III III IIII. United States Patent (19) Somerville et al. 5,598,327 *Jan. 28, Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent:
|
|
|
- Laurence Wilkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 United States Patent (19) Somerville et al. III III IIII USOO A 11 Patent Number: 45) Date of Patent: *Jan. 28, 1997 (54) PLANAR TRANSFORMER ASSEMBLY INCLUDING NON-OVERLAPPNG PRIMARY AND SECONDARY WINDINGS SURROUNDING A COMMON MAGNETIC FLUX PATH AREA 75 Inventors: Thomas A. Somerville; Walter B. Meinel; R. Mark Stitt, II, all of Tucson, Ariz. 73) Assignee: Burr-Brown Corporation, Tucson, Ariz. * Notice: The term of this patent shall not extend beyond the expiration date of Pat. No. 5,353, Appl. No.: 188,159 (22 Filed: Jan. 28, 1994 Related U.S. Application Data 63 Continuation-in-part of Ser. No.969,508, Oct. 30, 1992, Pat. No. 5,353,001, and Ser. No. 63,163, May 11, 1993, Pat. No. 5,304,917, which is a continuation-in-part of Ser. No. 850, 286, Mar. 12, 1992, abandoned, which is a continuation-in part of Ser. No. 621,014, Nov.30, 1990, Pat. No. 5,111,131, said Ser. No. 969,508, is a continuation of Ser. No. 645,224, Jan. 24, 1991, abandoned. (51) Int. Cl."... H02M 7/537; H01H 85/02 52 U.S. Cl /131; 336/83; 336/96; 336/200; 336/212; 336/232; 29/ Field of Search /200, 212, 336/232, 83, 96; 29/602.1, 606; 363/121 56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 3,833,872 9/1974 Marcus et al /83 4,012,703 3/1977 Chamberlayne /24 R 4,424,504 1/1984 Mitsui et al ,506,238 3/1985 Endoh et al /138 4,538,132 8/1985 Hiyama et al /22 4,628,148 12/1986 Endou PE 4,641,114 2/1987 Person /161 4,730,241 3/1988 Takaya /19 4,745,388 5/1988 Billings et al /92 4,800,356 1/1989 Ellis /184 4,864,486 9/1989 Spreen ,914,561 4/1990 Rice et al /126 4,939,494 7/1990 Massuda et al /96 5,353, /1994 Meinel et al /83 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS /1979 Japan... HOF 27/02 OTHER PUBLICATIONS IBM Technical Disclosure Bulletin, "Low-Modulus Encap sulation System', by R. Braune, vol. II, No. 8, Jan. 1969, p Primary Examiner-Jeffrey L. Sterrett Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Cahill, Sutton & Thomas P.L.C. 57 ABSTRACT A planar transformer assembly includes an insulative layer, a first spiral winding thereon circumscribing a magnetic flux path, a second spiral winding thereon in non-overlapping relation to the first spiral winding circumscribing the mag netic flux path, and a ferrite core assembly including first and Second core Sections defining a shallow gap or passage within which the spiral windings are disposed. In one embodiment, a plurality of laminated insulative layers are provided with a primary winding including a plurality of series-connected spiral subwindings and a non-overlapping secondary winding formed on the various insulative layers. The non-overlapping structure and the order of the various windings minimize electric field gradients and thereby mini mize electric field coupled noise currents. 22 Claims, 6 Drawing Sheets
2 U.S. Patent Jan. 28, 1997 Sheet 1 of 6 NSNS&N-1- NSNSN-w-s. ZZ ZZZ W N
3 U.S. Patent Jan. 28, 1997 Sheet 2 of 6 A7 G-f
4 U.S. Patent Jan. 28, 1997 Sheet 3 of 6
5 U.S. Patent Jan. 28, 1997 Sheet 4 of 6 N, 6A N-AA-AA-3- N-AAA/- G 2/ A 2-3 N-A: Af if
6 U.S. Patent Jan. 28, 1997 Sheet 5 of 6 /2-4
7 U.S. Patent Jan. 28, 1997 Sheet 6 of 6
8 1 PLANAR TRANSFORMER ASSEMBLY INCLUDING NON-OVERLAPPING PRIMARY AND SECONDARY WINDINGS SURROUNDING A COMMON MAGNETIC FLUX PATH AREA CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This application is a continuation-of-part of commonly assigned applications (1) Ser. No. 969,508, which issued as U.S. Pat. No. 5,353,001 on Oct. 4, 1995, by inventors Walter B. Meine and Mark R. Stitt entitled "HYBRID INTE GRATED CIRCUIT PLANAR TRANSFORMER'' filed Oct. 30, 1992, which is a continuation of application Ser. No. 645,224 filed Jan. 24, 1991, which is now abandoned, and (2) Ser. No. 063,163, by inventor Thomas A. Somerville entitled COMPACT LOW NOISE LOW POWER DUAL MODE BATTERY CHARGING CIRCUIT, filed May 11, 1993, which is now U.S. Pat. No. 5,304,917 which issued on Apr. 19, 1994 which is a continuation-in-part of application Ser. No. 850,286 filed Mar. 12, 1992, now abandoned, which is a continuation-in-part of application Ser. No. 621,014, filed Nov. 30, 1990, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,111,131 which issued on May 5, BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION The invention relates to low noise miniature transformers that are useful in hybrid integrated circuits, and more particularly to planar transformers having multiple, series connected primary windings and a non-overlapping second ary winding imprinted on various layers of a circuit board so as to minimize electromagnetic radiation and electric field coupling between primary and secondary windings, with a ferrite core formed by two ferrite sections, each including a thin, flat plate separated from the other by two spacer sections and also supported by the circuit board. There are a variety of electronic products which are powered by rechargeable batteries. The functional operation of some electronic products, including some powered by rechargeable batteries, is made unreliable by the presence of electrical noise. FCC regulations limit the amount of elec tromagnetic interference that can be radiated or conducted to the AC main power line by electronic devices. In some products, the presence of electrical noise causes sounds which are distracting to the user. Portable cellular telephones are an example of a noise-sensitive product. Some such products contain integral battery chargers that convert AC line voltage to low DC voltage levels at which conventional integrated circuit components can operate. It is important that the integral battery charger not introduce sufficient electrical noise to interfere with the reliable operation of the portable cellular telephone, not interfere with other products sharing the charger line voltage, or not violate FCC stan dards which are applied to electrical products to protect consumers from potential problems. There is an unmet need for a smaller, high efficiency, high frequency, low noise transformer that can be incorporated as part of an AC-to-DC converter or other circuit in a small hybrid integrated circuit package, such as a DIP package, or in a power connecter assembly. Hybrid electronic integrated circuits often are constructed using transfer molded packaging techniques to produce low cost electrical/electronic functions in a single conventional package, such as a dual-in-line package (DIP). Inclusion of magnetic components such as transformers in hybrid integrated circuits has always presented a major challenge, because the transformer cores required usually have large cross-sectional areas. Such large cross-sectional areas are inconsistent with the need to provide circuit functions in Small packages. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION Accordingly, it is an object of the invention to provide an improved, reduced size, hybrid integrated circuit trans former that is particularly suitable for low noise applica tions. It is another object of the invention to provide a hybrid integrated circuit transformer that can be included on a small printed circuit board as a component of a complete battery charger circuit and is easily encapsulated in a small power Connector. It is another object of the invention to provide a miniature integrated circuit transformer which can be encapsulated within a package having a thickness of as little as approxi mately 0.2 inches. It is another object of the invention to provide an improved planar hybrid integrated circuit transformer which can be incorporated in a thin conventional DIP package or the like. Briefly described, and in accordance with one embodi ment thereof, the invention provides a planar transformer assembly including a first insulative layer having a top surface and a bottom surface, a first spiral winding on the top surface, circumscribing a magnetic flux path area, a second spiral winding on the bottom surface circumscribing the magnetic flux path area, generally concentric with the first spiral winding, in non-overlapping relation to the first spiral winding, and a ferrite core assembly including a first core section including a thin, fiat first ferrite plate and a second core section including a thin, flat second ferrite plate. In one embodiment an elongated first ferrite spacer section sepa rates first ends of the first and second ferrite plates, and an elongated second ferrite spacer section separates second ends of the first and second ferrite plates. An elongated passage is defined by inner surfaces of the first and second ferrite plates and extends entirely through the ferrite core assembly. The first insulative layer passes entirely through the passage and extends outward from opposite sides of the ferrite core assembly. A securing element clamps the first and second ferrite plates and the first and second end spacer sections together. In one described embodiment of the invention, a plurality of laminated insulative layers are provided, wherein the first spiral winding is a subwinding of a primary winding includ ing a plurality of series-connected spiral subwindings formed on various surfaces, respectively, of the various insulative layers forming a multi-layer printed circuitboard, the spiral subwindings being connected in series by conduc tive vias passing through the various insulative layers. The second spiral winding is a secondary winding and surrounds the plurality of series-connected spiral subwindings of the primary winding. The secondary winding is formed on a second insulative layer adjacent to the first spiral subwind ing. A primary current supply circuit is connected to a first primary winding terminal that is connected to the first spiral subwinding. A switch connected to a second primary wind ing terminal is operated to produce Zero voltage switching of the primary current at a resonant frequency of the primary circuit. This arrangement separates the secondary winding as much as possible from the primary winding terminal on which large flyback voltages occur, reducing electric field gradients and the resulting electromagnetic radiation.
9 3 BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a partial perspective view of a planar transformer of the invention. FIG. 2 is an exploded partial perspective view of a preferred embodiment of the planar transformer of the present invention. FIG. 3 is a partial section view of the planar transformer of FIG. 2. FIG. 4 is a perspective view of the planar transformer of FIG. 2 showing portions of the printed circuitboard extend ing from opposite sides of the ferrite core and carrying associated circuitry. FIG. 5 is a schematic circuit diagram of the planar transformer of FIG. 4 and a resonant primary winding circuit thereof. FIGS. 6A-G are scale copies of the metal traces on each of the layers of the printed circuit board of the embodiment of FIG. 5. FIG. 7 is a section view diagram useful in explaining one aspect of the invention. FIG. 8 is a partial exploded perspective view of another embodiment of the planar transformer of the invention including conductive shields that contribute to electrically isolating the secondary windings from the primary winding. FIG. 9 is a perspective view of another embodiment of the planar transformer of the invention. FIG. 10 is a section view illustrating encapsulation of the embodiment of FIG. 9 in a molded DIP package. DETALED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS FIG. 1 shows a partial exploded view of one embodiment of the invention disclosed in the above-identified parent application, Ser. No. 969,508, now U.S. Pat. No. 5,353,001, incorporated herein by reference, in which printed circuit board 11 has a "tongue' section 11A on which windings 12 and 13 are formed generally concentrically, as spiral wind ings, around a common magnetic flux path area 14. This embodiment of the invention includes a ferrite core structure including an upper section 180 having two post or spacer sections 180A and 180B, one at each end. The two spacer sections 180A and 180B each can have the same width dimension 39 as the upper and lower core half sections 180 and 200. The lower ferrite core half section 200 is a thin flat plate. Spacer sections 180A and 180B are integral with the thin ferrite plate constituting the lower part of ferrite core half section 180. Core half sections 180 and 200 thereby form a shallow, rectangular passage 44, the height of which is inches, as indicated by arrows 32. The width 33 of passage 44 is 0.73 inches. The total thickness of the ferrite core thus formed is inches, its length is 1.0 inches, and its width is 0.63 inches, as indicated by dimension lines 38, 37, and 39, respectively. By making the cross-sectional areas of plates 180 and 200 thin and wide, the necessary inductance of typically 800 microhenrys for primary winding 12 is achieved, and the cross-sectional areas are made large enough to keep the magnetic flux density low enough to prevent saturation of the core material. Power loss due to saturation of the core is thereby avoided. The tongue section 11A of printed circuitboard 11 with all of the spiral windings printed thereon extends into rectangular hole 44. The width 39 of ferrite core 180, 200 completely subtends or confines all of the generally concentric windings 12, 13, etc. Note that the core 180,200 also could be formed of a single block of ferrite material with hole 44 milled out. The structure shown in FIG. 1 can be thought of as having a gap 32 of inches in the ferrite core 180,200. Gap 32 can be thought of as a gap in the center post of a "E' shaped ferrite core half section 180A,200A as a "limiting case' shown in FIG. 7, where the lengths of the center posts 48 are zero. That is, in the embodiment of FIG. 1, the post structure can be considered to be "infinitely shallow" so the lengths of such posts is zero. In the embodiment of FIG. 1 magnetic flux passes through gap 32 in the center magnetic flux area 14 of the primary and secondary windings, causing mutual inductive coupling therebetween. FIG. 2 shows a partial exploded view of a preferred embodiment of the planar transformer 10A, with the various insulating layers of a multi-layer printed circuit board 11 omitted for clarity. However, FIG. 3 shows a partial section view of six insulative layers and of a printed circuit board 111 (See FIG. 4) that extends entirely through the passage 44A,B defined by upper core 18 and lower core 20 in FIG. 2. (Note that identical or similar reference numerals are used to designate corresponding parts in the embodiment of FIG. 1 and the embodiment of FIGS. 2-4.) Referring to FIGS. 2 and 3, upper core section 18 includes a thin flat plate having enlarged, downwardly extending end spacer portions 18A and 18B which abut similar enlarged and upwardly extending end spacer portions 20A and 20B of an essentially identical bottom core section 20. Core sec tions 18 and 20 can be composed of H63B ferrite material, available from FDK America, Inc., of Irving, Tex. The length and width of each of core section 18 and 20 are 1.0 inches, and 0.63 inches respectively. The thickness of the central portion of each core section is inches and the thickness of the enlarged end sections is inches. The dimensions of the gap 44A, B defined by upper core section 18 and lower core section 20 are 0.73 inches by 0.63 inches by inches. Primary winding 12 includes five series-connected pri mary subwindings (only three of which are illustrated in FIG. 2, for convenience) and an auxiliary primary winding 21 (see FIGS. 3 and 5) which can be formed on the various surfaces of printed circuit board layers , respectively. Each of the five primary subwindings, which are collectively referred to by numeral 12, is generally coextensive with the others, so that they precisely overlap as indicated by dashed lines 26 and 27. One terminal of each of the primary subwindings 12-1, 12-2 etc. is connected to a terminal of another of the primary subwindings on an adjacent layer by a conductive via such as 50A, 50B or 50C. Each of the primary subwindings 12-1, 12-2 etc. circumscribes or surrounds an inner flux path region 14. The terminals of primary winding 12 are desig nated by numerals 30A and 30F. As shown in FIGS. 2 and 3, secondary winding 13 is formed on the top surface of printed circuit board layer and is precisely aligned in a non-overlapping fashion with the five primary subwind ings 12. The outer end of secondary winding 13 constitutes terminal 13A, and the inner end 13C is connected by conductive via 49 to metal trace 13B which constitutes the other secondary winding terminal. The inner portion of secondary winding 13 is generally coextensive with the outer portion of each of the five primary subwindings 12. The auxiliary power winding 21 is formed on the upper surface of insulative layer (FIG. 3). As shown in FIG. 4, a slightly narrowed portion 111A of printed circuit board 111 on which primary winding 12 and
10 S secondary winding 13 are formed extends entirely through the gap 44A,44B defined by the inner surfaces of upper core section 18 and lower core section 20 and the enlarged spacer portions 18AB and 20A.B. Numerals 57 and 58 generally designate various components, including some of the com ponents indicated in FIG. 5 on the left and right portions of printed circuit board 111 extending beyond the opposed sides of core sections 18 and 20. Core sections 18 and 20 are clamped together by a pair of inwardly biased spring clips 31. The entire assembly, includ ing printed circuit board 111 and planar transformer 10A thereon, then is inserted in a suitable package', for example, an enlarged housing for a male electrical plug, with conductors 42 and 43 leading to a rechargeable nickel cadmium battery in a mobile telephone unit or the like which is powered by the male electrical plug. Complete details of a "smart' battery charger circuit on printed circuit board 111 are set forth in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 063,163 filed May 11, 1993 and entitled "COMPACT LOW NOISE LOW POWER DUAL MODE BATTERY CHARGING CIR CUIT" which is incorporated herein by reference. Suitable potting material and/or features of the inside of the package prevent spring clips 31 from coming loose, e.g., as a result of vibration. Conductors 59 engage two prongs, respec tively, of the male electrical plug, and are connected to supply household current to the input of the battery charger formed by printed circuit board 111 and planar transformer 10A thereon. FIG. 8 shows another diagram similar to FIG. 2, in which a plurality of conductive shields are disposed between the five primary subwindings 12 and the one secondary winding 13, and are generally coextensive with the turns of secondary winding 13. Each shield has a narrow gap 16A to prevent flow of eddy currents, and a lead connected by the other shield leads by a suitable via, indicated by dotted line 25. The shields leads are electrically connected to a low impedance conductor carrying an AC ground voltage. The initial prototypes of the invention included shields such as Surprisingly, however, it was discovered that when they are eliminated, the electrical noise or interference, which results partly from coupling between the primary subwindings 12 and secondary winding 13, nevertheless is acceptably low to meet the specifications for which a marketable product is being designed. As explained in detail in the above-mentioned Somerville application, optimum overall circuit performance is obtained by combination of the planar transformer shown in FIGS. 2 and 3 and a resonant primary circuit as described in the above-identified Somerville application Ser. No. 063,163, especially if the turn off times of MOSFET 35 are adjusted in accordance with changes in the inductance of the primary subwindings occurring as a result of changes in the loading of the secondary winding 13. This results in reduced power dissipation in MOSFET35 in FIG.5 and also ensures that the fly-back voltage V returns to zero before MOSFET 19 is turned on, ensuring that "zero voltage switching' is achieved despite variations in the inductance of the primary winding 12 caused by varying load condi tions. This substantially reduces the generation of noise harmonics and the like. FIG. 5 is a simplified schematic diagram that shows the arrangement of the battery charger of the above-identified Somerville application Ser. No. 063,163. The components most closely related to the resonant primary circuit of the planar transformer 10A are shown. More specifically, the series connections of primary subwindings and the location of secondary winding 13 are shown in FIG. 5. Switching MOSFET35, a full wave rectifier D1-4, isolation barrier capacitors 54A,55A and 54B,55B also are shown. The auxiliary primary winding 21 used to generate power for circuitry on the primary side of planar transformer also is shown. In the circuit of FIG. 5, the 110 volt 60 hertz line current is rectified by the full wave rectifier including diodes D1, D2, D3 and D4 to produce the waveform V2s on conductor 28, which is connected to terminal 30A of primary winding 12. The other terminal 30F of primary winding 12 is connected to the drain electrode of MOSFET 35 and one terminal of flyback capacitor C. Terminal 30A of primary winding 12 also is connected to the other terminal of flyback capacitor C on which the 120 hertz full wave rectified signal is produced. The flyback voltage V occurs on conductor 30F MOSFET 35 is turned on and off at a 500 kilohertz to 1 megahertz rate, so that primary winding 12 is energized only for a part of the time which is centered about the times of occurrence of the peak levels of the voltage waveform on conductor 28. A feed-back loop Such as described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,111,131 involving primary winding 12 adjusts the on time of MOSFET35 to achieve a relatively constant primary winding current level. The primary winding 12 has a smaller average inductance during heavy loading of the secondary winding than during light loading. Accordingly, the off time of MOSFET 19 is adjusted to be less during high current loading conditions than during low current loading conditions, reducing power dissipation in the primary winding because the magnetic flux has time to return to Zero for each cycle of the primary winding resonant circuit. In the presently preferred embodiment of the invention, isolation barrier capacitors as described in U.S. Pat. No. 5,111,131 couple control signals produced by circuitry on the output or secondary winding side of printed circuitboard 111 to the input circuitry on the input or primary winding side of printed circuit board 111. In FIG. 5, a pair of capacitors 54A,55A are connected in series to provide one isolation barrier, and capacitors 54B and 55B are connected in series to form another isolation barrier. This pair of isolation barriers is used to convey control information from the secondary side of planar transformer to the primary side thereof. FIGS. 6A-6G show scale views of the various patterns of printed circuitboard 111 fabricated to implement the various planar transformer windings and subwindings (including the additional primary winding transformer 21 which rectifies the primary current to produce a power supply signal utilized to power the circuitry on the primary winding side of planar transformer 10A) connected in the order shown in FIG. 5. More specifically, FIG. 6A shows the pattern for secondary winding 13, which appears on top of the top layer FIG. 6B shows the pattern for primary subwinding 12-1, and also shows one pair of plates of isolation barrier capacitors 55A and 55B and their leads 61A and 61B to the secondary winding circuitry. Note that the leads 61A and 61B pass outside of the region 14 of concentrated magnetic field flux. FIG. 60 shows the primary subwinding pattern for primary winding 12-2 and also shows two of "floating isolation barrier capacitor plates which are provided to meet UL regulations unrelated to the present invention. FIG. 6D shows the pattern for auxiliary primary winding 21. FIG. 6E shows the pattern for primary subwinding FIG. 6F shows the pattern for primary subwinding FIG. 6G shows the pattern for primary subwinding 12-5.
11 7 For primary winding 12, the largest AC voltage is the flyback voltage V, which has peaks of approximately 500 volts. It occurs on primary terminal conductor 30F, and the smallest voltage changes, with peaks of approximately 167 volts, occur on primary terminal conductor 30A. Therefore, in accordance with the present embodiment of the invention, secondary winding 13 is provided on the printed circuit board layer adjacent to primary subwinding 12-1 on which the smallest voltage changes occur. This causes the physical location of secondary winding 13 to be separated by the maximum possible distance from conductor 30F on which the largest AC voltage peaks of approximately 500 volts occur. This minimizes the electric field gradients between primary winding 12 and secondary winding 13, and there fore reduces electromagnetic noise generation and also reduces the likelihood of current leakage or voltage break down between primary winding 12 and secondary winding 13. In accordance with the present invention, the parasitic capacitances 51 between primary subwindings and secondary winding 13 are minimized by the illustrated non-overlapping structure. This further minimizes electro magnetic noise generation. In some applications, especially if printed circuit board 111 is very thin, the end spacer portions 18A and 18B and 20A and 20B shown in FIG. 2 can be omitted, in which case the gap 44A,B extends over the entire length and width of the upper and lower ferrite core sections 18 and 20. FIG.9 shows such an implementation of the planar transformer, in which upper core section 18 is adhesively or otherwise attached to the upper surface of printed circuit board 111, and lower ferrite core section or plate 20 is adhesively or otherwise attached to the bottom surface of printed circuit board 111. In FIG. 10, numerals 45 designate adhesive attachment of ferrite cores 18 and 20 to the top and bottom surfaces of printed circuitboard 111. Gap 44 is equal to the thickness of printed circuit board 111 and extends throughout the entire region between upper core section 18 and lower core section 20. The printed primary winding and secondary winding, and also a shield similar to that described with reference to FIG. 8, can be provided on layers of printed circuit board 111 between ferrite core sections 18 and 20 in the manner previously described. This embodiment of the invention has lower inductance than the previously described embodi ments of the invention, but will be suitable for some applications. The planar transformer of FIG. 9 has several advantages, one being that it is more compact, as the ends of ferrite cores sections 18 and 19 need not extend around opposed edges of the printed circuit board 111. Another advantage is that gap 44 can be thinner, precisely equal to the thickness of the printed circuit board 111, whereas in the embodiments of FIGS. 1 and 2 the gap 44A,B must be slightly greater than the thickness of the printed circuit board because a small amount of clearance tolerance is needed to ensure that the end sections 18A,B and 20A,B properly abut. Furthermore, it is more convenient to adhesively attach ferrite core sections 18 and 20 to the surfaces of printed circuit board 111 in the planar transformer of FIG. 9 than in the earlier described embodiments. Another important advantage of the planar transformer of FIG. 9 is that it can be more conveniently encapsulated in a molded DIP package, as shown in FIG. 10, wherein numeral 65 designates the plastic injection-molded body of a DIP package in which the planar transformer and associated printed circuit board 111 are encapsulated. Numeral 63 designates the leads of the DIP, and numeral 64 designates conventional wire bonds of leads 63 to wire bond pads (not shown) on a surface of printed circuit board 111. Magneto strictive forces produced by ferrite core sections 18 and 20 can be absorbed by the material of which printed circuit board 111 is constructed, avoiding associated power loss and stresses on the DIP body material 65. Problems associated with leakage of the injected molding material between the surfaces of printed circuit board 111 and the inner surfaces of ferrite core sections 18 and 20 are avoided. Thus, a very small, efficient hybrid integrated circuit transformer with low core losses and low electromagnetic interference is achieved by the above described invention. While the invention has been described with reference to several embodiments thereof, those skilled in the art will be able to make various modifications to the described embodi ments without departing from the true spirit and scope of the invention. What is claimed is: 1. A planar transformer assembly comprising in combi nation: (a) an insulative layer having a top surface and a bottom surface; (b) a first spiral winding on the top surface, surrounding a magnetic flux path area; (c) a second spiral winding on the bottom surface, sur rounding the magnetic flux path area, concentric with the first spiral winding, in non-overlapping relation to the first spiral winding; (d) a ferrite core assembly including i. a first core section including a thin, flat first ferrite plate disposed on the top surface and subtending the first and second spiral windings, and ii. a second core section including a thin, flat second ferrite plate disposed on the bottom surface and subtending the first and second spiral windings. 2. The planar transformer assembly of claim 1 wherein the insulative layer includes a plurality of insulative sublayers, the first spiral winding being disposed on a first insulative sublayer, the second spiral winding being disposed on a second insulative sublayer, the planar transformer assembly including a conductive shield disposed between the first and second insulative sublayers and surrounding the magnetic flux path area and generally coextensive with one of the first and second spiral windings to reduce capacitive coupling between the first and second spiral windings and thereby reduce noise generation during operation of the planar transformer assembly. 3. The planar transformer assembly of claim 2 wherein the guard ring includes a gap to interrupt field coupled currents in the guard ring, and wherein the guard ring is coupled through a low impedance to a fixed voltage. 4. The planar transformer assembly of claim 1 wherein a portion of the insulative layer extends beyond the first and second core sections. 5. The planar transformer assembly of claim 4 including adhesive attaching the first core section to the top surface and adhesive attaching the second core section to the bottom surface. 6. The planar transformer assembly of claim 4 including an elongated first ferrite spacer section separating first ends of the first and second ferrite plates, and an elongated second ferrite spacer section separating second ends of the first and second ferrite plates, and material securing the first and second ferrite plates in fixed relation to the insulative layer. 7. The planar transformer assembly of claim 6 wherein the material includes an elastic clip engaging the first and second core sections to clamp them together.
12 9 8. The planar transformer assembly of claim 6 wherein the first ferrite spacer Section includes abutting first and second parts integral with the first ends of the first and second ferrite plates, respectively, and the second ferrite spacer section includes abutting third and fourth parts integral with the Second ends of the first and second ferrite plates, respec tivelv. 5the planar transformer assembly of claim 8 wherein the insulative layer includes a plurality of laminated insulative sublayers, wherein the first spiral winding is a subwinding of a primary winding including a plurality of series-connected spiral subwindings formed on various surfaces, respectively, of the various insulative sublayers, the spiral subwindings being connected in series by conductive vias passing through the various insulative sublayers. 10. The planar transformer assembly of claim 9 wherein the second spiral winding is a secondary winding all turns of which surround a region within which all turns of the subwindings of the primary windings are disposed. 11. The planar transformer assembly of claim 10 wherein the Sublayers are laminated together to form a multilayer printed circuit board, the planar transformer assembly including a primary current supply circuit disposed on the printed circuit board and connected to a first terminal of the primary winding, and also including a switching circuit disposed on the printed circuit board and connected to a second terminal of the primary winding. 12. The planar transformer assembly of claim 11 wherein the primary supply circuit supplies a relatively low first frequency rectified line voltage to the first terminal of the primary winding and the switching circuit couples and decouples the second terminal of the primary winding to a current return path at a relatively high second frequency equal to a resonant frequency of a primary winding circuit including a flyback capacitor, the second frequency being much greater than the first frequency. 13. The planar transformer assembly of claim 12 wherein the first frequency is approximately 60 hertz and the second frequency is approximately 500 kilohertz to one megahertz. 14. The planar transformer assembly of claim 12 wherein the information controls the switching circuit causing it to adjust the amount of time during which the second terminal of the primary winding is decoupled from the current return path in accordance with the amount of current loading of the Secondary winding by the secondary load circuit so as to ensure Zero-voltage switching of the primary winding despite changes in inductance of the primary winding caused by variations in the current loading of the secondary wind ing, thereby reducing noise generation of the planar trans former assembly. 15. The planar transformer assembly of claim 11 wherein the first terminal of the primary winding is connected to a first subwinding thereof, and wherein the secondary winding is disposed on a top insulative sublayer adjacent to another insulative sublayer on which the first subwinding is dis posed, and wherein the second terminal of the primary winding is connected to a second subwinding thereof dis posed on a bottom insulative sublayer, whereby the second ary winding is substantially separated from the second subwinding, to thereby reduce electrical field gradients and resulting electromagnetic radiation in the planar transformer assembly The planar transformer assembly of claim 15 wherein the primary winding has a predetermined number of turns in order to achieve a predetermined inductance, and wherein the number of subwindings is selected to allow a diameter of the primary winding to be small enough that all of the predetermined number of turns can be contained within the region surrounded by the turns of the secondary winding. 17. The planar transformer assembly of claim 15 includ ing first and second isolation barrier capacitors adapted to couple information between a secondary load circuit coupled to a terminal of the secondary winding and an input of the switching circuit, wherein conductive plates of each of the first and second isolation barrier capacitors and electrical conductors connected thereto are formed on vari ous laminated insulative layers outside of a magnetic flux path area surrounded by the primary and secondary wind ings. 18. A method of achieving reduced noise generation in a planar transformer assembly including a multilayer printed circuit board having a plurality of insulative layers, the method comprising the steps of: (a) forming a secondary winding by forming a first spiral winding surrounding a flux path area on a surface of a first insulative layer, (b) forming a primary winding having first and second terminals by forming a plurality of subwindings on a plurality of insulative layers, respectively, and connect ing the subwindings in series by means of conductive vias, the first terminal being adapted to receive a supply line voltage, the second terminal being adapted to be coupled to a switching circuit, all turns of the primary winding being contained in a region surrounded by the secondary winding, whereby the primary winding and secondary winding are non-overlapping and thereby reduce capacitive coupling and thereby reduce har monic noise generation during operation of the planar transformer assembly. 19. The method of claim 18 wherein the secondary winding has a predetermined secondary winding inductance, the method including selecting the number of subwindings so that a predetermined number of primary winding turns necessary to produce a predetermined primary winding inductance all can be included in the region surrounded by the secondary winding. 20. The method of claim 18 wherein the first insulative layer is adjacent to a second insulative layer, the method including forming one of the subwindings connected to the first terminal on the second insulative layer, and forming another of the subwindings connected to the second terminal on a third insulative layer, the first and third insulative layer being adjacent to opposite faces of the printed circuit board to thereby separate the secondary winding as much as possible from the second terminal, whereby voltage gradi ents between the primary and secondary windings are reduced and therefore generation of noise due to such gradients is reduced. 21. The method of claim 18 including supplying the line voltage as a rectified line voltage at a relatively low first frequency and operating the switching circuit to couple and decouple the second terminal to a current return path at a relatively high second frequency approximately equal to a resonant frequency of a primary winding circuit to provide improved transformer efficiency and further reduced har monic noise generation.
13 The method of claim 21 including measuring infor mation indicative of an amount of current loading of the secondary winding, coupling that information to the switch ing circuit, and operating the switching circuit in response to the information to adjust an amount of time during which the second terminal of the primary winding is decoupled from the current return path in accordance with the amount of current loading of the secondary winding so as to ensure 12 zero-voltage switching of the primary winding despite changes in inductance of the primary winding due to varia tions in the current loading of the secondary winding, thereby reducing noise generation of the planar transformer assembly.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1
 USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
USOO6177908B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6, 177,908 B1 Kawahata et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2001 (54) SURFACE-MOUNTING TYPE ANTENNA, 5,861,854 * 1/1999 Kawahate et al.... 343/700
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Kelley et al. 54 (75) 73 21) 22 INDUCTIVE COUPLED POWER SYSTEM Inventors: Arthur W. Kelley; William R. Owens, both of Rockford, Ill. Assignee: Sundstrand Corporation, Rockford,
United States Patent (19) Kelley et al. 54 (75) 73 21) 22 INDUCTIVE COUPLED POWER SYSTEM Inventors: Arthur W. Kelley; William R. Owens, both of Rockford, Ill. Assignee: Sundstrand Corporation, Rockford,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
(19) United States US 2015O108945A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0108945 A1 YAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) DEVICE FOR WIRELESS CHARGING (52) U.S. Cl. CIRCUIT
United States Patent (19) Nilssen
 United States Patent (19) Nilssen (4) HIGH-EFFICIENCY SINGLE-ENDED INVERTER CRCUIT 76) Inventor: Ole K. Nilssen, Caesar Dr. Rte. 4, Barrington, Ill. 60010 21 Appl. No.: 33,33 (22) Filed: Apr. 2, 1979 (1)
United States Patent (19) Nilssen (4) HIGH-EFFICIENCY SINGLE-ENDED INVERTER CRCUIT 76) Inventor: Ole K. Nilssen, Caesar Dr. Rte. 4, Barrington, Ill. 60010 21 Appl. No.: 33,33 (22) Filed: Apr. 2, 1979 (1)
Si,"Sir, sculptor. Sinitialising:
 (19) United States US 20090097281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0097281 A1 LIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2009 (54) LEAKAGE-INDUCTANCE ENERGY Publication Classification RECYCLING
(19) United States US 20090097281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0097281 A1 LIN (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 16, 2009 (54) LEAKAGE-INDUCTANCE ENERGY Publication Classification RECYCLING
II I III. United States Patent (19) Johnson, Jr. 73 Assignee: Exide Electronics Corporation,
 United States Patent (19) Johnson, Jr. (54) ISOLATED GATE DRIVE (75) Inventor: Robert W. Johnson, Jr., Raleigh, N.C. 73 Assignee: Exide Electronics Corporation, Raleigh, N.C. (21) Appl. No.: 39,932 22
United States Patent (19) Johnson, Jr. (54) ISOLATED GATE DRIVE (75) Inventor: Robert W. Johnson, Jr., Raleigh, N.C. 73 Assignee: Exide Electronics Corporation, Raleigh, N.C. (21) Appl. No.: 39,932 22
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
USOO9304615B2 (12) United States Patent Katsurahira (54) CAPACITIVE STYLUS PEN HAVING A TRANSFORMER FOR BOOSTING ASIGNAL (71) Applicant: Wacom Co., Ltd., Saitama (JP) (72) Inventor: Yuji Katsurahira, Saitama
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Mongoven et al. (54) 75 73) 21 22 (51) (52) 58) 56 POWER CRCUT FOR SERIES CONNECTED LOADS Inventors: Michael A. Mongoven, Oak Park; James P. McGee, Chicago, both of 1. Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Mongoven et al. (54) 75 73) 21 22 (51) (52) 58) 56 POWER CRCUT FOR SERIES CONNECTED LOADS Inventors: Michael A. Mongoven, Oak Park; James P. McGee, Chicago, both of 1. Assignee:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,770,955 B1
 USOO6770955B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Coccioli et al. () Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 2004 (54) SHIELDED ANTENNA INA 6,265,774 B1 * 7/2001 Sholley et al.... 7/728 SEMCONDUCTOR PACKAGE 6,282,095
USOO6770955B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Coccioli et al. () Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 2004 (54) SHIELDED ANTENNA INA 6,265,774 B1 * 7/2001 Sholley et al.... 7/728 SEMCONDUCTOR PACKAGE 6,282,095
United States Patent (19) Lee
 United States Patent (19) Lee (54) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT FOR DRIVING MAGNETRON 75 Inventor: Kyong-Keun Lee, Suwon, Rep. of Korea 73) Assignee: Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Suweon City, Rep. of Korea (21)
United States Patent (19) Lee (54) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT FOR DRIVING MAGNETRON 75 Inventor: Kyong-Keun Lee, Suwon, Rep. of Korea 73) Assignee: Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Suweon City, Rep. of Korea (21)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Kowalewski (54) RADIO FREQUENCY SWITCH EMPLOYING REED SWITCHES AND A QUARTER WAVE LINE 75) inventor: Rolf E. Kowalewski, Palatine, Ill. (73) Assignee: Motorola, Inc., Franklin
United States Patent (19) Kowalewski (54) RADIO FREQUENCY SWITCH EMPLOYING REED SWITCHES AND A QUARTER WAVE LINE 75) inventor: Rolf E. Kowalewski, Palatine, Ill. (73) Assignee: Motorola, Inc., Franklin
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O134516A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Du (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) DUAL BAND SLEEVE ANTENNA (52) U.S. Cl.... 3437790 (75) Inventor: Xin Du, Schaumburg,
(19) United States US 2005O134516A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Du (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) DUAL BAND SLEEVE ANTENNA (52) U.S. Cl.... 3437790 (75) Inventor: Xin Du, Schaumburg,
March 31, 1970 G. c. wilburn ET AL 3,504,318
 March 31, 1970 G. c. wilburn ET AL THREE-PHASE TRANSFORMER WITH FOUR LEGGED MAGNETIC CORE ( Nov, 1967 2. Sheets-Sheet l Original File W TO SOURCE OF ALTERNATING POTENTIAL WITNESSES i INVENTORS Gorlington
March 31, 1970 G. c. wilburn ET AL THREE-PHASE TRANSFORMER WITH FOUR LEGGED MAGNETIC CORE ( Nov, 1967 2. Sheets-Sheet l Original File W TO SOURCE OF ALTERNATING POTENTIAL WITNESSES i INVENTORS Gorlington
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160090275A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0090275 A1 Piech et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2016 (54) WIRELESS POWER SUPPLY FOR SELF-PROPELLED ELEVATOR
(19) United States US 20160090275A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0090275 A1 Piech et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2016 (54) WIRELESS POWER SUPPLY FOR SELF-PROPELLED ELEVATOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0021611A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021611 A1 Onizuka et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) BUS BAR STRUCTURE Related U.S. Application Data
US 2001 0021611A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0021611 A1 Onizuka et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 13, 2001 (54) BUS BAR STRUCTURE Related U.S. Application Data
Schaeff, LLP. 22 Filed: Nov. 2, 1998 (51) Int. Cl."... B21D 51/ U.S. Cl... 72/329; 72/ Field of Search... 72/327, 328, 329, 72/348
 United States Patent Turner et al. 19 USOO607.9249A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 27, 2000 54 METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR FORMING A BEADED CAN END 75 Inventors: Stephen B. Turner, Kettering;
United States Patent Turner et al. 19 USOO607.9249A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 27, 2000 54 METHODS AND APPARATUS FOR FORMING A BEADED CAN END 75 Inventors: Stephen B. Turner, Kettering;
/ 7. 2 LOWER CASE. (12) United States Patent US 6,856,819 B2. Feb. 15, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: 5 PARASITIC ELEMENT
 (12) United States Patent toh USOO6856819B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2005 (54) PORTABLE WIRELESS UNIT (75) Inventor: Ryoh Itoh, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: NEC Corporation, Tokyo (JP)
(12) United States Patent toh USOO6856819B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2005 (54) PORTABLE WIRELESS UNIT (75) Inventor: Ryoh Itoh, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: NEC Corporation, Tokyo (JP)
(51) Int. Cl... HoH 316 trolling a state of conduction of AC current between the
 USOO58599A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,8,599 ROSenbaum () Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54 GROUND FAULT CIRCUIT INTERRUPTER 57 ABSTRACT SYSTEM WITH UNCOMMITTED CONTACTS A ground fault
USOO58599A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,8,599 ROSenbaum () Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 1998 54 GROUND FAULT CIRCUIT INTERRUPTER 57 ABSTRACT SYSTEM WITH UNCOMMITTED CONTACTS A ground fault
A///X 2. N N-14. NetNNNNNNN N. / Et EY / E \ \ (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1. (19) United States
 (19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(19) United States US 20070170506A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0170506 A1 Onogi et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 26, 2007 (54) SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE (75) Inventors: Tomohide Onogi,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7768461 B2 (12) United States Patent Cheng et al. (54) ANTENNA DEVICE WITH INSERT-MOLDED ANTENNA PATTERN (75) Inventors: Yu-Chiang Cheng, Taipei (TW); Ping-Cheng Chang, Chaozhou Town (TW); Cheng-Zing
USOO7768461 B2 (12) United States Patent Cheng et al. (54) ANTENNA DEVICE WITH INSERT-MOLDED ANTENNA PATTERN (75) Inventors: Yu-Chiang Cheng, Taipei (TW); Ping-Cheng Chang, Chaozhou Town (TW); Cheng-Zing
III. United States Patent (19) Balakrishnan. 11 Patent Number: 5,469, Date of Patent: Nov. 21, 1995
 United States Patent (19) Balakrishnan (54) (75) (73) 21 22 60) (51) (52) 58) (56) PLASTIC QUAD-PACKAGED SWITCHED-MODE INTEGRATED CIRCUIT WITH INTEGRATED TRANSFORMER WINDINGS AND MOULDINGS FOR TRANSFORMER
United States Patent (19) Balakrishnan (54) (75) (73) 21 22 60) (51) (52) 58) (56) PLASTIC QUAD-PACKAGED SWITCHED-MODE INTEGRATED CIRCUIT WITH INTEGRATED TRANSFORMER WINDINGS AND MOULDINGS FOR TRANSFORMER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 US 201502272O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0227202 A1 BACKMAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
US 201502272O2A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0227202 A1 BACKMAN et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 13, 2015 (54) APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Publication Classification
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,804,867. Leighton et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 8, 1998
 USOO5804867A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,804,867 Leighton et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 8, 1998 54) THERMALLY BALANCED RADIO 5,107,326 4/1992 Hargasser... 257/579 FREQUENCY POWER TRANSISTOR
USOO5804867A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,804,867 Leighton et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 8, 1998 54) THERMALLY BALANCED RADIO 5,107,326 4/1992 Hargasser... 257/579 FREQUENCY POWER TRANSISTOR
Oct. 30, 1956 A. L. MUNZG 2,769,169 DIPOLE IMPEDANCE MATCHING DEVICE. 7W/-AAMMa. 7aawaaaaaay NSNNNN. r 2. a ava/7 Arroa Me
 Oct. 30, 1956 A. L. MUNZG DIPOLE IMPEDANCE MATCHING DEVICE Filed March 22, 1952 3. Sheets-Sheet l 7W/-AAMMa. 7aawaaaaaay NSNNNN r 2 a ava/7 Arroa Me Oct. 30, 1956 A. L. MUNZIG DIPOLE IMPEDANCE MATCHING
Oct. 30, 1956 A. L. MUNZG DIPOLE IMPEDANCE MATCHING DEVICE Filed March 22, 1952 3. Sheets-Sheet l 7W/-AAMMa. 7aawaaaaaay NSNNNN r 2 a ava/7 Arroa Me Oct. 30, 1956 A. L. MUNZIG DIPOLE IMPEDANCE MATCHING
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,673,489 Robel 45) Date of Patent: Oct. 7, 1997
 III USOO5673489A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,673,489 Robel 45) Date of Patent: Oct. 7, 1997 54 GRIDDED MEASUREMENT SYSTEM FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS CONSTRUCTION MATER ALS 529509 6/1955
III USOO5673489A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,673,489 Robel 45) Date of Patent: Oct. 7, 1997 54 GRIDDED MEASUREMENT SYSTEM FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS CONSTRUCTION MATER ALS 529509 6/1955
United States Patent Patent Number: 5,683,539 Qian et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997
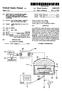 USOO5683539A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: Qian et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997 54 NDUCTIVELY COUPLED RF PLASMA 5,458,732 10/1995 Butler et al.... 216/61 REACTORWTH FLOATING COL 5,525,159
USOO5683539A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: Qian et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 4, 1997 54 NDUCTIVELY COUPLED RF PLASMA 5,458,732 10/1995 Butler et al.... 216/61 REACTORWTH FLOATING COL 5,525,159
Spring connection device and assembly in a jacquard harness
 Thursday, December 27, 2001 United States Patent: 6,302,154 Page: 1 ( 6 of 266 ) United States Patent 6,302,154 Bassi, et al. October 16, 2001 Spring connection device and assembly in a jacquard harness
Thursday, December 27, 2001 United States Patent: 6,302,154 Page: 1 ( 6 of 266 ) United States Patent 6,302,154 Bassi, et al. October 16, 2001 Spring connection device and assembly in a jacquard harness
United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822
 34.3a700 MS AU 26 EX l9/78 OR 4 gl30,822 United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822 Conroy Dec. 19, 1978 l2/ - (4) S A FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (7 Inventor: Peter J. Conroy, Scottsdale, Ariz. 10083 9/193
34.3a700 MS AU 26 EX l9/78 OR 4 gl30,822 United States Patent (19) (11) 4,130,822 Conroy Dec. 19, 1978 l2/ - (4) S A FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (7 Inventor: Peter J. Conroy, Scottsdale, Ariz. 10083 9/193
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,564,782 B2. Kimura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2017
 USO09564782B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kimura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2017 (54) WINDING, WINDING METHOD, AND (56) References Cited AUTOMOTIVE ROTATING ELECTRIC MACHINE U.S.
USO09564782B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Kimura et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 7, 2017 (54) WINDING, WINDING METHOD, AND (56) References Cited AUTOMOTIVE ROTATING ELECTRIC MACHINE U.S.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Schwab et al. US006335619B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR COMPRISING ARESONANT OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT RESPONDING TO CHANGES IN
(12) United States Patent Schwab et al. US006335619B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) INDUCTIVE PROXIMITY SENSOR COMPRISING ARESONANT OSCILLATORY CIRCUIT RESPONDING TO CHANGES IN
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent US007.961391 B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7.961,391 B2 Hua (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 14, 2011 (54) FREE SPACE ISOLATOR OPTICAL ELEMENT FIXTURE (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
(19) United States US 2005OO17592A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Fukushima (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 27, 2005 (54) ROTARY ELECTRIC MACHINE HAVING ARMATURE WINDING CONNECTED IN DELTA-STAR
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Takekuma USOO6850001B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (75) Inventor: Akira Takekuma, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: Agilent Technologies,
(12) United States Patent Takekuma USOO6850001B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) LIGHT EMITTING DIODE (75) Inventor: Akira Takekuma, Tokyo (JP) (73) Assignee: Agilent Technologies,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2
 USOO6543599B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2 Jasinetzky (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) STEP FOR ESCALATORS 5,810,148 A * 9/1998 Schoeneweiss... 198/333 6,398,003 B1
USOO6543599B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,543,599 B2 Jasinetzky (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2003 (54) STEP FOR ESCALATORS 5,810,148 A * 9/1998 Schoeneweiss... 198/333 6,398,003 B1
United States Patent (19) Archibald
 United States Patent (19) Archibald 54 ELECTROSURGICAL UNIT 75 Inventor: G. Kent Archibald, White Bear Lake, Minn. 73 Assignee: Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company, Saint Paul, Minn. (21) Appl.
United States Patent (19) Archibald 54 ELECTROSURGICAL UNIT 75 Inventor: G. Kent Archibald, White Bear Lake, Minn. 73 Assignee: Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company, Saint Paul, Minn. (21) Appl.
United States Patent (19) Rousseau et al.
 United States Patent (19) Rousseau et al. USOO593.683OA 11 Patent Number: 5,936,830 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 1999 54). IGNITION EXCITER FOR A GASTURBINE 58 Field of Search... 361/253, 256, ENGINE
United States Patent (19) Rousseau et al. USOO593.683OA 11 Patent Number: 5,936,830 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 10, 1999 54). IGNITION EXCITER FOR A GASTURBINE 58 Field of Search... 361/253, 256, ENGINE
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109. Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, a. Assistant Examiner-Alan B.
 H HHHHHHH US005299.109A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109 Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 1994 (54) LED EXIT LIGHT FIXTURE 5,138,782 8/1992 Mizobe... 40/219 75) Inventor: Daniel
H HHHHHHH US005299.109A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,299,109 Grondal. (45. Date of Patent: Mar. 29, 1994 (54) LED EXIT LIGHT FIXTURE 5,138,782 8/1992 Mizobe... 40/219 75) Inventor: Daniel
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 0004 175A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0004175 A1 Kelleher (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 21, 2001 (54) GENERATOR STATOR SLOT WEDGE Related U.S. Application
US 2001 0004 175A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0004175 A1 Kelleher (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 21, 2001 (54) GENERATOR STATOR SLOT WEDGE Related U.S. Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 20030085640A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085640 A1 Chan (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) FOLDABLE CABINET Publication Classification (76) Inventor:
US 20030085640A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085640 A1 Chan (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) FOLDABLE CABINET Publication Classification (76) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1
 USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
USOO6337722B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,337,722 B1 Ha () Date of Patent: *Jan. 8, 2002 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY PANEL HAVING ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE 5,195,010 A 5,220,443 A * 3/1993
(12) United States Patent
 US0092.59087B1 (12) United States Patent Hsiao (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.259,087 B1 Feb. 16, 2016 (54) FRONT CONNECTING DEVICE OF CONCEALED SLIDE (71) Applicant: Sun Chain Trading Co.,
US0092.59087B1 (12) United States Patent Hsiao (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.259,087 B1 Feb. 16, 2016 (54) FRONT CONNECTING DEVICE OF CONCEALED SLIDE (71) Applicant: Sun Chain Trading Co.,
United States Patent 19) 11 Patent Number: 5,442,436 Lawson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 1995
 I () US005442436A United States Patent 19) 11 Patent Number: Lawson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 1995 54 REFLECTIVE COLLIMATOR 4,109,304 8/1978 Khvalovsky et al.... 362/259 4,196,461 4/1980 Geary......
I () US005442436A United States Patent 19) 11 Patent Number: Lawson (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 1995 54 REFLECTIVE COLLIMATOR 4,109,304 8/1978 Khvalovsky et al.... 362/259 4,196,461 4/1980 Geary......
United States Patent (19) Shahan
 United States Patent (19) Shahan 54, HEAVY DUTY SHACKLE 75 Inventor: James B. Shahan, Tulsa, Okla. (73) Assignee: American Hoist & Derrick Company, Tulsa, Okla. (21) Appl. No.: 739,056 22 Filed: Nov. 5,
United States Patent (19) Shahan 54, HEAVY DUTY SHACKLE 75 Inventor: James B. Shahan, Tulsa, Okla. (73) Assignee: American Hoist & Derrick Company, Tulsa, Okla. (21) Appl. No.: 739,056 22 Filed: Nov. 5,
Kiuchi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2011
 (12) United States Patent US007902952B2 (10) Patent No.: Kiuchi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2011 (54) SHARED REACTOR TRANSFORMER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Hiroshi Kiuchi, Chiyoda-ku
(12) United States Patent US007902952B2 (10) Patent No.: Kiuchi et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2011 (54) SHARED REACTOR TRANSFORMER (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Hiroshi Kiuchi, Chiyoda-ku
- I 12 \ C LC2 N28. United States Patent (19) Swanson et al. EMITTERS (22) 11 Patent Number: 5,008,594 (45) Date of Patent: Apr.
 United States Patent (19) Swanson et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 1991 54 (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) SELF-BALANCNG CIRCUT FOR CONVECTION AIR ONZERS Inventors: Assignee: Appl.
United States Patent (19) Swanson et al. 11 Patent Number: () Date of Patent: Apr. 16, 1991 54 (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) SELF-BALANCNG CIRCUT FOR CONVECTION AIR ONZERS Inventors: Assignee: Appl.
rectifying smoothing circuit
 USOO648671.4B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ushida et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) HALF-BRIDGE INVERTER CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Atsuya Ushida, Oizumi-machi
USOO648671.4B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ushida et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 26, 2002 (54) HALF-BRIDGE INVERTER CIRCUIT (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Atsuya Ushida, Oizumi-machi
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,452,105 B2. Badii et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 17, 2002
 USOO64521 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Badii et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 17, 2002 (54) COAXIAL CABLE ASSEMBLY WITH A 3,970.969 A * 7/1976 Sirel et al.... 333/12 DISCONTINUOUS OUTERJACKET
USOO64521 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Badii et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 17, 2002 (54) COAXIAL CABLE ASSEMBLY WITH A 3,970.969 A * 7/1976 Sirel et al.... 333/12 DISCONTINUOUS OUTERJACKET
United States Patent (19)
 US006002389A 11 Patent Number: 6,002,389 Kasser (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 14, 1999 United States Patent (19) 54) TOUCH AND PRESSURE SENSING METHOD 5,398,046 3/1995 Szegedi et al.... 345/174 AND APPARATUS
US006002389A 11 Patent Number: 6,002,389 Kasser (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 14, 1999 United States Patent (19) 54) TOUCH AND PRESSURE SENSING METHOD 5,398,046 3/1995 Szegedi et al.... 345/174 AND APPARATUS
N St. Els"E"" (4) Atomy, Agent, or Firm Steina Brunda Garred &
 USOO6536045B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wilson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2003 (54) TEAR-OFF OPTICAL STACK HAVING 4,716,601. A 1/1988 McNeal... 2/434 PERPHERAL SEAL MOUNT 5,420,649
USOO6536045B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Wilson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2003 (54) TEAR-OFF OPTICAL STACK HAVING 4,716,601. A 1/1988 McNeal... 2/434 PERPHERAL SEAL MOUNT 5,420,649
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014.0062180A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0062180 A1 Demmerle et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH-VOLTAGE INTERLOCK LOOP (52) U.S. Cl. ("HVIL") SWITCH
(19) United States US 2014.0062180A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0062180 A1 Demmerle et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) HIGH-VOLTAGE INTERLOCK LOOP (52) U.S. Cl. ("HVIL") SWITCH
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) 11 US006023898A Patent Number: JOSey (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2000 54 METAL FRAME BUILDING 4,050,498 9/1977 Lucchetti... 52?657 X CONSTRUCTION 4,283,892 8/1981 Brown. 4,588,156
United States Patent (19) 11 US006023898A Patent Number: JOSey (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 15, 2000 54 METAL FRAME BUILDING 4,050,498 9/1977 Lucchetti... 52?657 X CONSTRUCTION 4,283,892 8/1981 Brown. 4,588,156
United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 LLP 57)
 III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
III US005621555A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,621,555 Park (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 15, 1997 (54) LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY HAVING 5,331,447 7/1994 Someya et al.... 359/59 REDUNDANT PXEL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1
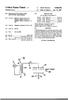
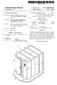 US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
US007458305B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.458,305 B1 Horlander et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 2, 2008 (54) MODULAR SAFE ROOM (58) Field of Classification Search... 89/36.01, 89/36.02,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,752,496 B2
 USOO6752496 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,752,496 B2 Conner (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 22, 2004 (54) PLASTIC FOLDING AND TELESCOPING 5,929.966 A * 7/1999 Conner... 351/118 EYEGLASS
USOO6752496 B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,752,496 B2 Conner (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 22, 2004 (54) PLASTIC FOLDING AND TELESCOPING 5,929.966 A * 7/1999 Conner... 351/118 EYEGLASS
58 Field of Search... 53/443, 448, 176, Spaced relation along the membrane and, portions of a
 USOO5918738A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Leistner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) TEE-NUT STRIP WITH EDGE MEMBRANES 4,955,476 9/1990 Nakata et al.... 206/346 5,762,190 6/1998 Leistner...
USOO5918738A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Leistner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 6, 1999 54) TEE-NUT STRIP WITH EDGE MEMBRANES 4,955,476 9/1990 Nakata et al.... 206/346 5,762,190 6/1998 Leistner...
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007124695B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,124.695 B2 Buechler (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2006 (54) MODULAR SHELVING SYSTEM 4,635,564 A 1/1987 Baxter 4,685,576 A 8, 1987 Hobson (76)
(12) United States Patent US007124695B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,124.695 B2 Buechler (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 24, 2006 (54) MODULAR SHELVING SYSTEM 4,635,564 A 1/1987 Baxter 4,685,576 A 8, 1987 Hobson (76)
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9463468B2 () Patent No.: Hiley (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2016 (54) COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE RF BO3B 5/08 (2006.01) GENERATOR USING A SELF-RESONANT GOIN 27/62 (2006.01) INDUCTOR
(12) United States Patent USOO9463468B2 () Patent No.: Hiley (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 11, 2016 (54) COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE RF BO3B 5/08 (2006.01) GENERATOR USING A SELF-RESONANT GOIN 27/62 (2006.01) INDUCTOR
United States Patent (19) Sun
 United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
United States Patent (19) Sun 54 INFORMATION READINGAPPARATUS HAVING A CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR 75 Inventor: Chung-Yueh Sun, Tainan, Taiwan 73 Assignee: Mustek Systems, Inc., Hsinchu, Taiwan 21 Appl. No. 916,941
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,959,246 Gretz (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 28, 1999
 USOO5959246A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,959,246 Gretz (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 28, 1999 54 ELECTRIC BOX EXTENDER AND 3,770,873 11/1973 Brown... 174/58 SUPPLEMENTAL PART 4,044,908 8/1977
USOO5959246A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,959,246 Gretz (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 28, 1999 54 ELECTRIC BOX EXTENDER AND 3,770,873 11/1973 Brown... 174/58 SUPPLEMENTAL PART 4,044,908 8/1977
United States Patent (19) Onuki et al.
 United States Patent (19) Onuki et al. 54). IGNITION APPARATUS FOR AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE 75 Inventors: Hiroshi Onuki; Takashi Ito, both of Hitachinaka, Katsuaki Fukatsu, Naka-gun; Ryoichi Kobayashi,
United States Patent (19) Onuki et al. 54). IGNITION APPARATUS FOR AN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE 75 Inventors: Hiroshi Onuki; Takashi Ito, both of Hitachinaka, Katsuaki Fukatsu, Naka-gun; Ryoichi Kobayashi,
United States Patent (19) Schnetzka et al.
 United States Patent (19) Schnetzka et al. 54 (75) GATE DRIVE CIRCUIT FOR AN SCR Inventors: Harold R. Schnetzka; Dean K. Norbeck; Donald L. Tollinger, all of York, Pa. Assignee: York International Corporation,
United States Patent (19) Schnetzka et al. 54 (75) GATE DRIVE CIRCUIT FOR AN SCR Inventors: Harold R. Schnetzka; Dean K. Norbeck; Donald L. Tollinger, all of York, Pa. Assignee: York International Corporation,
Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner. Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green
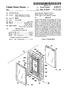 III United States Patent (19) 11) US005230172A Patent Number: 5,230,172 Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 1993 54 PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner o Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green 76)
III United States Patent (19) 11) US005230172A Patent Number: 5,230,172 Hsu (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 1993 54 PICTURE FRAME Primary Examiner-Kenneth J. Dorner o Assistant Examiner-Brian K. Green 76)
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
(12) United States Patent Suzuki et al. USOO6385294B2 (10) Patent No.: US 6,385,294 B2 (45) Date of Patent: May 7, 2002 (54) X-RAY TUBE (75) Inventors: Kenji Suzuki; Tadaoki Matsushita; Tutomu Inazuru,
324/334, 232, ; 340/551 producing multiple detection fields. In one embodiment,
 USOO5969528A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,969,528 Weaver (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 1999 54) DUAL FIELD METAL DETECTOR 4,605,898 8/1986 Aittoniemi et al.... 324/232 4,686,471 8/1987
USOO5969528A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,969,528 Weaver (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 19, 1999 54) DUAL FIELD METAL DETECTOR 4,605,898 8/1986 Aittoniemi et al.... 324/232 4,686,471 8/1987
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0043209A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043209 A1 Zhu (43) Pub. Date: (54) COIL DECOUPLING FORAN RF COIL (52) U.S. Cl.... 324/322 ARRAY (57) ABSTRACT
(19) United States US 2011 0043209A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0043209 A1 Zhu (43) Pub. Date: (54) COIL DECOUPLING FORAN RF COIL (52) U.S. Cl.... 324/322 ARRAY (57) ABSTRACT
52 U.S. Cl /587, 206/592: 229/87.02 planar Surfaces on which imprinting can appear. The molded
 USOO5806683A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Gale (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 15, 1998 54 WRAPPED PACKAGE AND METHOD USING Primary Examiner Paul T. Sewell MOLDED FIBER INNER STRUCTURE ASSistant
USOO5806683A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Gale (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 15, 1998 54 WRAPPED PACKAGE AND METHOD USING Primary Examiner Paul T. Sewell MOLDED FIBER INNER STRUCTURE ASSistant
(12) United States Patent
 US007098655B2 (12) United States Patent Yamada et al. (54) EDDY-CURRENT SENSOR WITH PLANAR MEANDER EXCITING COIL AND SPIN VALVE MAGNETORESISTIVE ELEMENT FOR NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING (75) Inventors: Sotoshi
US007098655B2 (12) United States Patent Yamada et al. (54) EDDY-CURRENT SENSOR WITH PLANAR MEANDER EXCITING COIL AND SPIN VALVE MAGNETORESISTIVE ELEMENT FOR NONDESTRUCTIVE TESTING (75) Inventors: Sotoshi
III IIII III. United States Patent (19) Cheng. 11) Patent Number: 5,529,288 (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 25, 1996
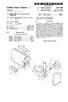 United States Patent (19) Cheng 54 STRUCTURE OF A HANDRAIL FOR A STARCASE 76 Inventor: Lin Cheng-I, P.O. Box 82-144, Taipei, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 284,223 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51 Int. Cl.... E04F 11/18
United States Patent (19) Cheng 54 STRUCTURE OF A HANDRAIL FOR A STARCASE 76 Inventor: Lin Cheng-I, P.O. Box 82-144, Taipei, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 284,223 22 Filed: Aug. 2, 1994 (51 Int. Cl.... E04F 11/18
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O151875A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0151875 A1 Lehr et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) LAMINATE INLAY PROCESS FOR SPORTS BOARDS (76) Inventors:
(19) United States US 2004O151875A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0151875 A1 Lehr et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) LAMINATE INLAY PROCESS FOR SPORTS BOARDS (76) Inventors:
FORM 2 THE PATENTS ACT, (39 of 1970) & The Patent Rules, 2003 COMPLETE SPECIFICATION
 FORM 2 THE PATENTS ACT, 1970 (39 of 1970) & The Patent Rules, 2003 COMPLETE SPECIFICATION 1. TITLE OF THE INVENTION: CURRENT TRANSFORMER 2. APPLICANTS: Name: SEARI ELECTRIC TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. Nationality:
FORM 2 THE PATENTS ACT, 1970 (39 of 1970) & The Patent Rules, 2003 COMPLETE SPECIFICATION 1. TITLE OF THE INVENTION: CURRENT TRANSFORMER 2. APPLICANTS: Name: SEARI ELECTRIC TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD. Nationality:
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,777,539 Folker et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998
 III USOO5777539A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,777,539 Folker et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998 54 INDUCTOR USING MULTILAYERED 5,521,573 5/1996 Inoh et al.... 336,200 PRINTED CIRCUIT
III USOO5777539A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,777,539 Folker et al. 45 Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998 54 INDUCTOR USING MULTILAYERED 5,521,573 5/1996 Inoh et al.... 336,200 PRINTED CIRCUIT
July 28, 1959 S. E. LOVER 2,896,49 1
 July 28, 1959 S. E. LOVER 2,896,49 1 MAGNETIC PICKUP FOR STRINGED MUSICAL INSTRUMENT Filed June 22, 1955 2 Sheets-Sheet 1 July 28, 1959 S. E. LOVER 2,896,49 1 MAGNETIC PICKUP FOi! STRING93 MUSICAL INSTRUMENT
July 28, 1959 S. E. LOVER 2,896,49 1 MAGNETIC PICKUP FOR STRINGED MUSICAL INSTRUMENT Filed June 22, 1955 2 Sheets-Sheet 1 July 28, 1959 S. E. LOVER 2,896,49 1 MAGNETIC PICKUP FOi! STRING93 MUSICAL INSTRUMENT
11) Patent Number: 5,323,091 Morris (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 21, STARTING SOURCE FOR ARC DISCHARGE 4,041,352 8/1977 McNeill et al...
 IIIHIIII USOO5323091A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,323,091 Morris (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 21, 1994 54 STARTING SOURCE FOR ARC DISCHARGE 4,041,352 8/1977 McNeill et al.... 315/248 LAMPS
IIIHIIII USOO5323091A United States Patent (19) 11) Patent Number: 5,323,091 Morris (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 21, 1994 54 STARTING SOURCE FOR ARC DISCHARGE 4,041,352 8/1977 McNeill et al.... 315/248 LAMPS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,848,291 B1
 USOO684.8291B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,848,291 B1 Johnson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) PRESS BRAKE TOOL AND TOOL HOLDER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
USOO684.8291B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,848,291 B1 Johnson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 1, 2005 (54) PRESS BRAKE TOOL AND TOOL HOLDER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Lin
 United States Patent (19) Lin 11) 45) Dec. 22, 1981 54) (76) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) BUILDING BLOCK SET Inventor: Wen-Ping Lin, 30, Chien-Yung St., Taichung, Taiwan Appl. No.: 187,618 Filed: Sep. 15,
United States Patent (19) Lin 11) 45) Dec. 22, 1981 54) (76) (21) 22 (51) (52) (58) (56) BUILDING BLOCK SET Inventor: Wen-Ping Lin, 30, Chien-Yung St., Taichung, Taiwan Appl. No.: 187,618 Filed: Sep. 15,
TEPZZ 879Z A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0354 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 879Z A_T (11) EP 2 879 023 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.06.1 Bulletin 1/23 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/034 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1419462. (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 879Z A_T (11) EP 2 879 023 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.06.1 Bulletin 1/23 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/034 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1419462. (22) Date of
58) Field of Seash, which is located on the first core leg. The fifth winding,
 US006043569A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Ferguson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 2000 54) ZERO PHASE SEQUENCE CURRENT Primary Examiner Richard T. Elms FILTER APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Attorney,
US006043569A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Ferguson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 28, 2000 54) ZERO PHASE SEQUENCE CURRENT Primary Examiner Richard T. Elms FILTER APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR Attorney,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,512,361 B1
 USOO6512361B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,512,361 B1 Becker (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 28, 2003 (54) 14/42-VOLTAUTOMOTIVE CIRCUIT 5,420.503 5/1995 Beha TESTER 5,517,183 A 5/1996 Bozeman,
USOO6512361B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,512,361 B1 Becker (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 28, 2003 (54) 14/42-VOLTAUTOMOTIVE CIRCUIT 5,420.503 5/1995 Beha TESTER 5,517,183 A 5/1996 Bozeman,
United States Patent 19 Perets
 United States Patent 19 Perets USOO5623875A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,623,875 Apr. 29, 1997 54 MULTI-COLOR AND EASY TO ASSEMBLE AUTOMATIC RUBBER STAMP 76 Inventor: Mishel Perets, clo M. Perets
United States Patent 19 Perets USOO5623875A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,623,875 Apr. 29, 1997 54 MULTI-COLOR AND EASY TO ASSEMBLE AUTOMATIC RUBBER STAMP 76 Inventor: Mishel Perets, clo M. Perets
United States Patent [19]
![United States Patent [19] United States Patent [19]](/thumbs/89/100382477.jpg) United States Patent [19] Simmonds et al. [54] APPARATUS FOR REDUCING LOW FREQUENCY NOISE IN DC BIASED SQUIDS [75] Inventors: Michael B. Simmonds, Del Mar; Robin P. Giffard, Palo Alto, both of Calif. [73]
United States Patent [19] Simmonds et al. [54] APPARATUS FOR REDUCING LOW FREQUENCY NOISE IN DC BIASED SQUIDS [75] Inventors: Michael B. Simmonds, Del Mar; Robin P. Giffard, Palo Alto, both of Calif. [73]
USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,272,450 Wisherd (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1993
 O HIHHHHHHHHHHHHIII USOO5272450A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,272,450 Wisherd (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1993 (54) DCFEED NETWORK FOR WIDEBANDRF POWER AMPLIFIER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS
O HIHHHHHHHHHHHHIII USOO5272450A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,272,450 Wisherd (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 1993 (54) DCFEED NETWORK FOR WIDEBANDRF POWER AMPLIFIER FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2
 USOO6663057B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2 Garelick et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADJUSTABLE PEDESTAL FOR BOAT 5,297.849 A * 3/1994 Chancellor... 297/344.
USOO6663057B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,663,057 B2 Garelick et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 16, 2003 (54) ADJUSTABLE PEDESTAL FOR BOAT 5,297.849 A * 3/1994 Chancellor... 297/344.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1
 USOO6386952B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1 White (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) SINGLE STATION BLADE SHARPENING 2,692.457 A 10/1954 Bindszus METHOD AND APPARATUS 2,709,874
USOO6386952B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,386,952 B1 White (45) Date of Patent: May 14, 2002 (54) SINGLE STATION BLADE SHARPENING 2,692.457 A 10/1954 Bindszus METHOD AND APPARATUS 2,709,874
United States Patent (19) Harnden
 United States Patent (19) Harnden 54) 75 (73) LMITING SHOOT THROUGH CURRENT INA POWER MOSFET HALF-BRIDGE DURING INTRINSIC DODE RECOVERY Inventor: Assignee: James A. Harnden, San Jose, Calif. Siliconix
United States Patent (19) Harnden 54) 75 (73) LMITING SHOOT THROUGH CURRENT INA POWER MOSFET HALF-BRIDGE DURING INTRINSIC DODE RECOVERY Inventor: Assignee: James A. Harnden, San Jose, Calif. Siliconix
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,650,825 B1
 USOO7650825B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 26, 2010 (54) CASE TRIMMER AND CHAMFER TOOL 4.325,282 A 4, 1982 Schaenzer... 86,24 4.385,546 A 5/1983 Lee...
USOO7650825B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lee et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 26, 2010 (54) CASE TRIMMER AND CHAMFER TOOL 4.325,282 A 4, 1982 Schaenzer... 86,24 4.385,546 A 5/1983 Lee...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090249965A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0249965 A1 Hauser (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIT REMOVER (75) Inventor: Lawrence M. Hauser, Auburn, WA (US) Correspondence
(19) United States US 20090249965A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0249965 A1 Hauser (43) Pub. Date: (54) PIT REMOVER (75) Inventor: Lawrence M. Hauser, Auburn, WA (US) Correspondence
6,064,277 A * 5/2000 Gilbert 331/117 R 6,867,658 Bl * 3/2005 Sibrai et al 331/185 6,927,643 B2 * 8/2005 Lazarescu et al. 331/186. * cited by examiner
 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US007274264B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 7,274,264 B2 Gabara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep.25,2007 (54) LOW-POWER-DISSIPATIO
111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US007274264B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 7,274,264 B2 Gabara et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep.25,2007 (54) LOW-POWER-DISSIPATIO
TEPZZ 48A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02M 3/335 ( ) H02M 1/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 48A T (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 3/33 (2006.01) H02M 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1178647.2 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 48A T (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 3/33 (2006.01) H02M 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1178647.2 (22)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Nakayama et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,916,413 Apr. 10, 1990 54 PACKAGE FOR PIEZO-OSCILLATOR (75) Inventors: Iwao Nakayama; Kazushige Ichinose; Hiroyuki Ogiso,
United States Patent (19) Nakayama et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: 4,916,413 Apr. 10, 1990 54 PACKAGE FOR PIEZO-OSCILLATOR (75) Inventors: Iwao Nakayama; Kazushige Ichinose; Hiroyuki Ogiso,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO695.9667B2 (10) Patent No.: BOrdelOn (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 1, 2005 (54) ANIMAL NAIL TRIMMER (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Lisa Bordelon, St. Petersburg, FL (US)
(12) United States Patent USOO695.9667B2 (10) Patent No.: BOrdelOn (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 1, 2005 (54) ANIMAL NAIL TRIMMER (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Lisa Bordelon, St. Petersburg, FL (US)
( 12 ) United States Patent
 THI NANIULUH TNICI UNTUK US009941606B1 ( 12 ) United States Patent Hashimoto et al. ( 54 ) COAXIAL CABLE CONNECTOR AND METHOD OF USE THEREOF ( 71 ) Applicant : DAI - ICHI SEIKO CO., LTD., Kyoto ( JP )
THI NANIULUH TNICI UNTUK US009941606B1 ( 12 ) United States Patent Hashimoto et al. ( 54 ) COAXIAL CABLE CONNECTOR AND METHOD OF USE THEREOF ( 71 ) Applicant : DAI - ICHI SEIKO CO., LTD., Kyoto ( JP )
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,187,032 B1
 US008187032B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,187,032 B1 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2012 (54) GUIDED MISSILE/LAUNCHER TEST SET (58) Field of Classification Search... 439/76.1.
US008187032B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,187,032 B1 Park et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 29, 2012 (54) GUIDED MISSILE/LAUNCHER TEST SET (58) Field of Classification Search... 439/76.1.
United States Patent (19) Morita et al.
 United States Patent (19) Morita et al. - - - - - 54. TEMPLATE 75 Inventors: Shiro Morita, Sakura; Kazuo Yoshitake, Tokyo, both of Japan 73 Assignee: Yoshitake Seisakujo Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl.
United States Patent (19) Morita et al. - - - - - 54. TEMPLATE 75 Inventors: Shiro Morita, Sakura; Kazuo Yoshitake, Tokyo, both of Japan 73 Assignee: Yoshitake Seisakujo Co., Inc., Tokyo, Japan (21) Appl.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0194836A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0194836A1 Morris et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOLATED FLYBACK CONVERTER WITH (52) U.S. Cl. EFFICIENT LIGHT
(19) United States US 2013 0194836A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0194836A1 Morris et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOLATED FLYBACK CONVERTER WITH (52) U.S. Cl. EFFICIENT LIGHT
IIII. United States Patent 19 Delorme. 11 Patent Number: 5,894,701 45) Date of Patent: Apr. 20, Attorney, Agent, or Firn-Swabey Ogilvy Renault
 United States Patent 19 Delorme 54) WOODEN MODULARPANELING FOR INTERFOR DECORATION 76 Inventor: Claude Delorme, 9141 Pierre Elliott Trudeau, St-Léonard, Québec, Canada, HR 3WA. 21 Appl. No.: 08/910,667
United States Patent 19 Delorme 54) WOODEN MODULARPANELING FOR INTERFOR DECORATION 76 Inventor: Claude Delorme, 9141 Pierre Elliott Trudeau, St-Léonard, Québec, Canada, HR 3WA. 21 Appl. No.: 08/910,667
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0325383A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0325383 A1 Xu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTRON BEAM MELTING AND LASER B23K I5/00 (2006.01) MILLING COMPOSITE
(19) United States US 2016.0325383A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0325383 A1 Xu et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) ELECTRON BEAM MELTING AND LASER B23K I5/00 (2006.01) MILLING COMPOSITE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US008238998B2 (10) Patent No.: Park (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 7, 2012 (54) TAB ELECTRODE 4,653,501 A * 3/1987 Cartmell et al.... 600,392 4,715,382 A * 12/1987 Strand...... 600,392
(12) United States Patent US008238998B2 (10) Patent No.: Park (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 7, 2012 (54) TAB ELECTRODE 4,653,501 A * 3/1987 Cartmell et al.... 600,392 4,715,382 A * 12/1987 Strand...... 600,392
IIH. United States Patent (19) Chen. (11) Patent Number: 5,318,090 (45. Date of Patent: Jun. 7, 1994
 United States Patent (19) Chen 54) ROLLER ASSEMBLY FORVENETIAN BLIND 76 Inventor: Cheng-Hsiung Chen, No. 228, Sec. 2, Chung-Te Rd., Taichung City, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 60,278 22 Filed: May 11, 1993 51)
United States Patent (19) Chen 54) ROLLER ASSEMBLY FORVENETIAN BLIND 76 Inventor: Cheng-Hsiung Chen, No. 228, Sec. 2, Chung-Te Rd., Taichung City, Taiwan 21 Appl. No.: 60,278 22 Filed: May 11, 1993 51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016.0342256A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0342256A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2016 (54) EMBEDDED CAPACITIVE TOUCH DISPLAY (52) U.S. CI.
(19) United States US 2016.0342256A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0342256A1 Zhou et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 24, 2016 (54) EMBEDDED CAPACITIVE TOUCH DISPLAY (52) U.S. CI.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1. Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 (19) United States US 2006OOO1503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0001503 A1 Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (54) MICROSTRIP TO WAVEGUIDE LAUNCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 333/26
(19) United States US 2006OOO1503A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0001503 A1 Stoneham (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 5, 2006 (54) MICROSTRIP TO WAVEGUIDE LAUNCH (52) U.S. Cl.... 333/26
