Fault Detection & Classification in UPFC Integrated Transmission Line Using DWT
|
|
|
- Lynne Snow
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive System (IJPEDS) Vol. 8, No. 4, December 217, pp. 1793~183 ISSN: , DOI: /ijpeds.v8i4.pp Fault Detection & Classification in UPFC Integrated Transmission Line Using DWT S.K Mishra 1, S.C Swain 2, L.N Tripathy 3 1,2 Department of Electrical Engineering, KIIT University 3 Department of Electrical Engineering, BijuPatnaik University of Technology Article Info Article history: Received Sep 17, 217 Revised Nov 14, 217 Accepted Dec 1, 217 Keyword: Fault Inception Angle (FIA) Fault resistance (Rf) Single-circuit line Source Impedance (SI) Spectral Energy (SE) Threshold (Th) ABSTRACT Fault detection and classification in UPFC (Unified Power Flow Controller) integrated transmission line using single terminal based DWT (Discrete Wavelet Transform) is proposed. The current is extracted from the sending end bus and processed through wavelet transform to evaluate the spectral energy (SE) using db4 mother wavelet. Three level decomposition is framed to extract the fundamental frequency component from non-stationary signal, considering sampling frequency of 2kHz system. The fundamental frequency component of respective phase currents are used to compute SE at sending end. The SE of individual phase current is the key factor for deciding the fault pattern detection and classification. The advantage of using this it requires less cost and protect entire transmission line with minimal fault detection time. The various types of fault (L-G, L-L, L-L-G, L-L-L) are simulated by considering the parameter like fault resistance, source impedance, fault inception angle, multi-location fault, reverse power flow and UPFC system parameter. The scheme works reliable and efficient to detect and classify the fault within a cycle of time period 2ms. Copyright 217 Institute of Advanced Engineering and Science. All rights reserved. Corresponding Author: S K Mishra, Departement of Electrical Engineering, KIIT University, Kathajodi campus, Patia, Bhubaneswar, India. mishra29y@yahoo.com 1. INTRODUCTION Transmission line integrated FACTS [1] (flexible AC transmission system) controllers are the emerging research in the field of power system protection. Now-a-days, FACTs [2] devices are integrated increasingly to the transmission line across many parts of the world. The most versatile FACTs controller device prevailing at present is the combination of both shunt and series controller device known as UPFC [3] (unified power flow controller). Not only it provides independent control parameter like active power, reactive power, impedance and voltage of transmission line but also enhances the transmission capacity of the line. It comprises of two linked self-commutating converters through both series and shunt transformers integrated to the line. UPFC [4] exists in the fault loop affects to some extent to voltage and current at the relaying point. This relay depicts the detail regarding fault detection and classification of the transmission line. The process of fault detection thereafter tripping signal issue to CB (circuit breaker) are to be coordinated in a well manner suitable using DWT based approach to detect fault pattern classification. The fault occurs in the transmission line includes, L G (line to-ground), L L (line to-line), LL G (double line to-ground) and L-L-L(triple line) and produces error in the measurement of conventional relaying scheme which can be overcome by applying digital relays. Conventional relaying scheme like distance relay [5] used for fault detection and classification based on the measurement of power frequency and lacks owing to the Journal homepage:
2 1794 ISSN: fault resistance, mutual coupling between the adjacent lines, location of fault, influence of reactance. To overcome conventional method, new approach is adopted to provide better accuracy and reliable operation. Digital relay operation based relaying is also possible in double circuit transmission line based on travelling wave [6] theory the problem in this is large expanse of hardware setup is needed to trip the signal. As the travelling wave contains high frequency signals, it is very difficult to separate the frequency components from interference as well as noise. Neural network based ANN [7] including fuzzy logic approach is also discussed in [8]. Fuzzy logic approach individually requires more computational time to analyse during the fault as it is sensitive to frequency changes. ANN based approach based on highly training and testing process is possible to analyse the fault. However during the process some neurons are missed due to phasor data computation which produces inaccurate result. In addition to that it requires more processing time compared to other approach. Ultra high speed relay for EHV/UHV transmission lines also discussed in [9] for different fault classification in the transmission line. Researchers have been identifying many new types of approach for faulty zone detection and classification. One of the approach in the field of protection is Kalman filtering discussed in [1], the problem in this is the requirement of a number of dissimilar filters. Another promising hybrid approach of machine intelligence and support vector machine (SVM) also discussed in [12] for fault identification and classification, but it is more prone to noise and interferences. In addition to this it provides result with higher inaccuracy when signal-to-noise ratio is considered for 3 db [11]. Fault identification using linear time-frequency distribution for VSI switch is discussed in [12], however it fails to explain fault detection time of different fault considered and its relay response time. In detection and classification of faults in matrix converter [13] also explains open circuit and short circuit fault of switching component but unable to detect and classify shunt fault occurred in transmission line propoerly. Fault current limiter [14] circuit explains to improve transient stability, but it unable to trace different shunt faults condition except short circuit fault. Classification of fault using wavelet multi-resolution analysis and neural network is also discussed in [15], however db4 wavelet at six level decomposition methods are discussed which require more processing time compared to proposed work of third level decomposition in addition to this it unable to explain fault detection time and proper classification of fault including system parameter change. In Adaline LMS control and DWT approach [16] based STATCOM integrated line explains the power quality improvement in adaptive linear neural network and DWT approach used for fault detection and classification but it unable to explain the fault detection time properly. Though fault detection and classification is explained in SVC integrated double circuit line using FDST [17] but fails to address the fault detection time. The decision tree [18] approach requires more processing time due to its burden. All these approach based detection and classification scheme are outlined excluding UPFC integrated line. However the transmission line integrated to UPFC then the scheme becomes very complex to analyse the fault. Therefore a strong motivation behind the scheme is to develop an algorithm which provides fast detection time or relay response time to process. This paper comprises five different section including introduction part in section-1. Section-2 discusses DWT based Signal Processing technique relaying scheme. Section-3 discusses studied system and explains proposed methodology effectively for evaluating fault detection and classification. Section-4 describes the discussion of simulation result considering the effect of parameter change. Section-5 explains conclusion part of proposed scheme. 2. SIGNAL PROCESSING TECHNIQUE The Signal processing tool have been used for evaluation of fault detection and classification. Out of many numerous tool used in power system protection, wavelet transform [19],[2] is considered to be a powerful tool for processing highly non-stationary signal containing different high order harmonics. To evaluate fundamental signal from the transient non-stationary signal occured during the fault analysis of window size is an impoertant issue to discuss which splits into number of adjustable size region according to its frequency. Therefore the accuracy becomes more and more with low-frequency data using longer time intervals whereas high-frequency data using shorter time interval. DWT offers time-frequency transformation rather than time-scale region. Further it is also used to decompose signal into a set of basic functions known as wavelets. Mother wavelet [21] of Daubechy s group db4 is decomposed into various scaled and shifted forms to achieve prototype wavelets. Selection of suitable mother wavelet Daubechy family [22] is considered to be best because its accuracy is higher compared to other type of mother wavelet. Number of filters like high pass (H.P) and low-pass (L.P) filters are used to obtain fundamental component of current discussed in Mallat s algorithm [2]. MRA approach of wavelet provides fast and short transients disturbances which is detected at lower scales. As discussed db4 [21], [22] performs well as compared to other type of mother wavelet.the Signal processing tool have been used for evaluation fault detection and IJPEDS Vol. 8, No. 4, December 217 :
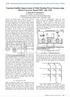
3 IJPEDS ISSN: classification accurately. Out of many tool used in power system protection, wavelet transform [19],[2] is considered to be the one of the powerful tool for processing highly non-stationary signal containing different higher order harmonics. The window size can be streched into number of adjustable size region according to its frequency range. Therefore the accuracy becomes more with low-frequency data using longer time intervals whereas high-frequency data can be found using shorter time interval window. DWT offers timefrequency transformation rather than time-scale region. Further it also used to decompose signal into a set of basic functions known as wavelets. Mother wavelet [21] of Daubechy s group db4 is decomposed into various scaled and shifted forms to achieve prototype wavelets. Selection of mother wavelet [22] is considered here for its higher accuracy compared to other type of mother wavelet. Number of filterslike high pass (H.P) and low-pass (L.P) filters used to obtain fundamental component of current discussed in Mallat s algorithm [2]. MRA approach used for fast and short transients disturbances are detected at lower scales. CWT signal x (t) is expressed as + 1 CWT(a, b) = a x(t) (t b) φ dt a (1) Where, φ a,b (t) = φ (t b) is known as mother wavelet; a and b are two parameters known as a dilation and translation parameter. DWT converts time signal to wavelet signal in discrete form and transforms into input series of HP (H i ) and LP (G i ) coefficients x, x 1,...x n ( length n/2 each). This is expressed by s 1 H i = x 2j n u n (z) n= s 1 G i = x 2j n v n (z) n= (2) (3) Where, u n (z) and v n (z) are known as wavelet filters and s is known to be filter length, j=,... [n/2]-1. The process starts with the extraction of individual current signal of phase (A, B, C) at sending end of the transmission line. The scheme has been considered for 2 khz sampling frequency (4 samples per cycle in 5 Hz system) for the simulation study. Signal decomposition is performed by considering three decomposition level. First level decomposition, a1 of 1kHz, d1 of 1 2 khz, second level decomposition, a2 of 5Hz, d2 of 5Hz 1kHz and third level decomposition a3 of 25Hz, d3 of 25 5Hz respectively. So, third level decomposition of a3 has fundamental component of frequency (5 Hz), 3 rd harmonics and 5 th harmonics component of current. In the 3 rd level, the reconstructed current signal of respective phase current (A3) from the approximate coefficient (a3) obtained at sending end terminal. From this reconstructed current signal r.m.s values of fundamental current signals are extracted. The current signal using DFT is used for computation of Spectral Energy [23]. 3. STUDIED SYSTEM The studied model of two substation each of having capacity of 4 kv voltage, 5 Hz frequency and short circuit level 15MVA between a transmission lines of 4km length depicted in Figure1(a). UPFC capacity of MVA is integrated at mid-point of line (Distributed model) and 48-pulse voltage source inverters (VSI) associated through two common DC capacitors of 25µF.STATCOM and SSSC are shunt and series connected through transformer 15kV/4kV and 15kV/22kV which injects/consumes reactive power to/from transmission system to regulate active power and bus voltage. The UPFC modelling and controller design presented in the scheme is referred [24], [25]. Spectral Energy [26] based one terminal (sending end bus) is the key point for deciding the fault pattern and classification. The relaying theory based application is referred [27]. Figure 1(b) and Figure1(c) depicts the schematic diagram and flow chart of the scheme respectively. In the Figure 1(a) substation voltage of sending end and receiving end are considered as V s and V r respectively and δ (in degree) is phase angle difference between them. Mathematically, V S = Vr =4 kv, δ =δs δr= Impedances Zs and Zr are considered for sending and receiving end. B se and B re are considered for sending end and receiving end bus. Transmission line is subdivided into four equal sub-sections of km line length having Z l1, Z l2, Z l3 and Z l4 respectively. Z 1 = (.1537Ω+j.2783Ω)/km and Z = (.4612Ω+j Ω)/km are considered for positive and zero sequence impedance of the proposed transmission line. Fault Detection & Classification in UPFC Integrated Transmission Line Using DWT (S.K Mishra)
4 1796 ISSN: Vs Z B B V s se Zl1 Zl 2B 1 B Z 2 l3 Z 3 l 4B r e r fault UPFC fault fault Figure 1(a). Proposed scheme of UPFC integrated transmission line 4kV B Transmission se B re V line s Vr 2 km 2 km Substation-1 Substation-2 Relay UPFC Figure 1(b). UPFC integrated at mid-point of transmission line length of 4km The flow chart of proposed scheme is depicted in Figure 1(c). The different types of parameter variations are considered for the proposed scheme to study fault detection and classification which are mentioned below. Variation of Fault resistance (Rf): to Ω. Variation of fault inception angle (FIA):,45,9. Variation of reverse power flow and normal power flow. Variation of source impedance (SI). Variation of UPFC parameter (Vse and θse). Series injected voltage variation (Vse varies from to 1% of the normal voltage). Series injected voltage angle variation (θse varies from 3 to 12 ). Variation of fault distance at different location CT-1 4kV Transmission line 2 km 2km UPFC B Substation-1 se Bre Substation-2 Extraction of current signals of individual phase,p from bus Bse Evaluation of Spectral Energy (SE) at sending end of respective phase currents I(p) of circuit. SEP = [I(p)]2, Spectral Energy of the Circuit, where p denote a particular phase either a, b or c SEP > Th, Fault occurs in phase p SEP < Th, No fault occurs in phase p Trip No Trip Figure 1(c). Flow chart of proposed scheme of UPFC integrated transmission line. Spectral Energy (SE) of phase current at sending end of the line is evaluated from the fundamental component of current magnitude using DWT. The SEp (SE of p-phase) is computed by using equation (5).The SEP obtained at sending end are compared with the set threshold (Th) values for fault detection and classification purposes. R21a Matlab platform is used for simulation study by considering fault initiation time at.3 second (6th sample of sampling frequency equal to 2 khz in 4 samples/cycle). The magnitude, phase angle of fundamental component current phase p is extracted from DWT reconstructed current signal and is expressed by, IJPEDS Vol. 8, No. 4, December 217 :
5 IJPEDS ISSN: Im I( p) I( p) I( p) tan Re I( p) (4) 1 Im I( p) where, I(p) & tan are magnitude and phase angle of fundamental component of current Re I( p) of phase p. The SE P of the current signals phase, p at sending end is given by SE P = I(p) 2 (5) The following mentioned case contributes information regarding detection and classification of fault. Case1:-SE P Th: The fault is within the circuit in p phase from sending end bus. Case2:-SE P Th: No fault occurs within the circuit in p phase from sending end bus. The threshold (Th) is carefully chosen as 25 for our test system, after conducting number of simulation for different fault types including wide parameter variation as well as UPFC parameters. 4. RESULT AND DISCUSSION Mat lab Simulink is prepared to model the proposed scheme of UPFC integrated transmission line. Different shunt faults L-G, LL-G, L-L, L-L-L and LLL-G are considered for simulation study, incepted at.3 seconds. Figure 2(a) depicts fault current retrieved from sending bus (B se ) of A-G fault incepted at.3 second. Table 1. Variation of Rf (1Ω -Ω) at FIA=, FDT (Fault detection time) and distance in km from B se Type of fault Rf=1 Ω from B se Rf=5Ω from B se Rf=Ω from B se Fault classification A-G 9ms, 1km 9ms,1km 1ms,1km A-phase A-G 9ms,39km 9ms,39km 9ms,39km A-phase AB-G 19ms,2km 18ms,2km 19ms,2km AB-phase BC-G 18ms,1km 19ms,1km 19ms,1km BC-phase ABC 15ms,km 16ms,km 18ms,km ABC-phase Figure 2(a). A-G fault at sending end (B se ), fault incepted at 6 sample Rf =1Ω, FIA=. Figure 2(b). A-G fault at 39km distance from B se at the Variation of Rf =1Ω, 5Ω and Ω, FIA= the Variation of Rf =1Ω, 5Ω and Ω, FIA= 4.1. Variation of fault resistance (Rf): The variation of Rf is an important parameter in the protection scheme. To test system performance as well as accuracy, Rf values are considered for variation from 1Ω to Ω. Figure 2(b) depicts BC-G fault occurs at 1km distance from B se at Rf=1Ω and FIA=. It shows that the spectral energy (SE) of fault current B and C grows higher and crosses the threshold, Th=25 and detects the fault at 36 sample (18ms) to issue the signal to trip circuit breaker. Therefore the fault is detected and classified as BC-G fault. Figure 2(c) depicts A-G fault occurs at 1km distance from B se at Rf=1Ω and FIA=. The figure shows that SE of A phase Fault Detection & Classification in UPFC Integrated Transmission Line Using DWT (S.K Mishra)
6 1798 ISSN: current grows higher as compared to B and C phase and crosses Th=25 to detect the fault in 18 sample (9ms) and classify the fault as A phase fault. Figure 2(d) depicts A-G fault at 39km distance from B se at Rf=1Ω, 5Ω and Ω, FIA=. It is seen from the figure that in all the three different case of Rf, SE grow higher and crosses Th value to detect fault in 18 sample (9ms). The Table1.Shows the variation of Rf=1Ω, 5Ω and Ω, FDT (fault detection time) and distance in km from B se respectively.the variation of Rf works fine under all different types of fault condition Variation of Source Impedance (SI): The variation of SI is also an important point to study for the system to be strong or weak under different types of fault condition. The different fault conditions are tested for different values of SI such asnormal SI (NSI), SI is increased by 5% of NSI, 1%, 15%, 2%, 25% then to 3%. Figure-3 depicts A-G fault occurs at 2km distance from B se at Rf=1Ω, FIA= and SI= to 3% increase of NSI, it shows that SE in all the case grows up word direction and crosses Th value and detects the fault in 18 sample (9ms).. Table2. Presents the variation of SI (5%, 1%,15%,2%,25% and 3% increase of NSI), FDT and distance in km from B se. Magnitudes of SE A,SE B,SE C A-G fault at 2km distance from sending end, Rf=1ohm, SI=% to 3% increase of NSI and FIA= degree 3 SE A (SI=NSI) SE 25 A (SI=5% increase in NSI) SE A (SI=1% increase in NSI) 2 SE A (SI=15%increase in NSI) SE A (SI=2% increase in NSI) 15 SE A (SI=25% increase in NSI) SE A (SI=3% increase in NSI) Th=25 A-G fault at 6 sample 5 fault detection sample=18-5 No. of sample Figure 3. A-G fault at 2km distance from B se at Rf =1Ω, SI=% to 3% increase of NSI and FIA= Table 2. Variation of SI (5% to 3% increase of NSI) at Rf =1Ω, fault distance in km from B se Fault type SI=5% +NSI, SI=1% +NSI, SI=15% +NSI, SI=2% +NSI, SI=25% +NSI, SI=3%+NSI, A-G 9ms,2km 9ms,2km 9ms,2km 9ms,2km 9ms,2km 9ms,2km AB-G 18ms,3km 18ms,3km 18ms,3km 18ms,3km 18ms,3km 18ms,3km CA 15ms,km 15ms,km 15ms,km 15ms,km 15ms,km 15ms,km ABC 19ms,399km 18ms,399km 17ms,399km 18ms,399km 18ms,399km 19ms,399km 4.3. Variation of Fault Inception Angle (FIA): The performance of FIAare also simulated by carrying out the number of simulations at FIA (3, 45 and 9 ). In Figure4, A-G fault occurs at 2km distance from B se at Rf =1Ω and FIA=3,45 and 9 in all the case SE of A-phase crosses Th value and detects the fault sample 27 (13.5ms) and classify as A phase fault. Further it is seen that the FIA of lower value has higher magnitude compared to FIA of higher value. Table3.Shows thevariation of FIA, FDT and distance in km from B se for different types of fault at Rf=1Ω, FIA (3,45 and9 ) respectively A-G fault at 2km distance from sending end,rf = 1 ohm with FIA=3, 45 and 9 degree degree FIA = 3 degree FIA =45 degree FIA =9 degree Magnitudes of SE A Th=25 A-G fault at 6 sample fault detection sample = No. of Sample Figure4. A-G fault at 2km distance from B se at Rf =1Ω, FIA=3, 45 and 9 IJPEDS Vol. 8, No. 4, December 217 :
7 IJPEDS ISSN: Table 3. Variation of FIA (, 3, 45 and 9 ) at Rf =1Ω, fault distance in km from B se Fault Type FIA= FIA=3 FIA=45 FIA=9 classification A-G 9ms, 2km 9ms,2km 9ms,2km 13.5ms,2km A-phase CA-G 16ms,km 16ms,km 16ms,km 18ms,km CA phase AB 15ms,3km 15ms,3km 15ms,2km 18ms,2km AB phase ABC 17ms,1km 17ms,1km 18ms,1km 19ms,2km ABC phase 4.4. Variation of Normal power flow and phase reversal: The phase reversal is critical issue while studying fault detection and classification under different types of fault in the power system protection. To validate proposed scheme, simulations are carried out to justify performance of the system. Figure 5 depicts C-G fault at 2km distance from B se at Rf=1Ω, FIA= with phase reversal. A comparative study is presented between normal power flow and reverse power flow. In case of normal flow of power angle, δ 1 =12 and δ 2 =, on the other hand in reverse flow of power, δ 1 = and δ 2 =12 are considered for phase reversal simulation. From these waveform it is clearly noticed that, SE of C-phase grows in up word direction and crosses Th value to detects the fault where as the FDT takes 27 sample (13.5ms) in reverse power flow and FDT is reduced to 18 sample (9ms) in normal power flow. Thus the C-phase fault is clearly detected and classified both in normal and reverse power flow. Table4. Presents variation of phase reversal and normal power flow, FDT and distance in km from B se C-G fault at 2 Km distance from sending end, Rf=1 ohm, FIA= degree with phase reversal Reverse Power flow Normal Power flow Magnitude of SE C 5 Th=25 C-G fault at 6 sample fault detection sample =27-5 No. of sample Figure 5. C-G fault at 2km distance from B se at Rf =1Ω, FIA= with phase reversal Table 4. Phase reversal and normal power flow at Rf =1Ω, FIA=, fault distance in km from B se Fault Type Normal power flow Reverse power flow classification C-G 1ms, 2km 13.5ms, 2km C-phase AB-G 12ms,km 15ms,km AB-phase BC 17ms,1km 19ms,1km BC-phase ABC 16ms,3km 19ms,3km ABC-phase 4.5. Variation of UPFC operating condition: UPFC variation such as series injected voltage, V se as well as series injected voltage phase variation, θ se are also an important parameter to study. It has significant impact in relation to performance of proposed scheme. Figure 6(a) depicts C-G fault at 2km distance from sending end, Rf=5Ω at V se = 5%,1% and 15% increase of V se in all the three case the SE increases in up word direction and crosses Th value, and the fault is detected within 27 sample (13.5ms). Further it is seen that the magnitude of SE reduces as the V se value reduces. Table-5 presents V se variation of UPFC (5%, 1% and 15% increase of V se ), FDT and distance in km from B se. Figure 6(b) depicts C-G fault at 2km distance from B se at Rf =1Ω, θ se of UPFC injected voltage (3 and 12 ), it is seen that the θ se =3 takes less sample as compared to θ se =12 and fault is detected in 18 sample and 27sample (9ms and 13.5ms) respectively and classified as C-phase fault. Table 6. Presents θ se of UPFC injected voltage (3, 6 and 12 ), in km from B se. Fault Detection & Classification in UPFC Integrated Transmission Line Using DWT (S.K Mishra)
8 18 ISSN: C-G fault at 2km distance from sending end, Rf=5 ohm at Vse of UPFC=5%,1% and 15% increase of Vse Vse=15%, Rf=5 ohm Vse=1%, Rf=5 ohm Vse=5%,Rf=5 ohm Magnitude of DSE C 5 Th=25 C-G fault at 6 sample fault detection sample= 27-5 No. of sample Figure 6(a). C-G fault at 2km distance from B se at Rf =5Ω, V se of UPFC= 5%, 1% and 15% increase of V se Table 5. V se of UPFC (5%, 1% and 15% increase of V se ) at Rf =5Ω, fault distance in km from B se Fault Type V se =5% FTD, distance V se =1% FTD, distance V se =15% FTD, distance Classification A-G 13.5ms, 2km 1ms, 2km 1ms,2km A-phase CA-G 16ms,km 14ms,km 14ms,km CA-phase AB 18ms,3km 16ms,3km 16ms,3km AB-phase ABC 19ms,399km 16ms,399km 16ms,399km ABC phase 2 15 C-G fault at 2km distance from SE, Rf=1ohm at injected seies voltage angle of UPFC=3 degree and 12 degree Angle of Vse of UPFC =3 degree Angle of V se of UPFC=12 degree Magnitudes of DSE C 5 Th=25 C-G fault at 6 sample fault detection sample=18 and 27-5 No. of sample Figure 6(b). C-G fault at 2km distance from B se at Rf =1Ω, θ se of UPFC injected voltage (3 and 12 ) Table 6. UPFC injected angle at Rf=1Ω, θ se =3, 6 and 12, fault distance in km from B se Fault Type θ se =3 θ se=12 Classification C-G 9ms, 2km 13.5ms, 2km C-phase AB-G 12ms,km 15ms,km AB-phase BC 15ms,399km 18ms,399km BC-phase ABC 16ms,1km 18ms,1km ABC-phase 4.6. Variation of fault distance at different location of UPFC: Different fault location of UPFC in B-phase fault km, 2km and 3km distance from B se are considered to justify the scheme accuracy depicted in Figure7. It is seen that the FDT in all three case are same as 9ms, irrespective of fault distance to detect and classify the fault. Very often this FDT changes as the parameter of the scheme changes. The magnitude of B-phase fault in case of km distance is higher compared to the B-phase fault of 3km distance. Table7. Shows the variation of distance with respect to FDT in different types of fault. It is seen that in all the case FDT remains within a cycle period of time 2ms. IJPEDS Vol. 8, No. 4, December 217 :
9 IJPEDS ISSN: B-G fault at different location of UPFC=km, 2km and 3 km distance from SE, Rf=1 ohm, FIA= degree km 2 km 3 km Magnitude of SE A Th=25 A-G fault at 6 sample 1cycle=4 sample=2 msec fault detection sample=18 fault detection time=9 msec -5 No. of sample Figure7. B-G fault at different distance (km, 2km and 3km) from B se at Rf =1Ω, FIA= Table 7. Variation of UPFC at distance (km, 2km and 3km) from B se, Rf =1Ω and FIA= Fault Type km, FDT 2km, FDT 3km, FDT Classification B-G 9ms 9ms 9ms B-phase BC-G 12ms 12ms 15ms BC-phase BC 13ms 15ms 15ms BC ABC 15ms 17ms 17ms ABC Table 8. A comparison study of spectral energy of phase in different types of fault before and after UPFC Absolute entropy Proposed scheme of Spectral Absolute entropy Proposed scheme of coefficients x 1 5 (before Energy of phase (before UPFC) coefficients x 1 5 (after Spectral Energy of phase UPFC) [28] UPFC) [28] (after UPFC) Fault type Phase A B C A B C A B C A B C AG BG CG AB BC CA ABG BCG CAG ABCG DISCUSSION Fault detection and classification in UPFC integrated transmission line using single terminal based DWT is proposed. From the above results it is observed that the scheme works fine in all the different variation of system parameters such as Rf, SI, FIA, phase reversal, fault location and UPFC condition. From the Figure 2 to Figure 7, it is clearly noticed that the fault is detected and classified within a cycle of time period (2ms). Table 1 to Table 7 presents the respective fault detection time (FDT) at different distance of fault occurrence under different types of fault and the fault classification. Table 8 presents a comparision study of spectral energy of different types of fault occurs before UPFC and after UPFC. The proposed scheme result has been compared to the existing wavelet entropy based scheme [28]. From this table it is noticed that the consideration of absolute entropy coefficient values from the literature [28] is found to be very high in the order of 1 5 (In AG fault 2.82х 1 5 for A-phase, 1.92х 1 5 for B-phase and 1.83х 1 5 for C- phase before UPFC) before UPFC and after UPFC condition compared to the proposed scheme shown in red numerical value (In AG fault for A-phase, for B-phase and 3.41 for C-phase before UPFC). If the absolute coefficient value is very high in the order of 1 5 then the processing time for fault detection requires high to detect the fault as a result of which the relay will take more time to detect the fault which affects the reliability and security of the costly equipment and is not acceptable in the relaying scheme. For this reason authors in the literature [28] are unable to address the fault detection time. However the proposed scheme clearly address the fault detection time by considering different parameters of transmission line and UPFC condition in Table 1 to Table 8 and it is found that in all situation the fault detection time remains within a cycle period of time (2ms). Further the bold red numerical value of Table 8 shows the value of spectral energy content of each phase before UPFC and after UPFC respectively.the numerical value more than threshold (Th=25) indicates the fault in that phase and the numerical value which is less than threshold (Th=25) indicates the healthy phase. All the spectral energy value of each phase are considered at a Fault Detection & Classification in UPFC Integrated Transmission Line Using DWT (S.K Mishra)
10 182 ISSN: sample after the incidence of fault. Therefore the proposed scheme is very effective, accurate and simple to detect the fault with minimum fault detection time to classify the fault. 6. CONCLUSION Fault detection and classification in a UPFC integrated transmission line using single terminal based DWT is proposed. The scheme of spectral energy based one terminal including UPFC using DWT has been successfully tested in matlab 21A simulation under the variation of different system parameters such as Rf, SI, FIA, phase reversal and UPFC operating condition V se and θ se. It is observed that the scheme works fine in all such variation to detect and classify the fault. Futher the fault detection time to detect the fault remains within a cycle period of time (2ms). The proposed scheme has been compared to the existing scheme and found to be effective to detect the fault within 2ms time. Therefore the proposed system of SE based one terminal scheme is very effective as it is less sensitive to synchronization error as compared to the time domain of differential current scheme. REFERENCES [1] N. G. Hingorani and L. Gyugyi, Understanding FACTS Concepts and Technology of Flexible AC Transmission Systems, New York: IEEE Press, 2. [2] S. R. Samantaray. A Data-Mining Model for Protection of FACTS-Based Transmission Line, in IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 213; 28(2): [3] L.N. Tripathy, M. K. Jena, S. R Samantray. Differential relaying scheme for tapped transmission line connecting UPFC and wind farm, International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 214; 6 (2): [4] L.N. Tripathy, S.R Samantray, P.K Dash. A fast time frequency transform based differential relaying scheme for UPFC based double-circuit transmission line, International Journal of Electrical and Power Energy system, 216; 77(1): [5] Zhou X, Wang H, R.K Agarwal, P. Beaumont. Performance of evaluation of distance relay as applied to a transmission system with UPFC, IEEE Transaction on Power Delivery, 26; 21(3): [6] M.H.J. Boolen. Traveling wave based protection of double circuit lines, Proceedings of Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers C- Generation, Transmission and Distribution, 1993; 14 (2): [7] SONG Y.H, A.T Johns, Q. Y. Xuan. Artificial neural network based protection scheme for controllable series compensated EHV transmission lines, IEE Proceeding on Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 1996; 143(1): [8] P.K. Dash, A. K Pradhan, G. Panda. A novel fuzzy neural network based distance relaying scheme, IEEE Transaction on Power Delivery, 2; 15(3): [9] M. Chamia, S. Liberman. Ultra high speed relay for EHV/UHV transmission lines, IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, 1978; 97(6): [1] S. R. Samantaray, P. K. Dash. High impedance fault detection in distribution feeders using extended kalman filter and support vector machine, European Transaction on Electrical Power, 21; 2(3): [11] V. L. Pham, K. P. Wong. Wavelet transform based algorithm for harmonic analysis of power system waveform, proceeding on Institutionof Electrical Engineering, Generation, Transmission and Distribution, 1999; 146(3): [12] M. F. Habban, M. Manap, A.R. Abdullah, M.H. Jopri, T. Sutikno. An Evaluation of linear time frequency distribution Analysis for VSI switch faults identification, International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive system, 217; 8(1): 1-9. [13] S. Azimi and M.V. Amiri. Concurrent Detection and Classification of faults in Matrix Converter using Transconductance, International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive system, 214; 5(1): 93-. [14] S. Dhara, A. K. Shrivastav, P. K. Sadhu, A. Ganguly. A fault current limiter circuit to improve transient stability in power system, International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive system, 216; 7(3): [15] Y. S Rao, G. Ravi Kumar, G. Keshab Rao. A new approach for classification of fault in transmission line with combination of wavelet multi resolution analysis and neural networks, International Journal of Power Electronics and Drive system, 217; 8(1): [16] S. K. Mishra, L.N Tripathy, S.C Swain. An Adaline LMS control and DWT approach based differential relaying STATCOM integrated line, International Journal of Control Theory and Applications, 217; 1 (37): [17] S. K. Mishra, L. N Tripathy, S.C Swain. The Detection & Classification of fault in a SVC integrated Double circuit Transmission line using FDST, International Journal of Control Theory and Applications, 217; 1 (37): [18] M. K. Jena, S. R. samantray, L. N. tripathy. Decision tree-induced fuzzy rule-based differential relaying for transmission line including unified power flow controller and wind-farms, in IET Generation, Transmission and Distribution, 214; 8 (12): [19] Ribeiro, P.F. Wavelet transform: an advanced tool for analyzing non-stationary harmonic distortions in power systems, The IEEE International Conference on Harmonics in power systems, Bologna, Italy, IJPEDS Vol. 8, No. 4, December 217 :
11 IJPEDS ISSN: [2] S. MalIat. A theory for multi-resolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation, IEEE Transaction on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1989; 11(7): [21] W. K. Ngui, M. S. Leong, L.M. Hee, A. M. Abdelrhman Mother wavelet Selection Method, Applied Mechanics and Materials, 213;393(1): [22] Daubechies I, Wavelet transform, time-frequency localization and signal analysis, IEEE Transaction on Information Theory, 199; 36(5): [23] H. A. Darwish, A. M. I. Talab, a.h Osman, N. M Mansur, O. P. Mallik. Spectral energy differential approach for transmission line protection, proceeding on PSCE, Atlanta: USA, 26: [24] L.N. Tripathy, M. K. jena, S. R Samantray. Differential relaying scheme for tapped transmission line connecting UPFC and wind farm, International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 214; 6 (2): [25] L.N. Tripathy, S.R Samantray, P.K Dash. Sparse S-transform for location of faults on transmission lines operating with unified power flow controller, in IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 215; 9(15): [26] A. Yadav, A. Swetapadma. A single ended directional fault section identifier and fault locator for double circuit transmission lines using combined wavelet and ANN approach, International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 215; 69 : [27] W. Elmore, Protective Relaying Theory and Applications, second ed., Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, 25. [28] El-Zonkoly and H. Desouki, "Wavelet Entropy Based Algorithm for Fault Detection and Classification in FACTS Compensated Transmission Line," Energy and Power Engineering, 211; 33 (8): Fault Detection & Classification in UPFC Integrated Transmission Line Using DWT (S.K Mishra)
A DWT Approach for Detection and Classification of Transmission Line Faults
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 3 Issue 02 July 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 A DWT Approach for Detection and Classification of Transmission Line Faults
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 3 Issue 02 July 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-6010 A DWT Approach for Detection and Classification of Transmission Line Faults
IDENTIFYING TYPES OF SIMULTANEOUS FAULT IN TRANSMISSION LINE USING DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM AND FUZZY LOGIC ALGORITHM
 International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control ICIC International c 2013 ISSN 1349-4198 Volume 9, Number 7, July 2013 pp. 2701 2712 IDENTIFYING TYPES OF SIMULTANEOUS FAULT IN TRANSMISSION
International Journal of Innovative Computing, Information and Control ICIC International c 2013 ISSN 1349-4198 Volume 9, Number 7, July 2013 pp. 2701 2712 IDENTIFYING TYPES OF SIMULTANEOUS FAULT IN TRANSMISSION
Discrete Wavelet Transform and Support Vector Machines Algorithm for Classification of Fault Types on Transmission Line
 Discrete Wavelet Transform and Support Vector Machines Algorithm for Classification of Fault Types on Transmission Line K. Kunadumrongrath and A. Ngaopitakkul, Member, IAENG Abstract This paper proposes
Discrete Wavelet Transform and Support Vector Machines Algorithm for Classification of Fault Types on Transmission Line K. Kunadumrongrath and A. Ngaopitakkul, Member, IAENG Abstract This paper proposes
Detection and classification of faults on 220 KV transmission line using wavelet transform and neural network
 International Journal of Smart Grid and Clean Energy Detection and classification of faults on 220 KV transmission line using wavelet transform and neural network R P Hasabe *, A P Vaidya Electrical Engineering
International Journal of Smart Grid and Clean Energy Detection and classification of faults on 220 KV transmission line using wavelet transform and neural network R P Hasabe *, A P Vaidya Electrical Engineering
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK SPECIAL ISSUE FOR NATIONAL LEVEL CONFERENCE "Technology Enabling Modernization
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK SPECIAL ISSUE FOR NATIONAL LEVEL CONFERENCE "Technology Enabling Modernization
A Novel Fuzzy Neural Network Based Distance Relaying Scheme
 902 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 15, NO. 3, JULY 2000 A Novel Fuzzy Neural Network Based Distance Relaying Scheme P. K. Dash, A. K. Pradhan, and G. Panda Abstract This paper presents a new
902 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON POWER DELIVERY, VOL. 15, NO. 3, JULY 2000 A Novel Fuzzy Neural Network Based Distance Relaying Scheme P. K. Dash, A. K. Pradhan, and G. Panda Abstract This paper presents a new
Fault Location Technique for UHV Lines Using Wavelet Transform
 International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 6, Number 1 (2013), pp. 77-88 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Fault Location Technique for UHV Lines
International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 6, Number 1 (2013), pp. 77-88 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Fault Location Technique for UHV Lines
Fault Detection Using Hilbert Huang Transform
 International Journal of Research in Advent Technology, Vol.6, No.9, September 2018 E-ISSN: 2321-9637 Available online at www.ijrat.org Fault Detection Using Hilbert Huang Transform Balvinder Singh 1,
International Journal of Research in Advent Technology, Vol.6, No.9, September 2018 E-ISSN: 2321-9637 Available online at www.ijrat.org Fault Detection Using Hilbert Huang Transform Balvinder Singh 1,
[Nayak, 3(2): February, 2014] ISSN: Impact Factor: 1.852
![[Nayak, 3(2): February, 2014] ISSN: Impact Factor: 1.852 [Nayak, 3(2): February, 2014] ISSN: Impact Factor: 1.852](/thumbs/96/128468304.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Classification of Transmission Line Faults Using Wavelet Transformer B. Lakshmana Nayak M.TECH(APS), AMIE, Associate Professor,
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Classification of Transmission Line Faults Using Wavelet Transformer B. Lakshmana Nayak M.TECH(APS), AMIE, Associate Professor,
Wavelet Based Fault Detection, Classification in Transmission System with TCSC Controllers
 ISSN: 2248-9622, Vol. 5, Issue 8, (Part - 3) August 215, pp.25-29 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Wavelet Based Fault Detection, Classification in Transmission System with TCSC Controllers 1 G.Satyanarayana,
ISSN: 2248-9622, Vol. 5, Issue 8, (Part - 3) August 215, pp.25-29 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Wavelet Based Fault Detection, Classification in Transmission System with TCSC Controllers 1 G.Satyanarayana,
A COMPARATIVE STUDY: FAULT DETECTION METHOD ON OVERHEAD TRANSMISSION LINE
 Volume 118 No. 22 2018, 961-967 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://acadpubl.eu/hub ijpam.eu A COMPARATIVE STUDY: FAULT DETECTION METHOD ON OVERHEAD TRANSMISSION LINE 1 M.Nandhini, 2 M.Manju,
Volume 118 No. 22 2018, 961-967 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://acadpubl.eu/hub ijpam.eu A COMPARATIVE STUDY: FAULT DETECTION METHOD ON OVERHEAD TRANSMISSION LINE 1 M.Nandhini, 2 M.Manju,
 http://dspace.nitrkl.ac.in/dspace A new approach to Power System Protection using Time-frequency analysis and Pattern Recognition Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award
http://dspace.nitrkl.ac.in/dspace A new approach to Power System Protection using Time-frequency analysis and Pattern Recognition Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award
A fast and accurate distance relaying scheme using an efficient radial basis function neural network
 Electric Power Systems Research 60 (2001) 1 8 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsr A fast and accurate distance relaying scheme using an efficient radial basis function neural network A.K. Pradhan *, P.K. Dash,
Electric Power Systems Research 60 (2001) 1 8 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsr A fast and accurate distance relaying scheme using an efficient radial basis function neural network A.K. Pradhan *, P.K. Dash,
Distribution System Faults Classification And Location Based On Wavelet Transform
 Distribution System Faults Classification And Location Based On Wavelet Transform MukeshThakre, Suresh Kumar Gawre & Mrityunjay Kumar Mishra Electrical Engg.Deptt., MANIT, Bhopal. E-mail : mukeshthakre18@gmail.com,
Distribution System Faults Classification And Location Based On Wavelet Transform MukeshThakre, Suresh Kumar Gawre & Mrityunjay Kumar Mishra Electrical Engg.Deptt., MANIT, Bhopal. E-mail : mukeshthakre18@gmail.com,
Performance Evaluation of Mho and Quadrilateral Characteristic Relays on UPFC Incorporated Transmission Line
 International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174 Volume 7, Number 8 (2014), pp. 827-835 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Performance Evaluation
International Journal of Electronic and Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2174 Volume 7, Number 8 (2014), pp. 827-835 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Performance Evaluation
Improvement of Power Quality Using a Hybrid Interline UPQC
 Improvement of Power Quality Using a Hybrid Interline UPQC M.K.Elango 1, C.Vengatesh Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering K.S.Rangasamy College of Technology Tiruchengode, Tamilnadu, India
Improvement of Power Quality Using a Hybrid Interline UPQC M.K.Elango 1, C.Vengatesh Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering K.S.Rangasamy College of Technology Tiruchengode, Tamilnadu, India
Online Diagnosis and Monitoring for Power Distribution System
 Energy and Power Engineering, 1,, 59-53 http://dx.doi.org/1.3/epe.1. Published Online November 1 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/epe) Online Diagnosis and Monitoring for Power Distribution System Atef Almashaqbeh,
Energy and Power Engineering, 1,, 59-53 http://dx.doi.org/1.3/epe.1. Published Online November 1 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/epe) Online Diagnosis and Monitoring for Power Distribution System Atef Almashaqbeh,
Comparison of Wavelet Transform and Fourier Transform based methods of Phasor Estimation for Numerical Relaying
 Comparison of Wavelet Transform and Fourier Transform based methods of Phasor Estimation for Numerical Relaying V.S.Kale S.R.Bhide P.P.Bedekar Department of Electrical Engineering, VNIT Nagpur, India Abstract
Comparison of Wavelet Transform and Fourier Transform based methods of Phasor Estimation for Numerical Relaying V.S.Kale S.R.Bhide P.P.Bedekar Department of Electrical Engineering, VNIT Nagpur, India Abstract
Single-Core Symmetrical Phase Shifting Transformer Protection Using Multi-Resolution Analysis
 IJEEE, Volume 3, Spl. Issue (1) Single-Core Symmetrical Phase Shifting Transformer Protection Using Multi-Resolution Analysis Meenakshi Sahu 1, Mr. Rahul Rahangdale 1, Department of ECE, School of Engineering
IJEEE, Volume 3, Spl. Issue (1) Single-Core Symmetrical Phase Shifting Transformer Protection Using Multi-Resolution Analysis Meenakshi Sahu 1, Mr. Rahul Rahangdale 1, Department of ECE, School of Engineering
Chapter -3 ANALYSIS OF HVDC SYSTEM MODEL. Basically the HVDC transmission consists in the basic case of two
 Chapter -3 ANALYSIS OF HVDC SYSTEM MODEL Basically the HVDC transmission consists in the basic case of two convertor stations which are connected to each other by a transmission link consisting of an overhead
Chapter -3 ANALYSIS OF HVDC SYSTEM MODEL Basically the HVDC transmission consists in the basic case of two convertor stations which are connected to each other by a transmission link consisting of an overhead
Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter Based UPFC with ANN
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 04, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Transient Stability Improvement of Multi Machine Power Systems using Matrix Converter
Selection of Mother Wavelet for Processing of Power Quality Disturbance Signals using Energy for Wavelet Packet Decomposition
 Volume 114 No. 9 217, 313-323 ISSN: 1311-88 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Selection of Mother Wavelet for Processing of Power Quality Disturbance
Volume 114 No. 9 217, 313-323 ISSN: 1311-88 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Selection of Mother Wavelet for Processing of Power Quality Disturbance
Improved first zone reach setting of artificial neural network-based directional relay for protection of double circuit transmission lines
 Published in IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution Received on 5th April 2013 Revised on 17th September 2013 Accepted on 24th September 2013 ISSN 1751-8687 Improved first zone reach setting of artificial
Published in IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution Received on 5th April 2013 Revised on 17th September 2013 Accepted on 24th September 2013 ISSN 1751-8687 Improved first zone reach setting of artificial
TRANSIENT STABILITY ENHANCEMENT OF POWER SYSTEM USING INTELLIGENT TECHNIQUE
 TRANSIENT STABILITY ENHANCEMENT OF POWER SYSTEM USING INTELLIGENT TECHNIQUE K.Satyanarayana 1, Saheb Hussain MD 2, B.K.V.Prasad 3 1 Ph.D Scholar, EEE Department, Vignan University (A.P), India, ksatya.eee@gmail.com
TRANSIENT STABILITY ENHANCEMENT OF POWER SYSTEM USING INTELLIGENT TECHNIQUE K.Satyanarayana 1, Saheb Hussain MD 2, B.K.V.Prasad 3 1 Ph.D Scholar, EEE Department, Vignan University (A.P), India, ksatya.eee@gmail.com
An Enhanced Symmetrical Fault Detection during Power Swing/Angular Instability using Park s Transformation
 Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Vol., No., April 6, pp. 3 ~ 3 DOI:.59/ijeecs.v.i.pp3-3 3 An Enhanced Symmetrical Fault Detection during Power Swing/Angular Instability
Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Vol., No., April 6, pp. 3 ~ 3 DOI:.59/ijeecs.v.i.pp3-3 3 An Enhanced Symmetrical Fault Detection during Power Swing/Angular Instability
Performance of DVR under various Fault conditions in Electrical Distribution System
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 8, Issue 1 (Nov. - Dec. 2013), PP 06-12 Performance of DVR under various Fault conditions
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 8, Issue 1 (Nov. - Dec. 2013), PP 06-12 Performance of DVR under various Fault conditions
SVC Compensated Multi Terminal Transmission System Digital Protection Scheme using Wavelet Transform Approach
 SVC Compensated Multi Terminal Transmission System Digital Protection Scheme using Wavelet Transform Approach J.Uday Bhaskar 1, S.S Tulasiram 2, G.Ravi Kumar 3 JNTUK 1, JNTUH 2, JNTUK 3 udayadisar@gmail.com
SVC Compensated Multi Terminal Transmission System Digital Protection Scheme using Wavelet Transform Approach J.Uday Bhaskar 1, S.S Tulasiram 2, G.Ravi Kumar 3 JNTUK 1, JNTUH 2, JNTUK 3 udayadisar@gmail.com
Interline Power Flow Controller: Review Paper
 Vol. (0) No. 3, pp. 550-554 ISSN 078-365 Interline Power Flow Controller: Review Paper Akhilesh A. Nimje, Chinmoy Kumar Panigrahi, Ajaya Kumar Mohanty Abstract The Interline Power Flow Controller (IPFC)
Vol. (0) No. 3, pp. 550-554 ISSN 078-365 Interline Power Flow Controller: Review Paper Akhilesh A. Nimje, Chinmoy Kumar Panigrahi, Ajaya Kumar Mohanty Abstract The Interline Power Flow Controller (IPFC)
Enhancement of Power Quality in Distribution System Using D-Statcom for Different Faults
 Enhancement of Power Quality in Distribution System Using D-Statcom for Different s Dr. B. Sure Kumar 1, B. Shravanya 2 1 Assistant Professor, CBIT, HYD 2 M.E (P.S & P.E), CBIT, HYD Abstract: The main
Enhancement of Power Quality in Distribution System Using D-Statcom for Different s Dr. B. Sure Kumar 1, B. Shravanya 2 1 Assistant Professor, CBIT, HYD 2 M.E (P.S & P.E), CBIT, HYD Abstract: The main
ISSN Vol.05,Issue.06, June-2017, Pages:
 WWW.IJITECH.ORG ISSN 2321-8665 Vol.05,Issue.06, June-2017, Pages:1061-1066 Fuzzy Logic Based Fault Detection and Classification of Unsynchronized Faults in Three Phase Double Circuit Transmission Lines
WWW.IJITECH.ORG ISSN 2321-8665 Vol.05,Issue.06, June-2017, Pages:1061-1066 Fuzzy Logic Based Fault Detection and Classification of Unsynchronized Faults in Three Phase Double Circuit Transmission Lines
Detection, localization, and classification of power quality disturbances using discrete wavelet transform technique
 From the SelectedWorks of Tarek Ibrahim ElShennawy 2003 Detection, localization, and classification of power quality disturbances using discrete wavelet transform technique Tarek Ibrahim ElShennawy, Dr.
From the SelectedWorks of Tarek Ibrahim ElShennawy 2003 Detection, localization, and classification of power quality disturbances using discrete wavelet transform technique Tarek Ibrahim ElShennawy, Dr.
LabVIEW Based Condition Monitoring Of Induction Motor
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS LabVIEW Based Condition Monitoring Of Induction Motor 1PG student Rushikesh V. Deshmukh Prof. 2Asst. professor Anjali U. Jawadekar Department of Electrical Engineering SSGMCE,
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS LabVIEW Based Condition Monitoring Of Induction Motor 1PG student Rushikesh V. Deshmukh Prof. 2Asst. professor Anjali U. Jawadekar Department of Electrical Engineering SSGMCE,
Wavelet Transform for Classification of Voltage Sag Causes using Probabilistic Neural Network
 International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 974-2158 Volume 4, Number 3 (211), pp. 299-39 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Wavelet Transform for Classification
International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 974-2158 Volume 4, Number 3 (211), pp. 299-39 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Wavelet Transform for Classification
Application of Fuzzy Logic Controller in UPFC to Mitigate THD in Power System
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 9, Issue 8 (January 2014), PP. 25-33 Application of Fuzzy Logic Controller in UPFC
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 9, Issue 8 (January 2014), PP. 25-33 Application of Fuzzy Logic Controller in UPFC
A Voltage Controlled D-STATCOM for Power Quality Improvement with DVR
 A Voltage Controlled D-STATCOM for Power Quality Improvement with DVR Rongali. Shiva Kumar P.G Student Scholar, Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Gokul Group Of Institutions Abstract:
A Voltage Controlled D-STATCOM for Power Quality Improvement with DVR Rongali. Shiva Kumar P.G Student Scholar, Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Gokul Group Of Institutions Abstract:
ENHANCED DISTANCE PROTECTION FOR SERIES COMPENSATED TRANSMISSION LINES
 ENHANCED DISTANCE PROTECTION FOR SERIES COMPENSATED TRANSMISSION LINES N. Perera 1, A. Dasgupta 2, K. Narendra 1, K. Ponram 3, R. Midence 1, A. Oliveira 1 ERLPhase Power Technologies Ltd. 1 74 Scurfield
ENHANCED DISTANCE PROTECTION FOR SERIES COMPENSATED TRANSMISSION LINES N. Perera 1, A. Dasgupta 2, K. Narendra 1, K. Ponram 3, R. Midence 1, A. Oliveira 1 ERLPhase Power Technologies Ltd. 1 74 Scurfield
Faults Detection in Single-Core Symmetrical Phase Shifting Transformers Based on Wavelets
 Faults Detection in Single-Core Symmetrical Phase Shifting Transformers Based on Wavelets 1 Meenakshi Sahu, 2 Rahul Rahangdale 1,2 Department Of Electronics And Communication Engineering School of Engineering
Faults Detection in Single-Core Symmetrical Phase Shifting Transformers Based on Wavelets 1 Meenakshi Sahu, 2 Rahul Rahangdale 1,2 Department Of Electronics And Communication Engineering School of Engineering
CHAPTER 3 COMBINED MULTIPULSE MULTILEVEL INVERTER BASED STATCOM
 CHAPTER 3 COMBINED MULTIPULSE MULTILEVEL INVERTER BASED STATCOM 3.1 INTRODUCTION Static synchronous compensator is a shunt connected reactive power compensation device that is capable of generating or
CHAPTER 3 COMBINED MULTIPULSE MULTILEVEL INVERTER BASED STATCOM 3.1 INTRODUCTION Static synchronous compensator is a shunt connected reactive power compensation device that is capable of generating or
DETECTION AND CLASSIFICATION OF POWER QUALITY DISTURBANCES
 DETECTION AND CLASSIFICATION OF POWER QUALITY DISTURBANCES Ph.D. THESIS by UTKARSH SINGH INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE ROORKEE-247 667 (INDIA) OCTOBER, 2017 DETECTION AND CLASSIFICATION OF POWER
DETECTION AND CLASSIFICATION OF POWER QUALITY DISTURBANCES Ph.D. THESIS by UTKARSH SINGH INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE ROORKEE-247 667 (INDIA) OCTOBER, 2017 DETECTION AND CLASSIFICATION OF POWER
Artificial Neural Network Based Fault Locator for Single Line to Ground Fault in Double Circuit Transmission Line
 DOI: 10.7763/IPEDR. 2014. V75. 11 Artificial Neural Network Based Fault Locator for Single Line to Ground Fault in Double Circuit Transmission Line Aravinda Surya. V 1, Ebha Koley 2 +, AnamikaYadav 3 and
DOI: 10.7763/IPEDR. 2014. V75. 11 Artificial Neural Network Based Fault Locator for Single Line to Ground Fault in Double Circuit Transmission Line Aravinda Surya. V 1, Ebha Koley 2 +, AnamikaYadav 3 and
Detection of Fault in Fixed Series Compensated Transmission Line during Power Swing Using Wavelet Transform
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 5, May 24 Detection of Fault in Fixed Series Compensated Transmission Line during Power Swing Using Wavelet Transform Rohan
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 5, May 24 Detection of Fault in Fixed Series Compensated Transmission Line during Power Swing Using Wavelet Transform Rohan
Application of Wavelet Transform in Power System Analysis and Protection
 Application of Wavelet Transform in Power System Analysis and Protection Neha S. Dudhe PG Scholar Shri Sai College of Engineering & Technology, Bhadrawati-Chandrapur, India Abstract This paper gives a
Application of Wavelet Transform in Power System Analysis and Protection Neha S. Dudhe PG Scholar Shri Sai College of Engineering & Technology, Bhadrawati-Chandrapur, India Abstract This paper gives a
Performance Evaluation of Traveling Wave Fault Locator for a 220kV Hoa Khanh-Thanh My Transmission Line
 Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research Vol. 8, No. 4, 2018, 3243-3248 3243 Performance Evaluation of Traveling Wave Fault Locator for a 220kV Hoa Khanh-Thanh My Transmission Line Kim Hung Le
Engineering, Technology & Applied Science Research Vol. 8, No. 4, 2018, 3243-3248 3243 Performance Evaluation of Traveling Wave Fault Locator for a 220kV Hoa Khanh-Thanh My Transmission Line Kim Hung Le
Wavelet Transform Based Islanding Characterization Method for Distributed Generation
 Fourth LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCET 6) Wavelet Transform Based Islanding Characterization Method for Distributed Generation O. A.
Fourth LACCEI International Latin American and Caribbean Conference for Engineering and Technology (LACCET 6) Wavelet Transform Based Islanding Characterization Method for Distributed Generation O. A.
CLASSIFICATION OF POWER QUALITY DISTURBANCES USING WAVELET TRANSFORM AND S-TRANSFORM BASED ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK
 CLASSIFICATION OF POWER QUALITY DISTURBANCES USING WAVELET TRANSFORM AND S-TRANSFORM BASED ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK P. Sai revathi 1, G.V. Marutheswar 2 P.G student, Dept. of EEE, SVU College of Engineering,
CLASSIFICATION OF POWER QUALITY DISTURBANCES USING WAVELET TRANSFORM AND S-TRANSFORM BASED ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK P. Sai revathi 1, G.V. Marutheswar 2 P.G student, Dept. of EEE, SVU College of Engineering,
Designing Of Distributed Power-Flow Controller
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) ISSN: 2278-1676 Volume 2, Issue 5 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 01-09 Designing Of Distributed Power-Flow Controller 1 R. Lokeswar Reddy (M.Tech),
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) ISSN: 2278-1676 Volume 2, Issue 5 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 01-09 Designing Of Distributed Power-Flow Controller 1 R. Lokeswar Reddy (M.Tech),
Power Quality Improvement using Hysteresis Voltage Control of DVR
 Power Quality Improvement using Hysteresis Voltage Control of DVR J Sivasankari 1, U.Shyamala 2, M.Vigneshwaran 3 P.G Scholar, Dept of EEE, M.Kumarasamy college of Engineering, Karur, Tamilnadu, India
Power Quality Improvement using Hysteresis Voltage Control of DVR J Sivasankari 1, U.Shyamala 2, M.Vigneshwaran 3 P.G Scholar, Dept of EEE, M.Kumarasamy college of Engineering, Karur, Tamilnadu, India
Dwt-Ann Approach to Classify Power Quality Disturbances
 Dwt-Ann Approach to Classify Power Quality Disturbances Prof. Abhijit P. Padol Department of Electrical Engineering, abhijit.padol@gmail.com Prof. K. K. Rajput Department of Electrical Engineering, kavishwarrajput@yahoo.co.in
Dwt-Ann Approach to Classify Power Quality Disturbances Prof. Abhijit P. Padol Department of Electrical Engineering, abhijit.padol@gmail.com Prof. K. K. Rajput Department of Electrical Engineering, kavishwarrajput@yahoo.co.in
A Novel Scheme of Transmission Line Faults Analysis and Detection by Using MATLAB Simulation
 A Novel Scheme of Transmission Line Faults Analysis and Detection by Using MATLAB Simulation Satish Karekar 1, Varsha Thakur 2, Manju 3 1 Parthivi College of Engineering and Management, Sirsakala, Bhilai-3,
A Novel Scheme of Transmission Line Faults Analysis and Detection by Using MATLAB Simulation Satish Karekar 1, Varsha Thakur 2, Manju 3 1 Parthivi College of Engineering and Management, Sirsakala, Bhilai-3,
Detection of fault location on transmission systems using Wavelet transform
 International Academic Institute for Science and Technology International Academic Journal of Science and Engineering Vol. 3, No. 4, 2016, pp. 23-32. ISSN 2454-3896 International Academic Journal of Science
International Academic Institute for Science and Technology International Academic Journal of Science and Engineering Vol. 3, No. 4, 2016, pp. 23-32. ISSN 2454-3896 International Academic Journal of Science
ENHANCING POWER SYSTEM STABILITY USING NEURO-FUZZY BASED UPFC
 ENHANCING POWER SYSTEM STABILITY USING NEURO-FUZZY BASED UPFC R.RAJA NIVEDHA 1, V.BHARATHI 2,P.S.DHIVYABHARATHI 3,V.RAJASUGUNA 4,N.SATHYAPRIYA 5 1 Assistant Professor, Department of EEE,Sri Eshwar college
ENHANCING POWER SYSTEM STABILITY USING NEURO-FUZZY BASED UPFC R.RAJA NIVEDHA 1, V.BHARATHI 2,P.S.DHIVYABHARATHI 3,V.RAJASUGUNA 4,N.SATHYAPRIYA 5 1 Assistant Professor, Department of EEE,Sri Eshwar college
Performance Of Distributed Power Flow Controller (DPFC) Under Fault Condition
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN CESS Performance Of Distributed Power Flow Controller (DPFC) Under Fault Condition Santosh Kumar Gupta M.Tech. Student, Department of Electrical Engineering National Institute of
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN CESS Performance Of Distributed Power Flow Controller (DPFC) Under Fault Condition Santosh Kumar Gupta M.Tech. Student, Department of Electrical Engineering National Institute of
Ultra Hight Voltge Transmission line Faults Identified and Analysis by using MATLAB Simulink
 International Seminar On Non-Conventional Energy Sources for Sustainable Development of Rural Areas, IJAERD- International Journal of Advance Engineering & Research Development e-issn: 2348-4470, p-issn:2348-6406
International Seminar On Non-Conventional Energy Sources for Sustainable Development of Rural Areas, IJAERD- International Journal of Advance Engineering & Research Development e-issn: 2348-4470, p-issn:2348-6406
Ferroresonance Signal Analysis with Wavelet Transform on 500 kv Transmission Lines Capacitive Voltage Transformers
 Signal Analysis with Wavelet Transform on 500 kv Transmission Lines Capacitive Voltage Transformers I Gusti Ngurah Satriyadi Hernanda, I Made Yulistya Negara, Adi Soeprijanto, Dimas Anton Asfani, Mochammad
Signal Analysis with Wavelet Transform on 500 kv Transmission Lines Capacitive Voltage Transformers I Gusti Ngurah Satriyadi Hernanda, I Made Yulistya Negara, Adi Soeprijanto, Dimas Anton Asfani, Mochammad
Keywords: Power System Computer Aided Design, Discrete Wavelet Transform, Artificial Neural Network, Multi- Resolution Analysis.
 GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES IDENTIFICATION AND CLASSIFICATION OF POWER QUALITY DISTURBANCES BY AN EFFECTIVE WAVELET BASED NEURAL CLASSIFIER Prof. A. P. Padol Department of Electrical
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES IDENTIFICATION AND CLASSIFICATION OF POWER QUALITY DISTURBANCES BY AN EFFECTIVE WAVELET BASED NEURAL CLASSIFIER Prof. A. P. Padol Department of Electrical
A Transient Current Based Wavelet-Fuzzy Approach for the Protection of Six-Terminal Transmission System
 Abstract International Journal of Exploration in Science and Technology A Transient Current Based Wavelet-Fuzzy Approach for the Protection of Six-Terminal Transmission System J.Uday Bhaskar 1, G.Ravi
Abstract International Journal of Exploration in Science and Technology A Transient Current Based Wavelet-Fuzzy Approach for the Protection of Six-Terminal Transmission System J.Uday Bhaskar 1, G.Ravi
CHAPTER 4 PV-UPQC BASED HARMONICS REDUCTION IN POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS
 66 CHAPTER 4 PV-UPQC BASED HARMONICS REDUCTION IN POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The use of electronic controllers in the electric power supply system has become very common. These electronic
66 CHAPTER 4 PV-UPQC BASED HARMONICS REDUCTION IN POWER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEMS INTRODUCTION The use of electronic controllers in the electric power supply system has become very common. These electronic
ANFIS based 48-Pulse STATCOM Controller for Enhancement of Power System Stability
 ANFIS based 48-Pulse STATCOM Controller for Enhancement of Power System Stility Subir Datta and Anjan Kumar Roy Abstract The paper presents a new ANFIS-based controller for enhancement of voltage stility
ANFIS based 48-Pulse STATCOM Controller for Enhancement of Power System Stility Subir Datta and Anjan Kumar Roy Abstract The paper presents a new ANFIS-based controller for enhancement of voltage stility
SIMULATION OF D-Q CONTROL SYSTEM FOR A UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER
 SIMULATION OF D-Q CONTROL SYSTEM FOR A UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER S. Tara Kalyani 1 and G. Tulasiram Das 1 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, Hyderabad,
SIMULATION OF D-Q CONTROL SYSTEM FOR A UNIFIED POWER FLOW CONTROLLER S. Tara Kalyani 1 and G. Tulasiram Das 1 1 Department of Electrical Engineering, Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University, Hyderabad,
Improvement of Power Quality in Distribution System using D-STATCOM With PI and PID Controller
 Improvement of Power Quality in Distribution System using D-STATCOM With PI and PID Controller Phanikumar.Ch, M.Tech Dept of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Bapatla Engineering College, Bapatla,
Improvement of Power Quality in Distribution System using D-STATCOM With PI and PID Controller Phanikumar.Ch, M.Tech Dept of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Bapatla Engineering College, Bapatla,
Performance Assessment of Distance Relay using MATLAB DibyaDarshiniMohanty, Ashwin Sharma, Ashutosh Varma M.S.I.T. M.S.I.T. M.S.I.
 Performance Assessment of Distance Relay using MATLAB DibyaDarshiniMohanty, Ashwin Sharma, Ashutosh Varma M.S.I.T. M.S.I.T. M.S.I.T Abstract This paper studies the performance of distance relay using MATLAB.
Performance Assessment of Distance Relay using MATLAB DibyaDarshiniMohanty, Ashwin Sharma, Ashutosh Varma M.S.I.T. M.S.I.T. M.S.I.T Abstract This paper studies the performance of distance relay using MATLAB.
Increasing Dynamic Stability of the Network Using Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC)
 Increasing Dynamic Stability of the Network Using Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) K. Manoz Kumar Reddy (Associate professor, Electrical and Electronics Department, Sriaditya Engineering College, India)
Increasing Dynamic Stability of the Network Using Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) K. Manoz Kumar Reddy (Associate professor, Electrical and Electronics Department, Sriaditya Engineering College, India)
Keywords: Wavelet packet transform (WPT), Differential Protection, Inrush current, CT saturation.
 IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Differential Protection of Three Phase Power Transformer Using Wavelet Packet Transform Jitendra Singh Chandra*, Amit Goswami
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Differential Protection of Three Phase Power Transformer Using Wavelet Packet Transform Jitendra Singh Chandra*, Amit Goswami
International Journal of Digital Application & Contemporary research Website: (Volume 2, Issue 10, May 2014)
 Digital Differential Protection of Power Transformer Gitanjali Kashyap M. Tech. Scholar, Dr. C. V. Raman Institute of Science and technology, Chhattisgarh (India) alisha88.ele@gmail.com Dharmendra Kumar
Digital Differential Protection of Power Transformer Gitanjali Kashyap M. Tech. Scholar, Dr. C. V. Raman Institute of Science and technology, Chhattisgarh (India) alisha88.ele@gmail.com Dharmendra Kumar
Bhavin Gondaliya 1st Head, Electrical Engineering Department Dr. Subhash Technical Campus, Junagadh, Gujarat (India)
 ISSN: 2349-7637 (Online) RESEARCH HUB International Multidisciplinary Research Journal (RHIMRJ) Research Paper Available online at: www.rhimrj.com Modeling and Simulation of Distribution STATCOM Bhavin
ISSN: 2349-7637 (Online) RESEARCH HUB International Multidisciplinary Research Journal (RHIMRJ) Research Paper Available online at: www.rhimrj.com Modeling and Simulation of Distribution STATCOM Bhavin
Feature Extraction of Magnetizing Inrush Currents in Transformers by Discrete Wavelet Transform
 Feature Extraction of Magnetizing Inrush Currents in Transformers by Discrete Wavelet Transform Patil Bhushan Prataprao 1, M. Mujtahid Ansari 2, and S. R. Parasakar 3 1 Dept of Electrical Engg., R.C.P.I.T.
Feature Extraction of Magnetizing Inrush Currents in Transformers by Discrete Wavelet Transform Patil Bhushan Prataprao 1, M. Mujtahid Ansari 2, and S. R. Parasakar 3 1 Dept of Electrical Engg., R.C.P.I.T.
Damping Power system Oscillation using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC)
 Damping Power system Oscillation using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) Girish Kumar Prasad 1, Dr. Malaya S Dash 2 1M-Tech Scholar, Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Technocrats
Damping Power system Oscillation using Static Synchronous Series Compensator (SSSC) Girish Kumar Prasad 1, Dr. Malaya S Dash 2 1M-Tech Scholar, Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Technocrats
Design Strategy for Optimum Rating Selection of Interline D-STATCOM
 International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 2 Issue 3 ǁ March. 2013 ǁ PP.12-17 Design Strategy for Optimum Rating Selection of Interline
International Journal of Engineering Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6734, ISSN (Print): 2319 6726 Volume 2 Issue 3 ǁ March. 2013 ǁ PP.12-17 Design Strategy for Optimum Rating Selection of Interline
ANALYSIS OF ACTIVE POWER FILTER FOR HARMONIC VOLTAGE RESONANCE SUPPRESSION IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
 ANALYSIS OF ACTIVE POWER FILTER FOR HARMONIC VOLTAGE RESONANCE SUPPRESSION IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM Original Research Article ISSN CODE: 456-1045 (Online) (ICV-EE/Impact Value): 3.08 (GIF) Impact Factor:.174
ANALYSIS OF ACTIVE POWER FILTER FOR HARMONIC VOLTAGE RESONANCE SUPPRESSION IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM Original Research Article ISSN CODE: 456-1045 (Online) (ICV-EE/Impact Value): 3.08 (GIF) Impact Factor:.174
AN ANN BASED FAULT DETECTION ON ALTERNATOR
 AN ANN BASED FAULT DETECTION ON ALTERNATOR Suraj J. Dhon 1, Sarang V. Bhonde 2 1 (Electrical engineering, Amravati University, India) 2 (Electrical engineering, Amravati University, India) ABSTRACT: Synchronous
AN ANN BASED FAULT DETECTION ON ALTERNATOR Suraj J. Dhon 1, Sarang V. Bhonde 2 1 (Electrical engineering, Amravati University, India) 2 (Electrical engineering, Amravati University, India) ABSTRACT: Synchronous
Classification of Voltage Sag Using Multi-resolution Analysis and Support Vector Machine
 Journal of Clean Energy Technologies, Vol. 4, No. 3, May 2016 Classification of Voltage Sag Using Multi-resolution Analysis and Support Vector Machine Hanim Ismail, Zuhaina Zakaria, and Noraliza Hamzah
Journal of Clean Energy Technologies, Vol. 4, No. 3, May 2016 Classification of Voltage Sag Using Multi-resolution Analysis and Support Vector Machine Hanim Ismail, Zuhaina Zakaria, and Noraliza Hamzah
Power Quality enhancement of a distribution line with DSTATCOM
 ower Quality enhancement of a distribution line with DSTATCOM Divya arashar 1 Department of Electrical Engineering BSACET Mathura INDIA Aseem Chandel 2 SMIEEE,Deepak arashar 3 Department of Electrical
ower Quality enhancement of a distribution line with DSTATCOM Divya arashar 1 Department of Electrical Engineering BSACET Mathura INDIA Aseem Chandel 2 SMIEEE,Deepak arashar 3 Department of Electrical
Power Quality Monitoring of a Power System using Wavelet Transform
 International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 3, Number 3 (2010), pp. 189--199 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Power Quality Monitoring of a Power
International Journal of Electrical Engineering. ISSN 0974-2158 Volume 3, Number 3 (2010), pp. 189--199 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Power Quality Monitoring of a Power
PERFORMANCE OF DISTRIBUTION STATIC COMPENSATOR IN LOW VOLTAGE DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
 PERFORMANCE OF DISTRIBUTION STATIC COMPENSATOR IN LOW VOLTAGE DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM Bhupali P. Kumbhar 1, Prof. V. V. Khatavkar 2 1 PG Student, Dept. of Electrical Engineering, 2 Asst. Professor, Dept. of
PERFORMANCE OF DISTRIBUTION STATIC COMPENSATOR IN LOW VOLTAGE DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM Bhupali P. Kumbhar 1, Prof. V. V. Khatavkar 2 1 PG Student, Dept. of Electrical Engineering, 2 Asst. Professor, Dept. of
Modified Approach for Harmonic Reduction in Transmission System Using 48-pulse UPFC Employing Series Zig-Zag Primary and Y-Y Secondary Transformer
 I.J. Intelligent Systems and Applications, 213, 11, 7-79 Published Online October 213 in MECS (http://www.mecs-press.org/) DOI: 1.5815/ijisa.213.11.8 Modified Approach for Harmonic Reduction in Transmission
I.J. Intelligent Systems and Applications, 213, 11, 7-79 Published Online October 213 in MECS (http://www.mecs-press.org/) DOI: 1.5815/ijisa.213.11.8 Modified Approach for Harmonic Reduction in Transmission
POWER FLOW CONTROL WITH UPFC IN POWER TRANSMISSION SYSTEM
 POWER FLOW CONTROL WITH UPFC IN POWER TRANSMISSION SYSTEM Ms.Dolly P.Raut 1, Asst.Prof.R.H.Adware 2 1 Department of Electrical engineering, G.H.Raisoni College of Engineering, India 2 Department of Electrical
POWER FLOW CONTROL WITH UPFC IN POWER TRANSMISSION SYSTEM Ms.Dolly P.Raut 1, Asst.Prof.R.H.Adware 2 1 Department of Electrical engineering, G.H.Raisoni College of Engineering, India 2 Department of Electrical
Fault Detection of Six-Phase Transmission Lines using Discrete Wavelet Transform
 Volume 114 No. 9 17, 31-37 ISSN: 1311-88 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Fault Detection of Six-Phase Transmission Lines using Discrete Wavelet Transform
Volume 114 No. 9 17, 31-37 ISSN: 1311-88 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Fault Detection of Six-Phase Transmission Lines using Discrete Wavelet Transform
Mitigation of voltage disturbances (Sag/Swell) utilizing dynamic voltage restorer (DVR)
 Research Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN 2278 9472 Mitigation of voltage disturbances (Sag/Swell) utilizing dynamic voltage restorer (DVR) Abstract Srishti Verma * and Anupama Huddar Electrical Engineering
Research Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN 2278 9472 Mitigation of voltage disturbances (Sag/Swell) utilizing dynamic voltage restorer (DVR) Abstract Srishti Verma * and Anupama Huddar Electrical Engineering
Stability Enhancement for Transmission Lines using Static Synchronous Series Compensator
 Stability Enhancement for Transmission Lines using Static Synchronous Series Compensator Ishwar Lal Yadav Department of Electrical Engineering Rungta College of Engineering and Technology Bhilai, India
Stability Enhancement for Transmission Lines using Static Synchronous Series Compensator Ishwar Lal Yadav Department of Electrical Engineering Rungta College of Engineering and Technology Bhilai, India
ISLANDING DETECTION IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM EMBEDDED WITH RENEWABLE-BASED DISTRIBUTED GENERATION. Saurabh Talwar
 ISLANDING DETECTION IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM EMBEDDED WITH RENEWABLE-BASED DISTRIBUTED GENERATION by Saurabh Talwar B. Eng, University of Ontario Institute of Technology, Canada, 2011 A Thesis Submitted
ISLANDING DETECTION IN DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM EMBEDDED WITH RENEWABLE-BASED DISTRIBUTED GENERATION by Saurabh Talwar B. Eng, University of Ontario Institute of Technology, Canada, 2011 A Thesis Submitted
Improving the Transient and Dynamic stability of the Network by Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC)
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 5, May 2012 1 Improving the Transient and Dynamic stability of the Network by Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) K. Manoz
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 5, May 2012 1 Improving the Transient and Dynamic stability of the Network by Unified Power Flow Controller (UPFC) K. Manoz
Protective Relaying of Power Systems Using Mathematical Morphology
 Q.H. Wu Z. Lu T.Y. Ji Protective Relaying of Power Systems Using Mathematical Morphology Springer List of Figures List of Tables xiii xxi 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction and Definitions 1 1.2 Historical
Q.H. Wu Z. Lu T.Y. Ji Protective Relaying of Power Systems Using Mathematical Morphology Springer List of Figures List of Tables xiii xxi 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction and Definitions 1 1.2 Historical
FAULT DETECTION, CLASSIFICATION AND LOCATION ON AN UNDERGROUND CABLE NETWORK USING WAVELET TRANSFORM
 90 FAULT DETECTION, CLASSIFICATION AND LOCATION ON AN UNDERGROUND CABLE NETWORK USING WAVELET TRANSFORM Hashim Hizam, Jasronita Jasni, Mohd Zainal Abidin Ab Kadir, Wan Fatinhamamah Wan Ahmad Department
90 FAULT DETECTION, CLASSIFICATION AND LOCATION ON AN UNDERGROUND CABLE NETWORK USING WAVELET TRANSFORM Hashim Hizam, Jasronita Jasni, Mohd Zainal Abidin Ab Kadir, Wan Fatinhamamah Wan Ahmad Department
Fault Diagnosis in H-Bridge Multilevel Inverter Drive Using Wavelet Transforms
 Fault Diagnosis in H-Bridge Multilevel Inverter Drive Using Wavelet Transforms V.Vinothkumar 1, Dr.C.Muniraj 2 PG Scholar, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, K.S.Rangasamy college of
Fault Diagnosis in H-Bridge Multilevel Inverter Drive Using Wavelet Transforms V.Vinothkumar 1, Dr.C.Muniraj 2 PG Scholar, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, K.S.Rangasamy college of
Power Quality Improvement in Distribution System Using D-STATCOM
 Power Quality Improvement in Distribution System Using D-STATCOM 1 K.L.Sireesha, 2 K.Bhushana Kumar 1 K L University, AP, India 2 Sasi Institute of Technology, Tadepalligudem, AP, India Abstract This paper
Power Quality Improvement in Distribution System Using D-STATCOM 1 K.L.Sireesha, 2 K.Bhushana Kumar 1 K L University, AP, India 2 Sasi Institute of Technology, Tadepalligudem, AP, India Abstract This paper
Manjeet Baniwal 1, U.Venkata Reddy 2, Gaurav Kumar Jha 3
 Application of to alleviate voltage sag and swell Manjeet Baniwal 1, U.Venkata Reddy 2, Gaurav Kumar Jha 3 123 (Electrical Engineering, AGPCE Nagpur/ RTMNU, INDIA) ABSTRACT : This paper deals with modelling
Application of to alleviate voltage sag and swell Manjeet Baniwal 1, U.Venkata Reddy 2, Gaurav Kumar Jha 3 123 (Electrical Engineering, AGPCE Nagpur/ RTMNU, INDIA) ABSTRACT : This paper deals with modelling
Comparison of Simulation Results of D-Facts & UPFC Used for Power Quality Improvement
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 9, September 2013 1 Comparison of Simulation Results of D-Facts & UPFC Used for Power Quality Improvement Dr.K.Ravichandrudu
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 9, September 2013 1 Comparison of Simulation Results of D-Facts & UPFC Used for Power Quality Improvement Dr.K.Ravichandrudu
II. BASIC STRUCTURE & FUNCTION OF UPFC
 Improvement of Power System Stability Using IPFC and UPFC Controllers VSN.Narasimha Raju 1 B.N.CH.V.Chakravarthi 2 Sai Sesha.M 3 1,2,3 Assistant Professor, EEE Department, Vishnu Institute of Technology,
Improvement of Power System Stability Using IPFC and UPFC Controllers VSN.Narasimha Raju 1 B.N.CH.V.Chakravarthi 2 Sai Sesha.M 3 1,2,3 Assistant Professor, EEE Department, Vishnu Institute of Technology,
Switching and Fault Transient Analysis of 765 kv Transmission Systems
 Third International Conference on Power Systems, Kharagpur, INDIA December >Paper #< Switching and Transient Analysis of 6 kv Transmission Systems D Thukaram, SM IEEE, K Ravishankar, Rajendra Kumar A Department
Third International Conference on Power Systems, Kharagpur, INDIA December >Paper #< Switching and Transient Analysis of 6 kv Transmission Systems D Thukaram, SM IEEE, K Ravishankar, Rajendra Kumar A Department
Traveling-Waves-Based Ground Fault Location Using Zero-Sequence Detection and Wavelet Transform
 Journal of Electrical Engineering, Electronics, Control and Computer Science JEEECCS, Volume 3, Issue 7, pages 7-12, 2017 Traveling-Waves-Based Ground Fault Location Using Zero-Sequence Detection and Wavelet
Journal of Electrical Engineering, Electronics, Control and Computer Science JEEECCS, Volume 3, Issue 7, pages 7-12, 2017 Traveling-Waves-Based Ground Fault Location Using Zero-Sequence Detection and Wavelet
DETECTION OF HIGH IMPEDANCE FAULTS BY DISTANCE RELAYS USING PRONY METHOD
 DETECTION OF HIGH IMPEDANCE FAULTS BY DISTANCE RELAYS USING PRONY METHOD Abilash Thakallapelli, Veermata Jijabai Technological Institute Abstract Transmission lines are usually suspended from steel towers
DETECTION OF HIGH IMPEDANCE FAULTS BY DISTANCE RELAYS USING PRONY METHOD Abilash Thakallapelli, Veermata Jijabai Technological Institute Abstract Transmission lines are usually suspended from steel towers
Harmonic Analysis of Power System Waveforms Based on Chaari Complex Mother Wavelet
 Proceedings of the 7th WSEAS International Conference on Power Systems, Beijing, China, September 15-17, 2007 7 Harmonic Analysis of Power System Waveforms Based on Chaari Complex Mother Wavelet DAN EL
Proceedings of the 7th WSEAS International Conference on Power Systems, Beijing, China, September 15-17, 2007 7 Harmonic Analysis of Power System Waveforms Based on Chaari Complex Mother Wavelet DAN EL
An Ellipse Technique Based Relay For Extra High Voltage Transmission Lines Protection
 Proceedings of the 14th International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON 10), Cairo University, Egypt, December 19-21, 2010, Paper ID 162. An Ellipse Technique Based Relay For Extra High Voltage
Proceedings of the 14th International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON 10), Cairo University, Egypt, December 19-21, 2010, Paper ID 162. An Ellipse Technique Based Relay For Extra High Voltage
SIMULATION OF D-STATCOM AND DVR IN POWER SYSTEMS
 SIMUATION OF D-STATCOM AND DVR IN POWER SYSTEMS S.V Ravi Kumar 1 and S. Siva Nagaraju 1 1 J.N.T.U. College of Engineering, KAKINADA, A.P, India E-mail: ravijntu@gmail.com ABSTRACT A Power quality problem
SIMUATION OF D-STATCOM AND DVR IN POWER SYSTEMS S.V Ravi Kumar 1 and S. Siva Nagaraju 1 1 J.N.T.U. College of Engineering, KAKINADA, A.P, India E-mail: ravijntu@gmail.com ABSTRACT A Power quality problem
Overcurrent relays coordination using MATLAB model
 JEMT 6 (2018) 8-15 ISSN 2053-3535 Overcurrent relays coordination using MATLAB model A. Akhikpemelo 1 *, M. J. E. Evbogbai 2 and M. S. Okundamiya 3 1 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering,
JEMT 6 (2018) 8-15 ISSN 2053-3535 Overcurrent relays coordination using MATLAB model A. Akhikpemelo 1 *, M. J. E. Evbogbai 2 and M. S. Okundamiya 3 1 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering,
factors that can be affecting the performance of a electrical power transmission system. Main problems which cause instability to a power system is vo
 2011 International Conference on Signal, Image Processing and Applications With workshop of ICEEA 2011 IPCSIT vol.21 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Location of FACTS devices for Real and Reactive
2011 International Conference on Signal, Image Processing and Applications With workshop of ICEEA 2011 IPCSIT vol.21 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Location of FACTS devices for Real and Reactive
Fault Detection and Classification Using Discrete Wavelet Transform
 Fault Detection and Classification Using Discrete Wavelet Transform Akanksha Malhotra, Purva Sharma Rajasthan College of Engineering for Women, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India Abstract: This research work aims
Fault Detection and Classification Using Discrete Wavelet Transform Akanksha Malhotra, Purva Sharma Rajasthan College of Engineering for Women, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India Abstract: This research work aims
Real and Reactive Power Control by using 48-pulse Series Connected Three-level NPC Converter for UPFC
 Real and Reactive Power Control by using 48-pulse Series Connected Three-level NPC Converter for UPFC A.Naveena, M.Venkateswara Rao 2 Department of EEE, GMRIT, Rajam Email id: allumalla.naveena@ gmail.com,
Real and Reactive Power Control by using 48-pulse Series Connected Three-level NPC Converter for UPFC A.Naveena, M.Venkateswara Rao 2 Department of EEE, GMRIT, Rajam Email id: allumalla.naveena@ gmail.com,
Comparison of Simulation and Experimental Results of UPFC used for Power Quality Improvement
 Comparison of Simulation and Experimental Results of UPFC used for Power Quality Improvement S. Muthukrishnan and Dr. A. Nirmal Kumar Abstract This paper deals with digital simulation and implementation
Comparison of Simulation and Experimental Results of UPFC used for Power Quality Improvement S. Muthukrishnan and Dr. A. Nirmal Kumar Abstract This paper deals with digital simulation and implementation
Design of Fast Real Time Controller for the Dynamic Voltage Restorer Based on Instantaneous Power Theory
 International Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 2016; 5(2-1): 1-6 Published online October 10, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com//epe) doi: 10.11648/.epe.s.2016050201.11 ISSN: 2326-957X
International Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 2016; 5(2-1): 1-6 Published online October 10, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com//epe) doi: 10.11648/.epe.s.2016050201.11 ISSN: 2326-957X
