13 Continuous-Time Modulation
|
|
|
- Louise Horn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 13 Continuous-Time Modulation Recommended Problems P13.1 c(t) x(t) x ;y(t) Figure P In the amplitude modulation system in Figure P13.1-1, the input x(t) has the Fourier transform shown in Figure P IX(W)i 4X(o) IT 2 2 Figure P For each choice of carrier c(t) in the following list, draw the magnitude and phase of Y(w), the Fourier transform of y(t). (a) c(t) = eisect (b) c(t) = es'cturm (c) c(t) = cos 3ct (d) c(t) = sin 3wct (e) c(t) = cos 3wct + sin 3wt P13.2 Consider the system in Figure P P13-1
2 Signals and Systems P13-2 x(t) X r X X Yy ~C WC CC WC s(t) m(t) d(t) Figure P The Fourier transform of s(t) is given by Figure P S(W) -2wC 0 2WC Figure P The Fourier transform of x(t) is given by Figure P X(W) Figure P For which of the following choices for m(t) and d(t) is y(t) nonzero? m(t) d(t) (a) 1 1 (b) cos oct cos Wct (c) sin wct sin wt (d) cos 2wet cos 2wet (e) cos 2wct cos oct P13.3 In Section 7.1 of the text, we discussed the effect of a loss in synchronization in phase between the carrier signals in the modulator and demodulator for sinusoidal amplitude modulation. Specifically, we showed that the output of the demodulator is attenuated by the cosine of the phase difference; in particular, when the modulator and demodulator have a phase difference of ir/2, the demodulator output is zero. As we demonstrate in this problem, it is also important to havefrequency synchronization between the modulator and demodulator.
3 Continuous-Time Modulation / Problems P13-3 Consider the amplitude modulation and demodulation systems in Figure P13.3-1, with 0e = 0 and with a change in frequency of the demodulator carrier such that where w(t) = y(t) cos wadt y(t) = x(t) cos Wct cos (oct + 0C) Lowpass filter cos (co t + 0e ) Figure P Let us denote the frequency difference between the modulator and demodulator as Aw [i.e., (Wd - Wc) = Aw]. Also, assume that x(t) is bandlimited with X(W) = 0 for Iwl > wm and assume that the cutoff frequency W of the lowpass filter in the demodulator satisfies the inequality (wm + IA ) < W < (2we + Awl -Mo) (a) Show that the output of the demodulator lowpass filter is proportional to x(t)cos(awt). (b) If the spectrum of x(t) is that shown in Figure P13.3-2, sketch the spectrum of the output of the demodulator. X(o) 1 - M P M Figure P13.3-2
4 Signals and Systems P13-4 You may find it useful to use the trigonometric identity cos A cos B = i[cos(a - B) + cos(a + B)] P13.4 Optional Problems P13.5 As discussed in Section of the text, asynchronous modulation-demodulation requires the injection of the carrier signal so that the modulated signal is of the form y(t) = [A + x(t)]cos(wet + Or), (P13.4-1) where [A + x(t)] > 0 for all t. The presence of the carrier means that more transmitter power is required, representing an inefficiency. (a) Let x(t) be given by x(t) = cos omt with wm < we and [A + x(t)] > 0. For a periodic signal y(t) with period T, the time average power P, is defined as P, = (1/T) fty 2 (t)dt. Determine and sketch Py for y(t) in eq. (P13.4-1). Express your answer as a function of the modulation index m, defined as the maximum absolute value of x(t) divided by A. (b) The efficiency of transmission of an amplitude-modulated signal is defined to be the ratio of the power in the sidebands of the signal to the total power in the signal. With x(t) = cos wmt and with wm < wc and [A + x(t)] > 0, determine and sketch the efficiency E of the modulated signal as a function of the modulation index m. Consider the modulated signal z(t) = A(t)cos(wc + 0,), where we, is known but 0c is unknown. We would like to recover A(t) from z(t). (a) Show that z(t) = x(t)cos wet + y(t)sin wet and express x(t) and y(t) in terms of A(t) and 0e,. (b) Show how to recover x(t) from z(t) by modulation followed by filtering. (c) Show how to recover y(t) from z(t) by modulation followed by filtering. (d) Express A(t) in terms of x(t) and y(t) with no reference to 0c and show in a block diagram how to recover A(t) from z(t). The following trigonometric identities may be useful: cos(a + B) = (cos A cos B) - cos 2 A = -(1 + cos 2A), sin 2 A = -(1 - cos 2A), sin 2A = 2 cos A sin A (sin A sin B), P13.6 A single-sideband modulation system with carrier frequency we, is shown in Figure P
5 Continuous-Time Modulation / Problems P13-5 x(t) y(t) cos Cos + c t Figure P Sketch the Fourier transform of si(t), s 2 (t), sa(t), s 4 (t), sr(t), s,(t), and y(t), thus showing that y(t) is x(t) single-sideband-modulated on the carrier We. Assume that x(t) has the real Fourier transform shown in Figure P and that H(w) is a lowpass filter as shown in Figure P X(O) H(w) 2 2 Figure P Figure P P13.7 Consider the system in Figure P13.7, which can be used to transmit two real signals over a single transmission channel. Y 1 (t) sin wo 0 t Figure P13.7 sin ot For y 1 (t) to be the same as s,(t), and y 2 (t) to be the same as s 2 (t), choose the proper filter H(w) and place the proper restrictions on the bandwidth of si(t) and s 2 (t).
6 Signals and Systems P13-6 P13.8 A commonly used system to maintain privacy in voice communications is a speech scrambler. As illustrated in Figure P13.8-1, the input to the system is a normal speech signal x(t) and the output is the scrambled version y(t). The signal y(t) is transmitted and then unscrambled at the receiver. x(t) --- Scrambler Y~)YM-Unscrambler x(t) (Normal speech) Figure P We assume that all inputs to the scrambler are real and bandlimited to frequency wm; that is, X(w) = 0 for IwI > WM. Given any such input, our proposed scrambler permutes different bands of the input signal spectrum. In addition, the output signal is real and bandlimited to the same frequency band; that is, Y(w) = 0 for IwI > wm. The specific permuting algorithm for our scrambler is Y(M) = X(W - WM), 0 <CO <COM, Y(M) = X(O + WM), -OM < CO <0 (a) If X(w) is given by the spectrum shown in Figure P13.8-2, sketch the spectrum of the scrambled signal y(t). X(O) 1 - -WM WM Figure P (b) Using amplifiers, multipliers, adders, oscillators, and whatever ideal filters you find necessary, draw the block diagram for such an ideal scrambler. (c) Again, using amplifiers, multipliers, adders, oscillators, and ideal filters, draw a block diagram for the associated unscrambler.
7 MIT OpenCourseWare Resource: Signals and Systems Professor Alan V. Oppenheim The following may not correspond to a particular course on MIT OpenCourseWare, but has been provided by the author as an individual learning resource. For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
13 Continuous-Time Modulation
 3 Continuous-Time Modulation Solutions to Recommended Problems S3. (a) By the shifting property, x(t)ejawc t - X(w - 3we) = Y(w) The magnitude and phase of Y(w) are given in Figure S3.-. IY(W)I 4Y(W) w..
3 Continuous-Time Modulation Solutions to Recommended Problems S3. (a) By the shifting property, x(t)ejawc t - X(w - 3we) = Y(w) The magnitude and phase of Y(w) are given in Figure S3.-. IY(W)I 4Y(W) w..
13 Continuous-Time Modulation
 13 Continuous-Time Modulation In this lecture, we begin the discussion of modulation. This is an important concept in communication systems and, as we will see in Lecture 15, also provides the basis for
13 Continuous-Time Modulation In this lecture, we begin the discussion of modulation. This is an important concept in communication systems and, as we will see in Lecture 15, also provides the basis for
18 Discrete-Time Processing of Continuous-Time Signals
 18 Discrete-Time Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Recommended Problems P18.1 Consider the system in Figure P18.1-1 for discrete-time processing of a continuoustime signal using sampling period T,
18 Discrete-Time Processing of Continuous-Time Signals Recommended Problems P18.1 Consider the system in Figure P18.1-1 for discrete-time processing of a continuoustime signal using sampling period T,
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM)
 Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
DT Filters 2/19. Atousa Hajshirmohammadi, SFU
 1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
15 Discrete-Time Modulation
 15 Discrete-Time Modulation The modulation property is basically the same for continuous-time and discrete-time signals. The principal difference is that since for discrete-time signals the Fourier transform
15 Discrete-Time Modulation The modulation property is basically the same for continuous-time and discrete-time signals. The principal difference is that since for discrete-time signals the Fourier transform
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Fall Semester, Introduction to EECS 2
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Fall Semester, 2006 6.082 Introduction to EECS 2 Modulation and Demodulation Introduction A communication system
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Fall Semester, 2006 6.082 Introduction to EECS 2 Modulation and Demodulation Introduction A communication system
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I)
 MODULATING A SIGNAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I) TRANSMITTING SIGNALS : In order to transmit the original low frequency baseband message efficiently over long distances, the signal
MODULATING A SIGNAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I) TRANSMITTING SIGNALS : In order to transmit the original low frequency baseband message efficiently over long distances, the signal
Communication Channels
 Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Amplitude Modulation. Ahmad Bilal
 Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
4.1 REPRESENTATION OF FM AND PM SIGNALS An angle-modulated signal generally can be written as
 1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
Laboratory Assignment 5 Amplitude Modulation
 Laboratory Assignment 5 Amplitude Modulation PURPOSE In this assignment, you will explore the use of digital computers for the analysis, design, synthesis, and simulation of an amplitude modulation (AM)
Laboratory Assignment 5 Amplitude Modulation PURPOSE In this assignment, you will explore the use of digital computers for the analysis, design, synthesis, and simulation of an amplitude modulation (AM)
Chapter 3: Analog Modulation Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved.
 Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
Amplitude Modulation Chapter 2. Modulation process
 Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Lecture 12 - Analog Communication (II)
 Lecture 12 - Analog Communication (II) James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu) Spring 2014 Colorado State University Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE423 1 / 12 Outline QAM: quadrature
Lecture 12 - Analog Communication (II) James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu) Spring 2014 Colorado State University Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE423 1 / 12 Outline QAM: quadrature
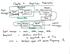 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II
 EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
6.02 Practice Problems: Modulation & Demodulation
 1 of 12 6.02 Practice Problems: Modulation & Demodulation Problem 1. Here's our "standard" modulation-demodulation system diagram: at the transmitter, signal x[n] is modulated by signal mod[n] and the
1 of 12 6.02 Practice Problems: Modulation & Demodulation Problem 1. Here's our "standard" modulation-demodulation system diagram: at the transmitter, signal x[n] is modulated by signal mod[n] and the
CME 312-Lab Communication Systems Laboratory
 Objective: By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the Modulation and Demodulation of the AM. 2. Observe the relation between modulation index and AM signal envelope.
Objective: By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the Modulation and Demodulation of the AM. 2. Observe the relation between modulation index and AM signal envelope.
3.1 Introduction 3.2 Amplitude Modulation 3.3 Double Sideband-Suppressed Carrier Modulation 3.4 Quadrature-Carrier Multiplexing 3.
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Outline 3.1 Introduction 3. Amplitude Modulation 3.3
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Outline 3.1 Introduction 3. Amplitude Modulation 3.3
1. Clearly circle one answer for each part.
 TB 1-9 / Exam Style Questions 1 EXAM STYLE QUESTIONS Covering Chapters 1-9 of Telecommunication Breakdown 1. Clearly circle one answer for each part. (a) TRUE or FALSE: Absolute bandwidth is never less
TB 1-9 / Exam Style Questions 1 EXAM STYLE QUESTIONS Covering Chapters 1-9 of Telecommunication Breakdown 1. Clearly circle one answer for each part. (a) TRUE or FALSE: Absolute bandwidth is never less
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS. MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications
 DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications Bandpass binary signalling The common techniques of bandpass binary signalling are: - On-off keying (OOK), also known as
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications Bandpass binary signalling The common techniques of bandpass binary signalling are: - On-off keying (OOK), also known as
Costas Loop. Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier
 Costas Loop Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier 0 Pre-Laboratory Reading Phase-shift keying that employs two discrete
Costas Loop Modules: Sequence Generator, Digital Utilities, VCO, Quadrature Utilities (2), Phase Shifter, Tuneable LPF (2), Multiplier 0 Pre-Laboratory Reading Phase-shift keying that employs two discrete
HW 6 Due: November 9, 4 PM
 Name ID3 ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2018/1 HW 6 Due: November 9, 4 PM Lecturer: Prapun Suksompong, Ph.D. Instructions (a) This assignment has 10 pages. (b) (1 pt) Work and write your answers
Name ID3 ECS 332: Principles of Communications 2018/1 HW 6 Due: November 9, 4 PM Lecturer: Prapun Suksompong, Ph.D. Instructions (a) This assignment has 10 pages. (b) (1 pt) Work and write your answers
I-Q transmission. Lecture 17
 I-Q Transmission Lecture 7 I-Q transmission i Sending Digital Data Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK): sending binary data over a single frequency band Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK): sending twice
I-Q Transmission Lecture 7 I-Q transmission i Sending Digital Data Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK): sending binary data over a single frequency band Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK): sending twice
Fourier Transform Analysis of Signals and Systems
 Fourier Transform Analysis of Signals and Systems Ideal Filters Filters separate what is desired from what is not desired In the signals and systems context a filter separates signals in one frequency
Fourier Transform Analysis of Signals and Systems Ideal Filters Filters separate what is desired from what is not desired In the signals and systems context a filter separates signals in one frequency
(Refer Slide Time: 3:11)
 Digital Communication. Professor Surendra Prasad. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi. Lecture-2. Digital Representation of Analog Signals: Delta Modulation. Professor:
Digital Communication. Professor Surendra Prasad. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi. Lecture-2. Digital Representation of Analog Signals: Delta Modulation. Professor:
EE4512 Analog and Digital Communications Chapter 6. Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation
 Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Amplitude Modulation Pages 306-309 309 The analytical signal for double sideband, large carrier amplitude modulation
Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Amplitude Modulation Pages 306-309 309 The analytical signal for double sideband, large carrier amplitude modulation
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications
 ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
Fundamentals of Communication Systems SECOND EDITION
 GLOBAL EDITIO Fundamentals of Communication Systems SECOD EDITIO John G. Proakis Masoud Salehi 78 Effect of oise on Analog Communication Systems Chapter 6 The noise power is P n = ow we can find the output
GLOBAL EDITIO Fundamentals of Communication Systems SECOD EDITIO John G. Proakis Masoud Salehi 78 Effect of oise on Analog Communication Systems Chapter 6 The noise power is P n = ow we can find the output
Module 4. Signal Representation and Baseband Processing. Version 2 ECE IIT, Kharagpur
 Module 4 Signal Representation and Baseband Processing Lesson 1 Nyquist Filtering and Inter Symbol Interference After reading this lesson, you will learn about: Power spectrum of a random binary sequence;
Module 4 Signal Representation and Baseband Processing Lesson 1 Nyquist Filtering and Inter Symbol Interference After reading this lesson, you will learn about: Power spectrum of a random binary sequence;
Solution to Chapter 4 Problems
 Solution to Chapter 4 Problems Problem 4.1 1) Since F[sinc(400t)]= 1 modulation index 400 ( f 400 β f = k f max[ m(t) ] W Hence, the modulated signal is ), the bandwidth of the message signal is W = 00
Solution to Chapter 4 Problems Problem 4.1 1) Since F[sinc(400t)]= 1 modulation index 400 ( f 400 β f = k f max[ m(t) ] W Hence, the modulated signal is ), the bandwidth of the message signal is W = 00
EXPERIMENT 3 - Part I: DSB-SC Amplitude Modulation
 OBJECTIVE To generate DSB-SC amplitude modulated signal. EXPERIMENT 3 - Part I: DSB-SC Amplitude Modulation PRELIMINARY DISCUSSION In the modulation process, the message signal (the baseband voice, video,
OBJECTIVE To generate DSB-SC amplitude modulated signal. EXPERIMENT 3 - Part I: DSB-SC Amplitude Modulation PRELIMINARY DISCUSSION In the modulation process, the message signal (the baseband voice, video,
Chapter 5. Amplitude Modulation
 Chapter 5 Amplitude Modulation So far we have developed basic signal and system representation techniques which we will now apply to the analysis of various analog communication systems. In particular,
Chapter 5 Amplitude Modulation So far we have developed basic signal and system representation techniques which we will now apply to the analysis of various analog communication systems. In particular,
Description of the AM Superheterodyne Radio Receiver
 Superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver Since the inception of the AM radio, it spread widely due to its ease of use and more importantly, it low cost. The low cost of most AM radios sold in the market is due
Superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver Since the inception of the AM radio, it spread widely due to its ease of use and more importantly, it low cost. The low cost of most AM radios sold in the market is due
EE3723 : Digital Communications
 EE3723 : Digital Communications Week 8-9: Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad - Digital Communications - EE3723 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation
EE3723 : Digital Communications Week 8-9: Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad - Digital Communications - EE3723 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation
Chapter 2 Direct-Sequence Systems
 Chapter 2 Direct-Sequence Systems A spread-spectrum signal is one with an extra modulation that expands the signal bandwidth greatly beyond what is required by the underlying coded-data modulation. Spread-spectrum
Chapter 2 Direct-Sequence Systems A spread-spectrum signal is one with an extra modulation that expands the signal bandwidth greatly beyond what is required by the underlying coded-data modulation. Spread-spectrum
PRODUCT DEMODULATION - SYNCHRONOUS & ASYNCHRONOUS
 PRODUCT DEMODULATION - SYNCHRONOUS & ASYNCHRONOUS INTRODUCTION...98 frequency translation...98 the process...98 interpretation...99 the demodulator...100 synchronous operation: ω 0 = ω 1...100 carrier
PRODUCT DEMODULATION - SYNCHRONOUS & ASYNCHRONOUS INTRODUCTION...98 frequency translation...98 the process...98 interpretation...99 the demodulator...100 synchronous operation: ω 0 = ω 1...100 carrier
The University of Texas at Austin Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm #2
 The University of Texas at Austin Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm #2 Date: November 18, 2010 Course: EE 313 Evans Name: Last, First The exam is scheduled to last 75 minutes. Open books
The University of Texas at Austin Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm #2 Date: November 18, 2010 Course: EE 313 Evans Name: Last, First The exam is scheduled to last 75 minutes. Open books
EE 438 Final Exam Spring 2000
 2 May 2000 Name: EE 438 Final Exam Spring 2000 You have 120 minutes to work the following six problems. Each problem is worth 25 points. Be sure to show all your work to obtain full credit. The exam is
2 May 2000 Name: EE 438 Final Exam Spring 2000 You have 120 minutes to work the following six problems. Each problem is worth 25 points. Be sure to show all your work to obtain full credit. The exam is
Signal Characteristics
 Data Transmission The successful transmission of data depends upon two factors:» The quality of the transmission signal» The characteristics of the transmission medium Some type of transmission medium
Data Transmission The successful transmission of data depends upon two factors:» The quality of the transmission signal» The characteristics of the transmission medium Some type of transmission medium
EE 460L University of Nevada, Las Vegas ECE Department
 EE 460L PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in the context of digital communications is a modulation process which imparts to a sinusoid two or more discrete amplitude levels. These are related
EE 460L PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in the context of digital communications is a modulation process which imparts to a sinusoid two or more discrete amplitude levels. These are related
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory Amplitude Modulation (AM)
 ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
CS311: Data Communication. Transmission of Analog Signal - I
 CS311: Data Communication Transmission of Analog Signal - I by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
CS311: Data Communication Transmission of Analog Signal - I by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
1B Paper 6: Communications Handout 2: Analogue Modulation
 1B Paper 6: Communications Handout : Analogue Modulation Ramji Venkataramanan Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering ramji.v@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term 16 1 / 3 Modulation Modulation
1B Paper 6: Communications Handout : Analogue Modulation Ramji Venkataramanan Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering ramji.v@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term 16 1 / 3 Modulation Modulation
ANALOG (DE)MODULATION
 ANALOG (DE)MODULATION Amplitude Modulation with Large Carrier Amplitude Modulation with Suppressed Carrier Quadrature Modulation Injection to Intermediate Frequency idealized system Software Receiver Design
ANALOG (DE)MODULATION Amplitude Modulation with Large Carrier Amplitude Modulation with Suppressed Carrier Quadrature Modulation Injection to Intermediate Frequency idealized system Software Receiver Design
REVIEW OF CIRCUIT IMPLEMENTATION OF SYNCHRONIZED CHAOS WITH APPLICATION TO COMMUNICATION BY: ABHISHEK SINGH AND DIVYA GROVER
 REVIEW OF CIRCUIT IMPLEMENTATION OF SYNCHRONIZED CHAOS WITH APPLICATION TO COMMUNICATION BY: ABHISHEK SINGH AND DIVYA GROVER INTRODUCTION: In this Project, we focus on the synchronizing properties of the
REVIEW OF CIRCUIT IMPLEMENTATION OF SYNCHRONIZED CHAOS WITH APPLICATION TO COMMUNICATION BY: ABHISHEK SINGH AND DIVYA GROVER INTRODUCTION: In this Project, we focus on the synchronizing properties of the
Neurophysiology. The action potential. Why should we care? AP is the elemental until of nervous system communication
 Neurophysiology Why should we care? AP is the elemental until of nervous system communication The action potential Time course, propagation velocity, and patterns all constrain hypotheses on how the brain
Neurophysiology Why should we care? AP is the elemental until of nervous system communication The action potential Time course, propagation velocity, and patterns all constrain hypotheses on how the brain
END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS ELEC321 Communication Systems (D2) Tuesday, 22 November 2005, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 10 minutes reading time.
 END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS 2005 Unit: Day and Time: Time Allowed: ELEC321 Communication Systems (D2) Tuesday, 22 November 2005, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 10 minutes reading time. Total Number of Questions:
END-OF-YEAR EXAMINATIONS 2005 Unit: Day and Time: Time Allowed: ELEC321 Communication Systems (D2) Tuesday, 22 November 2005, 9:20 a.m. Three hours plus 10 minutes reading time. Total Number of Questions:
Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM)
 Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) Modules: Integrate & Dump, Digital Utilities, Wideband True RMS Meter, Tuneable LPF, Audio Oscillator, Multiplier, Utilities, Noise Generator, Speech, Headphones. 0 Pre-Laboratory
Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) Modules: Integrate & Dump, Digital Utilities, Wideband True RMS Meter, Tuneable LPF, Audio Oscillator, Multiplier, Utilities, Noise Generator, Speech, Headphones. 0 Pre-Laboratory
Spread spectrum. Outline : 1. Baseband 2. DS/BPSK Modulation 3. CDM(A) system 4. Multi-path 5. Exercices. Exercise session 7 : Spread spectrum 1
 Spread spectrum Outline : 1. Baseband 2. DS/BPSK Modulation 3. CDM(A) system 4. Multi-path 5. Exercices Exercise session 7 : Spread spectrum 1 1. Baseband +1 b(t) b(t) -1 T b t Spreading +1-1 T c t m(t)
Spread spectrum Outline : 1. Baseband 2. DS/BPSK Modulation 3. CDM(A) system 4. Multi-path 5. Exercices Exercise session 7 : Spread spectrum 1 1. Baseband +1 b(t) b(t) -1 T b t Spreading +1-1 T c t m(t)
Module 3 : Sampling and Reconstruction Problem Set 3
 Module 3 : Sampling and Reconstruction Problem Set 3 Problem 1 Shown in figure below is a system in which the sampling signal is an impulse train with alternating sign. The sampling signal p(t), the Fourier
Module 3 : Sampling and Reconstruction Problem Set 3 Problem 1 Shown in figure below is a system in which the sampling signal is an impulse train with alternating sign. The sampling signal p(t), the Fourier
Some Old Exam Problems, EE 3350 Communication Systems 2/28/2011 Professor D. L. MacFarlane
 Some Old Eam Problems, EE 3350 Communication Systems 2/28/2011 Professor D. L. MacFarlane This document contains some eam problems that I have used in past semesters. I recommend that your pre test studying
Some Old Eam Problems, EE 3350 Communication Systems 2/28/2011 Professor D. L. MacFarlane This document contains some eam problems that I have used in past semesters. I recommend that your pre test studying
Linear Modulation: Amplitude Modulation
 1 Communication Systems Chapter Linear Modulation: Amplitude Modulation In the previous chapter, we have covered, what is modulation, its different types along with its need. Now here in this chapter we
1 Communication Systems Chapter Linear Modulation: Amplitude Modulation In the previous chapter, we have covered, what is modulation, its different types along with its need. Now here in this chapter we
CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL
 CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL PREPARATION... 22 carrier acquisition methods... 22 bandpass filter...22 the phase locked loop (PLL)....23 squaring...24 squarer plus PLL...26 the Costas loop...26 EXPERIMENT...
CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL PREPARATION... 22 carrier acquisition methods... 22 bandpass filter...22 the phase locked loop (PLL)....23 squaring...24 squarer plus PLL...26 the Costas loop...26 EXPERIMENT...
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 10 Single Sideband Modulation We will discuss, now we will continue
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 10 Single Sideband Modulation We will discuss, now we will continue
Spectrum. The basic idea of measurement. Instrumentation for spectral measurements Ján Šaliga 2017
 Instrumentation for spectral measurements Ján Šaliga 017 Spectrum Substitution of waveform by the sum of harmonics (sinewaves) with specific amplitudes, frequences and phases. The sum of sinewave have
Instrumentation for spectral measurements Ján Šaliga 017 Spectrum Substitution of waveform by the sum of harmonics (sinewaves) with specific amplitudes, frequences and phases. The sum of sinewave have
EE 400L Communications. Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation
 EE 400L Communications Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in
EE 400L Communications Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in
BIT SYNCHRONIZERS FOR PSK AND THEIR DIGITAL IMPLEMENTATION
 BIT SYNCHRONIZERS FOR PSK AND THEIR DIGITAL IMPLEMENTATION Jack K. Holmes Holmes Associates, Inc. 1338 Comstock Avenue Los Angeles, California 90024 ABSTRACT Bit synchronizers play an important role in
BIT SYNCHRONIZERS FOR PSK AND THEIR DIGITAL IMPLEMENTATION Jack K. Holmes Holmes Associates, Inc. 1338 Comstock Avenue Los Angeles, California 90024 ABSTRACT Bit synchronizers play an important role in
Project 2 - Speech Detection with FIR Filters
 Project 2 - Speech Detection with FIR Filters ECE505, Fall 2015 EECS, University of Tennessee (Due 10/30) 1 Objective The project introduces a practical application where sinusoidal signals are used to
Project 2 - Speech Detection with FIR Filters ECE505, Fall 2015 EECS, University of Tennessee (Due 10/30) 1 Objective The project introduces a practical application where sinusoidal signals are used to
3.1 Introduction to Modulation
 Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Principles of Communications ECS 332
 Principles of Communications ECS 332 Asst. Prof. Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th 5. Angle Modulation Office Hours: BKD, 6th floor of Sirindhralai building Wednesday 4:3-5:3 Friday 4:3-5:3 Example
Principles of Communications ECS 332 Asst. Prof. Dr. Prapun Suksompong prapun@siit.tu.ac.th 5. Angle Modulation Office Hours: BKD, 6th floor of Sirindhralai building Wednesday 4:3-5:3 Friday 4:3-5:3 Example
Problem Sheet for Amplitude Modulation
 Problem heet for Amplitude Modulation Q1: For the sinusoidaly modulated DB/LC waveform shown in Fig. below. a Find the modulation index. b ketch a line spectrum. c Calculated the ratio of average power
Problem heet for Amplitude Modulation Q1: For the sinusoidaly modulated DB/LC waveform shown in Fig. below. a Find the modulation index. b ketch a line spectrum. c Calculated the ratio of average power
(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]
![(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3] (b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]](/thumbs/85/91561193.jpg) Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. Semester 1 June COMMUNICATIONS IV (ELEC ENG 4035)
 EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. Semester 1 June 2007 101902 COMMUNICATIONS IV (ELEC ENG 4035) Official Reading Time: Writing Time: Total Duration: 10 mins 120 mins 130 mins Instructions: This is a closed
EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF B.E. Semester 1 June 2007 101902 COMMUNICATIONS IV (ELEC ENG 4035) Official Reading Time: Writing Time: Total Duration: 10 mins 120 mins 130 mins Instructions: This is a closed
Real and Complex Modulation
 Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
CHAPTER 2! AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM)
 CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
Amplitude Modulation, II
 Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
University of Toronto Electrical & Computer Engineering ECE 316, Winter 2015 Thursday, February 12, Test #1
 Name: Student No.: University of Toronto Electrical & Computer Engineering ECE 36, Winter 205 Thursday, February 2, 205 Test # Professor Dimitrios Hatzinakos Professor Deepa Kundur Duration: 50 minutes
Name: Student No.: University of Toronto Electrical & Computer Engineering ECE 36, Winter 205 Thursday, February 2, 205 Test # Professor Dimitrios Hatzinakos Professor Deepa Kundur Duration: 50 minutes
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier
 Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
The quality of the transmission signal The characteristics of the transmission medium. Some type of transmission medium is required for transmission:
 Data Transmission The successful transmission of data depends upon two factors: The quality of the transmission signal The characteristics of the transmission medium Some type of transmission medium is
Data Transmission The successful transmission of data depends upon two factors: The quality of the transmission signal The characteristics of the transmission medium Some type of transmission medium is
Fund. of Digital Communications Ch. 3: Digital Modulation
 Fund. of Digital Communications Ch. 3: Digital Modulation Klaus Witrisal witrisal@tugraz.at Signal Processing and Speech Communication Laboratory www.spsc.tugraz.at Graz University of Technology November
Fund. of Digital Communications Ch. 3: Digital Modulation Klaus Witrisal witrisal@tugraz.at Signal Processing and Speech Communication Laboratory www.spsc.tugraz.at Graz University of Technology November
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering
 Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I. Review. ELEC 350 Fall
 ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
M(f) = 0. Linear modulation: linear relationship between the modulated signal and the message signal (ex: AM, DSB-SC, SSB, VSB).
 4 Analog modulation 4.1 Modulation formats The message waveform is represented by a low-pass real signal mt) such that Mf) = 0 f W where W is the message bandwidth. mt) is called the modulating signal.
4 Analog modulation 4.1 Modulation formats The message waveform is represented by a low-pass real signal mt) such that Mf) = 0 f W where W is the message bandwidth. mt) is called the modulating signal.
Other Modulation Techniques - CAP, QAM, DMT
 Other Modulation Techniques - CAP, QAM, DMT Prof. David Johns (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (www.eecg.toronto.edu/~johns) slide 1 of 47 Complex Signals Concept useful for describing a pair of real signals Let
Other Modulation Techniques - CAP, QAM, DMT Prof. David Johns (johns@eecg.toronto.edu) (www.eecg.toronto.edu/~johns) slide 1 of 47 Complex Signals Concept useful for describing a pair of real signals Let
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING 1.6 Analog Filters 1.7 Applications of Analog Filters
 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING 1.6 Analog Filters 1.7 Applications of Analog Filters Copyright c 2005 Andreas Antoniou Victoria, BC, Canada Email: aantoniou@ieee.org July 14, 2018
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING 1.6 Analog Filters 1.7 Applications of Analog Filters Copyright c 2005 Andreas Antoniou Victoria, BC, Canada Email: aantoniou@ieee.org July 14, 2018
Final Exam Solutions June 14, 2006
 Name or 6-Digit Code: PSU Student ID Number: Final Exam Solutions June 14, 2006 ECE 223: Signals & Systems II Dr. McNames Keep your exam flat during the entire exam. If you have to leave the exam temporarily,
Name or 6-Digit Code: PSU Student ID Number: Final Exam Solutions June 14, 2006 ECE 223: Signals & Systems II Dr. McNames Keep your exam flat during the entire exam. If you have to leave the exam temporarily,
DSBSC GENERATION. PREPARATION definition of a DSBSC viewing envelopes multi-tone message... 37
 DSBSC GENERATION PREPARATION... 34 definition of a DSBSC... 34 block diagram...36 viewing envelopes... 36 multi-tone message... 37 linear modulation...38 spectrum analysis... 38 EXPERIMENT... 38 the MULTIPLIER...
DSBSC GENERATION PREPARATION... 34 definition of a DSBSC... 34 block diagram...36 viewing envelopes... 36 multi-tone message... 37 linear modulation...38 spectrum analysis... 38 EXPERIMENT... 38 the MULTIPLIER...
Charan Langton, Editor
 Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
AM Limitations. Amplitude Modulation II. DSB-SC Modulation. AM Modifications
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Midterm 1. Total. Name of Student on Your Left: Name of Student on Your Right: EE 20N: Structure and Interpretation of Signals and Systems
 EE 20N: Structure and Interpretation of Signals and Systems Midterm 1 12:40-2:00, February 19 Notes: There are five questions on this midterm. Answer each question part in the space below it, using the
EE 20N: Structure and Interpretation of Signals and Systems Midterm 1 12:40-2:00, February 19 Notes: There are five questions on this midterm. Answer each question part in the space below it, using the
Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6
 Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6 f f f LO audio baseband m http://www.technologyuk.net/telecommunications/telecom_principles/amplitude_modulation.shtml AM Modulation --
Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6 f f f LO audio baseband m http://www.technologyuk.net/telecommunications/telecom_principles/amplitude_modulation.shtml AM Modulation --
Universitas Sumatera Utara
 Amplitude Shift Keying & Frequency Shift Keying Aim: To generate and demodulate an amplitude shift keyed (ASK) signal and a binary FSK signal. Intro to Generation of ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK -
Amplitude Shift Keying & Frequency Shift Keying Aim: To generate and demodulate an amplitude shift keyed (ASK) signal and a binary FSK signal. Intro to Generation of ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK -
Amplitude Modulation II
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Contents. 7.1 Line Coding. Dr. Ali Muqaibel [Principles of Digital Transmission ]
![Contents. 7.1 Line Coding. Dr. Ali Muqaibel [Principles of Digital Transmission ] Contents. 7.1 Line Coding. Dr. Ali Muqaibel [Principles of Digital Transmission ]](/thumbs/96/128739202.jpg) Contents 7.1 Line Coding... 1 Performance Criteria of Line Codes... 4 Advanced Examples in Line Coding: High Density Bipolar (HDBN)... 5 7. Power Spectral Density of Line Codes... 5 7.3 Pulse shaping and
Contents 7.1 Line Coding... 1 Performance Criteria of Line Codes... 4 Advanced Examples in Line Coding: High Density Bipolar (HDBN)... 5 7. Power Spectral Density of Line Codes... 5 7.3 Pulse shaping and
Homework 4. Solution. a) Sketch the spectrum of m(t). b) Sketch the spectrum of the DSB-SC signal m(t)cos10,000πt.
 CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, BAKERSFIELD (CSUB) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING & COMPUTER SCIENCE ECE 423: DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS Homework 4 Solution QUESTION 1:(25 POINTS) You are given
CALIFORNIA STATE UNIVERSITY, BAKERSFIELD (CSUB) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING & COMPUTER SCIENCE ECE 423: DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS Homework 4 Solution QUESTION 1:(25 POINTS) You are given
CHAPTER 2. Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication ( )
 CHAPTER 2 Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication (2170710) Syllabus Chapter-2.3 Modulation Techniques Reasons for Choosing Encoding Techniques Digital data,
CHAPTER 2 Instructor: Mr. Abhijit Parmar Course: Mobile Computing and Wireless Communication (2170710) Syllabus Chapter-2.3 Modulation Techniques Reasons for Choosing Encoding Techniques Digital data,
Final Exam Solutions June 7, 2004
 Name: Final Exam Solutions June 7, 24 ECE 223: Signals & Systems II Dr. McNames Write your name above. Keep your exam flat during the entire exam period. If you have to leave the exam temporarily, close
Name: Final Exam Solutions June 7, 24 ECE 223: Signals & Systems II Dr. McNames Write your name above. Keep your exam flat during the entire exam period. If you have to leave the exam temporarily, close
Chapter 3. Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
CHANNEL ENCODING & DECODING. Binary Interface
 CHANNEL ENCODING & DECODING Input Source Encoder Channel Encoder Binary Interface Channel Output Source Decoder Channel Decoder 1 Simplest Example of channel encoding A sequence of binary digits is mapped,
CHANNEL ENCODING & DECODING Input Source Encoder Channel Encoder Binary Interface Channel Output Source Decoder Channel Decoder 1 Simplest Example of channel encoding A sequence of binary digits is mapped,
YEDITEPE UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING FACULTY COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS LABORATORY EE 354 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 YEDITEPE UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING FACULTY COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS LABORATORY EE 354 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS EXPERIMENT 3: SAMPLING & TIME DIVISION MULTIPLEX (TDM) Objective: Experimental verification of the
YEDITEPE UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING FACULTY COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS LABORATORY EE 354 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS EXPERIMENT 3: SAMPLING & TIME DIVISION MULTIPLEX (TDM) Objective: Experimental verification of the
Chpater 8 Digital Transmission through Bandlimited AWGN Channels
 Chapter 8. Digital Transmission through Bandlimited AWGN Channels - 1-1 st Semester, 008 Chpater 8 Digital Transmission through Bandlimited AWGN Channels Text. [1] J. G. Proakis and M. Salehi, Communication
Chapter 8. Digital Transmission through Bandlimited AWGN Channels - 1-1 st Semester, 008 Chpater 8 Digital Transmission through Bandlimited AWGN Channels Text. [1] J. G. Proakis and M. Salehi, Communication
Lab 0: Introduction to TIMS AND MATLAB
 TELE3013 TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 1 Lab 0: Introduction to TIMS AND MATLAB 1. INTRODUCTION The TIMS (Telecommunication Instructional Modelling System) system was first developed by Tim Hooper, then a
TELE3013 TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 1 Lab 0: Introduction to TIMS AND MATLAB 1. INTRODUCTION The TIMS (Telecommunication Instructional Modelling System) system was first developed by Tim Hooper, then a
Discrete-time Signals & Systems
 Discrete-time Signals & Systems S Wongsa Dept. of Control Systems and Instrumentation Engineering, KMU JAN, 2010 1 Overview Signals & Systems Continuous & Discrete ime Sampling Sampling in Frequency Domain
Discrete-time Signals & Systems S Wongsa Dept. of Control Systems and Instrumentation Engineering, KMU JAN, 2010 1 Overview Signals & Systems Continuous & Discrete ime Sampling Sampling in Frequency Domain
AMPLITUDE MODULATION
 AMPLITUDE MODULATION PREPARATION...2 theory...3 depth of modulation...4 measurement of m... 5 spectrum... 5 other message shapes.... 5 other generation methods...6 EXPERIMENT...7 aligning the model...7
AMPLITUDE MODULATION PREPARATION...2 theory...3 depth of modulation...4 measurement of m... 5 spectrum... 5 other message shapes.... 5 other generation methods...6 EXPERIMENT...7 aligning the model...7
