QPR No. 93 SOLID-STATE MICROWAVE ELECTRONICS" IV. Academic and Research Staff. Prof. R. P. Rafuse Dr. D. H. Steinbrecher.
|
|
|
- Rosalind Nicholson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IV. SOLID-STATE MICROWAVE ELECTRONICS" Academic and Research Staff Prof. R. P. Rafuse Dr. D. H. Steinbrecher Graduate Students W. G. Bartholomay D. F. Peterson R. W. Smith A. Y. Chen J. E. Rudzki R. E. Snyder R. D. Mohlere A. A. M. Saleh J. G. Webb A. 60-GHz MIXER The mixer has been assembled and tested. Using a 5-dB noise figure intermediatefrequency amplifier at 3. 1 GHz, we have measured an over-all receiver noise figure of db. This corresponds to a 7. 2-dB conversion loss mixer at GHz. The diodes used were gold gallium arsenide Schottky barrier diodes with a contact area of 5 pm. The diodes were self-biased with a DC current slightly in excess of 10 ma each. J. E. Rudzki B. 15-GHz DOUBLER With a new coupling pin designed by Dr. J. W. Majer, the input impedance measurements of a few diodes have been studied at GHz. A waveguide tuner is now being designed for the input port of the doubler. More theoretical aspects of the doubler are also being investigated. A. Y. Chen C. AVALANCHE DIODE ANALYSIS 1. Oscillator Analysis The variation in output power and noise of the fundamental of an avalanche diode oscillator has been investigated as a function of higher harmonic (the second and third, for the most part) tuning. This was accomplished by mounting the diode in a special circuit that provided reasonable isolation of the fundamental from the higher harmonics, as shown in Fig. IV-1. Tuning and coupling at the fundamental (~9 GHz) was provided by two movable copper slugs and an external double stub tuner (if necessary), while the tuning at the second (and third) harmonics was done by using a K-band adjustable waveguide backshort. The This work was supported by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (Grant NGL ); and in part by the Joint Services Electronics Programs (U.S. Army, U.S. Navy, and U.S. Air Force)under Contract DA AMC-02536(E).
2 OUTPUT COPPER TUNING SLUGS LOWPASS FILTER ( fo,10 GHz STANDARD K-BAND WAVEGUIDE Fig. IV-1. An imbedding network providing the necessary coupling and tuning for the fundamental. IDEAL FILTERS SDIODE JUNCTION V zl Fig. IV-2. Equivalent circuit.
3 (IV. SOLID-STATE MICROWAVE ELECTRONICS) movable short provides the same type of impedance variation at 3f as it does at 2f ; that is, X s = Zw tan P3 L, since the reduced height waveguide at the diode forces the third harmonic to propagate in the TE 3 0 mode. The output power was observed to be a function of the tuning at both ports, and for fixed tuning at the fundamental a 2-3 db variation in power level could be observed as the position of the adjustable short varied. The effect may be described in more quantitative fashion from consideration of the equivalent circuit (Fig. IV-2). The tuning at the fundamental was described by the change in the real part of Z1, and that at the 2nd and 3rd harmonics by the change in the position of the backshort relative to a given reference plane rp. X2S and X3S change together in some fashion, since each reactance is provided by the same adjustable short. The large series inductance of the cutoff waveguide essentially overwhelms any reactance change provided by the tuning slugs, thereby keeping the fundamental frequency nearly constant. Accordingly, this small variation in the reactive part of Z 1 allowed the tuning at fo to be characterized by its real part only. It should be mentioned that Z1 is the impedance seen by the junction at f, which can be found by the usual de-imbedding procedure. The imbedding networks at 2f and 3f were not calculated in this experiment. O o The procedure followed was to fix Re {Zl} at several appropriate values and then observe the power-level variations as a function of the position of the backshort. In this manner a contour map of power output at the fundamental vs the tuning at each frequency involved was constructed. There are relatively high power plateaus at the smaller values of R 1 (Re {Z 1 }), and its optimum value appears to be ~3. 0 i2 at 9. 2 GHz. the second and third harmonics are of consequence, since peaks and valleys occur at half-guide wavelengths of these frequencies (although there is some ambiguity, since the guide wavelength at 2fo ( in.) is nearly twice the guide wavelength at 3f (0.496 in.). Another consequence of the harmonic tuning was the variation it produced in the output noise, as seen on a spectrum analyzer. Both Figure IV-3 shows a typical power-level variation as a function of the position of the waveguide backshort. A rather profound variation in the noise performance was observed at each of the power-level droops. A sequence of photographs showing this effect is displayed in Fig. IV-4 where the letters below each picture correspond to the same letters in Fig. IV-3. the output with a matched load terminating the high-frequency port. Picture (f) represents a. Incremental Avalanche Impedance Measurements Incremental impedance measurements were made on an avalanche diode under nonoscillatory conditions to find its dependence on the direct avalanche current. The impedance was measured at some external reference plane using a slotted line or network analyzer, and then referred back to the diode junction through the appropriate coupling network. This coupling network was calculated from a knowledge of
4 FREQUENCY DEVIATION (MHz) (9.07 GHz CENTER FREQUENCY) o o -- o b o- - - _-_0-- b -- o POWER LEVEL (dbm) GUIDE WAVELENGTH AT 2f = 1.037" GUIDE WAVELENGTH AT 3f = 0.508" b\ 19.0 bi 0.50X 3,g (b) (c) (d) 1j A SIMILA R EFFECT WAS SEEr NI AS ER DROPS (e) (d) I I I I I I I I I I POSITION OF SHORT (inches) Fig. IV-3. Power and frequency deviation as a function of harmonic tuning. (Letters (a)-(e) refer to pictures in Fig. IV-4.)
5 (e) (f) Fig. IV-4. Spectrum analyzer display of the fundamental output as a function of harmonic tuning. Letters correspond to the positions of the short as shown in Fig. IV-3. The pictures were taken using the LOG scale of the spectrum analyzer, with 1-MHz bandwidth and 15-MHz dispersion.
6 NORMALIZED REAL PART I I I I I I I I I 0.0 V _ NETWORK ANALYZER DISPLAY OF IMPEDANCE VS BIAS AT THE EXTERNAL REFERENCE PLANE R-P. AVANANCHE BREAKDOWN IS 9.0 V AT Z = 0.5+ji V NORMALIZATION FACTOR = C min(vb +O) V > 62.0 V ma ,4 42, ma , RP 8.72 a j i44.72 S : j 9.32 Q NETWORK EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT AT 9.5 GHz Fig. IV-5. Incremental diode impedance vs bias.
7 (IV. SOLID-STATE MICROWAVE ELECTRONICS) NORMALIZED INCREMENTAL AVALANCHE RESISTANCE ,REAL PART 20.0 E 30.0 Z 40.0 U 50.0 u Z NORMALIZED INCREMENTAL AVALANCHE REACTANCE Fig. IV-6. Incremental diode impedance vs bias. three impedance values at the junction and the corresponding values at the external reference plane. The three values of junction impedance used correspond to the reactance of the depletion layer capacitance at 3 specified vias voltages above avalanche breakdown. Figure IV-5 shows the variation in impedance at the external reference plane (insert) and the corresponding variation at the junction after de-imbedding. In the display (insert), the bias was swept at 60 Hz and avalanche breakdown is at the intersection of the two arcs (the hysteresis is due to heating effects). Figure IV-6 shows the variation of both real and imaginary parts of the diode's incremental impedance; it appears to be a linear function of the avalanche current at 9. 5 GHz. b. Negative R Amplifier A Smith Chart plot of impedance vs bias at the output of the circuit of Fig. IV-i indicates that for certain values of bias the real part is negative. The amount of negative resistance depends on the diode and the circuit losses, but it was large enough in this case to be used as a negative R amplifier. By attaching a 4-port circulator to the output, and adjusting the DC bias to maximize the magnitude of r without permitting self-oscillation of the avalanche diode, gain and bandwidth
8 SLOPE ;-0.65 db/dbm GHz GHz I I I I I I 1 I I I I INPUT POWER (dbm) Fig. IV-7. Power gain vs input power with the as a negative resistance amplifier. avalanche diode used GAIN-BANDWIDTH PRODUCT BANDWIDTH z Z I I I I I I I I I INPUT POWER (dbm) Fig. IV-8. Bandwidth and gain-bandwidth product for the avalanche diode negative resistance amplifier at GHz.
9 (IV. SOLID-STATE MICROWAVE ELECTRONICS) measurements were made as a function of the input power. Since the network contained a rather highly tuned circuit, the bandwidth is quite narrow. Figure IV-7 shows the power gain vs input power at two closely spaced frequencies for a Varian Associates avalanche diode. The curve has a nearly constant slope of db/dbm. Figure IV-8 shows the bandwidth and gain-bandwidth product vs input power. The bandwidth might be stretched to 1 GHz with the proper circuit. Noise-figure measurements on this amplifier ranged between 30 db and 40 db, which is typical for amplifier circuits employing avalanche diodes as the negative R device. 2. Summary and Conclusions The results of the oscillator analysis seem to clearly imply a consideration of harmonic terminations in the design of avalanche diode circuits. The noise performance and power output might be further improved by providing independent tuning at the second, third, and possibly higher harmonics. Noise-figure measurements using the avalanche diode as the local oscillator for an X-band balanced mixer have shown a 6-8 db variation as the second harmonic was tuned with the adjustable backshort. This gives a sort of quantitative measure to the spectrum analyzer displays. Accordingly, a large-signal avalanche diode negative resistance amplifier might show noise-figure improvements with harmonic tuning. The incremental avalanche impedance appears to have a nearly linear relation to the direct avalanche current. This implies some sort of nonlinear relation between the instantaneous voltage and current, which can be found from a knowledge of the frequency behavior of the incremental impedance. This brings up the possibility of using the avalanche diode as a self-pumped parametric amplifier, that is, letting the oscillator signal be the pump. A further use might be in the area of harmonic generators. D. F. Peterson
10
Academic and Research Staff. Prof. P. L. Penfield, Jr. Prof. D. H. Steinbrecher. Graduate Students
 II. SOLID-STATE MICROWAVE ELECTRONICS Academic and Research Staff Prof. P. L. Penfield, Jr. Prof. D. H. Steinbrecher Graduate Students E. L. Caples R. H. S. Kwong D. F. Peterson A. Chu H. Po A. INTERMODULATION
II. SOLID-STATE MICROWAVE ELECTRONICS Academic and Research Staff Prof. P. L. Penfield, Jr. Prof. D. H. Steinbrecher Graduate Students E. L. Caples R. H. S. Kwong D. F. Peterson A. Chu H. Po A. INTERMODULATION
A 200 GHz Broadband, Fixed-Tuned, Planar Doubler
 A 200 GHz Broadband, Fixed-Tuned, Planar Doubler David W. Porterfield Virginia Millimeter Wave, Inc. 706 Forest St., Suite D Charlottesville, VA 22903 Abstract - A 100/200 GHz planar balanced frequency
A 200 GHz Broadband, Fixed-Tuned, Planar Doubler David W. Porterfield Virginia Millimeter Wave, Inc. 706 Forest St., Suite D Charlottesville, VA 22903 Abstract - A 100/200 GHz planar balanced frequency
LOW NOISE GHZ RECEIVERS USING SINGLE-DIODE HARMONIC MIXERS
 First International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Page 399 LOW NOISE 500-700 GHZ RECEIVERS USING SINGLE-DIODE HARMONIC MIXERS Neal R. Erickson Millitech Corp. P.O. Box 109 S. Deerfield, MA 01373
First International Symposium on Space Terahertz Technology Page 399 LOW NOISE 500-700 GHZ RECEIVERS USING SINGLE-DIODE HARMONIC MIXERS Neal R. Erickson Millitech Corp. P.O. Box 109 S. Deerfield, MA 01373
ENE324. Microwave experiments
 ENE324 Microwave experiments Gunn diodes are fabricated from a single piece of n-type semiconductor. The most common materials are gallium Arsenide, GaAs and Indium Phosphide,InP. However other materials
ENE324 Microwave experiments Gunn diodes are fabricated from a single piece of n-type semiconductor. The most common materials are gallium Arsenide, GaAs and Indium Phosphide,InP. However other materials
PRODUCT APPLICATION NOTES
 Extending the HMC189MS8 Passive Frequency Doubler Operating Range with External Matching General Description The HMC189MS8 is a miniature passive frequency doubler in a plastic 8-lead MSOP package. The
Extending the HMC189MS8 Passive Frequency Doubler Operating Range with External Matching General Description The HMC189MS8 is a miniature passive frequency doubler in a plastic 8-lead MSOP package. The
Millimeter- and Submillimeter-Wave Planar Varactor Sideband Generators
 Millimeter- and Submillimeter-Wave Planar Varactor Sideband Generators Haiyong Xu, Gerhard S. Schoenthal, Robert M. Weikle, Jeffrey L. Hesler, and Thomas W. Crowe Department of Electrical and Computer
Millimeter- and Submillimeter-Wave Planar Varactor Sideband Generators Haiyong Xu, Gerhard S. Schoenthal, Robert M. Weikle, Jeffrey L. Hesler, and Thomas W. Crowe Department of Electrical and Computer
Microwave Circuit Design and Measurements Lab. INTRODUCTION TO MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS: DETECTION OF RF POWER AND STANDING WAVES Lab #2
 EE 458/558 Microwave Circuit Design and Measurements Lab INTRODUCTION TO MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS: DETECTION OF RF POWER AND STANDING WAVES Lab #2 The purpose of this lab is to gain a basic understanding
EE 458/558 Microwave Circuit Design and Measurements Lab INTRODUCTION TO MICROWAVE MEASUREMENTS: DETECTION OF RF POWER AND STANDING WAVES Lab #2 The purpose of this lab is to gain a basic understanding
Impedance Matching Techniques for Mixers and Detectors. Application Note 963
 Impedance Matching Techniques for Mixers and Detectors Application Note 963 Introduction The use of tables for designing impedance matching filters for real loads is well known [1]. Simple complex loads
Impedance Matching Techniques for Mixers and Detectors Application Note 963 Introduction The use of tables for designing impedance matching filters for real loads is well known [1]. Simple complex loads
Schottky Barrier Diode Video Detectors. Application Note 923
 Schottky Barrier Diode Video Detectors Application Note 923 I. Introduction This Application Note describes the characteristics of Agilent Technologies Schottky Barrier Diodes intended for use in video
Schottky Barrier Diode Video Detectors Application Note 923 I. Introduction This Application Note describes the characteristics of Agilent Technologies Schottky Barrier Diodes intended for use in video
The Schottky Diode Mixer. Application Note 995
 The Schottky Diode Mixer Application Note 995 Introduction A major application of the Schottky diode is the production of the difference frequency when two frequencies are combined or mixed in the diode.
The Schottky Diode Mixer Application Note 995 Introduction A major application of the Schottky diode is the production of the difference frequency when two frequencies are combined or mixed in the diode.
MICROWAVE MICROWAVE TRAINING BENCH COMPONENT SPECIFICATIONS:
 Microwave section consists of Basic Microwave Training Bench, Advance Microwave Training Bench and Microwave Communication Training System. Microwave Training System is used to study all the concepts of
Microwave section consists of Basic Microwave Training Bench, Advance Microwave Training Bench and Microwave Communication Training System. Microwave Training System is used to study all the concepts of
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated RF Oscillator with Buffered Outputs. Typical Operating Circuit. 10nH 1000pF MAX2620 BIAS SUPPLY
 19-1248; Rev 1; 5/98 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated General Description The combines a low-noise oscillator with two output buffers in a low-cost, plastic surface-mount, ultra-small
19-1248; Rev 1; 5/98 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated General Description The combines a low-noise oscillator with two output buffers in a low-cost, plastic surface-mount, ultra-small
CHAPTER 4 LARGE SIGNAL S-PARAMETERS
 CHAPTER 4 LARGE SIGNAL S-PARAMETERS 4.0 Introduction Small-signal S-parameter characterization of transistor is well established. As mentioned in chapter 3, the quasi-large-signal approach is the most
CHAPTER 4 LARGE SIGNAL S-PARAMETERS 4.0 Introduction Small-signal S-parameter characterization of transistor is well established. As mentioned in chapter 3, the quasi-large-signal approach is the most
Part Number I s (Amps) n R s (Ω) C j (pf) HSMS x HSMS x HSCH x
 The Zero Bias Schottky Detector Diode Application Note 969 Introduction A conventional Schottky diode detector such as the Agilent Technologies requires no bias for high level input power above one milliwatt.
The Zero Bias Schottky Detector Diode Application Note 969 Introduction A conventional Schottky diode detector such as the Agilent Technologies requires no bias for high level input power above one milliwatt.
A Self-Biased Anti-parallel Planar Varactor Diode
 Page 356 A Self-Biased Anti-parallel Planar Varactor Diode Neal R. Erickson Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA 01003 Abstract A set of design criteria are presented
Page 356 A Self-Biased Anti-parallel Planar Varactor Diode Neal R. Erickson Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA 01003 Abstract A set of design criteria are presented
CHAPTER - 3 PIN DIODE RF ATTENUATORS
 CHAPTER - 3 PIN DIODE RF ATTENUATORS 2 NOTES 3 PIN DIODE VARIABLE ATTENUATORS INTRODUCTION An Attenuator [1] is a network designed to introduce a known amount of loss when functioning between two resistive
CHAPTER - 3 PIN DIODE RF ATTENUATORS 2 NOTES 3 PIN DIODE VARIABLE ATTENUATORS INTRODUCTION An Attenuator [1] is a network designed to introduce a known amount of loss when functioning between two resistive
PART MAX2605EUT-T MAX2606EUT-T MAX2607EUT-T MAX2608EUT-T MAX2609EUT-T TOP VIEW IND GND. Maxim Integrated Products 1
 19-1673; Rev 0a; 4/02 EVALUATION KIT MANUAL AVAILABLE 45MHz to 650MHz, Integrated IF General Description The are compact, high-performance intermediate-frequency (IF) voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs)
19-1673; Rev 0a; 4/02 EVALUATION KIT MANUAL AVAILABLE 45MHz to 650MHz, Integrated IF General Description The are compact, high-performance intermediate-frequency (IF) voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs)
MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) LAB MANUAL VI SEMESTER
 1 MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) LAB MANUAL VI SEMESTER RAO PAHALD SINGH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS BALANA(MOHINDERGARH)123029 Department Of Electronics and Communication
1 MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) MICROWAVE AND RADAR LAB (EE-322-F) LAB MANUAL VI SEMESTER RAO PAHALD SINGH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS BALANA(MOHINDERGARH)123029 Department Of Electronics and Communication
Application Note 106 IP2 Measurements of Wideband Amplifiers v1.0
 Application Note 06 v.0 Description Application Note 06 describes the theory and method used by to characterize the second order intercept point (IP 2 ) of its wideband amplifiers. offers a large selection
Application Note 06 v.0 Description Application Note 06 describes the theory and method used by to characterize the second order intercept point (IP 2 ) of its wideband amplifiers. offers a large selection
This article describes a computational
 Computer-Aided Design of Diode Frequency Multipliers This article describes the development and use of the MultFreq program for diode multipliers, and provides a practical example By Cezar A. A. Carioca,
Computer-Aided Design of Diode Frequency Multipliers This article describes the development and use of the MultFreq program for diode multipliers, and provides a practical example By Cezar A. A. Carioca,
MAHAVEER INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY. Microwave and Digital Communications Lab. Department Of Electronics and Communication Engineering
 MAHAVEER INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Microwave and Digital Communications Lab Department Of Electronics and Communication Engineering MICROWAVE ENGINEERING LAB List of Experiments: 1.Reflex Klystron
MAHAVEER INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Microwave and Digital Communications Lab Department Of Electronics and Communication Engineering MICROWAVE ENGINEERING LAB List of Experiments: 1.Reflex Klystron
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING TUTORIAL BANK Name : MICROWAVE ENGINEERING Code : A70442 Class : IV B. Tech I
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING TUTORIAL BANK Name : MICROWAVE ENGINEERING Code : A70442 Class : IV B. Tech I
Series and Parallel Resonant Circuits
 Series and Parallel Resonant Circuits Aim: To obtain the characteristics of series and parallel resonant circuits. Apparatus required: Decade resistance box, Decade inductance box, Decade capacitance box
Series and Parallel Resonant Circuits Aim: To obtain the characteristics of series and parallel resonant circuits. Apparatus required: Decade resistance box, Decade inductance box, Decade capacitance box
10MHz to 1050MHz Integrated RF Oscillator with Buffered Outputs
 9-24; Rev 2; 2/02 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 0MHz to 050MHz Integrated General Description The combines a low-noise oscillator with two output buffers in a low-cost, plastic surface-mount, ultra-small µmax
9-24; Rev 2; 2/02 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 0MHz to 050MHz Integrated General Description The combines a low-noise oscillator with two output buffers in a low-cost, plastic surface-mount, ultra-small µmax
Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent
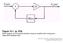 Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent feedback path. Figure 12-2 (p. 579) General circuit for a transistor oscillator. The transistor
Figure 12-1 (p. 578) Block diagram of a sinusoidal oscillator using an amplifier with a frequencydependent feedback path. Figure 12-2 (p. 579) General circuit for a transistor oscillator. The transistor
Using Enhanced Load-Pull Measurements for the Design of Base Station Power Amplifiers
 Application Note Using Enhanced Load-Pull Measurements for the Design of Base Station Power Amplifiers Overview Load-pull simulation is a very simple yet powerful concept in which the load or source impedance
Application Note Using Enhanced Load-Pull Measurements for the Design of Base Station Power Amplifiers Overview Load-pull simulation is a very simple yet powerful concept in which the load or source impedance
ECE 145A/218A, Lab Project #1b: Transistor Measurement.
 ECE 145A/218A, Lab Project #1b: Transistor Measurement. September 28, 2017 OVERVIEW... 2 GOALS:... 2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS:... 2 READING:... 2 TRANSISTOR RF CHARACTERIZATION.... 3 DC BIAS CIRCUITS... 3 TEST
ECE 145A/218A, Lab Project #1b: Transistor Measurement. September 28, 2017 OVERVIEW... 2 GOALS:... 2 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS:... 2 READING:... 2 TRANSISTOR RF CHARACTERIZATION.... 3 DC BIAS CIRCUITS... 3 TEST
A FIXED-TUNED 400 GHz SUBHARIVIONIC MIXER
 A FIXED-TUNED 400 GHz SUBHARIVIONIC MIXER USING PLANAR SCHOTTKY DIODES Jeffrey L. Hesler% Kai Hui, Song He, and Thomas W. Crowe Department of Electrical Engineering University of Virginia Charlottesville,
A FIXED-TUNED 400 GHz SUBHARIVIONIC MIXER USING PLANAR SCHOTTKY DIODES Jeffrey L. Hesler% Kai Hui, Song He, and Thomas W. Crowe Department of Electrical Engineering University of Virginia Charlottesville,
VSWR MEASUREMENT APPLICATION NOTE ANV004.
 APPLICATION NOTE ANV004 Bötelkamp 31, D-22529 Hamburg, GERMANY Phone: +49-40 547 544 60 Fax: +49-40 547 544 666 Email: info@valvo.com Introduction: VSWR stands for voltage standing wave ratio. The ratio
APPLICATION NOTE ANV004 Bötelkamp 31, D-22529 Hamburg, GERMANY Phone: +49-40 547 544 60 Fax: +49-40 547 544 666 Email: info@valvo.com Introduction: VSWR stands for voltage standing wave ratio. The ratio
A Single-Transistor, L-Band Telemetering Transmitter
 A Single-Transistor, L-Band Telemetering Transmitter Item Type text; Proceedings Authors D'Elio, C.; Poole, J. Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
A Single-Transistor, L-Band Telemetering Transmitter Item Type text; Proceedings Authors D'Elio, C.; Poole, J. Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
Low Cost Mixer for the 10.7 to 12.8 GHz Direct Broadcast Satellite Market
 Low Cost Mixer for the.7 to 12.8 GHz Direct Broadcast Satellite Market Application Note 1136 Introduction The wide bandwidth requirement in DBS satellite applications places a big performance demand on
Low Cost Mixer for the.7 to 12.8 GHz Direct Broadcast Satellite Market Application Note 1136 Introduction The wide bandwidth requirement in DBS satellite applications places a big performance demand on
ECEN 5014, Spring 2009 Special Topics: Active Microwave Circuits Zoya Popovic, University of Colorado, Boulder
 ECEN 5014, Spring 2009 Special Topics: Active Microwave Circuits Zoya opovic, University of Colorado, Boulder LECTURE 3 MICROWAVE AMLIFIERS: INTRODUCTION L3.1. TRANSISTORS AS BILATERAL MULTIORTS Transistor
ECEN 5014, Spring 2009 Special Topics: Active Microwave Circuits Zoya opovic, University of Colorado, Boulder LECTURE 3 MICROWAVE AMLIFIERS: INTRODUCTION L3.1. TRANSISTORS AS BILATERAL MULTIORTS Transistor
For this example, the required filter order is five, to theoretically meet the specifications. This then equates to the required susceptances as:
 For this example, the required filter order is five, to theoretically meet the specifications. This then equates to the required susceptances as: =1.0402 =2.7404 =3.7714 Likewise, the electrical lengths
For this example, the required filter order is five, to theoretically meet the specifications. This then equates to the required susceptances as: =1.0402 =2.7404 =3.7714 Likewise, the electrical lengths
DETECTOR. Figure 1. Diode Detector
 The Zero Bias Schottky Diode Detector at Temperature Extremes Problems and Solutions Application Note 9 Abstract The zero bias Schottky diode detector is ideal for RF/ID tag applications where it can be
The Zero Bias Schottky Diode Detector at Temperature Extremes Problems and Solutions Application Note 9 Abstract The zero bias Schottky diode detector is ideal for RF/ID tag applications where it can be
SOT-23/SOT-143 Package Lead Code Identification (top view) SINGLE 3 SERIES UNCONNECTED PAIR. SOT-323 Package Lead Code Identification (top view)
 Surface Mount Zero Bias Schottky Detector Diodes Technical Data HSMS-2850 Series Features Surface Mount SOT-2/ SOT-14 Packages Miniature SOT-2 and SOT-6 Packages High Detection Sensitivity: up to 50 mv/µw
Surface Mount Zero Bias Schottky Detector Diodes Technical Data HSMS-2850 Series Features Surface Mount SOT-2/ SOT-14 Packages Miniature SOT-2 and SOT-6 Packages High Detection Sensitivity: up to 50 mv/µw
A 600 GHz Varactor Doubler using CMOS 65nm process
 A 600 GHz Varactor Doubler using CMOS 65nm process S.H. Choi a and M.Kim School of Electrical Engineering, Korea University E-mail : hyperleonheart@hanmail.net Abstract - Varactor and active mode doublers
A 600 GHz Varactor Doubler using CMOS 65nm process S.H. Choi a and M.Kim School of Electrical Engineering, Korea University E-mail : hyperleonheart@hanmail.net Abstract - Varactor and active mode doublers
A Comparison of Harmonic Tuning Methods for Load Pull Systems
 MAURY MICROWAVE CORPORATION A Comparison of Harmonic Tuning Methods for Load Pull Systems Author: Gary Simpson, MSEE Director of Technical Development in Engineering, Maury Microwave Corporation July 2009
MAURY MICROWAVE CORPORATION A Comparison of Harmonic Tuning Methods for Load Pull Systems Author: Gary Simpson, MSEE Director of Technical Development in Engineering, Maury Microwave Corporation July 2009
RF Circuit Synthesis for Physical Wireless Design
 RF Circuit Synthesis for Physical Wireless Design Overview Subjects Review Of Common Design Tasks Break Down And Dissect Design Task Review Non-Synthesis Methods Show A Better Way To Solve Complex Design
RF Circuit Synthesis for Physical Wireless Design Overview Subjects Review Of Common Design Tasks Break Down And Dissect Design Task Review Non-Synthesis Methods Show A Better Way To Solve Complex Design
A NOVEL BIASED ANTI-PARALLEL SCHOTTKY DIODE STRUCTURE FOR SUBHARMONIC
 Page 342 A NOVEL BIASED ANTI-PARALLEL SCHOTTKY DIODE STRUCTURE FOR SUBHARMONIC Trong-Huang Lee', Chen-Yu Chi", Jack R. East', Gabriel M. Rebeiz', and George I. Haddad" let Propulsion Laboratory California
Page 342 A NOVEL BIASED ANTI-PARALLEL SCHOTTKY DIODE STRUCTURE FOR SUBHARMONIC Trong-Huang Lee', Chen-Yu Chi", Jack R. East', Gabriel M. Rebeiz', and George I. Haddad" let Propulsion Laboratory California
Microwave Fundamentals A Survey of Microwave Systems and Devices p. 3 The Relationship of Microwaves to Other Electronic Equipment p.
 Microwave Fundamentals A Survey of Microwave Systems and Devices p. 3 The Relationship of Microwaves to Other Electronic Equipment p. 3 Microwave Systems p. 5 The Microwave Spectrum p. 6 Why Microwave
Microwave Fundamentals A Survey of Microwave Systems and Devices p. 3 The Relationship of Microwaves to Other Electronic Equipment p. 3 Microwave Systems p. 5 The Microwave Spectrum p. 6 Why Microwave
Keysight Technologies Making Accurate Intermodulation Distortion Measurements with the PNA-X Network Analyzer, 10 MHz to 26.5 GHz
 Keysight Technologies Making Accurate Intermodulation Distortion Measurements with the PNA-X Network Analyzer, 10 MHz to 26.5 GHz Application Note Overview This application note describes accuracy considerations
Keysight Technologies Making Accurate Intermodulation Distortion Measurements with the PNA-X Network Analyzer, 10 MHz to 26.5 GHz Application Note Overview This application note describes accuracy considerations
ALMA Memo 436. Band 6 Receiver Noise Measurements using a Pre- Prototype YIG-Tunable LO
 Page: 1 of 11 ALMA Memo 436 Measurements using a Pre- Prototype Eric W. Bryerton, S. K. Pan, Dorsey Thacker, and Kamaljeet Saini National Radio Astronomy Obervatory Charlottesville, VA 2293, USA FEND-.1.6.-1-A-MEM
Page: 1 of 11 ALMA Memo 436 Measurements using a Pre- Prototype Eric W. Bryerton, S. K. Pan, Dorsey Thacker, and Kamaljeet Saini National Radio Astronomy Obervatory Charlottesville, VA 2293, USA FEND-.1.6.-1-A-MEM
Methodology for MMIC Layout Design
 17 Methodology for MMIC Layout Design Fatima Salete Correra 1 and Eduardo Amato Tolezani 2, 1 Laboratório de Microeletrônica da USP, Av. Prof. Luciano Gualberto, tr. 3, n.158, CEP 05508-970, São Paulo,
17 Methodology for MMIC Layout Design Fatima Salete Correra 1 and Eduardo Amato Tolezani 2, 1 Laboratório de Microeletrônica da USP, Av. Prof. Luciano Gualberto, tr. 3, n.158, CEP 05508-970, São Paulo,
NATIONAL RADIO ASTRONOMY OBSERVATORY Green Bank, West Virginia Electronics Division Internal Report No 105
 NATIONAL RADIO ASTRONOMY OBSERVATORY Green Bank, West Virginia Electronics Division Internal Report No 105 CHARACTERIZATION TESTS OF THE WESTERN ELECTRIC PARAMETRIC AMPLIFIER Dennis Sweeney SEPTEMBER 1971
NATIONAL RADIO ASTRONOMY OBSERVATORY Green Bank, West Virginia Electronics Division Internal Report No 105 CHARACTERIZATION TESTS OF THE WESTERN ELECTRIC PARAMETRIC AMPLIFIER Dennis Sweeney SEPTEMBER 1971
SIMPLIFIED COIL DESIGN (Part I) GE Ham News, Jan-Feb 1960 By B. H. Baidridge, W2OIQ
 SIMPLIFIED COIL DESIGN (Part I) GE Ham News, Jan-Feb 1960 By B. H. Baidridge, W2OIQ PROBLEM - HOW TO WIND COILS accurately for specific amateur radio applications. Solutions: 1. Calculating the coil inductance
SIMPLIFIED COIL DESIGN (Part I) GE Ham News, Jan-Feb 1960 By B. H. Baidridge, W2OIQ PROBLEM - HOW TO WIND COILS accurately for specific amateur radio applications. Solutions: 1. Calculating the coil inductance
Lecture 16 Microwave Detector and Switching Diodes
 Basic Building Blocks of Microwave Engineering Prof. Amitabha Bhattacharya Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 16 Microwave Detector
Basic Building Blocks of Microwave Engineering Prof. Amitabha Bhattacharya Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 16 Microwave Detector
L AND S BAND TUNABLE FILTERS PROVIDE DRAMATIC IMPROVEMENTS IN TELEMETRY SYSTEMS
 L AND S BAND TUNABLE FILTERS PROVIDE DRAMATIC IMPROVEMENTS IN TELEMETRY SYSTEMS Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Wurth, Timothy J.; Rodzinak, Jason Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering
L AND S BAND TUNABLE FILTERS PROVIDE DRAMATIC IMPROVEMENTS IN TELEMETRY SYSTEMS Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Wurth, Timothy J.; Rodzinak, Jason Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering
Chapter 5 DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF SWASTIKA-SHAPED FREQUENCY RECONFIGURABLE ANTENNA ON FR4 SUBSTRATE
 Chapter 5 DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF SWASTIKA-SHAPED FREQUENCY RECONFIGURABLE ANTENNA ON FR4 SUBSTRATE The same geometrical shape of the Swastika as developed in previous chapter has been implemented
Chapter 5 DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF SWASTIKA-SHAPED FREQUENCY RECONFIGURABLE ANTENNA ON FR4 SUBSTRATE The same geometrical shape of the Swastika as developed in previous chapter has been implemented
Vector-Receiver Load Pull Measurement
 MAURY MICROWAVE CORPORATION Vector-Receiver Load Pull Measurement Article Reprint of the Special Report first published in The Microwave Journal February 2011 issue. Reprinted with permission. Author:
MAURY MICROWAVE CORPORATION Vector-Receiver Load Pull Measurement Article Reprint of the Special Report first published in The Microwave Journal February 2011 issue. Reprinted with permission. Author:
Low Pass Filter Introduction
 Low Pass Filter Introduction Basically, an electrical filter is a circuit that can be designed to modify, reshape or reject all unwanted frequencies of an electrical signal and accept or pass only those
Low Pass Filter Introduction Basically, an electrical filter is a circuit that can be designed to modify, reshape or reject all unwanted frequencies of an electrical signal and accept or pass only those
Glossary of VCO terms
 Glossary of VCO terms VOLTAGE CONTROLLED OSCILLATOR (VCO): This is an oscillator designed so the output frequency can be changed by applying a voltage to its control port or tuning port. FREQUENCY TUNING
Glossary of VCO terms VOLTAGE CONTROLLED OSCILLATOR (VCO): This is an oscillator designed so the output frequency can be changed by applying a voltage to its control port or tuning port. FREQUENCY TUNING
Oct. 6, 1970 CHONG W. LEE " Filed June.28, 1967 PUSH-PULL TUNNEL DIODE AMPLIFIER. 4 Sheets-Sheet 1
 Oct. 6, 1970 CHONG W. LEE "313308 Filed June.28, 1967 4 Sheets-Sheet 1 Oct. 6, 1970 CHONG W. LEE Filed June 28, 1967 4 Sheets-Sheet 2 HIS ATTORNEY. Oct. 6, 1970 CHONG W. LEE Filed June 28, 1967 4 Sheets-Sheet
Oct. 6, 1970 CHONG W. LEE "313308 Filed June.28, 1967 4 Sheets-Sheet 1 Oct. 6, 1970 CHONG W. LEE Filed June 28, 1967 4 Sheets-Sheet 2 HIS ATTORNEY. Oct. 6, 1970 CHONG W. LEE Filed June 28, 1967 4 Sheets-Sheet
Design Considerations for a 1.9 THz Frequency Tripler Based on Membrane Technology
 Design Considerations for a.9 THz Frequency Tripler Based on Membrane Technology Alain Maestrini, David Pukala, Goutam Chattopadhyay, Erich Schlecht and Imran Mehdi Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California
Design Considerations for a.9 THz Frequency Tripler Based on Membrane Technology Alain Maestrini, David Pukala, Goutam Chattopadhyay, Erich Schlecht and Imran Mehdi Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California
CHAPTER 4. Practical Design
 CHAPTER 4 Practical Design The results in Chapter 3 indicate that the 2-D CCS TL can be used to synthesize a wider range of characteristic impedance, flatten propagation characteristics, and place passive
CHAPTER 4 Practical Design The results in Chapter 3 indicate that the 2-D CCS TL can be used to synthesize a wider range of characteristic impedance, flatten propagation characteristics, and place passive
Lecture - 19 Microwave Solid State Diode Oscillator and Amplifier
 Basic Building Blocks of Microwave Engineering Prof. Amitabha Bhattacharya Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 19 Microwave Solid
Basic Building Blocks of Microwave Engineering Prof. Amitabha Bhattacharya Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 19 Microwave Solid
A BACK-TO-BACK BARRIER-N-N P (bbbnn) DIODE TRIPLER AT 200 GHz
 Page 274 A BACK-TO-BACK BARRIER-N-N P (bbbnn) DIODE TRIPLER AT 200 GHz Debabani Choudhury, Antti V. Raisänen, R. Peter Smith, and Margaret A. Frerking Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute fo
Page 274 A BACK-TO-BACK BARRIER-N-N P (bbbnn) DIODE TRIPLER AT 200 GHz Debabani Choudhury, Antti V. Raisänen, R. Peter Smith, and Margaret A. Frerking Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute fo
Laboratory 4. Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes
 Laboratory 4 Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes Required Components: k resistor 0. F capacitor N94 small-signal diode LED 4. Objectives In the previous laboratory exercise you examined the effects of input
Laboratory 4 Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes Required Components: k resistor 0. F capacitor N94 small-signal diode LED 4. Objectives In the previous laboratory exercise you examined the effects of input
Limiter Diodes Features Description Chip Dimensions Model DOT Diameter (Typ.) Chip Number St l Style Inches 4 11
 Features Low Loss kw Coarse Limiters 200 Watt Midrange Limiters 10 mw Clean Up Limiters 210 20 Description Alpha has pioneered the microwave limiter diode. Because all phases of manufacturing, from design
Features Low Loss kw Coarse Limiters 200 Watt Midrange Limiters 10 mw Clean Up Limiters 210 20 Description Alpha has pioneered the microwave limiter diode. Because all phases of manufacturing, from design
Planar Frequency Doublers and Triplers for FIRST
 Planar Frequency Doublers and Triplers for FIRST N.R. Erickson and G. Narayanan Dept. of Physics and Astronomy University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA 01003 Introduction R.P. Smith, S.C. Martin and I.
Planar Frequency Doublers and Triplers for FIRST N.R. Erickson and G. Narayanan Dept. of Physics and Astronomy University of Massachusetts Amherst, MA 01003 Introduction R.P. Smith, S.C. Martin and I.
Complete Microstrip System
 Complete Microstrip System MST532-1 Description The increasing use of microwaves in applications, ranging from satellite and terrestrial communications to high-speed computing and data transmission, has
Complete Microstrip System MST532-1 Description The increasing use of microwaves in applications, ranging from satellite and terrestrial communications to high-speed computing and data transmission, has
EC6503 Transmission Lines and WaveguidesV Semester Question Bank
 UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines General Solution, Physicasignificance of the equations 1. Derive the two useful forms of equations for voltage and current
UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines General Solution, Physicasignificance of the equations 1. Derive the two useful forms of equations for voltage and current
There is a twenty db improvement in the reflection measurements when the port match errors are removed.
 ABSTRACT Many improvements have occurred in microwave error correction techniques the past few years. The various error sources which degrade calibration accuracy is better understood. Standards have been
ABSTRACT Many improvements have occurred in microwave error correction techniques the past few years. The various error sources which degrade calibration accuracy is better understood. Standards have been
Load Pull Validation of Large Signal Cree GaN Field Effect Transistor (FET) Model
 APPLICATION NOTE Load Pull Validation of Large Signal Cree GaN Field Effect Transistor (FET) Model Introduction Large signal models for RF power transistors, if matched well with measured performance,
APPLICATION NOTE Load Pull Validation of Large Signal Cree GaN Field Effect Transistor (FET) Model Introduction Large signal models for RF power transistors, if matched well with measured performance,
Design of Class F Power Amplifiers Using Cree GaN HEMTs and Microwave Office Software to Optimize Gain, Efficiency, and Stability
 White Paper Design of Class F Power Amplifiers Using Cree GaN HEMTs and Microwave Office Software to Optimize Gain, Efficiency, and Stability Overview This white paper explores the design of power amplifiers
White Paper Design of Class F Power Amplifiers Using Cree GaN HEMTs and Microwave Office Software to Optimize Gain, Efficiency, and Stability Overview This white paper explores the design of power amplifiers
Waveguides. Metal Waveguides. Dielectric Waveguides
 Waveguides Waveguides, like transmission lines, are structures used to guide electromagnetic waves from point to point. However, the fundamental characteristics of waveguide and transmission line waves
Waveguides Waveguides, like transmission lines, are structures used to guide electromagnetic waves from point to point. However, the fundamental characteristics of waveguide and transmission line waves
3. (a) Derive an expression for the Hull cut off condition for cylindrical magnetron oscillator. (b) Write short notes on 8 cavity magnetron [8+8]
![3. (a) Derive an expression for the Hull cut off condition for cylindrical magnetron oscillator. (b) Write short notes on 8 cavity magnetron [8+8] 3. (a) Derive an expression for the Hull cut off condition for cylindrical magnetron oscillator. (b) Write short notes on 8 cavity magnetron [8+8]](/thumbs/73/68588725.jpg) Code No: RR320404 Set No. 1 1. (a) Compare Drift space bunching and Reflector bunching with the help of Applegate diagrams. (b) A reflex Klystron operates at the peak of n=1 or 3 / 4 mode. The dc power
Code No: RR320404 Set No. 1 1. (a) Compare Drift space bunching and Reflector bunching with the help of Applegate diagrams. (b) A reflex Klystron operates at the peak of n=1 or 3 / 4 mode. The dc power
LBI-38642B. MAINTENANCE MANUAL RECEIVER FRONT END MODULE 19D902782G1: MHz 19D902782G2: MHz DESCRIPTION TABLE OF CONTENTS
 LBI-38642B MAINTENANCE MANUAL RECEIVER FRONT END MODULE 19D902782G1: 136-151 MHz 19D902782G2: 150-174 MHz TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION............................................... Front Cover SPECIFICATIONS.............................................
LBI-38642B MAINTENANCE MANUAL RECEIVER FRONT END MODULE 19D902782G1: 136-151 MHz 19D902782G2: 150-174 MHz TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION............................................... Front Cover SPECIFICATIONS.............................................
Research Article A Parallel-Strip Balun for Wideband Frequency Doubler
 Microwave Science and Technology Volume 213, Article ID 8929, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.11/213/8929 Research Article A Parallel-Strip Balun for Wideband Frequency Doubler Leung Chiu and Quan Xue Department
Microwave Science and Technology Volume 213, Article ID 8929, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.11/213/8929 Research Article A Parallel-Strip Balun for Wideband Frequency Doubler Leung Chiu and Quan Xue Department
Wideband Fixed-Tuned Millimeter and Submillimeter-Wave Frequency Multipliers
 Wideband Fixed-Tuned Millimeter and Submillimeter-Wave Frequency Multipliers N. R. Erickson Millitech Corp. PO Box 109 S. Deerfield, MA 01373 Abstract Varactor frequency multipliers have been built with
Wideband Fixed-Tuned Millimeter and Submillimeter-Wave Frequency Multipliers N. R. Erickson Millitech Corp. PO Box 109 S. Deerfield, MA 01373 Abstract Varactor frequency multipliers have been built with
ECEN 4634/5634, MICROWAVE AND RF LABORATORY
 ECEN 4634/5634, MICROWAVE AND RF LABORATORY Final Exam December 18, 2017 7:30-10:00pm 150 minutes, closed book, 1 sheet allowed, no calculators (estimates need to be within 3dB) Part 1 (60%). Briefly answer
ECEN 4634/5634, MICROWAVE AND RF LABORATORY Final Exam December 18, 2017 7:30-10:00pm 150 minutes, closed book, 1 sheet allowed, no calculators (estimates need to be within 3dB) Part 1 (60%). Briefly answer
Broadband Fixed-Tuned Subharmonic Receivers to 640 GHz
 Broadband Fixed-Tuned Subharmonic Receivers to 640 GHz Jeffrey Hesler University of Virginia Department of Electrical Engineering Charlottesville, VA 22903 phone 804-924-6106 fax 804-924-8818 (hesler@virginia.edu)
Broadband Fixed-Tuned Subharmonic Receivers to 640 GHz Jeffrey Hesler University of Virginia Department of Electrical Engineering Charlottesville, VA 22903 phone 804-924-6106 fax 804-924-8818 (hesler@virginia.edu)
A WIRELESS ENERGY HARVESTING SYSTEM WITH BEAMFORMING CAPABILITIES
 A WIRELESS ENERGY HARVESTING SYSTEM WITH BEAMFORMING CAPABILITIES by Daniel Schemmel A thesis submitted to the Faculty and the Board of Trustees of the Colorado School of Mines in partial fulfillment of
A WIRELESS ENERGY HARVESTING SYSTEM WITH BEAMFORMING CAPABILITIES by Daniel Schemmel A thesis submitted to the Faculty and the Board of Trustees of the Colorado School of Mines in partial fulfillment of
PUSH-PUSH DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OSCILLATOR USING SUBSTRATE INTEGRATED WAVEGUIDE POW- ER COMBINER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 30, 105 113, 2012 PUSH-PUSH DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OSCILLATOR USING SUBSTRATE INTEGRATED WAVEGUIDE POW- ER COMBINER P. Su *, Z. X. Tang, and B. Zhang School
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 30, 105 113, 2012 PUSH-PUSH DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OSCILLATOR USING SUBSTRATE INTEGRATED WAVEGUIDE POW- ER COMBINER P. Su *, Z. X. Tang, and B. Zhang School
ELEC4604. RF Electronics. Experiment 2
 ELEC4604 RF Electronics Experiment MICROWAVE MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES 1. Introduction and Objectives In designing the RF front end of a microwave communication system it is important to appreciate that the
ELEC4604 RF Electronics Experiment MICROWAVE MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUES 1. Introduction and Objectives In designing the RF front end of a microwave communication system it is important to appreciate that the
Schottky diode mixer for 5.8 GHz radar sensor
 AN_1808_PL32_1809_130625 Schottky diode mixer for 5.8 GHz radar sensor About this document Scope and purpose This application note shows a single balanced mixer for 5.8 GHz Doppler radar applications with
AN_1808_PL32_1809_130625 Schottky diode mixer for 5.8 GHz radar sensor About this document Scope and purpose This application note shows a single balanced mixer for 5.8 GHz Doppler radar applications with
AM036MX-QG-R 1 WATT, 2 GHz POWER AMPLIFIER
 AM036MX-QG-R 1 WATT, 2 GHz POWER AMPLIFIER AN136 January 2011 REV 3 INTRODUCTION This application note describes the design of a one-watt, single stage power amplifier at 2GHz using AMCOM s low cost surface
AM036MX-QG-R 1 WATT, 2 GHz POWER AMPLIFIER AN136 January 2011 REV 3 INTRODUCTION This application note describes the design of a one-watt, single stage power amplifier at 2GHz using AMCOM s low cost surface
NI AWR Design Environment Load-Pull Simulation Supports the Design of Wideband High-Efficiency Power Amplifiers
 Design NI AWR Design Environment Load-Pull Simulation Supports the Design of Wideband High-Efficiency Power Amplifiers The design of power amplifiers (PAs) for present and future wireless systems requires
Design NI AWR Design Environment Load-Pull Simulation Supports the Design of Wideband High-Efficiency Power Amplifiers The design of power amplifiers (PAs) for present and future wireless systems requires
Many applications. Mismatched Load Characterization for High-Power RF Amplifiers PA CHARACTERIZATION. This article discusses the
 From April 2004 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 2004 Summit Technical Media, LLC Mismatched Load Characterization for High-Power RF Amplifiers By Richard W. Brounley, P.E. Brounley Engineering Many
From April 2004 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 2004 Summit Technical Media, LLC Mismatched Load Characterization for High-Power RF Amplifiers By Richard W. Brounley, P.E. Brounley Engineering Many
MICROWAVE ENGINEERING LAB VIVA QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 MICROWAVE ENGINEERING LAB VIVA QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Why can t conventional tubes be used at microwave frequencies? Conventional tubes can t be used at microwave frequencies because of transit time effect.
MICROWAVE ENGINEERING LAB VIVA QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Why can t conventional tubes be used at microwave frequencies? Conventional tubes can t be used at microwave frequencies because of transit time effect.
Design of an Evanescent Mode Circular Waveguide 10 GHz Filter
 Design of an Evanescent Mode Circular Waveguide 10 GHz Filter NI AWR Design Environment, specifically Microwave Office circuit design software, was used to design the filters for a range of bandwidths
Design of an Evanescent Mode Circular Waveguide 10 GHz Filter NI AWR Design Environment, specifically Microwave Office circuit design software, was used to design the filters for a range of bandwidths
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Wireless and RF > APP 3571
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Wireless and RF > APP 3571 Keywords: automotive keyless entry, MAX2640, LNA, 315MHz, RKE, stability, automotive, keyless entry APPLICATION
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Wireless and RF > APP 3571 Keywords: automotive keyless entry, MAX2640, LNA, 315MHz, RKE, stability, automotive, keyless entry APPLICATION
ATF High Intercept Low Noise Amplifier for the MHz PCS Band using the Enhancement Mode PHEMT
 ATF-54143 High Intercept Low Noise Amplifier for the 185 191 MHz PCS Band using the Enhancement Mode PHEMT Application Note 1222 Introduction Avago Technologies ATF-54143 is a low noise enhancement mode
ATF-54143 High Intercept Low Noise Amplifier for the 185 191 MHz PCS Band using the Enhancement Mode PHEMT Application Note 1222 Introduction Avago Technologies ATF-54143 is a low noise enhancement mode
Design of an Evanescent Mode Circular Waveguide 10 GHz Filter
 Application Note Design of an Evanescent Mode Circular Waveguide 10 GHz Filter Overview Ham radio operation at 10 GHz is far removed from global shortwave communication typically operating below 30 MHz.
Application Note Design of an Evanescent Mode Circular Waveguide 10 GHz Filter Overview Ham radio operation at 10 GHz is far removed from global shortwave communication typically operating below 30 MHz.
Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering Department of ECE EC6701 RF and Microwave Engineering Unit 5 Microwave Measurements Part A
 Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering Department of ECE EC6701 RF and Microwave Engineering Unit 5 Microwave Measurements Part A 1. What is the principle by which high power measurements could be done by
Dhanalakshmi College of Engineering Department of ECE EC6701 RF and Microwave Engineering Unit 5 Microwave Measurements Part A 1. What is the principle by which high power measurements could be done by
Application Note 5057
 A 1 MHz to MHz Low Noise Feedback Amplifier using ATF-4143 Application Note 7 Introduction In the last few years the leading technology in the area of low noise amplifier design has been gallium arsenide
A 1 MHz to MHz Low Noise Feedback Amplifier using ATF-4143 Application Note 7 Introduction In the last few years the leading technology in the area of low noise amplifier design has been gallium arsenide
C. Mixers. frequencies? limit? specifications? Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device.
 9/13/2007 Mixers notes 1/1 C. Mixers Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device. HO: Mixers Q: How efficient is a typical mixer at creating signals
9/13/2007 Mixers notes 1/1 C. Mixers Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device. HO: Mixers Q: How efficient is a typical mixer at creating signals
ericssonz LBI-38642C MAINTENANCE MANUAL RECEIVER FRONT END MODULE 19D902782G1: MHz 19D902782G2: MHz DESCRIPTION TABLE OF CONTENTS
 LBI-38642C MAINTENANCE MANUAL RECEIVER FRONT END MODULE 19D902782G1: 136-151 MHz 19D902782G2: 150-174 MHz TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION............................................... Front Cover SPECIFICATIONS.............................................
LBI-38642C MAINTENANCE MANUAL RECEIVER FRONT END MODULE 19D902782G1: 136-151 MHz 19D902782G2: 150-174 MHz TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DESCRIPTION............................................... Front Cover SPECIFICATIONS.............................................
Circulator Construction
 ISOLATORS pg. 1 UNDERSTANDING COAXIAL AND DROP-IN CIRCULATORS AND ISOLATORS This article describes the basic operating principles of the stripline junction circulator. The following information has been
ISOLATORS pg. 1 UNDERSTANDING COAXIAL AND DROP-IN CIRCULATORS AND ISOLATORS This article describes the basic operating principles of the stripline junction circulator. The following information has been
LXI -Certified Multi-Harmonic Automated Tuners
 LXI -Certified Multi-Harmonic Automated Tuners DATA SHEET / 4T-050G03 MODELS: MT981ML01 MT982ML01 MT983ML01 // JANUARY 2018 What is load pull? Load Pull is the act of presenting a set of controlled impedances
LXI -Certified Multi-Harmonic Automated Tuners DATA SHEET / 4T-050G03 MODELS: MT981ML01 MT982ML01 MT983ML01 // JANUARY 2018 What is load pull? Load Pull is the act of presenting a set of controlled impedances
New Ultra-Fast Noise Parameter System... Opening A New Realm of Possibilities in Noise Characterization
 New Ultra-Fast Noise Parameter System... Opening A New Realm of Possibilities in Noise Characterization David Ballo Application Development Engineer Agilent Technologies Gary Simpson Chief Technology Officer
New Ultra-Fast Noise Parameter System... Opening A New Realm of Possibilities in Noise Characterization David Ballo Application Development Engineer Agilent Technologies Gary Simpson Chief Technology Officer
Cavity Filters. Waveguide Filters
 Cavity Cavity Filters K&L Microwave s series of cavity filters covers the frequency range from 30 MHz to 40 GHz. These filters are available with 2 to 17 resonant sections and bandwidths from 0.2% to 50%.
Cavity Cavity Filters K&L Microwave s series of cavity filters covers the frequency range from 30 MHz to 40 GHz. These filters are available with 2 to 17 resonant sections and bandwidths from 0.2% to 50%.
Negative Differential Resistance (NDR) Frequency Conversion with Gain
 Third International Symposium on Space Tcrahertz Technology Page 457 Negative Differential Resistance (NDR) Frequency Conversion with Gain R. J. Hwu, R. W. Aim, and S. C. Lee Department of Electrical Engineering
Third International Symposium on Space Tcrahertz Technology Page 457 Negative Differential Resistance (NDR) Frequency Conversion with Gain R. J. Hwu, R. W. Aim, and S. C. Lee Department of Electrical Engineering
Varactor-Tuned Oscillators. Technical Data. VTO-8000 Series
 Varactor-Tuned Oscillators Technical Data VTO-8000 Series Features 600 MHz to 10.5 GHz Coverage Fast Tuning +7 to +13 dbm Output Power ± 1.5 db Output Flatness Hermetic Thin-film Construction Description
Varactor-Tuned Oscillators Technical Data VTO-8000 Series Features 600 MHz to 10.5 GHz Coverage Fast Tuning +7 to +13 dbm Output Power ± 1.5 db Output Flatness Hermetic Thin-film Construction Description
High Intercept Low Noise Amplifier for 1.9 GHz PCS and 2.1 GHz W-CDMA Applications using the ATF Enhancement Mode PHEMT
 High Intercept Low Noise Amplifier for 1.9 GHz PCS and 2.1 GHz W-CDMA Applications using the ATF-55143 Enhancement Mode PHEMT Application Note 1241 Introduction Avago Technologies ATF-55143 is a low noise
High Intercept Low Noise Amplifier for 1.9 GHz PCS and 2.1 GHz W-CDMA Applications using the ATF-55143 Enhancement Mode PHEMT Application Note 1241 Introduction Avago Technologies ATF-55143 is a low noise
Vector Network Analyzer Application note
 Vector Network Analyzer Application note Version 1.0 Vector Network Analyzer Introduction A vector network analyzer is used to measure the performance of circuits or networks such as amplifiers, filters,
Vector Network Analyzer Application note Version 1.0 Vector Network Analyzer Introduction A vector network analyzer is used to measure the performance of circuits or networks such as amplifiers, filters,
A Stub Matched Lazy H for 17 M
 A Stub Matched Lazy H for 17 M Introduction The author has experimented with various configurations of the classic Lazy H antenna and a version optimised for operation on the 17 M band is shown in Figure
A Stub Matched Lazy H for 17 M Introduction The author has experimented with various configurations of the classic Lazy H antenna and a version optimised for operation on the 17 M band is shown in Figure
RF/Microwave Amplifier Design Using Harmonic Balance Simulation With Only S-parameter Data
 Application Note RF/Microwave Amplifier Design Using Harmonic Balance Simulation With Only S-parameter Data Overview It is widely held that S-parameters combined with harmonic balance (HB) alone cannot
Application Note RF/Microwave Amplifier Design Using Harmonic Balance Simulation With Only S-parameter Data Overview It is widely held that S-parameters combined with harmonic balance (HB) alone cannot
K-BAND HARMONIC DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OS- CILLATOR USING PARALLEL FEEDBACK STRUC- TURE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 34, 83 90, 2012 K-BAND HARMONIC DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OS- CILLATOR USING PARALLEL FEEDBACK STRUC- TURE Y. C. Du *, Z. X. Tang, B. Zhang, and P. Su School
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 34, 83 90, 2012 K-BAND HARMONIC DIELECTRIC RESONATOR OS- CILLATOR USING PARALLEL FEEDBACK STRUC- TURE Y. C. Du *, Z. X. Tang, B. Zhang, and P. Su School
Simulation of GaAs MESFET and HEMT Devices for RF Applications
 olume, Issue, January February 03 ISSN 78-6856 Simulation of GaAs MESFET and HEMT Devices for RF Applications Dr.E.N.GANESH Prof, ECE DEPT. Rajalakshmi Institute of Technology ABSTRACT: Field effect transistor
olume, Issue, January February 03 ISSN 78-6856 Simulation of GaAs MESFET and HEMT Devices for RF Applications Dr.E.N.GANESH Prof, ECE DEPT. Rajalakshmi Institute of Technology ABSTRACT: Field effect transistor
CUSTOM INTEGRATED ASSEMBLIES
 17 CUSTOM INTEGRATED ASSEMBLIES CUSTOM INTEGRATED ASSEMBLIES Cougar offers full first-level integration capabilities, providing not just performance components but also full subsystem solutions to help
17 CUSTOM INTEGRATED ASSEMBLIES CUSTOM INTEGRATED ASSEMBLIES Cougar offers full first-level integration capabilities, providing not just performance components but also full subsystem solutions to help
