Synchro and Resolver Conversion. Appendix F. Appendix F EFFECTS OF QUADRATURE SIGNALS ON SERVO SYSTEMS
|
|
|
- Geoffrey Smith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EFFECTS OF QUADRATURE SIGNALS ON SERVO SYSTEMS The usual arrangement of the Digital to Synchro converter in a control loop is shown in Chapter 4, Fig 4-38 The signal from the control transfmer is amplified and fed into a Phase sensitive detect (PSD) The DC output from the PSD fms the err signal f the control loop As can be seen from Fig 4-38, the PSD is driven from the reference signal and the operation of the PSD is such as to give a gain of + 1 when the reference is positive and a gain of -1 when the reference signal is negative Simple consideration of the PSD will show that, if an AC voltage at the same frequency as the reference voltage but shifted in phase by 90 degrees is introduced in series with the usual input from the CT, no errs will be caused (Errs could however be caused by the injection of such an AC voltage, if the voltage was of sufficient magnitude to cause asymmetric limiting in the amplifiers) Such an injection of a 90 0 phase shifted signal is not the same as the introduction of a real quadrature voltage caused by different phase shifts in the signal paths The following simple analysis shows the errs due to quadrature and how these errs are increased by a signal to reference phase shift The signals will be considered in Resolver fm to reduce the number of terms in the equations Referring to Fig F-1, we will consider the reference to be in phase with the input signals and then introduce a small phase shift on one signal relative to the other FIG F-1 A RESOLVER WITH A DIFFERENTIAL SIGNAL PHASE SHIFT A In a perfect system the voltages would be, Nth Atlantic Industries, Inc / (fax) SynchroHandbook_ 110 Wilbur Place, Bohemia, NY wwwnaiicom / Cage Code:0VGUI Page 1 of 7
2 Vs = V sinωt Sinφ Vc = V sinωt Cosφ V = V sinωt To show how the quadrature terms arises a phase shift of a will be applied to the carrier in Ye The three voltages are now: Vs = V sinωt Sinφ Vc = V sin( ωt + ) Cosφ V = V sinωt At a fixed angle θ the Resolver behaves like two transfmers with a common secondary where the ratios are: R Cos θ Sine input to rot and - R Sin θ Cosine input to rot The equivalent R f the Synchro control transfmer type 11CT4L, (9Ov L-L) is 064 The voltage in the rot winding will be the sum of the two voltages ie Vrot = (VSinωtsinφ) R Cos θ - [Vsin (ωt + ) Cos φ] R Sin θ (1) Where φ is the digital angle and θ is the angle of the resolver shaft and a is the phase shift introduced into the Cosine channel In equation (1) the next step is to expand the term by using the relationship: Sin (ωt + ) Sin (A + B) = Sin A Cos B + Cos A Sin B Doing this we get, V rot = RV[Sin ωt* Sin φ Cos θ - Cosφ Sinθ (SinωtCos + Cosωt **Sin)] *These terms are in phase ** This is the quadrature term Nth Atlantic Industries, Inc / (fax) SynchroHandbook_ 110 Wilbur Place, Bohemia, NY wwwnaiicom / Cage Code:0VGUI Page of 7
3 Collecting the in-phase and quadrature terms we have: Synchro and Resolver Conversion V rot = RV[Sinωt (SinφCos θ - CosφSinθCos) + Cosωt(CosφSinθSin)] () A properly designed control loop with a perfect phase sensitive detect will igne the term: Cosωt(CosφSinθSin) in equation () F such a properly designed servo loop there is an err which is very small due to the fact that Cos in the first term of equation () is not quite equal to 1 Befe proceeding to the case of the quadrature term itself we will find what the err would be in a loop which rejects the quadrature We make use of the fact that 4 Cos = 1+ + ( in radians) 4! and f small (which we are considering) Cos = 1 where is in radians Nth Atlantic Industries, Inc / (fax) SynchroHandbook_ 110 Wilbur Place, Bohemia, NY wwwnaiicom / Cage Code:0VGUI Page 3 of 7
4 Since we are concerned f the present with a good loop which rejects the quadrature signal, we can igne that term in the err signal Doing this and substituting f Cos as above gives: Vrot = RV {Sinωt[SinφCosθ- (1 /) Sin θcos φ]} The servo will alter θ to make Vrot = zero ie 0 = [SinφCosθ - SinθCosφ + / Sin θcos φ] (3) In equation (3), it is the term which gives rise to the err Sin θ Cos φ F φ θ, Sinθ Cos φ has a maximum of 05 at θ 45 0 And since Sin φ Cos θ - Sin θ Cos φ (φ- θ) radians, the err in radians is: ε = 0 5( and err are in radians) 05 err in degrees = ( in degrees) err in minutes = ( in degrees 57 ( in degrees) 4 ie ¼ arc minute f 10 of phase at wst angle of 45 0 We now look at the quadrature signal which should be rejected It is the term RV Cos ω t [Cos φ sin θ Sin ] of equation () F φ θ, the maximum Cos φ Sin θ is f φ θ = 45 0 and the value is 05 The peak value of the quadrature is Quadrature = RV x 05 ( is in radians) (Sin ) V = 90 R = 064 f the 11CT4b Control Transfmer (90 volts L-L) and f = 1/57 (1 degree) The rms value of the quadrature on the rot is volts per degree 57 rms Quadrature Voltage on rot = 05 volts per 1 degree of differential phase shift ie F l00mv rms the differential phase has to be 0 degrees Nth Atlantic Industries, Inc / (fax) SynchroHandbook_ 110 Wilbur Place, Bohemia, NY wwwnaiicom / Cage Code:0VGUI Page 4 of 7
5 The fegoing example of the effect of quadrature was based on the assumption that the signals and reference were in phase befe the small differential phase shift was introduced In practical systems there is often a phase shift of several degrees between the signals and reference This phase shift should be minimised in the design of Synchro systems Both control transmitter and control receiver Synchros give rise to phase leads between the input and output voltages and balancing phase leads are often introduced into the reference befe it is used to drive the phase sensitive detect DSC s generally give negligible phase shift between the input reference and output signals, if therefe a CX is replace by a DSC, the phase angle between the CT output voltage and the reference will be changed and a cresponding crection should be put in to the system at some point Nth Atlantic Industries, Inc / (fax) SynchroHandbook_ 110 Wilbur Place, Bohemia, NY wwwnaiicom / Cage Code:0VGUI Page 5 of 7
6 The following simple analysis shows the effects of quadrature signals in the presence of signal to reference phase shift Again to reduce the number of terms in the equations the resolver example will be considered The effect of reference to signal phase shift with quadrature Let the resolver fm signals be: Sin ωt Cos φ and Sin (ωt + ) Sin φ The control resolver rot voltage will be: where θ is the shaft angle Sinωt Cos φsinθ - Sin (ωt + )Sin φ Cos θ The action of the phase sensitive detect with a phase shifted reference where the phase shift is β is given by integrating the resolver rot output with respect to ωt from ωt = β to ωt = The control loop will set the result to zero ie: Expanding Sin (ωt +) and integrating gives: Cos φ Sinθ Sinωt dωt Sinφ Cosθ Sinωt dωt = 0 β β + Cos Sin3[ Coswt] β + Sinφ Cosθ Cos[ Cosωt] β Sinφ Cosθ[ Sinωt] β = 0 -Cosφ Sinθ Cosβ + Sinφ CosθCosCosβ - SinφCosθSin Sinβ = 0 β Now both β and are small so: where and β are in radians Cos 1 and Sin β β may be used Making these substitutions and rearranging the terms gives: β β 1 ( ) 1 = 0 Sin φ θ Sin φ Cos θ β Sin φ Cos θ The second and third terms in this expression are the ones which cause the err The coefficients Sinφ, Cos θ which occur in both these terms have a maximum value of 05 f φ θ Substituting 05 f Sinφ, Cos θ to give the maximum err (which is f θ φ = 45 degrees) gives: β β 1 ( ) 05[ 1 + ] = 0 Sin φ θ β Nth Atlantic Industries, Inc / (fax) SynchroHandbook_ 110 Wilbur Place, Bohemia, NY wwwnaiicom / Cage Code:0VGUI Page 6 of 7
7 And this fmula can be used to calculate the err, as an example f 1 5 = and β = ie 1 degree differential phase shift (which is large) and +5 degrees phase shift on the reference The err is very nearly equal to: 05 β radians radians, f 1 0 differential and 5 0 reference phase shift degrees arc minutes = 5 arc minutes This figure compares with the earlier figure of ¼ arc minute f the case with no reference phase shift It should be understood that the 1 0 differential phase shift taken in these examples is very large Quadrature voltages in converters and CTs jointly is me likely to crespond to an equivalent phase shift of 0 degrees less, ie the quadrature due to both the DRC and resolver will be less than 100 millivolts Nth Atlantic Industries, Inc / (fax) SynchroHandbook_ 110 Wilbur Place, Bohemia, NY wwwnaiicom / Cage Code:0VGUI Page 7 of 7
Power Electronics Single Phase Uncontrolled Half Wave Rectifiers. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Power Electronics Single Phase Uncontrolled Half Wave Rectifiers Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 Resistive Load 2 R-L Load 3 R-L Load with Freewheeling Diode 4 Half Wave Rectifier with a Capacitor
Power Electronics Single Phase Uncontrolled Half Wave Rectifiers Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of contents 1 Resistive Load 2 R-L Load 3 R-L Load with Freewheeling Diode 4 Half Wave Rectifier with a Capacitor
AC/Synchro/Resolver/Phase Definitions
 Instruments Apex Signal Logitek Astrosystems 110 Wilbur Place, Bohemia, NY 11716-2416 Phone 631-567-1100 Fax 631-567-1823 AC/Synchro/Resolver/Phase Definitions We are required to be familiar with a wide
Instruments Apex Signal Logitek Astrosystems 110 Wilbur Place, Bohemia, NY 11716-2416 Phone 631-567-1100 Fax 631-567-1823 AC/Synchro/Resolver/Phase Definitions We are required to be familiar with a wide
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM)
 Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
CHAPTER 9. Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 CHAPTER 9 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 9.1 The Sinusoidal Source A sinusoidal voltage source (independent or dependent) produces a voltage that varies sinusoidally with time. A sinusoidal current source
CHAPTER 9 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 9.1 The Sinusoidal Source A sinusoidal voltage source (independent or dependent) produces a voltage that varies sinusoidally with time. A sinusoidal current source
Circuit Analysis-II. Circuit Analysis-II Lecture # 2 Wednesday 28 th Mar, 18
 Circuit Analysis-II Angular Measurement Angular Measurement of a Sine Wave ü As we already know that a sinusoidal voltage can be produced by an ac generator. ü As the windings on the rotor of the ac generator
Circuit Analysis-II Angular Measurement Angular Measurement of a Sine Wave ü As we already know that a sinusoidal voltage can be produced by an ac generator. ü As the windings on the rotor of the ac generator
Model Phase Angle Voltmeter. Features: Description: Typical Applications:
 Model 2250 Phase Angle Voltmeter Features: 700Vpk Reference and Signal Inputs Wide Frequency Response Isolated Reference and Signal Inputs Up to 86 db Harmonic Rejection Ratio Measurement Capabilities
Model 2250 Phase Angle Voltmeter Features: 700Vpk Reference and Signal Inputs Wide Frequency Response Isolated Reference and Signal Inputs Up to 86 db Harmonic Rejection Ratio Measurement Capabilities
Sinusoids and Phasors (Chapter 9 - Lecture #1) Dr. Shahrel A. Suandi Room 2.20, PPKEE
 Sinusoids and Phasors (Chapter 9 - Lecture #1) Dr. Shahrel A. Suandi Room 2.20, PPKEE Email:shahrel@eng.usm.my 1 Outline of Chapter 9 Introduction Sinusoids Phasors Phasor Relationships for Circuit Elements
Sinusoids and Phasors (Chapter 9 - Lecture #1) Dr. Shahrel A. Suandi Room 2.20, PPKEE Email:shahrel@eng.usm.my 1 Outline of Chapter 9 Introduction Sinusoids Phasors Phasor Relationships for Circuit Elements
AN5161. Signal conditioning for resolver. Application note. Introduction
 Application note Signal conditioning for resolver Introduction This application note deals with the analog signal conditioning circuit used to drive a resolver and receive information from it. Some hints
Application note Signal conditioning for resolver Introduction This application note deals with the analog signal conditioning circuit used to drive a resolver and receive information from it. Some hints
Lab 9 - AC Filters and Resonance
 Lab 9 AC Filters and Resonance L9-1 Name Date Partners Lab 9 - AC Filters and Resonance OBJECTIES To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters. To understand resonance in circuits driven
Lab 9 AC Filters and Resonance L9-1 Name Date Partners Lab 9 - AC Filters and Resonance OBJECTIES To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters. To understand resonance in circuits driven
The period is the time required for one complete oscillation of the function.
 Trigonometric Curves with Sines & Cosines + Envelopes Terminology: AMPLITUDE the maximum height of the curve For any periodic function, the amplitude is defined as M m /2 where M is the maximum value and
Trigonometric Curves with Sines & Cosines + Envelopes Terminology: AMPLITUDE the maximum height of the curve For any periodic function, the amplitude is defined as M m /2 where M is the maximum value and
Dr.Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth Class. Operation and Analysis of the Three Phase Fully Controlled Bridge Converter
 Operation and Analysis of the Three Phase Fully Controlled Bridge Converter ١ Instructional Objectives On completion the student will be able to Draw the circuit diagram and waveforms associated with a
Operation and Analysis of the Three Phase Fully Controlled Bridge Converter ١ Instructional Objectives On completion the student will be able to Draw the circuit diagram and waveforms associated with a
Signal Levels and Leak Radiation of Loop Antennas for AM Home Transmitters
 Signal Levels and Leak Radiation of Loop Antennas for AM Home Transmitters Dipl.-Phys. Jochen Bauer 11/15/212 Abstract A considerable number of vintage radio sets for the AM broadcast bands use a build-in
Signal Levels and Leak Radiation of Loop Antennas for AM Home Transmitters Dipl.-Phys. Jochen Bauer 11/15/212 Abstract A considerable number of vintage radio sets for the AM broadcast bands use a build-in
LECTURE.3 : AC-DC CONVERSION
 LECTURE.3 : AC-DC CONVERSION (RECTIFICATIONS) 3.1Basic Rectifier Circuits Several types of rectifier circuits are available: single-phase and three-phase half-wave and full-wave, controlled and uncontrolled,
LECTURE.3 : AC-DC CONVERSION (RECTIFICATIONS) 3.1Basic Rectifier Circuits Several types of rectifier circuits are available: single-phase and three-phase half-wave and full-wave, controlled and uncontrolled,
Bucking Coils produce Energy Gain Cyril Smith, 2015
 Bucking Coils produce Energy Gain Cyril Smith, 015 1. Introduction There are many claims of overunity for systems that employ bucking coils. These are coils mounted on a common core and connected in series
Bucking Coils produce Energy Gain Cyril Smith, 015 1. Introduction There are many claims of overunity for systems that employ bucking coils. These are coils mounted on a common core and connected in series
Alternating voltages and currents
 Alternating voltages and currents Introduction - Electricity is produced by generators at power stations and then distributed by a vast network of transmission lines (called the National Grid system) to
Alternating voltages and currents Introduction - Electricity is produced by generators at power stations and then distributed by a vast network of transmission lines (called the National Grid system) to
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department. EE SOPHOMORE LABORATORY Experiment 5 RC Circuits Frequency Response
 POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department EE SOPHOMORE LORTORY Eperiment 5 RC Circuits Frequency Response Modified for Physics 18, rooklyn College I. Overview of Eperiment In this eperiment
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department EE SOPHOMORE LORTORY Eperiment 5 RC Circuits Frequency Response Modified for Physics 18, rooklyn College I. Overview of Eperiment In this eperiment
Goals. Introduction. To understand the use of root mean square (rms) voltages and currents.
 Lab 10. AC Circuits Goals To show that AC voltages cannot generally be added without accounting for their phase relationships. That is, one must account for how they vary in time with respect to one another.
Lab 10. AC Circuits Goals To show that AC voltages cannot generally be added without accounting for their phase relationships. That is, one must account for how they vary in time with respect to one another.
Complex Numbers in Electronics
 P5 Computing, Extra Practice After Session 1 Complex Numbers in Electronics You would expect the square root of negative numbers, known as complex numbers, to be only of interest to pure mathematicians.
P5 Computing, Extra Practice After Session 1 Complex Numbers in Electronics You would expect the square root of negative numbers, known as complex numbers, to be only of interest to pure mathematicians.
LRC Circuit PHYS 296 Your name Lab section
 LRC Circuit PHYS 296 Your name Lab section PRE-LAB QUIZZES 1. What will we investigate in this lab? 2. Figure 1 on the following page shows an LRC circuit with the resistor of 1 Ω, the capacitor of 33
LRC Circuit PHYS 296 Your name Lab section PRE-LAB QUIZZES 1. What will we investigate in this lab? 2. Figure 1 on the following page shows an LRC circuit with the resistor of 1 Ω, the capacitor of 33
Application Note (A12)
 Application Note (A2) The Benefits of DSP Lock-in Amplifiers Revision: A September 996 Gooch & Housego 4632 36 th Street, Orlando, FL 328 Tel: 47 422 37 Fax: 47 648 542 Email: sales@goochandhousego.com
Application Note (A2) The Benefits of DSP Lock-in Amplifiers Revision: A September 996 Gooch & Housego 4632 36 th Street, Orlando, FL 328 Tel: 47 422 37 Fax: 47 648 542 Email: sales@goochandhousego.com
So you say Bring on the SPAM?
 So you say Bring on the SPAM? Last Time s Lecture: Warm-ups about Transmitters Angle Modulation-->FM & PM How to get Modulation-->VCO Introduction to Oscillators: Feedback Perspective Timing-based (I.e.
So you say Bring on the SPAM? Last Time s Lecture: Warm-ups about Transmitters Angle Modulation-->FM & PM How to get Modulation-->VCO Introduction to Oscillators: Feedback Perspective Timing-based (I.e.
Phasor. Phasor Diagram of a Sinusoidal Waveform
 Phasor A phasor is a vector that has an arrow head at one end which signifies partly the maximum value of the vector quantity ( V or I ) and partly the end of the vector that rotates. Generally, vectors
Phasor A phasor is a vector that has an arrow head at one end which signifies partly the maximum value of the vector quantity ( V or I ) and partly the end of the vector that rotates. Generally, vectors
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 23 The Phase Locked Loop (Contd.) We will now continue our discussion
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 23 The Phase Locked Loop (Contd.) We will now continue our discussion
Grid Power Quality Analysis of 3-Phase System Using Low Cost Digital Signal Processor
 Grid Power Quality Analysis of 3-Phase System Using Low Cost Digital Signal Processor Sravan Vorem, Dr. Vinod John Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 56002 Email:
Grid Power Quality Analysis of 3-Phase System Using Low Cost Digital Signal Processor Sravan Vorem, Dr. Vinod John Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 56002 Email:
SD PROGRAMMABLE SYNCHRO/RESOLVER- TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER
 PROGRAMMABLE SYNCHRO/RESOLER- TO-DIGITAL CONERTER FEATURES Make sure the next Card you purchase has... TM Single + Power Supply Accuracy to. Arc-Minutes Pin Programmable Synchro/Resolver Input Option Pin
PROGRAMMABLE SYNCHRO/RESOLER- TO-DIGITAL CONERTER FEATURES Make sure the next Card you purchase has... TM Single + Power Supply Accuracy to. Arc-Minutes Pin Programmable Synchro/Resolver Input Option Pin
Lecture Note. Uncontrolled and Controlled Rectifiers
 Lecture Note 7 Uncontrolled and Controlled Rectifiers Prepared by Dr. Oday A Ahmed Website: https://odayahmeduot.wordpress.com Email: 30205@uotechnology.edu.iq Scan QR single-phase diode and SCR rectifiers
Lecture Note 7 Uncontrolled and Controlled Rectifiers Prepared by Dr. Oday A Ahmed Website: https://odayahmeduot.wordpress.com Email: 30205@uotechnology.edu.iq Scan QR single-phase diode and SCR rectifiers
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications
 ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
Electromagnetic Interference Reduction Study using a Self-Structuring Antenna
 Electromagnetic Interference Reduction Study using a Self-Structuring Antenna A. M. Patel (1), E. J. Rothwell* (1), L.C. Kempel (1), and J. E. Ross (2) (1) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Electromagnetic Interference Reduction Study using a Self-Structuring Antenna A. M. Patel (1), E. J. Rothwell* (1), L.C. Kempel (1), and J. E. Ross (2) (1) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
14595/96/97 accomplishes synchronization to a computer with the Converter Busy (CB) output and/or the Inhibit (INH) input.
 SD-49/9/97 SYNCHRO/RESOLER-TO-DIGITAL CONERTERS DESCRIPTION The SD-49 is a low-cost, high reliability, synchro- or resolver-to-digital converter with 4-bit-only, -bitonly or pin programmable 4-bit or -bit
SD-49/9/97 SYNCHRO/RESOLER-TO-DIGITAL CONERTERS DESCRIPTION The SD-49 is a low-cost, high reliability, synchro- or resolver-to-digital converter with 4-bit-only, -bitonly or pin programmable 4-bit or -bit
ELEC2202 Communications Engineering Laboratory Frequency Modulation (FM)
 ELEC Counications Engineering Laboratory ---- Frequency Modulation (FM) 1. Objectives On copletion of this laboratory you will be failiar with: Frequency odulators (FM), Modulation index, Bandwidth, FM
ELEC Counications Engineering Laboratory ---- Frequency Modulation (FM) 1. Objectives On copletion of this laboratory you will be failiar with: Frequency odulators (FM), Modulation index, Bandwidth, FM
13-3The The Unit Unit Circle
 13-3The The Unit Unit Circle Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz 2 Warm Up Find the measure of the reference angle for each given angle. 1. 120 60 2. 225 45 3. 150 30 4. 315 45 Find the exact value
13-3The The Unit Unit Circle Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz 2 Warm Up Find the measure of the reference angle for each given angle. 1. 120 60 2. 225 45 3. 150 30 4. 315 45 Find the exact value
Goals. Introduction. To understand the use of root mean square (rms) voltages and currents.
 Lab 10. AC Circuits Goals To show that AC voltages cannot generally be added without accounting for their phase relationships. That is, one must account for how they vary in time with respect to one another.
Lab 10. AC Circuits Goals To show that AC voltages cannot generally be added without accounting for their phase relationships. That is, one must account for how they vary in time with respect to one another.
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Currents. March 23, 2014 Chapter 30 1
 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Currents March 23, 2014 Chapter 30 1 Driven LC Circuit! The voltage V can be thought of as the projection of the vertical axis of the phasor V m representing the time-varying
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Currents March 23, 2014 Chapter 30 1 Driven LC Circuit! The voltage V can be thought of as the projection of the vertical axis of the phasor V m representing the time-varying
Radiation from Antennas
 Radiation from Antennas Ranga Rodrigo University of Moratuwa November 20, 2008 Ranga Rodrigo (University of Moratuwa) Radiation from Antennas November 20, 2008 1 / 32 Summary of Last Week s Lecture Radiation
Radiation from Antennas Ranga Rodrigo University of Moratuwa November 20, 2008 Ranga Rodrigo (University of Moratuwa) Radiation from Antennas November 20, 2008 1 / 32 Summary of Last Week s Lecture Radiation
MAE143A Signals & Systems - Homework 8, Winter 2013 due by the end of class Tuesday March 5, 2013.
 MAE43A Signals & Systems - Homework 8, Winter 3 due by the end of class uesday March 5, 3. Question Measuring frequency responses Before we begin to measure frequency responses, we need a little theory...
MAE43A Signals & Systems - Homework 8, Winter 3 due by the end of class uesday March 5, 3. Question Measuring frequency responses Before we begin to measure frequency responses, we need a little theory...
EE3723 : Digital Communications
 EE3723 : Digital Communications Week 8-9: Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad - Digital Communications - EE3723 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation
EE3723 : Digital Communications Week 8-9: Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad - Digital Communications - EE3723 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation
Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques. Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur
 Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur Data Conversion Circuits 2 Digital systems are being used
Data Conversion Circuits & Modulation Techniques Subhasish Chandra Assistant Professor Department of Physics Institute of Forensic Science, Nagpur Data Conversion Circuits 2 Digital systems are being used
Alternating current circuits- Series RLC circuits
 FISI30 Física Universitaria II Professor J.. ersosimo hapter 8 Alternating current circuits- Series circuits 8- Introduction A loop rotated in a magnetic field produces a sinusoidal voltage and current.
FISI30 Física Universitaria II Professor J.. ersosimo hapter 8 Alternating current circuits- Series circuits 8- Introduction A loop rotated in a magnetic field produces a sinusoidal voltage and current.
Lecture 4 - Three-phase circuits, transformer and transient analysis of RLC circuits. Figure 4.1
 Lecture 4 - Three-phase circuits, transformer and transient analysis of RLC circuits Power supply to sizeable power converters are often from three-phase AC source. A balanced three-phase source consists
Lecture 4 - Three-phase circuits, transformer and transient analysis of RLC circuits Power supply to sizeable power converters are often from three-phase AC source. A balanced three-phase source consists
THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM
 Chapter 11 THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM The sinusoidal waveform or sine wave is the fundamental type of alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage. It is also referred to as a sinusoidal wave or, simply,
Chapter 11 THE SINUSOIDAL WAVEFORM The sinusoidal waveform or sine wave is the fundamental type of alternating current (ac) and alternating voltage. It is also referred to as a sinusoidal wave or, simply,
CH 1. Large coil. Small coil. red. Function generator GND CH 2. black GND
 Experiment 6 Electromagnetic Induction "Concepts without factual content are empty; sense data without concepts are blind... The understanding cannot see. The senses cannot think. By their union only can
Experiment 6 Electromagnetic Induction "Concepts without factual content are empty; sense data without concepts are blind... The understanding cannot see. The senses cannot think. By their union only can
ELE636 Communication Systems
 ELE636 Communication Systems Chapter 5 : Angle (Exponential) Modulation 1 Phase-locked Loop (PLL) The PLL can be used to track the phase and the frequency of the carrier component of an incoming signal.
ELE636 Communication Systems Chapter 5 : Angle (Exponential) Modulation 1 Phase-locked Loop (PLL) The PLL can be used to track the phase and the frequency of the carrier component of an incoming signal.
EXPERIMENT 4: RC, RL and RD CIRCUITs
 EXPERIMENT 4: RC, RL and RD CIRCUITs Equipment List Resistor, one each of o 330 o 1k o 1.5k o 10k o 100k o 1000k 0.F Ceramic Capacitor 4700H Inductor LED and 1N4004 Diode. Introduction We have studied
EXPERIMENT 4: RC, RL and RD CIRCUITs Equipment List Resistor, one each of o 330 o 1k o 1.5k o 10k o 100k o 1000k 0.F Ceramic Capacitor 4700H Inductor LED and 1N4004 Diode. Introduction We have studied
13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions. Section 13.4
 13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions Section 13.4 1 13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions Section 13.4 2 Key Concept Section 13.4 3 Key Concept Section 13.4 4 Key Concept Section
13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions Section 13.4 1 13.4 Chapter 13: Trigonometric Ratios and Functions Section 13.4 2 Key Concept Section 13.4 3 Key Concept Section 13.4 4 Key Concept Section
Single-Phase Half-Wave Rectifiers
 ectifiers Single-Phase Half-Wave ectifiers A rectifier is a circuit that converts an ac signal into a unidirectional signal. A single-phase half-way rectifier is the simplest type. Although it is not widely
ectifiers Single-Phase Half-Wave ectifiers A rectifier is a circuit that converts an ac signal into a unidirectional signal. A single-phase half-way rectifier is the simplest type. Although it is not widely
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
Trigonometry Final Exam Study Guide Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The graph of a polar equation is given. Select the polar
Moving Forward Efficiently HEV/EV Traction Motor Lab
 Moving Forward Efficiently HEV/EV Traction Motor Lab A traction motor is an electric motor providing the primary rotational torque of a machine, usually for conversion into linear motion (traction). Renesas
Moving Forward Efficiently HEV/EV Traction Motor Lab A traction motor is an electric motor providing the primary rotational torque of a machine, usually for conversion into linear motion (traction). Renesas
1) Consider the circuit shown in figure below. Compute the output waveform for an input of 5kHz
 ) Consider the circuit shown in figure below. Compute the output waveform for an input of 5kHz Solution: a) Input is of constant amplitude of 2 V from 0 to 0. ms and 2 V from 0. ms to 0.2 ms. The output
) Consider the circuit shown in figure below. Compute the output waveform for an input of 5kHz Solution: a) Input is of constant amplitude of 2 V from 0 to 0. ms and 2 V from 0. ms to 0.2 ms. The output
Introduction. Transients in RLC Circuits
 Introduction In this experiment, we will study the behavior of simple electronic circuits whose response varies as a function of the driving frequency. One key feature of these circuits is that they exhibit
Introduction In this experiment, we will study the behavior of simple electronic circuits whose response varies as a function of the driving frequency. One key feature of these circuits is that they exhibit
JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 3.5. TRIGONOMETRY 5 (Trigonometric identities & wave-forms) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 3.5 TRIGONOMETRY 5 (Trigonometric identities & wave-forms by A.J.Hobson 3.5.1 Trigonometric identities 3.5. Amplitude, wave-length, frequency and phase-angle UNIT 3.5 - TRIGONOMETRY
JUST THE MATHS SLIDES NUMBER 3.5 TRIGONOMETRY 5 (Trigonometric identities & wave-forms by A.J.Hobson 3.5.1 Trigonometric identities 3.5. Amplitude, wave-length, frequency and phase-angle UNIT 3.5 - TRIGONOMETRY
Trigonometric Identities
 Trigonometric Identities Scott N. Walck September 1, 010 1 Prerequisites You should know the cosine and sine of 0, π/6, π/4, π/, and π/. Memorize these if you do not already know them. cos 0 = 1 sin 0
Trigonometric Identities Scott N. Walck September 1, 010 1 Prerequisites You should know the cosine and sine of 0, π/6, π/4, π/, and π/. Memorize these if you do not already know them. cos 0 = 1 sin 0
Weaver SSB Modulation/Demodulation - A Tutorial
 Weaver SSB odulation/demodulation - A Tutorial Derek Rowell February 18, 2017 1 Introduction In 1956 D. K. Weaver 1 proposed a new modulation scheme for single-sideband-suppressedcarrier (SSB) generation.
Weaver SSB odulation/demodulation - A Tutorial Derek Rowell February 18, 2017 1 Introduction In 1956 D. K. Weaver 1 proposed a new modulation scheme for single-sideband-suppressedcarrier (SSB) generation.
TEGAM INC. MODEL DSRS-5DA DECADE SYNCO/RESOLVER STANDARD
 TEGAM INC. MODEL DSRS-5DA DECADE SYNCO/RESOLVER STANDARD Instruction Manual PN# 500783-349 Publication Date: Novermber 2007 REV. A NOTE: This user s manual was as current as possible when this product
TEGAM INC. MODEL DSRS-5DA DECADE SYNCO/RESOLVER STANDARD Instruction Manual PN# 500783-349 Publication Date: Novermber 2007 REV. A NOTE: This user s manual was as current as possible when this product
250 MHz, Voltage Output 4-Quadrant Multiplier AD835
 a FEATURES Simple: Basic Function is W = XY + Z Complete: Minimal External Components Required Very Fast: Settles to.% of FS in ns DC-Coupled Voltage Output Simplifies Use High Differential Input Impedance
a FEATURES Simple: Basic Function is W = XY + Z Complete: Minimal External Components Required Very Fast: Settles to.% of FS in ns DC-Coupled Voltage Output Simplifies Use High Differential Input Impedance
Lab 8 - INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOLTAGES
 08-1 Name Date Partners ab 8 - INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOTAGES OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase, reactance, and impedance in AC circuits. To observe the behavior
08-1 Name Date Partners ab 8 - INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOTAGES OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase, reactance, and impedance in AC circuits. To observe the behavior
Lab 9 AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE
 09-1 Name Date Partners ab 9 A FITES AND ESONANE OBJETIES OEIEW To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven by A signals In a previous lab, you
09-1 Name Date Partners ab 9 A FITES AND ESONANE OBJETIES OEIEW To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven by A signals In a previous lab, you
Feedback Devices. By John Mazurkiewicz. Baldor Electric
 Feedback Devices By John Mazurkiewicz Baldor Electric Closed loop systems use feedback signals for stabilization, speed and position information. There are a variety of devices to provide this data, such
Feedback Devices By John Mazurkiewicz Baldor Electric Closed loop systems use feedback signals for stabilization, speed and position information. There are a variety of devices to provide this data, such
L02 Operational Amplifiers Applications 1
 L02 Operational Amplifiers Applications 1 Chapter 9 Ideal Operational Amplifiers and Op-Amp Circuits Donald A. Neamen (2009). Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design, 4th Edition, Mc-Graw-Hill Prepared
L02 Operational Amplifiers Applications 1 Chapter 9 Ideal Operational Amplifiers and Op-Amp Circuits Donald A. Neamen (2009). Microelectronics: Circuit Analysis and Design, 4th Edition, Mc-Graw-Hill Prepared
What is a Sine Function Graph? U4 L2 Relate Circle to Sine Activity.pdf
 Math 3 Unit 6, Trigonometry L04: Amplitude and Period of Sine and Cosine AND Translations of Sine and Cosine Functions WIMD: What I must do: I will find the amplitude and period from a graph of the sine
Math 3 Unit 6, Trigonometry L04: Amplitude and Period of Sine and Cosine AND Translations of Sine and Cosine Functions WIMD: What I must do: I will find the amplitude and period from a graph of the sine
Trigonometric Identities. Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 5 Trigonometric Identities Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 5.5 Double-Angle Double-Angle Identities An Application Product-to-Sum and Sum-to-Product Identities Copyright 2017, 2013,
5 Trigonometric Identities Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 5.5 Double-Angle Double-Angle Identities An Application Product-to-Sum and Sum-to-Product Identities Copyright 2017, 2013,
Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Tool Spindle
 Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Tool Spindle David. J. Hopkins, Paul Geraghty Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 7000 East Ave, MS/L-792, Livermore, CA. 94550 Abstract Proper configurations
Active Vibration Isolation of an Unbalanced Machine Tool Spindle David. J. Hopkins, Paul Geraghty Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 7000 East Ave, MS/L-792, Livermore, CA. 94550 Abstract Proper configurations
MAC 1114 REVIEW FOR EXAM #2 Chapters 3 & 4
 MAC 111 REVIEW FOR EXAM # Chapters & This review is intended to aid you in studying for the exam. This should not be the only thing that you do to prepare. Be sure to also look over your notes, textbook,
MAC 111 REVIEW FOR EXAM # Chapters & This review is intended to aid you in studying for the exam. This should not be the only thing that you do to prepare. Be sure to also look over your notes, textbook,
THE BENEFITS OF DSP LOCK-IN AMPLIFIERS
 THE BENEFITS OF DSP LOCK-IN AMPLIFIERS If you never heard of or don t understand the term lock-in amplifier, you re in good company. With the exception of the optics industry where virtually every major
THE BENEFITS OF DSP LOCK-IN AMPLIFIERS If you never heard of or don t understand the term lock-in amplifier, you re in good company. With the exception of the optics industry where virtually every major
1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine
 1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Exercise 1 Sketch a graph of y = cos(t). Label the multiples of π 2 and π 4 on your plot, as well as the amplitude and the period of the function. (Feel free to sketch the unit
1 Graphs of Sine and Cosine Exercise 1 Sketch a graph of y = cos(t). Label the multiples of π 2 and π 4 on your plot, as well as the amplitude and the period of the function. (Feel free to sketch the unit
11/8/2007 Antenna Pattern notes 1/1
 11/8/27 ntenna Pattern notes 1/1 C. ntenna Pattern Radiation Intensity is dependent on both the antenna and the radiated power. We can normalize the Radiation Intensity function to construct a result that
11/8/27 ntenna Pattern notes 1/1 C. ntenna Pattern Radiation Intensity is dependent on both the antenna and the radiated power. We can normalize the Radiation Intensity function to construct a result that
MHF4U. Advanced Functions Grade 12 University Mitchell District High School. Unit 4 Radian Measure 5 Video Lessons
 MHF4U Advanced Functions Grade 12 University Mitchell District High School Unit 4 Radian Measure 5 Video Lessons Allow no more than 1 class days for this unit! This includes time for review and to write
MHF4U Advanced Functions Grade 12 University Mitchell District High School Unit 4 Radian Measure 5 Video Lessons Allow no more than 1 class days for this unit! This includes time for review and to write
Moving Forward Efficiently HEV/EV Traction Motor Lab
 Moving Forward Efficiently HEV/EV Traction Motor Lab Mark Ramseyer, Staff Technical Application Engineer Terry Downs, Staff Technical Application Engineer A traction motor is an electric motor providing
Moving Forward Efficiently HEV/EV Traction Motor Lab Mark Ramseyer, Staff Technical Application Engineer Terry Downs, Staff Technical Application Engineer A traction motor is an electric motor providing
SCRIPT. Voltage Dividers
 SCRIPT Hello friends in our earlier discussion we talked about series resistive circuits, when connected in series, resistors form a "string" in which there is only one path for current. Ohm's law can
SCRIPT Hello friends in our earlier discussion we talked about series resistive circuits, when connected in series, resistors form a "string" in which there is only one path for current. Ohm's law can
Exercises Exercises. Multiple Choice 1. The average value of a constant (DC) voltage of 12 V is A. B.
 Exercises 8.5 Exercises Multiple Choice. he average value of a constant (DC) voltage of is A. D. 6. he average value of i 5+ cost A is A. D. 5+ A 5 A 5 A 5 A 3. he RMS value of a constant (DC) voltage
Exercises 8.5 Exercises Multiple Choice. he average value of a constant (DC) voltage of is A. D. 6. he average value of i 5+ cost A is A. D. 5+ A 5 A 5 A 5 A 3. he RMS value of a constant (DC) voltage
EE42: Running Checklist of Electronics Terms Dick White
 EE42: Running Checklist of Electronics Terms 14.02.05 Dick White Terms are listed roughly in order of their introduction. Most definitions can be found in your text. Terms2 TERM Charge, current, voltage,
EE42: Running Checklist of Electronics Terms 14.02.05 Dick White Terms are listed roughly in order of their introduction. Most definitions can be found in your text. Terms2 TERM Charge, current, voltage,
Exactly Evaluating Even More Trig Functions
 Exactly Evaluating Even More Trig Functions Pre/Calculus 11, Veritas Prep. We know how to find trig functions of certain, special angles. Using our unit circle definition of the trig functions, as well
Exactly Evaluating Even More Trig Functions Pre/Calculus 11, Veritas Prep. We know how to find trig functions of certain, special angles. Using our unit circle definition of the trig functions, as well
Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas
 Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege Bicycle ramps for advanced riders have a steeper incline than those designed for novices. Bicycle ramps made for competition (see [link])
Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas By: OpenStaxCollege Bicycle ramps for advanced riders have a steeper incline than those designed for novices. Bicycle ramps made for competition (see [link])
5/4/2005 Antenna Pattern present 1/1. C. Antenna Pattern
 5/4/2005 Antenna Pattern present 1/1 C. Antenna Pattern Radiation Intensity is dependent on both the antenna and the radiated power. We can normalize the Radiation Intensity function to construct a result
5/4/2005 Antenna Pattern present 1/1 C. Antenna Pattern Radiation Intensity is dependent on both the antenna and the radiated power. We can normalize the Radiation Intensity function to construct a result
The Periodogram. Use identity sin(θ) = (e iθ e iθ )/(2i) and formulas for geometric sums to compute mean.
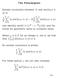 The Periodogram Sample covariance between X and sin(2πωt + φ) is 1 T T 1 X t sin(2πωt + φ) X 1 T T 1 sin(2πωt + φ) Use identity sin(θ) = (e iθ e iθ )/(2i) and formulas for geometric sums to compute mean.
The Periodogram Sample covariance between X and sin(2πωt + φ) is 1 T T 1 X t sin(2πωt + φ) X 1 T T 1 sin(2πωt + φ) Use identity sin(θ) = (e iθ e iθ )/(2i) and formulas for geometric sums to compute mean.
AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE
 July 22, 2008 AC Currents, Voltages, Filters, Resonance 1 Name Date Partners AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase,
July 22, 2008 AC Currents, Voltages, Filters, Resonance 1 Name Date Partners AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase,
Digital Signal Processing Lecture 1 - Introduction
 Digital Signal Processing - Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville August 20, 2015 Overview 1 2 3 4 Basic building blocks in DSP Frequency analysis Sampling Filtering
Digital Signal Processing - Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of Tennessee, Knoxville August 20, 2015 Overview 1 2 3 4 Basic building blocks in DSP Frequency analysis Sampling Filtering
Experiment 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase Locked Loops
 Experiment 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase Locked Loops Frequency Modulation Background Normally, we consider a voltage wave form with a fixed frequency of the form v(t) = V sin( ct + ), (1) where c
Experiment 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase Locked Loops Frequency Modulation Background Normally, we consider a voltage wave form with a fixed frequency of the form v(t) = V sin( ct + ), (1) where c
Trigonometric Identities. Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 5 Trigonometric Identities Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities Difference Identity for Cosine Sum Identity for Cosine Cofunction Identities Applications
5 Trigonometric Identities Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 5.3 Sum and Difference Identities Difference Identity for Cosine Sum Identity for Cosine Cofunction Identities Applications
Electrical Theory. Power Principles and Phase Angle. PJM State & Member Training Dept. PJM /22/2018
 Electrical Theory Power Principles and Phase Angle PJM State & Member Training Dept. PJM 2018 Objectives At the end of this presentation the learner will be able to: Identify the characteristics of Sine
Electrical Theory Power Principles and Phase Angle PJM State & Member Training Dept. PJM 2018 Objectives At the end of this presentation the learner will be able to: Identify the characteristics of Sine
About the HELM Project HELM (Helping Engineers Learn Mathematics) materials were the outcome of a three-year curriculum development project
 bout the HELM Project HELM (Helping Engineers Learn Mathematics) materials were the outcome of a three-year curriculum development project undertaken by a consortium of five English universities led by
bout the HELM Project HELM (Helping Engineers Learn Mathematics) materials were the outcome of a three-year curriculum development project undertaken by a consortium of five English universities led by
Module 5. DC to AC Converters. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 5 DC to AC Converters Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 37 Sine PWM and its Realization Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 After completion of this lesson, the reader shall be able to: 1. Explain
Module 5 DC to AC Converters Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 37 Sine PWM and its Realization Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 After completion of this lesson, the reader shall be able to: 1. Explain
ECEN689: Special Topics in High-Speed Links Circuits and Systems Spring 2010
 ECEN689: Special Topics in High-Speed Links Circuits and Systems Spring 010 Lecture 3: CDR Wrap-Up Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Announcements Exam is April 30 Will emphasize
ECEN689: Special Topics in High-Speed Links Circuits and Systems Spring 010 Lecture 3: CDR Wrap-Up Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Announcements Exam is April 30 Will emphasize
Costas Loop. Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier
 Costas Loop Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier 0 Pre-Laboratory Reading Phase-shift keying that employs two discrete
Costas Loop Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier 0 Pre-Laboratory Reading Phase-shift keying that employs two discrete
University of North Carolina-Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 4143/5195 Electrical Machinery Fall 2009
 University of North Carolina-Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 4143/5195 Electrical Machinery Fall 2009 Problem Set 3 Due: Monday September 28 Recommended Reading: Fitzgerald
University of North Carolina-Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 4143/5195 Electrical Machinery Fall 2009 Problem Set 3 Due: Monday September 28 Recommended Reading: Fitzgerald
EE152 F13 Midterm 1. Before starting, please check to make sure that you have all 6 pages Total 100. V0.
 EE152 F13 Midterm 1 Name: (please print) Solution In recognition of and in the spirit of the Stanford University Honor Code, I certify that I will neither give nor receive unpermitted aid on this exam.
EE152 F13 Midterm 1 Name: (please print) Solution In recognition of and in the spirit of the Stanford University Honor Code, I certify that I will neither give nor receive unpermitted aid on this exam.
rb Trip Code Resolver Troubleshooting
 Troubleshooting Guide CTTG #145 rb Trip Code Resolver Troubleshooting This guide pertains to drives using Resolver Feedback Problem: The drive shows rb in the display window or in the trip log. When using
Troubleshooting Guide CTTG #145 rb Trip Code Resolver Troubleshooting This guide pertains to drives using Resolver Feedback Problem: The drive shows rb in the display window or in the trip log. When using
Chapter 2 Shunt Active Power Filter
 Chapter 2 Shunt Active Power Filter In the recent years of development the requirement of harmonic and reactive power has developed, causing power quality problems. Many power electronic converters are
Chapter 2 Shunt Active Power Filter In the recent years of development the requirement of harmonic and reactive power has developed, causing power quality problems. Many power electronic converters are
Variable Resolution, 10-Bit to 16-Bit R/D Converter with Reference Oscillator AD2S1210
 Variable Resolution, 1-Bit to 16-Bit R/D Converter with Reference Oscillator ADS11 FEATURES Complete monolithic resolver-to-digital converter 315 rps maximum tracking rate (1-bit resolution) ±.5 arc minutes
Variable Resolution, 1-Bit to 16-Bit R/D Converter with Reference Oscillator ADS11 FEATURES Complete monolithic resolver-to-digital converter 315 rps maximum tracking rate (1-bit resolution) ±.5 arc minutes
6.1 - Introduction to Periodic Functions
 6.1 - Introduction to Periodic Functions Periodic Functions: Period, Midline, and Amplitude In general: A function f is periodic if its values repeat at regular intervals. Graphically, this means that
6.1 - Introduction to Periodic Functions Periodic Functions: Period, Midline, and Amplitude In general: A function f is periodic if its values repeat at regular intervals. Graphically, this means that
Solutions to Exercises, Section 5.6
 Instructor s Solutions Manual, Section 5.6 Exercise 1 Solutions to Exercises, Section 5.6 1. For θ = 7, evaluate each of the following: (a) cos 2 θ (b) cos(θ 2 ) [Exercises 1 and 2 emphasize that cos 2
Instructor s Solutions Manual, Section 5.6 Exercise 1 Solutions to Exercises, Section 5.6 1. For θ = 7, evaluate each of the following: (a) cos 2 θ (b) cos(θ 2 ) [Exercises 1 and 2 emphasize that cos 2
Initial Synchronization
 Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Initial Synchronization Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Contents Introduction and Over-sampling Downlink Synchronization
Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Initial Synchronization Institute of Communications Engineering National Sun Yat-sen University Contents Introduction and Over-sampling Downlink Synchronization
Differential Amp DC Analysis by Robert L Rauck
 Differential Amp DC Analysis by Robert L Rauck Amplifier DC performance is affected by a variety of Op Amp characteristics. Not all of these factors are commonly well understood. This analysis will develop
Differential Amp DC Analysis by Robert L Rauck Amplifier DC performance is affected by a variety of Op Amp characteristics. Not all of these factors are commonly well understood. This analysis will develop
Chapter 33. Alternating Current Circuits
 Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits Alternating Current Circuits Electrical appliances in the house use alternating current (AC) circuits. If an AC source applies an alternating voltage to a series
Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits Alternating Current Circuits Electrical appliances in the house use alternating current (AC) circuits. If an AC source applies an alternating voltage to a series
CHAPTER 3 DESIGN OF MICROSTRIP PATCH ARRAY ANTENNA
 CHAPTER 3 DESIGN OF MICROSTRIP PATCH ARRAY ANTENNA 3.1 Introduction This chapter is discussed on the various factors that affect the design of microstrips patch array antenna. This chapter will covered
CHAPTER 3 DESIGN OF MICROSTRIP PATCH ARRAY ANTENNA 3.1 Introduction This chapter is discussed on the various factors that affect the design of microstrips patch array antenna. This chapter will covered
Ac fundamentals and AC CIRCUITS. Q1. Explain and derive an expression for generation of AC quantity.
 Ac fundamentals and AC CIRCUITS Q1. Explain and derive an expression for generation of AC quantity. According to Faradays law of electromagnetic induction when a conductor is moving within a magnetic field,
Ac fundamentals and AC CIRCUITS Q1. Explain and derive an expression for generation of AC quantity. According to Faradays law of electromagnetic induction when a conductor is moving within a magnetic field,
UNIT Write short notes on travelling wave antenna? Ans: Travelling Wave Antenna
 UNIT 4 1. Write short notes on travelling wave antenna? Travelling Wave Antenna Travelling wave or non-resonant or aperiodic antennas are those antennas in which there is no reflected wave i.e., standing
UNIT 4 1. Write short notes on travelling wave antenna? Travelling Wave Antenna Travelling wave or non-resonant or aperiodic antennas are those antennas in which there is no reflected wave i.e., standing
17. Delta Modulation
 7. Delta Modulation Introduction So far, we have seen that the pulse-code-modulation (PCM) technique converts analogue signals to digital format for transmission. For speech signals of 3.2kHz bandwidth,
7. Delta Modulation Introduction So far, we have seen that the pulse-code-modulation (PCM) technique converts analogue signals to digital format for transmission. For speech signals of 3.2kHz bandwidth,
Figure 1. The unit circle.
 TRIGONOMETRY PRIMER This document will introduce (or reintroduce) the concept of trigonometric functions. These functions (and their derivatives) are related to properties of the circle and have many interesting
TRIGONOMETRY PRIMER This document will introduce (or reintroduce) the concept of trigonometric functions. These functions (and their derivatives) are related to properties of the circle and have many interesting
Low Cost, Complete 12-Bit Resolver-to-Digital Converter AD2S90
 a FEATURES Complete Monolithic Resolver-to-Digital Converter Incremental Encoder Emulation (102-Line) Absolute Serial Data (12-Bit) Differential Inputs 12-Bit Resolution Industrial Temperature Range 20-Pin
a FEATURES Complete Monolithic Resolver-to-Digital Converter Incremental Encoder Emulation (102-Line) Absolute Serial Data (12-Bit) Differential Inputs 12-Bit Resolution Industrial Temperature Range 20-Pin
Understanding VCO Concepts
 Understanding VCO Concepts OSCILLATOR FUNDAMENTALS An oscillator circuit can be modeled as shown in Figure 1 as the combination of an amplifier with gain A (jω) and a feedback network β (jω), having frequency-dependent
Understanding VCO Concepts OSCILLATOR FUNDAMENTALS An oscillator circuit can be modeled as shown in Figure 1 as the combination of an amplifier with gain A (jω) and a feedback network β (jω), having frequency-dependent
