STUDY OF CHIRPED PULSE COMPRESSION IN OPTICAL FIBER FOR ALL FIBER CPA SYSTEM
|
|
|
- Paula Hill
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJECE) ISSN(P): ; ISSN(E): X Vol. 4, Issue 6, Oct - Nov 15, 9-16 IASE SUDY OF CHIRPED PULSE COMPRESSION IN OPICAL FIBER FOR ALL FIBER CPA SYSEM ARPAN DUA Department of Physics, University of Burdwan, Burdwan, West Bengal, India ABSRAC Fiber lasers are highly regarded in present laser technological fields due to their high efficiency, beam quality and easy thermal management. Although, performance of fiber laser system is challenged by different nonlinear effects at high power. In case of ultra-short high power pulse fiber laser, nonlinearity plays significant role in pulse propagation through optical fiber as a result of presence of the high peak power of short pulses. Chirped pulse amplification (CPA) system can be incorporated in the design of such fiber laser as a way of increasing the pulse energy while mitigating the nonlinear effects. CPA system stretches the chirped pulses coming from fiber laser to reduce its peak power and then linearly amplified it. Amplified pulse experienced a pulse compressor made by bulk diffraction grating employed for recompression of the pulse. his bulk diffraction grating arrangement can be supplanted by specially design fiber arrangements to design all fiber CPA system using the nature of chirped pulse propagation in negative dispersion (anomalous) regime. In this paper, ultra-short chirped pulse propagation and compression in anomalous regime under the influence of Kerr nonlinearity, initial chirp and dispersion is studied using the nonlinear Schrödinger equation for optical fibers for all fiber CPA system. KEYWORDS: Anomalous Dispersion, Chirped Pulse Amplification, Kerr Effect, Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation, Self Phase Modulation INRODUCION Fiber lasers are become an essential part of present laser technologies due to their increasing popularity in various application fields. Efficient utilization of high power supporting capability of these lasers while maintaining the beam quality, makes them beneficial for industrial, defense and scientific applications. Although, in spite of all the acclaimed advantages of fiber lasers - stable light guidance over very long distances, large gain, high beam quality, alignment free laser system using narrowband reflectors (known as Fiber Bragg Grating or FBG) directly inside the fiber and combine or split light beams in a single fiber, fiber nonlinearities limit performance of fiber laser systems at high power. Due to the long path lengths of tightly confined light in the fiber core, the perfect conditions are created for inducing non linear effects even at modest power [1]. When high intensity light propagates through the core of the fiber, its refractive index (R.I.) profile is modified in a nonlinear way. he nonlinear dependence of the R.I. of a material on the intensity of light is produced by the Kerr effect [1]. his effect modifies the phase of a light through the nonlinear variation of the optical path. his effect has no significant role on continuous wave (CW) operation but for pulsed operation, Kerr effect produces an instantaneous phase shift which varies across the duration of the pulse. his effect is known as self phase modulation (SPM). In SPM effect, editor@iaset.us
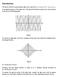
2 1 Arpan Dutta new frequency components are generated continuously as the pulse propagates through the fiber. hese SPM generated frequency components broaden the spectrum over its initial width. Chirp is the instantaneous frequency change in the pulse envelope. he chirp induced by SPM increases in magnitude with propagated distance and deviate the shape of the spectrum []. Ultra short pulse (generally in pico or femto second order) generation using pulsed operation of high power ultrafast fiber lasers yields shorter pulses with very high peak power. Due to high peak power of these pulses, nonlinear effects play significant role in fiber laser performance. Chirped pulse amplification (CPA) technique can be employed in high power ultrafast fiber lasers to increase pulse energy while mitigating the nonlinear effects. CPA can be used to prevent nonlinear effects in the fiber laser and amplifiers to enhance spectral quality of the pulse with pulse energies in order of micro joule to milijoule. CPA can generate sub picoseconds pulses with pulse energies of around 1 micro joule which are useful for many applications [3]. Figure 1: Chirped Pulse Amplification (CPA) System he working principle of CPA system can be understood from the block diagram given in figure 1. Fiber oscillator which is typically a mode locked fiber laser act as a short pulse source and deliver sub picoseconds pulses. hese short pulses are stretched by fiber stretcher, using the chromatic dispersion in several hundred meters of single mode fiber. Consequently, the peak power of the pulses is greatly reduced due to stretching and hence the nonlinear effects are mitigated. hese stretched pulses are linearly amplified by the fiber power amplifier. Amplified pulses are passes through a pulse compressor arrangement which can be made by a pair of bulk diffraction grating, inserted at the output of the power amplifier to reverse the chromatic dispersion induced by the stretcher and to recompress the pulses. he optical down converter is inserted to reduce the repetition rate of the oscillator pulses and thus to increase the pulse energy. By implementing the CPA system with current fiber technology, pulse stretching and recompression up to a factor 1, pulse energies of several mille joules and average powers of up to 1kW can be achieved [3]. o design an all fiber CPA system, all the main components of the CPA system should be based on optical fibers. In CPA system, oscillator, stretcher and power amplifier can be made by using optical fibers. If the use of bulk diffraction grating in compressor part replaced by specially designed fiber arrangements then all fiber CPA system can be achieved [4]. Now, pulse propagation in optical fiber mainly affected by the group velocity dispersion and fiber nonlinearity. Pulse, with presence or absence of chirp, propagating in nonlinear dispersive medium, experienced different effects at different propagation regime. Nonlinear effect like self phase modulation affects the pulse in spectral domain where as dispersion affect the pulse in temporal domain. Compression of positively chirped pulses also happens in negative dispersion (anomalous) regime [5]. So replacement of bulk diffraction grating in compressor part can be possible if the desired compression of pulse obtained by controlling the pulse as well as the optical fiber parameters. Chirped Pulse Propagation in Anomalous Regime Nonlinear Schrödinger equation (NLSE) governs the propagation of optical pulses in nonlinear dispersive medium Impact Factor (JCC): NAAS Rating: 3.6
3 Study of Chirped Pulse Compression in Optical 11 Fiber for all Fiber CPA System []. It is mathematically expressed as A i i A z A A A (1.) Where A (z, ) = slowly varying amplitude of the pulse envelope, α = fiber loss, β = nd order dispersion, = nonlinear coefficient. he three terms on the right hand side of equation (1.) signifies, respectively, the effects of fiber loss, dispersion and nonlinearity on pulses propagating inside the fibers. Depending upon the incident pulse parameters - peak power (P ) and initial width ( ) of the pulses, either dispersive or nonlinear effects dominate along the fiber. he values of dispersion length (L D ) and nonlinear length (L NL ) of the fiber provide length scaling over which dispersive or nonlinear effects become important for pulse evolution. Mathematically L D 1 L NL P. he sign of β (= s) implies two different dispersion regime in optical fiber. Positive value of s implies normal or positive dispersion regime where as negative value of s indicates the anomalous or negative dispersion regime. Pulse propagating in fiber experienced different effects in these two regimes. Again, Chirped and unchirped pulses also have different experience during propagation in these two regimes. Consider a linearly chirped pulse with Gaussian profile which is represented as (1 ic) A, ) exp[ ( ] (1.1) Where C is chirp parameter. If instantaneous frequency increases linearly from leading to trailing edge of the pulse then it is up chirp (C > ) and if opposite occurs then it is down chirp (C < ). he spectrum of A(, ) can be written as A(, ) ( ) 1 ic 1/ exp[ ] (1 ic) (1.) he full width half maximum (FWHM) value in spectral domain is 1/ ( 1 C ) / (1.3) In absence of chirp (C = ), spectral width is transform limited ( = 1) i.e. maintaining the time bandwidth product [6]. So presence of chirp enhance the spectral width of a pulse by factor of (1+C ) 1/ and equation (1.3) can be used to estimate the value of C. he transmitted pulse at any distance z is editor@iaset.us
4 1 Arpan Dutta A( z, ) [ i z(1 ic)] 1/ exp( [ (1 ic) ) i z(1 ic)] (1.4) distance z is So a chirped Gaussian pulse also maintains its shape during propagation. he pulse width after propagating a 1 C z [(1 ) z ( ) ] 1/ (1.5) he chirp parameter of the pulse changes as C1( z) C (1 C )( z / ) (1.6) Chirped pulses may broaden or compress depending upon whether C and β have same sign or not. If β C >, the chirped Gaussian pulses are broaden monotonically. his is because the dispersion induced chirp adds to the input chirp as the two contributions have same sign. If β C <, the dispersion induced chirp is opposite of input chirp. So pulse width decreases and minimum at a distance. he minimum value of the pulse width depends on input chirp parameter as min 1 ( 1 C 1/ ) (1.7) When the pulse attains its minimum width, C 1 = and pulse becomes transform limited such that = 1 where is the input spectral width of the pulse. So if a positively chirped (C > ) Gaussian pulse propagated through anomalous dispersion regime, then β C < and hence pulse compression occurs. If it is possible to control the amount of compression by controlling the pulse and fiber parameters, then the required pulse compressor can be designed. Simulation Results he effects of group velocity dispersion and SPM on pulse propagation in optical fiber can be realized by numerically solving the normalized form of NLSE. he standard numerical code for numerical solution of normalized NLSE written by G.P. Agrawal is used in this paper to study the chirped pulse compression in anomalous regime. he code implement split step Fourier method for solving the equation using MALAB []. he normalized NLSE expressed as A is A in A A (1.8) Where A () = slowly varying amplitude of the pulse envelope, normalized distance () z/l D, normalized time / and N = L D / L NL. N is actually related to the fiber and pulse parameters as Impact Factor (JCC): NAAS Rating: 3.6
5 Study of Chirped Pulse Compression in Optical 13 Fiber for all Fiber CPA System N ( P / ) (1.9) s = sign of β = ±1 (1 for normal regime and -1 for anomalous regime). In the numerical code, total fiber length is defined in units of the L D. N and s should be specified together with input amplitude A(,) for any numerical solution of equation (1.8). he input amplitude is related to the shape and amount of chirp of the pulse as A(, ) f ( )exp( ic / ) Where f() represents the pulse shape. In the code, an integer m is used to define the pulse shape. For Gaussian profile, the value of m = 1. For m = 1 1 A(, ) exp[ (1 ic) ] Now, pulse compression can be achieved in anomalous regime if the pulse is initially positively chirped. Compression can be controlled using the chirp parameter of the pulse. In numerical code, by setting s = -1 (anomalous dispersion regime), m = 1 (Gaussian pulse) and N = 1, pulse propagation examined by assigning the chirp parameter.5,1 and and varying the fiber length from.1 to.5 by.1 steps (in units of the dispersion length). Observations of the pulse propagation are done in temporal and spectrum domain. In each case, the value of C implies the initial pulse is positively chirped. o design an all fiber CPA system, replacement of bulk diffraction grating in the pulse compressor part is only possible if the required compression is achieved by specially designed fiber arrangements. he study in this paper also finds the optimized fiber length with fixed fiber and pulse parameters for required pulse compression. An experimentally obtained output pulse of a mode locked fiber laser system was taken for this study. Pulse and fiber parameters are - peak power (P ) = 55W, nonlinearity parameter () = 3.5 / W / km, FWHM = 5ps, N = 15.5 and 1 6 Figure : Chirped Pulse Propagation in Anomalous Dispersion Regime with C =.5 editor@iaset.us
6 14 Arpan Dutta Figure 3: Chirped Pulse Propagation in Anomalous Dispersion Regime with C = 1 Figure 4: Chirped Pulse Propagation in Anomalous Dispersion Regime with C = Figure 5: Compression of an Experimentally Obtained Pulse in Anomalous Dispersion Regime CONCLUSIONS According to figure to figure 4, it can be concluded that positively chirped pulse propagation in anomalous regime results pulse compression in temporal domain while no change in spectral domain. In all the three cases i.e. C =.5,1 and, pulse width reaches its minimum value at.5l D. When the pulse attains its minimum width, it becomes transform limited. hus to maintain the transform limit, no change occur in spectral width of the pulse and hence no change occur in spectral domain. Pulse compression i.e. the minimum value of the pulse width depends on the input chirp parameter by equation (1.7). If we move from figure to figure 4, we can conclude that increment in positive chirp results Impact Factor (JCC): NAAS Rating: 3.6
7 Study of Chirped Pulse Compression in Optical 15 Fiber for all Fiber CPA System increment in pulse compression in temporal domain but no change in spectral domain. More the input pulse is initially chirped, more pulse compression occurs temporally. Figure 5 shows the compression of the experimentally obtained pulse. he initial pulse has FWHM = 5ps before propagation. At fiber length.3l D, the pulse width becomes minimum and we get compressed pulse with FWHM = 1ps after propagation. So the key results of this study are Optimized fiber length =.3L D = 37.5m (as L D = 1.5km). FWHM before propagation = 5ps and FWHM after propagation = 1ps. So Compression factor =.. Estimated Chirp parameter using equation (1.7), C = 4.9 Unlike the previous results, figure 5 shows a significant change in pulse spectra. he spectrum of the pulse becomes a multi peak structure due to the SPM induced chirp. his happens due to the high value of N. N = 15.5 imply dominant nonlinear effects on the pulse. Higher value of N can cause optical wave breaking due to high nonlinearity. So from the overall study we can inferred that pulse compression can be controlled using the initial chirp of the input pulse without affecting the pulse spectra and fiber lengths can be optimized with fixed pulse and fiber parameters for required compression. hese important facts lead us to the design of an efficient pulse compressor for all fiber CPA system. ACKNOWLEDGEMENS I would like to express my heartiest gratitude to Dr. Mrinmay Pal, Senior Scientist, Fiber Optics and Photonics Division (FOPD), CSIR-Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute (CGCRI), for his valuable guidance and cooperation to complete this work. I am also thankful to the Director of the CSIR-CGCRI for giving me the opportunity to use the CGCRI laboratory and scientific software for my work. REFERENCES 1. Cesar Jauregui, Jens Limpert and Andreas ünnermann, High Power Fiber laser, nature photonics vol.7, nov. 13, pg G. P. Agarwal, Nonlinear Fiber Optics, Academic press. 3. Martin E. Fermann and Ingmar Hartl, ultra fast Fiber lasers, nature photonics vol.7 november 13, pg N.G.R. Broderick, D. J. Richardson, D. averner, J.E. Caplen, L. Dong, M. Ibsen, High Power Chirped Pulse all fiber amplification system based on large mode area fiber components, Optics Letters, Vol.4, Issue 8, 1999, pp S. V. Smirnov, S. M. Kobtsev and S. V. Kukarin, Linear compression of chirped pulses in optical fiber with large step-index mode area, 3 Feb 15, Vol. 3, No. 4, Optics Express Aaron Webster, Useful Mathematical Formulas for ransform Limited Pulses, Dover publications, editor@iaset.us
8 16 Arpan Dutta Arpan Dutta received his B.ech degree in Electronics & Communication Engineering from West Bengal University of echnology, West Bengal, India, in 1 and the M.ech degree in Electronics & Communication Engineering (Microwaves) from University of Burdwan, Burdwan, West Bengal, India, in 15. He was an M.ech project trainee in CSIR-Central Glass and Ceramic Research Institute (CGCRI) in His research interests include Fiber Optics, Semiconductor Optoelectronics, Fiber Lasers and Nonlinear Fiber Optics. Impact Factor (JCC): NAAS Rating: 3.6
Design of Highly stable Femto Second Fiber laser in Similariton regime for Optical Communication application
 International Journal of Innovation and Scientific Research ISSN 2351-814 Vol. 9 No. 2 Sep. 214, pp. 518-525 214 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijisr.issr-journals.org/ Design
International Journal of Innovation and Scientific Research ISSN 2351-814 Vol. 9 No. 2 Sep. 214, pp. 518-525 214 Innovative Space of Scientific Research Journals http://www.ijisr.issr-journals.org/ Design
WDM Transmitter Based on Spectral Slicing of Similariton Spectrum
 WDM Transmitter Based on Spectral Slicing of Similariton Spectrum Leila Graini and Kaddour Saouchi Laboratory of Study and Research in Instrumentation and Communication of Annaba (LERICA), Department of
WDM Transmitter Based on Spectral Slicing of Similariton Spectrum Leila Graini and Kaddour Saouchi Laboratory of Study and Research in Instrumentation and Communication of Annaba (LERICA), Department of
C. J. S. de Matos and J. R. Taylor. Femtosecond Optics Group, Imperial College, Prince Consort Road, London SW7 2BW, UK
 Multi-kilowatt, all-fiber integrated chirped-pulse amplification system yielding 4 pulse compression using air-core fiber and conventional erbium-doped fiber amplifier C. J. S. de Matos and J. R. Taylor
Multi-kilowatt, all-fiber integrated chirped-pulse amplification system yielding 4 pulse compression using air-core fiber and conventional erbium-doped fiber amplifier C. J. S. de Matos and J. R. Taylor
Pulse stretching and compressing using grating pairs
 Pulse stretching and compressing using grating pairs A White Paper Prof. Dr. Clara Saraceno Photonics and Ultrafast Laser Science Publication Version: 1.0, January, 2017-1 - Table of Contents Dispersion
Pulse stretching and compressing using grating pairs A White Paper Prof. Dr. Clara Saraceno Photonics and Ultrafast Laser Science Publication Version: 1.0, January, 2017-1 - Table of Contents Dispersion
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG)
 Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 35. Self-Phase-Modulation
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 35 Self-Phase-Modulation (SPM) Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 35 Self-Phase-Modulation (SPM) Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
Fundamental Optics ULTRAFAST THEORY ( ) = ( ) ( q) FUNDAMENTAL OPTICS. q q = ( A150 Ultrafast Theory
 ULTRAFAST THEORY The distinguishing aspect of femtosecond laser optics design is the need to control the phase characteristic of the optical system over the requisite wide pulse bandwidth. CVI Laser Optics
ULTRAFAST THEORY The distinguishing aspect of femtosecond laser optics design is the need to control the phase characteristic of the optical system over the requisite wide pulse bandwidth. CVI Laser Optics
Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier
 Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.2 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Fiber lasers offer advantages in maintaining stable operation over
Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.2 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Fiber lasers offer advantages in maintaining stable operation over
A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method.
 PULSE GATING : A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method. Picosecond lasers can be found in many fields of applications from research to industry. These lasers are very common in bio-photonics, non-linear
PULSE GATING : A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method. Picosecond lasers can be found in many fields of applications from research to industry. These lasers are very common in bio-photonics, non-linear
All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration
 1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
How to build an Er:fiber femtosecond laser
 How to build an Er:fiber femtosecond laser Daniele Brida 17.02.2016 Konstanz Ultrafast laser Time domain : pulse train Frequency domain: comb 3 26.03.2016 Frequency comb laser Time domain : pulse train
How to build an Er:fiber femtosecond laser Daniele Brida 17.02.2016 Konstanz Ultrafast laser Time domain : pulse train Frequency domain: comb 3 26.03.2016 Frequency comb laser Time domain : pulse train
Enhanced spectral compression in nonlinear optical
 Enhanced spectral compression in nonlinear optical fibres Sonia Boscolo, Christophe Finot To cite this version: Sonia Boscolo, Christophe Finot. Enhanced spectral compression in nonlinear optical fibres.
Enhanced spectral compression in nonlinear optical fibres Sonia Boscolo, Christophe Finot To cite this version: Sonia Boscolo, Christophe Finot. Enhanced spectral compression in nonlinear optical fibres.
Figure1. To construct a light pulse, the electric component of the plane wave should be multiplied with a bell shaped function.
 Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II
 Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II Generating negative groupdelay dispersion angular dispersion Pulse compression Prisms Gratings Chirped mirrors Chirped vs. transform-limited A transform-limited pulse:
Dispersion and Ultrashort Pulses II Generating negative groupdelay dispersion angular dispersion Pulse compression Prisms Gratings Chirped mirrors Chirped vs. transform-limited A transform-limited pulse:
Simultaneous pulse amplification and compression in all-fiber-integrated pre-chirped large-mode-area Er-doped fiber amplifier
 Simultaneous pulse amplification and compression in all-fiber-integrated pre-chirped large-mode-area Er-doped fiber amplifier Gong-Ru Lin 1 *, Ying-Tsung Lin, and Chao-Kuei Lee 2 1 Graduate Institute of
Simultaneous pulse amplification and compression in all-fiber-integrated pre-chirped large-mode-area Er-doped fiber amplifier Gong-Ru Lin 1 *, Ying-Tsung Lin, and Chao-Kuei Lee 2 1 Graduate Institute of
High Power Compact Fiber Chirped Pulse Amplifiers at 1558-nm using Er/Yb LMA Fibers and Chirped Volume Bragg Grating Compressors
 High Power Compact Fiber Chirped Pulse Amplifiers at 1558-nm using Er/Yb LMA Fibers and Chirped Volume Bragg Grating Compressors Ming-Yuan Cheng, Almantas Galvanauskas University of Michigan Vadim Smirnov,
High Power Compact Fiber Chirped Pulse Amplifiers at 1558-nm using Er/Yb LMA Fibers and Chirped Volume Bragg Grating Compressors Ming-Yuan Cheng, Almantas Galvanauskas University of Michigan Vadim Smirnov,
ANALYSIS OF DISPERSION COMPENSATION IN A SINGLE MODE OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
 ANAYSIS OF DISPERSION COMPENSATION IN A SINGE MODE OPTICA FIBER COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Sani Abdullahi Mohammed 1, Engr. Yahya Adamu and Engr. Matthew Kwatri uka 3 1,,3 Department of Electrical and Electronics
ANAYSIS OF DISPERSION COMPENSATION IN A SINGE MODE OPTICA FIBER COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Sani Abdullahi Mohammed 1, Engr. Yahya Adamu and Engr. Matthew Kwatri uka 3 1,,3 Department of Electrical and Electronics
Yb-doped Mode-locked fiber laser based on NLPR Yan YOU
 Yb-doped Mode-locked fiber laser based on NLPR 20120124 Yan YOU Mode locking method-nlpr Nonlinear polarization rotation(nlpr) : A power-dependent polarization change is converted into a power-dependent
Yb-doped Mode-locked fiber laser based on NLPR 20120124 Yan YOU Mode locking method-nlpr Nonlinear polarization rotation(nlpr) : A power-dependent polarization change is converted into a power-dependent
Directly Chirped Laser Source for Chirped Pulse Amplification
 Directly Chirped Laser Source for Chirped Pulse Amplification Input pulse (single frequency) AWG RF amp Output pulse (chirped) Phase modulator Normalized spectral intensity (db) 64 65 66 67 68 69 1052.4
Directly Chirped Laser Source for Chirped Pulse Amplification Input pulse (single frequency) AWG RF amp Output pulse (chirped) Phase modulator Normalized spectral intensity (db) 64 65 66 67 68 69 1052.4
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression
 Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
Spatial distribution clamping of discrete spatial solitons due to three photon absorption in AlGaAs waveguide arrays
 Spatial distribution clamping of discrete spatial solitons due to three photon absorption in AlGaAs waveguide arrays Darren D. Hudson 1,2, J. Nathan Kutz 3, Thomas R. Schibli 1,2, Demetrios N. Christodoulides
Spatial distribution clamping of discrete spatial solitons due to three photon absorption in AlGaAs waveguide arrays Darren D. Hudson 1,2, J. Nathan Kutz 3, Thomas R. Schibli 1,2, Demetrios N. Christodoulides
Fiber Laser and Amplifier Simulations in FETI
 Fiber Laser and Amplifier Simulations in FETI Zoltán Várallyay* 1, Gábor Gajdátsy* 1, András Cserteg* 1, Gábor Varga* 2 and Gyula Besztercey* 3 Fiber lasers are displaying an increasing demand and a presence
Fiber Laser and Amplifier Simulations in FETI Zoltán Várallyay* 1, Gábor Gajdátsy* 1, András Cserteg* 1, Gábor Varga* 2 and Gyula Besztercey* 3 Fiber lasers are displaying an increasing demand and a presence
Continuum White Light Generation. WhiteLase: High Power Ultrabroadband
 Continuum White Light Generation WhiteLase: High Power Ultrabroadband Light Sources Technology Ultrafast Pulses + Fiber Laser + Non-linear PCF = Spectral broadening from 400nm to 2500nm Ultrafast Fiber
Continuum White Light Generation WhiteLase: High Power Ultrabroadband Light Sources Technology Ultrafast Pulses + Fiber Laser + Non-linear PCF = Spectral broadening from 400nm to 2500nm Ultrafast Fiber
Performance Analysis of dispersion compensation using Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG) in Optical Communication
 Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347-5161 214 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Performance
Research Article International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 416, P-ISSN 2347-5161 214 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Performance
Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks
 363 Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks CHAOUI Fahd 3, HAJAJI Anas 1, AGHZOUT Otman 2,4, CHAKKOUR Mounia 3, EL YAKHLOUFI Mounir
363 Chirped Bragg Grating Dispersion Compensation in Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Optical Long-Haul Networks CHAOUI Fahd 3, HAJAJI Anas 1, AGHZOUT Otman 2,4, CHAKKOUR Mounia 3, EL YAKHLOUFI Mounir
Development of Nano Second Pulsed Lasers Using Polarization Maintaining Fibers
 Development of Nano Second Pulsed Lasers Using Polarization Maintaining Fibers Shun-ichi Matsushita*, * 2, Taizo Miyato*, * 2, Hiroshi Hashimoto*, * 2, Eisuke Otani* 2, Tatsuji Uchino* 2, Akira Fujisaki*,
Development of Nano Second Pulsed Lasers Using Polarization Maintaining Fibers Shun-ichi Matsushita*, * 2, Taizo Miyato*, * 2, Hiroshi Hashimoto*, * 2, Eisuke Otani* 2, Tatsuji Uchino* 2, Akira Fujisaki*,
Lecture 3 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 3, Slide 1
 Lecture 3 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion Limitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
Lecture 3 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion Limitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
Chad A. Husko 1,, Sylvain Combrié 2, Pierre Colman 2, Jiangjun Zheng 1, Alfredo De Rossi 2, Chee Wei Wong 1,
 SOLITON DYNAMICS IN THE MULTIPHOTON PLASMA REGIME Chad A. Husko,, Sylvain Combrié, Pierre Colman, Jiangjun Zheng, Alfredo De Rossi, Chee Wei Wong, Optical Nanostructures Laboratory, Columbia University
SOLITON DYNAMICS IN THE MULTIPHOTON PLASMA REGIME Chad A. Husko,, Sylvain Combrié, Pierre Colman, Jiangjun Zheng, Alfredo De Rossi, Chee Wei Wong, Optical Nanostructures Laboratory, Columbia University
Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 9: December 11, 2015
 Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 9: December 11, 2015 Chapter 9: Optical Parametric Amplifiers and Oscillators 9.8 Noncollinear optical parametric amplifier (NOPA) 9.9 Optical parametric chirped-pulse
Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 9: December 11, 2015 Chapter 9: Optical Parametric Amplifiers and Oscillators 9.8 Noncollinear optical parametric amplifier (NOPA) 9.9 Optical parametric chirped-pulse
Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion
 36 Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion Supreet Singh 1, Kulwinder Singh 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi
36 Analysis of Self Phase Modulation Fiber nonlinearity in Optical Transmission System with Dispersion Supreet Singh 1, Kulwinder Singh 2 1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Punjabi
ASE Suppression in a Diode-Pumped Nd:YLF Regenerative Amplifier Using a Volume Bragg Grating
 ASE Suppression in a Diode-Pumped Nd:YLF Regenerative Amplifier Using a Volume Bragg Grating Spectral density (db) 0 10 20 30 40 Mirror VBG 1053.0 1053.3 1053.6 Wavelength (nm) Frontiers in Optics 2007/Laser
ASE Suppression in a Diode-Pumped Nd:YLF Regenerative Amplifier Using a Volume Bragg Grating Spectral density (db) 0 10 20 30 40 Mirror VBG 1053.0 1053.3 1053.6 Wavelength (nm) Frontiers in Optics 2007/Laser
Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta RP Photonics Consulting GmbH. Competence Area: Fiber Devices
 Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta RP Photonics Consulting GmbH Competence Area: Fiber Devices Topics in this Area Fiber lasers, including exotic types Fiber amplifiers, including telecom-type devices and high power
Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta RP Photonics Consulting GmbH Competence Area: Fiber Devices Topics in this Area Fiber lasers, including exotic types Fiber amplifiers, including telecom-type devices and high power
High Power Femtosecond Fiber Chirped Pulse Amplification System for High Speed Micromachining
 High Power Femtosecond Fiber Chirped Pulse Amplification System for High Speed Micromachining Lawrence SHAH and Martin E. FERMANN IMRA America, Inc., 1044 Woodridge Avenue, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA, 48105
High Power Femtosecond Fiber Chirped Pulse Amplification System for High Speed Micromachining Lawrence SHAH and Martin E. FERMANN IMRA America, Inc., 1044 Woodridge Avenue, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA, 48105
Single Mode Optical Fiber - Dispersion
 Single Mode Optical Fiber - Dispersion 1 OBJECTIVE Characterize analytically and through simulation the effects of dispersion on optical systems. 2 PRE-LAB A single mode fiber, as the name implies, supports
Single Mode Optical Fiber - Dispersion 1 OBJECTIVE Characterize analytically and through simulation the effects of dispersion on optical systems. 2 PRE-LAB A single mode fiber, as the name implies, supports
atom physics seminar ultra short laser pulses
 atom physics seminar ultra short laser pulses creation and application ultra short laser pulses overview what? - why? - how? creation and optimisation typical experimental setup properties of existing
atom physics seminar ultra short laser pulses creation and application ultra short laser pulses overview what? - why? - how? creation and optimisation typical experimental setup properties of existing
Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber
 Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber I. H. M. Nadzar 1 and N. A.Awang 1* 1 Faculty of Science, Technology and Human Development, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Johor,
Study of Multiwavelength Fiber Laser in a Highly Nonlinear Fiber I. H. M. Nadzar 1 and N. A.Awang 1* 1 Faculty of Science, Technology and Human Development, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Johor,
Simultaneous Amplification and Compression of Ultrashort Solitons in an Erbium-Doped Nonlinear Amplifying Fiber Loop Mirror
 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 39, NO. 4, APRIL 2003 555 Simultaneous Amplification and Compression of Ultrashort Solitons in an Erbium-Doped Nonlinear Amplifying Fiber Loop Mirror Ping Kong
IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 39, NO. 4, APRIL 2003 555 Simultaneous Amplification and Compression of Ultrashort Solitons in an Erbium-Doped Nonlinear Amplifying Fiber Loop Mirror Ping Kong
Spectral broadening of frequency combs via pulse apodization prior to nonlinear propagation
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Open Access Theses Theses and Dissertations Spring 2015 Spectral broadening of frequency combs via pulse apodization prior to nonlinear propagation Oscar E. Sandoval Purdue
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Open Access Theses Theses and Dissertations Spring 2015 Spectral broadening of frequency combs via pulse apodization prior to nonlinear propagation Oscar E. Sandoval Purdue
Large-aperture chirped volume Bragg grating based fiber CPA system
 Large-aperture chirped volume Bragg grating based fiber CPA system * Kai-Hsiu Liao 1, Ming-Yuan Cheng 1, Emilie Flecher 3, Vadim I. Smirnov 2, Leonid B. Glebov 3, and Almantas Galvanauskas 1 1 EECS Department,
Large-aperture chirped volume Bragg grating based fiber CPA system * Kai-Hsiu Liao 1, Ming-Yuan Cheng 1, Emilie Flecher 3, Vadim I. Smirnov 2, Leonid B. Glebov 3, and Almantas Galvanauskas 1 1 EECS Department,
The Realization of Ultra-Short Laser Sources. with Very High Intensity
 Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 3, 2009, no. 10, 359-367 The Realization of Ultra-Short Laser Sources with Very High Intensity Arqile Done University of Gjirokastra, Department of Mathematics Computer
Adv. Studies Theor. Phys., Vol. 3, 2009, no. 10, 359-367 The Realization of Ultra-Short Laser Sources with Very High Intensity Arqile Done University of Gjirokastra, Department of Mathematics Computer
Propagation, Dispersion and Measurement of sub-10 fs Pulses
 Propagation, Dispersion and Measurement of sub-10 fs Pulses Table of Contents 1. Theory 2. Pulse propagation through various materials o Calculating the index of refraction Glass materials Air Index of
Propagation, Dispersion and Measurement of sub-10 fs Pulses Table of Contents 1. Theory 2. Pulse propagation through various materials o Calculating the index of refraction Glass materials Air Index of
Lecture 7 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 7, Slide 1
 Dispersion management Lecture 7 Dispersion compensating fibers (DCF) Fiber Bragg gratings (FBG) Dispersion-equalizing filters Optical phase conjugation (OPC) Electronic dispersion compensation (EDC) Fiber
Dispersion management Lecture 7 Dispersion compensating fibers (DCF) Fiber Bragg gratings (FBG) Dispersion-equalizing filters Optical phase conjugation (OPC) Electronic dispersion compensation (EDC) Fiber
The Development of a High Quality and a High Peak Power Pulsed Fiber Laser With a Flexible Tunability of the Pulse Width
 The Development of a High Quality and a High Peak Power Pulsed Fiber Laser With a Flexible Tunability of the Pulse Width Ryo Kawahara *1, Hiroshi Hashimoto *1, Jeffrey W. Nicholson *2, Eisuke Otani *1,
The Development of a High Quality and a High Peak Power Pulsed Fiber Laser With a Flexible Tunability of the Pulse Width Ryo Kawahara *1, Hiroshi Hashimoto *1, Jeffrey W. Nicholson *2, Eisuke Otani *1,
Fibre Bragg Grating. Minoli Arumugam Photonics and Optical Communications Instructor: Prof. Dietmar Knipp Jacobs University Bremen Spring 2007
 Fibre Bragg Grating Minoli Arumugam Photonics and Optical Communications Instructor: Prof. Dietmar Knipp Jacobs University Bremen Spring 2007 What is a Fibre Bragg Grating? It is a type of distributed
Fibre Bragg Grating Minoli Arumugam Photonics and Optical Communications Instructor: Prof. Dietmar Knipp Jacobs University Bremen Spring 2007 What is a Fibre Bragg Grating? It is a type of distributed
Chromatic Dispersion Compensation in Optical Fiber Communication System and its Simulation
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology Supplementary Article Chromatic Dispersion Compensation in Optical Fiber Communication System and its Simulation R. Udayakumar 1 *, V. Khanaa 2 and T. Saravanan
Indian Journal of Science and Technology Supplementary Article Chromatic Dispersion Compensation in Optical Fiber Communication System and its Simulation R. Udayakumar 1 *, V. Khanaa 2 and T. Saravanan
Pulse breaking recovery in fiber lasers
 Pulse breaking recovery in fiber lasers L. M. Zhao 1,, D. Y. Tang 1 *, H. Y. Tam 3, and C. Lu 1 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798 Department
Pulse breaking recovery in fiber lasers L. M. Zhao 1,, D. Y. Tang 1 *, H. Y. Tam 3, and C. Lu 1 School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798 Department
J-KAREN-P Session 1, 10:00 10:
 J-KAREN-P 2018 Session 1, 10:00 10:25 2018 5 8 Outline Introduction Capabilities of J-KAREN-P facility Optical architecture Status and implementation of J-KAREN-P facility Amplification performance Recompression
J-KAREN-P 2018 Session 1, 10:00 10:25 2018 5 8 Outline Introduction Capabilities of J-KAREN-P facility Optical architecture Status and implementation of J-KAREN-P facility Amplification performance Recompression
Comprehensive Numerical Modelling of a Low-Gain Optical Parametric Amplifier as a Front-End Contrast Enhancement Unit
 Comprehensive Numerical Modelling of a Low-Gain Optical Parametric Amplifier as a Front-End Contrast Enhancement Unit arxiv:161.5558v1 [physics.optics] 21 Jan 216 A. B. Sharba, G. Nersisyan, M. Zepf, M.
Comprehensive Numerical Modelling of a Low-Gain Optical Parametric Amplifier as a Front-End Contrast Enhancement Unit arxiv:161.5558v1 [physics.optics] 21 Jan 216 A. B. Sharba, G. Nersisyan, M. Zepf, M.
Compensation of Dispersion in 10 Gbps WDM System by Using Fiber Bragg Grating
 International Journal of Computational Engineering & Management, Vol. 15 Issue 5, September 2012 www..org 16 Compensation of Dispersion in 10 Gbps WDM System by Using Fiber Bragg Grating P. K. Raghav 1,
International Journal of Computational Engineering & Management, Vol. 15 Issue 5, September 2012 www..org 16 Compensation of Dispersion in 10 Gbps WDM System by Using Fiber Bragg Grating P. K. Raghav 1,
Generation of Complex Microwave and Millimeter-Wave Pulses Using Dispersion and Kerr Effect in Optical Fiber Systems
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 21, NO. 5, MAY 2003 1179 Generation of Complex Microwave and Millimeter-Wave Pulses Using Dispersion and Kerr Effect in Optical Fiber Systems Oren Levinson and Moshe
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 21, NO. 5, MAY 2003 1179 Generation of Complex Microwave and Millimeter-Wave Pulses Using Dispersion and Kerr Effect in Optical Fiber Systems Oren Levinson and Moshe
Ultra-fast all-optical wavelength conversion in silicon waveguides using femtosecond pulses
 Ultra-fast all-optical wavelength conversion in silicon waveguides using femtosecond pulses R.Dekker a, J. Niehusmann b, M. Först b, and A. Driessen a a Integrated Optical Micro Systems, Mesa+, University
Ultra-fast all-optical wavelength conversion in silicon waveguides using femtosecond pulses R.Dekker a, J. Niehusmann b, M. Först b, and A. Driessen a a Integrated Optical Micro Systems, Mesa+, University
Optical Communications and Networking 朱祖勍. Sept. 25, 2017
 Optical Communications and Networking Sept. 25, 2017 Lecture 4: Signal Propagation in Fiber 1 Nonlinear Effects The assumption of linearity may not always be valid. Nonlinear effects are all related to
Optical Communications and Networking Sept. 25, 2017 Lecture 4: Signal Propagation in Fiber 1 Nonlinear Effects The assumption of linearity may not always be valid. Nonlinear effects are all related to
Coherent temporal imaging with analog timebandwidth
 Coherent temporal imaging with analog timebandwidth compression Mohammad H. Asghari 1, * and Bahram Jalali 1,2,3 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095,
Coherent temporal imaging with analog timebandwidth compression Mohammad H. Asghari 1, * and Bahram Jalali 1,2,3 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095,
A PIECE WISE LINEAR SOLUTION FOR NONLINEAR SRS EFFECT IN DWDM FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 9 A PIECE WISE LINEAR SOLUION FOR NONLINEAR SRS EFFEC IN DWDM FIBER OPIC COMMUNICAION SYSEMS M. L. SINGH and I. S. HUDIARA Department of Electronics echnology Guru Nanak Dev University Amritsar-005, India
9 A PIECE WISE LINEAR SOLUION FOR NONLINEAR SRS EFFEC IN DWDM FIBER OPIC COMMUNICAION SYSEMS M. L. SINGH and I. S. HUDIARA Department of Electronics echnology Guru Nanak Dev University Amritsar-005, India
All optical wavelength converter based on fiber cross-phase modulation and fiber Bragg grating
 All optical wavelength converter based on fiber cross-phase modulation and fiber Bragg grating Pavel Honzatko a, a Institute of Photonics and Electronics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, v.v.i.,
All optical wavelength converter based on fiber cross-phase modulation and fiber Bragg grating Pavel Honzatko a, a Institute of Photonics and Electronics, Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic, v.v.i.,
Spectral Characteristics of Uniform Fiber Bragg Grating With Different Grating Length and Refractive Index Variation
 Spectral Characteristics of Uniform Fiber Bragg Grating With Different Grating Length and efractive Index Variation Chiranjit Ghosh 1, Quazi Md. Alfred 2, Biswajit Ghosh 3 ME (EIE) Student, University
Spectral Characteristics of Uniform Fiber Bragg Grating With Different Grating Length and efractive Index Variation Chiranjit Ghosh 1, Quazi Md. Alfred 2, Biswajit Ghosh 3 ME (EIE) Student, University
Performance scaling of laser amplifiers via coherent combination of ultrashort pulses
 Performance scaling of laser amplifiers via coherent combination of ultrashort pulses Dissertation zur Erlangung des akademischen Grades doctor rerum naturalium (Dr. rer. nat.) vorgelegt dem Rat der Physikalisch-Astronomischen
Performance scaling of laser amplifiers via coherent combination of ultrashort pulses Dissertation zur Erlangung des akademischen Grades doctor rerum naturalium (Dr. rer. nat.) vorgelegt dem Rat der Physikalisch-Astronomischen
Soliton stability conditions in actively modelocked inhomogeneously broadened lasers
 Lu et al. Vol. 20, No. 7/July 2003 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1473 Soliton stability conditions in actively modelocked inhomogeneously broadened lasers Wei Lu,* Li Yan, and Curtis R. Menyuk Department of Computer
Lu et al. Vol. 20, No. 7/July 2003 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1473 Soliton stability conditions in actively modelocked inhomogeneously broadened lasers Wei Lu,* Li Yan, and Curtis R. Menyuk Department of Computer
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy
 Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 93 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 93 (016 ) 647 654 6th International Conference On Advances In Computing & Communications, ICACC 016, 6-8 September 016,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 93 (016 ) 647 654 6th International Conference On Advances In Computing & Communications, ICACC 016, 6-8 September 016,
Ultrafast Optical Physics II (SoSe 2017) Lecture 9, June 16
 Ultrafast Optical Physics II (SoSe 2017) Lecture 9, June 16 9 Pulse Characterization 9.1 Intensity Autocorrelation 9.2 Interferometric Autocorrelation (IAC) 9.3 Frequency Resolved Optical Gating (FROG)
Ultrafast Optical Physics II (SoSe 2017) Lecture 9, June 16 9 Pulse Characterization 9.1 Intensity Autocorrelation 9.2 Interferometric Autocorrelation (IAC) 9.3 Frequency Resolved Optical Gating (FROG)
TO meet the demand for high-speed and high-capacity
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 16, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1998 1953 A Femtosecond Code-Division Multiple-Access Communication System Test Bed H. P. Sardesai, C.-C. Chang, and A. M. Weiner Abstract This
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 16, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 1998 1953 A Femtosecond Code-Division Multiple-Access Communication System Test Bed H. P. Sardesai, C.-C. Chang, and A. M. Weiner Abstract This
Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3000 cm 1
 Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3 cm A.C.W. van Rhijn, S. Postma, J.P. Korterik, J.L. Herek, and H.L. Offerhaus Mesa + Research Institute for Nanotechnology, University
Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3 cm A.C.W. van Rhijn, S. Postma, J.P. Korterik, J.L. Herek, and H.L. Offerhaus Mesa + Research Institute for Nanotechnology, University
Theoretical Investigation of Optical Fiber-Length-Dependent Phase Noise in Opto-Electronic Oscillators
 Theoretical Investigation of Optical Fiber-Length-Dependent Phase Noise in Opto-Electronic Oscillators The effects of optical propagation on RF signal and noise Andrew Docherty, Olukayode Okusaga, Curtis
Theoretical Investigation of Optical Fiber-Length-Dependent Phase Noise in Opto-Electronic Oscillators The effects of optical propagation on RF signal and noise Andrew Docherty, Olukayode Okusaga, Curtis
Determination of ideal Fibre Bragg Grating (FBG) length for Optical Transmission System
 Determination of ideal Fibre Bragg Grating (FBG) length for Optical Transmission System Aastha Singhal SENSE school, VIT University Vellore, India Akanksha Singh SENSE school, VIT University Vellore, India
Determination of ideal Fibre Bragg Grating (FBG) length for Optical Transmission System Aastha Singhal SENSE school, VIT University Vellore, India Akanksha Singh SENSE school, VIT University Vellore, India
All-fiber, all-normal dispersion ytterbium ring oscillator
 Early View publication on www.interscience.wiley.com (issue and page numbers not yet assigned; citable using Digital Object Identifier DOI) Laser Phys. Lett. 1 5 () / DOI./lapl.9 1 Abstract: Experimental
Early View publication on www.interscience.wiley.com (issue and page numbers not yet assigned; citable using Digital Object Identifier DOI) Laser Phys. Lett. 1 5 () / DOI./lapl.9 1 Abstract: Experimental
Impact of Fiber Non-Linearities in Performance of Optical Communication
 Impact of Fiber Non-Linearities in Performance of Optical Communication Narender Kumar Sihval 1, Vivek Kumar Malik 2 M. Tech Students in ECE Department, DCRUST-Murthal, Sonipat, India Abstract: Non-linearity
Impact of Fiber Non-Linearities in Performance of Optical Communication Narender Kumar Sihval 1, Vivek Kumar Malik 2 M. Tech Students in ECE Department, DCRUST-Murthal, Sonipat, India Abstract: Non-linearity
Optical spectra beyond the amplifier bandwidth limitation in dispersion-managed mode-locked fiber lasers
 Optical spectra beyond the amplifier bandwidth limitation in dispersion-managed mode-locked fiber lasers Souad Chouli, 1,* José M. Soto-Crespo, and Philippe Grelu 1 1 Laboratoire Interdisciplinaire Carnot
Optical spectra beyond the amplifier bandwidth limitation in dispersion-managed mode-locked fiber lasers Souad Chouli, 1,* José M. Soto-Crespo, and Philippe Grelu 1 1 Laboratoire Interdisciplinaire Carnot
Optical solitons in a silicon waveguide
 Optical solitons in a silicon waveguide Jidong Zhang 1, Qiang Lin 2, Giovanni Piredda 2, Robert W. Boyd 2, Govind P. Agrawal 2, and Philippe M. Fauchet 1,2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Optical solitons in a silicon waveguide Jidong Zhang 1, Qiang Lin 2, Giovanni Piredda 2, Robert W. Boyd 2, Govind P. Agrawal 2, and Philippe M. Fauchet 1,2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF OPTICAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM USING FBG AND BESSEL FILTERS
 PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF OPTICAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM USING FBG AND BESSEL FILTERS Antony J. S., Jacob Stephen and Aarthi G. ECE Department, School of Electronics Engineering, VIT University, Vellore, Tamil
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF OPTICAL TRANSMISSION SYSTEM USING FBG AND BESSEL FILTERS Antony J. S., Jacob Stephen and Aarthi G. ECE Department, School of Electronics Engineering, VIT University, Vellore, Tamil
Simulation of semiconductor modelocked ring lasers with monolithically integrated pulse shaping elements
 Simulation of semiconductor modelocked ring lasers with monolithically integrated pulse shaping elements Martijn Heck, Yohan Barbarin, Erwin Bente Daan Lenstra Meint Smit Richard Nötzel, Xaveer Leijtens,
Simulation of semiconductor modelocked ring lasers with monolithically integrated pulse shaping elements Martijn Heck, Yohan Barbarin, Erwin Bente Daan Lenstra Meint Smit Richard Nötzel, Xaveer Leijtens,
Packet clock recovery using a bismuth oxide fiber-based optical power limiter
 Packet clock recovery using a bismuth oxide fiber-based optical power limiter Ch. Kouloumentas 1*, N. Pleros 1, P. Zakynthinos 1, D. Petrantonakis 1, D. Apostolopoulos 1, O. Zouraraki 1, A. Tzanakaki,
Packet clock recovery using a bismuth oxide fiber-based optical power limiter Ch. Kouloumentas 1*, N. Pleros 1, P. Zakynthinos 1, D. Petrantonakis 1, D. Apostolopoulos 1, O. Zouraraki 1, A. Tzanakaki,
Rogério Nogueira Instituto de Telecomunicações Pólo de Aveiro Departamento de Física Universidade de Aveiro
 Fiber Bragg Gratings for DWDM Optical Networks Rogério Nogueira Instituto de Telecomunicações Pólo de Aveiro Departamento de Física Universidade de Aveiro Overview Introduction. Fabrication. Physical properties.
Fiber Bragg Gratings for DWDM Optical Networks Rogério Nogueira Instituto de Telecomunicações Pólo de Aveiro Departamento de Física Universidade de Aveiro Overview Introduction. Fabrication. Physical properties.
Soliton Resonances in Dispersion Oscillating Optical Fibers
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 5, 2009 416 Soliton Resonances in Dispersion Oscillating Optical Fibers Andrey Konyukhov 1, Leonid Melnikov 1, Vladimir Khopin 2, Vladimir Stasuyk 3, and Alexej Sysoliatin 4 1
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 5, 2009 416 Soliton Resonances in Dispersion Oscillating Optical Fibers Andrey Konyukhov 1, Leonid Melnikov 1, Vladimir Khopin 2, Vladimir Stasuyk 3, and Alexej Sysoliatin 4 1
Widely Wavelength-tunable Soliton Generation and Few-cycle Pulse Compression with the Use of Dispersion-decreasing Fiber
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 5, 29 421 Widely Wavelength-tunable Soliton Generation and Few-cycle Pulse Compression with the Use of Dispersion-decreasing Fiber Alexey Andrianov 1, Sergey Muraviev 1, Arkady
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 5, NO. 5, 29 421 Widely Wavelength-tunable Soliton Generation and Few-cycle Pulse Compression with the Use of Dispersion-decreasing Fiber Alexey Andrianov 1, Sergey Muraviev 1, Arkady
Self-phase-modulation induced spectral broadening in silicon waveguides
 Self-phase-modulation induced spectral broadening in silicon waveguides Ozdal Boyraz, Tejaswi Indukuri, and Bahram Jalali University of California, Los Angeles Department of Electrical Engineering, Los
Self-phase-modulation induced spectral broadening in silicon waveguides Ozdal Boyraz, Tejaswi Indukuri, and Bahram Jalali University of California, Los Angeles Department of Electrical Engineering, Los
Lecture 8 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 8, Slide 1
 Lecture 8 Bit error rate The Q value Receiver sensitivity Sensitivity degradation Extinction ratio RIN Timing jitter Chirp Forward error correction Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 8, Slide Bit error
Lecture 8 Bit error rate The Q value Receiver sensitivity Sensitivity degradation Extinction ratio RIN Timing jitter Chirp Forward error correction Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 8, Slide Bit error
Fiber-Optic Communication Systems
 Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Second Edition GOVIND P. AGRAWAL The Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY A WILEY-iNTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. NEW YORK / CHICHESTER
Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Second Edition GOVIND P. AGRAWAL The Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY A WILEY-iNTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. NEW YORK / CHICHESTER
First published on: 22 February 2011 PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by: [University of California, Irvine] On: 24 April 2011 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 923037147] Publisher Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in
This article was downloaded by: [University of California, Irvine] On: 24 April 2011 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 923037147] Publisher Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in
Dispersion Pre-Compensation for a Multi-wavelength Erbium Doped Fiber Laser Using Cascaded Fiber Bragg Gratings
 Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 5(10): 1744749, 009 009, INSInet Publication Dispersion Pre-Compensation for a Multi-wavelength Erbium Doped Fiber Laser Using Cascaded Fiber Bragg Gratings 1 1 1
Journal of Applied Sciences Research, 5(10): 1744749, 009 009, INSInet Publication Dispersion Pre-Compensation for a Multi-wavelength Erbium Doped Fiber Laser Using Cascaded Fiber Bragg Gratings 1 1 1
Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p.
 Preface p. xiii Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p. 6 Plastic Optical Fibers p. 9 Microstructure Optical
Preface p. xiii Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p. 6 Plastic Optical Fibers p. 9 Microstructure Optical
Divided-pulse amplification for terawatt-class fiber lasers
 Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 224, 2567 2571 (2015) EDP Sciences, Springer-Verlag 2015 DOI: 10.1140/epjst/e2015-02566-8 THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL SPECIAL TOPICS Review Divided-pulse amplification for
Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 224, 2567 2571 (2015) EDP Sciences, Springer-Verlag 2015 DOI: 10.1140/epjst/e2015-02566-8 THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL SPECIAL TOPICS Review Divided-pulse amplification for
Mitigation of Chromatic Dispersion using Different Compensation Methods in Optical Fiber Communication: A Review
 Volume-4, Issue-3, June-2014, ISSN No.: 2250-0758 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Available at: www.ijemr.net Page Number: 21-25 Mitigation of Chromatic Dispersion using Different
Volume-4, Issue-3, June-2014, ISSN No.: 2250-0758 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Available at: www.ijemr.net Page Number: 21-25 Mitigation of Chromatic Dispersion using Different
Phase Sensitive Amplifier Based on Ultrashort Pump Pulses
 Phase Sensitive Amplifier Based on Ultrashort Pump Pulses Alexander Gershikov and Gad Eisenstein Department of Electrical Engineering, Technion, Haifa, 32000, Israel. Corresponding author: alexger@campus.technion.ac.il
Phase Sensitive Amplifier Based on Ultrashort Pump Pulses Alexander Gershikov and Gad Eisenstein Department of Electrical Engineering, Technion, Haifa, 32000, Israel. Corresponding author: alexger@campus.technion.ac.il
Performance Analysis of Chromatic Dispersion Compensation of a Chirped Fiber Grating on a Differential Phase-shift-keyed Transmission
 Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 13, No. 1, March 2009, pp. 107-111 DOI: 10.3807/JOSK.2009.13.1.107 Performance Analysis of Chromatic Dispersion Compensation of a Chirped Fiber Grating on a
Journal of the Optical Society of Korea Vol. 13, No. 1, March 2009, pp. 107-111 DOI: 10.3807/JOSK.2009.13.1.107 Performance Analysis of Chromatic Dispersion Compensation of a Chirped Fiber Grating on a
Analytical method for designing gratingcompensated dispersion-managed soliton systems
 706 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 1, No. 4/ April 004 Kwan et al. Analytical method for designing gratingcompensated dispersion-managed soliton systems Y. H. C. Kwan, K. Nakkeeran, and P. K. A. Wai Photonics
706 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 1, No. 4/ April 004 Kwan et al. Analytical method for designing gratingcompensated dispersion-managed soliton systems Y. H. C. Kwan, K. Nakkeeran, and P. K. A. Wai Photonics
Investigation of the impact of fiber Bragg grating bandwidth on the efficiency of a fiber Raman laser
 Investigation of the impact of fiber Bragg grating bandwidth on the efficiency of a fiber Raman laser US-Australia meeting May12, 2015 Leanne J. Henry, Michael Klopfer (1), and Ravi Jain (1) (1) University
Investigation of the impact of fiber Bragg grating bandwidth on the efficiency of a fiber Raman laser US-Australia meeting May12, 2015 Leanne J. Henry, Michael Klopfer (1), and Ravi Jain (1) (1) University
Optimized Dispersion Compensation with Post Fiber Bragg Grating in WDM Optical Network
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 10, October-2012 1 Optimized Dispersion Compensation with Post Fiber Bragg Grating in WDM Optical Network P.K. Raghav, M. P.
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 3, Issue 10, October-2012 1 Optimized Dispersion Compensation with Post Fiber Bragg Grating in WDM Optical Network P.K. Raghav, M. P.
Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for High-Energy Optical Pulse Formation
 Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for High-Energy Optical Pulse Formation Yong-Won Song Center for Energy Materials Research, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul 136-791, Korea E-mail: ysong@kist.re.kr
Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for High-Energy Optical Pulse Formation Yong-Won Song Center for Energy Materials Research, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul 136-791, Korea E-mail: ysong@kist.re.kr
Mechanism of intrinsic wavelength tuning and sideband asymmetry in a passively mode-locked soliton fiber ring laser
 28 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/Vol. 17, No. 1/January 2000 Man et al. Mechanism of intrinsic wavelength tuning and sideband asymmetry in a passively mode-locked soliton fiber ring laser W. S. Man, H. Y. Tam, and
28 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/Vol. 17, No. 1/January 2000 Man et al. Mechanism of intrinsic wavelength tuning and sideband asymmetry in a passively mode-locked soliton fiber ring laser W. S. Man, H. Y. Tam, and
Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania
 Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania Razvan Dabu, Daniel Ursescu INFLPR, Magurele, Romania Contents GiWALAS laser facility TEWALAS laser facility CETAL project
Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania Razvan Dabu, Daniel Ursescu INFLPR, Magurele, Romania Contents GiWALAS laser facility TEWALAS laser facility CETAL project
Performance Analysis of Designing a Hybrid Optical Amplifier (HOA) for 32 DWDM Channels in L-band by using EDFA and Raman Amplifier
 Performance Analysis of Designing a Hybrid Optical Amplifier (HOA) for 32 DWDM Channels in L-band by using EDFA and Raman Amplifier Aied K. Mohammed, PhD Department of Electrical Engineering, University
Performance Analysis of Designing a Hybrid Optical Amplifier (HOA) for 32 DWDM Channels in L-band by using EDFA and Raman Amplifier Aied K. Mohammed, PhD Department of Electrical Engineering, University
Performance Analysis of SOA-MZI based All-Optical AND & XOR Gate
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2016 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Utkarsh
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology E-ISSN 2277 4106, P-ISSN 2347 5161 2016 INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Utkarsh
Analysis of Dispersion of Single Mode Optical Fiber
 Daffodil International University Institutional Repository Proceedings of NCCIS November 007 007-11-4 Analysis of Dispersion of Single Mode Optical Fiber Hossen, Monir Daffodil International University
Daffodil International University Institutional Repository Proceedings of NCCIS November 007 007-11-4 Analysis of Dispersion of Single Mode Optical Fiber Hossen, Monir Daffodil International University
2-R REGENERATION EXPLOITING SELF-PHASE MODULATION IN A SEMICONDUCTOR OPTICAL AMPLIFIER
 2-R REGENERATION EXPLOITING SELF-PHASE MODULATION IN A SEMICONDUCTOR OPTICAL AMPLIFIER Gianluca Meloni,^ Antonella Bogoni,^ and Luca Poti^ Scuola Superiore Sunt'Anna, P.zza dei Martin della Libertd 33,
2-R REGENERATION EXPLOITING SELF-PHASE MODULATION IN A SEMICONDUCTOR OPTICAL AMPLIFIER Gianluca Meloni,^ Antonella Bogoni,^ and Luca Poti^ Scuola Superiore Sunt'Anna, P.zza dei Martin della Libertd 33,
Cross-Phase modulation of laser pulses by strong single-cycle terahertz pulse
 Cross-Phase modulation of laser pulses by strong single-cycle terahertz pulse Nan Yang 1, Hai-Wei Du * 1 Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (Ministry of Education) and Department of Physics, Shanghai Jiaotong
Cross-Phase modulation of laser pulses by strong single-cycle terahertz pulse Nan Yang 1, Hai-Wei Du * 1 Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (Ministry of Education) and Department of Physics, Shanghai Jiaotong
Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion
 Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion M. A. Khayer Azad and M. S. Islam Institute of Information and Communication
Performance Limitations of WDM Optical Transmission System Due to Cross-Phase Modulation in Presence of Chromatic Dispersion M. A. Khayer Azad and M. S. Islam Institute of Information and Communication
Picosecond Pulses for Test & Measurement
 Picosecond Pulses for Test & Measurement White Paper PN 200-0100-00 Revision 1.1 September 2003 Calmar Optcom, Inc www.calamropt.com Overview Calmar s picosecond laser sources are actively mode-locked
Picosecond Pulses for Test & Measurement White Paper PN 200-0100-00 Revision 1.1 September 2003 Calmar Optcom, Inc www.calamropt.com Overview Calmar s picosecond laser sources are actively mode-locked
High Energy Non - Collinear OPA
 High Energy Non - Collinear OPA Basics of Operation FEATURES Pulse Duration less than 10 fs possible High Energy (> 80 microjoule) Visible Output Wavelength Tuning Computer Controlled Tuning Range 250-375,
High Energy Non - Collinear OPA Basics of Operation FEATURES Pulse Duration less than 10 fs possible High Energy (> 80 microjoule) Visible Output Wavelength Tuning Computer Controlled Tuning Range 250-375,
Spectral Changes Induced by a Phase Modulator Acting as a Time Lens
 Spectral Changes Induced by a Phase Modulator Acting as a Time Lens Introduction First noted in the 196s, a mathematical equivalence exists between paraxial-beam diffraction and dispersive pulse broadening.
Spectral Changes Induced by a Phase Modulator Acting as a Time Lens Introduction First noted in the 196s, a mathematical equivalence exists between paraxial-beam diffraction and dispersive pulse broadening.
