Optimal Operation and Dispatch of Voltage Regulation Devices Considering High Penetrations of Distributed Photovoltaic Generation
|
|
|
- Avice Grant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Optimal Operation and Dispatch of Voltage Regulation Devices Considering High Penetrations of Distributed Photovoltaic Generation Gyu-Jung Cho, Yun-Sik Oh, Min-Sung Kim, Ji-Soo Kim, Chul-Hwan Kim, Barry Mather, and Bri-Mathias Hodge Abstract Voltage regulation devices have been traditionally installed and utilized to support distribution voltages. Installations of distributed energy resources (DERs) in distribution systems are rapidly increasing, and many of these generation resources have variable and uncertain power output. These generators can significantly change the voltage profile for a feeder; therefore, in the distribution system planning stage of the optimal operation and dispatch of voltage regulation devices, possible high penetrations of DERs should be considered. In this paper, we model the IEEE -bus test feeder, including all essential equipment. An optimization method is adopted to determine the optimal siting and operation of the voltage regulation devices in the presence of distributed solar power generation. Finally, we verify the optimal configuration of the entire system through the optimization and simulation results. Keywords: IEEE -bus test feeder, distribution system planning, optimization, PV integration, step-voltage regulator V I. INTRODUCTION oltage regulation devices such as capacitor banks or step voltage regulators (SVRs) have been installed and utilized for the improvement of the power factor or mitigation of voltage drops in current distribution system operational practice [] [2]. Recently, distributed energy resources (DERs) have begun to be extensively installed in the distribution system as auxiliary generation resources. The power output of renewable DERs is normally variable and uncertain because the characteristics of the input from the DERs are affected by the daily solar radiation or wind profile. If the distribution system operator plans to install new voltage regulation devices in the distribution system, it is clear that the output of the DERs will affect each device s location and This work was partially funded by the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract No. DE_AC--GO2 with the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Korea government (No. 2RA2AA2). G. J. Cho, Y. S. Oh, M. S. Kim, J. S. Kim, and C. H. Kim are with the College of Information and Communication Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon,, Republic of Korea ( tom@skku.edu; fivebal2@skku.edu; michelle2@skku.edu; high@skku.edu; chkim@skku.edu). B. Mather and B.-M. Hodge are with the Power System Design and Studies Group, NREL, Golden, CO USA ( Barry.Mather@nrel.gov; Bri.Mathias.Hodge@nrel.gov). operating schedule. Moreover, if the operator focuses on maximizing the DER capacity in the distribution system, the operation schedule or voltage device sizing and siting will be affected by the configuration of the DER installation and the resulting net load profile. Therefore, a study is needed on the optimal operation and dispatch of the voltage regulation devices that simultaneously considers the size of highly distributed DERs and the resulting net load profile. Recently, several papers have addressed the optimization problem of the size and location of the capacitor banks [] [] or the location and tap setting of the SVRs [] []. Many authors have focused on the performance of the optimization method. However, there have been very few optimization studies considering highly distributed DERs, the variable power output of the DERs, and the resulting operation of the voltage regulation devices simultaneously. In this paper, we consider a monthly load profile from the summer of 2 in Southern California. Open-source yearly solar radiation profiles from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory s National Solar Radiation Database (NSRDB) [] are used to model the highly distributed photovoltaic (PV) generation. We utilize the IEEE -bus system as our target distribution system. First, loads are allocated to the target distribution system based on a proportional representation from the original feeder load factors. 2 loads are individually placed on separate buses in the modified IEEE -bus test feeder, and each of the loads has a relevant profile according to certain criteria of the load capacity. The optimization variables including the size and location of the PV, capacitor banks, and SVR settings are assigned to the distribution system via the Open-Source Distribution System Simulator (OpenDSS) [] using the COM interface. The optimization is performed by the Design Analysis Kit for Optimization and Terascale Applications (DAKOTA) []. The objective function values are calculated at every simulation iteration to evaluate the input parameters. Finally, we utilize a quasi-static time-series (QSTS) simulation to consider the actual load and solar profiles to evaluate the monthly operation of the SVR, any voltage deviations, and the cumulative circuit power losses to calculate the constraints and economics of the system. Paper submitted to the International Conference on Power Systems Transients (IPST2) in Seoul, Republic of Korea, June 2 2, 2
2 II. TARGET SYSTEM AND EQUIPMENT TOPOLOGY A. Quasi-Static Time-Series Simulation Based on the IEEE -Bus Test Feeder System When a high penetration level of DERs is expected in a newly planned distribution system, power flow analysis of the target distribution system considering the cooperation among the voltage regulation devices, such as SVR and capacitor banks, is required to determine the optimal equipment dispatch as well as the operation schedule of the other devices. Because the QSTS simulation shows a series of simulation results of the static (snapshot) power flow results at each time step [], it is well suited for these types of problems, and an appropriate time step that is able to accommodate the time interval for the operation of the power system equipment is needed. In this paper, we use a modified IEEE -bus test feeder system and consider the actual load profile of a distribution feeder in Southern California. We use a monthly load profile from the summer of 2 with solar radiation data added for distributed PV from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory s National Solar Radiation Database (NSRDB) []. B. Configuration of the Load and the PV Allocation Fig. shows the different types of the daily load profile and daily irradiance pattern from the NSRDB for an example day. PV output [p.u.] IND COM DOM Fig.. Four types of load profiles and PV power output on June, 2 We assume that each PV system is distributed with a rooftop configuration and that all of the PV systems are distributed throughout all of the load buses in the IEEE -bus test feeder system. A total of 2 buses among buses (including the midpoint between each bus) of the target system are selected; the bus names, capacity of each load, and load types for each of the buses are shown in Table I. Four types of load profiles are adopted to consider the actual load pattern. The classified load types represent domestic single/multiple (DOM), small commercial (COM), industrial (IND), and street and area lightning (SL) load. The static load patterns of each load type can be obtained from []. Loads are dispatched in accordance with certain criteria of the load capacity []. The SL capacities of the PV systems are calculated according to the rating of the PV inverters. We assume that the PV inverters are rated at 2% of the maximum PV power output in peak radiation. The PV systems are assumed to be located at each of the 2 buses shown in Table I. The highlighted buses are locations where capacitor banks may be installed, as is introduced in the next section. TABLE I SIZES AND TYPES OF EACH LOAD Bus Name Load Size [kva] Load Type Bus Name Load Size [kva] Load Type Mid DOM Mid DOM Mid 2 DOM 2 IND Mid2 SL Mid DOM Mid2 DOM Mid DOM Mid22 2 COM IND Mid2 DOM Mid SL Mid2 SL Mid SL Mid SL Mid 2 COM DOM IND Mid 22 DOM Mid 2 DOM Mid DOM Mid 2 DOM Mid DOM IND IND C. Configuration of the Voltage Regulation Devices Fig. 2 shows a single-line configuration of the IEEE -bus test feeder system with the voltage regulation devices. There are two SVRs, and the operation of these devices will be defined by the setting of the target voltage of the SVRs and the band gap of the tap operation. PV installed Bus mid mid mid mid mid mid mid mid mid SVR mid22 mid2 mid mid mid SVR 2 Fig. 2. Configuration of the IEEE -bus test feeder system mid2 mid2 mid2 mid mid Seventeen buses of the IEEE -bus test feeder, where the capacitor banks can be installed, are chosen for the capacitor bank dispatching. There are three-phase loads on each bus, and these buses are highlighted in Table I. Two fixed-type capacitor banks are already installed in two of the buses of the
3 original IEEE -bus test feeder system, and ; however, the size of these banks is quite large size compared to the size of the load at each bus, so a large amount of reverse reactive power flows in the lines adjacent to the two buses. To evaluate the test feeder, we eliminated the original two capacitor banks from the test feeder system. New capacitor banks, which have various sizes, will be dispatched to determine the optimal size and location of the capacitor banks according to the simulation conditions. Each capacitor bank is considered a fixed type because it has a relatively smaller size than the feeder transformer. III. OPTIMAL OPERATION AND DISPATCH OF THE VOLTAGE REGULATION DEVICES FOR HIGHLY DISTRIBUTED DERS A. Problem Definition A final purpose of the simulation is to determine the optimal capacity, siting of the capacitor banks, and the operational settings of the SVR. Table II shows the targets of the optimization to determine the optimal capacity and location of the newly installed capacitor banks considering highly distributed PV and the operation of the SVR. TABLE II TARGETS FOR THE OPTIMIZATION PROBLEM Equipment PV Allowable Range PV Size 2 kva Location Every bus that has loads Capacitor Size kvar bank Location Every bus that has three-phase loads SVR Target voltage 2 2 V The above parameters are used as inputs to the optimization problem. We change each parameter of the equipment as variables, and we evaluate each objective function at each simulation time step i.e., every minutes. Because the capacity of the PV and capacitor banks varies from to 2 kva or kvar, we can effectively estimate the PV and capacitor bank installation. Through this, we can also evaluate the optimal location and the capacity of each piece of equipment to be located among the fixed target buses. In addition, we can estimate the SVR tap setting. Because various setting values are used for the simulation, the optimal set can be obtained from the simulation results. Multiple objective functions are utilized because distribution planning, like most optimization problems, has many competing objectives. The three objective functions used in this work are defined in () (), where PV indicates the Ν size of each PV; is the total number of the installed PV systems; PF is the average power factor of the whole PV PV during the simulation period; and i C Cap, C Loss, and C SVR calculate the maintenance cost due to the capacitor banks, circuit power loss, and SVR operation, respectively. Among these objective functions, F and F 2 are to be maximized, whereas F is to be minimized. F N F PV i i C C F 2 PF PV Cap Loss CSVR Equation () represents the total size of the installed PV, and we aim to obtain the final PV hosting capacity (PVHC) of the system to the maximum extent possible. The purpose of this study is to determine the optimal operation of the voltage regulation devices in higher penetration levels of DER than general conditions; therefore, we maximize the PVHC as one of the objective functions, and we do not distinguish the penetration levels of the DER among each case. Equation (2) shows the average operating power factor of the whole system s PV inverters. We adopt a simple power factor control algorithm to improve the power factor of the point of common coupling at the location of the PV installation. Equation () represents the total cost due to maintenance of each equipment and circuit power loss. It needs to be minimized to obtain a decreasing effect on the operating cost of the distribution system. We can calculate each term of () by following () (): M C C Cap Q i i Loss P l, total L a e Cs - Ca A i T C SVR i where Μ is the total number of the installed capacitor banks; is the size of each capacitor bank; P is the total Q i circuit power loss; Cs Ca l, total is the investment cost of the SVR; is the maintenance cost of the SVR; and is a capital recovery factor, which is a function of annual interest rate and expected life of the SVR [] [2]. Each coefficient to calculate the cumulative cost of the capacitor banks and circuit power losses is considered []. Fig. shows the flowchart of the optimization procedure. After the initialization, DAKOTA inputs an initial set of system parameters for the PVHC, capacitor banks, and SVR, as shown in Table II. OpenDSS calculates the power flow during the simulation time step, which is minutes in this study. Constraints for the voltage, conductor ampacity, and the reverse power flow are evaluated subsequently. Objective functions are calculated via the COM interface, and if there are any violations in the system, penalty values are added to the objective functions. Finally, DAKOTA resolves the optimization problem, which has multiple objective functions, by using a genetic algorithm. DAKOTA defines the best set of input variables i.e., the size A -
4 of the installed PV, capacity of each capacitor bank, and setting for each SVR in the system according to the values of the three objective functions as measured by the OpenDSS QSTS simulations through an iterative process. Obj. Function (F ) START Initialization Power Flow Calculation For Simulation Duration Coming into the Constraints? END Yes Obj. Function 2 (F 2 ) (PVHC N // CAP N // SVR N) = Optimal System Setting Fig.. Flowchart of the simulation procedure Parameter Sets (PVHC N // CAP N // SVR N) No Penalty Value Obj. Function (F ) B. Simulation Result: Overall DAKOTA Variables (initial set, N=n=) N=n+ No Optimized? Yes Objective Function Fig. shows the overall simulation results. The upper plot shows the relationship among the three objective functions; the lower plots verify the relationship between the PVHC and the other objective functions. Pareto optimal front, and the small dots represent other solutions tested during the optimization procedure. We obtained Pareto optimal solutions from the simulation. We can draw the three-dimensional Pareto front approximately, which is highlighted by the bold line; and the Pareto surface, which is a three-dimensional convex hull shape. Fig. shows the tendency of each objective function. The results are divided into regions based on average operating power factor of the PV. If the distribution system has a purpose of dispatching a large amount PV, daily maintenance cost will be increased, and the PV operating power factor will be decreased. It seems that this trade-off means that the operation of the SVR is increased to maintain the overall voltage of the bus. C. Simulation Result: Capacitor Banks Fig. shows the relationship between the total size of the installed capacitor banks and the daily maintenance cost; it is obtained from the parameter sets corresponding to feasible solutions on the Pareto surface. The filled triangles show results that are calculated in a condition such that the average PV operating power factor is less than.. For the majority of the power factor values above., the total size of the capacitor banks should be increased to reduce the daily maintenance cost. Capcitor Bank Size [kvar] Daily Maintenance Cost [$] Fig.. Results of the capacitor bank size and daily cost P.F. under. P.F. over. Fig. shows the relationship between the PVHC and the total size of the capacitor banks. The straight line in the upper subplot represents a tendency of the PVHC according to the total size of the capacitor banks, which is shown in the lower subplot Power Factor Fig.. Results of the overall simulation Large stars in the figure denote feasible solutions on the Size [kvar] 2 2 PVHC Power Factor 2 Total capacity of capacitor Fig.. Results of the capacitor bank size and other objective functions.
5 The size of the installed capacitor banks does not seem to affect the PVHC of the distribution system; however, each capacitor bank has its own allowable PVHC, and it is affected by the PV operating power factor. For example, a dotted box in the upper subplot shows a result of the total of the -kvar capacitor banks. In this case, if the PV operating power factor maintains a high value, more than., the PVHC is decreased. As the PV operating power factor increases, this phenomenon becomes even worse. Therefore, if the objective is to operate PV in a high power factor, the trade-off relationship between PVHC and the PV operating power factor needs to be resolved to find the optimal values. D. Simulation Result: SVR Fig. shows the relationship between the PVHC and the determined setting of each phase of the SVR. Three subplots in the first column represent the a, b, and c phase of SVR s optimized setting results, respectively; and the second column shows the same results for SVR Fig.. Results of the SVR Unlike the case of the capacitor bank, each setting value of the SVR is almost unchanged with the different amounts of PVHC, daily maintenance cost, and PV operating power factor. This means that the optimal setting values of each SVR can be fixed as a result. E. Optimal Operation and Dispatch of the Voltage Regulation Devices We can obtain possible optimal sets of the capacitor bank dispatch and the SVRs setting by considering the high penetration level of PV. We chose the two best cases based on the minimum daily maintenance cost. Fig. shows the overall results of the installed PV and capacitor banks. According to the distance from the substation, the PV and capacitor banks show a similar tendency for each solution, respectively. In Bus, which experiences the most severe voltage drop, the PV and capacitor banks tend to be installed most frequently. In particular, the capacitor banks installed in each branch tend to be close to the substation, such as at buses and mid. The optimal setting for each SVR is shown in Table III. Compared to the original setting value, the optimized tap band values tend to be widened, and the target voltages are slightly decreased. This result reflects the effect of cost due to the SVR operation, and it shows that the setting value of the SVR is optimized to reduce the number of tap-changing operations. TABLE III OPTIMIZED SETTING VALUES FOR EACH PHASE OF THE SVRS Original Best Solution 2 nd Best Solution Target V [V] Tap Band Target V [V] Tap Band Target V [V] Tap Band SVR a 2 SVR b 2 SVR c 2 2 SVR 2a 2 SVR 2b 2 SVR 2c 2 The whole result shows a possible configuration of the voltage regulation devices with highly distributed PV in the IEEE -bus test feeder. Note that the result in this section focusses only on cost-effectiveness. In distribution system PV Size [kva] 2 Best solution-pvhc 2nd best solution-pvhc Best solution-cap 2nd best solution-cap 2 Capacitor Bank [kvar] Mid Mid Mid2 Mid2 Mid2 Mid Mid2 Mid Mid22 Mid Mid Mid Mid Mid Mid Mid Mid Mid Mid Busname (The order of distance from substation) Fig.. Result plots of PVHC and capacitor banks size for the 2 best cases having cost-effectiveness
6 planning, the focus of the distribution system operator and the best solution sets will vary with the relevant aspects. Although we have been able to suggest a method to determine the optimal operation and dispatch of the voltage regulation devices through the optimization problem solving, an extended study is needed to reflect more realistic phenomena and the capacity of equipment. IV. CONCLUSIONS We have studied the optimal operation and dispatch of the voltage regulation devices using an optimization approach. The IEEE -bus test feeder was used as a test system, and modeling of the distribution system was performed by using OpenDSS with the COM interface. We used the DAKOTA program to resolve the optimization problem, and a genetic algorithm was used as the optimization method. To drive the simulation model, we proposed an optimization problem with multiple objective functions, including PVHC, daily maintenance cost of the equipment, and the PV operating power factor. As a result of the simulationoptimization for the target distribution system, various Pareto sets were obtained. During the planning of a distribution system with a high penetration level of DERs, a simulation model such as that shown by the results of this paper can be used to understand the various trade-offs made in the design. V. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The U.S. Government retains and the publisher, by accepting the article for publication, acknowledges that the U.S. Government retains a nonexclusive, paid-up, irrevocable, worldwide license to publish or reproduce the published form of this work, or allow others to do so, for U.S. Government purposes. distributed generation units production, IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, vol., no. 2, pp.,,, Aug. 2. [] Y. A. Baysal and I. H. Altas, Cuckoo search algorithm for power loss minimization by optimal capacitor allocation in radial power systems, 2 International Symposium on INnovations in Intelligent SysTems and Applications (INISTA), Sinaia, 2, pp.. [] M. B. Jannat and A. S. Savić, Optimal capacitor placement in distribution networks regarding uncertainty in active power load and distributed generation units production, IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, vol., no. 2, pp.,,, 2. [] R. Shigenobu, A. Yona, T. Senjyu, and T. Funabashi, Multi-objective optimization of SVR considering optimum placement and weather conditions in distribution systems, 2 th International Conference on Intelligent System Application to Power Systems (ISAP), Porto, 2, pp.. [] A. S. Safigianni and G. J. Salis, Optimum voltage regulator placement in a radial power distribution network, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., vol., no. 2, pp., May 2. [2] C. A. N. Pereira and C. A. Castro, Optimal placement of voltage regulators in distribution systems, 2 IEEE Bucharest PowerTech, Bucharest, 2, pp.. [] B. A. Robbins, H. Zhu, and A. D. Domínguez-García, Optimal tap setting of voltage regulation transformers in unbalanced distribution systems, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., vol., no., pp. 2 2, Jan. 2. [] NREL Measurement and Data Center (MIDC) Solar Radiation Research Laboratory (SRRL) Baseline Measurement System (BMS), online resource: accessed Jan. 2. [] OpenDSS electric power distribution system simulator, online resource: accessed Oct. 2. [] B. M. Adams, L. E. Bauman, W. J. Bohnhoff, K. R. Dalbey, M. S. Ebeida, J. P. Eddy, et al., Dakota, a multilevel parallel object-oriented framework for design optimization, parameter estimation, uncertainty quantification, and sensitivity analysis: Version. user s manual, Sandia Technical Report SAND2-, May 2. [] B. A. Mather, Quasi-static time-series test feeder for PV integration analysis on distribution systems, 22 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, San Diego, CA, 22. [] Southern California Edison, 2 Static Load Profiles, online resource: accessed Oct. 2. VI. REFERENCES [] T. Senjyu, Y. Miyazato, A. Yona, N. Urasaki, and T. Funabashi, Optimal distribution voltage control and coordination with distributed generation, IEEE Trans. Power Del., vol. 2, no. 2, pp.,2,22, Apr. 2. [2] T. E. Grebe, Application of distribution system capacitor banks and their impact on power quality, IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., vol. 2, no., pp., Jun.. [] R. A. Gallego, A. J. Monticelli, and R. Romero, Optimal capacitor placement in radial distribution networks, IEEE Trans. Power Syst., vol., no., pp., Nov. 2. [] A. A. El-Fergany and A. Y. Abdelaziz, Efficient heuristic-based approach for multi-objective capacitor allocation in radial distribution networks, IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, vol., no., pp., Jan. 2. [] D. P. Montoya, J. M. Ramirez and J. R. Zuluaga, Multi-objective optimization for reconfiguration and capacitor allocation in distribution systems, North American Power Symposium (NAPS), 2, Pullman, WA, 2, pp. -. [] A. K. Fard and T. Niknam, Optimal stochastic capacitor placement problem from the reliability and cost views using firefly algorithm, IET Science, Measurement & Technology, vol., no., pp. 2 2, Sept. 2. [] M. B. Jannat and A. S. Savić, Optimal capacitor placement in distribution networks regarding uncertainty in active power load and
Voltage Unbalance Reduction in Low Voltage Feeders by Dynamic Switching of Residential Customers among Three Phases
 Voltage Unbalance Reduction in Low Voltage Feeders by Dynamic Switching of Residential Customers among Three Phases Farhad Shahnia, Peter Wolfs and Arindam Ghosh 3 Centre of Smart Grid and Sustainable
Voltage Unbalance Reduction in Low Voltage Feeders by Dynamic Switching of Residential Customers among Three Phases Farhad Shahnia, Peter Wolfs and Arindam Ghosh 3 Centre of Smart Grid and Sustainable
Minimization of Power Loss and Improvement of Voltage Profile in a Distribution System Using Harmony Search Algorithm
 Minimization of Power Loss and Improvement of Voltage Profile in a Distribution System Using Harmony Search Algorithm M. Madhavi 1, Sh. A. S. R Sekhar 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Electrical and Electronics
Minimization of Power Loss and Improvement of Voltage Profile in a Distribution System Using Harmony Search Algorithm M. Madhavi 1, Sh. A. S. R Sekhar 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Electrical and Electronics
Aggregated Rooftop PV Sizing in Distribution Feeder Considering Harmonic Distortion Limit
 Aggregated Rooftop PV Sizing in Distribution Feeder Considering Harmonic Distortion Limit Mrutyunjay Mohanty Power Research & Development Consultant Pvt. Ltd., Bangalore, India Student member, IEEE mrutyunjay187@gmail.com
Aggregated Rooftop PV Sizing in Distribution Feeder Considering Harmonic Distortion Limit Mrutyunjay Mohanty Power Research & Development Consultant Pvt. Ltd., Bangalore, India Student member, IEEE mrutyunjay187@gmail.com
Suppression of Voltage Violation in PV Connected Distribution System via Cooperation of Battery Energy Storage System and SVR
 Suppression of Voltage Violation in PV Connected Distribution System via Cooperation of Battery Energy Storage System and SVR YanQingyuan, Mutsumi Aoki Abstract--Nowadays, considering of environment protection,
Suppression of Voltage Violation in PV Connected Distribution System via Cooperation of Battery Energy Storage System and SVR YanQingyuan, Mutsumi Aoki Abstract--Nowadays, considering of environment protection,
Determination of Smart Inverter Power Factor Control Settings for Distributed Energy Resources
 21, rue d Artois, F-758 PARIS CIGRE US National Committee http : //www.cigre.org 216 Grid of the Future Symposium Determination of Smart Inverter Power Factor Control Settings for Distributed Energy Resources
21, rue d Artois, F-758 PARIS CIGRE US National Committee http : //www.cigre.org 216 Grid of the Future Symposium Determination of Smart Inverter Power Factor Control Settings for Distributed Energy Resources
INVESTIGATING THE BENEFITS OF MESHING REAL UK LV NETWORKS
 INVESTIGATING THE BENEFITS OF MESHING REAL UK LV NETWORKS Muhammed S. AYDIN Alejandro NAVARRO Espinosa Luis F. OCHOA The University of Manchester UK The University of Manchester UK The University of Manchester
INVESTIGATING THE BENEFITS OF MESHING REAL UK LV NETWORKS Muhammed S. AYDIN Alejandro NAVARRO Espinosa Luis F. OCHOA The University of Manchester UK The University of Manchester UK The University of Manchester
Genetic Algorithm based Voltage Regulator Placement in Unbalanced Radial Distribution Systems
 Volume 50, Number 4, 2009 253 Genetic Algorithm based Voltage Regulator in Unbalanced Radial Distribution Systems Ganesh VULASALA, Sivanagaraju SIRIGIRI and Ramana THIRUVEEDULA Abstract: In rural power
Volume 50, Number 4, 2009 253 Genetic Algorithm based Voltage Regulator in Unbalanced Radial Distribution Systems Ganesh VULASALA, Sivanagaraju SIRIGIRI and Ramana THIRUVEEDULA Abstract: In rural power
Modelling Parameters. Affect on DER Impact Study Results
 Modelling Parameters Affect on DER Impact Study Results Agenda Distributed Energy Resources (DER) Impact Studies DER Challenge Study Steps Lessons Learned Modeling Reverse Power Transformer Configuration
Modelling Parameters Affect on DER Impact Study Results Agenda Distributed Energy Resources (DER) Impact Studies DER Challenge Study Steps Lessons Learned Modeling Reverse Power Transformer Configuration
Annamacharya Institute of Technology and Sciences, Tirupathi, A.P, India
 Active Power Loss Minimization Using Simultaneous Network Reconfiguration and DG Placement with AGPSO Algorithm K.Sandhya,Venkata Supura Vemulapati 2,2 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Active Power Loss Minimization Using Simultaneous Network Reconfiguration and DG Placement with AGPSO Algorithm K.Sandhya,Venkata Supura Vemulapati 2,2 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Maximum Allowable PV Penetration by Feeder Reconfiguration Considering Harmonic Distortion Limits
 Maximum Allowable PV Penetration by Feeder Reconfiguration Considering Harmonic Distortion Limits Vemula Mahesh Veera Venkata Prasad #1, R. Madhusudhana Rao *, Mrutyunjay Mohanty #3 #1 M.Tech student,
Maximum Allowable PV Penetration by Feeder Reconfiguration Considering Harmonic Distortion Limits Vemula Mahesh Veera Venkata Prasad #1, R. Madhusudhana Rao *, Mrutyunjay Mohanty #3 #1 M.Tech student,
Identifying Long Term Voltage Stability Caused by Distribution Systems vs Transmission Systems
 Identifying Long Term Voltage Stability Caused by Distribution Systems vs Transmission Systems Amarsagar Reddy Ramapuram M. Ankit Singhal Venkataramana Ajjarapu amar@iastate.edu ankit@iastate.edu vajjarapu@iastate.edu
Identifying Long Term Voltage Stability Caused by Distribution Systems vs Transmission Systems Amarsagar Reddy Ramapuram M. Ankit Singhal Venkataramana Ajjarapu amar@iastate.edu ankit@iastate.edu vajjarapu@iastate.edu
Active Power Sharing and Frequency Control of Multiple Distributed Generators in A Microgrid
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, PP 01-07 www.iosrjournals.org Active Power Sharing and Frequency Control of Multiple Distributed
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, PP 01-07 www.iosrjournals.org Active Power Sharing and Frequency Control of Multiple Distributed
Feeder Protection Challenges with High Penetration of Inverter Based Distributed Generation
 Feeder Protection Challenges with High Penetration of Inverter Based Distributed Generation Harag Margossian 1, Florin Capitanescu 2, Juergen Sachau 3 Interdisciplinary Centre for Security, Reliability
Feeder Protection Challenges with High Penetration of Inverter Based Distributed Generation Harag Margossian 1, Florin Capitanescu 2, Juergen Sachau 3 Interdisciplinary Centre for Security, Reliability
Voltage Control of Distribution Networks with Distributed Generation using Reactive Power Compensation
 Voltage Control of Distribution Networks with Distributed Generation using Reactive Power Compensation Author Mahmud, M., Hossain, M., Pota, H., M Nasiruzzaman, A. Published 2011 Conference Title Proceedings
Voltage Control of Distribution Networks with Distributed Generation using Reactive Power Compensation Author Mahmud, M., Hossain, M., Pota, H., M Nasiruzzaman, A. Published 2011 Conference Title Proceedings
State of Charge (SOC)-Based Active Power Sharing Method for Distributed Generations in an Islanded Microgrid
 International Conference on Circuits and Systems (CAS 2015) State of Charge (SOC)-Based Active Power Sharing Method for Distributed Generations in an Islanded Microgrid Yun-Su Kim and Seung-Il Moon School
International Conference on Circuits and Systems (CAS 2015) State of Charge (SOC)-Based Active Power Sharing Method for Distributed Generations in an Islanded Microgrid Yun-Su Kim and Seung-Il Moon School
A VOLTAGE SAG/SWELL ALONG WITH LOAD REACTIVE POWER COMPENSATION BY USING SERIES INVERTER of UPQC-S
 A VOLTAGE SAG/SWELL ALONG WITH LOAD REACTIVE POWER COMPENSATION BY USING SERIES INVERTER of UPQC-S M.L.SAMPATH KUMAR*1, FIROZ-ALI-MD*2 M.Tech Student, Department of EEE, NCET, jupudi, Ibrahimpatnam, Vijayawada,
A VOLTAGE SAG/SWELL ALONG WITH LOAD REACTIVE POWER COMPENSATION BY USING SERIES INVERTER of UPQC-S M.L.SAMPATH KUMAR*1, FIROZ-ALI-MD*2 M.Tech Student, Department of EEE, NCET, jupudi, Ibrahimpatnam, Vijayawada,
THERE has been a growing interest in the optimal operation
 648 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 22, NO. 2, MAY 2007 A New Optimal Routing Algorithm for Loss Minimization and Voltage Stability Improvement in Radial Power Systems Joong-Rin Shin, Member,
648 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 22, NO. 2, MAY 2007 A New Optimal Routing Algorithm for Loss Minimization and Voltage Stability Improvement in Radial Power Systems Joong-Rin Shin, Member,
NSGA Based Optimal Volt / Var Control in Distribution System with Dispersed Generation
 NSGA Based Optimal Volt / Var Control in Distribution System with Dispersed Generation P. N. Hrisheekesha, and Jaydev Sharma Abstract In this paper, a method based on Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm
NSGA Based Optimal Volt / Var Control in Distribution System with Dispersed Generation P. N. Hrisheekesha, and Jaydev Sharma Abstract In this paper, a method based on Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm
A Novel Approach to Simultaneous Voltage Sag/Swell and Load Reactive Power Compensations Using UPQC
 A Novel Approach to Simultaneous Voltage Sag/Swell and Load Reactive Power Compensations Using UPQC N. Uma Maheshwar, Assistant Professor, EEE, Nalla Narasimha Reddy Group of Institutions. T. Sreekanth,
A Novel Approach to Simultaneous Voltage Sag/Swell and Load Reactive Power Compensations Using UPQC N. Uma Maheshwar, Assistant Professor, EEE, Nalla Narasimha Reddy Group of Institutions. T. Sreekanth,
Harmony Search and Nonlinear Programming Based Hybrid Approach to Enhance Power System Performance with Wind Penetration
 Abstract Wind generation existence in power system greatly affects power system transient stability and it also greatly affects steady state conditions. FACTS devices are proposed as a solution to this
Abstract Wind generation existence in power system greatly affects power system transient stability and it also greatly affects steady state conditions. FACTS devices are proposed as a solution to this
Modelling and Simulation of High Step up Dc-Dc Converter for Micro Grid Application
 Vol.3, Issue.1, Jan-Feb. 2013 pp-530-537 ISSN: 2249-6645 Modelling and Simulation of High Step up Dc-Dc Converter for Micro Grid Application B.D.S Prasad, 1 Dr. M Siva Kumar 2 1 EEE, Gudlavalleru Engineering
Vol.3, Issue.1, Jan-Feb. 2013 pp-530-537 ISSN: 2249-6645 Modelling and Simulation of High Step up Dc-Dc Converter for Micro Grid Application B.D.S Prasad, 1 Dr. M Siva Kumar 2 1 EEE, Gudlavalleru Engineering
Optimal Placement of AVR in RDS Using Modified Cuckoo Search Algorithm
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 11, Issue 2 Ver. I (Mar. Apr. 2016), PP 54-65 www.iosrjournals.org Optimal Placement of AVR
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 11, Issue 2 Ver. I (Mar. Apr. 2016), PP 54-65 www.iosrjournals.org Optimal Placement of AVR
Modeling and Validation of an Unbalanced LV Network Using Smart Meter and SCADA Inputs
 Modeling and Validation of an Unbalanced LV Network Using Smart Meter and SCADA Inputs Derek C. Jayasuriya, Max Rankin, Terry Jones SP AusNet Melbourne, Australia Julian de Hoog, Doreen Thomas, Iven Mareels
Modeling and Validation of an Unbalanced LV Network Using Smart Meter and SCADA Inputs Derek C. Jayasuriya, Max Rankin, Terry Jones SP AusNet Melbourne, Australia Julian de Hoog, Doreen Thomas, Iven Mareels
Voltage Support and Reactive Power Control in Micro-grid using DG
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Voltage Support and Reactive Power Control in Micro-grid using DG Nagashree. J. R 1, Vasantha Kumara. T. M 2, Narasimhegowda 3 1
International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Voltage Support and Reactive Power Control in Micro-grid using DG Nagashree. J. R 1, Vasantha Kumara. T. M 2, Narasimhegowda 3 1
Voltage Level Management of Low Voltage Radial Distribution Networks with High Penetration of Rooftop PV Systems
 Voltage Level Management of Low Voltage Radial Distribution Networks with High Penetration of Rooftop PV Systems Piyadanai Pachanapan and Surachet Kanprachar Abstract The increasing of rooftop photovoltaic
Voltage Level Management of Low Voltage Radial Distribution Networks with High Penetration of Rooftop PV Systems Piyadanai Pachanapan and Surachet Kanprachar Abstract The increasing of rooftop photovoltaic
Stability Issues of Smart Grid Transmission Line Switching
 Preprints of the 19th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Stability Issues of Smart Grid Transmission Line Switching Garng. M. Huang * W. Wang* Jun An** *Texas A&M University,
Preprints of the 19th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control Stability Issues of Smart Grid Transmission Line Switching Garng. M. Huang * W. Wang* Jun An** *Texas A&M University,
GA BASED CAPACITOR PLACEMENT FOR VOLTAGE OPTIMIZATION IN 33-BUS RADIAL DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
 International Journal of Information Technology and Knowledge Management July-December 2011, Volume 4, No. 2, pp. 713-718 GA BASED CAPACITOR PLACEMENT FOR VOLTAGE OPTIMIZATION IN 33-BUS RADIAL DISTRIBUTION
International Journal of Information Technology and Knowledge Management July-December 2011, Volume 4, No. 2, pp. 713-718 GA BASED CAPACITOR PLACEMENT FOR VOLTAGE OPTIMIZATION IN 33-BUS RADIAL DISTRIBUTION
DISTRIBUTION NETWORK RECONFIGURATION FOR LOSS MINIMISATION USING DIFFERENTIAL EVOLUTION ALGORITHM
 DISTRIBUTION NETWORK RECONFIGURATION FOR LOSS MINIMISATION USING DIFFERENTIAL EVOLUTION ALGORITHM K. Sureshkumar 1 and P. Vijayakumar 2 1 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Velammal
DISTRIBUTION NETWORK RECONFIGURATION FOR LOSS MINIMISATION USING DIFFERENTIAL EVOLUTION ALGORITHM K. Sureshkumar 1 and P. Vijayakumar 2 1 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Velammal
Voltage Controller for Radial Distribution Networks with Distributed Generation
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 3, March 2014 1 Voltage Controller for Radial Distribution Networks with Distributed Generation Christopher Kigen *, Dr. Nicodemus
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 3, March 2014 1 Voltage Controller for Radial Distribution Networks with Distributed Generation Christopher Kigen *, Dr. Nicodemus
Optimal Allocation of TCSC Devices Using Genetic Algorithms
 Proceedings of the 14 th International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON 10), Cairo University, Egypt, December 19-21, 2010, Paper ID 195. Optimal Allocation of TCSC Devices Using Genetic Algorithms
Proceedings of the 14 th International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON 10), Cairo University, Egypt, December 19-21, 2010, Paper ID 195. Optimal Allocation of TCSC Devices Using Genetic Algorithms
II. SC SYSTEM. A. Configuration of SC system Fig. 1 shows a circuit configuration of SC system. This
 Verification of the Effects of the Harmonic Voltages in the Distribution System by Single-Phase SCs for Suppressing Voltage Unbalance. Y. Ikai, M. Aoki, Y. Fujita, H. Kobayashi, M. Oguri, T.Yamada Abstract
Verification of the Effects of the Harmonic Voltages in the Distribution System by Single-Phase SCs for Suppressing Voltage Unbalance. Y. Ikai, M. Aoki, Y. Fujita, H. Kobayashi, M. Oguri, T.Yamada Abstract
Power Quality Improvement By Using DSTATCOM Controller
 Power Quality Improvement By Using DSTATCOM Controller R.Srikanth 1 E. Anil Kumar 2 Assistant Professor, Assistant Professor, Dept. of EEE, BITS Vizag Dept. of EEE, BITS Vizag Email id : srikanthreddypalli@gmail.com
Power Quality Improvement By Using DSTATCOM Controller R.Srikanth 1 E. Anil Kumar 2 Assistant Professor, Assistant Professor, Dept. of EEE, BITS Vizag Dept. of EEE, BITS Vizag Email id : srikanthreddypalli@gmail.com
Model Predictive Control Based MPPT Using Quasi Admittance converters for photovoltaic system
 Model Predictive Control Based MPPT Using Quasi Admittance converters for photovoltaic system S. Karthick 1, J. Johndavidraj 2, S. Divya 3 1 Student, No:44, New Raja Colony, Beema Nagar, Trichy-620001.
Model Predictive Control Based MPPT Using Quasi Admittance converters for photovoltaic system S. Karthick 1, J. Johndavidraj 2, S. Divya 3 1 Student, No:44, New Raja Colony, Beema Nagar, Trichy-620001.
Embedded Generation Connection Application Form
 Embedded Generation Connection Application Form This Application Form provides information required for an initial assessment of the Embedded Generation project. All applicable sections must be completed
Embedded Generation Connection Application Form This Application Form provides information required for an initial assessment of the Embedded Generation project. All applicable sections must be completed
Frequency Prediction of Synchronous Generators in a Multi-machine Power System with a Photovoltaic Plant Using a Cellular Computational Network
 2015 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence Frequency Prediction of Synchronous Generators in a Multi-machine Power System with a Photovoltaic Plant Using a Cellular Computational Network
2015 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence Frequency Prediction of Synchronous Generators in a Multi-machine Power System with a Photovoltaic Plant Using a Cellular Computational Network
LOAD REACTIVE POWER COMPENSATION BY USING SERIES INVERTER OF UPQC
 International Journal of Advances in Applied Science and Engineering (IJAEAS) ISSN (P): 2348-1811; ISSN (E): 2348-182X Vol-1, Iss.-3, JUNE 2014, 220-225 IIST LOAD REACTIVE POWER COMPENSATION BY USING SERIES
International Journal of Advances in Applied Science and Engineering (IJAEAS) ISSN (P): 2348-1811; ISSN (E): 2348-182X Vol-1, Iss.-3, JUNE 2014, 220-225 IIST LOAD REACTIVE POWER COMPENSATION BY USING SERIES
TRANSFORMER LESS H6-BRIDGE CASCADED STATCOM WITH STAR CONFIGURATION FOR REAL AND REACTIVE POWER COMPENSATION
 International Journal of Technology and Engineering System (IJTES) Vol 8. No.1 Jan-March 2016 Pp. 01-05 gopalax Journals, Singapore available at : www.ijcns.com ISSN: 0976-1345 TRANSFORMER LESS H6-BRIDGE
International Journal of Technology and Engineering System (IJTES) Vol 8. No.1 Jan-March 2016 Pp. 01-05 gopalax Journals, Singapore available at : www.ijcns.com ISSN: 0976-1345 TRANSFORMER LESS H6-BRIDGE
New Pulse Multiplication Technique Based on Six-Pulse Thyristor Converters for High-Power Applications
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS, VOL. 38, NO. 1, JANUARY/FEBRUARY 2002 131 New Pulse Multiplication Technique Based on Six-Pulse Thyristor Converters for High-Power Applications Sewan Choi,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRY APPLICATIONS, VOL. 38, NO. 1, JANUARY/FEBRUARY 2002 131 New Pulse Multiplication Technique Based on Six-Pulse Thyristor Converters for High-Power Applications Sewan Choi,
Embedded Generation Connection Application Form
 Embedded Generation Connection Application Form This Application Form provides information required for an initial assessment of the Embedded Generation project. All applicable sections must be completed
Embedded Generation Connection Application Form This Application Form provides information required for an initial assessment of the Embedded Generation project. All applicable sections must be completed
Identification of weak buses using Voltage Stability Indicator and its voltage profile improvement by using DSTATCOM in radial distribution systems
 IOSR Journal of Electrical And Electronics Engineering (IOSRJEEE) ISSN : 2278-1676 Volume 2, Issue 4 (Sep.-Oct. 2012), PP 17-23 Identification of weak buses using Voltage Stability Indicator and its voltage
IOSR Journal of Electrical And Electronics Engineering (IOSRJEEE) ISSN : 2278-1676 Volume 2, Issue 4 (Sep.-Oct. 2012), PP 17-23 Identification of weak buses using Voltage Stability Indicator and its voltage
Sensitivity Analysis for 14 Bus Systems in a Distribution Network With Distributed Generators
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 10, Issue 3 Ver. I (May Jun. 2015), PP 21-27 www.iosrjournals.org Sensitivity Analysis for
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 10, Issue 3 Ver. I (May Jun. 2015), PP 21-27 www.iosrjournals.org Sensitivity Analysis for
2012 Grid of the Future Symposium. Impacts of the Decentralized Photovoltaic Energy Resources on the Grid
 21, rue d Artois, F-75008 PARIS CIGRE US National Committee http : //www.cigre.org 2012 Grid of the Future Symposium Impacts of the Decentralized Photovoltaic Energy Resources on the Grid B. ENAYATI, C.
21, rue d Artois, F-75008 PARIS CIGRE US National Committee http : //www.cigre.org 2012 Grid of the Future Symposium Impacts of the Decentralized Photovoltaic Energy Resources on the Grid B. ENAYATI, C.
Harmonics Issues that Limit Solar Photovoltaic Generation on Distribution Circuits
 WREF 01 Paper # 048 Harmonics Issues that Limit Solar Photovoltaic Generation on Distribution Circuits Ketut Dartawan Ricardo Austria, Le Hui and Mark Suehiro* Pterra Consulting Maui Electric Company*
WREF 01 Paper # 048 Harmonics Issues that Limit Solar Photovoltaic Generation on Distribution Circuits Ketut Dartawan Ricardo Austria, Le Hui and Mark Suehiro* Pterra Consulting Maui Electric Company*
An Improved Single Input Multiple Output Converter
 International Conference on Advanced Trends in Engineering and Technology-04 (FORSCHUNG) 07 An Improved Single Input Multiple Output Parvathy and David E Abstract The aim of this study is to develop a
International Conference on Advanced Trends in Engineering and Technology-04 (FORSCHUNG) 07 An Improved Single Input Multiple Output Parvathy and David E Abstract The aim of this study is to develop a
Fault Location Using Sparse Wide Area Measurements
 319 Study Committee B5 Colloquium October 19-24, 2009 Jeju Island, Korea Fault Location Using Sparse Wide Area Measurements KEZUNOVIC, M., DUTTA, P. (Texas A & M University, USA) Summary Transmission line
319 Study Committee B5 Colloquium October 19-24, 2009 Jeju Island, Korea Fault Location Using Sparse Wide Area Measurements KEZUNOVIC, M., DUTTA, P. (Texas A & M University, USA) Summary Transmission line
UPQC for Improvement Power Quality.
 International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 2278-7461, p-issn: 2319-6491 Volume 4, Issue 4 [Sep 2014] PP: 07-19 UPQC for Improvement Power Quality. Dr.S Kamakshaiah 1 Ashwini Kumar 2 1,2, Dept
International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 2278-7461, p-issn: 2319-6491 Volume 4, Issue 4 [Sep 2014] PP: 07-19 UPQC for Improvement Power Quality. Dr.S Kamakshaiah 1 Ashwini Kumar 2 1,2, Dept
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF TAP CHANGER CONTROL ALGORITHMS FOR DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS WITH HIGH PENETRATION OF RENEWABLES
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF TAP CHANGER CONTROL ALGORITHMS FOR DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS WITH HIGH PENETRATION OF RENEWABLES Marianne HARTUNG Eva-Maria BAERTHLEIN Ara PANOSYAN GE Global Research Germany GE Global
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF TAP CHANGER CONTROL ALGORITHMS FOR DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS WITH HIGH PENETRATION OF RENEWABLES Marianne HARTUNG Eva-Maria BAERTHLEIN Ara PANOSYAN GE Global Research Germany GE Global
EMERGING distributed generation technologies make it
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 20, NO. 4, NOVEMBER 2005 1757 Fault Analysis on Distribution Feeders With Distributed Generators Mesut E. Baran, Member, IEEE, and Ismail El-Markaby, Student Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 20, NO. 4, NOVEMBER 2005 1757 Fault Analysis on Distribution Feeders With Distributed Generators Mesut E. Baran, Member, IEEE, and Ismail El-Markaby, Student Member,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Computer Science 92 (2016 ) 36 41
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 92 (2016 ) 36 41 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Communication & Convergence (ICCC-2016) Srikanta
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 92 (2016 ) 36 41 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Communication & Convergence (ICCC-2016) Srikanta
Online Dynamic Assessment of Transmission Ratings for Transmission Constraint Management in Power System and Market Operations
 Online Dynamic Assessment of Transmission Ratings for Transmission Constraint Management in Power System and Market Operations Kwok W. Cheung, Ph.D., PE, PMP, FIEEE R&D Director, Network Management Solutions
Online Dynamic Assessment of Transmission Ratings for Transmission Constraint Management in Power System and Market Operations Kwok W. Cheung, Ph.D., PE, PMP, FIEEE R&D Director, Network Management Solutions
ASSESSMENT OF HARMONIC DISTORTION LEVELS IN LV NETWORKS WITH INCREASING PENETRATION LEVELS OF INVERTER CONNECTED EMBEDDED GENERATION
 ASSESSMENT OF HARMONIC DISTORTION LEVELS IN LV NETWORKS WITH INCREASING PENETRATION LEVELS OF INVERTER CONNECTED EMBEDDED GENERATION Adam DYŚKO, Graeme M. BRT, James R. McDONALD niversity of Strathclyde
ASSESSMENT OF HARMONIC DISTORTION LEVELS IN LV NETWORKS WITH INCREASING PENETRATION LEVELS OF INVERTER CONNECTED EMBEDDED GENERATION Adam DYŚKO, Graeme M. BRT, James R. McDONALD niversity of Strathclyde
The Impact of Superconducting Fault Current Limiter Locations on Voltage Sag in Power Distribution System
 Amirkabir University of Technology (Tehran Polytechnic) Vol. 47, No. 2, Fall 215, pp. 49-6 Amirkabir International Journal of Science& Research )AIJ-EEE) The Impact of Superconducting Fault Current Limiter
Amirkabir University of Technology (Tehran Polytechnic) Vol. 47, No. 2, Fall 215, pp. 49-6 Amirkabir International Journal of Science& Research )AIJ-EEE) The Impact of Superconducting Fault Current Limiter
Impact of Distributed Generation on Voltage Regulation by ULTC Transformer using Various Existing Methods
 Proceedings of the th WSEAS International Conference on Power Systems, Beijing, China, September -, 200 Impact of Distributed Generation on Voltage Regulation by ULTC Transformer using Various Existing
Proceedings of the th WSEAS International Conference on Power Systems, Beijing, China, September -, 200 Impact of Distributed Generation on Voltage Regulation by ULTC Transformer using Various Existing
Downloaded from
 Proceedings of The Intl. Conf. on Information, Engineering, Management and Security 2014 [ICIEMS 2014] 330 Power Quality Improvement Using UPQC Chandrashekhar Reddy S Assoc.Professor, Dept.of Electrical
Proceedings of The Intl. Conf. on Information, Engineering, Management and Security 2014 [ICIEMS 2014] 330 Power Quality Improvement Using UPQC Chandrashekhar Reddy S Assoc.Professor, Dept.of Electrical
Voltage Sag Index Calculation Using an Electromagnetic Transients Program
 International Conference on Power Systems Transients IPST 3 in New Orleans, USA Voltage Sag Index Calculation Using an Electromagnetic Transients Program Juan A. Martinez-Velasco, Jacinto Martin-Arnedo
International Conference on Power Systems Transients IPST 3 in New Orleans, USA Voltage Sag Index Calculation Using an Electromagnetic Transients Program Juan A. Martinez-Velasco, Jacinto Martin-Arnedo
POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BY USING ACTIVE POWER FILTERS
 POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BY USING ACTIVE POWER FILTERS Ramesh Kumar V 1, Dr. Dalvinder Kaur Mangal 2 1 Research Scholar, Department of Electrical Engineering, Sunrise University, Alwar 2 Asso. Prof.,
POWER QUALITY IMPROVEMENT BY USING ACTIVE POWER FILTERS Ramesh Kumar V 1, Dr. Dalvinder Kaur Mangal 2 1 Research Scholar, Department of Electrical Engineering, Sunrise University, Alwar 2 Asso. Prof.,
Multi-agent Coordination of DG Inverters for Improving the Voltage Profile of the Distribution Grid
 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORIES http://www.merl.com Multi-agent Coordination of DG Inverters for Improving the Voltage Profile of the Distribution Grid Polymeneas, E.; Benosman, M. TR2014-112
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RESEARCH LABORATORIES http://www.merl.com Multi-agent Coordination of DG Inverters for Improving the Voltage Profile of the Distribution Grid Polymeneas, E.; Benosman, M. TR2014-112
LOAD BALANCING IN PRIMARY DISTRIBUTION FEEDERS BY COMBINATION OF RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCE AND VOLTAGE SOURCE INVERTER
 Paper ID: EE14 LOAD BALANCING IN PRIMARY DISTRIBUTION FEEDERS BY COMBINATION OF RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCE AND VOLTAGE SOURCE INVERTER Metkari Vishal T., Department of Electrical, Sanjeevan Engineering &
Paper ID: EE14 LOAD BALANCING IN PRIMARY DISTRIBUTION FEEDERS BY COMBINATION OF RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCE AND VOLTAGE SOURCE INVERTER Metkari Vishal T., Department of Electrical, Sanjeevan Engineering &
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July-2013 377 Self-Healing Framework for Distribution Systems Fazil Haneef, S.Angalaeswari Abstract - The self healing framework
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 7, July-2013 377 Self-Healing Framework for Distribution Systems Fazil Haneef, S.Angalaeswari Abstract - The self healing framework
An Interleaved High Step-Up Boost Converter With Voltage Multiplier Module for Renewable Energy System
 An Interleaved High Step-Up Boost Converter With Voltage Multiplier Module for Renewable Energy System Vahida Humayoun 1, Divya Subramanian 2 1 P.G. Student, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
An Interleaved High Step-Up Boost Converter With Voltage Multiplier Module for Renewable Energy System Vahida Humayoun 1, Divya Subramanian 2 1 P.G. Student, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) International Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology (IJEET), ISSN 0976 ISSN 0976 6545(Print) ISSN 0976 6553(Online) Volume
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJEET) International Journal of Electrical Engineering and Technology (IJEET), ISSN 0976 ISSN 0976 6545(Print) ISSN 0976 6553(Online) Volume
Multilevel Inverter for Grid-Connected PV SystemEmploying MPPT and PI Controller
 Multilevel Inverter for Grid-Connected PV SystemEmploying MPPT and PI Controller Seena M Varghese P. G. Student, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Saintgits College of Engineering,
Multilevel Inverter for Grid-Connected PV SystemEmploying MPPT and PI Controller Seena M Varghese P. G. Student, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Saintgits College of Engineering,
Cost Based Dynamic Load Dispatch for an Autonomous Parallel Converter Hybrid AC-DC Microgrid
 Cost Based Dynamic Load Dispatch for an Autonomous Parallel Converter Hybrid AC-DC Microgrid M. A. Hasan, N. K. Vemula and S. K. Parida Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology,
Cost Based Dynamic Load Dispatch for an Autonomous Parallel Converter Hybrid AC-DC Microgrid M. A. Hasan, N. K. Vemula and S. K. Parida Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology,
Power-Quality Improvement with a Voltage-Controlled DSTATCOM
 Power-Quality Improvement with a Voltage-Controlled DSTATCOM R.Pravalika MTech Student Paloncha, Khammam, India V.Shyam Kumar Associate Professor Paloncha, Khammam, India. Mr.Chettumala Ch Mohan Rao Associate
Power-Quality Improvement with a Voltage-Controlled DSTATCOM R.Pravalika MTech Student Paloncha, Khammam, India V.Shyam Kumar Associate Professor Paloncha, Khammam, India. Mr.Chettumala Ch Mohan Rao Associate
Neural Network Based Loading Margin Approximation for Static Voltage Stability in Power Systems
 Neural Network Based Loading Margin Approximation for Static Voltage Stability in Power Systems Arthit Sode-Yome, Member, IEEE, and Kwang Y. Lee, Fellow, IEEE Abstract Approximate loading margin methods
Neural Network Based Loading Margin Approximation for Static Voltage Stability in Power Systems Arthit Sode-Yome, Member, IEEE, and Kwang Y. Lee, Fellow, IEEE Abstract Approximate loading margin methods
THE DESERT KNOWLEDGE AUSTRALIA SOLAR CENTRE: HIGH VOLTAGE EFFECTS ON INVERTER PERFORMANCE.
 THE DESERT KNOWLEDGE AUSTRALIA SOLAR CENTRE: HIGH VOLTAGE EFFECTS ON INVERTER PERFORMANCE. Paul Rodden, Ga Rick Lee & Lyndon Frearson CAT Projects PO Box 8044, Desert Knowledge Precinct, Alice Springs,
THE DESERT KNOWLEDGE AUSTRALIA SOLAR CENTRE: HIGH VOLTAGE EFFECTS ON INVERTER PERFORMANCE. Paul Rodden, Ga Rick Lee & Lyndon Frearson CAT Projects PO Box 8044, Desert Knowledge Precinct, Alice Springs,
AS the power distribution networks become more and more
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 21, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2006 153 A Unified Three-Phase Transformer Model for Distribution Load Flow Calculations Peng Xiao, Student Member, IEEE, David C. Yu, Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS, VOL. 21, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2006 153 A Unified Three-Phase Transformer Model for Distribution Load Flow Calculations Peng Xiao, Student Member, IEEE, David C. Yu, Member,
Power Quality Improvement by Simultaneous Controlling of Active and Reactive Powers in UPQC-S
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal ISSN: 2249-6645 Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Power Quality Improvement by Simultaneous Controlling of Active and Reactive Powers in UPQC-S Dr.Chandrashekhar
International OPEN ACCESS Journal ISSN: 2249-6645 Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Power Quality Improvement by Simultaneous Controlling of Active and Reactive Powers in UPQC-S Dr.Chandrashekhar
AUTOMATIC IMPLEMENTATION OF FIR FILTERS ON FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS
 AUTOMATIC IMPLEMENTATION OF FIR FILTERS ON FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Satish Mohanakrishnan and Joseph B. Evans Telecommunications & Information Sciences Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering
AUTOMATIC IMPLEMENTATION OF FIR FILTERS ON FIELD PROGRAMMABLE GATE ARRAYS Satish Mohanakrishnan and Joseph B. Evans Telecommunications & Information Sciences Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering
,, N.Loganayaki 3. Index Terms: PV multilevel inverter, grid connected inverter, coupled Inductors, self-excited Induction Generator.
 Modeling Of PV and Wind Energy Systems with Multilevel Inverter Using MPPT Technique,, N.Loganayaki 3 Abstract -The recent upsurge is in the demand of hybrid energy systems which can be accomplished by
Modeling Of PV and Wind Energy Systems with Multilevel Inverter Using MPPT Technique,, N.Loganayaki 3 Abstract -The recent upsurge is in the demand of hybrid energy systems which can be accomplished by
High Gain Step Up DC-DC Converter For DC Micro-Grid Application
 High Gain Step Up DC-DC Converter For DC Micro-Grid Application Manoranjan Sahoo Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India Email: mailmrsahoo@gmail.com Siva Kumar
High Gain Step Up DC-DC Converter For DC Micro-Grid Application Manoranjan Sahoo Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad, India Email: mailmrsahoo@gmail.com Siva Kumar
Impact Assessment Generator Form
 Impact Assessment Generator Form This connection impact assessment form provides information for the Connection Assessment and Connection Cost Estimate. Date: (dd/mm/yyyy) Consultant/Developer Name: Project
Impact Assessment Generator Form This connection impact assessment form provides information for the Connection Assessment and Connection Cost Estimate. Date: (dd/mm/yyyy) Consultant/Developer Name: Project
An efficient power flow algorithm for distribution systems with polynomial load
 An efficient power flow algorithm for distribution systems with polynomial load Jianwei Liu, M. M. A. Salama and R. R. Mansour Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo,
An efficient power flow algorithm for distribution systems with polynomial load Jianwei Liu, M. M. A. Salama and R. R. Mansour Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo,
Neural Network based Multi-Dimensional Feature Forecasting for Bad Data Detection and Feature Restoration in Power Systems
 Neural Network based Multi-Dimensional Feature Forecasting for Bad Data Detection and Feature Restoration in Power Systems S. P. Teeuwsen, Student Member, IEEE, I. Erlich, Member, IEEE, Abstract--This
Neural Network based Multi-Dimensional Feature Forecasting for Bad Data Detection and Feature Restoration in Power Systems S. P. Teeuwsen, Student Member, IEEE, I. Erlich, Member, IEEE, Abstract--This
IMPLEMENTATION OF ADVANCED DISTRIBUTION AUTOMATION IN U.S.A. UTILITIES
 IMPLEMENTATION OF ADVANCED DISTRIBUTION AUTOMATION IN U.S.A. UTILITIES (Summary) N S Markushevich and A P Berman, C J Jensen, J C Clemmer Utility Consulting International, JEA, OG&E Electric Services,
IMPLEMENTATION OF ADVANCED DISTRIBUTION AUTOMATION IN U.S.A. UTILITIES (Summary) N S Markushevich and A P Berman, C J Jensen, J C Clemmer Utility Consulting International, JEA, OG&E Electric Services,
WITH THE advent of advanced power-electronics technologies,
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 29, NO. 4, AUGUST 2014 1859 Impact of Unified Power-Quality Conditioner Allocation on Line Loading, Losses, and Voltage Stability of Radial Distribution Systems
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 29, NO. 4, AUGUST 2014 1859 Impact of Unified Power-Quality Conditioner Allocation on Line Loading, Losses, and Voltage Stability of Radial Distribution Systems
Enhancement of Fault Current and Overvoltage by Active Type superconducting fault current limiter (SFCL) in Renewable Distributed Generation (DG)
 Enhancement of Fault Current and Overvoltage by Active Type superconducting fault current limiter (SFCL) in Renewable Distributed Generation (DG) PATTI.RANADHEER Assistant Professor, E.E.E., PACE Institute
Enhancement of Fault Current and Overvoltage by Active Type superconducting fault current limiter (SFCL) in Renewable Distributed Generation (DG) PATTI.RANADHEER Assistant Professor, E.E.E., PACE Institute
Discussion on the Deterministic Approaches for Evaluating the Voltage Deviation due to Distributed Generation
 Discussion on the Deterministic Approaches for Evaluating the Voltage Deviation due to Distributed Generation TSAI-HSIANG CHEN a NIEN-CHE YANG b Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University
Discussion on the Deterministic Approaches for Evaluating the Voltage Deviation due to Distributed Generation TSAI-HSIANG CHEN a NIEN-CHE YANG b Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University
Comparison of Bias-Voltage and Reflection-Coefficient Based Reconfiguration of a Tunable-Varactor Matching Network for Adaptive Amplifiers
 Comparison of Bias-Voltage and Reflection-Coefficient Based Reconfiguration of a Tunable-Varactor Matching Network for Adaptive Amplifiers Lucilia Lamers 1, Zachary Hays 1, Christopher Kappelmann 1, Sarvin
Comparison of Bias-Voltage and Reflection-Coefficient Based Reconfiguration of a Tunable-Varactor Matching Network for Adaptive Amplifiers Lucilia Lamers 1, Zachary Hays 1, Christopher Kappelmann 1, Sarvin
Design of a Dual Active Bridge DC-DC Converter for Photovoltaic System Application. M.T. Tsai, C.L. Chu, Y.Z. Yang and D. R Wu
 ICIC Express etters ICIC International c16 ISSN 185-766 Volume 7, Number 8, August 16 pp. 185-181 Design of a Dual Active Bridge DC-DC Converter for Photovoltaic System Application M.T. Tsai, C.. Chu,
ICIC Express etters ICIC International c16 ISSN 185-766 Volume 7, Number 8, August 16 pp. 185-181 Design of a Dual Active Bridge DC-DC Converter for Photovoltaic System Application M.T. Tsai, C.. Chu,
Enhancement of Power Quality using active power filter in a Medium-Voltage Distribution Network switching loads
 Vol.2, Issue.2, Mar-Apr 2012 pp-431-435 ISSN: 2249-6645 Enhancement of Power Quality using active power filter in a Medium-Voltage Distribution Network switching loads M. CHANDRA SEKHAR 1, B. KIRAN BABU
Vol.2, Issue.2, Mar-Apr 2012 pp-431-435 ISSN: 2249-6645 Enhancement of Power Quality using active power filter in a Medium-Voltage Distribution Network switching loads M. CHANDRA SEKHAR 1, B. KIRAN BABU
Real-time Volt/Var Optimization Scheme for Distribution Systems with PV Integration
 Grid-connected Advanced Power Electronic Systems Real-time Volt/Var Optimization Scheme for Distribution Systems with PV Integration 02-15-2017 Presenter Name: Yan Chen (On behalf of Dr. Benigni) Outline
Grid-connected Advanced Power Electronic Systems Real-time Volt/Var Optimization Scheme for Distribution Systems with PV Integration 02-15-2017 Presenter Name: Yan Chen (On behalf of Dr. Benigni) Outline
Short Circuit Calculation in Networks with a High Share of Inverter Based Distributed Generation
 Short Circuit Calculation in Networks with a High Share of Inverter Based Distributed Generation Harag Margossian, Juergen Sachau Interdisciplinary Center for Security, Reliability and Trust University
Short Circuit Calculation in Networks with a High Share of Inverter Based Distributed Generation Harag Margossian, Juergen Sachau Interdisciplinary Center for Security, Reliability and Trust University
A PV Based Thirteen Level Inverter For Microgrid Mr.K.sairam, M. Saritha Reddy, K.S. Mann, M. Narendra Kumar
 A PV Based Thirteen Level Inverter For Microgrid Mr.K.sairam, M. Saritha Reddy, K.S. Mann, M. Narendra Kumar Sairam.kammari@outlook.com ABSTRACT- MicroGrid connected Photovoltaic (PV) system uses to have
A PV Based Thirteen Level Inverter For Microgrid Mr.K.sairam, M. Saritha Reddy, K.S. Mann, M. Narendra Kumar Sairam.kammari@outlook.com ABSTRACT- MicroGrid connected Photovoltaic (PV) system uses to have
Optimum Rate Allocation for Two-Class Services in CDMA Smart Antenna Systems
 810 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 51, NO. 5, MAY 2003 Optimum Rate Allocation for Two-Class Services in CDMA Smart Antenna Systems Il-Min Kim, Member, IEEE, Hyung-Myung Kim, Senior Member,
810 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 51, NO. 5, MAY 2003 Optimum Rate Allocation for Two-Class Services in CDMA Smart Antenna Systems Il-Min Kim, Member, IEEE, Hyung-Myung Kim, Senior Member,
D-UPFC Application as the Series Power Device in the Massive Roof-top PVs and Domestic Loads
 Current Photovoltaic Research 4(4) 131-139 (2016) pissn 2288-3274 DOI:https://doi.org/10.21218/CPR.2016.4.4.131 eissn 2508-125X D-UPFC Application as the Series Power Device in the Massive Roof-top PVs
Current Photovoltaic Research 4(4) 131-139 (2016) pissn 2288-3274 DOI:https://doi.org/10.21218/CPR.2016.4.4.131 eissn 2508-125X D-UPFC Application as the Series Power Device in the Massive Roof-top PVs
VOLTAGE CONTROL STRATEGY IN WEAK DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS WITH HYBRIDS GENERATION SYSTEMS
 VOLTAGE CONTROL STRATEGY IN WEAK DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS WITH HYBRIDS GENERATION SYSTEMS Marcelo CASSIN Empresa Provincial de la Energía de Santa Fe Argentina mcassin@epe.santafe.gov.ar ABSTRACT In radial
VOLTAGE CONTROL STRATEGY IN WEAK DISTRIBUTION NETWORKS WITH HYBRIDS GENERATION SYSTEMS Marcelo CASSIN Empresa Provincial de la Energía de Santa Fe Argentina mcassin@epe.santafe.gov.ar ABSTRACT In radial
Document C-29. Procedures for System Modeling: Data Requirements & Facility Ratings. January 5 th, 2016 TFSS Revisions Clean Open Process Posting
 Document C-29 Procedures for System Modeling: January 5 th, 2016 TFSS Revisions Clean Open Process Posting Prepared by the SS-37 Working Group on Base Case Development for the Task Force on System Studies.
Document C-29 Procedures for System Modeling: January 5 th, 2016 TFSS Revisions Clean Open Process Posting Prepared by the SS-37 Working Group on Base Case Development for the Task Force on System Studies.
Smart Time-Division-Multiplexing Control Strategy for Voltage Multiplier Rectifier
 Smart Time-Division-Multiplexing Control Strategy for Voltage Multiplier Rectifier Bin-Han Liu, Jen-Hao Teng, Yi-Cheng Lin Department of Electrical Engineering, National Sun Yat-Sen University, Kaohsiung,
Smart Time-Division-Multiplexing Control Strategy for Voltage Multiplier Rectifier Bin-Han Liu, Jen-Hao Teng, Yi-Cheng Lin Department of Electrical Engineering, National Sun Yat-Sen University, Kaohsiung,
Improve Distribution System Energy Efficiency With Coordinated Reactive Power Control
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS 1 Improve Distribution System Energy Efficiency With Coordinated Reactive Power Control Fang Yang, Member, IEEE, and Zhao Li, Member,IEEE Abstract In the distribution
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER SYSTEMS 1 Improve Distribution System Energy Efficiency With Coordinated Reactive Power Control Fang Yang, Member, IEEE, and Zhao Li, Member,IEEE Abstract In the distribution
Impact of High PV Penetration on Grid Operation. Yahia Baghzouz Professor of Electrical engineering University of Nevada Las Vegas
 Impact of High PV Penetration on Grid Operation Yahia Baghzouz Professor of Electrical engineering University of Nevada Las Vegas Overview Introduction/Background Effects of High PV Penetration on Distribution
Impact of High PV Penetration on Grid Operation Yahia Baghzouz Professor of Electrical engineering University of Nevada Las Vegas Overview Introduction/Background Effects of High PV Penetration on Distribution
MODELING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF POWER ELECTRONICS BASED VOLTAGE REGULATORS ON DISTRIBUTION VOLTAGE DISTURBANCES
 MODELING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF POWER ELECTRONICS BASED VOLTAGE REGULATORS ON DISTRIBUTION VOLTAGE DISTURBANCES James SIMONELLI Olivia LEITERMANN Jing HUANG Gridco Systems USA Gridco Systems USA Gridco Systems
MODELING THE EFFECTIVENESS OF POWER ELECTRONICS BASED VOLTAGE REGULATORS ON DISTRIBUTION VOLTAGE DISTURBANCES James SIMONELLI Olivia LEITERMANN Jing HUANG Gridco Systems USA Gridco Systems USA Gridco Systems
VOLTAGE MANAGEMENT BY THE APPORTIONMENT OF TOTAL VOLTAGE DROP IN THE PLANNING AND OPERATION OF COMBINED MEDIUM AND LOW VOLTAGE DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
 66 SOUTH AFRICAN INSTITUTE OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERS Vol.97(1) March 2006 VOLTAGE MANAGEMENT BY THE APPORTIONMENT OF TOTAL VOLTAGE DROP IN THE PLANNING AND OPERATION OF COMBINED MEDIUM AND LOW VOLTAGE DISTRIBUTION
66 SOUTH AFRICAN INSTITUTE OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERS Vol.97(1) March 2006 VOLTAGE MANAGEMENT BY THE APPORTIONMENT OF TOTAL VOLTAGE DROP IN THE PLANNING AND OPERATION OF COMBINED MEDIUM AND LOW VOLTAGE DISTRIBUTION
Industry Webinar. Reactive Power Planning. NERC System Analysis and Modeling Subcommittee (SAMS) March 2017
 Industry Webinar Reactive Power Planning NERC System Analysis and Modeling Subcommittee (SAMS) March 2017 Webinar Topics Reliability Guideline on Reactive Power Planning Webinar Topics Fundamentals of
Industry Webinar Reactive Power Planning NERC System Analysis and Modeling Subcommittee (SAMS) March 2017 Webinar Topics Reliability Guideline on Reactive Power Planning Webinar Topics Fundamentals of
Smart Grid Reconfiguration Using Genetic Algorithm and NSGA-II
 Smart Grid Reconfiguration Using Genetic Algorithm and NSGA-II 1 * Sangeeta Jagdish Gurjar, 2 Urvish Mewada, 3 * Parita Vinodbhai Desai 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, AIT, Gujarat Technical University,
Smart Grid Reconfiguration Using Genetic Algorithm and NSGA-II 1 * Sangeeta Jagdish Gurjar, 2 Urvish Mewada, 3 * Parita Vinodbhai Desai 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, AIT, Gujarat Technical University,
Study of a 3kW High-Efficient Wide-Bandgap DC- DC Power Converter for Solar Power Integration in 400V DC Distribution Networks
 IEEE PEDS 2017, Honolulu, USA 12 15 December 2017 Study of a 3kW High-Efficient Wide-Bandgap DC- DC Power Converter for Solar Power Integration in 400V DC Distribution Networks Yucheng Zhang, Yashwanth
IEEE PEDS 2017, Honolulu, USA 12 15 December 2017 Study of a 3kW High-Efficient Wide-Bandgap DC- DC Power Converter for Solar Power Integration in 400V DC Distribution Networks Yucheng Zhang, Yashwanth
Planning of Distributed Generation and Capacitor in an Unbalanced Radial Distribution System using Cuckoo Search Algorithm
 Planning of Distributed Generation and Capacitor in an Unbalanced Radial Distribution System using Cuckoo Search Algorithm Padarbinda Samal, Sanjeeb Mohanty and Sanjib Ganguly Department of Electrical
Planning of Distributed Generation and Capacitor in an Unbalanced Radial Distribution System using Cuckoo Search Algorithm Padarbinda Samal, Sanjeeb Mohanty and Sanjib Ganguly Department of Electrical
A Variable Step Size MPPT Method for Stand-Alone PV Energy Systems
 Journal of Energy and Natural Resources 2016; 5(1-1): 1-5 Published online January 12, 2016 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/jenr) doi: 10.11648/j.jenr.s.2016050101.11 ISSN: 2330-7366 (Print);
Journal of Energy and Natural Resources 2016; 5(1-1): 1-5 Published online January 12, 2016 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/jenr) doi: 10.11648/j.jenr.s.2016050101.11 ISSN: 2330-7366 (Print);
Study on the Improvement of the Special Protection Scheme (SPS) in the Korean power system
 Study on the Improvement of the Special Protection Scheme (SPS) in the Korean power system Jeonghoon Shin, Suchul Nam, Seungtae Cha, Jaegul Lee, Taekyun Kim, Junyoen Kim, Taeok Kim, Hwachang Song Abstract--This
Study on the Improvement of the Special Protection Scheme (SPS) in the Korean power system Jeonghoon Shin, Suchul Nam, Seungtae Cha, Jaegul Lee, Taekyun Kim, Junyoen Kim, Taeok Kim, Hwachang Song Abstract--This
OpenDSS PVSystem Element Model Version 1
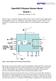 OpenDSS PVSystem Element Model Version 1 Wednesday, February 23, 2011 Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of the PVSystem device model recently implemented into OpenDSS version 7.4.1 at Build 28. This model
OpenDSS PVSystem Element Model Version 1 Wednesday, February 23, 2011 Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of the PVSystem device model recently implemented into OpenDSS version 7.4.1 at Build 28. This model
