High-quality Crystal Filter Design and Realization
|
|
|
- Scarlett Parrish
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 118 Telfor Journal, Vol. 5, No. 2, High-quality rystal Filter Design and Realization Dragi M. Dujković, Snežana Dedić Nešić, Lenkica Grubišić, na Gavrovska, Member, IEEE, and Irini Reljin, Senior Member, IEEE 1 bstract nalog oscillators and filters are still very important devices in modern telecommunication and measurement equipment. Quartz crystal units are used for high-quality oscillators and filters, due to their extremely stable resonant frequency and Q-factor. In this paper the design and realization of a high-quality bandpass quartz crystal filter with a possible application to antenna circuitry is described. Keywords rystal units, crystal filters, filter design, filter realization, communications, digital communications. I. INTRODUTION RYSTL units are electromechanical devices, based on piezoelectricity. When cutting them in an appropriate way regarding crystal axes, they are characterized by an extremely stable resonant frequency and a very high quality factor (Q-factor). Once designed, crystal units have advantages of high-quality performances and relatively low cost production [1] [ 9]. n approximate equivalent model of a crystal unit, which is valid at frequencies near to crystal resonant frequency, is depicted in Fig. 1 [3]. Mechanical vibrations are modeled with serial elements, R m, m, L m, which are internal parameters. apacitance 0 comes from crystal electrodes and parasitic capacitances and even can be added externally. R m Fig. 1. Equivalent model of a crystal unit. typical plot of the reactance vs. frequency, of the circuit in Fig. 1, is depicted in Fig. 2. Serial (resonant) frequency, f S, is determined by parameters L m and m and This research is particularly funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technological Development, Republic of Serbia, under the grant TR Dragi M. Dujković is with the School of Electrical Engineering, University of Belgrade, Bul. kralja leksandra 73, Belgrade, Serbia (phone: ; dragi@etf.rs). Snežana Dedić Nešić, is with the Mihajlo Pupin Institute, Volgina 15, Belgrade, Serbia; ( snezanadn@gmail.com). Lenkica Grubišić, is with the Mihajlo Pupin Institute, Volgina 15, Belgrade, Serbia; ( lenkica.grubisic@gmail.com). na Gavrovska is with the Innovation enter of the School of Electrical Engineering, Bul. kralja leksandra 73, Belgrade, Serbia (phone: ; anaga777@gmail.com). Irini S. Reljin is with the School of Electrical Engineering, University of Belgrade, Bul. kralja leksandra 73, Belgrade, Serbia (phone: ; irini@etf.rs). Lm o m has the following value: 1 fs (1) 2 Lm m Parallel (antiresonant) frequency, f P, is defined by: 1 m 0 fp fs(1 m / 2 0 ) (2) 2 L 0 m m m 0 Internal losses described by serial resistance, R m, are small, leading to an extremely high Q-factor of the order of 10 6 [4]. Since parallel capacitance 0 is significantly greater than m frequencies f S and f P are very close, as indicated in Fig. 2. rystal units operate in the range between f S and f P, when the reactance has an inductive nature. Manufacturers of crystal units usually cut and handle crystals in such a way that the resonant frequency of unloaded crystal is higher than required. By adding external parallel capacitance P the frequency can be fine tuned to a desired (lower) frequency. X fs { 1 2 f 0 Fig. 2. Typical plot of the reactance of crystal unit vs. Frequency. II. BSIS OF RYSTL FILTER DESIGN rystal units are normally used in band pass and band reject filters. The extremely high Q-factor of unloaded crystal unit permits a very narrow bandwidth and sharp separation between passband and stopband. The simplest scheme of a filter with a single crystal unit (denoted as ) is depicted in Fig. 3. By several filter sections, usually in a cascade connection, a desired transfer function can be realized. When designing crystal filters one needs to pay attention to several important requirements [10] combining electrical and mechanical demands. Electrical demands relate to the choice of filter function (Butterworth, fp f
2 Dujković et al.: High-quality rystal Filter Design and Realization 119 R in 1 2 R out Fig. 3. Basic filter section realized with single crystal unit. hebyshev, etc.) and the filter order for satisfying given specifications: required attenuation limits in passband (max attenuation) and stopband (min attenuation), permitted ripple in the passband, lowest and highest frequencies in the passband (or stopband) region, the width of transition regions, phase and delay requirements, etc. lso, input and output resistances (impedances) should be matched with the source and the load, for satisfying VSWR or return loss requirements. Regarding mechanical demands, note that crystal units are electromechanical devices with a precise (mechanical) resonant frequency. Due to that they are very sensitive to external vibrations and shocks, so special attention should be addressed to the mounting and housing. lso, some interharmonical modes of vibrations may occur producing spurious responses very narrow responses, generally located at high frequencies, which considerably differ from desired values. If they appear in the stopband, the attenuation is decreased, while in the passband they will introduce an unwanted notch. Fortunately, spurious responses are very narrow and they usually don t cause a serious problem unless for signals at just these frequencies. dditional requirements may be addressed to environmental conditions, such as temperature range, humidity, etc., in which the crystal filter has to operate. The number of crystal units is dictated by a desired filter order, because each crystal unit is characterized by one complex pole (see Fig. 2). Therefore, the filter with N crystals is often referred to as a filter with N poles. Parallel capacitances, denoted as 0 in Fig. 1, reduce the bandwidth, but this effect can be minimized by adding low-loss parallel inductances. By adding serial capacitances between crystal units their coupling and impedance matching can be obtained. ctually, there are only a few global manufacturers that offer the possibility of crystal filters realization satisfying specific customer s requirements. More often, manufacturers produce standard (typical) crystal units and filter types. By following previous theoretical considerations [11] and rich professional experience of researchers at the School of Electrical Engineering and the Institute Mihajlo Pupin in Belgrade [12] [15], we have derived a procedure for the design and realization of the high-quality crystal filter QF2106, which will be described in the following sections. III. REQUIREMENTS FOR FILTER QF2106 band-pass filter QF2106, suitable for a high frequency range [1] [10] (as in antenna circuits), was designed and realized, according to strict requirements that meet the specifications for basic and special conditions, which are set by the customer. One of the important demands was to achieve as high as possible attenuation in the stop-band, and to reduce spurious responses in the range of interest. Regarding the desired attenuation, an appropriate filter order (the number of crystal units) was determined, while the reduction of spurious responses was obtained by choosing the optimal diameter of the crystal unit [2] and by an appropriate arrangement of components on the printed circuit board. The filter central frequency of MHz in the passband provides relative attenuation smaller than 3 db in the frequency range of 7.5 khz and attenuation greater than 40 db outside the band of 40 khz. In the range within 50 khz, the relative decline is more than 40 db. In Table I, we present technical characteristics of the proposed filter QF2106, required by our customer. Minimal transducer attenuation in the passband should be less than 6dB. Input and output filter impedances are 50Ω. Operating temperature range is -20 º to +70 º, while storage temperature range is -40 º to +85 º. The filter should be placed in the housing G10 BN of the size 61x26x2 (dimensions in mm). The manufacturing process applied to filters QF2106 can be used for the production of all the types of crystal filters, which have strict requirements regarding the level of guaranteed attenuation in the stopband and strictly defined ripple and phase characteristic of the passband. TBLE 1: REQUIRED TEHNIL HRTERISTIS OF THE FILTER QF210. Parameter Value Reference frequency MHz Bandwidth at 3 db 7.5 khz min Pass band ripple 1 db max Transition band to attn. 20dB 30 khz max Transition band to attn. 40dB 60 khz max Relative attenuation (min) 40 db Min. transducer attenuation 6 db max Input impedance 50 Ω Output impedance 50 Ω Values of spurious responses 10 db max Operating temperature range -20 º to +70 º Storage temperature range -40 º to +85 º Maximum drive level + 10 dbm Housing G10 BN IV. DESIGN OF THE RYSTL FILTER QF2106 The whole filter design has been performed through two basic parts: the circuit design and design of crystal units. ircuit design relates to electrical requirements (approximation function, filter order, the number of crystal units, etc.), after that particular design of crystal units is performed. Both designing parts are mutually dependent in some way and design process should be derived through several iterations, which needs high designers experience.
3 120 Telfor Journal, Vol. 5, No. 2, ircuit design The circuit is designed by using transformation techniques for the cascade of lattice sections. The transfer function and filter topology are determined according to specified requirements. Based on the specifications of the amplitude response in stop- and pass-band, the approximation function, filter order and corresponding filter topology are determined (Fig. 4). The circuit is designed under the assumption of real (non-ideal) filter elements. ircuit design defines the requirements for the crystal unit [1], [7], [9], [11]. s an assistant tool for testing filter design we used computer program developed for such purposes [15]. The filter order determines the number of crystals required. s depicted in Fig. 4, the filter is composed of four quartz resonators in a semi-lattice network, with two types of crystal units, denoted as and B. The choice of crystal unit has a major impact on the overall filter performances. For instance, inappropriate choice of crystal unit may produce high spurious response, then, units having a low Q-factor may degrade amplitude and/or phase response, etc. fter determining filter order and topology, the next step is to choose crystal units (usually called crystal resonators) having parameters which are well suited to given requirements. V in R in T L 1 L2 2 L 1 T Rout B B Fig. 4. Electrical scheme of the crystal filter QF2106. Furthermore, it is very important to design the layout of printed circuit board (PB). The position of components in the PB is essential, due to parasite effects, electromagnetic noise and other internal and external influences. B. Design of crystal units For the given project, we decided to use crystal units with T-cut, of 66 μm thickness which operate in the 5 th overtone mode. Realization of crystal units corresponds to the preliminary list of technical characteristics and requirements for such crystal units (given in Table II). In crystal units design it is very important to make an appropriate selection of electrodes and the coating film. Here we used electrodes with thickness of d=0.89mm. For realizing such electrodes we developped a new technology, based on aluminium as an appropriate material regarding electromechanical demands. Frequency adjustment is done with a sodium chemical process (maximal deviation after group evaporation is less than - 35kHz), and with anode oxidation (max +60kHz) which provides very stable l 2 O 3 films. fter this process and cementation, all crystal units are being treated for 24 hours on air for making a thin film of stable oxide. rystal units V out are plan-parael (PP) with a diameter of Φ=5mm in a cold welded (W) housing (H-45 type). For assuring high rejection of spurious responses, extremely high plan parallelism of crystal plates is necessary [11] [14]. This is a very challenging technology problem and only a few manufacturers in the global market can resolve it. Item TBLE 2: REQUIRED TEHNIL HRTERISTIS FOR RYSTL UNITS USED IN FILTER QF2106. Value Housing H-45 rystal unit frequency f = kHz f B = kHz Q-factor > 60,000 Dynamic capacity m = mpf±10% Parallel capacity 0 = 0.9 pf±5% Dynamic resistance R 1 < 190Ώ Frequency adjustment df/f = ±10ppm Frequency tolerance df/f = ±15ppm ging df/f = 1ppm/yr Spurious frequencies (f n ). f 0 +80kHz, without f n B. f n >35dB, f 0 ±1MHz Operating temperature range -20 º to +70 º Storage temperature range -40 º to +85 º Notes: Frequencies f and f B are crystal unit frequencies (unit and B). Both units have the same Q-factor. apacitance m, 0 and resistance R 1 are from the equivalent scheme depicted in Fig 1. and they were assumed the same for both crystal unit types. Matching, deviation, and spurious frequencies are typical data required for design of crystal units. V. FINL RELIZTION. Production The final step was the production of designed filter. This process is also very demanding, which includes preparation of all processes which are necessary for each production phase. The production consists of two global phases: production of filter units and the encapsulation of filters. Production of crystal filter units is realized by applying all necessary mechanical, chemical and testing (adjusting) processes. It includes crystal cutting, rounding, grinding, polishing, deposition of thin l film electrodes, and finally mounting the units into the housing, cementing and vacuum enclosing. Between all processing steps a number of different control measurements and correction processes are applied, assuring high quality and high precision of realized units. fter the production of crystal units, special attention is devoted to the choice of additional electronic components: resistors, capacitors and inductors, regarding their tolerances, temperature dependence, aging, dimensions and quality, in general. Some components, like inductors, have to be realized and tuned manually. The second production phase consists of mounting and soldering components on the PB. fter that, the
4 Dujković et al.: High-quality rystal Filter Design and Realization 121 connecting input/output access points are mounted and the complete PB is encapsulated into the housing. The final step is adjusting the encapsulated filter by fine tuning of variable components, by using a high precision network analyzer. When filter characteristics satisfy a required specification, filter housing will be hermetically closed. Since the filter QF2106 is designed for outdoor purposes, the housing G10 BN was used. In Fig. 5. the technical drawing of the housing G10 BN is depicted, while the photo of final product, the realized filter F2106, is presented in Fig max * * ±0.2 Fig. 5. Housing G10 BN for filter QF2106. Fig. 6. Final product: filter QF2106. rystal filter QF2106 was produced using the newest technologies in crystal units realization, derived as joint work of Institute Mihajlo Pupin and Innovation enter and School of Electrical Engineering, University of Belgrade. B. Measurement results Requirements are completely satisfied and they are approved by measurement results. In Fig. 7. the measurement results for realized band-pass filter QF 106 are presented. In the upper part of Fig. 7. the measured values of most relevant filter parameters are presented, such as nominal centre frequency, bandwidth, etc. In the bottom of Fig. 7. transfer the function is presented in the narrower frequency range (upper diagram) and in the wider range (lower diagram). M3 ± ± max min. VI. ONLUSION new band-pass crystal filter was designed, according to severe requirements assuming special conditions. Testing results performed on realized filters confirm their quality and potential application in high-quality professional devices. In the world market there are only a few global manufacturers producing high-quality crystal filters based on specific requirements for a specific consumer. For such type of production, highly qualified, educated and experienced researchers, designers and manufacturers are required. Nowadays, in view of economic aspects, it is necessary to establish collaboration between more institutions and manufacturers. The Institute Mihajlo Pupin, Belgrade, has a long tradition and great experience in the realization of these types of electronic components based on specific requirements. From cooperative work with the Innovation enter and the School of Electrical Engineering, University of Belgrade, it is expectable to realize even better results in the future. REFERENES [1] R. G. Kinsman, History of rystal Filters, IEEE Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency ontrol Society, 1998 [2] Robert G. Kinsman, rystal Filters: Design, Manufacture and pplication, John Willey and Sons Inc., [3] H. Stader, J.. Hardcastle, rystal Ladder Filters for ll, QEX, pp.14-18, Nov-Dec 2009 [4] I. Poole, Quartz crystal filter, Radio-Electronics.com vailable at: [5] lexander I. Zverev, Handbook of Filter Synthesis, John Wiley and Sons Inc., [6] H. J. Blinchikoff,. I. Zverev, Filtering in the Time and Frequency Domains, John Wiley and Sons Inc., [7] D. S. Humpherys, The nalysis, Design and Synthesis of Electrical Filters, Prentice Hall, Englewood lifs, N.J [8] L. Weinberg, Network nalysis and Synthesis, Mc. Graw- Hill ompany Inc., [9] W. S. otter, omplete Wireless Design, Second Edition, McGraw- Hill Inc., [10] J. Pivnichny, Ladder rystal Filters, MFJ Publishing, 1st edition, [11] S. Dedić-Nešić, ontribution to Design of rystal Filters with Linear Phase haracteristic, (in Serbian), Master Thesis, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, University of Belgrade, [12] D. Dujković, S. Dedić Nešić, L. Grubišić,. Gavrovska, Irini Reljin, new crystal filter F106, in Proc. 20th Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR), 2012, pp , Beograd, Serbia, [13] D. Dujković, L. Grubišić, S. Dedić Nešić,. Gavrovska, B. Reljin, new technological process of chemical polishing of S cut crystal units, used for high quality crystal oscillators, in Proc. 20th Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR), 2012, pp , Beograd, Serbia, [14] D. Dujković, S. Dedić Nešić, L. Grubišić, B. Reljin, I. Reljin, rystal Filter 50 MHz for pplications in Specific Environmental onditions, in Proc. 10th International onference on Telecommunication in Modern Satellite able and Broadcasting Services (TELSIKS), 2011, vol. 1. pp , Nis, Serbia, [15] M. Slavković,. Gavrovska, M. Paskaš, S. Dedić Nešić, B. Reljin, omputer nalysis of a rystal Filter with Four rystal Units in Proc. 20th Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR), 2012, pp , Beograd, Serbia, 2012.
5 122 Telfor Journal, Vol. 5, No. 2, Fig. 7. Measurement results for realized crystal filter QF2106.
Characteristics of Crystal. Piezoelectric effect of Quartz Crystal
 Characteristics of Crystal Piezoelectric effect of Quartz Crystal The quartz crystal has a character when the pressure is applied to the direction of the crystal axis, the electric change generates on
Characteristics of Crystal Piezoelectric effect of Quartz Crystal The quartz crystal has a character when the pressure is applied to the direction of the crystal axis, the electric change generates on
Crystal Filter. n Precautions for Use. n How to Adjust the Transformer in the Connected Section of MC
 n How to Adjust the Transformer in the Connected Section of MC n How to Adjust the Transformer in the Connected Section of The figure below shows a circuit when the input/output section and the connected
n How to Adjust the Transformer in the Connected Section of MC n How to Adjust the Transformer in the Connected Section of The figure below shows a circuit when the input/output section and the connected
List of Crystal XXXXXXXX Unit Model Names kHz
 List of Crystal Unit Model Names Products Family Model Name For Automotive Number of Terminals Frequency Range (MHz) 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 7 1 2 Tuning Fork Crystal Unit (khz range) N161SA 2 N212SA 2 32.768kHz
List of Crystal Unit Model Names Products Family Model Name For Automotive Number of Terminals Frequency Range (MHz) 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 7 1 2 Tuning Fork Crystal Unit (khz range) N161SA 2 N212SA 2 32.768kHz
Keywords: ISM, RF, transmitter, short-range, RFIC, switching power amplifier, ETSI
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Wireless and RF > APP 4929 Keywords: ISM, RF, transmitter, short-range, RFIC, switching power amplifier, ETSI APPLICATION NOTE 4929 Adapting
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Wireless and RF > APP 4929 Keywords: ISM, RF, transmitter, short-range, RFIC, switching power amplifier, ETSI APPLICATION NOTE 4929 Adapting
Communication Circuit Lab Manual
 German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 3 Crystal Oscillator Eng. Anas Alashqar
German Jordanian University School of Electrical Engineering and IT Department of Electrical and Communication Engineering Communication Circuit Lab Manual Experiment 3 Crystal Oscillator Eng. Anas Alashqar
Design of Duplexers for Microwave Communication Systems Using Open-loop Square Microstrip Resonators
 International Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications 2016, 6(1): 7-12 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijea.20160601.02 Design of Duplexers for Microwave Communication Charles U. Ndujiuba 1,*, Samuel N. John 1, Taofeek
International Journal of Electromagnetics and Applications 2016, 6(1): 7-12 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijea.20160601.02 Design of Duplexers for Microwave Communication Charles U. Ndujiuba 1,*, Samuel N. John 1, Taofeek
Application Note Receivers MLX71120/21 With LNA1-SAW-LNA2 configuration
 Designing with MLX71120 and MLX71121 receivers using a SAW filter between LNA1 and LNA2 Scope Many receiver applications, especially those for automotive keyless entry systems require good sensitivity
Designing with MLX71120 and MLX71121 receivers using a SAW filter between LNA1 and LNA2 Scope Many receiver applications, especially those for automotive keyless entry systems require good sensitivity
Design note for YIC Quartz Crystal Unit
 Design note for YIC Quartz Crystal Unit CRYSTAL EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT The equivalent circuit of a quartz crystal is shown to explain the basic elements governing the crystal characteristics and performance.
Design note for YIC Quartz Crystal Unit CRYSTAL EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT The equivalent circuit of a quartz crystal is shown to explain the basic elements governing the crystal characteristics and performance.
Electrical Circuits II (ECE233b)
 Electrical ircuits II (EE33b) ariablefrequency Network Performance (Part 3) Anestis Dounavis The University of Western Ontario Faculty of Engineering Science Scaling Often the values of circuit parameters
Electrical ircuits II (EE33b) ariablefrequency Network Performance (Part 3) Anestis Dounavis The University of Western Ontario Faculty of Engineering Science Scaling Often the values of circuit parameters
Chapter 2. The Fundamentals of Electronics: A Review
 Chapter 2 The Fundamentals of Electronics: A Review Topics Covered 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels 2-2: Tuned Circuits 2-3: Filters 2-4: Fourier Theory 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels Most circuits
Chapter 2 The Fundamentals of Electronics: A Review Topics Covered 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels 2-2: Tuned Circuits 2-3: Filters 2-4: Fourier Theory 2-1: Gain, Attenuation, and Decibels Most circuits
PART MAX2605EUT-T MAX2606EUT-T MAX2607EUT-T MAX2608EUT-T MAX2609EUT-T TOP VIEW IND GND. Maxim Integrated Products 1
 19-1673; Rev 0a; 4/02 EVALUATION KIT MANUAL AVAILABLE 45MHz to 650MHz, Integrated IF General Description The are compact, high-performance intermediate-frequency (IF) voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs)
19-1673; Rev 0a; 4/02 EVALUATION KIT MANUAL AVAILABLE 45MHz to 650MHz, Integrated IF General Description The are compact, high-performance intermediate-frequency (IF) voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs)
The Impedance Variation with Feed Position of a Microstrip Line-Fed Patch Antenna
 SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 11, No. 1, February 2014, 85-96 UDC: 621.396.677.5:621.3.011.21 DOI: 10.2298/SJEE131121008S The Impedance Variation with Feed Position of a Microstrip Line-Fed
SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 11, No. 1, February 2014, 85-96 UDC: 621.396.677.5:621.3.011.21 DOI: 10.2298/SJEE131121008S The Impedance Variation with Feed Position of a Microstrip Line-Fed
CHAPTER 14. Introduction to Frequency Selective Circuits
 CHAPTER 14 Introduction to Frequency Selective Circuits Frequency-selective circuits Varying source frequency on circuit voltages and currents. The result of this analysis is the frequency response of
CHAPTER 14 Introduction to Frequency Selective Circuits Frequency-selective circuits Varying source frequency on circuit voltages and currents. The result of this analysis is the frequency response of
An Oscillator Scheme for Quartz Crystal Characterization.
 An Oscillator Scheme for Quartz Crystal Characterization. Wes Hayward, 15Nov07 The familiar quartz crystal is modeled with the circuit shown below containing a series inductor, capacitor, and equivalent
An Oscillator Scheme for Quartz Crystal Characterization. Wes Hayward, 15Nov07 The familiar quartz crystal is modeled with the circuit shown below containing a series inductor, capacitor, and equivalent
A Novel Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Resonator (FBAR) Duplexer for Wireless Applications
 Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 7, No. 2, pp. 67 71 (24) 67 A Novel Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Resonator (FBAR) Duplexer for Wireless Applications C. H. Tai 1, T. K. Shing 1 *, Y. D. Lee
Tamkang Journal of Science and Engineering, Vol. 7, No. 2, pp. 67 71 (24) 67 A Novel Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Resonator (FBAR) Duplexer for Wireless Applications C. H. Tai 1, T. K. Shing 1 *, Y. D. Lee
Impedance Matching Techniques for Mixers and Detectors. Application Note 963
 Impedance Matching Techniques for Mixers and Detectors Application Note 963 Introduction The use of tables for designing impedance matching filters for real loads is well known [1]. Simple complex loads
Impedance Matching Techniques for Mixers and Detectors Application Note 963 Introduction The use of tables for designing impedance matching filters for real loads is well known [1]. Simple complex loads
An Application of Bandpass Filters. Jeff Crawford - K ZR October 15, 2016
 An Application of Bandpass Filters Jeff Crawford - K ZR October 15, 2016 1 Goals for this Discussion: Cover some general filter theory Apply this theory to an amateur radio need SO2R (Single Operator 2
An Application of Bandpass Filters Jeff Crawford - K ZR October 15, 2016 1 Goals for this Discussion: Cover some general filter theory Apply this theory to an amateur radio need SO2R (Single Operator 2
Test Your Understanding
 074 Part 2 Analog Electronics EXEISE POBLEM Ex 5.3: For the switched-capacitor circuit in Figure 5.3b), the parameters are: = 30 pf, 2 = 5pF, and F = 2 pf. The clock frequency is 00 khz. Determine the
074 Part 2 Analog Electronics EXEISE POBLEM Ex 5.3: For the switched-capacitor circuit in Figure 5.3b), the parameters are: = 30 pf, 2 = 5pF, and F = 2 pf. The clock frequency is 00 khz. Determine the
CRYSTAL FILTERS & CRYSTAL UNITS
 & he following section contains information about rystal ilters & rystal nits (717) 486-3411 X (717) 486-5920 eference ables PG G umber of Poles ilter ype utterworth hebyshev 0.1 d hebyshev 0.5 d heoretical
& he following section contains information about rystal ilters & rystal nits (717) 486-3411 X (717) 486-5920 eference ables PG G umber of Poles ilter ype utterworth hebyshev 0.1 d hebyshev 0.5 d heoretical
Commercially available GaAs MMIC processes allow the realisation of components that can be used to implement passive filters, these include:
 Sheet Code RFi0615 Technical Briefing Designing Digitally Tunable Microwave Filter MMICs Tunable filters are a vital component in broadband receivers and transmitters for defence and test/measurement applications.
Sheet Code RFi0615 Technical Briefing Designing Digitally Tunable Microwave Filter MMICs Tunable filters are a vital component in broadband receivers and transmitters for defence and test/measurement applications.
Design of an Evanescent Mode Circular Waveguide 10 GHz Filter
 Design of an Evanescent Mode Circular Waveguide 10 GHz Filter NI AWR Design Environment, specifically Microwave Office circuit design software, was used to design the filters for a range of bandwidths
Design of an Evanescent Mode Circular Waveguide 10 GHz Filter NI AWR Design Environment, specifically Microwave Office circuit design software, was used to design the filters for a range of bandwidths
FILTRONETICS INC. Quality Technology by Quality People
 FILTRONETICS INC. www.filtro.net Quality Technology by Quality People INTRODUCTION Filtronetics, Inc offers a broad line of frequency control products for diverse applications. We have been in business
FILTRONETICS INC. www.filtro.net Quality Technology by Quality People INTRODUCTION Filtronetics, Inc offers a broad line of frequency control products for diverse applications. We have been in business
A MINIATURIZED OPEN-LOOP RESONATOR FILTER CONSTRUCTED WITH FLOATING PLATE OVERLAYS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 14, 131 145, 21 A MINIATURIZED OPEN-LOOP RESONATOR FILTER CONSTRUCTED WITH FLOATING PLATE OVERLAYS C.-Y. Hsiao Institute of Electronics Engineering National
Progress In Electromagnetics Research C, Vol. 14, 131 145, 21 A MINIATURIZED OPEN-LOOP RESONATOR FILTER CONSTRUCTED WITH FLOATING PLATE OVERLAYS C.-Y. Hsiao Institute of Electronics Engineering National
Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator
 Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator Modeling the Piezo Electric Quartz Crystal Most oscillators employed for RF and microwave applications use a resonator to set the frequency of oscillation. It is desirable to
Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator Modeling the Piezo Electric Quartz Crystal Most oscillators employed for RF and microwave applications use a resonator to set the frequency of oscillation. It is desirable to
sensors ISSN by MDPI
 Sensors 2006, 6, 746-755 Full Research Paper sensors ISSN 424-8220 2006 by MDPI http://www.mdpi.org/sensors A Comparison of Freuency Pullability in Oscillators Using a Single AT-Cut Quartz Crystal and
Sensors 2006, 6, 746-755 Full Research Paper sensors ISSN 424-8220 2006 by MDPI http://www.mdpi.org/sensors A Comparison of Freuency Pullability in Oscillators Using a Single AT-Cut Quartz Crystal and
PHYS225 Lecture 15. Electronic Circuits
 PHYS225 Lecture 15 Electronic Circuits Last lecture Difference amplifier Differential input; single output Good CMRR, accurate gain, moderate input impedance Instrumentation amplifier Differential input;
PHYS225 Lecture 15 Electronic Circuits Last lecture Difference amplifier Differential input; single output Good CMRR, accurate gain, moderate input impedance Instrumentation amplifier Differential input;
Design of Wideband Printed Antenna Array in Corner Reflector with Cosecant Square-Shaped Beam Pattern
 98 Telfor Journal, Vol. 8, No., 016. Design of Wideband Printed Antenna Array in Corner Reflector with Cosecant Square-Shaped Beam Pattern Marija Milijić, Graduate Student Member, IEEE, Aleksandar Nešić,
98 Telfor Journal, Vol. 8, No., 016. Design of Wideband Printed Antenna Array in Corner Reflector with Cosecant Square-Shaped Beam Pattern Marija Milijić, Graduate Student Member, IEEE, Aleksandar Nešić,
SAW Filter PCB Layout
 SAW Filter PCB Layout by Allan Coon Director, Filter Product Marketing Murata Electronics North America, c. 1999 troduction The performance of surface acoustic wave (SAW) filters depends on a number of
SAW Filter PCB Layout by Allan Coon Director, Filter Product Marketing Murata Electronics North America, c. 1999 troduction The performance of surface acoustic wave (SAW) filters depends on a number of
Design and Demonstration of a Passive, Broadband Equalizer for an SLED Chris Brinton, Matthew Wharton, and Allen Katz
 Introduction Design and Demonstration of a Passive, Broadband Equalizer for an SLED Chris Brinton, Matthew Wharton, and Allen Katz Wavelength Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Networks (WDM PONs) have
Introduction Design and Demonstration of a Passive, Broadband Equalizer for an SLED Chris Brinton, Matthew Wharton, and Allen Katz Wavelength Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Networks (WDM PONs) have
Analog Design-filters
 Analog Design-filters Introduction and Motivation Filters are networks that process signals in a frequency-dependent manner. The basic concept of a filter can be explained by examining the frequency dependent
Analog Design-filters Introduction and Motivation Filters are networks that process signals in a frequency-dependent manner. The basic concept of a filter can be explained by examining the frequency dependent
Design and Simulation of Folded Arm Miniaturized Microstrip Low Pass Filter
 813 Design and Simulation of Folded Arm Miniaturized Microstrip Low Pass 1 Inder Pal Singh, 2 Praveen Bhatt 1 Shinas College of Technology P.O. Box 77, PC 324, Shinas, Oman 2 Samalkha Group of Institutions,
813 Design and Simulation of Folded Arm Miniaturized Microstrip Low Pass 1 Inder Pal Singh, 2 Praveen Bhatt 1 Shinas College of Technology P.O. Box 77, PC 324, Shinas, Oman 2 Samalkha Group of Institutions,
Concept of Dual-Band and Multistage Bandpass Filters with Antiparallel Configuration
 December, 018 Concept of Dual-Band and Multistage Bandpass Filters with Antiparallel Configuration iniša Jovanović, Bratislav Milovanović 1 Abstract This paper explores the application of band pass filters
December, 018 Concept of Dual-Band and Multistage Bandpass Filters with Antiparallel Configuration iniša Jovanović, Bratislav Milovanović 1 Abstract This paper explores the application of band pass filters
Waveguide E-Plane All-Metal Inserted Diplexer
 SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 1, No. 3, November 2004, 79-87 Waveguide E-Plane All-Metal Inserted Diplexer M. Rakić 1, B. Jokanović 1, Dj. Budimir 2 Abstract: This paper presents the procedure
SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 1, No. 3, November 2004, 79-87 Waveguide E-Plane All-Metal Inserted Diplexer M. Rakić 1, B. Jokanović 1, Dj. Budimir 2 Abstract: This paper presents the procedure
1, Bandwidth (Hz) ,
 A Crystal Filter Tutorial Abstract: The general topic of crystal filters will be discussed in a manner that is intended to help the user to better understand, specify, test, and use them. The center frequency
A Crystal Filter Tutorial Abstract: The general topic of crystal filters will be discussed in a manner that is intended to help the user to better understand, specify, test, and use them. The center frequency
Chapter-2 LOW PASS FILTER DESIGN 2.1 INTRODUCTION
 Chapter-2 LOW PASS FILTER DESIGN 2.1 INTRODUCTION Low pass filters (LPF) are indispensable components in modern wireless communication systems especially in the microwave and satellite communication systems.
Chapter-2 LOW PASS FILTER DESIGN 2.1 INTRODUCTION Low pass filters (LPF) are indispensable components in modern wireless communication systems especially in the microwave and satellite communication systems.
Index. bias current, 61, 145 critical, 61, 64, 108, 161 start-up, 109 bilinear function, 11, 43, 167
 Bibliography 1. W. G. Cady. Method of Maintaining Electric Currents of Constant Frequency, US patent 1,472,583, filed May 28, 1921, issued Oct. 30, 1923. 2. G. W. Pierce, Piezoelectric Crystal Resonators
Bibliography 1. W. G. Cady. Method of Maintaining Electric Currents of Constant Frequency, US patent 1,472,583, filed May 28, 1921, issued Oct. 30, 1923. 2. G. W. Pierce, Piezoelectric Crystal Resonators
Crystal Resonator Terminology
 Acceleration Sensitivity This property of the resonator (also called g-sensitivity) is the dependence of frequency on acceleration, usually observed as vibration-induced sidebands. Under acceleration,
Acceleration Sensitivity This property of the resonator (also called g-sensitivity) is the dependence of frequency on acceleration, usually observed as vibration-induced sidebands. Under acceleration,
A NOVEL MICROSTRIP LC RECONFIGURABLE BAND- PASS FILTER
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 36, 171 179, 213 A NOVEL MICROSTRIP LC RECONFIGURABLE BAND- PASS FILTER Qianyin Xiang, Quanyuan Feng *, Xiaoguo Huang, and Dinghong Jia School of Information
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 36, 171 179, 213 A NOVEL MICROSTRIP LC RECONFIGURABLE BAND- PASS FILTER Qianyin Xiang, Quanyuan Feng *, Xiaoguo Huang, and Dinghong Jia School of Information
Design of an Evanescent Mode Circular Waveguide 10 GHz Filter
 Application Note Design of an Evanescent Mode Circular Waveguide 10 GHz Filter Overview Ham radio operation at 10 GHz is far removed from global shortwave communication typically operating below 30 MHz.
Application Note Design of an Evanescent Mode Circular Waveguide 10 GHz Filter Overview Ham radio operation at 10 GHz is far removed from global shortwave communication typically operating below 30 MHz.
Low-Sensitivity, Lowpass Filter Design
 Low-Sensitivity, Lowpass Filter Design Introduction This Application Note covers the design of a Sallen-Key (also called KRC or VCVS [voltage-controlled, voltage-source]) lowpass biquad with low component
Low-Sensitivity, Lowpass Filter Design Introduction This Application Note covers the design of a Sallen-Key (also called KRC or VCVS [voltage-controlled, voltage-source]) lowpass biquad with low component
Electromagnetic Modelling of UHF RFID Tags*
 SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 8, No. 1, February 2011, 1-7 UDK: 621.396.029:537.531 Electromagnetic Modelling of UHF RFID Tags* Nemanja Milošević 1, Branko Kolundžija 1 Abstract: Paper
SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 8, No. 1, February 2011, 1-7 UDK: 621.396.029:537.531 Electromagnetic Modelling of UHF RFID Tags* Nemanja Milošević 1, Branko Kolundžija 1 Abstract: Paper
Introduction (cont )
 Active Filter 1 Introduction Filters are circuits that are capable of passing signals within a band of frequencies while rejecting or blocking signals of frequencies outside this band. This property of
Active Filter 1 Introduction Filters are circuits that are capable of passing signals within a band of frequencies while rejecting or blocking signals of frequencies outside this band. This property of
VI TELEFILTER Resonator specification TFR 868D 1/5
 VI TELEFILTER Resonator specification TFR 868D 1/5 Measurement condition Ambient temperature: 25 C Input power level: 0 dbm Terminating impedance * for input: 50Ω for output: 50Ω Characteristics Remark:
VI TELEFILTER Resonator specification TFR 868D 1/5 Measurement condition Ambient temperature: 25 C Input power level: 0 dbm Terminating impedance * for input: 50Ω for output: 50Ω Characteristics Remark:
COMPACT DESIGN AND SIMULATION OF LOW PASS MICROWAVE FILTER ON MICROSTRIP TRANSMISSION LINE AT 2.4 GHz
 International Journal of Management, IT & Engineering Vol. 7 Issue 7, July 2017, ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor: 7.119 Journal Homepage: Double-Blind Peer Reviewed Refereed Open Access International Journal
International Journal of Management, IT & Engineering Vol. 7 Issue 7, July 2017, ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor: 7.119 Journal Homepage: Double-Blind Peer Reviewed Refereed Open Access International Journal
Linearization of Broadband Microwave Amplifier
 SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 11, No. 1, February 2014, 111-120 UDK: 621.396:004.72.057.4 DOI: 10.2298/SJEE131130010D Linearization of Broadband Microwave Amplifier Aleksandra Đorić 1,
SERBIAN JOURNAL OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Vol. 11, No. 1, February 2014, 111-120 UDK: 621.396:004.72.057.4 DOI: 10.2298/SJEE131130010D Linearization of Broadband Microwave Amplifier Aleksandra Đorić 1,
Design of a Wideband Band-Pass Filter Using Semi-lumped and Semi-distributed Technology
 3rd International Conference on Science and Social Research (ICSSR 2014) Design of a Wideband Band-Pass Filter Using Semi-lumped and Semi-distributed Technology Ying Liu 1, Jiayu Xie 1, Junling Huang 1
3rd International Conference on Science and Social Research (ICSSR 2014) Design of a Wideband Band-Pass Filter Using Semi-lumped and Semi-distributed Technology Ying Liu 1, Jiayu Xie 1, Junling Huang 1
Piezo-Ceramic Glossary
 Version: March 1, 2017 Electronics Tech. Piezo-Ceramic Glossary Web: www.direct-token.com Email: rfq@direct-token.com Direct Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. China: 12F, Zhong Xing Industry Bld., Chuang
Version: March 1, 2017 Electronics Tech. Piezo-Ceramic Glossary Web: www.direct-token.com Email: rfq@direct-token.com Direct Electronics Industry Co., Ltd. China: 12F, Zhong Xing Industry Bld., Chuang
INF 5490 RF MEMS. L12: Micromechanical filters. S2008, Oddvar Søråsen Department of Informatics, UoO
 INF 5490 RF MEMS L12: Micromechanical filters S2008, Oddvar Søråsen Department of Informatics, UoO 1 Today s lecture Properties of mechanical filters Visualization and working principle Design, modeling
INF 5490 RF MEMS L12: Micromechanical filters S2008, Oddvar Søråsen Department of Informatics, UoO 1 Today s lecture Properties of mechanical filters Visualization and working principle Design, modeling
Methodology for MMIC Layout Design
 17 Methodology for MMIC Layout Design Fatima Salete Correra 1 and Eduardo Amato Tolezani 2, 1 Laboratório de Microeletrônica da USP, Av. Prof. Luciano Gualberto, tr. 3, n.158, CEP 05508-970, São Paulo,
17 Methodology for MMIC Layout Design Fatima Salete Correra 1 and Eduardo Amato Tolezani 2, 1 Laboratório de Microeletrônica da USP, Av. Prof. Luciano Gualberto, tr. 3, n.158, CEP 05508-970, São Paulo,
DESIGN OF MICROWAVE WAVEGUIDE FILTERS WITH EFFECTS OF FABRICATION IMPERFECTIONS
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Series: Electronics and Energetics Vol. 3, N o 4, December 217, pp. 431-458 DOI: 1.2298/FUEE174431M DESIGN OF MICROWAVE WAVEGUIDE FILTERS WITH EFFECTS OF FABRICATION IMPERFECTIONS Marija
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Series: Electronics and Energetics Vol. 3, N o 4, December 217, pp. 431-458 DOI: 1.2298/FUEE174431M DESIGN OF MICROWAVE WAVEGUIDE FILTERS WITH EFFECTS OF FABRICATION IMPERFECTIONS Marija
Bandpass Filters Using Capacitively Coupled Series Resonators
 8.8 Filters Using Coupled Resonators 441 B 1 B B 3 B N + 1 1 3 N (a) jb 1 1 jb jb 3 jb N jb N + 1 N (b) 1 jb 1 1 jb N + 1 jb N + 1 N + 1 (c) J 1 J J Z N + 1 0 Z +90 0 Z +90 0 Z +90 0 (d) FIGURE 8.50 Development
8.8 Filters Using Coupled Resonators 441 B 1 B B 3 B N + 1 1 3 N (a) jb 1 1 jb jb 3 jb N jb N + 1 N (b) 1 jb 1 1 jb N + 1 jb N + 1 N + 1 (c) J 1 J J Z N + 1 0 Z +90 0 Z +90 0 Z +90 0 (d) FIGURE 8.50 Development
INF 5490 RF MEMS. LN10: Micromechanical filters. Spring 2012, Oddvar Søråsen Department of Informatics, UoO
 INF 5490 RF MEMS LN10: Micromechanical filters Spring 2012, Oddvar Søråsen Department of Informatics, UoO 1 Today s lecture Properties of mechanical filters Visualization and working principle Modeling
INF 5490 RF MEMS LN10: Micromechanical filters Spring 2012, Oddvar Søråsen Department of Informatics, UoO 1 Today s lecture Properties of mechanical filters Visualization and working principle Modeling
Lowpass Filters. Microwave Filter Design. Chp5. Lowpass Filters. Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu. Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University
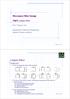 Microwave Filter Design Chp5. Lowpass Filters Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Lowpass Filters Design steps Select an appropriate lowpass filter prototype
Microwave Filter Design Chp5. Lowpass Filters Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Lowpass Filters Design steps Select an appropriate lowpass filter prototype
Figure Main frame of IMNLab.
 IMNLab Tutorial This Tutorial guides the user to go through the design procedure of a wideband impedance match network for a real circuit by using IMNLab. Wideband gain block TQP3M97 evaluation kit from
IMNLab Tutorial This Tutorial guides the user to go through the design procedure of a wideband impedance match network for a real circuit by using IMNLab. Wideband gain block TQP3M97 evaluation kit from
Electric Circuit Theory
 Electric Circuit Theory Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Chapter 15 Active Filter Circuits Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Contents and Objectives 3 Chapter Contents 15.1 First-Order
Electric Circuit Theory Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Chapter 15 Active Filter Circuits Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Contents and Objectives 3 Chapter Contents 15.1 First-Order
A NOVEL DUAL-BAND BANDPASS FILTER USING GENERALIZED TRISECTION STEPPED IMPEDANCE RESONATOR WITH IMPROVED OUT-OF-BAND PER- FORMANCE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 21, 31 40, 2011 A NOVEL DUAL-BAND BANDPASS FILTER USING GENERALIZED TRISECTION STEPPED IMPEDANCE RESONATOR WITH IMPROVED OUT-OF-BAND PER- FORMANCE X.
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 21, 31 40, 2011 A NOVEL DUAL-BAND BANDPASS FILTER USING GENERALIZED TRISECTION STEPPED IMPEDANCE RESONATOR WITH IMPROVED OUT-OF-BAND PER- FORMANCE X.
Tunable Microstrip Low Pass Filter with Modified Open Circuited Stubs
 International Journal of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science Vol. 2, No. 3, 2017, pp. 11-15 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ijeecs Tunable Microstrip Low Pass Filter with Modified Open Circuited
International Journal of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science Vol. 2, No. 3, 2017, pp. 11-15 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ijeecs Tunable Microstrip Low Pass Filter with Modified Open Circuited
A 1-W GaAs Class-E Power Amplifier with an FBAR Filter Embedded in the Output Network
 A 1-W GaAs Class-E Power Amplifier with an FBAR Filter Embedded in the Output Network Kyle Holzer and Jeffrey S. Walling University of Utah PERFIC Lab, Salt Lake City, UT 84112, USA Abstract Integration
A 1-W GaAs Class-E Power Amplifier with an FBAR Filter Embedded in the Output Network Kyle Holzer and Jeffrey S. Walling University of Utah PERFIC Lab, Salt Lake City, UT 84112, USA Abstract Integration
Compact Microstrip Low-pass Filter with Wide Stop-band Using P-Shaped Resonator
 309 Compact Microstrip Low-pass Filter with Wide Stop-band Using P-Shaped Resonator Mohsen Hayati, Masoom Validi Department of Electrical Engineering, Kermanshah Branch, Islamic Azad University, Kermanshah,
309 Compact Microstrip Low-pass Filter with Wide Stop-band Using P-Shaped Resonator Mohsen Hayati, Masoom Validi Department of Electrical Engineering, Kermanshah Branch, Islamic Azad University, Kermanshah,
DESIGN OF COMPACT MICROSTRIP LOW-PASS FIL- TER WITH ULTRA-WIDE STOPBAND USING SIRS
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 18, 179 186, 21 DESIGN OF COMPACT MICROSTRIP LOW-PASS FIL- TER WITH ULTRA-WIDE STOPBAND USING SIRS L. Wang, H. C. Yang, and Y. Li School of Physical
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 18, 179 186, 21 DESIGN OF COMPACT MICROSTRIP LOW-PASS FIL- TER WITH ULTRA-WIDE STOPBAND USING SIRS L. Wang, H. C. Yang, and Y. Li School of Physical
A study of switched-capacitor filters
 University of Arkansas, Fayetteville ScholarWorks@UARK Electrical Engineering Undergraduate Honors Theses Electrical Engineering 12-2008 A study of switched-capacitor filters Kacie Thomas University of
University of Arkansas, Fayetteville ScholarWorks@UARK Electrical Engineering Undergraduate Honors Theses Electrical Engineering 12-2008 A study of switched-capacitor filters Kacie Thomas University of
RFIC DESIGN EXAMPLE: MIXER
 APPENDIX RFI DESIGN EXAMPLE: MIXER The design of radio frequency integrated circuits (RFIs) is relatively complicated, involving many steps as mentioned in hapter 15, from the design of constituent circuit
APPENDIX RFI DESIGN EXAMPLE: MIXER The design of radio frequency integrated circuits (RFIs) is relatively complicated, involving many steps as mentioned in hapter 15, from the design of constituent circuit
INF 5490 RF MEMS. LN10: Micromechanical filters. Spring 2011, Oddvar Søråsen Jan Erik Ramstad Department of Informatics, UoO
 INF 5490 RF MEMS LN10: Micromechanical filters Spring 2011, Oddvar Søråsen Jan Erik Ramstad Department of Informatics, UoO 1 Today s lecture Properties of mechanical filters Visualization and working principle
INF 5490 RF MEMS LN10: Micromechanical filters Spring 2011, Oddvar Søråsen Jan Erik Ramstad Department of Informatics, UoO 1 Today s lecture Properties of mechanical filters Visualization and working principle
INVENTION DISCLOSURE- ELECTRONICS SUBJECT MATTER IMPEDANCE MATCHING ANTENNA-INTEGRATED HIGH-EFFICIENCY ENERGY HARVESTING CIRCUIT
 INVENTION DISCLOSURE- ELECTRONICS SUBJECT MATTER IMPEDANCE MATCHING ANTENNA-INTEGRATED HIGH-EFFICIENCY ENERGY HARVESTING CIRCUIT ABSTRACT: This paper describes the design of a high-efficiency energy harvesting
INVENTION DISCLOSURE- ELECTRONICS SUBJECT MATTER IMPEDANCE MATCHING ANTENNA-INTEGRATED HIGH-EFFICIENCY ENERGY HARVESTING CIRCUIT ABSTRACT: This paper describes the design of a high-efficiency energy harvesting
Electrical Design of Narrow Band Filters. Giuseppe Macchiarella Polytechnic of Milan, Italy Electronic and Information Department
 Electrical Design of Narrow Band Filters Giuseppe Macchiarella Polytechnic of Milan, Italy Electronic and Information Department Introduction The design of a narrow band microwave filter starts with the
Electrical Design of Narrow Band Filters Giuseppe Macchiarella Polytechnic of Milan, Italy Electronic and Information Department Introduction The design of a narrow band microwave filter starts with the
Design Choice: Crystal vs. Crystal Oscillator
 A B S T R A C T When doing a new design that requires controlled timing, a common consideration is to determine if the timing device is to be a crystal or an oscillator. This Application Note compares
A B S T R A C T When doing a new design that requires controlled timing, a common consideration is to determine if the timing device is to be a crystal or an oscillator. This Application Note compares
Tfs248e.doc version VI TELEFILTER Filter specification TFS 248 E 1/5. D a t a typ. Value Limit
 Filter specification TFS 248 E 1/5 Measurement condition Ambient temperature: 23 C Input power level: 0 dbm Terminating impedances at f c *) Input: 560 Ω -5.9pF Characteristics Output: 500 Ω -6.3 pf Remark:
Filter specification TFS 248 E 1/5 Measurement condition Ambient temperature: 23 C Input power level: 0 dbm Terminating impedances at f c *) Input: 560 Ω -5.9pF Characteristics Output: 500 Ω -6.3 pf Remark:
PRACTICAL BROADBAND MICROSTRIP FILTER DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION METHOD
 IJRRAS 9 (3) December 20 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol9issue3/ijrras_9_3_0.pdf PRACTICAL BROADBAND MICROSTRIP FILTER DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION METHOD Abdullah Eroglu, Tracy Cline & Bill Westrick Indiana
IJRRAS 9 (3) December 20 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol9issue3/ijrras_9_3_0.pdf PRACTICAL BROADBAND MICROSTRIP FILTER DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION METHOD Abdullah Eroglu, Tracy Cline & Bill Westrick Indiana
Compact microstrip stepped-impedance lowpass filter with wide stopband using SICMRC
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.9, No.22, 1742 1747 Compact microstrip stepped-impedance lowpass filter with wide stopband using SICMRC Mohsen Hayati 1,2a) and Hamed Abbasi 1 1 Electrical and Electronics
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.9, No.22, 1742 1747 Compact microstrip stepped-impedance lowpass filter with wide stopband using SICMRC Mohsen Hayati 1,2a) and Hamed Abbasi 1 1 Electrical and Electronics
S. Jovanovic Institute IMTEL Blvd. Mihaila Pupina 165B, Belgrade, Serbia and Montenegro
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 76, 223 228, 2007 MICROSTRIP BANDPASS FILTER AT S BAND USING CAPACITIVE COUPLED RESONATOR S. Prabhu and J. S. Mandeep School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER 76, 223 228, 2007 MICROSTRIP BANDPASS FILTER AT S BAND USING CAPACITIVE COUPLED RESONATOR S. Prabhu and J. S. Mandeep School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Lecture 16 Date: Frequency Response (Contd.)
 Lecture 16 Date: 03.10.2017 Frequency Response (Contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) not every transfer function has all seven factors. To sketch the Bode plots for a generic
Lecture 16 Date: 03.10.2017 Frequency Response (Contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) not every transfer function has all seven factors. To sketch the Bode plots for a generic
APPLICATION NOTE 052. A Design Flow for Rapid and Accurate Filter Prototyping
 APPLICATION NOTE 052 A Design Flow for Rapid and Accurate Filter Prototyping Introduction Filter designers for RF/microwave requirements are challenged with meeting an often-conflicting set of performance
APPLICATION NOTE 052 A Design Flow for Rapid and Accurate Filter Prototyping Introduction Filter designers for RF/microwave requirements are challenged with meeting an often-conflicting set of performance
Active Filter Design Techniques
 Active Filter Design Techniques 16.1 Introduction What is a filter? A filter is a device that passes electric signals at certain frequencies or frequency ranges while preventing the passage of others.
Active Filter Design Techniques 16.1 Introduction What is a filter? A filter is a device that passes electric signals at certain frequencies or frequency ranges while preventing the passage of others.
Short Tutorial on Quartz Crystals and Oscillators
 Short Tutorial on Quartz Crystals and Oscillators Contents 1. Quartz Crystals...2 1.1 Equivalent circuit of a quartz crystal...2 1.2. Quartz crystal in 'series resonance'...5 1.2.1. Influence of the shunt
Short Tutorial on Quartz Crystals and Oscillators Contents 1. Quartz Crystals...2 1.1 Equivalent circuit of a quartz crystal...2 1.2. Quartz crystal in 'series resonance'...5 1.2.1. Influence of the shunt
DEFECTED MICROSTRIP STRUCTURE BASED BANDPASS FILTER
 DEFECTED MICROSTRIP STRUCTURE BASED BANDPASS FILTER M.Subhashini, Mookambigai college of engineering, Tamilnadu, India subha6688@gmail.com ABSTRACT A defected microstrip structure (DMS) unit is proposed
DEFECTED MICROSTRIP STRUCTURE BASED BANDPASS FILTER M.Subhashini, Mookambigai college of engineering, Tamilnadu, India subha6688@gmail.com ABSTRACT A defected microstrip structure (DMS) unit is proposed
Chapter 15: Active Filters
 Chapter 15: Active Filters 15.1: Basic filter Responses A filter is a circuit that passes certain frequencies and rejects or attenuates all others. The passband is the range of frequencies allowed to pass
Chapter 15: Active Filters 15.1: Basic filter Responses A filter is a circuit that passes certain frequencies and rejects or attenuates all others. The passband is the range of frequencies allowed to pass
Application Note SAW-Components
 RF360 Europe GmbH A Qualcomm TDK Joint Venture Application Note SAW-Components App. Note 19 Abstract: The characteristics of surface acoustic wave (SAW) filters are presented in order to find a suitable
RF360 Europe GmbH A Qualcomm TDK Joint Venture Application Note SAW-Components App. Note 19 Abstract: The characteristics of surface acoustic wave (SAW) filters are presented in order to find a suitable
Surface Mount Package SOT-363 (SC-70) Pin Connections and Package Marking. OUTPUT and V d 5 GND 4 V CC
 3. GHz Low Noise Silicon MMIC Amplifier Technical Data INA-5463 Features Ultra-Miniature Package Single 5 V Supply (29 ma) 21.5 db Gain (1.9 GHz) 8. dbm P 1dB (1.9 GHz) Positive Gain Slope Unconditionally
3. GHz Low Noise Silicon MMIC Amplifier Technical Data INA-5463 Features Ultra-Miniature Package Single 5 V Supply (29 ma) 21.5 db Gain (1.9 GHz) 8. dbm P 1dB (1.9 GHz) Positive Gain Slope Unconditionally
Internal Model of X2Y Chip Technology
 Internal Model of X2Y Chip Technology Summary At high frequencies, traditional discrete components are significantly limited in performance by their parasitics, which are inherent in the design. For example,
Internal Model of X2Y Chip Technology Summary At high frequencies, traditional discrete components are significantly limited in performance by their parasitics, which are inherent in the design. For example,
L AND S BAND TUNABLE FILTERS PROVIDE DRAMATIC IMPROVEMENTS IN TELEMETRY SYSTEMS
 L AND S BAND TUNABLE FILTERS PROVIDE DRAMATIC IMPROVEMENTS IN TELEMETRY SYSTEMS Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Wurth, Timothy J.; Rodzinak, Jason Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering
L AND S BAND TUNABLE FILTERS PROVIDE DRAMATIC IMPROVEMENTS IN TELEMETRY SYSTEMS Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Wurth, Timothy J.; Rodzinak, Jason Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering
Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator
 Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator Modeling the Piezo Electric Quartz Crystal Most oscillators employed for RF and microwave applications use a resonator to set the frequency of oscillation. It is desirable to
Lab 4. Crystal Oscillator Modeling the Piezo Electric Quartz Crystal Most oscillators employed for RF and microwave applications use a resonator to set the frequency of oscillation. It is desirable to
Oscillators III. by Werner Wiesbeck and Manfred Thumm. Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe in der Helmholtz - Gemeinschaft
 Oscillators III by Werner Wiesbeck and Manfred Thumm Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe in der Helmholtz - Gemeinschaft Universität Karlsruhe (TH) Research University founded 1825 Electrical Properties (I) The
Oscillators III by Werner Wiesbeck and Manfred Thumm Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe in der Helmholtz - Gemeinschaft Universität Karlsruhe (TH) Research University founded 1825 Electrical Properties (I) The
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF 2-BIT LOADED LINE PHASE SHIFTER
 Proceedings of the 8 th National onference on DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF -BIT LOADED LINE PHASE SHIFTER MERY.J 1 MUTHUKUMARAN.P 1 M.E ommunication Systems, Sri Venkateswara ollege of Engineering, Sriprembudur,
Proceedings of the 8 th National onference on DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF -BIT LOADED LINE PHASE SHIFTER MERY.J 1 MUTHUKUMARAN.P 1 M.E ommunication Systems, Sri Venkateswara ollege of Engineering, Sriprembudur,
Simple Quartz Crystal Models: A Review
 Simple Quartz Crystal Models: A Review Wes Hayward, w7zoi, 2 May 2017 A recent Internet posting ask about quartz crystals and the way the properties, mainly stability, change as the package and size change,
Simple Quartz Crystal Models: A Review Wes Hayward, w7zoi, 2 May 2017 A recent Internet posting ask about quartz crystals and the way the properties, mainly stability, change as the package and size change,
A TUNABLE GHz BANDPASS FILTER BASED ON SINGLE MODE
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 135, 261 269, 2013 A TUNABLE 1.4 2.5 GHz BANDPASS FILTER BASED ON SINGLE MODE Yanyi Wang *, Feng Wei, He Xu, and Xiaowei Shi National Laboratory of Science and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 135, 261 269, 2013 A TUNABLE 1.4 2.5 GHz BANDPASS FILTER BASED ON SINGLE MODE Yanyi Wang *, Feng Wei, He Xu, and Xiaowei Shi National Laboratory of Science and
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 59 66, 2009
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 59 66, 2009 QUASI-LUMPED DESIGN OF BANDPASS FILTER USING COMBINED CPW AND MICROSTRIP M. Chen Department of Industrial Engineering and Managenment
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 9, 59 66, 2009 QUASI-LUMPED DESIGN OF BANDPASS FILTER USING COMBINED CPW AND MICROSTRIP M. Chen Department of Industrial Engineering and Managenment
Keywords: op amp filters, Sallen-Key filters, high pass filter, opamps, single op amp
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Tutorials > Amplifier and Comparator Circuits > APP 738 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Tutorials > Audio Circuits > APP 738 Maxim > Design
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Tutorials > Amplifier and Comparator Circuits > APP 738 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Tutorials > Audio Circuits > APP 738 Maxim > Design
Tunable Lumped-Element Notch Filter with Constant Bandwidth
 Tunable Lumped-Element Notch Filter with Constant Bandwidth Douglas R. Jachowski Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC 20375 USA E-mail: doug.jachowski@nrl.navy.mil I. Introduction Interference can
Tunable Lumped-Element Notch Filter with Constant Bandwidth Douglas R. Jachowski Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, DC 20375 USA E-mail: doug.jachowski@nrl.navy.mil I. Introduction Interference can
AN INTEGRATED ULTRASOUND TRANSDUCER DRIVER FOR HIFU APPLICATIONS. Wai Wong, Carlos Christoffersen, Samuel Pichardo, Laura Curiel
 AN INTEGRATED ULTRASOUND TRANSDUCER DRIVER FOR HIFU APPLICATIONS Wai Wong, Carlos Christoffersen, Samuel Pichardo, Laura Curiel Lakehead University, Thunder Bay, ON, P7B 5E Department of Electrical and
AN INTEGRATED ULTRASOUND TRANSDUCER DRIVER FOR HIFU APPLICATIONS Wai Wong, Carlos Christoffersen, Samuel Pichardo, Laura Curiel Lakehead University, Thunder Bay, ON, P7B 5E Department of Electrical and
Surface Mount SOT-363 (SC-70) Package. Pin Connections and Package Marking 4 V CC. Note: Package marking provides orientation and identification.
 1.5 GHz Low Noise Silicon MMIC Amplifier Technical Data INA-52063 Features Ultra-Miniature Package Single 5 V Supply (30 ma) 22 db Gain 8 dbm P 1dB Unconditionally Stable Applications Amplifier for Cellular,
1.5 GHz Low Noise Silicon MMIC Amplifier Technical Data INA-52063 Features Ultra-Miniature Package Single 5 V Supply (30 ma) 22 db Gain 8 dbm P 1dB Unconditionally Stable Applications Amplifier for Cellular,
HT32 Series Crystal Oscillator, ADC Design Note and PCB Layout Guide
 HT32 Series rystal Oscillator, AD Design Note and PB Layout Guide HT32 Series rystal Oscillator, AD Design Note and PB Layout Guide D/N:AN0301E Introduction This application note provides some hardware
HT32 Series rystal Oscillator, AD Design Note and PB Layout Guide HT32 Series rystal Oscillator, AD Design Note and PB Layout Guide D/N:AN0301E Introduction This application note provides some hardware
Surface Mount SOT-363 (SC-70) Package. Pin Connections and Package Marking GND 1 4 V CC
 GHz Low Noise Silicon MMIC Amplifier Technical Data INA-63 Features Ultra-Miniature Package Internally Biased, Single 5 V Supply (12 ma) db Gain 3 db NF Unconditionally Stable Applications Amplifier for
GHz Low Noise Silicon MMIC Amplifier Technical Data INA-63 Features Ultra-Miniature Package Internally Biased, Single 5 V Supply (12 ma) db Gain 3 db NF Unconditionally Stable Applications Amplifier for
REALIZATION OF TEMPERATURE COMPENSATED ALUMINUM NITRIDE MICRORESONATOR FILTERS WITH BANDWIDTHS BEYOND kt2 LIMIT
 University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Electrical and Computer Engineering ETDs Engineering ETDs 2-14-2014 REALIZATION OF TEMPERATURE COMPENSATED ALUMINUM NITRIDE MICRORESONATOR FILTERS WITH BANDWIDTHS
University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Electrical and Computer Engineering ETDs Engineering ETDs 2-14-2014 REALIZATION OF TEMPERATURE COMPENSATED ALUMINUM NITRIDE MICRORESONATOR FILTERS WITH BANDWIDTHS
Experiment #10: Passive Filter Design
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEEING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPATMENT OF ELECTICAL AND COMPUTE ENGINEEING ECE 2110: CICUIT THEOY LABOATOY Experiment #10: Passive Filter Design EQUIPMENT Lab Equipment Equipment Description
SCHOOL OF ENGINEEING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPATMENT OF ELECTICAL AND COMPUTE ENGINEEING ECE 2110: CICUIT THEOY LABOATOY Experiment #10: Passive Filter Design EQUIPMENT Lab Equipment Equipment Description
Narrowband Microstrip Filter Design With NI AWR Microwave Office
 Narrowband Microstrip Filter Design With NI AWR Microwave Office Daniel G. Swanson, Jr. DGS Associates, LLC Boulder, CO dan@dgsboulder.com www.dgsboulder.com Narrowband Microstrip Filters There are many
Narrowband Microstrip Filter Design With NI AWR Microwave Office Daniel G. Swanson, Jr. DGS Associates, LLC Boulder, CO dan@dgsboulder.com www.dgsboulder.com Narrowband Microstrip Filters There are many
Multi-pole Microstrip Directional Filters for Multiplexing Applications
 Multi-pole Microstrip Directional Filters for Multiplexing Applications Humberto Lobato-Morales, Alonso Corona-Chávez, J. Luis Olvera-Cervantes, D.V.B. Murthy Instituto Nacional de Astrofísica, Óptica
Multi-pole Microstrip Directional Filters for Multiplexing Applications Humberto Lobato-Morales, Alonso Corona-Chávez, J. Luis Olvera-Cervantes, D.V.B. Murthy Instituto Nacional de Astrofísica, Óptica
ACTR Features: ACTR DCC6C v1.1
 Features: ACTR9028-934.6-DCC6C v1.1 1-port Resonator Provides reliable, fundamental mode, quartz frequency stabilization i.e. in transmitters or local oscillators Surface Mounted Technology (SMT) Lead-free
Features: ACTR9028-934.6-DCC6C v1.1 1-port Resonator Provides reliable, fundamental mode, quartz frequency stabilization i.e. in transmitters or local oscillators Surface Mounted Technology (SMT) Lead-free
Application Note SAW-Components
 RF360 Europe GmbH A Qualcomm TDK Joint Venture Application Note SAW-Components App. Note #18 Abstract: Surface Acoustic Wave filters are crucial to improve the performance of Remote Keyless Entry (RKE)
RF360 Europe GmbH A Qualcomm TDK Joint Venture Application Note SAW-Components App. Note #18 Abstract: Surface Acoustic Wave filters are crucial to improve the performance of Remote Keyless Entry (RKE)
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN
 LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
EKT 356 MICROWAVE COMMUNICATIONS CHAPTER 4: MICROWAVE FILTERS
 EKT 356 MICROWAVE COMMUNICATIONS CHAPTER 4: MICROWAVE FILTERS 1 INTRODUCTION What is a Microwave filter? linear 2-port network controls the frequency response at a certain point in a microwave system provides
EKT 356 MICROWAVE COMMUNICATIONS CHAPTER 4: MICROWAVE FILTERS 1 INTRODUCTION What is a Microwave filter? linear 2-port network controls the frequency response at a certain point in a microwave system provides
