Experimental investigation about influences of longitudinal-mode structure of pumping source on a Ti:sapphire laser
|
|
|
- Lucinda Jackson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Experiental investigation about influences of longitudinal-ode structure of puping source on a Ti:sapphire laser Huadong Lu, Jing Su,* Changde Xie, and Kunchi Peng State Key Laboratory of Quantu Optics and Quantu Optics Devices, Institute of Opto-Electronics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan, Shanxi , China * jingsu@sxu.edu.cn Abstract: Using a ulti-longitudinal-ode (MLM) and a singlelongitudinal-ode (SLM) all-solid-state green lasers to be the puping sources of a continuous-wave Ti:sapphire laser, respectively, the intensitynoise dependence of the Ti:sapphire laser on the longitudinal-ode structure of puping sources is experientally studied. The coparison between the theoretical prediction based on the quantu-echanical odel and the experiental easureent for the intensity-noise spectra is presented. 011 Optical Society of Aerica OCIS codes: (70.500) Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise; ( ) Lasers, frequency doubled; ( ) Lasers, ring; ( ) Lasers, titaniu. References and links 1. P. F. Moulton, Spectroscopic and laser characteristics of Ti:Al O 3, J. Opt. Soc. A. B 3(1), (1986).. S. Qaar, H. Xiong, and M. S. Zubairy, Influence of pup-phase fluctuations on entangleent generation using a correlated spontaneous-eission laser, Phys. Rev. A 75(6), (007). 3. D. Wang, Y. Shang, Z. Yan, W. Wang, X. Jia, C. Xie, and K. Peng, Experiental investigation about the influence of pup phase noise on phase-correlation of output optical fields fro a non-degenerate paraetric oscillator, Europhys. Lett. 8(), 4003 (008). 4. D. Wang, Y. Shang, X. Jia, C. Xie, and K. Peng, Dependence of quantu correlations of twin beas on the pup finesse of an optical paraetric oscillator, J. Phys. At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 41(3), (008). 5. T. C. Ralph, C. C. Harb, and H. A. Bachor, Intensity noise of injection-locked lasers: Quantu theory using a linearized input-output ethod, Phys. Rev. A 54(5), (1996). 6. C. C. Harb, T. C. Ralph, E. H. Huntington, D. E. McClelland, H.-A. Bachor, and I. Freitag, Intensity-noise dependence of Nd:YAG lasers on their diode-laser pup source, J. Opt. Soc. A. B 14(11), (1997). 7. Z. Jing, Z. Kuanshou, C. Yanli, Z. Tiancai, X. Changde, and P. Kunchi, Intensity noise properties of LD puped single-frequency ring laser, Acta Opt. Sin. 0(10), (000). 8.. Zhang, Y. Cheng, T. Zhang, K. Zhang, C. Xie, and K. Peng, Investigation of the characteristics of the intensity noise of singly resonant active second-haronic generation, J. Opt. Soc. A. B 17(10), (000). 9. M. Tsunekane, N. Taguchi, and H. Inaba, High-power, efficient, low-noise, continuous-wave all-solid-state Ti:sapphire laser, Opt. Lett. 1(3), (1996). 10. J. Belfi, J. Galli, G. Giusfredi, and F. Marin, Intensity noise of an injection-locked Ti:sapphire laser: analysis of the phase-noise-to-aplitude-noise conversion, J. Opt. Soc. A. B 3(7), (006). 11. S. Witte, R. T. Zinkstok, W. Hogervorst, and K. S. E. Eikea, Control and precise easureent of carrierenvelope phase dynaics, Appl. Phys. B 78(1), 5 1 (004). 1. Y. Yaaoto, S. Machida, and O. Nilsson, Aplitude squeezing in a pup-noise-suppressed laser oscillator, Phys. Rev. A 34(5), (1986). 13. A. Lucianetti, Th. Graf, R. Weber, and H. P. Weber, Thero-optical properties of transversely puped coposite YAG rods with Nd-doped core, IEEE J. Quantu Electron. 36(), 0 7 (000). 14. L. Fengqin, Y. Lin, S. Yuei, Z. Yaohui, Z. Kuanshou, and P. Kunchi, All-solid-state CW 1.9 W TEM 00 ode green laser, Chin. J. Lasers 36(6), (009). 15. Y. Zheng, F. Li, Y. Wang, K. Zhang, and K. Peng, High-stability single-frequency green laser with a wedge Nd:YVO 4 as a polarizing bea splitter, Opt. Coun. 83(), (010). 16. M. Bouafia, H. Bencheikh, L. Bouaaa, and H. Weber, M quality factor as a key to astering laser bea propagation, Proc. SPIE 5456, (004). 17. L. Huadong, S. Jing, L. Fengqin, W. Wenzhe, C. Yougui, and P. Kunchi, Copact, stable, tunable Ti:Sapphire laser, Chin. J. Lasers 37(5), (010). 18. H. P. Yuen, and V. W. S. Chan, Noise in hoodyne and heterodyne detection, Opt. Lett. 8(3), (1983). 19. W. Yiin, L. Yupu, and Z. Yinghua, Influence of the pup bea ode in a longitudinally puped CW Ti:sapphire laser, Chin. J. Lasers A3(), (1996). (C) 011 OSA 17 January 011 / Vol. 19, No. / OPTICS EXPRESS 1344
2 0. J. Harrison, A. Finch, D. M. Rines, G. A. Rines, and P. F. Moulton, Low-threshold, cw, all-solid-state Ti:Al( )O( 3) laser, Opt. Lett. 16(8), (1991). 1. A. J. Alfrey, Modeling of longitudinally puped CW Ti:Sapphire laser oscillators, IEEE J. Quantu Electron. 5(4), (1989).. C. C. Harb, T. C. Ralph, E. H. Huntington, I. Freitag I, D. E. McClelland, and H. A. Bachor, Intensity-noise properties of injection-locked lasers, Phys. Rev. A 54(5), (1996). 3. C. Becher, and K.-J. Boller, Intensity noise properties of Nd:YVO 4 icrochip lasers puped with an aplitude squeezed diode laser, Opt. Coun. 147(4-6), (1998). 4. H. Nagai, M. Kue, I. Otha, H. Shiizu, and M. Kazuura, Noise generation in laser diode-puped solid state lasers due to ode hopping of puping laser diodes, in Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Vol. 1 of 199 OSA Technical Digest Series (Optical Society of Aerica, Washington, D. C., 199), paper CWG T. Baer, Large-aplitude fluctuations due to longitudinal ode coupling in diode-puped intracavity-doubled Nd:YAG lasers, J. Opt. Soc. A. B 3(9), (1986). 1. Introduction All-solid-state continuous-wave (CW) single-frequency tunable Ti:sapphire lasers with copact configuration and high efficiency have been extensively applied to high-sensitive laser spectroscopy, quantu counications, high-precision interferoetry and so on owing to their broad tunable wavelength range fro 700 n to 1000 n [1]. Recent years, when Ti:sapphire lasers are used in the experiental researches of laser cooling of atos, quantu optics and quantu inforation, ore and ore attentions have to be paid in reducing intensity noises of their output light since the extra noises on laser sources will severely influence the experiental results [ 4]. Ralph and Harb established a theoretical odel based on quantu echanics to express the effect of different noise sources on the intensity noises of the output light fro lasers [5]. Successively, Harb et al. experientally copared the intensity noises of two sets of Nd:YAG ring lasers puped by a single-eleent diode laser (SEDL) or by a diode-laser array (DLA), respectively [6]. They showed that the intensity noise of the Nd:YAG laser depends on vacuu fluctuations as well as on puping source noise and deonstrated that the seiclassical rate-equation odel was not sufficient to describe the noise behavior of the lasers since it is unable to involve the influence of nonclassical vacuu fluctuations on the intensity-noise spectru. Using the quantu echanical odel suggested in Ref [5], they successful described the observed intensity-noise spectru of the lasers. Later the odel was used to study the intensity noise of LD-puped Nd:YVO 4, Nd:YAP lasers [7] and single-frequency-doubling lasers [8], respectively. In 1996, Masaki Tsunekane et al. copared the intensity noises of tunable Ti:sapphire lasers puped by an Ar-ion laser with that puped by an all-solid-state green laser and showed that the intensity noises of the output light fro the Ti:sapphire laser puped by Ar-ion laser was orders of agnitude around 0.5 MHz higher than that puped by the all-solid-state laser [9]. However, they didn t consider the influence of the longitudinal-ode construction of the puping source. In 006, Jacopo Belfi et al. studied the noise properties of an injectionlocked Ti:sapphire laser and deonstrated the strong influence of the phase-noises of the injected seed-laser on the intensity noises of the output light [10]. In 004, S. Witter et al. studied the influences of the puping source on the carrier-envelope offset phase of a 10-fs pulse Ti:sapphire laser, and pointed out that the use of a single-longitudinal-ode puping source is advantageous when the carrier-envelope phase stabilization is required [11]. So far, the influences of the longitudinal-ode structure of puping sources on the operating characteristics of a CW single-frequency Ti:sapphire laser have not been discussed to the best of our knowledge. To investigate the influences of the longitudinal-ode structure of the puping sources on the intensity noises of the output light fro a puped CW Ti:sapphire laser, we design and build two sets of all-solid-state green lasers which have different configuration and longitudinal-ode structure: one with single-transverse-ode but ulti-longitudinal odes (MLM) and another one with single-longitudinal-ode (SLM). The intensity noise spectra of the SLM and MLM and the puped Ti:sapphire lasers are experientally easured with selfhoodyne detectors, respectively. The experiental results point out that the noise features of the output light of the Ti:sapphire laser puped by the SLM syste are significantly (C) 011 OSA 17 January 011 / Vol. 19, No. / OPTICS EXPRESS 1345
3 iproved in coparison with that puped by the MLM syste, and the puping efficiency of the SLM syste is uch higher than that of the MLM syste. When the MLM puping syste was replaced by the SLM puping syste, the intensity noise of the Ti:sapphire laser at the resonant relaxation oscillation (RRO) frequency was decreased fro 4 db to 19 db, the critical frequency reaching the quantu noise liit (QNL) was reduced fro 7 MHz to.5 MHz, and the threshold puping power was decreased fro 5.6 W to.1 W. By eans of the transfer-function-type theories [1] and the solutions developed by Ralph et al. [5] as well as the technique and the procedure outlined by Harb et al. [6], we obtained the theoretical predictions of the intensity noise spectra of the Ti:sapphire laser output based on the experiental paraeters for the MLM and the SLM puping systes, respectively. It is shown that the easured noise spectru of the SLM puping syste basically agrees with the theoretical prediction but for the MLM puping syste, the agreeent is not very well. The physical reasons of the disagreeent will be analyzed in the section 4.. Experiental setups At first, we briefly introduce the configurations of the MLM and SLM puping systes (T- IVB and F-VII B, Yu Guang Co., Ltd.). Both of the are the intracavity frequency-doubled all-solid-state lasers with the fundaental wavelength of 1064 n and doubling-frequency wavelength of 53 n, the puping sources of which are the CW fiber-bundled laser diodes (LDs) with the axiu output powers of 30 W for the MLM syste and 60 W for the SLM syste respectively (FB01L4511 and LIMO60-F400-DL 808-EX116, LIMO Lissotschenko Mikrooptik GbH). The diaeter and the Nuerical Aperture (NA) of the output coupling fiber for both LDs are 400 μ and 0.. The coposite Nd:YVO 4 -YVO 4 rod consisting of the undoped end cap of 5 -length and 0.3 (0.) at. % Nd-doped part of 8 (15) -length serves as the laser aterial for the MLM (SLM) syste. The use of the coposite laser crystal can iniize the effect of the theral lens during the laser operation [13]. The lithiu triborate LiB 3 O 5 (LBO) crystals with the diensions of 3 3 and are used for the frequency-doubling crystals in the MLM and the SLM syste, respectively. The teperature of the LBO crystals is well controlled at the phase-atching teperature of 148 C by a teperature controller with a precision of 0.1 C (YG-1HC, Yu Guang Co., Ltd.). The resonant cavities of the MLM and the SLM systes are the threeirror folded cavity [14] and the four-irror ring cavity [15], respectively. To ensure unidirectional operation of the SLM syste, an optical diode is inserted into its ring cavity. The axial output power of 8 W at 53 n is obtained under the LD puping powers of 8 W (40 W) at 808 n for the MLM (SLM) puping syste. Although both MLM and SLM systes are in a single-transverse-ode configuration, the easured quality-factors (M ) for the MLM and the SLM syste at the sae power of 8 W are less than 1.5 and 1.1, respectively. The larger the value of M is, the worse the quality of the bea transverse-ode is [16]. Thus the SLM syste has saller spot size at the focus in the Ti:sapphire crystal than that of the MLM syste, which results in that the SLM syste has higher puping efficiency than that of the MLM syste. (C) 011 OSA 17 January 011 / Vol. 19, No. / OPTICS EXPRESS 1346
4 Fig. 1. (Color online) Experiental setup of easuring the intensity noise of all-solid-state CW single-frequency tunable Ti:sapphire laser. f 1, f : Lens, BRF: Birefringent filter, OD: Optical diode, HWP 1, HWP, HWP 3: Half-wave 53 n, HWP 4, HWP 5: Half-wave 780 n, PBS 1, PBS : 53 n, PBS 3, PBS 4: 780 n, PD 1, PD, PD 3, PD 4: Photo-detector. The scheatic diagra of the all-solid-state frequency-tunable and single-frequency CW Ti:sapphire laser (CTSL-I, Yu Guang Co., Ltd.) is shown in Fig. 1. The puping source is the MLM or the SLM syste. The lenses f 1 and f for an optical coupling syste to couple the puping laser at 53 n into the resonant cavity of the Ti:sapphire laser. A sall part of the puping laser is reflected by a bea-splitter (M 1 ) for the easureents of the puping noises and the puping power. The ring resonator of the Ti:sapphire laser consists of four irrors (M -M 5 ) in a figure-eight configuration [17]. A Brewster-cut gain aterial (Ti:sapphire crystal), a ulti-plate birefringent filter (BRF) for tuning in a broad frequencyband, an optical diode (OD) for ensuring unidirectional operation of laser and an etalon for ode-selecting are placed in the resonator. The input coupler (M ) is coated with 95% transission at 53 n and the output coupler is coated with 3.1% transission at n. The half-wave plate HWP 1 is used for the polarization alignent of the puping laser with respect to the optical axis of the Ti:sapphire crystal. HWP 3 (HWP 5 ), the polarizing-beasplitter PBS (PBS 4 ) and the two silicon photo-diodes PD 1, PD (PD 3, PD 4 ) (S3399) copose the self-hoodyne-detector for easuring the intensity noises of the puping sources (Ti:sapphire laser). The optical signals detected by PD 1 -PD 4 are aplified by the integrated aplifiers (CLC45) and then the aplified photo currents of PD 1 and PD (PD 3 and PD 4 ) are cobined with a negative or positive power cobiner (+/). The su and the subtract photocurrents stand for the intensity noise and the corresponding quantu noise liit (QNL), respectively [18]. Finally, the noise spectra of the su (subtract) photocurrents are analyzed by a spectral analyzer (SA) with the resolution bandwidth (RBW) of 30 khz and the video bandwidth (VBW) of 30 Hz. HWP (HWP 4 ) and PBS 1 (PBS 3 ) are used for controlling the laser power detected by the self-hoodyne-detector and the power eter serves as the power onitor. (C) 011 OSA 17 January 011 / Vol. 19, No. / OPTICS EXPRESS 1347
5 3. Experiental results Fig.. (Color online) Longitudinal-ode structure of the puping sources. (a) The SLM puping syste. (b) The MLM puping syste. Figure (a) and (b) show the longitudinal-ode structures of the SLM (a) and the MLM (b) puping source which are obtained by scanning the F-P interferoeter. The MLM puping syste has coplex and rando longitudinal-ode configuration, thus it can be concluded that the severe ode-hopping and ode-copetition effects exist in the puping syste which ust significantly change the intensity noise property of the puped Ti:sapphire laser. The dependences of the output powers of the Ti:sapphire laser upon the puping powers fro the SLM (a) and the MLM (b) syste are shown in Fig. 3. The threshold puping powers for the SLM and MLM syste are.1 W and 5.6 W, respectively. The obtained power of Ti:sapphire laser puped by the SLM syste is uch higher than that puped by the MLM syste under sae puping power, that is because the transverse-ode quality of the SLM puping syste (M -1.1) is uch better than that of the MLM puping syste (M -1.5), thus using the SLM puping syste we can obtain the saller waist spot of the puping light in the Ti:sapphire crystal and the higher puping efficiency [19 1]. (C) 011 OSA 17 January 011 / Vol. 19, No. / OPTICS EXPRESS 1348
6 Fig. 3. (Color online) Output power of CW single-frequency tunable Ti:sapphire laser versus puping power with different puping sources. (a) The SLM syste as puping source. (b) The MLM syste as puping source. Fig. 4. (Color online) Intensity noise spectru of the Ti:sapphire laser copared with that of the SLM puping source. (a) Intensity noise of the SLM puping syste. (b) Intensity noise of the Ti:sapphire laser. Figure 4 and 5 show the intensity noise spectra of the Ti:sapphire laser (b) copared with that of the puping source (a) for the SLM (Fig. 4) and the MLM (Fig. 5) syste, respectively. In the experient the power of both SLM and MLM puping systes with the wavelength of 53 n is aintained at 8 W. Under this puping level the output powers of the Ti:sapphire laser at 780 n are about W and 700 W for the SLM and the MLM puping syste, respectively (See Fig. 3 for details). For perforing the noise spectru easureents in Fig. 4 and 5, the laser power injected into the hoodyne detectors for all four optical beas is precisely adjusted to 30 W with the intensity adjusters consisting of half-wave plates (HWP -HWP 5 ) and polarizing-bea-splitters (PBS 1 -PBS 4 ). The optical attenuations for the puping laser of 8 W and the Ti:sapphire laser of W (700 W) are 0.03/8 and 0.03/ (0.03/0.7), respectively. The extra attenuation of the puping power, which is 4-ties (11.5-ties) larger than the attenuation of the Ti:sapphire laser puped by the SLM (MLM) syste, has been taken into account in the noise spectra of Fig. 4 and 5 by appropriate (C) 011 OSA 17 January 011 / Vol. 19, No. / OPTICS EXPRESS 1349
7 noralization []. The intensity-noise spectra are plotted relative to the QNL on a log-log scale, i. e. 10log 10 (V f ) versus log 10 (ω/π) and 0 db indicates that the noise level equals to the QNL. The frequency and the agnitude of the RRO for the Ti:sapphire laser puped by the SLM (MLM) syste are 850 khz (75 khz) and 19 db (4 db) above the QNL. At lower frequencies fro 0.1 MHz to 0.6 MHz (close to the RRO) the intensity noise level of the Ti:sapphire laser puped by the SLM syste (Fig. 4(b)) is basically atched with that of the puping source (Fig. 4(a)), but at the region higher than 0.6 MHz, the intensity noise profile of the Ti:sapphire laser is not in good agreeent with that of the puping source. For the MLM puping syste (Fig. 5(b)) only at the frequency region fro 100 khz to 175 khz, the intensity noise level of the Ti:sapphire laser agrees with that of the puping source (Fig. 5(a)). At frequencies higher than 175 khz, the intensity noise of the Ti:sapphire laser is higher than that of the puping source. It eans that only at lower frequency the intensity noise fro the puping sources was transferred to the Ti:sapphire laser. In both SLM and the MLM systes, the intensity noise of Ti:sapphire laser reaches the QNL alost siultaneously with its puping source [.5 MHz for SLM (Fig. 4); 7MHz for MLM (Fig. 5)]. It should be entioned that the easureents of the noise spectra are ipleented fro 0.1 MHz to 10 MHz in our experients, since below 0.1 MHz the influences of the electronic noise fro the detectors cannot be neglected and the gain of the electronic aplifiers is less than the required value, thus the observed noise spectra cannot represent the real intensity noise of the easured laser and above 10 MHz all noise spectra have reached the QNL. Fig. 5. (Color online) Intensity noise spectru of the Ti:sapphire laser copared with that of the MLM puping source. (a) Intensity noise of the MLM puping syste. (b) Intensity noise of the Ti:sapphire laser. 4. Quantu theoretical prediction copared with experiental easureent According to the transfer-function forula of the noise sources developed in Ref [5], the intensity-noise spectru of the Ti:sapphire laser is expressed by V f : G G 4 8 l l V 1 V f V vac p r l r l GJ 3 t G J 4 t 3 l V l V spont dipole V losses r l r l r l (1) (C) 011 OSA 17 January 011 / Vol. 19, No. / OPTICS EXPRESS 1350
8 where V vac, V p, V spont, V dipole and V losses are the noise inputs fro vacuu noise entering the output coupler (V vac ), pup-source intensity-noise spectru (V p ), spontaneous-eission noise (V spont ), dipole fluctuation noise (V dipole ) and noise introduced fro intracavity losses (V losses ), respectively. ω is the noise frequency. The total cavity decay rate is κ = (κ + κ l ), the coefficients κ and κ l derive fro the output coupling and intracavity losses, respectively. α is the intracavity photon nuber per ato of the lasing ode and is given by Γ is the puping rate; J 3 G t J3 () is the occupation probability of the upper lasing level; G describes the coupling of the lasing transition to the laser ode and is proportional to the stiulated-eission cross section of the transition, γ t is the rate of spontaneous eission fro the upper lasing level. G r is the frequency of the RRO. l G t is the daping rate of the RRO. The experientally easured intensity-noise spectra of the Ti:sapphire laser for the SLM (a) and the MLM (b) puping syste copared with that of the theoretical prediction based on Eq. (1) [(c) for SLM and (d) for MLM] are shown in Fig. 6. The paraeters for calculating the traces (c) and (d) are listed in Table 1. Table 1. Paraeters used to calculate the noise spectra of Fig. 6(c) and 6(d) Paraeter Trace (c) Trace (d) f RRO (khz) G (s 1 ) κ (s 1 ) γ t (s 1 ) J 3 per ato α per ato N (atos) Γ (s 1 ) These values presented here are deterined by the technique outlined by Harb et al. []. For deterining the predicted noise levels we deterined the shape for one of the noise spectra firstly, then adjusted V p and Γ to coincide with their easured values, and then produce all the other noise-spectra predictions. We selected the paraeters to ake the calculated RRO peak overlapping with the experiental RRO peak in both SLM and MLM puping cases, respectively. The RRO frequency for the SLM puping syste is 850 khz which is higher 15 khz than that for the MLM puping syste (75 khz). The agnitude of the RRO peak for the SLM puping syste is 19 db above the QNL which is 5 db lower than that of the MLM puping syste (4 db). The results are in good agreeent with the predictions of the quantu theory. Since the SLM puping laser has a saller waist spot and saller ode volue in the Ti:sapphire crystal than that of the MLM puping laser, the puping rate of the SLM syste ust be faster than that of the MLM syste under the sae puping power, which results in that the RRO frequency of the SLM syste is higher and its RRO peaks is lower [3]. Copared with the RRO peak LD-puped Nd:YAG laser presented in Ref [6], the width of RRO peak of Ti:sapphire laser is wider. That is because the life tie of the laser upper level of the Ti:sapphire crystal is uch shorter than that of Nd:YAG, thus the Ti:sapphire active ediu has higher daping. For the SLM puping syste, the theoretical prediction (c) and the experiental noise spectru (a) agree quite well at and beyond the RRO frequency. However, for the MLM puping syste, the predicted width of the RRO peak (d) is wider than that experientally easured (b) and the easured noise spectru beyond the RRO frequency is higher than that of theoretical prediction (d). We can see that beyond the RRO frequency the three traces of Fig. 6(a), 6(c) and 6(d) alost overlap, which eans that just as the quantu theoretical prediction the noise spectru of the Ti:sapphire laser puped by the SLM syste was not affected by the puping noise beyond the RRO frequency. However, for the MLM syste the intensity noise of Ti:sapphire laser (b) is uch (C) 011 OSA 17 January 011 / Vol. 19, No. / OPTICS EXPRESS 1351
9 higher. It eans that the severe ode-hopping phenoena exist in the MLM puping syste which change significantly the intensity noise spectru of Ti:sapphire laser as pointed out in Ref [6]. and [4]. Fig. 6. (Color online) Ti:sapphire intensity noise spectra copared with the quantu prediction for the noise profile. (a), (b) Measured intensity noise profiles when the Ti:sapphire is puped with the SLM and the MLM syste, respectively. (c), (d) The corresponding calculated profiles. Fro Fig. 4 and 5 we can see below the RRO frequency the intensity noise of the Ti:sapphire laser is ainly doinated by the noise spectru of the puping source. Not like the LD puping source with white noises used in Ref [6], an intensity-noise distribution exists in both SLM and MLM puping sources. When we drew the traces (c) and (d) of Fig. 6 using quantu odel of Ref [5], only a value of the puping noises was utilized and the distribution of the puping noise did not considered. Thus the experiental spectra below the RRO are higher than that predicted theoretically and only around the RRO peak the prediction (c) for the SLM syste agrees with the experiental trace (a). We believe that if the noise spectru distribution of the puping source is involved in the procedure for deterining the predicted noise level, the quantu theoretical prediction will be in better agreeent with the experiental results, especially for the SLM puping syste. 5. Conclusions We experientally studied the dependences of the Ti:sapphire laser upon the longitudinalode structure of the puping sources. We found that when the single-longitudinal-ode laser serves as the puping source not only the puping efficiency is enhanced but also the noise feature of the Ti:sapphire laser is iproved significantly. The laser systes with higher puping efficiency and better intensity noise spectru are very useful in scientific research and practical application. Our works provide feasible reference for designing and building high quality all-solid-state lasers. The configuration of the laser transition levels of Ti:sapphire crystal is a broad-band twolevel syste. In this case the ode-hop and the ode-copetition of the puping laser will severely affect the operation of the puped laser and increase the intensity noise of the output laser. On the other side in the MLM intracavity frequency-doubled Nd:YVO 4 puping syste with higher power of 8 W there are possibly the intercrossing saturation effect and the green proble [5] due to the existence of the frequency-doubling crystal. These effects are not involved in the Eq. (1), so the easured noise spectru of the MLM puped Ti:sapphire laser exists larger disagreeent with that predicted theoretically. For the SLM puping syste, the noise spectru at and after the RRO frequency is in good agreeent with the quantu (C) 011 OSA 17 January 011 / Vol. 19, No. / OPTICS EXPRESS 135
10 theoretical prediction. But at lower frequency the experiental curve of Fig. 6(a) and the theoretical curve of Fig. 6(c) disagree, that is because the theoretical curve of Fig. 6(c) is drew with a given value of puping noises, which is taken only for reaching good agreeent with the experiental easureent at the RRO frequency. However, the puping noise is not the white noise and thus has different value at different frequency. The noise spectru distribution of the puping source was not involved in the calculation. We believe that if the noise distribution of the puping source is considered, the theoretical calculation will be in better agreeent with the experiental results for the SLM syste. To the MLM syste, ore physical effects, such as ode-hop, ode-copetition and so on should be involved in the theoretical forula for achieving better atch between theory and experient. Acknowledgeents This research was supported by the National Basic Research Progra (973 Progra) (No. 010CB93103), NSFC Project for Excellent Research Tea (No ), and the Key Progra of NSFC (No ). (C) 011 OSA 17 January 011 / Vol. 19, No. / OPTICS EXPRESS 1353
Single frequency Ti:sapphire laser with continuous frequency-tuning and low intensity noise by means of the additional intracavity nonlinear loss
 Single frequency Ti:sapphire laser with continuous frequency-tuning and low intensity noise by means of the additional intracavity nonlinear loss Huadong Lu, Xuejun Sun, Meihong Wang, Jing Su, and Kunchi
Single frequency Ti:sapphire laser with continuous frequency-tuning and low intensity noise by means of the additional intracavity nonlinear loss Huadong Lu, Xuejun Sun, Meihong Wang, Jing Su, and Kunchi
Optical fiber beamformer for processing two independent simultaneous RF beams
 Optical fiber beaforer for processing two independent siultaneous RF beas M. Jaeger, S. Granieri *, and A. Siahakoun Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering, Rose-Hulan Institute of Technology Terre
Optical fiber beaforer for processing two independent siultaneous RF beas M. Jaeger, S. Granieri *, and A. Siahakoun Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering, Rose-Hulan Institute of Technology Terre
Mode spectrum of multi-longitudinal mode pumped near-degenerate OPOs with volume Bragg grating output couplers
 Mode spectru of ulti-longitudinal ode puped near-degenerate OPOs with volue Bragg grating output couplers Markus Henriksson 12 * Lars Sjöqvist 1 Valdas Pasiskevicius 2 and Fredrik Laurell 2 1 Laser Systes
Mode spectru of ulti-longitudinal ode puped near-degenerate OPOs with volue Bragg grating output couplers Markus Henriksson 12 * Lars Sjöqvist 1 Valdas Pasiskevicius 2 and Fredrik Laurell 2 1 Laser Systes
Fundamental study for measuring microflow with Michelson interferometer enhanced by external random signal
 Bulletin of the JSME Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systes, and Manufacturing Vol.8, No.4, 2014 Fundaental study for easuring icroflow with Michelson interferoeter enhanced by external rando signal
Bulletin of the JSME Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design, Systes, and Manufacturing Vol.8, No.4, 2014 Fundaental study for easuring icroflow with Michelson interferoeter enhanced by external rando signal
Self-injection locked CW single-frequency tunable Ti:sapphire laser
 Vol. 25, No. 18 4 Sep 2017 OPTICS EXPRESS 21379 Self-injection locked CW single-frequency tunable Ti:sapphire laser Y IXIAO W EI, 1 H UADONG L U, 1,2,* P IXIAN J IN, 1 AND K UNCHI P ENG 1,2 1 State Key
Vol. 25, No. 18 4 Sep 2017 OPTICS EXPRESS 21379 Self-injection locked CW single-frequency tunable Ti:sapphire laser Y IXIAO W EI, 1 H UADONG L U, 1,2,* P IXIAN J IN, 1 AND K UNCHI P ENG 1,2 1 State Key
Stable, 12 W, continuous-wave single-frequency Nd:YVO 4 green laser polarized and dual-end pumped at 880 nm
 Stable, 12 W, continuous-wave single-frequency Nd:YVO 4 green laser polarized and dual-end pumped at 880 nm Jianli Liu, Zhiyong Wang, Hong Li, Qin Liu, Kuanshou Zhang* State Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics
Stable, 12 W, continuous-wave single-frequency Nd:YVO 4 green laser polarized and dual-end pumped at 880 nm Jianli Liu, Zhiyong Wang, Hong Li, Qin Liu, Kuanshou Zhang* State Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics
Ignition and monitoring technique for plasma processing of multicell superconducting radio frequency cavities
 Ignition and onitoring technique for plasa processing of ulticell superconducting radio frequency cavities Marc Doleans Oak Ridge ational Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee 3783, USA E ail: doleans@ornl.gov
Ignition and onitoring technique for plasa processing of ulticell superconducting radio frequency cavities Marc Doleans Oak Ridge ational Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tennessee 3783, USA E ail: doleans@ornl.gov
Optical Cavity Designs for Interferometric Gravitational Wave Detectors. Pablo Barriga 17 August 2009
 Optical Cavity Designs for Interferoetric Gravitational Wave Detectors Pablo Barriga 7 August 9 Assignents.- Assuing a cavity of 4k with an ITM of 934 radius of curvature and an ETM of 45 radius of curvature.
Optical Cavity Designs for Interferoetric Gravitational Wave Detectors Pablo Barriga 7 August 9 Assignents.- Assuing a cavity of 4k with an ITM of 934 radius of curvature and an ETM of 45 radius of curvature.
Performance Analysis of Atmospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays
 Perforance Analysis of Atospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays Aniceto Belonte* a, Joseph M. Kahn b a Technical Univ. of Catalonia, Dept. of Signal Theory and Coun., 08034 Barcelona, Spain; b Stanford
Perforance Analysis of Atospheric Field Conjugation Adaptive Arrays Aniceto Belonte* a, Joseph M. Kahn b a Technical Univ. of Catalonia, Dept. of Signal Theory and Coun., 08034 Barcelona, Spain; b Stanford
HIGH FREQUENCY LASER BASED ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY USING A CW GENERATION SOURCE
 HIGH FREQUENCY LASER BASED ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY USING A CW GENERATION SOURCE T.W. Murray, O. Balogun, and N. Pratt Departent of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, Boston University, Boston MA 0225 Abstract:
HIGH FREQUENCY LASER BASED ACOUSTIC MICROSCOPY USING A CW GENERATION SOURCE T.W. Murray, O. Balogun, and N. Pratt Departent of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, Boston University, Boston MA 0225 Abstract:
Adaptive Harmonic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor
 Journal of Counication and Coputer (4 484-49 doi:.765/548-779/4.6. D DAVID PUBLISHING Adaptive Haronic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor Li Tan, Jean Jiang, and Liango
Journal of Counication and Coputer (4 484-49 doi:.765/548-779/4.6. D DAVID PUBLISHING Adaptive Haronic IIR Notch Filter with Varying Notch Bandwidth and Convergence Factor Li Tan, Jean Jiang, and Liango
Experiment 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase Locked Loops October 11, 2006
 Experient 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase ocked oops October 11, 2006 Frequency Modulation Norally, we consider a voltage wave for with a fixed frequency of the for v(t) = V sin(ω c t + θ), (1) where
Experient 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase ocked oops October 11, 2006 Frequency Modulation Norally, we consider a voltage wave for with a fixed frequency of the for v(t) = V sin(ω c t + θ), (1) where
CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT
 CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT In this chapter, the experimental results for fine-tuning of the laser wavelength with an intracavity liquid crystal element
CHAPTER 5 FINE-TUNING OF AN ECDL WITH AN INTRACAVITY LIQUID CRYSTAL ELEMENT In this chapter, the experimental results for fine-tuning of the laser wavelength with an intracavity liquid crystal element
LOW COST PRODUCTION PHASE NOISE MEASUREMENTS ON MICROWAVE AND MILLIMETRE WAVE FREQUENCY SOURCES
 Page 1 of 10 LOW COST PRODUCTION PHASE NOISE MEASUREMENTS ON MICROWAVE AND MILLIMETRE WAVE FREQUENCY SOURCES Hugh McPherson Spectral Line Systes Ltd, Units 1,2&3 Scott Road, Tarbert, Isle of Harris. www.spectral-line-systes.co.uk
Page 1 of 10 LOW COST PRODUCTION PHASE NOISE MEASUREMENTS ON MICROWAVE AND MILLIMETRE WAVE FREQUENCY SOURCES Hugh McPherson Spectral Line Systes Ltd, Units 1,2&3 Scott Road, Tarbert, Isle of Harris. www.spectral-line-systes.co.uk
PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK
 PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? W Wei A Cooke J Havie-Clark Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead,
PREDICTING SOUND LEVELS BEHIND BUILDINGS - HOW MANY REFLECTIONS SHOULD I USE? W Wei A Cooke J Havie-Clark Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead, UK Apex Acoustics Ltd, Gateshead,
UWB System for Time-Domain Near-Field Antenna Measurement
 UWB Syste for Tie-Doain Near-Field Antenna Measureent B. Levitas #, M. Drozdov #, I. Naidionova #, S. Jefreov #, S. Malyshev *2, A. Chizh *3 www.geozondas.co # Geozondas Ltd., 6, Shevchenko Str., LT-3,
UWB Syste for Tie-Doain Near-Field Antenna Measureent B. Levitas #, M. Drozdov #, I. Naidionova #, S. Jefreov #, S. Malyshev *2, A. Chizh *3 www.geozondas.co # Geozondas Ltd., 6, Shevchenko Str., LT-3,
Design and Implementation of Serial Port Ultrasonic Distance Measurement System Based on STC12 Jian Huang
 International Conference on Education, Manageent and Coputer Science (ICEMC 2016) Design and Ipleentation of Serial Port Ultrasonic Distance Measureent Syste Based on STC12 Jian Huang Xijing University,
International Conference on Education, Manageent and Coputer Science (ICEMC 2016) Design and Ipleentation of Serial Port Ultrasonic Distance Measureent Syste Based on STC12 Jian Huang Xijing University,
Exploring the Electron Tunneling Behavior of Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) tip and n-type Semiconductor
 Page 110 Exploring the of Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) tip and n-type Seiconductor M. A. Rahan * and J. U. Ahed Departent of Applied Physics, Electronics & Counication Engineering, University of
Page 110 Exploring the of Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) tip and n-type Seiconductor M. A. Rahan * and J. U. Ahed Departent of Applied Physics, Electronics & Counication Engineering, University of
240-GHz continuously frequency-tuneable Nd:YVO 4 /LBO laser with two intra-cavity locked etalons
 240-GHz continuously frequency-tuneable Nd:YVO 4 /LBO laser with two intra-cavity locked etalons Daba Radnatarov, 1,* Sergey Kobtsev, 1,2 Sergey Khripunov, 1 and Vladimir Lunin 1,2 1 Division of Laser
240-GHz continuously frequency-tuneable Nd:YVO 4 /LBO laser with two intra-cavity locked etalons Daba Radnatarov, 1,* Sergey Kobtsev, 1,2 Sergey Khripunov, 1 and Vladimir Lunin 1,2 1 Division of Laser
Fiber Bragg grating based four-bit optical beamformer
 Fiber Bragg grating based four-bit optical beaforer Sean Durrant a, Sergio Granieri a, Azad Siahakoun a, Bruce Black b a Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering b Departent of Electrical and Coputer
Fiber Bragg grating based four-bit optical beaforer Sean Durrant a, Sergio Granieri a, Azad Siahakoun a, Bruce Black b a Departent of Physics and Optical Engineering b Departent of Electrical and Coputer
2-Dimensional beamsteering using dispersive deflectors and wavelength tuning
 2-Diensional beasteering using dispersive deflectors and wavelength tuning Trevor Chan, 1,* Evgeny Myslivets, 1 and Joseph E. Ford, 1 1 Departent of Electrical and Coputer Engineering, University of California,
2-Diensional beasteering using dispersive deflectors and wavelength tuning Trevor Chan, 1,* Evgeny Myslivets, 1 and Joseph E. Ford, 1 1 Departent of Electrical and Coputer Engineering, University of California,
Tunable single frequency fiber laser based on FP-LD injection locking
 Tunable single frequency fiber laser based on FP-LD injection locking Aiqin Zhang, Xinhuan Feng, * Minggui Wan, Zhaohui Li, and Bai-ou Guan Institute of Photonics Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou,
Tunable single frequency fiber laser based on FP-LD injection locking Aiqin Zhang, Xinhuan Feng, * Minggui Wan, Zhaohui Li, and Bai-ou Guan Institute of Photonics Technology, Jinan University, Guangzhou,
Real Time Etch-depth Measurement Using Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, (8): -7, 1 ISSN 1991-8178 Real Tie Etch-depth Measureent Using Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor 1 Reza Hosseini, Navid Rahany, 3 Behrad Soltanbeigi, Rouzbeh
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, (8): -7, 1 ISSN 1991-8178 Real Tie Etch-depth Measureent Using Surface Acoustic Wave Sensor 1 Reza Hosseini, Navid Rahany, 3 Behrad Soltanbeigi, Rouzbeh
Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio
 Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio In our discussion in the past few lectures, we have coputed the C/N ratio of the received signals at different points of the satellite transission syste. The C/N
Relation between C/N Ratio and S/N Ratio In our discussion in the past few lectures, we have coputed the C/N ratio of the received signals at different points of the satellite transission syste. The C/N
The following tutorial will serve as an outline of the fundamental elements involved in the
 ACOUSTO-OPTICS TUTORIAL G. Ivtsenkov, Ph.D. & V. Pachkov, Ph.D. Light Manageent Group Inc. Research & Developent Burlington, Ontario, Canada INTRODUCTION THE ACOUSTO-OPTIC SWITCH PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS
ACOUSTO-OPTICS TUTORIAL G. Ivtsenkov, Ph.D. & V. Pachkov, Ph.D. Light Manageent Group Inc. Research & Developent Burlington, Ontario, Canada INTRODUCTION THE ACOUSTO-OPTIC SWITCH PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS
R. J. Jones Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017
 R. J. Jones Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Semiconductor Lasers (2 weeks) Semiconductor (diode) lasers are by far the most widely used lasers today. Their small size and properties of the light output
R. J. Jones Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Semiconductor Lasers (2 weeks) Semiconductor (diode) lasers are by far the most widely used lasers today. Their small size and properties of the light output
Cost-effective wavelength-tunable fiber laser using self-seeding Fabry-Perot laser diode
 Cost-effective wavelength-tunable fiber laser using self-seeding Fabry-Perot laser diode Chien Hung Yeh, 1* Fu Yuan Shih, 2 Chia Hsuan Wang, 3 Chi Wai Chow, 3 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Information and Communications
Cost-effective wavelength-tunable fiber laser using self-seeding Fabry-Perot laser diode Chien Hung Yeh, 1* Fu Yuan Shih, 2 Chia Hsuan Wang, 3 Chi Wai Chow, 3 and Sien Chi 2, 3 1 Information and Communications
NINTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION, ICSV9 PASSIVE CONTROL OF LAUNCH NOISE IN ROCKET PAYLOAD BAYS
 first nae & faily nae: Rick Morgans Page nuber: 1 NINTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION, ICSV9 PASSIVE CONTROL OF LAUNCH NOISE IN ROCKET PAYLOAD BAYS Rick Morgans, Ben Cazzolato, Anthony
first nae & faily nae: Rick Morgans Page nuber: 1 NINTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION, ICSV9 PASSIVE CONTROL OF LAUNCH NOISE IN ROCKET PAYLOAD BAYS Rick Morgans, Ben Cazzolato, Anthony
REPORT ITU-R SA Telecommunication characteristics and requirements for space VLBI systems
 Rep. ITU-R SA.2132 1 REPORT ITU-R SA.2132 Telecounication characteristics and requireents for space VLBI systes (2008) This Report describes the characteristics of the space VLBI systes. These characteristics
Rep. ITU-R SA.2132 1 REPORT ITU-R SA.2132 Telecounication characteristics and requireents for space VLBI systes (2008) This Report describes the characteristics of the space VLBI systes. These characteristics
Block Diagram of FM Receiver
 FM Receivers FM receivers, like AM receivers, utilize the superheterodyne principle, but they operate at uch higher frequencies (88-108 MHz). A liiter is often used to ensure the received signal is constant
FM Receivers FM receivers, like AM receivers, utilize the superheterodyne principle, but they operate at uch higher frequencies (88-108 MHz). A liiter is often used to ensure the received signal is constant
Quantum measurements with an amplitude-squeezed-light beam splitter
 Quantum measurements with an amplitude-squeezed-light beam splitter Junxiang Zhang, Tiancai Zhang, Ruifang Dong, Jing Zhang, Changde Xie, and Kunchi Peng Quantum measurement of amplitude fluctuation is
Quantum measurements with an amplitude-squeezed-light beam splitter Junxiang Zhang, Tiancai Zhang, Ruifang Dong, Jing Zhang, Changde Xie, and Kunchi Peng Quantum measurement of amplitude fluctuation is
Ring cavity tunable fiber laser with external transversely chirped Bragg grating
 Ring cavity tunable fiber laser with external transversely chirped Bragg grating A. Ryasnyanskiy, V. Smirnov, L. Glebova, O. Mokhun, E. Rotari, A. Glebov and L. Glebov 2 OptiGrate, 562 South Econ Circle,
Ring cavity tunable fiber laser with external transversely chirped Bragg grating A. Ryasnyanskiy, V. Smirnov, L. Glebova, O. Mokhun, E. Rotari, A. Glebov and L. Glebov 2 OptiGrate, 562 South Econ Circle,
ACCURATE DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT BASED ON THE FREQUENCY VARIATION MONITORING OF ULTRASONIC SIGNALS
 XVII IMEKO World Congress Metrology in 3rd Millenniu June 22 27, 2003, Dubrovnik, Croatia ACCURATE DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT BASED ON THE FREQUENCY VARIATION MONITORING OF ULTRASONIC SIGNALS Ch. Papageorgiou
XVII IMEKO World Congress Metrology in 3rd Millenniu June 22 27, 2003, Dubrovnik, Croatia ACCURATE DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT BASED ON THE FREQUENCY VARIATION MONITORING OF ULTRASONIC SIGNALS Ch. Papageorgiou
Design of efficient high-power diode-end-pumped TEMoo Nd:YVO4. laser. Yung Fu Chen*, Chen Cheng Liaob, Yu Pin Lanb, S. C. Wangb
 Design of efficient high-power diode-end-pumped TEMoo Nd:YVO4 laser Yung Fu Chen*, Chen Cheng Liaob, Yu Pin Lanb, S. C. Wangb ADepartment of Electrophysics, National Chiao Tung University Hsinchu, Taiwan,
Design of efficient high-power diode-end-pumped TEMoo Nd:YVO4 laser Yung Fu Chen*, Chen Cheng Liaob, Yu Pin Lanb, S. C. Wangb ADepartment of Electrophysics, National Chiao Tung University Hsinchu, Taiwan,
LIGO-P R. High-Power Fundamental Mode Single-Frequency Laser
 LIGO-P040053-00-R High-Power Fundamental Mode Single-Frequency Laser Maik Frede, Ralf Wilhelm, Dietmar Kracht, Carsten Fallnich Laser Zentrum Hannover, Hollerithallee 8, 30419 Hannover, Germany Phone:+49
LIGO-P040053-00-R High-Power Fundamental Mode Single-Frequency Laser Maik Frede, Ralf Wilhelm, Dietmar Kracht, Carsten Fallnich Laser Zentrum Hannover, Hollerithallee 8, 30419 Hannover, Germany Phone:+49
Optical Magnetic Response in a Single Metal Nanobrick. Jianwei Tang, Sailing He, et al.
 Optical Magnetic Response in a Single Metal Nanobrick Jianwei Tang, Sailing He, et al. Abstract: Anti-syetric localized surface plasons are deonstrated on a single silver nanostrip sandwiched by SiC layers.
Optical Magnetic Response in a Single Metal Nanobrick Jianwei Tang, Sailing He, et al. Abstract: Anti-syetric localized surface plasons are deonstrated on a single silver nanostrip sandwiched by SiC layers.
POWER QUALITY ASSESSMENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIMATION NUMERICAL ALGORITHM
 POWER QUALITY ASSESSENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIATION NUERICAL ALGORITH Vladiir Terzia ABB Gerany vadiir.terzia@de.abb.co Vladiir Stanoevic EPS Yugoslavia vla_sta@hotail.co artin axiini ABB Gerany
POWER QUALITY ASSESSENT USING TWO STAGE NONLINEAR ESTIATION NUERICAL ALGORITH Vladiir Terzia ABB Gerany vadiir.terzia@de.abb.co Vladiir Stanoevic EPS Yugoslavia vla_sta@hotail.co artin axiini ABB Gerany
Characteristics of absorption and dispersion for rubidium D 2 lines with the modulation transfer spectrum
 Characteristics of absorption and dispersion for rubidium D 2 lines with the modulation transfer spectrum Jing Zhang, Dong Wei, Changde Xie, and Kunchi Peng The State Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics and
Characteristics of absorption and dispersion for rubidium D 2 lines with the modulation transfer spectrum Jing Zhang, Dong Wei, Changde Xie, and Kunchi Peng The State Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics and
Long-Period Grating Thermal Sensitivity Dependence on the External Medium Refractive Index
 Long-Period Grating Theral Sensitivity Dependence on the External Mediu Refractive Index Ricardo C. Kaikawachi, Gustavo R. C. Possetti, Márcia Muller and José L. Fabris Federal University of Technology
Long-Period Grating Theral Sensitivity Dependence on the External Mediu Refractive Index Ricardo C. Kaikawachi, Gustavo R. C. Possetti, Márcia Muller and José L. Fabris Federal University of Technology
Low Noise High Power Ultra-Stable Diode Pumped Er-Yb Phosphate Glass Laser
 Low Noise High Power Ultra-Stable Diode Pumped Er-Yb Phosphate Glass Laser R. van Leeuwen, B. Xu, L. S. Watkins, Q. Wang, and C. Ghosh Princeton Optronics, Inc., 1 Electronics Drive, Mercerville, NJ 8619
Low Noise High Power Ultra-Stable Diode Pumped Er-Yb Phosphate Glass Laser R. van Leeuwen, B. Xu, L. S. Watkins, Q. Wang, and C. Ghosh Princeton Optronics, Inc., 1 Electronics Drive, Mercerville, NJ 8619
A Preprocessing Method to Increase High Frequency Response of A Parametric Loudspeaker
 A Preprocessing Method to Increase High Frequency Response of A Paraetric Loudspeaker Chuang Shi * and Woon-Seng Gan Digital Processing Laboratory School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang
A Preprocessing Method to Increase High Frequency Response of A Paraetric Loudspeaker Chuang Shi * and Woon-Seng Gan Digital Processing Laboratory School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Nanyang
DEVELOPMENT OF CW AND Q-SWITCHED DIODE PUMPED ND: YVO 4 LASER
 DEVELOPMENT OF CW AND Q-SWITCHED DIODE PUMPED ND: YVO 4 LASER Gagan Thakkar 1, Vatsal Rustagi 2 1 Applied Physics, 2 Production and Industrial Engineering, Delhi Technological University, New Delhi (India)
DEVELOPMENT OF CW AND Q-SWITCHED DIODE PUMPED ND: YVO 4 LASER Gagan Thakkar 1, Vatsal Rustagi 2 1 Applied Physics, 2 Production and Industrial Engineering, Delhi Technological University, New Delhi (India)
Modeling Beam forming in Circular Antenna Array with Directional Emitters
 International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volue 5 Issue 3 ǁ Mar. 2017 ǁ PP.01-05 Modeling Bea foring in Circular Antenna Array
International Journal of Research in Engineering and Science (IJRES) ISSN (Online): 2320-9364, ISSN (Print): 2320-9356 Volue 5 Issue 3 ǁ Mar. 2017 ǁ PP.01-05 Modeling Bea foring in Circular Antenna Array
Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorithm Zhong Danmei 1, a, Wang zhan 1, a, Cheng zhu 1, a, Huang Da 1, a
 2nd International Conference on Electrical, Coputer Engineering and Electronics (ICECEE 25 Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorith Zhong Danei, a, Wang zhan, a, Cheng
2nd International Conference on Electrical, Coputer Engineering and Electronics (ICECEE 25 Mitigation of GPS L 2 signal in the H I observation based on NLMS algorith Zhong Danei, a, Wang zhan, a, Cheng
A 243mJ, Eye-Safe, Injection-Seeded, KTA Ring- Cavity Optical Parametric Oscillator
 Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Space Dynamics Lab Publications Space Dynamics Lab 1-1-2011 A 243mJ, Eye-Safe, Injection-Seeded, KTA Ring- Cavity Optical Parametric Oscillator Robert J. Foltynowicz
Utah State University DigitalCommons@USU Space Dynamics Lab Publications Space Dynamics Lab 1-1-2011 A 243mJ, Eye-Safe, Injection-Seeded, KTA Ring- Cavity Optical Parametric Oscillator Robert J. Foltynowicz
Multi-Wavelength, µm Tunable, Tandem OPO
 Multi-Wavelength, 1.5-10-µm Tunable, Tandem OPO Yelena Isyanova, Alex Dergachev, David Welford, and Peter F. Moulton Q-Peak, Inc.,135 South Road, Bedford, MA 01730 isyanova@qpeak.com Introduction Abstract:
Multi-Wavelength, 1.5-10-µm Tunable, Tandem OPO Yelena Isyanova, Alex Dergachev, David Welford, and Peter F. Moulton Q-Peak, Inc.,135 South Road, Bedford, MA 01730 isyanova@qpeak.com Introduction Abstract:
S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique
 S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique Chien-Hung Yeh 1, *, Ming-Ching Lin 3, Ting-Tsan Huang 2, Kuei-Chu Hsu 2 Cheng-Hao Ko 2, and Sien Chi
S-band gain-clamped grating-based erbiumdoped fiber amplifier by forward optical feedback technique Chien-Hung Yeh 1, *, Ming-Ching Lin 3, Ting-Tsan Huang 2, Kuei-Chu Hsu 2 Cheng-Hao Ko 2, and Sien Chi
[Jambhulkar*, 4.(7): July, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785
![[Jambhulkar*, 4.(7): July, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785 [Jambhulkar*, 4.(7): July, 2015] ISSN: (I2OR), Publication Impact Factor: 3.785](/thumbs/77/76046661.jpg) [Jabhulkar*, 4.(7): July, 25] ISSN: 2277-9655 IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY A REVIEW: OPTICAL FREQUENCY COMB GENERATOR (OFCG) Sneha Jabhulkar*, P. B. Borole
[Jabhulkar*, 4.(7): July, 25] ISSN: 2277-9655 IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY A REVIEW: OPTICAL FREQUENCY COMB GENERATOR (OFCG) Sneha Jabhulkar*, P. B. Borole
A simple charge sensitive preamplifier for experiments with a small number of detector channels
 A siple charge sensitive preaplifier for experients with a sall nuber of detector channels laudio Arnaboldi and Gianluigi Pessina Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN) Università degli Studi di
A siple charge sensitive preaplifier for experients with a sall nuber of detector channels laudio Arnaboldi and Gianluigi Pessina Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN) Università degli Studi di
High-power operation of Tm:YLF, Ho:YLF and Er:YLF lasers
 High-power operation of Tm:YLF, Ho:YLF and Er:YLF lasers Peter F. Moulton Solid State and Diode Laser Technology Review 2003 20 May Albuquerque, NM Outline High-power Tm:YLF-pumped Ho:YLF laser ZGP OPO
High-power operation of Tm:YLF, Ho:YLF and Er:YLF lasers Peter F. Moulton Solid State and Diode Laser Technology Review 2003 20 May Albuquerque, NM Outline High-power Tm:YLF-pumped Ho:YLF laser ZGP OPO
Generation of 11.5 W coherent red-light by intra-cavity frequency-doubling of a side-pumped Nd:YAG laser in a 4-cm LBO
 Optics Communications 241 (2004) 167 172 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Generation of 11.5 W coherent red-light by intra-cavity frequency-doubling of a side-pumped Nd:YAG laser in a 4-cm LBO Zhipei Sun
Optics Communications 241 (2004) 167 172 www.elsevier.com/locate/optcom Generation of 11.5 W coherent red-light by intra-cavity frequency-doubling of a side-pumped Nd:YAG laser in a 4-cm LBO Zhipei Sun
EXPERIMENTATION FOR ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL
 CHPTER - 6 EXPERIMENTTION FOR CTIVE VIBRTION CONTROL 6. INTRODUCTION The iportant issues in vibration control applications are odeling the sart structure with in-built sensing and actuation capabilities
CHPTER - 6 EXPERIMENTTION FOR CTIVE VIBRTION CONTROL 6. INTRODUCTION The iportant issues in vibration control applications are odeling the sart structure with in-built sensing and actuation capabilities
All-Optical Clock Division Using Period-one Oscillation of Optically Injected Semiconductor Laser
 International Conference on Logistics Engineering, Management and Computer Science (LEMCS 2014) All-Optical Clock Division Using Period-one Oscillation of Optically Injected Semiconductor Laser Shengxiao
International Conference on Logistics Engineering, Management and Computer Science (LEMCS 2014) All-Optical Clock Division Using Period-one Oscillation of Optically Injected Semiconductor Laser Shengxiao
A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier
 Science in China Ser. G Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2004 Vol.47 No.6 767 772 767 A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier ZHU Heyuan, XU Guang, WANG Tao, QIAN Liejia & FAN Dianyuan State
Science in China Ser. G Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 2004 Vol.47 No.6 767 772 767 A CW seeded femtosecond optical parametric amplifier ZHU Heyuan, XU Guang, WANG Tao, QIAN Liejia & FAN Dianyuan State
101 W of average green beam from diode-side-pumped Nd:YAG/LBO-based system in a relay imaged cavity
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 75, No. 5 journal of November 2010 physics pp. 935 940 101 W of average green beam from diode-side-pumped Nd:YAG/LBO-based system in a relay imaged cavity S K
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 75, No. 5 journal of November 2010 physics pp. 935 940 101 W of average green beam from diode-side-pumped Nd:YAG/LBO-based system in a relay imaged cavity S K
Fiber-laser-pumped Ti:sapphire laser
 Fiber-laser-pumped Ti:sapphire laser G. K. Samanta, 1,* S. Chaitanya Kumar, 1 Kavita Devi, 1 and M. Ebrahim-Zadeh 1,2 1 ICFO-Institut de Ciencies Fotoniques, Mediterranean Technology Park, 08860 Castelldefels,
Fiber-laser-pumped Ti:sapphire laser G. K. Samanta, 1,* S. Chaitanya Kumar, 1 Kavita Devi, 1 and M. Ebrahim-Zadeh 1,2 1 ICFO-Institut de Ciencies Fotoniques, Mediterranean Technology Park, 08860 Castelldefels,
Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature
 Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature Donghui Zhao.a, Xuewen Shu b, Wei Zhang b, Yicheng Lai a, Lin Zhang a, Ian Bennion a a Photonics Research Group,
Stable dual-wavelength oscillation of an erbium-doped fiber ring laser at room temperature Donghui Zhao.a, Xuewen Shu b, Wei Zhang b, Yicheng Lai a, Lin Zhang a, Ian Bennion a a Photonics Research Group,
High-power semiconductor lasers for applications requiring GHz linewidth source
 High-power semiconductor lasers for applications requiring GHz linewidth source Ivan Divliansky* a, Vadim Smirnov b, George Venus a, Alex Gourevitch a, Leonid Glebov a a CREOL/The College of Optics and
High-power semiconductor lasers for applications requiring GHz linewidth source Ivan Divliansky* a, Vadim Smirnov b, George Venus a, Alex Gourevitch a, Leonid Glebov a a CREOL/The College of Optics and
Intermediate-Node Initiated Reservation (IIR): A New Signaling Scheme for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion
 Interediate-Node Initiated Reservation IIR): A New Signaling Schee for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion Kejie Lu, Jason P. Jue, Tiucin Ozugur, Gaoxi Xiao, and Irich Chlatac The Center
Interediate-Node Initiated Reservation IIR): A New Signaling Schee for Wavelength-Routed Networks with Sparse Conversion Kejie Lu, Jason P. Jue, Tiucin Ozugur, Gaoxi Xiao, and Irich Chlatac The Center
SEVERAL benchmark tests for beam propagation methods
 JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 16, NO. 10, OCTOBER 1998 1921 A COST 240 Benchark Test for Bea Propagation Methods Applied to an Electrooptical Modulator Based on Surface Plasons H. J. W. M. Hoekstra,
JOURNAL OF LIGHTWAVE TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 16, NO. 10, OCTOBER 1998 1921 A COST 240 Benchark Test for Bea Propagation Methods Applied to an Electrooptical Modulator Based on Surface Plasons H. J. W. M. Hoekstra,
An orthogonal multi-beam based MIMO scheme. for multi-user wireless systems
 An orthogonal ulti-bea based IO schee for ulti-user wireless systes Dong-chan Oh o and Yong-Hwan Lee School of Electrical Engineering and IC, Seoul ational University Kwana P.O. Box 34, Seoul, 151-600,
An orthogonal ulti-bea based IO schee for ulti-user wireless systes Dong-chan Oh o and Yong-Hwan Lee School of Electrical Engineering and IC, Seoul ational University Kwana P.O. Box 34, Seoul, 151-600,
Optical design of shining light through wall experiments
 Optical design of shining light through wall experiments Benno Willke Leibniz Universität Hannover (member of the ALPS collaboration) Vistas in Axion Physics: A Roadmap for Theoretical and Experimental
Optical design of shining light through wall experiments Benno Willke Leibniz Universität Hannover (member of the ALPS collaboration) Vistas in Axion Physics: A Roadmap for Theoretical and Experimental
A Dynamic Simulink Model For Erbium-Doped Fiber Amplifiers Overmodulation in Presence of Amplified Spontaneous Emission Effect
 J. Basic. Appl. ci. Res., (3)834-84,, TextRoad Publication IN 9-434 Journal of Basic and Applied cientific Research www.textroad.co A Dynaic iulink Model For Erbiu-Doped Fiber Aplifiers Overodulation in
J. Basic. Appl. ci. Res., (3)834-84,, TextRoad Publication IN 9-434 Journal of Basic and Applied cientific Research www.textroad.co A Dynaic iulink Model For Erbiu-Doped Fiber Aplifiers Overodulation in
POD-001 PolaDetect. Operation Manual
 POD-001 PolaDetect In-line high speed polarieter Operation Manual August 31, 2005 General Photonics Corp. Ph: (909) 590-5473 5228 Edison Ave. Fax: (909) 902-5536 Chino, CA 91710 USA www.generalphotonics.co
POD-001 PolaDetect In-line high speed polarieter Operation Manual August 31, 2005 General Photonics Corp. Ph: (909) 590-5473 5228 Edison Ave. Fax: (909) 902-5536 Chino, CA 91710 USA www.generalphotonics.co
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Student Name Date MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161 Modern Optics Project Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 6 Fall 2010 Solid-State
Student Name Date MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161 Modern Optics Project Laboratory Laboratory Exercise No. 6 Fall 2010 Solid-State
LOPUT Laser: A novel concept to realize single longitudinal mode laser
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 82, No. 2 journal of February 2014 physics pp. 185 190 LOPUT Laser: A novel concept to realize single longitudinal mode laser JGEORGE, KSBINDRAand SMOAK Solid
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 82, No. 2 journal of February 2014 physics pp. 185 190 LOPUT Laser: A novel concept to realize single longitudinal mode laser JGEORGE, KSBINDRAand SMOAK Solid
WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0?
 WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0? Iproveents/new features introduced in v12.0 are: 1. Extended - Extree Liits a. Extreely LOW contrast aterials b. Extended resolution for radiation pattern c. Extreely
WIPL-D Pro: What is New in v12.0? Iproveents/new features introduced in v12.0 are: 1. Extended - Extree Liits a. Extreely LOW contrast aterials b. Extended resolution for radiation pattern c. Extreely
RAKE Receiver. Tommi Heikkilä S Postgraduate Course in Radio Communications, Autumn II.
 S-72333 Postgraduate Course in Radio Counications, Autun 2004 1 RAKE Receiver Toi Heikkilä toiheikkila@teliasoneraco Abstract RAKE receiver is used in CDMA-based (Code Division Multiple Access) systes
S-72333 Postgraduate Course in Radio Counications, Autun 2004 1 RAKE Receiver Toi Heikkilä toiheikkila@teliasoneraco Abstract RAKE receiver is used in CDMA-based (Code Division Multiple Access) systes
Multiwavelength Single-Longitudinal-Mode Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Laser. Citation IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., 2013, v. 25, p.
 Title Multiwavelength Single-Longitudinal-Mode Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Laser Author(s) ZHOU, Y; Chui, PC; Wong, KKY Citation IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., 2013, v. 25, p. 385-388 Issued Date 2013 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/189009
Title Multiwavelength Single-Longitudinal-Mode Ytterbium-Doped Fiber Laser Author(s) ZHOU, Y; Chui, PC; Wong, KKY Citation IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett., 2013, v. 25, p. 385-388 Issued Date 2013 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/189009
DIGITAL Communications
 DIGITAL Counications Contents Introduction to Counication Systes Analogue Modulation AM, DSBSC, SB, SSB, FM, PM, Narrow band FM, PLL Deodulators, and FLL Loops Sapling Systes Tie and Frequency Division
DIGITAL Counications Contents Introduction to Counication Systes Analogue Modulation AM, DSBSC, SB, SSB, FM, PM, Narrow band FM, PLL Deodulators, and FLL Loops Sapling Systes Tie and Frequency Division
Optical generation of frequency stable mm-wave radiation using diode laser pumped Nd:YAG lasers
 Optical generation of frequency stable mm-wave radiation using diode laser pumped Nd:YAG lasers T. Day and R. A. Marsland New Focus Inc. 340 Pioneer Way Mountain View CA 94041 (415) 961-2108 R. L. Byer
Optical generation of frequency stable mm-wave radiation using diode laser pumped Nd:YAG lasers T. Day and R. A. Marsland New Focus Inc. 340 Pioneer Way Mountain View CA 94041 (415) 961-2108 R. L. Byer
Passively Q-switched m intracavity optical parametric oscillator
 Passively Q-switched 1.57- m intracavity optical parametric oscillator Yuri Yashkir and Henry M. van Driel We demonstrate an eye-safe KTP-based optical parametric oscillator OPO driven intracavity by a
Passively Q-switched 1.57- m intracavity optical parametric oscillator Yuri Yashkir and Henry M. van Driel We demonstrate an eye-safe KTP-based optical parametric oscillator OPO driven intracavity by a
Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber
 Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber H. Ahmad 1, S. Shahi 1 and S. W. Harun 1,2* 1 Photonics Research Center, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Department
Multi-wavelength laser generation with Bismuthbased Erbium-doped fiber H. Ahmad 1, S. Shahi 1 and S. W. Harun 1,2* 1 Photonics Research Center, University of Malaya, 50603 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia 2 Department
Sound recording with the application of microphone arrays
 Coputer Applications in Electrical Engineering Sound recording with the application of icrophone arrays Eugeniusz Kornatowski West Poeranian University of Technology 7-26 Szczecin, 26 Kwietnia, e-ail:
Coputer Applications in Electrical Engineering Sound recording with the application of icrophone arrays Eugeniusz Kornatowski West Poeranian University of Technology 7-26 Szczecin, 26 Kwietnia, e-ail:
] (1) Problem 1. University of California, Berkeley Fall 2010 EE142, Problem Set #9 Solutions Prof. Jan Rabaey
![] (1) Problem 1. University of California, Berkeley Fall 2010 EE142, Problem Set #9 Solutions Prof. Jan Rabaey ] (1) Problem 1. University of California, Berkeley Fall 2010 EE142, Problem Set #9 Solutions Prof. Jan Rabaey](/thumbs/81/84143587.jpg) University of California, Berkeley Fall 00 EE4, Proble Set #9 Solutions Ain Arbabian Prof. Jan Rabaey Proble Since the ixer is a down-conversion type with low side injection f LO 700 MHz and f RF f IF
University of California, Berkeley Fall 00 EE4, Proble Set #9 Solutions Ain Arbabian Prof. Jan Rabaey Proble Since the ixer is a down-conversion type with low side injection f LO 700 MHz and f RF f IF
Power Improvement in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Embedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3
 Power Iproveent in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Ebedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3 1 Departent of ECE, GTBKIET, Chhapianwali Malout, Punjab 2 Director, Principal,
Power Iproveent in 64-Bit Full Adder Using Ebedded Technologies Er. Arun Gandhi 1, Dr. Rahul Malhotra 2, Er. Kulbhushan Singla 3 1 Departent of ECE, GTBKIET, Chhapianwali Malout, Punjab 2 Director, Principal,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: /NPHOTON
 Supplementary Methods and Data 1. Apparatus Design The time-of-flight measurement apparatus built in this study is shown in Supplementary Figure 1. An erbium-doped femtosecond fibre oscillator (C-Fiber,
Supplementary Methods and Data 1. Apparatus Design The time-of-flight measurement apparatus built in this study is shown in Supplementary Figure 1. An erbium-doped femtosecond fibre oscillator (C-Fiber,
Single-frequency operation of a Cr:YAG laser from nm
 Single-frequency operation of a Cr:YAG laser from 1332-1554 nm David Welford and Martin A. Jaspan Paper CThJ1, CLEO/QELS 2000 San Francisco, CA May 11, 2000 Outline Properties of Cr:YAG Cr:YAG laser design
Single-frequency operation of a Cr:YAG laser from 1332-1554 nm David Welford and Martin A. Jaspan Paper CThJ1, CLEO/QELS 2000 San Francisco, CA May 11, 2000 Outline Properties of Cr:YAG Cr:YAG laser design
High-power diode-end-pumped laser with multisegmented Nd-doped yttrium vanadate
 High-power diode-end-pumped laser with multisegmented Nd-doped yttrium vanadate Y. J. Huang and Y. F. Chen * Department of Electrophysics, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan * yfchen@cc.nctu.edu.tw
High-power diode-end-pumped laser with multisegmented Nd-doped yttrium vanadate Y. J. Huang and Y. F. Chen * Department of Electrophysics, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan * yfchen@cc.nctu.edu.tw
Coupling of light from microdisk lasers into plasmonic nano-antennas
 Coupling of light fro icrodisk lasers into plasonic nano-antennas Haroldo T. Hattori 1, *, Ziyuan Li 1, Danyu Liu 2, Ivan D. Rukhlenko 3, and Malin Prearatne 3 1 School of Engineering and Inforation Technology,
Coupling of light fro icrodisk lasers into plasonic nano-antennas Haroldo T. Hattori 1, *, Ziyuan Li 1, Danyu Liu 2, Ivan D. Rukhlenko 3, and Malin Prearatne 3 1 School of Engineering and Inforation Technology,
High power VCSEL array pumped Q-switched Nd:YAG lasers
 High power array pumped Q-switched Nd:YAG lasers Yihan Xiong, Robert Van Leeuwen, Laurence S. Watkins, Jean-Francois Seurin, Guoyang Xu, Alexander Miglo, Qing Wang, and Chuni Ghosh Princeton Optronics,
High power array pumped Q-switched Nd:YAG lasers Yihan Xiong, Robert Van Leeuwen, Laurence S. Watkins, Jean-Francois Seurin, Guoyang Xu, Alexander Miglo, Qing Wang, and Chuni Ghosh Princeton Optronics,
Demonstration of a 1-W injection-locked continuous-wave titanium:sapphire laser
 Demonstration of a 1-W injection-locked continuous-wave titanium:sapphire laser Elizabeth A. Cummings, Malcolm S. Hicken, and Scott D. Bergeson We report on a 1-W injection-locked cw titanium:sapphire
Demonstration of a 1-W injection-locked continuous-wave titanium:sapphire laser Elizabeth A. Cummings, Malcolm S. Hicken, and Scott D. Bergeson We report on a 1-W injection-locked cw titanium:sapphire
Solid-State Laser Engineering
 Walter Koechner Solid-State Laser Engineering Fourth Extensively Revised and Updated Edition With 449 Figures Springer Contents 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Optical Amplification 1 1.2 Interaction of Radiation
Walter Koechner Solid-State Laser Engineering Fourth Extensively Revised and Updated Edition With 449 Figures Springer Contents 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Optical Amplification 1 1.2 Interaction of Radiation
Comparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls
 Coparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls Ali Mahbod 1, Abdolghafar Ghorbani Pour 2, Abdollah Tabaroei 3, Sina Mokhtar 2 1- Departent of Civil Engineering, Shahid Bahonar University,
Coparison Between PLAXIS Output and Neural Network in the Guard Walls Ali Mahbod 1, Abdolghafar Ghorbani Pour 2, Abdollah Tabaroei 3, Sina Mokhtar 2 1- Departent of Civil Engineering, Shahid Bahonar University,
Selective Harmonic Elimination for Multilevel Inverters with Unbalanced DC Inputs
 Selective Haronic Eliination for Multilevel Inverters with Unbalanced DC Inputs Abstract- Selective haronics eliination for the staircase voltage wavefor generated by ultilevel inverters has been widely
Selective Haronic Eliination for Multilevel Inverters with Unbalanced DC Inputs Abstract- Selective haronics eliination for the staircase voltage wavefor generated by ultilevel inverters has been widely
High-efficiency continuously tunable single-frequency doubly resonant optical parametric oscillator
 High-efficiency continuously tunable single-frequency doubly resonant optical parametric oscillator Chunchun Liu, Xiaomin Guo, Zengliang Bai, Xuyang Wang, and Yongmin Li* State Key Laboratory of Quantum
High-efficiency continuously tunable single-frequency doubly resonant optical parametric oscillator Chunchun Liu, Xiaomin Guo, Zengliang Bai, Xuyang Wang, and Yongmin Li* State Key Laboratory of Quantum
ELEC2202 Communications Engineering Laboratory Frequency Modulation (FM)
 ELEC Counications Engineering Laboratory ---- Frequency Modulation (FM) 1. Objectives On copletion of this laboratory you will be failiar with: Frequency odulators (FM), Modulation index, Bandwidth, FM
ELEC Counications Engineering Laboratory ---- Frequency Modulation (FM) 1. Objectives On copletion of this laboratory you will be failiar with: Frequency odulators (FM), Modulation index, Bandwidth, FM
A tunable and switchable single-longitudinalmode dual-wavelength fiber laser with a simple linear cavity
 A tunable and switchable single-longitudinalmode dual-wavelength fiber laser with a simple linear cavity Xiaoying He, 1 Xia Fang, 1 Changrui Liao, 1 D. N. Wang, 1,* and Junqiang Sun 2 1 Department of Electrical
A tunable and switchable single-longitudinalmode dual-wavelength fiber laser with a simple linear cavity Xiaoying He, 1 Xia Fang, 1 Changrui Liao, 1 D. N. Wang, 1,* and Junqiang Sun 2 1 Department of Electrical
Improving the output beam quality of multimode laser resonators
 Improving the output beam quality of multimode laser resonators Amiel A. Ishaaya, Vardit Eckhouse, Liran Shimshi, Nir Davidson and Asher A. Friesem Department of Physics of Complex Systems, Weizmann Institute
Improving the output beam quality of multimode laser resonators Amiel A. Ishaaya, Vardit Eckhouse, Liran Shimshi, Nir Davidson and Asher A. Friesem Department of Physics of Complex Systems, Weizmann Institute
TESTING OF ADCS BY FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS IN MULTI-TONE MODE
 THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volue 5, Nuber /004, pp.000-000 TESTING OF ADCS BY FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS IN MULTI-TONE MODE Daniel BELEGA
THE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF THE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volue 5, Nuber /004, pp.000-000 TESTING OF ADCS BY FREQUENCY-DOMAIN ANALYSIS IN MULTI-TONE MODE Daniel BELEGA
Overlapping Signal Separation in DPX Spectrum Based on EM Algorithm. Chuandang Liu 1, a, Luxi Lu 1, b
 nd International Worshop on Materials Engineering and Coputer Sciences (IWMECS 015) Overlapping Signal Separation in DPX Spectru Based on EM Algorith Chuandang Liu 1, a, Luxi Lu 1, b 1 National Key Laboratory
nd International Worshop on Materials Engineering and Coputer Sciences (IWMECS 015) Overlapping Signal Separation in DPX Spectru Based on EM Algorith Chuandang Liu 1, a, Luxi Lu 1, b 1 National Key Laboratory
Alternative Encoding Techniques for Digital Loudspeaker Arrays
 Alternative Encoding Techniques for Digital Loudspeaer Arrays Fotios Kontoichos, Nicolas Alexander Tatlas, and John Mourjopoulos Audio and Acoustic Technology Group, Wire Counications Laboratory, Electrical
Alternative Encoding Techniques for Digital Loudspeaer Arrays Fotios Kontoichos, Nicolas Alexander Tatlas, and John Mourjopoulos Audio and Acoustic Technology Group, Wire Counications Laboratory, Electrical
Energy-Efficient Cellular Communications Powered by Smart Grid Technology
 Energy-Efficient Cellular Counications Powered by Sart Grid Technology Itiaz Nasi, Mostafa Zaan Chowdhury, and Md. Syadus Sefat Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Khulna University of Engineering
Energy-Efficient Cellular Counications Powered by Sart Grid Technology Itiaz Nasi, Mostafa Zaan Chowdhury, and Md. Syadus Sefat Departent of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Khulna University of Engineering
Keywords: International Mobile Telecommunication (IMT) Systems, evaluating the usage of frequency bands, evaluation indicators
 2nd International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Inforatics (AMEII 206) Entropy Method based Evaluation for Spectru Usage Efficiency of International Mobile Telecounication
2nd International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Inforatics (AMEII 206) Entropy Method based Evaluation for Spectru Usage Efficiency of International Mobile Telecounication
Trace-gas detection based on the temperature-tuning periodically poled MgO: LiNbO 3 optical parametric oscillator
 JOUNAL OF OPTOELECTONICS AND ADVANCED MATEIALS Vol. 8, No. 4, August 2006, p. 1438-14 42 Trace-gas detection based on the temperature-tuning periodically poled MgO: LiNbO 3 optical parametric oscillator
JOUNAL OF OPTOELECTONICS AND ADVANCED MATEIALS Vol. 8, No. 4, August 2006, p. 1438-14 42 Trace-gas detection based on the temperature-tuning periodically poled MgO: LiNbO 3 optical parametric oscillator
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Technology 24 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.co ScienceDirect Procedia Technology 4 (16 ) 834 841 International Conference on Eerging Trends in Engineering, Science and Technology (ICETEST - 15) An Intensity
Available online at www.sciencedirect.co ScienceDirect Procedia Technology 4 (16 ) 834 841 International Conference on Eerging Trends in Engineering, Science and Technology (ICETEST - 15) An Intensity
G. Norris* & G. McConnell
 Relaxed damage threshold intensity conditions and nonlinear increase in the conversion efficiency of an optical parametric oscillator using a bi-directional pump geometry G. Norris* & G. McConnell Centre
Relaxed damage threshold intensity conditions and nonlinear increase in the conversion efficiency of an optical parametric oscillator using a bi-directional pump geometry G. Norris* & G. McConnell Centre
Torsion System. Encoder #3 ( 3 ) Third encoder/disk for Model 205a only. Figure 1: ECP Torsion Experiment
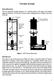 Torsion Syste Introduction This lab experient studies dynaics of a torsional syste with single and ultiple degrees of freedo. The effects of various control configurations are studied in later part of
Torsion Syste Introduction This lab experient studies dynaics of a torsional syste with single and ultiple degrees of freedo. The effects of various control configurations are studied in later part of
Conductively cooled 1-kHz single-frequency Nd:YAG laser for remote sensing
 Conductively cooled 1-kHz single-frequency Nd:YAG laser for remote sensing Juntao Wang ( ), Ren Zhu (ý ), Jun Zhou ( ), Huaguo Zang ( ÙÁ), Xiaolei Zhu (ý ), and Weibiao Chen (í Á) Shanghai Key Laboratory
Conductively cooled 1-kHz single-frequency Nd:YAG laser for remote sensing Juntao Wang ( ), Ren Zhu (ý ), Jun Zhou ( ), Huaguo Zang ( ÙÁ), Xiaolei Zhu (ý ), and Weibiao Chen (í Á) Shanghai Key Laboratory
Fast Widely-Tunable CW Single Frequency 2-micron Laser
 Fast Widely-Tunable CW Single Frequency 2-micron Laser Charley P. Hale and Sammy W. Henderson Beyond Photonics LLC 1650 Coal Creek Avenue, Ste. B Lafayette, CO 80026 Presented at: 18 th Coherent Laser
Fast Widely-Tunable CW Single Frequency 2-micron Laser Charley P. Hale and Sammy W. Henderson Beyond Photonics LLC 1650 Coal Creek Avenue, Ste. B Lafayette, CO 80026 Presented at: 18 th Coherent Laser
