International Journal of Optics and Applications 27, 7(3): 49-54 DOI:.5923/j.optics.2773. Analysis and Design of Semiconductor Photonic Crystal Double Bandpass Filter for CWDM Systems Leila Hajshahvaladi,
International Journal of Optics and Applications 27, 7(3): 49-54 DOI:.5923/j.optics.2773. Analysis and Design of Semiconductor Photonic Crystal Double Bandpass Filter for CWDM Systems Leila Hajshahvaladi,
CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER
 CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER As we discussed in chapter 1, silicon photonics has received much attention in the last decade. The main reason is
CHAPTER 2 POLARIZATION SPLITTER- ROTATOR BASED ON A DOUBLE- ETCHED DIRECTIONAL COUPLER As we discussed in chapter 1, silicon photonics has received much attention in the last decade. The main reason is
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG)
 Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
WDM Transmitter Based on Spectral Slicing of Similariton Spectrum
 WDM Transmitter Based on Spectral Slicing of Similariton Spectrum Leila Graini and Kaddour Saouchi Laboratory of Study and Research in Instrumentation and Communication of Annaba (LERICA), Department of
WDM Transmitter Based on Spectral Slicing of Similariton Spectrum Leila Graini and Kaddour Saouchi Laboratory of Study and Research in Instrumentation and Communication of Annaba (LERICA), Department of
Investigation of the tapered waveguide structures for terahertz quantum cascade lasers
 Invited Paper Investigation of the tapered waveguide structures for terahertz quantum cascade lasers T. H. Xu, and J. C. Cao * Key Laboratory of Terahertz Solid-State Technology, Shanghai Institute of
Invited Paper Investigation of the tapered waveguide structures for terahertz quantum cascade lasers T. H. Xu, and J. C. Cao * Key Laboratory of Terahertz Solid-State Technology, Shanghai Institute of
Electronically switchable Bragg gratings provide versatility
 Page 1 of 5 Electronically switchable Bragg gratings provide versatility Recent advances in ESBGs make them an optimal technological fabric for WDM components. ALLAN ASHMEAD, DigiLens Inc. The migration
Page 1 of 5 Electronically switchable Bragg gratings provide versatility Recent advances in ESBGs make them an optimal technological fabric for WDM components. ALLAN ASHMEAD, DigiLens Inc. The migration
Ultracompact and low power optical switch based on silicon. photonic crystals
 Ultracompact and low power optical switch based on silicon photonic crystals Daryl M. Beggs 1, *, Thomas P. White 1, Liam O Faolain 1 and Thomas F. Krauss 1 1 School of Physics and Astronomy, University
Ultracompact and low power optical switch based on silicon photonic crystals Daryl M. Beggs 1, *, Thomas P. White 1, Liam O Faolain 1 and Thomas F. Krauss 1 1 School of Physics and Astronomy, University
NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN DIGITALLY TUNABLE OPTICAL FILTER SYSTEM FOR WAVELENGTH SELEC- TIVE SWITCHING BASED OPTICAL NETWORKS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 93 100, 2009 NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN DIGITALLY TUNABLE OPTICAL FILTER SYSTEM FOR WAVELENGTH SELEC- TIVE SWITCHING BASED OPTICAL NETWORKS A. Banerjee
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 93 100, 2009 NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN DIGITALLY TUNABLE OPTICAL FILTER SYSTEM FOR WAVELENGTH SELEC- TIVE SWITCHING BASED OPTICAL NETWORKS A. Banerjee
A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method.
 PULSE GATING : A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method. Picosecond lasers can be found in many fields of applications from research to industry. These lasers are very common in bio-photonics, non-linear
PULSE GATING : A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method. Picosecond lasers can be found in many fields of applications from research to industry. These lasers are very common in bio-photonics, non-linear
Title. Author(s)Saitoh, Fumiya; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori. CitationOptics Express, 18(5): Issue Date Doc URL.
 Title A design method of a fiber-based mode multi/demultip Author(s)Saitoh, Fumiya; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Express, 18(5): 4709-4716 Issue Date 2010-03-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/46825
Title A design method of a fiber-based mode multi/demultip Author(s)Saitoh, Fumiya; Saitoh, Kunimasa; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Express, 18(5): 4709-4716 Issue Date 2010-03-01 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/46825
Packet clock recovery using a bismuth oxide fiber-based optical power limiter
 Packet clock recovery using a bismuth oxide fiber-based optical power limiter Ch. Kouloumentas 1*, N. Pleros 1, P. Zakynthinos 1, D. Petrantonakis 1, D. Apostolopoulos 1, O. Zouraraki 1, A. Tzanakaki,
Packet clock recovery using a bismuth oxide fiber-based optical power limiter Ch. Kouloumentas 1*, N. Pleros 1, P. Zakynthinos 1, D. Petrantonakis 1, D. Apostolopoulos 1, O. Zouraraki 1, A. Tzanakaki,
The effect of the input energy on the SOA gain with non-uniform biasing
 The effect of the input energy on the SOA gain with non-uniform biasing A. Abd El Aziz, W. P. Ng, Z. Ghassemlooy, Moustafa Aly, R. Ngah 3, M. F. Chiang Optical Communications Research Group, NCRLab Northumbria
The effect of the input energy on the SOA gain with non-uniform biasing A. Abd El Aziz, W. P. Ng, Z. Ghassemlooy, Moustafa Aly, R. Ngah 3, M. F. Chiang Optical Communications Research Group, NCRLab Northumbria
Chromatic Dispersion Compensation in Optical Fiber Communication System and its Simulation
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology Supplementary Article Chromatic Dispersion Compensation in Optical Fiber Communication System and its Simulation R. Udayakumar 1 *, V. Khanaa 2 and T. Saravanan
Indian Journal of Science and Technology Supplementary Article Chromatic Dispersion Compensation in Optical Fiber Communication System and its Simulation R. Udayakumar 1 *, V. Khanaa 2 and T. Saravanan
FIVE-PORT POWER SPLITTER BASED ON PILLAR PHOTONIC CRYSTAL *
 IJST, Transactions of Electrical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. E1, pp 93-100 Printed in The Islamic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shiraz University FIVE-PORT POWER SPLITTER BASED ON PILLAR PHOTONIC CRYSTAL * M. MOHAMMADI
IJST, Transactions of Electrical Engineering, Vol. 39, No. E1, pp 93-100 Printed in The Islamic Republic of Iran, 2015 Shiraz University FIVE-PORT POWER SPLITTER BASED ON PILLAR PHOTONIC CRYSTAL * M. MOHAMMADI
A NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN DIGITALLY TUNABLE OPTICAL FILTER SYSTEM FOR DWDM OPTICAL NETWORKS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 11, 213 223, 2010 A NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN DIGITALLY TUNABLE OPTICAL FILTER SYSTEM FOR DWDM OPTICAL NETWORKS A. Banerjee Department of Electronics and Communication
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 11, 213 223, 2010 A NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN DIGITALLY TUNABLE OPTICAL FILTER SYSTEM FOR DWDM OPTICAL NETWORKS A. Banerjee Department of Electronics and Communication
Arbitrary Power Splitting Couplers Based on 3x3 Multimode Interference Structures for All-optical Computing
 Arbitrary Power Splitting Couplers Based on 3x3 Multimode Interference Structures for All-optical Computing Trung-Thanh Le Abstract--Chip level optical links based on VLSI photonic integrated circuits
Arbitrary Power Splitting Couplers Based on 3x3 Multimode Interference Structures for All-optical Computing Trung-Thanh Le Abstract--Chip level optical links based on VLSI photonic integrated circuits
Design and Simulation of Optical Power Splitter By using SOI Material
 J. Pure Appl. & Ind. Phys. Vol.3 (3), 193-197 (2013) Design and Simulation of Optical Power Splitter By using SOI Material NAGARAJU PENDAM * and C P VARDHANI 1 * Research Scholar, Department of Physics,
J. Pure Appl. & Ind. Phys. Vol.3 (3), 193-197 (2013) Design and Simulation of Optical Power Splitter By using SOI Material NAGARAJU PENDAM * and C P VARDHANI 1 * Research Scholar, Department of Physics,
Deliverable Report. Deliverable No: D2.9 Deliverable Title: OAM waveguide transmission
 Deliverable Report Deliverable No: D2.9 Deliverable Title: OAM waveguide transmission Grant Agreement number: 255914 Project acronym: PHORBITECH Project title: A Toolbox for Photon Orbital Angular Momentum
Deliverable Report Deliverable No: D2.9 Deliverable Title: OAM waveguide transmission Grant Agreement number: 255914 Project acronym: PHORBITECH Project title: A Toolbox for Photon Orbital Angular Momentum
Performance Analysis of SOA-MZI based All-Optical AND & XOR Gate
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2016 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Utkarsh
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2016 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Utkarsh
Mach Zehnder Interferometer True Time Delay Line
 Mach Zehnder Interferometer True Time Delay Line Terna Engineering College Nerul, Navi Mumbai ABSTRACT In this paper we propose an optical true time delay (TTD) line for Phased array antenna beam forming,
Mach Zehnder Interferometer True Time Delay Line Terna Engineering College Nerul, Navi Mumbai ABSTRACT In this paper we propose an optical true time delay (TTD) line for Phased array antenna beam forming,
Tuning of Photonic Crystal Ring Resonators for Application in Analog to Digital Converter Systems
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 2013 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 4 (12): 4242-4247 Science Explorer Publications Tuning of Photonic Crystal Ring
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 2013 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 4 (12): 4242-4247 Science Explorer Publications Tuning of Photonic Crystal Ring
Optical solitons in a silicon waveguide
 Optical solitons in a silicon waveguide Jidong Zhang 1, Qiang Lin 2, Giovanni Piredda 2, Robert W. Boyd 2, Govind P. Agrawal 2, and Philippe M. Fauchet 1,2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Optical solitons in a silicon waveguide Jidong Zhang 1, Qiang Lin 2, Giovanni Piredda 2, Robert W. Boyd 2, Govind P. Agrawal 2, and Philippe M. Fauchet 1,2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
The Design of Optical Signal Transforms Based on Planar Waveguides on a Silicon on Insulator Platform
 IACSIT International Journal of Engineering and Technology, Vol., No.3, June ISSN: 793-836 The Design of Optical Signal Transforms Based on Planar Waveguides on a Silicon on Insulator Platform Trung-Thanh
IACSIT International Journal of Engineering and Technology, Vol., No.3, June ISSN: 793-836 The Design of Optical Signal Transforms Based on Planar Waveguides on a Silicon on Insulator Platform Trung-Thanh
Slow-light Enhanced Nonlinear Optics in Silicon Photonic Crystal Waveguides
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 6, NO. 3, 2010 273 Slow-light Enhanced Nonlinear Optics in Silicon Photonic Crystal Waveguides D. J. Moss 1, B. Corcoran 1, C. Monat 1, C. Grillet 1, T. P. White 2, L. O Faolain 2, T.
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 6, NO. 3, 2010 273 Slow-light Enhanced Nonlinear Optics in Silicon Photonic Crystal Waveguides D. J. Moss 1, B. Corcoran 1, C. Monat 1, C. Grillet 1, T. P. White 2, L. O Faolain 2, T.
Principles of Optics for Engineers
 Principles of Optics for Engineers Uniting historically different approaches by presenting optical analyses as solutions of Maxwell s equations, this unique book enables students and practicing engineers
Principles of Optics for Engineers Uniting historically different approaches by presenting optical analyses as solutions of Maxwell s equations, this unique book enables students and practicing engineers
A Novel Vertical Directional Coupler Switch With Switching-Operation-Induced Section and Extinction-Ratio-Enhanced Section
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 20, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2002 1773 A Novel Vertical Directional Coupler Switch With Switching-Operation-Induced Section and Extinction-Ratio-Enhanced Section Sung-Chan
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 20, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2002 1773 A Novel Vertical Directional Coupler Switch With Switching-Operation-Induced Section and Extinction-Ratio-Enhanced Section Sung-Chan
Figure1. To construct a light pulse, the electric component of the plane wave should be multiplied with a bell shaped function.
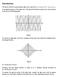 Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Non-reciprocal phase shift induced by an effective magnetic flux for light
 Non-reciprocal phase shift induced by an effective magnetic flux for light Lawrence D. Tzuang, 1 Kejie Fang, 2,3 Paulo Nussenzveig, 1,4 Shanhui Fan, 2 and Michal Lipson 1,5 1 School of Electrical and Computer
Non-reciprocal phase shift induced by an effective magnetic flux for light Lawrence D. Tzuang, 1 Kejie Fang, 2,3 Paulo Nussenzveig, 1,4 Shanhui Fan, 2 and Michal Lipson 1,5 1 School of Electrical and Computer
Widely Wavelength-tunable Soliton Generation and Few-cycle Pulse Compression with the Use of Dispersion-decreasing Fiber
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 5, 29 421 Widely Wavelength-tunable Soliton Generation and Few-cycle Pulse Compression with the Use of Dispersion-decreasing Fiber Alexey Andrianov 1, Sergey Muraviev 1, Arkady
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 5, 29 421 Widely Wavelength-tunable Soliton Generation and Few-cycle Pulse Compression with the Use of Dispersion-decreasing Fiber Alexey Andrianov 1, Sergey Muraviev 1, Arkady
Title. Author(s)Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanori. CitationOptics Letters, 31(1): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type.
 Title Polarization-independent optical directional coupler Author(s)Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Letters, 31(1): 56-58 Issue Date 2006 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/948 Rights
Title Polarization-independent optical directional coupler Author(s)Fujisawa, Takeshi; Koshiba, Masanori CitationOptics Letters, 31(1): 56-58 Issue Date 2006 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/948 Rights
SELF COLLIMATION IN PILLAR TYPE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL USING COMSOL
 SELF COLLIMATION IN PILLAR TYPE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL USING COMSOL S.Hemalatha 1, K.Shanthalakshmi 2 1 ME Communication Systems Department of ECE Adhiyamaan College Of Engineering, Hosur, India 2 Associate
SELF COLLIMATION IN PILLAR TYPE PHOTONIC CRYSTAL USING COMSOL S.Hemalatha 1, K.Shanthalakshmi 2 1 ME Communication Systems Department of ECE Adhiyamaan College Of Engineering, Hosur, India 2 Associate
Optical Polarization Filters and Splitters Based on Multimode Interference Structures using Silicon Waveguides
 International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume No. 7, July, 01 Optical Polarization Filters and Splitters Based on Multimode Interference Structures using Silicon Waveguides 1 Trung-Thanh Le,
International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume No. 7, July, 01 Optical Polarization Filters and Splitters Based on Multimode Interference Structures using Silicon Waveguides 1 Trung-Thanh Le,
Ultra-Compact Photonic Crystal Based Water Temperature Sensor
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 3, 2016: 274 278 Ultra-Compact Photonic Crystal Based Water Temperature Sensor Mahmoud NIKOUFARD *, Masoud KAZEMI ALAMOUTI, and Alireza ADEL Department of Electronics, Faculty
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 6, No. 3, 2016: 274 278 Ultra-Compact Photonic Crystal Based Water Temperature Sensor Mahmoud NIKOUFARD *, Masoud KAZEMI ALAMOUTI, and Alireza ADEL Department of Electronics, Faculty
A Low-loss Integrated Beam Combiner based on Polarization Multiplexing
 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORIES http://www.merl.com A Low-loss Integrated Beam Combiner based on Polarization Multiplexing Wang, B.; Kojima, K.; Koike-Akino, T.; Parsons, K.; Nishikawa, S.; Yagyu,
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORIES http://www.merl.com A Low-loss Integrated Beam Combiner based on Polarization Multiplexing Wang, B.; Kojima, K.; Koike-Akino, T.; Parsons, K.; Nishikawa, S.; Yagyu,
AMACH Zehnder interferometer (MZI) based on the
 1284 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 23, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 Optimal Design of Planar Wavelength Circuits Based on Mach Zehnder Interferometers and Their Cascaded Forms Qian Wang and Sailing He, Senior
1284 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 23, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 Optimal Design of Planar Wavelength Circuits Based on Mach Zehnder Interferometers and Their Cascaded Forms Qian Wang and Sailing He, Senior
Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion
 36 Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion Supreet Singh 1, Kulwinder Singh 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi
36 Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion Supreet Singh 1, Kulwinder Singh 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi
Hybrid Integration Technology of Silicon Optical Waveguide and Electronic Circuit
 Hybrid Integration Technology of Silicon Optical Waveguide and Electronic Circuit Daisuke Shimura Kyoko Kotani Hiroyuki Takahashi Hideaki Okayama Hiroki Yaegashi Due to the proliferation of broadband services
Hybrid Integration Technology of Silicon Optical Waveguide and Electronic Circuit Daisuke Shimura Kyoko Kotani Hiroyuki Takahashi Hideaki Okayama Hiroki Yaegashi Due to the proliferation of broadband services
Semiconductor Optical Communication Components and Devices Lecture 39: Optical Modulators
 Semiconductor Optical Communication Components and Devices Lecture 39: Optical Modulators Prof. Utpal Das Professor, Department of Electrical Engineering, Laser Technology Program, Indian Institute of
Semiconductor Optical Communication Components and Devices Lecture 39: Optical Modulators Prof. Utpal Das Professor, Department of Electrical Engineering, Laser Technology Program, Indian Institute of
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression
 Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
THz Filter Using the Transverse-electric (TE 1 ) Mode of the Parallel-plate Waveguide
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea ol. 13 No. December 9 pp. 3-7 DOI: 1.387/JOSK.9.13..3 THz Filter Using the Transverse-electric (TE 1 ) Mode of the Parallel-plate Waveguide Eui Su Lee and Tae-In
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea ol. 13 No. December 9 pp. 3-7 DOI: 1.387/JOSK.9.13..3 THz Filter Using the Transverse-electric (TE 1 ) Mode of the Parallel-plate Waveguide Eui Su Lee and Tae-In
Silica polygonal micropillar resonators: Fano line shapes tuning by using a Mach-Zehnder interferometer
 Silica polygonal micropillar resonators: Fano line shapes tuning by using a Mach-Zehnder interferometer Kam Yan Hon and Andrew W. Poon Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The Hong Kong
Silica polygonal micropillar resonators: Fano line shapes tuning by using a Mach-Zehnder interferometer Kam Yan Hon and Andrew W. Poon Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The Hong Kong
A new design of a 4-channel optical demultiplexer based on photonic crystal ring resonator using a modified Y-branch
 Optica Applicata, Vol. XLVIII, No. 2, 2018 DOI: 10.5277/oa180203 A new design of a 4-channel optical demultiplexer based on photonic crystal ring resonator using a modified Y-branch VAHID FALLAHI, MAHMOOD
Optica Applicata, Vol. XLVIII, No. 2, 2018 DOI: 10.5277/oa180203 A new design of a 4-channel optical demultiplexer based on photonic crystal ring resonator using a modified Y-branch VAHID FALLAHI, MAHMOOD
Generation of Complex Microwave and Millimeter-Wave Pulses Using Dispersion and Kerr Effect in Optical Fiber Systems
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 21, NO. 5, MAY 2003 1179 Generation of Complex Microwave and Millimeter-Wave Pulses Using Dispersion and Kerr Effect in Optical Fiber Systems Oren Levinson and Moshe
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 21, NO. 5, MAY 2003 1179 Generation of Complex Microwave and Millimeter-Wave Pulses Using Dispersion and Kerr Effect in Optical Fiber Systems Oren Levinson and Moshe
Cross-Phase modulation of laser pulses by strong single-cycle terahertz pulse
 Cross-Phase modulation of laser pulses by strong single-cycle terahertz pulse Nan Yang 1, Hai-Wei Du * 1 Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (Ministry of Education) and Department of Physics, Shanghai Jiaotong
Cross-Phase modulation of laser pulses by strong single-cycle terahertz pulse Nan Yang 1, Hai-Wei Du * 1 Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (Ministry of Education) and Department of Physics, Shanghai Jiaotong
Soliton Resonances in Dispersion Oscillating Optical Fibers
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 5, 2009 416 Soliton Resonances in Dispersion Oscillating Optical Fibers Andrey Konyukhov 1, Leonid Melnikov 1, Vladimir Khopin 2, Vladimir Stasuyk 3, and Alexej Sysoliatin 4 1
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 5, 2009 416 Soliton Resonances in Dispersion Oscillating Optical Fibers Andrey Konyukhov 1, Leonid Melnikov 1, Vladimir Khopin 2, Vladimir Stasuyk 3, and Alexej Sysoliatin 4 1
Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings
 Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu Optical Engineering 52(9), 091708 (September 2013) Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu
Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu Optical Engineering 52(9), 091708 (September 2013) Silicon photonic devices based on binary blazed gratings Zhiping Zhou Li Yu
Improved Extinction Ratios for Both Cross and Bar States Using Two-Section Ultra Short Vertical Directional Couplers
 Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Vol. 39 (000) pp. 6555 6559 Part 1, No. 1A, Decemer 000 c 000 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Improved Extinction Ratios for Both Cross and Bar States Using Two-Section Ultra Short
Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Vol. 39 (000) pp. 6555 6559 Part 1, No. 1A, Decemer 000 c 000 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Improved Extinction Ratios for Both Cross and Bar States Using Two-Section Ultra Short
- no emitters/amplifiers available. - complex process - no CMOS-compatible
 Advantages of photonic integrated circuits (PICs) in Microwave Photonics (MWP): compactness low-power consumption, stability flexibility possibility of aggregating optics and electronics functionalities
Advantages of photonic integrated circuits (PICs) in Microwave Photonics (MWP): compactness low-power consumption, stability flexibility possibility of aggregating optics and electronics functionalities
Elements of Optical Networking
 Bruckner Elements of Optical Networking Basics and practice of optical data communication With 217 Figures, 13 Tables and 93 Exercises Translated by Patricia Joliet VIEWEG+ TEUBNER VII Content Preface
Bruckner Elements of Optical Networking Basics and practice of optical data communication With 217 Figures, 13 Tables and 93 Exercises Translated by Patricia Joliet VIEWEG+ TEUBNER VII Content Preface
Optics and Lasers. Matt Young. Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides
 Matt Young Optics and Lasers Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides Fourth Revised Edition With 188 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Matt Young Optics and Lasers Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides Fourth Revised Edition With 188 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
OPTICAL NETWORKS. Building Blocks. A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005
 OPTICAL NETWORKS Building Blocks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction An introduction to WDM devices. optical fiber optical couplers optical receivers optical filters optical amplifiers
OPTICAL NETWORKS Building Blocks A. Gençata İTÜ, Dept. Computer Engineering 2005 Introduction An introduction to WDM devices. optical fiber optical couplers optical receivers optical filters optical amplifiers
CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING
 CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING Siti Aisyah bt. Ibrahim and Chong Wu Yi Photonics Research Center Department of Physics,
CHIRPED FIBER BRAGG GRATING (CFBG) BY ETCHING TECHNIQUE FOR SIMULTANEOUS TEMPERATURE AND REFRACTIVE INDEX SENSING Siti Aisyah bt. Ibrahim and Chong Wu Yi Photonics Research Center Department of Physics,
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy
 Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices
 644 Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices Kin Seng Chiang,* Sin Yip Cheng, Hau Ping Chan, Qing Liu, Kar Pong Lor, and Chi Kin Chow Department of Electronic Engineering,
644 Realization of Polarization-Insensitive Optical Polymer Waveguide Devices Kin Seng Chiang,* Sin Yip Cheng, Hau Ping Chan, Qing Liu, Kar Pong Lor, and Chi Kin Chow Department of Electronic Engineering,
ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES
 ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN: 1995-0772 Published BYAENSI Publication EISSN: 1998-1090 http://www.aensiweb.com/anas 2017 May 11(7):pages 36-40 Open Access Journal Designing of All Optical
ADVANCES in NATURAL and APPLIED SCIENCES ISSN: 1995-0772 Published BYAENSI Publication EISSN: 1998-1090 http://www.aensiweb.com/anas 2017 May 11(7):pages 36-40 Open Access Journal Designing of All Optical
Numerical Analysis and Optimization of a Multi-Mode Interference Polarization Beam Splitter
 Numerical Analysis and Optimization of a Multi-Mode Interference Polarization Beam Splitter Y. D Mello*, J. Skoric, M. Hui, E. Elfiky, D. Patel, D. Plant Department of Electrical Engineering, McGill University,
Numerical Analysis and Optimization of a Multi-Mode Interference Polarization Beam Splitter Y. D Mello*, J. Skoric, M. Hui, E. Elfiky, D. Patel, D. Plant Department of Electrical Engineering, McGill University,
Wavelength-independent coupler from fiber to an on-chip cavity, demonstrated over an 850nm span
 Wavelength-independent coupler from fiber to an on-chip, demonstrated over an 85nm span Tal Carmon, Steven Y. T. Wang, Eric P. Ostby and Kerry J. Vahala. Thomas J. Watson Laboratory of Applied Physics,
Wavelength-independent coupler from fiber to an on-chip, demonstrated over an 85nm span Tal Carmon, Steven Y. T. Wang, Eric P. Ostby and Kerry J. Vahala. Thomas J. Watson Laboratory of Applied Physics,
GRENOUILLE.
 GRENOUILLE Measuring ultrashort laser pulses the shortest events ever created has always been a challenge. For many years, it was possible to create ultrashort pulses, but not to measure them. Techniques
GRENOUILLE Measuring ultrashort laser pulses the shortest events ever created has always been a challenge. For many years, it was possible to create ultrashort pulses, but not to measure them. Techniques
ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 2016
 ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 2016 Lecture 9: Mach-Zehnder Modulator Transmitters Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Mach-Zehnder
ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 2016 Lecture 9: Mach-Zehnder Modulator Transmitters Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Mach-Zehnder
Demonstration of tunable optical delay lines based on apodized grating waveguides
 Demonstration of tunable optical delay lines based on apodized grating waveguides Saeed Khan 1, 2 and Sasan Fathpour 1,2,* 1 CREOL, The College of Optics and Photonics, University of Central Florida, Orlando,
Demonstration of tunable optical delay lines based on apodized grating waveguides Saeed Khan 1, 2 and Sasan Fathpour 1,2,* 1 CREOL, The College of Optics and Photonics, University of Central Florida, Orlando,
Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 9: December 11, 2015
 Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 9: December 11, 2015 Chapter 9: Optical Parametric Amplifiers and Oscillators 9.8 Noncollinear optical parametric amplifier (NOPA) 9.9 Optical parametric chirped-pulse
Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 9: December 11, 2015 Chapter 9: Optical Parametric Amplifiers and Oscillators 9.8 Noncollinear optical parametric amplifier (NOPA) 9.9 Optical parametric chirped-pulse
Session 2: Silicon and Carbon Photonics (11:00 11:30, Huxley LT311)
 Session 2: Silicon and Carbon Photonics (11:00 11:30, Huxley LT311) (invited) Formation and control of silicon nanocrystals by ion-beams for photonic applications M Halsall The University of Manchester,
Session 2: Silicon and Carbon Photonics (11:00 11:30, Huxley LT311) (invited) Formation and control of silicon nanocrystals by ion-beams for photonic applications M Halsall The University of Manchester,
Integrated photonic circuit in silicon on insulator for Fourier domain optical coherence tomography
 Integrated photonic circuit in silicon on insulator for Fourier domain optical coherence tomography Günay Yurtsever *,a, Pieter Dumon a, Wim Bogaerts a, Roel Baets a a Ghent University IMEC, Photonics
Integrated photonic circuit in silicon on insulator for Fourier domain optical coherence tomography Günay Yurtsever *,a, Pieter Dumon a, Wim Bogaerts a, Roel Baets a a Ghent University IMEC, Photonics
Wavelength and bandwidth-tunable silicon comb filter based on Sagnac loop mirrors with Mach- Zehnder interferometer couplers
 Wavelength and bandwidth-tunable silicon comb filter based on Sagnac loop mirrors with Mach- Zehnder interferometer couplers Xinhong Jiang, 1 Jiayang Wu, 1 Yuxing Yang, 1 Ting Pan, 1 Junming Mao, 1 Boyu
Wavelength and bandwidth-tunable silicon comb filter based on Sagnac loop mirrors with Mach- Zehnder interferometer couplers Xinhong Jiang, 1 Jiayang Wu, 1 Yuxing Yang, 1 Ting Pan, 1 Junming Mao, 1 Boyu
Integrated grating-assisted coarse/dense WDM multiplexers
 Integrated grating-assisted coarse/dense WDM multiplexers Linping Shen *a, Chenglin Xu b, and Wei-Ping Huang b a Apollo Inc., 1057 Main Street W., Hamilton, ON, Canada L8S 1B7 * lpshen@apollophotonics.com;
Integrated grating-assisted coarse/dense WDM multiplexers Linping Shen *a, Chenglin Xu b, and Wei-Ping Huang b a Apollo Inc., 1057 Main Street W., Hamilton, ON, Canada L8S 1B7 * lpshen@apollophotonics.com;
High-Speed Optical Modulators and Photonic Sideband Management
 114 High-Speed Optical Modulators and Photonic Sideband Management Tetsuya Kawanishi National Institute of Information and Communications Technology 4-2-1 Nukui-Kita, Koganei, Tokyo, Japan Tel: 81-42-327-7490;
114 High-Speed Optical Modulators and Photonic Sideband Management Tetsuya Kawanishi National Institute of Information and Communications Technology 4-2-1 Nukui-Kita, Koganei, Tokyo, Japan Tel: 81-42-327-7490;
Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature
 Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature Donghui Zhao.a, Xuewen Shu b, Wei Zhang b, Yicheng Lai a, Lin Zhang a, Ian Bennion a a Photonics Research Group,
Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature Donghui Zhao.a, Xuewen Shu b, Wei Zhang b, Yicheng Lai a, Lin Zhang a, Ian Bennion a a Photonics Research Group,
Optical Communications and Networking 朱祖勍. Sept. 25, 2017
 Optical Communications and Networking Sept. 25, 2017 Lecture 4: Signal Propagation in Fiber 1 Nonlinear Effects The assumption of linearity may not always be valid. Nonlinear effects are all related to
Optical Communications and Networking Sept. 25, 2017 Lecture 4: Signal Propagation in Fiber 1 Nonlinear Effects The assumption of linearity may not always be valid. Nonlinear effects are all related to
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 4
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 4 Modal Propagation of Light in an Optical Fiber Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar,
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 4 Modal Propagation of Light in an Optical Fiber Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar,
Self-phase-modulation induced spectral broadening in silicon waveguides
 Self-phase-modulation induced spectral broadening in silicon waveguides Ozdal Boyraz, Tejaswi Indukuri, and Bahram Jalali University of California, Los Angeles Department of Electrical Engineering, Los
Self-phase-modulation induced spectral broadening in silicon waveguides Ozdal Boyraz, Tejaswi Indukuri, and Bahram Jalali University of California, Los Angeles Department of Electrical Engineering, Los
Title. Author(s)Koshiba, Masanori. CitationJOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, 19(12): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights.
 Title Wavelength division multiplexing and demultiplexing Author(s)Koshiba, Masanori CitationJOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, 19(12): 1970-1975 Issue Date 2001-12 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/5582
Title Wavelength division multiplexing and demultiplexing Author(s)Koshiba, Masanori CitationJOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, 19(12): 1970-1975 Issue Date 2001-12 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/5582
Enhanced spectral compression in nonlinear optical
 Enhanced spectral compression in nonlinear optical fibres Sonia Boscolo, Christophe Finot To cite this version: Sonia Boscolo, Christophe Finot. Enhanced spectral compression in nonlinear optical fibres.
Enhanced spectral compression in nonlinear optical fibres Sonia Boscolo, Christophe Finot To cite this version: Sonia Boscolo, Christophe Finot. Enhanced spectral compression in nonlinear optical fibres.
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 93 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 93 (016 ) 647 654 6th International Conference On Advances In Computing & Communications, ICACC 016, 6-8 September 016,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 93 (016 ) 647 654 6th International Conference On Advances In Computing & Communications, ICACC 016, 6-8 September 016,
Index of refraction varies significantly for broadband pulses
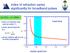 Index of refraction varies significantly for broadband pulses Δt=10 fs Δλ =90nm index of refraction may vary by nearly 1% phase speed depends on n v φ (λ) = c n(λ) n phase relations will be lost as pulse
Index of refraction varies significantly for broadband pulses Δt=10 fs Δλ =90nm index of refraction may vary by nearly 1% phase speed depends on n v φ (λ) = c n(λ) n phase relations will be lost as pulse
Single-mode lasing in PT-symmetric microring resonators
 CREOL The College of Optics & Photonics Single-mode lasing in PT-symmetric microring resonators Matthias Heinrich 1, Hossein Hodaei 2, Mohammad-Ali Miri 2, Demetrios N. Christodoulides 2 & Mercedeh Khajavikhan
CREOL The College of Optics & Photonics Single-mode lasing in PT-symmetric microring resonators Matthias Heinrich 1, Hossein Hodaei 2, Mohammad-Ali Miri 2, Demetrios N. Christodoulides 2 & Mercedeh Khajavikhan
21. (i) Briefly explain the evolution of fiber optic system (ii) Compare the configuration of different types of fibers. or 22. (b)(i) Derive modal eq
 Unit-1 Part-A FATIMA MICHAEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Senkottai Village, Madurai Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai - 625 020. [An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution] DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND
Unit-1 Part-A FATIMA MICHAEL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY Senkottai Village, Madurai Sivagangai Main Road, Madurai - 625 020. [An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution] DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND
UNIT - 7 WDM CONCEPTS AND COMPONENTS
 UNIT - 7 WDM CONCEPTS AND COMPONENTS WDM concepts, overview of WDM operation principles, WDM standards, Mach-Zehender interferometer, multiplexer, Isolators and circulators, direct thin film filters, active
UNIT - 7 WDM CONCEPTS AND COMPONENTS WDM concepts, overview of WDM operation principles, WDM standards, Mach-Zehender interferometer, multiplexer, Isolators and circulators, direct thin film filters, active
Suppression of Four Wave Mixing Based on the Pairing Combinations of Differently Linear-Polarized Optical Signals in WDM System
 The Quarterly Journal of Optoelectronical Nanostructures Islamic Azad University Spring 2016 / Vol. 1, No.1 Suppression of Four Wave Mixing Based on the Pairing Combinations of Differently Linear-Polarized
The Quarterly Journal of Optoelectronical Nanostructures Islamic Azad University Spring 2016 / Vol. 1, No.1 Suppression of Four Wave Mixing Based on the Pairing Combinations of Differently Linear-Polarized
Concepts of optical signal processing and optical communications
 Concepts of optical signal processing and optical communications Electronic components allowing to control electric currents with electric currents (or voltages) and integration of a large number of such
Concepts of optical signal processing and optical communications Electronic components allowing to control electric currents with electric currents (or voltages) and integration of a large number of such
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF APPLIED ENGINEERING RESEARCH, DINDIGUL Volume 1, No 3, 2010
 All Optical Half Adder Design Using Equations Governing XGM and FWM Effect in Semiconductor Optical Amplifier V. K. Srivastava, V. Priye Indian School of Mines University, Dhanbad srivastavavikrant@hotmail.com
All Optical Half Adder Design Using Equations Governing XGM and FWM Effect in Semiconductor Optical Amplifier V. K. Srivastava, V. Priye Indian School of Mines University, Dhanbad srivastavavikrant@hotmail.com
Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise
 Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise Ben Wu, * Zhenxing Wang, Bhavin J. Shastri, Matthew P. Chang, Nicholas A. Frost, and Paul R. Prucnal
Temporal phase mask encrypted optical steganography carried by amplified spontaneous emission noise Ben Wu, * Zhenxing Wang, Bhavin J. Shastri, Matthew P. Chang, Nicholas A. Frost, and Paul R. Prucnal
Analysis of Dispersion of Single Mode Optical Fiber
 Daffodil International University Institutional Repository Proceedings of NCCIS November 007 007-11-4 Analysis of Dispersion of Single Mode Optical Fiber Hossen, Monir Daffodil International University
Daffodil International University Institutional Repository Proceedings of NCCIS November 007 007-11-4 Analysis of Dispersion of Single Mode Optical Fiber Hossen, Monir Daffodil International University
A photonic analog-to-digital converter based on an unbalanced Mach-Zehnder quantizer
 A photonic analog-to-digital converter based on an unbalanced Mach-Zehnder quantizer Chris H. Sarantos and Nadir Dagli* Department of Electrical Engineering, University of California Santa Barbara, CA,
A photonic analog-to-digital converter based on an unbalanced Mach-Zehnder quantizer Chris H. Sarantos and Nadir Dagli* Department of Electrical Engineering, University of California Santa Barbara, CA,
Communication using Synchronization of Chaos in Semiconductor Lasers with optoelectronic feedback
 Communication using Synchronization of Chaos in Semiconductor Lasers with optoelectronic feedback S. Tang, L. Illing, J. M. Liu, H. D. I. barbanel and M. B. Kennel Department of Electrical Engineering,
Communication using Synchronization of Chaos in Semiconductor Lasers with optoelectronic feedback S. Tang, L. Illing, J. M. Liu, H. D. I. barbanel and M. B. Kennel Department of Electrical Engineering,
Crosstalk Reduction using Cascading Configuration in Multiplexer/Demultiplexer Based Array Waveguide Grating in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing
 International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 5, Issue 1, October 214] 2 ISSN 247-3338 Reduction using Cascading Configuration in Multiplexer/Demultiplexer Based Array Waveguide
International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 5, Issue 1, October 214] 2 ISSN 247-3338 Reduction using Cascading Configuration in Multiplexer/Demultiplexer Based Array Waveguide
Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating. Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel
 Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel Zhijun Yan *, Pouneh Saffari, Kaiming Zhou, Adedotun Adebay, Lin Zhang Photonic Research Group, Aston
Optical RI sensor based on an in-fiber Bragg grating Fabry-Perot cavity embedded with a micro-channel Zhijun Yan *, Pouneh Saffari, Kaiming Zhou, Adedotun Adebay, Lin Zhang Photonic Research Group, Aston
THE WIDE USE of optical wavelength division multiplexing
 1322 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 35, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 1999 Coupling of Modes Analysis of Resonant Channel Add Drop Filters C. Manolatou, M. J. Khan, Shanhui Fan, Pierre R. Villeneuve, H.
1322 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 35, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 1999 Coupling of Modes Analysis of Resonant Channel Add Drop Filters C. Manolatou, M. J. Khan, Shanhui Fan, Pierre R. Villeneuve, H.
Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors
 846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
846 PIERS Proceedings, Cambridge, USA, July 6, 8 Design and Analysis of Resonant Leaky-mode Broadband Reflectors M. Shokooh-Saremi and R. Magnusson Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University
Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier
 Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.2 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Fiber lasers offer advantages in maintaining stable operation over
Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.2 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Fiber lasers offer advantages in maintaining stable operation over
