A Driver Circuit of Spatial Light Modulator
|
|
|
- Elizabeth Garrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 , pp A Driver Circuit of Spatial Light Modulator Lan Wu 1, Fu-na Zhou 2,* and Minghao Zhu 3 1 College of Electrical Engineering, Henan University of Technology, Zhengzhou, China 2 College of Computer and information engineering, Henan University, Kaifeng, China 3 Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Chinese Academy of Science wulan@haut.edu.cn and zhoufn2002@henu.edu.cn Abstract Spatial light modulator (SLM) driving circuit is an important constituent of photoelectric signal conversion system which has a very broad application prospects in various fields such as image display, image recognition, high-speed optical computing and optical communication system. In this study, a high speed and high precision driving circuit was developed, which was applied in 2 level grayscale image processing. This driving circuit adopted Charter.35µm technology. The testing results demonstrated that detection signal was able to follow the driving voltage of modulator and control the modulator on optical signal modulation. Keywords: Spatial light modulator (SLM), driving circuit, grayscale 1. Introduction The driving circuit which is based on multi-quantum well spatial light modulator (SLM) plays an important part in implementation of photoelectric signal conversion. It is also a bridge connecting the optical signal and the high speed circuit, which has a broad application in diverse fields such as optical computing, optical interconnection and free space optical communication, etc. Modulator based on multi-quantum (nucleation) are particularly interested in its response to a single pixel can be greater than 5 GHZ, faster than the SLMs based on other materials [l]. Into the SLMs photoelectric signal processing and optical computing have made outstanding achievements. A new optical digital signal processing (DSP) based on nucleation SLM 8000 Giga MAC/s and 5 mw/giga power consumption of the MAC [2]. SLMs development set the new request driver circuit at a higher speed, lower power consumption and higher precision. Previously, some reports have described a multi-chip module array CMOS driving and four pieces of digital to analog converter (DAC) [3-9].This solution allows high frame rate and high power consumption. In addition, the clock signal pathways in motherboard need synchronous drive and 4 DAC chip. Further extension, e lock synchronize all pieces of the path is too long, to support high-speed transmission. Put forward the construction of a sewage DAC each pixel as a possible solution. It integrates all blocks in a chip, reduce the energy consumption and solve the problem of data synchronization, the disadvantage is that the accuracy of the DAC depends on its integral capacitance value significantly limited processing technology. In this application, the output of the relative error is 10% or more of the serious capacitor mismatch, it should not be ignored. In some image display and graphics recognition systems, usually only the spatial light modulator whose reflected lights show a change in brightness is needed. Therefore, a two level gray-scale modulator driving circuit is designed. The driving circuit of two level gray-scale modular is only required to produce high and low electrical levels, thus the unit ISSN: IJFGCN Copyright c 2016 SERSC
2 pixel can be simply designed as two latch units whose converters are cascade connected. However, many uncertain factors exit in flip chip bonding technology, which may cause damage to modulator and driving chip as well as make short-circuit during indium bump interconnection. Therefore, we need to have a full understanding of the data storage status in driving chip before and after the flip chip bonding. Thus, the driving circuit is required not only to drive modulator chip, but also to read each pixel signal which reflects the effects of processing technology on chip. 2. Circuit Design Since the unit pixel in two level grayscale SLM driving circuit only receives 0 and 1 control signal, thereby outputting low and high driving voltage respectively, therefore, only one digit input signal is required per pixel per frame. Take 112x112 array SLM driving circuit as an example, whose structure is shown in Figure bit parallel port input is adopted. 28 bit digital input signal is converted to 112-bit wide signal through shift register, which is then transmitted to level conversion circuit after being cached by input register. Level conversion circuit converts 3.3V digital signal to 4V analog signal and transmits it to unit array. The digital control circuit on the left side (Ctrl Cir) is used to gate corresponding pixel, while the output circuit on the right side is applied in detecting storage signal. This circuit can not only realize the modulator driving, but also detect the accuracy of the storage signal in driving circuit chip after devices flip chip bonding. 28 Bit Ctrl Cir. Shift Register 112 Bit Input Register Level Shift Driving Pixels Output Stage Figure 1. The Structure of SLM Driver Circuit 2.1. Circuit Working States Driving circuit has 4 working states including Scan mode (SCAN), Test mode (TEST), Reset mode (RESET) and set mode (SET). 1. SCAN mode (By default): control circuit gates drive unit in line- by- line form until completing scanning of one frame. Drive unit is similar to a latch where the input data is stored. 2. TEST mode (TEST is set high): there is no data input. Drive units are inter cascade connected. The stored signals are readout via the output circuit through shift operation. 3. RESET mode (RESET is set high): all pixel outputs are 0, namely the minimum potential. 4. SET mode (SET is set high): all pixel outputs are 1, namely the supply voltage. 256 Copyright c 2016 SERSC
3 2.2. Drive Unit Circuit Drive unit is shown in Figure 2, which is composed of a dual 2- circuit (MUX 2 to 1), register (D flip-flop), and a large CMOS switch. TEST, SET, TEST are state control signals, DATA signal is an input digital signal from level conversion circuit. Lin_scan/CLK signal can switch between row selection control signal and clock signal. Vframe is frame refreshing signal which can control a unifying output of a frame signal. CELL_OUT of each drive unit not only serve as modulator drive, but also is connected to the CELL_IN in the previous drive unit. Figure 2. The Pixel Structure of Driver Circuit The input to circuit is selected by using a dual 2 circuit. By default, the TEST is set 0, DATA serves as drive unit input. Under the control of line scan signal (Line_scan), the data is stored by D flip-flop. When the circuit is converted to TEST mode, TEST signal is set 1, signal CELL_IN serves as drive unit input. Since CELL_IN in each unit is connected to CELL_OUT in previous unit, so the unit arrays can be considered as cascade connection of 112x112 D flip-flops. The trigger signal of D flip-flop is converted to clock by row scan signal, through which the stored data is shifted out Digital Control Circuit The digital control circuit of two level grayscale driving circuit includes pipeline cache, controller of array circuit, row cache deserializer module, and main control logic of system control digital circuit. The main function of digital circuit is to continuously read in 28-digit data through pipeline cache, and then to transmit data to each pixel of driving circuit through controller Layout Design With respect to 112x112 SLM driving circuit, its driving unit circuit is designed within 42x42 µm2 pixel. The driving circuit is located in the middle of pixel, surrounded by power line, ground wire and control signals which are overspread on the entire chip. There is a 20x20 µm2 PAD in each of pixel which is used for voltage output. During fipchip bonding, indium ball with about 20 µm diameter is generated in the PAD. 3. Testing Results and Analysis 3.1. The Results of Simulation and Analysis The simulation was conducted on entire driving circuit based on HSIM simulator. Because an innovative hierarchical data storage and isomorphism algorithm were adopted, there is no restrictions for the circuit scale of simulation. The simulation speed is also much quicker than that of simulators such as HSPICE and Spectra. Although HSIM shows a shortcoming in simulation accuracy, it is a very ideal simulation software for large scale digital circuits. By using 50MHZ reference clock, simulation made the circuit completely store 112x112 random 0, 1 input signals in SCAN mode first, and then let the circuit output Copyright c 2016 SERSC 257
4 signals in TEST mode. The output data is sorted in accordance with the end-to-end order of drive unit, which is not the same with the input signal. Therefore, the sequence of input data was adjusted by using MATLAB, which was compared with that of output data and confirmed to be consistent. In addition, the timing function of the entire chip was also tested to be successful. Figure 3 is the part of simulation results. Figure 3. The Contrast of Input and Output Simulation Results Due to influence of factors such as synchronous switch noise, a stable 3.3V or 4V voltage was not guaranteed by power when chip were working. To observe the effects of voltage changes on chip performance, we respectively simulated D.C. supply change of digital control part from 2.8V to 3.8V, as well as level shifter within chip, pixel array, and the change of D.C. supply of two non-overlapping clock generating circuit from 3.8V to 4.2V. The results show that the chip can work normally. To prevent noise ripple effect on chip, a large amount of filter capacitors were added into chip. In addition, power of triangular wave with 10mV peak value was superposed in the simulation. The results demonstrated that the outputs were still correct, indicating that the noise ripple with 10mV peak value didn t affect chip function Chip Testing Results and Analysis Chip circuit testing is divided into two parts, electrical testing and optical testing. Electrical testing is to verify whether the driving chip can accurately output expected voltage to drive modulator chip. Optical testing is to test the capacity of circuit and modulator chip to process optical signal after flip flop bonding. The results of optical testing can be confirmed by that of electrical testing to determine the effect of flip flop bonding. (1) The electrical testing The electrical testing system of driving circuit is shown in Figure 4, including a twoway D.C. supply which supplies 3.3V or 4V power; FPGA which is used to generate clock, control signal and input data; PCB board, shown in Figure 5, was used to generate chip required bias voltage and power signal filtering; oscilloscope or logic analyzer which was used to observe output signal. In order to prevent light path block, COB encapsulation mode was adopted. And the chip was measured by directly fixing on PCB board. 258 Copyright c 2016 SERSC
5 Power Control Control Signal Driving Circuit oscilloscope Input Signal Figure 4. The Electrical Test System of Driver Circuit Figure 5. The Test PCB To test whether the modulator outputs expected voltage controlled by driving chip. The driving voltage was serial shift outputted through driving unit cascade connection, and then compared with input signal. 28-bit input signal was composed of 14 0 and Therefore, the output signal is also a 14 alternating armaments of 0 and 1. Namely, 28 1 will appear in odd line breaks, while 0 will appear in even line breaks. The testing results are shown in Figure 6. The chip output data were compared to be the same with input data after transpose in MATLAB, indicating driving circuit working normally. Figure 6. The Electrical Test Results Copyright c 2016 SERSC 259
6 (2) Optical testing Optical testing system is composed of 850nm wavelength laser, an actuator, a magnifying lens, a projection lens and a photosensitive detector. To reduce the influence of mixed lights on the testing results, two irises are added in optical path which reassures that the signal received by detector are completely from the reflection of modulator, as shown in Figure 7. Figure 7. Optical Test System Figure 8 shows observation results in oscilloscope, with 3.5V supply voltage and 5V supply voltage shown in Figure 8 (a) and Figure 8 (b) respectively. The top of each figure is driving voltage input, while the bottom is detecting results. When the modulator voltage changes between 0V and 3.5V, the detected signal intensity by detector is 58.6nV, the strength of modulation signal is 5.3 mv, modulation depth is 9%, and modulation frequency is 2 Hz. When driving voltage changes from 3.5V to 5V, modulation depth jumped to 7.1mV/67.4mV=10.5%. The results indicate that detection signal of detector coordinates well with driving voltage of modulator, therefore driving circuit can control the modulator to modulate the optical signal. (a) Figure 8. The Detector Output with the Change of the Driving Voltage 4. Conclusion A two-level gray-scale driver circuit of MQW SLM is designed in this paper. It can produce high and low two-level driver voltage, the pixel is designed to a latch unit with two inverters in cascade. The testing results show that the detection signal from the detector and the driving voltage of the modulator followed very well, the driver circuit can control modulator optical signal modulation. (b) 260 Copyright c 2016 SERSC
7 Acknowledgements This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No , U Reference [1] S. Eisenbach, Optical Signal Processing, Confidential and Proprietary Information of Lenslet, (2003), [2] K. Goossen, J. Walker and L. D Asaro, GaAs MQW modulators integrated with silicon CMOS, IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, vol. 7, no. 4, (1995), pp [3] T. K. Woodward, A. V. Krishnamoorthy and K. W.Goossen, Modulator-Driver Circuits for Optoelectronic VLSI, Photonics Technology Letters, IEEE, vol. 9, no. 6, (1997), p [4] C. Garvin, J. A. Trezza and J. S. Ahearn, Overview of hign-speed multiple quantum well optical modulator devices at Lockheed Marth Sanders, OSA/SLM, (1999), SMC1-3:26. [5] M. H. Weiler, J. S. Ahearn and S. B. Adams, Large scale modulator arrays for beam steering and optical modulator applications, IEEEAC paper #458, (2002). [6] S. Serati, K. Bauchert and P. Millett, Development of large-array spatial light modulators, Society of Photo Instrumentation Engineers, (2004). [7] L. Wu, N. Yu and Y. Zhang, A universal programmable drive circuit for spatial light modulators, Journal of Semiconductors, vol. 30, no. 7, (2009), pp [8] R. Y. Nian, L. K. Qiang, Z. Z. Wei, Research on Flip-chip Key Technologies, Journal of Soochow University (Engineering science edition), vol. 24, no. 5, (2004), pp [9] R. C. Ling, L. Kai and D. R. Zheng, Flip Chip Technology and Its Application, Electronics & Packaging, vol. 9, no. 3, (2009), pp Authors Wu Lan, she received the Ph.D. degree in micro-electronics and solid-electronic from Xi an University of technology and Suzhou Institute of Nano-tech and Nano-bionics in Presently she is a Associate Professor of Henan University of Technology. She researches in IC design, system modeling, and nonlinear prediction control. Funa Zhou, she received the Master degree from Henan University, Kaifeng, China in 2004 and the Ph.D. degree from Shanghai Maritime University, Shanghai, China in She is currently an associate professor with the School of Computer and Information Engineering, Henan University, Kaifeng, China. Dr. Zhou has published over twenty peer-reviewed international journal papers, and her current research interests include data driven fault diagnosis and information fusion. Corresponding author. Copyright c 2016 SERSC 261
8 262 Copyright c 2016 SERSC
Course Outcome of M.Tech (VLSI Design)
 Course Outcome of M.Tech (VLSI Design) PVL108: Device Physics and Technology The students are able to: 1. Understand the basic physics of semiconductor devices and the basics theory of PN junction. 2.
Course Outcome of M.Tech (VLSI Design) PVL108: Device Physics and Technology The students are able to: 1. Understand the basic physics of semiconductor devices and the basics theory of PN junction. 2.
A new Photon Counting Detector: Intensified CMOS- APS
 A new Photon Counting Detector: Intensified CMOS- APS M. Belluso 1, G. Bonanno 1, A. Calì 1, A. Carbone 3, R. Cosentino 1, A. Modica 4, S. Scuderi 1, C. Timpanaro 1, M. Uslenghi 2 1-I.N.A.F.-Osservatorio
A new Photon Counting Detector: Intensified CMOS- APS M. Belluso 1, G. Bonanno 1, A. Calì 1, A. Carbone 3, R. Cosentino 1, A. Modica 4, S. Scuderi 1, C. Timpanaro 1, M. Uslenghi 2 1-I.N.A.F.-Osservatorio
A new Photon Counting Detector: Intensified CMOS- APS
 A new Photon Counting Detector: Intensified CMOS- APS M. Belluso 1, G. Bonanno 1, A. Calì 1, A. Carbone 3, R. Cosentino 1, A. Modica 4, S. Scuderi 1, C. Timpanaro 1, M. Uslenghi 2 1- I.N.A.F.-Osservatorio
A new Photon Counting Detector: Intensified CMOS- APS M. Belluso 1, G. Bonanno 1, A. Calì 1, A. Carbone 3, R. Cosentino 1, A. Modica 4, S. Scuderi 1, C. Timpanaro 1, M. Uslenghi 2 1- I.N.A.F.-Osservatorio
A 42 fj 8-bit 1.0-GS/s folding and interpolating ADC with 1 GHz signal bandwidth
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.11, No.2, 1 9 A 42 fj 8-bit 1.0-GS/s folding and interpolating ADC with 1 GHz signal bandwidth Mingshuo Wang a), Fan Ye, Wei Li, and Junyan Ren b) State Key Laboratory
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.11, No.2, 1 9 A 42 fj 8-bit 1.0-GS/s folding and interpolating ADC with 1 GHz signal bandwidth Mingshuo Wang a), Fan Ye, Wei Li, and Junyan Ren b) State Key Laboratory
Dual-Function Detector Modulator Smart-Pixel Module
 Dual-Function Detector Modulator Smart-Pixel Module A. V. Krishnamoorthy, T. K. Woodward, K. W. Goossen, J. A. Walker, S. P. Hui, B. Tseng, J. E. Cunningham, W. Y. Jan, F. E. Kiamilev, and D. A. B. Miller
Dual-Function Detector Modulator Smart-Pixel Module A. V. Krishnamoorthy, T. K. Woodward, K. W. Goossen, J. A. Walker, S. P. Hui, B. Tseng, J. E. Cunningham, W. Y. Jan, F. E. Kiamilev, and D. A. B. Miller
Copyright 2000 Society of Photo Instrumentation Engineers.
 Copyright 2000 Society of Photo Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in SPIE Proceedings, Volume 4043 and is made available as an electronic reprint with permission of SPIE. One print or
Copyright 2000 Society of Photo Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in SPIE Proceedings, Volume 4043 and is made available as an electronic reprint with permission of SPIE. One print or
VLSI Implementation of Image Processing Algorithms on FPGA
 International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174 Volume 3, Number 3 (2010), pp. 139--145 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com VLSI Implementation
International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174 Volume 3, Number 3 (2010), pp. 139--145 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com VLSI Implementation
The Architecture of the BTeV Pixel Readout Chip
 The Architecture of the BTeV Pixel Readout Chip D.C. Christian, dcc@fnal.gov Fermilab, POBox 500 Batavia, IL 60510, USA 1 Introduction The most striking feature of BTeV, a dedicated b physics experiment
The Architecture of the BTeV Pixel Readout Chip D.C. Christian, dcc@fnal.gov Fermilab, POBox 500 Batavia, IL 60510, USA 1 Introduction The most striking feature of BTeV, a dedicated b physics experiment
A10-Gb/slow-power adaptive continuous-time linear equalizer using asynchronous under-sampling histogram
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.10, No.4, 1 8 A10-Gb/slow-power adaptive continuous-time linear equalizer using asynchronous under-sampling histogram Wang-Soo Kim and Woo-Young Choi a) Department
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.10, No.4, 1 8 A10-Gb/slow-power adaptive continuous-time linear equalizer using asynchronous under-sampling histogram Wang-Soo Kim and Woo-Young Choi a) Department
Design and Implementation of a Low Power Successive Approximation ADC. Xin HUANG, Xiao-ning XIN, Jian REN* and Xin-lei CHEN
 2018 International Conference on Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology (ICMEIT 2018) ISBN: 978-1-60595-548-3 Design and Implementation of a Low Power Successive Approximation ADC Xin HUANG,
2018 International Conference on Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology (ICMEIT 2018) ISBN: 978-1-60595-548-3 Design and Implementation of a Low Power Successive Approximation ADC Xin HUANG,
ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 2016
 ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 2016 Lecture 10: Electroabsorption Modulator Transmitters Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Announcements
ECEN689: Special Topics in Optical Interconnects Circuits and Systems Spring 2016 Lecture 10: Electroabsorption Modulator Transmitters Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Announcements
A 3 Mpixel ROIC with 10 m Pixel Pitch and 120 Hz Frame Rate Digital Output
 A 3 Mpixel ROIC with 10 m Pixel Pitch and 120 Hz Frame Rate Digital Output Elad Ilan, Niv Shiloah, Shimon Elkind, Roman Dobromislin, Willie Freiman, Alex Zviagintsev, Itzik Nevo, Oren Cohen, Fanny Khinich,
A 3 Mpixel ROIC with 10 m Pixel Pitch and 120 Hz Frame Rate Digital Output Elad Ilan, Niv Shiloah, Shimon Elkind, Roman Dobromislin, Willie Freiman, Alex Zviagintsev, Itzik Nevo, Oren Cohen, Fanny Khinich,
Module -18 Flip flops
 1 Module -18 Flip flops 1. Introduction 2. Comparison of latches and flip flops. 3. Clock the trigger signal 4. Flip flops 4.1. Level triggered flip flops SR, D and JK flip flops 4.2. Edge triggered flip
1 Module -18 Flip flops 1. Introduction 2. Comparison of latches and flip flops. 3. Clock the trigger signal 4. Flip flops 4.1. Level triggered flip flops SR, D and JK flip flops 4.2. Edge triggered flip
Decision Based Median Filter Algorithm Using Resource Optimized FPGA to Extract Impulse Noise
 Journal of Embedded Systems, 2014, Vol. 2, No. 1, 18-22 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/jes/2/1/4 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/jes-2-1-4 Decision Based Median Filter Algorithm
Journal of Embedded Systems, 2014, Vol. 2, No. 1, 18-22 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/jes/2/1/4 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/jes-2-1-4 Decision Based Median Filter Algorithm
ABSTRACT. Keywords: 0,18 micron, CMOS, APS, Sunsensor, Microned, TNO, TU-Delft, Radiation tolerant, Low noise. 1. IMAGERS FOR SPACE APPLICATIONS.
 Active pixel sensors: the sensor of choice for future space applications Johan Leijtens(), Albert Theuwissen(), Padmakumar R. Rao(), Xinyang Wang(), Ning Xie() () TNO Science and Industry, Postbus, AD
Active pixel sensors: the sensor of choice for future space applications Johan Leijtens(), Albert Theuwissen(), Padmakumar R. Rao(), Xinyang Wang(), Ning Xie() () TNO Science and Industry, Postbus, AD
Image Acquisition Method Based on TMS320DM642
 Journal of Computer and Communications, 2017, 5, 119-124 http://www.scirp.org/journal/jcc ISSN Online: 2327-5227 ISSN Print: 2327-5219 Image Acquisition Method Based on TMS320DM642 Li Liu, Yining Liu Liaoning
Journal of Computer and Communications, 2017, 5, 119-124 http://www.scirp.org/journal/jcc ISSN Online: 2327-5227 ISSN Print: 2327-5219 Image Acquisition Method Based on TMS320DM642 Li Liu, Yining Liu Liaoning
A 14-bit 2.5 GS/s DAC based on Multi-Clock Synchronization. Hegang Hou*, Zongmin Wang, Ying Kong, Xinmang Peng, Haitao Guan, Jinhao Wang, Yan Ren
 Joint International Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology Conference (JIMET 2015) A 14-bit 2.5 GS/s based on Multi-Clock Synchronization Hegang Hou*, Zongmin Wang, Ying Kong, Xinmang Peng,
Joint International Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology Conference (JIMET 2015) A 14-bit 2.5 GS/s based on Multi-Clock Synchronization Hegang Hou*, Zongmin Wang, Ying Kong, Xinmang Peng,
A New Capacitive Sensing Circuit using Modified Charge Transfer Scheme
 78 Hyeopgoo eo : A NEW CAPACITIVE CIRCUIT USING MODIFIED CHARGE TRANSFER SCHEME A New Capacitive Sensing Circuit using Modified Charge Transfer Scheme Hyeopgoo eo, Member, KIMICS Abstract This paper proposes
78 Hyeopgoo eo : A NEW CAPACITIVE CIRCUIT USING MODIFIED CHARGE TRANSFER SCHEME A New Capacitive Sensing Circuit using Modified Charge Transfer Scheme Hyeopgoo eo, Member, KIMICS Abstract This paper proposes
A 2-bit/step SAR ADC structure with one radix-4 DAC
 A 2-bit/step SAR ADC structure with one radix-4 DAC M. H. M. Larijani and M. B. Ghaznavi-Ghoushchi a) School of Engineering, Shahed University, Tehran, Iran a) ghaznavi@shahed.ac.ir Abstract: In this letter,
A 2-bit/step SAR ADC structure with one radix-4 DAC M. H. M. Larijani and M. B. Ghaznavi-Ghoushchi a) School of Engineering, Shahed University, Tehran, Iran a) ghaznavi@shahed.ac.ir Abstract: In this letter,
Ultralight Weight Optical Systems using Nano-Layered Synthesized Materials
 Ultralight Weight Optical Systems using Nano-Layered Synthesized Materials Natalie Clark, PhD NASA Langley Research Center and James Breckinridge University of Arizona, College of Optical Sciences Overview
Ultralight Weight Optical Systems using Nano-Layered Synthesized Materials Natalie Clark, PhD NASA Langley Research Center and James Breckinridge University of Arizona, College of Optical Sciences Overview
High-Speed Interconnect Technology for Servers
 High-Speed Interconnect Technology for Servers Hiroyuki Adachi Jun Yamada Yasushi Mizutani We are developing high-speed interconnect technology for servers to meet customers needs for transmitting huge
High-Speed Interconnect Technology for Servers Hiroyuki Adachi Jun Yamada Yasushi Mizutani We are developing high-speed interconnect technology for servers to meet customers needs for transmitting huge
Comparison between Analog and Digital Current To PWM Converter for Optical Readout Systems
 Comparison between Analog and Digital Current To PWM Converter for Optical Readout Systems 1 Eun-Jung Yoon, 2 Kangyeob Park, 3* Won-Seok Oh 1, 2, 3 SoC Platform Research Center, Korea Electronics Technology
Comparison between Analog and Digital Current To PWM Converter for Optical Readout Systems 1 Eun-Jung Yoon, 2 Kangyeob Park, 3* Won-Seok Oh 1, 2, 3 SoC Platform Research Center, Korea Electronics Technology
A LOW POWER SINGLE PHASE CLOCK DISTRIBUTION USING 4/5 PRESCALER TECHNIQUE
 A LOW POWER SINGLE PHASE CLOCK DISTRIBUTION USING 4/5 PRESCALER TECHNIQUE MS. V.NIVEDITHA 1,D.MARUTHI KUMAR 2 1 PG Scholar in M.Tech, 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of E.C.E,Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute
A LOW POWER SINGLE PHASE CLOCK DISTRIBUTION USING 4/5 PRESCALER TECHNIQUE MS. V.NIVEDITHA 1,D.MARUTHI KUMAR 2 1 PG Scholar in M.Tech, 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of E.C.E,Srinivasa Ramanujan Institute
Power And Area Optimization of Pulse Latch Shift Register
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 12, Issue 6 (June 2016), PP.41-45 Power And Area Optimization of Pulse Latch Shift
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 12, Issue 6 (June 2016), PP.41-45 Power And Area Optimization of Pulse Latch Shift
LSI and Circuit Technologies for the SX-8 Supercomputer
 LSI and Circuit Technologies for the SX-8 Supercomputer By Jun INASAKA,* Toshio TANAHASHI,* Hideaki KOBAYASHI,* Toshihiro KATOH,* Mikihiro KAJITA* and Naoya NAKAYAMA This paper describes the LSI and circuit
LSI and Circuit Technologies for the SX-8 Supercomputer By Jun INASAKA,* Toshio TANAHASHI,* Hideaki KOBAYASHI,* Toshihiro KATOH,* Mikihiro KAJITA* and Naoya NAKAYAMA This paper describes the LSI and circuit
Digital Design and System Implementation. Overview of Physical Implementations
 Digital Design and System Implementation Overview of Physical Implementations CMOS devices CMOS transistor circuit functional behavior Basic logic gates Transmission gates Tri-state buffers Flip-flops
Digital Design and System Implementation Overview of Physical Implementations CMOS devices CMOS transistor circuit functional behavior Basic logic gates Transmission gates Tri-state buffers Flip-flops
Design of a Hardware/Software FPGA-Based Driver System for a Large Area High Resolution CCD Image Sensor
 PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 4, No. 3, 2014: 274 280 Design of a Hardware/Software FPGA-Based Driver System for a Large Area High Resolution CCD Image Sensor Ying CHEN 1,2*, Wanpeng XU 3, Rongsheng ZHAO 1,
PHOTONIC SENSORS / Vol. 4, No. 3, 2014: 274 280 Design of a Hardware/Software FPGA-Based Driver System for a Large Area High Resolution CCD Image Sensor Ying CHEN 1,2*, Wanpeng XU 3, Rongsheng ZHAO 1,
The Design of SET-CMOS Hybrid Logic Style of 1-Bit Comparator
 The Design of SET-CMOS Hybrid Logic Style of 1-Bit Comparator A. T. Fathima Thuslim Department of Electronics and communication Engineering St. Peters University, Avadi, Chennai, India Abstract: Single
The Design of SET-CMOS Hybrid Logic Style of 1-Bit Comparator A. T. Fathima Thuslim Department of Electronics and communication Engineering St. Peters University, Avadi, Chennai, India Abstract: Single
99. Sun sensor design and test of a micro satellite
 99. Sun sensor design and test of a micro satellite Li Lin 1, Zhou Sitong 2, Tan Luyang 3, Wang Dong 4 1, 3, 4 Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun
99. Sun sensor design and test of a micro satellite Li Lin 1, Zhou Sitong 2, Tan Luyang 3, Wang Dong 4 1, 3, 4 Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun
ALTHOUGH zero-if and low-if architectures have been
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 40, NO. 6, JUNE 2005 1249 A 110-MHz 84-dB CMOS Programmable Gain Amplifier With Integrated RSSI Function Chun-Pang Wu and Hen-Wai Tsao Abstract This paper describes
IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 40, NO. 6, JUNE 2005 1249 A 110-MHz 84-dB CMOS Programmable Gain Amplifier With Integrated RSSI Function Chun-Pang Wu and Hen-Wai Tsao Abstract This paper describes
A design of 16-bit adiabatic Microprocessor core
 194 A design of 16-bit adiabatic Microprocessor core Youngjoon Shin, Hanseung Lee, Yong Moon, and Chanho Lee Abstract A 16-bit adiabatic low-power Microprocessor core is designed. The processor consists
194 A design of 16-bit adiabatic Microprocessor core Youngjoon Shin, Hanseung Lee, Yong Moon, and Chanho Lee Abstract A 16-bit adiabatic low-power Microprocessor core is designed. The processor consists
AND 5GHz ABSTRACTT. easily detected. the transition. for half duration. cycle highh voltage is send. this. data bit frame. the the. data.
 COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT DESIGNS OF MANCHES STER ENCODER DESIGNED D WITH CMOS INVERTERS USING 32NM UMC CMOS TECHNOLOGY AT 1GHz, 2.5GHz AND 5GHz M. Tech student, Department of ECE, Gyan Vihar School of Engineering
COMPARISON OF DIFFERENT DESIGNS OF MANCHES STER ENCODER DESIGNED D WITH CMOS INVERTERS USING 32NM UMC CMOS TECHNOLOGY AT 1GHz, 2.5GHz AND 5GHz M. Tech student, Department of ECE, Gyan Vihar School of Engineering
A Low Power Single Phase Clock Distribution Multiband Network
 A Low Power Single Phase Clock Distribution Multiband Network A.Adinarayana Asst.prof Princeton College of Engineering and Technology. Abstract : Frequency synthesizer is one of the important elements
A Low Power Single Phase Clock Distribution Multiband Network A.Adinarayana Asst.prof Princeton College of Engineering and Technology. Abstract : Frequency synthesizer is one of the important elements
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF POWER EFFICIENT ALL DIGITAL PHASE LOCKED LOOP
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering and Management (ICETEM14) ISSN 0976
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) Proceedings of the International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering and Management (ICETEM14) ISSN 0976
A CMOS image sensor working as high-speed photo receivers as well as a position sensor for indoor optical wireless LAN systems
 A CMOS image sensor working as high-speed photo receivers as well as a position sensor for indoor optical wireless LAN systems Keiichiro Kagawa a, Tomohiro Nishimura a, Hiroaki Asazu a, Tomoaki Kawakami
A CMOS image sensor working as high-speed photo receivers as well as a position sensor for indoor optical wireless LAN systems Keiichiro Kagawa a, Tomohiro Nishimura a, Hiroaki Asazu a, Tomoaki Kawakami
Study on OFDM Symbol Timing Synchronization Algorithm
 Vol.7, No. (4), pp.43-5 http://dx.doi.org/.457/ijfgcn.4.7..4 Study on OFDM Symbol Timing Synchronization Algorithm Jing Dai and Yanmei Wang* College of Information Science and Engineering, Shenyang Ligong
Vol.7, No. (4), pp.43-5 http://dx.doi.org/.457/ijfgcn.4.7..4 Study on OFDM Symbol Timing Synchronization Algorithm Jing Dai and Yanmei Wang* College of Information Science and Engineering, Shenyang Ligong
A passive circuit based RF optimization methodology for wireless sensor network nodes. Article (peer-reviewed)
 Title Author(s) Editor(s) A passive circuit based RF optimization methodology for wireless sensor network nodes Zheng, Liqiang; Mathewson, Alan; O'Flynn, Brendan; Hayes, Michael; Ó Mathúna, S. Cian Wu,
Title Author(s) Editor(s) A passive circuit based RF optimization methodology for wireless sensor network nodes Zheng, Liqiang; Mathewson, Alan; O'Flynn, Brendan; Hayes, Michael; Ó Mathúna, S. Cian Wu,
Optical Interconnection and Clocking for Electronic Chips
 1 Optical Interconnection and Clocking for Electronic Chips Aparna Bhatnagar and David A. B. Miller Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University, Stanford CA 9430 ABSTRACT As the speed of electronic
1 Optical Interconnection and Clocking for Electronic Chips Aparna Bhatnagar and David A. B. Miller Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University, Stanford CA 9430 ABSTRACT As the speed of electronic
Development of a 20 GS/s Sampling Chip in 130nm CMOS Technology
 Development of a 20 GS/s Sampling Chip in 130nm CMOS Technology 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Orlando, Florida, October 28 th 2009 Jean-Francois Genat On behalf of Mircea Bogdan 1, Henry J. Frisch
Development of a 20 GS/s Sampling Chip in 130nm CMOS Technology 2009 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium, Orlando, Florida, October 28 th 2009 Jean-Francois Genat On behalf of Mircea Bogdan 1, Henry J. Frisch
Implementation of Pixel Array Bezel-Less Cmos Fingerprint Sensor
 Article DOI: 10.21307/ijssis-2018-013 Issue 0 Vol. 0 Implementation of 144 64 Pixel Array Bezel-Less Cmos Fingerprint Sensor Seungmin Jung School of Information and Technology, Hanshin University, 137
Article DOI: 10.21307/ijssis-2018-013 Issue 0 Vol. 0 Implementation of 144 64 Pixel Array Bezel-Less Cmos Fingerprint Sensor Seungmin Jung School of Information and Technology, Hanshin University, 137
LSI and Circuit Technologies of the SX-9
 TANAHASHI Toshio, TSUCHIDA Junichi, MATSUZAWA Hajime NIWA Kenji, SATOH Tatsuo, KATAGIRI Masaru Abstract This paper outlines the LSI and circuit technologies of the SX-9 as well as their inspection technologies.
TANAHASHI Toshio, TSUCHIDA Junichi, MATSUZAWA Hajime NIWA Kenji, SATOH Tatsuo, KATAGIRI Masaru Abstract This paper outlines the LSI and circuit technologies of the SX-9 as well as their inspection technologies.
MAR2100 MARADIN MEMS DRIVE AND CONTROL
 MAR2100 MARADIN MEMS DRIVE AND CONTROL The MAR2100 is a Drive and control IC for Maradin's MAR1100 dual-axis MEMS based scanning mirror. MAR2100 is targeted for miniature laser projectors and laser steering
MAR2100 MARADIN MEMS DRIVE AND CONTROL The MAR2100 is a Drive and control IC for Maradin's MAR1100 dual-axis MEMS based scanning mirror. MAR2100 is targeted for miniature laser projectors and laser steering
Basic Logic Circuits
 Basic Logic Circuits Required knowledge Measurement of static characteristics of nonlinear circuits. Measurement of current consumption. Measurement of dynamic properties of electrical circuits. Definitions
Basic Logic Circuits Required knowledge Measurement of static characteristics of nonlinear circuits. Measurement of current consumption. Measurement of dynamic properties of electrical circuits. Definitions
Design of Low Power CMOS Startup Charge Pump Based on Body Biasing Technique
 Design of Low Power CMOS Startup Charge Pump Based on Body Biasing Technique Juliet Abraham 1, Dr. B. Paulchamy 2 1 PG Scholar, Hindusthan institute of Technology, coimbtore-32, India 2 Professor and HOD,
Design of Low Power CMOS Startup Charge Pump Based on Body Biasing Technique Juliet Abraham 1, Dr. B. Paulchamy 2 1 PG Scholar, Hindusthan institute of Technology, coimbtore-32, India 2 Professor and HOD,
Research on the Effective Detection Methods of Large Scale IC Fault Signals. Junhong LI
 International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering (ICCSE 2015) Research on the Effective Detection Methods of Large Scale IC Fault Signals Junhong LI Engineering Technology and Information
International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering (ICCSE 2015) Research on the Effective Detection Methods of Large Scale IC Fault Signals Junhong LI Engineering Technology and Information
MBI5031 Application Note
 MBI5031 Application Note Foreword MBI5031 is specifically designed for D video applications using internal Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) control, unlike the traditional D drivers with external PWM control,
MBI5031 Application Note Foreword MBI5031 is specifically designed for D video applications using internal Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) control, unlike the traditional D drivers with external PWM control,
X-ray Detectors: What are the Needs?
 X-ray Detectors: What are the Needs? Sol M. Gruner Physics Dept. & Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source (CHESS) Ithaca, NY 14853 smg26@cornell.edu 1 simplified view of the Evolution of Imaging Synchrotron
X-ray Detectors: What are the Needs? Sol M. Gruner Physics Dept. & Cornell High Energy Synchrotron Source (CHESS) Ithaca, NY 14853 smg26@cornell.edu 1 simplified view of the Evolution of Imaging Synchrotron
Image sensor combining the best of different worlds
 Image sensors and vision systems Image sensor combining the best of different worlds First multispectral time-delay-and-integration (TDI) image sensor based on CCD-in-CMOS technology. Introduction Jonathan
Image sensors and vision systems Image sensor combining the best of different worlds First multispectral time-delay-and-integration (TDI) image sensor based on CCD-in-CMOS technology. Introduction Jonathan
DESIGN AND VERIFICATION OF ANALOG PHASE LOCKED LOOP CIRCUIT
 DESIGN AND VERIFICATION OF ANALOG PHASE LOCKED LOOP CIRCUIT PRADEEP G CHAGASHETTI Mr. H.V. RAVISH ARADHYA Department of E&C Department of E&C R.V.COLLEGE of ENGINEERING R.V.COLLEGE of ENGINEERING Bangalore
DESIGN AND VERIFICATION OF ANALOG PHASE LOCKED LOOP CIRCUIT PRADEEP G CHAGASHETTI Mr. H.V. RAVISH ARADHYA Department of E&C Department of E&C R.V.COLLEGE of ENGINEERING R.V.COLLEGE of ENGINEERING Bangalore
WITH the rapid evolution of liquid crystal display (LCD)
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 43, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2008 371 A 10-Bit LCD Column Driver With Piecewise Linear Digital-to-Analog Converters Chih-Wen Lu, Member, IEEE, and Lung-Chien Huang Abstract
IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 43, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2008 371 A 10-Bit LCD Column Driver With Piecewise Linear Digital-to-Analog Converters Chih-Wen Lu, Member, IEEE, and Lung-Chien Huang Abstract
Coherent Detection Gradient Descent Adaptive Control Chip
 MEP Research Program Test Report Coherent Detection Gradient Descent Adaptive Control Chip Requested Fabrication Technology: IBM SiGe 5AM Design No: 73546 Fabrication ID: T57WAD Design Name: GDPLC Technology
MEP Research Program Test Report Coherent Detection Gradient Descent Adaptive Control Chip Requested Fabrication Technology: IBM SiGe 5AM Design No: 73546 Fabrication ID: T57WAD Design Name: GDPLC Technology
Light gathering Power: Magnification with eyepiece:
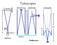 Telescopes Light gathering Power: The amount of light that can be gathered by a telescope in a given amount of time: t 1 /t 2 = (D 2 /D 1 ) 2 The larger the diameter the smaller the amount of time. If
Telescopes Light gathering Power: The amount of light that can be gathered by a telescope in a given amount of time: t 1 /t 2 = (D 2 /D 1 ) 2 The larger the diameter the smaller the amount of time. If
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 5, May ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 5, May-2013 2190 Biquad Infinite Impulse Response Filter Using High Efficiency Charge Recovery Logic K.Surya 1, K.Chinnusamy
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 5, May-2013 2190 Biquad Infinite Impulse Response Filter Using High Efficiency Charge Recovery Logic K.Surya 1, K.Chinnusamy
Delay-Locked Loop Using 4 Cell Delay Line with Extended Inverters
 International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering Vol. 2, No. 4, December, 2014 Delay-Locked Loop Using 4 Cell Delay Line with Extended Inverters Jefferson A. Hora, Vincent Alan Heramiz,
International Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering Vol. 2, No. 4, December, 2014 Delay-Locked Loop Using 4 Cell Delay Line with Extended Inverters Jefferson A. Hora, Vincent Alan Heramiz,
A 10Gbps Analog Adaptive Equalizer and Pulse Shaping Circuit for Backplane Interface
 Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on CIRCUITS, SYSTEMS, ELECTRONICS, CONTROL & SIGNAL PROCESSING, Dallas, USA, November 1-3, 2006 225 A 10Gbps Analog Adaptive Equalizer and Pulse Shaping Circuit
Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS Int. Conf. on CIRCUITS, SYSTEMS, ELECTRONICS, CONTROL & SIGNAL PROCESSING, Dallas, USA, November 1-3, 2006 225 A 10Gbps Analog Adaptive Equalizer and Pulse Shaping Circuit
SWITCHED CAPACITOR BASED IMPLEMENTATION OF INTEGRATE AND FIRE NEURAL NETWORKS
 Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 54, NO. 7-8, 23, 28 212 SWITCHED CAPACITOR BASED IMPLEMENTATION OF INTEGRATE AND FIRE NEURAL NETWORKS Daniel Hajtáš Daniela Ďuračková This paper is dealing with
Journal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 54, NO. 7-8, 23, 28 212 SWITCHED CAPACITOR BASED IMPLEMENTATION OF INTEGRATE AND FIRE NEURAL NETWORKS Daniel Hajtáš Daniela Ďuračková This paper is dealing with
CS302 - Digital Logic Design Glossary By
 CS302 - Digital Logic Design Glossary By ABEL : Advanced Boolean Expression Language; a software compiler language for SPLD programming; a type of hardware description language (HDL) Adder : A digital
CS302 - Digital Logic Design Glossary By ABEL : Advanced Boolean Expression Language; a software compiler language for SPLD programming; a type of hardware description language (HDL) Adder : A digital
The Medipix3 Prototype, a Pixel Readout Chip Working in Single Photon Counting Mode with Improved Spectrometric Performance
 26 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record NM1-6 The Medipix3 Prototype, a Pixel Readout Chip Working in Single Photon Counting Mode with Improved Spectrometric Performance R. Ballabriga, M. Campbell,
26 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record NM1-6 The Medipix3 Prototype, a Pixel Readout Chip Working in Single Photon Counting Mode with Improved Spectrometric Performance R. Ballabriga, M. Campbell,
Low Power Design of Successive Approximation Registers
 Low Power Design of Successive Approximation Registers Rabeeh Majidi ECE Department, Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Worcester MA USA rabeehm@ece.wpi.edu Abstract: This paper presents low power design
Low Power Design of Successive Approximation Registers Rabeeh Majidi ECE Department, Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Worcester MA USA rabeehm@ece.wpi.edu Abstract: This paper presents low power design
DESIGN OF MULTIPLYING DELAY LOCKED LOOP FOR DIFFERENT MULTIPLYING FACTORS
 DESIGN OF MULTIPLYING DELAY LOCKED LOOP FOR DIFFERENT MULTIPLYING FACTORS Aman Chaudhary, Md. Imtiyaz Chowdhary, Rajib Kar Department of Electronics and Communication Engg. National Institute of Technology,
DESIGN OF MULTIPLYING DELAY LOCKED LOOP FOR DIFFERENT MULTIPLYING FACTORS Aman Chaudhary, Md. Imtiyaz Chowdhary, Rajib Kar Department of Electronics and Communication Engg. National Institute of Technology,
Synchronous Mirror Delays. ECG 721 Memory Circuit Design Kevin Buck
 Synchronous Mirror Delays ECG 721 Memory Circuit Design Kevin Buck 11/25/2015 Introduction A synchronous mirror delay (SMD) is a type of clock generation circuit Unlike DLLs and PLLs an SMD is an open
Synchronous Mirror Delays ECG 721 Memory Circuit Design Kevin Buck 11/25/2015 Introduction A synchronous mirror delay (SMD) is a type of clock generation circuit Unlike DLLs and PLLs an SMD is an open
Fractional- N PLL with 90 Phase Shift Lock and Active Switched- Capacitor Loop Filter
 J. Park, F. Maloberti: "Fractional-N PLL with 90 Phase Shift Lock and Active Switched-Capacitor Loop Filter"; Proc. of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, CICC 2005, San Josè, 21 September
J. Park, F. Maloberti: "Fractional-N PLL with 90 Phase Shift Lock and Active Switched-Capacitor Loop Filter"; Proc. of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, CICC 2005, San Josè, 21 September
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 28 Course Wrap Up. Recap 1
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 28 Course Wrap Up Dec. 5, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John Wawrzynek)
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 28 Course Wrap Up Dec. 5, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John Wawrzynek)
Keywords: VLSI; CMOS; Pass Transistor Logic (PTL); Gate Diffusion Input (GDI); Parellel In Parellel Out (PIPO); RAM. I.
 Comparison and analysis of sequential circuits using different logic styles Shofia Ram 1, Rooha Razmid Ahamed 2 1 M. Tech. Student, Dept of ECE, Rajagiri School of Engg and Technology, Cochin, Kerala 2
Comparison and analysis of sequential circuits using different logic styles Shofia Ram 1, Rooha Razmid Ahamed 2 1 M. Tech. Student, Dept of ECE, Rajagiri School of Engg and Technology, Cochin, Kerala 2
Dead-Time Control System for a Synchronous Buck dc-dc Converter
 Dead-Time Control System for a Synchronous Buck dc-dc Converter Floriberto Lima Chipidea Microelectronics berto@chipidea.com Marcelino Santos IST / INESC-ID marcelino.santos@ist.utl.pt José Barata IST,
Dead-Time Control System for a Synchronous Buck dc-dc Converter Floriberto Lima Chipidea Microelectronics berto@chipidea.com Marcelino Santos IST / INESC-ID marcelino.santos@ist.utl.pt José Barata IST,
Design of Phase Locked Loop as a Frequency Synthesizer Muttappa 1 Akalpita L Kulkarni 2
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 03, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Design of Phase Locked Loop as a Frequency Synthesizer Muttappa 1 Akalpita L Kulkarni
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 03, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Design of Phase Locked Loop as a Frequency Synthesizer Muttappa 1 Akalpita L Kulkarni
A 12-bit 100kS/s SAR ADC for Biomedical Applications. Sung-Chan Rho 1 and Shin-Il Lim 2. Seoul, Korea. Abstract
 , pp.17-22 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijunesst.2016.9.8.02 A 12-bit 100kS/s SAR ADC for Biomedical Applications Sung-Chan Rho 1 and Shin-Il Lim 2 1 Department of Electronics and Computer Engineering, Seokyeong
, pp.17-22 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijunesst.2016.9.8.02 A 12-bit 100kS/s SAR ADC for Biomedical Applications Sung-Chan Rho 1 and Shin-Il Lim 2 1 Department of Electronics and Computer Engineering, Seokyeong
Marvell 88E1000-RJJ Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver Partial Circuit Analysis
 October 5, 2004 Marvell 88E1000-RJJ Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver Partial Circuit Analysis Introduction... Page 1 List of Figures... Page 2 Device Summary Sheet... Page 9 Analog Front-end Top Level...Tab
October 5, 2004 Marvell 88E1000-RJJ Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver Partial Circuit Analysis Introduction... Page 1 List of Figures... Page 2 Device Summary Sheet... Page 9 Analog Front-end Top Level...Tab
Used in Image Acquisition Area CCD Driving Circuit Design
 Used in Image Acquisition Area CCD Driving Circuit Design Yanyan Liu Institute of Electronic and Information Engineering Changchun University of Science and Technology Room 318, BLD 1, No.7089, Weixing
Used in Image Acquisition Area CCD Driving Circuit Design Yanyan Liu Institute of Electronic and Information Engineering Changchun University of Science and Technology Room 318, BLD 1, No.7089, Weixing
MM5452/MM5453 Liquid Crystal Display Drivers
 MM5452/MM5453 Liquid Crystal Display Drivers General Description The MM5452 is a monolithic integrated circuit utilizing CMOS metal gate, low threshold enhancement mode devices. It is available in a 40-pin
MM5452/MM5453 Liquid Crystal Display Drivers General Description The MM5452 is a monolithic integrated circuit utilizing CMOS metal gate, low threshold enhancement mode devices. It is available in a 40-pin
An Fpga Implementation Of N/N+1 Prescaler For A Low Power Single Phase Clock Distribution System
 An Fpga Implementation Of N/N+1 Prescaler For A Low Power Single Phase Clock Distribution System V Satya Deepthi 1, SnehaSuprakash 2, USBK MahaLakshmi 3 1 M.Tech student, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Assistant
An Fpga Implementation Of N/N+1 Prescaler For A Low Power Single Phase Clock Distribution System V Satya Deepthi 1, SnehaSuprakash 2, USBK MahaLakshmi 3 1 M.Tech student, 2 Assistant Professor, 3 Assistant
DESIGN OF A 500MHZ, 4-BIT LOW POWER ADC FOR UWB APPLICATION
 DESIGN OF A 500MHZ, 4-BIT LOW POWER ADC FOR UWB APPLICATION SANTOSH KUMAR PATNAIK 1, DR. SWAPNA BANERJEE 2 1,2 E & ECE Department, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur, Kharagpur, India Abstract-This
DESIGN OF A 500MHZ, 4-BIT LOW POWER ADC FOR UWB APPLICATION SANTOSH KUMAR PATNAIK 1, DR. SWAPNA BANERJEE 2 1,2 E & ECE Department, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur, Kharagpur, India Abstract-This
Delay-based clock generator with edge transmission and reset
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.11, No.15, 1 8 Delay-based clock generator with edge transmission and reset Hyunsun Mo and Daejeong Kim a) Department of Electronics Engineering, Graduate School,
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.11, No.15, 1 8 Delay-based clock generator with edge transmission and reset Hyunsun Mo and Daejeong Kim a) Department of Electronics Engineering, Graduate School,
Digital micro-mirror device based modulator for microscope illumination
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 002 (2009) 000 000 87 91 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia Frontier Research in Nanoscale Science and Technology Digital micro-mirror device based
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 002 (2009) 000 000 87 91 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia Frontier Research in Nanoscale Science and Technology Digital micro-mirror device based
A Readout ASIC for CZT Detectors
 A Readout ASIC for CZT Detectors L.L.Jones a, P.Seller a, I.Lazarus b, P.Coleman-Smith b a STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Didcot, OX11 0QX, UK b STFC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington WA4 4AD, UK
A Readout ASIC for CZT Detectors L.L.Jones a, P.Seller a, I.Lazarus b, P.Coleman-Smith b a STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Didcot, OX11 0QX, UK b STFC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington WA4 4AD, UK
Highly Reliable Frequency Multiplier with DLL-Based Clock Generator for System-On-Chip
 Highly Reliable Frequency Multiplier with DLL-Based Clock Generator for System-On-Chip B. Janani, N.Arunpriya B.E, Dept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Panimalar Engineering College/ Anna
Highly Reliable Frequency Multiplier with DLL-Based Clock Generator for System-On-Chip B. Janani, N.Arunpriya B.E, Dept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Panimalar Engineering College/ Anna
AN EFFICIENT ALGORITHM FOR THE REMOVAL OF IMPULSE NOISE IN IMAGES USING BLACKFIN PROCESSOR
 AN EFFICIENT ALGORITHM FOR THE REMOVAL OF IMPULSE NOISE IN IMAGES USING BLACKFIN PROCESSOR S. Preethi 1, Ms. K. Subhashini 2 1 M.E/Embedded System Technologies, 2 Assistant professor Sri Sai Ram Engineering
AN EFFICIENT ALGORITHM FOR THE REMOVAL OF IMPULSE NOISE IN IMAGES USING BLACKFIN PROCESSOR S. Preethi 1, Ms. K. Subhashini 2 1 M.E/Embedded System Technologies, 2 Assistant professor Sri Sai Ram Engineering
Digital Logic ircuits Circuits Fundamentals I Fundamentals I
 Digital Logic Circuits Fundamentals I Fundamentals I 1 Digital and Analog Quantities Electronic circuits can be divided into two categories. Digital Electronics : deals with discrete values (= sampled
Digital Logic Circuits Fundamentals I Fundamentals I 1 Digital and Analog Quantities Electronic circuits can be divided into two categories. Digital Electronics : deals with discrete values (= sampled
Low-Power Digital CMOS Design: A Survey
 Low-Power Digital CMOS Design: A Survey Krister Landernäs June 4, 2005 Department of Computer Science and Electronics, Mälardalen University Abstract The aim of this document is to provide the reader with
Low-Power Digital CMOS Design: A Survey Krister Landernäs June 4, 2005 Department of Computer Science and Electronics, Mälardalen University Abstract The aim of this document is to provide the reader with
Development of a sampling ASIC for fast detector signals
 Development of a sampling ASIC for fast detector signals Hervé Grabas Work done in collaboration with Henry Frisch, Jean-François Genat, Eric Oberla, Gary Varner, Eric Delagnes, Dominique Breton. Signal
Development of a sampling ASIC for fast detector signals Hervé Grabas Work done in collaboration with Henry Frisch, Jean-François Genat, Eric Oberla, Gary Varner, Eric Delagnes, Dominique Breton. Signal
A Reset-Free Anti-Harmonic Programmable MDLL- Based Frequency Multiplier
 JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, OL.13, NO.5, OCTOBER, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2013.13.5.459 A Reset-Free Anti-Harmonic Programmable MDLL- Based Frequency Multiplier Geontae
JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, OL.13, NO.5, OCTOBER, 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2013.13.5.459 A Reset-Free Anti-Harmonic Programmable MDLL- Based Frequency Multiplier Geontae
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 15 - CMOS Implementation Technologies. Overview of Physical Implementations
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 15 - CMOS Implementation Technologies Mar 12, 2013 John Wawrzynek Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec15-CMOS Page 1 Overview of Physical Implementations Integrated Circuits (ICs)
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 15 - CMOS Implementation Technologies Mar 12, 2013 John Wawrzynek Spring 2013 EECS150 - Lec15-CMOS Page 1 Overview of Physical Implementations Integrated Circuits (ICs)
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9 - CMOS Implementation Technologies
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9 - CMOS Implementation Technologies Feb 14, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec09-CMOS Page 1 Overview of Physical Implementations Integrated Circuits (ICs)
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9 - CMOS Implementation Technologies Feb 14, 2012 John Wawrzynek Spring 2012 EECS150 - Lec09-CMOS Page 1 Overview of Physical Implementations Integrated Circuits (ICs)
Ultra fast single photon counting chip
 Ultra fast single photon counting chip P. Grybos, P. Kmon, P. Maj, R. Szczygiel Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Automatics, Computer Science and Biomedical Engineering AGH University of Science and
Ultra fast single photon counting chip P. Grybos, P. Kmon, P. Maj, R. Szczygiel Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Automatics, Computer Science and Biomedical Engineering AGH University of Science and
DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS A DESIGN PERSPECTIVE 2 N D E D I T I O N
 DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS A DESIGN PERSPECTIVE 2 N D E D I T I O N Jan M. Rabaey, Anantha Chandrakasan, and Borivoje Nikolic CONTENTS PART I: THE FABRICS Chapter 1: Introduction (32 pages) 1.1 A Historical
DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS A DESIGN PERSPECTIVE 2 N D E D I T I O N Jan M. Rabaey, Anantha Chandrakasan, and Borivoje Nikolic CONTENTS PART I: THE FABRICS Chapter 1: Introduction (32 pages) 1.1 A Historical
An Efficient Method for Implementation of Convolution
 IAAST ONLINE ISSN 2277-1565 PRINT ISSN 0976-4828 CODEN: IAASCA International Archive of Applied Sciences and Technology IAAST; Vol 4 [2] June 2013: 62-69 2013 Society of Education, India [ISO9001: 2008
IAAST ONLINE ISSN 2277-1565 PRINT ISSN 0976-4828 CODEN: IAASCA International Archive of Applied Sciences and Technology IAAST; Vol 4 [2] June 2013: 62-69 2013 Society of Education, India [ISO9001: 2008
Design and implementation of readout circuit on glass substrate with digital correction for touch-panel applications
 Design and implementation of readout circuit on glass substrate with digital correction for touch-panel applications Tzu-Ming Wang (SID Student Member) Ming-Dou Ker Abstract A readout circuit on glass
Design and implementation of readout circuit on glass substrate with digital correction for touch-panel applications Tzu-Ming Wang (SID Student Member) Ming-Dou Ker Abstract A readout circuit on glass
DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF A HIGH PERFORMANCE CMOS VOLTAGE DOUBLERS USING CHARGE REUSE TECHNIQUE
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 12, No. 12 (2017) 3344-3357 School of Engineering, Taylor s University DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF A HIGH PERFORMANCE CMOS VOLTAGE DOUBLERS USING CHARGE
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 12, No. 12 (2017) 3344-3357 School of Engineering, Taylor s University DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF A HIGH PERFORMANCE CMOS VOLTAGE DOUBLERS USING CHARGE
NEW DIGITAL ANGLE MEASUREMENT FACILITY BASED ON FPGA
 30 th ovember 202. Vol. 45 o.2 ISS: 992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISS: 87-395 EW DIGITAL AGLE MEASUREMET FACILITY BASED O FPGA HAO ZHAO, 2 HAO FEG Jiaxing University, Jiaxing Zhejiang China 2 Hangzhou Dianzi
30 th ovember 202. Vol. 45 o.2 ISS: 992-8645 www.jatit.org E-ISS: 87-395 EW DIGITAL AGLE MEASUREMET FACILITY BASED O FPGA HAO ZHAO, 2 HAO FEG Jiaxing University, Jiaxing Zhejiang China 2 Hangzhou Dianzi
BEE 2233 Digital Electronics. Chapter 1: Introduction
 BEE 2233 Digital Electronics Chapter 1: Introduction Learning Outcomes Understand the basic concept of digital and analog quantities. Differentiate the digital and analog systems. Compare the advantages
BEE 2233 Digital Electronics Chapter 1: Introduction Learning Outcomes Understand the basic concept of digital and analog quantities. Differentiate the digital and analog systems. Compare the advantages
Millimeter-wave CMOS Transceiver Techniques for Automotive Radar Systems
 Millimeter-wave CMOS Transceiver Techniques for Automotive Radar Systems Yoichi Kawano Hiroshi Matsumura Ikuo Soga Yohei Yagishita Recently, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) with the keyword of
Millimeter-wave CMOS Transceiver Techniques for Automotive Radar Systems Yoichi Kawano Hiroshi Matsumura Ikuo Soga Yohei Yagishita Recently, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) with the keyword of
6-Bit Charge Scaling DAC and SAR ADC
 6-Bit Charge Scaling DAC and SAR ADC Meghana Kulkarni 1, Muttappa Shingadi 2, G.H. Kulkarni 3 Associate Professor, Department of PG Studies, VLSI Design and Embedded Systems, VTU, Belgavi, India 1. M.Tech.
6-Bit Charge Scaling DAC and SAR ADC Meghana Kulkarni 1, Muttappa Shingadi 2, G.H. Kulkarni 3 Associate Professor, Department of PG Studies, VLSI Design and Embedded Systems, VTU, Belgavi, India 1. M.Tech.
Model 305 Synchronous Countdown System
 Model 305 Synchronous Countdown System Introduction: The Model 305 pre-settable countdown electronics is a high-speed synchronous divider that generates an electronic trigger pulse, locked in time with
Model 305 Synchronous Countdown System Introduction: The Model 305 pre-settable countdown electronics is a high-speed synchronous divider that generates an electronic trigger pulse, locked in time with
Energy Efficient and High Speed Charge-Pump Phase Locked Loop
 Energy Efficient and High Speed Charge-Pump Phase Locked Loop Sherin Mary Enosh M.Tech Student, Dept of Electronics and Communication, St. Joseph's College of Engineering and Technology, Palai, India.
Energy Efficient and High Speed Charge-Pump Phase Locked Loop Sherin Mary Enosh M.Tech Student, Dept of Electronics and Communication, St. Joseph's College of Engineering and Technology, Palai, India.
Innovative ultra-broadband ubiquitous Wireless communications through terahertz transceivers ibrow
 Project Overview Innovative ultra-broadband ubiquitous Wireless communications through terahertz transceivers ibrow Mar-2017 Presentation outline Project key facts Motivation Project objectives Project
Project Overview Innovative ultra-broadband ubiquitous Wireless communications through terahertz transceivers ibrow Mar-2017 Presentation outline Project key facts Motivation Project objectives Project
IT FR R TDI CCD Image Sensor
 4k x 4k CCD sensor 4150 User manual v1.0 dtd. August 31, 2015 IT FR 08192 00 R TDI CCD Image Sensor Description: With the IT FR 08192 00 R sensor ANDANTA GmbH builds on and expands its line of proprietary
4k x 4k CCD sensor 4150 User manual v1.0 dtd. August 31, 2015 IT FR 08192 00 R TDI CCD Image Sensor Description: With the IT FR 08192 00 R sensor ANDANTA GmbH builds on and expands its line of proprietary
Design of CMOS Based PLC Receiver
 Available online at: http://www.ijmtst.com/vol3issue10.html International Journal for Modern Trends in Science and Technology ISSN: 2455-3778 :: Volume: 03, Issue No: 10, October 2017 Design of CMOS Based
Available online at: http://www.ijmtst.com/vol3issue10.html International Journal for Modern Trends in Science and Technology ISSN: 2455-3778 :: Volume: 03, Issue No: 10, October 2017 Design of CMOS Based
A Novel Integrated Circuit Driver for LED Lighting
 Circuits and Systems, 014, 5, 161-169 Published Online July 014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs http://dx.doi.org/10.436/cs.014.57018 A Novel Integrated Circuit Driver for LED Lighting Yanfeng
Circuits and Systems, 014, 5, 161-169 Published Online July 014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs http://dx.doi.org/10.436/cs.014.57018 A Novel Integrated Circuit Driver for LED Lighting Yanfeng
Design of High-Precision Infrared Multi-Touch Screen Based on the EFM32
 Sensors & Transducers 204 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Design of High-Precision Infrared Multi-Touch Screen Based on the EFM32 Zhong XIAOLING, Guo YONG, Zhang WEI, Xie XINGHONG,
Sensors & Transducers 204 by IFSA Publishing, S. L. http://www.sensorsportal.com Design of High-Precision Infrared Multi-Touch Screen Based on the EFM32 Zhong XIAOLING, Guo YONG, Zhang WEI, Xie XINGHONG,
IN RECENT years, we have often seen three-dimensional
 622 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 39, NO. 4, APRIL 2004 Design and Implementation of Real-Time 3-D Image Sensor With 640 480 Pixel Resolution Yusuke Oike, Student Member, IEEE, Makoto Ikeda,
622 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 39, NO. 4, APRIL 2004 Design and Implementation of Real-Time 3-D Image Sensor With 640 480 Pixel Resolution Yusuke Oike, Student Member, IEEE, Makoto Ikeda,
