Name Section 2 (4 5:50PM, Monday and Thursday) Draw circuit diagrams for all problems, especially as you simplify the circuits.
|
|
|
- Kory Evans
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Part B (80 Points) Name Section 2 (4 5:50PM, Monday and Thursday) 1. (10 Pts) 2. (10 Pts) 3. (10 Pts) 4. (30 Pts) 5. (10 Pts) 6. (10 Pts) Total Draw circuit diagrams for all problems, especially as you simplify the circuits. Be sure to fully annotate plots, even when the problem does not ask you to do this. Show all of your work Almost all problems can be solved using more than one method. Check your answers by using a second method. At least skim through the entire quiz before you begin and then start with the problems you know best. The proctor will only answer clarification questions where wording is unclear or where there may be errors/typos. No other questions will be responded to. K. Connor, J. Braunstein Revised: 28 November 2016
2 First Radio Broadcast of Election Results 7 November 1916 Radio station 2XG, also known as the "Highbridge station" after its location at 1391 Sedgewick Ave. in the Bronx, was an experimental station licensed to the De Forest Radio Telephone and Telegraph Company from & It was the first radio station employing a vacuum-tube transmitter to make news and entertainment broadcasts on a regular schedule. On the night of the November 7, 1916 Wilson-Hughes presidential election, 2XG, in conjunction with the New York American, broadcast election returns that for the first time were in full audio instead of Morse code. This program featured telephoned bulletins supplied by the newspaper which hailed the effort as "the first time the wireless telephone has been demonstrated as a practical, serviceable carrier of election news and comment" and read over the air by "unassuming chap" Walter Schare. Also featured were Columbia recordings that included "'The Star Spangled Banner,' 'Columbia, the Gem of the Ocean,' 'Dixie,' 'America' and other airs long loved by Americans." Just before shutting down at 11:00 PM, the station incorrectly announced that Charles Evans Hughes had won, however the next day it was learned that late totals from California had tilted the election in Woodrow Wilson's favor. It was estimated that 7,000 persons received the broadcast. The concerts continued, with listeners reported as far away at Cape Hatteras, North Carolina. A "radio dance" held in Morristown, New Jersey at the end of the year received widespread publicity. However, with the entry of the United States into World War One on April 6, 1917, all civilian radio stations were ordered shut down, and 2XG was silenced for the duration of the conflict. The broadcast location is now part of the I-87 on-ramp near the Yankee Stadium Howard Johnson Motel. First Woman Elected to Congress 7 November 1916 Jeannette Pickering Rankin (June 11, 1880 May 18, 1973) was the first woman to hold federal office in the United States when, in 1916, she was elected to the U.S. House of Representatives by the state of Montana. She won a second House term 24 years later, in Each of Rankin's Congressional terms coincided with initiation of U.S. military intervention in each of the World Wars. A lifelong pacifist, she was one of 50 House members (total of 56 in both chambers) who opposed the war declaration of 1917, and the only member of Congress to vote against declaring war on Japan after the attack on Pearl Harbor in Rankin was also instrumental in initiating the legislation that eventually became the 19th Constitutional Amendment, granting unrestricted voting rights to women; and she championed the causes of gender equality and civil rights throughout a career that spanned more than six decades. Source: Wikipedia K. Connor, J. Braunstein 2 Revised: 28 November 2016
3 Inductance Specs From Digilent Parts Kit Website K. Connor, J. Braunstein 3 Revised: 28 November 2016
4 K. Connor, J. Braunstein 4 Revised: 28 November 2016
5 Standard Capacitor Values K. Connor, J. Braunstein 5 Revised: 28 November 2016
6 Problem 1 (10 Pts) Experimentally Determining an Input Impedance Nearly all loads can be characterized by some kind of simple input impedance. For example, the two analog input channels on the Analog Discovery board have an input resistance of 1MΩ and an input capacitance of 24pF. The circuit at the right is set up to determine the resistance of a Photocell (aka Light Dependent Resistor or LDR) under two lighting conditions. The source voltage Vsource is 9V and the known resistor R is 8.2k. We plan to use the photocell to control a nightlight so we need to measure its nominal resistance when the room is brightly lit (nightlight should be off) and dark (night light should be fully on). The data for these two conditions are given below. Trial Light Level V(OUT) 1 Low 7.5V 2 High 2.4V a. (5 Pts) Determine the unknown resistance LDR for low light conditions. b. (5 Pts) Determine the unknown resistance LDR for high light conditions K. Connor, J. Braunstein 6 Revised: 28 November 2016
7 Problem 2 (10 Points) Phase In the Matlab generated plot below, two cosinusoidal voltages are shown vs time. V ( t) cos( t) and U ( t) cos( t ). The magnitudes of the two voltages are not the same. The vertical scale is 0.5V/Div and the horizontal scale is 0.5ms/Div a. (2 Pts) Determine the frequency f in Hertz and ω in Radians. b. (2 Pts) Determine the phase of U in degrees. Be sure to specify its sign and remember it can have any value from -360 degrees to +360 degrees. K. Connor, J. Braunstein 7 Revised: 28 November 2016
8 c. (2 Pts) What is the amplitude of U in Volts? ~ d. (2 Pts) What is the phasor form of U? e. (2 Pts) Plot the point for the phasor voltage on the complex plane. Plot the point that represents its value as a complex number. Be sure to fully label the plot. Imag Real K. Connor, J. Braunstein 8 Revised: 28 November 2016
9 Problem 3 (10 Pts) Transistor as a Switch In the circuit below, the 2N2222 NPN transistor is being used as a switch. The pulsed source produces a triangular voltage wave with a 1V amplitude and a 1V offset. R1 = 2kΩ and R2 = 10kΩ. a. (3 Pts) Determine the voltage across resistor R2 when the source voltage Vsource (V2) is at or near its maximum value. Is the switch ON or OFF? b. (3 Pts) Determine the voltage across the resistor R2 when the source voltage Vsource (V2) is at or near its minimum value. Is the switch ON or OFF? K. Connor, J. Braunstein 9 Revised: 28 November 2016
10 c. (2 Pts) Which of the following is true? a. The transistor is ON more than half the time b. The transistor is OFF more than half the time c. The transistor is ON half the time and OFF half the time d. There is not enough information to select an answer from the choices above d. (2 Pts) A plot of the input voltage V(IN) is shown below. Sketch and label the Base voltage V(Base) and the output voltage V(OUT) as functions of time on the same plot. The vertical scale is 0.5V/div and the horizontal scale is 0.3ms/div. K. Connor, J. Braunstein 10 Revised: 28 November 2016
11 Problem 4 (30 Points) Phasor Analysis of Filters A simple filter is configured with an inductor and a resistor, as shown. For parts a-d of this problem, you are asked for the general functional form of expressions (i.e. in terms of ω, R, L, V1, V(OUT), V(IN)). Do not plug in numbers until you are asked to do so. a. (2 Pts) Is this a high pass or a low pass filter? b. (2 Pts) What are the general forms for the impedances of an inductor and a resistor as functions of frequency? Z Z R L c. (3 Pts) This circuit is of the general form shown at the right which is a voltage divider built with two general impedances rather than resistors. Write the general expression for Vout in terms of Vin, Z1 and Z2. d. (3 Pts) Find the general form of the filter transfer function ~ VOUT H j ~? V IN For the remainder of this problem, plug in actual numbers for components, voltages, etc. e. (4 Pts) Evaluate your expression from part d for the given frequency (17.31kHz) and component values. Your answer should be complex, but you do not need to simplify it yet. K. Connor, J. Braunstein 11 Revised: 28 November 2016
12 f. (4 pts) Find the real and imaginary parts of your answer to part e. Re H j? Im H j? g. (4 Pts) Using your answers to part f, write the transfer function in polar form. That is find the magnitude and phase (in radians and degrees). Hint: The phase should be near π/n where n is some integer from 1 to 12. H j H j H j e? h. (2 Pts) The input voltage is given as t 2cos t V IN. That is, it has a magnitude of 2V, no phase and is at the given frequency. Write the input voltage in phasor form V ~? IN ~ i. (3 Pts) Solve for the output voltage in phasor form V?. OUT j. (3 Pts) Convert the output voltage back to time varying form t? V OUT K. Connor, J. Braunstein 12 Revised: 28 November 2016
13 Problem 5 (10 Pts) Damped Harmonic Oscillator The voltage shown below is for a typical damped harmonic oscillator. The vertical scale is 1.0V/Div and the horizontal scale is 0.005s/Div. a. (3 Pts) Determine the frequency of the oscillation f. b. (3 Pts) Determine the damping constant of the oscillation 1 c. (4 Pts) Write the mathematical expression for the voltage as a function of time in the t form V( t) V e cos t. o K. Connor, J. Braunstein 13 Revised: 28 November 2016
14 Problem 6 (10 Pts) Diodes, Current, Voltage and Power In the diode circuit shown, a 1N914 high speed signal diode is used. The voltage source is DC and equal to 6V. The resistor R1 is 500Ω. Note that you are not given the load line for this diode, so you must assume standard diode parameters. Explain all answers and indicate any assumptions. a. (1 Pt) Is the diode ON or OFF in this circuit with the given values for V1 and R1? b. (2 Pts) Given your answer to part a, what is the voltage across the diode? c. (2 Pts) What is the current through the diode? Hint: It is the current through the resistor. The diode orientation is now reversed, as shown. d. (1 Pt) Is the diode ON or OFF in this circuit, with the given values for V1 and R1? e. (2 Pts) Given your answer to part a, what is the voltage across the diode? f. (2 Pts) What is the current through the diode? Hint: It is the current through the resistor. K. Connor, J. Braunstein 14 Revised: 28 November 2016
Name. For partial credit in some question, you may want to re-draw circuit diagrams as you simplify the circuits.
 Quiz I Fall 2017 Name Part B (80 Points) 1. (10 Pts) 2. (8 Pts) 3. (16 Pts) 5. (12 Pts) 6. (16 Pts) 7. (11 Pts) 4. (7 Pts) Total Be sure to simplify circuits into standard forms. For partial credit in
Quiz I Fall 2017 Name Part B (80 Points) 1. (10 Pts) 2. (8 Pts) 3. (16 Pts) 5. (12 Pts) 6. (16 Pts) 7. (11 Pts) 4. (7 Pts) Total Be sure to simplify circuits into standard forms. For partial credit in
Name. Draw circuit diagrams for all problems, especially as you simplify the circuits.
 Quiz I Spring 2016 Name Part B (80 Points) 1. (10 Pts) 2. (15 Pts) 3. (10 Pts) 4. (10 Pts) 5. (5 Pts) 6. (10 Pts) 7. (16 Pts) 8. (4 Pts) Total Draw circuit diagrams for all problems, especially as you
Quiz I Spring 2016 Name Part B (80 Points) 1. (10 Pts) 2. (15 Pts) 3. (10 Pts) 4. (10 Pts) 5. (5 Pts) 6. (10 Pts) 7. (16 Pts) 8. (4 Pts) Total Draw circuit diagrams for all problems, especially as you
Name Section 1 (12 1:50PM, Monday and Thursday) Draw circuit diagrams for all problems, especially as you simplify the circuits.
 Quiz I Fall 2016 Name Section 1 (12 1:50PM, Monday and Thursday) Part B (80 Points) 1. (10 Pts) 2. (16 Pts) 3. (10 Pts) 4. (5 Pts) 5. (9 Pts) 6. (10 Pts) 7. (16 Pts) 8. (4 Pts) Total Draw circuit diagrams
Quiz I Fall 2016 Name Section 1 (12 1:50PM, Monday and Thursday) Part B (80 Points) 1. (10 Pts) 2. (16 Pts) 3. (10 Pts) 4. (5 Pts) 5. (9 Pts) 6. (10 Pts) 7. (16 Pts) 8. (4 Pts) Total Draw circuit diagrams
Name Section 1 (12 1:50PM, Monday and Thursday) Draw circuit diagrams for all problems, especially as you simplify the circuits.
 Name Section 1 (12 1:50PM, Monday and Thursday) Part B (80 Points) 1. (10 Pts) 2. (16 Pts) 3. (10 Pts) 4. (5 Pts) 5. (9 Pts) 6. (10 Pts) 7. (16 Pts) 8. (4 Pts) Total Draw circuit diagrams for all problems,
Name Section 1 (12 1:50PM, Monday and Thursday) Part B (80 Points) 1. (10 Pts) 2. (16 Pts) 3. (10 Pts) 4. (5 Pts) 5. (9 Pts) 6. (10 Pts) 7. (16 Pts) 8. (4 Pts) Total Draw circuit diagrams for all problems,
Name. Draw circuit diagrams for all problems, especially as you simplify the circuits.
 Name Part A (20 Points) 1. (3 Pts) 2. (3 Pts) 3. (4 Pts) 4. (3 Pts) 5. (4 Pts) 6. (3 Pts) Part B (80 Points) 1. (10 Pts) 2. (5 Pts) 3. (10 Pts) 4. (15 Pts) 5. (10 Pts) 6. (10 Pts) 7. (15 Pts) 8. (5 Pts)
Name Part A (20 Points) 1. (3 Pts) 2. (3 Pts) 3. (4 Pts) 4. (3 Pts) 5. (4 Pts) 6. (3 Pts) Part B (80 Points) 1. (10 Pts) 2. (5 Pts) 3. (10 Pts) 4. (15 Pts) 5. (10 Pts) 6. (10 Pts) 7. (15 Pts) 8. (5 Pts)
Solution. Draw circuit diagrams for all problems, especially as you simplify the circuits.
 Solution Part A (20 Points) 1. (3 Pts) 2. (3 Pts) 3. (4 Pts) 4. (3 Pts) 5. (4 Pts) 6. (3 Pts) Part B (80 Points) 1. (10 Pts) 2. (5 Pts) 3. (10 Pts) 4. (15 Pts) 5. (10 Pts) 6. (10 Pts) 7. (15 Pts) 8. (5
Solution Part A (20 Points) 1. (3 Pts) 2. (3 Pts) 3. (4 Pts) 4. (3 Pts) 5. (4 Pts) 6. (3 Pts) Part B (80 Points) 1. (10 Pts) 2. (5 Pts) 3. (10 Pts) 4. (15 Pts) 5. (10 Pts) 6. (10 Pts) 7. (15 Pts) 8. (5
Name. Part A (25 Points) Complete on Blackboard. A. (25 Pts) Part B (75 Points) 1. (12 Pts) 2. (12 Pts) 3. (10 Pts) 4. (8 Pts) 5. (11 Pts) 6.
 Name Part A (25 Points) Complete on Blackboard A. (25 Pts) Part B (75 Points) 1. (12 Pts) 2. (12 Pts) 3. (10 Pts) 4. (8 Pts) 5. (11 Pts) 6. (6 Pts) 7. (13 Pts) 8. (3 Pts) Total Annotate the circuit diagrams
Name Part A (25 Points) Complete on Blackboard A. (25 Pts) Part B (75 Points) 1. (12 Pts) 2. (12 Pts) 3. (10 Pts) 4. (8 Pts) 5. (11 Pts) 6. (6 Pts) 7. (13 Pts) 8. (3 Pts) Total Annotate the circuit diagrams
Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited
 Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited In this experiment you will revisit the voltage oscillations of a simple LC circuit. Then you will address circuits made by combining resistors
Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited In this experiment you will revisit the voltage oscillations of a simple LC circuit. Then you will address circuits made by combining resistors
Class #9: Experiment Diodes Part II: LEDs
 Class #9: Experiment Diodes Part II: LEDs Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the properties and uses of LEDs, particularly as a communication device. This is a continuation
Class #9: Experiment Diodes Part II: LEDs Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the properties and uses of LEDs, particularly as a communication device. This is a continuation
Class #16: Experiment Matlab and Data Analysis
 Class #16: Experiment Matlab and Data Analysis Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to add to our Matlab skill set so that data can be easily plotted and analyzed with simple tools. Background:
Class #16: Experiment Matlab and Data Analysis Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to add to our Matlab skill set so that data can be easily plotted and analyzed with simple tools. Background:
Name. Part A (25 Points) Complete on Blackboard. A. (25 Pts) Part B (75 Points) 1. (14 Pts) 2. (4 Pts) 3. (12 Pts) 4. (12 Pts) 5.
 Name Part A (25 Points) Complete on Blackboard A. (25 Pts) Part B (75 Points) 1. (14 Pts) 2. (4 Pts) 3. (12 Pts) 4. (12 Pts) 5. (15 Pts) 6. (15 Pts) 7. (3 Pts) Total Draw circuit diagrams for all problems,
Name Part A (25 Points) Complete on Blackboard A. (25 Pts) Part B (75 Points) 1. (14 Pts) 2. (4 Pts) 3. (12 Pts) 4. (12 Pts) 5. (15 Pts) 6. (15 Pts) 7. (3 Pts) Total Draw circuit diagrams for all problems,
AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE
 July 22, 2008 AC Currents, Voltages, Filters, Resonance 1 Name Date Partners AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase,
July 22, 2008 AC Currents, Voltages, Filters, Resonance 1 Name Date Partners AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase,
STUDENT NUMBER Letter VCE VET ELECTRONICS. Written examination. Monday 31 October 2005
 Victorian CertiÞcate of Education 2005 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Figures Words STUDENT NUMBER Letter VCE VET ELECTRONICS Written examination Monday 31 October 2005 Reading time: 9.00 am
Victorian CertiÞcate of Education 2005 SUPERVISOR TO ATTACH PROCESSING LABEL HERE Figures Words STUDENT NUMBER Letter VCE VET ELECTRONICS Written examination Monday 31 October 2005 Reading time: 9.00 am
ENGR4300 Test 3A Fall 2002
 1. 555 Timer (20 points) Figure 1: 555 Timer Circuit For the 555 timer circuit in Figure 1, find the following values for R1 = 1K, R2 = 2K, C1 = 0.1uF. Show all work. a) (4 points) T1: b) (4 points) T2:
1. 555 Timer (20 points) Figure 1: 555 Timer Circuit For the 555 timer circuit in Figure 1, find the following values for R1 = 1K, R2 = 2K, C1 = 0.1uF. Show all work. a) (4 points) T1: b) (4 points) T2:
Class #8: Experiment Diodes Part I
 Class #8: Experiment Diodes Part I Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the properties and uses of diodes. We used a 1N914 diode in two previous experiments, but now we
Class #8: Experiment Diodes Part I Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to become familiar with the properties and uses of diodes. We used a 1N914 diode in two previous experiments, but now we
Physics 132 Quiz # 23
 Name (please (please print) print) Physics 132 Quiz # 23 I. I. The The current in in an an ac ac circuit is is represented by by a phasor.the value of of the the current at at some time time t t is is
Name (please (please print) print) Physics 132 Quiz # 23 I. I. The The current in in an an ac ac circuit is is represented by by a phasor.the value of of the the current at at some time time t t is is
332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #2 Title: Function Generators and Oscilloscopes Suggested Equipment:
 RUTGERS UNIVERSITY The State University of New Jersey School of Engineering Department Of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #2 Title:
RUTGERS UNIVERSITY The State University of New Jersey School of Engineering Department Of Electrical and Computer Engineering 332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Laboratory Experiment #2 Title:
ENGR-2300 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 3 Spring 2015
 ENGR-23 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 3 Spring 215 On all questions: SHOW ALL WORK. BEGIN WITH FORMULAS, THEN SUBSTITUTE VALUES AND UNITS. No credit will be given for answers that appear without justification.
ENGR-23 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 3 Spring 215 On all questions: SHOW ALL WORK. BEGIN WITH FORMULAS, THEN SUBSTITUTE VALUES AND UNITS. No credit will be given for answers that appear without justification.
Class #3: Experiment Signals, Instrumentation, and Basic Circuits
 Class #3: Experiment Signals, Instrumentation, and Basic Circuits Purpose: The objectives of this experiment are to gain some experience with the tools we use (i.e. the electronic test and measuring equipment
Class #3: Experiment Signals, Instrumentation, and Basic Circuits Purpose: The objectives of this experiment are to gain some experience with the tools we use (i.e. the electronic test and measuring equipment
ECE 2006 University of Minnesota Duluth Lab 11. AC Circuits
 1. Objective AC Circuits In this lab, the student will study sinusoidal voltages and currents in order to understand frequency, period, effective value, instantaneous power and average power. Also, the
1. Objective AC Circuits In this lab, the student will study sinusoidal voltages and currents in order to understand frequency, period, effective value, instantaneous power and average power. Also, the
Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects
 Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects 11.2.1: Signals with Multiple Frequency Components Overview: In this lab project, we will calculate the magnitude response of an electrical circuit and
Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects 11.2.1: Signals with Multiple Frequency Components Overview: In this lab project, we will calculate the magnitude response of an electrical circuit and
INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE
 AC Filters & Resonance 167 Name Date Partners INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE OBJECTIVES To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven
AC Filters & Resonance 167 Name Date Partners INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE OBJECTIVES To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven
Laboratory 4. Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes
 Laboratory 4 Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes Required Components: k resistor 0. F capacitor N94 small-signal diode LED 4. Objectives In the previous laboratory exercise you examined the effects of input
Laboratory 4 Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes Required Components: k resistor 0. F capacitor N94 small-signal diode LED 4. Objectives In the previous laboratory exercise you examined the effects of input
EE 462G Laboratory #1 Measuring Capacitance
 EE 462G Laboratory #1 Measuring Capacitance Drs. A.V. Radun and K.D. Donohue (1/24/07) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Updated 8/31/2007 by
EE 462G Laboratory #1 Measuring Capacitance Drs. A.V. Radun and K.D. Donohue (1/24/07) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 Updated 8/31/2007 by
California State University, Northridge Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering. Senior Design Final Project Report.
 California State University, Northridge Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Senior Design Final Project Report FM Transmitter Josh Rothe Jonathan Rodriguez Pattrawut Phochana Jamell Jordan
California State University, Northridge Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Senior Design Final Project Report FM Transmitter Josh Rothe Jonathan Rodriguez Pattrawut Phochana Jamell Jordan
Week 8 AM Modulation and the AM Receiver
 Week 8 AM Modulation and the AM Receiver The concept of modulation and radio transmission is introduced. An AM receiver is studied and the constructed on the prototyping board. The operation of the AM
Week 8 AM Modulation and the AM Receiver The concept of modulation and radio transmission is introduced. An AM receiver is studied and the constructed on the prototyping board. The operation of the AM
Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope
 PAGE 1/14 Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope Student ID Major Name Team No. Experiment Lecturer Student's Mentioned Items Experiment Class Date Submission
PAGE 1/14 Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope Student ID Major Name Team No. Experiment Lecturer Student's Mentioned Items Experiment Class Date Submission
Electronics and Instrumentation ENGR-4300 Spring 2004 Section Experiment 5 Introduction to AC Steady State
 Experiment 5 Introduction to C Steady State Purpose: This experiment addresses combinations of resistors, capacitors and inductors driven by sinusoidal voltage sources. In addition to the usual simulation
Experiment 5 Introduction to C Steady State Purpose: This experiment addresses combinations of resistors, capacitors and inductors driven by sinusoidal voltage sources. In addition to the usual simulation
ENGR-2300 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 2 Spring 2016
 ENGR-23 Quiz 2 Spring 216 ENGR-23 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 2 Spring 216 On all questions: SHOW ALL WORK. BEGIN WITH FORMULAS, THEN SUBSTITUTE VALUES AND UNITS. No credit will be given for numbers
ENGR-23 Quiz 2 Spring 216 ENGR-23 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 2 Spring 216 On all questions: SHOW ALL WORK. BEGIN WITH FORMULAS, THEN SUBSTITUTE VALUES AND UNITS. No credit will be given for numbers
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II
 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II LAB 5 INTRO: INTRODUCTION TO INVERTING AMPLIFIERS AND OTHER OP-AMP CIRCUITS GOALS In this lab, you will characterize the gain and frequency dependence of inverting op-amp
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II LAB 5 INTRO: INTRODUCTION TO INVERTING AMPLIFIERS AND OTHER OP-AMP CIRCUITS GOALS In this lab, you will characterize the gain and frequency dependence of inverting op-amp
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER
 University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER Issued 10/27/2008 Report due in Lecture 11/10/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize a 2N3904 NPN
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER Issued 10/27/2008 Report due in Lecture 11/10/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize a 2N3904 NPN
Lab 13 AC Circuit Measurements
 Lab 13 AC Circuit Measurements Objectives concepts 1. what is impedance, really? 2. function generator and oscilloscope 3. RMS vs magnitude vs Peak-to-Peak voltage 4. phase between sinusoids skills 1.
Lab 13 AC Circuit Measurements Objectives concepts 1. what is impedance, really? 2. function generator and oscilloscope 3. RMS vs magnitude vs Peak-to-Peak voltage 4. phase between sinusoids skills 1.
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS (INTRODUCTION TO MULTISIM SOFTWARE)
 PROJECT 1B DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS (INTRODUCTION TO MULTISIM SOFTWARE) (i) FSK SYSTEM (MODULATOR / DEMODULATOR) Abstract: In this project, students are required to design a complete circuit of FSK SYSTEM.
PROJECT 1B DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS (INTRODUCTION TO MULTISIM SOFTWARE) (i) FSK SYSTEM (MODULATOR / DEMODULATOR) Abstract: In this project, students are required to design a complete circuit of FSK SYSTEM.
ECE 363 FINAL (F16) 6 problems for 100 pts Problem #1: Fuel Pump Controller (18 pts)
 ECE 363 FINAL (F16) NAME: 6 problems for 100 pts Problem #1: Fuel Pump Controller (18 pts) You are asked to design a high-side switch for a remotely operated fuel pump. You decide to use the IRF9520 power
ECE 363 FINAL (F16) NAME: 6 problems for 100 pts Problem #1: Fuel Pump Controller (18 pts) You are asked to design a high-side switch for a remotely operated fuel pump. You decide to use the IRF9520 power
Designing Information Devices and Systems II Spring 2019 A. Sahai, J. Roychowdhury, K. Pister Homework 2
 EECS 16B Designing Information Devices and Systems II Spring 2019 A. Sahai, J. Roychowdhury, K. Pister Homework 2 This homework is due on Wednesday, February 13, 2019, at 11:59PM. Self-grades are due on
EECS 16B Designing Information Devices and Systems II Spring 2019 A. Sahai, J. Roychowdhury, K. Pister Homework 2 This homework is due on Wednesday, February 13, 2019, at 11:59PM. Self-grades are due on
Experiment 9 AC Circuits
 Experiment 9 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits
Experiment 9 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits
Name Date: Course number: MAKE SURE TA & TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START EXPERIMENT 10. Electronic Circuits
 Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 10 Electronic Circuits 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. How are you going to determine the capacitance of the unknown
Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 10 Electronic Circuits 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1. How are you going to determine the capacitance of the unknown
CHAPTER 6. Motor Driver
 CHAPTER 6 Motor Driver In this lab, we will construct the circuitry that your robot uses to drive its motors. However, before testing the motor circuit we will begin by making sure that you are able to
CHAPTER 6 Motor Driver In this lab, we will construct the circuitry that your robot uses to drive its motors. However, before testing the motor circuit we will begin by making sure that you are able to
E84 Lab 3: Transistor
 E84 Lab 3: Transistor Cherie Ho and Siyi Hu April 18, 2016 Transistor Testing 1. Take screenshots of both the input and output characteristic plots observed on the semiconductor curve tracer with the following
E84 Lab 3: Transistor Cherie Ho and Siyi Hu April 18, 2016 Transistor Testing 1. Take screenshots of both the input and output characteristic plots observed on the semiconductor curve tracer with the following
Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance
 E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
ENGR-2300 Quiz 2 Fall ENGR-2300 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 2 Fall Solution. Name Section. Question III (25 points)
 ENGR-23 Quiz 2 Fall 212 ENGR-23 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 2 Fall 212 Solution Name Section Question I (25 points) Question II (25 points) Question III (25 points) Question IV (25 points) Total (1
ENGR-23 Quiz 2 Fall 212 ENGR-23 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 2 Fall 212 Solution Name Section Question I (25 points) Question II (25 points) Question III (25 points) Question IV (25 points) Total (1
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5)
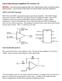 Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Positive to Negative Buck-Boost Converter Using LM267X SIMPLE SWITCHER Regulators
 Positive to Negative Buck-Boost Converter Using LM267X SIMPLE SWITCHER Regulators Abstract The 3rd generation Simple Switcher LM267X series of regulators are monolithic integrated circuits with an internal
Positive to Negative Buck-Boost Converter Using LM267X SIMPLE SWITCHER Regulators Abstract The 3rd generation Simple Switcher LM267X series of regulators are monolithic integrated circuits with an internal
Field Effect Transistors
 Field Effect Transistors Purpose In this experiment we introduce field effect transistors (FETs). We will measure the output characteristics of a FET, and then construct a common-source amplifier stage,
Field Effect Transistors Purpose In this experiment we introduce field effect transistors (FETs). We will measure the output characteristics of a FET, and then construct a common-source amplifier stage,
PHYS 235: Homework Problems
 PHYS 235: Homework Problems 1. The illustration is a facsimile of an oscilloscope screen like the ones you use in lab. sinusoidal signal from your function generator is the input for Channel 1, and your
PHYS 235: Homework Problems 1. The illustration is a facsimile of an oscilloscope screen like the ones you use in lab. sinusoidal signal from your function generator is the input for Channel 1, and your
University of Utah Electrical Engineering Department ECE 2100 Experiment No. 2 Linear Operational Amplifier Circuits II
 University of Utah Electrical Engineering Department ECE 2100 Experiment No. 2 Linear Operational Amplifier Circuits II Minimum required points = 51 Grade base, 100% = 85 points Recommend parts should
University of Utah Electrical Engineering Department ECE 2100 Experiment No. 2 Linear Operational Amplifier Circuits II Minimum required points = 51 Grade base, 100% = 85 points Recommend parts should
Wireless Communication
 Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
Electronics and Instrumentation Name ENGR-4220 Fall 1998 Section Quiz 2
 Quiz 2 1. RLC Circuits You should recognize the circuits shown below from Experiment 5 and Gingrich s notes. Given below are several possible expressions for transfer functions for such circuits. Indicate
Quiz 2 1. RLC Circuits You should recognize the circuits shown below from Experiment 5 and Gingrich s notes. Given below are several possible expressions for transfer functions for such circuits. Indicate
LAB 4 : FET AMPLIFIERS
 LEARNING OUTCOME: LAB 4 : FET AMPLIFIERS In this lab, students design and implement single-stage FET amplifiers and explore the frequency response of the real amplifiers. Breadboard and the Analog Discovery
LEARNING OUTCOME: LAB 4 : FET AMPLIFIERS In this lab, students design and implement single-stage FET amplifiers and explore the frequency response of the real amplifiers. Breadboard and the Analog Discovery
EECS40 RLC Lab guide
 EECS40 RLC Lab guide Introduction Second-Order Circuits Second order circuits have both inductor and capacitor components, which produce one or more resonant frequencies, ω0. In general, a differential
EECS40 RLC Lab guide Introduction Second-Order Circuits Second order circuits have both inductor and capacitor components, which produce one or more resonant frequencies, ω0. In general, a differential
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering. ESE 206: Electrical Circuits and Systems II - Lab
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE 206: Electrical Circuits and Systems II - Lab AC POWER ANALYSIS AND DESIGN I. Purpose and Equipment: Provide experimental
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE 206: Electrical Circuits and Systems II - Lab AC POWER ANALYSIS AND DESIGN I. Purpose and Equipment: Provide experimental
Introduction to oscilloscope. and time dependent circuits
 Physics 9 Intro to oscilloscope, v.1.0 p. 1 NAME: SECTION DAY/TIME: TA: LAB PARTNER: Introduction to oscilloscope and time dependent circuits Introduction In this lab, you ll learn the basics of how to
Physics 9 Intro to oscilloscope, v.1.0 p. 1 NAME: SECTION DAY/TIME: TA: LAB PARTNER: Introduction to oscilloscope and time dependent circuits Introduction In this lab, you ll learn the basics of how to
Figure 1: Closed Loop System
 SIGNAL GENERATORS 3. Introduction Signal sources have a variety of applications including checking stage gain, frequency response, and alignment in receivers and in a wide range of other electronics equipment.
SIGNAL GENERATORS 3. Introduction Signal sources have a variety of applications including checking stage gain, frequency response, and alignment in receivers and in a wide range of other electronics equipment.
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING
 ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING Objectives: To familiarize the student with the concepts of signal conditioning. At the end of the lab, the student should be able to: Understand the
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING Objectives: To familiarize the student with the concepts of signal conditioning. At the end of the lab, the student should be able to: Understand the
Homework Assignment 12
 Homework Assignment 12 Question 1 Shown the is Bode plot of the magnitude of the gain transfer function of a constant GBP amplifier. By how much will the amplifier delay a sine wave with the following
Homework Assignment 12 Question 1 Shown the is Bode plot of the magnitude of the gain transfer function of a constant GBP amplifier. By how much will the amplifier delay a sine wave with the following
University of North Carolina, Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 EE Design II Fall 2009
 University of North Carolina, Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 EE Design II Fall 2009 Lab 1 Power Amplifier Circuits Issued August 25, 2009 Due: September 11, 2009
University of North Carolina, Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 EE Design II Fall 2009 Lab 1 Power Amplifier Circuits Issued August 25, 2009 Due: September 11, 2009
Lab 9 - INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOLTAGES
 145 Name Date Partners Lab 9 INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOLTAGES V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To learn the meanings of peak voltage and frequency for AC signals. To observe the behavior of resistors in
145 Name Date Partners Lab 9 INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOLTAGES V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To learn the meanings of peak voltage and frequency for AC signals. To observe the behavior of resistors in
A 3-STAGE 5W AUDIO AMPLIFIER
 ECE 2201 PRELAB 7x BJT APPLICATIONS A 3-STAGE 5W AUDIO AMPLIFIER UTILIZING NEGATIVE FEEDBACK INTRODUCTION Figure P7-1 shows a simplified schematic of a 3-stage audio amplifier utilizing three BJT amplifier
ECE 2201 PRELAB 7x BJT APPLICATIONS A 3-STAGE 5W AUDIO AMPLIFIER UTILIZING NEGATIVE FEEDBACK INTRODUCTION Figure P7-1 shows a simplified schematic of a 3-stage audio amplifier utilizing three BJT amplifier
LABORATORY 7 v2 BOOST CONVERTER
 University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Bernhard Boser LABORATORY 7 v2 BOOST CONVERTER In many situations circuits require a different
University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Bernhard Boser LABORATORY 7 v2 BOOST CONVERTER In many situations circuits require a different
ECE 342 Fall 2017 Optoelectronic Link Project Lab 2: Active Bandpass Filters
 ECE 342 Fall 2017 Optoelectronic Link Project Lab 2: Active Bandpass Filters Overview The performance of any electronic circuit, analog or digital, is limited by the noise floor. In a classical system,
ECE 342 Fall 2017 Optoelectronic Link Project Lab 2: Active Bandpass Filters Overview The performance of any electronic circuit, analog or digital, is limited by the noise floor. In a classical system,
2.0 AC CIRCUITS 2.1 AC VOLTAGE AND CURRENT CALCULATIONS. ECE 4501 Power Systems Laboratory Manual Rev OBJECTIVE
 2.0 AC CIRCUITS 2.1 AC VOLTAGE AND CURRENT CALCULATIONS 2.1.1 OBJECTIVE To study sinusoidal voltages and currents in order to understand frequency, period, effective value, instantaneous power and average
2.0 AC CIRCUITS 2.1 AC VOLTAGE AND CURRENT CALCULATIONS 2.1.1 OBJECTIVE To study sinusoidal voltages and currents in order to understand frequency, period, effective value, instantaneous power and average
Component modeling. Resources and methods for learning about these subjects (list a few here, in preparation for your research):
 Component modeling This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Component modeling This worksheet and all related files are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, version 1.0. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/1.0/,
Sophomore Physics Laboratory (PH005/105) Analog Electronics Phase Locked Loop (PLL)
 CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PHYSICS MATHEMATICS AND ASTRONOMY DIVISION Sophomore Physics Laboratory (PH005/105) Analog Electronics Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Copyright c Virgínio de Oliveira Sannibale,
CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY PHYSICS MATHEMATICS AND ASTRONOMY DIVISION Sophomore Physics Laboratory (PH005/105) Analog Electronics Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Copyright c Virgínio de Oliveira Sannibale,
Experiment 8: An AC Circuit
 Experiment 8: An AC Circuit PART ONE: AC Voltages. Set up this circuit. Use R = 500 Ω, L = 5.0 mh and C =.01 μf. A signal generator built into the interface provides the emf to run the circuit from Output
Experiment 8: An AC Circuit PART ONE: AC Voltages. Set up this circuit. Use R = 500 Ω, L = 5.0 mh and C =.01 μf. A signal generator built into the interface provides the emf to run the circuit from Output
Lecture 16 Date: Frequency Response (Contd.)
 Lecture 16 Date: 03.10.2017 Frequency Response (Contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) not every transfer function has all seven factors. To sketch the Bode plots for a generic
Lecture 16 Date: 03.10.2017 Frequency Response (Contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) not every transfer function has all seven factors. To sketch the Bode plots for a generic
AC CIRCUITS - CAPACITORS AND INDUCTORS
 EXPRIMENT#8 AC CIRCUITS - CAPACITORS AND INDUCTORS NOTE: Two weeks are allocated for this experiment. Before performing this experiment, review the Proper Oscilloscope Use section of Experiment #7. Objective
EXPRIMENT#8 AC CIRCUITS - CAPACITORS AND INDUCTORS NOTE: Two weeks are allocated for this experiment. Before performing this experiment, review the Proper Oscilloscope Use section of Experiment #7. Objective
Miniproject: AM Radio
 Objective UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE05 Lab Experiments Miniproject: AM Radio Until now, the labs have focused
Objective UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE05 Lab Experiments Miniproject: AM Radio Until now, the labs have focused
Operational Amplifiers: Part II
 1. Introduction Operational Amplifiers: Part II The name "operational amplifier" comes from this amplifier's ability to perform mathematical operations. Three good examples of this are the summing amplifier,
1. Introduction Operational Amplifiers: Part II The name "operational amplifier" comes from this amplifier's ability to perform mathematical operations. Three good examples of this are the summing amplifier,
ENGR-4300 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 2 Fall 2011 Name Section
 ENGR-43 Quiz 2 Fall 211 ENGR-43 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 2 Fall 211 Name Section Question I (2 points) Question II (2 points) Question III (2 points) Question I (2 points) Question (2 points) Total
ENGR-43 Quiz 2 Fall 211 ENGR-43 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 2 Fall 211 Name Section Question I (2 points) Question II (2 points) Question III (2 points) Question I (2 points) Question (2 points) Total
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN
 LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
Lab 5 Second Order Transient Response of Circuits
 Lab 5 Second Order Transient Response of Circuits Lab Performed on November 5, 2008 by Nicole Kato, Ryan Carmichael, and Ti Wu Report by Ryan Carmichael and Nicole Kato E11 Laboratory Report Submitted
Lab 5 Second Order Transient Response of Circuits Lab Performed on November 5, 2008 by Nicole Kato, Ryan Carmichael, and Ti Wu Report by Ryan Carmichael and Nicole Kato E11 Laboratory Report Submitted
FREQUENCY RESPONSE AND PASSIVE FILTERS LABORATORY
 FREQUENCY RESPONSE AND PASSIVE FILTERS LABORATORY In this experiment we will analytically determine and measure the frequency response of networks containing resistors, AC source/sources, and energy storage
FREQUENCY RESPONSE AND PASSIVE FILTERS LABORATORY In this experiment we will analytically determine and measure the frequency response of networks containing resistors, AC source/sources, and energy storage
Class #3: Experiment Signals, Instrumentation, and Basic Circuits
 Class #3: Experiment Signals, Instrumentation, and Basic Circuits Purpose: The objectives of this experiment are to gain some experience with the tools we use (i.e. the electronic test and measuring equipment
Class #3: Experiment Signals, Instrumentation, and Basic Circuits Purpose: The objectives of this experiment are to gain some experience with the tools we use (i.e. the electronic test and measuring equipment
Lab 6: MOSFET AMPLIFIER
 Lab 6: MOSFET AMPLIFIER NOTE: This is a "take home" lab. You are expected to do the lab on your own time (still working with your lab partner) and then submit your lab reports. Lab instructors will be
Lab 6: MOSFET AMPLIFIER NOTE: This is a "take home" lab. You are expected to do the lab on your own time (still working with your lab partner) and then submit your lab reports. Lab instructors will be
1. What is the unit of electromotive force? (a) volt (b) ampere (c) watt (d) ohm. 2. The resonant frequency of a tuned (LRC) circuit is given by
 Department of Examinations, Sri Lanka EXAMINATION FOR THE AMATEUR RADIO OPERATORS CERTIFICATE OF PROFICIENCY ISSUED BY THE DIRECTOR GENERAL OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS, SRI LANKA 2004 (NOVICE CLASS) Basic Electricity,
Department of Examinations, Sri Lanka EXAMINATION FOR THE AMATEUR RADIO OPERATORS CERTIFICATE OF PROFICIENCY ISSUED BY THE DIRECTOR GENERAL OF TELECOMMUNICATIONS, SRI LANKA 2004 (NOVICE CLASS) Basic Electricity,
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters
 Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes
 Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes Equipment: function generator, oscilloscope, two BNC cables, BNC T connector, BNC banana adapter, breadboards, wire packs, some banana cables, three
Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes Equipment: function generator, oscilloscope, two BNC cables, BNC T connector, BNC banana adapter, breadboards, wire packs, some banana cables, three
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department. EE 204 Electrical Engineering Lab
 University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 204 Electrical Engineering Lab EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT DEVICES Prepared by: Prof. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 204 Electrical Engineering Lab EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT DEVICES Prepared by: Prof. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3)
 Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Homework Assignment 01
 Homework Assignment 01 In this homework set students review some basic circuit analysis techniques, as well as review how to analyze ideal op-amp circuits. Numerical answers must be supplied using engineering
Homework Assignment 01 In this homework set students review some basic circuit analysis techniques, as well as review how to analyze ideal op-amp circuits. Numerical answers must be supplied using engineering
Physics 309 Lab 3 Bipolar junction transistor
 Physics 39 Lab 3 Bipolar junction transistor The purpose of this third lab is to learn the principles of operation of a bipolar junction transistor, how to characterize its performances, and how to use
Physics 39 Lab 3 Bipolar junction transistor The purpose of this third lab is to learn the principles of operation of a bipolar junction transistor, how to characterize its performances, and how to use
Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier
 ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier Objectives In this lab exercise you will use the power supply to power the stereo amplifier built in the previous
ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier Objectives In this lab exercise you will use the power supply to power the stereo amplifier built in the previous
Basic Analog Circuits
 Basic Analog Circuits Overview This tutorial is part of the National Instruments Measurement Fundamentals series. Each tutorial in this series, will teach you a specific topic of common measurement applications,
Basic Analog Circuits Overview This tutorial is part of the National Instruments Measurement Fundamentals series. Each tutorial in this series, will teach you a specific topic of common measurement applications,
EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES
 EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES LAB #3: VOLTAGE AND CURRENT MEASUREMENTS This lab features a tutorial on the instrumentation that you will be using throughout the semester. More specifically, you will see
EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES LAB #3: VOLTAGE AND CURRENT MEASUREMENTS This lab features a tutorial on the instrumentation that you will be using throughout the semester. More specifically, you will see
UC Berkeley, EECS Department
 UC Berkeley, EECS Department B. Boser EECS 4 Lab LAB5: Boost Voltage Supply UID: Boost Converters We have tried to use resistors (voltage dividers) to transform voltages but found that these solutions
UC Berkeley, EECS Department B. Boser EECS 4 Lab LAB5: Boost Voltage Supply UID: Boost Converters We have tried to use resistors (voltage dividers) to transform voltages but found that these solutions
Electronic Instrumentation ENGR-4300 Fall 2002 Project 2: Optical Communications Link
 Project 2: Optical Communications Link For this project, each group will build a transmitter circuit and a receiver circuit. It is suggested that 1 or 2 students build and test the individual components
Project 2: Optical Communications Link For this project, each group will build a transmitter circuit and a receiver circuit. It is suggested that 1 or 2 students build and test the individual components
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology. EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments. Masood Ejaz
 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
University of North Carolina-Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 Electrical Engineering Design II Fall 2013
 Exercise 1: PWM Modulator University of North Carolina-Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 Electrical Engineering Design II Fall 2013 Lab 3: Power-System Components and
Exercise 1: PWM Modulator University of North Carolina-Charlotte Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 3157 Electrical Engineering Design II Fall 2013 Lab 3: Power-System Components and
CI-22. BASIC ELECTRONIC EXPERIMENTS with computer interface. Experiments PC1-PC8. Sample Controls Display. Instruction Manual
 CI-22 BASIC ELECTRONIC EXPERIMENTS with computer interface Experiments PC1-PC8 Sample Controls Display See these Oscilloscope Signals See these Spectrum Analyzer Signals Instruction Manual Elenco Electronics,
CI-22 BASIC ELECTRONIC EXPERIMENTS with computer interface Experiments PC1-PC8 Sample Controls Display See these Oscilloscope Signals See these Spectrum Analyzer Signals Instruction Manual Elenco Electronics,
Experiment 9: AC circuits
 Experiment 9: AC circuits Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 Introduction Last week (RC circuit): This week:
Experiment 9: AC circuits Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 Introduction Last week (RC circuit): This week:
Low Cost, General Purpose High Speed JFET Amplifier AD825
 a FEATURES High Speed 41 MHz, 3 db Bandwidth 125 V/ s Slew Rate 8 ns Settling Time Input Bias Current of 2 pa and Noise Current of 1 fa/ Hz Input Voltage Noise of 12 nv/ Hz Fully Specified Power Supplies:
a FEATURES High Speed 41 MHz, 3 db Bandwidth 125 V/ s Slew Rate 8 ns Settling Time Input Bias Current of 2 pa and Noise Current of 1 fa/ Hz Input Voltage Noise of 12 nv/ Hz Fully Specified Power Supplies:
Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response
 ES 3: Introduction to Electrical Systems Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response I. GOALS: In this laboratory, you will build an audio amplifier using an LM386 integrated circuit.
ES 3: Introduction to Electrical Systems Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response I. GOALS: In this laboratory, you will build an audio amplifier using an LM386 integrated circuit.
LABORATORY 3: Transient circuits, RC, RL step responses, 2 nd Order Circuits
 LABORATORY 3: Transient circuits, RC, RL step responses, nd Order Circuits Note: If your partner is no longer in the class, please talk to the instructor. Material covered: RC circuits Integrators Differentiators
LABORATORY 3: Transient circuits, RC, RL step responses, nd Order Circuits Note: If your partner is no longer in the class, please talk to the instructor. Material covered: RC circuits Integrators Differentiators
LABORATORY 4. Palomar College ENGR210 Spring 2017 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17
 LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
CHARACTERIZATION OF OP-AMP
 EXPERIMENT 4 CHARACTERIZATION OF OP-AMP OBJECTIVES 1. To sketch and briefly explain an operational amplifier circuit symbol and identify all terminals. 2. To list the amplifier stages in a typical op-amp
EXPERIMENT 4 CHARACTERIZATION OF OP-AMP OBJECTIVES 1. To sketch and briefly explain an operational amplifier circuit symbol and identify all terminals. 2. To list the amplifier stages in a typical op-amp
SIMULATIONS WITH THE BUCK-BOOST TOPOLOGY EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY. Modified February 2006
 SIMULATIONS WITH THE BUCK-BOOST TOPOLOGY EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified February 2006 Page 1 of 13 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the Buck-Boost converter
SIMULATIONS WITH THE BUCK-BOOST TOPOLOGY EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified February 2006 Page 1 of 13 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the Buck-Boost converter
A 40m Direct Conversion Receiver project to upgrade from ZR to ZS
 A 40m Direct Conversion Receiver project to upgrade from ZR to ZS Hannes Coetzee, ZS6BZP, B.Eng Elektronic (Pretoria) A simple receiver with a low component count is described for the 40m Amateur band.
A 40m Direct Conversion Receiver project to upgrade from ZR to ZS Hannes Coetzee, ZS6BZP, B.Eng Elektronic (Pretoria) A simple receiver with a low component count is described for the 40m Amateur band.
EE-4022 Experiment 2 Amplitude Modulation (AM)
 EE-4022 MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING 2015 Page 2-1 Student objectives: EE-4022 Experiment 2 Amplitude Modulation (AM) In this experiment the student will use laboratory modules to implement operations
EE-4022 MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING 2015 Page 2-1 Student objectives: EE-4022 Experiment 2 Amplitude Modulation (AM) In this experiment the student will use laboratory modules to implement operations
ENGR-2300 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 1 Fall 2018 Name SOLUTIONS Section. Question III (20 points)
 ENGR-2300 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 1 Fall 2018 Name SOLUTIONS Section Question I (20 points) Question II (20 points) Question III (20 points) Question IV (20 points) LMS Question (20 points) (graded
ENGR-2300 Electronic Instrumentation Quiz 1 Fall 2018 Name SOLUTIONS Section Question I (20 points) Question II (20 points) Question III (20 points) Question IV (20 points) LMS Question (20 points) (graded
Fields and Waves I Spring 2008 Homework 1
 Fields and Waves I Spring 28 Due 23 January 28 at : pm Some of the solution is found in the text below, some is attached at the end. 1. Waves and Phasor Notation Be sure that you read the following questions
Fields and Waves I Spring 28 Due 23 January 28 at : pm Some of the solution is found in the text below, some is attached at the end. 1. Waves and Phasor Notation Be sure that you read the following questions
