MOSFET-v. Op Amp Balancing Comparison
|
|
|
- Nigel Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MOSFET-v. Op Amp Balancing Comparison By reducing leakage current, SAB MOSFET device balance individual cell voltage with current balancing and cut power dissipation compared to op amp-based voltage balancing As the use of two or more supercapacitor cells becomes prevalent in the design of a variety of battery operated systems, designers are looking for ways to optimize the circuitry around the cells configured in a series. Designs with greater power efficiency are high in demand because they must also extend battery life by reducing energy consumption. One essential fact of using two or more cells in a series is that each supercapacitor cell has to be referenced against the others in the series in order to be balanced to prevent over-voltage of any one of the cells. Over-voltage causes stress and eventual failure of the devices. There are two widely used methods of balancing cells: One method uses an operational amplifier circuit to balance voltage in each cell, by essentially forcing a mid-point voltage between the supercapacitor cells. The other method uses a MOSFET array to balance the leakage currents in each cell by exponentially varying currents relative to its selected operating voltages. This method compensates for leakage current imbalances with small voltage imbalances so that the maximum rated voltage limits are not violated. For applications that depend on the lowest power dissipation to preserve battery life, current balancing method provides superior energy efficiency for the supercapacitors, batteries and system. It also requires far fewer circuit components, reduced board space, lower cost and greater reliability. Below, a graph will demonstrate how power dissipation of a supercapacitor series-connected stack differs in each method. Figure 1 charts leakage current (µa) versus cell voltage. It offers a comparison of individual cell leakage current both with op amp-based voltage balancing and MOSFET-based current balancing.
2 Figure 1. Figure 1 shows the difference between op amp-based voltage balancing versus MOSFET-based current balancing for two supercapacitor cells used in a series. Note that IC1 and Cell1 is a near vertical line that shows the ALD SAB MOSFET used for the current balancing, which forces Cell 1 to increase its total leakage current exponentially with incremental voltages. The contrast between the two different methods of supercapacitor cell balancing is best illustrated with an example. In this example, the first assumption is that the total charge voltage (power supply) across two cells shown in Figure 1 is 4.6V. The second assumption is that the cell capacitance of each of supercapacitors is equal, thus C1 = C2. Thirdly, the cell balance assumption occurs when cell leakage currents are equal, where IC1 = IC2. Fourth, the individual Cell 1 and Cell 2 leakage currents each follows a specific leakage current versus cell voltage relationship. This specific relationship is part of the individual characteristics of each supercapacitor cell being manufactured, which the manufacturer cannot control and which can vary over a wide range of values and shapes, even for supercapacitors made with the same material by the same manufacturer at the same time of manufacture. Most supercapacitor manufacturers would only specify a maximum leakage current value, with some efforts to match but not guarantee leakage currents by housing two or more supercapacitors within a single package. Without any external intervention or external cell balancing, the natural cell balancing occurs where both cells have leakage currents at 1.1 ua, where Cell 2 settles to 1.7V and Cell 1 settles to 2.9V (see
3 dotted lines). Cell 1, having exceeded its rated voltage of 2.7V, deteriorate rapidly and becomes damaged prematurely. When op amp-based voltage balancing is applied, Cell1 (C1) is forced to a mid-point voltage of 2.3V at 0.8µA. Cell 2 (C2) is also forced to 2.3V at 2.8 µa leakage current plus 1µA for op amp current, which equals 3.8µA for total power dissipation. The first vertical line on the left in the graph above shows opamp voltage balancing. The solid horizontal line in Figure 1 demonstrates MOSFET-based current balancing. Using the ALD device, Cell 2 balances at 2.27V at 2.6µA and Cell 1 balances at 2.33V at 2.6µA. When MOSFET-based current balancing is used, with careful selection of SAB MOSFET part numbers and the charge voltages, the leakage current of one of the two MOSFETs is at zero, dissipating zero power dissipation. Each supercapacitor cell balances at a leakage current level that is less than the maximum leakage of either one of the two cells. The actual balance current is less than whichever is higher of the two supercapacitor leakage itself, because the circuit is forcing that voltage a little bit lower. The dotted horizontal line shows the supercapacitors with no balancing, but this is just a reference point because unbalanced supercapacitors cannot actually exist for long in a series without this balancing. It will cause cell damage and actual failure, eventually. The rule for supercapacitors of two or more linked in a series is that whichever cell exhibits the greatest leakage, it forces its companion to exceed its rated voltage limit, which damages the materials in that cell. Once that cell is damaged, resulting in, for example, a short circuit, then the full voltage of 4.6V applies across the original leakier cell, causing the cell to become damaged as well, in a domino effect. The MOSFET current balancing technique is very different from op-amp balancing, which uses balanced voltage balancing. An op-amp circuit will try to force the two cells to the same voltage mid-point of 2.3 volt and it burns power in doing so. If the two cells capacitances are not balanced, even ever so slightly, then there is additional current burn (read: energy wasted) directly out of one of the supercapacitor cells. Depending upon the actual in-balance in supercapacitor capacitance, and hence their respective natural voltages, this additional current burn may be substantially more than any of the leakage currents. In an op-amp balancing scheme, Cell 1 is going to be set at 2.3V and 0.8 µa leakage current and Cell 2 is going to be forced to 2.3V at 2.8 µa leakage current. Assuming the op-amp also burns an extra 1µA, so then total power dissipation will be 3.8µA altogether.
4 With MOSFET current balancing, leakage current is reduced to 2.6µA for both cells, which is less leakage current produced by the individual supercapacitor at 2.8µA. By balancing the current, MOSFETs also automatically balance the voltage of each cell (C1-2.27V, C2 2.33) to be near voltage balance so that neither of them can damage the other with voltage that exceeds the supercapacitor limits of 2.7V. As the leakage (drain-gate) current of each MOSFET varies exponentially with its cell voltage, the little apparent voltage imbalance between the two cells is actually a benefit, as each cells settles to a voltage that it is comfortable and more natural with without dissipating any excessive leakage currents or discharge currents. Nevertheless, it can be challenging to series-connect a whole string of supercapacitors to a much higher voltage than the 4.6V in this example. Carefully matched supercapacitor cells and matched MOSFETs lend themselves more readily to seriesconnected high voltage, high power applications such as 50V or 100V systems. All of the results demonstrated in Figure 1 have been successfully re-produced during their third-party developer testing. Op-amp circuits are non-trivial, both in terms of component count and power draw. Even if a micro power op-amp is used, the circuit could draw much more power than the 3.8µA demonstrated in Fig. 1 if the supercapacitor cells aren t nearly balanced in both capacitance values and leakage currents. Op-amp circuits can be less forgiving of supercapacitor capacitance mismatches between the cells. Op-amps have some unknown variables associated with them because they force a mid-point voltage of each cell. Any time the super-capacitor stack wants to deviate from that voltage, it can create a tremendous amount of problem for the op-amp. This requires tightly matched capacitance values. Supercapacitors are essentially low voltage, high current devices. If you try force them to a different voltage, it takes a tremendous amount of current. Power consumption is non-trivial for many battery operated systems, such as back-up power supplies or remotely located monitoring equipment where supercapacitors are used. These systems typically have to operate off the grid for long periods of time on battery charges. Reliability for water-level monitoring devices used on rivers or weather stations have to wake up occasionally, turn on sensors, record data and send it wirelessly to a collection point. Every milliwatt is important for these types of equipment to operate reliably between service calls and battery charges. As supercapacitors used in a series of two or more becomes more prevalent in systems described above, engineers need to optimize efficiency, board space and cost. MOSFETs that provide current balancing
5 for supercapacitor cells are more energy efficient than those using op amp voltage balancing. They are also a little more forgiving to mismatched supercapacitor cells.
ALD810023/ALD810024/ALD810025/ ALD810026/ALD810027/ALD QUAD SUPERCAPACITOR AUTO BALANCING (SAB ) MOSFET ARRAY ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC.
 TM ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC. QUAD SUPERCAPACITOR AUTO BALANCING (SAB ) MOSFET ARRAY e EPAD ALD802/ALD802/ALD8025/ ALD802/ALD802/ALD8028 E N A B L E D GENERAL DESCRIPTION The ALD80xx and ALD0xx family
TM ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC. QUAD SUPERCAPACITOR AUTO BALANCING (SAB ) MOSFET ARRAY e EPAD ALD802/ALD802/ALD8025/ ALD802/ALD802/ALD8028 E N A B L E D GENERAL DESCRIPTION The ALD80xx and ALD0xx family
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O126826A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0126826 A1 CHAO (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR BALANCING Publication Classification
US 2016O126826A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0126826 A1 CHAO (43) Pub. Date: May 5, 2016 (54) CIRCUIT AND METHOD FOR BALANCING Publication Classification
CHAPTER 3. Instrumentation Amplifier (IA) Background. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Instrumentation Amplifier Architecture and Configurations
 CHAPTER 3 Instrumentation Amplifier (IA) Background 3.1 Introduction The IAs are key circuits in many sensor readout systems where, there is a need to amplify small differential signals in the presence
CHAPTER 3 Instrumentation Amplifier (IA) Background 3.1 Introduction The IAs are key circuits in many sensor readout systems where, there is a need to amplify small differential signals in the presence
Current Mirrors. Current Source and Sink, Small Signal and Large Signal Analysis of MOS. Knowledge of Various kinds of Current Mirrors
 Motivation Current Mirrors Current sources have many important applications in analog design. For example, some digital-to-analog converters employ an array of current sources to produce an analog output
Motivation Current Mirrors Current sources have many important applications in analog design. For example, some digital-to-analog converters employ an array of current sources to produce an analog output
Using the isppac-powr1208 MOSFET Driver Outputs
 January 2003 Introduction Using the isppac-powr1208 MOSFET Driver Outputs Application Note AN6043 The isppac -POWR1208 provides a single-chip integrated solution to power supply monitoring and sequencing
January 2003 Introduction Using the isppac-powr1208 MOSFET Driver Outputs Application Note AN6043 The isppac -POWR1208 provides a single-chip integrated solution to power supply monitoring and sequencing
MOSFET Amplifier Biasing
 MOSFET Amplifier Biasing Chris Winstead April 6, 2015 Standard Passive Biasing: Two Supplies V D V S R G I D V SS To analyze the DC behavior of this biasing circuit, it is most convenient to use the following
MOSFET Amplifier Biasing Chris Winstead April 6, 2015 Standard Passive Biasing: Two Supplies V D V S R G I D V SS To analyze the DC behavior of this biasing circuit, it is most convenient to use the following
TOP VIEW. OUTPUT PRESET 2.5V TO 5V 200mA SHDN 3 4 BP GND. Maxim Integrated Products 1
 19-2584; Rev ; 1/2 Low-Noise, Low-Dropout, 2mA General Description The low-noise, low-dropout linear regulator operates from a 2.5V to 6.5V input and delivers up to 2mA. Typical output noise is 3µV RMS,
19-2584; Rev ; 1/2 Low-Noise, Low-Dropout, 2mA General Description The low-noise, low-dropout linear regulator operates from a 2.5V to 6.5V input and delivers up to 2mA. Typical output noise is 3µV RMS,
Flyback Converter for High Voltage Capacitor Charging
 Flyback Converter for High Voltage Capacitor Charging Tony Alfrey (tonyalfrey at earthlink dot net) A Flyback Converter is a type of switching power supply that may be used to generate an output voltage
Flyback Converter for High Voltage Capacitor Charging Tony Alfrey (tonyalfrey at earthlink dot net) A Flyback Converter is a type of switching power supply that may be used to generate an output voltage
An introduction to Depletion-mode MOSFETs By Linden Harrison
 An introduction to Depletion-mode MOSFETs By Linden Harrison Since the mid-nineteen seventies the enhancement-mode MOSFET has been the subject of almost continuous global research, development, and refinement
An introduction to Depletion-mode MOSFETs By Linden Harrison Since the mid-nineteen seventies the enhancement-mode MOSFET has been the subject of almost continuous global research, development, and refinement
High temperature linear operation of paralleled power MOSFETs
 Paper to be presented at HTEN 27 conference, September 7-9, St. Catherine s College, Oxford, UK. High temperature linear operation of paralleled power MOSFETs Steven A. Morris Baker Hughes/NTEQ 2 Rankin
Paper to be presented at HTEN 27 conference, September 7-9, St. Catherine s College, Oxford, UK. High temperature linear operation of paralleled power MOSFETs Steven A. Morris Baker Hughes/NTEQ 2 Rankin
Designing High Power Parallel Arrays with PRMs
 APPLICATION NOTE AN:032 Designing High Power Parallel Arrays with PRMs Ankur Patel Applications Engineer August 2015 Contents Page Introduction 1 Arrays for Adaptive Loop / Master-Slave Operation 1 High
APPLICATION NOTE AN:032 Designing High Power Parallel Arrays with PRMs Ankur Patel Applications Engineer August 2015 Contents Page Introduction 1 Arrays for Adaptive Loop / Master-Slave Operation 1 High
Traditional PWM vs. Morningstar s TrakStar MPPT Technology
 Traditional PWM vs. Morningstar s TrakStar MPPT Technology Introduction: Morningstar MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) controllers utilize Morningstar s own advanced TrakStar Maximum Power Point Tracking
Traditional PWM vs. Morningstar s TrakStar MPPT Technology Introduction: Morningstar MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) controllers utilize Morningstar s own advanced TrakStar Maximum Power Point Tracking
RT9167/A. Low-Noise, Fixed Output Voltage, 300mA/500mA LDO Regulator Features. General Description. Applications. Ordering Information RT9167/A-
 General Description The RT9167/A is a 3mA/mA low dropout and low noise micropower regulator suitable for portable applications. The output voltages range from 1.V to.v in 1mV increments and 2% accuracy.
General Description The RT9167/A is a 3mA/mA low dropout and low noise micropower regulator suitable for portable applications. The output voltages range from 1.V to.v in 1mV increments and 2% accuracy.
THAT Corporation APPLICATION NOTE 102
 THAT Corporation APPLICATION NOTE 0 Digital Gain Control With Analog VCAs Abstract In many cases, a fully analog signal path provides the least compromise to sonic integrity, and ultimately delivers the
THAT Corporation APPLICATION NOTE 0 Digital Gain Control With Analog VCAs Abstract In many cases, a fully analog signal path provides the least compromise to sonic integrity, and ultimately delivers the
3 Circuit Theory. 3.2 Balanced Gain Stage (BGS) Input to the amplifier is balanced. The shield is isolated
 Rev. D CE Series Power Amplifier Service Manual 3 Circuit Theory 3.0 Overview This section of the manual explains the general operation of the CE power amplifier. Topics covered include Front End Operation,
Rev. D CE Series Power Amplifier Service Manual 3 Circuit Theory 3.0 Overview This section of the manual explains the general operation of the CE power amplifier. Topics covered include Front End Operation,
NOVEMBER 29, 2017 COURSE PROJECT: CMOS TRANSIMPEDANCE AMPLIFIER ECG 720 ADVANCED ANALOG IC DESIGN ERIC MONAHAN
 NOVEMBER 29, 2017 COURSE PROJECT: CMOS TRANSIMPEDANCE AMPLIFIER ECG 720 ADVANCED ANALOG IC DESIGN ERIC MONAHAN 1.Introduction: CMOS Transimpedance Amplifier Avalanche photodiodes (APDs) are highly sensitive,
NOVEMBER 29, 2017 COURSE PROJECT: CMOS TRANSIMPEDANCE AMPLIFIER ECG 720 ADVANCED ANALOG IC DESIGN ERIC MONAHAN 1.Introduction: CMOS Transimpedance Amplifier Avalanche photodiodes (APDs) are highly sensitive,
PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS OF EPAD PRECISION MATCHED PAIR MOSFET ARRAY
 TM ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC. e EPAD E N A B L E D PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS OF EPAD PRECISION MATCHED PAIR MOSFET ARRAY GENERAL DESCRIPTION ALDxx/ALD9xx/ALDxx/ALD9xx are high precision monolithic
TM ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC. e EPAD E N A B L E D PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS OF EPAD PRECISION MATCHED PAIR MOSFET ARRAY GENERAL DESCRIPTION ALDxx/ALD9xx/ALDxx/ALD9xx are high precision monolithic
DESIGN OF A NOVEL CURRENT MIRROR BASED DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER DESIGN WITH LATCH NETWORK. Thota Keerthi* 1, Ch. Anil Kumar 2
 ISSN 2277-2685 IJESR/October 2014/ Vol-4/Issue-10/682-687 Thota Keerthi et al./ International Journal of Engineering & Science Research DESIGN OF A NOVEL CURRENT MIRROR BASED DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER DESIGN
ISSN 2277-2685 IJESR/October 2014/ Vol-4/Issue-10/682-687 Thota Keerthi et al./ International Journal of Engineering & Science Research DESIGN OF A NOVEL CURRENT MIRROR BASED DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER DESIGN
DISCONTINUED PRODUCT FOR REFERENCE ONLY COMPLEMENTARY OUTPUT POWER HALL LATCH 5275 COMPLEMENTARY OUTPUT POWERHALL LATCH FEATURES
 5275 POWER HALL LATCH Data Sheet 27632B X V CC 1 SUPPLY ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS at T A = +25 C Supply Voltage, V CC............... 14 V Magnetic Flux Density, B...... Unlimited Type UGN5275K latching
5275 POWER HALL LATCH Data Sheet 27632B X V CC 1 SUPPLY ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS at T A = +25 C Supply Voltage, V CC............... 14 V Magnetic Flux Density, B...... Unlimited Type UGN5275K latching
CONVERTING 1524 SWITCHING POWER SUPPLY DESIGNS TO THE SG1524B
 LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS PS-5 CONVERTING 1524 SWITCHING POWER SUPPLY DESIGNS TO THE SG1524B Stan Dendinger Manager, Advanced Product Development Silicon General, Inc. INTRODUCTION Many power control
LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS PS-5 CONVERTING 1524 SWITCHING POWER SUPPLY DESIGNS TO THE SG1524B Stan Dendinger Manager, Advanced Product Development Silicon General, Inc. INTRODUCTION Many power control
Logic signal voltage levels
 Logic signal voltage levels Logic gate circuits are designed to input and output only two types of signals: "high" (1) and "low" (0), as represented by a variable voltage: full power supply voltage for
Logic signal voltage levels Logic gate circuits are designed to input and output only two types of signals: "high" (1) and "low" (0), as represented by a variable voltage: full power supply voltage for
150mA, Low-Dropout Linear Regulator with Power-OK Output
 9-576; Rev ; /99 5mA, Low-Dropout Linear Regulator General Description The low-dropout (LDO) linear regulator operates from a +2.5V to +6.5V input voltage range and delivers up to 5mA. It uses a P-channel
9-576; Rev ; /99 5mA, Low-Dropout Linear Regulator General Description The low-dropout (LDO) linear regulator operates from a +2.5V to +6.5V input voltage range and delivers up to 5mA. It uses a P-channel
CAP-XX APPLICATION NOTE No. 1002
 Units 9-0/2 Mars Road Tel +6 2 9420 0690 CAP-XX (Australia) Pty Ltd Lane Cove NSW 2066 Fax +6 2 9420 0692 ABN 28 077 060 872 Australia www.cap-xx.com ACN 077 060 872 CAP-XX APPLICATION NOTE No. 002 Start-Up
Units 9-0/2 Mars Road Tel +6 2 9420 0690 CAP-XX (Australia) Pty Ltd Lane Cove NSW 2066 Fax +6 2 9420 0692 ABN 28 077 060 872 Australia www.cap-xx.com ACN 077 060 872 CAP-XX APPLICATION NOTE No. 002 Start-Up
CMOS LOW VOLTAGE, LOW CHARGE INJECTION QUAD SPST ANALOG SWITCHES
 ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC. ALD421/ALD422M CMOS LOW VOLTAGE, LOW CHARGE INJECTION QUAD SPST ANALOG SWITCHES GENERAL DESCRIPTION The ALD421/ALD422M are quad SPST CMOS analog switches specifically developed
ADVANCED LINEAR DEVICES, INC. ALD421/ALD422M CMOS LOW VOLTAGE, LOW CHARGE INJECTION QUAD SPST ANALOG SWITCHES GENERAL DESCRIPTION The ALD421/ALD422M are quad SPST CMOS analog switches specifically developed
MIC2291. General Description. Features. Applications. Typical Application. 1.2A PWM Boost Regulator Photo Flash LED Driver
 1.2A PWM Boost Regulator Photo Flash LED Driver General Description The is a 1.2MHz Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), boost-switching regulator that is optimized for high-current, white LED photo flash applications.
1.2A PWM Boost Regulator Photo Flash LED Driver General Description The is a 1.2MHz Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), boost-switching regulator that is optimized for high-current, white LED photo flash applications.
OUTPUT UP TO 300mA C2 TOP VIEW FAULT- DETECT OUTPUT. Maxim Integrated Products 1
 19-1422; Rev 2; 1/1 Low-Dropout, 3mA General Description The MAX886 low-noise, low-dropout linear regulator operates from a 2.5 to 6.5 input and is guaranteed to deliver 3mA. Typical output noise for this
19-1422; Rev 2; 1/1 Low-Dropout, 3mA General Description The MAX886 low-noise, low-dropout linear regulator operates from a 2.5 to 6.5 input and is guaranteed to deliver 3mA. Typical output noise for this
New lossless clamp for single ended converters
 New lossless clamp for single ended converters Nigel Machin & Jurie Dekter Rectifier Technologies Pacific 24 Harker St Burwood, Victoria, 3125 Australia information@rtp.com.au Abstract A clamp for single
New lossless clamp for single ended converters Nigel Machin & Jurie Dekter Rectifier Technologies Pacific 24 Harker St Burwood, Victoria, 3125 Australia information@rtp.com.au Abstract A clamp for single
Field Effect Transistors
 Field Effect Transistors Purpose In this experiment we introduce field effect transistors (FETs). We will measure the output characteristics of a FET, and then construct a common-source amplifier stage,
Field Effect Transistors Purpose In this experiment we introduce field effect transistors (FETs). We will measure the output characteristics of a FET, and then construct a common-source amplifier stage,
Analog CMOS Interface Circuits for UMSI Chip of Environmental Monitoring Microsystem
 Analog CMOS Interface Circuits for UMSI Chip of Environmental Monitoring Microsystem A report Submitted to Canopus Systems Inc. Zuhail Sainudeen and Navid Yazdi Arizona State University July 2001 1. Overview
Analog CMOS Interface Circuits for UMSI Chip of Environmental Monitoring Microsystem A report Submitted to Canopus Systems Inc. Zuhail Sainudeen and Navid Yazdi Arizona State University July 2001 1. Overview
±2.5 C ( 55 to +130 C) mv/ C Typ. Ta = 30 C: V Typ. Ta = +30 C: V Typ. Ta = +130 C: V Typ. ±0.4% Typ.
 Rev.1.2_00 CMOS TEMPERATURE SENSOR IC The is a high-accuracy temperature sensor IC on a single chip, provides output voltage which is linear against the temperature change. Each chip consists of a temperature
Rev.1.2_00 CMOS TEMPERATURE SENSOR IC The is a high-accuracy temperature sensor IC on a single chip, provides output voltage which is linear against the temperature change. Each chip consists of a temperature
UNDERSTANDING HORIZONTAL OUTPUT STAGES OF COMPUTER MONITORS
 UNDERSTANDING HORIZONTAL OUTPUT STAGES OF COMPUTER MONITORS Today's computer, medical, security, design and industrial video display monitors operate at a host of different horizontal resolutions or scanning
UNDERSTANDING HORIZONTAL OUTPUT STAGES OF COMPUTER MONITORS Today's computer, medical, security, design and industrial video display monitors operate at a host of different horizontal resolutions or scanning
TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
Methods for Reducing Emissions from Switching Power Circuits. A. McDowell, C. Zhu and T. Hubing
 Methods for Reducing Emissions from Switching Power Circuits A. McDowell, C. Zhu and T. Hubing 1 Objective To reduce radiated emissions and other forms of interference from power inverter circuits, by
Methods for Reducing Emissions from Switching Power Circuits A. McDowell, C. Zhu and T. Hubing 1 Objective To reduce radiated emissions and other forms of interference from power inverter circuits, by
Some Proprietary LED Current Balancing Techniques. Introduction. by Sanjaya Maniktala. Method 1 (see Figure 1)
 Introduction This App Note is intended to provide a brief explanation of proprietary LED control modes, current balancing, and special synchronous operation, in particular those based on US Patent Application
Introduction This App Note is intended to provide a brief explanation of proprietary LED control modes, current balancing, and special synchronous operation, in particular those based on US Patent Application
LINEAR INTEGRATED SYSTEMS, INC.
 LINEAR INTEGRATED SYSTEMS, INC. 4042 Clipper Court Fremont, CA 94538-6540 sales@linearsystems.com A Linear Integrated Systems, Inc. White Paper Consider the Discrete JFET When You Have a Priority Performance
LINEAR INTEGRATED SYSTEMS, INC. 4042 Clipper Court Fremont, CA 94538-6540 sales@linearsystems.com A Linear Integrated Systems, Inc. White Paper Consider the Discrete JFET When You Have a Priority Performance
Low-Cost, Micropower, High-Side Current-Sense Amplifier + Comparator + Reference ICs
 9-63; Rev ; /3 Low-Cost, Micropower, High-Side Current-Sense General Description The low-cost, micropower, high-side current-sense supervisors contain a highside current-sense amplifier, bandgap reference,
9-63; Rev ; /3 Low-Cost, Micropower, High-Side Current-Sense General Description The low-cost, micropower, high-side current-sense supervisors contain a highside current-sense amplifier, bandgap reference,
New Current-Sense Amplifiers Aid Measurement and Control
 AMPLIFIER AND COMPARATOR CIRCUITS BATTERY MANAGEMENT CIRCUIT PROTECTION Mar 13, 2000 New Current-Sense Amplifiers Aid Measurement and Control This application note details the use of high-side current
AMPLIFIER AND COMPARATOR CIRCUITS BATTERY MANAGEMENT CIRCUIT PROTECTION Mar 13, 2000 New Current-Sense Amplifiers Aid Measurement and Control This application note details the use of high-side current
Switched capacitor circuitry
 Switched capacitor circuitry This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the reative ommons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Switched capacitor circuitry This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the reative ommons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
PREVIEW COPY. Amplifiers. Table of Contents. Introduction to Amplifiers...3. Single-Stage Amplifiers...19
 Amplifiers Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Amplifiers...3 Single-Stage Amplifiers...19 Amplifier Performance and Multistage Amplifiers...35 Lesson Four Op Amps...51
Amplifiers Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Amplifiers...3 Single-Stage Amplifiers...19 Amplifier Performance and Multistage Amplifiers...35 Lesson Four Op Amps...51
Constant Current Control for DC-DC Converters
 Constant Current Control for DC-DC Converters Introduction...1 Theory of Operation...1 Power Limitations...1 Voltage Loop Stability...2 Current Loop Compensation...3 Current Control Example...5 Battery
Constant Current Control for DC-DC Converters Introduction...1 Theory of Operation...1 Power Limitations...1 Voltage Loop Stability...2 Current Loop Compensation...3 Current Control Example...5 Battery
S-5813A/5814A Series CMOS TEMPERATURE SENSOR IC. Rev.1.2_00. Features. Applications. Package. Seiko Instruments Inc. 1
 The is a family of high-precision temperature sensor ICs on a single chip with a linear output voltage for temperature changes. Each chip is composed of a temperature sensor, a constant current circuit,
The is a family of high-precision temperature sensor ICs on a single chip with a linear output voltage for temperature changes. Each chip is composed of a temperature sensor, a constant current circuit,
Synchronous Buck Converter Controller
 Product is End of Life 3/204 Synchronous Buck Converter Controller Si950 DESCRIPTION The Si950 synchronous buck regulator controller is ideally suited for high-efficiency step down converters in battery-powered
Product is End of Life 3/204 Synchronous Buck Converter Controller Si950 DESCRIPTION The Si950 synchronous buck regulator controller is ideally suited for high-efficiency step down converters in battery-powered
MIC2196 OSRAM LED LIGHTING
 MIC2196 OSRAM LED LIGHTING Osram OSTAR : Micrel LED Driver Advancements Introduction Today s high current LEDs are finding applications that replace conventional lamps including filament and fluorescent
MIC2196 OSRAM LED LIGHTING Osram OSTAR : Micrel LED Driver Advancements Introduction Today s high current LEDs are finding applications that replace conventional lamps including filament and fluorescent
A Solution to Simplify 60A Multiphase Designs By John Lambert & Chris Bull, International Rectifier, USA
 A Solution to Simplify 60A Multiphase Designs By John Lambert & Chris Bull, International Rectifier, USA As presented at PCIM 2001 Today s servers and high-end desktop computer CPUs require peak currents
A Solution to Simplify 60A Multiphase Designs By John Lambert & Chris Bull, International Rectifier, USA As presented at PCIM 2001 Today s servers and high-end desktop computer CPUs require peak currents
CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION
 168 CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION 7.1 OVERVIEW In the previous chapters discussed about the design and simulation of Discrete controller for ZVS Buck, Interleaved Boost, Buck-Boost, Double Frequency
168 CHAPTER 7 HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATION 7.1 OVERVIEW In the previous chapters discussed about the design and simulation of Discrete controller for ZVS Buck, Interleaved Boost, Buck-Boost, Double Frequency
CPC1590 Application Technical Information
 Application Note: AN- CPC59 Application Technical Information AN--R www.ixysic.com AN- Using the CPC59 Isolated Gate Driver IC The CPC59 is an excellent choice for remote switching of DC and low frequency
Application Note: AN- CPC59 Application Technical Information AN--R www.ixysic.com AN- Using the CPC59 Isolated Gate Driver IC The CPC59 is an excellent choice for remote switching of DC and low frequency
Performance of Revised TVC Circuit. PSD8C Version 2.0. Dr. George L. Engel
 Performance of Revised TVC Circuit PSD8C Version 2. Dr. George L. Engel May, 21 I) Introduction This report attempts to document the performance of the revised TVC circuit. The redesign tried to correct
Performance of Revised TVC Circuit PSD8C Version 2. Dr. George L. Engel May, 21 I) Introduction This report attempts to document the performance of the revised TVC circuit. The redesign tried to correct
Statistical Pulse Measurements using USB Power Sensors
 Statistical Pulse Measurements using USB Power Sensors Today s modern USB Power Sensors are capable of many advanced power measurements. These Power Sensors are capable of demodulating the signal and processing
Statistical Pulse Measurements using USB Power Sensors Today s modern USB Power Sensors are capable of many advanced power measurements. These Power Sensors are capable of demodulating the signal and processing
Silicon-Gate Switching Functions Optimize Data Acquisition Front Ends
 Silicon-Gate Switching Functions Optimize Data Acquisition Front Ends AN03 The trend in data acquisition is moving toward ever-increasing accuracy. Twelve-bit resolution is now the norm, and sixteen bits
Silicon-Gate Switching Functions Optimize Data Acquisition Front Ends AN03 The trend in data acquisition is moving toward ever-increasing accuracy. Twelve-bit resolution is now the norm, and sixteen bits
Measuring Power Supply Switching Loss with an Oscilloscope
 Measuring Power Supply Switching Loss with an Oscilloscope Our thanks to Tektronix for allowing us to reprint the following. Ideally, the switching device is either on or off like a light switch, and instantaneously
Measuring Power Supply Switching Loss with an Oscilloscope Our thanks to Tektronix for allowing us to reprint the following. Ideally, the switching device is either on or off like a light switch, and instantaneously
Fundamentals of Microelectronics
 Fundamentals of Microelectronics CH1 Why Microelectronics? CH2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors CH3 Diode Circuits CH4 Physics of Bipolar Transistors CH5 Bipolar Amplifiers CH6 Physics of MOS Transistors
Fundamentals of Microelectronics CH1 Why Microelectronics? CH2 Basic Physics of Semiconductors CH3 Diode Circuits CH4 Physics of Bipolar Transistors CH5 Bipolar Amplifiers CH6 Physics of MOS Transistors
The Design and Characterization of an 8-bit ADC for 250 o C Operation
 The Design and Characterization of an 8-bit ADC for 25 o C Operation By Lynn Reed, John Hoenig and Vema Reddy Tekmos, Inc. 791 E. Riverside Drive, Bldg. 2, Suite 15, Austin, TX 78744 Abstract Many high
The Design and Characterization of an 8-bit ADC for 25 o C Operation By Lynn Reed, John Hoenig and Vema Reddy Tekmos, Inc. 791 E. Riverside Drive, Bldg. 2, Suite 15, Austin, TX 78744 Abstract Many high
Capacitive Touch Sensing Tone Generator. Corey Cleveland and Eric Ponce
 Capacitive Touch Sensing Tone Generator Corey Cleveland and Eric Ponce Table of Contents Introduction Capacitive Sensing Overview Reference Oscillator Capacitive Grid Phase Detector Signal Transformer
Capacitive Touch Sensing Tone Generator Corey Cleveland and Eric Ponce Table of Contents Introduction Capacitive Sensing Overview Reference Oscillator Capacitive Grid Phase Detector Signal Transformer
TLE4916-1K. Datasheet. Sense & Control. Low Power Automotive Hall Switch. Rev.1.0,
 Low Power Automotive Hall Switch Datasheet Rev.1.0, 2010-02-23 Sense & Control This datasheet has been downloaded from http://www.digchip.com at this page Edition 2010-02-23 Published by Infineon Technologies
Low Power Automotive Hall Switch Datasheet Rev.1.0, 2010-02-23 Sense & Control This datasheet has been downloaded from http://www.digchip.com at this page Edition 2010-02-23 Published by Infineon Technologies
THE increased complexity of analog and mixed-signal IC s
 134 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 34, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 1999 An Integrated Low-Voltage Class AB CMOS OTA Ramesh Harjani, Member, IEEE, Randy Heineke, Member, IEEE, and Feng Wang, Member, IEEE
134 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 34, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 1999 An Integrated Low-Voltage Class AB CMOS OTA Ramesh Harjani, Member, IEEE, Randy Heineke, Member, IEEE, and Feng Wang, Member, IEEE
Introduction What is an Isolated
 Introduction What is an Isolated Gate Driver? Multiple Choice Quiz TI Precision Labs Isolation 1 1. Gate drivers can be found in these electrical systems a. Commercial b. Automotive c. Industrial d. All
Introduction What is an Isolated Gate Driver? Multiple Choice Quiz TI Precision Labs Isolation 1 1. Gate drivers can be found in these electrical systems a. Commercial b. Automotive c. Industrial d. All
Supertex inc. HV7801 HV7801. High Side Current Monitor 8.0 to 450V Voltage Gain of 5. Features. General Description. Applications
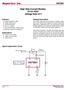 High Side Current Monitor 80 to 450V Voltage Gain of 5 Features Supply voltage 8V to 450V Voltage output device Typical gain 50±1% Max 500mV Fast rise and fall time, 700ns to 20µs Maximum quiescent current
High Side Current Monitor 80 to 450V Voltage Gain of 5 Features Supply voltage 8V to 450V Voltage output device Typical gain 50±1% Max 500mV Fast rise and fall time, 700ns to 20µs Maximum quiescent current
AUDIO OSCILLATOR DISTORTION
 AUDIO OSCILLATOR DISTORTION Being an ardent supporter of the shunt negative feedback in audio and electronics, I would like again to demonstrate its advantages, this time on the example of the offered
AUDIO OSCILLATOR DISTORTION Being an ardent supporter of the shunt negative feedback in audio and electronics, I would like again to demonstrate its advantages, this time on the example of the offered
OHM S LAW. Ohm s Law The relationship between potential difference (V) across a resistor of resistance (R) and the current (I) passing through it is
 OHM S LAW Objectives: a. To find the unknown resistance of an ohmic resistor b. To investigate the series and parallel combination of resistors c. To investigate the non-ohmic resistors Apparatus Required:
OHM S LAW Objectives: a. To find the unknown resistance of an ohmic resistor b. To investigate the series and parallel combination of resistors c. To investigate the non-ohmic resistors Apparatus Required:
MAX8863T/S/R, MAX8864T/S/R. Low-Dropout, 120mA Linear Regulators. General Description. Benefits and Features. Ordering Information.
 General Description The MAX8863T/S/R and low-dropout linear regulators operate from a +2.5V to +6.5V input range and deliver up to 12mA. A PMOS pass transistor allows the low, 8μA supply current to remain
General Description The MAX8863T/S/R and low-dropout linear regulators operate from a +2.5V to +6.5V input range and deliver up to 12mA. A PMOS pass transistor allows the low, 8μA supply current to remain
IN the design of the fine comparator for a CMOS two-step flash A/D converter, the main design issues are offset cancelation
 JOURNAL OF STELLAR EE315 CIRCUITS 1 A 60-MHz 150-µV Fully-Differential Comparator Erik P. Anderson and Jonathan S. Daniels (Invited Paper) Abstract The overall performance of two-step flash A/D converters
JOURNAL OF STELLAR EE315 CIRCUITS 1 A 60-MHz 150-µV Fully-Differential Comparator Erik P. Anderson and Jonathan S. Daniels (Invited Paper) Abstract The overall performance of two-step flash A/D converters
16.2 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERSION
 240 16. DC MEASUREMENTS In the context of contemporary instrumentation systems, a digital meter measures a voltage or current by performing an analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion. A/D converters produce
240 16. DC MEASUREMENTS In the context of contemporary instrumentation systems, a digital meter measures a voltage or current by performing an analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion. A/D converters produce
New Rail-to-Rail Output Op Amps Bring Precision Performance to Low Voltage Systems
 New Rail-to-Rail Output Op Amps Bring Precision Performance to Low oltage Systems Introduction Linear Technology has recently released several new high precision op amps for use in low voltage systems.
New Rail-to-Rail Output Op Amps Bring Precision Performance to Low oltage Systems Introduction Linear Technology has recently released several new high precision op amps for use in low voltage systems.
BICMOS Technology and Fabrication
 12-1 BICMOS Technology and Fabrication 12-2 Combines Bipolar and CMOS transistors in a single integrated circuit By retaining benefits of bipolar and CMOS, BiCMOS is able to achieve VLSI circuits with
12-1 BICMOS Technology and Fabrication 12-2 Combines Bipolar and CMOS transistors in a single integrated circuit By retaining benefits of bipolar and CMOS, BiCMOS is able to achieve VLSI circuits with
Difference between BJTs and FETs. Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)
 Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
R 3 V D. V po C 1 PIN 13 PD2 OUTPUT
 MASSACHUSETTS STITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.0 Feedback Systems Spring Term 008 Issued : April, 008 PLL Design Problem Due : Friday, May 9, 008 In this
MASSACHUSETTS STITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.0 Feedback Systems Spring Term 008 Issued : April, 008 PLL Design Problem Due : Friday, May 9, 008 In this
Chapter 13: Introduction to Switched- Capacitor Circuits
 Chapter 13: Introduction to Switched- Capacitor Circuits 13.1 General Considerations 13.2 Sampling Switches 13.3 Switched-Capacitor Amplifiers 13.4 Switched-Capacitor Integrator 13.5 Switched-Capacitor
Chapter 13: Introduction to Switched- Capacitor Circuits 13.1 General Considerations 13.2 Sampling Switches 13.3 Switched-Capacitor Amplifiers 13.4 Switched-Capacitor Integrator 13.5 Switched-Capacitor
ECE ECE285. Electric Circuit Analysis I. Spring Nathalia Peixoto. Rev.2.0: Rev Electric Circuits I
 ECE285 Electric Circuit Analysis I Spring 2014 Nathalia Peixoto Rev.2.0: 140124. Rev 2.1. 140813 1 Lab reports Background: these 9 experiments are designed as simple building blocks (like Legos) and students
ECE285 Electric Circuit Analysis I Spring 2014 Nathalia Peixoto Rev.2.0: 140124. Rev 2.1. 140813 1 Lab reports Background: these 9 experiments are designed as simple building blocks (like Legos) and students
Four-Channel Sample-and-Hold Amplifier AD684
 a FEATURES Four Matched Sample-and-Hold Amplifiers Independent Inputs, Outputs and Control Pins 500 ns Hold Mode Settling 1 s Maximum Acquisition Time to 0.01% Low Droop Rate: 0.01 V/ s Internal Hold Capacitors
a FEATURES Four Matched Sample-and-Hold Amplifiers Independent Inputs, Outputs and Control Pins 500 ns Hold Mode Settling 1 s Maximum Acquisition Time to 0.01% Low Droop Rate: 0.01 V/ s Internal Hold Capacitors
1MHz, 3A Synchronous Step-Down Switching Voltage Regulator
 FEATURES Guaranteed 3A Output Current Efficiency up to 94% Efficiency up to 80% at Light Load (10mA) Operate from 2.8V to 5.5V Supply Adjustable Output from 0.8V to VIN*0.9 Internal Soft-Start Short-Circuit
FEATURES Guaranteed 3A Output Current Efficiency up to 94% Efficiency up to 80% at Light Load (10mA) Operate from 2.8V to 5.5V Supply Adjustable Output from 0.8V to VIN*0.9 Internal Soft-Start Short-Circuit
UM mA, 600kHz Step-Up DC-DC Converter UM3433 SOT23-6. General Description. Rev.05 Dec /9
 General Description UM3433 600mA, 600kHz Step-Up DC-DC Converter UM3433 SOT23-6 The UM3433 is synchronous rectified, fixed frequency, step-up DC/DC converter series delivering high efficiency in a low
General Description UM3433 600mA, 600kHz Step-Up DC-DC Converter UM3433 SOT23-6 The UM3433 is synchronous rectified, fixed frequency, step-up DC/DC converter series delivering high efficiency in a low
Features. Functional Configuration IN+
 IttyBitty Rail-to-Rail Input Comparator General Description The MIC7211 and MIC7221 are micropower comparators featuring rail-to-rail input performance in Micrel s IttyBitty SOT-23-5 package. The MIC7211/21
IttyBitty Rail-to-Rail Input Comparator General Description The MIC7211 and MIC7221 are micropower comparators featuring rail-to-rail input performance in Micrel s IttyBitty SOT-23-5 package. The MIC7211/21
REV. B. NOTES 1 At Pin 1. 2 Calculated as average over the operating temperature range. 3 H = Hermetic Metal Can; N = Plastic DIP.
 SPECIFICATIONS (@ V IN = 15 V and 25 C unless otherwise noted.) Model AD584J AD584K AD584L Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit OUTPUT VOLTAGE TOLERANCE Maximum Error 1 for Nominal Outputs of: 10.000
SPECIFICATIONS (@ V IN = 15 V and 25 C unless otherwise noted.) Model AD584J AD584K AD584L Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit OUTPUT VOLTAGE TOLERANCE Maximum Error 1 for Nominal Outputs of: 10.000
Technical Article A DIRECT QUADRATURE MODULATOR IC FOR 0.9 TO 2.5 GHZ WIRELESS SYSTEMS
 Introduction As wireless system designs have moved from carrier frequencies at approximately 9 MHz to wider bandwidth applications like Personal Communication System (PCS) phones at 1.8 GHz and wireless
Introduction As wireless system designs have moved from carrier frequencies at approximately 9 MHz to wider bandwidth applications like Personal Communication System (PCS) phones at 1.8 GHz and wireless
Self-timed Refreshing Approach for Dynamic Memories
 Self-timed Refreshing Approach for Dynamic Memories Jabulani Nyathi and Jos6 G. Delgado-F'rias Department of Electrical Engineering State University of New York Binghamton, NY 13902-6000 Abstract Refreshing
Self-timed Refreshing Approach for Dynamic Memories Jabulani Nyathi and Jos6 G. Delgado-F'rias Department of Electrical Engineering State University of New York Binghamton, NY 13902-6000 Abstract Refreshing
Using the EnerChip in Pulse Current Applications
 Using the EnerChip in Pulse Current Applications Introduction EnerChips are solid state, reflow solder tolerant batteries packaged in standard surface mount, low profile packages. They can be placed onto
Using the EnerChip in Pulse Current Applications Introduction EnerChips are solid state, reflow solder tolerant batteries packaged in standard surface mount, low profile packages. They can be placed onto
LC 2 MOS Precision 5 V Quad SPST Switches ADG661/ADG662/ADG663
 a FEATURE +5 V, 5 V Power upplies Ultralow Power issipation (
a FEATURE +5 V, 5 V Power upplies Ultralow Power issipation (
LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF442 dual low power operational amplifiers provide many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM1458 while
LF442 Dual Low Power JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description The LF442 dual low power operational amplifiers provide many of the same AC characteristics as the industry standard LM1458 while
Ultra Low Static Power OTA with Slew Rate Enhancement
 ECE 595B Analog IC Design Design Project Fall 2009 Project Proposal Ultra Low Static Power OTA with Slew Rate Enhancement Patrick Wesskamp PUID: 00230-83995 1) Introduction In this design project I plan
ECE 595B Analog IC Design Design Project Fall 2009 Project Proposal Ultra Low Static Power OTA with Slew Rate Enhancement Patrick Wesskamp PUID: 00230-83995 1) Introduction In this design project I plan
1.2A, 23V, 1.4MHz Step-Down Converter
 1.2A, 23, 1.4MHz Step-Down Converter General Description The is a buck regulator with a built-in internal power MOSFET. It can provide 1.2A continuous output current over a wide input supply range with
1.2A, 23, 1.4MHz Step-Down Converter General Description The is a buck regulator with a built-in internal power MOSFET. It can provide 1.2A continuous output current over a wide input supply range with
Lab 1: Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements
 Abstract: Lab 1: Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements This lab exercise introduces the basic measurement instruments that will be used throughout the course. These instruments include multimeters, oscilloscopes,
Abstract: Lab 1: Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements This lab exercise introduces the basic measurement instruments that will be used throughout the course. These instruments include multimeters, oscilloscopes,
TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier
 TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
TL082 Wide Bandwidth Dual JFET Input Operational Amplifier General Description These devices are low cost, high speed, dual JFET input operational amplifiers with an internally trimmed input offset voltage
MT6303 Series Omni-polar, Low Power, MR Switch Sensor
 Feature AMR+CMOS monolithic structure High sensitivity B OP = 18Gauss, B RP = 13Gauss Low power consumption Average supply current
Feature AMR+CMOS monolithic structure High sensitivity B OP = 18Gauss, B RP = 13Gauss Low power consumption Average supply current
BM192-VCEB-CE. One-Cell Li Battery Protectors. General Description. Features. Applications. Typical Application Circuit. Battery Pack.
 一级代理 : 深圳市鼎瑞诚实业有限公司官方网站 :www.dingruicheng.com.cn BYD Microelectronics Co., Ltd. One-Cell Li Battery Protectors General Description The is protector for lithium-ion and lithium polymer rechargeable battery
一级代理 : 深圳市鼎瑞诚实业有限公司官方网站 :www.dingruicheng.com.cn BYD Microelectronics Co., Ltd. One-Cell Li Battery Protectors General Description The is protector for lithium-ion and lithium polymer rechargeable battery
Integration of Supercapacitors into Wirelessly Charged Biomedical Sensors
 Integration of s into Wirelessly Charged Biomedical Sensors Amit Pandey, Fadi Allos, Aiguo Patrick Hu, David Budgett The Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Auckland Auckland,
Integration of s into Wirelessly Charged Biomedical Sensors Amit Pandey, Fadi Allos, Aiguo Patrick Hu, David Budgett The Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Auckland Auckland,
Lecture 19 Real Semiconductor Switches and the Evolution of Power MOSFETS A.. Real Switches: I(D) through the switch and V(D) across the switch
 Lecture 19 Real Semiconductor Switches and the Evolution of Power MOSFETS 1 A.. Real Switches: I(D) through the switch and V(D) across the switch 1. Two quadrant switch implementation and device choice
Lecture 19 Real Semiconductor Switches and the Evolution of Power MOSFETS 1 A.. Real Switches: I(D) through the switch and V(D) across the switch 1. Two quadrant switch implementation and device choice
Automotive Surge Suppression Devices Can Be Replaced with High Voltage IC
 Automotive Surge Suppression Devices Can Be Replaced with High Voltage IC By Bruce Haug, Senior Product Marketing Engineer, Linear Technology Background Truck, automotive and heavy equipment environments
Automotive Surge Suppression Devices Can Be Replaced with High Voltage IC By Bruce Haug, Senior Product Marketing Engineer, Linear Technology Background Truck, automotive and heavy equipment environments
Photovoltaic Systems I EE 446/646
 Photovoltaic Systems I EE 446/646 PV System Types & Goal Types of PV Systems: Grid-tied systems that feed power directly into the utility grid, Residential Systems (1-10kW) Commercial/industrial systems
Photovoltaic Systems I EE 446/646 PV System Types & Goal Types of PV Systems: Grid-tied systems that feed power directly into the utility grid, Residential Systems (1-10kW) Commercial/industrial systems
A new class AB folded-cascode operational amplifier
 A new class AB folded-cascode operational amplifier Mohammad Yavari a) Integrated Circuits Design Laboratory, Department of Electrical Engineering, Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, Iran a) myavari@aut.ac.ir
A new class AB folded-cascode operational amplifier Mohammad Yavari a) Integrated Circuits Design Laboratory, Department of Electrical Engineering, Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, Iran a) myavari@aut.ac.ir
Bridge Measurement Systems
 Section 5 Outline Introduction to Bridge Sensors Circuits for Bridge Sensors A real design: the ADS1232REF The ADS1232REF Firmware This presentation gives an overview of data acquisition for bridge sensors.
Section 5 Outline Introduction to Bridge Sensors Circuits for Bridge Sensors A real design: the ADS1232REF The ADS1232REF Firmware This presentation gives an overview of data acquisition for bridge sensors.
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD UB24205 Preliminary CMOS IC
 UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD UB24205 Preliminary CMOS IC LITHIUM-ION/POLYMER BATTERY PROTECTION IC DESCRIPTION The UTC UB24205 is a lithium-ion / lithium-polymer rechargeable battery protection IC with
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD UB24205 Preliminary CMOS IC LITHIUM-ION/POLYMER BATTERY PROTECTION IC DESCRIPTION The UTC UB24205 is a lithium-ion / lithium-polymer rechargeable battery protection IC with
High Side MOSFET Gate Drive: The Power of Well. Implemented Pulse Transformers
 High Side MOSFET Gate Drive: The Power of Well Author: Fritz Schlunder SHEF Systems AN-1 Implemented Pulse Transformers Many different techniques and circuits are available for providing high side N-Channel
High Side MOSFET Gate Drive: The Power of Well Author: Fritz Schlunder SHEF Systems AN-1 Implemented Pulse Transformers Many different techniques and circuits are available for providing high side N-Channel
Review Energy Bands Carrier Density & Mobility Carrier Transport Generation and Recombination
 Review Energy Bands Carrier Density & Mobility Carrier Transport Generation and Recombination Current Transport: Diffusion, Thermionic Emission & Tunneling For Diffusion current, the depletion layer is
Review Energy Bands Carrier Density & Mobility Carrier Transport Generation and Recombination Current Transport: Diffusion, Thermionic Emission & Tunneling For Diffusion current, the depletion layer is
LM , -8.2, -8.4, -12.6, Lithium-Ion Battery Charge Controller
 LM3420-4.2, -8.2, -8.4, -12.6, -16.8 Lithium-Ion Battery Charge Controller General Description The LM3420 series of controllers are monolithic integrated circuits designed for charging and end-of-charge
LM3420-4.2, -8.2, -8.4, -12.6, -16.8 Lithium-Ion Battery Charge Controller General Description The LM3420 series of controllers are monolithic integrated circuits designed for charging and end-of-charge
Analysis and Reduction of On-Chip Inductance Effects in Power Supply Grids
 Analysis and Reduction of On-Chip Inductance Effects in Power Supply Grids Woo Hyung Lee Sanjay Pant David Blaauw Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science {leewh, spant, blaauw}@umich.edu
Analysis and Reduction of On-Chip Inductance Effects in Power Supply Grids Woo Hyung Lee Sanjay Pant David Blaauw Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science {leewh, spant, blaauw}@umich.edu
D8020. Universal High Integration Led Driver Description. Features. Typical Applications
 Universal High Integration Led Driver Description The D8020 is a highly integrated Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) high efficiency LED driver IC. It requires as few as 6 external components. This IC allows
Universal High Integration Led Driver Description The D8020 is a highly integrated Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) high efficiency LED driver IC. It requires as few as 6 external components. This IC allows
DS1669 Dallastat TM Electronic Digital Rheostat
 Dallastat TM Electronic Digital Rheostat www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Replaces mechanical variable resistors Electronic interface provided for digital as well as manual control Wide differential input voltage
Dallastat TM Electronic Digital Rheostat www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Replaces mechanical variable resistors Electronic interface provided for digital as well as manual control Wide differential input voltage
MAX1686HEUA -40 C to +85 C 8 µmax TOP VIEW IN
 9-376; Rev ; 2/98 3V to 5V Regulating General Description The MAX686 provides power for dual-voltage subscriber ID module (SIM) cards in portable applications such as GSM cellular phones. Designed to reside
9-376; Rev ; 2/98 3V to 5V Regulating General Description The MAX686 provides power for dual-voltage subscriber ID module (SIM) cards in portable applications such as GSM cellular phones. Designed to reside
Applications Overview
 Applications Overview Galvanic Cycling of Rechargeable Batteries I-V Characterization of Solar Cells and Panels Making Low Resistance Measurements Using High Current DC I-V Characterization of Transistors
Applications Overview Galvanic Cycling of Rechargeable Batteries I-V Characterization of Solar Cells and Panels Making Low Resistance Measurements Using High Current DC I-V Characterization of Transistors
Experiment 1: Amplifier Characterization Spring 2019
 Experiment 1: Amplifier Characterization Spring 2019 Objective: The objective of this experiment is to develop methods for characterizing key properties of operational amplifiers Note: We will be using
Experiment 1: Amplifier Characterization Spring 2019 Objective: The objective of this experiment is to develop methods for characterizing key properties of operational amplifiers Note: We will be using
