H01C RESISTORS. Definition statement. References. Limiting references CPC - H01C
|
|
|
- Darlene Simon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 H01C RESISTORS Definition statement This place covers: Passive two-terminal electrical components per se that implement electrical resistance as a circuit element, thereby enabling typically a direct proportion between the current and the voltage across the component's terminals. Non-adjustable metal resistors made of wire or ribbon, per se, e.g. iron-filament ballast resistors, or metallic glasses therefor, coiled, woven or formed as grids. Configurations thereof may include flexible or folding resistors, changes in dimensions or characteristics of the resistive element from one terminal to another, resistors having sinusoidal or zig-zag configurations or arranged for reducing self-induction, capacitance or variation with frequency. Non-adjustable resistors formed as one or more layers or coatings; Non-adjustable resistors made from powdered conducting material or powdered semi-conducting material (excluding loose powder or granular material) with or without insulating material. Resistors whose effective value is varied non-mechanically such as by temperature (thermistors, e.g. exhibiting positive or negative temperature coefficient), voltage (varistors and overvoltage protection resistors) or current (including over-current protection resistors) and having a non-linear behaviour, e.g. typically a sharp change in resistance values upon reaching critical or threshold values of non-mechanical parameters. Compositions and arrangements thereof. Non-adjustable resistors consisting of loose powdered or granular conducting, or powdered or granular semi-conducting material, e.g. coherers or like imperfect resistors for detecting electromagnetic waves; overvoltage protection resistors or arresters. Non-adjustable liquid resistors. Electrical resistors whose effective value is mechanically adjustable, including liquid resistors or adjustable resistors structurally comprising a plurality of resistors, with changing dimensions and/ or forms of the resistors, arrangements of fixed resistors with intervening connector or structurally in combination with switching arrangements. Resistors whose resistance is adjustable by shortcircuiting different amounts of the resistive element, by mechanical pressure or force, by auxiliary driving means, by resistor movement or by action of actuation means, e.g. contacts, said contacts rocking or rolling along resistive element or taps, sliding along resistive element, e.g. moving along a straight path, in an accurate path or along turns of a helical resistive element. Resistors not provided for elsewhere, e.g. structural combinations of resistors excluding impedance networks. Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing resistors adapted for manufacturing resistor chips, for manufacturing resistors with envelope or housing, for winding the resistive element or for coating resistive material on a base, e.g. by thick (including precursor compositions therefor) or thin film techniques (e.g. vapour or chemical deposition, sputtering or flame spraying) by pirolytic processes or by resistor foil bonding; adapted for trimming, for applying terminals or for baking. Details common to two or more main types of devices or processes covered by this subclass, e.g. special adaption for mounting; housings, encapsulations; Arrangements for distinguishing marks (e.g. colour coding), electrostatic or electromagnetic shielding, cooling, heating and ventilating or of current collectors; Terminals or tapping points. Variable resistors, the value of which is changed non-mechanically, e.g. by voltage, current or temperature. Selection of specified materials as dielectric H01B 3/00 1
2 H01C (continued) CPC - H01C Trimming of resistors for integrated circuits Passive two-terminal components without a potential-jump or surface barrier for integrated circuits H01L21/66 H01L 28/00 Resistors with a potential-jump or surface barrier H01L 29/86 Photoresistors and similar semiconductor devices in which radiation controls flow of current through the device Magnetic-field-controlled resistors and similar devices using galvanomagnetic or similar magnetic effects H01L 31/08 H01L 43/08 Bulk negative resistance effect devices H01L 47/00 Apparatus or processes for filling or compressing insulating material in heating element tubes H05B 3/52 Application-oriented references Examples of places where the subject matter of this place is covered when specially adapted, used for a particular purpose, or incorporated in a larger system: Resistance strain gauges for measuring linear expansion or contraction G01B Measuring temperature using resistive elements G01K 7/16 Measuring force or stress by measuring variations in ohmic resistance of solid materials G01L 1/20 Resistors used for electric measuring electrical or magnetic variables G01R 1/203 Thin- or thick-film integrated circuits; Resistors as components of an integrated circuit Impedance networks H01L 27/00 H03H Powder metallurgy B22F Trimming of electrical components B23K 26/351 Layered products Compositions of ceramic materials, e.g. for resistors, varistors and based on zinc oxides Compositions of ceramic materials, e.g. for resistors, thermistors, and based on titanium oxide or titanates Compositions of ceramic materials, e.g. for resistors, thermistors, and based on zirconium oxides or zirconates Compositions of ceramic materials, e.g. for resistors, thermistors, and based on vanadium, niobium, tantalum, molybdenum or tungsten oxides or vanadates, niobates, tantalates, molybdates or tungstates B32B C04B 35/453 C04B 35/46 C04B 35/48 C04B 35/495 Polymeric films or sheets C08J 5/18 Indicating or measuring liquid level, or level of fluent solid material by measuring variations of resistance of resistors due to contact with conductor fluid G01F 23/24 Investigating or analyzing material by investigating resistance G01N 27/04 Arrangements for measuring resistance G01R 27/00 2
3 H01C (continued) CPC - H01C Measuring dielectric properties, e.g. dielectric constants G01R 27/2617 Devices using superconductivity or hyperconductivity H01L 39/00 Solid state devices for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating, or switching without a potential-jump barrier or surface barrier H01L 45/00 Thin- or thick-film solid state devices H01L 49/02 Terminals or tapping points in general H01R Overvoltage arresters using spark gaps H01T 4/00 Emergency protective circuit arrangements responsive to excess current H02H 9/02 Emergency protective circuit arrangements responsive to excess voltage H02H 9/04 Ohmic-resistance heating H05B 3/00 Printed circuits incorporating printed electric components, e.g. printed resistor, capacitor, inductor Printed circuits structurally associated with non-printed electric components H05K 1/16 H05K 1/18 Casings for electrical apparatus in general H05K 5/00 Special rules of classification Variable resistors, the value of which is changed non-mechanically, e.g. by voltage or temperature, are classified in group H01C 7/00. Electrodes and terminals for resistors in main group H01C 7/00 are covered by main group H01C 1/00, more specifically subgroups H01C 1/14 and lower. Glossary of terms In this place, the following terms or expressions are used with the meaning indicated: Thermistor Varistor Adjustable Type of resistor whose resistance varies significantly with temperature, typically as sharp or sudden change, when a threshold temperature value is reached. Also referred as Voltage Dependent Resistor is a resistor that conducts significantly increased current when voltage is excessive. Mechanically adjustable Synonyms and Keywords In patent documents the following expressions/words are often used as synonyms: Varistor Voltage dependent resistor H01C 1/00 Details Definition statement This place covers: Mounting, Supporting Color coding 3
4 H01C 1/00 (continued) CPC - H01C Shielding arrangements Current collectors Terminals Resistor networks H01C 1/012 the base extending along and imparting rigidity or reinforcement to the resistive element (H01C 1/016 takes precedence; the resistive element being formed in two or more coils or loops as a spiral, helical or toroidal winding H01C 3/18, H01C 3/20; the resistive element being formed as one or more layers or coatings on a base H01C 7/00) Compensation for resistor expansion or contraction H01C 1/016 Resistive elements being formed in two or more coils or loops as a spiral, helical or toroidal winding Resistive elements being formed as one or more layers or coatings on a base H01C 3/18, H01C 3/20 H01C 7/00 H01C 1/014 the resistor being suspended between and being supported by two supporting sections (H01C 1/016 takes precedence) Compensation for resistor expansion or contraction H01C 1/016 H01C 1/024 the housing or enclosure being hermetically sealed (H01C 1/028, H01C 1/032, H01C 1/034 take precedence) Resistive elements being embedded in insulation with outer enclosing sheath H01C 1/028 Plural layers surrounding the resistive element H01C 1/032 Housing or enclosure being formed as coating or mold without outer sheath H01C 1/034 4
5 H01C 1/032 plural layers surrounding the resistive element (H01C 1/028 takes precedence) Resistive elements being embedded in insulation with outer enclosing sheath H01C 1/028 H01C 1/034 the housing or enclosure being formed as coating or mould without outer sheath (H01C 1/032 takes precedence) Plural layers surrounding the resistive element H01C 1/032 H01C 1/14 Terminals or tapping points {or electrodes} specially adapted for resistors (in general H01R); Arrangements of terminals or tapping points {or electrodes} on resistors Terminals or tapping points in general H01R H01C 1/148 the terminals embracing or surrounding the resistive element (H01C 1/142 takes precedence) Terminals or tapping points being coated on the resistive element H01C 1/142 5
6 H01C 3/14 the resistive element being formed in two or more coils or loops continuously wound as a spiral, helical or toroidal winding (H01C 3/02 - H01C 3/12 take precedence) Resistors arranged or constructed for reducing self-induction, capacitance or variation with frequency Iron-filament ballast resistors; Other resistors having variable temperature coefficient Flexible or folding resistors, whereby such a resistor can be looped or collapsed upon itself Dimension or characteristic of resistive element changing gradually or in discrete steps from one terminal to another H01C 3/02 H01C 3/04 H01C 3/06 H01C 3/08 Resistive element having zig-zag or sinusoidal configuration H01C 3/10 Lying in one plane H01C 3/12 H01C 3/18 wound on a flat or ribbon base (H01C 3/16 takes precedence) Resistive elements including two or more distinct wound elements or two or more winding patterns H01C 3/16 H01C 3/20 wound on cylindrical or prismatic base (H01C 3/16 takes precedence) Resistive elements including two or more distinct wound elements or two or more winding patterns H01C 3/16 6
7 H01C 7/00 Non-adjustable resistors formed as one or more layers or coatings; Nonadjustable resistors made from powdered conducting material or powdered semi-conducting material with or without insulating material (consisting of loose powdered or granular material H01C 8/00; {measuring deformation in a solid state using the change in resistance formed by printed-circuit technique G01B 7/20; insulating materials H01B 3/00; passive thin-film or thick-film semiconductor or solid state devices H01L 27/00; resistors without a potentialjump or surface barrier specially adapted for integrated circuits, details thereof, multistep manufacturing processes therefor H01L 28/20}; resistors with a potential-jump barrier or surface barrier, e.g. field effect resistors H01L 29/00; semiconductor devices sensitive to electromagnetic or corpuscular radiation, e.g. photoresistors, H01L 31/00; devices using superconductivity H01L 39/00; devices using galvanomagnetic or similar magnetic effects, e.g. magnetic-fieldcontrolled resistors, H01L 43/00; solid state devices for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching without a potential-jump barrier or surface barrier H01L 45/00; bulk negative resistance effect devices H01L 47/00; {ohmic resistance heating H05B 3/00; printed circuits H05K}) Resistors consisting of loose powdered or granular material H01C 8/00 Passive thin-film or thick-film semiconductor or solid state devices H01L 27/00 Resistors without a potential-jump or surface barrier specially adapted for integrated circuits Resistors with a potential-jump barrier or surface barrier, e.g. field effect resistors Semiconductor devices sensitive to electro-magnetic or corpuscular radiation, e.g. photoresistors Devices using galvanomagnetic or similar magnetic effects, e.g. magnetic-field-controlled resistors H01L 28/20 H01L 29/00 H01L 31/00 H01L 43/00 Bulk negative resistance effect devices H01L 47/00 Measuring deformation in a solid state using the change in resistance formed by printed-circuit technique G01B 7/20 Insulating materials H01B 3/00 Devices using superconductivity H01L 39/00 Solid state devices for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching without a potential-jump barrier or surface barrier H01L 45/00 Ohmic resistance heating H05B 3/00 Printed circuits H05K 7
8 H01C 7/04 having negative temperature coefficient {(thermometers using resistive elements G01K 7/16)} Thermometers using resistive elements G01K 7/16 H01C 7/102 Varistor boundary, e.g. surface layers (H01C 7/12 takes precedence) Overvoltage protection resistors H01C 7/12 H01C 7/105 Varistor cores (H01C 7/12 takes precedence) Overvoltage protection resistors H01C 7/12 H01C 7/12 Overvoltage protection resistors {(series resistors structurally associated with spark gaps H01T 1/16)} Series resistors structurally associated with spark gaps H01T 1/16 H01C 7/13 current responsive Special rules of classification Groups H01C 7/02 - H01C 7/13 take precedence over groups H01C 7/18 - H01C 7/22. 8
9 H01C 10/00 Adjustable resistors Special rules of classification Groups H01C 10/02 - H01C 10/26 take precedence over groups H01C 10/28 - H01C 10/50. H01C 10/22 resistive element dimensions changing gradually in one direction, e.g. tapered resistive element (H01C 10/04 takes precedence) With specified mathematical relationship between movement of resistor actuating means and value of resistance, other than direct proportional relationship H01C 10/04 H01C 10/26 resistive element moving (H01C 10/16, H01C 10/24 take precedence) Plural resistive elements H01C 10/16 Contacts moving along turns of a helical resistive element, or vice versa H01C 10/24 H01C 10/44 the contact bridging and sliding along resistive element and parallel conducting bar or collector (H01C 10/42 takes precedence) Contact bridging and sliding along resistive element and parallel conducting bar or collector H01C 10/42 9
10 H01C 10/46 Arrangements of fixed resistors with intervening connectors, e.g. taps (H01C 10/28, H01C 10/30 take precedence) Contact rocking or rolling along resistive element or taps H01C 10/28 Contact sliding along resistive element H01C 10/30 H01C 10/50 structurally combined with switching arrangements (H01C 10/36 takes precedence) Contact moving in an arcuate path structurally combined with switching arrangements H01C 10/36 H01C 13/02 Structural combinations of resistors (impedance networks per se H03H) Impedance networks per se H03H H01C 17/00 Apparatus or processes specially adapted for manufacturing resistors (providing fillings for housings or enclosures H01C 1/02; reducing insulation surrounding a resistor to powder H01C 1/03; manufacture of thermally variable resistors H01C 7/02, H01C 7/04) Providing fillings for housings or enclosures H01C 1/02 Reducing insulation surrounding a resistor to powder H01C 1/03 Manufacture of thermally variable resistors H01C 7/02, H01C 7/04 10
11 H01C 17/24 by removing or adding resistive material (H01C 17/23, H01C 17/232, H01C 17/235 take precedence) By opening or closing resistor geometric tracks of predetermined resistive values, e.g. snapistors Adjusting the temperature coefficient; Adjusting value of resistance by adjusting temperature coefficient of resistance H01C 17/23 H01C 17/232 Initial adjustment of potentiometer parts for calibration H01C 17/235 H01C 17/242 by laser {(trimming by laser in general B23K 26/351)} Trimming by laser in general B23K 26/351 11
COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION
 CPC H H02 COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION ELECTRICITY (NOTE omitted) GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS (indicating or signalling undesired
CPC H H02 COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION ELECTRICITY (NOTE omitted) GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER EMERGENCY PROTECTIVE CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS (indicating or signalling undesired
5. The Different Types of Resistors
 5. The Different Types of Resistors Resistors ( R ), are the most fundamental and commonly used of all the electronic components, to the point where they are almost taken for granted. There are many different
5. The Different Types of Resistors Resistors ( R ), are the most fundamental and commonly used of all the electronic components, to the point where they are almost taken for granted. There are many different
5. Transducers Definition and General Concept of Transducer Classification of Transducers
 5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION
 CPC H H03 COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION ELECTRICITY (NOTE omitted) BASIC ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY H03B GENERATION OF OSCILLATIONS, DIRECTLY OR BY FREQUENCY-CHANGING, BY CIRCUITS EMPLOYING ACTIVE ELEMENTS
CPC H H03 COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION ELECTRICITY (NOTE omitted) BASIC ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY H03B GENERATION OF OSCILLATIONS, DIRECTLY OR BY FREQUENCY-CHANGING, BY CIRCUITS EMPLOYING ACTIVE ELEMENTS
COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION
 CPC H H02 COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION ELECTRICITY (NOTE omitted) GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER H02M APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN
CPC H H02 COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION ELECTRICITY (NOTE omitted) GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER H02M APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN
Voltage and current regulation circuits operating according to the non-switched (linear) principle are classified in subclass G05F
 CPC - H02M - 2017.08 H02M APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER
CPC - H02M - 2017.08 H02M APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER
What is a Resistor? Token Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. Version: January 12, Web:
 Version: January 12, 2017 What is a Resistor? Web: www.token.com.tw Email: rfq@token.com.tw Token Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. Taiwan: No.137, Sec. 1, Zhongxing Rd., Wugu District, New Taipei City, Taiwan,
Version: January 12, 2017 What is a Resistor? Web: www.token.com.tw Email: rfq@token.com.tw Token Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. Taiwan: No.137, Sec. 1, Zhongxing Rd., Wugu District, New Taipei City, Taiwan,
Electronic component
 Electronic component Electronic component: An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. 2 TYPES OF
Electronic component Electronic component: An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. 2 TYPES OF
Techo notes. Resistors. Composition Resistors. Resistor Symbol
 Resistors Techo notes Resistors (R), are the most commonly used of all electronic components, to the point where they are almost taken for granted. There are many different resistor types available with
Resistors Techo notes Resistors (R), are the most commonly used of all electronic components, to the point where they are almost taken for granted. There are many different resistor types available with
The manufacture of abrasive articles or shaped materials containing macromolecular substances, e.g. as bonding agent, is covered by C08J5/14.
 CPC - B24D - 2016.11 B24D TOOLS FOR GRINDING, BUFFING, OR SHARPENING (tools for grinding or polishing optical surfaces on lenses or surfaces of similar shape B24B 13/01; grinding heads B24B 41/00; manufacture
CPC - B24D - 2016.11 B24D TOOLS FOR GRINDING, BUFFING, OR SHARPENING (tools for grinding or polishing optical surfaces on lenses or surfaces of similar shape B24B 13/01; grinding heads B24B 41/00; manufacture
This place covers: Demodulation or transference of signals modulated on a sinusoidal carrier or on electromagnetic waves.
 CPC - H03D - 2017.08 H03D DEMODULATION OR TRANSFERENCE OF MODULATION FROM ONE CARRIER TO ANOTHER (masers, lasers H01S; circuits capable of acting both as modulator and demodulator H03C; details applicable
CPC - H03D - 2017.08 H03D DEMODULATION OR TRANSFERENCE OF MODULATION FROM ONE CARRIER TO ANOTHER (masers, lasers H01S; circuits capable of acting both as modulator and demodulator H03C; details applicable
COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION
 CPC H 2014.07 Interleaved page 1 CPC H COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION ELECTRICITY These notes cover the basic principles and general instructions for use of section H. Section H covers : basic electric
CPC H 2014.07 Interleaved page 1 CPC H COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION ELECTRICITY These notes cover the basic principles and general instructions for use of section H. Section H covers : basic electric
What is an Inductor? Token Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. Version: January 16, Web:
 Version: January 16, 2017 What is an Inductor? Web: www.token.com.tw Email: rfq@token.com.tw Token Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. Taiwan: No.137, Sec. 1, Zhongxing Rd., Wugu District, New Taipei City,
Version: January 16, 2017 What is an Inductor? Web: www.token.com.tw Email: rfq@token.com.tw Token Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. Taiwan: No.137, Sec. 1, Zhongxing Rd., Wugu District, New Taipei City,
NIRMA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT EE101: Elements of Electrical Engineering DC CIRCUIT
 NIRMA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT EE101: Elements of Electrical Engineering DC CIRCUIT Learning Objective: Resistance, Effect of temperature on resistance, temperature
NIRMA UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT EE101: Elements of Electrical Engineering DC CIRCUIT Learning Objective: Resistance, Effect of temperature on resistance, temperature
(51) Int Cl.: G01R 15/06 ( ) (54) Combined current and voltage measurement transformer of the capacitor bushing type
 (19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 624 311 A1 (43) Date of publication: 08.02.2006 Bulletin 2006/06 (51) Int Cl.:
(19) Europäisches Patentamt European Patent Office Office européen des brevets (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (11) EP 1 624 311 A1 (43) Date of publication: 08.02.2006 Bulletin 2006/06 (51) Int Cl.:
9/28/2010. Chapter , The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
This place covers: Devices with electromagnetic waves being generated by stimulated emission
 H01S DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION Devices with electromagnetic waves being generated by stimulated emission Details specific to the laser or maser action Amplification by stimulated emission inside
H01S DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION Devices with electromagnetic waves being generated by stimulated emission Details specific to the laser or maser action Amplification by stimulated emission inside
The term "optical" applies not only to visible light but also to ultra-violet, infra-red radiations or Terahertz (G02F 1/3534).
 G02F DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS, THE OPTICAL OPERATION OF WHICH IS MODIFIED BY CHANGING THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIUM OF THE DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF THE INTENSITY, COLOUR, PHASE,
G02F DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS, THE OPTICAL OPERATION OF WHICH IS MODIFIED BY CHANGING THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIUM OF THE DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF THE INTENSITY, COLOUR, PHASE,
High-Voltage Test Techniques
 High-Voltage Test Techniques Dieter Kind Kurt Feser 2nd Revised and Enlarged Edition With 211 Figures and 12 Laboratory Experiments Translated from the German by Y. Narayana Rao Professor of Electrical
High-Voltage Test Techniques Dieter Kind Kurt Feser 2nd Revised and Enlarged Edition With 211 Figures and 12 Laboratory Experiments Translated from the German by Y. Narayana Rao Professor of Electrical
Basic Principles and Operation of Transformer
 Basic Principles and Operation of Transformer CONSTRUCTIONAL ASPECTS Cores In order to enhance core s magnetic properties, it is constructed from an iron and silicon mixture (alloy). The magnetic core
Basic Principles and Operation of Transformer CONSTRUCTIONAL ASPECTS Cores In order to enhance core s magnetic properties, it is constructed from an iron and silicon mixture (alloy). The magnetic core
TEPZZ 48A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02M 3/335 ( ) H02M 1/00 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 48A T (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 3/33 (2006.01) H02M 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1178647.2 (22)
(19) TEPZZ 48A T (11) (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 04.01.2017 Bulletin 2017/01 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 3/33 (2006.01) H02M 1/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 1178647.2 (22)
This place covers: Generation of oscillations in a non-switching manner, i.e. by harmonic oscillators providing sinusoidal signals.
 CPC - H03B - 2018.01 H03B GENERATION OF OSCILLATIONS, DIRECTLY OR BY FREQUENCY- CHANGING, BY CIRCUITS EMPLOYING ACTIVE ELEMENTS WHICH OPERATE IN A NON-SWITCHING MANNER; GENERATION OF NOISE BY SUCH CIRCUITS
CPC - H03B - 2018.01 H03B GENERATION OF OSCILLATIONS, DIRECTLY OR BY FREQUENCY- CHANGING, BY CIRCUITS EMPLOYING ACTIVE ELEMENTS WHICH OPERATE IN A NON-SWITCHING MANNER; GENERATION OF NOISE BY SUCH CIRCUITS
Joining glass to glass or other materials by fusing, by specially adapted adhesive, interlayer
 CPC - C03C - 2018.01 C03C CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF GLASSES, GLAZES, OR VITREOUS ENAMELS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF GLASS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF FIBRES OR FILAMENTS MADE FROM GLASS, MINERALS OR SLAGS; JOINING
CPC - C03C - 2018.01 C03C CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF GLASSES, GLAZES, OR VITREOUS ENAMELS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF GLASS; SURFACE TREATMENT OF FIBRES OR FILAMENTS MADE FROM GLASS, MINERALS OR SLAGS; JOINING
Constructional details or arrangements, e.g. housings, packages, cooling, electrodes.
 H01S DEVICES USING THE PROCESS OF LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION [LASER] TO AMPLIFY OR GENERATE LIGHT; DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN WAVE RANGES
H01S DEVICES USING THE PROCESS OF LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION [LASER] TO AMPLIFY OR GENERATE LIGHT; DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN WAVE RANGES
Categorized by the type of core on which inductors are wound:
 Inductors Categorized by the type of core on which inductors are wound: air core and magnetic core. The magnetic core inductors can be subdivided depending on whether the core is open or closed. Equivalent
Inductors Categorized by the type of core on which inductors are wound: air core and magnetic core. The magnetic core inductors can be subdivided depending on whether the core is open or closed. Equivalent
 VIDYARTHIPLUS - ANNA UNIVERSITY ONLINE STUDENTS COMMUNITY UNIT 1 DC MACHINES PART A 1. State Faraday s law of Electro magnetic induction and Lenz law. 2. Mention the following functions in DC Machine (i)
VIDYARTHIPLUS - ANNA UNIVERSITY ONLINE STUDENTS COMMUNITY UNIT 1 DC MACHINES PART A 1. State Faraday s law of Electro magnetic induction and Lenz law. 2. Mention the following functions in DC Machine (i)
TEPZZ 879Z A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G06F 3/0354 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 879Z A_T (11) EP 2 879 023 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.06.1 Bulletin 1/23 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/034 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1419462. (22) Date of
(19) TEPZZ 879Z A_T (11) EP 2 879 023 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 03.06.1 Bulletin 1/23 (1) Int Cl.: G06F 3/034 (13.01) (21) Application number: 1419462. (22) Date of
carbons and other pressure-sensitive layers or coatings specifically adapted for manifolding;
 CPC - B41L - 2017.08 B41L APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR MANIFOLDING, DUPLICATING, OR PRINTING FOR OFFICE OR OTHER COMMERCIAL PURPOSES; ADDRESSING MACHINES OR LIKE SERIES-PRINTING MACHINES (printing presses
CPC - B41L - 2017.08 B41L APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR MANIFOLDING, DUPLICATING, OR PRINTING FOR OFFICE OR OTHER COMMERCIAL PURPOSES; ADDRESSING MACHINES OR LIKE SERIES-PRINTING MACHINES (printing presses
EUROPEAN PATENT OFFICE U.S. PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CPC NOTICE OF CHANGES 461 DATE: FEBRUARY 1, 2018 PROJECT MP0388 F21K 2/00 F21K 5/00
 EUROPEAN PATENT OFFICE U.S. PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CPC NOTICE OF CHANGES 461 The following classification changes will be effected by this Notice of Changes: Action Subclass Group(s) SCHEME: Titles
EUROPEAN PATENT OFFICE U.S. PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CPC NOTICE OF CHANGES 461 The following classification changes will be effected by this Notice of Changes: Action Subclass Group(s) SCHEME: Titles
Electric testing of analogue or digital electric devices, apparatus or networks, or measuring their characteristics.
 G01R MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES (measuring physical variables of any kind by conversion into electric variables, see Note (4) following the title of class G01; measuring
G01R MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES (measuring physical variables of any kind by conversion into electric variables, see Note (4) following the title of class G01; measuring
SHEETS TEMPORARILY ATTACHED TOGETHER; FILING APPLIANCES; FILE CARDS; INDEXING (reading desks A47B 19/00; book rests A47B 23/00)
 CPC - B42F - 2016.11 B42F SHEETS TEMPORARILY ATTACHED TOGETHER; FILING APPLIANCES; FILE CARDS; INDEXING (reading desks A47B 19/00; book rests A47B 23/00) Sheets temporarily attached together,with or without
CPC - B42F - 2016.11 B42F SHEETS TEMPORARILY ATTACHED TOGETHER; FILING APPLIANCES; FILE CARDS; INDEXING (reading desks A47B 19/00; book rests A47B 23/00) Sheets temporarily attached together,with or without
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3.
 Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
Reactor and inductor are names used interchangeably for this circuit device.
 Recommended Design Criteria for Air-Cooled Reactor for Line and Track Circuits Revised 2015 (7 Pages) A. Purpose This Manual Part recommends design criteria for an air-cooled reactor for line and track
Recommended Design Criteria for Air-Cooled Reactor for Line and Track Circuits Revised 2015 (7 Pages) A. Purpose This Manual Part recommends design criteria for an air-cooled reactor for line and track
CAPACITIVE SENSORS. Series KS. Key-Features:
 CAPACITIVE SENSORS Series KS Key-Features: Content: Introduction Applications...2 Technical Data Sensor Heads...3 Technical Drawing...4 Sensor Cabels...5 1 Channel Electronics...6 Description Electronics
CAPACITIVE SENSORS Series KS Key-Features: Content: Introduction Applications...2 Technical Data Sensor Heads...3 Technical Drawing...4 Sensor Cabels...5 1 Channel Electronics...6 Description Electronics
Systems Engineering. Passive Components. v1.2 March itic.
 Systems Engineering Passive Components Pere Palà itic http://itic.cat v1.2 March 2012 Resistors Resistor Types Resistors Ubiquitous Uncritical Surface mount chip Metal film Carbon Wirewound Precision resistors
Systems Engineering Passive Components Pere Palà itic http://itic.cat v1.2 March 2012 Resistors Resistor Types Resistors Ubiquitous Uncritical Surface mount chip Metal film Carbon Wirewound Precision resistors
Coating of the fibre during the drawing process C03C 25/10 Optical fibres per se with polarisation maintaining properties in light guides
 CPC - C03B - 2017.08 C03B MANUFACTURE, SHAPING, OR SUPPLEMENTARY PROCESSES Relationships with other classification places C03B concerns all aspects of glass manufacture processes, apparatus and C03C relates
CPC - C03B - 2017.08 C03B MANUFACTURE, SHAPING, OR SUPPLEMENTARY PROCESSES Relationships with other classification places C03B concerns all aspects of glass manufacture processes, apparatus and C03C relates
Classification within G01B into the main groups is to a large extent based on the underlying measurement principle:
 CPC - G01B - 2017.08 G01B MEASURING LENGTH, THICKNESS OR SIMILAR LINEAR DIMENSIONS; MEASURING ANGLES; MEASURING AREAS; MEASURING IRREGULARITIES OF SURFACES OR CONTOURS {(measuring human body, see the relevant
CPC - G01B - 2017.08 G01B MEASURING LENGTH, THICKNESS OR SIMILAR LINEAR DIMENSIONS; MEASURING ANGLES; MEASURING AREAS; MEASURING IRREGULARITIES OF SURFACES OR CONTOURS {(measuring human body, see the relevant
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION. Model Answer. Subject Code: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
 Subject Code: 17215 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Subject Code: 17215 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Inductor Glossary. Token Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. Version: January 16, Web:
 Version: January 16, 2017 Inductor Glossary Web: www.token.com.tw Email: rfq@token.com.tw Token Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. Taiwan: No.137, Sec. 1, Zhongxing Rd., Wugu District, New Taipei City, Taiwan,
Version: January 16, 2017 Inductor Glossary Web: www.token.com.tw Email: rfq@token.com.tw Token Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. Taiwan: No.137, Sec. 1, Zhongxing Rd., Wugu District, New Taipei City, Taiwan,
Integrated diodes. The forward voltage drop only slightly depends on the forward current. ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI
 1 Integrated diodes pn junctions of transistor structures can be used as integrated diodes. The choice of the junction is limited by the considerations of switching speed and breakdown voltage. The forward
1 Integrated diodes pn junctions of transistor structures can be used as integrated diodes. The choice of the junction is limited by the considerations of switching speed and breakdown voltage. The forward
It further covers the following parts and devices related to those apparatus:
 CPC - B21D - 2017.08 B21D WORKING OR PROCESSING OF SHEET METAL OR METAL TUBES, RODS OR PROFILES WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL (working or processing of wire B21F) Processes and
CPC - B21D - 2017.08 B21D WORKING OR PROCESSING OF SHEET METAL OR METAL TUBES, RODS OR PROFILES WITHOUT ESSENTIALLY REMOVING MATERIAL; PUNCHING METAL (working or processing of wire B21F) Processes and
EUROPEAN PATENT OFFICE U.S. PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CPC NOTICE OF CHANGES 466 DATE: JANUARY 1, 2018 PROJECT MP0394
 EUROPEAN PATENT OFFICE U.S. PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CPC NOTICE OF CHANGES 466 The following classification changes will be effected by this Notice of Changes: Action Subclass Group(s) SCHEME: s Changed:
EUROPEAN PATENT OFFICE U.S. PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CPC NOTICE OF CHANGES 466 The following classification changes will be effected by this Notice of Changes: Action Subclass Group(s) SCHEME: s Changed:
4/30/2012. General Class Element 3 Course Presentation. Circuit CoCircuit Componentsmponents. Subelement G6. 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups
 General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G6 Circuit Components 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3
General Class Element 3 Course Presentation ti ELEMENT 3 SUB ELEMENTS General Licensing Class Subelement G6 Circuit Components 3 Exam Questions, 3 Groups G1 Commission s Rules G2 Operating Procedures G3
Inductors & Resonance
 Inductors & Resonance The Inductor This figure shows a conductor carrying a current. A magnetic field is set up around the conductor as concentric circles. If a coil of wire has a current flowing through
Inductors & Resonance The Inductor This figure shows a conductor carrying a current. A magnetic field is set up around the conductor as concentric circles. If a coil of wire has a current flowing through
Special Lecture Series Biosensors and Instrumentation
 !1 Special Lecture Series Biosensors and Instrumentation Lecture 6: Micromechanical Sensors 1 This is the first part of the material on micromechanical sensors which deals with piezoresistive and piezoelectric
!1 Special Lecture Series Biosensors and Instrumentation Lecture 6: Micromechanical Sensors 1 This is the first part of the material on micromechanical sensors which deals with piezoresistive and piezoelectric
Attention is drawn to the following places, which may be of interest for search:
 CPC - B22D - 2017.08 B22D CASTING OF METALS; CASTING OF OTHER SUBSTANCES BY THE SAME PROCESSES OR DEVICES (shaping of plastics or substances in a plastic state B29C; metallurgical processing, selection
CPC - B22D - 2017.08 B22D CASTING OF METALS; CASTING OF OTHER SUBSTANCES BY THE SAME PROCESSES OR DEVICES (shaping of plastics or substances in a plastic state B29C; metallurgical processing, selection
CAPACITIVE FOR WINDING ELECTRIC MOTORS, TRANSFORMERS AND ELECTRO-MAGNETS
 CAPACITIVE FOR WINDING ELECTRIC MOTORS, TRANSFORMERS AND ELECTRO-MAGNETS The invention relates to a capacitive coil of copper wire that can be used for all electromagnetic energy converters and their inductive
CAPACITIVE FOR WINDING ELECTRIC MOTORS, TRANSFORMERS AND ELECTRO-MAGNETS The invention relates to a capacitive coil of copper wire that can be used for all electromagnetic energy converters and their inductive
Construction Hints and Techniques
 Construction Hints and Techniques You just get finished building a Microwave project and it looks beautiful. After admiring it for awhile you decide to spark it up. All of the voltages and currents look
Construction Hints and Techniques You just get finished building a Microwave project and it looks beautiful. After admiring it for awhile you decide to spark it up. All of the voltages and currents look
Custom Resistors for High Pulse Applications
 White Paper Custom Resistors for High Pulse Applications Issued in June 2017 The contents of this White Paper are protected by copyright and must not be reproduced without permission 2017 Riedon Inc. All
White Paper Custom Resistors for High Pulse Applications Issued in June 2017 The contents of this White Paper are protected by copyright and must not be reproduced without permission 2017 Riedon Inc. All
COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION
 CPC D COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION TEXTILES; PAPER TEXTILES OR FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR D04 BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS,
CPC D COOPERATIVE PATENT CLASSIFICATION TEXTILES; PAPER TEXTILES OR FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR D04 BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS,
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY
 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY UNIT III THEORY OF METAL CUTTING Broad classification of Engineering Manufacturing Processes. It is extremely difficult to tell the exact number of various manufacturing processes
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY UNIT III THEORY OF METAL CUTTING Broad classification of Engineering Manufacturing Processes. It is extremely difficult to tell the exact number of various manufacturing processes
BASIC ELECTRONICS PROF. T.S. NATARAJAN DEPT OF PHYSICS IIT MADRAS LECTURE-2 ELECTRONIC DEVICES -1 RESISTOR, IDEAL SOURCE VOLTAGE & CAPACITOR
 BASIC ELECTRONICS PROF. T.S. NATARAJAN DEPT OF PHYSICS IIT MADRAS LECTURE-2 ELECTRONIC DEVICES -1 RESISTOR, IDEAL SOURCE VOLTAGE & CAPACITOR In the last lecture we saw the importance of learning about
BASIC ELECTRONICS PROF. T.S. NATARAJAN DEPT OF PHYSICS IIT MADRAS LECTURE-2 ELECTRONIC DEVICES -1 RESISTOR, IDEAL SOURCE VOLTAGE & CAPACITOR In the last lecture we saw the importance of learning about
ELECTRONICS & INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT
 ELECTRONICS & INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT Our Ref: LITD G/25/LITD 05 25.02.2015 Subject: Reaffirmation of Indian Standards pertaining to Electronic Components And Modules Sectional Committee, LITD
ELECTRONICS & INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT Our Ref: LITD G/25/LITD 05 25.02.2015 Subject: Reaffirmation of Indian Standards pertaining to Electronic Components And Modules Sectional Committee, LITD
1. A transducer converts
 1. A transducer converts a. temperature to resistance b. force into current c. position into voltage d. one form of energy to another 2. Whose of the following transducers the output is a change in resistance?
1. A transducer converts a. temperature to resistance b. force into current c. position into voltage d. one form of energy to another 2. Whose of the following transducers the output is a change in resistance?
Pressure Transducer Handbook
 123 Pressure Transducer Handbook Date: February 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 - Introduction 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Product Overview SECTION 2 - Kulite Sensing Technology 2.1 Pressure Transducers 2.2
123 Pressure Transducer Handbook Date: February 2004 TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 - Introduction 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Product Overview SECTION 2 - Kulite Sensing Technology 2.1 Pressure Transducers 2.2
Matrix Multimedia Limited Tel Fax
 matrix multimedia Electronic Circuits and Components v2.0 Course material with Virtual Laboratories that stimulate, teach & test. This second version of Electronic Circuits and Components is bigger and
matrix multimedia Electronic Circuits and Components v2.0 Course material with Virtual Laboratories that stimulate, teach & test. This second version of Electronic Circuits and Components is bigger and
SHIELDING EFFECTIVENESS
 SHIELDING Electronic devices are commonly packaged in a conducting enclosure (shield) in order to (1) prevent the electronic devices inside the shield from radiating emissions efficiently and/or (2) prevent
SHIELDING Electronic devices are commonly packaged in a conducting enclosure (shield) in order to (1) prevent the electronic devices inside the shield from radiating emissions efficiently and/or (2) prevent
Prepared by Mick Maytum
 IEC Technical Committee 109: Standards on insulation co-ordination for low-voltage equipment Warning Prepared by Mick Maytum mjmaytum@gmail.com The document content is of a general nature only and is not
IEC Technical Committee 109: Standards on insulation co-ordination for low-voltage equipment Warning Prepared by Mick Maytum mjmaytum@gmail.com The document content is of a general nature only and is not
Part Derating Parameters
 Part Derating Parameters Capacitors Fixed Aluminum (Electrolytic) Fixed Ceramic Fixed Mica/Glass Fixed Paper/Plastic Fixed Tantalum (Non- Solid) Reverse Voltage Fixed Tantalum (Solid) Reverse Voltage Variable
Part Derating Parameters Capacitors Fixed Aluminum (Electrolytic) Fixed Ceramic Fixed Mica/Glass Fixed Paper/Plastic Fixed Tantalum (Non- Solid) Reverse Voltage Fixed Tantalum (Solid) Reverse Voltage Variable
Sensors. Chapter 3. Storey: Electrical & Electronic Systems Pearson Education Limited 2004 OHT 3.1
 Sensors Chapter 3 Introduction Describing Sensor Performance Temperature Sensors Light Sensors Force Sensors Displacement Sensors Motion Sensors Sound Sensors Sensor Interfacing Storey: Electrical & Electronic
Sensors Chapter 3 Introduction Describing Sensor Performance Temperature Sensors Light Sensors Force Sensors Displacement Sensors Motion Sensors Sound Sensors Sensor Interfacing Storey: Electrical & Electronic
Development of Passive Component using Carbon Powder for Electronic Circuit Board
 Development of Passive Component using Carbon Powder for Electronic Circuit Board K. W. E. Cheng 1, W.T.Wu 1, Y.W.Wong 2 Department of Electrical Engineering 1, Department of Applied Physics 2, The Hong
Development of Passive Component using Carbon Powder for Electronic Circuit Board K. W. E. Cheng 1, W.T.Wu 1, Y.W.Wong 2 Department of Electrical Engineering 1, Department of Applied Physics 2, The Hong
Electronic Components. Identification of components and handling precautions to protect them from damage due to electrostatic discharge
 Electronic Components Identification of components and handling precautions to protect them from damage due to electrostatic discharge 1 Passive Components Resistors Capacitors Inductors Diodes Interface
Electronic Components Identification of components and handling precautions to protect them from damage due to electrostatic discharge 1 Passive Components Resistors Capacitors Inductors Diodes Interface
Handling of articles in general is found in B65G and handling of sheet material in general is found in B65H.
 G07D HANDLING OF COINS OR OF PAPER CURRENCY OR SIMILAR VALUABLE PAPERS, e.g. TESTING, SORTING BY DENOMINATIONS, COUNTING, DISPENSING, CHANGING OR DEPOSITING This subclass covers handling of "coins" or
G07D HANDLING OF COINS OR OF PAPER CURRENCY OR SIMILAR VALUABLE PAPERS, e.g. TESTING, SORTING BY DENOMINATIONS, COUNTING, DISPENSING, CHANGING OR DEPOSITING This subclass covers handling of "coins" or
An Instrumentation System
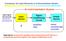 Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Electronic Systems - B1 23/04/ /04/ SisElnB DDC. Chapter 2
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS. Introduction. B1 - Sensors and actuators. Introduction
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Transducer transmitter BILT 4 II 2(1) G. Technical Manual
 GB Transducer transmitter BILT 4 II 2(1) G Technical Manual Transducer transmitter BILT 4 Contents Introduction General... 3 Ex.safety description... 4 Technical data... 5 Installation General... 6 Mechanical
GB Transducer transmitter BILT 4 II 2(1) G Technical Manual Transducer transmitter BILT 4 Contents Introduction General... 3 Ex.safety description... 4 Technical data... 5 Installation General... 6 Mechanical
NOTICE. The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should be addressed to:
 Serial Number 09/548.387 Filing Date 11 April 2000 Inventor Theodore R. Anderson Edward R. Javor NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should
Serial Number 09/548.387 Filing Date 11 April 2000 Inventor Theodore R. Anderson Edward R. Javor NOTICE The above identified patent application is available for licensing. Requests for information should
PRECISION-POWER-RF-NIKKOHM
 1. Application of resistors for industrial use Nikkohm Co., Ltd is a manufacturer of resistors for industrial use that feature the world s first class performance. Resistors for industrial use are not
1. Application of resistors for industrial use Nikkohm Co., Ltd is a manufacturer of resistors for industrial use that feature the world s first class performance. Resistors for industrial use are not
PIEZOELECTRIC TRANSFORMER FOR INTEGRATED MOSFET AND IGBT GATE DRIVER
 1 PIEZOELECTRIC TRANSFORMER FOR INTEGRATED MOSFET AND IGBT GATE DRIVER Prasanna kumar N. & Dileep sagar N. prasukumar@gmail.com & dileepsagar.n@gmail.com RGMCET, NANDYAL CONTENTS I. ABSTRACT -03- II. INTRODUCTION
1 PIEZOELECTRIC TRANSFORMER FOR INTEGRATED MOSFET AND IGBT GATE DRIVER Prasanna kumar N. & Dileep sagar N. prasukumar@gmail.com & dileepsagar.n@gmail.com RGMCET, NANDYAL CONTENTS I. ABSTRACT -03- II. INTRODUCTION
CLAIMS 1. A suspension board with circuit, characterized in that, it comprises a metal support layer, an insulating layer formed on the metal support
 [19] State Intellectual Property Office of the P.R.C [51] Int. Cl 7 G11B 5/48 H05K 1/11 [12] Patent Application Publication G11B 21/16 [21] Application No.: 00133926.5 [43] Publication Date: 5.30.2001
[19] State Intellectual Property Office of the P.R.C [51] Int. Cl 7 G11B 5/48 H05K 1/11 [12] Patent Application Publication G11B 21/16 [21] Application No.: 00133926.5 [43] Publication Date: 5.30.2001
TRAFTOR WINDINGS CHANGING THE RULES TOROIDAL INDUCTORS & TRANSFORMERS SOLUTIONS PROVIDER AND MANUFACTURER
 TRAFTOR WINDINGS CHANGING THE RULES TOROIDAL INDUCTORS & TRANSFORMERS SOLUTIONS PROVIDER AND MANUFACTURER PRODUCT RANGE POWER INDUCTORS Toroidal technology, driven by 20 years of R&D. POWER TRANSFORMERS
TRAFTOR WINDINGS CHANGING THE RULES TOROIDAL INDUCTORS & TRANSFORMERS SOLUTIONS PROVIDER AND MANUFACTURER PRODUCT RANGE POWER INDUCTORS Toroidal technology, driven by 20 years of R&D. POWER TRANSFORMERS
HARMONICS CAUSES AND EFFECTS
 HARMONICS CAUSES AND EFFECTS What is Harmonics? Harmonics is defined as the content of the signal whose frequency is an integral multiple of the system frequency of the fundamentals. Harmonics current
HARMONICS CAUSES AND EFFECTS What is Harmonics? Harmonics is defined as the content of the signal whose frequency is an integral multiple of the system frequency of the fundamentals. Harmonics current
V I S H A y I n T E R T E C H n O l O G y, I n C. In D u C T O R S In S T R u C TIO n A l INDuCtOR 101 Gu ID E w w w. v i s h a y.
 VISHAY INTERTECHNOLOGY, INC. INDUCTORS INDUCTOR 101 instructional Guide www.vishay.com Inductor 101 Inductor A passive component designed to resist changes in current. Inductors are often referred to as
VISHAY INTERTECHNOLOGY, INC. INDUCTORS INDUCTOR 101 instructional Guide www.vishay.com Inductor 101 Inductor A passive component designed to resist changes in current. Inductors are often referred to as
ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICITY
 INTRODUCTION ELECTRONICS ND ELECTRICITY The science of Electronics and Electricity makes a very important contribution to our everyday existence. Electricity is concerned with the generation, transmission
INTRODUCTION ELECTRONICS ND ELECTRICITY The science of Electronics and Electricity makes a very important contribution to our everyday existence. Electricity is concerned with the generation, transmission
New Materials and Method for Laser Trimmable NTC Thermistors
 New Materials and Method for Laser Trimmable NTC Thermistors By David J. Nabatian Gene A. Perschnick Chuck Rosenwald KOARTAN EMC Technology Corporation Artek Corporation Microelectronic Interconnect Materials
New Materials and Method for Laser Trimmable NTC Thermistors By David J. Nabatian Gene A. Perschnick Chuck Rosenwald KOARTAN EMC Technology Corporation Artek Corporation Microelectronic Interconnect Materials
This Manual Part recommends design criteria for resistors suitable for railway signaling circuits other than electronic.
 2016 Part 14.2.15 Recommended Design Criteria for Resistors Revised 2016 (6 Pages) A. Purpose z00381hn 3/12/15 8:34 AM z00381hn 3/12/15 8:37 AM This Manual Part recommends design criteria for resistors
2016 Part 14.2.15 Recommended Design Criteria for Resistors Revised 2016 (6 Pages) A. Purpose z00381hn 3/12/15 8:34 AM z00381hn 3/12/15 8:37 AM This Manual Part recommends design criteria for resistors
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER
 VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
Embedded Systems Analog Electronics
 Embedded Systems Analog Electronics Units physical units = length [meter], mass [kilogram], time [second] force - [Newton]: kg m/s 2 (F=ma) torque - [N m] energy - [joule]: 1N acting through distance of
Embedded Systems Analog Electronics Units physical units = length [meter], mass [kilogram], time [second] force - [Newton]: kg m/s 2 (F=ma) torque - [N m] energy - [joule]: 1N acting through distance of
Sectional Design Standard for Flexible/Rigid-Flexible Printed Boards
 Sectional Design Standard for Flexible/Rigid-Flexible Printed Boards Developed by the Flexible Circuits Design Subcommittee (D-) of the Flexible Circuits Committee (D-0) of IPC Supersedes: IPC-2223C -
Sectional Design Standard for Flexible/Rigid-Flexible Printed Boards Developed by the Flexible Circuits Design Subcommittee (D-) of the Flexible Circuits Committee (D-0) of IPC Supersedes: IPC-2223C -
Shades of blinds for greenhouses A01G 9/22 Shop furniture Picture frames
 CPC - E06B - 2018.01 E06B FIXED OR MOVABLE CLOSURES FOR OPENINGS IN BUILDINGS, VEHICLES, FENCES OR LIKE ENCLOSURES IN GENERAL, e.g. DOORS, WINDOWS, BLINDS, GATES (shades or blinds for greenhouses A01G
CPC - E06B - 2018.01 E06B FIXED OR MOVABLE CLOSURES FOR OPENINGS IN BUILDINGS, VEHICLES, FENCES OR LIKE ENCLOSURES IN GENERAL, e.g. DOORS, WINDOWS, BLINDS, GATES (shades or blinds for greenhouses A01G
 Page 1 of 6 A Historical Perspective From Aristotle to Hawking Force & Its Effects Measurement Limitations The Strain Gage Sensor Designs Measuring Circuits Application & Installation Process Pressure
Page 1 of 6 A Historical Perspective From Aristotle to Hawking Force & Its Effects Measurement Limitations The Strain Gage Sensor Designs Measuring Circuits Application & Installation Process Pressure
Figure Cutaway view of the Phasitron tube, which is used as the modulator and upon which the operation of the GE f-m transmitter is based.
 FM Transmission and Reception Pages 130-135 Rider, John. F., and Seymour D. Uslan John F. Rider Publisher, Inc., 1948. THE GENERAL ELECTRIC TRANSMITTER The original f-m transmitters manufactured by the
FM Transmission and Reception Pages 130-135 Rider, John. F., and Seymour D. Uslan John F. Rider Publisher, Inc., 1948. THE GENERAL ELECTRIC TRANSMITTER The original f-m transmitters manufactured by the
KNOW MORE ABOUT THE TRANSFORMERS. Glossary Transformers
 KNOW MORE ABOUT THE TRANSFORMERS Glossary Transformers Ambient temperature The existing temperature of the atmosphere surrounding a transformer installation. Ampere The practical unit of electric current.
KNOW MORE ABOUT THE TRANSFORMERS Glossary Transformers Ambient temperature The existing temperature of the atmosphere surrounding a transformer installation. Ampere The practical unit of electric current.
CURRENT ELECTRICITY. 1. The S.I. unit of power is (a) Henry (b) coulomb (c) watt (d) watt-hour Ans: c
 CURRENT ELECTRICITY 1. The S.I. unit of power is (a) Henry (b) coulomb (c) watt (d) watt-hour 2. Electric pressure is also called (a) resistance (b) power (c) voltage (d) energy 3. The substances which
CURRENT ELECTRICITY 1. The S.I. unit of power is (a) Henry (b) coulomb (c) watt (d) watt-hour 2. Electric pressure is also called (a) resistance (b) power (c) voltage (d) energy 3. The substances which
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS 1. At room temperature the current in an intrinsic semiconductor is due to A. holes B. electrons C. ions D. holes and electrons 2. Work function is the maximum energy required
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS 1. At room temperature the current in an intrinsic semiconductor is due to A. holes B. electrons C. ions D. holes and electrons 2. Work function is the maximum energy required
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17215 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17215 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
CHAPTER 6 CARBON NANOTUBE AND ITS RF APPLICATION
 CHAPTER 6 CARBON NANOTUBE AND ITS RF APPLICATION 6.1 Introduction In this chapter we have made a theoretical study about carbon nanotubes electrical properties and their utility in antenna applications.
CHAPTER 6 CARBON NANOTUBE AND ITS RF APPLICATION 6.1 Introduction In this chapter we have made a theoretical study about carbon nanotubes electrical properties and their utility in antenna applications.
Power Transformers Basics
 Power Transformers Basics Transformer Basic Objective Introduce Basic Transformer Theory as it Relates to Diagnostics Provide a Better Understanding of the Diagnostic Test Environment Identify Important
Power Transformers Basics Transformer Basic Objective Introduce Basic Transformer Theory as it Relates to Diagnostics Provide a Better Understanding of the Diagnostic Test Environment Identify Important
RISE WINTER 2015 UNDERSTANDING AND TESTING SELF SENSING MCKIBBEN ARTIFICIAL MUSCLES
 RISE WINTER 2015 UNDERSTANDING AND TESTING SELF SENSING MCKIBBEN ARTIFICIAL MUSCLES Khai Yi Chin Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Michigan Abstract Due to their compliant properties,
RISE WINTER 2015 UNDERSTANDING AND TESTING SELF SENSING MCKIBBEN ARTIFICIAL MUSCLES Khai Yi Chin Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Michigan Abstract Due to their compliant properties,
High Power Capacitors
 High Power Capacitors Calculation Form DESIGN Specification Capacitance C (µf) Working voltage V w (V) Rms current I rms (A rms ) Frequency F (Hz) Ripple voltage V r (V) Ambient temperature θ amb ( C)
High Power Capacitors Calculation Form DESIGN Specification Capacitance C (µf) Working voltage V w (V) Rms current I rms (A rms ) Frequency F (Hz) Ripple voltage V r (V) Ambient temperature θ amb ( C)
Part 10: Transducers
 Part 10: Transducers 10.1: Classification of Transducers An instrument may be defined as a device or a system which is designed to maintain a functional relationship between prescribed properties of physical
Part 10: Transducers 10.1: Classification of Transducers An instrument may be defined as a device or a system which is designed to maintain a functional relationship between prescribed properties of physical
Design and Fabrication of Tesla Coil
 Design and Fabrication of Tesla Coil Prof. S. M. Shaikh 1, Mr. Harshad Dube 2, Mrs. Sushmita Walunj 3, Mrs. Namita Thorat 4, 1 Assistant Professor, Electrical Engineering, AISSMS s IOIT, Maharashtra, India
Design and Fabrication of Tesla Coil Prof. S. M. Shaikh 1, Mr. Harshad Dube 2, Mrs. Sushmita Walunj 3, Mrs. Namita Thorat 4, 1 Assistant Professor, Electrical Engineering, AISSMS s IOIT, Maharashtra, India
BM6312 FEATURES GENERAL DESCRIPTION APPLICATIONS. High-performance current mode PWM Controller. Product Specification
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION BM6312 is a high-performance current mode PWM control IC designed for AC/DC convertor, which built-in high-voltage power switch tube and supplies continuous output power of 12W within
GENERAL DESCRIPTION BM6312 is a high-performance current mode PWM control IC designed for AC/DC convertor, which built-in high-voltage power switch tube and supplies continuous output power of 12W within
"Material fields per se" such as polymer materials or compositions and kind of fibrous web.
 D06N WALL, FLOOR OR LIKE COVERING MATERIALS, e.g. LINOLEUM, OILCLOTH, ARTIFICIAL LEATHER, ROOFING FELT, CONSISTING OF A FIBROUS WEB COATED WITH A LAYER OF MACROMOLECULAR MATERIAL; FLEXIBLE SHEET MATERIAL
D06N WALL, FLOOR OR LIKE COVERING MATERIALS, e.g. LINOLEUM, OILCLOTH, ARTIFICIAL LEATHER, ROOFING FELT, CONSISTING OF A FIBROUS WEB COATED WITH A LAYER OF MACROMOLECULAR MATERIAL; FLEXIBLE SHEET MATERIAL
Integrated Circuits: FABRICATION & CHARACTERISTICS - 4. Riju C Issac
 Integrated Circuits: FABRICATION & CHARACTERISTICS - 4 Riju C Issac INTEGRATED RESISTORS Resistor in a monolithic IC is very often obtained by the bulk resistivity of one of the diffused areas. P-type
Integrated Circuits: FABRICATION & CHARACTERISTICS - 4 Riju C Issac INTEGRATED RESISTORS Resistor in a monolithic IC is very often obtained by the bulk resistivity of one of the diffused areas. P-type
Chapter 8. Digital and Analog Interfacing Methods
 Chapter 8 Digital and Analog Interfacing Methods Lesson 16 MCU Based Instrumentation Outline Resistance and Capacitance based Sensor Interface Inductance based Sensor (LVDT) Interface Current based (Light
Chapter 8 Digital and Analog Interfacing Methods Lesson 16 MCU Based Instrumentation Outline Resistance and Capacitance based Sensor Interface Inductance based Sensor (LVDT) Interface Current based (Light
Laboratory no. 3 FLUORESCENT LAMPS FITTINGS
 Laboratory no. 3 FLUORESCENT LAMPS FITTINGS 3.1 General information The fluorescent lamps powered at industrial frequency voltage act as nonlinear resistors, non-inertial, with a dynamic symmetric volt-ampere
Laboratory no. 3 FLUORESCENT LAMPS FITTINGS 3.1 General information The fluorescent lamps powered at industrial frequency voltage act as nonlinear resistors, non-inertial, with a dynamic symmetric volt-ampere
PCB DESIGN AND ASSEMBLY FOR POWER SUPPLIES
 PCB DESIGN AND ASSEMBLY FOR POWER SUPPLIES Power supplies come in large varieties, can have different topologies, and feature numerous safeguards. Design of printed circuit boards (PCBs) for powers supplies
PCB DESIGN AND ASSEMBLY FOR POWER SUPPLIES Power supplies come in large varieties, can have different topologies, and feature numerous safeguards. Design of printed circuit boards (PCBs) for powers supplies
Lesson Plan. Electronics 1-Total 51 Hours
 Lesson Plan. Electronics 1-Total 5s Unit I: Electrical Engineering materials:(10) Crystal structure & defects; Ceramic materials-structures, composites, processing and uses; Insulating laminates for electronics,
Lesson Plan. Electronics 1-Total 5s Unit I: Electrical Engineering materials:(10) Crystal structure & defects; Ceramic materials-structures, composites, processing and uses; Insulating laminates for electronics,
